Attached files
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
|
x |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2014
OR
|
¨ |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission File Number 001-36642
VIVINT SOLAR, INC.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its Charter)
|
Delaware |
|
45-5605880 |
|
( State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
|
(I.R.S. Employer |
3301 N. Thanksgiving Way, Suite 500
Lehi, UT
84043
(Address of principal executive offices) (Zip Code)
(877) 404-4129
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
Common Stock, Par Value $0.01 Per Share; |
|
Common stock traded on the New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. YES ¨ NO x
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. YES ¨ NO x
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. YES x NO ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to submit and post such files). YES x NO ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of Registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. x
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definition of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer”, and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
|
Large accelerated filer |
|
¨ |
|
Accelerated filer |
|
¨ |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Non-accelerated filer |
|
x (Do not check if a small reporting company) |
|
Small reporting company |
|
¨ |
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). YES ¨ NO x
As of June 30, 2014, the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second quarter, there was no established public market for the registrant’s common stock. The registrant’s common stock began trading on the New York Stock Exchange on October 1, 2014.
As of March 2, 2015, there were 105,303,122 shares of registrant’s common stock outstanding.
Portions of the Registrant’s Definitive Proxy Statement relating to the Annual Meeting of Shareholders, scheduled to be held on June 4, 2015, are incorporated by reference into Part III of this report.
Table of Contents
|
|
|
Page |
|
PART I |
|
|
|
Item 1. |
1 |
|
|
Item 1A. |
8 |
|
|
Item 1B. |
34 |
|
|
Item 2. |
34 |
|
|
Item 3. |
35 |
|
|
Item 4. |
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PART II |
|
|
|
Item 5. |
36 |
|
|
Item 6. |
37 |
|
|
Item 7. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
39 |
|
Item 7A. |
63 |
|
|
Item 8. |
64 |
|
|
Item 9. |
Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
102 |
|
Item 9A. |
102 |
|
|
Item 9B. |
104 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PART III |
|
|
|
Item 10. |
105 |
|
|
Item 11. |
105 |
|
|
Item 12. |
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
105 |
|
Item 13. |
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
105 |
|
Item 14. |
105 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PART IV |
|
|
|
Item 15. |
106 |
i
Forward-looking Statements
This report, including the sections entitled “Business,” “Risk Factors,” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and certain information incorporated by reference into this report contain forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. Forward-looking statements are identified by words such as “believe,” “anticipate,” “expect,” “intend,” “plan,” “will,” “may,” “seek” and other similar expressions. You should read these statements carefully because they discuss future expectations, contain projections of future results of operations or financial condition or state other “forward-looking” information. These statements relate to our future plans, objectives, expectations, intentions and financial performance and the assumptions that underlie these statements.
These forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to:
|
· |
federal, state and local regulations and policies governing the electric utility industry; |
|
· |
the regulatory regime for our offerings and for third-party owned solar energy systems; |
|
· |
technical limitations imposed by operators of the power grid; |
|
· |
the continuation of tax rebates, credits and incentives, including changes to the rates of the income tax credit, or ITC, beginning in 2017; |
|
· |
the price of utility-generated electricity and electricity from other sources; |
|
· |
our ability to finance the installation of solar energy systems; |
|
· |
our ability to sustain and manage growth; |
|
· |
our ability to further penetrate existing markets, expand into new markets and expand into markets for non-residential solar energy systems; |
|
· |
our ability to develop new product offerings and distribution channels; |
|
· |
our relationships with our sister company Vivint, Inc., or Vivint, and our sponsor The Blackstone Group, L.P., which is referred to in this report as Blackstone or our sponsor; |
|
· |
our ability to manage our supply chain; |
|
· |
the cost of solar panels and the residual value of solar panels after the expiration of our customer contracts; |
|
· |
our ability to maintain our brand and protect our intellectual property; and |
|
· |
our expectations regarding remediation of the material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting. |
In combination with the risk factors we have identified, we cannot assure you that the forward-looking statements in this report will prove to be accurate. Further, if our forward-looking statements prove to be inaccurate, the inaccuracy may be material. In light of the significant uncertainties in these forward-looking statements, you should not regard these statements as a representation or warranty by us or any other person that we will achieve our objectives and plans in any specified time frame, or at all, or as predictions of future events. Moreover, neither we nor any other person assumes responsibility for the accuracy and completeness of the forward-looking statements. We undertake no obligation to publicly update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law.
BUSINESS
Overview
We offer distributed solar energy — electricity generated by a solar energy system installed at or near customers’ locations — to residential customers based on 20-year contracts at prices below their current utility rates. Our customers pay little to no money upfront, and typically save 20% to 40% on solar-generated electricity rates relative to utility-generated electricity rates following system interconnection to the power grid and continue to benefit from locked-in energy prices over the term of their contracts, insulating them against unpredictable increases in utility rates.
1
Our 20-year customer contracts generate predictable, recurring cash flows and establish a long-term relationship with homeowners. Through our investment funds, we own an interest in the solar energy systems we install and ownership of the solar energy systems allows us and the other fund investors to benefit from various local, state and federal incentives. We obtain financing based on these cash flows and incentives. When customers decide to move or sell the home prior to the end of their contract term, the customer contracts allow our customers to transfer their obligations to the new home buyer, subject to a creditworthiness determination. If the home buyer is not creditworthy or does not wish to assume the customer’s obligations, the contract allows us to require the customer to purchase the system. Our sources of financing are used to offset our direct installation costs and most, if not all, of our allocated overhead expenses. Our direct relationship with homeowners also facilitates our ability to control quality and provide high levels of customer service and provides us with an opportunity to offer additional value-added products and services to our customers.
From our inception in May 2011 through December 31, 2014, we have experienced rapid growth, installing solar energy systems with an aggregate of 228.2 megawatts of capacity at more than 35,700 homes in seven states for an average solar energy system capacity of approximately 6.4 kilowatts. According to GTM Research, an industry research firm, we were the second largest installer of solar energy systems to the U.S. residential market in 2013, and have continued to increase our market share, capturing approximately 16% market share in the third quarter of 2014, up from approximately 8% in the third quarter of 2013. We believe the key ingredients to our success include the following:
|
· |
High growth industry with a significant addressable market. The market for residential distributed solar energy is growing rapidly and disrupting the traditional electricity market. According to GTM Research, the U.S. residential solar energy market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate, or CAGR, of approximately 27% from 2013 through 2018. Residential distributed solar has currently penetrated less than 1% of its total addressable market in the United States. |
|
· |
Differentiated and highly scalable platform. We have developed an integrated approach to providing distributed solar energy where we fully control the lifecycle of our customers’ experience including the initial professional consultation, design and engineering process, installation and ongoing monitoring and service. We deploy our sales force on a neighborhood-by-neighborhood basis, which allows us to cultivate a geographically concentrated customer base that reduces our costs and increases our operating efficiency. We couple this model with repeatable and highly scalable processes to establish warehouse facilities, assemble and train sales and installation teams and open new offices. We believe that our processes enable us to expand rapidly within existing markets and into new markets. We also believe that our direct sales model and integrated approach represent a differentiated platform, unique in the industry that accelerates our growth by maximizing sales effectiveness, delivering high levels of customer satisfaction and driving cost efficiency. |
|
· |
Long-term, highly visible, recurring cash flow. Our customers typically sign 20-year contracts for solar electricity generated by the system owned by us and pay us directly over the term of their contracts. These customer contracts generate recurring monthly customer payments. As of December 31, 2014, the average estimated nominal contracted payment for our customer contracts was approximately $30,000, and there is the potential for additional payments if customers choose to renew their contracts at the end of the term. The solar energy systems we install are eligible for investment tax credits, or ITCs, accelerated tax depreciation and other utility and governmental incentives. We have historically financed the assets created by substantially all of these contracts through investment funds, which reduces our cost of capital to finance our operations. |
As of February 28, 2015, we had raised 13 investment funds to which investors such as banks have committed to invest approximately $673 million which will enable us to install solar energy systems of total fair market value approximating $1.6 billion. As of February 28, 2015, we had remaining tax equity commitments to fund approximately 71 megawatts of future deployments, which we estimate to be sufficient to fund solar energy systems with a total fair market value of approximately $331 million.
2
Our Approach
We secure financing that enables our customers to access solar energy for little to no upfront cost to them. The key elements of our integrated approach to providing distributed solar energy include:
|
· |
Professional consultation. We deploy our direct-to-home sales force to provide in-person professional consultations to prospective customers to evaluate the feasibility of installing a solar energy system at their residence. Our sales closing and referral rates are enhanced by homeowners’ responsiveness to our direct-to-home, neighborhood-by-neighborhood outreach strategy. |
|
· |
Design and engineering. We have developed a streamlined process that enables us to design and install a custom solar energy system that delivers significant customer savings. This process, which incorporates proprietary software, standardized templates and data derived from on-site surveys, allows us to design each system to comply with complex and varied state and local regulations and optimize system performance on a per panel basis. We continue to pursue technology innovation to integrate accurate system design into the initial in-person sales consultation as a competitive tool to enhance the customer experience and increase sales close rates. |
|
· |
Installation. We are a licensed contractor in the markets we serve and are responsible for each customer installation. Once we complete the system design, we obtain the necessary building permits and begin installation. Upon completion, we schedule the required inspections and arrange for interconnection to the power grid. By directly handling these logistics, we control quality and streamline the system installation process for our customers. Throughout this process, we apprise our customers of the project status with regular updates from our account representatives. We minimize costs, ensure quality and deliver high levels of customer satisfaction by controlling the entire installation process. |
|
· |
Monitoring and service. We monitor the performance of our solar energy systems, leveraging a combination of internally developed solutions as well as capabilities provided by our suppliers. Currently, a substantial majority of our existing solar energy systems use Enphase Energy, Inc.’s, or Enphase’s, communications gateway device paired with its monitoring service. We leverage the Enphase communications gateway and monitoring service to collect performance data and use this data to ensure we deliver quality operations and maintenance services for our solar energy systems. If services are required, our strong local presence enables rapid response times. |
|
· |
Referrals. We believe our commitment to delivering high levels of customer satisfaction and our concentrated geographic deployment strategy have generated a significant amount of sales through customer referrals, which increase our neighborhood penetration rates, lower our customer acquisition costs and accelerate our growth. Our financial returns also benefit from the cost savings derived from increasing the density of installations in a neighborhood. |
Our Strategy
Our goal is to become the premier provider of distributed solar energy. Key elements of our strategy include:
|
· |
Further penetrating our existing markets. While we have chosen to initially introduce our solar energy systems in states whose utility prices, sun exposure, climate conditions and regulatory policies provide for the most compelling market for distributed solar energy, we believe even those states are still significantly underpenetrated. Accordingly, we intend to increase our presence in these markets by introducing our solar energy systems into new neighborhoods and communities in states in which we already have operations. We intend to leverage our brand and existing customer base to grow in these markets at lower customer acquisition and installation costs relative to our competitors. In addition, we intend to complement our existing go-to-market strategy with outright sales of and consumer loan products for solar energy systems. |
|
· |
Expanding into new locations and commercial markets. To enlarge our addressable market, we plan to expand our presence to new states and we intend to enter the commercial and industrial market, which includes small businesses such as community retailers as well as larger retailers and manufacturers. We plan to pursue similar debt, equity and other financing strategies consistent with our approach in the residential market, including creating investment funds, to help finance our commercial and industrial operations. We are making investments to introduce our solar energy systems into the residential market in other states that we believe present attractive economics for us and homeowners. We have a track record of entering new markets quickly and efficiently. In 2014, we established 23 new sales offices to sell to residential customers in addition to the 16 previously existing sales offices. |
3
|
· |
Capitalizing on opportunities to increase sales and lower costs. We intend to capitalize on our opportunities to increase sales and lower costs through internal development initiatives, acquisitions and alternative financing structures. We plan to make additional investments in new technologies related to our system design and installation and ongoing customer service practices. Such investments will enable us to continue to improve our operating efficiency, cost structure and customer satisfaction. In addition, our management team has significant experience in successfully integrating acquisitions into their businesses, and we believe there are opportunities to acquire related businesses, talent and technology to drive sales and lower costs. |
|
· |
Building and leveraging strategic relationships. We plan to build and leverage strategic relationships with new and existing partners to grow our business and drive cost reductions. For example, in addition to our direct sales channel, we are currently exploring opportunities to sell solar energy systems to customers through a number of distribution channels including relationships with homebuilders, home improvement stores, large construction, electrical and roofing companies and other third parties that have access to large numbers of potential customers. Our ongoing relationship with our sister company Vivint will give us continued cross-selling opportunities and we expect to benefit from Blackstone’s network of strategic relationships. Additionally, we intend to lower our cost of capital through alternative financing sources such as securitization by pooling and transferring certain of our solar energy systems and associated customer contracts into special purpose entities, or SPEs, and subsequently issuing and selling interests in these SPEs as securities. |
Customer Contracts
As of December 31, 2014, the average FICO score of our customers was approximately 750. Our solar energy customers purchase energy or lease solar energy systems from us pursuant to one of two types of long-term contracts: a power purchase agreement or a lease. Prior to the first quarter of 2014, all of our long-term contracts were structured as power purchase agreements. In the first quarter of 2014, we began offering leases in connection with our entry into certain markets. Of our over 22,400 installations in 2014, approximately 540 systems were leased.
In the power purchase agreement structure, we charge customers a fee per kilowatt hour based on the amount of electricity the solar energy system actually produces. In the lease structure, the customer’s monthly payment is fixed based on a calculation that takes into account expected solar energy generation. The lease includes a performance guarantee under which we agree to refund a proportion of the customer payments if the leased solar energy system does not meet the annual guaranteed energy production level. The power purchase agreement and lease terms are typically for 20 years, and all of the prices that we charge to our customers are subject to pre-determined annual fixed percentage price escalations as specified in the customer contract. Since January 2014, substantially all of our customer contracts have included an annual price escalator of 2.9%. Over the term of these agreements, we operate the systems and agree to maintain them in good condition. Customers who buy energy from us under power purchase agreements or lease systems are covered by our workmanship warranty equal to the length of the term of these agreements.
Sales and Marketing
We place our integrated residential solar energy systems through a scalable sales organization that uses a direct-to-home sales model. We believe that a high-touch, customer-focused selling process is important before, during and after the sale of our products to maximize our sales success. The members of our sales force typically reside and work within the market they serve. We also generate a significant amount of sales through customer referrals. We have found that customer referrals increase in relation to our penetration in a particular market and shortly after entering a new market become an increasingly effective way to market our solar energy systems. In addition to direct sales, we are currently exploring opportunities to sell solar energy systems to customers through a number of distribution channels, including relationships with home builders, home improvement stores, large construction, electrical and roofing companies and other third parties that have access to large numbers of potential customers.
We establish a sales office in each market that we enter. A typical sales team may consist of 15 to 20 sales representatives, depending on the sales region, which we refer to as sales managers, and one to two district managers. Sales managers are typically recruited by district managers. These sales teams are supported by approximately 30 installation technicians and an operations manager. There are also regional managers who generally oversee 10 to 20 sales offices. Historically, we have recruited a majority of our sales personnel from Vivint. However, pursuant to a non-competition agreement entered into in connection with our initial public offering, we and Vivint have agreed not to solicit for employment any of the other’s employees who primarily manage sales, installation or servicing of the other’s products and services. In 2014, we established 23 sales offices.
Our sales managers participate in a comprehensive training program, which includes operating as a team in existing markets prior to deployment to newly established offices. We believe this approach significantly accelerates the time we can effectively sell in a particular market after establishing a new office, and has in the past allowed us to obtain executed contracts within a day of opening a new office. Our sales managers also receive ongoing training throughout the year.
4
We train our sales managers on sales techniques and applicable laws and regulations. We also train our sales managers to customize their consultative presentation according to the individual homeowner, based on guidelines and principles outlined in our training materials. We provide sales managers with real-time data on potential customers through a proprietary application provided to our sales managers to help them to sell in an efficient manner. Through the application, a sales manager can pre-screen potential customers directly from his or her mobile device, view maps of the sales area and track data for current and potential customers.
Operations and Suppliers
We purchase solar panels directly from multiple manufacturers. Historically, our solar panel suppliers were Trina Solar Limited, Yingli Green Energy Americas, Inc. and Canadian Solar, Inc. During 2014, Trina Solar Limited and Yingli Green Energy Americas, Inc. accounted for substantially all of our solar photovoltaic module purchases and Enphase accounted for substantially all of our inverter purchases. Historically, we procured racking systems primarily from Zep Solar, Inc., or Zep, which was acquired by one of our competitors in 2013. In 2014, we diversified our racking providers. We have successfully transitioned away from using racking systems procured from Zep, although we currently have a limited inventory remaining in certain of our markets which we are using primarily as replacement parts on service calls. We believe that our new racking system providers will be able to meet all of our needs going forward, and we do not expect any interruption to our business as a result of this transition. We generally source the other products related to our solar energy systems, such as fasteners, wiring and electrical fittings, through a variety of distributors.
If we fail to develop, maintain and expand our relationships with these or other suppliers, our ability to meet anticipated demand for our solar energy systems may be adversely affected, or we may only be able to offer our systems at higher costs or after delays. If one or more of the suppliers that we rely upon to meet anticipated demand ceases or reduces production due to its financial condition, acquisition by a competitor or otherwise, it may be difficult to quickly identify alternative suppliers or to qualify alternative products on commercially reasonable terms, and our ability to satisfy this demand may be adversely affected.
We screen all suppliers and components based on expected cost, reliability, warranty coverage, ease of installation and other ancillary costs. We typically enter into master contract arrangements with our major suppliers that define the general terms and conditions of our purchases, including warranties, product specifications, indemnities, delivery and other customary terms. We typically purchase solar panels, inverters and racking on an as-needed basis from our suppliers at then prevailing prices pursuant to purchase orders issued under our master contract arrangements.
The declining cost of solar panels and the raw materials necessary to manufacture them has been a key driver in the price we charge for electricity and customer adoption of solar energy. According to industry experts, solar panel and raw material prices are not expected to continue to decline at the same rate as they have over the past several years. The resulting prices could slow our growth and cause our financial results to suffer. In addition, in the past we have purchased virtually all of the solar panels used in our solar energy systems from manufacturers based in China which have benefited from favorable governmental policies by the Chinese government.
As of February 28, 2015, we operate in Arizona, California, Hawaii, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York and Utah. Our corporate headquarters are located in Utah. We manage inventory through our local warehouses and maintain a fleet of more than 470 trucks and other vehicles to support our installers and operations. This operational scale is fundamental to our business, as our field teams completed on average approximately 1,870 residential installations per month during the year ended December 31, 2014, while our project management teams simultaneously manage thousands of projects as they move through the stages of engineering, permitting, installation, maintenance and monitoring.
We offer an installation warranty that the solar energy systems under our customer contracts will be free from material defects in design and workmanship for the term of the contract as well as a limited warranty on roof penetrations. We are also obligated to maintain the solar energy systems in good condition for the term of the contract, usually 20 years.
We provide a performance guarantee to our lease customers that requires us to refund money to the lessee if the solar energy system fails to generate the minimum amount of electricity in a given term, as specified in the lease. We offer performance guarantees in certain leasing-only markets such as Arizona. In these markets, we compensate customers if their systems produce less energy than the guaranteed amount in any given year by making a payment to customers with under-performing systems. As of December 31, 2014, we have not compensated any customers per the terms of these contracts. We expect to begin making payments in the second half of 2015 for any under-performing systems. As of the date of this report, a relatively small number of our installations had been leased. As a result, we expect payments for underperforming systems will not be material initially, but as the number of leased systems grows, such payments will increase over time and may vary from period-to-period based on a number of factors, including weather conditions in the areas in which we lease systems, which may adversely impact our results of operations.
5
We further offer a range of warranties on our solar energy systems to our investment funds. All of our systems feature a workmanship warranty during which we are obligated, at our cost and expense, to correct defects in our installation work, which depending on the particular investment fund, is for a period of either five or ten years. Generally our maintenance obligations to our investment funds do not include the cost of panels, inverters or racking, should such major components require replacement. The cost of such components are borne instead by the applicable investment fund, although we are obligated to install such equipment as part of our services covered by the agreed maintenance services fee. This obligation is satisfied by Vivint Solar Provider, LLC, which provides operations and maintenance services to each of our investment funds. As part of Vivint Solar Provider’s operations and maintenance work, we provide a pass-through of the inverter and panel manufacturers’ warranty coverage to our customers, which generally range from 10 to 25 years. We also provide ongoing service and repair during the entire term of the customer relationship, regardless of whether or not such repairs are covered by our or a manufacturer’s warranty. Costs associated with such ongoing service and repair have not been material.
Competition
We believe that our primary competitors are the traditional utilities that supply electricity to our potential customers. We compete with these traditional utilities primarily based on price (cents per kilowatt hour), predictability of future prices (by providing pre-determined annual price escalations) and the ease by which customers can switch to electricity generated by our solar energy systems. We believe that we compete favorably with traditional utilities based on these factors in the states where we offer our solar power purchase and solar energy leasing services.
We also compete with companies that are not regulated like traditional utilities but that have access to the traditional utility electricity transmission and distribution infrastructure pursuant to state and local pro-competitive and consumer choice policies and with solar companies with business models that are similar to ours, such as SolarCity Corporation. We believe that we compete favorably with these companies based on our customer service, including our speed from signing a customer agreement to installation, our in-house installation, operations and maintenance teams, and a results-focused back office that quickly and efficiently addresses customer inquiries.
In addition, we compete with solar companies in the downstream value chain of solar energy. For example, we face competition from purely finance driven organizations that acquire customers and then subcontract out the installation of solar energy systems, from installation businesses that seek financing from external parties, from large construction companies and utilities and increasingly from sophisticated electrical and roofing companies. These distributed energy competitors typically work in contractual arrangements with third parties, leaving the customer in the position of having to deal with different companies for different aspects of their solar energy systems. We believe that we compete favorably with these companies because we offer an integrated approach to residential solar energy systems, which includes in-house sales, financing, engineering, installation, maintenance and monitoring. Many of our competitors offer only a subset of the services we provide. Aside from simple cost efficiency, we offer distinct practical benefits as an all-in-one provider such as providing a single point of contact and accountability for our offerings during the relationship with our customers. Further, we are not dependent on installation subcontractors, enabling us to better scale our business while maintaining quality control.
Technology and Intellectual Property
As of December 31, 2014, we, directly or through our wholly owned subsidiary Solmetric Corporation, or Solmetric, had five patents and seven pending applications with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. These patents and applications relate to shade and site analysis. Our issued patents start expiring in 2026. We intend to file additional patent applications as we innovate through our research and development efforts.
Solmetric is best known for the “SunEye” hardware and “PV Designer” software product lines. The SunEye is a handheld electronic tool that provides shade analysis. PV Designer allows layout and energy production estimates for the optimum photovoltaic design on a customer’s home. These products provide more accurate solar energy assessments during the pre-install process and fast and accurate performance testing during commissioning and operations and management. In February 2015, we decided to discontinue external sales of the SunEye and PV Designer products, which were at the end of their product life cycles. We will continue selling the PV Analyzer product, which is commercially used in commissioning, auditing, operating, maintaining and troubleshooting issues with photovoltaic systems. We will continue to develop and produce SunEye and PV Designer products for internal use only. The Solmetric development team will be known as Vivint Solar Labs, a research and development team focused on proprietary photovoltaic installation instruments and software.
As part of our strategy, we plan to continue to expand our technological capabilities through targeted acquisitions such as Solmetric, licensing technology and intellectual property from third parties, joint development relationships with partners and suppliers and other strategic initiatives as we strive to offer the industry’s best operational efficiency, performance prediction, operations and management.
6
Government Regulation, Policies and Incentives
Government Regulation
We are not regulated as a public utility in the United States under current applicable national, state or other local regulatory regimes where we conduct business.
To operate our systems we obtain interconnection permission from the applicable local primary electric utility. Depending on the size of the solar energy system and local law requirements, interconnection permission is provided by the local utility and us and/or our customer. In almost all cases, interconnection permissions are issued on the basis of a standard process that has been pre-approved by the local public utility commission or other regulatory body with jurisdiction over net metering procedures. As such, no additional regulatory approvals are required once interconnection permission is given. We maintain a utility administration function, with primary responsibility for engaging with utilities and ensuring our compliance with interconnection rules.
Our operations are subject to stringent and complex federal, state and local laws, including regulations governing the occupational health and safety of our employees and wage regulations. For example, we are subject to the requirements of the federal Occupational Safety and Health Act, as amended, or OSHA, the U.S. Department of Transportation, or DOT, and comparable state laws that protect and regulate employee health and safety. We strive to maintain compliance with applicable OSHA, DOT and similar government regulations; however, as discussed in the section captioned “Risk Factors—Compliance with occupational safety and health requirements and best practices can be costly, and noncompliance with such requirements may result in potentially significant monetary penalties, operational delays and adverse publicity,” there have been instances in which we experienced workplace accidents and received citations from regulators, resulting in fines. Such instances have not materially impacted our business or relations with our employees.
Government Policies
Net metering is one of several key policies that have enabled the growth of distributed solar in the United States. Net metering allows a homeowner to pay his or her local traditional utility only for their power usage net of production from the solar energy system installed on his or her roof. Where the customer’s utility provides for net metering, the customer typically pays for the net energy used or receives a credit against future bills at the retail rate if more energy is produced than consumed. Homeowners receive credit for the energy that the solar installation exports to the local power grid, and are reimbursed by the utility for net excess generation in some utility markets, including some of those in which we operate. Forty-four states, Puerto Rico and the District of Columbia have adopted some form of net metering law or regulation. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, or EIA, the total number of net metered customers in the United States has grown at a CAGR of approximately 48%, from approximately 19,000 households in 2005 to approximately 437,000 households in 2013. Despite this rapid growth, in 2013 only 0.3% of all electricity consumers were engaged in some form of net metering. In 2014, however, net metering programs were subject to regulatory scrutiny in Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada and Utah. Regulators in these states have considered imposing limits on the aggregate capacity of net metering generation, reducing the rate that net metering customers are paid for the power that they deliver back to the grid and allegations that homeowners with net metered solar systems shift the costs of maintaining the electric grid onto non-solar ratepayers. Despite these considerations, regulators have generally upheld the programs in their current form, though some were subject to minor modification and others, including California, Hawaii and Utah, have been designated for additional review in the next few years.
Government Incentives
Federal, state and local government bodies and utilities provide incentives to various parties, including owners, end users, distributors, system integrators and manufacturers of solar energy systems to promote solar energy. These incentives come in various forms, including rebates, tax credits and other financial incentives such as system performance payments, payments for renewable energy credits associated with renewable energy generation and exclusion of solar energy systems from property tax assessments. These incentives enable us to lower the price we charge customers for energy from, and to lease, our solar energy systems, helping to catalyze customer acceptance of solar energy as an alternative to utility-provided power.
The Federal government currently offers a 30% ITC under Section 48(a) of the Internal Revenue Code for the installation of certain solar power facilities; this 30% rate continues until December 31, 2016. By statute, this tax credit is scheduled to decrease to 10% on January 1, 2017, and we expect the reduction in the ITC to negatively impact the availability of tax equity financing and the economics of distributed solar energy financed using tax equity structures. This scheduled reduction in the ITC will likely adversely impact growth in the distributed solar energy market. Nevertheless, decreasing system costs, combined with increasing retail utility rates, are expected to partially mitigate the impact of such reduction. In addition, industry sources have suggested that the reduction in the ITC in 2017 may be stepped down gradually over time, which we believe would further mitigate the impact of such reduction.
7
The economics of purchasing a solar energy system are also improved by eligibility for accelerated depreciation, also known as the modified accelerated cost recovery system, or MACRS, which allows for the depreciation of equipment according to an accelerated schedule established by the Internal Revenue Service. The acceleration of depreciation creates a valuable tax benefit that reduces the overall cost of the solar energy system and increases the return on investment.
Approximately half of the states in which we operate offer a personal and/or corporate investment or production tax credit for solar energy that is additive to the ITC. Further, most of the states and local jurisdictions have established property tax incentives for renewable energy systems that include exemptions, exclusions, abatements and credits.
Many state governments, traditional utilities, municipal utilities and co-operative utilities offer a rebate or other cash incentive for the installation and operation of a solar energy system or energy efficiency measures. Capital costs or “up-front” rebates provide funds to solar customers or developers or systems owners such as us based on the cost, size or expected production of a customer’s solar energy system. Performance-based incentives provide cash payments to solar customers or a system owner based on the energy generated by the solar energy system during a pre-determined period.
Many states also have adopted procurement requirements for renewable energy production. Thirty states and the District of Columbia have adopted a renewable portfolio standard that requires regulated utilities to procure a specified percentage of total electricity delivered to customers in the state from eligible renewable energy sources, such as solar energy systems, by a specified date. To prove compliance with such mandates, utilities usually must surrender solar renewable energy certificates, or SRECs to the applicable authority. Solar energy system owners such as our investment funds often are able to sell SRECs to utilities directly or in SREC markets.
Workforce
As of December 31, 2014, we had a total workforce of 2,294, including 456 service providers in sales and marketing, 589 employees in operations, 1,067 employees in installation, 168 employees in general and administrative and 14 employees in research and development. Our sales and marketing headcount includes 420 active direct sellers. We consider a direct sales person to be active if they completed at least four customer pre-surveys in the prior four weeks. Our operations personnel work primarily in installation, design and account management. Our general and administrative personnel work primarily in finance, business development, capital markets and human resources. None of our service providers are represented by a labor union and we consider relations with our workers to be good.
You should carefully consider the following risk factors, together with all of the other information included in this report, including the section of this report captioned “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our financial statements and related notes. If any of the following risks occurred, it could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition or operating results. This report also contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. Our actual results could differ materially from those anticipated in the forward-looking statements as a result of factors that are described below and elsewhere in this report.
8
Risks Related to our Business
We need to enter into substantial additional financing arrangements to facilitate our customers’ access to our solar energy systems, and if financing is not available to us on acceptable terms when needed, our ability to continue to grow our business would be materially adversely impacted.
Our future success depends on our ability to raise capital from third-party investors on competitive terms to help finance the deployment of our solar energy systems. We seek to minimize our cost of capital in order to maintain the price competitiveness of the electricity produced by, or the lease payments for, our solar energy systems. If we are unable to establish new investment funds when needed, or upon desirable terms, to enable our customers’ access to our solar energy systems with little to no upfront cost to them, we may be unable to finance installation of our customers’ systems or our cost of capital could increase, either of which would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. As of February 28, 2015, we had raised 13 investment funds to which investors such as banks and other large financial investors have committed to invest approximately $673 million which will enable us to install solar energy systems of total fair market value approximating $1.6 billion. As of February 28, 2015, we had remaining tax equity commitments to fund approximately 71 megawatts of future deployments, which we estimate to be sufficient to fund solar energy systems with a total fair market value of approximately $331 million. The contract terms in certain of our investment fund documents impose conditions on our ability to draw on financing commitments from the fund investors, including if an event occurs that could reasonably be expected to have a material adverse effect on the fund or on us. If we do not satisfy such conditions due to events related to our business or a specific investment fund or developments in our industry or otherwise, and as a result we are unable to draw on existing commitments, our inability to draw on such commitments could have a material adverse effect on our business, liquidity, financial condition and prospects.
To meet the capital needs of our growing business, we will need to obtain additional financing from new investors and investors with whom we currently have arrangements. If any of the financial institutions that currently provide financing decide not to invest in the future due to general market conditions, concerns about our business or prospects or any other reason, or decide to invest at levels that are inadequate to support our anticipated needs or materially change the terms under which they are willing to provide future financing, we will need to identify new financial institutions and companies to provide financing and negotiate new financing terms.
In the past, we have sometimes been unable to timely establish investment funds in accordance with our plans, due in part to the relatively limited number of investors attracted to such types of funds, competition for such capital and the complexity associated with negotiating the agreements with respect to such funds. Delays in raising financing could cause us to delay expanding in existing markets or entering into new markets and hiring additional personnel in support of our planned growth. Any future delays in capital raising could similarly cause us to delay deployment of a substantial number of solar energy systems for which we have signed power purchase agreements or leases with customers. Our future ability to obtain additional financing depends on banks’ and other financing sources’ continued confidence in our business model and the renewable energy industry as a whole. It could also be impacted by the liquidity needs of such financing sources themselves. We face intense competition from a variety of other companies, technologies and financing structures for such limited investment capital. If we are unable to continue to offer a competitive investment profile, we may lose access to these funds or they may only be available to us on terms that are less favorable than those received by our competitors. For example, if we experience higher customer default rates than we currently experience in our existing investment funds, this could make it more difficult or costly to attract future financing. In our experience, there are a relatively small number of investors that generate sufficient profits and possess the requisite financial sophistication that can benefit from and have significant demand for the tax benefits that our investment funds can provide. Historically, in the distributed solar energy industry, investors have typically been large financial institutions and a few large, profitable corporations. Our ability to raise investment funds is limited by the relatively small number of such investors. Any inability to secure financing could lead us to cancel planned installations, could impair our ability to accept new customers and could increase our borrowing costs, any of which would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
9
A material reduction in the retail price of traditional utility-generated electricity or electricity from other sources or other reduction in the cost of such electricity would harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We believe that a significant number of our customers decide to buy solar energy because they want to pay less for electricity than what is offered by the traditional utilities. However, distributed residential solar energy has yet to achieve broad market adoption as evidenced by the fact that distributed solar has penetrated less than 1% of its total addressable market in the U.S. residential sector.
The customer’s decision to choose solar energy may also be affected by the cost of other renewable energy sources. Decreases in the retail prices of electricity from the traditional utilities or from other renewable energy sources would harm our ability to offer competitive pricing and could harm our business. The cost of electricity from traditional utilities could decrease as a result of:
|
· |
construction of new power generation plants, including plants utilizing natural gas, nuclear, coal, renewable energy or other generation technologies; |
|
· |
relief of transmission constraints that enable local centers to generate energy less expensively; |
|
· |
reductions in the price of natural gas or other fuel sources; |
|
· |
utility rate adjustment and customer class cost reallocation; |
|
· |
energy conservation technologies and public initiatives to reduce electricity consumption; |
|
· |
widespread deployment of existing or development of new or lower-cost energy storage technologies that have the ability to reduce a customer’s average cost of electricity by shifting load to off-peak times; and |
|
· |
development of new energy generation technologies that provide less expensive energy. |
A reduction in utility electricity costs would make the purchase of electricity under our power purchase agreements or the lease of our solar energy systems less economically attractive. If the cost of energy available from traditional utilities were to decrease due to any of these reasons, or other reasons, we would be at a competitive disadvantage, we may be unable to attract new customers and our growth would be limited.
Electric utility industry policies and regulations may present technical, regulatory and economic barriers to the purchase and use of solar energy systems that may significantly reduce demand for electricity from our solar energy systems.
Federal, state and local government regulations and policies concerning the electric utility industry, utility rate structures, interconnection procedures, and internal policies of electric utilities, heavily influence the market for electricity generation products and services. These regulations and policies often relate to electricity pricing and the interconnection of distributed electricity generation systems to the power grid. Policies and regulations that promote renewable energy and customer-sited energy generation have been challenged by traditional utilities and questioned by those in government and others arguing for less governmental spending and involvement in the energy market. To the extent that such views are reflected in government policy, the changes in such policies and regulations could adversely affect our results of operations, cost of capital and growth prospects.
In the United States, governments and the state public service commissions that determine utility rates continuously modify these regulations and policies. These regulations and policies could result in a significant reduction in the potential demand for electricity from our solar energy systems and could deter customers from entering into contracts with us. In addition, depending on the region, electricity generated by solar energy systems competes most effectively with the most expensive retail rates for electricity from the power grid, rather than the less expensive average price of electricity. Modifications to the utilities’ peak hour pricing policies or rate design, such as to a flat rate, would make our current products less competitive with the price of electricity from the power grid. For example, a shift in the timing of peak rates for utility-generated electricity to a time of day when solar energy generation is less efficient could make our solar energy system offerings less competitive and reduce demand for our offerings. In addition, since we are required to obtain interconnection permission for each solar energy system from the local utility, changes in a local utility’s regulations, policies or interconnection process have in the past delayed and in the future could delay or prevent the completion of our solar energy systems. This in turn has delayed and in the future could delay or prevent us from generating revenues from such solar energy systems or cause us to redeploy solar energy systems, adversely impacting our results of operations.
10
In addition, any changes to government or internal utility regulations and policies that favor electric utilities could reduce our competitiveness and cause a significant reduction in demand for our offerings or increase our costs or the prices we charge our customers. Certain jurisdictions have proposed allowing traditional utilities to assess fees on customers purchasing energy from solar energy systems or have imposed or proposed new charges or rate structures that would disproportionately impact solar energy system customers who utilize net metering, either of which would increase the cost of energy to those customers and could reduce demand for our solar energy systems. For example, California has adopted and is in the process of implementing Assembly Bill 327, which has lifted the capacity caps on net metering applicable to each utility in the state, but also allows fixed charges or minimum bills of up to $10 to be imposed on future net metering customers and allows the California Public Utilities Commission to alter the net metering rates. This may result in monthly charges being imposed on our customers in California and less favorable rates for the export of electricity by California customers. Additionally, certain utilities in Arizona have recently approved increased rates and charges for net metering customers, and in January 2015, Hawaiian Electric Company proposed material changes to the net metering program on the islands of Hawaii, Oahu and Maui, which are currently being reviewed by Hawaii’s Public Utilities Commission. These policy changes may be less favorable to our customers and affect demand for our solar energy systems, and similar changes to net metering policies may occur in other states. It is also possible that these or other changes could be imposed on our current customers, as well as future customers. Due to the concentration of our solar energy systems in states such as California and Hawaii and expected continued concentration of our business in California, any such changes in these markets would be particularly harmful to our reputation, customer relations, business, results of operations and future growth in these areas. We may be similarly adversely affected if our business becomes concentrated in other jurisdictions.
Our business currently depends on the availability of rebates, tax credits and other financial incentives. The expiration, elimination or reduction of these rebates, credits or incentives could adversely impact our business.
Federal, state and local government and regulatory bodies provide for tariff structures and incentives to various parties including owners, end users, distributors, system integrators and manufacturers of solar energy systems to promote solar energy in various forms, including rebates, tax credits and other financial incentives such as system performance payments, renewable energy credits associated with renewable energy generation, exclusion of solar energy systems from property tax assessments and net metering. We rely on these governmental and regulatory programs to finance solar energy system installations, which enables us to lower the price we charge customers for energy from, and to lease, our solar energy systems, helping to catalyze customer acceptance of solar energy with those customers as an alternative to utility-provided power. However, these programs may expire on a particular date, end when the allocated funding is exhausted or be reduced or terminated as solar energy adoption rates increase. These reductions or terminations often occur without warning. In addition, the financial value of certain incentives decreases over time. For example, the value of solar renewable energy certificates, or SRECs, in a market tends to decrease over time as the supply of SREC-producing solar energy systems installed in that market increases. If we overestimate the future value of these incentives, it could adversely impact our financial results.
The federal government currently offers a 30% investment tax credit, or the ITC, under Section 48(a) of the Internal Revenue Code for the installation of certain solar power facilities; the 30% rate continues until December 31, 2016. By statute, the ITC is scheduled to decrease to 10% of the fair market value of a solar energy system on January 1, 2017, and the amounts that fund investors are willing to invest could decrease or we may be required to provide a larger allocation of customer payments to the fund investors as a result of this scheduled decrease. To the extent we have a reduced ability to raise investment funds as a result of this reduction, the rate of growth of installations of our residential solar energy systems would be negatively impacted. The ITC has been a significant driver of the financing supporting the adoption of residential solar energy systems in the United States and its scheduled reduction beginning in 2017, unless modified by an intervening change in law, will significantly impact the attractiveness of solar to these investors and could potentially harm our business. In addition, as we approach the scheduled decrease in the ITC, delays in obtaining interconnection approval from the local utility as a result of changes to regulations, policies or interconnection process or other reasons may result in the loss of our ability to obtain the higher 30% ITC for systems installed in the months and weeks approaching the end of 2016, which would be harmful to our business.
Applicable authorities may adjust or decrease incentives from time to time or include provisions for minimum domestic content requirements or other requirements to qualify for these incentives. Reductions in, eliminations or expirations of or additional application requirements for, governmental incentives could adversely impact our results of operations and ability to compete in our industry by increasing our cost of capital, causing us to increase the prices of our energy and solar energy systems and reducing the size of our addressable market. In addition, this would adversely impact our ability to attract investment partners and to form new investment funds and our ability to offer attractive financing to prospective customers.
11
We rely on net metering and related policies to offer competitive pricing to our customers in all of our current markets, and changes to net metering policies may significantly reduce demand for electricity from our solar energy systems.
Our business benefits significantly from favorable net metering policies in states in which we operate. Net metering allows a homeowner to pay his or her local electric utility only for their power usage net of production from the solar energy system, transforming the conventional relationship between customers and traditional utilities. Homeowners receive credit for the energy that the solar installation generates in excess of that needed by the home to offset energy usage at times when the solar installation is not generating energy. In states that provide for net metering, the customer typically pays for the net energy used or receives a credit against future bills at the retail rate if more energy is produced by the solar installation than consumed. In some states and utility territories, customers are also reimbursed by the electric utility for net excess generation on a periodic basis.
Forty-four states, Puerto Rico and the District of Columbia have adopted some form of net metering. Each of the states where we currently serve customers has adopted some form of a net metering policy. In recent years, net metering programs have been subject to regulatory scrutiny in some states, such as Arizona, California, Colorado, Hawaii and Utah. Generally, the programs have been upheld in their current form, though some were subject to minor modification and others, including Arizona, California and Hawaii, are undergoing additional regulatory review. In California, for example, the current net metering rules, as applied to the state’s three large investor-owned utilities (San Diego Gas and Electric Company, Southern California Edison Company and Pacific Gas and Electric Company), would generally be grandfathered for a period of 20 years, but only for systems installed prior to the earlier of July 1, 2017 or the date the applicable utility reaches its statutory net metering cap. This net metering cap is measured based on the nameplate capacity of net metered systems within the applicable utility’s service territory. Currently, the net metering caps for the three large investor-owned utilities are: 607 megawatts for San Diego Gas and Electric Company; 2,240 megawatts for Southern California Edison Company; and 2,409 megawatts for Pacific Gas and Electric Company. Once the net metering cap is reached for one of the three investor-owned utilities, customers of that utility seeking to net meter will be required to take service under the new net metering tariff. As reflected in their most recent reports required by statute, these investor-owned utilities have approximately 37%, 55% and 42% of capacity remaining under their respective net metering caps. The statute providing the current caps also provides that, once the new net metering rules are effective, there will be no net metering caps applied to these utilities.
If net metering caps in certain jurisdictions are reached while they are still in effect, if the value of the credit that customers receive for net metering is significantly reduced, if utility rate structures are altered, or if fees are imposed on net metering customers, future customers may be unable to recognize the same level of cost savings associated with net metering that current customers enjoy. The absence of favorable net metering policies or of net metering entirely, or the imposition of new charges that only or disproportionately impact customers that use net metering would significantly limit customer demand for our solar energy systems and the electricity they generate and could adversely impact our business, results of operations and future growth.
Technical and regulatory limitations may significantly reduce our ability to sell electricity from our solar energy systems in certain markets.
Technical and regulatory limits may curb our growth in certain key markets. For example, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, in promulgating the first form small generator interconnection procedures, recommended limiting customer-sited intermittent generation resources, such as our solar energy systems, to a certain percentage of peak load on a given electrical feeder circuit. Similar limits have been adopted by many states as a de facto standard and could constrain our ability to market to customers in certain geographic areas where the concentration of solar installations exceeds this limit. For example, Hawaiian electric utilities have adopted certain policies that limit distributed electricity generation in parts of their service territories. While these limits have constrained our growth in Hawaii, legislative and regulatory developments in Hawaii have generally allowed distributed electricity generation penetration beyond the electric utility imposed limitations. Future revisions, however, could result in limitations on deployment of solar energy systems in Hawaii, which in 2014, accounted for approximately 4% of our total installations, and 2% of our fourth quarter installations, and such limitations would negatively impact our business. Furthermore, in certain areas, we benefit from policies that allow for expedited or simplified procedures related to connecting solar energy systems to the power grid. If such procedures are changed or cease to be available, our ability to sell the electricity generated by solar energy systems we install may be adversely impacted. As adoption of solar distributed generation rises along with the commercial operation of utility scale solar generation in key markets such as California, the amount of solar energy being fed into the power grid will surpass the amount planned for relative to the amount of aggregate demand. Some traditional utilities claim that in less than five years, solar generation resources may reach a level capable of producing an over-generation situation, which may require some solar generation resources to be curtailed to maintain operation of the grid. While the prospect of such curtailment is somewhat speculative, the adverse effects of such curtailment without compensation could adversely impact our business, results of operations and future growth.
12
We are not currently regulated as an electric utility under applicable law, but we may be subject to regulation as an electric utility in the future.
We are not regulated as an electric utility in any of the markets in which we currently operate. As a result, we are not subject to the various federal, state and local standards, restrictions and regulatory requirements applicable to traditional utilities. Any federal, state, or local regulations that cause us to be treated as an electric utility, or to otherwise be subject to a similar regulatory regime of commission-approved operating tariffs, rate limitations, and related mandatory provisions, could place significant restrictions on our ability to operate our business and execute our business plan by prohibiting, restricting or otherwise regulating our sale of electricity. If we were subject to the same state or federal regulatory authorities as public electric utilities in the United States or if new regulatory bodies were established to oversee our business in the United States, then our operating costs would materially increase.
Our business depends in part on the regulatory treatment of third-party owned solar energy systems.
Retail sales of electricity by non-utilities such as us face regulatory hurdles in some states and jurisdictions, including states and jurisdictions that we intend to enter where the laws and regulatory policies have not historically embraced competition to the service provided by the incumbent, vertically integrated electric utility. Some of the principal challenges pertain to whether non-customer owned systems qualify for the same levels of rebates or other non-tax incentives available for customer-owned solar energy systems, whether third-party owned systems are eligible at all for these incentives and whether third-party owned systems are eligible for net metering and the associated significant cost savings. Furthermore, in some states and utility territories third parties are limited in the way that they may deliver solar to their customers. In jurisdictions such as Arizona, the District of Columbia, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, North Carolina and Utah and in Los Angeles, California, laws have been interpreted to prohibit the sale of electricity pursuant to our standard power purchase agreement, leading residential solar energy system providers to use leases in lieu of power purchase agreements. Changes in law, reductions in, eliminations of or additional application requirements for, these benefits could reduce demand for our systems, adversely impact our access to capital and could cause us to increase the price we charge our customers for energy.
If the Internal Revenue Service or the U.S. Treasury Department makes a determination that the fair market value of our solar energy systems is materially lower than what we have reported in our fund tax returns or cash grant applications, we may have to pay significant amounts to our investment funds, to our fund investors and/or the U.S. government. Such determinations could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and prospects.
We report in our fund tax returns and we and our fund investors claim the ITC based on the fair market value of our solar energy systems. While we are not aware of any audits or results of audits related to our appraisals or fair market value determinations of any of our investment funds by the Internal Revenue Service, or IRS, scrutiny with respect to fair market value determinations has increased industry-wide in recent years. If as part of an examination the IRS were to review the fair market value that we used to establish our basis for claiming ITCs and determine that the ITCs previously claimed should be reduced, we would owe certain of our investment funds or our fund investors an amount equal to 30% of the investor’s share of the difference between the fair market value used to establish our basis for claiming ITCs and the adjusted fair market value determined by the IRS, plus any costs and expenses associated with a challenge to that fair market value, plus a gross up to pay for additional taxes. We could also be subject to tax liabilities, including interest and penalties based on our share of claimed ITCs. To date, we have not been required to make such payments under any of our investment funds.
Solar energy systems that began construction or satisfied a safe harbor by incurring eligible project costs prior to the end of 2011 were eligible to receive a 30% federal cash grant paid by the U.S. Treasury Department under Section 1603 of the “American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009,” or the U.S. Treasury grant. Separate from the IRS fair market value determination for purposes of ITCs, the U.S. Treasury Department has issued subpoenas related to its cash grant program and reviewed the fair market value determinations of a number of other significant participants in residential solar investment funds. Although we were not a target of this investigation, after discussions with the U.S. Treasury Department in early 2013, we accepted approximately $2.5 million less in cash grant payments than we had originally anticipated, a reduction of approximately 12%, which reduction affected a single investment fund. Although we were not obligated to make any payments to the investor in such fund, this resulted in a reduction of the fund investor’s overall investment by approximately $1.0 million. We had no other existing cash grant investment funds as of December 31, 2014, but if we were to enter into such funds in the future we may be required to engage in further discussions with, or otherwise be subject to investigation by, the U.S. Treasury Department in relation to applications for cash grants made by such funds.
13
Our ability to provide solar energy systems to customers on an economically viable basis depends on our ability to finance these systems with fund investors who require particular tax and other benefits.
Substantially all of our solar energy systems installed to date have been eligible for ITCs or U.S. Treasury grants, as well as accelerated depreciation benefits. We have relied on, and will continue to rely on, financing structures that monetize a substantial portion of those benefits and provide financing for our solar energy systems. If, for any reason, we were unable to continue to monetize those benefits through these arrangements, we may be unable to provide solar energy systems for new customers and maintain solar energy systems for new and existing customers on an economically viable basis.
The availability of this tax-advantaged financing depends upon many factors, including:
|
· |
our ability to compete with other renewable energy companies for the limited number of potential investment fund investors, each of which has limited funds and limited appetite for the tax benefits associated with these financings; |
|
· |
the state of financial and credit markets; |
|
· |
changes in the legal or tax risks associated with these financings; and |
|
· |
non-renewal of these incentives or decreases in the associated benefits. |
Solar energy system owners are currently allowed to claim the ITC that is equal to 30% of the system’s eligible tax basis, which is generally the fair market value of the system. By statute, the ITC is scheduled to decrease to 10% on January 1, 2017. Moreover, potential fund investors must remain satisfied that the structures we offer qualify for the tax benefits associated with solar energy systems available to these investors, which depends both on the investors’ assessment of tax law and the absence of any unfavorable interpretations of that law. Changes in existing law and interpretations by the IRS and the courts could reduce the willingness of fund investors to invest in funds associated with these solar energy system investments. We cannot assure you that this type of financing will be available to us. Alternatively, new investment fund structures or other financing mechanisms may become available, and if we are unable to take advantage of these fund structures and financing mechanisms it may place us at a competitive disadvantage. If, for any reason, we are unable to finance solar energy systems through tax-advantaged structures or if we are unable to realize or monetize depreciation benefits, or if we are otherwise unable to structure investment funds in ways that are both attractive to investors and allow us to provide desirable pricing to customers, we may no longer be able to provide solar energy systems to new customers on an economically viable basis. This would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Rising interest rates could adversely impact our business.
Changes in interest rates could have an adverse impact on our business by increasing our cost of capital. For example, rising interest rates would increase our cost of capital and may negatively impact our ability to secure financing on favorable terms needed to build our solar energy systems.
The majority of our cash flows to date have been from customer contracts that have been partially monetized under various investment fund structures. One of the components of this monetization is the present value of the payment streams from the customers who enter into these contracts. If the rate of return required by the fund investor rises as a result of a rise in interest rates, the present value of the customer payment stream and the total value that we are able to derive from monetizing the payment stream will each be reduced. Interest rates are at historically low levels, partially as a result of intervention by the U.S. Federal Reserve. The Federal Reserve has taken actions to taper off this intervention, and should these actions continue, it is likely that interest rates will rise in 2015, which would cause our costs of capital to increase and could impede our ability to secure financing. Rising interest rates could harm our business and financial condition.
Our investment funds contain arrangements which provide for priority distributions to fund investors until they receive their targeted rates of return. In addition, under the terms of certain of our investment funds, we may be required to make payments to the fund investors if certain tax benefits that are allocated to such fund investors are not realized as expected. Our financial condition may be adversely impacted if a fund is required to make these priority distributions for a longer period than anticipated to achieve the fund investors’ targeted rates of return or if we are required to make any tax-related payments.
Our fund investors expect returns partially in the form of cash and, to enable such returns, our investment funds contain terms that contractually require the funds to make priority distributions to the fund investor, to the extent cash is available, until it achieves its targeted rate of return. The amounts of potential future distributions under these arrangements depends on the amounts and timing of receipt of cash flows into the investment fund, almost all of which is generated from customer payments related to solar energy systems that have been previously purchased (or leased, as applicable) by such fund. If such cash flows are lower than expected, the priority distributions to the investor may continue for longer than initially anticipated. Additionally, certain of our investment funds require that, under certain circumstances, we forego distributions from the fund that we are otherwise contractually entitled to so that such distributions can be redirected to the fund investor until it achieves the targeted return.
14
Our fund investors also expect returns partially in the form of tax benefits and, to enable such returns, our investment funds contain terms that contractually require us to make payments to the funds that are then used to make payments to the fund investor in certain circumstances so that the fund investor receives value equivalent to the tax benefits it expected to receive when entering into the transaction. The amounts of potential tax payments under these arrangements depend on the tax benefits that accrue to such investors from the funds’ activities.
Due to uncertainties associated with estimating the timing and amounts of these cash distributions and allocations of tax benefits to such investors, we cannot determine the potential maximum future impact on our cash flows or payments that we could have to make under these arrangements. We may agree to similar terms in the future if market conditions require it. Any significant payments that we may be required to make or distributions to us that are reduced or diverted as a result of these arrangements could adversely affect our financial condition.
We may incur substantially more debt or take other actions that could restrict our ability to pursue our business strategies.
In September 2014, we entered into an aggregation credit facility, which was subsequently amended in February 2015, pursuant to which we may borrow up to an aggregate of $375.0 million and, upon the satisfaction of certain conditions and the approval of the lenders, up to an aggregate of $175.0 million in additional borrowings. In addition, in March 2015, we entered into a revolving credit facility pursuant to which we may borrow up to an aggregate of $131.0 million and, upon the satisfaction of certain conditions and the approval of the lenders, we may increase the aggregate amount of the revolving credit facility to $150.0 million. These credit facilities restrict our ability to dispose of assets, incur indebtedness, incur liens, pay dividends or make other distributions to holders of our capital stock, repurchase our capital stock, make specified investments or engage in transactions with our affiliates. We and our subsidiaries may incur substantial additional debt in the future and any debt instrument we enter into in the future may contain similar restrictions. In addition, certain of our affiliates, including our sister company Vivint Inc., or Vivint, are and may in the future be restricted in engaging in transactions with us pursuant to the terms of the instruments governing indebtedness incurred by them. These restrictions could inhibit our ability to pursue our business strategies. Furthermore, if we default on one of our debt instruments, and such event of default is not cured or waived, the lenders could terminate commitments to lend and cause all amounts outstanding with respect to the debt to be due and payable immediately, which in turn could result in cross acceleration under other debt instruments. Our assets and cash flow may not be sufficient to fully repay borrowings under all of our outstanding debt instruments if some or all of these instruments are accelerated upon a default.
Furthermore, there is no assurance that we will be able to enter into new debt instruments on acceptable terms. If we are unable to satisfy financial covenants and other terms under existing or new instruments or obtain waivers or forbearance from our lenders or if we are unable to obtain refinancing or new financings for our working capital, equipment and other needs on acceptable terms if and when needed, our business would be adversely affected.
Our business is concentrated in certain markets, putting us at risk of region specific disruptions.
As of December 31, 2014, approximately 48% and 10% of our cumulative installations were in California and Hawaii, and 22 of our 39 offices were located in these states. In addition, we expect future growth to occur in California, which could further concentrate our customer base and operational infrastructure. Accordingly, our business and results of operations are particularly susceptible to adverse economic, regulatory, political, weather and other conditions in such markets and in other markets that may become similarly concentrated.
It is difficult to evaluate our business and prospects due to our limited operating history.
Since our formation in 2011, we have focused our efforts exclusively on the sales, financing, engineering, installation, maintenance and monitoring of solar energy systems for residential customers. We may be unsuccessful in significantly broadening our customer base through installation of solar energy systems within our current markets or in new markets we may enter. Our limited operating history, combined with the rapidly evolving and competitive nature of our industry, may not provide an adequate basis for you to evaluate our operating and financial results and business prospects. In addition, we have limited insight into emerging trends that may adversely impact our business, prospects and operating results.
Additionally, due to our limited operating history, we do not have empirical evidence of the effect of our systems on the resale value of our customers’ houses. Due to the length of our customer contracts, the system deployed on a customer’s roof may be outdated prior to the expiration of the term of the customer contract reducing the likelihood of renewal of our contracts at the end of the 20-year term, and possibly increasing the occurrence of defaults. This could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flow. As a result, our limited operating history may impair our ability to accurately forecast our future performance and to invest accordingly.
15
We have identified a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting relating to inadequate financial statement preparation and review procedures in connection with the preparation of our consolidated financial statements that resulted in the restatement of certain of our financial statements, and we may identify material weaknesses in the future.
In connection with the preparation, audits and interim reviews of our consolidated financial statements, we and our independent registered public accounting firm identified a material weakness in internal control over financial reporting. This material weakness was further evidenced by errors discovered during the preparation and review of our consolidated financial statements as of and for the six months ended June 30, 2014 which resulted in the restatement of our consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2013 and as of and for the three months ended March 31, 2014. These errors included, but were not limited to: (1) incorrectly accounting for income taxes, (2) incorrect inputs in the hypothetical liquidation at book value, or HLBV, method of attributing net income or loss to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests and (3) the incorrect classification of paid-in-kind interest in our statement of cash flows.
Under standards established by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board, a material weakness is a deficiency or combination of deficiencies in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of our annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected and corrected on a timely basis. This material weakness resulted from several control deficiencies.
Specifically and in addition to the errors that resulted in the restatement discussed above, we and our independent registered public accounting firm identified a number of material errors and other audit adjustments and determined that we did not design and implement sufficient controls and processes and did not have a sufficient number of qualified accounting and finance personnel. Additionally, the nature of our investment funds increases the complexity of our accounting for the allocation of net income (loss) between our stockholders and non-controlling interests under the HLBV method and the calculation of our tax provision. As we enter into additional investment funds, which may have contractual provisions different from those of our existing funds, the calculation under the HLBV method and the calculation of our tax provision could become increasingly complicated. This additional complexity could increase the chance that we experience additional errors in the future, particularly because we have a material weakness in internal controls. In addition, our need to devote our resources to addressing this complexity could delay or prolong our remediation efforts and thereby prolong the existence of the material weakness. As a result, we and our independent registered public accounting firm determined that we did not have adequate procedures and controls and adequate personnel to ensure that accurate financial statements could be prepared on a timely basis.
To remediate this material weakness and to prevent future material weaknesses, we believe that we must continue to add qualified accounting, finance and tax personnel, formalize and implement written policies and procedures for the review of account analyses, tax provisions, reconciliations and journal entries, and implement and improve systems to automate certain financial reporting processes and to improve efficiency and accuracy.
We have begun taking numerous steps and plan to take additional steps to remediate the underlying causes of the material weakness. The actions that we are taking are subject to ongoing senior management review as well as audit committee oversight. We cannot estimate how long it will take to remediate the material weakness, and our initiatives may not prove to be successful in remediating this material weakness.
If in future periods we determine that this material weakness has not been remediated or we identify other material weaknesses in internal control over financial reporting, we will be unable to assert that our internal control over financial reporting is effective, which could result in the loss of investor confidence. In addition, to date, the audit of our consolidated financial statements by our independent registered public accounting firm has included a consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis of designing their audit procedures, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting. When we cease to be an emerging growth company we will be required to have our independent registered accounting firm perform such an evaluation, and additional material weaknesses or other control deficiencies may be identified.
If we are unable to successfully remediate our current material weakness or avoid or remediate any future material weakness, our stock price may be adversely affected and we may be unable to maintain compliance with applicable stock exchange listing requirements.
16
We have incurred operating losses and may be unable to achieve or sustain profitability in the future.
We have incurred operating losses since our inception. We incurred net losses of $165.9 million and $56.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. We expect to continue to incur net losses from operations as we increase our spending to finance the expansion of our operations, expand our installation, engineering, administrative, sales and marketing staffs, and implement internal systems and infrastructure to support our growth. In addition, as a public company, we will incur significant additional legal, accounting and other expenses that we did not incur as a private company. We do not know whether our revenue will grow rapidly enough to absorb these costs, and our limited operating history makes it difficult to assess the extent of these expenses or their impact on our operating results. Our ability to achieve profitability depends on a number of factors, including:
|
· |
growing our customer base; |
|
· |
finding investors willing to invest in our investment funds; |
|
· |
maintaining and further lowering our cost of capital; |
|
· |
reducing the cost of components for our solar energy systems; and |
|
· |
reducing our operating costs by optimizing our sales, design and installation processes and supply chain logistics. |
Even if we do achieve profitability, we may be unable to sustain or increase our profitability in the future.
Substantially all of our business is conducted primarily using one channel, direct-selling.
While we are in the process of evaluating different distribution channels, currently substantially all of our business is conducted using direct-selling. We compete against companies that sell solar energy systems to customers through a number of distribution channels, including homebuilders, home improvement stores, large construction, electrical and roofing companies and other third parties and companies that access customers through relationships with third parties in addition to other direct-selling companies. This single distribution channel may place us at a disadvantage with consumers who prefer to purchase products through these other distribution channels. Additionally, we are vulnerable to changes in laws related to direct marketing as regulations have limited unsolicited residential sales calls and may impose additional restrictions. If additional laws affecting direct marketing are passed in the markets in which we operate, it would take time to train our sales force to comply with such laws, and we may be exposed to fines or other penalties for violations of such laws. If we fail to compete effectively through our direct-selling efforts or are not successful in executing our strategy to sell our solar energy systems through other channels, our financial condition, results of operations and growth prospects will be adversely affected.
We are highly dependent on our ability to attract, train and retain an effective sales force.
The success of our direct-selling channel efforts depends upon the recruitment, retention and motivation of a large number of sales personnel to compensate for a high turnover rate among sales personnel, which is a common characteristic of a direct-selling business. In order to grow our business, we need to recruit, train and retain sales personnel on a continuing basis. Historically, we have recruited a large portion of our sales personnel from our sister company, Vivint, particularly in California, where a significant portion of our business is concentrated. Pursuant to a non-competition agreement entered into in connection with our initial public offering, we and Vivint have agreed not to solicit for employment any of the other’s employees who primarily manage sales, installation or servicing of the other’s products and services. The commitment not to solicit those employees lasts for 180 days after the employee finishes employment with us or Vivint. In the future, we will need to recruit greater numbers of our sales personnel from other sources and we may be unable to successfully do so. Sales personnel are attracted to direct-selling by competitive earnings opportunities and so direct-sellers typically compete for sales personnel by providing a more competitive earnings opportunity than that offered by the competition. Competitors devote substantial effort to determining the effectiveness of such incentives so that they can invest in incentives that are the most cost effective or produce the best return on incentive. For example, we have historically compensated our sales personnel on a commission basis, based on the size of the solar energy systems they sell. Some sales personnel may prefer a compensation structure that also includes a salary and equity incentive component. We may need to adjust our compensation model to include such components, and these adjustments could adversely impact our operating results and financial performance.
17
In addition to our sales compensation model, our ability to recruit, train and retain effective sales personnel could be harmed by additional factors, including:
|
· |
any adverse publicity regarding us, our solar energy systems, our distribution channel or our industry; |
|
· |
lack of interest in, or the technical failure of, our solar energy systems; |
|
· |
lack of a compelling product or income opportunity that generates interest for potential new sales personnel, or perception that other product or income opportunities are more attractive; |
|
· |
any negative public perception of our sales personnel and direct-selling businesses in general; |
|
· |
any regulatory actions or charges against us or others in our industry; |
|
· |
general economic and business conditions; and |
|
· |
potential saturation or maturity levels in a given market which could negatively impact our ability to attract and retain sales personnel in such market. |
We are subject to significant competition for the recruitment of sales personnel from other direct-selling companies and from other companies that sell solar energy systems in particular. Furthermore, the regional and district managers of our sales personnel are instrumental in recruiting, retaining and motivating our sales personnel. From time to time, when managers have elected to leave us and join other companies, the sales personnel they supervise have left with them. We expect to experience similar attrition in our sales personnel in the future which may impact our results of operations and growth. The impact of such attrition could be particularly acute in those jurisdictions, such as California, where contractual non-competition agreements for service providers are not enforceable or subject to significant limitations.
It is therefore continually necessary to innovate and enhance our direct-selling and service model as well as to recruit and retain new sales personnel. If we are unable to do so, our business will be adversely affected.
A failure to hire and retain a sufficient number of employees in key functions would constrain our growth and our ability to timely complete our customers’ projects.
To support our growth, we need to hire, train, deploy, manage and retain a substantial number of skilled installers and electricians in the relevant markets. Competition for qualified personnel in our industry is increasing, particularly for skilled electricians and other personnel involved in the installation of solar energy systems. We also compete with the homebuilding and construction industries for skilled labor. As these industries seek to hire additional workers, our cost of labor may increase. Historically, we compensated our installers and electricians based on the number of solar energy systems they install. Companies with whom we compete to hire installers may offer an hourly rate or equity incentive component, which certain installers may prefer. We periodically assess the compensation policies for our service providers, including our installers and electricians, and expect to decide to compensate them on the basis of an hourly rate and productivity incentives. Our installers and electricians may not react well to any such change which in turn could adversely affect retention, motivation and productivity.
Furthermore, trained installers are typically able to more efficiently install solar energy systems. Shortages of skilled labor could significantly delay installations or otherwise increase our costs. While we do not currently have any unionized employees, we have expanded, and may continue to expand, into areas such as the Northeast, where labor unions are more prevalent. The unionization of our labor force could also increase our labor costs. In addition, a significant portion of our business has been concentrated in states such as California, where market conditions are particularly favorable to distributed solar energy generation. We have experienced and may in the future experience greater than expected turnover in our installers in those jurisdictions which would adversely impact the geographic mix of new solar energy system installations.
Because we are a licensed electrical contractor in every jurisdiction in which we operate, we are required to employ licensed electricians. As we expand into new markets, we are required to hire and/or contract with seasoned licensed electricians in order for us to qualify for the requisite state and local licenses. Because of the high demand for these seasoned licensed electricians, these individuals currently or in the future may demand greater compensation. In addition, our inability to attract and retain these qualifying electricians may adversely impact our ability to continue operations in current markets or expand into new areas.
If we cannot meet our hiring, retention and efficiency goals, we may be unable to complete our customers’ projects on time, in an acceptable manner or at all. Any significant failures in this regard would materially impair our growth, reputation, business and financial results. If we are required to pay higher compensation than we anticipate, these greater expenses may also adversely impact our financial results and the growth of our business.
18
Historically, we have only provided our offerings to residential customers, which could put us at a disadvantage relative to companies who also compete in other markets.
We have historically only provided our offerings to residential customers. We compete with companies who sell solar energy systems in the commercial, industrial and government markets, in addition to the residential market. While we intend to enter the commercial and industrial market, and while we believe that in the future we may have opportunities to expand our operations into other markets, there are no assurances that our design and installation systems will work for non-residential customers or that we will be able to compete successfully with companies with historical presences in such markets. Additionally, there is intense competition in the residential solar energy market in the markets in which we operate. As new entrants continue to enter into these markets, we may be unable to gain or maintain market share and we may be unable to compete with companies that earn revenue in both the residential market and non-residential markets.
We face competition from traditional regulated electric utilities, from less-regulated third party energy service providers and from new renewable energy companies.
The solar energy and renewable energy industries are both highly competitive and continually evolving as participants strive to distinguish themselves within their markets and compete with large traditional utilities. We believe that our primary competitors are the traditional utilities that supply electricity to our potential customers. Traditional utilities generally have substantially greater financial, technical, operational and other resources than we do. As a result, these competitors may be able to devote more resources to the research, development, promotion and sale of their products or respond more quickly to evolving industry standards and changes in market conditions than we can. Traditional utilities could also offer other value-added products or services that could help them to compete with us even if the cost of electricity they offer is higher than ours. In addition, a majority of utilities’ sources of electricity is non-solar, which may allow utilities to sell electricity more cheaply than electricity generated by our solar energy systems.
We also compete with companies that are not regulated like traditional utilities but that have access to the traditional utility electricity transmission and distribution infrastructure pursuant to state and local pro-competitive and consumer choice policies. These energy service companies are able to offer customers electricity supply-only solutions that are competitive with our solar energy system options on both price and usage of renewable energy technology while avoiding the long-term agreements and physical installations that our current fund-financed business model requires. This may limit our ability to attract new customers, particularly those who wish to avoid long-term contracts or have an aesthetic or other objection to putting solar panels on their roofs.
We also compete with solar companies with business models that are similar to ours. In addition, we compete with solar companies in the downstream value chain of solar energy. For example, we face competition from purely finance driven organizations that acquire customers and then subcontract out the installation of solar energy systems, from installation businesses that seek financing from external parties, from large construction companies and utilities, and increasingly from sophisticated electrical and roofing companies. Some of these competitors specialize in the residential solar energy market, and some may provide energy at lower costs than we do. Some of our competitors offer or may offer alternative sales strategies to investment fund strategy, such as direct outright sales of and consumer loan products for solar energy systems. Further, some of our competitors are integrating vertically in order to ensure supply and to control costs. Many of our competitors also have significant brand name recognition and have extensive knowledge of our target markets. For us to remain competitive, we must distinguish ourselves from our competitors by offering an integrated approach that successfully competes with each level of products and services offered by our competitors at various points in the value chain. If our competitors develop an integrated approach similar to ours including sales, financing, engineering, manufacturing, installation, maintenance and monitoring services, this will reduce our marketplace differentiation.
As the solar industry grows and evolves, we will also face new competitors who are not currently in the market. Our industry is characterized by low technological barriers to entry and well-capitalized companies could choose to enter the market and compete with us. Our failure to adapt to changing market conditions and to compete successfully with existing or new competitors will limit our growth and will have a material adverse effect on our business and prospects.
Developments in alternative technologies or improvements in distributed solar energy generation may materially adversely affect demand for our offerings.
Significant developments in alternative technologies, such as advances in other forms of distributed solar power generation, storage solutions such as batteries, the widespread use or adoption of fuel cells for residential or commercial properties or improvements in other forms of centralized power production may materially and adversely affect our business and prospects in ways we do not currently anticipate. Any failure by us to adopt new or enhanced technologies or processes, or to react to changes in existing technologies, could materially delay deployment of our solar energy systems, which could result in product obsolescence, the loss of competitiveness of our systems, decreased revenue and a loss of market share to competitors.
19
We depend on a limited number of suppliers of solar energy system components and technologies to adequately meet anticipated demand for our solar energy systems. Due to the limited number of suppliers in our industry, the acquisition of any of these suppliers by a competitor or any shortage, delay, price change, imposition of tariffs or duties or other limitation in our ability to obtain components or technologies we use could result in sales and installation delays, cancellations and loss of market share.
We purchase solar panels, inverters and other system components from a limited number of suppliers, making us susceptible to quality issues, shortages and price changes. In 2014, Trina Solar Limited and Yingli Green Energy Americas, Inc. accounted for substantially all of our solar photovoltaic module purchases and Enphase Energy, Inc. accounted for substantially all of our inverter purchases. If we fail to develop, maintain and expand our relationships with these or other suppliers, our ability to adequately meet anticipated demand for our solar energy systems may be adversely affected, or we may only be able to offer our systems at higher costs or after delays. If one or more of the suppliers that we rely upon to meet anticipated demand ceases or reduces production due to its financial condition, acquisition by a competitor or otherwise, is unable to increase production as industry demand increases or is otherwise unable to allocate sufficient production to us, it may be difficult to quickly identify alternative suppliers or to qualify alternative products on commercially reasonable terms, and our ability to satisfy this demand may be adversely affected. There are a limited number of suppliers of solar energy system components and technologies. While we believe there are other sources of supply for these products available, transitioning to a new supplier may result in additional costs and delays in acquiring our solar products and deploying our systems. These issues could harm our business or financial performance.
In addition, the acquisition of a component supplier or technology provider by one of our competitors could limit our access to such components or technologies and require significant redesigns of our solar energy systems or installation procedures and have a material adverse effect on our business. For example, one of our competitors acquired Zep Solar, Inc., or Zep, in 2013. Zep sold us virtually all of the racking systems used in our hardware in 2013, and the resulting limitation in our ability to acquire Zep products required us to redesign certain aspects of our systems to accommodate alternative racking hardware. In addition, some of our investment funds require the use of designated equipment, and our inability to obtain any such required equipment could limit our ability to finance solar energy systems that we intend to place in those funds.
There have also been periods of industry-wide shortages of key components, including solar panels, in times of rapid industry growth. The manufacturing infrastructure for some of these components has a long lead-time, requires significant capital investment and relies on the continued availability of key commodity materials, potentially resulting in an inability to meet demand for these components. The solar industry is currently experiencing rapid growth and, as a result, shortages of key components, including solar panels, may be more likely to occur, which in turn may result in price increases for such components. Even if industry-wide shortages do not occur, suppliers may decide to allocate key components with high demand or insufficient production capacity to more profitable customers, customers with long-term supply agreements or customers other than us and our supply of such components may be reduced as a result.
Historically, we purchased the components for our solar energy systems on an as-needed basis and did not operate under long-term supply agreements. Recently, we have begun to enter into multi-year agreements with our major suppliers. All of these purchases under these purchase orders are denominated in U.S. dollars. Since our revenue is also generated in U.S. dollars we are mostly insulated from currency fluctuations. However, since our suppliers often incur a significant amount of their costs by purchasing raw materials and generating operating expenses in foreign currencies, if the value of the U.S. dollar depreciates significantly or for a prolonged period of time against these other currencies this may cause our suppliers to raise the prices they charge us, which could harm our financial results. Since we purchase almost all of the solar photovoltaic modules we use from China, we are particularly exposed to exchange rate risk from increases in the value of the Chinese Renminbi. In addition, the U.S. government has imposed tariffs on solar cells produced and assembled in China and Taiwan. These tariffs, and any tariffs or duties, or shortages, delays, price changes or other limitation in our ability to obtain components or technologies we use could limit our growth, cause cancellations or adversely affect our profitability, and result in loss of market share and damage to our brand.
Our operating results may fluctuate from quarter to quarter and year to year, which could make our future performance difficult to predict and could cause our operating results for a particular period to fall below expectations, resulting in a severe decline in the price of our common stock.
Our quarterly and annual operating results are difficult to predict and may fluctuate significantly in the future. We have experienced seasonal and quarterly fluctuations in the past. However, given that we are an early-stage company operating in a rapidly growing industry, the true extent of these fluctuations may have been masked by our recent growth rates and thus may not be readily apparent from our historical operating results and may be difficult to predict. For example, the amount of revenue we recognize in a given period from our customer contracts is dependent in part on the amount of energy generated by solar energy systems under such contracts. As a result, revenue derived from power purchase agreements is impacted by seasonally shorter daylight hours in winter months. In addition, our ability to install solar energy systems is impacted by weather, as for example during the winter months in the Northeastern United States. Such delays can impact the timing of when we can install and begin to generate revenue from solar energy systems. As such, our past quarterly operating results may not be good indicators of future performance.
20
In addition to the other risks described in this “Risk Factors” section, the following factors could cause our operating results to fluctuate:
|
· |
the expiration or initiation of any rebates or incentives; |
|
· |
significant fluctuations in customer demand for our offerings; |
|
· |
our ability to complete installations in a timely manner; |
|
· |
the availability and costs of suitable financing; |
|
· |
the amount and timing of sales of SRECs; |
|
· |
our ability to continue to expand our operations, and the amount and timing of expenditures related to this expansion; |
|
· |
actual or anticipated changes in our growth rate relative to our competitors; |
|
· |
announcements by us or our competitors of significant acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures or capital-raising activities or commitments; |
|
· |
changes in our pricing policies or terms or those of our competitors, including traditional utilities; and |
|
· |
actual or anticipated developments in our competitors’ businesses or the competitive landscape. |
For these or other reasons, the results of any prior quarterly or annual periods should not be relied upon as indications of our future performance. In addition, our actual revenue, key operating metrics and other operating results in future periods may fall short of the expectations of investors and financial analysts, which could have an adverse effect on the trading price of our common stock.
Our business has benefited from the declining cost of solar panels, and our financial results may be harmed now that the cost of solar panels has stabilized and could increase in the future.
The declining cost of solar panels and the raw materials necessary to manufacture them has been a key driver in the price we charge for electricity and customer adoption of solar energy. According to industry experts, solar panel and raw material prices are not expected to continue to decline at the same rate as they have over the past several years. In addition, growth in the solar industry and the resulting increase in demand for solar panels and the raw materials necessary to manufacture them may also put upward pressure on prices. The resulting prices could slow our growth and cause our financial results to suffer. In addition, in the past we have purchased virtually all of the solar panels used in our solar energy systems from manufacturers based in China which have benefited from favorable governmental policies by the Chinese government. If this governmental support were to decrease or be eliminated, our ability to purchase these products on competitive terms or to access specialized technologies from China could be restricted.
Even if this support were to continue, the U.S. government could impose additional tariffs on solar cells manufactured in China. In 2012, the U.S. government imposed anti-dumping tariffs on Chinese crystalline silicon photovoltaic cells on a manufacturer specific basis with rates ranging from approximately 18.3% to 250.0%, and applicable countervailing duty rates ranging from approximately 14.8% to 16.0%. In 2014, the U.S. government broadened its investigation of Chinese pricing practices in this area to include solar panels and modules produced in China containing solar cells manufactured in other countries. In December 2014, the U.S. government announced antidumping duties ranging from 26.7% to 165.04% on imports of the majority of solar panels made in China, and rates ranging from 11.5% to 27.6% on imported solar cells made in Taiwan. Countervailing duties ranging from 27.6% to 49.8% for Chinese modules were also announced. In January 2015, the antidumping duties were confirmed by a determination of the U.S. International Trade Commission that material harm to the U.S. solar industry had occurred. These combined tariffs would make such solar cells less competitively priced in the United States, and the Chinese and Taiwanese manufacturers may choose to limit the amount of solar equipment they sell into the United States. As a result, it may be easier for solar cell manufacturers located outside of China or Taiwan to increase the prices of the solar cells they sell into the United States. If we are required to pay higher prices, accept less favorable terms or purchase solar panels or other system components from alternative, higher-priced sources, our financial results will be adversely affected.
21
The residual value of our solar energy systems at the end of the associated term of the lease or power purchase agreement may be lower than projected today and adversely affect our financial performance and valuation.
We intend to amortize the costs of our solar energy systems over a 30 year estimated useful life, which exceeds the period of the component warranties and the corresponding payment streams from our contracts with our customers. If we incur repair and maintenance costs on these systems after the warranties have expired, and if they then fail or malfunction, we will be liable for the expense of repairing these systems without a chance of recovery from our suppliers. We are also contractually obligated to remove, store and reinstall the solar energy systems for a nominal fee if customers need to replace or repair their roofs. The nominal fee is market standard; however, it may not cover our costs to remove, store and reinstall the solar energy systems. In addition, we typically bear the cost of removing the solar energy systems at the end of the term of the customer contract if the customer does not renew his or her contract at the end of its term. Furthermore, it is difficult to predict how future environmental regulations may affect the costs associated with the removal, disposal or recycling of our solar energy systems. If the residual value of the systems is less than we expect at the end of the customer contract, after giving effect to any associated removal and redeployment costs, we may be required to accelerate all or some of the remaining unamortized costs. This could materially impair our future operating results and estimated retained value.
We act as the licensed general contractor for our customers and are subject to risks associated with construction, cost overruns, delays, regulatory compliance and other contingencies, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
We are a licensed contractor in every market we service and we are responsible for every customer installation. We are the general contractor, electrician, construction manager and installer for all our solar energy systems. We may be liable to customers for any damage we cause to their home, belongings or property during the installation of our systems. For example, we penetrate our customers’ roofs during the installation process and may incur liability for the failure to adequately weatherproof such penetrations following the completion of installation of solar energy systems. In addition, because the solar energy systems we deploy are high-voltage energy systems, we may incur liability for the failure to comply with electrical standards and manufacturer recommendations. Furthermore, prior to obtaining permission to operate our solar energy systems, the systems must pass various inspections. Any delay in passing, or inability to pass, such inspections, would adversely affect our results of operations. Because our profit on a particular installation is based in part on assumptions as to the cost of such project, cost overruns, delays or other execution issues may cause us to not achieve our expected results or cover our costs for that project.
In addition, the installation of solar energy systems is subject to oversight and regulation in accordance with national, state and local laws and ordinances relating to building, fire and electrical codes, safety, environmental protection, utility interconnection and metering, and related matters. We also rely on certain of our employees to maintain professional licenses in many of the jurisdictions in which we operate, and our failure to employ properly licensed personnel could adversely affect our licensing status in those jurisdictions. It is difficult and costly to track the requirements of every authority having jurisdiction over our operations and our solar energy systems. Any new government regulations or utility policies pertaining to our systems, or changes to existing government regulations or utility policies pertaining to our systems, may result in significant additional expenses to us and our customers and, as a result, could cause a significant reduction in demand for our systems.
Compliance with occupational safety and health requirements and best practices can be costly, and noncompliance with such requirements may result in potentially significant monetary penalties, operational delays and adverse publicity.
The installation of solar energy systems requires our employees to work at heights with complicated and potentially dangerous electrical systems. The evaluation and modification of buildings as part of the installation process requires our employees to work in locations that may contain potentially dangerous levels of asbestos, lead, mold or other materials known or believed to be hazardous to human health. We also maintain a fleet of more than 470 trucks and other vehicles to support our installers and operations. There is substantial risk of serious injury or death if proper safety procedures are not followed. Our operations are subject to regulation under the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Act, or OSHA, the U.S. Department of Transportation, or DOT, and equivalent state laws. Changes to OSHA or DOT requirements, or stricter interpretation or enforcement of existing laws or regulations, could result in increased costs. If we fail to comply with applicable OSHA regulations, even if no work-related serious injury or death occurs, we may be subject to civil or criminal enforcement and be required to pay substantial penalties, incur significant capital expenditures or suspend or limit operations. Because our installation employees are compensated on a per project basis, they are incentivized to work more quickly than installers that are compensated on an hourly basis. While we have not experienced a high level of injuries to date, this incentive structure may result in higher injury rates than others in the industry and could accordingly expose us to increased liability. In the past, we have had workplace accidents and received citations from OSHA regulators for alleged safety violations, resulting in fines. Any such accidents, citations, violations, injuries or failure to comply with industry best practices may subject us to adverse publicity, damage our reputation and competitive position and adversely affect our business.
22
Problems with product quality or performance may cause us to incur expenses, may lower the residual value of our solar energy systems and may damage our market reputation and adversely affect our financial results.
We agree to maintain the solar energy systems installed on our customers’ homes during the length of the term of our customer contracts, which is typically 20 years. We are exposed to any liabilities arising from the systems’ failure to operate properly and are generally under an obligation to ensure that each system remains in good condition during the term of the agreement. As part of our operations and maintenance work, we provide a pass-through of the inverter and panel manufacturers’ warranty coverage to our customers, which generally range from 10 to 25 years. One or more of these third-party manufacturers could cease operations and no longer honor these warranties, leaving us to fulfill these potential obligations to our customers or to our fund investors without underlying warranty coverage. In most of our investment funds, the fund itself would bear this cost; however, in certain funds we would bear this cost with respect to such major equipment. Even if the investment fund bears the direct expense of such replacement equipment, we could suffer financial losses associated with a loss of production from the solar energy systems.
Beginning in 2014, we began structuring some customer contracts as solar energy system leases. To be competitive in the market and to comply with the requirements of jurisdictions where we offer leases, our solar energy system leases contain a performance guarantee in favor of the lessee. Leases with performance guarantees require us to refund money to the lessee if the solar energy system fails to generate a stated minimum amount of electricity in a 12-month period. We may also suffer financial losses associated with such refunds if significant performance guarantee payments are triggered.
Although we have not incurred material quality or performance expenses in the past, we may incur material expenses in the future. Our failure to accurately predict future liabilities could result in unexpected volatility in our financial condition. Because of the limited operating history of our solar energy systems, we have been required to make assumptions and apply judgments regarding a number of factors, including our anticipated rate of warranty claims, and the durability, performance and reliability of our solar energy systems. We have made these assumptions based on the historic performance of similar systems or on accelerated life cycle testing. Our assumptions could prove to be materially different from the actual performance of our systems, causing us to incur substantial expense to repair or replace defective solar energy systems in the future or to compensate customers for systems that do not meet their performance guarantees. Equipment defects, serial defects or operational deficiencies also would reduce our revenue from customer contracts because the customer payments under such agreements are dependent on system production or would require us to make refunds under performance guarantees. Any widespread product failures or operating deficiencies may damage our market reputation and adversely impact our financial results.
We are responsible for providing maintenance, repair and billing on solar energy systems that are owned or leased by our investment funds on a fixed fee basis, and our financial performance could be adversely affected if our cost of providing such services is higher than we project.
We typically provide a five-year workmanship warranty to our investment funds for every system we sell to them. We are also generally contractually obligated to cover the cost of maintenance, repair and billing on any solar energy systems that we sell or lease to our investment funds. We are subject to a maintenance services agreement under which we are required to operate and maintain the system, and perform customer billing services for a fixed fee that is calculated to cover our future expected maintenance and servicing costs of the solar energy systems in each investment fund over the term of the lease or power purchase agreement with the covered customers. If our solar energy systems require an above-average amount of repairs or if the cost of repairing systems were higher than our estimate, we would need to perform such repairs without additional compensation. If our solar energy systems, a majority of which are located in California and Hawaii, are damaged in the event of a natural disaster beyond our control, such as an earthquake, tsunami or hurricane, losses could be outside the scope of insurance policies or exceed insurance policy limits, and we could incur unforeseen costs that could harm our business and financial condition. We may also incur significant costs for taking other actions in preparation for, or in reaction to, such events. When required to do so under the terms of a particular investment fund, we purchase property and business interruption insurance with industry standard coverage and limits approved by the investor’s third-party insurance advisors to hedge against such risk, but such coverage may not cover our losses, and we have not acquired such coverage for all of our funds.
Product liability claims against us or accidents could result in adverse publicity and potentially significant monetary damages.
If one of our solar energy systems injured someone, we could be exposed to product liability claims. In addition, it is possible that our products could injure our customer or third parties, or that our products could cause property damage as a result of product malfunctions, defects, improper installation, fire or other causes. We rely on our general liability insurance to cover product liability claims. Any product liability claim we face could be expensive to defend and divert management’s attention. The successful assertion of product liability claims against us could result in potentially significant monetary damages, penalties or fines, subject us to adverse publicity, damage our reputation and competitive position and adversely affect sales of our systems and other products. In addition, product liability claims, injuries, defects or other problems experienced by other companies in the residential solar industry could lead to unfavorable market conditions to the industry as a whole, and may have an adverse effect on our ability to attract new customers, thus affecting our growth and financial performance.
23
Failure by our component suppliers to use ethical business practices and comply with applicable laws and regulations may adversely affect our business.
We do not control our suppliers or their business practices. Accordingly, we cannot guarantee that they follow ethical business practices such as fair wage practices and compliance with environmental, safety and other local laws. A lack of demonstrated compliance could lead us to seek alternative suppliers, which could increase our costs and result in delayed delivery of our products, product shortages or other disruptions of our operations. Violation of labor or other laws by our suppliers or the divergence of a supplier’s labor or other practices from those generally accepted as ethical in the United States or other markets in which we do business could also attract negative publicity for us and harm our business.
Damage to our brand and reputation, or change or loss of use of our brand, would harm our business and results of operations.
We depend significantly on our reputation for high-quality products, best-in-class customer service and the brand name “Vivint Solar” to attract new customers and grow our business. If we fail to continue to deliver our solar energy systems within the planned timelines, if our offerings do not perform as anticipated or if we damage any of our customers’ properties or delay or cancel projects, our brand and reputation could be significantly impaired. Future technical improvements may allow us to offer lower prices or offer new technology to new customers; however, technical limitations in our current solar energy systems may prevent us from offering such lower prices or new technology to our existing customers. The inability of our current customers to benefit from technological improvements could cause our existing customers to lower the value they perceive our existing products offer and impair our brand and reputation.
We have focused particular attention on growing our direct sales force, leading us in some instances to take on candidates who we later determined did not meet our standards. In addition, given our direct sales business model and the sheer number of interactions our sales and other personnel have with customers and potential customers, it is inevitable that some customers’ and potential customers’ interactions with our company will be perceived as less than satisfactory. This has led to instances of customer complaints, some of which have affected our digital footprint on rating websites such as that for Yelp and the Better Business Bureau. If we cannot manage our hiring and training processes to avoid or minimize to the extent possible, these issues, our reputation may be harmed and our ability to attract new customers would suffer.
Given our past relationship with our sister company Vivint and the similarity in our names, customers may associate us with any problems experienced with Vivint, such as complaints with the Better Business Bureau. Because we have no control over Vivint, we may not be able to take remedial action to cure any issues Vivint has with its customers, and our brand and reputation may be harmed if we are mistaken for the same company.
In addition, if we were to no longer use, lose the right to continue to use, or if others use, the “Vivint Solar” brand, we could lose recognition in the marketplace among customers, suppliers and partners, which could affect our growth and financial performance, and would require financial and other investment, and management attention in new branding, which may not be as successful.
Marketplace confidence in our liquidity and long-term business prospects is important for building and maintaining our business.
Our financial condition, operating results and business prospects may suffer materially if we are unable to establish and maintain confidence about our liquidity and business prospects among consumers and within our industry. Our solar energy systems require ongoing maintenance and support. If we were to reduce operations, even years from now, buyers of our systems from years earlier might have difficulty in having us repair or service our systems, which remain our responsibility under the terms of our customer contracts. As a result, consumers may be less likely to purchase our solar energy systems now if they are uncertain that our business will succeed or that our operations will continue for many years. Similarly, suppliers and other third parties will be less likely to invest time and resources in developing business relationships with us if they are not convinced that our business will succeed. Accordingly, in order to build and maintain our business, we must maintain confidence among customers, suppliers and other parties in our liquidity and long-term business prospects. We may not succeed in our efforts to build this confidence.
If we fail to manage our recent and future growth effectively, we may be unable to execute our business plan, maintain high levels of customer service or adequately address competitive challenges.
We have experienced significant growth in recent periods with the cumulative capacity of our solar energy systems growing from 72.8 megawatts as of December 31, 2013 to 228.2 megawatts as of December 31, 2014, and we intend to continue to expand our business significantly within existing markets and in a number of new locations in the future. This growth has placed, and any future growth may place, a significant strain on our management, operational and financial infrastructure. In particular, we will be required to expand, train and manage our growing employee base and scale and otherwise improve our IT infrastructure in tandem with that headcount growth. Our management will also be required to maintain and expand our relationships with customers, suppliers and other third parties and attract new customers and suppliers, as well as manage multiple geographic locations.
24
In addition, our current and planned operations, personnel, IT and other systems and procedures might be inadequate to support our future growth and may require us to make additional unanticipated investments in our infrastructure. Our success and ability to further scale our business will depend, in part, on our ability to manage these changes in a cost-effective and efficient manner. If we cannot manage our growth, we may be unable to take advantage of market opportunities, execute our business strategies or respond to competitive pressures. This could also result in declines in quality or customer satisfaction, increased costs, difficulties in introducing new offerings or other operational difficulties. Any failure to effectively manage growth could adversely impact our business and reputation.
We may not realize the anticipated benefits of past or future acquisitions, and integration of these acquisitions may disrupt our business and management.
We acquired Solmetric Corporation in January 2014 and in the future we may acquire additional companies, project pipelines, products or technologies or enter into joint ventures or other strategic initiatives. We may not realize the anticipated benefits of this acquisition or any other future acquisition, and any acquisition has numerous risks. These risks include the following:
|
· |
difficulty in assimilating the operations and personnel of the acquired company; |
|
· |
difficulty in effectively integrating the acquired technologies or products with our current technologies; |
|
· |
difficulty in maintaining controls, procedures and policies during the transition and integration; |
|
· |
disruption of our ongoing business and distraction of our management and employees from other opportunities and challenges due to integration issues; |
|
· |
difficulty integrating the acquired company’s accounting, management information and other administrative systems; |
|
· |
inability to retain key technical and managerial personnel of the acquired business; |
|
· |
inability to retain key customers, vendors and other business partners of the acquired business; |
|
· |
inability to achieve the financial and strategic goals for the acquired and combined businesses; |
|
· |
incurring acquisition-related costs or amortization costs for acquired intangible assets that could impact our operating results; |
|
· |
potential failure of the due diligence processes to identify significant issues with product quality, intellectual property infringement and other legal and financial liabilities, among other things; |
|
· |
potential inability to assert that internal controls over financial reporting are effective; and |
|
· |
potential inability to obtain, or obtain in a timely manner, approvals from governmental authorities, which could delay or prevent such acquisitions. |
Mergers and acquisitions of companies are inherently risky, and if we do not complete the integration of acquired businesses successfully and in a timely manner, we may not realize the anticipated benefits of the acquisitions to the extent anticipated, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations.
The loss of one or more members of our senior management or key employees may adversely affect our ability to implement our strategy.
We depend on our experienced management team, and the loss of one or more key executives could have a negative impact on our business. In particular, we are dependent on the services of our chief executive officer, Greg Butterfield. We also depend on our ability to retain and motivate key employees and attract qualified new employees. None of our key executives are bound by employment agreements for any specific term and we do not maintain key person life insurance policies on any of our executive officers. In addition, two-thirds of the outstanding options to purchase shares of our common stock granted to our key executives and other employees under our 2013 Omnibus Incentive Plan will vest if 313 Acquisition LLC receives a return on its invested capital at pre-established thresholds, subject to the employee’s continued service through the receipt of such return. While our initial public offering did not itself constitute an event that would trigger vesting, subsequent sales by 313 Acquisition LLC of our common stock could result in the vesting of such options. As a result, the retention incentives associated with these options could lapse for all employees holding these options under our 2013 Omnibus Incentive Plan at the same time or times. This decrease in retention incentive could cause significant turnover after these options vest. We may be unable to replace key members of our management team and key employees if we lose their services. Integrating new employees into our team could prove disruptive to our operations, require substantial resources and management attention and ultimately prove unsuccessful. An inability to attract and retain sufficient managerial personnel who have critical industry experience and relationships could limit or delay our strategic efforts, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
25
The execution of our business plan and development strategy may be seriously harmed if integration of our senior management team is not successful.
Since August 2013, we have experienced and we may continue to experience significant changes in our senior management team. Specifically, nine members of our senior management team, including our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, have joined us since August 2013 and only two members of our senior management team have prior experience in the distributed solar energy industry. This lack of long-term experience working together and limited experience in the distributed solar energy industry may adversely impact our senior management team’s ability to effectively manage our business and accurately forecast our results, including revenue from our distributed solar energy systems and sales.
The requirements of being a public company may strain our resources, divert management’s attention and affect our ability to attract and retain qualified board members and officers.
As a public company, we are subject to the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act, the listing requirements of the New York Stock Exchange, or NYSE, and other applicable securities rules and regulations. Compliance with these rules and regulations has increased our legal and financial compliance costs, made some activities more difficult, time-consuming or costly and increased demand on our systems and resources. The Exchange Act requires, among other things, that we file annual, quarterly and current reports with respect to our business and operating results and maintain effective disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting. To maintain and, if required, improve our disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting to meet this standard, significant resources and management oversight may be required. As a result, management’s attention may be diverted from other business concerns which could harm our business and operating results. Although we have already hired additional employees to comply with these requirements, we may need to hire more employees in the future which will increase our costs and expenses. Moreover, in the preparation of our financial statements, we and our independent registered public accounting firm identified a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting in connection with the preparation, audits and interim reviews of our consolidated financial statements, and if we fail to remediate this material weakness or, in the future, we or our independent registered public accounting firm identify deficiencies in our internal control over financial reporting that are deemed to be material weaknesses, the market price of our stock could decline and we could be subject to sanctions or investigations by the SEC or other regulatory authorities, which would require additional financial and management resources.
Being a public company has also made it more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance, and in the future, we may be required to accept reduced coverage or incur substantially higher costs to continue coverage. These factors could also make it more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified executive officers and members of our board of directors, particularly to serve on our audit committee and compensation committee.
We may be subject to intellectual property rights claims by third parties, which are extremely costly to defend, could require us to pay significant damages and could limit our ability to use certain technologies.
Third parties, including our competitors, may own patents or other intellectual property rights that cover aspects of our technology or business methods. Such parties may claim we have misappropriated, misused, violated or infringed third party intellectual property rights, and, if we gain greater recognition in the market, we face a higher risk of being the subject of claims that we have violated others’ intellectual property rights. Any claim that we violate a third party’s intellectual property rights, whether with or without merit, could be time-consuming, expensive to settle or litigate and could divert our management’s attention and other resources. If we do not successfully settle or defend an intellectual property claim, we could be liable for significant monetary damages and could be prohibited from continuing to use certain technology, business methods, content or brands. To avoid a prohibition, we could seek a license from third parties, which could require us to pay significant royalties, increasing our operating expenses. If a license is not available at all or not available on reasonable terms, we may be required to develop or license a non-violating alternative, either of which could require significant effort and expense. If we cannot license or develop a non-violating alternative, we would be forced to limit or stop sales of our offerings and may be unable to effectively compete. Any of these results would adversely affect our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. To deter other companies from making intellectual property claims against us or to gain leverage in settlement negotiations, we may be forced to significantly increase the size of our intellectual property portfolio through internal efforts and acquisitions from third parties, both of which could require significant expenditures. However, a robust intellectual property portfolio may provide little or no deterrence, particularly for patent holding companies or other patent owners that have no relevant product revenues.
26
We use “open source” software in our solutions, which may restrict how we distribute our offerings, require that we release the source code of certain software subject to open source licenses or subject us to possible litigation or other actions that could adversely affect our business.
We currently use in our solutions, and expect to continue to use in the future, software that is licensed under so-called “open source,” “free” or other similar licenses. Open source software is made available to the general public on an “as-is” basis under the terms of a non-negotiable license. We currently combine our proprietary software with open source software but not in a manner that we believe requires the release of the source code of our proprietary software to the public. We do not plan to integrate our proprietary software with open source software in ways that would require the release of the source code of our proprietary software to the public, however, our use and distribution of open source software may entail greater risks than use of third-party commercial software. Open source licensors generally do not provide warranties or other contractual protections regarding infringement claims or the quality of the code. In addition, if we combine our proprietary software with open source software in a certain manner, we could, under certain open source licenses, be required to release the source code of our proprietary software to the public. This would allow our competitors to create similar offerings with lower development effort and time and ultimately could result in a loss of sales. We may also face claims alleging noncompliance with open source license terms or infringement or misappropriation of proprietary software. These claims could result in litigation, require us to purchase a costly license or require us to devote additional research and development resources to change our software, any of which would have a negative effect on our business and operating results. In addition, if the license terms for open source software that we use change, we may be forced to re-engineer our solutions, incur additional costs or discontinue the sale of our offerings if re-engineering could not be accomplished on a timely basis. Although we monitor our use of open source software to avoid subjecting our offerings to unintended conditions, few courts have interpreted open source licenses, and there is a risk that these licenses could be construed in a way that could impose unanticipated conditions or restrictions on our ability to commercialize our offerings. We cannot guarantee that we have incorporated open source software in our software in a manner that will not subject us to liability, or in a manner that is consistent with our current policies and procedures.
The installation and operation of solar energy systems depends heavily on suitable solar and meteorological conditions. If meteorological conditions are unexpectedly unfavorable, the electricity production from our solar energy systems may be substantially below our expectations and our ability to timely deploy new systems may be adversely impacted.
The energy produced and revenue and cash receipts generated by a solar energy system depend on suitable solar, atmospheric and weather conditions, all of which are beyond our control. Furthermore, components of our systems, such as panels and inverters, could be damaged by severe weather, such as hailstorms or lightning. Although we maintain insurance to cover for many such casualty events, our investment funds would be obligated to bear the expense of repairing the damaged solar energy systems, sometimes subject to limitations based on our ability to successfully make warranty claims. Our economic model and projected returns on our systems require us to achieve certain production results from our systems and, in some cases, we guarantee these results for both our consumers and our investors. If the systems underperform for any reason, our financial results could suffer. Sustained unfavorable weather also could delay our installation of solar energy systems, leading to increased expenses and decreased revenue and cash receipts in the relevant periods. We have experienced seasonal fluctuations in our operations. For example, the amount of revenue we recognize in a given period from power purchase agreements is dependent in part on the amount of energy generated by solar energy systems under such contracts. As a result, operating leases and incentives revenue is impacted by seasonally shorter daylight hours in winter months. In addition, our ability to install solar energy systems is impacted by weather. For example, we have limited ability to install solar energy systems during the winter months in the Northeastern United States. Such delays can impact the timing of when we can install and begin to generate revenue from solar energy systems. However, given that we are an early stage company operating in a rapidly growing industry, the true extent of these fluctuations may have been masked by our recent growth rates and thus may not be readily apparent from our historical operating results and may be difficult to predict. As such, our historical operating results may not be indicative of future performance. Furthermore, weather patterns could change, making it harder to predict the average annual amount of sunlight striking each location where we install a solar energy system. This could make our solar energy systems less economical overall or make individual systems less economical. Any of these events or conditions could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
27
Disruptions to our solar monitoring systems could negatively impact our revenues and increase our expenses.
Our ability to accurately charge our customers for the energy produced by our solar energy systems depends on customers maintaining a broadband internet connection so that we may receive data regarding solar energy systems production from their home networks. We could incur significant expenses or disruptions of our operations in connection with failures of our solar monitoring systems, including failures of our customers’ home networks that would prevent us from accurately monitoring solar energy production. In addition, sophisticated hardware and operating system software and applications that we procure from third parties may contain defects in design or manufacture, including “bugs” and other problems that could unexpectedly interfere with the operation of our systems. The costs to us to eliminate or alleviate viruses and bugs, or any problems associated with failures of our customers’ home networks could be significant, and the efforts to address these problems could result in interruptions, delays or cessation of service that may impede our sales, distribution or other critical functions. We have in the past experienced periods where some of our customers’ networks have been unavailable and, as a result, we have been forced to estimate the production of their solar energy systems. Such estimates may prove inaccurate and could cause us to underestimate the power being generated by our solar energy systems and undercharge our customers, thereby harming our results of operations.
We are exposed to the credit risk of our customers.
Our solar energy customers purchase energy or lease solar energy systems from us pursuant to one of two types of long-term contracts: a power purchase agreement or a lease. The power purchase agreement and lease terms are typically for 20 years, and require the customer to make monthly payments to us. Accordingly, we are subject to the credit risk of our customers. As of December 31, 2014, the average FICO score of our customers was approximately 750. However, as we grow our business, we expect that the risk of customer defaults will increase. As a result, our reserve for this exposure is estimated to be $0.6 million as of December 31, 2014, and our future exposure may exceed the amount of such reserves.
The Office of the Inspector General of the U.S. Department of Treasury has issued subpoenas to a number of significant participants in the rooftop solar energy installation industry and may take further action based on this ongoing investigation or for other reasons.
In July 2012, other companies that are significant participants in both the solar industry and the U.S. Treasury grant program received subpoenas from the U.S. Department of Treasury’s Office of the Inspector General to deliver certain documents in their possession related to their applications for U.S. Treasury grants and communications with certain other solar development companies or certain firms that appraise solar energy property for U.S. Treasury grant application purposes. The Inspector General is working with the Civil Division of the U.S. Department of Justice to investigate the administration and implementation of the U.S. Treasury grant program, including possible misrepresentations concerning the fair market value of the solar power systems submitted in grant applications by companies in the solar industry. While we have not been a direct target of this investigation to date, given our participation in the U.S. Treasury grant program, the Inspector General or the Department of Justice could broaden the investigation to include us. If it were broadened to include us, the period of time necessary to resolve the investigation would be uncertain, and the matter could require significant management and financial resources that could otherwise be devoted to the operation of our business. The Department of Justice could also decide to bring a civil action to recover amounts it believes were improperly paid to us. If it were successful in asserting this action, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, liquidity, financial condition and prospects.
A failure to comply with laws and regulations relating to our interactions with current or prospective residential customers could result in negative publicity, claims, investigations and litigation, and adversely affect our financial performance.
Our business substantially focuses on contracts and transactions with residential customers. We must comply with numerous federal, state and local laws and regulations that govern matters relating to our interactions with residential consumers, including those pertaining to privacy and data security, consumer financial and credit transactions, home improvement contracts, warranties and door-to-door solicitation. These laws and regulations are dynamic and subject to potentially differing interpretations, and various federal, state and local legislative and regulatory bodies may initiate investigations, expand current laws or regulations, or enact new laws and regulations, regarding these matters. Changes in these laws or regulations or their interpretation could dramatically affect how we do business, acquire customers, and manage and use information we collect from and about current and prospective customers and the costs associated therewith. We strive to comply with all applicable laws and regulations relating to our interactions with residential customers. It is possible, however, that these requirements may be interpreted and applied in a manner that is inconsistent from one jurisdiction to another and may conflict with other rules or our practices. For example, members of the U.S. House of Representatives have recently sent letters to the Consumer Financial Protection Board, or CFPB, and the Federal Trade Commission, or FTC, requesting that these agencies investigate the sales practices of companies providing solar energy system leases to residential consumers. While we believe our sales practices comply with all applicable laws and regulations, if the CFPB or FTC were to initiate an investigation against us or enact regulations relating to the marketing of solar leases to residential consumers, responding to such investigation or complying with such regulations could require us to modify our operations and incur significant additional expenses, which could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. Additionally, our non-compliance
28
with any such law or regulations could also expose us to claims, proceedings, litigation and investigations by private parties and regulatory authorities, as well as substantial fines and negative publicity, each of which may materially and adversely affect our business. We have incurred, and will continue to incur, significant expenses to comply with such laws and regulations.
Any unauthorized access to, or disclosure or theft of personal information we gather, store or use could harm our reputation and subject us to claims or litigation.
We receive, store and use personal information of our customers, including names, addresses, e-mail addresses, credit information and other housing and energy use information. We also store and use personal information of our employees. In addition, we currently utilize certain shared information and technology systems with Vivint. We take certain steps in an effort to protect the security, integrity and confidentiality of the personal information we collect, store or transmit, but there is no guarantee that inadvertent or unauthorized use or disclosure will not occur or that third parties will not gain unauthorized access to this information despite our efforts. Because techniques used to obtain unauthorized access or sabotage systems change frequently and generally are not identified until they are launched against a target, we and our suppliers or vendors, including Vivint, may be unable to anticipate these techniques or to implement adequate preventative or mitigation measures.
Unauthorized use or disclosure of, or access to, any personal information maintained by us or on our behalf, whether through breach of our systems, breach of the systems of our suppliers or vendors, including Vivint, by an unauthorized party, or through employee or contractor error, theft or misuse, or otherwise, could harm our business. If any such unauthorized use or disclosure of, or access to, such personal information were to occur, our operations could be seriously disrupted and we could be subject to demands, claims and litigation by private parties, and investigations, related actions, and penalties by regulatory authorities. In addition, we could incur significant costs in notifying affected persons and entities and otherwise complying with the multitude of federal, state and local laws and regulations relating to the unauthorized access to, or use or disclosure of, personal information. Finally, any perceived or actual unauthorized access to, or use or disclosure of, such information could harm our reputation, substantially impair our ability to attract and retain customers and have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We are involved, and may become involved in the future, in legal proceedings that, if adversely adjudicated or settled, could adversely affect our financial results.
We are, and may in the future become, party to litigation. For example, in September 2014, two of our former installation technicians, on behalf of themselves and individuals the plaintiffs claim to be similarly situated, filed a purported class action complaint in the Superior Court of the State of California, County of San Diego. This action alleges certain violations of the California Labor Code and the California Business and Professions Code based on, among other things, alleged improper classification of installer technicians, installer helpers, electrician technicians and electrician helpers, failure to pay minimum and overtime wages, failure to provide accurate itemized wage statements, and failure to provide wages on termination. We believe that we have strong defenses to the claims asserted in this matter, and we intend to defend the case vigorously.
In addition, in November and December 2014, two putative class action lawsuits were filed in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York against us, our directors, certain of our officers and the underwriters of our initial public offering of common stock alleging violation of securities laws and seeking unspecified damages. In January 2015, the Court ordered these cases to be consolidated into the earlier filed case, Hyatt v. Vivint Solar, Inc. et al., 14-cv-9283 (KBF). The plaintiffs filed a consolidated amended complaint in February 2015. We believe this lawsuit is without merit, and we intend to defend the case vigorously.
While we intend to defend against these actions vigorously, the ultimate outcomes of these cases are presently not determinable as they are in a preliminary phase. In general, litigation claims can be expensive and time consuming to bring or defend against, may result in the diversion of management attention and resources from our business and business goals and could result in settlements or damages that could significantly affect financial results and the conduct of our business. It is not possible to predict the final resolution of the litigation to which we currently are or may in the future become party, and the impact of certain of these matters on our business, prospects, financial condition, liquidity, results of operations and cash flows.
Risks Related to our Relationship with Vivint
Vivint provides us with certain key services for our business. If Vivint fails to perform its obligations to us or if we do not find appropriate replacement services, we may be unable to perform these services or implement substitute arrangements on a timely and cost-effective basis on terms favorable to us.
We have historically relied on the technical, administrative and operational support of Vivint to run our business. Some of the Vivint resources we are using include information technology and infrastructure, employee benefits and certain other services. In addition, historically we have recruited a majority of our sales personnel from Vivint. We continue to separate our operations from those of Vivint and are working to either create our own financial, administrative, operational and other support systems or contract with third parties to replace Vivint’s systems and services that will not be provided to us under the terms of continuing services agreements between us and Vivint. The implementation of new software support systems requires significant management time,
29
support and cost, and there are inherent risks associated with implementing, developing, improving and expanding our core systems. We cannot be sure that these systems will be fully or effectively implemented on a timely basis, if at all. If we do not successfully implement these systems, our operations may be disrupted and our operating results could be harmed. In addition, the new systems may not operate as we expect them to, and we may be required to expend significant resources to correct problems or find alternative sources for performing these functions.
In order to successfully transition to our own systems, services and service providers and operate as a stand-alone business, we entered into various agreements with Vivint in connection with our public offering. These include a master framework agreement providing the overall terms of the relationship and a transition services agreement detailing various information technology and back office support services that Vivint will provide. Vivint will provide each service until we agree that support from Vivint is no longer required for that service. The services provided under the transition services agreement may not be sufficient to meet our needs and we may not be able to replace these services at favorable costs and on favorable terms, if at all. Any failure or significant downtime in our own financial or administrative systems or in Vivint’s financial or administrative systems during the transition period and any difficulty in separating our operations from Vivint’s operations and integrating newly developed or acquired services into our business could result in unexpected costs, impact our results or prevent us from paying our suppliers and employees and performing other technical, administrative and operations services on a timely basis and could materially harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Our historical financial information may not be representative of future results as a stand-alone public company.
The historical financial information we have included in this report does not necessarily reflect what our financial position, results of operations or cash flows would have been had we operated separately from Vivint during the historical periods presented. The historical costs and expenses reflected in our consolidated financial statements include charges to certain corporate functions historically provided to us by Vivint. We and Vivint believe these charges are reasonable reflections of the historical utilization levels of these services in support of our business; however, these charges may not include all of the expenses that would have been incurred had we operated separately from Vivint during the historical periods presented. As a result, our historical financial information is not necessarily indicative of our future results of operations, financial position, cash flows or costs and expenses.
Our inability to resolve any disputes that arise between us and Vivint with respect to our past and ongoing relationships may adversely affect our financial results, and such disputes may also result in claims for indemnification.
Disputes may arise between Vivint and us in a number of areas relating to our past and ongoing relationships, including the following:
|
· |
intellectual property, labor, tax, employee benefits, indemnification and other matters arising from our separation from Vivint; |
|
· |
employee retention and recruiting; |
|
· |
our ability to use, modify and enhance the intellectual property that we have licensed from Vivint; |
|
· |
business combinations involving us; |
|
· |
pricing for shared and transitional services; |
|
· |
exclusivity arrangements; |
|
· |
the nature, quality and pricing of products and services Vivint agrees to provide to us; and |
|
· |
business opportunities that may be attractive to both Vivint and us. |
We have entered into certain agreements with Vivint. Pursuant to the terms of the Non-Competition Agreement we have entered into with Vivint, we and Vivint each define our areas of business and our competitors, and agree not to directly or indirectly engage in the other’s business for three years. This agreement may limit our ability to pursue attractive opportunities that we may have otherwise pursued.
Additionally, this agreement prohibits, for a period of five years, either Vivint or us from soliciting for employment any member of the other’s executive or senior management team, or any of the other’s employees who primarily manage sales, installation or services of the other’s products and services. The commitment not to solicit each other’s employees lasts for 180 days after such employee finishes employment with us or Vivint. Historically we have recruited a majority of our sales personnel from Vivint. This agreement may require us to obtain personnel from other sources, and may limit our ability to continue scaling our business if we are unable to do so.
30
Pursuant to the terms of the Marketing and Customer Relations Agreement we have entered into with Vivint, we and Vivint are required to compensate one another for sales leads that result in sales. Vivint may direct sales leads to other solar energy companies in markets in which we have not entered. However, once we enter a market, Vivint must exclusively direct to us all leads for customers and potential customers with an interest in solar energy. Vivint’s ability to sell leads to other solar energy providers in markets where we are not currently operating may adversely affect our ability to scale rapidly if we subsequently enter into such market as many of Vivint’s customers with solar energy inclinations may have already been referred to another company by the time we enter into such market.
We may not be able to resolve any potential conflicts relating to these agreements or otherwise, and even if we do, the resolution may be less favorable than if we were dealing with an unaffiliated party. In addition, we have indemnification obligations under the intercompany services agreements we entered into with Vivint, and disputes between us and Vivint may result in claims for indemnification. However, we do not currently expect that these indemnification obligations will materially affect our potential liability compared to what it would be if we did not enter into these agreements with Vivint.
Risks Related to Our Common Stock
The price of our common stock may be volatile, and the value of your investment could decline.
The trading price of our common stock may be highly volatile. For example, from our initial public offering to the date of this report, the closing price of our common stock has ranged from a high of $16.01 to a low of $7.94. Our stock price could continue to be subject to wide fluctuations in response to various factors, some of which are beyond our control. These factors include:
|
· |
changes in laws or regulations applicable to our industry or offerings; |
|
· |
additions or departures of key personnel; |
|
· |
the failure of securities analysts to cover our common stock; |
|
· |
actual or anticipated changes in expectations regarding our performance by investors or securities analysts; |
|
· |
securities litigation involving us; |
|
· |
price and volume fluctuations in the overall stock market; |
|
· |
volatility in the market price and trading volume of companies in our industry or companies that investors consider comparable; |
|
· |
share price and volume fluctuations attributable to inconsistent trading volume levels of our shares; |
|
· |
our ability to protect our intellectual property and other proprietary rights; |
|
· |
sales of our common stock by us or our stockholders; |
|
· |
the expiration of contractual lock-up agreements; |
|
· |
litigation or disputes involving us, our industry or both; |
|
· |
major catastrophic events; and |
|
· |
general economic and market conditions. |
Further, the stock markets have experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that have affected and continue to affect the market prices of equity securities of many companies. These fluctuations often have been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of those companies. In addition, the stock prices of many renewable energy companies have experienced wide fluctuations that have often been unrelated to the operating performance of those companies. These broad market and industry fluctuations, as well as general economic, political and market conditions such as recessions, interest rate changes or international currency fluctuations, may cause the market price of our common stock to decline. If the market price of our common stock decreases, investors may not realize any return on investment and may lose some or all of their investments.
In the past, companies that have experienced volatility in the market price of their stock have been subject to securities class action litigation. We are currently subject to two putative class action lawsuits filed in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York, alleging certain misrepresentations by us in connection with our initial public offering. We may become the target of additional securities litigation in the future, which could result in substantial costs and divert our management’s attention from other business concerns, which could seriously harm our business.
31
As an emerging growth company within the meaning of the Securities Act, we will utilize certain modified disclosure requirements, and we cannot be certain if these reduced requirements will make our common stock less attractive to investors.
We are an emerging growth company, and, for as long as we continue to be an emerging growth company, we may choose to take advantage of exemptions from various reporting requirements applicable to other public companies but not to “emerging growth companies” including, but not limited to, not being required to have our independent registered public accounting firm audit our internal control over financial reporting under Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports and proxy statements, and exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. We have utilized, and we plan in future filings with the SEC to continue to utilize, the modified disclosure requirements available to emerging growth companies. As a result, our stockholders may not have access to certain information they may deem important.
In addition, Section 107 of the JOBS Act also provides that an emerging growth company can utilize the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act for complying with new or revised accounting standards. Thus, an emerging growth company can delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. We have irrevocably elected not to avail ourselves of this exemption from new or revised accounting standards and, therefore, we will be subject to the same new or revised accounting standards as other public companies that are not “emerging growth companies.”
We could remain an ‘‘emerging growth company’’ for up to five years, or until the earliest of (1) the last day of the first fiscal year in which our annual gross revenue exceeds $1 billion, (2) the date that we become a ‘‘large accelerated filer’’ as defined in Rule 12b-2 under the Exchange Act, which would occur if we become a seasoned issuer and the market value of our common stock that is held by non-affiliates exceeds $700 million as of the last business day of our most recently completed second fiscal quarter or (3) the date on which we have issued more than $1 billion in non-convertible debt during the preceding three-year period.
Our stock price could decline due to the large number of outstanding shares of our common stock eligible for future sale.
Sales of substantial amounts of our common stock in the public market, or the perception that these sales could occur, could cause the market price of our common stock to decline. These sales could also make it more difficult for us to sell equity or equity-related securities in the future at a time and price that we deem appropriate.
As of December 31, 2014, we had 105.3 million outstanding shares of common stock. We, 313 Acquisition LLC and all of our directors and officers, as well as the other holders of substantially all shares of our common stock outstanding immediately prior to the completion of our initial public offering, agreed with the underwriters, subject to certain exceptions, not to dispose of or hedge any of their common stock until 180 days following the date of such offering, except with the prior written consent of the representatives of the underwriters. After the expiration of the 180-day restricted period on March 29, 2015, these shares may be sold in the public market in the United States, subject to prior registration in the United States, if required, or reliance upon an exemption from U.S. registration, including, in the case of shares held by affiliates or control persons, compliance with the volume restrictions of Rule 144. Participants in the reserved share program, which provided for the sale of up to 5% of the shares offered in our initial public offering, have agreed to similar restrictions for 180 days following the date of such offering, which restrictions may be waived with the prior written consent of the representatives of the underwriters.
In addition, 0.7 million shares of our common stock reserved for future issuance under our Long-Term Incentive Plan will issue, vest and be immediately tradable without restriction on the date that is six months after the closing of our initial public offering. An additional 2.7 million shares of our common stock reserved for future issuance under our Long-Term Incentive Plan will issue, vest and be immediately tradable without restriction at the later of (1) the date our sponsor and its affiliates achieve a specified return on their invested capital and (2) the date that is six months after the closing of our initial public offering. On the date that is 18 months after the closing of our initial public offering, 0.7 million shares reserved for future issuance under our Long-Term Incentive Plan will issue, vest and be immediately tradable without restriction. For more information regarding the shares reserved under our Long Term Incentive Plan see the section of the Prospectus captioned “Shares Eligible for Future Sale.”
Further, options to purchase 10.1 million shares of common stock remained outstanding as of December 31, 2014, one-third of which are subject to ratable time-based vesting over a five year period and will become immediately tradable once vested. The remaining two-thirds are subject to vesting upon certain performance conditions and the achievement of certain investment return thresholds by 313 Acquisition LLC and will vest and become immediately tradable as follows: (1) one-half of the shares vest (a) if 313 Acquisition LLC receives cash proceeds with respect to its holdings of our common stock in an amount that equals $250 million more than its cumulative investment in our common stock (which amount shall be equal to $75 million plus any amounts invested after November 16, 2012) or (b) if 240 days after the completion of our initial public offering, our aggregate equity market capitalization exceeds $1 billion and (2) one-half of the shares vest when 313 Acquisition LLC receives cash proceeds with respect to its holdings of our common stock in an amount that equals $500 million more than its cumulative investment in our common stock (which amount shall be equal to $75 million plus any amounts invested after November 16, 2012).
32
Following March 29, 2015, the date that is 180 days after the completion of our initial public offering, stockholders owning an aggregate of 84.7 million shares of our common stock will be entitled, under contracts providing for registration rights, to require us to register shares of our common stock owned by them for public sale in the United States, subject to the restrictions of Rule 144. On October 1, 2014, we filed a registration statement on Form S-8 to register 22.9 million shares previously issued or reserved for future issuance under our equity compensation plans and agreements. Upon effectiveness of this registration statement, subject to the satisfaction of applicable exercise periods and, in certain cases, lock-up agreements with the representatives of the underwriters referred to above, the shares of common stock issued upon exercise of outstanding options will be available for immediate resale in the United States in the open market. Sales of our common stock as restrictions end or pursuant to registration rights may make it more difficult for us to sell equity securities in the future at a time and at a price that we deem appropriate. These sales also could cause our stock price to fall and make it more difficult for you to sell shares of our common stock.
Our sponsor and its affiliates control us and their interests may conflict with ours or yours in the future.
As of December 31, 2014, 313 Acquisition LLC, which is controlled by our sponsor and its affiliates, beneficially owned approximately 78% of our common stock. Moreover, under our organizational documents and the stockholders agreement with 313 Acquisition LLC, for so long as our existing owners and their affiliates retain significant ownership of us, we will agree to nominate to our board individuals designated by our sponsor, whom we refer to as the sponsor directors. In addition, for so long as 313 Acquisition LLC continues to own shares representing a majority of the total voting power, we will agree to nominate to our board individuals appointed by Summit Partners and Todd Pedersen. Even when our sponsor and its affiliates and certain of its co-investors cease to own shares of our stock representing a majority of the total voting power, for so long as our sponsor and its affiliates continue to own a significant percentage of our stock our sponsor will still be able to significantly influence the composition of our board of directors and the approval of actions requiring stockholder approval. In addition, under the stockholders agreement, affiliates of our sponsor will have consent rights with respect to certain actions involving our company, provided a certain aggregate ownership threshold is maintained collectively by our sponsor and its affiliates, together with Summit Partners, Todd Pedersen and Alex Dunn and their respective affiliates. Accordingly, for such period of time, our sponsor and certain of its co-investors will have significant influence with respect to our management, business plans and policies, including the appointment and removal of our officers. In particular, for so long as our sponsor and its affiliates continue to own a significant percentage of our stock, our sponsor will be able to cause or prevent a change of control of our company or a change in the composition of our board of directors and could preclude any unsolicited acquisition of our company. The concentration of ownership could deprive you of an opportunity to receive a premium for your shares of common stock as part of a sale of our company and ultimately might affect the market price of our common stock.
Our sponsor and its affiliates engage in a broad spectrum of activities, including investments in the energy sector. In the ordinary course of their business activities, our sponsor and its affiliates may from time to time acquire and hold interests in businesses that compete directly or indirectly with us. For example, affiliates of our sponsor regularly invest in utility companies that compete with solar energy and renewable energy companies such as ours. In addition, affiliates of our sponsor own interests in one of the largest solar power developers in India and may in the future make other investments in solar power, including in the United States. Our certificate of incorporation provides that none of our sponsor, any of its affiliates or any director who is not employed by us (including any non-employee director who serves as one of our officers in both his or her director and officer capacities) or his or her affiliates will have any duty to refrain from engaging, directly or indirectly, in the same business activities or similar business activities or lines of business in which we operate. Our sponsor also may pursue acquisition opportunities that may be complementary to our business, and, as a result, those acquisition opportunities may not be available to us. In addition, our sponsor may have an interest in pursuing acquisitions, divestitures and other transactions that, in its judgment, could enhance its investment, even though such transactions might involve risks to you.
We have elected to take advantage of the “controlled company” exemption to the corporate governance rules for NYSE-listed companies, which could make our common stock less attractive to some investors or otherwise harm our stock price.
Because we qualify as a “controlled company” under the corporate governance rules for NYSE-listed companies, we are not required to have a majority of our board of directors be independent, nor are we required to have a compensation committee or an independent nominating function. In light of our status as a controlled company, in the future we could elect not to have a majority of our board of directors be independent or not to have a compensation committee or nominating and governance committee. Accordingly, should the interests of 313 Acquisition LLC or our sponsor differ from those of other stockholders, the other stockholders may not have the same protections afforded to stockholders of companies that are subject to all of the corporate governance rules for NYSE-listed companies. Our status as a controlled company could make our common stock less attractive to some investors or otherwise harm our stock price.
33
Provisions in our certificate of incorporation, bylaws, stockholders agreement and under Delaware law might discourage, delay or prevent a change of control of our company or changes in our management and, therefore, depress the trading price of our common stock.
Our certificate of incorporation, bylaws and stockholders agreement contain provisions that could depress the trading price of our common stock by discouraging, delaying or preventing a change of control of our company or changes in our management that the stockholders of our company may believe advantageous. These provisions include:
|
· |
establishing a classified board of directors so that not all members of our board of directors are elected at one time; |
|
· |
authorizing “blank check” preferred stock that our board of directors could issue to increase the number of outstanding shares to discourage a takeover attempt; |
|
· |
limiting the ability of stockholders to call a special stockholder meeting; |
|
· |
limiting the ability of stockholders to act by written consent; |
|
· |
providing that the board of directors is expressly authorized to make, alter or repeal our bylaws; |
|
· |
establishing advance notice requirements for nominations for elections to our board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted upon by stockholders at stockholder meetings; |
|
· |
requiring our sponsor to consent to certain actions, as described under the section of the Prospectus captioned “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions—Agreements with Our Sponsor—Stockholders Agreement,” for so long as our sponsor, Summit Partners, Todd Pedersen and Alex Dunn or their respective affiliates collectively own, in the aggregate, at least 30% of our outstanding shares of common stock; |
|
· |
the removal of directors only for cause and only upon the affirmative vote of the holders of at least 66 2/3% in voting power of all the then-outstanding shares of stock of our company entitled to vote thereon, voting together as a single class, if Blackstone and its affiliates beneficially own, in the aggregate, less than 30% in voting power of the stock of our company entitled to vote generally in the election of directors; and |
|
· |
that certain provisions may be amended only by the affirmative vote of the holders of at least 66 2/3% in voting power of all the then-outstanding shares of stock of our company entitled to vote thereon, voting together as a single class, if Blackstone and its affiliates beneficially own, in the aggregate, less than 30% in voting power of the stock of our company entitled to vote generally in the election of directors. |
If securities or industry analysts do not publish or cease publishing research or reports about us, our business or our market, or if they change their recommendations regarding our stock adversely, our stock price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our common stock will be influenced by the research and reports that industry or securities analysts may publish about us, our business, our market or our competitors. If any of the analysts who do now, or may in the future, cover us change their recommendation regarding our stock adversely, or provide more favorable relative recommendations about our competitors, our stock price would likely decline. If any analyst who may cover us were to cease coverage of our company or fail to regularly publish reports on us, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which in turn could cause our stock price or trading volume to decline.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
None.
Our corporate headquarters and executive offices are currently located in Lehi, Utah, where we occupy approximately 37,229 square feet of office space. We lease 90,675 square feet of office space with TCO-Canyon Park, LLC in Orem, Utah. We also entered into a lease with T-Stat One, LLC for approximately 150,000 square feet of office space that will replace our current corporate headquarters and executive offices once the building is completed in early 2016. We anticipate entering into a lease for an additional studio building on that site for approximately 13,000 square feet. Our other locations include warehouses that range from approximately 3,000 to 23,000 square feet in Arizona, California, Connecticut, Hawaii, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey and New York.
We lease all of our facilities and we do not own any real property. We believe that our Utah offices are sufficient to meet our immediate needs, but we are actively seeking additional office space to accommodate our planned growth. We believe that we will be able to obtain additional facilities on commercially reasonable terms.
34
In the normal course of business, we may from time to time be named as a party to various legal claims, actions and complaints. It is impossible to predict with certainty whether any resulting liability would have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In December 2013, one of our former sales representatives, on behalf of himself and a purported class, filed a complaint for unspecified damages, injunctive relief and restitution in the Superior Court of the State of California in and for the County of San Diego against Vivint Solar Developer, LLC, one of our subsidiaries, and unnamed John Doe defendant alleging violations of the California Labor Code and the California Business and Professions Code and seeking penalties of an unspecified amount, interest on all economic damages and reasonable attorney’s fees and costs. In addition, the complaint requests an injunction, which would enjoin us from similar violations of California’s Labor Code and Business and Professions Code, and restitution of costs to the plaintiff and purported class members under California’s unfair competition law. In January 2014, we filed an answer denying the allegations in the complaint and asserting various affirmative defenses. In late 2014, the parties agreed to terms of settlement to resolve this case, depending on class participation. The final settlement agreement is subject to court approval, which we anticipate to occur sometime mid-2015. We have recorded a $0.4 million reserve related to this proceeding in our condensed consolidated financial statements.
In September 2014, two of our former installation technicians, on behalf of themselves and a purported class, filed a complaint for damages, injunctive relief and restitution in the Superior Court of the State of California in and for the County of San Diego against us and unnamed John Doe defendants. The complaint alleges certain violations of the California Labor Code and the California Business and Professions Code based on, among other things, alleged improper classification of installer technicians, installer helpers, electrician technicians and electrician helpers, failure to pay minimum and overtime wages, failure to provide accurate itemized wage statements, and failure to provide wages on termination. In December 2014, the original plaintiffs and three additional plaintiffs filed an amended complaint with essentially the same allegations. On February 5, 2015, we filed an answer to the amended complaint, denying liability and asserting a number of defenses. We believe that we have strong defenses to the claims asserted in this matter, and we intend to defend the case vigorously. Although we cannot predict with certainty the ultimate resolution of this suit, we do not believe this matter will have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, cash flows or financial condition.
Beginning in November 2014, two putative class action lawsuits were filed in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York against us, our directors, certain of our officers and the underwriters of our initial public offering of common stock alleging violation of securities laws and seeking unspecified damages. In January 2015, the Court ordered these cases to be consolidated into the earlier filed case, Hyatt v. Vivint Solar, Inc. et al., 14-cv-9283 (KBF). The plaintiffs filed a consolidated amended complaint in February 2015. We believe this lawsuit is without merit, and we intend to defend the case vigorously. We are unable to estimate a range of loss, if any, that could result were there to be an adverse final decision. If an unfavorable outcome were to occur in this case, it is possible that the impact could be material to our results of operations in the period(s) in which any such outcome becomes probable and estimable.
Also in May 2014, Vivint made us aware that the U.S. Attorney’s office for the State of Utah is engaged in an investigation that Vivint believes relates to certain political contributions made by some of Vivint’s executive officers that are our directors and some of Vivint’s employees. We have no reason to believe that Vivint Solar, its executive officers or its employees are targets of such investigation.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures.
Not applicable.
35
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
Our common stock has been traded on the New York Stock Exchange since October 1, 2014 under the symbol “VSLR.” Prior to October 1, 2014, there was no established public trading market for our common stock. The following table sets forth the high and low sales price for our common stock as reported by the New York Stock Exchange for the period indicated.
|
|
High |
|
Low |
|
|
|
Fourth quarter 2014 |
18.71 |
|
|
7.42 |
|
As of March 2, 2015, we had approximately three stockholders of record of our common stock. This does not include the number of persons whose stock is in nominee or “street name” accounts through brokers.
Stock Performance Graph
This following graph is not “soliciting material,” is not deemed “filed” with the SEC and is not to be incorporated by reference into any filing of Vivint Solar, Inc. under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), or the Exchange Act, whether made before or after the date hereof and irrespective of any general incorporation language in any such filing.
The following graph compares for the period from October 1, 2014 through December 31, 2014, the total cumulative stockholder return on our common stock with the total cumulative return of the New York Stock Exchange Composite Index, the MAC Global Solar Energy Index and a group of publicly traded peer companies. Measurement points are October 1, 2014—the initial trading day of our common stock; October 31, 2014; November 30, 2014 and December 31, 2014. The graph assumes a $100 investment at the beginning of the period in our common stock, the stocks represented in the New York Stock Exchange Composite Index, the MAC Global Solar Energy Index and a group of publicly traded peer companies, and reinvestment of any dividends. Historical stock price performance should not be relied upon as an indication of future stock price performance:
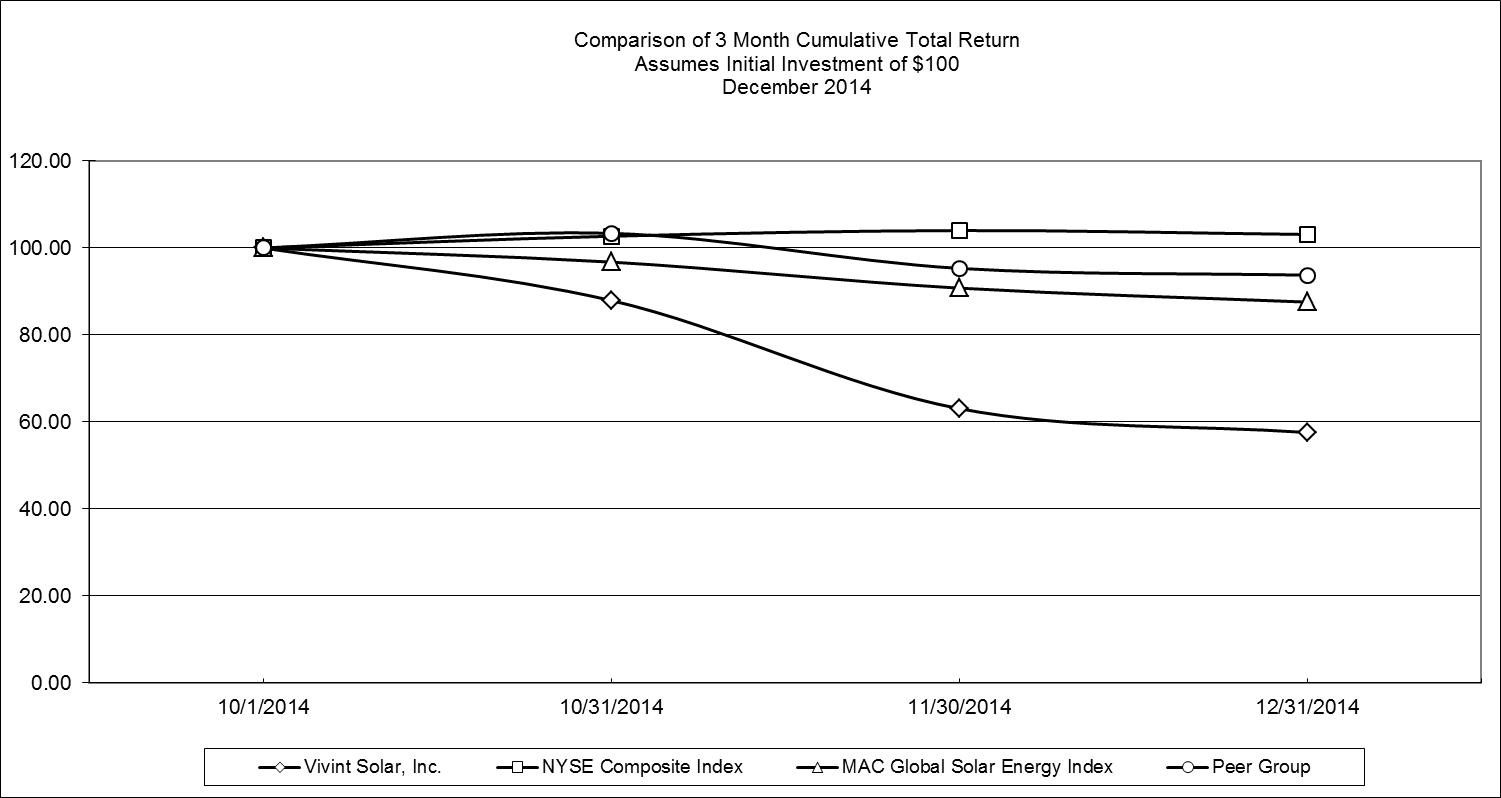
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
In August 2014, we issued and sold an aggregate of 2.7 million shares of common stock to 313 Acquisition LLC for $10.667 per share for aggregate proceeds of $28.5 million. In September 2014, we issued and sold an aggregate of 7.0 million additional shares to 313 Acquisition LLC and two of its directors for $10.667 per share for aggregate gross proceeds of $75.0 million. See Note 12— Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests, Equity and Preferred Stock in the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
No underwriters were involved in the foregoing sales of securities. The issuances of the securities described above were deemed to be exempt from registration under the Securities Act in reliance on Section 4(2) of the Securities Act. The recipients of securities in each such transaction represented their intention to acquire securities for investment only and not with a view to or for sale in connection with any distribution thereof and appropriate legends were affixed to the stock certificates issued in such transactions. All recipients had adequate access, through their relationships with us, to information about us.
36
Use of Proceeds
We filed a Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-198372) for an initial public offering of our common stock, which was declared effective by the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 30, 2014. On October 6, 2014, we closed our initial public offering in which we sold 20.6 million shares of our common stock at a public offering price of $16.00 per share, resulting in net proceeds, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and $8.8 million in offering expenses, of $300.6 million.
During the quarter ended December 31, 2014, we used the cash from the net proceeds of our initial public offering to repay an aggregate of $58.7 million in borrowings and accrued interest under lines of credit with Vivint and also used approximately $34.7 million for working capital and other general corporate purposes, including growing our corporate and sales staff to support the growth of the business. We expect to use the remainder of net proceeds for working capital and general corporate purposes. We maintain the proceeds received in cash and cash equivalents.
Issuer Purchase of Equity Securities
None.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock. We currently intend to retain any future earnings to fund our growth; and therefore, we do not anticipate declaring or paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. In addition, the terms of our future debt instruments may prohibit us from paying cash dividends on our common stock. Any future determination to declare cash dividends will be made at the discretion of our board of directors, subject to applicable laws and provisions of our debt instruments and organizational documents, after taking into account our financial condition, results of operations, capital requirements, general business conditions and other factors that our board of directors may deem relevant.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
The following table sets forth selected historical consolidated financial and other data for the periods ended and at the dates indicated below. On November 16, 2012, we were acquired by our sponsor. We refer to the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 and the period from November 17, 2012 through December 31, 2012 as the Successor Periods or Successor, and the period from January 1, 2012 through November 16, 2012 as the Predecessor Period or Predecessor. Our selected historical consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, the period from November 17, 2012 to December 31, 2012 and the Predecessor Period presented in this table and the balance sheet data as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 have been derived from our historical audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this report. Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected in the future. The following selected financial data should be read in conjunction with the sections of this document captioned “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this report.
37
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except per share data) |
|
||||||||||||||
|
Statement of Operations Data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating leases and incentives |
|
$ |
21,688 |
|
|
$ |
5,864 |
|
|
$ |
109 |
|
|
|
$ |
183 |
|
|
Solar energy system and product sales |
|
|
3,570 |
|
|
|
306 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
157 |
|
|
Total revenue |
|
|
25,258 |
|
|
|
6,170 |
|
|
|
109 |
|
|
|
|
340 |
|
|
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of revenue—operating leases and incentives |
|
|
67,984 |
|
|
|
19,004 |
|
|
|
1,018 |
|
|
|
|
3,302 |
|
|
Cost of revenue—solar energy system and product sales |
|
|
1,997 |
|
|
|
123 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
95 |
|
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
21,869 |
|
|
|
7,348 |
|
|
|
533 |
|
|
|
|
1,471 |
|
|
Research and development |
|
|
1,892 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
78,899 |
|
|
|
16,438 |
|
|
|
971 |
|
|
|
|
7,789 |
|
|
Amortization of intangible assets |
|
|
14,911 |
|
|
|
14,595 |
|
|
|
1,824 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
|
187,552 |
|
|
|
57,508 |
|
|
|
4,346 |
|
|
|
|
12,657 |
|
|
Loss from operations |
|
|
(162,294 |
) |
|
|
(51,338 |
) |
|
|
(4,237 |
) |
|
|
|
(12,317 |
) |
|
Interest expense |
|
|
9,323 |
|
|
|
3,144 |
|
|
|
96 |
|
|
|
|
881 |
|
|
Other expense |
|
|
1,372 |
|
|
|
1,865 |
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
|
|
240 |
|
|
Loss before income taxes |
|
|
(172,989 |
) |
|
|
(56,347 |
) |
|
|
(4,377 |
) |
|
|
|
(13,438 |
) |
|
Income tax (benefit) expense |
|
|
(7,070 |
) |
|
|
123 |
|
|
|
(1,074 |
) |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
Net loss |
|
|
(165,919 |
) |
|
|
(56,470 |
) |
|
|
(3,303 |
) |
|
|
|
(13,445 |
) |
|
Net loss attributable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
|
(137,036 |
) |
|
|
(62,108 |
) |
|
|
(699 |
) |
|
|
|
(1,771 |
) |
|
Net (loss attributable) income available to stockholders |
|
|
(28,883 |
) |
|
|
5,638 |
|
|
|
(2,604 |
) |
|
|
|
(11,674 |
) |
|
Accretion to redemption value of Series B redeemable preferred stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
(20,000 |
) |
|
Net (loss attributable) income available to common stockholders |
|
$ |
(28,883 |
) |
|
$ |
5,638 |
|
|
$ |
(2,604 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(31,674 |
) |
|
Net (loss attributable) income available per share to common stockholders(1): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
$ |
(0.35 |
) |
|
$ |
0.08 |
|
|
$ |
(0.03 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(0.42 |
) |
|
Diluted |
|
$ |
(0.35 |
) |
|
$ |
0.07 |
|
|
$ |
(0.03 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(0.42 |
) |
|
Weighted-average shares used in computing net (loss attributable) income available per share to common stockholders(1): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
|
83,446 |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
Diluted |
|
|
83,446 |
|
|
|
75,223 |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
(1) See Note 17—Basic and Diluted Net Income (Loss) Per Share to our Consolidated Financial Statements for an explanation of the method used to calculate basic and diluted net (loss attributable) income available per share to common stockholders and the weighted-average number of shares used in the computation of the per share amounts.
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Balance Sheet Data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
261,649 |
|
|
$ |
6,038 |
|
|
$ |
11,650 |
|
|
Solar energy systems, net |
|
|
588,167 |
|
|
|
188,058 |
|
|
|
47,089 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
|
1,064,324 |
|
|
|
297,707 |
|
|
|
132,087 |
|
|
Revolving lines of credit, related party |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
41,412 |
|
|
|
15,000 |
|
|
Long-term debt |
|
|
105,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
|
128,427 |
|
|
|
73,265 |
|
|
|
17,741 |
|
|
Total equity |
|
|
613,136 |
|
|
|
80,621 |
|
|
|
71,323 |
|
38
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
Overview
You should read the following discussion together with Item 6 “Selected Financial Data” and our Consolidated Financial Statements and the related Notes included in Item 8 of this report. This discussion contains forward-looking statements about our business and operations. Our actual results may differ materially from those we currently anticipate as a result of the many factors, including those we describe under “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this report. See “Forward-Looking Statements.”
Business Overview
We offer distributed solar energy to residential customers based on long-term contracts at prices below their current utility rates. Our customer focus, neighborhood-driven direct-to-home sales model, brand and operational efficiency have driven our rapid growth in solar energy installations. We believe our continued growth is disrupting the traditional electricity market by satisfying customers’ demand for increased energy independence and less expensive, more socially responsible electricity generation.
We sell the electricity that our solar energy systems produce through long-term power purchase agreements or we lease our solar energy systems through long-term leases. Prior to 2014, all of our long-term customer contracts were structured as power purchase agreements. In 2014, we began offering leases to residential customers in connection with our entry into certain markets. Under either contract type, we install our solar energy system at our customer’s home and bill the customer monthly. In the power purchase agreement structure, we charge customers a fee per kilowatt hour based on the amount of electricity the solar energy system actually produces. In the lease structure, the customer’s monthly payment is fixed based on a calculation that takes into account expected solar energy generation. We provide our lease customers a performance guarantee, under which we agree to make a payment at the end of each year to the customer if the solar energy system does not meet the guaranteed production level in the prior 12-month period. The power purchase agreement and lease terms are typically for 20 years, and virtually all the prices that we charge to our customers are subject to pre-determined annual fixed percentage price escalations as specified in the customer contract. Since the beginning of 2014, substantially all of our customer contracts have included an annual price escalator of 2.9%. We do not believe that either form of long-term customer contract is materially more advantageous to us than the other.
We compete mainly with traditional utilities. In the markets we serve, our strategy is to price the energy we sell below prevailing retail electricity rates. As a result, the price our customers pay to buy energy from us varies depending on the state where the customer is located and the local traditional utility. In markets that are also served by other distributed solar energy system providers, the price we charge also depends on customer price sensitivity, the need to offer a compelling financial benefit and the price other solar energy companies charge in the region.
Our ability to offer long-term customer contracts depends in part on our ability to finance the installation of the solar energy systems by co-investing or entering into lease arrangements with fund investors who value the resulting customer receivables and investment tax credits, accelerated tax depreciation and other incentives related to the solar energy systems through structured investments known as “tax equity.” Tax equity investments are generally structured as non-recourse project financings. In the context of the distributed solar energy market, tax equity investors make an upfront advance payment to a sponsor through an investment fund in exchange for a share of the tax attributes and cash flows emanating from an underlying portfolio of solar energy systems. In these tax equity investments, the U.S. federal tax attributes offset taxes that otherwise would have been payable on the investors’ other operations. As of February 28, 2015, we had raised 13 investment funds to which investors such as banks and other large financial investors have committed to invest approximately $673 million, which will enable us to install solar energy systems of total fair market value approximating $1.6 billion. As of February 28, 2015, we had tax equity commitments to fund approximately 71 megawatts of future deployments, which we estimate to be sufficient to fund solar energy systems with a total fair market value of approximately $331 million. The terms and conditions of each investment fund vary significantly by investor and by fund. We continue to negotiate with financial investors to create additional investment funds.
Our investment funds have adopted either the partnership or inverted lease structures. Under partnership structures, we and our fund investors contribute cash into a partnership company. The partnership uses this cash to acquire solar energy systems developed by us and sells energy from such systems to customers or directly leases the solar energy systems to customers. Under our existing inverted lease structure, we and the fund investor set up a multi-tiered investment vehicle, comprised of two partnership entities, that facilitates the pass through of the tax benefits to the fund investors. In this structure we contribute solar energy systems to a lessor partnership entity in exchange for interests in the lessor partnership and the fund investors contribute cash to a lessee partnership in exchange for interests in the lessee partnership which in turn makes an investment in the lessor partnership entity in exchange for interests in the lessor partnership. The lessor partnership distributes the cash contributions received from the lessee partnership to our wholly owned subsidiary that contributed the projects to the lessor partnership. The lessor partnership leases the contributed solar energy systems to the lessee partnership under a master lease, and the lessee partnership pays the lessor partnership rent for those systems.
39
We have determined that we are the primary beneficiary in these partnership and inverted lease structures for accounting purposes. Accordingly, we consolidate the assets and liabilities and operating results of these partnerships in our consolidated financial statements. We recognize the fund investors’ share of the net assets of the investment funds as non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests in our condensed consolidated balance sheets. These income or loss allocations, reflected on our condensed consolidated statement of operations, can have a significant impact on our reported results of operations.
Recent Developments
Working Capital Credit Facility
In March 2015, we entered into a credit agreement with certain financial institutions for which Goldman Sachs Lending Partners LLC is acting as administrative agent and collateral agent, under which we may from time to time incur up to an aggregate principal amount of $131.0 million in revolver borrowings. Upon the satisfaction of certain conditions and the approval of the lenders, we may increase the aggregate amount of revolver borrowings to $150.0 million. Loans under the revolving credit facility will be used for the construction and acquisition of solar energy systems, and letters of credit may be issued under the revolving credit facility for working capital and general corporate purposes. The revolving credit facility matures in March 2020.
Increase of Aggregation Facility
In February 2015, we with Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, entered into an amendment to our aggregation credit facility, or the Aggregation Facility, that increased the funding commitment by $25.0 million pursuant to which we may borrow up to an aggregate of $375.0 million. In addition, the right to which we may request additional borrowing capacity upon the satisfaction of certain conditions and the approval of the lenders was reduced to $175.0 million, such that the total potential capacity under the facility remains at $550.0 million. The other terms of the Aggregation Facility remained unchanged.
Discontinuance of Solmetric Products
In February 2015, we decided to discontinue the external sales of Solmetric’s SunEye and PV Designer products, which were at the end of their product life cycles. We will continue selling the Solmetric PV Analyzer product. We will continue to produce and develop the SunEye and PV Designer products for internal use only. The Solmetric development team will be known as Vivint Solar Labs, a research and development team focused on proprietary photovoltaic installation instruments and software. As a result of the discontinuance of these products, we will be recording a noncash impairment charge of approximately $4.0 million to $5.0 million for intangible and other assets related to these two products in the first quarter of 2015. In 2014, these two products accounted for approximately $2.1 million of revenue.
Investment Funds
During the fourth quarter of 2014, we formed two solar investment funds with fund investors. The total commitment under these investment funds was $80.0 million. In February 2015, we also entered into a solar investment fund arrangement with an existing investor. The total commitment under this investment fund arrangement is $50.0 million.
Key Operating Metrics
We regularly review a number of metrics, including the following key operating metrics, to evaluate our business, measure our performance, identify trends affecting our business, formulate financial projections and make strategic decisions. Some of our key operating metrics are estimates. These estimates are based on our management’s beliefs and assumptions and on information currently available to management. Although we believe that we have a reasonable basis for each of these estimates, these estimates are based on a combination of assumptions that may not prove to be accurate over time, particularly given that a number of them involve estimates of cash flows up to 30 years in the future. Underperformance of the solar energy systems, payment defaults by our customers, cancellation of signed contracts, competition from other distributed solar energy companies, development in the distributed solar energy market and the energy market more broadly, technical innovation or other factors described under the section of this report captioned “Risk Factors” could cause our actual results to differ materially from our calculations. Furthermore, while we believe we have calculated these key metrics in a manner consistent with those used by others in our industry, other companies may in fact calculate these metrics differently than we do now or in the future, which would reduce their usefulness as a comparative measure.
|
· |
Solar energy system installations. Solar energy system installations represents the number of solar energy systems installed on customers’ premises. Cumulative solar energy system installations represents the aggregate number of solar energy systems that have been installed on customers’ premises. We track the number of solar energy system installations as of the end of a given period as an indicator of our historical growth and as an indicator of our rate of growth from period to period. |
40
|
· |
Megawatts installed. Megawatts installed represents the aggregate megawatt nameplate capacity of solar energy systems that have been installed during the applicable period. Cumulative megawatts installed represents the aggregate megawatt nameplate capacity of solar energy systems that have been installed. We track the nameplate capacity of our solar energy systems as measured in megawatts DC STC, or direct current standard test conditions. Because the size of solar energy systems varies greatly, we believe that tracking the aggregate megawatt nameplate capacity of the systems is an indicator of our growth rate. We track megawatts installed in a given period as an indicator of asset growth in the period and cumulative megawatts installed as of the end of a given period as an indicator of our historical growth. |
|
· |
Estimated nominal contracted payments remaining. Estimated nominal contracted payments remaining equals the sum of the remaining cash payments that our customers are expected to pay over the term of their agreements with us for systems installed as of the measurement date. For a power purchase agreement, we multiply the contract price per kilowatt-hour by the estimated annual energy output of the associated solar energy system to determine the estimated nominal contracted payments. For a customer lease, we include the monthly fees and upfront fee, if any, as set forth in the lease. We use the nominal contracted payments, together with the value attributable to investment tax credits, accelerated depreciation, solar renewable energy certificates, or SRECs, state tax benefits and rebates, to cover the fixed and variable costs associated with installing solar energy systems. Estimated nominal contracted payments remaining is a reporting metric forecasted as of specified dates. It is a forward-looking number, and we use judgment in developing the assumptions used to calculate it. The primary assumption in the calculation is the annual energy output of the associated solar energy systems, which is estimated based on typical annual sun hours given the system’s location, nameplate production capacity of the system, and estimated declines in the solar equipment productivity over the life of the system. Those assumptions may not prove to be accurate over time. Estimated retained value and estimated retained value per watt amounts do not consider the impact of other events that could adversely affect the cash flows generated by the solar energy system during the contract term and anticipated renewal period. These events could include, but are not limited to, non-payment of obligated amounts by the customer, declines in utility rates for residential electricity or early contract termination by the customer as a result of the customer purchasing the solar energy system in connection with the sale of the home on which the solar energy system is installed. |
|
· |
Estimated retained value. Estimated retained value represents the net cash flows discounted at 6% that we expect to receive from customers pursuant to long-term customer contracts net of estimated cash distributions to fund investors and estimated operating expenses for systems installed as of the measurement date. Estimated retained value, and the other metrics that are based on estimated retained value, are key operating metrics because these amounts reflect the net cash flows we expect to receive from customers pursuant to long-term customer contracts and represent valuable future revenue streams created by our operations, but which are not yet recognized on our financial statements. |
|
· |
Estimated retained value under energy contracts. Estimated retained value under energy contracts represents the estimated retained value from the solar energy systems during the typical 20-year term of our contracts. |
|
· |
Estimated retained value of renewal. Estimated retained value of renewal represents the estimated retained value associated with an assumed 10-year renewal term following the expiration of the initial contract term. To calculate estimated retained value of renewal, we assume all contracts are renewed at 90% of the contractual price in effect at the expiration of the initial term. |
|
· |
Estimated retained value per watt. Estimated retained value per watt is calculated by dividing the estimated retained value as of the measurement date by the aggregate nameplate capacity of solar energy systems under long-term customer contracts that have been installed as of such date, and is subject to the same assumptions and uncertainties as estimated retained value. We have chosen to initially introduce our solar energy systems in states where utility rates, solar resource and regulatory policies provide for the most compelling market for distributed solar energy. Although we believe there are many other markets that have attractive economics for us, estimated retained value per watt will decrease over time because these markets are not as attractive as the ones in which we currently operate. We may experience disproportionate growth in markets that offer attractive incentives such as SRECs, the value of which is not reflected in estimated retained value. In addition, the estimated retained value associated with commercial and industrial solar energy systems is typically less than that for residential solar energy systems. To the extent we expand into the commercial and industrial market, estimated retained value per watt will also be adversely affected. Furthermore, other companies may calculate estimated retained value per watt (or a similar metric) differently than we do, which reduces its usefulness as a comparative measure. |
41
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|||
|
Solar energy system installations |
|
|
22,424 |
|
|
|
10,521 |
|
|
|
2,669 |
|
|
Megawatts installed |
|
|
155.4 |
|
|
|
58.0 |
|
|
|
14.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|||
|
Cumulative solar energy system installations |
|
|
35,720 |
|
|
|
13,296 |
|
|
|
2,775 |
|
|
Cumulative megawatts installed |
|
|
228.2 |
|
|
|
72.8 |
|
|
|
14.8 |
|
|
Estimated nominal contracted payments remaining (in millions) |
|
$ |
1,030.5 |
|
|
$ |
394.1 |
|
|
$ |
89.2 |
|
|
Estimated retained value under energy contracts (in millions) |
|
$ |
383.1 |
|
|
$ |
151.2 |
|
|
$ |
33.1 |
|
|
Estimated retained value of renewal (in millions) |
|
$ |
97.9 |
|
|
$ |
39.2 |
|
|
$ |
8.5 |
|
|
Estimated retained value (in millions) |
|
$ |
480.9 |
|
|
$ |
190.4 |
|
|
$ |
41.6 |
|
|
Estimated retained value per watt |
|
$ |
2.11 |
|
|
$ |
2.62 |
|
|
$ |
2.83 |
|
Factors Affecting Our Performance
Availability of Capital
Our future success depends on our ability to raise capital from third-party investors on competitive terms to help finance the deployment of our residential solar energy systems. There are a limited number of potential investment fund investors and the competition for these investments is intense. The principal tax credit on which fund investors in our industry rely is the investment tax credits, or ITC. By statute, the ITC is scheduled to decrease to 10% of the fair market value of a solar energy system on January 1, 2017 from 30% today, and the amounts that fund investors are willing to invest could decrease or we may be required to provide a larger allocation of customer payments to the fund investors as a result of this scheduled decrease. We intend to create additional investment funds with financial investors and corporate investors. We also use debt, equity or other financing strategies to fund our operations, including our obligations to make contributions to investment funds. Such other financing strategies may increase our cost of capital.
Incentives; Net Metering
Our cost of capital, the price we can charge for electricity, the cost of our systems and the demand for residential distributed solar energy is impacted by a number of federal, state and local government incentives and regulations, including: tax credits, particularly the ITC; tax abatements; rebate programs; net metering; SRECs and to a lesser extent, cash grants, particularly the U.S. Treasury grant program. These programs have on occasion been challenged by incumbent utilities and questioned by those in government and others arguing for less governmental spending and involvement in the energy market. For example, in 2014 net metering programs were subject to regulatory scrutiny in Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada and Utah where regulators have considered imposing limits on the aggregate capacity of net metering generation and reducing the rate that net metering customers are paid for the power that they deliver back to the grid based on claims that homeowners with net metered solar systems shift the costs of maintaining the electric grid onto other ratepayers. To the extent that such views are reflected in government policy, the reduction of such incentives could adversely affect our results of operations, cost of capital and growth prospects. We also apply for and receive SRECs and other state-level incentives in certain jurisdictions for power generated by our solar energy systems, which comprise a significant portion of the value to us of the associated solar energy systems. The market for SRECs is extremely volatile and sellers are often able to obtain better unit pricing by selling a large quantity of SRECs. As a result, we may sell SRECs infrequently, at opportune times and in large quantities and the timing and volume of our SREC sales may lead to fluctuations in our quarterly results. While we have received U.S. Treasury grants with respect to some of the solar energy systems that we have installed in the past, we have no other existing cash grant investment funds. If we were to enter into cash grant funds in the future we may be required to engage in further discussions with, or otherwise be subject to investigation by, the U.S. Treasury Department in relation to applications for cash grants made by such funds.
42
Cost of Solar Energy Systems
Since our inception, the cost of solar panels and the components necessary to manufacture them has declined, which has been a key driver in the price we charge for electricity and customer adoption of solar energy. We have purchased substantially all of the solar panels used in our solar energy systems from manufacturers based in China which have benefited from favorable governmental policies and subsidies by the Chinese government. More recently, solar panel and component prices have stabilized and could increase in the future. In recent years, the U.S. government has imposed anti-dumping duties and countervailing duties on solar panels and other system components produced in China and Taiwan. See “Risk Factors—Risk Related to our Business—Our business has benefited from the declining cost of solar panels, and our financial results may be harmed now that the cost of solar panels has stabilized and could increase in the future.” As a result, we have begun sourcing solar cells from manufacturers located outside of China or Taiwan. The cost of other components, such as inverters, racking systems and other electrical equipment, may also vary from period to period. If solar energy system costs begin to increase, whether as a result of these tariffs or because of the removal of government subsidies, we may be forced to pass these costs on to our customers and the value proposition for customers would decrease. Alternatively, our financial results would decrease if we did not pass these costs on to our customers.
Expansion into New Markets
As of February 28, 2015, we operate in Arizona, California, Hawaii, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York and Utah. We chose to initially introduce our solar energy systems in these states based on the utility prices, sun exposure, climate conditions and regulatory policies in those states. We believe that these states remain underpenetrated. Accordingly, we intend to further penetrate these markets by introducing our solar energy systems into new neighborhoods and communities in states where we already have operations.
In recent years, the combination of declining solar energy system costs and increasing retail electricity prices have made distributed solar energy a cost effective power source for homeowners in an increasing number of markets. We plan to enlarge our addressable market by expanding into new states that present attractive economics for us and homeowners. We believe our scalable approach to entering new geographic markets significantly accelerates the time required for us to effectively sell in a particular market after establishing a new office.
During 2015 we plan to open at least 20 new offices in states in which we currently have operations and new states into which we are expanding.
Utility rates, availability of state incentives, other state, regional and local regulations, sun exposure and weather conditions, which can impact sales, installation and system productivity, vary by market. For example, markets in California typically have higher utility rates than markets in the Eastern United States. As a result, systems in California typically have a higher retained value than systems in the Eastern United States. However, we are entitled to receive SRECs and other state incentives in many Eastern states that are not available in Western United States. Although the impact of such incentives is not reflected in the retained value of the associated systems, they do generate value for us. As a result our financial and operating results will be affected by the geographic mix of the systems we install.
Additionally, we intend to enter the commercial and industrial market, which includes small businesses such as community retailers as well as larger retailers and manufacturers. We plan to pursue similar debt, equity and other financing strategies consistent with our approach in the residential market, including creating investment funds, to help finance such solar energy systems.
Sales Channels
We employ a direct-to-home sales model because we believe it improves sales effectiveness. Currently, we ask potential customers to sign long-term customer contracts at no upfront cost to them and prior to us conducting a formal assessment of the home, designing a system, obtaining permits and other actions required prior to installation. As may be expected with a direct sales model, a large number of potential customers who sign long-term customer contracts ultimately elect not to have a system installed or the potential customers fail to meet our underwriting standards. We believe there are opportunities to improve the rate at which potential customers ultimately move forward through system installation, including by conducting the formal assessment of the home or installing a control panel on the day the contract is signed, or requiring potential customers to commit to a modest upfront fee that would be credited against payments under our contracts with them. We are currently evaluating such changes to determine if they can improve our signing to installation rate.
In addition to direct sales, we are currently exploring opportunities to sell solar energy systems to customers through a number of distribution channels, including relationships with home builders, large construction, electrical and roofing companies and other third parties, such as home improvement stores, kiosks and retail stores. We believe that such initiatives will contribute to our revenue growth. The potential impact of these initiatives on our financial results, however, is uncertain because while the price per kilowatt we can charge may be lower, we expect to benefit from more favorable cost structures by virtue of the larger nature of the installations.
43
Operations as a Stand-Alone Company
Historically, we have relied on the administrative and operational support of our sister company Vivint Inc., or Vivint, to run our business. Some of the Vivint resources we have used include office space, information and technology resources and systems, purchasing services, operational and fleet services and marketing services. As such, our historical financial information does not necessarily reflect what our financial position, results of operations, cash flows or costs and expenses would have been had we operated separately from Vivint during the historical periods presented in this report. The historical costs and expenses reflected in our consolidated financial statements include charges to certain corporate functions historically provided to us by Vivint. We and Vivint believe these charges are reasonable reflections of the historical utilization levels of these services in support of our business.
Although we have made and are continuing to make investments to support our near and longer-term growth as a fully independent company, we will continue to have an ongoing relationship with Vivint which will provide services such as information technology and infrastructure, employee benefits and certain other services. Our continued expansion may exceed the capacity that Vivint is able to provide under the terms of such agreement. If Vivint is unable to satisfy its obligations thereunder on a timely basis, we may face difficulties in providing these services internally or implementing acceptable, substitute arrangements with third-party providers. Furthermore, as we transition IT and other systems and certain corporate functions from Vivint and rely on our own infrastructure, we may experience interruptions or inefficiencies that adversely affect our operations, customer satisfaction and increase our costs.
Components of Results of Operations
Revenue
We classify and account for our long-term power purchase agreements as operating leases, and recognize revenue from these contracts based on the actual amount of power generated at rates specified under the contracts. In 2014, we began offering solar energy systems to customers pursuant to legal-form leases in certain markets. We recognize revenue based on the amount of power generated at rates specified under the contracts and establish a reserve for those lease contracts for which we may have to make a payment at the end of each year to the customer if the solar energy systems do not meet a guaranteed production level in the prior 12-month period.
We consider the proceeds from solar energy system rebate incentives offered by certain state and local governments to form part of the payments under our operating leases and recognize such payments as revenue over the contract term. We record revenue from our operating leases over the term of our long-term customer contracts, which is typically 20 years. We also apply for and receive SRECs in certain jurisdictions for power generated by our solar energy systems. We generally recognize revenue related to the sale of SRECs upon delivery. The market for SRECs is extremely volatile and sellers are often able to obtain better unit pricing by selling a large quantity of SRECs. As a result, we may sell SRECs infrequently, at opportune times and in large quantities and the timing and volume of our SREC sales may lead to fluctuations in our quarterly results. For the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, approximately 10% and 5% of our revenue was attributable to SREC sales, and less than 1% of our revenue was attributable to state and local rebates and incentives in both periods. On occasion we have sold solar energy systems for cash. In these instances, the revenue is recognized upon the solar energy system passing inspection by the responsible city department. Subsequent to our acquisition of Solmetric Corporation, or Solmetric, in the first quarter of 2014, we began recognizing revenue related to the sale of photovoltaic installation software products and devices, a portion of which consists of post-contract customer support, or PCS. PCS includes the implied right to receive, on a when and if available basis, future unspecified software upgrades and features as well as bug fixes, email and telephone support. Because we are not able to determine vendor-specific objective evidence of fair value, or VSOE for the PCS, revenue from the entire arrangement is recognized ratably over four years, which is the economic life over which the upgrades are expected to be provided.
For a breakout of our revenue by major product type, see Note 2—Summary of Significant Accounting Policies.
44
Operating Expenses
Cost of Revenue. Cost of operating leases and incentives is comprised of the depreciation of the cost of the solar energy systems, which are depreciated for accounting purposes over 30 years; the amortization of initial direct costs, which are amortized over the term of the long-term customer contract; and the indirect costs related to the processing, account creation, design, installation, interconnection and servicing of solar energy systems, which are not capitalized, such as personnel costs not directly associated to a solar energy system installation, warehouse rent, utilities and fleet vehicle executory costs. Under our direct sales model, a vast majority of payments to our direct sales personnel consist of commissions attributable to long-term customer contract acquisition. Capitalized initial direct costs consist of these commissions and other customer acquisition expenses. The cost of operating leases and incentives related to the sales of SRECs is limited to broker fees, which are only paid in connection with certain transactions. Accordingly, the sale of SRECs in a quarter favorably impacts our operating results for that period. In future periods, we anticipate that our costs on a per watt value basis will decrease due to expected decreases in material costs. However, we expect our cost of operating leases and incentives revenue will continue to increase in absolute dollars as we continue to grow our volume of installations and increase headcount related to support and operations.
Cost of solar energy system and product sales consists of direct and indirect material and labor costs for solar energy systems. It also consists of materials, personnel costs, depreciation, facilities costs, other overhead costs and infrastructure expenses associated with the manufacturing of the photovoltaic installation software products and devices.
Sales and Marketing Expenses. Sales and marketing expenses include personnel costs, such as salaries, benefits, bonuses and stock-based compensation for our corporate sales and marketing employees and exclude costs related to our direct sales personnel that are accounted for as cost of revenue. Sales and marketing expenses also include advertising, promotional and other marketing-related expenses; certain allocated corporate overhead costs related to facilities and information technology; travel and professional services. In future periods, we anticipate sales and marketing costs to increase significantly in absolute dollars as we continue to grow our headcount for sales employees and undertake marketing initiatives to continue growing our business.
Research and Development. Research and development expense is comprised primarily of salaries and benefits and other costs related to the development of photovoltaic installation software products and devices. Research and development costs are charged to expense when incurred. In future periods we anticipate research and development costs to increase slightly in absolute dollars.
General and Administrative Expenses. General and administrative expenses include personnel costs, such as salaries, bonuses and stock-based compensation related to our general and administrative personnel; professional fees related to legal, human resources, accounting and structured finance services; travel; and certain allocated corporate overhead costs related to facilities and information technology. In future periods, we expect that general and administrative expenses will increase slightly in absolute dollars in order to support the growth in our business, to build a corporate infrastructure separate from Vivint, to operate as a public reporting company and to manage an increasing number of investment fund arrangements. Our historical financial results include charges for the use of services provided by Vivint centralized departments and shared facilities. These costs were based on the actual cost incurred by Vivint without mark-up. The charges to us may not be representative of what the costs would have been had we operated separately from the Vivint businesses during the periods presented. However, we believe the amounts charged are representative of the incremental cost to Vivint to provide these services to us. In future periods, we expect to continue to use certain of these services, such as information and technology resources and systems and marketing services, from Vivint as part of the transition services agreements, which provide that we continue to be charged for actual costs incurred.
Amortization of Intangible Assets. We recorded intangible assets at their fair value of $43.8 million as of November 17, 2012, the date of our acquisition by 313 Acquisition LLC. Such intangible assets are being amortized over their estimated useful life of three years. In addition, we recorded finite-lived intangible assets of $3.7 million with useful lives ranging from five to ten years as part of the Solmetric acquisition in January 2014. As part of the Solmetric acquisition, we also recorded intangible assets of $2.1 million related to in-process research and development which are subject to amortization upon completion of the project or impairment if the project is subsequently abandoned. In 2014, we also recorded $0.4 million of capitalized software development costs related to the development of an internal-use software application that is intended to improve the sales process and to the development of an internal use inventory tracking system.
45
Non-Operating Expenses
Interest Expense. Interest expense primarily consists of the interest charges associated with our indebtedness including the amortization of deferred financing costs and the interest component of capital lease obligations. In the future we may incur additional indebtedness to fund our operations and our interest expense would correspondingly increase.
Other Expense. Other expense consists primarily of interest and penalties primarily associated with employee payroll withholding tax payments which were not paid in a timely manner.
Income Tax (Benefit) Expense. All of our business is conducted in the United States, and therefore income tax (benefit) expense consists of current and deferred income taxes incurred in U.S federal, state and local jurisdictions.
Net (Loss Attributable) Income Available to Stockholders
We determine the net (loss attributable) income available to stockholders by deducting from net loss the net loss attributable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests. The net loss attributable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests represents the investment fund investors’ allocable share in the results of operations of the investment funds, which we consolidate.
We have determined that the legal provisions in the contractual arrangements of the investment funds represent substantive profit-sharing arrangements, where the allocation to the partners differ from the stated ownership percentages. We have further determined that the appropriate methodology for attributing income and loss to the non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests each period is a balance sheet approach using the hypothetical liquidation at book value, or HLBV, method. Under the HLBV method, the amounts of income and loss attributed to the non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests in the consolidated statements of operations reflect changes in the amounts the fund investors would hypothetically receive at each balance sheet date under the liquidation provisions of the contractual agreements of these funds, assuming the net assets of the respective investment funds were liquidated at recorded amounts determined in accordance with GAAP. The fund investors’ interest in the results of operations of these investment funds is determined as the difference in the fund investors’ claim under the HLBV method at the start and end of each reporting period, after taking into account any capital transactions between the fund and the fund investors. For all of our investment funds, the application of HLBV is performed consistently. However, the results of that application and its impact on the income or loss allocated between us and the non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests depend on the respective funds’ specific contractual liquidation provisions. For all of our investment funds, the HLBV results are generally affected by, among other factors, the tax attributes allocated to the fund investors including tax bonus depreciation and investment tax credits or U.S. Treasury grants received in lieu of the investment tax credits, the amount of preferred returns that have been paid to the fund investors by the investment funds, and the allocation of taxable income or losses in a liquidation scenario.
Regardless of the investment fund structure, the contractual liquidation provisions of our existing funds provide that the allocation percentages between us and the investor change, or “flip,” under certain circumstances. Prior to the point at which the allocation percentage flips, the investor is entitled to receive a contractually agreed upon allocation of the value generated by the solar energy systems. The allocation of cash payments received from customers may differ from the allocation of other tax benefits. Afterwards, we are entitled to receive the majority of the value generated by the solar energy systems. The difference between our current inverted lease structures and our current partnership structures that drives a significant impact on our results from the application of the HLBV method is how the flip point is determined. The result of this difference is described in detail in the following paragraphs.
For our existing investment funds that have adopted the partnership structure, the flip point is tied to the achievement of the fund investor’s targeted after tax rate of return. The receipt of tax benefits by the fund investor count towards the achievement of such target, which reduces the amount distributable to the fund investor in a hypothetical liquidation under these funds’ contractual liquidation provisions. This generally results in a net loss attributable to the fund investor in the period in which these tax benefits are received as a result of our application of the HLBV method.
For our existing investment funds that have adopted the inverted lease structure, the flip point is typically tied to the passage of a period of time that corresponds to the expiration of the recapture period associated with ITCs. An investor in a fund with an inverted lease fund structure will receive tax benefits similar to an investor in a fund that has adopted a partnership structure; however, unlike the partnership investment fund structure, the receipt of tax benefits by the fund investor does not impact the amount distributable to the fund investor in a hypothetical liquidation under these funds’ contractual liquidation provisions. At the flip point, which typically corresponds to the end of the ITC recapture period, the fund investor’s claims on the net assets of the investment fund generally decreases. This is expected to result in a net loss attributable to the fund investor in the period when the flip occurs as a result of our application of the HLBV method.
46
These differences are a result of the specific contractual provisions for each of our existing funds and are not necessarily indicative of terms for our future partnership or inverted lease structures. Future investment funds may contain different features than those that we currently employ and, as a result, would not necessarily impact the HLBV calculation and resulting allocation of net income or loss in the same way that our existing funds do.
The HLBV calculation for both fund structures is also impacted by the difference between the cash received by us from the investment funds and the carrying value of the solar energy systems contributed to the investment funds. The purchase price paid for solar energy systems by an investment fund is based on the fair market value, as determined by an independent appraiser. As we consolidate both the subsidiary that develops the solar energy systems and the investment fund, the sales of the solar energy systems are considered transactions under common control and are therefore reflected at their historical cost, or their carryover basis. Cash received in excess of the installed purchased solar energy systems’ carryover basis is treated as deemed distributions from the investment fund to us. In most cases, any excess of the purchase price over the carryover basis of the solar energy systems would result in allocations of income to us.
The HLBV calculation for both fund structures may also be affected by the timing of an investor’s cash contribution to the investment fund relative to the timing of the contribution or sale of the solar energy systems to the applicable investment fund. A portion of the solar energy systems purchased by, or contributed to, an investment fund are not installed at the time of purchase or contribution and therefore do not have any carryover basis allocated to them. Our wholly owned subsidiary has an obligation to purchase, install and provide the solar energy system equipment to an investment fund for any in-progress projects that were previously purchased by such fund. If our wholly owned subsidiary does not ultimately provide the investment fund with the solar energy systems that it purchased, it is required to refund the purchase price to the investment fund. In these specific cases, we determined that the portion of the cash purchase price paid by an investment fund that relates to in-progress projects should be recorded as a receivable by the investment fund, representing the investment fund’s right to receive solar panels and related equipment for solar energy systems that are installed after the project is purchased by the investment fund. Given that our subsidiary controls the investment fund, we have accounted for the receivable balance as a reduction in the investment fund’s members’ equity in accordance with GAAP. Initially this may result in allocations of losses amongst the partners, as the GAAP equity balance is less than the tax capital account. The allocations of such losses amongst the partners follow the contractual liquidation provisions of the partnership agreements. When such solar energy systems are subsequently installed, the systems are recorded at their carryover basis as a common control transaction and the receivable balance is eliminated. With the elimination of the receivable, the investment fund’s member’s equity is increased to the extent of the carrying amount of the assets contributed, which results in the reversal of a portion of the prior allocation of losses. In most cases, the reversal of such losses occurs within a short period of time, approximately three to six months. As discussed above, the difference between the receivable balance eliminated and the carryover basis of the installed solar energy systems is treated as deemed distributions from the investment fund to us, and as a result, that portion of the prior allocation of losses is not reversed over time.
If the redemption value of our redeemable non-controlling interests exceeds their carrying value after attribution of income or loss under the HLBV method in any period, we will make an additional attribution of income to our redeemable non-controlling interests such that their carrying value will at least equal the redemption value.
We apply the HLBV method consistently across our investment funds. However, the impact on non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests may vary significantly period-to-period depending on the structure of the funds we enter into, the contractual liquidation provisions of such investment funds, the age of such investment funds and the timing of an investor’s cash contribution to the investment fund relative to the timing of the contribution or sale by us of the solar energy system to the applicable investment fund.
47
Results of Operations
The results of operations presented below should be reviewed in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this report.
The following table sets forth selected consolidated statements of operations data for each of the periods indicated.
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating leases and incentives |
|
$ |
21,688 |
|
|
$ |
5,864 |
|
|
$ |
109 |
|
|
|
$ |
183 |
|
|
Solar energy system and product sales |
|
|
3,570 |
|
|
|
306 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
157 |
|
|
Total revenue |
|
|
25,258 |
|
|
|
6,170 |
|
|
|
109 |
|
|
|
|
340 |
|
|
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of revenue—operating leases and incentives |
|
|
67,984 |
|
|
|
19,004 |
|
|
|
1,018 |
|
|
|
|
3,302 |
|
|
Cost of revenue—solar energy system and product sales |
|
|
1,997 |
|
|
|
123 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
95 |
|
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
21,869 |
|
|
|
7,348 |
|
|
|
533 |
|
|
|
|
1,471 |
|
|
Research and development |
|
|
1,892 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
78,899 |
|
|
|
16,438 |
|
|
|
971 |
|
|
|
|
7,789 |
|
|
Amortization of intangible assets |
|
|
14,911 |
|
|
|
14,595 |
|
|
|
1,824 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
|
187,552 |
|
|
|
57,508 |
|
|
|
4,346 |
|
|
|
|
12,657 |
|
|
Loss from operations |
|
|
(162,294 |
) |
|
|
(51,338 |
) |
|
|
(4,237 |
) |
|
|
|
(12,317 |
) |
|
Interest expense |
|
|
9,323 |
|
|
|
3,144 |
|
|
|
96 |
|
|
|
|
881 |
|
|
Other expense |
|
|
1,372 |
|
|
|
1,865 |
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
|
|
240 |
|
|
Loss before income taxes |
|
|
(172,989 |
) |
|
|
(56,347 |
) |
|
|
(4,377 |
) |
|
|
|
(13,438 |
) |
|
Income tax (benefit) expense |
|
|
(7,070 |
) |
|
|
123 |
|
|
|
(1,074 |
) |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
Net loss |
|
|
(165,919 |
) |
|
|
(56,470 |
) |
|
|
(3,303 |
) |
|
|
|
(13,445 |
) |
|
Net loss attributable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
|
(137,036 |
) |
|
|
(62,108 |
) |
|
|
(699 |
) |
|
|
|
(1,771 |
) |
|
Net (loss attributable) income available to stockholders |
|
|
(28,883 |
) |
|
|
5,638 |
|
|
|
(2,604 |
) |
|
|
|
(11,674 |
) |
|
Accretion to redemption value of Series B redeemable preferred stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
(20,000 |
) |
|
Net (loss attributable) income available to common stockholders |
|
$ |
(28,883 |
) |
|
$ |
5,638 |
|
|
$ |
(2,604 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(31,674 |
) |
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2014 and 2013
Revenue
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
$ Change |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2014 from 2013 |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
||||||||||
|
Total revenue |
|
$ |
25,258 |
|
|
$ |
6,170 |
|
|
$ |
19,088 |
|
|
The increase in total revenue of $19.1 million was primarily the result of an increase of $13.4 million related to operating lease and incentives and an increase of $2.3 million in the sale of SRECs as the number of installed solar energy systems in service increased 154%. In addition, subsequent to the Solmetric acquisition in January 2014, we recognized revenue of $3.2 million related to the sale of photovoltaic installation software products and devices. We did not recognize revenue related to the sale of photovoltaic installation software products and devices in 2013 as the Solmetric acquisition occurred in January 2014.
48
Operating Expenses
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
$ Change |
|
||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2014 from 2013 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of revenue—operating leases and incentives |
|
$ |
67,984 |
|
|
$ |
19,004 |
|
|
$ |
48,980 |
|
|
Cost of revenue—solar energy system and product sales |
|
|
1,997 |
|
|
|
123 |
|
|
|
1,874 |
|
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
21,869 |
|
|
|
7,348 |
|
|
|
14,521 |
|
|
Research and development |
|
|
1,892 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,892 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
78,899 |
|
|
|
16,438 |
|
|
|
62,461 |
|
|
Amortization of intangible assets |
|
|
14,911 |
|
|
|
14,595 |
|
|
|
316 |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
$ |
187,552 |
|
|
$ |
57,508 |
|
|
$ |
130,044 |
|
Cost of Revenue. The increase in cost of revenue—operating leases and incentives of $49.0 million was in part due to a $21.6 million increase in compensation and benefit costs that were expensed in the period related to the design, installation and interconnection of solar energy systems to the power grid primarily due to growth in installation and operations employee headcount of 127% in 2014 and the increase in the number of installed solar energy systems. Other direct installation costs increased $6.8 million and were comprised of items such as rentals and purchases of tools and equipment, inventory obsolescence, insurance and supplies. In addition, depreciation and amortization of solar energy systems increased $6.1 million primarily due to the increase in the number of installed solar energy systems consistent with the significant growth in revenue over these periods. Facility and information technology expenses increased $5.9 million due to our increased headcount and increased utilization of office space by our employees. Other factors contributing to the increase in these expenses were the increases in fleet vehicle maintenance, insurance, warehouse and other related costs of $4.9 million; travel costs related to design and installation activities of $1.4 million; and stock-based compensation of $1.1 million.
The increase in cost of revenue—solar energy system and product sales of $1.9 million was primarily due to the costs of photovoltaic installation software products following the Solmetric acquisition in January 2014.
Sales and Marketing Expense. The increase in sales and marketing expense of $14.5 million was attributable primarily to our continued efforts to grow our business by entering into new markets, opening new sales offices in various locations and increased hiring of sales and marketing personnel, resulting in a sales and marketing employee headcount increase of 120% in 2014. Additionally, the increase in expenses was primarily due to increased compensation and benefits expense of $7.2 million due to the increased headcount, including an increase of $0.8 million related to stock-based compensation; an increase in costs related to advertising, promotional and other marketing-related expenses of $2.7 million; an increase in travel and housing expenses of $2.3 million; and an increase in sales and marketing related administrative costs of $1.7 million.
Research and Development Expense. The $1.9 million increase in research and development expense was attributable to photovoltaic installation software product and device development in 2014. Prior to the Solmetric acquisition in January 2014, we did not incur any research and development expenses.
General and Administrative Expense. The increase in general and administrative expenses of $62.5 million primarily resulted from an increase in professional service fees and stock-based compensation expense. Our professional service fees increased $17.4 million driven primarily from costs related to our initial public offering and preparations to become a public reporting company. Stock-based compensation increased $21.5 million, of which $14.8 million related to purchases of our stock by two of our directors in September 2014 (see Note 12—Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests, Equity and Preferred Stock for more details on this transaction). Our compensation and benefits increased $12.8 million as our employee headcount increased by 310% in 2014 across our general and administrative functions to a level necessary to support the growth of the business. Fees related to the initiation of tax equity investment funds increased by $6.6 million as we closed seven tax equity investment funds during 2014.
Amortization of Intangible Assets. The increase in amortization of intangible assets relates directly to the intangible assets acquired as part of the Solmetric Acquisition.
49
Non-Operating Expenses
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
$ Change |
|
||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2014 from 2013 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Interest expense |
|
$ |
9,323 |
|
|
$ |
3,144 |
|
|
$ |
6,179 |
|
|
Other expense |
|
|
1,372 |
|
|
|
1,865 |
|
|
|
(493 |
) |
Interest Expense. The increase in interest expense of $6.2 million was primarily due to additional borrowings in 2014. Of the $6.2 million increase, $4.9 million related to our term loan credit facility and the Aggregation Facility entered into with Bank of America in 2014, and $1.5 million related to our revolving lines of credit with Vivint. Of the $4.9 million in interest expense related to our credit facilities with Bank of America, $2.2 million related to the amortization of loan origination fees. These increases in interest expense were partially offset by a decrease of $0.2 million in interest expense related to the revolving line of credit that was terminated in June 2013.
Other Expense. The decrease in other expenses of $0.5 million was primarily due to a decrease in interest and penalties associated with payroll taxes from 2012 and 2013 that were not paid in a timely manner and which were paid during 2014.
Income Taxes
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
$ Change |
|
||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2014 from 2013 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Income tax (benefit) expense |
|
$ |
(7,070 |
) |
|
$ |
123 |
|
|
$ |
(7,193 |
) |
The change in income tax (benefit) expense of $7.2 million to a $7.1 million income tax benefit was primarily due to an increase in pre-tax book losses in proportion to permanent tax adjustments, such as non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests, tax credits and other nondeductible expenses.
Net Loss Attributable to Non-controlling Interests and Redeemable Non-controlling Interests
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
$ Change |
|
||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2014 from 2013 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||
|
Net loss attributable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
$ |
(137,036 |
) |
|
$ |
(62,108 |
) |
|
$ |
(74,928 |
) |
The allocation of net loss to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests as a percentage of our total net loss was 83% and 110% for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. Generally, gains and losses that are allocated to the fund investors under the HLBV method relate to hypothetical liquidation gains and losses resulting from differences between the net assets of the investment fund and the partners’ respective tax capital accounts in the investment fund. Losses allocated to the fund investors were also driven by a reduction in certain fund investors’ claims on net assets due to the agreement of the partnership to take bonus depreciation allowances under Internal Revenue Code Section 168(k), as well as the receipt of ITCs that were primarily allocated to fund investors.
50
Comparison of Year Ended December 31, 2013, Successor Period Ended December 31, 2012 and Predecessor Period Ended November 16, 2012
Amounts in the “$ Change 2012 to 2013” column equal results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2013 less combined results of operations for the Successor Period from November 17, 2012 through December 31, 2012 and the results of operations for the Predecessor Period from January 1, 2012 through November 16, 2012.
Revenue
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|
$ Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
|
2013 from 2012 |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
||||||||||||||
|
Total revenue |
|
$ |
6,170 |
|
|
$ |
109 |
|
|
|
$ |
340 |
|
|
$ |
5,721 |
|
The increase in total revenue of $5.7 million was primarily attributable to an increase of $5.2 million related to operating leases and incentives as the number of installed solar energy systems in service increased significantly from 2012 to 2013. In addition, sales of SRECs increased to $0.3 million in 2013 from a de minimis amount in 2012, and were recognized within operating leases and incentives revenue. We also had an increase of $0.1 million in solar energy system sales.
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|
$ Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
|
2013 from 2012 |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
||||||||||||||
|
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of revenue—operating leases and incentives |
|
$ |
19,004 |
|
|
$ |
1,018 |
|
|
|
$ |
3,302 |
|
|
$ |
14,684 |
|
|
Cost of revenue—solar energy system and product sales |
|
|
123 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
95 |
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
7,348 |
|
|
|
533 |
|
|
|
|
1,471 |
|
|
|
5,344 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
16,438 |
|
|
|
971 |
|
|
|
|
7,789 |
|
|
|
7,678 |
|
|
Amortization of intangible assets |
|
|
14,595 |
|
|
|
1,824 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
12,771 |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
$ |
57,508 |
|
|
$ |
4,346 |
|
|
|
$ |
12,657 |
|
|
$ |
40,505 |
|
Cost of Revenue. The increase in cost of revenue—operating leases and incentives of $14.7 million was primarily due to a $9.4 million increase in indirect costs related to the design, installation and interconnection of solar energy systems to the power grid that were expensed in the period and a $1.9 million increase in depreciation and amortization of solar energy systems, consistent with the significant growth in revenue over these periods. The facility and information technology expenses related to our agreements with Vivint and allocated to cost of revenue increased by $1.8 million due to our increased headcount as well as increased square footage utilized by our employees. Warehouse and other related costs increased by $1.1 million. We also experienced a $0.3 million increase in fleet vehicle maintenance and insurance and a $0.3 million increase in travel costs related to design and installation activities.
Sales and Marketing Expense. The increase in sales and marketing expense of $5.3 million was attributable to our continued efforts to grow our business by entering into new markets, opening new sales offices in various locations and increased hiring of sales and marketing personnel. Specifically, the higher expense level was attributable to increased compensation and benefits expense of $3.0 million, increased costs related to advertising, promotional and other related expenses of $2.0 million and increased travel expenses of $0.4 million.
General and Administrative Expense. The increase in general and administrative expenses of $7.7 million primarily resulted from a $5.1 million increase in compensation and benefits as we increased headcount to support our growth. In addition, professional service fees increased by $3.8 million, office supplies and postage increased by $0.6 million, information technology related to our agreement with Vivint allocated to general and administrative expenses increased by $0.4 million, insurance costs increased by $0.4 million, travel expenses increased by $0.4 million and banking service charges increased by $0.2 million. These increases were partially offset by costs related to the Successor’s acquisition of the Predecessor consisting of $2.7 million of special retention bonuses and other payments to employees and $1.0 million of transaction fees that were expensed in the Predecessor Period which did not occur in the Successor Periods.
51
Amortization of Intangible Assets. In connection with the Successor’s acquisition of the Predecessor, we recorded intangible assets at their fair value of $43.8 million as of the date of the acquisition for which amortization is reflected in the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2013 and 2012.
Non-Operating Expenses
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|
$ Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
|
2013 to 2012 |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
||||||||||||||
|
Interest expense |
|
$ |
3,144 |
|
|
$ |
96 |
|
|
|
$ |
881 |
|
|
$ |
2,167 |
|
|
Other expense |
|
|
1,865 |
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
|
|
240 |
|
|
|
1,581 |
|
Interest Expense. The increase in interest expense was primarily the result of additional borrowings under our revolving lines of credit with Vivint.
Other Expense. The increase in other expenses was comprised primarily of interest and penalties associated with payroll taxes that were not paid in a timely manner in 2012 and 2013.
Income Tax (Benefit) Expense
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|
$ Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
|
2013 from 2012 |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
||||||||||||||
|
Income tax (benefit) expense |
|
$ |
123 |
|
|
$ |
(1,074 |
) |
|
|
$ |
7 |
|
|
$ |
1,190 |
|
The $1.2 million increase in income tax expense (benefit) was a result of an increase in taxable income resulting from adjustments for permanent items, such as increases in losses attributable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests, intercompany sales, tax credits and other nondeductible expenses.
Net Loss Attributable to Non-Controlling Interests and Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|
$ Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
|
2013 from 2012 |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
||||||||||||||
|
Net loss attributable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
$ |
(62,108 |
) |
|
$ |
(699 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(1,771 |
) |
|
$ |
(59,638 |
) |
The allocation of net loss to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests as a percentage of our total net loss was 110%, 21%, and 13% for the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 and the Predecessor Period. The increase in net loss attributable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests was mainly due to the $57.5 million loss allocation from funds into which we were selling assets. The losses to the fund investors for the period ending December 31, 2013 are primarily driven by a reduction in certain fund investors’ claims on net assets due to the agreement of the partnership to take bonus depreciation allowances under Internal Revenue Code Section 168(k), as well as the receipt of investment tax credits which were primarily allocated to fund investors.
52
Accretion to Redemption Value of Series B Redeemable Preferred Stock
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|
$ Change |
|
||||
|
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
|
2013 to 2012 |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
||||||||||||||
|
Accretion to redemption value of Series B redeemable preferred stock |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
$ |
(20,000 |
) |
|
$ |
20,000 |
|
Immediately prior to the Successor’s acquisition of the Predecessor, we had 8,342 shares of Series B redeemable preferred stock outstanding. Due to the change in control upon the acquisition, we recorded $20.0 million to accrete Series B redeemable preferred stock to redemption value in relation to the redemption of such preferred stock in the Predecessor Period. We do not expect to incur similar charges in future periods as we no longer have redeemable preferred stock outstanding after the acquisition.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based upon our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. GAAP require us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenue and expenses, cash flows and related footnote disclosures. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from these estimates. Our future consolidated financial statements will be affected to the extent that our actual results materially differ from these estimates.
We believe that the assumptions and estimates associated with our principles of consolidation, revenue recognition, solar energy systems, net, performance guarantees, impairment of long-lived assets, goodwill impairment analysis, stock-based compensation, provision for income taxes and non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests have the greatest potential impact on our consolidated financial statements. Therefore, we consider these to be our critical accounting policies and estimates.
Principles of Consolidation
We consider each of our investment funds to be a separate variable interest entity, or VIE. We use a qualitative approach in assessing the consolidation requirement for these VIEs. This approach focuses on determining whether we have the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly affect the VIE’s economic performance and whether we have the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits that could potentially be significant to the VIE. All of these determinations involve significant management judgments and estimates. We have determined that we are the primary beneficiary in all of our operational VIEs. We evaluate our relationships with the VIEs on an ongoing basis to ensure that we continue to be the primary beneficiary. All intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
U.S. Treasury Grants and Investment Tax Credits
Certain solar energy systems were eligible to receive U.S. Treasury grants under Section 1603 of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, as amended by the Tax Relief Unemployment Insurance Reauthorization and Job Creation Act of December 2010. Prior to installation of such eligible systems, we submitted an application to receive a grant. After installation was completed and the solar energy system was interconnected to the power grid, we requested disbursement of the funds, typically based on 30% of the tax basis of eligible solar energy systems. Once we were notified that the U.S. Treasury Department approved the disbursement of the grant proceeds for a solar energy system, we recorded a reduction in the basis of the solar energy system in the amount of cash to be received, at the grant approval date.
For the solar energy systems that are not eligible to receive U.S. Treasury grants, we apply for and receive investment tax credits under Section 48(a) of the Internal Revenue Code. The amount for the investment tax credit is equal to 30% of the value of eligible solar property. We receive minimal allocations of investment tax credits as the majority of such credits are allocated to the fund investors. Some of our investment funds obligate us to make certain fund investors whole for losses that the investors may suffer in certain limited circumstances resulting from the disallowance or recapture of investment tax credits as a result of the Internal Revenue Service’s, or the IRS, assessment of the fair value of such systems. We have concluded that the likelihood of a recapture event is remote and consequently has not recorded any liability in the consolidated financial statements for any potential recapture exposure. If it becomes probable that a U.S. Treasury grant is required to be repaid, we will assess whether it is necessary to derecognize any grant (or portion thereof) in accordance with Account Standards Codification section 450.
53
Solar Energy Systems, Net
Solar energy systems are stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation and amortization. As discussed in the section captioned “U.S. Treasury Grants and Investment Tax Credits” above, we also applied for and received U.S. Treasury grants related to our solar energy systems. We record the U.S. Treasury grants as a reduction in the basis of the solar energy systems at the approval date of the grant. This accounting treatment results in decreased depreciation expense related to these solar energy systems over their useful lives.
Depreciation and amortization expense is calculated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets as follows:
|
|
|
Useful Lives |
|
System equipment costs |
|
30 years |
|
Initial direct costs related to solar energy systems |
|
Lease term (20 years) |
We commence depreciation of our solar energy systems once the respective systems have been installed and interconnected to the power grid.
The determination of the useful lives of assets included within solar energy systems involves significant management judgment.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets and Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets
The carrying amounts of our long-lived assets, including solar energy systems, property and intangible assets subject to depreciation and amortization, are periodically reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of these assets may not be recoverable or that the useful life is shorter than originally estimated. Factors that we consider in deciding when to perform an impairment review include significant negative industry or economic trends, and significant changes or planned changes in our use of the assets. Recoverability of these assets is measured by comparison of the carrying amount of each asset to the future undiscounted cash flows the asset is expected to generate over its remaining life. If the asset is considered to be impaired, the amount of any impairment is measured as the difference between the carrying value and the fair value of the impaired asset. If the useful life is shorter than originally estimated, we amortize the remaining carrying value over the new shorter useful life.
We will test indefinite-lived intangible assets that were acquired as part of the acquisition of Solmetric Corporation for impairment on an annual basis, or whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the fair value is less than its carrying value. To test these intangible assets for impairment, we compare the fair value of the indefinite-lived asset with its carrying amount. In the event the carrying value exceeds the fair value of the assets, the assets are written down to their fair value.
Goodwill Impairment Analysis
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price of an acquired business over the fair value of the net assets acquired. We have recorded goodwill as a result of push-down accounting from 313 Acquisition LLC applied as of the Acquisition date and our acquisition of Solmetric Corporation in January 2014. We have determined that we operate as one reporting unit. We perform our annual impairment test of goodwill as of October 1st of each fiscal year or whenever events or circumstances change or occur that would indicate that goodwill might be impaired. Triggering events that may indicate impairment include, but are not limited to, a significant adverse change in the business climate, unanticipated competition, loss of key personnel, significant changes in the manner we use the acquired assets or the strategy for the overall business, significant negative industry or economic trends or significant underperformance relative to historical operations or projected future results of operations.
In conducting the impairment test, we first assess qualitative factors, including those stated previously, to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount as a basis for determining whether it is necessary to perform the two-step goodwill impairment test. If the qualitative step is not passed, we perform a two-step impairment test whereby in the first step we must compare the fair value of the reporting unit with its carrying amount. If the carrying amount exceeds its fair value, we perform the second step of the goodwill impairment test to determine the amount of impairment. The second step, measuring the impairment loss, compares the implied fair value of the goodwill with the carrying value of the goodwill. Any excess of the goodwill carrying value over the implied fair value is recognized as an impairment loss.
Solar Energy Performance Guarantees
Under our customer agreements that are structured as legal-form leases, we provide a performance guarantee where we agree to make payments on an annual basis to our customers if the solar energy systems do not meet a guaranteed production level in the prior 12-month period. As of December 31, 2014, the amounts accrued under the performance guarantees were de minimis.
54
Revenue Recognition
We sell the electricity that our solar energy systems produce through long-term power purchase agreements or we lease our solar energy systems through long-term leases. Prior to 2014, all of our long-term customer contracts were structured as power purchase agreements. In 2014, we began offering leases to residential customers in certain markets. We also generate revenue through sales of SRECs, solar energy system and photovoltaic installation software products and devices and receipt of rebate incentives. We recognize revenue when all of the following criteria are met: (1) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, (2) delivery or performance has occurred, (3) the sales price is fixed or determinable and (4) collectability is reasonably assured. Revenue associated with power purchase agreements and solar energy system leases, SRECs and rebate incentives are included within operating leases and incentives revenue. Revenue from the sale of photovoltaic installation software products and devices and solar energy systems sales is recognized within solar energy system and product sales.
Operating Leases and Incentives Revenue
Our primary revenue-generating activity consists of entering into long-term power purchase agreements with residential customers, under which the customer agrees to purchase all of the power generated by the solar energy system for the term of the contract, which is 20 years. The agreement includes a fixed price per kilowatt hour with a fixed annual price escalation percentage (to address the impact of inflation and utility rate increases over the period of the contract). Customers have not historically been charged for installation or activation of the solar energy system. For all power purchase agreements, we assess the probability of collectability on a customer-by-customer basis through a credit review process that evaluates their financial condition and ability to pay.
We have determined that power purchase agreements should be accounted for as operating leases after evaluating and concluding that none of the following capitalized lease classification criteria are met: no transfer of ownership or bargain purchase option exists at the end of the lease, the lease term is not greater than 75% of the useful life or the present value of minimum lease payments does not exceed 90% of the fair value at lease inception. As customer payments under a power purchase agreement are dependent on power generation, they are considered contingent rentals and are excluded from future minimum annual lease payments. Revenue from power purchase agreements is recognized based on the actual amount of power generated at rates specified under the contracts, assuming the other revenue recognition criteria discussed above are met.
Operating leases and incentives revenue is recorded net of sales tax collected.
In 2014, we began offering solar energy system to customers pursuant to legal-form leases in certain markets. The customer agreements are structured as legal-form leases due to local regulations that can be read to prohibit the sale of electricity pursuant to our standard power purchase agreement. Pursuant to the lease agreements, the customers’ monthly payments are pre-determined fixed monthly amounts and include an annual fixed percentage price escalation to address the impact of inflation and utility rate increases over the period of the contracts, which is 20 years. We provide our legal-form lease customers a performance guarantee, under which we agree to potentially refund a portion of the fixed lease payments at the end of each year to the customer if the solar energy systems do not meet a guaranteed production level in the prior 12-month period. Solar energy performance guarantees were de minimis as of December 31, 2014.
We apply for and receive SRECs in certain jurisdictions for power generated by our solar energy systems. When SRECs are granted, we typically sell them to other companies directly, or to brokers, to assist them in meeting their own mandatory emission reduction or conservation requirements. We recognize revenue related to the sale of these certificates upon delivery, assuming the other revenue recognition criteria discussed above are met.
We consider upfront rebate incentives earned from our solar energy systems to be minimum lease payments and recognize revenue for those payments on a straight-line basis over the life of the long-term customer contracts, assuming the other revenue recognition criteria discussed above are met.
Solar Energy System and Product Sales
Revenue from solar energy system sales is recognized upon the solar energy system passing an inspection by the responsible city department after completion of system installation assuming the remaining revenue recognition criteria discussed above have been met.
Revenue from the sale of photovoltaic installation software products and devices is recognized upon delivery of the product to the customer assuming the remaining revenue recognition criteria discussed above have been met.
55
Multiple-Element Arrangements
We enter into revenue arrangements from the sale of photovoltaic installation software products and devices that consist of multiple elements. Each element in a multiple element arrangement must be evaluated to determine whether it represents a separate unit of account. An element constitutes a separate unit of account when it has standalone value and delivery of an undelivered element is both probable and within our control.
Our typical multiple-element arrangements involve sales of (1) photovoltaic installation hardware devices containing software essential to the hardware product’s functionality, or photovoltaic device, and (2) standalone software, both including the implied right for the customer to receive post-contract customer support, or PCS, with the purchase of our products. PCS includes the implied right to receive, on a when and if available basis, future unspecified software upgrades and features as well as bug fixes, email and telephone support.
For sales of photovoltaic devices, we allocate revenue between (1) the photovoltaic device and (2) PCS using the relative selling price method. Because we have not sold these deliverables separately, vendor-specific objective evidence of fair value, or VSOE, is not available. Additionally, we are unable to reliably determine the selling prices of similar competitor products and upgrades on a standalone basis to determine third-party evidence of selling price. As such, the allocation of revenue is based on our best estimate of selling price, or BESP.
We determine BESP for a product or service by considering multiple factors including, but not limited to, market conditions, competitive landscape, internal costs, gross margin objectives and pricing practices. The determination of BESP is made through consultation with and formal approval by management, taking into consideration our marketing strategy.
The consideration allocated to the delivered photovoltaic device is recognized at the time of shipment provided that the four general revenue recognition criteria discussed above have been met. The consideration allocated to the PCS is deferred and recognized ratably over the four year estimated life of the devices and the period during which the related PCS is expected to be provided.
For sales of software with PCS, revenue is recognized based on software revenue recognition accounting guidance. Because we are not able to determine VSOE for the PCS, revenue from the entire arrangement is recognized ratably over four years, which is the economic life over which the upgrades are expected to be provided.
Provision for Income Taxes
We account for income taxes under an asset and liability approach. Deferred income taxes reflect the impact of temporary differences between assets and liabilities recognized for financial reporting purposes and the amounts recognized for income tax reporting purposes, net operating loss carryforwards and other tax credits measured by applying currently enacted tax laws. A valuation allowance is provided when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to an amount that is more likely than not to be realized.
We sell solar energy systems to the partnership flip-structured investment funds. As the investment funds are consolidated by us, the gain on the sale of the solar energy systems is not recognized in the consolidated financial statements. However, this gain is recognized for tax reporting purposes. Since these transactions are intercompany sales for book purposes, any tax expense incurred related to these intercompany sales is deferred and recorded as a prepaid tax asset and amortized over the estimated useful life of the underlying solar energy systems, which has been estimated to be 30 years.
We determine whether a tax position is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination, including resolution of any related appeals or litigation processes, based on the technical merits of the position. We use a two-step approach to recognizing and measuring uncertain tax positions. The first step is to evaluate the tax position for recognition by determining if the weight of available evidence indicates that it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon tax authority examination, including resolution of related appeals or litigation processes, if any. The second step is to measure the tax benefit as the largest amount that is more than 50% likely of being realized upon ultimate settlement.
Our policy is to include interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits, if any, within the provision for taxes in the consolidated statements of operations.
56
Stock-Based Compensation
Expense related to stock-based compensation granted to employees is measured and recognized in the financial statements based on the grant-date fair value of the awards. The fair value of each time-based award is estimated on the grant date using the Black-Scholes-Merton stock option pricing valuation model. The fair value of each performance-based employee stock option is estimated on the date of grant using the Monte Carlo simulation model. The stock-based compensation expense, net of forfeitures, is recognized on an accelerated attribution basis over the requisite service period of an award, which is generally the award’s vesting period.
Stock-based compensation expense for equity instruments issued to non-employees is recognized based on the estimated fair value of the equity instrument. The fair value of the non- employee awards is subject to remeasurement at each reporting period until services required under the arrangement are completed, which is the vesting date.
Use of the Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model requires the input of highly subjective assumptions, including (1) the fair value of the underlying common stock, (2) the expected term of the option, (3) the expected volatility of the price of our common stock, (4) risk-free interest rates and (5) the expected dividend yield of our common stock. The assumptions used in the option-pricing model represent our best estimates. These estimates involve inherent uncertainties and the application of our judgment. If factors change and different assumptions are used, our stock-based compensation expense could be materially different in the future.
We have granted options at an exercise price per share not less than what the board of directors had determined was the fair market value per share of our underlying common stock on each date of grant. Up until the time of our initial public offering, our common stock valuations were determined in accordance with the guidelines outlined in the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants Practice Aid, Valuation of Privately-Held-Company Equity Securities Issued as Compensation. Because our common stock was not publicly traded, the board of directors exercised significant judgment in determining the fair value of our common stock. Changes in judgments could have a material impact on our results of operations and financial position. Now that our common stock is publicly traded, estimates regarding the fair value of our common stock will not be necessary.
The board of directors is comprised of a majority of non-employee directors that we believe had the relevant experience and expertise to determine a fair value of our common stock on each respective grant date. In the absence of a public trading market for our common stock at that time, the board of directors, with input from management, considered numerous objective and subjective factors to determine the common stock’s fair value as of the date of each option grant, including our operating and financial performance, financial condition, current business conditions and projections, the market performance of companies in the industry in which we compete, the hiring of key personnel and the availability of tax equity and debt financing.
In addition to assumptions used in the Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model, we must also estimate a forfeiture rate to calculate the stock-based compensation expense for our awards. Our forfeiture rate is based on an analysis of our actual forfeitures since the adoption of our equity award plan. We routinely evaluate the appropriateness of the forfeiture rate based on actual forfeiture experience, analysis of employee turnover and expectations of future option exercise behavior. Changes in the estimated forfeiture rate can have a significant impact on our stock-based compensation expense as the cumulative effect of adjusting the forfeiture rate is recognized in the period the forfeiture estimate is changed. If a revised forfeiture rate is higher than the previously estimated forfeiture rate, an adjustment is made that will result in a decrease to the stock-based compensation expense recognized in the financial statements. If a revised forfeiture rate is lower than the previously estimated forfeiture rate, an adjustment is made that will result in an increase to the stock-based compensation expense recognized in the financial statements.
We will continue to use judgment in evaluating the expected term, expected volatility and forfeiture rate related to our stock-based compensation expense on a prospective basis. As we continue to accumulate additional data related to our common stock, we may have refinements to the estimates of our expected volatility, expected terms and forfeiture rates, which could materially impact our future stock-based compensation expense as it relates to the future grants of our stock-based awards.
57
Non-Controlling Interests and Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests
Our non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests represent fund investors’ interests in the net assets of certain investment funds, which we consolidate, that we have entered into in order to finance the costs of solar energy systems under long-term customer contracts. We have determined that the provisions in the contractual arrangements of the investment funds represent substantive profit-sharing arrangements, which gives rise to the non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests. We have further determined that the appropriate methodology for attributing income and loss to the non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests each period is a balance sheet approach using the HLBV method. Under the HLBV method, the amounts of income and loss attributed to the non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests in the consolidated statements of operations reflect changes in the amounts the fund investors would hypothetically receive at each balance sheet date under the liquidation provisions of the contractual agreements of these funds, assuming the net assets of these respective investment funds were liquidated at recorded amounts. The fund investors’ interest in the results of operations of these investment funds is determined as the difference in the non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interest’s claim under the HLBV method at the start and end of each reporting period, after taking into account any capital transactions between the fund and the fund investors.
Attributing income and loss to the non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests under the HLBV method requires the use of significant assumptions and estimates to calculate the amounts that fund investors would receive upon a hypothetical liquidation. Changes in these assumptions and estimates can have a significant impact on the amount that fund investors would receive upon a hypothetical liquidation. The use of the HLBV methodology to allocate income to the non-controlling and redeemable non-controlling interest holders may create volatility in our consolidated statements of operations as the application of HLBV can drive changes in net income available and loss attributable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests from quarter to quarter.
We classify certain non-controlling interests with redemption features that are not solely within our control outside of permanent equity on our consolidated balance sheets. Redeemable non-controlling interests are reported using the greater of their carrying value at each reporting date as determined by the HLBV method or their estimated redemption value in each reporting period.
Estimating the redemption value of the redeemable non-controlling interests requires the use of significant assumptions and estimates. Changes in these assumptions and estimates can have a significant impact on the calculation of the redemption value.
58
Quarterly Results of Operations
The following table presents our unaudited consolidated statement of operations for each of the eight quarters in the 24 month period ended December 31, 2014. Our consolidated statement of operations for each of these quarters have been prepared on a basis consistent with our audited annual consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this report and, in the opinion of management, include all adjustments necessary for the fair presentation of our consolidated results of operations for these quarters. You should read this information together with our Consolidated Financial Statements and the related Notes included elsewhere in this report. The results of operations for any quarter are not necessarily indicative of the results of operations for any future period.
|
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
September 30, |
|
June 30, |
|
March 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
September 30, |
|
June 30, |
|
March 31, |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
2014 |
|
2014 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
2013 |
|
2013 |
|
2013 |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
(In thousands, except per share data) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating leases and incentives |
|
$ |
5,890 |
|
$ |
7,131 |
|
$ |
5,804 |
|
$ |
2,863 |
|
$ |
1,948 |
|
$ |
2,123 |
|
$ |
1,225 |
|
$ |
568 |
|
|
Solar energy system and product sales |
|
|
970 |
|
|
1,202 |
|
|
754 |
|
|
644 |
|
|
23 |
|
|
151 |
|
|
108 |
|
|
24 |
|
|
Total revenue |
|
|
6,860 |
|
|
8,333 |
|
|
6,558 |
|
|
3,507 |
|
|
1,971 |
|
|
2,274 |
|
|
1,333 |
|
|
592 |
|
|
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of revenue—operating leases and incentives |
|
|
20,823 |
|
|
19,515 |
|
|
16,459 |
|
|
11,187 |
|
|
6,180 |
|
|
4,811 |
|
|
4,396 |
|
|
3,617 |
|
|
Cost of revenue—solar energy system and product sales |
|
|
487 |
|
|
627 |
|
|
485 |
|
|
398 |
|
|
15 |
|
|
32 |
|
|
61 |
|
|
15 |
|
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
5,640 |
|
|
5,220 |
|
|
5,790 |
|
|
5,219 |
|
|
2,353 |
|
|
2,105 |
|
|
1,673 |
|
|
1,217 |
|
|
Research and development |
|
|
489 |
|
|
431 |
|
|
500 |
|
|
472 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
15,623 |
|
|
37,170 |
|
|
13,752 |
|
|
12,354 |
|
|
6,471 |
|
|
5,135 |
|
|
3,036 |
|
|
1,796 |
|
|
Amortization of intangible assets |
|
|
3,756 |
|
|
3,727 |
|
|
3,691 |
|
|
3,737 |
|
|
3,649 |
|
|
3,649 |
|
|
3,648 |
|
|
3,649 |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
|
46,818 |
|
|
66,690 |
|
|
40,677 |
|
|
33,367 |
|
|
18,668 |
|
|
15,732 |
|
|
12,814 |
|
|
10,294 |
|
|
Loss from operations |
|
|
(39,958 |
) |
|
(58,357 |
) |
|
(34,119 |
) |
|
(29,860 |
) |
|
(16,697 |
) |
|
(13,458 |
) |
|
(11,481 |
) |
|
(9,702 |
) |
|
Interest expense |
|
|
1,988 |
|
|
3,261 |
|
|
2,673 |
|
|
1,401 |
|
|
1,190 |
|
|
963 |
|
|
566 |
|
|
425 |
|
|
Other expense |
|
|
(90 |
) |
|
297 |
|
|
277 |
|
|
888 |
|
|
802 |
|
|
541 |
|
|
354 |
|
|
168 |
|
|
Loss before income taxes |
|
|
(41,856 |
) |
|
(61,915 |
) |
|
(37,069 |
) |
|
(32,149 |
) |
|
(18,689 |
) |
|
(14,962 |
) |
|
(12,401 |
) |
|
(10,295 |
) |
|
Income tax (benefit) expense |
|
|
(3,784 |
) |
|
(10,222 |
) |
|
2,542 |
|
|
4,394 |
|
|
47 |
|
|
31 |
|
|
(440 |
) |
|
485 |
|
|
Net loss |
|
|
(38,072 |
) |
|
(51,693 |
) |
|
(39,611 |
) |
|
(36,543 |
) |
|
(18,736 |
) |
|
(14,993 |
) |
|
(11,961 |
) |
|
(10,780 |
) |
|
Net loss attributable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
|
(31,933 |
) |
|
(16,415 |
) |
|
(45,104 |
) |
|
(43,584 |
) |
|
(21,953 |
) |
|
(37,848 |
) |
|
(186 |
) |
|
(2,121 |
) |
|
Net (loss attributable) income available to common stockholders |
|
$ |
(6,139 |
) |
$ |
(35,278 |
) |
$ |
5,493 |
|
$ |
7,041 |
|
$ |
3,217 |
|
$ |
22,855 |
|
$ |
(11,775 |
) |
$ |
(8,659 |
) |
|
Net (loss attributable) income available per share to common stockholders: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
$ |
(0.06 |
) |
$ |
(0.45 |
) |
$ |
0.07 |
|
$ |
0.09 |
|
$ |
0.04 |
|
$ |
0.30 |
|
$ |
(0.16 |
) |
$ |
(0.12 |
) |
|
Diluted |
|
$ |
(0.06 |
) |
$ |
(0.45 |
) |
$ |
0.07 |
|
$ |
0.09 |
|
$ |
0.04 |
|
$ |
0.30 |
|
$ |
(0.16 |
) |
$ |
(0.12 |
) |
|
Weighted-average shares used in computing net (loss attributable) income available per share to common stockholders: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
|
105,079 |
|
|
78,428 |
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
Diluted |
|
|
105,079 |
|
|
78,428 |
|
|
76,267 |
|
|
76,064 |
|
|
75,825 |
|
|
75,001 |
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
75,000 |
|
Seasonality
We have experienced seasonal fluctuations in our operations. For example, the amount of revenue we recognize in a given period from power purchase agreements is dependent in part on the amount of energy generated by solar energy systems under such contracts. As a result, operating leases and incentives revenue is impacted by seasonally shorter daylight hours in winter months. In addition, our ability to install solar energy systems is impacted by weather. For example, we have limited ability to install solar energy systems during the winter months in the Northeastern United States. Such delays can impact the timing of when we can install and begin to generate revenue from solar energy systems. However, given that we are an early stage company operating in a rapidly growing industry, the true extent of these fluctuations may have been masked by our recent growth rates and thus may not be readily apparent from our historical operating results and may be difficult to predict. As such, our historical operating results may not be indicative of future performance.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of December 31, 2014, we had cash and cash equivalents of $261.6 million, which consisted principally of cash and time deposits with high-credit-quality financial institutions. On October 6, 2014, we closed our initial public offering in which we sold 20.6 million shares of our common stock at a price of $16.00 per share, resulting in net proceeds of $300.6 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and $8.8 million in offering expenses payable by us.
59
Besides the proceeds from our initial public offering, we have also financed our solar energy system-related operations from investment fund arrangements that we have formed with fund investors and from borrowings. Our principal uses of cash are funding our operations, including the costs of acquisition and installation of solar energy systems, satisfaction of our obligations under our debt instruments and other working capital requirements. We believe our cash and cash equivalents, investment fund commitments, projected investment fund contributions and available borrowings as further described below will be sufficient to meet our anticipated cash needs for at least the next 12 months.
Sources of Funds
Sale of Equity Securities
On October 6, 2014, we closed our initial public offering in which we sold 20.6 million shares of our common stock at a price of $16.00 per share, resulting in net proceeds of $300.6 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and $8.8 million in offering expenses payable by us.
In August and September 2014, we issued and sold an aggregate of 9.7 million shares of common stock to 313 Acquisition LLC and two of our directors for $10.667 per share for aggregate gross proceeds of $103.5 million. For additional discussion regarding these transactions, refer to Note 12—Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests, Equity and Preferred Stock.
Investment Fund Commitments
As of February 28, 2015, we have raised 13 investment funds to which investors such as banks and other large financial investors have committed to invest approximately $673 million, which will enable us to install solar energy systems of total fair market value approximating $1.6 billion. The undrawn committed capital for these funds as of February 28, 2015 is approximately $155 million, which includes approximately $47 million in payments that will be received from fund investors upon interconnection to the respective utility grid of solar energy systems that have already been allocated to investment funds. As of February 28, 2015, we had tax equity commitments to fund approximately 71 megawatts of future deployments, which we estimate to be sufficient to fund solar energy systems with a total fair market value of approximately $331 million.
Debt Instruments
Working Capital Credit Facility. In March 2015, we entered into a credit agreement with certain financial institutions for which Goldman Sachs Lending Partners LLC is acting as administrative agent and collateral agent, under which we may from time to time incur up to an aggregate of principal amount of $131.0 million in revolver borrowings. Upon the satisfaction of certain conditions and the approval of the lenders, we may increase the aggregate amount of the revolver borrowings to $150.0 million. Loans under the revolving credit facility will be used for the construction and acquisition of solar energy systems, and letters of credit may be issued under the revolving credit facility for working capital and general corporate purposes. The revolving credit facility matures in March 2020.
Aggregation Credit Facility. In September 2014, we entered into the Aggregation Facility pursuant to which we may borrow up to an aggregate of $350.0 million and, subject to the satisfaction of certain conditions and the approval of the lenders, up to an additional aggregate of $200.0 million in borrowings with certain financial institutions for which Bank of America, N.A. is acting as administrative agent. As of December 31, 2014, we had incurred an aggregate of $105.0 million in term loan borrowings under this agreement, of which approximately $75.7 million was used to repay the outstanding principal and accrued and unpaid interest under the May 2014 credit facility with Bank of America, N.A. As of December 31, 2014, we had a remaining borrowing capacity of $245.0 million under this facility. In February 2015, we entered into an amendment to the Aggregation Facility that increased the funding commitment by $25.0 million pursuant to which we may borrow up to an aggregate of $375.0 million. In addition, the right to which we may request additional borrowing capacity upon the satisfaction of certain conditions and the approval of the lenders was reduced to $175.0 million, such that the total potential capacity under facility remains at $550.0 million.
Prepayments are permitted under the Aggregation Facility and the principal and accrued interest on any outstanding loans mature on March 12, 2018. Under the aggregation credit facility, interest on borrowings accrues at a floating rate equal to (1) a margin that varies between 3.25% during the period during which we may incur borrowings and 3.50% after such period plus either of (2)(a) LIBOR or (b) the greatest of (i) the Federal Funds Rate plus 0.5%, (ii) the administrative agent’s prime rate and (iii) LIBOR plus 1%. As of December 31, 2014, the borrowings under the Aggregation Facility accrued interest at 3.5%.
60
The borrower under the Aggregation Facility is Vivint Solar Financing I, LLC, one of our indirect wholly owned subsidiaries, that in turn holds our interests in the managing members in our existing investment funds. These managing members guarantee the borrower’s obligations under the Aggregation Facility. In addition, Vivint Solar Holdings, Inc. has pledged its interests in the borrower, and the borrower has pledged its interests in the guarantors as security for the borrower’s obligations under the aggregation credit facility. The aggregation credit facility includes customary events of default, conditions to borrowing and covenants, including covenants that restrict, subject to certain exceptions, the borrower’s and the guarantors’ ability to incur indebtedness, incur liens, make investments, make fundamental changes to their business, dispose of assets, make certain types of restricted payments or enter into certain related party transactions, as well as maintain certain financial ratios. As of December 31, 2014, we were in compliance with such covenants.
Uses of Funds
Our principal uses of cash are funding our operations, including the costs of acquisition and installation of solar energy systems, satisfaction of our obligations under our debt instruments and other working capital requirements. During the quarter ended December 31, 2014, we used the cash from the net proceeds of our initial public offering to repay an aggregate $58.7 million in borrowings and accrued interest under lines of credit with Vivint and also used approximately $34.7 million for working capital and other general corporate purposes, including growing our corporate and sales staff to support the growth of the business. We expect to use the remainder of net proceeds for working capital and general corporate purposes. We maintain the proceeds received in cash and cash equivalents.
Over the past two years, our operating expenses have increased from year to year due to the significant growth of our business. Over the past two years, our capital expenditures excluding our solar energy systems have been minimal; however, our capital expenditures have increased in 2014 and are expected to continue to increase as we continue to grow our business.
We expect our operating cash requirements to increase in the future as we increase sales and marketing activities to expand into new markets and increase sales coverage in markets in which we currently operate. In addition, the agreements governing each of our investment funds include options that, when exercised, either require us to purchase, or allow us to elect to purchase, our fund investor’s interest in the investment fund. No options have been exercised or become exercisable to date, however, such options are expected to become exercisable in the future and the exercise of one or more options could require us to expend significant funds. Regardless of whether these options are exercised, we will need to raise financing to support our operations, and such financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. If we are unable to raise financing when needed, our operations and ability to execute our business strategy could be adversely affected. We may seek to raise financing through the sale of equity, equity-linked securities or the incurrence of indebtedness. Additional equity or equity-linked financing may be dilutive to our stockholders. If we raise funding through the incurrence of indebtedness, such indebtedness would have rights that are senior to holders of our equity securities and could contain covenants that restrict our operations.
Historical Cash Flows
The primary drivers of our uses and sources of cash are described in the sections above. The following table summarizes our cash flows for the periods indicated:
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|||||||
|
Consolidated cash flow data: |
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
||||
|
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
||||||||||||||
|
Net cash used in operating activities |
|
$ |
(135,918 |
) |
|
$ |
(20,873 |
) |
|
$ |
(1,209 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(2,890 |
) |
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
(400,763 |
) |
|
|
(127,522 |
) |
|
|
(8,014 |
) |
|
|
|
(15,308 |
) |
|
Net cash provided by financing activities |
|
|
792,292 |
|
|
|
142,783 |
|
|
|
20,873 |
|
|
|
|
18,113 |
|
|
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
255,611 |
|
|
|
(5,612 |
) |
|
|
11,650 |
|
|
|
|
(85 |
) |
61
Operating Activities
In 2014, we had a net cash outflow from operations of $135.9 million. This outflow was partially offset by noncash adjustments of $23.7 million for stock-based compensation and $15.0 million for the amortization of intangible assets.
Investing Activities
In 2014, we used $400.8 million in investing activities primarily to purchase $383.5 million associated with the design, acquisition and installation of solar energy systems and $12.0 million related to the Solmetric acquisition.
Financing Activities
In 2014, we generated $792.3 million from financing activities, of which $412.9 million was from the issuance of common stock and $339.5 million was from the proceeds from investments by non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests into our investment funds.
Contractual Obligations
Our contractual commitments and obligations were as follows as of December 31, 2014:
|
|
Payments Due by Period(1) |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
Less than |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
More than |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
1 Year |
|
|
1-3 Years |
|
|
3-5 Years |
|
|
5 Years |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||
|
|
(In thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Long-term debt |
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
105,000 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
105,000 |
|
|
Distributions payable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests(2) |
|
6,780 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
6,780 |
|
|
Capital lease obligations and interest |
|
4,029 |
|
|
|
5,891 |
|
|
|
715 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
10,635 |
|
|
Operating lease obligations |
|
7,077 |
|
|
|
15,043 |
|
|
|
7,529 |
|
|
|
4,080 |
|
|
|
33,729 |
|
|
Total |
$ |
17,886 |
|
|
$ |
20,934 |
|
|
$ |
113,244 |
|
|
$ |
4,080 |
|
|
$ |
156,144 |
|
|
(1) |
Does not include amounts related to redeemable put options held by fund investors. The redemption price for the fund investors’ interest in the respective fund is equal to the sum of: (a) any unpaid, accrued priority return, and (i) the greater of: (x) a fixed price and (b) the fair market value of such interest at the date the option is exercised. Due to uncertainties associated with estimating the timing and amount of the redemption price, we cannot determine the potential future payments that we could have to make under these redemption options. For additional information regarding the redeemable put options, see Note 12—Redeemable Non-Controlling Interest, Equity and Preferred Stock to our Consolidated Financial Statements. As of December 31, 2014, all fund investors have contributed an aggregate of $480.2 million into the funds. For additional information regarding our investment funds, see Note 11—Investment Funds to our Consolidated Financial Statements. |
|
(2) |
Includes a $4.0 million accrued distribution reimbursement to a fund investor in order to true up the investor’s expected rate of return due to a delay in systems being interconnected to the utility grid. However, does not include any other potential contractual obligations that may arise as a result of the contractual guarantees we have made with certain investors in our investment funds. The amounts of any potential payments we may be required to make depend on the amount and timing of future distributions to the relevant fund investors and the investment tax credits that accrue to such investors from the funds’ activities. Due to uncertainties associated with estimating the timing and amounts of distributions and likelihood of an event that may trigger repayment of any forfeiture or recapture of investment tax credits to such investors, we cannot determine the potential maximum future payments that we could have to make under these guarantees. As a result of these guarantees, as of December 31, 2014, we were required to hold a minimum balance of $5.0 million in the aggregate, which is classified as restricted cash on our consolidated balance sheet. For additional information, see Note 11—Investment Funds to our Consolidated Financial Statements. |
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We include in our condensed consolidated financial statements all assets and liabilities and results of operations of investment fund arrangements that we have entered into. We do not have any off-balance sheet arrangements.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2015, the Financial Accounting Services Board, or FASB, issued Accounting Standards Update, or ASU, 2015-02, Consolidation (Topic 810): Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis. This update makes some targeted changes to current consolidation guidance. These changes impact both the voting and the variable interest consolidation models. In particular, the update will change how companies determine whether limited partnerships or similar entities are variable interest entities. The update is effective in fiscal years, including interim periods, beginning after December 15, 2015, and early adoption is permitted. We currently consolidate several variable interest entities, and we do not anticipate that ASU 2015-02 will have a significant impact on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
62
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, which requires an entity to recognize the amount of revenue to which it expects to be entitled for the transfer of promised goods or services to customers. The ASU will replace most existing revenue recognition guidance in U.S. GAAP when it becomes effective. The new standard is effective for us on January 1, 2017. Early application is not permitted. The standard permits the use of either the retrospective or cumulative effect transition method. We are evaluating the effect that ASU 2014-09 will have on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures. We have not yet selected a transition method nor have we determined the effect of the standard on our ongoing financial reporting.
Emerging Growth Company Status
Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that an “emerging growth company” can take advantage of the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act for complying with new or revised accounting standards. In other words, an “emerging growth company” can delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. We have irrevocably elected not to avail ourselves of this exemption from new or revised accounting standards and, therefore, we will be subject to the same new or revised accounting standards as other public companies that are not “emerging growth companies.”
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
Our exposure to market risk for changes in interest rates relates primarily to our cash and cash equivalents and our indebtedness.
As of December 31, 2014, we had cash and cash equivalents of $261.6 million. Our cash equivalents are money market accounts and time deposits with maturities of three months or less at the time of purchase. Our primary exposure to market risk on these funds is interest income sensitivity, which is affected by changes in the general level of the interest rates in the United States. However, because of the short-term nature of the instruments in our portfolio, a sudden change in market interest rates would not be expected to have a material impact on our condensed consolidated financial statements.
In September 2014, we entered into an aggregation credit facility pursuant to which we may borrow up to an aggregate of $350.0 million and, upon the satisfaction of certain conditions and the approval of the lenders, up to an additional aggregate of $200.0 million in borrowings with certain financial institutions for which Bank of America, N.A. is acting as administrative agent. As of December 31, 2014, we incurred an aggregate of $105.0 million in term loan borrowings under this agreement, which accrued interest at a floating rate, which was approximately 3.5% as of December 31, 2014. If the aggregation facility had been fully drawn at December 31, 2013 and remained outstanding for all of 2014, the effect of a hypothetical 10% change in our floating interest rate on these borrowings would increase or decrease interest expense by approximately $1.2 million.
All of our operations are in the United States and all purchases of our solar energy system components are denominated in U.S. dollars. However, our suppliers often incur a significant amount of their costs by purchasing raw materials and generating operating expenses in foreign currencies. If the value of the U.S. dollar depreciates significantly or for a prolonged period of time against these currencies (particularly the Chinese Renminbi), our suppliers may raise the prices they charge us, which could have a negative impact on our financial results.
63
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
|
|
Page |
|
|
|
|
|
|
65 |
|
|
|
66 |
|
|
|
67 |
|
|
|
68 |
|
|
|
69 |
|
|
|
70 |
64
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Vivint Solar, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Vivint Solar, Inc. as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, redeemable preferred stock, redeemable non-controlling interests and equity, and cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, the period from November 17, 2012 through December 31, 2012 (Successor), and the period from January 1, 2012 through November 16, 2012 (Predecessor). These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. We were not engaged to perform an audit of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of Vivint Solar, Inc. at December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, the period from November 17, 2012 through December 31, 2012 (Successor) and the period from January 1, 2012 to November 16, 2012 (Predecessor), in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Salt Lake City, Utah
March 13, 2015
65
(In thousands, except per share data and footnote 1)
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
||
|
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
261,649 |
|
|
$ |
6,038 |
|
|
Accounts receivable, net |
|
|
1,837 |
|
|
|
608 |
|
|
Inventories |
|
|
774 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
16,806 |
|
|
|
5,938 |
|
|
Total current assets |
|
|
281,066 |
|
|
|
12,584 |
|
|
Restricted cash |
|
|
6,516 |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
Solar energy systems, net |
|
|
588,167 |
|
|
|
188,058 |
|
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
13,024 |
|
|
|
3,640 |
|
|
Intangible assets, net |
|
|
18,487 |
|
|
|
27,364 |
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
36,601 |
|
|
|
29,545 |
|
|
Prepaid tax asset, net |
|
|
111,910 |
|
|
|
30,738 |
|
|
Other non-current assets, net |
|
|
8,553 |
|
|
|
778 |
|
|
TOTAL ASSETS(1) |
|
$ |
1,064,324 |
|
|
$ |
297,707 |
|
|
LIABILITIES, REDEEMABLE NON-CONTROLLING INTERESTS AND EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable |
|
$ |
51,354 |
|
|
$ |
25,356 |
|
|
Accounts payable—related party |
|
|
2,132 |
|
|
|
3,068 |
|
|
Distributions payable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
|
6,780 |
|
|
|
1,576 |
|
|
Accrued compensation |
|
|
16,794 |
|
|
|
15,491 |
|
|
Current portion of deferred revenue |
|
|
314 |
|
|
|
68 |
|
|
Current portion of capital lease obligation |
|
|
3,502 |
|
|
|
1,275 |
|
|
Accrued and other current liabilities |
|
|
14,016 |
|
|
|
10,307 |
|
|
Total current liabilities |
|
|
94,892 |
|
|
|
57,141 |
|
|
Capital lease obligation, net of current portion |
|
|
6,176 |
|
|
|
2,486 |
|
|
Revolving lines of credit—related party |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
41,412 |
|
|
Long-term debt |
|
|
105,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Deferred tax liability, net |
|
|
112,227 |
|
|
|
41,510 |
|
|
Deferred revenue, net of current portion |
|
|
4,466 |
|
|
|
1,272 |
|
|
Total liabilities(1) |
|
|
322,761 |
|
|
|
143,821 |
|
|
Commitments and contingencies (Note 16) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
|
128,427 |
|
|
|
73,265 |
|
|
Stockholders' equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock, $0.01 par value—1,000,000 authorized, 105,303 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2014; 100,000 authorized, 75,000 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2013 |
|
|
1,053 |
|
|
|
750 |
|
|
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
502,785 |
|
|
|
75,049 |
|
|
(Accumulated deficit) retained earnings |
|
|
(25,849 |
) |
|
|
3,034 |
|
|
Total stockholders' equity |
|
|
477,989 |
|
|
|
78,833 |
|
|
Non-controlling interests |
|
|
135,147 |
|
|
|
1,788 |
|
|
Total equity |
|
|
613,136 |
|
|
|
80,621 |
|
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES, REDEEMABLE NON-CONTROLLING INTERESTS AND EQUITY |
|
$ |
1,064,324 |
|
|
$ |
297,707 |
|
|
(1) |
The Company’s consolidated assets as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 include $540.1 million and $156.2 million consisting of assets of variable interest entities, or VIEs, that can only be used to settle obligations of the VIEs. These assets include solar energy systems, net, of $525.9 million and $152.6 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013; cash and cash equivalents of $12.6 million and $3.1 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013; and accounts receivable, net, of $1.6 million and $0.5 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013. The Company’s consolidated liabilities as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 included $11.4 million and $2.9 million of liabilities of VIEs whose creditors have no recourse to the Company. These liabilities include distributions payable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests of $6.8 million and $1.6 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013; and deferred revenue of $4.6 million and $1.3 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013. See further description in Note 11—Investment Funds. |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
66
Vivint Solar, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(In thousands, except per share data)
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
||||
|
Revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating leases and incentives |
|
$ |
21,688 |
|
|
$ |
5,864 |
|
|
$ |
109 |
|
|
|
$ |
183 |
|
|
Solar energy system and product sales |
|
|
3,570 |
|
|
|
306 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
157 |
|
|
Total revenue |
|
|
25,258 |
|
|
|
6,170 |
|
|
|
109 |
|
|
|
|
340 |
|
|
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of revenue—operating leases and incentives |
|
|
67,984 |
|
|
|
19,004 |
|
|
|
1,018 |
|
|
|
|
3,302 |
|
|
Cost of revenue—solar energy system and product sales |
|
|
1,997 |
|
|
|
123 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
95 |
|
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
21,869 |
|
|
|
7,348 |
|
|
|
533 |
|
|
|
|
1,471 |
|
|
Research and development |
|
|
1,892 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
78,899 |
|
|
|
16,438 |
|
|
|
971 |
|
|
|
|
7,789 |
|
|
Amortization of intangible assets |
|
|
14,911 |
|
|
|
14,595 |
|
|
|
1,824 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
|
187,552 |
|
|
|
57,508 |
|
|
|
4,346 |
|
|
|
|
12,657 |
|
|
Loss from operations |
|
|
(162,294 |
) |
|
|
(51,338 |
) |
|
|
(4,237 |
) |
|
|
|
(12,317 |
) |
|
Interest expense |
|
|
9,323 |
|
|
|
3,144 |
|
|
|
96 |
|
|
|
|
881 |
|
|
Other expense |
|
|
1,372 |
|
|
|
1,865 |
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
|
|
240 |
|
|
Loss before income taxes |
|
|
(172,989 |
) |
|
|
(56,347 |
) |
|
|
(4,377 |
) |
|
|
|
(13,438 |
) |
|
Income tax (benefit) expense |
|
|
(7,070 |
) |
|
|
123 |
|
|
|
(1,074 |
) |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
Net loss |
|
|
(165,919 |
) |
|
|
(56,470 |
) |
|
|
(3,303 |
) |
|
|
|
(13,445 |
) |
|
Net loss attributable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
|
(137,036 |
) |
|
|
(62,108 |
) |
|
|
(699 |
) |
|
|
|
(1,771 |
) |
|
Net (loss attributable) income available to stockholders |
|
$ |
(28,883 |
) |
|
$ |
5,638 |
|
|
$ |
(2,604 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(11,674 |
) |
|
Accretion to redemption value of Series B redeemable preferred stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
(20,000 |
) |
|
Net (loss attributable) income available to common stockholders |
|
$ |
(28,883 |
) |
|
$ |
5,638 |
|
|
$ |
(2,604 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(31,674 |
) |
|
Net (loss attributable) income available per share to common stockholders: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
$ |
(0.35 |
) |
|
$ |
0.08 |
|
|
$ |
(0.03 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(0.42 |
) |
|
Diluted |
|
$ |
(0.35 |
) |
|
$ |
0.07 |
|
|
$ |
(0.03 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(0.42 |
) |
|
Weighted-average shares used in computing net (loss attributable) income available per share to common stockholders: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
|
83,446 |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
Diluted |
|
|
83,446 |
|
|
|
75,223 |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
67
Vivint Solar, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Redeemable Preferred Stock, Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests and Equity
(In thousands)
|
|
Series B |
|
|
Redeemable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Retained |
|
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
Redeemable |
|
|
Non- |
|
|
|
Series A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional |
|
|
Earnings |
|
|
Stockholders’ |
|
|
Non- |
|
|
Total |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
Preferred Stock |
|
|
Controlling |
|
|
|
Preferred Stock |
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
Paid-in |
|
|
(Accumulated |
|
|
Equity |
|
|
Controlling |
|
|
Equity |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Interests |
|
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Deficit) |
|
|
(Deficit) |
|
|
Interests |
|
|
(Deficit) |
|
||||||||||||
|
Predecessor: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance — January 1, 2012 |
|
4 |
|
|
$ |
5,000 |
|
|
$ |
224 |
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
$ |
1 |
|
|
$ |
1,378 |
|
|
$ |
(2,164 |
) |
|
$ |
(785 |
) |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
(785 |
) |
|
Issuance of Series B redeemable preferred stock |
|
4 |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Accretion to redemption value of Series B redeemable preferred stock |
|
— |
|
|
|
20,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(5,542 |
) |
|
|
(14,458 |
) |
|
|
(20,000 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(20,000 |
) |
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
155 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
155 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
155 |
|
|
Noncash contributions for services |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,009 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,009 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,009 |
|
|
Contributions from redeemable non- controlling interests |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
9,193 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Distributions to redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(197 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Net loss |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(1,771 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(11,674 |
) |
|
|
(11,674 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(11,674 |
) |
|
Balance — November 16, 2012 |
|
8 |
|
|
|
30,000 |
|
|
|
7,449 |
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(28,296 |
) |
|
|
(28,295 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(28,295 |
) |
|
Successor: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Noncash capital contribution related to the Acquisition |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
10,620 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
750 |
|
|
|
72,380 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
73,130 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
73,130 |
|
|
Noncash contributions for services |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
797 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
797 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
797 |
|
|
Contributions from redeemable non- controlling interests |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
8,147 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Distributions to redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(327 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Net loss |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(699 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(2,604 |
) |
|
|
(2,604 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(2,604 |
) |
|
Balance — December 31, 2012 |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
17,741 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
750 |
|
|
|
73,177 |
|
|
|
(2,604 |
) |
|
|
71,323 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
71,323 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
294 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
294 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
294 |
|
|
Noncash contributions for services |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
160 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
160 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
160 |
|
|
Capital contribution from Parent |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,418 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,418 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,418 |
|
|
Contributions from non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
63,154 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
60,000 |
|
|
|
60,000 |
|
|
Distributions to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(3,064 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(670 |
) |
|
|
(670 |
) |
|
Net income (loss) |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(4,566 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,638 |
|
|
|
5,638 |
|
|
|
(57,542 |
) |
|
|
(51,904 |
) |
|
Balance — December 31, 2013 |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
73,265 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
750 |
|
|
|
75,049 |
|
|
|
3,034 |
|
|
|
78,833 |
|
|
|
1,788 |
|
|
|
80,621 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
23,687 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
23,687 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
23,687 |
|
|
Noncash contributions for services |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
Issuance of common stock |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
30,303 |
|
|
|
303 |
|
|
|
412,609 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
412,912 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
412,912 |
|
|
Costs related to issuance of common stock |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(8,760 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(8,760 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(8,760 |
) |
|
Contributions from non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
63,735 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
275,777 |
|
|
|
275,777 |
|
|
Deemed dividend |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
43,430 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
43,430 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
43,430 |
|
|
Return of capital adjustment |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(43,430 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(43,430 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(43,430 |
) |
|
Distributions to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(5,154 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(8,801 |
) |
|
|
(8,801 |
) |
|
Net loss |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(3,419 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(28,883 |
) |
|
|
(28,883 |
) |
|
|
(133,617 |
) |
|
|
(162,500 |
) |
|
Balance — December 31, 2014 |
|
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
128,427 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
105,303 |
|
|
$ |
1,053 |
|
|
$ |
502,785 |
|
|
$ |
(25,849 |
) |
|
$ |
477,989 |
|
|
$ |
135,147 |
|
|
$ |
613,136 |
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
68
Vivint Solar, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(In thousands)
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss |
|
$ |
(165,919 |
) |
|
$ |
(56,470 |
) |
|
$ |
(3,303 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(13,445 |
) |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
8,523 |
|
|
|
1,984 |
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
72 |
|
|
Amortization of intangible assets |
|
|
15,042 |
|
|
|
14,595 |
|
|
|
1,824 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
23,687 |
|
|
|
294 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
155 |
|
|
Amortization of deferred financing costs |
|
|
2,232 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
161 |
|
|
Noncash contributions for services |
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
160 |
|
|
|
797 |
|
|
|
|
4,009 |
|
|
Noncash interest expense |
|
|
4,280 |
|
|
|
2,930 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
74,848 |
|
|
|
30,927 |
|
|
|
(1,075 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of acquisitions: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable, net |
|
|
(1,018 |
) |
|
|
(512 |
) |
|
|
(52 |
) |
|
|
|
(41 |
) |
|
Inventories |
|
|
(195 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
(10,486 |
) |
|
|
(3,605 |
) |
|
|
(102 |
) |
|
|
|
(988 |
) |
|
Prepaid tax asset, net |
|
|
(81,172 |
) |
|
|
(30,738 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Other non-current assets, net |
|
|
(8,451 |
) |
|
|
(741 |
) |
|
|
(19 |
) |
|
|
|
(9 |
) |
|
Accounts payable |
|
|
1,905 |
|
|
|
1,425 |
|
|
|
286 |
|
|
|
|
363 |
|
|
Accounts payable—related party |
|
|
(935 |
) |
|
|
2,592 |
|
|
|
741 |
|
|
|
|
1,701 |
|
|
Accrued compensation |
|
|
(1,073 |
) |
|
|
10,367 |
|
|
|
498 |
|
|
|
|
375 |
|
|
Deferred revenue |
|
|
3,387 |
|
|
|
1,340 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Accrued and other current liabilities |
|
|
(773 |
) |
|
|
4,579 |
|
|
|
(822 |
) |
|
|
|
4,757 |
|
|
Net cash used in operating activities |
|
|
(135,918 |
) |
|
|
(20,873 |
) |
|
|
(1,209 |
) |
|
|
|
(2,890 |
) |
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Payments for the cost of solar energy systems |
|
|
(383,522 |
) |
|
|
(134,138 |
) |
|
|
(11,083 |
) |
|
|
|
(18,306 |
) |
|
Payment in connection with business acquisition, net of cash acquired |
|
|
(12,040 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Payments for property and equipment |
|
|
(3,505 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Change in restricted cash |
|
|
(1,516 |
) |
|
|
(3,500 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
(152 |
) |
|
Purchase of intangible assets |
|
|
(370 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Proceeds from U.S. Treasury grants |
|
|
190 |
|
|
|
10,116 |
|
|
|
3,069 |
|
|
|
|
3,150 |
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
(400,763 |
) |
|
|
(127,522 |
) |
|
|
(8,014 |
) |
|
|
|
(15,308 |
) |
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of common stock |
|
|
412,912 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Payments for deferred offering costs |
|
|
(8,066 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Proceeds from investment by non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
|
339,512 |
|
|
|
123,154 |
|
|
|
8,147 |
|
|
|
|
9,193 |
|
|
Distributions paid to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
|
(8,751 |
) |
|
|
(2,284 |
) |
|
|
(274 |
) |
|
|
|
(80 |
) |
|
Proceeds from long-term debt |
|
|
105,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Proceeds from short-term debt |
|
|
75,500 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Payments on short-term debt |
|
|
(75,500 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Proceeds from revolving lines of credit—related party |
|
|
154,500 |
|
|
|
83,482 |
|
|
|
15,000 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Payments on revolving lines of credit—related party |
|
|
(200,192 |
) |
|
|
(60,000 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Proceeds from revolving line of credit |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,500 |
|
|
|
|
4,000 |
|
|
Payments on revolving lines of credit |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(2,000 |
) |
|
|
(4,500 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Principal payments on capital lease obligations |
|
|
(2,623 |
) |
|
|
(987 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Capital contribution from Parent |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,418 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of redeemable preferred stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
Net cash provided by financing activities |
|
|
792,292 |
|
|
|
142,783 |
|
|
|
20,873 |
|
|
|
|
18,113 |
|
|
NET INCREASE (DECREASE) IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
|
|
255,611 |
|
|
|
(5,612 |
) |
|
|
11,650 |
|
|
|
|
(85 |
) |
|
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS—Beginning of period |
|
|
6,038 |
|
|
|
11,650 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
85 |
|
|
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS—End of period |
|
$ |
261,649 |
|
|
$ |
6,038 |
|
|
$ |
11,650 |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURES OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid for interest |
|
$ |
4,473 |
|
|
$ |
206 |
|
|
$ |
96 |
|
|
|
$ |
313 |
|
|
Cash paid for income taxes |
|
$ |
4,350 |
|
|
$ |
4 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
$ |
1 |
|
|
NONCASH INVESTING AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vehicles acquired under capital leases |
|
$ |
8,541 |
|
|
$ |
4,749 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Accretion to redemption value of Series B redeemable preferred stock |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
$ |
20,000 |
|
|
Accrued distributions to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
$ |
5,204 |
|
|
$ |
1,450 |
|
|
$ |
53 |
|
|
|
$ |
117 |
|
|
Capital contribution related to the Acquisition |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
71,658 |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Costs of solar energy systems included in accounts payable, accrued compensation and other accrued liabilities |
|
$ |
25,990 |
|
|
$ |
19,946 |
|
|
$ |
(439 |
) |
|
|
$ |
13,243 |
|
|
Receivable for tax credit recorded as a reduction to solar energy system costs |
|
$ |
4,132 |
|
|
$ |
2,122 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
69
Vivint Solar, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
|
1. |
Organization |
Vivint Solar, Inc. (the “Company” and formerly known as V Solar Holdings, Inc.) was incorporated as a Delaware corporation on August 12, 2011. Vivint Solar, Inc. and its subsidiaries are collectively referred to as the “Company.” The Company commenced operations in May 2011. The Company offers solar energy to residential customers through long-term customer contracts, such as power purchase agreements and solar energy system leases. The Company enters into these long-term customer contracts through a sales organization that uses a direct-to-home sales model. The long-term customer contracts are typically for 20 years and require the customer to make monthly payments to the Company. Through the acquisition of Solmetric Corporation (“Solmetric”) in the first quarter of 2014, the Company also offers photovoltaic installation software products and devices.
The Company has formed various investment funds and entered into a long-term debt facility to monetize the recurring customer payments under its long-term customer contracts and the investment tax credits, accelerated tax depreciation and other incentives associated with residential solar energy systems. The Company uses the cash received from the investment funds to finance a portion of the Company’s variable and fixed costs associated with installing the residential solar energy systems. In addition, the obligations of the Company are in no event obligations of the investment funds.
On November 16, 2012 (the “Acquisition Date”), investment funds affiliated with The Blackstone Group L.P. (the “Sponsor”) and certain co-investors (collectively, the “Investors”), through 313 Acquisition LLC (“313” or “Parent”), acquired 100% of the equity interests of APX Group, Inc. (“Vivint”) and the Company (the “Acquisition”). The Acquisition was accomplished through certain mergers and related reorganization transactions pursuant to which the Company became a direct wholly owned subsidiary of 313, an entity owned by the Investors. The impact of the mergers resulted in a change to the Company’s capital structure which is reflected as a noncash capital contribution related to the Acquisition in the Company’s consolidated statements of redeemable preferred stock, redeemable non-controlling interests and equity. See Note 4—Business Acquisitions.
Since inception and continuing after the Acquisition, the Company has relied upon Vivint and certain of its affiliates for many of its administrative, managerial, account management and operational services. The Company was consolidated by Vivint as a variable interest entity prior to the Acquisition, and continues to be an affiliated entity and related party subsequent to the Acquisition. The Company has entered into various agreements and transactions with Vivint and its affiliates related to these services. See Note 15—Related Party Transactions.
|
2. |
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
Basis of Presentation and Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) and applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) and reflect the accounts and operations of the Company, its subsidiaries in which the Company has a controlling financial interest and the investment funds formed to fund the purchase of solar energy systems, which are consolidated as variable interest entities (“VIEs”). The Company uses a qualitative approach in assessing the consolidation requirement for VIEs. This approach focuses on determining whether the Company has the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly affect the VIE’s economic performance and whether the Company has the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits that could potentially be significant to the VIE. For all periods presented, the Company has determined that it is the primary beneficiary in all of its operational VIEs. The Company evaluates its relationships with the VIEs on an ongoing basis to ensure that it continues to be the primary beneficiary. All intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation. For additional information regarding these VIEs, see Note 11—Investment Funds.
The years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 and the period from November 17, 2012 through December 31, 2012 are referred to as the Successor Periods or Successor and the period from January 1, 2012 through November 16, 2012 as the Predecessor Period or Predecessor. The consolidated financial statements are presented as four separate periods: the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, the period from November 17, 2012 through December 31, 2012 and the Predecessor Period. The Company’s assets and liabilities were adjusted to fair value on the closing date of the Acquisition by application of push-down accounting. Due to the change in the basis of accounting resulting from the Acquisition, the consolidated financial statements for the Successor Periods and the Predecessor Period are not necessarily comparable.
70
The consolidated financial statements reflect all of the costs of doing business, including the allocation of expenses incurred by Vivint on behalf of the Company. For additional information, see Note 15—Related Party Transactions. These expenses were allocated to the Company on a basis that was considered to reasonably reflect the utilization of the services provided to, or the benefit obtained by, the Company. The allocations may not, however, reflect the expense the Company would have incurred as an independent company for the periods presented, and may not be indicative of the Company’s future results of operations and financial position.
Stock Split
In July 2013, the board of directors approved a 750,000-for-1 stock split of common stock. All share and per share information for the Successor Periods referenced throughout the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes have been retroactively adjusted to reflect this stock split.
Segment Information
The Company’s chief operating decision maker is its Chief Executive Officer. The Chief Executive Officer reviews financial information presented on a consolidated basis for purposes of allocating resources and evaluating financial performance. The Company has one business activity and no segment managers are accountable for operations or operating results beyond revenues. Accordingly, the Company operates as a single operating and reporting segment.
The following table sets forth the Company’s revenue by major product (in thousands):
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
||||
|
Revenue: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating leases and incentives |
|
$ |
21,688 |
|
|
$ |
5,864 |
|
|
$ |
109 |
|
|
|
$ |
183 |
|
|
Photovoltaic installation devices and software |
|
|
3,213 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Solar energy system sales |
|
|
357 |
|
|
|
306 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
157 |
|
|
Total revenue |
|
$ |
25,258 |
|
|
$ |
6,170 |
|
|
$ |
109 |
|
|
|
$ |
340 |
|
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. The Company regularly makes significant estimates and assumptions including, but not limited to, estimates that affect the Company’s principles of consolidation, revenue recognition, the useful lives of solar energy systems, the valuation and recoverability of intangible assets and goodwill acquired, useful lives of intangible assets, recoverability of long-lived assets, the recognition and measurement of loss contingencies, the valuation of stock-based compensation, the determination of valuation allowances associated with deferred tax assets, and the valuation of non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests. The Company bases its estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions believed to be reasonable, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ materially from those estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with maturities of three months or less at the time of purchase to be cash and cash equivalents. Cash equivalents consist principally of time deposits and money market accounts with high quality financial institutions.
Restricted Cash
The Company’s guaranty agreements with certain of its fund investors require the maintenance of minimum cash balances of $5.0 million. For additional information, see Note 11—Investment Funds. The Company was also required to deposit $1.5 million into a separate interest reserve account in accordance with the terms of its loan credit facility with Bank of America, N.A. For additional information, see Note 10—Debt Obligations. These minimum cash balances are classified as restricted cash.
71
Accounts Receivable, Net
Accounts receivable are recorded at the invoiced amount, net of allowance for doubtful accounts. Accounts receivable also include unbilled accounts receivable, which result from monthly power generation under power purchase agreements not yet invoiced as of the end of the reporting period. The Company estimates its allowance for doubtful accounts based upon the collectability of the receivables in light of historical trends and adverse situations that may affect customers’ ability to pay. Revisions to the allowance are recorded as an adjustment to bad debt expense. After appropriate collection efforts are exhausted, specific accounts receivable deemed to be uncollectible are charged against the allowance in the period they are deemed uncollectible. Recoveries of accounts receivable previously written-off are recorded as credits to bad debt expense. The Company had an allowance for doubtful accounts of $0.6 million and a de minimis amount as of December 31, 2014 and 2013.
Inventories
Inventories consist of components related to photovoltaic installation software products and devices and are stated at the lower of cost, on an average cost basis, or market. The Company did not have inventories prior to the acquisition of Solmetric in January 2014.
Concentrations of Risk
Financial instruments which potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents and accounts receivable. The associated risk of concentration for cash and cash equivalents is mitigated by banking with creditworthy institutions. At certain times, amounts on deposit exceed Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation insurance limits. The Company does not require collateral or other security to support accounts receivable. The Company is not dependent on any single customer. The loss of a customer would not adversely impact the Company’s operating results or financial position.
The Company purchases solar panels, inverters and other system components from a limited number of suppliers. Two suppliers accounted for approximately 50% and 40% of the solar photovoltaic module purchases for the year ended December 31, 2014. The same two suppliers each individually accounted for over 48% of these purchases for the year ended December 31, 2013. The same two suppliers accounted for approximately 63% and 20% of these purchases for the year ended December 31, 2012. One supplier accounted for a substantial majority of the Company’s inverter purchases for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. If these suppliers fail to satisfy the Company’s requirements on a timely basis or if the Company fails to develop, maintain and expand its relationship with these suppliers, the Company could suffer delays in being able to deliver or install its solar energy systems, experience a possible loss of revenue, or incur higher costs, any of which could adversely affect its operating results.
As of December 31, 2014, the Company’s customers under long-term customer contracts are primarily located in Arizona, California, Hawaii, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey and New York. Future operations could be affected by changes in the economic conditions in these and other geographic areas, by changes in the demand for renewable energy generated by solar panel systems or by changes or eliminations of solar energy related government incentives.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Assets and liabilities recorded at fair value on a recurring basis in the consolidated balance sheets are categorized based upon the level of judgment associated with the inputs used to measure their fair values. Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or an exit price that would be paid to transfer a liability in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value must maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The authoritative guidance on fair value measurements establishes a three-tier fair value hierarchy for disclosure of fair value measurements as follows:
|
· |
Level I—Inputs are unadjusted, quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities at the measurement date; |
|
· |
Level II—Inputs are observable, unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for similar assets or liabilities, unadjusted quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active, or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the related assets or liabilities; and |
|
· |
Level III—Unobservable inputs that are significant to the measurement of the fair value of the assets or liabilities that are supported by little or no market data. |
The Company’s financial instruments consist of Level I and Level II assets and liabilities. See Note 3—Fair Value Measurements.
72
U.S. Treasury Grants and Investment Tax Credits
Certain solar energy systems were eligible to receive U.S. Treasury grants under Section 1603 of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, as amended by the Tax Relief Unemployment Insurance Reauthorization and Job Creation Act of December 2010. Prior to installation of such eligible systems, the Company submitted an application to receive a grant. After installation was completed and the solar energy system was interconnected to the power grid, the Company requested disbursement of the funds, typically based on 30% of the tax basis of eligible solar energy systems. Once the Company was notified that the U.S. Treasury Department approved the disbursement of the grant proceeds for a solar energy system, the Company recorded a reduction in the basis of the solar energy system in the amount of cash to be received, at the grant approval date. If it becomes probable that a U.S. Treasury grant is required to be repaid, the Company will assess whether it is necessary to derecognize any grant (or portion thereof) in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification section 450.
For the solar energy systems that are not eligible to receive U.S. Treasury grants, the Company will apply for and receive investment tax credits under Section 48(a) of the Internal Revenue Code. The amount for the investment tax credit is equal to 30% of the value of eligible solar property. The Company receives minimal allocations of investment tax credits as the majority of such credits are allocated to the fund investor. Some of the Company’s investment funds obligate it to make certain fund investors whole for losses that the investors may suffer in certain limited circumstances resulting from the disallowance or recapture of investment tax credits as a result of the Internal Revenue Service’s (the “IRS”) assessment of the fair value of such systems. The Company has concluded that the likelihood of a recapture event is remote and consequently has not recorded any liability in the consolidated financial statements for any potential recapture exposure.
Solar Energy Systems, Net
The Company sells energy to customers through power purchase agreements or leases solar energy systems to customers under legal-form lease agreements. From inception through December 31, 2013, customers only purchased energy under the power purchase agreement structure. The Company has determined that these contracts should be accounted for as operating leases and, accordingly, solar energy systems are stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation and amortization. In the first quarter of 2014, the Company began offering leases to customers in connection with its entry into the Arizona market. As of December 31, 2014 the Company had interconnected approximately 140 of its leased solar energy systems to the power grid and began depreciation and amortization on these solar energy systems.
Solar energy systems, net is comprised of system equipment costs and initial direct costs related to solar energy systems. System equipment costs include components such as solar panels, inverters, racking systems and other electrical equipment, as well as costs for design and installation activities once a long-term customer contract has been executed. Initial direct costs related to solar energy systems consist of sales commissions and other direct customer acquisition expenses. System equipment costs and initial direct costs are capitalized and recorded within solar energy systems, net.
As noted under the heading “U.S. Treasury Grants and Investment Tax Credits”, the Company applies for and receives U.S. Treasury grants related to its solar energy systems. The Company records the U.S. Treasury grants as a reduction in the basis of the solar energy systems at the approval date of the grant. This accounting treatment results in decreased depreciation of such solar energy systems over their useful lives.
Depreciation and amortization is calculated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets as follows:
|
|
|
Useful Lives |
|
System equipment costs |
|
30 years |
|
Initial direct costs related to solar energy systems |
|
Lease term (20 years) |
System equipment costs are depreciated and initial direct costs are amortized once the respective systems have been installed and interconnected to the power grid. As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company had recorded costs of $598.4 million and $190.1 million in solar energy systems, of which $407.7 million and $132.3 million related to systems that had been interconnected to the power grid, with accumulated depreciation and amortization of $10.2 million and $2.1 million.
73
The Company’s property and equipment is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are calculated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Vehicles leased under capital leases are depreciated over the life of the lease term, which is typically three years. The estimated useful lives of computer equipment, furniture, fixtures and purchased software are three years. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of the lease term or the estimated useful lives of the assets. The estimated useful lives of leasehold improvements currently range from one to three years. Repairs and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred. Major renewals and improvements that extend the useful lives of existing assets are capitalized and depreciated over their estimated useful lives.
Intangible Assets
Finite-lived intangible assets, which consist of customer contracts, customer relationships, trademarks/trade names and developed technology acquired in business combinations are initially recorded at fair value and presented net of accumulated amortization. These intangible assets are amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives. The Company amortizes customer contracts over three years, customer relationships over five years, trademarks/trade names over 10 years and developed technology over five to eight years.
In-process research and development reflects research and development projects that have not yet been completed and are capitalized as indefinite-lived intangibles subject to amortization upon completion or impairment if the assets are subsequently impaired or abandoned. In-process research and development projects were acquired in January 2014 as part of the Solmetric acquisition. See Note 4—Business Acquisitions. The Company assesses (or tests) indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment on an annual basis, or whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the fair value is less than its carrying value. To test these intangible assets for impairment, the Company compares the fair value of the indefinite-lived asset with its carrying amount. In the event the carrying value exceeds the fair value of the assets, the assets are written down to their fair value. There has been no impairment of indefinite-lived intangible assets during any of the periods presented.
Capitalization of Internal Use-Software Costs
The Company capitalizes costs incurred in the development of internal-use software during the application development stage. Costs related to preliminary project activities and post-implementation activities are expensed as incurred. Internal-use software is amortized on a straight-line basis over its estimated useful life. The Company tests these assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances occur that could impact the recoverability of these assets. In 2014, the Company incurred third-party costs related to the development of internal-use software applications that will be subject to amortization over expected useful lives of three years. No amortization was recorded for internal-use software in the any of the periods presented.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The carrying amounts of the Company’s long-lived assets, including solar energy systems, property and equipment and finite-lived intangible assets are periodically reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of these assets may not be recoverable or that the useful life is shorter than originally estimated. Factors that the Company considers in deciding when to perform an impairment review include significant negative industry or economic trends, and significant changes or planned changes in the Company’s use of the assets. Recoverability of these assets is measured by comparison of the carrying amount of each asset to the future undiscounted cash flows the asset is expected to generate over its remaining life. If the asset is considered to be impaired, the amount of any impairment is measured as the difference between the carrying value and the fair value of the impaired asset. If the useful life is shorter than originally estimated, the Company amortizes the remaining carrying value over the new shorter useful life. No impairment of any long-lived assets was identified for the periods presented.
Goodwill and Impairment Analysis
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price of an acquired business over the fair value of the net tangible and intangible assets acquired. The Company has goodwill recorded on its books as a result of push-down accounting applied as of the Acquisition Date as well as its acquisition of Solmetric. See Note 4—Business Acquisitions. The Company’s impairment test is based on a single operating segment and reporting unit structure.
The Company performs its annual impairment test of goodwill as of October 1st of each fiscal year or whenever events or circumstances change that would indicate that goodwill might be impaired. Triggering events that may indicate impairment include, but are not limited to, a significant adverse change in the business climate, unanticipated competition, loss of key personnel, significant changes in the manner the Company uses the acquired assets or the strategy for the overall business, significant negative industry or economic trends or significant underperformance relative to historical operations or projected future results of operations.
74
In conducting the impairment test, the Company first assesses qualitative factors, including those stated previously, to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount as a basis for determining whether it is necessary to perform the two-step goodwill impairment test. If the qualitative step is not passed, the Company performs a two-step impairment test whereby in the first step, the Company must compare the fair value of the reporting unit with its carrying amount. If the carrying amount exceeds its fair value, the Company performs the second step of the goodwill impairment test to determine the amount of impairment. The second step, measuring the impairment loss, compares the implied fair value of the goodwill with the carrying value of the goodwill. Any excess of the goodwill carrying value over the implied fair value is recognized as an impairment loss.
The Company determined the second step test was not necessary based on the results of its qualitative assessments and concluded that it was more likely than not that the fair value of its reporting unit was greater than its respective carrying value as of October 1, 2014 and October 1, 2013. The Company did not have any goodwill prior to the Acquisition.
Prepaid Tax Asset, Net
The Company sells solar energy systems to the investment funds. As the investment funds are consolidated by the Company, the gain on the sale of the solar energy systems is not recognized in the consolidated financial statements. However, this gain is recognized for tax reporting purposes. Since these transactions are intercompany sales for book purposes, any tax expense incurred related to these intercompany sales is deferred and recorded as a prepaid tax asset and amortized over the estimated useful life of the underlying solar energy systems, which has been estimated to be 30 years.
Other Non-Current Assets
Other non-current assets primarily consist of deferred financing costs and advances receivable due from related parties. Costs incurred in connection with obtaining debt financing are deferred and amortized utilizing the straight-line method, which approximates the effective-interest method, over the term of the related financing. On occasion, the Company provides advance payments of compensation to direct-sales personnel. The advance is repaid as a reduction of the direct-sales personnel’s future compensation. The Company has established an allowance related to advances to direct-sales personnel who have terminated their employment agreement with the Company. These are non-interest bearing advances.
Distributions Payable to Non-Controlling Interests and Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests
As discussed in Note 11—Investment Funds, the Company and fund investors have formed various investment funds that the Company consolidates as the Company has determined that it is the primary beneficiary of these VIEs. These VIEs are required to pay cumulative cash distributions to their respective fund investors. The Company accrues amounts payable to fund investors in distributions payable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests in its consolidated balance sheets.
Deferred Revenue
Deferred revenue includes rebates and incentives received from utility companies and various government agencies and are recognized as revenue over the related lease term of 20 years. Additionally, subsequent to the Solmetric acquisition in January 2014, the Company also defers revenue from its multiple element arrangements. See Revenue Recognition below.
Warranties
The Company warrants solar energy systems sold to customers for one year against defects in material or installation workmanship. The manufacturers’ warranties on the solar energy system components, which is typically passed through to the customers, has a typical product warranty period of 10 years and a limited performance warranty period of 25 years. The Company warrants its photovoltaic installation software products and devices for one to two years against defects in materials or installation workmanship.
The Company generally provides for the estimated cost of warranties at the time the related revenue is recognized. The Company assesses the accrued warranty regularly and adjusts the amounts as necessary based on actual experience and changes in future estimates. Accrued warranty is recorded as a component of accrued and other current liabilities on the consolidated balance sheets and was not significant as of December 31, 2014 and 2013.
75
Solar Energy Performance Guarantees
In 2014, the Company entered into customer agreements that are structured as legal-form leases. Under these leases the Company guarantees a certain annual minimum solar energy production output for the solar energy systems. Failure to reach the minimum thresholds specified in the legal-form leases could result in the Company being required to pay back a portion of the previously remitted lease payments from customers. The Company monitors the solar energy systems to ensure that these minimum levels of energy production are being achieved and evaluates if any amounts are due to its customers. Solar energy performance guarantee liabilities were de minimis as of December 31, 2014.
Comprehensive Loss
As the Company had no other comprehensive income or loss, comprehensive loss is the same as net loss for all periods presented.
Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue when all of the following criteria are met: (1) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, (2) delivery or performance has occurred, (3) the sales price is fixed or determinable and (4) collectability is reasonably assured. The Company generates revenue through power purchase agreements and solar energy system leases, solar renewable energy certificates (“SRECs”) sales, rebate incentives and solar energy system sales. Revenue associated with power purchase agreements and solar energy system leases, SRECs and rebate incentives are included within operating leases and incentives revenue. The Company also recognizes revenue related to the sale of photovoltaic installation software products and devices within solar energy system and product sales.
Operating Leases and Incentives Revenue
The Company’s primary revenue-generating activity consists of entering into long-term power purchase agreements with residential customers, under which the customer agrees to purchase all of the power generated by the solar energy system for the term of the contract, which is 20 years. The agreement includes a fixed price per kilowatt hour with a fixed annual price escalation percentage (to address the impact of inflation and utility rate increases over the period of the contract). Customers have not historically been charged for installation or activation of the solar energy system. For all power purchase agreements, the Company assesses the probability of collectability on a customer-by-customer basis through a credit review process that evaluates their financial condition and ability to pay.
The Company has determined that power purchase agreements should be accounted for as operating leases after evaluating and concluding that none of the following capitalized lease classification criteria are met: no transfer of ownership or bargain purchase option exists at the end of the lease, the lease term is not greater than 75% of the useful life or the present value of minimum lease payments does not exceed 90% of the fair value at lease inception. As customer payments under a power purchase agreement are dependent on power generation, they are considered contingent rentals and are excluded from future minimum annual lease payments. Revenue from power purchase agreements is recognized based on the actual amount of power generated at rates specified under the contracts, assuming the other revenue recognition criteria discussed above are met.
Operating leases and incentives revenue is recorded net of sales tax collected.
In 2014, the Company began offering solar energy systems to customers pursuant to legal-form leases in certain markets. The customer agreements are structured as legal-form leases due to local regulations that can be read to prohibit the sale of electricity pursuant to the Company’s standard power purchase agreement. Pursuant to the lease agreements, the customers’ monthly payments are a pre-determined amount calculated based on the expected solar energy generation by the system and includes an annual fixed percentage price escalation (to address the impact of inflation and utility rate increases) over the period of the contracts, which is 20 years. The Company provides its legal-form lease customers a performance guarantee, under which the Company agrees to make a payment at the end of each year to the customer if the solar energy systems do not meet a guaranteed production level in the prior 12-month period. Solar energy performance guarantee liabilities were de minimis as of December 31, 2014.
The Company applies for and receives SRECs in certain jurisdictions for power generated by its solar energy systems. When SRECs are granted, the Company typically sells them to other companies directly, or to brokers, to assist them in meeting their own mandatory emission reduction or conservation requirements. The Company recognizes revenue related to the sale of these certificates upon delivery, assuming the other revenue recognition criteria discussed above are met. The portion of SRECs included in operating leases and incentives was $2.6 million, $0.3 million and de minimis for the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 and the Predecessor Period. There were no SRECs recognized within operating leases and incentives revenue for the Successor Period ended December 31, 2012.
76
The Company considers upfront rebate incentives earned from its solar energy systems to be minimum lease payments and are recognized on a straight-line basis over the life of the long-term customer contracts, assuming the other revenue recognition criteria discussed above are met. The portion of rebates recognized within operating leases and incentives was $0.2 million and de minimis for the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. There were no rebates recognized within operating leases and incentives revenue for the Predecessor Period and the Successor Period ended December 31, 2012.
Solar Energy System and Product Sales
Revenue from solar energy system sales is recognized upon the solar energy system passing an inspection by the responsible city department after completion of system installation assuming the remaining revenue recognition criteria discussed above have been met.
Revenue from the sale of photovoltaic installation software products and devices is recognized upon delivery of the product to the customer assuming the remaining revenue recognition criteria discussed above have been met.
Multiple-Element Arrangements
The Company enters into revenue arrangements from the sale of photovoltaic installation software products and devices that consist of multiple elements. Each element in a multiple element arrangement must be evaluated to determine whether it represents a separate unit of account. An element constitutes a separate unit of account when it has standalone value and delivery of an undelivered element is both probable and within the Company’s control.
The Company’s typical multiple-element arrangements involve sales of (1) photovoltaic installation hardware devices containing software essential to the hardware product’s functionality (“photovoltaic device”) and (2) stand-alone software, both including the implied right for the customer to receive post-contract customer support (“PCS”) with the purchase of the Company’s products. PCS includes the implied right to receive, on a when and if available basis, future unspecified software upgrades and features as well as bug fixes, email and telephone support.
For sales of photovoltaic devices, the Company allocates revenue between (1) the photovoltaic device and (2) PCS using the relative selling price method. Because the Company has not sold these deliverables separately, vendor-specific objective evidence of fair value (“VSOE”) is not available. Additionally, the Company is unable to reliably determine the selling prices of similar competitor products and upgrades on a standalone basis to determine third-party evidence of selling price. As such, the allocation of revenue is based on the Company’s best estimate of selling price (“BESP”).
The Company determines BESP for a product or service by considering multiple factors including, but not limited to, market conditions, competitive landscape, internal costs, gross margin objectives and pricing practices. The determination of BESP is made through consultation with and formal approval by the Company’s management, taking into consideration the Company’s marketing strategy.
The consideration allocated to the delivered photovoltaic device is recognized at the time of shipment provided that the four general revenue recognition criteria discussed above have been met. The consideration allocated to the PCS is deferred and recognized ratably over the four year estimated life of the devices and the period during which the related PCS is expected to be provided.
For sales of software with PCS, revenue is recognized based on software revenue recognition accounting guidance. Because the Company is not able to determine VSOE for the PCS, revenue from the entire arrangement is recognized ratably over four years, which is the economic life over which the upgrades are expected to be provided.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of Revenue—Operating Leases and Incentives
Cost of revenue—operating leases and incentives includes the depreciation of the cost of the solar energy systems and the amortization of capitalized initial direct costs. It also includes other costs related to the processing, account creation, design, installation, interconnection and servicing of solar energy systems that are not capitalized, such as personnel costs not directly associated to a solar energy system installation, warehouse rent and utilities, and fleet vehicle executory costs. The cost of revenue for the sales of SRECs is limited to broker fees which are paid in connection with certain SREC transactions.
77
Cost of Revenue—Solar Energy System and Product Sales
Cost of revenue—solar energy system and product sales consists of direct and indirect material and labor costs for solar energy systems. It also consists of materials, personnel costs, depreciation, facilities costs, other overhead costs and infrastructure expenses associated with the manufacturing of the photovoltaic installation software products and devices.
Research and Development
Research and development expense is primarily comprised of salaries and benefits associated with research and development personnel and other costs related to photovoltaic installation software product and device development. Research and development costs are charged to expense when incurred. The Company’s research and development expense was $1.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. Prior to the acquisition of Solmetric in January 2014, the Company did not incur any research and development expenses.
Advertising Costs
Advertising costs are expensed when incurred and are included in sales and marketing expenses in the consolidated statements of operations. The Company’s advertising expense was $3.5 million, $1.3 million, $0.2 million and $0.2 million for the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 and the Predecessor Period.
Other Expense
The Company incurred interest and penalties primarily associated with employee payroll withholding tax payments that were not paid in a timely manner of $1.4 million, $1.9 million, a de minimis amount and $0.2 million for the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 and the Predecessor Period.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes under an asset and liability approach. Deferred income taxes reflect the impact of temporary differences between assets and liabilities recognized for financial reporting purposes and the amounts recognized for income tax reporting purposes, net operating loss carryforwards, and other tax credits measured by applying currently enacted tax laws. A valuation allowance is provided when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to an amount that is more likely than not to be realized.
The Company determines whether a tax position is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination, including resolution of any related appeals or litigation processes, based on the technical merits of the position. The Company uses a two-step approach to recognizing and measuring uncertain tax positions. The first step is to evaluate the tax position for recognition by determining if the weight of available evidence indicates that it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon tax authority examination, including resolution of related appeals or litigation processes, if any. The second step is to measure the tax benefit as the largest amount that is more than 50% likely of being realized upon ultimate settlement.
The Company’s policy is to include interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits, if any, within income tax expense (benefit) in the consolidated statements of operations.
Stock-Based Compensation Expense
Stock-based compensation expense for equity instruments issued to employees is measured based on the grant-date fair value of the awards. The fair value of each time-based employee stock option is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes-Merton stock option pricing valuation model. The fair value of each performance-based employee stock option is estimated on the date of grant using the Monte Carlo simulation model. The Company recognizes compensation costs using the accelerated attribution method for all employee stock-based compensation awards that are expected to vest over the requisite service period of the awards, which is generally the awards’ vesting period. Forfeitures are required to be estimated at the time of grant and revised, if necessary, in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates.
Stock-based compensation expense for equity instruments issued to non-employees is recognized based on the estimated fair value of the equity instrument. The fair value of the non-employee awards is subject to remeasurement at each reporting period until services required under the arrangement are completed, which is the vesting date.
78
Post-Employment Benefits
The Company participates in a 401(k) Plan sponsored by Vivint that covers all of the Company’s eligible employees. The Company did not provide a discretionary company match to employee contributions during any of the periods presented.
Non-Controlling Interests and Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests
Non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests represent fund investors’ interest in the net assets of certain consolidated investment funds, which have been entered into by the Company in order to finance the costs of solar energy systems under long-term customer contracts. The Company has determined that the provisions in the contractual arrangements represent substantive profit-sharing arrangements. The Company has further determined that the appropriate methodology for attributing income and loss to the non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests each period is a balance sheet approach referred to as the hypothetical liquidation at book value (“HLBV”) method. Under the HLBV method, the amounts of income and loss attributed to the non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests in the consolidated statements of operations reflect changes in the amounts the fund investors would hypothetically receive at each balance sheet date under the liquidation provisions of the contractual agreements of these structures, assuming the net assets of these funding structures were liquidated at recorded amounts. The fund investors’ non-controlling interest in the results of operations of these funding structures is determined as the difference in the non-controlling interests’ claim under the HLBV method at the start and end of each reporting period, after taking into account any capital transactions, such as contributions or distributions, between the fund and the fund investors. The use of the HLBV methodology to allocate income to the non-controlling and redeemable non-controlling interest holders may create volatility in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations as the application of HLBV can drive changes in net income available and loss attributable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests from quarter to quarter.
The Company classifies certain non-controlling interests with redemption features that are not solely within the control of the Company outside of permanent equity on its consolidated balance sheets. Redeemable non-controlling interests are reported using the greater of their carrying value at each reporting date as determined by the HLBV method or their estimated redemption value in each reporting period.
Loss Contingencies
The Company is subject to the possibility of various loss contingencies arising in the ordinary course of business. The Company considers the likelihood of loss or impairment of an asset, or the incurrence of a liability, as well as the Company’s ability to reasonably estimate the amount of loss, in determining loss contingencies. An estimated loss contingency is accrued when it is probable that an asset has been impaired or a liability has been incurred and the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. If the Company determines that a loss is possible and the range of the loss can be reasonably determined, then the Company discloses the range of the possible loss. The Company regularly evaluates current information available to determine whether an accrual is required, an accrual should be adjusted or a range of possible loss should be disclosed.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2015, the Financial Accounting Services Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2015-02, Consolidation (Topic 810): Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis. This update makes some targeted changes to current consolidation guidance. These changes impact both the voting and the variable interest consolidation models. In particular, the update will change how companies determine whether limited partnerships or similar entities are VIEs. The update is effective in fiscal years, including interim periods, beginning after December 15, 2015, and early adoption is permitted. The Company currently consolidates several VIEs and does not anticipate that ASU 2015-02 will have a significant impact on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, which requires an entity to recognize the amount of revenue to which it expects to be entitled for the transfer of promised goods or services to customers. The ASU will replace most existing revenue recognition guidance in GAAP when it becomes effective. The new standard is effective for the Company on January 1, 2017. Early application is not permitted. The standard permits the use of either the retrospective or cumulative effect transition method. The Company is evaluating the effect that ASU 2014-09 will have on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures. The Company has not yet selected a transition method nor has it determined the effect of the standard on its ongoing financial reporting.
79
|
3. |
Fair Value Measurements |
The Company measures and reports its cash equivalents at fair value. The following tables set forth the fair value of the Company’s financial assets measured on a recurring basis by level within the fair value hierarchy (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, 2014 |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
Level I |
|
|
Level II |
|
|
Level III |
|
|
Total |
|
||||
|
Financial Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Time deposits |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
1,900 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
1,900 |
|
|
Money market funds |
|
|
607 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
607 |
|
|
Total financial assets |
|
$ |
607 |
|
|
$ |
1,900 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
2,507 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2013 |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
Level I |
|
|
Level II |
|
|
Level III |
|
|
Total |
|
||||
|
Financial Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Time deposits |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
1,900 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
1,900 |
|
|
Money market funds |
|
|
620 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
620 |
|
|
Total financial assets |
|
$ |
620 |
|
|
$ |
1,900 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
2,520 |
|
The carrying amounts of certain financial instruments of the Company, consisting of cash and cash equivalents excluding time deposits; accounts receivable; accounts payable; accounts payable—related party and distributions payable to redeemable non-controlling interests (all Level I) approximate fair value due to their relatively short maturities. Time deposits (Level II) approximate fair value due to their short-term nature (30 days) and, upon renewal, the interest rate is adjusted based on current market rates. The Company’s long-term debt is carried at cost and was $105.0 million as of December 31, 2014. The Company estimated the fair value of long-term debt to approximate its carrying value as interest accrues at a floating rate based on market rates. The Company’s revolving lines of credit—related party were comprised of two lines of credit and were carried at cost of $41.4 million as of December 31, 2013. The Company estimated the fair value of its related party revolving lines of credit to be $39.0 million as of December 31, 2013 based on rates for companies with similar credit ratings and issuances at approximately the same time period and in the same market environment. The Company did not have realized gains or losses related to financial assets for any of the periods presented.
|
4. |
Business Acquisitions |
Acquisition of the Company by Investors
As described in Note 1—Organization, the Acquisition was completed on November 16, 2012. The purchase price agreed to in the purchase agreement with the Investors was $75.0 million. The purchase price was subsequently adjusted to $73.1 million based on the carrying balances of the liabilities assumed and a net worth adjustment of $0.4 million. The net purchase consideration transferred was (in thousands):
|
Cash |
|
$ |
73,130 |
|
|
Less: Cash acquired |
|
|
(1,472 |
) |
|
Total purchase consideration |
|
$ |
71,658 |
|
In connection with the Acquisition, the total consideration of $71.7 million paid by the Investors was used for the purchase of all outstanding stock, settlement of the Predecessor’s subordinated debt and related party payables with Vivint and its subsidiaries, settlement of other liabilities of the Predecessor incurred in connection with the Acquisition and settlement of stock-based awards. The Acquisition is reflected as a noncash supplemental disclosure on the consolidated statements of cash flows as no cash flowed through the Company’s accounts. The Company incurred $2.7 million of costs related to special retention bonuses and other payments to employees directly related to the Acquisition and $1.0 million of transaction fees, comprised of investment banking, advisory, legal and accounting fees that were expensed in the Predecessor Period. These expenses are included in general and administrative expenses in the Predecessor Period in the consolidated statements of operations.
Pursuant to the terms of the purchase agreement, $9.5 million of the purchase consideration was placed in escrow for general representations and warranties, rather than specific contingencies or specific assets or liabilities of the Company and was released in 2014. The Company had no right to these funds, nor did it have a direct obligation associated with them. Accordingly, the Company did not include the escrow funds in its consolidated balance sheets.
80
The estimated fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed are based on information obtained from various sources including third party valuations, management’s internal valuation and historical experience. The fair values of the customer contracts intangible asset and the redeemable non-controlling interest were determined using the income approach and significant estimates relate to assumptions as to the future economic benefits to be received, cash flow projections and discount rates.
The following table summarizes the estimated fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed (in thousands):
|
Current assets acquired |
|
$ |
171 |
|
|
Solar energy systems |
|
|
39,532 |
|
|
Customer contracts |
|
|
43,783 |
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
29,545 |
|
|
Current liabilities assumed |
|
|
(15,111 |
) |
|
Deferred tax liability, net |
|
|
(11,643 |
) |
|
Revolving line of credit |
|
|
(4,000 |
) |
|
Redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
|
(10,619 |
) |
|
Total |
|
$ |
71,658 |
|
The redeemable non-controlling interests represent the fair value of an investor’s interest in the investment funds acquired as part of the Acquisition. The Company has determined that it is the primary beneficiary of the investment funds and, accordingly, consolidates the financial position and results of operations of the investment funds in the consolidated financial statements.
Goodwill, which represents the purchase price in excess of the fair value of net assets acquired, is not expected to be deductible for income tax purposes. This goodwill is reflective of the expected growth in the business, partly based on historical performance, related to the operating leases and incentives revenue that will be generated over the next 20 years from current customers and the expected continued growth of the Company’s customer base through its existing and growing sales channels.
For tax purposes, the acquired intangible assets are not amortized. Accordingly, a deferred tax liability of $16.3 million was recorded for the difference between the book and tax basis related to the intangible assets. Additionally, a deferred tax asset of $4.7 million was recorded as a result of the Company’s net operating losses.
Unaudited Pro Forma Information
The following pro forma financial information is based on the historical financial statements of the Company and presents the Company’s results as if the Acquisition had occurred as of January 1, 2012 (in thousands):
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
Pro forma revenue |
|
$ |
449 |
|
|
Pro forma net loss |
|
|
(26,604 |
) |
|
Pro forma net loss attributable to common stockholders |
|
|
(24,134 |
) |
The unaudited pro forma financial information combines the Company’s results of operations as if the Acquisition had occurred as of January 1, 2012. The pro forma results include the acquisition accounting effects resulting from the Acquisition such as the amortization charges from acquired intangible assets, reversal of interest expense related to the revolving line of credit, reversal of costs related to special retention bonuses and other payments to employees and transaction costs directly related to the Acquisition and reversal of the accretion to redemption value of Series B redeemable preferred stock and related tax effects. The pro forma information presented does not purport to present what the actual results would have been had the Acquisition actually occurred on January 1, 2012, nor is the information intended to project results for any future period.
81
Solmetric Acquisition
In January 2014, the Company completed the acquisition of Solmetric (the “Solmetric Acquisition”), a developer and manufacturer of photovoltaic installation software products and devices. The purchase price agreed to in the purchase agreement with Solmetric was $12.0 million plus a net working capital adjustment resulting in total cash purchase consideration of $12.2 million. In connection with the Solmetric Acquisition, the total consideration of $12.2 million was used for the purchase of all outstanding stock and options of Solmetric, settlement of Solmetric’s short-term promissory note, and settlement of other liabilities including employee-related liabilities of Solmetric incurred in connection with the acquisition. The Company incurred $0.3 million of costs related to retention bonuses to key Solmetric employees and $0.1 million of transaction fees, all of which have been included in the various line items of the consolidated statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Pursuant to the terms of the purchase agreement, $1.0 million of the purchase consideration was placed in escrow and is being held for general representations and warranties, rather than specific contingencies or specific assets or liabilities of the Company. The Company has no right to these funds, nor does it have a direct obligation associated with them. Accordingly, the Company does not include the escrow funds in its consolidated balance sheets. Notwithstanding any prior claims to the escrow fund due to a breach of representations and warranties, the escrow was released on the one year anniversary of the Solmetric Acquisition.
The estimated fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed are based on information obtained from various sources including third party valuations, management’s internal valuation and historical experience. The fair values of the intangible assets related to customer relationships, trade names and trademarks, developed technology and in-process research and development were determined using the income approach and significant estimates relate to assumptions as to the future economic benefits to be received, cash flow projections and discount rates.
The purchase price was allocated based on the estimated fair value of net assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of the acquisition. The purchase price allocation was finalized as of December 31, 2014.
The following table summarizes the estimated fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed (in thousands):
|
Cash acquired |
|
$ |
139 |
|
|
Inventories |
|
|
580 |
|
|
Other current assets acquired |
|
|
221 |
|
|
Property |
|
|
77 |
|
|
Customer relationships |
|
|
738 |
|
|
Trademarks/trade names |
|
|
1,664 |
|
|
Developed technology |
|
|
1,295 |
|
|
In-process research and development |
|
|
2,097 |
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
7,056 |
|
|
Deferred tax liability, net |
|
|
(1,478 |
) |
|
Current liabilities assumed |
|
|
(210 |
) |
|
Total |
|
$ |
12,179 |
|
Goodwill, which represents the purchase price in excess of the fair value of net assets acquired, is not expected to be deductible for income tax purposes. This goodwill is reflective of the value derived from the Company utilizing Solmetric’s advanced technology to improve the installation and efficacy of its solar panels as well as the expected growth in the Solmetric business, based on its historical performance and the expectation of continued growth as the solar industry expands.
For tax purposes, the acquired intangible assets are not amortized. Accordingly, a deferred tax liability of $2.5 million was recorded for the difference between the book and tax basis related to the intangible assets. Additionally, a deferred tax asset of $1.0 million was recorded mainly as a result of Solmetric’s net operating losses.
Financial results for Solmetric since the acquisition date are included in the results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2014. Solmetric contributed $3.2 million of revenues and $0.4 million of net income for the year ended December 31, 2014.
82
Unaudited Solmetric Pro Forma Information
The following pro forma financial information is based on the historical financial statements of the Company and presents the Company’s results as if the Solmetric Acquisition had occurred as of January 1, 2013 (in thousands):
|
|
|
Years Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
||
|
Pro forma revenue |
|
$ |
25,380 |
|
|
$ |
9,122 |
|
|
Pro forma net loss |
|
|
(165,734 |
) |
|
|
(57,046 |
) |
|
Pro forma net (loss attributable) income available to common stockholders |
|
|
(28,698 |
) |
|
|
5,062 |
|
The unaudited pro forma results include the accounting effects resulting from the Solmetric Acquisition, such as the amortization charges from acquired intangible assets, reversal of costs related to special retention bonuses and other payments to employees and transaction costs directly related to the Solmetric Acquisition, elimination of intercompany sales and reversal of the related tax effects. The pro forma information presented does not purport to present what the actual results would have been had the Solmetric Acquisition actually occurred on January 1, 2013, nor is the information intended to project results for any future period.
|
5. |
Solar Energy Systems |
Solar energy systems, net consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
||
|
System equipment costs |
|
$ |
478,502 |
|
|
$ |
155,101 |
|
|
Initial direct costs related to solar energy systems |
|
|
75,349 |
|
|
|
22,250 |
|
|
|
|
|
553,851 |
|
|
|
177,351 |
|
|
Less: Accumulated depreciation and amortization |
|
|
(10,186 |
) |
|
|
(2,075 |
) |
|
|
|
|
543,665 |
|
|
|
175,276 |
|
|
Solar energy system inventory |
|
|
44,502 |
|
|
|
12,782 |
|
|
Solar energy systems, net |
|
$ |
588,167 |
|
|
$ |
188,058 |
|
Solar energy system inventory represents the solar components and materials used in the installation of solar energy systems prior to being installed on customers’ roofs. As such, no depreciation is recorded related to this line item. The Company recorded depreciation and amortization expense related to solar energy systems of $8.1 million and $2.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
|
6. |
Property and Equipment |
Property and equipment, net consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
|
|
Estimated |
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
Useful Lives |
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
||
|
Vehicles acquired under capital leases |
|
3 years |
|
$ |
13,351 |
|
|
$ |
4,796 |
|
|
Furniture and computer and other equipment |
|
3 years |
|
|
2,183 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Leasehold improvements |
|
1-3 years |
|
|
2,088 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17,622 |
|
|
|
4,796 |
|
|
Less: Accumulated depreciation and amortization |
|
|
|
|
(4,598 |
) |
|
|
(1,156 |
) |
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
|
$ |
13,024 |
|
|
$ |
3,640 |
|
83
The Company recorded depreciation and amortization expense related to property and equipment of $3.4 million and $1.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. Prior to December 31, 2013, the Company did not have any recorded property and equipment, and therefore, did not record related depreciation and amortization expense in the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 and the Predecessor Period.
The Company leases fleet vehicles that are accounted for as capital leases and are included in property and equipment, net. Depreciation on vehicles under capital leases totaling $3.0 million and $1.2 million was capitalized in solar energy systems, net for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. For the year ended December 31, 2014, a de minimis amount of depreciation was also expensed. There was no depreciation on vehicles under capital leases for the Successor Period ended December 31, 2012 or the Predecessor Period.
Future minimum lease payments under capital leases as of December 31, 2014 were as follows (in thousands):
|
Years Ending December 31, |
|
|
|
|
|
2015 |
|
$ |
4,029 |
|
|
2016 |
|
|
3,266 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2,625 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
669 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
46 |
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
— |
|
|
Total minimum lease payments |
|
|
10,635 |
|
|
Less: interest |
|
|
957 |
|
|
Present value of capital lease obligations |
|
|
9,678 |
|
|
Less: current portion |
|
|
3,502 |
|
|
Long-term portion |
|
$ |
6,176 |
|
|
7. |
Intangible Assets and Goodwill |
Intangible assets consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
||
|
Cost: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer contracts |
|
$ |
43,783 |
|
|
$ |
43,783 |
|
|
Customer relationships |
|
|
738 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Trademarks/trade names |
|
|
1,664 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Developed technology |
|
|
1,295 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
In-process research and development |
|
|
2,097 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Internal-use software |
|
|
370 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Total carrying value |
|
|
49,947 |
|
|
|
43,783 |
|
|
Accumulated amortization: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer contracts |
|
|
(31,013 |
) |
|
|
(16,419 |
) |
|
Customer relationships |
|
|
(135 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Trademarks/trade names |
|
|
(152 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Developed technology |
|
|
(160 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Total accumulated amortization |
|
|
(31,460 |
) |
|
|
(16,419 |
) |
|
Total intangible assets, net |
|
$ |
18,487 |
|
|
$ |
27,364 |
|
The Company recorded amortization expense of $14.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, of which $0.1 million was recorded in cost of revenue-solar energy system and product sales. Amortization expense was $14.6 million and $1.8 million for the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2013 and 2012. Prior to the Acquisition on November 16, 2012, the Company did not have any recorded intangible assets, and therefore, no amortization expense was incurred in the Predecessor Period.
84
As of December 31, 2014, expected amortization expense for the unamortized intangible assets is as follows (in thousands):
|
Years Ending December 31, |
|
|
|
|
|
2015 |
|
$ |
13,376 |
|
|
2016 |
|
|
611 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
611 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
494 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
323 |
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
975 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
16,390 |
|
In-process research and development reflects projects that have not yet been completed and are not subject to amortization as of December 31, 2014.
The changes in the carrying amounts of goodwill during the year ended December 31, 2014 were as follows (in thousands):
|
Balance as of December 31, 2013 |
|
$ |
29,545 |
|
|
Goodwill acquired in Solmetric acquisition |
|
|
7,056 |
|
|
Balance as of December 31, 2014 |
|
$ |
36,601 |
|
|
8. |
Accrued Compensation |
Accrued compensation consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
||
|
Accrued payroll |
|
$ |
9,888 |
|
|
$ |
3,142 |
|
|
Accrued commissions |
|
|
6,575 |
|
|
|
4,206 |
|
|
Accrued employee taxes |
|
|
331 |
|
|
|
8,143 |
|
|
Total accrued compensation |
|
$ |
16,794 |
|
|
$ |
15,491 |
|
|
9. |
Accrued and Other Current Liabilities |
Accrued and other current liabilities consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
||
|
Sales and use tax payable |
|
$ |
5,052 |
|
|
$ |
5,299 |
|
|
Income tax payable |
|
|
4,097 |
|
|
|
3,061 |
|
|
Accrued professional fees |
|
|
1,289 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Deferred rent |
|
|
1,090 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Accrued unused commitment fees and interest |
|
|
478 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Fleet expenses |
|
|
470 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Accrued penalties and interest |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,909 |
|
|
Other accrued expenses |
|
|
1,540 |
|
|
|
38 |
|
|
Total accrued and other current liabilities |
|
$ |
14,016 |
|
|
$ |
10,307 |
|
85
|
10. |
Debt Obligations |
Debt obligations consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
||
|
Long-term debt |
|
$ |
105,000 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Revolving lines of credit—related party |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
41,412 |
|
|
Total debt |
|
$ |
105,000 |
|
|
$ |
41,412 |
|
Bank of America, N.A. Aggregation Credit Facility
In September 2014, the Company entered into an aggregation credit facility (the “Aggregation Facility”) pursuant to which the Company may borrow up to an aggregate of $350.0 million and, upon the satisfaction of certain conditions and the approval of the lenders, up to an additional aggregate of $200.0 million in borrowings with certain financial institutions for which Bank of America, N.A. is acting as administrative agent. For accounting purposes, the Aggregation Facility is considered a modification of a term loan credit facility entered into in May 2014 described below.
Prepayments are permitted under the Aggregation Facility, and the principal and accrued interest on any outstanding loans mature on March 12, 2018. Under the Aggregation Facility, interest on borrowings accrues at a floating rate equal to either (1)(a) the London Interbank Offer Rate (“LIBOR”) or (b) the greatest of (i) the Federal Funds Rate plus 0.5%, (ii) the administrative agent’s prime rate and (iii) LIBOR plus 1% and (2) a margin that varies between 3.25% during the period during which the Company may incur borrowings and 3.50% after such period. Interest is payable at the end of each interest period that the Company may elect as a term of either one, two or three months.
The borrower under the Aggregation Facility is Vivint Solar Financing I, LLC, one of the Company’s indirect wholly owned subsidiaries, which in turn holds the Company’s interests in the managing members in the Company’s existing investment funds. These managing members guarantee the borrower’s obligations under the Aggregation Facility. In addition, Vivint Solar Holdings, Inc. has pledged its interests in the borrower, and the borrower has pledged its interests in the guarantors as security for the borrower’s obligations under the Aggregation Facility. The related solar energy systems are not subject to any security interest of the lenders, and there is no recourse to the Company in the case of a default.
The Aggregation Facility includes customary covenants, including covenants that restrict, subject to certain exceptions, the borrower’s, and the guarantors’ ability to incur indebtedness, incur liens, make investments, make fundamental changes to their business, dispose of assets, make certain types of restricted payments or enter into certain related party transactions. Among other restrictions, the Aggregation Facility provides that the borrower may not incur any indebtedness other than that related to the Aggregation Facility or in respect of permitted swap agreements, and that the guarantors may not incur any indebtedness other than that related to the Aggregation Facility or as permitted under existing investment fund transaction documents. These restrictions do not impact the Company’s ability to enter into investment funds, including those that are similar to those entered into previously. As of December 31, 2014, the Company was in compliance with such covenants.
As of December 31, 2014, the Company had incurred an aggregate of $105.0 million in term loan borrowings, of which approximately $75.7 million was used to repay the outstanding principal and accrued and unpaid interest under the May 2014 term loan credit facility discussed below. The remaining borrowing capacity was $245.0 million as of December 31, 2014. However, the Company does not have immediate access to the remaining $245.0 million balance as future borrowings are dependent on when it has solar energy system revenue to collateralize the borrowings.
The Aggregation Facility also contains certain customary events of default. If an event of default occurs, lenders under the Aggregation Facility will be entitled to take various actions, including the acceleration of amounts due under the Aggregation Facility and foreclosure on the interests of the borrower and the guarantors that have been pledged to the lenders.
Interest expense was approximately $1.4 million in the year ended December 31, 2014. As of December 31, 2014, the current portion of deferred financing costs of $2.5 million was recorded in prepaid expenses and other current assets, and the long-term portion of deferred financing costs of $5.5 million was recorded in other non-current assets, net in the consolidated balance sheet. In addition, a $1.5 million interest reserve amount was deposited in an interest reserve account with the administrative agent and is included in restricted cash.
86
Bank of America, N.A. Term Loan Credit Facility
In May 2014, the Company entered into a term loan credit facility for an aggregate principal amount of $75.5 million with certain financial institutions for which Bank of America, N.A. acted as administrative agent. In September 2014 in connection with the entry into the Aggregation Facility, the Company repaid the then outstanding $75.5 million in aggregate borrowings and terminated the agreement. Under this credit facility, the Company incurred interest on the term borrowings that accrued at a floating rate based on (1) LIBOR plus a margin equal to 4%, or (2) a rate equal to 3% plus the greatest of (a) the Federal Funds Rate plus 0.5%, (b) the administrative agent’s prime rate and (c) LIBOR plus 1%. Interest expense from inception of this credit facility in May 2014 through payoff in September 2014 was approximately $1.3 million.
The credit facility included customary covenants, including covenants that restricted, subject to certain exceptions, the Company’s ability to incur indebtedness, incur liens, make investments, make fundamental changes to the Company’s business, dispose of assets, make certain types of restricted payments or enter into certain related party transactions. As of the day on which borrowings under the credit facility were repaid, the Company was in compliance with all such covenants. In addition, the $1.6 million interest reserve amount that was deposited in an interest reserve account with the administrative agent was released upon termination of the credit facility.
Revolving Lines of Credit—Related Party
On October 9, 2014, the Company repaid $58.8 million in aggregate borrowings and interest owed to Vivint under the 2013 Loan Agreement and the 2012 Loan Agreement defined below. These loan agreements were terminated upon repayment.
In May 2013, the Company entered into a Subordinated Note and Loan Agreement with APX Parent Holdco, Inc., pursuant to which the Company was able to incur up to $20.0 million in revolver borrowings (“2013 Loan Agreement”). From May 2013 through December 2013, the Company incurred $18.5 million in principal borrowings under the agreement. Interest accrued on these borrowings at 12% per year through November 2013 and 20% per year thereafter, and accrued interest was paid-in-kind through additions to the principal amount on a semi-annual basis. In January 2014, the Company amended and restated the 2013 Loan Agreement, pursuant to which the Company was able to incur an additional $30.0 million in revolver borrowings, resulting in a total borrowing capacity of $50.0 million, with interest on the borrowings accruing at a rate of 12% per year. From January 2014 through September 2014, the Company incurred an aggregate of $154.5 million in revolver borrowings under the 2013 Loan Agreement of which $141.5 million was repaid within one to eight days from the respective borrowing date. None of these borrowings individually exceeded the borrowing capacity of $50.0 million. Interest expense was $3.1 million and $1.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. There was no associated interest expense incurred during the Successor Period ended December 31, 2012 and the Predecessor Period.
In December 2012 and amended in July 2013, the Company entered into a Subordinated Note and Loan Agreement with Vivint pursuant to which the Company could incur revolver borrowings of up to $20.0 million (“2012 Loan Agreement”). In December 2012, the Company incurred $15.0 million in revolver borrowings. From January 2013 through May 2013, the Company incurred an additional $5.0 million in revolver borrowings. Interest accrued on these borrowings at 7.5% per year, and accrued interest was paid-in-kind through additions to the principal amount on a semi-annual basis. Interest expense was $1.3 million, $1.5 million and de minimis for the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. There was no interest expense incurred during the Predecessor Period.
In November 2013, the Company entered into a Subordinated Note and Loan Agreement with APX Parent Holdco, Inc. for a one day loan of $20.0 million to obtain funding for an investment fund and repaid the full amount the next day. The imputed interest on the principal amount was not significant.
In July 2013, the Company entered into a Subordinated Note and Loan Agreement with APX Parent Holdco, Inc. for a one day loan of $40.0 million to obtain funding for an investment fund and repaid the full amount the next day. The imputed interest on the principal amount was not significant.
Revolving Line of Credit
In July 2012, the Company entered into a credit agreement with a financial institution pursuant to which it could incur up to $15.0 million in revolver borrowings. In 2012, the Company incurred $6.5 million in principal borrowings under the agreement. The interest rate on these borrowings accrued at a rate equal to the LIBOR plus 10%. The weighted-average interest rate of short-term borrowings was 10.5% for both the Predecessor Period and the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2012 and 2013. The Company repaid all borrowings and terminated the agreement in June 2013. Interest expense was approximately $0.2 million, $0.1 million and $0.1 million in the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 and the Predecessor Period. No interest expense was recorded for the year ended December 31, 2014 as the agreement was terminated in June 2013.
87
|
11. |
Investment Funds |
As of December 31, 2014, the Company had formed 12 investment funds for the purpose of funding the purchase of solar energy systems. The Company has aggregated the financial information of the investment funds in the table below. The aggregate carrying value of these funds’ assets and liabilities (after elimination of intercompany transactions and balances) in the Company’s consolidated balance sheets were as follows (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
||
|
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
12,641 |
|
|
$ |
3,092 |
|
|
Accounts receivable, net |
|
|
1,542 |
|
|
|
544 |
|
|
Total current assets |
|
|
14,183 |
|
|
|
3,636 |
|
|
Solar energy systems, net |
|
|
525,903 |
|
|
|
152,565 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
540,086 |
|
|
$ |
156,201 |
|
|
Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Distributions payable to non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
$ |
6,780 |
|
|
$ |
1,576 |
|
|
Current portion of deferred revenue |
|
|
237 |
|
|
|
68 |
|
|
Total current liabilities |
|
|
7,017 |
|
|
|
1,644 |
|
|
Deferred revenue, net of current portion |
|
|
4,335 |
|
|
|
1,272 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
$ |
11,352 |
|
|
$ |
2,916 |
|
The Company consolidates the investment funds, and all intercompany balances and transactions between the Company and the investment funds are eliminated in the consolidated financial statements. The Company determined that each of these investment funds meets the definition of a VIE. The Company uses a qualitative approach in assessing the consolidation requirement for VIEs that focuses on determining whether the Company has the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly affect the VIE’s economic performance and whether the Company has the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits that could potentially be significant to the VIE.
The Company has considered the provisions within the contractual arrangements that grant it power to manage and make decisions that affect the operation of these VIEs, including determining the solar energy systems and associated long term customer contracts to be sold or contributed to the VIE, and installation, operation and maintenance of the solar energy systems. The Company considers that the rights granted to the other investors under the contractual arrangements are more protective in nature rather than participating rights. As such, the Company has determined it is the primary beneficiary of the VIEs for all periods presented. The Company evaluates its relationships with the VIEs on an ongoing basis to ensure that it continues to be the primary beneficiary.
Fund investors for three of the funds are managed indirectly by the Sponsor and accordingly are considered related parties. As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the cumulative total of contributions into the VIEs by all investors was $480.2 million and $140.7 million, of which $110.0 million and $60.0 million were contributed by related parties.
The Company had an arrangement with a large financial institution that was not operational through 2014. In December 2014, this arrangement was terminated. All funds, except for one, were operational as of December 31, 2014. The Company did not have any assets, liabilities or activity associated with this non-operational fund. Total available committed capital under this fund was $75.0 million as of December 31, 2014.
Under the related agreements, cash distributions of income and other receipts by the fund, net of agreed-upon expenses and estimated expenses, tax benefits and detriments of income and loss, and tax benefits of tax credits, are assigned to the fund investor and Company’s subsidiary as specified in contractual arrangements. Certain of these arrangements have call and put options to acquire the investor’s equity interest as specified in the contractual agreements.
88
Guarantees
With respect to the investment funds, the Company and the fund investors have entered into guaranty agreements under which the Company guarantees the performance of certain financial obligations of its subsidiaries to the investment funds. These guarantees do not result in the Company being required to make payments to the fund investors unless such payments are mandated by the investment fund governing documents and the investment fund fails to make such payment.
The Company is contractually obligated to make certain VIE investors whole for losses that the investors may suffer in certain limited circumstances resulting from the disallowance or recapture of investment tax credits. The Company has concluded that the likelihood of a recapture event is remote and consequently has not recorded any liability in the consolidated financial statements for any potential recapture exposure. The maximum potential future payments that the Company could have to make under this obligation would depend on the IRS successfully asserting upon audit that the fair market values of the solar energy systems sold or transferred to the funds as determined by the Company exceeded the allowable basis for the systems for purposes of claiming ITCs. The fair market values of the solar energy systems and related ITCs are determined and the ITCs are allocated to the fund investors in accordance with the funds governing agreements. Due to uncertainties associated with estimating the timing and amounts of distributions, the likelihood of an event that may trigger repayment, forfeiture or recapture of ITCs to such investors, and the fact that the Company cannot determine how the IRS will evaluate system values used in claiming ITCs, the Company cannot determine the potential maximum future payments that are required under these guarantees.
For a certain fund, if it does not have sufficient cash flows to make a stated cash distribution to the fund investor each annual period, the Company’s subsidiary (which is the managing member of the fund) is obligated to contribute additional cash sufficient to allow the investment fund to make such distribution to the fund investor. The Company has not made payments under its guarantee of performance of the obligations of the subsidiary in prior periods because the fund has generated sufficient cash flow to make the stated cash distributions to the fund investor. The Company has determined that the maximum potential exposure under the guarantee to the fund is not significant.
In December 2014, the Company accrued an adjustment to reimburse the investor of one of its investment funds a portion of capital contributed and to reduce the anticipated customer revenue in order to true up the investor’s expected rate of return due to a delay in solar energy systems being interconnected to the utility grid. As such, the Company recorded a $4.0 million accrued distribution as of December 31, 2014.
As a result of the guaranty arrangements in certain funds, as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company is required to hold minimum cash balances of $5.0 million in the aggregate for both periods, which are classified as restricted cash on the consolidated balance sheets.
|
12. |
Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests, Equity and Preferred Stock |
Common Stock
The Company has 1.0 billion authorized shares of common stock. As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company had 105.3 million and 75.0 million shares of common stock issued and outstanding.
The Company had shares of common stock reserved for issuance as follows (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
||
|
Awards issued and outstanding |
|
|
10,053 |
|
|
|
6,609 |
|
|
Awards available for grant under equity incentive plans |
|
|
8,783 |
|
|
|
2,567 |
|
|
Long-term incentive plan |
|
|
4,059 |
|
|
|
4,059 |
|
|
Total |
|
|
22,895 |
|
|
|
13,235 |
|
On October 6, 2014, the Company closed its initial public offering in which 20.6 million shares of its common stock were sold at a public offering price of $16.00 per share, which generated net proceeds, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and $8.8 million in offering expenses, of $300.6 million.
89
In August 2014, the Company issued and sold an aggregate of 2.7 million shares of common stock to 313 for $10.667 per share for aggregate proceeds of $28.5 million. In September 2014, the Company issued and sold an aggregate of 7.0 million additional shares to 313 and two of its directors for $10.667 per share for aggregate gross proceeds of $75.0 million. The Company intended for the proceeds from such sales to fund its growing operations and to bolster its financial condition in advance of its initial public offering. The transactions were negotiated on an arms’ length basis and represented what the Company believed to be the most agreeable alternative at the time. Subsequent to such transactions, the Company set the preliminary price range for its initial public offering, the mid-point of which was $17.00 per share. The Company has determined that, for financial reporting purposes, it is appropriate to record the aggregate difference between the per share purchase price and mid-point of the preliminary price range for its initial public offering with respect to the shares sold to the two directors, or $14.8 million, as stock-based compensation expense, which was recorded in general and administrative expense. Regarding the shares of common stock sold to 313, the Company has also determined that for financial reporting purposes, it is appropriate to record the aggregate difference of $43.4 million as a deemed distribution within additional paid-in capital.
Immediately prior to the Acquisition, the Company had 25,000 shares of Series A common stock and 25,000 shares of Series B common stock outstanding. In connection with the Acquisition, all outstanding shares of Series A common stock and Series B common stock were purchased and subsequently cancelled. After the Acquisition the Company had 75.0 million shares of common stock issued and outstanding.
Non-Controlling Interests and Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests
Four of the funds each include a right for the non-controlling interest holder to elect to require the Company’s wholly owned subsidiary to purchase all of its membership interests in the fund after a stated period of time (each, a “Put Option”). In one of the funds, the Company’s wholly owned subsidiary has the right to elect to require the non-controlling interest holder to sell all of its membership units to the Company’s wholly owned subsidiary (the “Call Option”) after the expiration of the non-controlling interest holder’s Put Option. In the three other funds, the Company’s wholly owned subsidiary has a Call Option for a stated period prior to the effectiveness of the Put Option. In the remaining eight funds there is a Call Option which is exercisable after a stated period of time.
The purchase price for the fund investor’s interest in the four funds under the Put Options is the greater of fair market value at the time the option is exercised and a specified amount, ranging from $0.7 million to $4.1 million. The Put Options for these four funds are exercisable beginning on the date that specified conditions are met for each respective fund. None of the Put Options are expected to become exercisable prior to 2017.
Because the Put Options represent redemption features that are not solely within the control of the Company, the non-controlling interests in these funds is presented outside of permanent equity. Redeemable non-controlling interests are reported using the greater of their carrying value at each reporting date (which is impacted by attribution under the hypothetical liquidation at book value method) or their estimated redemption value in each reporting period. The carrying value of redeemable non-controlling interests at December 31, 2014 and 2013 was greater than the redemption value.
The purchase price for the fund investors’ interests under the Call Options varies by fund, but is generally the greater of a specified amount, which ranges from approximately $0.7 million to $7.0 million, the fair market value of such interest at the time the option is exercised, or an amount that causes the fund investor to achieve a specified return on investment. The Call Options for all 12 funds are exercisable beginning on the date that specified conditions are met for each respective fund. None of the Call Options are expected to become exercisable prior to 2018.
Preferred Stock
In October 2014, the Company authorized 10.0 million shares of preferred stock that is issuable in series. As of December 31, 2014, there were no series of preferred stock issued or designated.
In January 2012, the Company issued 4,171 shares of Series B redeemable preferred stock at $1,199 per share for aggregate gross proceeds of $5.0 million. The Company classified the Series B redeemable preferred stock outside of permanent equity as it was redeemable at the option of the holder or upon a change in control.
Immediately prior to the Acquisition, the Company had 25,000 shares of Series A preferred stock and 8,342 shares of Series B redeemable preferred stock outstanding. Due to the change in control upon the Acquisition, the Company recorded accretion of $20.0 million in relation to the redemption of the Series B redeemable preferred stock. All outstanding shares of the Series A preferred stock were purchased and subsequently cancelled in connection with the Acquisition. Accordingly, the Company did not have any authorized or outstanding redeemable preferred stock or preferred stock as of December 31, 2013.
90
|
13. |
Equity Compensation Plans |
2014 Equity Incentive Plan
The Company adopted the 2014 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2014 Plan”), which became effective the first business day prior to the effectiveness of the Company’s registration statement on Form S-1, which occurred on September 30, 2014. Under the 2014 Plan, the Company may grant stock options, restricted stock, restricted stock units, stock appreciation rights, performance units, performance shares and performance awards to its employees, directors and consultants, and its parent and subsidiary corporations’ employees and consultants.
Under the 2014 Plan, a total of 8.8 million shares of common stock initially are reserved for issuance, subject to adjustment in the case of certain events, of which 22,400 awards were issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2014. In addition, any shares that otherwise would be returned to the Omnibus Plan (as defined below) as the result of the expiration or termination of options, may be added to the 2014 Plan. During 2014, 5,000 shares were forfeited in the Omnibus Plan (as defined below) and returned to the 2014 Plan. The number of shares available for issuance under the 2014 Plan is subject to an annual increase on the first day of each year beginning in 2015, equal to the least of 8.8 million shares, 4% of the outstanding shares of common stock as of the last day of the immediately preceding fiscal year and an amount of shares as determined by the Company.
2013 Omnibus Incentive Plan; Non-plan Option Grant
In July 2013, the Company adopted the 2013 Omnibus Incentive Plan (the “Omnibus Plan”), which was terminated in connection with the adoption of the 2014 Plan in September 2014, and accordingly no additional shares are available for issuance under the Omnibus Plan. The Omnibus Plan will continue to govern outstanding awards granted under the plan. In August 2013, the Company granted an option to purchase 617,647 shares of common stock outside of the Omnibus Plan; however the provisions of this option were substantially similar to those of the options granted pursuant to the Omnibus Plan.
During 2014 and 2013, the Company granted options of which one-third are subject to ratable time-based vesting over a five year period and two-thirds are subject to vesting upon certain performance conditions and the achievement of certain investment return thresholds by 313. The options have a ten-year contractual period.
In April 2014, the Company amended the vesting schedules of certain options outstanding under the Omnibus Plan and an option granted outside of the Omnibus Plan described above to provide that a portion of each of these options vests upon the Company’s aggregate market capitalization (using the 30-day, volume-weighted average closing bid price listed on the New York Stock Exchange) being equal to or exceeding $1.0 billion at the end of any trading day at least 240 days following the completion of the Company’s public offering.
During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company recorded $5.8 million in stock-based compensation related to the performance conditions as the performance conditions were met. As of December 31, 2014, there were 6.7 million shares subject to outstanding options that are subject to performance and market conditions.
A summary of stock option activity is as follows (in thousands, except term and per share amounts):
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted- |
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Average |
|
|
Remaining |
|
|
Aggregate |
|
||||
|
|
|
Underlying |
|
|
Exercise |
|
|
Contractual |
|
|
Intrinsic |
|
||||
|
|
|
Options |
|
|
Price |
|
|
Term |
|
|
Value |
|
||||
|
Outstanding—December 31, 2013 |
|
|
6,609 |
|
|
$ |
1.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
12,755 |
|
|
Granted |
|
|
3,493 |
|
|
|
1.60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercised |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cancelled |
|
|
(49 |
) |
|
|
1.03 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding—December 31, 2014 |
|
|
10,053 |
|
|
$ |
1.21 |
|
|
|
8.8 |
|
|
$ |
80,790 |
|
|
Options vested and exercisable—December 31, 2013 |
|
|
186 |
|
|
$ |
1.00 |
|
|
|
9.5 |
|
|
$ |
359 |
|
|
Options vested and exercisable—December 31, 2014 |
|
|
764 |
|
|
$ |
1.06 |
|
|
|
8.7 |
|
|
$ |
6,241 |
|
|
Options vested and expected to vest—December 31, 2013 |
|
|
2,001 |
|
|
$ |
1.00 |
|
|
|
9.6 |
|
|
$ |
3,862 |
|
|
Options vested and expected to vest—December 31, 2014 |
|
|
8,559 |
|
|
$ |
1.21 |
|
|
|
8.8 |
|
|
$ |
68,463 |
|
91
The following table summarizes stock option activity by range of exercise price as of December 31, 2014 (number of awards in thousands):
|
|
|
Awards Outstanding |
|
|
Awards Exercisable |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted Average |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of Awards |
|
|
Remaining |
|
Weighted Average |
|
|
Number of Awards |
|
Weighted Average |
|
|||
|
Range of Exercise Price |
|
Outstanding |
|
|
Contractual Life |
|
Exercise Price |
|
|
Exercisable |
|
Exercise Price |
|
|||
|
$0.00 - $1.00 |
|
|
6,565 |
|
|
8.6 |
|
$ |
1.00 |
|
|
620 |
|
$ |
1.00 |
|
|
$1.01 - $2.00 |
|
|
3,156 |
|
|
9.1 |
|
|
1.30 |
|
|
144 |
|
1.30 |
|
|
|
$2.01 - $10.00 |
|
320 |
|
|
9.5 |
|
|
4.14 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
||
|
$10.01 - $16.00 |
|
12 |
|
|
9.7 |
|
|
16.00 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
||
|
Total |
|
|
10,053 |
|
|
8.8 |
|
$ |
1.21 |
|
|
764 |
|
$ |
1.06 |
|
The weighted-average grant-date fair value of time-based options granted during the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 was $4.69 and $0.91 per share. The weighted-average grant-date fair value of performance-based options granted during the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 was $2.80 and $2.23 per share. There were no options exercised during the periods presented. Intrinsic value is calculated as the difference between the exercise price of the underlying options and the fair value of the common stock for the options that had exercise prices that were lower than the fair value per share of the common stock.
As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, there were approximately $12.5 million and $4.9 million of total unrecognized stock-based compensation expense, net of estimated forfeitures related to nonvested time-based and performance condition stock options. As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the time-based awards are expected to be recognized over the weighted average period of 2.6 years and 2.7 years. As of December 31, 2014, the performance-based awards are expected to be recognized over a weighted period of 1.9 years.
During 2014, a total of 22,400 restricted stock units were granted to two members of the Company’s Board of Director’s. During 2014, a total of $0.1 million of expense was recorded related to this grant. These units vest in June 2015. The total fair value of options vested for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 was $1.0 million and $0.1 million.
Long-term Incentive Plan
In July 2013, the Company’s board of directors approved 4.1 million shares of common stock for six Long-term Incentive Plan Pools (“LTIP Pools”) that comprise the 2013 Long-term Incentive Plan (the “LTIP”). The purpose of the LTIP is to attract and retain key service providers and strengthen their commitment to the Company by providing incentive compensation measured by reference to the value of the shares of the Company’s common stock. Eligible participants include nonemployees, which is comprised of direct sales personnel, who sell the solar energy system contracts, employees that install and maintain the solar energy systems and employees that recruit new employees to the Company.
Based on the terms of the agreement, participants are allocated a portion of the LTIP Pools relative to the performance of other participants. LTIP awards to employees are considered to be granted when the allocation of the LTIP Pools to each participant is fixed which occurs once performance and service conditions are met. The performance conditions include the execution of a public offering or change of control or a declaration of a payment by the compensation committee. In addition, after the performance condition is achieved, participants must fulfill service or other conditions based on shareholder return to vest in the award. Expense associated with the units will be recognized once the units have been granted to individual participants.
The Company amended five of six of the LTIP Pools in April 2014 and the final pool in August 2014. The amendment modified the date on which each participant’s award is fixed from the date of a public offering to a subsequent date based on fulfilling certain service or other performance conditions based on stockholder returns, which will be the same date on which the award vests. No LTIP awards have been granted to specific employees as of December 31, 2014.
Nonemployee awards are granted and will be measured on the date on which the performance is complete, which is the date the service or other performance conditions are achieved. The Company recognizes stock-based compensation expense based on the lowest aggregate fair value of the non-employee awards at the reporting date. The Company has not recognized any expense related to the LTIP in any of the periods presented.
92
Determination of Fair Value of Stock Options
The Company estimates the fair value of the time-based stock options granted on each grant date using the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing model and applies the accelerated attribution method for expense recognition. The Company estimates the fair value and the vesting period of the performance-based options granted on each grant date using the Monte Carlo simulation method.
The fair values using the Black-Scholes-Merton method were estimated on each grant date using the following weighted-average assumptions:
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
||||
|
Expected term (in years) |
|
6.2 |
|
|
|
6.3 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
6.3 |
|
|
|
Volatility |
|
|
87.1 |
% |
|
|
80.0 |
% |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
67.0 |
% |
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
1.9 |
% |
|
|
1.7 |
% |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
1.2 |
% |
|
Dividend yield |
|
|
0.0 |
% |
|
|
0.0 |
% |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
0.0 |
% |
Use of the Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model requires the input of highly subjective assumptions, including (1) the fair value of the underlying common stock, (2) the expected term of the option, (3) the expected volatility of the price of the Company’s common stock, (4) risk-free interest rates and (5) the expected dividend yield of the Company’s common stock. The assumptions used in the option-pricing model represent management’s best estimates. These estimates involve inherent uncertainties and the application of management’s judgment. If factors change and different assumptions are used, the Company’s stock-based compensation expense could be materially different in the future.
These assumptions and estimates are as follows:
|
· |
Fair Value of Common Stock. As the Company’s common stock is publicly traded, the fair value of the Company’s common stock is the close price on the grant date. Prior to the initial public offering, the fair value of common stock was estimated. The fair values of the common stock underlying the Company’s stock-based awards were determined by the Company’s board of directors, which considered numerous objective and subjective factors to determine the fair value of common stock at each grant date. These factors included, but were not limited to, the lack of marketability of the Company’s common stock and developments in the business. A significant factor considered for awards granted approaching the initial public offering was the expected offering price. |
|
· |
Expected Term. The expected term represents the period that the Company’s option awards are expected to be outstanding. The Company utilized the simplified method in estimating the expected term of its options granted. The simplified method deems the term to be the average of the time to vesting and the contractual life of the options. The Company also considered additional factors including the expected lives used by a peer group of companies within the industry that it considers to be comparable to its business. |
|
· |
Expected Volatility. The volatility is derived from the average historical stock volatilities of a peer group of public companies within the Company’s industry that it considers to be comparable to its business over a period equivalent to the expected term of the stock-based grants. The Company did not rely on implied volatilities of traded options in the industry peers’ common stock because of the low volume of activity. |
|
· |
Risk-Free Interest Rate. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant for zero-coupon U.S. Treasury notes with maturities approximately equal to the option’s expected term. |
|
· |
Dividend Yield. The Company has never declared or paid any cash dividends and does not presently plan to pay cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Consequently, the Company used an expected dividend yield of zero. |
The Company estimates potential forfeitures of stock grants and adjusts stock-based compensation expense accordingly. The estimate of forfeitures will be adjusted over the requisite service period to the extent that actual forfeitures differ, or are expected to differ, from such estimates. Changes in estimated forfeitures will be recognized in the period of change and will also impact the amount of stock-based compensation expenses to be recognized in future periods.
93
The fair values using the Monte Carlo Simulation method were estimated on each grant date using the following weighted-average assumptions:
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
||
|
Volatility |
|
|
80.0 |
% |
|
|
80.0 |
% |
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
|
2.7 |
% |
|
|
2.6 |
% |
Stock-based compensation was included in operating expenses as follows (in thousands):
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
20121 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
||||
|
Cost of revenue—operating leases and incentives |
|
$ |
1,105 |
|
|
$ |
6 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
860 |
|
|
|
51 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
21,722 |
|
|
|
237 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
155 |
|
|
Total stock-based compensation |
|
$ |
23,687 |
|
|
$ |
294 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
$ |
155 |
|
(1) No stock options were outstanding during the Successor Period from November 17, 2012 through December 31, 2012.
In September 2014, the Company recorded $14.8 million of stock-based compensation expense in general and administrative expense related to the sale of shares of common stock to two of its directors as discussed in Note 12—Redeemable Non-controlling Interests, Equity and Preferred Stock.
|
14. |
Income Taxes |
The income tax (benefit) expense is composed of the following (in thousands):
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
||||
|
Current: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal |
|
$ |
1,358 |
|
|
$ |
2,492 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
State |
|
|
4,035 |
|
|
|
569 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
Total current expense |
|
|
5,393 |
|
|
|
3,061 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
Deferred: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal |
|
|
(9,636 |
) |
|
|
(2,900 |
) |
|
|
(932 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
State |
|
|
(2,827 |
) |
|
|
(38 |
) |
|
|
(143 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Total deferred benefit |
|
|
(12,463 |
) |
|
|
(2,938 |
) |
|
|
(1,075 |
) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Income tax (benefit) expense |
|
$ |
(7,070 |
) |
|
$ |
123 |
|
|
$ |
(1,074 |
) |
|
|
$ |
7 |
|
94
The Company operates in only one federal jurisdiction, the United States. The following table presents a reconciliation of the tax benefit computed at the statutory federal rate and the Company’s tax (benefit) expense (in thousands):
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
||||
|
Income tax benefit—computed as 35% of pretax loss |
|
$ |
(60,546 |
) |
|
$ |
(19,721 |
) |
|
$ |
(1,488 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(4,569 |
) |
|
Effect of non-controlling interests and redeemable non-controlling interests |
|
|
47,962 |
|
|
|
21,737 |
|
|
|
238 |
|
|
|
|
602 |
|
|
Effect of nondeductible acquisition costs |
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
270 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Effect of nondeductible expenses |
|
|
6,617 |
|
|
|
1,439 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
State and local income tax expenses |
|
|
616 |
|
|
|
343 |
|
|
|
(94 |
) |
|
|
|
(378 |
) |
|
Amortization of prepaid tax asset |
|
|
2,199 |
|
|
|
474 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Valuation allowance |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
4,325 |
|
|
Effect of tax credits |
|
|
(3,939 |
) |
|
|
(4,472 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Other |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
323 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
Income tax (benefit) expense |
|
$ |
(7,070 |
) |
|
$ |
123 |
|
|
$ |
(1,074 |
) |
|
|
$ |
7 |
|
Deferred income taxes reflect the impact of temporary differences between assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts recognized for income tax reporting purposes, net operating loss carryforwards and other tax credits measured by applying currently enacted tax laws. The significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities were as follows (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
||
|
Deferred tax assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity compensation |
|
$ |
3,738 |
|
|
$ |
174 |
|
|
Accruals and reserves |
|
|
3,335 |
|
|
|
540 |
|
|
Tax credits |
|
|
399 |
|
|
|
2,776 |
|
|
Net operating losses |
|
|
198 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Investment in solar funds |
|
|
146 |
|
|
|
166 |
|
|
Gross deferred tax assets |
|
|
7,816 |
|
|
|
3,656 |
|
|
Valuation allowance |
|
|
(222 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Net deferred tax assets |
|
|
7,594 |
|
|
|
3,656 |
|
|
Deferred tax liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investment in solar funds |
|
|
(106,664 |
) |
|
|
(31,039 |
) |
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
(9,493 |
) |
|
|
(10,993 |
) |
|
Gross deferred tax liabilities |
|
|
(116,157 |
) |
|
|
(42,032 |
) |
|
Net deferred tax liabilities |
|
$ |
(108,563 |
) |
|
$ |
(38,376 |
) |
The Company sells solar energy systems to the investment funds. As the investment funds are consolidated by the Company, the gain on the sale of the solar energy systems is not recognized in the consolidated financial statements. However, this gain is recognized for tax reporting purposes. Since these transactions are intercompany sales, any tax expense incurred related to these intercompany sales should be deferred and amortized over the estimated useful life of the underlying solar energy systems, which has been estimated to be 30 years. Accordingly, the Company has recorded a prepaid tax asset, net of $111.9 million and $30.7 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013.
The current portion of deferred tax assets of $3.7 million and $3.1 million was included in prepaid and other current assets as of December 31, 2014 and 2013. The future reversal of deferred tax liabilities is expected to produce a sufficient source of future taxable income of the necessary character and in the necessary periods and jurisdictions to support the realization of these deferred tax assets. As such, no valuation allowance is required.
95
The Company had net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $0.3 million and zero related to federal and $1.5 million and zero related to state (collectively the “NOLs”), available to offset future taxable income as of December 31, 2014 and 2013. These NOLs expire in varying amounts from 2031 through 2034 for federal tax purposes and from 2025 through 2034 for state tax purposes if unused. The Company anticipates existing federal NOLs will be utilized by taxable gains in future periods. The Company recognized a valuation allowance of $0.2 million for the existing state NOLs due to state-imposed limitations on their utilization.
The Company reported federal business tax credits, primarily composed of federal investment tax credits, of $3.9 million and $4.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. The Company accounts for its federal business tax credits as a reduction of income tax expense in the year in which the credits arise.
Uncertain Tax Positions
As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company had no unrecognized tax benefits. There were no interest and penalties accrued for any uncertain tax positions as of December 31, 2014 and 2013. The Company does not have any tax positions for which it is reasonably possible the total amount of gross unrecognized benefits will increase or decrease within 12 months of the year ended December 31, 2014. The Company is subject to taxation and files income tax returns in the United States, and various state and local jurisdictions. Substantially all of the Company’s federal, state and local income tax returns since inception are still subject to audit.
|
15. |
Related Party Transactions |
The Company’s operations included the following expenses from related party transactions (in thousands):
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
||||
|
Cost of revenue—operating leases and incentives |
|
$ |
7,834 |
|
|
$ |
1,558 |
|
|
$ |
73 |
|
|
|
$ |
246 |
|
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
2,312 |
|
|
|
866 |
|
|
|
131 |
|
|
|
|
406 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
5,909 |
|
|
|
2,323 |
|
|
|
614 |
|
|
|
|
3,624 |
|
|
Interest expense(1) |
|
|
4,481 |
|
|
|
2,924 |
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
(1) |
Includes revolving lines of credit—related party. See Note 10—Debt Obligations. |
Vivint Services
The Company entered into a number of agreements with Vivint related to services and other support that Vivint would provide to the Company, which agreements became effective in connection with the Company’s initial public offering. Among these agreements included the following:
|
· |
Master Intercompany Framework Agreement. This agreement establishes a framework for the relationship between the Company and Vivint, including master terms regarding the protection of each other’s confidential information, and master procedural terms, such as notice procedures, restrictions on assignment, interpretive provisions, governing law and dispute resolution. |
|
· |
Non-competition Agreement. This agreement defines each company’s current areas of business and competitors, and the Company and Vivint agree not to directly or indirectly engage in the other’s business for three years. |
|
· |
Transition Services Agreement. Pursuant to this agreement Vivint provides the Company various enterprise services that it has historically provided to the Company. Under this agreement, Vivint agreed to provide the services at the same degree of care and diligence that it takes in performing services for its own operations. These services include information technology and infrastructure, employee benefits and certain other services. In exchange, the Company pays Vivint for the services, which represents Vivint’s good faith estimate of their full cost of providing the services to the Company, without markup or surcharge. |
|
· |
Marketing and Customer Relations Agreement. This agreement governs various cross-marketing initiatives between the companies, in particular the provision of sales leads from each company to the other. The commission rate is based on the amount paid to subcontractors for performing similar lead generation services. The term of this agreement, including the term of the schedules defining the terms of the mutual lead generation program, is three years. |
96
|
· |
Bill of Sale. Under this agreement, Vivint transferred certain assets such as office equipment from Vivint to the Company. |
|
· |
Trademark License Agreement. Pursuant to this agreement, the licensor, a subsidiary majority-owned by Vivint and minority-owned by the Company, granted to the Company a royalty-free exclusive license to the trademark “VIVINT SOLAR” in the field of selling renewable energy or energy storage products and services. The agreement is perpetual but may be terminated voluntarily by the Company or by the licensor upon certain specified termination events. Vivint retains ownership of the Vivint trademark and the Company has no right to use “Vivint” except as part of “VIVINT SOLAR”. |
The Company incurred fees under these agreements of $2.2 million in 2014 following the Company’s initial public offering that reflect the amount of services provided by Vivint on behalf of the Company.
In June 2013, the Company entered into a full service sublease agreement (the “Sublease Agreement”) with Vivint, which was applied retroactively to be in effect as of January 1, 2013. Under the Sublease Agreement, Vivint provided various administrative services, such as management, human resources, information technology, facilities and use of corporate office space to the Company. The Company paid Vivint a monthly services fee and rent based on headcount and square footage used. In connection with the Company’s initial public offering, the Sublease Agreement was amended to focus exclusively on real estate issues. In 2011, and amended June 2013, the Company entered into a trademark / service mark license agreement (“Trademark Agreement”) with Vivint, pursuant to which the Company paid Vivint a monthly fee in exchange for rights to use certain trademarks, based on kilowatt hours produced by the solar energy systems each month. In June 2013, the Trademark Agreement was amended and restated to grant the Company a royalty-free, non-exclusive license to use certain Vivint marks, subject to certain quality control requirements and was applied retroactively to be in effect as of January 1, 2013. The Trademark Agreement was terminated in connection with the entry into the Trademark License Agreement described above.
The Company incurred fees under the Sublease and Trademark agreements of $7.2 million, $2.9 million, $0.8 million and $4.1 million for the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 and the Predecessor Period, which reflect the amount of services provided by Vivint on behalf of the Company.
Payables to Vivint recorded in accounts payable—related party were $2.1 million and $3.1 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013. These payables include amounts due to Vivint related to the fees incurred under the service agreements noted above, as well as other miscellaneous intercompany payables including freight, healthcare cost reimbursements and other pass-through purchases.
313 Incentive Units Plan
Incentive units from 313 have been granted to certain board members of the Company. Such board members are also employees of Vivint. As a result, the related compensation expense has been allocated between the two companies based on the net equity of the respective companies at the Acquisition. The Company recorded expense of $0.2 million and corresponding noncash capital contributions from 313 during each of the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. The noncash capital contributions were reported as noncash contributions for services on the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows and Redeemable Preferred Stock, Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests and Equity. The incentive units are subject to time-based and performance-based vesting conditions, with one-third subject to ratable time-based vesting over a five year period and two-thirds subject to the achievement of certain investment return thresholds by the sponsor and its affiliates. 313 has determined that it is not probable that the performance conditions will be achieved, and as such, all allocated stock compensation expense is related to the time-based vesting conditions during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. The fair value of stock-based awards is measured at the grant date and is recognized as expense over the board members’ requisite service period.
Advisory Agreements
In May 2014, the Company entered into an advisory agreement with Blackstone Advisory Partners L.P., an affiliate of the Sponsor (“BAP”), under which BAP will provide financial advisory and placement services related to the Company’s financing of residential solar energy systems. Under the agreement, the Company is required under certain circumstances to pay a placement fee to BAP ranging from 0.75% to 1.5% of the transaction capital, depending on the identity of the investor and whether the financing relates to residential or commercial projects. This agreement replaced the 2013 advisory agreement described below.
Effective May 2013, the Company entered into an advisory agreement with BAP that provided financial advisory and placement services related to the Company’s financing of residential solar energy systems. Under the agreement, BAP was paid a placement fee ranging from 0% to 2% of the transaction capital, depending on the identity of the investor and how contact with the investor was established.
97
The Company incurred fees under these agreements of $4.5 million and $1.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. No fees were incurred during the Successor Period ended December 31, 2012 and the Predecessor Period. The amounts were recorded in general and administrative expense in the Company’s consolidated statement of operations.
At the time of the Acquisition, the Company entered into a support and services agreement with Blackstone Capital Partners VI LP (“BCP”) and Blackstone Management Partners LLC (“BMP”), under which BCP and BMP would provide advice to the Company on, among other things, finance, operations, human resources and legal. Under the agreement, BCP and BMP were paid, in aggregate, an annual management fee in the amount of the greater of a minimum annual fee, which was initially defined as $0, or 1.5% of consolidated earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization. No annual management fee was paid under this agreement for any of the periods presented. The support and services agreement expired upon the Company’s initial public offering.
Terminated Advisory Agreements
Prior to the Acquisition, the Company had a management agreement with certain of its former investors (“Jupiter Parties”), pursuant to which they were paid an annual management fee. Jupiter Parties received management fees of $0.2 million during the Predecessor Period, which were included in general and administrative expense in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations. The agreement was terminated in conjunction with the Acquisition, and as such no fees were paid during the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
Advances Receivable—Related Party
Amounts due from direct-sales personnel were $1.2 million and $0.7 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013. The Company provided a reserve of $0.9 million and $0.4 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 related to advances to direct-sales personnel who have terminated their employment agreement with the Company.
Transactions with 313 and Directors
In August and September 2014, the Company issued and sold shares of its common stock to 313 and two of its directors as discussed in Note 12—Redeemable Non-controlling Interests, Equity and Preferred Stock. In April 2013, the Company received a $1.4 million capital contribution from 313. No other cash contributions were received during the periods presented.
Investment Funds
Fund investors for three of the funds are indirectly managed by the Sponsor and accordingly are considered related parties. See Note 11—Investment Funds. In July 2014, the Company also entered into a Backup Maintenance Servicing Agreement with Vivint in which Vivint will provide maintenance servicing of the fund assets in the event that the Company is removed as the service provider for two of the funds. No services have been performed by Vivint under this agreement.
|
16. |
Commitments and Contingencies |
Non-Cancellable Operating Leases
In May 2014, the Company entered into non-cancellable leases in anticipation of relocating its corporate office space to Lehi, Utah (the “Prior Leases”). Pursuant to a termination agreement and new leases (the “New Leases”) in September 2014, the Company entered into a non-cancellable lease with an affiliate of the landlord under the Prior Leases whereby the Company will move into another building being constructed by the affiliate in the same general location. It is anticipated that this new building will be completed during the first quarter of 2016. At the time the new building is completed, the Prior Leases will be cancelled. The terms of the New Leases are similar to those of the Prior Leases, with the exception that the Company will be leasing additional space. The Company will be deemed the owner of the building for accounting purposes during the construction period due to the terms of the New Leases.
In July 2014, the Company entered into non-cancellable operating leases in anticipation of moving certain of its operations to Orem, Utah.
The Company entered into lease agreements for warehouses and related equipment from 2011 through 2014, located in states in which the Company conducts operations. The warehouse lease agreements range from a term of one to seven years, with the majority having a term of three years. The equipment lease agreements, the longest of which is 12-months, include basic renewal options for an additional set period, continued renting by the month, or return of the unit.
98
For all non-cancellable lease arrangements, there are no bargain renewal options, penalties for failure to renew, or any guarantee by the Company of the lessor’s debt or a loan from the Company to the lessor related to the leased property. These leases have been classified and accounted for as non-cancellable operating leases. Aggregate operating lease expense was $4.3 million, $1.2 million, $0.1 million and $0.3 million for the Successor Periods ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 and the Predecessor Period.
Future minimum lease payments under non-cancelable operating leases as of December 31, 2014 were as follows (in thousands):
|
Years Ending December 31, |
|
|
|
|
|
2015 |
|
$ |
7,077 |
|
|
2016 |
|
|
8,647 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
6,396 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
3,748 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
3,781 |
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
4,080 |
|
|
Total minimum lease payments |
|
$ |
33,729 |
|
Letters of Credit
As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company had a $1.8 million stand-by letter of credit related to a three-year forward contract to sell SRECs entered into in November 2013. The agreement expires in January 2017. As the Company expects to be able to deliver the SRECs required under the forward contracts, no liability has been accrued.
Indemnification Obligations
From time to time, the Company enters into contracts that contingently require it to indemnify parties against claims. These contracts primarily relate to provisions in the Company’s services agreements with related parties that may require the Company to indemnify the related parties against services rendered; and certain agreements with the Company’s officers and directors under which the Company may be required to indemnify such persons for liabilities. In addition, under the terms of the agreements related to the Company’s investment funds and other material contracts, the Company may also be required to indemnify fund investors and other third parties for liabilities. As of December 31, 2014, the Company recorded a $4.0 million accrued distribution to reimburse a fund investor a portion of its capital contribution in order to true-up the investor’s expected rate of return due to a delay in solar energy systems being interconnected to the utility grid.
Legal Proceedings
In December 2013, one of the Company’s former sales representatives, on behalf of himself and a purported class, filed a complaint for unspecified damages, injunctive relief and restitution in the Superior Court of the State of California in and for the County of San Diego against Vivint Solar Developer, LLC, one of the Company’s subsidiaries, and unnamed John Doe defendants alleging violations of the California Labor Code and the California Business and Professions Code and seeking penalties of an unspecified amount, interest on all economic damages and reasonable attorney’s fees and costs. In January 2014, the Company filed an answer denying the allegations in the complaint and asserting various affirmative defenses. In late 2014, the parties agreed to terms of settlement to resolve this case, depending on class participation. The final settlement agreement is subject to court approval, which the Company anticipates to occur sometime mid-2015. The Company has recorded a $0.4 million reserve related to this proceeding in its consolidated financial statements.
In May 2014, Vivint made the Company aware that the U.S. Attorney’s office for the State of Utah is engaged in an investigation that Vivint believes relates to certain political contributions made by some of Vivint’s executive officers that are directors of the Company and some of Vivint’s employees. The Company has no reason to believe that it, the executive officers or employees are targets of such investigation.
99
In September 2014, two former installation technicians of the Company, on behalf of themselves and a purported class, filed a complaint for damages, injunctive relief and restitution in the Superior Court of the State of California in and for the County of San Diego against the Company and unnamed John Doe defendants. The complaint alleges certain violations of the California Labor Code and the California Business and Professions Code based on, among other things, alleged improper classification of installer technicians, installer helpers, electrician technicians and electrician helpers, failure to pay minimum and overtime wages, failure to provide accurate itemized wage statements, and failure to provide wages on termination. In December 2014, the original plaintiffs and three additional plaintiffs filed an amended complaint with essentially the same allegations. On February 5, 2015, the Company filed an answer to the amended complaint, denying liability and asserting a number of defenses. The Company believes that it has strong defenses to the claims asserted in this matter, and the Company intends to defend the case vigorously. Although the Company cannot predict with certainty the ultimate resolution of this suit, it does not believe this matter will have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, results of operations, cash flows or financial condition.
In November and December 2014, two putative class action lawsuits were filed in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York against the Company, its directors, certain of its officers and the underwriters of the Company’s initial public offering of common stock alleging violation of securities laws and seeking unspecified damages. In January 2015, the Court ordered these cases to be consolidated into the earlier filed case, Hyatt v. Vivint Solar, Inc. et al., 14-cv-9283 (KBF). The plaintiffs filed a consolidated amended complaint in February 2015. The Company believes this lawsuit is without merit and intends to defend the case vigorously. The Company is unable to estimate a range of loss, if any, that could result were there to be an adverse final decision. If an unfavorable outcome were to occur in this case, it is possible that the impact could be material to the Company’s results of operations in the period(s) in which any such outcome becomes probable and estimable.
In addition to the matters discussed above, in the normal course of business, the Company has from time to time been named as a party to various legal claims, actions and complaints. While the outcome of these matters cannot be predicted with certainty, the Company does not currently believe that the outcome of any of these claims will have a material adverse effect, individually or in the aggregate, on its consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
The Company accrues for losses that are probable and can be reasonably estimated. The Company evaluates the adequacy of its legal reserves based on its assessment of many factors, including interpretations of the law and assumptions about the future outcome of each case based on available information.
100
|
17. |
Basic and Diluted Net Income (Loss) Per Share |
The Company computes basic income (loss) per share by dividing net income available or loss attributable to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted earnings per share reflects the potential dilution of securities that could be exercised or converted into common shares, and is computed by dividing net earnings available to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding plus the effect of potentially dilutive shares to purchase common stock.
The following table sets forth the computation of the Company’s basic and diluted net (loss attributable) income available per share to common stockholders for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Successor Period ended December 31, 2012 and the Predecessor Period (in thousands, except per share amounts):
|
|
|
Successor |
|
|
|
Predecessor |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
Period from |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
November 17, |
|
|
|
January 1, |
|
||
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
through |
|
|
|
through |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
November 16, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2013 |
|
|
2012 |
|
|
|
2012 |
|
||||
|
Numerator: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net (loss attributable) income available to common stockholders |
|
$ |
(28,883 |
) |
|
$ |
5,638 |
|
|
$ |
(2,604 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(31,674 |
) |
|
Denominator: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares used in computing net (loss attributable) income available per share to common stockholders, basic |
|
|
83,446 |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
Weighted-average effect of potentially dilutive shares to purchase common stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
223 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Shares used in computing net (loss attributable) income available per share to common stockholders, diluted |
|
|
83,446 |
|
|
|
75,223 |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
Net (loss attributable) income available per share to common stockholders |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
$ |
(0.35 |
) |
|
$ |
0.08 |
|
|
$ |
(0.03 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(0.42 |
) |
|
Diluted |
|
$ |
(0.35 |
) |
|
$ |
0.07 |
|
|
$ |
(0.03 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(0.42 |
) |
For the year ended December 31, 2014, the Successor Period ended December 31, 2012 and the Predecessor Period, the Company incurred net losses attributable to common stockholders. As such, the potentially dilutive shares were anti-dilutive and were not considered in weighted average number of common shares outstanding for those periods. As of December 31, 2013, stock options underlying 4.4 million shares of common stock granted under the Omnibus Plan and an option award granted outside of the Omnibus Plan with terms substantially similar to those granted under the Omnibus Plan were subject to performance condition which had not yet been met. Accordingly, these options were not included in the computation of diluted EPS.
|
18. |
Subsequent Events |
Working Capital Credit Facility
In March 2015, the Company entered into a credit agreement with certain financial institutions for which Goldman Sachs Lending Partners LLC is acting as administrative agent and collateral agent, under which the Company may from time to time incur up to an aggregate of principal amount of $131.0 million in revolver borrowings. Upon the satisfaction of certain conditions and the approval of the lenders, the Company may increase the aggregate amount of revolver borrowings to $150.0 million. Loans under the revolving credit facility will be used for the construction and acquisition of solar energy systems, and letters of credit may be issued under the revolving credit facility for working capital and general corporate purposes. The revolving credit facility matures in March 2020.
101
Increase of Aggregation Facility
In February 2015, the Company with Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, entered into an amendment to the Aggregation Facility that increased the funding commitment by $25.0 million pursuant to which the Company may borrow up to an aggregate of $375.0 million. In addition, the right to which the Company may request additional borrowing capacity, upon the satisfaction of certain conditions and the approval of the lenders, was reduced to $175.0 million, such that the total potential capacity under facility remains at $550.0 million. The other terms of the Aggregation Facility remained unchanged.
Investment Fund
In February 2015, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company entered into a solar investment fund arrangement with an existing fund investor. The total commitment under the solar investment fund arrangement is $50.0 million. The Company’s wholly owned subsidiary has the right to elect to require the fund investor to sell all of its membership units to the Company’s wholly owned subsidiary beginning on the date that certain conditions are met. The purchase price for the fund investor’s interest is $1.2 million plus any accrued but unpaid preferred distributions. The Company has not yet completed its assessment of whether the fund arrangement is a VIE.
Discontinuance of Solmetric Products
In February 2015, the Company decided to discontinue the external sales of Solmetric’s SunEye and PV Designer products, which were at the end of their product life cycles. The Company will continue selling the Solmetric PV Analyzer product. The Company will continue to develop and produce SunEye and PV Designer products for internal use only. As a result of the discontinuance of these products, the Company will be recording in the first quarter of 2015 a noncash impairment charge of approximately $4.0 million to $5.0 million for intangible and other assets related to these two products. In 2014, these two products accounted for approximately $2.1 million of revenue.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures.
Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
(a)Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2014 pursuant to Rule 13a-15 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). The term “disclosure controls and procedures,” as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act, means controls and other procedures of a company that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to the company’s management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Based on the evaluation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2014, our chief executive officer and chief financial officer concluded that, as a result of material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting as previously disclosed in our Prospectus, our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective as of December 31, 2014.
Material Weakness
In connection with the preparation, audits and interim reviews of our consolidated financial statements, we and our independent registered public accounting firm identified a material weakness in internal control over financial reporting. Under standards established by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board of the United States, a material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of our annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis.
102
Specifically, we and our independent registered public accounting firm identified a number of material errors and other audit adjustments in connection with the preparation, audits and interim reviews of our consolidated financial statements which resulted in the restatement of our consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2013 and as of and for the three months ended March 31, 2014.
As of December 31, 2014, we had not designed and implemented sufficient controls and processes and did not have a sufficient number of qualified accounting, finance and tax personnel. Additionally, the nature of our investment funds increases the complexity of our accounting for the allocation of net income (loss) between our stockholders and non-controlling interests under the HLBV method and the calculation of our tax provision. As we enter into additional investment funds, which may have contractual provisions different from those of our existing funds, the calculation under the HLBV method and the calculation of our tax provision could become increasingly complicated. This additional complexity could increase the chance that we experience additional errors in the future, particularly because we have a material weakness in internal controls. In addition, our need to devote our resources to addressing this complexity could delay or prolong our remediation efforts and thereby prolong the existence of the material weakness. As a result, we and our independent registered public accounting firm determined that we do not have adequate procedures and controls and an adequate number of personnel to ensure that accurate financial statements could be prepared on a timely basis.
We have begun taking numerous steps and plan to take additional steps to remediate the underlying causes of the material weakness. In November 2013, we hired a new chief financial officer and a new vice president of finance and in January 2014, we hired a new corporate controller as well as additional finance and accounting personnel since January 2014, including a director of internal audit in January 2015, which significantly increases our finance and accounting team’s experience in GAAP and financial reporting for publicly traded companies. We are also in the process of formalizing and implementing written policies and procedures for the review of account analyses, reconciliations and journal entries. In January 2014, we engaged third-party consultants to provide support over our accounting and financial reporting process including assisting us with our evaluation of complex technical accounting matters. In addition, we expect to retain consultants to advise us on making further improvements to our internal controls over financial reporting. We believe that these additional resources will enable us to broaden the scope and quality of our controls relating to the oversight and review of financial statements and our application of relevant accounting policies. Furthermore, we plan to implement and improve systems to automate certain financial reporting processes and to improve information accuracy. However, these remediation efforts are still in process and have not yet been completed. Because of this material weakness, there is heightened risk that a material misstatement of our annual or quarterly financial statements will not be prevented or detected. We plan to complete this remediation process as quickly as possible. Although we expect it will take at least a year, we cannot estimate how long it will take to remediate this material weakness. In addition, the remediation steps we have taken, are taking and expect to take may not effectively remediate the material weakness, in which case our internal control over financial reporting would continue to be ineffective. We cannot guarantee that we will be able to complete our remedial actions successfully. Even if we are able to complete these actions successfully, these measures may not adequately address our material weakness and may take more than a year to complete. In addition, it is possible that we will discover additional material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting or that our existing material weakness will result in additional errors in or restatements of our financial statements.
We will be required to furnish a report by management on, among other things, the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting commencing with the filing of our second annual report on Form 10-K. This assessment will need to include disclosure of any material weaknesses identified by our management in our internal control over financial reporting. In addition, we will be required to engage an independent registered public accounting firm to opine on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting beginning at the date we are no longer an “emerging growth company” as defined in the JOBS Act. At such time, our management may conclude that our internal control over financial reporting is not effective. Moreover, even if our management concludes that our internal control over financial reporting is effective, our independent registered public accounting firm may issue a report that is adverse if such firm is not satisfied with the level at which our controls are documented, designed, operated or reviewed. As a result, we may need to undertake various actions, such as implementing new internal controls and procedures and hiring accounting or internal audit staff. Our remediation efforts may not enable us to avoid a material weakness in the future. In addition, as a public company, our reporting obligations may place a significant strain on our management, operational and financial resources and systems for the foreseeable future.
(b)Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2014 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting, other than those described above.
103
Inherent Limitation on the Effectiveness of Internal Control
The effectiveness of any system of internal control over financial reporting, including ours, is subject to inherent limitations, including the exercise of judgment in designing, implementing, operating, and evaluating the controls and procedures, and the inability to eliminate misconduct completely. Accordingly, any system of internal control over financial reporting, including ours, no matter how well designed and operated, can only provide reasonable, not absolute assurances. In addition, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. We intend to continue to monitor and upgrade our internal controls as necessary or appropriate for our business, but cannot assure you that such improvements will be sufficient to provide us with effective internal control over financial reporting.
None.
104
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
The information required by this Item 10 of Form 10-K that is found in our 2014 Proxy Statement to be filed with the SEC in connection with the solicitation of proxies for our 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, or the 2014 Proxy Statement, is incorporated by reference to our 2014 Proxy Statement. The 2014 Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year to which this report relates.
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
The information required by Item 11 of Form 10-K is found in our 2014 Proxy Statement and is incorporated here by reference to our 2014 Proxy Statement.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
The information required by Item 12 of Form 10-K is found in our 2014 Proxy Statement and is incorporated here by reference to our 2014 Proxy Statement.
Equity Compensation Plan Information
The following table provides information as of December 31, 2014 with respect to the shares of our common stock that may be issued under existing equity compensation plans (shares in thousands):
|
|
|
A |
|
|
B |
|
|
C |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of Securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remaining Available |
|
|
|
|
|
Number of Securities to be |
|
|
Weighted Average |
|
|
for Future Issuance |
|
|||
|
|
|
Issued Upon Exercise of |
|
|
Exercise Price |
|
|
Under Equity Compensation |
|
|||
|
|
|
Outstanding Options, |
|
|
of Outstanding Options, |
|
|
Plans (Excluding Securities |
|
|||
|
Plan Category |
|
Warrants and Rights |
|
|
Warrants and Rights |
|
|
Reflected in Column A) |
|
|||
|
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders |
|
|
10,053(1) |
|
|
$ |
1.21 |
|
|
|
12,842(2) |
|
|
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Total |
|
|
10,053(1) |
|
|
$ |
1.21 |
|
|
|
12,842(2) |
|
(1) Consists of awards granted under the 2013 Omnibus Incentive Plan and an option award granted outside of the Omnibus Plan with terms substantially similar to those granted under the Omnibus Plan.
(2) Represents the number of securities remaining available for future issuance under the 2014 Equity Incentive Plan and the Long-term Incentive Plan. The number of shares available for issuance under the 2014 Plan is subject to an annual increase on the first day of each year beginning in 2015, equal to the least of 8.8 million shares or 4% of the outstanding shares of common stock as of the last day of the immediately preceding fiscal year and an amount of shares we determine.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
The information required by Item 13 of Form 10-K is found in our 2014 Proxy Statement and is incorporated here by reference to our 2014 Proxy Statement.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services.
The information required by Item 14 of Form 10-K is found in our 2014 Proxy Statement and is incorporated here by reference to our 2014 Proxy Statement.
105
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.
(a)(1.) Consolidated Financial Statements:
The following documents are filed as a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for Vivint Solar, Inc.:
Report of Ernst & Young LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2014 and 2013.
Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 and the Successor Period from November 17 through December 31, 2012 and the Predecessor Period from January 1 through November 16, 2012.
Consolidated Statements of Redeemable Preferred Stock, Redeemable Non-Controlling Interest and Stockholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 and the Successor Period from November 17 through December 31, 2012 and the Predecessor Period from January 1 through November 16, 2012.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 and the Successor Period from November 17 through December 31, 2012 and the Predecessor Period from January 1 through November 16, 2012.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
(2.) Financial Statement Schedules:
Financial statement schedules are omitted because they are not required, not applicable or because the required information is shown in the Consolidated Financial Statements or Notes thereto.
(3.) Exhibits:
Required exhibits are incorporated by reference or are filed with this Annual Report as set forth in the following Exhibit Index, which immediately precedes such exhibits.
106
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
|
Vivint Solar, Inc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date: March 13, 2015 |
|
By: |
/s/ Gregory S. Butterfield |
|
|
|
|
Gregory S. Butterfield |
|
|
|
|
Chief Executive Officer and President |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
Name |
|
Title |
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Gregory S. Butterfield |
|
Chief Executive Officer and President, Director |
|
March 13, 2015 |
|
Gregory S. Butterfield |
|
(Principal Executive Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Dana C. Russell |
|
Chief Financial Officer and Executive Vice President |
|
March 13, 2015 |
|
Dana C. Russell |
|
(Principal Accounting and Financial Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ David F. D’Alessandro |
|
Director |
|
March 13, 2015 |
|
David F. D’Alessandro |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Alex J. Dunn |
|
Director |
|
March 13, 2015 |
|
Alex J. Dunn |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Bruce McEvoy |
|
Director |
|
March 13, 2015 |
|
Bruce McEvoy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Todd R. Pedersen |
|
Director |
|
March 13, 2015 |
|
Todd R. Pedersen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Joseph F. Trustey |
|
Director |
|
March 13, 2015 |
|
Joseph F. Trustey |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Peter F. Wallace |
|
Director |
|
March 13, 2015 |
|
Peter F. Wallace |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Joseph S. Tibbetts, Jr. |
|
Director |
|
March 13, 2015 |
|
Joseph S. Tibbetts, Jr. |
|
|
|
|
107
Exhibit Index
|
Exhibit Number |
|
Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Incorporated by Reference |
|
Filing Date |
|
3.1 |
|
Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Company |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
3.1 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
3.2 |
|
Amended and Restated Bylaws of the Company |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
3.2 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
4.1* |
|
Registration Rights Agreement by and among the Company and the investors named therein, dated October 6, 2014 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.1+ |
|
Form of Director and Executive Officer Indemnification Agreement |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.1 |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.2+ |
|
2013 Omnibus Incentive Plan, as amended |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.2 |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.3 |
|
Form of Stock Option Agreement under the 2013 Omnibus Incentive Plan |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.17 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
10.4+ |
|
2014 Equity Incentive Plan |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.3 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.5 |
|
Form of Notice of Stock Option Grant and Stock Option Agreement under the 2014 Equity Incentive Plan |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.15 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
10.6 |
|
Form of Notice of Restricted Stock Unit Grant and Restricted Stock Unit Agreement under the 2014 Equity Incentive Plan |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.16 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
10.7+ |
|
Amended and Restated 2013 Long-Term Incentive Pool Plan for District Sales Managers, and forms of agreements thereunder |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.4A |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.8+ |
|
Amended and Restated 2013 Long-Term Incentive Pool Plan for Operations Leaders, and forms of agreements thereunder |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.4B |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.9+* |
|
Amended and Restated 2013 Long-Term Incentive Pool Plan for Recruiting Regional Sales Managers, and forms of agreements thereunder |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.10+ |
|
Amended and Restated 2013 Long-Term Incentive Pool Plan for Regional Managers (Technicians), and forms of agreements thereunder |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.4D |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.11+ |
|
Amended and Restated 2013 Long-Term Incentive Pool Plan for Regional Sales Managers, and forms of agreements thereunder |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.4E |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.12+ |
|
Amended and Restated 2013 Long-Term Incentive Pool Plan for Sales Managers, and forms of agreements thereunder |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.4F |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
Exhibit Number |
|
Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Incorporated by Reference |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.13+ |
|
Form of 313 Acquisition LLC Unit Plan |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.5 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.14+ |
|
Executive Incentive Compensation Plan, and forms of agreements thereunder |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.6 |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.15+ |
|
Form of Involuntary Termination Protection Agreement between the Company and certain of its officers |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.7 |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.16+ |
|
Letter Agreement, dated August 28, 2014, with Gregory S. Butterfield |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.8 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.17+* |
|
Letter Agreement, dated August 28, 2014, with Dana C. Russell |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.18+* |
|
Letter Agreement, dated August 28, 2014, with Shawn J. Lindquist |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.19 |
|
Subordinated Note and Loan Agreement between the Company and APX Group, Inc., dated December 27, 2012 |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.11 |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.20 |
|
First Amendment to Note and Loan Agreement between the Company and APX Group, Inc., dated July 26, 2013 |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.11A |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.21 |
|
Amended and Restated Subordinated Note and Loan Agreement between the Company and APX Parent Holdco, Inc., dated January 20, 2014 |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.12 |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.22 |
|
First Amendment to Amended and Restated Subordinated Note and Loan Agreement between the Company and APX Parent Holdco, Inc., dated April 25, 2014 |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.12A |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.23† |
|
Credit Agreement between the Company, as a guarantor, Vivint Solar Holdings, Inc., as the borrower, and Bank of America, N.A. as administrative agent, collateral agent and lender, dated May 1, 2014 |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.13 |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.24* |
|
Stockholders Agreement by and among the Company and other parties thereto, dated October 6, 2014 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.25 |
|
Master Intercompany Framework Agreement between the Company and Vivint, Inc., dated September 30, 2014 |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.1 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
10.26 |
|
Transition Services Agreement between the Company and Vivint, Inc., September 30, 2014 |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.2 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
10.27 |
|
Non-Competition Agreement between the Company and Vivint, Inc., dated September 30, 2014 |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.3 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
Exhibit Number |
|
Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Incorporated by Reference |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.28 |
|
Product Development and Supply Agreement between Vivint Solar Developer, LLC and Vivint, Inc., dated September 30, 2014 |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.4 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
10.29 |
|
Marketing and Customer Relations Agreement between Vivint Solar Developer, LLC and Vivint, Inc., dated September 30, 2014 |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.5 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
10.30 |
|
Trademark Assignment Agreement between Vivint Solar Licensing LLC and Vivint, Inc., dated September 30, 2014 |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.6 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
10.31 |
|
Trademark Assignment Agreement between the Company and Vivint, Inc., dated September 30, 2014 |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.7 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
10.32 |
|
Termination Agreement (Turnkey Full-Service Sublease Agreement) between Vivint Solar Holdings, Inc., and Vivint, Inc., dated September 30, 2014 |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.8 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
10.33 |
|
Bill of Sale and Assignment between the Company and Vivint, Inc., dated September 30, 2014 |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.9 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
10.34 |
|
Limited Liability Company Agreement of Vivint Solar Licensing, LLC, between the Company and Vivint, Inc., dated September 30, 2014 |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.10 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
10.35 |
|
Trademark License Agreement between the Company and Vivint Solar Licensing, LLC, dated September 30, 2014 |
|
10-Q |
|
001-36642 |
|
10.11 |
|
November 12, 2014 |
|
10.36 |
|
Engagement Letter between the Company and Blackstone Advisory Partners L.P. dated as of May 30, 2014 |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.25 |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.37 |
|
Lease Agreement between the Company and Thanksgiving Park Five, LLC dated as of May 5, 2014 |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.26 |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.38 |
|
Sublease Agreement between the Company, Thanksgiving Park LLC and Durham Jones & Pinegar, P.C., dated as of May 19, 2014 |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.27 |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.39 |
|
Canyon Park Technology Center Office Building Lease Agreement between the Company and TCU-Canyon Park, LLC |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.28 |
|
August 26, 2014 |
|
10.40† |
|
Limited Liability Company Agreement of Vivint Solar Mia Project Company, LLC, between Vivint Solar Mia Manager, LLC and Blackstone Holdings Finance Co. L.L.C., dated as of July 16, 2013 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.29 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
Exhibit Number |
|
Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Incorporated by Reference |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.41† |
|
First Amendment to the Limited Liability Company Agreement of Vivint Solar Mia Project Company, LLC, between Vivint Solar Mia Manager, LLC and Blackstone Holdings Finance Co. L.L.C., dated as of September 12, 2013 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.29A |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.42 |
|
Second Amendment to Limited Liability Company Agreement of Vivint Solar Mia Project Company, LLC, between Vivint Solar Mia Manager, LLC and Blackstone Holdings Finance Co. L.L.C., dated as of August 31, 2013 |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.29B |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.43† |
|
Development, EPC and Purchase Agreement by and among, Vivint Solar Developer, LLC, Vivint Solar Holdings, Inc., and Vivint Solar Mia Project Company, LLC, dated as of July 16, 2013 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.30 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.44 |
|
First Amendment to Development, EPC and Purchase Agreement by and among Vivint Solar Developer, LLC, Vivint Solar Holdings, Inc., and Vivint Solar Mia Project Company, LLC, dated as of January 13, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.30A |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.45 |
|
Second Amendment to Development, EPC and Purchase Agreement by and among, Vivint Solar Developer, LLC, Vivint Solar Holdings, Inc., and Vivint Solar Mia Project Company, LLC dated as of April 25, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.30B |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.46 |
|
Maintenance Services Agreement between Vivint Solar Provider, LLC and Vivint Solar Mia Project Company, LLC, dated as of July 16, 2013 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.31 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.47 |
|
Guaranty by the Company in favor of Blackstone Holdings Finance Co. L.L.C. and Vivint Solar Mia Project Company, LLC, dated as of July 16, 2013 |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.32 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.48† |
|
Limited Liability Company Agreement of Vivint Solar Aaliyah Project Company, LLC, between Vivint Solar Aaliyah Manager, LLC and Stoneco IV Corporation, dated as of November 5, 2013 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.33 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
Exhibit Number |
|
Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Incorporated by Reference |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.49† |
|
First Amendment to Limited Liability Company Agreement of Vivint Solar Aaliyah Project Company, LLC, between Vivint Solar Aaliyah Manager, LLC and Stoneco IV Corporation, dated as of January 13, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.33A |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.50† |
|
Development, EPC and Purchase Agreement by and among Vivint Solar Developer, LLC, Vivint Solar Holdings, Inc., and Vivint Solar Aaliyah Project Company, LLC, dated as of November 5, 2013 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.34 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.51 |
|
First Amendment to Development, EPC and Purchase Agreement by and among, Vivint Solar Developer, LLC, Vivint Solar Holdings, Inc., and Vivint Solar Aaliyah Project Company, LLC, dated as of January 13, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.34A |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.52† |
|
Second Amendment to Development, EPC and Purchase Agreement by and among Vivint Solar Developer, LLC, Vivint Solar Holdings, Inc., and Vivint Solar Aaliyah Project Company, LLC, dated as of February 13, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.34B |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.53 |
|
Maintenance Services Agreement between Vivint Solar Provider, LLC and Vivint Solar Aaliyah Project Company, LLC, dated as of November 5, 2013 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.35 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.54 |
|
Guaranty by Vivint Solar, Inc. in favor of Stoneco IV Corporation, LLC and Vivint Solar Aaliyah Project Company, LLC, dated November 5, 2013 |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.36 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.55† |
|
Limited Liability Company Agreement of Vivint Solar Rebecca Project Company, LLC between Vivint Solar Rebecca Manager, LLC and Blackstone Holdings I L.P., dated as of February 13, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.37 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.56† |
|
Development, EPC and Purchase Agreement by and among Vivint Solar Developer, LLC, Vivint Solar Holdings, Inc., and Vivint Solar Rebecca Project Company, LLC, dated as of February 13, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.38 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.57 |
|
Maintenance Services Agreement between Vivint Solar Provider, LLC and Vivint Solar Rebecca Project Company, LLC, dated as of February 13, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.39 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
Exhibit Number |
|
Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Incorporated by Reference |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.58 |
|
Guaranty by Vivint Solar, Inc. in favor of Blackstone Holdings I L.P. and Vivint Solar Rebecca Project Company, LLC, dated as of February 13, 2014 |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.40 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.59 |
|
Subscription Agreement between the Company and 313 Acquisition LLC, dated August 14, 2014 |
|
S-1 |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.41 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.60 |
|
Subscription Agreement between the Company and the investors named therein, dated September 3, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.43 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.61† |
|
Loan Agreement, among Vivint Solar Financing I, LLC, Bank of America, N.A. and the parties named therein, dated as of September 12, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.44 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.62† |
|
Collateral Agency and Depositary Agreement among Vivint Solar Financing I, LLC, Bank of America, N.A. and the parties named therein, dated as of September 12, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.45 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.63† |
|
Pledge and Security Agreement among Vivint Solar Financing I, LLC, Bank of America, N.A. and the parties named therein, dated as of September 12, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.46 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.64 |
|
Lease Termination Agreement between the Company and Thanksgiving Park Five, LLC, dated September 15, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.47 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
10.65 |
|
Lease Agreement between the Company and T-Stat One, LLC, dated August 12, 2014 |
|
S-1/A |
|
333-198372 |
|
10.48 |
|
September 18, 2014 |
|
21.1* |
|
List of subsidiaries of the Company |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.1* |
|
Consent of Ernst & Young LLP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24.1* |
|
Powers of Attorney (contained on signature page). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.1* |
|
Certification of Principal Executive Officer Pursuant to Rules 13a-14(a) and 15d-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.2* |
|
Certification of Principal Financial Officer Pursuant to Rules 13a-14(a) and 15d-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exhibit Number |
|
Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Incorporated by Reference |
|
Filing Date |
|
32.1* |
|
Certification of Principal Executive Officer Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32.2* |
|
Certification of Principal Financial Officer Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.INS* |
|
XBRL Instance Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.SCH* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.CAL* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.DEF* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.LAB* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.PRE* |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Legend: |
|
|
+ |
Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan. |
|
† |
Confidential treatment has been requested with respect to certain portions of this exhibit. Omitted portions have been filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
|
* |
Filed herewith. |
