Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-21 - EX-21 - McEwen Mining Inc. | a2223369zex-21.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - McEwen Mining Inc. | a2223369zex-23_1.htm |
| EX-32 - EX-32 - McEwen Mining Inc. | a2223369zex-32.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - McEwen Mining Inc. | a2223369zex-31_1.htm |
| EXCEL - IDEA: XBRL DOCUMENT - McEwen Mining Inc. | Financial_Report.xls |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - McEwen Mining Inc. | a2223369zex-31_2.htm |
Use these links to rapidly review the document
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
ý |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2014 |
||
o |
TRANSITION REPORT UNDER SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
For the transition period from to |
||
Commission file number 001-33190
MCEWEN MINING INC.
(Name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Colorado (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
84-0796160 (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
|
150 King Street West, Suite 2800, Toronto, Ontario Canada (Address of principal executive offices) |
M5H 1J9 (Zip Code) |
(866) 441-0690
(Registrant's telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Common Stock, no par value | NYSE | |
|---|---|---|
| Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No ý
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No ý
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer" and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer o | Accelerated filer ý | Non-accelerated filer o (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) |
Smaller reporting company o |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No ý
As of June 30, 2014 (the last business day of the registrant's second fiscal quarter), the aggregate market value of the registrant's voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the registrant was $639,507,249 based on the closing price of $2.88 per share as reported on the NYSE. There were 272,114,148 shares of common stock outstanding (and 27,985,731 exchangeable shares exchangeable into McEwen Mining Inc. common stock on a one-for-one basis) on March 2, 2015.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE: Portions of the Proxy Statement for the 2014 Annual Meeting of Shareholders are incorporated into Part III, Items 10 through 14 of this report.
Descriptions of agreements or other documents in this report are intended as summaries and are not necessarily complete. Please refer to the agreements or other documents filed or incorporated herein by reference as exhibits. Please see the Exhibit Index at the end of this report for a complete list of those exhibits.
1
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Please see the note under "ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS," for a description of special factors potentially affecting forward-looking statements included in this report.
CAUTIONARY NOTE TO UNITED STATES INVESTORS—INFORMATION CONCERNING
PREPARATION OF RESOURCE AND RESERVE ESTIMATES
McEwen Mining Inc. ("McEwen Mining," "we", "our", "us" or the "Company") is required to prepare reports under the Canadian Securities Administrators' National Instrument 43-101 "Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects" ("NI 43-101"), under the Canadian securities laws because we are listed on the Toronto Stock Exchange ("TSX") and subject to Canadian securities laws. These standards are materially different from the standards generally permitted in reports filed with the United States ("U.S.") Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC").
Definitions of terms under NI 43-101 differ materially from the definitions of those and related terms in Industry Guide 7 ("Industry Guide 7") promulgated by the SEC. Under U.S. standards, mineralization may not be classified as a "reserve" unless a determination has been made that the mineralization could be economically and legally produced or extracted at the time the reserve determination is made. Under Industry Guide 7 standards, a "Final" or "Bankable" feasibility study or other report is required to report reserves, the three-year historical average precious metals prices are used in any reserve or cash flow analysis to designate reserves and the primary environmental analysis or report must be filed with the appropriate government authority.
One consequence of these differences is that "reserves" calculated in accordance with Canadian standards may not be "reserves" under Industry Guide 7 standards. U.S. investors should be aware that McEwen Mining's properties located in Argentina (with the exception of the San José mine), Mexico and the United States do not have "reserves" as defined by Industry Guide 7 and are cautioned not to assume that any part or all of the disclosed mineralized material will be confirmed or converted into Industry Guide 7 compliant "reserves".
Further, since we have no reserves on some of our properties as defined in Industry Guide 7, we have in the past and will continue to expense substantially all design, construction and development costs with regard to those properties, even though these expenditures are expected to have a future economic benefit in excess of one year. Only certain types of property and equipment which have alternative uses or significant salvage value may be capitalized without proven and probable reserves. We also expense our asset retirement obligations on those properties. Companies that have reserves under Industry Guide 7 typically capitalize these costs, and subsequently depreciate or amortize them on a units-of-production basis as reserves are mined. Unlike these other companies, we depreciate or amortize any capitalized costs on a straight-line basis based on the estimated useful life of the mine, as determined by our internal mine plans. As a result of these and other differences, our financial statements may not be comparable to the financial statements of mining companies that have established reserves.
Under NI 43-101, we report measured, indicated and inferred resources, which are measurements that are generally not permitted in filings made with the SEC. The estimation of measured resources and indicated resources involve greater uncertainty as to their existence and economic feasibility than the estimation of proven and probable reserves under Industry Guide 7. U.S. investors are cautioned not to assume that any part of measured or indicated resources will ever be converted into economically mineable reserves. The estimation of inferred resources involves far greater uncertainty as to their existence and economic viability than the estimation of other categories of resources. It cannot be assumed that all or any part of inferred resources will ever be upgraded to a higher category.
2
Therefore, U.S. investors are also cautioned not to assume that all or any part of inferred resources exist, or that they can be mined legally or economically.
Canadian regulations permit the disclosure of resources in terms of "contained ounces" provided that the tonnes and grade for each resource are also disclosed; however, the SEC only permits issuers to report "mineralized material" in tonnage and average grade without reference to contained ounces. Under U.S. regulations, the tonnage and average grade described herein and other information disseminated to you would be characterized as mineralized material. We provide such disclosure about our properties to allow a means of comparing our projects to those of other companies in the mining industry, many of which are Canadian and report pursuant to NI 43-101, and to comply with applicable disclosure requirements.
We also note that drill results are not indicative of mineralized material in other areas where we have mining interests. Furthermore, mineralized material identified on our properties does not and may never have demonstrated economic or legal viability.
Minera Santa Cruz S.A., the owner of the San José mine, is responsible for and has supplied to us all reported results from the San José mine. The technical information contained herein with regard to the San José mine is, with few exceptions as noted, based entirely on information provided to us by Minera Santa Cruz S.A. Our joint venture partner, a subsidiary of Hochschild Mining plc, and its affiliates other than MSC do not accept responsibility for the use of project data or the adequacy or accuracy of this information.
3
History and Organization
We are a mining and minerals exploration company focused on precious and base metals in Argentina, Mexico and the United States. We were organized under the laws of the State of Colorado on July 24, 1979 under the name Silver State Mining Corporation. On June 21, 1988, we changed our name to U.S. Gold Corporation and on March 16, 2007, we changed our name to US Gold Corporation. On January 24, 2012, we changed our name to McEwen Mining Inc. after the completion of the acquisition of Minera Andes Inc. ("Minera Andes") by way of a statutory plan of arrangement under the laws of the Province of Alberta, Canada.
We operate in Argentina, Mexico and the United States. As at December 31, 2014, we had an aggregate land position consisting primarily of mining claims, leases of mining claims or concessions of 814 square miles (2,109 square kilometers) in Argentina, 697 square miles (1,807 square kilometers) in Mexico, and 241 square miles (625 square kilometers) in Nevada. We own a 49% interest in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. ("MSC"), owner and operator of the producing San José mine in Santa Cruz, Argentina, which is controlled by the majority owner of the joint venture, Hochschild Mining plc ("Hochschild"). We also own the El Gallo 1 gold mine in Sinaloa, Mexico. In addition to our operating properties, we also hold interests in numerous exploration stage properties and projects in Argentina, Mexico and the United States, including the Gold Bar ("Gold Bar") and Los Azules ("Los Azules") projects.
Our objective is to increase the value of our shares through the exploration, development, and extraction of gold, silver and other valuable minerals. Other than the San José mine in Argentina, we generally conduct our exploration activities as sole operator, but we may enter into arrangements with other companies through joint venture or similar agreements in an effort to achieve our strategic objectives. We hold our mineral interests and property and operate our business through various subsidiary companies, each of which is owned entirely, directly, or indirectly, by us.
Our principal executive office is located at 150 King Street West, Suite 2800, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5H 1J9 and our telephone number is (866) 441-0690. We also maintain offices in San Juan, Argentina; Guamuchil, Mexico; Elko and Reno, Nevada. Our website is www.mcewenmining.com. We make available our periodic reports and news releases on our website. Our common stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange ("NYSE") and on the Toronto Stock Exchange ("TSX"), in each case under the symbol "MUX". Exchangeable shares of McEwen Mining—Minera Andes Acquisition Corp. are listed on the TSX under the symbol "MAQ".
In this report, "McEwen Mining", the "Company", "our" and "we" refer to McEwen Mining Inc. together with our subsidiaries, unless otherwise noted. "Au" represents gold; "Ag" represents silver; "oz" represents ounce; "gpt" represents grams per metric tonne; "ft." represents feet; "m" represents meter; "km" represents kilometer; and "sq." represents square, and C$ refers to Canadian dollars. All of our financial information is reported in United States (U.S.) dollars, unless otherwise noted.
4
Segment Information
Our operating segments include Argentina, Mexico and the United States. Our sales and long-lived assets are geographically distributed as follows.
| |
Sales | Long-Lived Assets | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||
Mexico |
100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 2 | % | 1 | % | 1 | % | |||||||
Argentina |
0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | 82 | % | 78 | % | 78 | % | |||||||
United States |
0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | 16 | % | 20 | % | 21 | % | |||||||
Other |
0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | |||||||
Products
The end product at our gold and silver operations is either in the form of doré or concentrate. Production from the San José mine generally consists of approximately 45% doré production and 55% of concentrate production, while the El Gallo 1 mine produces primarily doré. Doré is an alloy consisting primarily of gold and silver but also containing other metals. Doré is sent to refiners to produce bullion that meets the required market standard of 99.95% gold and 99.9% silver. Under the terms of our refining agreements, the doré bars are refined for a fee, and our share of the refined gold and silver is credited to our account. Ore concentrate, or simply concentrate, is raw ore that has been ground finely to a powdery product where gangue (waste) is removed, thus concentrating the metal component. Concentrates from the San José mine are shipped to third-party smelters and refineries for further processing to produce useful metals.
During 2014, we reported consolidated production attributable to us of 84,351 gold ounces and 3,195,733 silver ounces, for a total of 137,612 gold equivalent ounces (using a silver to gold ratio of 60:1). Of our consolidated gold and silver production, approximately 55% and 99%, respectively, came from the San José mine in Argentina and 45% and 1%, respectively, came from our El Gallo 1 mine in Mexico.
Gold and silver doré produced from the San José mine is sold at the prevailing spot market price based on the London A.M. fix, while concentrates are sold at the prevailing spot market price based on either the London P.M. fix or average of the London A.M. and London P.M fix depending on the sales contract. Concentrates are provisionally priced, whereby the selling price is subject to final adjustments at the end of a period ranging from 30 to 90 days after delivery to the customer. The final price is based on the market price at the relevant quotation point stipulated in the contract. Due to the time elapsed between shipment and the final settlement with the buyer, MSC must estimate the prices at which sales of metals will be settled. At the end of each financial reporting period, previously recorded provisional sales are adjusted to estimated settlement metals prices based on relevant forward market prices until final settlement with the buyer.
Gold and silver doré produced in Mexico are generally sold at the prevailing spot market price.
During 2014, total gold and silver sales for the San José mine were $213.0 million. However, our share of earnings or losses under the equity method of accounting for the year ended December 31, 2014 was a loss of $5.3 million. Total gold and silver sales for the El Gallo 1 mine were $45.3 million during 2014. See Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations for additional information regarding production and operating results for our properties, and Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies—Investments, for additional information regarding the equity method of accounting.
5
The following table presents the annual high, low and average daily London P.M. fix prices per ounce for gold and silver over the past three years and 2015 to the most recent practical date on the London Bullion Market:
| |
Gold | Silver | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Year
|
High | Low | Average | High | Low | Average | |||||||||||||
| |
(in dollar per ounce) |
||||||||||||||||||
2012 |
$ | 1,792.00 | $ | 1,540.00 | $ | 1,669.00 | $ | 37.23 | $ | 26.67 | $ | 31.15 | |||||||
2013 |
1,694 | 1,192 | 1,411 | 32.23 | 18.61 | 23.79 | |||||||||||||
2014 |
1,385 | 1,142 | 1,266 | 22.05 | 15.28 | 19.08 | |||||||||||||
2015 (through March 2, 2015) |
1,296 | 1,172 | 1,239 | 18.23 | 15.71 | 16.97 | |||||||||||||
On March 2, 2015, the London P.M. fix for gold was $1,213 per ounce and silver was $16.63 per ounce.
Gold and Silver Processing Methods
Gold and silver are extracted from mineralized material, by either milling or heap leaching, depending on, among other things, the amount of gold and silver contained in the material, whether the material is naturally oxidized or not oxidized, the accessibility of the mineralized material, the amenability of the material to treatment and related capital and operating costs. The mineralized material is extracted by underground (San José mine) and open pit (El Gallo 1 mine) mining methods.
The processing plant at the San José mine is composed of conventional crushing, grinding and flotation circuits. Approximately half of the silver-gold flotation concentrate is processed in an intensive cyanide leaching circuit with the dissolved gold and silver recovered by electrowinning of a clarified solution followed by smelting to produce doré. The doré is then sent to refiners to produce a purer product. The balance of the flotation concentrate is filtered and shipped to a smelter. Flotation and leached tailings are stored in side-by-side engineered, zero discharge facilities. Starting in 2015, flotation tailings started being stored in a newly constructed pond, after the original pond reached the end of its useful life at the end of the year 2014. A Merrill Crowe circuit recovers small amounts of gold and silver from the electrowinning discharge solution. Beginning in 2012, the crushing circuit was modified to accommodate a 10% increase in mill throughput, from a nominal 1,500 to 1,650 metric tonnes per day. The modifications were completed in 2013.
At the El Gallo 1 mine, mineralized material is processed using heap leaching. Heap leaching consists of stacking crushed material on impermeable pads, where a weak cyanide solution is applied to the surface of the heap to dissolve the gold and silver. The gold and silver-bearing solution is then collected and pumped to an Adsorption-Desorption-Recovery ("ADR") processing plant consisting of carbon columns, stripping circuits and a precious metal refinery to process gold and silver into doré bars. Doré bars are then shipped from the mine to a third party refiner to obtain a purer, final product.
Gold and Silver Reserves
The following table presents the portion of proven and probable gold and silver reserves attributable to McEwen Mining from our 49% equity interest in the San José mine. The reserves as presented are in-place and include mining dilution and mining losses, but do not include allowances for mill or smelter recoveries.
6
San José Reserves and Resources—49% attributable basis
Reserve Category
|
Tonnes (in thousands) |
Silver (grams/tonne) |
Silver ounces (in millions) |
Gold (grams/tonne) |
Gold ounces (in thousands) |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Proven |
465.5 | 597 | 8.9 | 7.82 | 117.0 | |||||||||||
Probable |
422.87 | 426 | 5.8 | 6.15 | 83.6 | |||||||||||
Proven & Probable |
888.37 | 515 | 14.7 | 7.03 | 200.6 | |||||||||||
The 2013 information is the most recent available to us and does not account for depletion from 2014 production or reserves delineated during 2014. We expect that Hochschild Mining plc. will report updated reserves as at December 31, 2014 by the first quarter of 2015. For additional information about our reserves on this property, including tonnage and grade, see Item 2. Properties—San José Mine, Argentina, on page 31.
There are no proven and probable reserves at El Gallo 1 in Mexico or any of our other properties.
Competitive Business Conditions
We compete with many companies in the mining and mineral exploration industry, including large, established mining companies with substantial capabilities, personnel, and financial resources. There is a limited supply of desirable mineral lands available for claim-staking, lease, or acquisition in Argentina, Mexico, or the United States, and other areas where we may conduct exploration activities. We may be at a competitive disadvantage in acquiring mineral properties, since we compete with these individuals and companies, many of which have greater financial resources and larger technical staffs than we do. From time to time, specific properties or areas which would otherwise be attractive to us for exploration or acquisition may be unavailable due to their previous acquisition by other companies or our lack of financial resources.
Competition in the industry is not limited to the acquisition of mineral properties, but also extends to the technical expertise to find, advance, and operate such properties; the labor to operate the properties; and the capital for the purpose of funding such exploration and development. Many competitors not only explore for and mine precious and base metals, but conduct refining and marketing operations on a world-wide basis. Such competition may result in our company being unable not only to acquire desired properties, but to recruit or retain qualified employees or to acquire the capital necessary to fund our operation and advance our properties. Our inability to compete with other companies for these resources would have a material adverse effect on our results of operation, financial condition and cash flows.
General Government Regulations
Argentina
Mining in Argentina is subject to numerous federal, provincial and local laws, regulations and ordinances governing mineral rights, operations and environmental protection.
Mineral Concession Rights. Under Argentine Law, mining concessions are real property, which can be transferred freely and can also be pledged. Concessions are granted by provincial governments for unlimited periods of time, subject to the following conditions:
- (a)
- the
payment twice a year of a mining fee or canón ranging between 160 to 1,600 Argentine
pesos per mining claim, or pertenencia, depending on the type of mining claim; and
- (b)
- the filing of a minimum investment plan and compliance with a minimum investment in the concession equal to 300 times the relevant canón over a five year period.
Failure to comply with these conditions may result in the termination of the concession.
7
Surface Rights. A mining license alone is not sufficient to permit mining operations. An agreement for access and occupation of the surface land is also required from the surface owner and occupier before mining may commence. Surface rights in Argentina are not automatically granted with title to either a mining lease or a claim and must be negotiated with the landowner.
Water Rights. Water rights are granted for the land or industry they have been applied for. Water rights cannot be separately seized or expropriated from the land or mining concession for which the use of water has been granted as long as the use for the mining concession is required and the obligations by the title holder are complied with.
Mining Royalties. As legal owners of the mineral resources, provinces are entitled to request royalties from mine operators. Regulations vary from province to province. Under a Mining Tax Stability Agreement between the Province of Santa Cruz where the San José mine is located and MSC, the mining royalty was fixed at 1.85% of the mine-site value per year when the final product is doré and 2.55% when the final products are concentrates or precipitates. Starting in November 2012, MSC increased its royalty payments to the Province to the legal maximum of 3% for all products. Royalties are paid monthly.
Reserve Tax Law. In June 2013, the Province of Santa Cruz passed amendments to the Provincial Tax Code and Provincial Tax Law, which imposes a new tax on mining reserves in the Province. The law came into effect on July 5, 2013. The tax will amount to 1% of the value of mine reserves reported in feasibility studies and financial statements inclusive of variations resulting from ongoing operations. Regulations require that the tax be calculated on "measured" reserves, and MSC has interpreted this to mean "proven" reserves. The Province has not disputed this interpretation but has not provided further clarification on the definition of "measured" reserves, and the outcome is not clear at the time. MSC has filed a legal claim disputing the legality of the new tax and has paid the initial installments under protest.
Environmental Law. The Environmental Protection Section of the National Mining Code of Argentina, enacted in 1995, requires that each Provincial government monitor and enforce the laws pertaining to prescribed development and protection of the environment. The Argentine Constitution establishes that the Federal Government is required to set the minimum standards. In 2002, the National Congress established such minimum standards for the sustainable management and protection of the environment and biodiversity, which are applicable throughout Argentina. Provinces are entitled to strengthen those standards. Further, the Argentine Constitution, as amended in 1994, allows any individual who believes a third party may be damaging the environment to initiate an action against such party. Existing and proposed legislation at both the federal and state levels in Argentina governing the protection of glaciers and the management of natural resources, including mining activity, in the vicinity of glaciers, may impact the Company's ability to develop its projects.
Mining Permits. Prior to conducting mining operations, companies must submit an Environmental Impact Report ("EIR") to the provincial government. The EIR must describe the proposed operation and the methods that will be used to prevent undue environmental damage and must be updated biennially. Mine operators are liable for environmental damage and violators of environmental standards may be required to shut down mining operations. An EIR must be submitted every two years in accordance with Argentine Law.
Mexico
Mining in Mexico is also subject to numerous federal, state and local laws, regulations and ordinances governing mineral rights, operations and environmental protection.
8
Mineral Concession Rights. Exploration and exploitation of minerals in Mexico may be carried out through Mexican companies incorporated under Mexican law by means of obtaining mining concessions. Mining concessions are granted by the Mexican government for a period of fifty years from the date of their recording in the Public Registry of Mining and are renewable for a further period of fifty years upon application within five years prior to the expiration of such concession in accordance with the Mining Law and its regulations.
Mining concessions are subject to annual work requirements and payment of annual surface taxes which are assessed and levied on a semi-annual basis. Such concessions may be transferred or assigned by their holders, but such transfers or assignments must be registered with the Public Registry of Mining in order to be valid against third parties.
The holder of a concession must pay semi-annual duties in January and July of each year on a per hectare basis and in accordance with the amounts provided by the Federal Fees Law.
During the month of May of each year, the concessionaire must file with the General Bureau of Mines, the work assessment reports made on each concession or group of concessions for the preceding calendar year. The regulations of the Mining Law provide tables containing the minimum investment amounts that must be made on a concession. This amount is updated annually in accordance with the changes in the Consumer Price Index.
Surface Rights. In Mexico, while mineral rights are administered by the federal government through federally issued mining concession, ejidos (communal owners of land recognized by the federal laws in Mexico) control surface access rights to the land. An ejido may sell or lease lands directly to a private entity. While the Company has agreements or is in the process of negotiating agreements with the ejidos that impact all of its projects in Mexico, some of these agreements may be subject to renegotiations.
Water Rights. Water rights are managed by the Comisión Nacional del Aqua ("CONAGUA"). According to the Mexican water rights legislation, industrial users such as mining companies must pay for the right to use national waters regardless of how their rights were obtained, with the rates being determined by the availability of water and the method of extraction. We are not required to obtain water rights. According to CONAGUA, the El Gallo Complex is located in the Sinaloa River Aquifer and is termed Zona de Libre Alumbramiento, meaning a free zone because of excess capacity. However, water usage costs $0.40 per cubic meter consumed.
Mining Royalties. In October 2013, the Mexican lower house passed a bill levying a tax-deductible mining royalty of 7.5% on earnings before the deduction of interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization, along with an additional 0.5% surcharge on precious metals revenue for mining companies. The effective date of the law was January 1, 2014. Although there are a number of uncertainties surrounding the scope, calculation and enforcement of the royalty, based on the Company's current interpretation of the bill, the royalty or surcharge was not material for 2014. Further, the Company has filed an Amparo, a legal recourse seeking remedy for the protection of constitutional rights In November 2014, the Company received an unfavourable decision from the District Court in respect of this Amparo. The Company has appealed the decision by submitting a Revision Recourse (Recurso de Revisión) that will be decided by the Federal Circuit Courts.
Environmental Law. The Environmental Law in Mexico, called the "General Law of Ecological Balance and Protection to the Environment" ("General Law"), provides for general environmental policies, with specific requirements for certain activities such as exploration set forth in regulations called "Mexican official norms". Responsibility for enforcement of the General Law, the regulations and the Mexican official norms is with the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources, which regulate all environmental matters with the assistance of Procuraduría Federal de Protección al Ambiente ("PROFEPA").
9
The primary laws and regulations used by the State of Sinaloa where our El Gallo property is located in order to govern environmental protection for mining and exploration are: the General Law, Forestry Law, Residues Law, as well as their specific regulations on air, water and residues, and the Mexican official norms ("NOM-120"). In order to comply with the environmental regulations, a concessionaire must obtain a series of permits during the exploitation and exploration stage. The time required to obtain the required permits is dependent on a number of factors including the type of vegetation and trees impacted by proposed activities.
Mining Permits. The Secretariat of Environmental and Natural Resources, the Mexican Government environmental authority ("SEMARNAT"), is responsible for issuing environmental permits associated with mining. Three main permits required before construction can begin are: Environmental Impact Statement (known in Mexico as Manifesto Impacto Ambiental) ("MIA"), Land Use Change (known in Mexico as Estudio Justificativo Para Cambio Uso Sueldo) ("ETJ"), and Risk Analysis (known in Mexico as Analisis de Riesgo) ("RA"). A construction permit is required from the local municipality and an archaeological release letter from the National Institute of Anthropology and History ("INAH"). An explosives permit is required from the ministry of defense before construction can begin. The MIA is required to be prepared by a third-party contractor and submitted to SEMARNAT and must include a detailed analysis of climate, air quality, water, soil, vegetation, wildlife, cultural resources and socio-economic impacts. The RA study (which is included into the MIA and submitted as one complete document) identifies potential environmental releases of hazardous substances and evaluates the risks in order to establish methods to prevent, respond to, and control environmental emergencies. The ETJ requires that an evaluation be made of the existing conditions of the land, including a plant and wildlife study, an evaluation of the current and proposed use of the land, impacts to naturally occurring resources, and an evaluation of reclamation/re-vegetation plans.
United States
Mining in the United States is also subject to numerous federal, state and local laws. Three types of laws are of particular importance to our U.S. mineral properties: those affecting land ownership and mining rights; those regulating mining operations; and those dealing with the environment.
Land Ownership and Mining Rights. Our Nevada properties are primarily located on lands owned by the United States (Federal Lands) and are governed by the General Mining Law of 1872 ("General Mining Law") as amended. The General Mining Law allows the location of mining claims on certain Federal Lands upon the discovery of a valuable mineral deposit and proper compliance with claim location requirements. A valid mining claim provides the holder with the right to conduct mining operations for the removal of minerals, subject to compliance with the General Mining Law and state law governing the staking and registration of mining claims, as well as compliance with various federal, state and local operating and environmental laws, regulations and ordinances. As the owner or lessee of the unpatented mining claims, we have the right to conduct mining operations on the lands subject to the prior procurement of required operating permits and approvals, compliance with the terms and conditions of any applicable mining lease, and compliance with applicable federal, state, and local laws, regulations and ordinances.
Mining Operations. The exploration of mining properties and development and operation of mines are governed by federal, state and local laws. Our Nevada properties are primarily administered by the United States Department of the Interior, Bureau of Land Management, which we refer to as the U.S. Bureau of Land Management ("BLM"). In general, the federal laws that govern mining claim location and maintenance and mining operations on Federal Lands are administered by the BLM. Additional federal laws, such as those governing the purchase, transport or storage of explosives, and those governing mine safety and health, also apply.
10
The State of Nevada likewise requires various permits and approvals before mining operations can begin, although the state and federal regulatory agencies usually cooperate to minimize duplication of permitting efforts. Among other things, a detailed reclamation plan must be prepared and approved, with bonding in the amount of projected reclamation costs. The bond is used to ensure that proper reclamation takes place, and the bond will not be released until this is completed. The Nevada Department of Environmental Protection ("NDEP") is the state agency that administers the reclamation permits, mine permits and related closure plans on our Nevada properties. Local jurisdictions (such as county governments) may also impose permitting requirements (such as conditional use permits or zoning approvals).
Environmental Law. The development, operation, closure, and reclamation of mining projects in the United States requires numerous notifications, permits, authorizations, and public agency decisions. Compliance with environmental and related laws and regulations requires us to obtain permits from regulatory agencies, and to file various reports and keep records of our operations. Certain of these permits require periodic renewal or review of their conditions and may be subject to a public review process during which opposition to our proposed operations may be encountered. We are currently operating under various permits for activities connected to mineral exploration, reclamation, and environmental requirements.
Proposed mineral processing at our Gold Bar property will require additional permitting prior to production. Various federal agencies and departments within the State of Nevada and local governments will be cooperating to review applications for any mining development and process facilities at the site. Although not expected, potential external events such as public or cooperating agency opposition could lengthen the schedule for permit acquisition. Because of previously permitted mining activity at the site, we currently have no reason to believe that permits to mine the mineral resources at Gold Bar could not be obtained from local, state and Federal regulatory agencies without unreasonable effort and expense. Production water for the Gold Bar property can be appropriated pursuant to regulations implemented by the State of Nevada. The permit for production water was received from the NDEP in July 2014.
Customers
During the year ended December 31, 2014, 73% of total sales from the San José mine were made to Argor-Heraeus S.A., LS-Nikko Copper Inc., and Republic Metals. Argor-Heraeus S.A., a Swiss company, is a purchaser of doré, which accounted for 20% of total sales. LS-Nikko Copper Inc., a Korean company, is a purchaser of concentrate, which accounted for 33% of total sales. Republic Metals., an American company, is a purchaser of concentrate and accounted for 20% of total sales.
MSC has sales agreement with each of these purchasers. MSC has already allocated all of its 2015 concentrate and doré production to its existing customers. However, any interruption of production or loss of one of these customers could temporarily disrupt the sale of metals and adversely affect its operating results.
At our El Gallo 1 mine, we either sell refined metal on the spot market, or doré under the terms set out in a doré purchase agreement the Company entered into with The Bank of Nova Scotia ("Scotia"), a Canadian financial institution. Under the terms of that agreement, dated in July 2012, the Company has the option to sell approximately 90% of the gold and silver contained in doré bars produced at the El Gallo 1 mine prior to the completion of refining by the third party refiner, which normally takes approximately 15 business days. During the year ended December 31, 2014, approximately 90% our sales from El Gallo 1 in Mexico were made through this doré purchase agreement. We also have an agreement to sell refined metal with a second Canadian financial institution.
11
Employees
As of March 2, 2015, we had 273 employees including 238 employees based in Mexico, 5 in Argentina, 8 in the United States, and 22 in Canada. All of our employees based in Canada work in an executive, technical or administrative position, while our employees in Mexico, Argentina and the United States include laborers, engineers, geologists, permitting specialists, information technologists, and office administrators. Some of our employees in Mexico are covered by union labor contracts and the Company believes we have good relations with our employees and their unions. We also frequently engage independent contractors in connection with certain administrative matters and the exploration of our properties, such as drillers, geophysicists, geologists, and other technical disciplines. As of March 2, 2015, MSC had 1,162 employees in Argentina.
This report, including Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, contains forward-looking statements that may be affected by several risk factors. The following information summarizes all material risks known to us as of the date of filing this report:
Risks Relating to Our Company
We have incurred substantial losses since our inception in 1979 and may never be profitable.
Since our inception in 1979, we have never been profitable. As of December 31, 2014, our accumulated deficit, including non-cash impairment charges, was $919.6 million, including a net loss of $311.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. In the future, our ability to become profitable will depend on the profitability of the San José and El Gallo 1 mines, our ability to bring the El Gallo 2 and Gold Bar projects into production and generate revenue sufficient to cover our costs and expenses, and our ability to advance, sell or otherwise monetize our other properties, including the Los Azules copper project. In pursuit of that objective, we will seek to identify additional mineralization that can be extracted economically at operating and exploration properties. For our non-operating properties that we believe demonstrate economic potential, we need to either develop our properties, locate and enter into agreements with third party operators, or sell the properties. We may suffer significant additional losses in the future and may never be profitable. Even if we do achieve profitability, we may not be able to sustain or increase profitability on a quarterly or annual basis.
Our business requires substantial capital investment and we may be unable to raise additional funding on favorable terms to develop additional mining operations.
We will need to obtain additional financing, either in the form of debt or equity financing, to fund development of additional mining operations such as the El Gallo 2 or Gold Bar projects and to continue our administrative activities. Our working capital balance, along with expected cash generated from mining operations at El Gallo 1 and any dividends received from MSC, is not expected to be sufficient to allow us to develop El Gallo 2, the next anticipated mine project, or to continue our operations indefinitely. Our ability to obtain necessary funding, in turn, depends upon a number of factors, including the state of the economy and applicable commodity prices. We may not be successful in obtaining the required financing for El Gallo 2 or other purposes, on terms that are favorable to us or at all, in which case, our ability to continue operating would be adversely affected. Failure to obtain such additional financing could result in delay or indefinite postponement of further exploration or potential development and the possible partial or total loss of our interest in certain properties.
12
The feasibility of mining at our El Gallo and Gold Bar properties has not been established in accordance with Industry Guide 7, and any funds spent by us on exploration and development could be lost.
A "reserve," as defined by Industry Guide 7 of the SEC, is that part of a mineral deposit which could be economically and legally extracted or produced at the time of the reserve determination. A reserve requires a SEC-compliant feasibility study or other report demonstrating with reasonable certainty that the deposit can be economically extracted and produced. Since we have not received a SEC-compliant report on any of our properties, we currently have no reserves as defined by Industry Guide 7, except for our 49% interest in the San José mine, and there are no assurances that we will be able to prove that there are reserves on our properties.
The mineralized material identified on our properties, including the El Gallo 1 mine where we are currently in production, does not and may never demonstrate economic viability. Substantial expenditures are required to establish reserves through drilling and additional study and there is no assurance that reserves will be established. The feasibility of mining at El Gallo, Gold Bar, or any other property has not been, and may never be, established. Whether a mineral deposit can be commercially viable depends upon a number of factors, including the particular attributes of the deposit, including size, grade, metallurgical recoveries and proximity to infrastructure; metal prices, which can be highly variable; and government regulations, including environmental and reclamation obligations. If we are unable to establish some or all of our mineralized material as proven or probable reserves in sufficient quantities to justify commercial operations, our investment in that property may be lost, and the market value of our securities may suffer.
We are required to prepare and file with the Canadian securities regulators estimates of mineralized material in accordance with NI 43-101. These standards are substantially different from the standards generally permitted to report reserve and other estimates in reports and other materials filed with the SEC. Under NI 43-101, we report measured, indicated and inferred resources, measurements which are generally not permitted in filings made with the SEC. U.S. investors are cautioned not to assume that all or any part of measured or indicated resources reported in our Canadian filings will ever be converted into Industry Guide 7 compliant reserves.
There are significant risks and uncertainty associated with construction, commencing or expanding production or changing production plans without a current feasibility, pre-feasibility or scoping study. As such, the El Gallo Complex and Gold Bar properties may ultimately be determined to lack one or more geological, engineering, legal, operating, economic, social, environmental, and other relevant factors reasonably required to serve as the basis for a final decision to successfully complete all or part of these projects.
The figures for our estimated mineralized material are based on interpretation and assumptions and may yield less mineral production under actual conditions than is currently estimated.
Unless otherwise indicated, mineralization figures presented in our filings with securities regulatory authorities including the SEC, news releases and other public statements that may be made from time to time are based upon estimates made by independent geologists and our internal geologists. When making determinations about whether to advance any of our projects to development, we must rely upon such estimated calculations as to the mineralized material and grades of mineralization on our properties. Until ore is actually mined and processed, mineralized material and grades of mineralization must be considered as estimates only.
These estimates are imprecise and depend upon geological interpretation and statistical inferences drawn from drilling and sampling analysis, which may prove to be unreliable. We cannot ensure that:
- •
- these estimates will be accurate;
- •
- mineralization estimates will be accurate; or
13
- •
- this mineralization can be mined or processed profitably.
Any material changes in mineral estimates and grades of mineralization may affect the economic viability of placing a property into production and such property's return on capital. There can be no assurance that minerals recovered in small scale tests will be recovered in large-scale tests under on-site conditions or in production scale. The estimates contained in our public filings have been determined and valued based on assumed future prices, cut-off grades and operating costs that may prove to be inaccurate. Extended declines in market prices for gold and/or silver may render portions of our mineralization estimates uneconomic and result in reduced reported mineralization or adversely affect the commercial viability of one or more of our properties. Any material reductions in estimates of mineralization, or of our ability to extract this mineralization, could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations or financial condition.
We own our 49% interest in the San José mine and the other 51% is owned Hochschild Mining plc., under the terms of an option and joint venture agreement ("OJVA"), and therefore we are unable to control all aspects of the exploration and development of and production from this property.
Our interest in the San José mine is subject to the risks normally associated with the conduct of joint ventures. A disagreement between joint venture partners on how to conduct business efficiently, the inability of joint venture partners to meet their obligations to the joint venture or third parties, or litigation arising between joint venture partners regarding joint venture matters could have a material adverse effect on the viability of our interests held through the joint venture.
Our operations in Argentina and Mexico are subject to changes in political conditions, regulations and crime.
Although all of our operations are subject to changes in political conditions, regulations and crime, the Company has substantial investments in Argentina and Mexico and is therefore subject to risks normally associated with the conduct of business in foreign countries. Further, both Argentina and Mexico have undergone significant government regulations with respect to, but not limited to, restrictions on production, price controls, export controls, currency remittance, importation of parts and supplies, income and other taxes, expropriation of property, foreign investment, maintenance of claims, environmental legislation, land use, land claims of local people, water use and mine safety. Changes, if any, in mining or investment policies or shifts in political attitude in any of the jurisdictions in which the Company operates may adversely affect the Company's operations or profitability. There also is the risk of political violence and increased social tension in both Mexico and Argentina as these countries have experienced periods of crime, and civil and labor unrest. Certain political and economic events such as acts, or failures to act, by a government authorities in Argentina and Mexico, and acts of political violence could have a material adverse effect on our ability to operate in the country.
With respect to our San José mine, there are risks relating to an uncertain or unpredictable political and economic environment in Argentina. For instance, Argentina defaulted on foreign debt repayments and on the repayment on a number of official loans to multinational organizations in 2002 and 2003, and defaulted again on its bonds in 2014 after failing to reach an agreement with certain of its bondholders. In 2008, the Argentine government also reassessed its policy and practice in respect of export duties and began levying export duties on mining companies operating in the country. In 2012, Argentina's President announced the nationalization of the majority stake of Yacimientos Petrolíferos Fiscales (YPF), Argentina's largest oil company. In 2013, Argentina's federal Income Tax Statute was amended to include a 10% income tax withholding on dividend distributions by Argentine corporations, and the capital gains exception for non-resident taxpayers was repealed. Although these particular changes have not affected the San José mine, there can be no assurance that the Argentine government will not unilaterally take other action which could have a material adverse effect on our projects in the country or that Argentina will continue to honor any fiscal agreements or tax stability rights provided to MSC.
14
There also exist current restrictions to imports and provisions relating to local sourcing of transports and substitution of imports of goods and services. These measures may impact the quality and supply of products and services required for our Argentine operations, including specifically the San José mine. Other unanticipated changes by the Argentine government could adversely impact the profitability of the San José mine or affect our ability to explore or develop all or part of our Los Azules project or other exploration properties in Argentina. Political and economic events such as acts, or failures to act, by a government authority in Argentina, and acts of political violence in Argentina, could have a material adverse effect on our ability to operate.
With respect to our El Gallo 1 mine in Mexico, in recent years, there has been a marked increase in the level of violence and crime relating to drug cartels in Sinaloa state, where we operate, and in other regions of Mexico. This may disrupt our ability to carry out exploration and mining activities and affect the safety and security of our employees and contractors. Our exploration and mining activities may be adversely affected in varying degrees by changing government regulations relating to the mining industry or shifts in political conditions, including as a result of periodic elections, that could increase the costs related to our activities or maintaining our properties.
Legislation has been enacted that significantly and adversely affects the mining industry.
In Argentina, in June 2013, the Province of Santa Cruz passed amendments to the Provincial Tax Code and Provincial Tax Law, which imposes a new tax on mining reserves in the Province. The law came into effect on July 5, 2013. The tax will amount to 1% of the value of mine reserves reported in feasibility studies and financial statements inclusive of variations resulting from ongoing operations. Regulations require that the tax be calculated on "measured" reserves, and MSC has interpreted this to mean "proven" reserves. The Province has not disputed this interpretation but has not provided further clarification on the definition of "measured" reserves, and the outcome is not clear at the time. MSC has filed a legal claim disputing the legality of the new tax and has paid the initial installments under protest.
In Mexico, in October 2013, the Mexican lower house passed a bill proposing a tax-deductible mining royalty of 7.5% on earnings before the deduction of interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization, along with an additional 0.5% on precious metals revenue for precious metals mining companies. In addition the long term corporate tax rate is expected to remain at 30% rather than being reduced to 28% as originally planned. The Mexican Senate approved the provisions of the Tax Reform on October 31, 2013. The effective date of the law was effective January 1, 2014.
Periodically, members of the U.S. Congress have introduced bills which would supplant or alter the provisions of the General Mining Law of 1872, which governs the unpatented claims that we control with respect to our U.S. properties. One such amendment has become law and has imposed a moratorium on the patenting of mining claims, which reduced the security of title provided by unpatented claims such as those on our U.S. properties. If additional legislation is enacted, it could substantially increase the cost of holding unpatented mining claims by requiring payment of royalties, and could significantly impair our ability to develop mineral estimates on unpatented mining claims. Such bills have proposed, among other things, to make permanent the patent moratorium, to impose a federal royalty on production from unpatented mining claims and to declare certain lands as unsuitable for mining. Although it is impossible to predict at this time what royalties may be imposed in the future, the imposition of such royalties could adversely affect the potential for development of such mining claims, and the economics of existing operating mines on federal unpatented mining claims. Passage of such legislation could adversely affect our business.
15
Recent Argentine foreign exchange regulations and export revenue repatriation requirements could adversely affect our liquidity and operations.
In October 2011, Argentina announced a decree under which a previously granted exemption was eliminated, therefore requiring mining companies to repatriate mining revenues to Argentine currency before distributing revenue either locally or overseas. Fluctuation in the value of the Argentine peso as a result of the repatriation requirement and the repatriation requirement may create inefficiencies in our ability to transfer our revenue from Argentina and result in substantial transaction costs. Further, there are additional transaction costs imposed by the central bank for transferring funds from and within Argentina.
In April 2012, Argentina announced further rules which initially reduced the number of days mining companies have to repatriate funds relating to exports sales to 15 days and then subsequently in July 2012, relaxed the repatriation requirement to 79 days on the export of doré and 180 days on the sale of concentrates for certain mining companies including MSC which operates the San José mine.
Further, under current regulations, Argentine residents, including MSC, are not allowed to purchase in the foreign exchange market relevant amounts of foreign currency without a specific purpose, which includes foreign currency to be held in Argentina and other cross-border transfers. While Argentine companies may freely acquire and transfer foreign currency abroad to pay profits and dividends to foreign shareholders (provided that they relate to final and audited financial statements), in an attempt to stop capital flight and control the dollar, the government has continued restricting, by means of a "de facto" measure, the transfer of dividends abroad.
These restrictions and any additional restrictions on the Argentine foreign exchange regime or export repatriation requirements could affect our liquidity and operations in Argentina, and our ability to access such funds.
Our business is subject to U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and similar worldwide anti-bribery laws, a breach or violation of which could lead to civil and criminal fines and penalties, loss of licenses or permits and reputational harm.
We operate in certain jurisdictions that have experienced governmental and private sector corruption to some degree, and, in certain circumstances, strict compliance with anti-bribery laws may conflict with certain local customs and practices. For example, the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and anti-bribery laws in other jurisdictions, generally prohibit companies and their intermediaries from making improper payments for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business or other commercial advantage, and often carry substantial penalties. There can be no assurance that our internal control policies and procedures always will protect it from recklessness, fraudulent behavior, dishonesty or other inappropriate acts committed by the Company's affiliates, employees or agents. As such, our corporate policies and processes may not prevent all potential breaches of law or other governance practices. Violations of these laws, or allegations of such violations, could lead to civil and criminal fines and penalties, litigation, and loss of operating licenses or permits, and may damage the Company's reputation, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial position and results of operations or cause the market value of our common shares to decline.
We are subject to foreign currency risk.
While we transact most of our business in U.S. dollars, expenses, such as labor, operating supplies, and property and equipment, are denominated in Canadian dollars, Mexican pesos or Argentine pesos. As a result, currency exchange fluctuations may impact our operating costs. The appreciation of non-U.S. dollar currencies against the U.S. dollar increases costs and the cost of purchasing property and equipment in U.S. dollar terms in Mexico, Argentina and Canada, which can adversely impact our operating results and cash flows. Conversely, a depreciation of non-U.S. dollar currencies usually
16
decreases operating costs and property and equipment purchases in U.S. dollar terms in foreign countries.
The value of cash and cash equivalents denominated in foreign currencies also fluctuates with changes in currency exchange rates. Appreciation of non-U.S. dollar currencies results in a foreign currency gain on such investments and a depreciation in non-U.S. dollar currencies results in a loss. We have not utilized market risk sensitive instruments to manage our exposure to foreign currency exchange rates but may in the future actively manage our exposure to foreign currency exchange rate risk. We also hold portions of our cash reserves in Canadian, Mexican and Argentine currency.
Fluctuating precious metals and copper prices could negatively impact our business.
The potential for profitability of our gold and silver mining operations and the value of our mining properties are directly related to the market price of gold, silver and copper. The price of gold, silver and copper may also have a significant influence on the market price of our common stock. The market price of gold and silver historically has fluctuated significantly, including a significant downward trend from 2012 to 2014, and is affected by numerous factors beyond our control. These factors include supply and demand fundamentals, expectations with respect to the rate of inflation, the relative strength of the U.S. dollar and other currencies, interest rates, gold and silver sales and loans by central banks, forward sales by metal producers, accumulation and divestiture by exchange traded funds, global or regional political, economic or banking crises, and a number of other factors. The market price of silver is also affected by industrial demand. The selection of a property for exploration or development, the determination to construct a mine and place it into production, and the dedication of funds necessary to achieve such purposes are decisions that must be made long before the first revenues, if any, from production will be received. Price fluctuations between the time that such decisions are made and the commencement of production can have a material adverse effect on the economics of a mine.
The volatility of mineral prices represents a substantial risk which no amount of planning or technical expertise can fully eliminate. In the event mineral prices decline and remain low for prolonged periods of time, we might be unable to develop our properties, which may adversely affect our results of operations, financial performance and cash flows. Our results of operations have been and could continue to be materially and adversely affected by the impairment of assets. An asset impairment charge may result from the occurrence of unexpected adverse events that impact our estimates of expected cash flows generated from our producing properties or the market value of our non-producing properties. The deteriorating economic outlook for companies in the mineral exploration and extraction sector and declines in commodity prices are likely to reduce the recoverable amount of our investment in MSC, El Gallo 1 mine, and other, non-producing mineral property interests including the Los Azules project, and therefore may increase our impairment charges in the future.
The volatility in gold, silver and copper prices is illustrated by the following table, which sets forth, for the periods indicated, the average market prices in U.S. dollars per ounce of gold and silver, based on the average daily London P.M. fix, and per pound of copper based on the London Metal Exchange Grade A copper settlement price.
Metal
|
2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Gold |
$ | 1,224 | $ | 1,572 | $ | 1,669 | $ | 1,411 | $ | 1,266 | ||||||
Silver |
20.19 | 35.12 | 31.15 | 23.79 | 19.08 | |||||||||||
Copper |
3.42 | 4.00 | 3.61 | 3.32 | 3.11 | |||||||||||
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, and as of the date of this report, mineral prices have continued to experience a downward trend, especially with respect to silver and copper. As at March 2, 2015, gold, silver and copper prices were of $1,241 per ounce, $17.22 per ounce, and $2.58 per pound,
17
respectively. Should these downward trends continue, there is a possibility that we may record additional impairment charges in 2015 or future years.
Increased operating and capital costs could affect our profitability.
Costs at any particular mining location are subject to variation due to a number of factors, such as variable ore grade, changing metallurgy and revisions to mine plans in response to the physical shape and location of the ore body, as well as the age and utilization rates for the mining and processing-related facilities and equipment. In addition, costs are affected by the price and availability of input commodities, such as fuel, electricity, labor, chemical reagents, explosives, steel and concrete and mining and processing-related equipment and facilities. Reported costs may also be affected by changes in accounting standards. A material increase in costs at any significant location could have a significant effect on our profitability and operating cash flow.
We could have significant increases in capital and operating costs over the next several years in connection with the development of new projects in challenging jurisdictions and in the sustaining and/or expansion of existing mining and processing operations. Costs associated with capital expenditures have escalated on an industry-wide basis over the last several years, as a result of factors beyond our control, including the prices of oil, steel and other commodities and labor, as well as the demand for certain mining and processing equipment. Increased capital expenditures may have an adverse effect on the profitability of and cash flow generated from existing operations, as well as the economic returns anticipated from new projects.
Our estimated timetables to achieve production for the El Gallo 2 and Gold Bar properties may not be accurate.
The final decision to proceed with the construction of our El Gallo 2 project, for which a feasibility study was completed in 2012, has not been made. The Company plans to complete its cost savings studies and review financing alternatives. Any decision to proceed would be based on silver prices and securing financing on terms that we believe are more favorable to us than those that were available to us at the time of filing this report. With respect to the Gold Bar project, based on the 2012 preliminary feasibility study, we believe production may be achieved in 2016. However, the Gold Bar preliminary feasibility study is preliminary in nature and is subject to change due to factors within and outside of our control. There is no certainty that the economics estimated in the preliminary feasibility study will be realized or that we will be able to begin production within the timelines estimated, if at all.
Further, we may also be unable to obtain the necessary permits in a timely manner, on reasonable terms or on terms that provide us sufficient resources to develop our properties. These and other factors may cause us to delay production at El Gallo 2 and our Gold Bar properties beyond our current expectations, or cancel our plans entirely.
Development at Los Azules presents development challenges that may negatively affect, if not completely negate, the feasibility of development of the property.
The Los Azules property is located in a remote location that is accessed by 75 miles (120 kilometers) of unimproved dirt road with eight river crossings and two mountain passes both above 13,451 feet (4,100 meters). Even assuming that technical difficulties associated with this remote location can be overcome, the capital costs may make the project uneconomical. According to a new NI 43-101 Preliminary Economic Assessment ("PEA") filed on November 7, 2013 with an effective date of August 1, 2013, capital costs were estimated to be $3.9 billion initially and $5.5 billion over the life of the mine with an accuracy target of plus or minus 35%. In order for Los Azules to be economically feasible for development, the price of copper would have to achieve and remain at a level high enough
18
to justify the high capital costs estimated for the project. There can be no assurance that these capital cost estimates are accurate, given the inflationary pressure in the mining industry and in Argentina in particular. If the long term price of copper were to remain low or decrease significantly below the current price or capital cost estimates increase significantly, Los Azules may not be feasible for development, and we may have to write-off the remaining carrying value of the asset. Furthermore, the project's economic feasibility has not yet been demonstrated through a full feasibility study. The PEA is preliminary in nature, includes NI 43-101 mineral resources that are considered too speculative geologically to have economic considerations applied to them that would allow them to be categorized as mineral reserves either under Industry Guide 7 or NI 43-101, and there is no certainty that the PEA will be realized. Finally, we may not be able to raise sufficient capital to develop the property; we may not receive the required permits or environmental approvals; we may not be able to construct the necessary power and infrastructure assets; and, we may not be able to attract qualified workers to build such a project, any of which could result in the delay or indefinite postponement of development at the property. Such a result would have a material adverse effect on our Company.
We may acquire additional exploration stage properties and we may face negative reactions if reserves are not located on acquired properties.
We have in the past and may in the future acquire additional exploration stage properties. There can be no assurance that we have or will be able to complete the acquisition of such properties at reasonable prices or on favorable terms and that reserves will be identified on any properties that we acquire. We may also experience negative reactions from the financial markets if we are unable to successfully complete acquisitions of additional properties or if reserves are not located on acquired properties. These factors may adversely affect the trading price of our common stock or our financial condition or results of operations.
The nature of mineral exploration and production activities involves a high degree of risk and the possibility of uninsured losses that could materially and adversely affect our operations.
Exploration for and production of minerals is highly speculative and involves greater risk than many other businesses. Many exploration programs do not result in the discovery of mineralization, and any mineralization discovered may not be of sufficient quantity or quality to be profitably mined. Few properties that are explored are ultimately advanced to production. Our current exploration efforts are, and future development and mining operations we conduct will be, subject to all of the operating hazards and risks normally incident to exploring for and developing mineral properties, such as, but not limited to:
- •
- economically insufficient mineralized material;
- •
- fluctuations in production costs that may make mining uneconomical;
- •
- availability of labor, contractors, engineers, power, transportation and infrastructure;
- •
- labor disputes;
- •
- potential delays related to social, public health, and community issues;
- •
- unanticipated variations in grade and other geologic problems;
- •
- environmental hazards;
- •
- water conditions;
- •
- difficult surface or underground conditions;
- •
- industrial accidents;
19
- •
- metallurgical and other processing problems;
- •
- mechanical and equipment performance problems;
- •
- failure of pit walls or dams;
- •
- unusual or unexpected rock formations;
- •
- personal injury, fire, flooding, cave-ins and landslides; and
- •
- decrease in reserves or mineralized material due to a lower silver, gold or copper price.
Any of these risks can materially and adversely affect, among other things, the development of properties, production quantities and rates, costs and expenditures, potential revenues and production dates. We currently have no insurance to guard against any of these risks, except in very limited circumstances. If we determine that capitalized costs associated with any of our mineral interests are not likely to be recovered, we would incur a write-down of our investment in these interests. All of these factors may result in losses in relation to amounts spent which are not recoverable.
We do not insure against all risks to which we may be subject in our operations.
While we currently maintain insurance to insure against general commercial liability claims and physical assets at our properties in Argentina, Mexico, and the United States, we do not maintain insurance to cover all of the potential risks associated with our operations. Our other exploration projects have no existing infrastructure for which we insure. We may also be unable to obtain insurance to cover other risks at economically feasible premiums or at all. Insurance coverage may not continue to be available, or may not be adequate to cover liabilities. We might also become subject to liability for environmental, pollution or other hazards associated with mineral exploration and production which may not be insured against, which may exceed the limits of our insurance coverage or which we may elect not to insure against because of premium costs or other reasons. Losses from these events may cause us to incur significant costs that could materially adversely affect our financial condition and our ability to fund activities on our property. A significant loss could force us to reduce or terminate our operations.
Shortages of critical parts and equipment may adversely affect our operations and development projects.
The mining industry has been impacted, from time to time, by increased demand for critical resources such as input commodities, drilling equipment, trucks, shovels and tires. These shortages have, at times, impacted the efficiency of our operations, and resulted in cost increases and delays in construction of projects; thereby impacting operating costs, capital expenditures and production and construction schedules.
Our operations are subject to permitting requirements which could require us to delay, suspend or terminate our operations on our mining properties.
Our mining operations, including ongoing exploration drilling programs, require permits from the state and federal governments, including permits for the use of water and for drilling wells for water. We may be unable to obtain these permits in a timely manner, on reasonable terms or on terms that provide us sufficient resources to develop our properties, or at all. Even if we are able to obtain such permits, the time required by the permitting process can be significant. If we cannot obtain or maintain the necessary permits, or if there is a delay in receiving these permits, our timetable and business plan for exploration of our properties will be adversely affected, which may in turn adversely affect our results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and market price of our securities.
20
Title to mineral properties can be uncertain, and we are at risk of loss of ownership of one or more of our properties.
Our ability to explore and operate our properties depends on the validity of our title to that property. Our U.S. mineral properties include leases of unpatented mining claims, as well as unpatented mining and millsite claims which we control directly. Unpatented mining claims provide only possessory title and their validity is often subject to contest by third parties or the federal government, which makes the validity of unpatented mining claims uncertain and generally more risky. Our concessions in Mexico are subject to continuing government regulation and failure to adhere to such regulations will result in termination of the concession. Similarly, under Argentine Law, failure to comply with applicable conditions may result in the termination of the concession. Uncertainties inherent in mineral properties relate to such things as the sufficiency of mineral discovery, proper posting and marking of boundaries, assessment work and possible conflicts with other claims not determinable from public record. We have not obtained title opinions covering our entire property, with the attendant risk that title to some claims, particularly title to undeveloped property, may be defective. There may be valid challenges to the title to our property which, if successful, could impair development and/or operations.
We cannot ensure that we will have an adequate supply of water to complete desired exploration or development of our mining properties.
Our mining operations require significant quantities of water for mining, ore processing and related support facilities. Our operations in Argentina, Mexico and the United States are in areas where water is scarce and competition among users for continuing access to water is significant. Continuous production at our mines is dependent on our ability to maintain our water rights and claims and to defeat claims adverse to our current water uses in legal proceedings. Although each of our operations currently has sufficient water rights and claims to cover its operational demands, we cannot predict the potential outcome of pending or future legal proceedings relating to our water rights, claims and uses. Water shortages may also result from weather or environmental and climate impacts out of the Company's control.
Our continuing reclamation obligations at Tonkin, El Gallo and other properties could require significant additional expenditures.
We are responsible for the reclamation obligations related to disturbances located on all of our properties, including the Tonkin Complex. We have posted a surety bond in the amount of the estimated reclamation obligation at the Tonkin Complex. We submitted a mine closure plan to the BLM for the Tonkin Complex during the fourth quarter of 2010. The closure plan for the Tonkin mine is currently undergoing an environmental review pursuant to the National Environmental Policy Act. The plan was accepted by the NDEP in March 2012 but is still under review by the BLM pursuant to the National Environmental Policy Act. It is possible that reclamation plan cost estimates and bonding requirements may increase as a result of this review. The Company, however, is unable to meaningfully estimate possible increases at this time. We have not posted a bond in Mexico relating to the El Gallo Complex, as none is required but have recorded a liability based on the estimated amount of our reclamation obligations. There is a risk that any surety bond or recorded liability, even if increased based on the analysis and work performed to update the reclamation obligations, could be inadequate to cover the actual costs of reclamation when carried out. The satisfaction of bonding requirements and continuing reclamation obligations will require a significant amount of capital. There is a risk that we will be unable to fund these additional bonding requirements, that the surety bonds may no longer be accepted by the governmental agencies as satisfactory reclamation coverage, in which case we would be required to replace the surety bonding with cash, and further, that the regulatory authorities may increase reclamation and bonding requirements to such a degree that it would not be commercially
21
reasonable to continue exploration activities, which may adversely affect our results of operations, financial performance and cash flows.
Our ongoing operations and past mining activities are subject to environmental risks, which could expose us to significant liability and delay, suspension or termination of our operations.
All phases of our operations are subject to Argentine, Mexican and American federal, state and local environmental regulation. These regulations mandate, among other things, the maintenance of air and water quality standards and land reclamation. They also set forth limitations on the generation, transportation, storage and disposal of solid and hazardous waste, including cyanide. Environmental legislation is evolving in a manner which will require stricter standards and enforcement, increased fines and penalties for non-compliance, more stringent environmental assessments of proposed projects, and a heightened degree of responsibility for us and our officers, directors and employees. Future changes in environmental regulation, if any, may adversely affect our operations, make our operations prohibitively expensive, or prohibit them altogether. Environmental hazards may exist on our properties that are unknown to us at the present and that have been caused by us, or previous owners or operators, or that may have occurred naturally. Mining properties from the companies we have acquired may cause us to be liable for remediating any damage that those companies may have caused. The liability could include response costs for removing or remediating the release and damage to natural resources, including ground water, as well as the payment of fines and penalties. Failure to comply with applicable environmental laws, regulations and permitting requirements may also result in enforcement actions thereunder, including orders issued by regulatory or judicial authorities, causing operations to cease or be curtailed, and may include corrective measures requiring capital expenditures, installation of additional equipment, or remedial actions.
We have transferred our interest in several mining properties over past years, some of which are now being operated by third parties. Under applicable U.S. federal and state environmental laws, as prior owner of these properties, we may be liable for remediating any damage that we may have caused. The liability could include response costs for removing or remediating the release and damage to natural resources, including ground water, as well as the payment of fines and penalties.
Due to an increased level of non-governmental organization activity targeting the mining industry, the potential for the government to delay the issuance of permits or impose new requirements or conditions upon mining operations may be increased. Any changes in government policies may be costly to comply with and may delay mining operations. Future changes in such laws and regulations, if any, may adversely affect our operations, make our operations prohibitively expensive, or prohibit them altogether. If our interests are materially adversely affected as a result of a violation of applicable laws, regulations, or permitting requirements or a change in applicable law or regulations, it would have a significant negative impact on the value of our company and could have a significant impact on our stock price.
Global climate change is an international concern, and could impact our ability to conduct future operations.
Global climate change is an international issue and receives a substantial amount of publicity. We would expect that the imposition of international treaties or Argentina, Mexican, and American federal, state, provincial or local laws or regulations pertaining to mandatory reductions in energy consumption or emissions of greenhouse gasses could affect the feasibility of our mining projects and increase our operating costs.
Our industry is highly competitive, attractive mineral lands are scarce, and we may not be able to obtain quality properties.
We compete with many companies in the mining industry, including large, established mining companies with substantial capabilities, personnel and financial resources. There is a limited supply of
22
desirable mineral lands available for claim staking, lease or acquisition in Argentina, Mexico and the United States, and other areas where we may conduct exploration activities. We may be at a competitive disadvantage in acquiring mineral properties, since we compete with these individuals and companies, many of which have greater financial resources and larger technical staffs than we do. From time to time, specific properties or areas which would otherwise be attractive to us for exploration or acquisition may be unavailable to us due to their previous acquisition by other companies or our lack of financial resources. Competition in the industry is not limited to the acquisition of mineral properties but also extends to the technical expertise to find, advance, and operate such properties; the labor to operate the properties; and the capital for the purpose of funding such properties. Many competitors not only explore for and mine precious metals, but conduct refining and marketing operations on a world-wide basis. Such competition may result in our Company being unable not only to acquire desired properties, but to recruit or retain qualified employees or to acquire the capital necessary to fund our operation and advance our properties. Our inability to compete with other companies for these resources would have a material adverse effect on our results of operation, financial condition and cash flows.
Our lack of operating experience may cause us difficulty in managing our growth.
Our management team, as a whole, has limited experience in developing and operating a mine. We are currently working towards the development of El Gallo 2 in Mexico and our Gold Bar project in Nevada. If we are unable to successfully finance and place these projects into production, our stock price may suffer and you may lose some or all of your investment. Our ability to manage the anticipated growth that we expect will accompany placing one or more of those properties into production will require us to improve and expand our management and our operational systems and controls. If our management is unable to manage growth effectively, our business and financial condition would be materially harmed. In addition, if rapid growth occurs, it may strain our operational, managerial and financial resources.
To the extent that we seek to expand our operations and increase our reserves through acquisitions, we may experience issues in executing acquisitions or integrating acquired operations.
From time to time, we examine opportunities to make selective acquisitions in order to provide increased returns to our shareholders and to expand our operations and reported reserves and, potentially, generate synergies. The success of any acquisition would depend on a number of factors, including, but not limited to:
- •
- Identifying suitable candidates for acquisition and negotiating acceptable terms;
- •
- Obtaining approval from regulatory authorities and potentially the Company's shareholders;
- •
- Maintaining our financial and strategic focus and avoiding distraction of management during the process of integrating the acquired
business;
- •
- Implementing our standards, controls, procedures and policies at the acquired business and addressing any pre-existing liabilities or
claims involving the acquired business; and
- •
- To the extent the acquired operations are in a country in which we have not operated historically, understanding the regulations and challenges of operating in that new jurisdiction.
There can be no assurance that we will be able to conclude any acquisitions successfully, or that any acquisition will achieve the anticipated synergies or other positive results. Any material problems that we encounter in connection with such an acquisition could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial position.
23
We rely on contractors to conduct a significant portion of our operations and construction projects.
A significant portion of our operations and construction projects are currently conducted in whole or in part by contractors, including specifically our mining contractor at the El Gallo 1 mine. As a result, our operations are subject to a number of risks, some of which are outside our control, including:
- •
- Negotiating agreements with contractors on acceptable terms;
- •
- The inability to replace a contractor and its operating equipment in the event that either party terminates the agreement;
- •
- Reduced control and oversight over those aspects of operations which are the responsibility of the contractor;
- •
- Failure of a contractor to perform under its agreement;
- •
- Interruption of operations or increased costs in the event that a contractor ceases its business due to insolvency or other unforeseen
events;
- •
- Failure of a contractor to comply with applicable legal and regulatory requirements, to the extent it is responsible for such
compliance; and
- •
- Problems of a contractor with managing its workforce, labor unrest or other related employment issues.
In addition, we may incur liability to third parties as a result of the actions of our contractors. The occurrence of one or more of these risks could adversely affect our results of operations and financial position.
We depend on a limited number of personnel and the loss of any of these individuals could adversely affect our business.
Our company is dependent on key management, namely our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer; our Chief Financial Officer, our Chief Operating Officer; our Managing Director, our Vice President, Argentina; our Vice President, Projects; our Vice President, Corporate Development; and our Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary. Robert R. McEwen, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, is responsible for strategic direction and the oversight of our business. Nathan Stubina, our Managing Director; William Faust, our Chief Operating Officer; Simon Quick, our Vice President, Projects; and Andrew Elinesky, our Vice President, Argentina, oversee project development in Mexico, Nevada and Argentina. Perry Y. Ing, our Chief Financial Officer, is responsible for our public reporting and administrative functions. Craig Stanley, our Vice President, Corporate Development, is responsible for corporate development activities, including the evaluation of potential transactions. Nils F. Engelstad, our Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary, is responsible for overseeing the legal and corporate affairs of our Company. We rely heavily on these individuals for the conduct of our business. The loss of any of these officers may significantly and adversely affect our business. In that event, we would be forced to identify and retain an individual to replace the departed officer. We may not be able to replace one or more of these individuals on terms acceptable to us. We have no life insurance on the life of any officer.
Some of our directors may have conflicts of interest as a result of their involvement with other natural resource companies.
Some of our directors are directors or officers of other natural resource or mining-related companies, or may be involved in related pursuits that could present conflicts of interest with their roles at our Company. These associations may give rise to conflicts of interest from time to time. In the event that any such conflict of interest arises, a director who has such a conflict is required to disclose the conflict to the other directors and may be required to abstain from voting on the matter.
24
The laws of the State of Colorado, our Articles of Incorporation and agreements with certain officers and directors may protect our directors from certain types of lawsuits.
The laws of the State of Colorado provide that our directors will not be liable to us or our shareholders for monetary damages for all but certain types of conduct as directors of the Company. Our Articles of Incorporation permit us to indemnify our directors and officers against all damages incurred in connection with our business to the fullest extent provided or allowed by law, including through stand-alone indemnity agreements. We have also entered into indemnification agreements with our executive officers and directors which require that we indemnify them against certain liabilities incurred by them in their capacity as such. The exculpation provisions may have the effect of preventing shareholders from recovering damages against our directors caused by their negligence, poor judgment or other circumstances. The indemnification provisions may require us to use our limited assets to defend our directors and officers against claims, including claims arising out of their negligence, poor judgment, or other circumstances.
We are currently the subject of an inquiry by the SEC Division of Enforcement with respect to the accounting treatment of Los Azules.
We are currently the subject of an inquiry by the SEC's Division of Enforcement requesting certain information from us (the "Inquiry"). The Inquiry commenced in late November 2013. The SEC has stated that the Inquiry should not be construed as an indication by the SEC or its staff that any violation of law has occurred, nor should it be considered a reflection on any person, entity or security. Based on our assessment of the questions asked and documents requested by the SEC, we believe the Inquiry concerns the accounting treatment of the Company's Los Azules project for the period ending June 30, 2013 ("Q2 2013") and specifically why the Los Azules project was not classified as "held for sale" pursuant to ASC 360, Property, Plant, and Equipment, and why we did not record an impairment relating to Los Azules during Q2 2013, at which time the Company's precious metals assets in Argentina were impaired and during which time the Company was engaging in a sales process for the Los Azules project.
The Company conducts a review of potential impairment triggers for all its mineral projects on a quarterly basis. The Company found no indicators of impairment in Q1 2013. In Q2 2013, there were adverse changes in the economic environment for mining companies, which was considered to be an indicator of impairment under ASC 360-10-35-21a. Consequently, the Company performed impairment tests for all its Argentine assets, including Los Azules. The results of the impairment tests indicated that, although certain of our precious metal assets in Argentina were impaired, there was no impairment for Los Azules. In Q3 2013, no indicators of impairment were identified for Los Azules. For Q4 2013, annual impairment testing was performed on all assets and no impairment of Los Azules was recorded. In Q1 2014, no indicators of impairment were identified for Los Azules. In Q2 2014, as described in Note 6, Mineral Property Interests and Asset Retirement Obligations, indicators of impairment for Los Azules were identified due to the sale of Lumina Copper Corp.'s Taca Taca copper project to First Quantum Minerals Ltd. The Company consequently recorded an impairment charge of $120.4 million relating to Los Azules during Q2 2014. In Q3 2014, no indicators of impairment were identified for Los Azules. For Q4 2014, annual impairment testing was performed on all assets. The Company noted a further decline in the observed market value of comparable transactions, which the Company considered to be an indicator of impairment. As a result, the Company recorded an additional impairment of $107.9 million in Q4 2014. Refer to Note 6, Mineral Property Interests and Asset Retirement Obligations for further details.
The Company believes that the "asset held for sale" criteria under ASC 360 were never satisfied for Los Azules in any of the periods presented above. In addition, our financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 were audited by our independent registered public accounting firm,
25
KPMG LLP, who issued an unqualified opinion on our 2014 and 2013 annual consolidated financial statements.
We have cooperated fully and intend to continue to cooperate fully with the SEC. Following a meeting with the SEC in Washington, DC on April 7, 2014, we delivered our responses to the SEC's third request for documents in late April 2014. On September 30, 2014, we received a fourth request for documents. We delivered our responses to that request on October 30, 2014. At this point, we are unable to predict what, if any, consequences the Inquiry may have on us. However, the Inquiry may continue to result in considerable legal expenses and divert management's attention from other business concerns. If the SEC were to commence legal action, we could be required to pay significant penalties or other amounts and could become subject to injunctions, an administrative cease and desist order or other equitable remedies. The resolution of the Inquiry could require the filing of restatements of our prior financial statements or require that we take other actions not presently contemplated. We can provide no assurances as to the outcome of the Inquiry, and the outcome could have a material adverse impact on our business.
We are subject to litigation risks.
All industries, including the mining industry, are subject to legal claims, with and without merit. Defense and settlement costs can be substantial, even with respect to claims that have no merit. Due to the inherent uncertainty of the litigation process, the resolution of any particular legal proceeding, including regulatory proceedings, could have a material adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations.
Risks Relating to Our Common Stock
A small number of existing shareholders own a significant portion of McEwen Mining common stock, which could limit your ability to influence the outcome of any shareholder vote.
As of March 2, 2015, Mr. McEwen beneficially owned approximately 25%, or 75.2 million shares, of the 300.1 million shares of McEwen Mining common stock (assuming all outstanding Exchangeable shares not held by McEwen Mining or its subsidiaries are exchanged for an equivalent amount of McEwen Mining common stock). Under our Articles of Incorporation and the laws of the State of Colorado, the vote of the holders of a majority of the shares voting at a meeting at which a quorum is present is generally required to approve most shareholder action. As a result, Mr. McEwen will be able to significantly influence the outcome of shareholder votes for the foreseeable future, including votes concerning the election of directors, amendments to our Articles of Incorporation or proposed mergers, acquisitions or other significant corporate transactions.
Our stock price may be volatile, and as a result you could lose all or part of your investment.
In addition to other risk factors identified herein and to volatility associated with equity securities in general, the value of your investment could decline due to the impact of any of the following factors upon the market price of our common stock:
- •
- Changes in the worldwide price for gold, silver and/or copper;
- •
- Volatility in the equities markets;
- •
- Disappointing results from our exploration or production efforts;
- •
- Producing at rates lower than those targeted;
- •
- Political and regulatory risks;
- •
- Weather conditions, including unusually heavy rains;
- •
- Failure to meet our revenue or profit goals or operating budget;
26
- •
- Decline in demand for our common stock;
- •
- Downward revisions in securities analysts' estimates or changes in general market conditions;
- •
- Technological innovations by competitors or in competing technologies;
- •
- Investor perception of our industry or our prospects;
- •
- Actions by government central banks; and
- •
- General economic trends.
During the 2014 calendar year the price of our stock has ranged from a low of $0.92 to a high of $3.56. In addition, stock markets in general have experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations and the market prices of securities have been highly volatile. These fluctuations are often unrelated to operating performance and may adversely affect the market price of our common stock. As a result, you may be unable to resell your shares at a desired price.
We have never paid a dividend on our common stock and we do not anticipate paying one in the foreseeable future.
We have not paid a dividend on our common stock to date, and we do not expect to be in a position to pay dividends in the foreseeable future. Any earnings from the San José mine will likely be retained to finance our growth. Any future dividends will depend upon any future earnings, our then-existing financial requirements and other factors, and will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors.
Gain recognized by non-U.S. holders and non-U.S. persons holding any interest in the Company other than solely as a creditor (including, for example, interests in the form of our convertible debt, if any) on the sale or other disposition of our securities may be subject to U.S. federal income tax.
We believe that we currently are a "United States real property holding corporation" under section 897(c) of the Internal Revenue Code (the "Code"), or USRPHC, and that there is a substantial likelihood that we will continue to be a USRPHC in the future. Subject to certain exceptions, securities (other than securities that provide no interest in a corporation other than solely as a creditor) issued by a corporation that has been a USRPHC at any time during the preceding five years (or the non-U.S. holder's holding period for such securities, if shorter) are treated as U.S. real property interests, or USRPIs, and a gain recognized by a non-U.S. holder on the sale or other disposition of a USRPI is subject to regular U.S. federal income tax, on a net basis at graduated rates, as if such gain were effectively connected with the conduct by such holder of a U.S. trade or business. If gain recognized by a non-U.S. holder from the sale or other disposition of McEwen Mining common stock or other securities is subject to regular net basis income tax under these rules, the transferee of such McEwen Mining common stock or other securities may be required to deduct and withhold a tax equal to 10% of the gross amount paid to the non-U.S. holder with respect to the sale or other disposition, unless certain exceptions apply. Any tax withheld may be credited against the U.S. federal income tax owed by the non-U.S. holder for the year in which the sale or other disposition occurs.
The exercise of options and the future issuances of McEwen Mining common stock will dilute current shareholders and may reduce the market price of McEwen Mining common stock.
Under certain circumstances, McEwen Mining's board of directors (the "McEwen Mining Board") has the authority to authorize the offer and sale of additional securities without the vote of or notice to existing shareholders. McEwen Mining may issue equity in the future in connection with acquisitions, strategic transactions or for other purposes. Based on the need for additional capital to fund expected growth, it is likely that we will issue additional securities to provide such capital and that such additional issuances may involve a significant number of shares of McEwen Mining common stock.
27
Issuance of additional securities in the future will dilute the percentage interest of existing shareholders of McEwen Mining and may reduce the market price of McEwen Mining common stock and other securities.
Furthermore, the sale of a significant amount of McEwen Mining common stock by any selling security holders, specifically Mr. Robert R. McEwen ("Mr. McEwen"), our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, may depress the price of McEwen Mining common stock. As a result, you may lose all or a portion of your investment.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
We classify our mineral properties into two categories: "Production Properties" and "Exploration Properties". Our designation of certain properties as "Production Properties" should not suggest that we have proven or probable reserves at those properties as defined by the SEC. Our significant production and exploration properties are described below.
Production Properties
San José Mine, Argentina (49%)
For detailed information on the San José mine production statistics and financial results, refer to Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
Overview and History
The San José mine is an underground mine located in Santa Cruz Province, Argentina, and operated by a subsidiary of Hochschild, MSC. The San José mine is part of a larger property, which covers a total area of approximately 730 sq. miles. (1,892 sq. km) and consists of 108 mining concessions (consisting of 19 Minas or approved mining claims; 79 Manifestaciones de Descubrimiento, or claims that are in the application process for mining claim status; and 10 Cateos, or claims that are for exploration only). This includes the mineral rights that were transferred to MSC pursuant to a vend-in agreement between the Company and Hochschild (described in further detail in Item 2—Properties, Other Argentina Properties, below), which was completed in October 2013. Under this agreement, we agreed to contribute to MSC the mining rights to a certain number of our Santa Cruz exploration properties, totaling approximately 50,000 hectares, with Hochschild also contributing to MSC certain of its mineral properties located in the same region, totaling approximately 89,200 hectares. The registration of title change for these 57 mining concessions, consisting of 46 Manifestaciones de Descubrimiento, and 11 Cateos,(claims that are for exploration only) were finalized in the second quarter of 2014.
We acquired our interest in this property in connection with the acquisition of Minera Andes in January 2012. The property was acquired by Minera Andes in 1997, following completion of a regional geological study. Minera Andes embarked on an exploration program from 1997 to 2001, which led to the discovery of the silver and gold bearing Huevos Verdes and Saavedra West Zones. In March 2001 (and subsequently amended by agreements dated May 14, 2002, August 27, 2002, September 10, 2004, and September 17, 2010), an option and joint venture agreement was signed between Minera Andes (49%) and Hochschild (51%) covering the San José property. Under the terms of the OJVA, a subsidiary of Hochschild acquired a majority interest in the property and title to the San José property and the San José mine is held by MSC, the holding and operating company set up under the terms of the OJVA. MSC has purchased the land and corresponding occupation rights that are necessary to conduct its operations. All of the known mineralized zones, mineral resources and mineral reserves and active mine workings, existing tailing ponds and waste are within MSC's concessions.
28
Location and Access
The San José property is located in the District of Perito Moreno, in Santa Cruz, Argentina, lying approximately between latitude 46°41'S and 46°47'S and longitude 70°17'W and 70°00'W. The mine is 1,087 miles (1,750 kilometers) south-southwest of Buenos Aires and 217 miles (350 kilometers) southwest of the Atlantic port of Comodoro Rivadavia. The principal access route to the San José property is an unsealed dirt road section of 20 miles (32 kilometers) and then tarmac road to the port of Comodoro Rivadavia, a total distance of 217 miles (350 kilometers). Comodoro Rivadavia has scheduled national air services to Buenos Aires, the capital of Argentina, with international air connections. The nearest town is Perito Moreno, which is approximately 19 miles (30 kilometers) west of the San José property.
The following map depicts the location of the San José property in relation to other third-party properties at the time of filing this report.
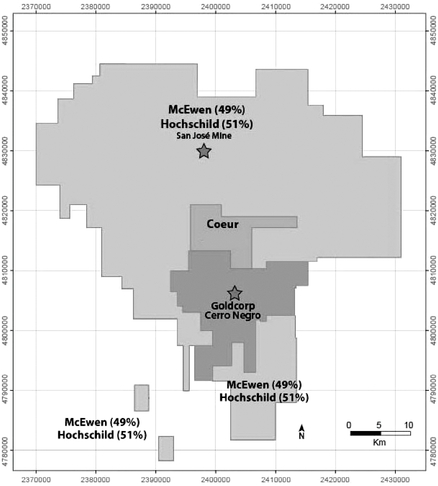
The San José property is within an arid to semi-arid area of Argentina, with short, warm summers reaching temperatures above 70°F (21°C) and winters with temperatures commonly below 32°F (0°C). Strong and persistent winds are common especially during the warmer months (October to May). Average rainfall at the site is estimated to be 5.7 inches (144 millimeters) and snowfall amounts to 1.3 inches (32.5 millimeters). Annual average temperature is 48°F (8.9°C). MSC has maintained a weather station at the property since January 2005. Mining and exploration continue year round in this part of Argentina.
29
Vegetation is comprised of low scrub bushes and grass, typical of harsh climate and poor soils. Fauna consists of birds, small mammals and reptiles. Most of the property area is uninhabited; however, it is used by local farmers for sheep and cattle grazing.
Geology and Mineralization
The San José property is approximately located in the northwest corner of the 23,166 sq. mile (60,000 sq. km) Deseado Massif of the Santa Cruz Province, Argentina. The Deseado Massif consists of Paleozoic metamorphic basement rocks unconformably overlain by Middle to Upper Jurassic bimodal andesitic and rhyolitic volcanics and volcaniclastics. Cretaceous sediments and Tertiary to Quaternary basalts overlie the Jurassic volcanics. The Jurassic Bajo Pobre Formation is the main host of gold and silver vein mineralization at the mine as well as many regional prospects. The Formation also hosts some of the mineralization at Saavedra West Zone. The formation is comprised of a lower andesite volcaniclastic unit and an upper andesite lava flow and has a maximum thickness of 394 ft. (120 m). Mineralization in the San José area occurs as low sulfidation epithermal quartz veins, breccias and stockwork systems accompanying normal-sinistral faults striking 330° to 340°. The main structural trend of fault and vein systems on the property is west-northwest to north-northwest.
Facilities and Infrastructure
Infrastructure of the property consists of camp facilities that can accommodate up to approximately 1,100 personnel, a medical clinic, a security building, a maintenance shop, a laboratory, processing facilities, a mine and process facility warehouse, a surface tailings impoundment, support buildings and mine portals, a change house, a core warehouse, an administration building and offices. The laboratory is equipped to process all assays (core, chips, soil) and incorporates fire assaying and atomic absorption equipment. MSC has installed a satellite-based telephone/data/internet communication system.
The San José mine is a ramp access underground mining operation. The San José veins are accessed from three main portals: the Tehuelche Portal, the Kospi Portal and the Güer Aike Portal. The main ramps are located about 164 ft. (50 m) from the vein, depending on the dip of the ore. Cross-cuts to the ramp are centrally positioned on the vein and usually have an ore pass and a waste/backfill pass.
Electricity is provided by an 81-mile (130 km) 132 kV electric transmission line, which was constructed in 2009 and connects the San José mine processing facility to the national power grid.
The processing plant at the San José mine is composed of conventional crushing, grinding and flotation circuits. Approximately one-half of the silver-gold flotation concentrate is processed in an intensive cyanide leaching circuit with the dissolved gold and silver recovered by electrowinning of a clarified solution followed by smelting to produce doré. The balance of the flotation concentrate is filtered and shipped to a smelter. Flotation and leached tailings are stored in side-by-side engineered, zero discharge facilities. A Merrill Crowe circuit recovers small amounts of gold and silver from the electrowinning discharge solution. In 2012, modifications were undertaken to modify the crushing circuit, in order to increase the mill throughput capacity by 10%, from a nominal 1,500 tonnes per day to 1,650 tonnes per day. The modifications were completed in 2013. In 2013, the capacity of the flotation tailing dam was also increased, followed by the construction of a new tailing dam in 2014. Construction was completed in the fourth quarter of 2014, and operational in the first quarter 2015.
Exploration Activities
Exploration by Minera Andes on the San José property from 1997 to 2001 was concentrated over the northern part of the property and consisted of geological mapping, sampling, trenching, geophysics, alteration and metallurgical studies and reverse circulation ("RC") and diamond drilling. In 2001, an
30
extensive exploration program was undertaken which included detailed topographic surveying of the property, induced polarization ("IP") geophysics and drilling. Exploration during 2003-2004 consisted of underground exploration/development, environmental and metallurgical studies and the construction and commissioning of a pilot plant at the Huevos Verdes Vein. Surveying of the topography, planned access and infrastructure in the Huevos Verdes and Frea areas was carried out during 2005 to 2007. From 2007 to 2008, a total of 193 diamond drill holes totaling 155,108 ft. (47,277 m) and focused on regional prospects as well as strike extensions of known veins with most of the drilling concentrated on the Ayelén, Frea and Odin veins. From 2009 to 2014, a total of approximately 898,620 ft. (273,900 m) of diamond core drilling was completed. During 2014, a total of 54,520 ft. (16,618 m) of drilling was performed and exploration was focused on definition of the Karina, Guadalupe and Nueva Ramona veins as well as drilling in the Los Pinos area. Detailed surface mapping and sampling over the Los Pinos vein, over an area of 3,500 hectares, was also completed. Mapping of the south side of the San José area covering an area of 520 acres (211 hectares) was also carried out.
Reserves
The following is the reserve information calculated by Hochschild for the San José mine as at December 31, 2013 and therefore does not account for depletion from 2014 production, or reserves delineated during 2014. The 2013 information is the most recent available to us. We expect that Hochschild will report updated reserves as at December 31, 2014 during the first quarter of 2015.
These figures, reported on a 100% basis, were prepared by Hochschild and audited by P&E Mining Consultants Inc. whose report dated March 6, 2014, concluded that the reserve estimates for the San José mine prepared by Hochschild at December 31, 2013 provide a reliable estimation of reserves in accordance with the standards of the Joint Ore Reserve Committee of the Australian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy ("JORC"), NI 43-101, the Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum ("CIM") best practices and Industry Guide 7. The mineral reserves were estimated using metal prices of $1,200 per ounce of gold and $20 per ounce of silver with a marginal revenue cut-off value of $94.76 per tonne. The reserves as presented are in-place and include mining dilution and mining losses, but do not include allowances for mill or smelter recoveries.
San José Reserves and Resources—100%
Reserve Category
|
Tonnes (in thousands) |
Silver (grams/tonne) |
Silver ounces (in millions) |
Gold (grams/tonne) |
Gold ounces (in thousands) |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Proven |
950 | 597 | 18.2 | 7.82 | 238.8 | |||||||||||
Probable |
863 | 426 | 11.8 | 6.15 | 170.6 | |||||||||||
Proven & Probable |
1,813 | 515 | 30.1 | 7.03 | 409.4 | |||||||||||
El Gallo Complex, Mexico (100%)
For detailed information on the El Gallo 1 mine production statistics and financial results, refer to Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
Overview and History
The Company owns a group of properties in Sinaloa State, Mexico, which includes the El Gallo 1 mine and the El Gallo 2 project. The El Gallo property consists of approximately 697 sq. miles (1,807 sq. km) of mineral or mining concessions held through ownership of Pangea Resources Inc., which in turn holds 100% ownership of Compañia Minera Pangea S.A. de C.V. ("Minera Pangea"). Concession titles are granted under Mexican mining law and are issued by the Secretaria de Economía, Coordinación General de Minera, Dirección General de Minas. McEwen Mining acquired El Gallo and the surrounding
31
mineral concessions when it completed its acquisition of Nevada Pacific Gold Ltd. ("Nevada Pacific") in 2007.
El Gallo 1 refers to the open-pit mine, heap leach operation formerly known as the Magistral mine. The El Gallo 1 mine produced approximately 70,000 ounces of gold from 2002 to 2005 while owned by predecessor companies. Operations at El Gallo 1 were shut down in July 2005 due to higher than anticipated operating costs, a lack of working capital, and poor gold recoveries. In October 2006, while still owned by Nevada Pacific, the El Gallo 1 mine was placed on care and maintenance with the operating permit remaining in place. We purchased the mine as part of our 2007 acquisition of Nevada Pacific.
In 2012, we re-commissioned the mine, at a cost of $13.5 million, which included the costs of upgrading existing infrastructure, such as the heap leach pad and assay lab, as well as installing a three-stage crushing plant and construction of the ADR plant. As we have no proven or probable reserves at the El Gallo 1 mine, the estimated capital expenditures required were based on internal studies. We poured the first gold pour in September 2012, with commercial production commencing January 1, 2013. Since production has restarted, El Gallo 1 has produced a total of 75,807 ounces of gold and 51,039 ounces of silver.
El Gallo 2 refers to the project which, should the Company proceed with its development and construction, would process mineralization from the El Gallo and Palmarito silver deposits through open-pit mining. The El Gallo deposit is a new discovery made by our geology team in November 2008. Although there is a long history of mining in the area, based on field observations, only a minimal amount of artisanal mining appears to have taken place at the El Gallo deposit. There is no recorded history of prior exploration having occurred at the El Gallo deposit. The Palmarito silver deposit is a historic silver producing area that has an estimated historical production of 15,300,000 million ounces of silver and 49,250 ounces of gold from open pit and underground workings before mining ceased in 1950. Palmarito is considered to be one of the major historical producers of silver in Sinaloa State.
An annual lease agreement for surface access to El Gallo 1 and 2 is currently in place between Minera Pangea and certain of our employees who hold the surface rights. These lease agreements provide for access and site preparation to accommodate exploration activities and drilling. The employees who hold the surface rights have commenced the required legal process to convert the land into private ownership so it can be sold to us. We are not required to make any additional payments, as the purchase price was agreed to and paid at the time of the lease agreements. Although the agreements cover a large area around the project, there can be no assurances that additional surface rights will not be required.
Various environmental permits are required in order perform exploration drilling in Sinaloa State. Permitting requirements are dependent upon the level of disturbance. Exemptions can generally be obtained if drilling occurs in areas where no new disturbance will occur and vegetation will not be removed (agricultural areas, dirt roads, previously mined sites). If drilling occurs on previously undisturbed land and vegetation will be removed, an Environmental Impact Study and Land Use Change are required. Each of the areas where we are currently conducting exploration drilling has the required permit or exemption.
As of the date of this report, the El Gallo 1 mine has all necessary permits for current operations, which must be renewed in June 2022. Specific permit-required conditions must be followed during operations such as, but are not limited to; groundwater quality monitoring at four points, recycling of used oil, and the development of an accident prevention plan.
All required permits for construction and operation of El Gallo 2, including environmental permits such as the MIA, ETJ and the RA, have been received. The final environmental permit, relating to the Change of Land Use was received from the SEMARNAT in January 2014.
32
Two additional permits were submitted in 2014. The first permit is in relation to the mining of the Palmarito deposit, which represents approximately 15% of the projected annual silver production at El Gallo 2. The second permit relates to the right-of-way for a 4.6-mile (7.5 km) 115 kV electric transmission line that would connect the El Gallo 2 processing plant to the national power grid. In the meantime, construction of the mine could begin with power provided by generators with the option of connecting to the grid when the permit is received. Delays in receiving either of these two these permits would not be expected to delay eventual construction from proceeding.
A feasibility study ("FS") was completed on the El Gallo 2 project in September 2012. The FS included a NI 43-101 compliant resource estimate of 24 million tonnes of mineralized material with a weighted average grade of 68.9 gpt silver and 0.1 gpt gold, including measured and indicated resources only. Initial capital expenditures for the project based on the FS are estimated at $180 million, although we are conducting cost savings studies to reduce the initial capital investment required while minimizing the impact on potential production. Potential changes include reducing the number of leach tanks and transformers, building a smaller process plant / refinery and using modular crushers. The complete FS technical report (which does not reflect any of the aforementioned potential changes) was filed on SEDAR on September 28, 2012. We also filed an updated NI 43-101 compliant resource estimate for the El Gallo Complex on August 29, 2013, with an effective date of June 30, 2013. Both reports are available on SEDAR under the Company's profile, and are subject to the assumptions and conditions set forth therein.
A final decision to proceed with the construction of El Gallo 2 has not been made and alternatives to reduce capital and operating costs continue to be examined. Any decision to proceed would be based on improved silver price expectations, improved project economics, and securing financing on terms that are more favorable than those that were available to the Company at the time of filing this report. The Company has procured long-lead time equipment such as the ball mill. The fabrication of the ball mill, which is the longest lead time item associated with the mine, was completed in 2014. Pending a decision to proceed with the development of El Gallo 2, the ball mill will kept in storage at the manufacturer's facilities.
Location and Access
The El Gallo Complex is located in northwestern Mexico, within Sinaloa State, Mocorito Municipality. It is situated approximately 60 miles (100 kilometers) by air northwest of the Sinaloa state capital city of Culiacan in the western foothills of the Sierra Madre Occidental mountain range. The concessions are located approximately 2.5 miles (4.0 kilometers) by road from the village of Mocorito, approximately 10 miles (16 kilometers) from the town of Guamuchil. Access is either by paved or well maintained, two-way, dirt roads.
33
The following map depicts the location of the El Gallo Complex:
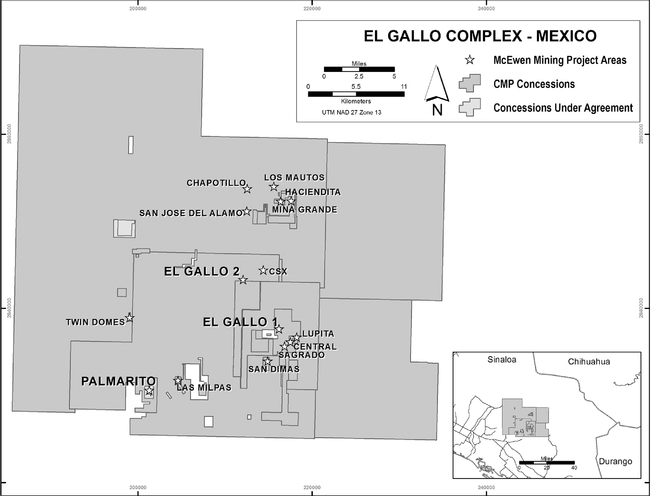
Geology and Mineralization
Gold mineralization in the El Gallo 1 mine area occurs in six deposits along two distinct structural trends, northwest and northeast. A northwest trending structural zone hosts the Samaniego and San Rafael deposits. San Dimas also is hosted by a northwest-striking structure. The second structural trend is northeast-striking and includes the Sagrado Corazón, Lupita and Central deposits. Along these structural trends the mineralization is located within numerous sub-structures that may be parallel, oblique or even perpendicular to the principal trends. The third structural trend is north-south and includes the San Dimas deposit. Mineralization among the various deposits of the El Gallo 1 area is generally similar, with the individual structural zones consisting of quartz stockwork, breccia, and local quartz vein mineralization occurring within propylitically altered andesitic volcanic rocks. The Samaniego, San Rafael, Lupita, Sagrado Corazon and Central deposits are characterized by gold accompanied by iron oxide and variable copper; the San Dimas deposit is polymetallic containing gold, silver, copper, lead and zinc.
Silver mineralization at El Gallo 2 is hosted in siliceous breccia zones and quartz stockwork zones within the dominantly andesitic rock package. These zones often occur at lithologic contacts, particularly contacts of Tertiary porphyry intrusions. Multi-lithologic breccias zones are often adjacent to these contacts and these breccias are locally mineralized. Mineral zones commonly have gently-dipping tabular geometry. Often, these zones reflect control by sill contacts of the Tertiary intrusives.
34
Silver mineralization at Palmarito occurs along or near the contact of andesitic-dacitic volcanic country rocks and a Tertiary rhyolite intrusive forming a horseshoe-shaped zone which wraps around the margin of the intrusive. The strongest mineralization in the main Palmarito orebody occurs along a northeast-trending zone which appears to represent the intersection of two contact structures. Generally, mineralization occurs in a breccia zone and is associated with strong silicification in the form of siliceous breccia, stockwork veining and silica flooding.
Facilities and Infrastructure
The El Gallo property has well-developed infrastructure including electricity and well developed roads. At the El Gallo 1 mine, significant mining has occurred in the past and most recent operations included open pit mining in two pits, with gold and silver ores processed in a heap leaching facility. There is a truck shop, a warehouse, two core logging facilities, heap leach pad, process ponds, laboratory, three stage crushing plant, an ADR process plant and an administrative office. The laboratory is equipped to process all assays (blasthole samples from the mine, core, chips, soil) and incorporates fire assaying and atomic absorption equipment. Included also is a metallurgical lab capable of processing bottle rolls and columns to determine gold and silver recoveries of ores amenable to cyanide leaching.
The crushing and process plant had an initial capacity of 3,000 tonnes per day. In 2014, an expansion to the processing capacity of the plant was completed, increasing from 3,000 to 4,500 tonnes per day, at a cost of approximately of $2.8 million. Commissioning commenced during the second quarter of 2014, and was fully operational by the fourth quarter of 2014.
There is also access to a local work force that is familiar with mining operations. Mining operations and site security are performed by contractors and the Company has its own workforce in the administrative and processing areas.
Primary water supply for El Gallo 1 comes from two currently operating water wells located 0.9 miles (1.5 km) from the process facility. Wells are powered by a generator that pumps water into a raw water pond, and it is then used for operations. The well field combined with local annual precipitation of 32 inches (~830 mm) provide sufficient supply for El Gallo 1 production.
Primary water supply for El Gallo 2 will come from three locally drilled water wells. Sufficient water yields required for the El Gallo 2 project were confirmed through several long-term pumping tests during the 2013 hydraulic aquifer investigation. Each well is located within 1.2 miles (2 km) of the proposed El Gallo process facility. Wells will be powered by electricity and pump water into a raw water storage tank for mine usage.
Exploration Activities
Modern exploration activities at the El Gallo 1 mine property started in early 1995, initially for Mogul Mining NL and subsequently for Santa Cruz Gold Inc ("Santa Cruz Gold"). From mid-1995 to early 1997, extensive drilling was conducted by Minera Pangea/Santa Cruz Gold on the San Rafael and Samaniego Hill deposit areas, as well as locally extensive drilling on the Sagrado Corazón-Central-Lupita deposit area. In 1998, Santa Cruz conducted a limited amount of additional drilling for metallurgical samples, reverse circulation grade verification, in-fill purposes, and condemnation of potential surface facility locations. In 1999, after a merger with Santa Cruz Gold, Queenstake Resources Ltd. ("Queenstake") conducted a limited drilling program to step-out/in-fill drill in the Samaniego Hill deposit and to obtain pit-slope geotechnical samples from both the San Rafael and Samaniego Hill deposits. Queenstake conducted a drilling campaign from late 2001 to early 2002 in the La Prieta Zone of the Samaniego Hill deposit to delineate extensions of the high grade La Prieta zone along strike and down dip. Between 2004 and 2005, Nevada Pacific Gold Ltd. conducted further drilling on the Samaniego Hill and Lupita areas and determined that the mineralized intercepts expanded the
35
Lupita envelope at depth to the southeast. Between 2008 and 2013, McEwen Mining also conducted drilling in the Samaniego Hill, San Rafael, Sagrado Corazon, Lupita and Central areas and determined that mineralized intercepts within those holes show continued down dip extension and lateral extension of the Lupita and Sagrado Corazon deposits, in particular. We continue to drill at El Gallo 1 with the objective of extending the mine life, which, based on our mine plan as of December 31, 2014, is estimated to end in 2017. Between 2011 and 2014, we drilled a total of approximately 190,000 feet (60,370 meters) of core drilling at El Gallo 1.
We initiated exploration in the El Gallo area in January 2008. The first evidence of additional mineralization at El Gallo occurred in the summer of 2008 when rock samples from surface outcropping returned encouraging silver values. McEwen Mining has been the sole operator of the El Gallo project since drilling began in January 2009. By December 2014, a total of 427,370 feet (130,262 meters) of core drilling had been completed. Drilling was conducted throughout the El Gallo project area and included condemnation drilling done for planned mine facilities and infrastructure peripheral to the mineralized material.
We have also recently focused our drilling efforts within other areas of the El Gallo Complex, which include CSX, Mina Grande and Twin Domes, in order to expand mineralization for potential El Gallo 1 and 2 production. As of the date of this report, one core drill has continued to operate, with plans to add an additional drill in the year 2015.
No Proven or Probable Reserves
We have not yet demonstrated the existence of proven or probable reserves at the El Gallo Complex as defined by Industry Guide 7.
Royalties
Coeur Mining Inc. a NYSE and TSX listed company, holds a sliding scale net smelter return royalty ("NSR") on gold or gold equivalent recovered from the El Gallo 1 mine and the El Gallo mineralized material area. The royalty is calculated at a rate of 1% of NSR on the initial 30,000 ounces of gold equivalent production, at a rate of 3.5% of NSR on the next 350,000 ounces of gold equivalent production, and thereafter, at a rate of 1% of NSR on gold recovered from the areas, in perpetuity. Cumulatively, on a life-of-mine basis through to December 31, 2014, approximately 148,000 gold and gold equivalent ounces have been produced from mineralized material within the scope of the NSR agreement. The NSR was previously held by Gold Royalty Corp., a private Canadian Corporation, which was acquired by Coeur Mining Inc. in December 2013.
For Palmarito, a 2% NSR exists on certain mineral claims around the area that were optioned from a third party. The NSR affects strike extensions and down-dip portions of the in-situ mineralized material and the majority of historic tailings.
Exploration Properties
Gold Bar Project, Nevada (100%)
Overview and History
The Gold Bar Project is a proposed mine project consisting of a conventional open pit mine with an oxide gold heap leach recovery circuit. The project is located within the Battle Mountain-Eureka-Cortez gold trend in Eureka County, central Nevada, and covers an area of 71 square miles (185 square kilometers) consisting of 71 claims. The property was previously mined from 1987 to 1994 by Atlas Precious Metals Inc. The Gold Bar project is currently in the permitting phase. The timeline to obtain permits is uncertain, but similar projects on public lands in Nevada have required between 36-60 months. The formal permitting process began in 2012.
36
A pre-feasibility study ("PFS") was completed by SRK Consulting and filed on February 27, 2012 with an effective date of November 28, 2011. We have yet not demonstrated the existence of proven or probable reserves for the Gold Bar Project as defined by Industry Guide 7. The PFS included a NI 43-101 resource estimate of 19.5 million tonnes of mineralized material at a grade of 0.95 gpt gold. Based on the PFS, initial capital expenditures for the project are estimated at $53.1 million including an allocation of $7.2 million for contingencies. The full PFS technical report is available on SEDAR at www.sedar.com under the Company's profile, and is subject to the assumptions and conditions set forth therein.
Location and Access
The Gold Bar Complex is in the Roberts Creek Mountains, in Eureka County, Nevada, approximately 30 miles (48 km) northwest of the town of Eureka, Nevada, primarily in Township 22 North; Range 50 East (N39°48'16.5"; W116°21'09.65").
The project site is accessed by traveling 40 km west on US Highway 50 from Eureka, NV, the nearest town, or 72 km east on US Highway 50 from Austin, NV to the Three Bars Road. Travel is then 26 km north on the Three Bars Road, a gravel, all weather road maintained by Eureka County. The project area is approximately 15 miles (24 km) from the Three Bars Road, and is accessed through unimproved dirt roads that are not maintained by the county.
The following map depicts the location of the Gold Bar Complex:
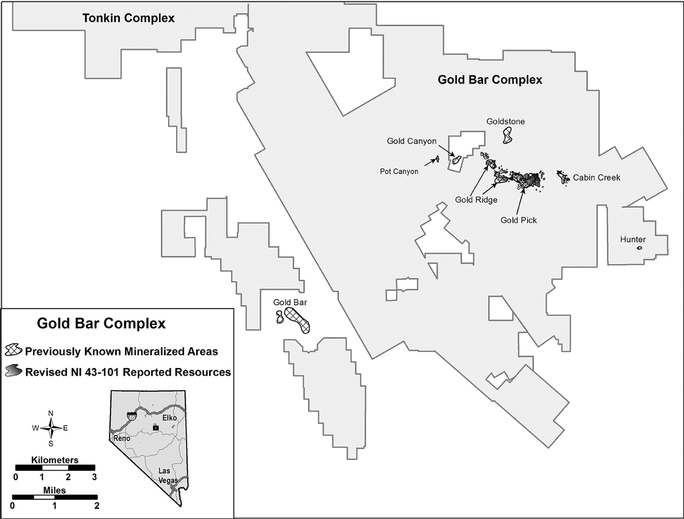
37
Geology and Mineralization
The Gold Pick-Gold Ridge area occurs on the Battle Mountain-Eureka mineral belt in a large window of lower-plate carbonate rocks surrounded by upper-plate rocks. The lower-plate carbonates at Gold Pick-Gold Ridge consist of an east-dipping section of Silurian Lone Mountain Dolomite, Devonian McColley Canyon Formation, Devonian Denay Formation, and Devonian Devils Gate Limestone (from oldest to youngest). Northwest-trending and northeast-trending structures cut the area; the Gold Pick mineralization is localized in an apparent northwest-trending horst of McColley Canyon Formation which is cut by a series of northeast-trending structures.
Gold mineralization is hosted primarily in the Bartine Member of the McColley Canyon Formation, which consists of carbonate wackestones and packstones approximately 250 to 380 feet thick. Minor amounts of mineralization are found in the underlying dolomitic limestone Kobeh Member of the McColley Canyon Formation when it is adjacent to apparent feeder structures. Gold Pick-Gold Ridge is "Carlin-Type" sediment-hosted gold mineralization with typical associated alteration (decalcification, silicification) and trace elements (antimony, arsenic, mercury, and barium). Carlin-Type deposits are deposits that are restricted to a small part of the North American Cordillera in northern Nevada and northwest Utah.
Three-dimensional modeling by our geologists has led to the identification of an unconformity (erosional surface) between the basement and gold host rocks at the Gold Bar Project. Channels in this unconformity were filled with porous limestone, which then acted as preferred pathways for gold mineralization. Much of the gold mineralization in the Gold Pick-Gold Ridge area occurs in the porous limestones above these channels.
Exploration Activities
Since 2012, we have continued to advance the permitting process for construction and production. Since the formal permitting process began, we are unable to perform any drilling activities at the project. During this time, we continue to advance the Gold Bar project by completing baseline studies in support of the BLM and State of Nevada permitting required for mine development and construction. We also drilled and pump-tested one potential water well location for future mining operations.
We submitted our Plan Of Operations ("POO") permit application in 2013. The POO was determined complete and the BLM has determined that an Environmental Impact Statement ("EIS") is necessary to fulfill the requirements under the National Environmental Policy Act ("NEPA"). Upon completion of the EIS, the BLM will be able to proceed with the approval determination of the POO. A Request for Proposal has been issued and a third-party consulting firm has been contracted to assist the BLM in the preparation of an EIS for the Gold Bar project. Final permit approval is scheduled for the third quarter of 2016.
No Proven or Probable Reserves
We have not yet demonstrated the existence of proven or probable reserves at the Gold Bar Complex as defined by Industry Guide 7.
Los Azules Copper Project, Argentina (100%)
The Los Azules copper project is a 100% owned advanced-stage porphyry copper exploration project located in the cordilleran region of San Juan Province, Argentina near the border with Chile. We acquired this property, along with other Argentina exploration properties, in connection with the acquisition of Minera Andes in January 2012. Located at approximately 31o 13'30" south latitude and 70o 13'50" west longitude, Los Azules is 4 miles (6 km) east of the Chilean-Argentine border. It is
38
accessible by unimproved dirt roads except for seasonal closures in winter. The elevation at site ranges between 11,500 feet - 14,750 feet (3,500 m - 4,500 m) above sea level.
The following map illustrates the location of the Los Azules Copper Project as well as our other properties in the Province of San Juan:
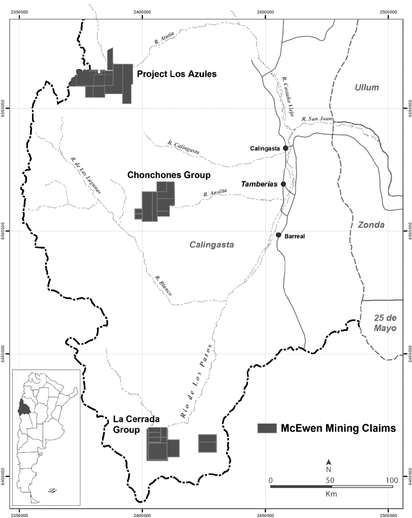
The deposit is located within a copper porphyry belt that is host to some of the world's largest copper mines. The upper part of the system consists of a barren leached cap, which is underlain by a high-grade secondary enrichment blanket. Primary mineralization below the secondary enrichment zone has been intersected in drilling up to a depth of more than 3,280 feet (1,000 meters) below surface. The property encompasses 127 square miles (328 square kilometers) and surrounds a large alteration zone that is approximately 5 miles (8 kilometers) long by 1.2 miles (2 kilometers) wide.
Drilling programs have been undertaken at Los Azules between 1998 and 2014 by four different mineral exploration companies: Battle Mountain Gold (now Newmont Mining Inc.), Mount Isa Mines S.A. (now Xstrata Copper Plc.), Minera Andes and McEwen Mining. Drilling, including early reverse circulation programs, focused initially on gold exploration and subsequently on diamond drilling for porphyry style copper mineralization. Drilling conditions are difficult, especially in highly faulted zones and in areas of unconsolidated surface scree or talus. Due to snow conditions on two mountain passes on the access road to the site, seasonal exploration typically commences in December and extends into late April or early May. From 1998 to the end of 2014, a total of 195,210 feet (59,500 meters) were drilled on the property. No significant drilling took place during the year 2013-2014
39
season, as we focused on baseline studies regarding flora, fauna, water quality and other environmental compliance matters.
In November 2013, we filed a NI 43-101 Preliminary Economic Assessment ("PEA") prepared by Samuel Engineering Inc. The PEA was expanded to include an updated mineralized material estimate, which we released in May 2013, indicating a mineralized material base of 0.4 billion tonnes of mineralized material with a weighted average grade of 0.63 percent copper. Note this mineralized material includes indicated resources only, and does not include estimates of inferred resources.
The PEA also considers new metallurgical processes and an increased production profile. The updated PEA contemplates the construction of a mine and process plant operating over a 35-year mine life at a throughput of 120,000 tonnes per day. The proposed mine is projected to produce copper cathode via a pressure oxidative leach process, in addition to heap leaching the lower grade mineralized material. The advantages of being able to produce copper cathode rather than copper concentrate would be to eliminate the capital intensive concentrate pipeline through Chile, reduce the applicable export tax from 10% on concentrate to 5% on cathode, and remove the treatment and refining charges from the smelting process. The complete technical report was filed on November 7, 2013. It is available on SEDAR under the Company's profile, and is subject to the assumptions and conditions set forth therein.
In October 2014, the Company terminated the option held by TNR Gold Corp ("TNR") to acquire a minority ownership position in Los Azules (the "Back-In Right Option"). The Back-In Right Option gave TNR the option of owning up to 25% in the northern portion of Los Azules. Based on the estimated resources for those northern claims, this would represent approximately 13% of the total deposit. In exchange for the termination of the Back-In Right Option, the Company issued 850,000 shares of the Company's common stock to TNR, and granted a 0.4% net smelter royalty on Los Azules. Further, if Company sells all of its interest in the project within thirty six months of closing the transaction on October 16, 2014, the Company will grant a bonus payment equal to 1% of the gross proceeds of such transaction to TNR.
Other Argentina Exploration Properties
In addition to the San José mine and the Los Azules project, the Company also owns a 100% interest in numerous exploration properties totaling 409 sq. miles (1,060 sq. km), located in the Province of Santa Cruz, and 278 sq. miles (720 sq. km) in the Province of San Juan, where generally limited exploration has been performed. We do not presently consider these properties significant to our exploration program or our operations.
40
The following map depicts the location of our exploration properties in the Province of Santa Cruz (after the transfer of the properties that were part of the vend-in agreement discussed above):
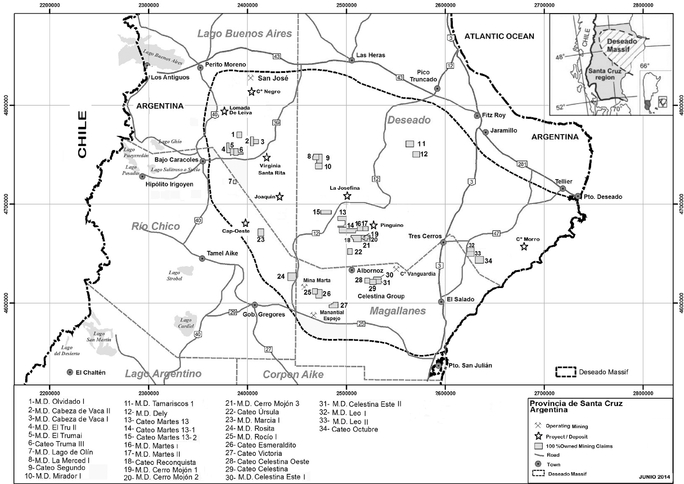
41
The following map depicts the location of our exploration properties in the Province of San Juan:
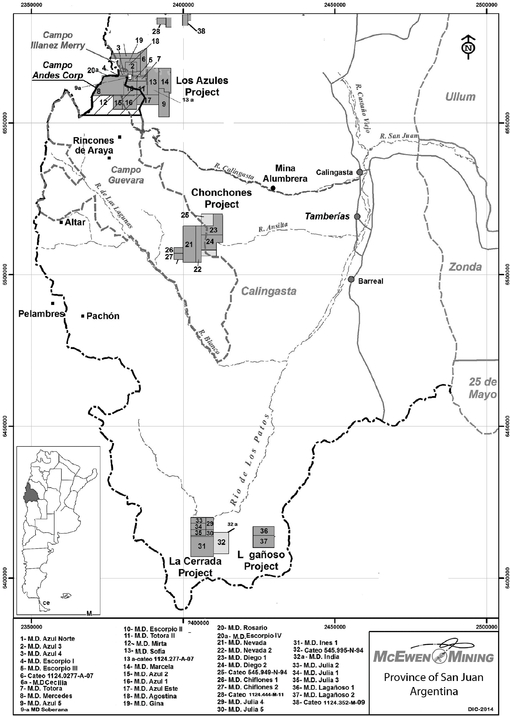
No significant drilling took place during the year 2014. As of the date of this report, the Company has made the decision to rationalize its mineral property interests in an effort to focus its exploration efforts on more prospective areas, and as a result, does not intend to pursue the exploration of the Santa Cruz or San Juan properties.
In October 2013, the Company and Hochschild entered into a vend-in agreement with MSC pursuant to which we agreed to contribute to MSC the mining rights to a certain number of our Santa Cruz exploration properties. The properties transferred, totaling approximately 48,900 hectares, included amongst others the Telken, Piramides, Tobias, and Este tenements, and are in close proximity to or abutting the properties comprising the San José mine. Hochschild also contributed to MSC
42
certain of its mineral properties located in the same region, totaling approximately 82,700 hectares. The agreement also contains a 2% net smelter return royalty payable to the Company or Hochschild based on any of MSC's production from the respective mineral properties contributed by each party. Registration of title changes with the Argentine government were finalized in the second quarter of 2014.
The following maps illustrate the location of the respective Santa Cruz exploration properties contributed by the Company and Hochschild pursuant to the vend-in agreement, and the combined properties after completion of the vend-in agreement:
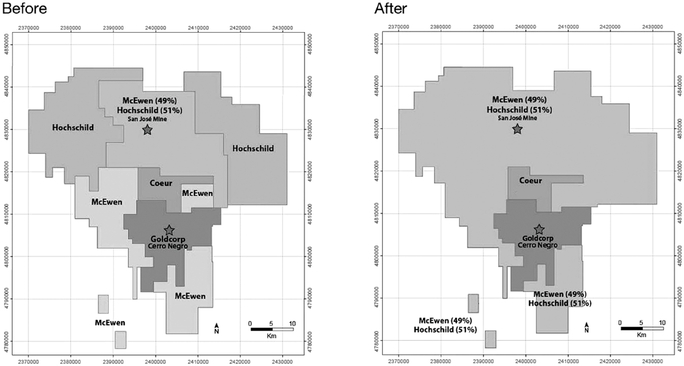
Nevada Exploration Properties
The following table summarizes the Nevada land position of our Company as of December 31, 2014:
Nevada Mineral Property Interest
|
Number of Claims |
Square Miles |
Square Kilometers |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Gold Bar Complex |
2,353 | 71 | 185 | |||||||
Tonkin Complex |
3,100 | 94 | 244 | |||||||
Limo Complex |
1,100 | 35 | 90 | |||||||
Battle Mountain Complex |
648 | 19 | 49 | |||||||
Other United Stated Properties |
652 | 22 | 58 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Nevada Properties |
7,853 | 241 | 625 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Of all the Nevada properties held by the Company, only Gold Bar, discussed in more detail above, is considered to be of significance to the Company's development plans at the time of filing this report. No significant drilling or exploration activities took place during the year 2014. As of the date of this report, the Company has made the decision to rationalize its mineral property interests in an effort to focus its exploration efforts on more prospective areas, and as a result, does not intend to pursue the exploration of its Nevada properties, with the exception of the Gold Bar, Tonkin and North Battle Mountain properties.
43
We generally hold mineral interests in Nevada through unpatented mining and mill site claims, leases of unpatented mining claims, and joint venture and other agreements. Unpatented mining claims are held subject to paramount title in the United States. In order to retain these claims, we must pay annual maintenance fees to the BLM, and to the counties within which the claims are located. Rates for these jurisdictions vary and may change over time. Other obligations which must be met include continuing assessment work, obtaining and maintaining necessary regulatory permits, and lease and option payments to claim owners.
The following map illustrates the general location of the trends and our properties in Nevada:
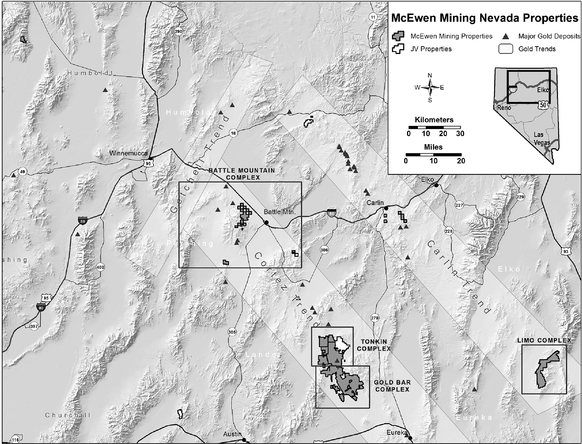
Tonkin Complex
The Tonkin Complex represents our largest holding in the State of Nevada at approximately 94 sq. miles (244 sq. km). The Tonkin Project is a gold mining property located within the Battle Mountain-Eureka Trend in Eureka County, Nevada. From 1985 through 1989, Tonkin produced approximately 30,000 ounces gold utilizing an oxide heap leach and a separate ball mill involving bioxidation to treat the problematic sulphide ore. Due to cost escalation and recovery issues associated with the refractory and preg-robbing carbonaceous mineralogy, the operation was shut down.
We are not currently subject to any material legal proceedings, and to the best of our knowledge, no such proceeding is threatened, the results of which would have a material impact on our properties, results of operations, or financial condition. Nor, to the best of our knowledge, are any of our officers or directors involved in any legal proceedings in which we are an adverse party.
44
Notwithstanding the foregoing, although no legal action has been commenced, we point the reader to Item 1A. Risk factors—"We are currently the subject of an enquiry by the SEC Division of Enforcement with respect to the accounting treatment of Los Azules", on page 25.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
As we have no mines located in the U.S. or any of its territories, the disclosure required by this Item is not applicable.
45
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market Information
On January 24, 2012, our common stock commenced trading on the NYSE and TSX under the symbol "MUX", subsequent to the completion of the acquisition of Minera Andes. Prior to that, our common stock traded on the NYSE and TSX under the symbol "UXG". McEwen Mining—Minera Andes Canadian Acquisition Corp. exchangeable shares are traded on the TSX, under the symbol "MAQ".
The table below sets forth the high and low sales prices for our common stock on a quarterly basis as reported by the NYSE and TSX from January 1, 2013 to December 31, 2014.
| |
NYSE | TSX (C$) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
High | Low | High | Low | |||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2014 |
|||||||||||||
First Quarter |
$ | 3.56 | $ | 2.07 | $ | 3.93 | $ | 2.23 | |||||
Second Quarter |
3.03 | 2.07 | 3.27 | 2.25 | |||||||||
Third Quarter |
3.10 | 1.96 | 3.33 | 2.20 | |||||||||
Fourth Quarter |
1.92 | 0.92 | 2.15 | 1.07 | |||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2013 |
|||||||||||||
First Quarter |
$ | 3.96 | $ | 2.28 | $ | 3.92 | $ | 2.34 | |||||
Second Quarter |
2.82 | 1.67 | 2.87 | 1.75 | |||||||||
Third Quarter |
2.89 | 1.65 | 3.03 | 1.76 | |||||||||
Fourth Quarter |
2.51 | 1.73 | 2.57 | 1.82 | |||||||||
As of March 2, 2015, there were outstanding 272,114,148 shares of our common stock, which were held by approximately 5,592 stockholders of record. As of March 2, 2015, there were outstanding 27,985,731 exchangeable shares, which were held by approximately 67 holders of record. The exchangeable shares are exchangeable at the option of the holders into our common stock on a one-for-one basis.
Transfer Agent
Computershare Investor Services Inc. is the transfer agent for our common stock. The principal office of Computershare is 250 Royall Street, Canton, Massachusetts, 02021 and their telephone number is (303) 262-0600. The transfer agent in Canada and transfer agent for exchangeable shares is Computershare Investor Services at 100 University Ave., 9th Floor, Toronto ON, M5J 2Y1 and their telephone number is 1-800-564-6253.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid dividends on our common stock. Payment of future dividends, if any, will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors after taking into account various factors, including the terms of any credit arrangements, our financial condition, operating results, current and anticipated cash needs and plans for growth. Our initial earnings, if any, will likely be retained to finance our growth. At the present time, we are not party to any agreement that would limit our ability to pay dividends.
46
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
Set out below is information as of December 31, 2014 with respect to compensation plans (including individual compensation arrangements) under which our equity securities are authorized for issuance. This information relates to our Equity Incentive Plan.
Plan Category
|
Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options |
Weighted-average exercise price per share of outstanding options |
Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders |
4,649,634 | $3.35 | 3,090,137 | |||||||
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders(1) |
199,143 | C$ | 5.11 | — | ||||||
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders(2) |
301,650 | C$ | 2.30 | — | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
TOTAL |
5,150,427 | 3,090,137 | ||||||||
- (1)
- In
connection with certain acquisitions completed in 2007, we assumed stock options covering 812,918 shares of our common stock. Following certain exercises
and expirations of 613,775 options between 2007 and 2014, a total of 199,143 options remain exercisable at December 31, 2014.
- (2)
- In connection with the acquisition of Minera Andes in 2012, we assumed stock options covering 1,735,650 shares of our common stock. Following certain exercises and expirations/cancellations of 1,434,000 options between 2012 and 2014, a total of 301,650 options remain exercisable at December 31, 2014.
The options that we assumed in connection with the 2007 acquisitions were not approved by our security holders. These options are exercisable at prices ranging from C$4.30 to C$6.70 and expire on dates between 2015 and 2017. The options outstanding as at December 31, 2014 that we assumed in connection with the acquisition of Minera Andes in 2012 were not approved by our security holders either. The options outstanding as at December 31, 2014 are exercisable at prices ranging from C$2.27 to C$2.51 and expire on dates in 2015. The weighted average exercise price of these options reflects the original exercise price of the options, modified to reflect the exchange ratios associated with the acquisitions. We are not authorized to issue any additional options under any of these plans.
On January 19, 2012, shareholders approved an amendment to our Equity Incentive Plan to increase the number of shares of common stock reserved for issuance thereunder from 9,000,000 to 13,500,000 shares. The number of securities shown in the table above as remaining available for future issuance is net of securities previously issued and exercised.
47
Performance Graph
The following graph compares our cumulative total shareholder return for the five years ended December 31, 2014 with (i) the NYSE Arca Gold Bugs Index, which is an index of companies involved in the gold industry and (ii) the NYSE Composite Index, which is a performance indicator of the overall stock market. The graph assumes a $100 investment on December 31, 2009 in our common stock and the two other stock market indices, and assumes the reinvestment of dividends, if any.
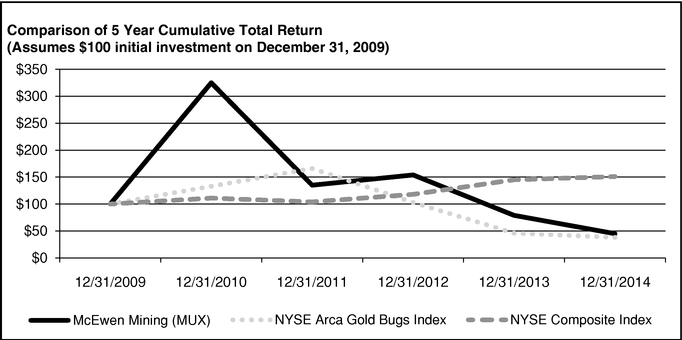
| |
December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | |||||||||||||
McEwen Mining (MUX) |
$ | 100 | $ | 325 | $ | 135 | $ | 154 | $ | 79 | $ | 45 | |||||||
NYSE Arca Gold Bugs Index |
100 | 133 | 166 | 103 | 46 | 38 | |||||||||||||
NYSE Composite Index |
100 | 111 | 104 | 118 | 145 | 151 | |||||||||||||
48
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The following table summarizes certain selected historical financial data about our Company for the last five years. The data has been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements for the years indicated. The data for 2012 reflects the acquisition of Minera Andes effective January 24, 2012. You should read this data in conjunction with the MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS and our audited consolidated financial statements contained herein. All amounts are stated in thousands of U.S. dollars unless otherwise indicated.
| |
For the year ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||||||||
Operating data |
||||||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 45,303 | $ | 45,982 | $ | 5,966 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
(Loss) income on investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. |
(5,284 | ) | 846 | 20,835 | — | — | ||||||||||
Operating loss(1) |
(410,165 | ) | (200,397 | ) | (91,405 | ) | (60,185 | ) | (35,783 | ) | ||||||
Other (expenses) income |
(8,948 | ) | (710 | ) | (2,493 | ) | (1,867 | ) | 694 | |||||||
Net loss(1) |
(311,943 | ) | (147,742 | ) | (66,654 | ) | (61,872 | ) | (33,091 | ) | ||||||
Basic and diluted loss per share(2) |
$ | (1.05 | ) | $ | (0.50 | ) | $ | (0.26 | ) | $ | (0.42 | ) | $ | (0.25 | ) | |
Weighted average number of shares(2) |
297,763 | 297,041 | 261,233 | 147,692 | 132,633 | |||||||||||
| |
As at December 31, | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||||||||
Balance sheet data |
||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 12,380 | $ | 24,321 | $ | 70,921 | $ | 13,416 | $ | 6,818 | ||||||
Short-term investments |
— | — | — | 3,933 | — | |||||||||||
Marketable equity securities |
1,082 | 2 | 3 | 1,480 | 4,576 | |||||||||||
Gold and silver bullion |
— | — | 1,690 | 22,810 | 4,569 | |||||||||||
IVA taxes receivable |
11,739 | 11,591 | 9,150 | 2,983 | 769 | |||||||||||
Inventories |
12,404 | 8,800 | 7,262 | 139 | 164 | |||||||||||
Property and equipment, net |
17,896 | 15,143 | 12,767 | 11,772 | 4,391 | |||||||||||
Mineral property interests |
287,812 | 642,968 | 767,067 | 245,454 | 235,153 | |||||||||||
Investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. |
177,018 | 212,947 | 273,948 | — | — | |||||||||||
Other assets |
2,627 | 7,294 | 8,129 | 8,368 | 5,185 | |||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets |
$ | 522,958 | $ | 923,066 | $ | 1,150,937 | $ | 310,355 | $ | 261,625 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Current liabilities |
$ | 24,082 | $ | 11,189 | $ | 25,195 | $ | 6,124 | $ | 3,680 | ||||||
Deferred income tax liability |
51,899 | 158,855 | 229,522 | 78,786 | 78,573 | |||||||||||
Other long-term liabilities |
5,763 | 6,255 | 6,629 | 6,141 | 6,092 | |||||||||||
Shareholders' equity |
441,214 | 746,767 | 889,591 | 219,304 | 173,280 | |||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and shareholders' equity |
$ | 522,958 | $ | 923,066 | $ | 1,150,937 | $ | 310,355 | $ | 261,625 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- Includes
a non-cash expense of $353,736, $62,963, $18,468 and $5,878 relating to the write-downs of mineral property interests, and property and equipment
in 2014, 2013, 2012, and 2010, respectively. Also includes a non-cash expense of $21,162 and $95,878 relating to the write-down of our investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. in 2014 and 2013,
respectively.
- (2)
- Includes a retroactive adjustment on the weighted average number of shares outstanding for 2011, 2010, and 2009 as a result of a rights offering in 2012, as the rights offering was offered to all existing shareholders and was considered to contain a bonus element.
49
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Introduction
The following discussion updates our plan of operation as of March 9, 2015 for the foreseeable future. It also summarizes what management believes is relevant to our results of operations for three fiscal years ended December 31, 2014 and our financial condition at December 31, 2014 and 2013, with a particular emphasis on the year ended December 31, 2014. With regard to properties or projects that are not in production, we provide some details of our plan of operation.
The discussion also presents certain Non-GAAP financial performance measures, such as earnings from mining operations, adjusted net loss, total cash costs, total cash cost per ounce, all-in sustaining costs, all-in sustaining cost per ounce, all-in costs, all-in cost per ounce, and average realized price per ounce, that are important to management in its evaluation of our operating results and which are used by management to compare our performance to what we perceive to be peer group mining companies and relied on as part of management's decision-making process. Management believes these measures may also be important to investors in evaluating our performance. For a detailed description of each of the Non-GAAP financial performance measures and certain limitations inherent in such measures, please see the discussion under "Non-GAAP Financial Performance Measures" below, beginning on page 69.
The information in this section should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto included in this annual report.
Reliability of Information: MSC, the owner of the San José mine, is responsible for and has supplied to us all reported results from the San José mine. The technical information contained herein is, with few exceptions as noted, based entirely on information provided to us by MSC. Our joint venture partner, a subsidiary of Hochschild Mining plc, and its affiliates other than MSC do not accept responsibility for the use of project data or the adequacy or accuracy of this document.
50
Selected Financial and Operating Results
| |
Three months ended December 31, |
Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||
| |
(in thousands, unless otherwise indicated) |
|||||||||||||||
Gold and silver sales |
$ | 13,683 | $ | 10,247 | $ | 45,303 | $ | 45,982 | $ | 5,966 | ||||||
(Loss) income on investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A., net of amortization |
$ | (5,434 | ) | $ | 594 | $ | (5,284 | ) | $ | 846 | $ | 20,835 | ||||
Earnings from mining operations(1)(3) |
$ | 8,218 | $ | 6,532 | $ | 25,455 | $ | 37,634 | $ | 137,038 | ||||||
Net loss |
$ | (212,775 | ) | $ | (11,343 | ) | $ | (311,943 | ) | $ | (147,742 | ) | $ | (66,654 | ) | |
Net loss per common share—basic and diluted |
$ | (0.71 | ) | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (1.05 | ) | $ | (0.50 | ) | $ | (0.26 | ) | |
Adjusted net loss(3) |
$ | (9,744 | ) | $ | (5,204 | ) | $ | (32,998 | ) | $ | (30,965 | ) | $ | (78,559 | ) | |
Adjusted net loss per common share—basic and diluted(3) |
$ | (0.03 | ) | $ | (0.02 | ) | $ | (0.11 | ) | $ | (0.10 | ) | $ | (0.26 | ) | |
Consolidated gold ounces(1): |
||||||||||||||||
Produced |
27.4 | 20.7 | 84.4 | 79.2 | 58.5 | |||||||||||
Sold |
26.0 | 20.4 | 80.3 | 79.1 | 58.8 | |||||||||||
Consolidated silver ounces(1): |
||||||||||||||||
Produced |
973 | 857 | 3,196 | 3,135 | 2,278 | |||||||||||
Sold |
1,068 | 859 | 3,114 | 3,099 | 2,240 | |||||||||||
Consolidated gold equivalent ounces(1)(2): |
||||||||||||||||
Produced |
43.6 | 37.2 | 137.6 | 139.5 | 102.3 | |||||||||||
Sold |
43.8 | 36.9 | 132.2 | 138.7 | 101.9 | |||||||||||
Consolidated average realized price ($/ounce)(1)(3): |
||||||||||||||||
Gold |
$ | 1,182 | $ | 1,220 | $ | 1,248 | $ | 1,328 | $ | 1,665 | ||||||
Silver |
$ | 15.49 | $ | 19.45 | $ | 17.68 | $ | 21.28 | $ | 30.65 | ||||||
Consolidated costs per gold equivalent ounce sold ($/ounce)(1)(2): |
||||||||||||||||
Total cash costs(3)(4) |
$ | 709 | $ | 751 | $ | 817 | $ | 776 | $ | 811 | ||||||
All-in sustaining costs(3)(5) |
$ | 1,063 | $ | 1,102 | $ | 1,198 | $ | 1,178 | $ | 1,371 | ||||||
All-in costs(3)(5) |
$ | 1,194 | $ | 1,215 | $ | 1,368 | $ | 1,412 | $ | 2,238 | ||||||
Silver : gold ratio(2) |
60 : 1 | 52 : 1 | 60 : 1 | 52 : 1 | 52 : 1 | |||||||||||
- (1)
- Includes
production attributable to us from our 49% owned San José mine.
- (2)
- Silver
production is presented as a gold equivalent. Gold equivalent ounces calculations are based on prevailing spot prices at the beginning of the year.
The silver to gold ratio used for 2014 was 60:1, while the ratio for 2013 and prior was 52:1. For 2015, the silver to gold ratio has been set to 75:1.
- (3)
- Earnings
from mining operations, adjusted net loss, total cash costs, all-in sustaining costs, all-in costs, and average realized prices are non-GAAP
financial performance measures with no standardized definition under U.S. GAAP. See "Non-GAAP Financial Performance Measures" beginning on page 69 for additional information, including
definitions of these terms.
- (4)
- In
2013, the Company revised its allocation of general and administrative expenses to total cash costs to conform to the Gold Institute Production Cost
standard. 2012 figures have been adjusted to conform to the current methodology.
- (5)
- In 2013, the Company adopted the new guidance on all-in sustaining and all-in costs published by the World Gold Council on June 27, 2013. 2012 figures have been adjusted to conform to the current methodology.
51
Operating and Financial Highlights
- •
- Both the San José and El Gallo 1 mines met 2014
production guidance. Gold equivalent production in the year 2014 totaled 137,612 ounces, which includes 98,969 gold equivalent ounces
attributable to us from our 49% interest in the San José mine (compared to 2014 guidance of 97,180 gold equivalent ounces), and 38,643 gold equivalent ounces from the El Gallo 1
mine (compared to guidance of 37,500 gold equivalent ounces). The production challenges experienced in the third quarter of 2014 at El Gallo 1 due to severe rainfall were compensated by the mining and
processing of high grade ore in the fourth quarter of 2014. Processing capacity in the fourth quarter of 2014 was also increased through the use of a portable crusher to process ore in stockpile.
- •
- Both the San José and El Gallo 1 mines met or were
below 2014 cost guidance. Total cash costs, all-in sustaining costs and all-in costs per gold equivalent ounce sold for the year ended
December 31, 2014 for all of our operations on a consolidated basis totaled $817, $1,198 and $1,368 per ounce, respectively. Total cash costs and all-in sustaining costs at the San
José mine for the year 2014 were $795 and $1,086 per gold equivalent ounce, respectively, which compare favorably to the 2014 cost guidance of $750-$850 and $1,100-$1,200 per gold
equivalent ounce, respectively. Total cash costs and all-in sustaining cash costs at our El Gallo 1 mine totaled $875 and $1,194 per gold equivalent ounce, respectively. These also compare favorably
to the updated 2014 guidance we published as part of our results for the third quarter of 2014, of $950-$1,050 and $1,200-$1,300 per gold equivalent ounce, respectively. Costs at the El Gallo 1 mine
were below guidance due to the higher than expected average grade of metal processed in the fourth quarter of 2014.
- •
- The Company expects consolidated production for 2015 to be of 96,500
ounces of gold and 3,120,000 ounces of silver. This is comprised of 46,500 ounces of gold and 3,100,000 ounces of silver from the San
José mine, and 50,000 ounces of gold and 20,000 ounces of silver from the El Gallo 1 mine. Using a silver to gold ratio of 75:1 for the year 2015, this represents projected consolidated
production of 138,100 gold equivalent ounces. The silver to gold ratio is reviewed annually based on prevailing spot prices at the beginning of the year. The silver to gold ratio for the year 2014 was
of 60:1, while the ratio for 2013 and prior was 52:1.
- •
- 2015 consolidated cost guidance is forecasted at $675-$775 per gold
equivalent ounce for total cash costs and $1,075-$1,175 per gold equivalent ounce for all-in sustaining costs. Total cash costs and
all-in sustaining costs at the San José mine are forecasted at $775-875 per gold equivalent ounce and $1,175-1,275, respectively, while at El Gallo 1, forecasted costs are $500-600 per
gold equivalent ounce and $700-800 per gold equivalent ounce, respectively. These are based on a based on a silver to gold ratio of 75:1.
- •
- Consolidated gold equivalent ounces sold in year ended
December 31, 2014 totaled 132,227 ounces. This includes 96,304 gold equivalent ounces attributable to us from our 49% interest in
the San José mine, and 35,923 gold equivalent ounces from El Gallo 1. The year-over-year increase in gold and silver ounces sold reflects the increase in production at both mines.
However, the increase in sales volume was offset by lower average realized prices.
- •
- The consolidated average realized prices for the year 2014 were $1,248 per ounce of gold sold, and $17.68 per ounce of silver sold. The decrease year-over-year reflects the downward trend of gold and silver prices during the year 2014. Average realized prices are presented net of adjustments of provisionally priced sales of concentrates.
52
- •
- We reported a consolidated net loss of $311.9 million, or $1.05 per
share for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to $147.7 million, or $0.50 per share in 2013. The net loss for year 2014
includes impairment charges on our Los Azules project, Nevada and Argentina properties, of $228.3 million, $98.4 million and $27.0 million, respectively, along with a corresponding deferred income tax
recovery of $41.8 million, $31.6 million and $3.2 million, respectively. These impairment charges reflect a significant reduction in our planned exploration program and land optimization initiative
across most of our properties, as well as a decline in the observed market value of comparable transactions. With respect to our El Gallo 1 mine, although we produced and sold higher quantities of
gold and silver from our El Gallo 1 mine in the year 2014 than in 2013, there was a slight decrease in revenues due to lower average realized prices, which did not compensate for the increase in
production costs applicable to sales. In addition, we also recorded an impairment of $21.2 million relating to our investment in MSC, and incurred registration taxes of $6.8 million relating to
intercompany financing agreements with certain of our subsidiaries.
- •
- Our adjusted net loss for the year ended December 31, 2014, was
$33.0 million, or $0.11 per share. This compares to a loss of $31.0 million, or $0.10 per share, for 2013. Adjusted net
loss removes the impact of impairment charges and foreign currency gains or losses resulting from the devaluation of the Argentine peso, Mexican peso and Canadian dollar relative to the U.S. dollar,
as well as non recurring items such as registration taxes.
- •
- Our earning from mining operations for the year ended
December 31, 2014 was $25.5 million, compared to $37.6 million in 2013. The decrease compared to 2013 was due to
lower average metal prices on sales realized in the year 2014.
- •
- We ended the year with $15.9 million in cash, investments and precious metals and no bank debt.
Development and Exploration Activities
El Gallo Complex, Mexico
El Gallo 1
During 2013, we commenced work on the expansion of El Gallo 1 in order to increase processing capacity from a nominal 3,000 tonnes per day to 4,500 tonnes per day. The commissioning commenced during the second quarter of 2014, with the expansion fully operational by the fourth quarter of 2014. During the year ended December 31, 2014, we spent $1.2 million on the expansion, primarily relating to the installation of a new series of pumps, generators and carbon columns, upgrading the electro-winning cells at the ADRO process plant, and expanding the heap leach pad to accommodate the increased throughput and subsequent ore delivery rate. We also incurred $0.3 million on an induction furnace to handle the expected increased doré production. The final cost of the expansion, including this last item, totaled $2.8 million.
In addition to costs relating to the expansion, mine constructions costs incurred in the year ended December 31, 2014 include $0.3 million on road construction from the Lupita pit to the crusher.
In 2015, we expect to spend approximately $3.0 million on sustaining capital, including the expansion of our leach pads to accommodate the increased processing capacity at El Gallo 1, and other capital expenditures.
El Gallo 2
We received the final environmental permit required for the potential construction and operation of the mine. The final environmental permit, relating to the Change of Land Use was received from
53
the SEMARNAT in January 2014. Further, we submitted two additional permits in 2014. The first permit is in relation to the mining of the Palmarito deposit, which represents approximately 15% of the projected annual silver production at El Gallo 2. The second permit relates to the right-of-way for a 4.6-mile (7.5 km) 115 kV electric transmission line that would connect the El Gallo 2 processing plant to the national power grid. In the meantime, construction of the mine could begin with power provided by generators with the option of connecting to the grid when the permit is received. Delays in receiving either of these two these permits would not be expected to delay eventual construction from proceeding.
A final decision to proceed with the construction of El Gallo 2 has not been made. Any decision to proceed would be based on silver price expectations and securing financing on terms that are more favorable than those that were available to us at the time of filing this report. We believe approximately $150 million in financing would be required in order to construct the mine. In order to prepare for a possible construction decision in the future, we have been evaluating possible debt financing alternatives and advancing the construction of the ball mill, which is the longest lead time item associated with the mine. The ball mill is now substantially complete. Pending a decision to proceed with the development of El Gallo 2, we are storing the mill at the manufacturer's facilities. We expect to disburse the final payment of $1.0 million for the ball mill in the first half of 2015.
We are also conducting cost-saving studies to identify opportunities that would allow us to reduce the initial capital investment required while minimizing the impact on potential production. Potential changes include reducing the number of leach tanks and transformers, building a smaller process plant / refinery, and using modular crushers. The El Gallo 2 Feasibility Study, which provided an estimate of $180 million for initial capital expenditures, has not been updated to reflect these possible changes.
For the year ended December 31, 2014, we spent $1.8 million on mine development costs. For 2015, budgeted costs primarily relate to the storage of the ball mill at the manufacturer's facilities and test work.
Exploration
In 2014, approximately 76,530 ft. (23,326 m) of drilling was completed. This included 69,114 ft. (21,066 m) at the El Gallo 1 mine, where exploration and geotechnical holes were drilled in the Samaniego pit, Lupita, Central and Veta Nueva area, before moving to the San José del Alamo project approximately 9 miles (14 km) to the north for infill drilling on the existing resource. Further infill drilling on the preliminary resource at Twin Domes, 7 miles (11 km) to the west is being carried out with the objective of adding to the overall El Gallo 1 mineralized material base. Additional exploration activities included continuing the blast hole program in conjunction with rock and soil sampling at prospects within our existing license grounds. Drilling efforts were also focused within other areas of the broader El Gallo tenement including Carrisalejo and Mina Grande with the objective of increasing the mineralized material base within the El Gallo 2 area, where we drilled 7,411 ft. (2,259 m).
As of the date of this report, one core drill has continued to operate, with plans to add an additional drill in 2015. For 2015, we have budgeted $5.5 million in total exploration costs at El Gallo, which includes drilling of approximately 88,580 ft. (27,000 m). The exploration program will be focused on core drilling, blast hole drilling and surface mapping, which will include rock and soil sampling.
Gold Bar Project, Nevada, U.S.
Gold Bar is located primarily on public lands managed by the BLM. During 2014, we continued to advance the Gold Bar project by completing baseline studies in support of the BLM and State of Nevada permitting required for mine development and construction. We also drilled and pump-tested one potential water well location for future mining operations.
54
We submitted our Plan Of Operations ("POO") permit application during the fourth quarter of 2013. The POO was determined complete and the BLM has determined that an Environmental Impact Statement ("EIS") is necessary to fulfill the requirements under the National Environmental Policy Act ("NEPA"). Upon completion of the EIS, the BLM will be able to proceed with the approval determination of the POO. A third-party consulting firm has been contracted to assist the BLM in the preparation of an EIS for the Gold Bar project. Due to reduced staffing levels and personnel turnover at the BLM Mount Lewis Field office, final permit approval, which was previously scheduled for the second quarter of 2014, is expected for the third quarter of 2016.
For 2015, we have budgeted $1.4 million in for the Gold Bar project, primarily for the advancement of the EIS, as well as a drill program of approximately 10,000 ft (3,050 m).
Los Azules Copper Project, Argentina
The 2013-2014 exploration season started in December 2013 and was completed in March 2014. No significant exploration work was conducted during this 2013-2014 season. Expenditures for the year ended December 31, 2014 totaled $0.7 million, and related to baseline studies regarding flora, fauna, water quality and other environmental compliance matters.
For 2015, we have budgeted $0.7 million for Los Azules. While no significant exploration work or drilling program is expected, we will continue to advance the project with baseline environmental studies.
Rationalization of Exploration Program—Nevada, Santa Cruz and San Juan Properties
We performed a strategic review of our property holdings in Nevada and Argentina. In an effort to conserve resources, we have made the decision to rationalize our exploration efforts to focus on our core assets, namely our Los Azules, Gold Bar, Tonkin and North Battle Mountain properties. We have recorded impairment charges on non-core properties and reduced their carrying values to nil.
Results of Operations—MSC (on a 100% basis)
Overview
The following discussion relates only to MSC. The following table sets out production totals, sales totals, total cash costs and all-in sustaining costs (on a co-product and gold equivalent basis) for the San José mine for the periods presented, on a 100% basis. Also included below are the production figures on a 49% attributable basis. As noted in Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies—Investments, we account for investments over which we exert significant influence but do not control through majority ownership using the equity method of accounting. In applying the equity method of accounting to our 49% Investment in MSC, MSC's financial statements, which are originally prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board, have been adjusted to conform with U.S. GAAP. As such, the summarized financial data presented under this heading is in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
55
| |
Three months ended December 31, |
Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||
| |
(in thousands, unless otherwise indicated) |
|||||||||||||||
San José Mine—100% |
||||||||||||||||
Tonnes of ore mined |
161 | 159 | 539 | 550 | 548 | |||||||||||
Average grade (gpt): |
||||||||||||||||
Gold |
6.11 | 7.31 | 6.06 | 6.70 | 5.40 | |||||||||||
Silver |
490 | 469 | 448 | 462 | 422 | |||||||||||
Tonnes of ore processed |
153 | 156 | 571 | 537 | 510 | |||||||||||
Average grade (gpt): |
||||||||||||||||
Gold |
6.19 | 6.03 | 5.77 | 6.42 | 5.79 | |||||||||||
Silver |
454 | 399 | 404 | 425 | 417 | |||||||||||
Average recovery (%): |
||||||||||||||||
Gold |
89.6 | 87.6 | 88.8 | 89.2 | 90.4 | |||||||||||
Silver |
87.8 | 87.0 | 87.2 | 86.7 | 86.6 | |||||||||||
Gold ounces: |
||||||||||||||||
Produced |
27 | 27 | 94 | 99 | 86 | |||||||||||
Sold |
30 | 25 | 91 | 95 | 84 | |||||||||||
Silver ounces: |
||||||||||||||||
Produced |
1,959 | 1,741 | 6,469 | 6,357 | 5,953 | |||||||||||
Sold |
2,163 | 1,742 | 6,316 | 6,278 | 5,897 | |||||||||||
Gold equivalent ounces(1): |
||||||||||||||||
Produced |
60 | 60 | 202 | 221 | 200 | |||||||||||
Sold |
66 | 59 | 197 | 215 | 198 | |||||||||||
Net sales |
$ | 64,627 | $ | 58,692 | $ | 213,013 | $ | 240,723 | $ | 310,384 | ||||||
Gross average realized price ($/ounce)(2): |
||||||||||||||||
Gold |
$ | 1,165 | $ | 1,187 | $ | 1,236 | $ | 1,284 | $ | 1,650 | ||||||
Silver |
$ | 15.49 | $ | 19.44 | $ | 17.68 | $ | 21.26 | $ | 30.65 | ||||||
Total cash costs(2) |
$ | 46,856 | $ | 43,903 | $ | 156,224 | $ | 169,091 | $ | 160,353 | ||||||
Total cash costs per ounce sold ($/ounce)(2)(3): |
||||||||||||||||
Gold |
$ | 812 | $ | 832 | $ | 874 | $ | 876 | $ | 835 | ||||||
Silver |
$ | 10.36 | $ | 13.15 | $ | 12.11 | $ | 13.71 | $ | 15.28 | ||||||
Gold equivalent(1) |
$ | 708 | $ | 747 | $ | 795 | $ | 785 | $ | 811 | ||||||
All-in sustaining costs(2) |
$ | 67,767 | $ | 59,593 | $ | 213,384 | $ | 228,080 | $ | 236,574 | ||||||
All-in sustaining costs per ounce sold ($/ounce)(2)(4): |
||||||||||||||||
Gold |
$ | 1,174 | $ | 1,129 | $ | 1,193 | $ | 1,182 | $ | 1,231 | ||||||
Silver |
$ | 14.98 | $ | 17.84 | $ | 16.54 | $ | 18.49 | $ | 22.54 | ||||||
Gold equivalent(1) |
$ | 1,024 | $ | 1,014 | $ | 1,086 | $ | 1,058 | $ | 1,197 | ||||||
Silver : gold ratio(1) |
60 : 1 | 52 : 1 | 60 : 1 | 52 : 1 | 52 : 1 | |||||||||||
McEwen Mining—49% attributable share |
||||||||||||||||
Ounces produced: |
||||||||||||||||
Gold |
13 | 13 | 46 | 48 | 42 | |||||||||||
Silver |
960 | 853 | 3,170 | 3,115 | 2,917 | |||||||||||
Gold equivalent(1) |
29 | 28 | 99 | 108 | 98 | |||||||||||
- (1)
- Silver production is presented as a gold equivalent. Gold equivalent ounces calculations are based on prevailing spot prices at the beginning of the year. The silver to gold ratio used for 2014 was 60:1, while the ratio for 2013 and prior was 52:1. For 2015, the silver to gold ratio has been set to 75:1.
- (2)
- Average realized prices, total cash costs, all-in sustaining costs, and all-in costs are non-GAAP financial performance measures with no standardized definition under U.S. GAAP. See "Non-GAAP Financial Performance Measures" beginning on page 69 for additional information, including definitions of these terms.
56
- (3)
- In 2013, the Company revised its allocation of general and administrative expenses to total cash costs to conform to the Gold Institute Production Cost standard. 2012 figures have been adjusted to conform to the current methodology.
- (4)
- In 2013, the Company adopted the new guidance on all-in sustaining and all-in costs published by the World Gold Council on June 27, 2013. 2012 figures have been adjusted to conform to the current methodology.
Production
Gold production for the year ended December 31, 2014 was 94,161 ounces. While gold production exceeded the 2014 guidance of 90,000 gold ounces by 4% as a result of higher than forecasted average grade and recovery rates production declined 5% when compared to 2013 due to the exceptionally high average gold grade processed in that year.
Silver production was relatively in line with 2014 guidance of 6,500,000 silver ounces, with 6,469,022 ounces produced in the year ended December 31, 2014. This was slightly higher than silver production in the year ended December 31, 2013, due to the increase in tonnes processed, coupled with higher average silver recovery rates, in the year 2014 compared to 2013. These benefits were partly offset by a year-over-year decrease in average silver grade.
Tonnes processed increased to 571,018 in 2014, an increase of 6% from 536,937 tonnes in 2013, as a result of the expansion in mill throughput capacity which was commissioned at the beginning of 2013 and fully operational for the entirety of the year 2014. In addition to the increased mill capacity, tonnes processed were higher in 2014 than in 2013 due to fewer days of labour interruptions in 2014. Production in 2013 was impacted by 22 days of stoppage, which included a ten-day stoppage in the first quarter of 2013 due to an outbreak of a food-transmitted illness. Comparatively, labour interruptions at the mine in 2014 totaled eight days, primarily due to employee travel being affected by national strikes throughout Argentina.
Sales
For year ended December 31, 2014, net sales realized by MSC from the sale of gold and silver decreased by 12% to $213.0 million from $240.7 million in 2013. The decrease was primarily a result of lower average realized prices, coupled with the fewer number of ounces of gold sold due to the decrease in gold production in 2014 compared to 2013. Sales volumes in 2014 were 91,276 ounces of gold and 6,315,799 ounces of silver, compared to 94,758 ounces of gold and 6,277,837 ounces of silver sold in 2013. Sales in the third quarter of 2014 had been unusually low due to shipment delays at the port from which concentrate is typically shipped. The build-up of concentrate inventory was resolved in the fourth quarter of 2014.
The average gross sale price for gold sold, after mark-to-market provisional price adjustments, discussed below, for the year ended December 31, 2014 was $1,236 per ounce, a decrease of 4% compared to $1,284 per ounce realized in 2013. In comparison, the average London P.M. fix price for gold was $1,266 per ounce in 2014, and $1,411 per ounce in 2013.
The average gross sale price for silver sold, after mark-to-market provisional price adjustments, for the year ended December 31, 2014 was $17.68 per ounce, a decrease of 17% compared to an average $21.26 per ounce realized in 2013. In comparison, the average London P.M. fix price for silver was $19.08 per ounce in 2014, and $23.79 per ounce in 2013.
The difference between the average gross realized sale price per ounce of gold and silver sold by MSC and the average London fix prices noted above is due to negative adjustments of provisionally priced shipments of concentrates as a result of the downward trend of gold and silver prices during the latter half of 2014. Sales revenue on provisionally priced sales of concentrates is recognized based on estimates of the final pricing receivable based on relevant forward market prices. At each reporting
57
date, provisionally priced metal is marked to market based on the forward selling price for the quotational period of the sales contract.
Total Cash Costs and All-In Sustaining Costs
Total cash costs for the San José mine per gold equivalent ounce sold for the year ended December 31, 2014 were within the 2014 guidance range of $750-850 per gold equivalent ounce, ending at $795 per ounce based on a 60:1 ratio, compared to $785 per ounce sold in 2013 based on a silver to gold ratio of 52:1, or $848 based on a 60:1 ratio. On a co-product basis (gold and silver), total cash costs for both the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 were $874 per ounce of gold, and $12.11 per ounce of silver, compared to $876 per ounce of gold, and $13.71 per ounce of silver in 2013. Total cash costs on an aggregate basis decreased from $169.1 million to $156.2 million, reflecting lower sales volume due to lower levels of production in the year 2014 compared to 2013. Total cash costs also decreased as a result of continued cost cutting measures implemented by MSC and a sharp devaluation of the Argentine peso during the first half of the year 2014. These effects were partly offset by high inflation in Argentina.
All-in sustaining costs were below the 2014 guidance range of $1,100-$1,200 per gold equivalent ounce, due to significant reductions in capital and exploration expenditures as part of MSC's continued cost cutting measures. All-in sustaining cash costs per gold equivalent ounce sold for the year ended December 31, 2014 were $1,086 per ounce based on a 60:1 ratio, compared to $1,058 per ounce in 2013 based on a silver to gold ratio of 52:1, or $1,144 based on a 60:1 ratio. On a co-product basis, all-in sustaining costs for the year ended December 31, 2014 were $1,193 per ounce of gold, compared to $1,182 per ounce in 2013, and $16.54 per ounce of silver, compared to $18.49 per ounce in 2013. On an aggregate basis, all-in sustaining costs decreased year-over-year from $228.1 million to $213.4 million.
Exploration
During 2014, a total of 54,520 ft. (16,618 m) of drilling was performed and exploration was focused on definition of the Karina, Guadalupe and Nueva Ramona veins as well as drilling in the Los Pinos area. Detailed surface mapping and sampling over the Los Pinos vein, over an area of 3,500 hectares, was also completed. Mapping of the south side of the San José area covering an area of 520 acres (211 hectares) was also carried out.
2015 Guidance
We expect 2015 production at MSC, on a 100% basis, to be approximately 6,300,000 million ounces of silver and 95,000 ounces of gold, for a 49% share attributable to us of approximately 87,800 gold equivalent ounces (3.1 million ounces of silver and 46,500 ounces of gold, using a silver to gold ratio of 75:1). The decrease in forecasted production for 2015 compared to 2014 reflects a slight decrease in the number of tonnes processed of 550,000 and lower recovery rates of 87.1% and 86.7% for gold and silver, respectively. Average grades are expected to be 6.15 g/t and 414 g/t, respectively. Total cash costs and all-in sustaining costs per gold equivalent ounce are expected to be between $775-$875 per ounce and $1,175-$1,275 per ounce, respectively.
Exploration expenditures in 2015 are budgeted to be approximately $0.7 million. Depending on the outcome of these activities, we may also focus on the Colorado Grande area, and on the Los Pinos and Los Pinitos veins, for a total of 3,000 m (9,840 ft) of drilling, as well as the identification and mapping of new structures.
58
Investment in MSC (49%)
Our 49% attributable share of operations from our investment in MSC was a loss of $5.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to income of $0.9 million in 2013. The loss of $5.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 is net of the amortization of the fair value increments arising from the purchase price allocation, of $13.2 million, and related deferred income tax recovery of $10.5 million. Included in the income tax recovery is the impact of fluctuations in the exchange rate between the Argentine peso and the U.S. dollar on the peso-denominated deferred tax liability associated with the investment in MSC recorded as part of the acquisition of Minera Andes. As a devaluation of the Argentine peso relative to the U.S. dollar results in a recovery of deferred income taxes, the impact has been a decrease in the loss from our investment in MSC for the year ended December 31, 2014.
A summary of the financial results from MSC, including our 49% attributable share of operations from our investment in MSC, for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, and for the period from January 25, 2012 (after the closing of the acquisition of Minera Andes) to December 31, 2012, is as follows.
| |
For the year ended December 31, |
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
For the period ended December 31, 2012 |
|||||||||
| |
2014 | 2013 | ||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Minera Santa Cruz S.A. (100%) |
||||||||||
Net sales |
$ | 213,013 | $ | 240,723 | $ | 290,848 | ||||
Production costs applicable to sales |
(173,274 | ) | (190,281 | ) | (155,915 | ) | ||||
(Loss) income from operations before extraordinary items |
(5,300 | ) | 4,338 | 51,634 | ||||||
Net (loss) income |
(5,300 | ) | 4,338 | 51,634 | ||||||
Portion attributable to McEwen Mining Inc. (49%) |
||||||||||
Net (loss) income |
$ | (2,597 | ) | $ | 2,126 | $ | 25,301 | |||
Amortization of fair value increments |
(13,190 | ) | (18,424 | ) | (22,682 | ) | ||||
Income tax recovery |
10,503 | 17,144 | 18,217 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
(Loss) income from investment in MSC, net of amortization |
$ | (5,284 | ) | $ | 846 | $ | 20,835 | |||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
In addition to our attributable loss on our investment in MSC of $5.3 million, we recorded an impairment charge in the year ended December 31, 2014, primarily as a result of the significant decline in silver market prices during the year 2014, as well as in the observed market value of comparable transactions in South America, indicating a potential significant decrease in the market price of the exploration properties owned by MSC. As the decline in the estimated fair value of our investment in MSC was considered other than temporary, we recorded an impairment charge of $21.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. Refer to Note 7, Investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. ("MSC")—San José Mine, and Note 17, Fair Value Accounting, of the accompanying financial statements for further details on the valuation and impairment of our investment in MSC.
During the year ended December 31, 2014, we received $9.5 million in dividends from MSC, compared to $1.8 million in 2013.
59
Changes in our investment in MSC for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 are as follows:
| |
2014 | 2013 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Investment in MSC, beginning balance |
$ | 212,947 | $ | 273,948 | |||
Attributable net (loss) income from MSC |
(2,597 | ) | 2,126 | ||||
Amortization of fair value increments |
(13,190 | ) | (18,425 | ) | |||
Income tax recovery |
10,503 | 17,145 | |||||
Dividend distribution received |
(9,483 | ) | (1,826 | ) | |||
Impairment of investment in MSC |
(21,162 | ) | (95,878 | ) | |||
Contribution of Santa Cruz exploration properties, net of tax |
— | 35,857 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Investment in MSC, ending balance |
$ | 177,018 | $ | 212,947 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
As at December 31, 2014, MSC had current assets of $113.3 million, total assets of $540.6 million, current liabilities of $67.0 million and total liabilities of $179.4 million. These balances include the increase in fair value and amortization of the fair value increments arising from the purchase price allocation and are net of the impairment charges recorded in 2014 and 2013. Excluding the fair value increments from the purchase price allocation and impairment charges, MSC had current assets of $111.5 million, total assets of $311.5 million, current liabilities of $67.0 million, and total liabilities of $102.7 million as at December 31, 2014.
Results of Operations—El Gallo 1
Overview
The following table sets out production totals, sales totals, total cash costs, and all-in sustaining cash costs (on a gold equivalent basis) for El Gallo 1 for the three months ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, and for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. The mine achieved commercial production, for accounting purposes, after its initial gold pour in September 2012. For operational purposes, commercial production was declared as of January 1, 2013. As production for operational
60
purposes was only achieved on January 1, 2013, certain measures such as total cash costs and all-in sustaining costs have no comparative figures for 2012.
| |
Three months ended December 31, |
Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||
| |
(in thousands, unless otherwise indicated) |
|||||||||||||||
Tonnes of ore mined |
369 | 351 | 1,271 | 1,278 | 357 | |||||||||||
Average grade gold (gpt) |
2.20 | 1.27 | 1.40 | 1.31 | 1.21 | |||||||||||
Tonnes of ore processed |
522 | 324 | 1,462 | 1,255 | 340 | |||||||||||
Average grade gold (gpt) |
2.39 | 1.17 | 1.58 | 1.22 | 1.05 | |||||||||||
Gold ounces: |
||||||||||||||||
Produced |
14.1 | 7.7 | 38.2 | 30.7 | 6.9 | |||||||||||
Sold |
11.3 | 8.0 | 35.6 | 32.7 | 3.2 | |||||||||||
Silver ounces: |
||||||||||||||||
Produced |
13.5 | 3.8 | 25.9 | 20.7 | 4.5 | |||||||||||
Sold |
8.0 | 5.5 | 19.4 | 22.7 | 0.3 | |||||||||||
Gold equivalent ounces(1): |
||||||||||||||||
Produced |
14.3 | 7.8 | 38.7 | 31.1 | 6.9 | |||||||||||
Sold |
11.4 | 8.1 | 35.9 | 33.1 | 3.2 | |||||||||||
Net sales |
$ | 13,683 | $ | 10,247 | $ | 45,303 | $ | 45,982 | $ | 45,982 | ||||||
Average realized price ($/ounce)(2): |
||||||||||||||||
Gold |
$ | 1,203 | $ | 1,270 | $ | 1,263 | $ | 1,389 | $ | 1,853 | ||||||
Silver |
$ | 16.08 | $ | 20.55 | $ | 17.89 | $ | 23.92 | $ | 32.90 | ||||||
Total cash costs(2)(3) |
$ | 8,106 | $ | 6,182 | $ | 31,418 | $ | 24,821 | $ | — | ||||||
Total cash cost per gold equivalent ounce sold ($/ounce)(1)(2)(3) |
$ | 711 | $ | 765 | $ | 875 | $ | 749 | $ | — | ||||||
All-in sustaining costs(2)(4) |
$ | 10,618 | $ | 8,664 | $ | 42,895 | $ | 38,575 | $ | — | ||||||
All-in sustaining cost per gold equivalent ounce sold ($/ounce)(1)(2)(4) |
$ | 931 | $ | 1,071 | $ | 1,194 | $ | 1,164 | $ | — | ||||||
Silver : gold ratio(1) |
60 : 1 | 52 : 1 | 60 : 1 | 52 : 1 | 52 : 1 | |||||||||||
- (1)
- Silver production presented as a gold equivalent. Gold equivalent ounces calculations are based on prevailing spot prices at the beginning of the year. The silver to gold ratio used for 2014 was 60:1, while the ratio for 2013 and prior was 52:1. For 2015, the silver to gold ratio has been set to 75:1.
- (2)
- Average realized prices, total cash costs, all-in sustaining costs, and all-in costs are non-GAAP financial performance measures with no standardized definition under U.S. GAAP. See "Non-GAAP Financial Performance Measures" beginning on page 69 for additional information, including definitions of these terms.
- (3)
- In 2013, the Company revised its allocation of general and administrative expenses to total cash costs to conform to the Gold Institute Production Cost standard. 2012 figures have been adjusted to conform to the current methodology.
- (4)
- In 2013, the Company adopted the new guidance on all-in sustaining and all-in costs published by the World Gold Council on June 27, 2013. 2012 figures have been adjusted to conform to the current methodology.
Production
Production at El Gallo 1 for the year ended December 31, 2014 increased by 24% to 38,643 gold equivalent ounces, from 31,129 gold equivalent ounces in 2013, exceeding the 2014 production guidance of 37,500 gold equivalent ounces. While tonnes mined in 2014 remained relatively consistent with 2013, tonnes processed increased 17% to 1,462,496 in 2014 from 1,255,314 in 2013. The increase in tonnes
61
processed was due to the installation of a portable crusher in the fourth quarter of 2014 to increase crushing capacity and compensate for the production shortfall in the third quarter of 2014 resulting from heavy rainfalls in that quarter. Additional tonnes processed through this portable crusher totaled 156,037 tonnes in the fourth quarter of 2014, with an additional 75,922 tonnes processed in January 2015. The portable crusher was demobilized in the first quarter of 2015, after the ore stockpiles were drawn down. In addition to the increase in tonnes crushed, production increased due to the mining of deeper, higher-grade ore in the fourth quarter of 2014. Grades in the fourth quarter of 2014 averaged 2.39 g/t, resulting in an average grade for the year 2014 of 1.58 g/t, compared to 1.22 g/t in 2013.
Tonnes mined represent tonnes of ore extracted, while tonnes processed represent tonnes of ore crushed and placed on the leach pads. The difference between tonnes mined of 1,270,888 and tonnes processed of 1,462,496 was draw down from the existing stockpile inventory. Due to long process cycles, actual recoveries from the heap are difficult to measure and may fluctuate significantly based on the timing, quantity and metallurgical attributes of new mineralized material placed on the leach pads, amongst other variables. The cumulative recovery rate for gold production from September 1, 2012 (start of production at the El Gallo 1 mine) to December 31, 2014 is estimated at 56%. This is lower than the estimated cumulative recovery rate of 61% as at December 31, 2013, as a significant amount of mineralized material was placed on the leach pads at the end of the year 2014. The recovery of the ounces contained from this mineralized material will be realized in the first quarter of 2015.
Sales
For the year ended December 31, 2014, sales from El Gallo 1 amounted to $45.3 million, a slight decrease compared to $46.0 million in 2013. Despite an increase of 8% in ounces sold from 33,142 gold ounces in 2013 to 35,923 gold ounces in 2014, the benefit of increased sales volume was negated by lower average realized prices. The average realized price of gold was $1,263 per ounce in 2014, compared to $1,389 per ounce in 2013.
Total Cash Costs and All-In Sustaining Costs
Total cash costs for the El Gallo 1 mine per gold equivalent ounce sold for the year ended December 31, 2014 increased to $875 per ounce, compared to $749 per ounce in 2013. On an aggregate basis, total cash costs increased by 27% to $31.4 million in 2014, compared to $24.8 million in 2013. The increase in total cash costs in the 2014 period both on a dollar and per ounce basis is primarily a reflection of the operating challenges resulting from the severe rainfall, as discussed above, as well as a higher strip ratio in the areas being mined in 2014. Further, haulage costs have increased year-over-year, as we are currently mining areas in the pits farther away from the processing plant and waste dumps. Total cash costs were below the updated 2014 guidance of $950-$1,050 per gold equivalent ounces primarily as a result of the average higher grade processed of 2.39 g/t compared to a forecast of 1.80 g/t for the fourth quarter of 2014.
All-in sustaining costs for the year ended December 31, 2014 were $1,194 per gold equivalent ounce in 2014 compared to $1,164 per ounce in 2013. On an aggregate basis, all-in sustaining costs increased by 11% to $42.9 million in of 2014, compared to $38.6 million in 2013, due to the operating challenges noted above. All-in sustaining costs also include $0.3 million related to the construction of the road between the Lupita pit and the crusher. All-in sustaining costs were below the updated 2014 guidance of $1,200-$1,300 per gold equivalent ounces primarily as a result of the average higher grade processed in the fourth quarter of 2014, as noted above.
2015 Guidance
For 2015, El Gallo 1 is forecasted to produce approximately 50,200 gold equivalent ounces (50,000 gold ounces and 20,000 silver ounces, using a silver to gold ratio of 75:1), as we benefit from a full year
62
of increased processing capacity at El Gallo 1, with the expansion project now complete and fully operational, and higher expected average grades. Total cash costs and all-in sustaining costs per gold equivalent ounce are expected to be between $500-$600 per ounce and $700-$800 per ounce, respectively, as we continue to mine deeper in the pit for higher grades. For the year 2015, we expect average grades of 2.6 g/t, thereby leading to reduced costs on a per ounce basis.
Results of Consolidated Operations
Year ended December 31, 2014 compared to 2013
General. For the year ended December 31, 2014, our net loss was $311.9 million or $1.05 per share, compared to $147.7 million or $0.50 per share in 2013. Although we produced and sold higher quantities of gold and silver from our El Gallo 1 mine in the year 2014 than in 2013, there was a slight decrease in revenues due to lower average realized prices, which did not compensate for the increase in production costs applicable to sales. Further, significant impairment charges relating to our mineral property interests were recorded in both 2014 and 2013, of $353.7 million and $63.0 million, respectively. Impairments recorded in the year ended December 31, 2014 related to all of our exploration properties across Nevada and Argentina, including Gold Bar and Los Azules, while those recorded in the year 2013 related to the Argentina exploration properties and certain Nevada properties. Impairments of $21.2 million and $95.8 million were also recorded on our investment in MSC in 2014 and 2013, respectively. In the year 2014, we also recorded a non-recurring expense of $6.8 million relating to registration taxes payable for intercompany financing agreements with certain of our subsidiaries.
Revenue. Gold and silver sales in the year ended December 31, 2014 totaled $45.3 million. This compares to $46.0 million in 2013. The decrease was driven by the decrease in average realized metals prices, which more than offset the increase in ounces sold from our El Gallo 1 mine.
Costs and Expenses. Total costs and expenses, excluding impairment charges, in the year ended December 31, 2014 totaled $80.6 million, compared to $87.5 million in 2013. The decrease was largely a result of reduced exploration costs and general and administrative expenses, partly offset by higher production costs applicable to sales. The 2013 period also included a loss on disposal of $6.8 million relating to the sale of certain Nevada properties.
Production costs applicable to sales at El Gallo 1 were $40.6 million in the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to $34.6 million in 2013. While the increase is partly a reflection of the higher number of ounces sold, production costs applicable to sales on a per ounce basis also increased due to a higher average strip ratio, higher haulage cost and operating challenges due to severe rainfalls in 2014. Production costs in the 2014 period also include $2.0 million in inventory write-down, and expenditures of $0.4 million to repair and improve the integrity of the excess pond liners and foundation of the ADR plant, as well as to provide a higher margin of safety in the event of extraordinary rainfall.
Mine construction costs were $1.7 million in the year 2014 compared to $1.4 million in 2013. Mine construction costs both in 2014 and 2013 were primarily incurred in relation to the El Gallo 1 processing capacity expansion, which was substantially completed in the second quarter of 2014, and fully operational in the fourth quarter of 2014. The 2014 period also includes costs incurred on the purchase of an induction furnace of $0.3 million, and the construction of a road from the Lupita pit to the crusher of $0.3 million.
Mine development costs, which are comprised of engineering and development costs for El Gallo 2, were $1.8 million in the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to $0.8 million in 2013, and included a payment of $1.4 million for the Land Use Change permit in January 2014. As
63
mentioned previously, during the year, we continued to pursue long-term items for a new mill, even though no final production decision has been made.
Exploration costs in the year 2014 decreased to $11.3 million from $24.8 million in 2013, reflecting a reduction in exploration expenditures and drilling activities across most projects in 2014 in an effort to conserve capital. During the year 2014, we incurred $2.5 million in exploration expenditures in Argentina. This amount includes the value of the 850,000 shares we issued to TNR to terminate the Back-In Right Option on a portion of the Los Azules project, as described in Item 2. Properties—Los Azules Copper Project, and in Note 10, Stock Based Compensation. The remainder of the exploration expenses relate to basic geological work primarily on Los Azules. This compares to $14.8 million in exploration expenditures in 2013. For Mexico, during the 2014 period, we spent $5.5 million in exploration expenditures, including approximately 76,500 ft. (23,325 m) of drilling primarily at the El Gallo 1 mine, compared to $6.7 million in 2013 for 89,650 ft. (27,334 m) of drilling. For Nevada, we spent $3.1 million in 2014 in exploration expenditures, which include drilling of approximately 7,180 ft. (2,190 m) at the South Roberts project and 2,670 ft. (810 m) at the Grass Valley project, compared to $3.0 million in 2013.
Property holding costs increased year-over-year, to $6.4 million in the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to $4.6 million in 2013. The increase compared to 2013 relates primarily to an additional accrual of $1.4 million for our obligation relating to the long-term trust fund required by the BLM for the closure of the Tonkin mine in Nevada. Our accrual for this obligation totals $2.5 million as at December 31, 2014. The liability is recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities on our Consolidated Balance Sheet as at December 31, 2014.
General and administrative costs decreased in the 2014 year to $12.1 million compared to $14.0 million in 2013.
Loss on investment in MSC, net of amortization of fair value increments, during the year ended December 31, 2014 was $5.3 million, compared to income of $0.8 million in 2013. The decrease in earnings is primarily a result of lower average realized prices in the 2014 period compared to 2013.
In addition to our attributable loss on investment in MSC of $5.3 million, we also recorded an impairment charge on our investment in the year ended December 31, 2014. The impairment in 2014 was triggered by the unexpected and significant decline of silver prices during the year, as well as a decline in the observed market value of comparable transactions in South America, indicating a potential significant decrease in the market price of the exploration properties owned by MSC. As the decline in the estimated fair value of our investment in MSC was considered other than temporary, we recorded an impairment charge of $21.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. This compares to an impairment of $95.9 million in the year 2013.
Impairment of mineral property interests for the year ended December 31, 2014 included $228.3 million relating to our Los Azules project, $98.4 million in relation to our Nevada properties, and $27.0 million with respect to our Argentina properties. The first impairment of Los Azules was recorded in the second quarter of 2014, for an amount of $120.4 million, and was primarily triggered by a contemporaneous acquisition of a copper project located in Argentina, which we believed shared similarities with Los Azules. In the fourth quarter of 2014, we recorded an additional impairment of $107.9 million as a result of a further decline in the observed market value of comparable transactions in the second half of 2014. With respect to the Nevada and Argentina properties, the impairments of $98.4 million and $27.0 million, respectively, were primarily as a result of significant declines in the observed market value of comparable transactions noted as part of our year-end annual impairment analysis, which indicated a decrease in the market value of our properties, as well as the strategic review of our exploration program, pursuant to which we have made the decision to focus primarily on core assets, namely our Los Azules, Gold Bar, Tonkin and North Battle Mountain properties. These
64
events resulted in a total impairment charge of $353.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, along with a deferred income tax recovery of $76.6 million.
By comparison, for the year ended December 31, 2013, the impairment of $63.0 million related to certain exploration properties in Santa Cruz, Argentina and Nevada, with a deferred income tax recovery of $14.6 million.
Other income (expenses). Other expenses in the year ended December 31, 2014 totaled $8.9 million, and primarily consisted of $6.8 million in registration taxes payable in relation to intercompany financing agreements with certain of our subsidiaries. The liability is recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities on our Consolidated Balance Sheet as at December 31, 2014. Timing of payment is yet to be determined.
Recovery of income taxes. Recovery of income taxes was $107.2 million in 2014, compared to $53.4 million in 2013. The income tax recovery in 2014 includes tax recoveries of $41.8 million, $31.6 million and $3.2 million relating to the impairments of the Los Azules, Nevada and Argentina properties, respectively. In addition, a tax recovery of $23.6 million due to the impact of the devaluating Argentine peso on peso-denominated deferred income tax liabilities, and an adjustment of $5.8 million to record the tax effect of temporary differences related to exploration expenditures incurred in Argentina in prior years and deductible for tax purposes in future years, were also recorded in the year ended December 31, 2014.
Year Ended December 31, 2013 compared to 2012
As a result of the completion of the acquisition of Minera Andes on January 24, 2012, our operating results for the year ended December 31, 2012 included the operations of Minera Andes beginning on January 25, 2012 (after the date of acquisition).
General. For the year ended December 31, 2013, we recorded a net loss of $147.7 million or $0.50 per share, compared to a net loss of $66.7 million or $0.26 per share for the same period in 2012. The increase in net loss is due to the impairments of our investment in MSC of $95.9 million, and of certain mineral property interests in Nevada and in the Province of Santa Cruz, Argentina, of $63.0 million, as well as a loss on disposal of assets of $6.7 million, of which $6.4 million related to the sale of certain mining claims in Nevada in the second quarter of 2013. These impairment charges and losses were partly offset by our gold and silver sales from the El Gallo 1 mine, coupled with an increase in the recovery of income taxes.
Revenue. Gold and silver sales in the year ended December 31, 2013 from our El Gallo 1 mine in Mexico totaled $46.0 million. This compares to only $6.0 million in 2012 as the El Gallo 1 mine only started commercial production for accounting purposes on September 1, 2012.
Costs and Expenses. Total costs and expenses in the year ended December 31, 2013, excluding impairment charges discussed above, totaled $87.5 million, compared to $78.9 million in the 2012 period. Production costs applicable to the sales at El Gallo 1 increased our total costs and expenses, although these were partly offset by the decrease in mine construction and mine operating costs that were incurred in 2012 prior to the El Gallo 1 mine starting production activities for accounting purposes on September 1, 2012. We also incurred no acquisition costs in 2013, compared to the same period in 2012 when we incurred costs for the acquisition of Minera Andes
Production costs applicable to sales at El Gallo were $34.6 million in the year ended December 31, 2013. Production costs consist of direct mining costs which include contract mining services, processing costs, personnel costs, certain general and administrative costs, energy costs, operating materials and supplies, repairs and maintenance costs, transport fees, royalty expense and third-party refining costs. Production costs applicable to sales is calculated based on the weighted average cost of ounces sold during the period. This compares to $3.9 million for the same period in 2012, as the El Gallo 1 mine only started production for accounting purposes on September 1, 2012.
65
Income on investment in MSC during the year ended December 31, 2013, net of amortization and excluding the impairment charges discussed below, was $0.8 million, compared to $20.8 million in 2012. The decline is primarily a result of lower average realized gold and silver prices and increased operating costs due to several labor stoppages during 2013 and inflationary pressure on labor costs, materials and supplies within Argentina, which more than offset the higher sales volumes.
Impairment of investment in MSC for year ended December 31, 2013 was $95.9 million, compared to nil in the same period in 2012. In the second quarter of 2013, we concluded there were indicators that there was a loss in value in our investment in MSC that was other than temporary based on a significant decline in gold and silver market prices and rising operating costs in Argentina, coupled with the new tax on mining reserves in the Province of Santa Cruz. We tested the recoverability and determined the fair value of our investment in MSC using a discounted cash flow approach and determined that the carrying value of our investment in MSC exceeded its estimated fair value and as the loss in value was considered to be other than temporary, we recorded an impairment charge of $95.9 million in the second quarter of 2013.
Impairment of mineral property interests and property and equipment was $63.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2013, compared to $18.5 million in 2012. Of this, $28.9 million related to our exploration properties in Nevada, which were affected by an unexpected significant decline in gold prices during the year, and $27.7 million related to our exploration properties located in the Province of Santa Cruz, which were also affected by the decrease in gold and silver market prices, as well as continued inflationary pressures in Argentina and the new tax on mining reserves discussed above. We concluded that there were indicators that the carrying values of these properties may not be recoverable. We determined their fair value under the market approach by using the observed market value per square mile based on comparable transactions in South America, and concluded that the carrying value of these mineral property interests exceeded their estimated fair value. In the third quarter of 2013, we recorded an additional impairment charge of $6.3 million on certain claims in Nevada which we allowed to lapse in an effort to focus on our exploration activities in more prospective areas.
Mine construction costs were $1.4 million in the year ended December 31, 2013 compared to $14.3 million in 2012. Mine construction costs in 2013 were incurred in relation to the El Gallo 1 mill expansion from a nominal 3,000 tonnes per day to 4,500 tonnes per day. Costs in 2012 related to the initial construction of El Gallo 1, and included construction of the crushing and processing plant, mobilization and demobilization of mining equipment, road construction, pre-stripping costs, earth work for the leach pad and management costs to oversee the construction. As noted in our Critical Accounting Polices in this report, these costs were expensed rather than capitalized as we have not demonstrated the existence of proven or probable reserves at El Gallo 1.
Mine development costs were $0.8 million in the year ended December 31, 2013 and related to engineering and development costs for El Gallo 2. There were no similar costs in 2012.
Exploration costs decreased in 2013 by $22.4 million to $24.8 million from $47.2 million in 2012, reflecting lower exploration activities on all of our exploration projects as we seek to conserve working capital. During 2013, we spent $14.8 million in exploration expenditures in Argentina. Of this, $12.9 million was spent on Los Azules, which included approximately 21,000 ft. (6,407 m) of drilling activities. The remainder was spent on the Telken Norte and Octubre exploration properties in Santa Cruz province, which included 3,300 ft. (1,014 m) of drilling activities. This compares to $25.1 million in exploration expenditures in Argentina for the period from January 25, 2012 to December 31, 2012. Of this, $20.8 million was spent on Los Azules where we drilled approximately 32,000 ft. (9,800 m). The remainder was spent on exploration activities in the Santa Cruz province, which included approximately 68,000 ft. (20,800 m) of drilling activities. For Mexico, we spent $6.7 million in exploration expenditures during 2013, which included approximately 89,700 ft. (27,334 m) of drilling, compared to $15.9 million
66
and approximately 131,500 ft. (40,077 m) drilled in 2012. For Nevada, we spent $3.0 million in exploration expenditures in 2013, which relate primarily to permitting efforts for the Gold Bar project in Nevada as well as drilling of 2,150 ft. (655 m), compared to $5.1 million in 2012, during which we drilled approximately 7,000 ft. (2,000 m).
Property holding costs for the year ended December 31, 2013 were lower than those incurred in the 2012 period, at $4.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2013 compared to $7.2 million in 2012. The decrease is due to the number of claims we sold or allowed to lapse in Nevada, and the claims related to the Santa Cruz exploration properties we transferred to MSC as part of a vend-in agreement.
General and administrative costs decreased in 2013 by $2.8 million to $14.0 million, compared to $16.8 million in 2012, mostly as a result of lower stock based compensation expense as all stock options assumed from the Minera Andes acquisition in 2012 have now vested.
Loss on sale of assets was $6.7 million for 2013, compared to a gain of $1.1 million in the same period in 2012, and related primarily to the sale of certain mining claims in the Limo Complex, in Nevada. The claims, which had a carrying value of $7.2 million, were sold for a sales price of $0.8 million. As the carrying value exceeded the proceeds from the sales agreement, we recorded a loss on disposal of $6.4 million for these claims.
Other Income (Expenses). Gain on litigation settlement relates to the 1,000,000 shares issued as part of the settlement of the lawsuit with TNR Gold Corp. in November 2012 with respect to Los Azules. The shares were issued in January 2013, thus resulting in the elimination of the liability and a gain on settlement of $0.6 million for the 2013 period as the market price of the shares decreased from December 2012 to January 2013.
Recovery of income taxes. Recovery of income taxes was $53.4 million in 2013, compared to $27.2 million in 2012. The 2013 amount includes $36.3 million from the revaluation of the deferred income tax liability balance denoted in Argentine pesos to U.S. dollars, compared to $21.1 million for the period between January 24, 2012 (date of the Minera Andes acquisition) and December 31, 2012; $14.6 million related to the impairment charges on our mineral properties in Argentina and Nevada; and $2.5 million related to the loss on sale of the mining claims in the Limo Complex, in Nevada.
Total Cash Costs, All-In Sustaining Costs, and All-In Costs
Total cash costs for all of our operating properties on a consolidated basis for the year ended December 31, 2014 were $817 per gold equivalent ounce sold, based on a silver to gold ratio of 60:1, compared to $776 per gold equivalent ounce in 2013, based on a silver to gold ratio of 52:1. Using a 60:1 conversion ratio, total cash costs per gold equivalent ounce for the year 2013 would have been $823 per ounce. On an aggregate basis, total cash costs slightly increased from $107.7 million in 2013 to $108.0 million in 2014. The increase in total cash costs on an aggregate basis was a result of the higher number of ounces sold both at the San José and El Gallo 1 mines, coupled with the increased operating costs at the El Gallo 1 mine. These factors were partly offset by lower operating costs at the San José mine, as a result of MSC's ongoing cost optimization initiatives. The Argentine peso also experienced a significant devaluation during the first half of the year 2014, although the benefit of the devaluation was mostly offset by continued high inflation.
Consolidated all-in sustaining costs, which include corporate general and administrative expenses not separately allocated to either the El Gallo 1 or San José mine, for the year ended December 31, 2014 were $1,198 per gold equivalent ounce, compared to $1,178 per gold equivalent ounce in 2013, based on a silver to gold ratio of 52:1. Using a 60:1 conversion ratio, all-in sustaining costs per gold equivalent ounce for 2013 would have been $1,249. On an aggregate basis, all-in sustaining costs decreased from $163.4 million in 2013 to $158.3 million in 2014. The higher operating costs at the
67
El Gallo 1 mine were more than offset by the reduction in exploration and capital expenditures both at the San José and at the El Gallo 1 mine. Corporate general and administrative expenses also decreased during in 2014 compared to 2013.
Consolidated all-in costs for the year ended December 31, 2014 were $1,368 per gold equivalent ounce sold, compared to $1,412 per gold equivalent ounce in 2013, based on a silver to gold ratio of 52:1. Using a 60:1 conversion ratio, all-in costs per gold equivalent ounce for 2013 would have been $1,498. On an aggregate basis, all-in costs decreased from $195.9 million in 2013 to $180.9 million in 2014, primarily as a result of lower exploration costs at our Los Azules and Santa Cruz exploration properties.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of December 31, 2014, we had working capital of $15.6 million, comprised of current assets of $39.7 million and current liabilities of $24.1 million. This represents a decrease of approximately $20.0 million from the working capital balance of $35.6 million as of December 31, 2013. During the year ended December 31, 2014, we received $9.5 million in dividends from MSC, and collected $5.0 million in Value Added Taxes ("VAT") receivable. Offsetting these benefits to our working capital was the overall decrease in our cash balance due to our operating cash outflow, and an increase in accounts payable and accruals, which includes $6.7 million related to the registration taxes on intercompany financing agreements with certain of our subsidiaries, and $2.5 million for our long-term trust fund obligation for the closure of the Tonkin mine in Nevada. Timing of payment of these obligations is yet to be determined and are accordingly recorded as current liabilities.
We believe our working capital at December 31, 2014 is sufficient to fund ongoing exploration and corporate activities over the next 12 months. Our sources of working capital at December 31, 2014 include cash on hand, other current assets and cash flows from El Gallo 1.
However, in order to fund the development of El Gallo 2, if we make a positive production decision, we would need to raise additional capital of approximately $150 million, given that the estimated capital cost significantly exceeds our available working capital. In such case, we would explore several financing methods to complete the development and construction of El Gallo 2, which may include incurring debt, issuing additional equity, equipment leasing and other forms of financing. Our ability to build El Gallo 2 is dependent on one or several of the alternatives being completed.
Net cash used in operations for the year ended December 31, 2014 decreased to $14.9 million from $42.4 million in 2013. Our El Gallo 1 mine contributed $43.8 million in gold and silver sales to operating cash flows in the year 2014 compared to $44.4 million in 2013. As noted above, we received $9.5 million in dividends from our investment in MSC, compared to $1.8 million in 2013. However, these cash inflows were more than offset by cash paid to suppliers and employees of $69.0 million in 2014, compared to $90.4 million in 2013. Cash paid to suppliers and employees decreased year-over-year primarily due to the collection of VAT taxes receivable of $5.0 million, as well as a lower level of exploration activities in the 2014 period than in 2013.
Cash from investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2014 were an inflow of $1.5 million, due to the release of $5.2 million in restricted time deposits for reclamation bonding on our Tonkin property in Nevada. These restricted deposits were replaced by surety bonds, as discussed in Note 13, Rental Expense, Commitments and Contingencies, of the accompanying financial statements. Partially offsetting this inflow was $2.8 million of additions to property and equipment which include the advances for the El Gallo 2 ball mill, and leasehold improvements for the relocation of our corporate office. Cash used in investing activities for the comparable period in 2013 totaled $3.0 million.
68
Cash provided by financing activities for year ended December 31, 2014 was $2.3 million, and related to issuances of common stock as part of our Equity Incentive Plan. This compares to $0.2 million for the comparable period in 2013.
Overall, cash decreased by $11.9 million from December 31, 2013 to December 31, 2014. Comparatively, the cash decrease from December 31, 2013 to December 31, 2012 was $46.6 million.
In an effort to manage our liquidity, during the third quarter of 2013, we entered into an agreement with one of our mining contractors to settle parts of our expected account payable with shares of our common stock, up to a maximum of 2,500,000 shares, as discussed in Note 11, Stock Based Compensation. As at December 31, 2014, we were required to issue a cumulative total of approximately 712,830 common shares, of which approximately 393,190 were issued in the year ended December 31, 2014. The fair value of the remaining 319,640 outstanding shares of $0.4 million is included in accounts payable and accrued liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheet as at December 31, 2014. The agreement was subsequently terminated on February 1, 2015.
Contractual Obligations
The following table presents certain payments due by the Company under contractual obligations with minimum firm commitments as of December 31, 2014, and excludes amounts already recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheet:
| |
|
Payments due by period | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Contractual Obligations
|
Total | Less than 1 year | 1-3 years | 4-5 years | More than 5 years |
|||||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||||||||
Operating Lease Obligations |
$ | 4,302 | $ | 928 | $ | 1,007 | $ | 938 | $ | 1,429 | ||||||
Purchase Obligations |
17 | 17 | — | — | — | |||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 4,319 | $ | 945 | $ | 1,007 | $ | 938 | $ | 1,429 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating lease obligations include long-term leases covering office space, exploration expenditures, option payments and option payments on properties.
Contingencies
We have surety bonds outstanding to provide bonding for our environmental reclamation obligations in the United States. These surety bonds are available for draw down in the event we do not perform our reclamation obligations. When the specific reclamation requirements are met, the beneficiary of the surety bonds will cancel and/or return the instrument to the issuing entity. As of December 31, 2014, no liability has been recognized for our surety bonds of $4.8 million.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of December 31, 2014, we did not have any off-balance sheet arrangements (as that phrase is defined by SEC rules applicable to this report) which have or are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations or liquidity.
Non-GAAP Financial Performance Measures
In this report, we have provided information prepared or calculated according to U.S. GAAP, as well as provided some Non-U.S. GAAP financial performance measures. Because the Non-GAAP performance measures do not have any standardized meaning prescribed by U.S. GAAP, they may not be comparable to similar measures presented by other companies. These measures should not be considered in isolation or as substitute for measures of performance prepared in accordance with
69
GAAP. There are limitations associated with the use of such Non-GAAP measures. Since these measures do not incorporate revenues, changes in working capital and non-operating cash costs, they are not necessarily indicative of operating profit or loss, or cash flow from operations as determined in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
Earnings (Loss) from Mining Operations
The term Earnings or Loss from Mining Operations used in this report is a non-GAAP financial measure. We use and report this measure because we believe it provides investors and analysts with a useful measure of the underlying earnings or loss from our mining operations.
We define Earnings from Mining Operations as Gold and Silver Sales from our El Gallo 1 mine and our 49% attributable share of the San José mine's Net Sales, less their respective Production Costs Applicable to Sales. To the extent that Production Costs Applicable to Sales may include depreciation and amortization expense related to the fair value increments on historical business acquisitions (fair value paid in excess of the carrying value of the underlying assets and liabilities assumed on the date of acquisition), we deduct this expense in order to arrive at Production Costs Applicable to Sales that only include depreciation and amortization expense incurred at the mine-site level. The San José mine Net Sales and Production Costs Applicable to Sales are presented, on a 100% basis, in Note 7 of the accompanying financial statements.
The following table presents a reconciliation of Earnings from Mining Operations to Gross Profit, a GAAP financial measure.
| |
Three months ended December 31, |
Year ended December 31, |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
El Gallo 1 earnings from mining operations |
|||||||||||||
Gold and silver sales |
$ | 13,683 | $ | 10,247 | $ | 45,303 | $ | 45,982 | |||||
Production costs applicable to sales |
(10,184 | ) | (7,816 | ) | (40,608 | ) | (34,594 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gross (loss) profit |
3,499 | 2,431 | 4,695 | 11,388 | |||||||||
Add: Amortization related to fair value increments on historical acquisitions included in Production Costs Applicable to Sales |
322 | 287 | 1,288 | 1,530 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
El Gallo 1 earnings from mining operations |
3,821 | 2,718 | 5,983 | 12,918 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
San José earnings from mining operations (49% attributable basis) |
|||||||||||||
Net sales |
31,667 | 28,759 | 104,376 | 117,954 | |||||||||
Production costs applicable to sales |
(27,270 | ) | (24,945 | ) | (84,904 | ) | (93,238 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gross profit |
4,397 | 3,814 | 19,472 | 24,716 | |||||||||
Add: Amortization related to fair value increments on historical acquisitions included in Production Costs Applicable to Sales |
— | — | — | — | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
San José earnings from mining operations |
4,397 | 3,814 | 19,472 | 24,716 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Consolidated earnings from mining operations |
8,218 | 6,532 | 25,455 | 37,634 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
70
Adjusted Net loss, and Adjusted Net Loss Per Share
The terms adjusted net loss and adjusted net loss per share used in this report are non-GAAP financial measures. We use and report these measures because we believe they provide investors and analysts with useful measures of the underlying operating performance of our core mining business.
Adjusted net income (loss) excludes the following items from net income (loss):
- •
- impairment charges (including inventory and VAT receivable write-downs, and impairments of long-lived assets), and the related income
tax recovery;
- •
- foreign currency gains and losses, including the impact of foreign currency fluctuations on our deferred income tax liabilities
denominated in Argentine peso; and
- •
- other non-recurring items, as applicable.
The following table presents a reconciliation of Adjusted Net Loss to Net Loss, a GAAP financial measure.
| |
Three months ended December 31, |
Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||
Net loss |
$ | (212,775 | ) | $ | (11,343 | ) | $ | (311,943 | ) | $ | (147,742 | ) | $ | (66,654 | ) | |
Write-down of VAT receivable |
— | — | 340 | — | — | |||||||||||
Impairment of investment in MSC |
21,162 | — | 21,162 | 95,878 | — | |||||||||||
Impairment of mineral property interests, net of income taxes |
179,159 | 18,816 | 277,100 | 48,322 | 12,387 | |||||||||||
Loss on sale of assets, net of income taxes |
— | — | — | 4,268 | — | |||||||||||
Registration taxes on intercompany financing agreements (non-recurring) |
76 | — | 6,788 | — | 6,788 | |||||||||||
Foreign currency loss |
1,487 | 215 | 2,419 | 1,309 | (456 | ) | ||||||||||
Portion of income on investment in MSC resulting from foreign currency fluctuations |
1,053 | (3,028 | ) | (5,263 | ) | (9,411 | ) | (9,910 | ) | |||||||
Portion of income tax recovery resulting from foreign currency fluctuations |
94 | (9,863 | ) | (23,601 | ) | (23,589 | ) | (23,589 | ) | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjusted net loss |
(9,744 | ) | (5,204 | ) | (32,998 | ) | (30,965 | ) | (81,434 | ) | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjusted net loss per share—basic |
$ | (0.03 | ) | $ | (0.02 | ) | $ | (0.11 | ) | $ | (0.10 | ) | $ | (0.27 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average common shares outstanding (thousands)—basic |
299,009 | 297,125 | 297,763 | 297,001 | 297,763 | |||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Cash Costs, All-In Sustaining Costs and All-In Costs
The terms total cash costs, total cash cost per ounce, all-in sustaining costs, all-in sustaining cost per ounce, all-in costs and all-in cost per ounce used in this report are non-GAAP financial measures. We report these measures to provide additional information regarding operational efficiencies both on a consolidated and an individual mine basis (San José mine and El Gallo 1 mine), and believe these measures provide investors and analysts with useful information about our underlying costs of operations. For the San José mine, where we hold a 49% share in the production through our 49% interest in MSC, we exclude the share of gold or silver production attributable to the controlling interest.
71
The measure total cash costs and total cash cost per ounce are calculated in accordance with the Production Cost Standard developed by The Gold Institute, which was a worldwide association of suppliers of gold and gold products and included leading North American gold producers. The Gold Institute ceased operations in 2002, but we believe the standard is still the accepted standard of reporting cash costs of production in North America. Adoption of the standard is voluntary and the cost measures presented may not be comparable to other similarly titled measures of other companies.
The measures all-in sustaining costs, all-in sustaining costs per ounce, all-in costs and all-in costs per ounce were adopted by us in 2013, as we believe that the these measures better represents the total costs associated with producing gold. We have adopted this reporting methodology based on the standard from the World Gold Council (as promulgated in their June 27, 2013 press release, World Gold Council's Guidance Note on Non-GAAP Metrics—All-In Sustaining Costs and All-In Costs). There is no assurance that these measures are necessarily comparable to our industry peers.
Total cash costs consists of mining, processing, on-site general and administrative costs, community and permitting costs related to current operations, royalty costs, refining and treatment charges (for both doré and concentrate products), sales costs, export taxes and operational stripping costs, and exclude depreciation and amortization. In order to arrive at our consolidated total cash costs, we also include our attributable share of total cash costs from operations where we hold less than a 100% economic share in the production, such as MSC where we hold a 49% interest. The sum of these costs is divided by the corresponding gold equivalent ounces sold to determine a per ounce amount.
All-in sustaining costs consists of total cash costs (as described above), plus environmental rehabilitation costs and amortization of the asset retirement costs related to operating sites, sustaining exploration and development costs, and sustaining capital expenditures. In order to arrive at our consolidated all-in sustaining costs, we also include our attributable share of all-in sustaining costs from operations where we hold less than a 100% economic share in the production, as well as attributable corporate general and administrative expenses. The sum of these costs is divided by the corresponding gold equivalent ounces sold to determine a per ounce amount.
All-in costs include community, permitting and reclamation and remediation costs not related to current operations, non-sustaining exploration and development costs and non-sustaining capital expenditures. As these costs do not relate to any particular producing operation, we divide the sum of these costs by the consolidated gold equivalent ounces sold, including our attributable share of any operation where we hold less than a 100% interest, and do not provide this measure on a per mine basis.
Costs excluded from total cash costs, sustaining all-in sustaining costs and all-in costs are income tax expense, all financing charges, costs related to business combinations, asset acquisitions and asset disposal, and any items that are deducted for the purpose of normalizing items, as described in Adjusted Net loss, and Adjusted Net Loss Per Share above.
For MSC, co-product total cash costs and all-in sustaining costs are calculated by dividing the respective proportionate share of the total cash costs, all-in sustaining costs, and all-in costs for each metal sold for the period by the ounces of each respective metal sold. The respective proportionate share of each metal sold is calculated based on their pro-rated sales value. Approximately 51% of the value of the sales in the fourth quarter of 2014 was derived from gold and 49% was derived from silver. This compares to 47% and 53% for gold and silver, respectively, for the same period in 2013. For the year ended December 31, 2014, approximately 50% of the value of the sales was derived from gold and 50% from silver, compared to 48% and 52% in 2013, respectively.
72
The following tables reconcile these non-GAAP measures to the most directly comparable GAAP measure, Production Costs Applicable to Sales. Total cash costs, all-in sustaining costs, all-in costs and ounces of gold and silver sold for the San José mine are provided to us by MSC.
| |
Three months ended December 31, |
Year ended December 31, |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
| |
(in thousands, except per ounce) |
(in thousands, except per ounce) |
|||||||||||
Production costs applicable to sales |
$ | 10,184 | $ | 7,816 | $ | 40,608 | $ | 34,594 | |||||
Less: Depreciation |
(322 | ) | (287 | ) | (1,288 | ) | (1,530 | ) | |||||
Less: Pre-stripping costs for future pit access |
(2,052 | ) | (1,686 | ) | (8,763 | ) | (9,197 | ) | |||||
On-site general and administrative expenses |
296 | 339 | 1,174 | 927 | |||||||||
Property holding costs |
— | — | 27 | 27 | |||||||||
Other non-cash adjustments |
— | — | (340 | ) | — | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total cash costs (El Gallo 1 Mine) |
$ | 8,106 | $ | 6,182 | $ | 31,418 | $ | 24,821 | |||||
McEwen's share of MSC total cash costs (49%) |
22,959 | 21,512 | 76,550 | 82,855 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Consolidated total cash costs |
$ | 31,065 | $ | 27,694 | $ | 107,967 | $ | 107,676 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Per gold equivalent ounce sold: |
|||||||||||||
Total cash costs (El Gallo 1 Mine) |
$ | 711 | $ | 765 | $ | 875 | $ | 749 | |||||
McEwen's share of MSC total cash costs (49%) |
708 | 747 | 795 | 785 | |||||||||
Consolidated total cash costs (including McEwen's share of MSC) |
709 | 751 | 817 | 776 | |||||||||
Reconciliation of All-In Sustaining Costs to Total Cash Costs
| |
Three months ended December 31, |
Year ended December 31, |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
| |
(in thousands, except per ounce) |
(in thousands, except per ounce) |
|||||||||||
Total cash costs (excluding McEwen's share of MSC) |
$ | 8,106 | $ | 6,182 | $ | 31,418 | $ | 24,821 | |||||
Operating site reclamation accretion and amortization |
200 | 153 | 802 | 737 | |||||||||
On-site exploration expenses |
260 | 643 | 1,592 | 3,820 | |||||||||
Mine construction and capital expenditures (sustaining) |
— | — | 320 | — | |||||||||
Pre-stripping costs for future pit access |
2,052 | 1,686 | 8,763 | 9,197 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
All-in sustaining costs (El Gallo 1 Mine) |
$ | 10,618 | $ | 8,664 | $ | 42,895 | $ | 38,575 | |||||
McEwen's share of MSC all-in sustaining costs (49%) |
33,206 | 29,201 | 104,558 | 111,759 | |||||||||
Corporate general and administrative expenses |
2,784 | 2,757 | 10,895 | 13,074 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Consolidated all-in sustaining costs (including McEwen's share of MSC) |
$ | 46,608 | $ | 40,622 | $ | 158,348 | $ | 163,408 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Per gold equivalent ounce sold: |
|||||||||||||
All-in sustaining costs (El Gallo 1 Mine) |
$ | 931 | $ | 1,071 | $ | 1,194 | $ | 1,164 | |||||
McEwen's share of MSC all-in sustaining costs (49%) |
1,024 | 1,014 | 1,086 | 1,058 | |||||||||
Consolidated all-in sustaining costs (including McEwen's share of MSC) |
1,063 | 1,102 | 1,198 | 1,178 | |||||||||
73
Reconciliation of All-In Costs to All-In Sustaining Costs
| |
Three months ended December 31, |
Year ended December 31, |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
| |
(in thousands, except per ounce) |
(in thousands, except per ounce) |
|||||||||||
Consolidated all-in sustaining costs (including McEwen's share of MSC) |
$ | 46,608 | $ | 40,622 | $ | 158,348 | $ | 163,408 | |||||
Property holding costs (non-sustaining) |
1,797 | 507 | 6,338 | 4,557 | |||||||||
Reclamation accretion and amortization (non-operating sites) |
310 | 56 | 407 | 229 | |||||||||
Exploration expenses (non-sustaining) |
3,449 | 2,122 | 9,740 | 21,159 | |||||||||
Mine development (non-sustaining) |
75 | 672 | 3,264 | 4,741 | |||||||||
Mine construction and capital expenditures (non-sustaining) |
97 | 838 | 2,756 | 1,795 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Consolidated all-in costs (including McEwen's share of MSC) |
$ | 52,336 | $ | 44,817 | $ | 180,853 | $ | 195,889 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Per gold equivalent ounce sold: |
|||||||||||||
Consolidated all-in costs (including McEwen's share of MSC) |
$ | 1,194 | $ | 1,215 | $ | 1,368 | $ | 1,412 | |||||
The following table summarizes the consolidated number of gold equivalent ounces sold used to calculate total cash costs, all-in sustaining costs and all-in costs on a per ounce basis, as discussed above. Gold equivalent ounces are calculated using an average silver to gold ratio of 52:1 for 2013 and prior.
| |
Three months ended December 31, |
Year ended December 31, |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Gold equivalent ounces sold (El Gallo 1 Mine) |
11,406 | 8,086 | 35,924 | 33,142 | |||||||||
McEwen's share of MSC gold equivalent ounces sold |
32,425 | 28,790 | 96,304 | 105,588 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Consolidated gold equivalent ounces sold (including McEwen's share of MSC) |
43,831 | 36,876 | 132,228 | 138,730 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Silver : gold ratio |
60 : 1 | 52 : 1 | 60 : 1 | 52 : 1 | |||||||||
Average realized prices
The term average realized price per ounce used in this report is also a Non-GAAP financial measure. We report this measure to better understand the price realized in each reporting period for gold and silver.
Average realized price is calculated as gross sales of gold and silver (excluding commercial deductions) over the number of net ounces sold in the period (net of deduction units).
74
The following table reconciles this Non-GAAP measure to the most directly comparable U.S. GAAP measure, Sales of Gold and Silver. Ounces of gold and silver sold for the San José mine are provided to us by MSC.
| |
Three months ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||||
| |
(in thousands, except ounce and per ounce) |
||||||||||||||||||
| |
El Gallo Phase 1 |
MSC (49% interest) |
Total | El Gallo Phase 1 |
MSC (49% interest) |
Total | |||||||||||||
Gold sales |
$ | 13,555 | $ | 17,207 | $ | 30,762 | $ | 10,134 | $ | 14,347 | $ | 24,481 | |||||||
Silver sales |
129 | 16,409 | 16,538 | 113 | 16,170 | 16,283 | |||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gold and silver sales |
$ | 13,683 | $ | 33,617 | $ | 47,300 | $ | 10,247 | $ | 30,517 | $ | 40,764 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gold ounces sold |
11,272 | 14,764 | 26,036 | 7,980 | 12,091 | 20,071 | |||||||||||||
Silver ounces sold |
8,000 | 1,059,669 | 1,067,669 | 5,500 | 831,700 | 837,200 | |||||||||||||
Gold equivalent ounces sold |
11,406 | 32,425 | 43,831 | 8,086 | 28,084 | 36,171 | |||||||||||||
Average realized price per gold ounce sold |
$ |
1,203 |
$ |
1,165 |
$ |
1,182 |
$ |
1,270 |
$ |
1,187 |
$ |
1,220 |
|||||||
Average realized price per silver ounce sold |
$ | 16.08 | $ | 15.49 | $ | 15.49 | $ | 20.55 | $ | 19.44 | $ | 19.45 | |||||||
Average realized price per gold equivalent ounce sold |
$ | 1,200 | $ | 1,037 | $ | 1,079 | $ | 1,267 | $ | 1,087 | $ | 1,127 | |||||||
| |
Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||||
| |
(in thousands, except ounce and per ounce) |
||||||||||||||||||
| |
El Gallo Phase 1 |
MSC (49% interest) |
Total | El Gallo Phase 1 |
MSC (49% interest) |
Total | |||||||||||||
Gold sales |
$ | 44,956 | $ | 55,268 | $ | 100,223 | $ | 45,439 | $ | 59,241 | $ | 104,680 | |||||||
Silver sales |
347 | 54,711 | 55,058 | 543 | 64,921 | $ | 65,464 | ||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gold and silver sales |
$ | 45,303 | $ | 109,979 | $ | 155,282 | $ | 45,982 | $ | 124,162 | $ | 170,144 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gold ounces sold |
35,600 | 44,725 | 80,325 | 32,705 | 46,148 | 78,853 | |||||||||||||
Silver ounces sold |
19,417 | 3,094,742 | 3,114,159 | 22,700 | 3,054,245 | 3,076,945 | |||||||||||||
Gold equivalent ounces sold |
35,924 | 96,304 | 132,228 | 33,142 | 104,883 | 138,025 | |||||||||||||
Average realized price per gold ounce sold |
$ |
1,263 |
$ |
1,236 |
$ |
1,248 |
$ |
1,389 |
$ |
1,284 |
$ |
1,328 |
|||||||
Average realized price per silver ounce sold |
$ | 17.89 | $ | 17.68 | $ | 17.68 | $ | 23.92 | $ | 21.26 | $ | 21.28 | |||||||
Average realized price per gold equivalent ounce sold |
$ | 1,261 | $ | 1,142 | $ | 1,174 | $ | 1,387 | $ | 1,184 | $ | 1,233 | |||||||
Critical Accounting Policies
Listed below are the accounting policies that require significant judgments and estimates that we believe are critical to our consolidated financial statements.
Investments—Equity Method and Joint Ventures: The Company accounts for investments over which the Company exerts significant influence but does not control through majority ownership using the equity method of accounting pursuant to ASC Topic 323, Investments—Equity Method and Joint Ventures. Under this method, the Company's share of earnings and losses is included in the Consolidated Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss and the balance of the investment is
75
adjusted by a like amount. Under the equity method, dividends received from an investee are recorded as decreases in the investment account, not as income. If and when there has been a loss in value that is other than a temporary decline, the carrying value is reduced to its fair value.
Stockpiles, Material on Leach Pads, In-process Inventory, Precious Metals Inventory and Materials and Supplies: Stockpiles, material on leach pads, in-process inventory, precious metals inventory and materials and supplies are carried at the lower of average cost or net realizable value. Net realizable value represents the estimated future sales price of the product based on current and long-term metals prices, less the estimated costs to complete production and bring the product to sale. Write-downs of stockpiles, material on leach pads, in-process inventory, precious metals inventory and materials and supplies, resulting from net realizable value impairments, are reported as a component of production costs applicable to sales. The current portion of stockpiles, material on leach pad, in-process inventory and materials and supplies is determined based on the expected amounts to be processed within the next 12 months. Stockpiles, material on leach pads, in-process inventory and materials and supplies not expected to be processed within the next 12 months, if any, are classified as long-term.
Stockpiles represent mineralized material that has been extracted from the mine and is available for further processing. Stockpiles are measured by estimating the number of tonnes added and removed from the stockpile, an estimate of the contained metals (based on assay data) and the estimated metallurgical recovery rates. Costs are allocated to stockpiles based on relative values of material stockpiled and processed using current mining costs incurred up to the point of stockpiling the mineralized material. Material is removed from the stockpile at an average cost per tonne. Since the Company only achieved production for accounting purposes in September 2012, no value was allocated to stockpiles prior to then.
Mineralized material on leach pads is the ore that is placed on pads where it is treated with a chemical solution that dissolves the gold contained in the ore over a period of months. Costs are attributed to the ore on leach pads based on current mining costs incurred up to the point of placing the ore on the pad. Costs are removed from the leach pad based on the average cost per estimated recoverable ounce of gold on the leach pad as the gold is recovered. The estimates of recoverable gold on the leach pads are calculated from the quantities of ore placed on the leach pads (measured tons added to the leach pads), the grade of ore placed on the leach pads (based on assay data) and a recovery percentage. In general, leach pads recover between 50% and 95% of the recoverable ounces in the first year of leaching, declining each year thereafter until the leaching is complete. The cumulative metallurgical recovery rate for gold production at the El Gallo 1 mine from September 2012 (start of production) to December 31, 2014 was approximately 56% (2013—61%). Although the quantities of recoverable gold placed on the leach pads are reconciled by comparing the grades of ore placed on the pads to the quantities of gold actually recovered (metallurgical balancing), the nature of the leaching process inherently limits the ability to precisely monitor inventory levels. As a result, the metallurgical balancing process is constantly monitored and the engineering estimates are refined based on actual results over time.
In-process inventories represent materials that are currently in the process of being converted to a saleable product. The El Gallo 1 conversion process uses an Adsorption-Desorption-Recovery ("ADR") processing plant utilizing carbon columns for recovery. In-process material is measured based on assays of the material fed into the process and the projected recoveries of the respective plants. Costs are allocated to in-process inventories based on the costs of the material fed into the process attributable to the source material coming from the mines, stockpiles and/or leach pads plus the in-process conversion costs incurred to that point in the process.
76
Precious metal inventories include gold and silver bullion that is unsold and held at the Company's or the refinery's facilities. Costs are allocated to precious metal inventories based on costs of the respective in-process inventories incurred prior to the refining process plus applicable refining costs.
Materials and supplies inventories are comprised of chemicals, reagents and consumable parts used in drilling and other operating activities. They are valued at the lower of average cost or net realizable value. Cost includes applicable taxes and freight.
Proven and Probable Reserves: The definition of proven and probable reserves is set forth in Industry Guide 7. Proven reserves are reserves for which (a) quantity is computed from dimensions revealed in outcrops, trenches, workings or drill holes, grade and/or quality are computed from the results of detailed sampling and (b) the sites for inspection, sampling and measurement are spaced so closely and the geological character is so well defined that size, shape, depth and mineral content of the reserves are well-established. Probable reserves are reserves for which quantity and grade and/or quality are computed from information similar to that used for proven (measured) reserves, but the sites for inspection, sampling, and measurement are farther apart or are otherwise less adequately spaced. The degree of assurance, although lower than that for proven (measured) reserves, is high enough to assume continuity between points of observations.
As of December 31, 2014, except for the Company's 49% interest in the San José mine, none of the Company's properties contain resources that satisfy the definition of proven and probable reserves. The Company classifies the development of its properties, including the El Gallo 1 mine, as exploration stage projects since no proven or probable reserves have been established.
Property and Equipment: As described in Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies—Design, Construction and Development Costs below, substantially all costs, including design, engineering, construction, and installation of equipment are expensed as incurred as the Company has not established proven and probable reserves on any of its properties except for the Company's 49% interest in the San José mine. Only certain types of equipment which has alternative uses or significant salvage value, may be capitalized without proven and probable reserves. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method with the exception of mining equipment. Mining equipment is depreciated using the units-of-production method based on tonnes processed over the estimated total mine life. Office furniture, equipment and light vehicles are being depreciated over estimated economic lives ranging from 3 to 5 years. Leasehold improvements, which relate to the Company's corporate office, are being amortized over the term of the lease of 10 years. Trailers, heavy vehicles and other site equipment are being depreciated over estimated economic lives from 5 to 15 years. Buildings are being depreciated over an estimated economic life of 20 years.
Design, Construction, and Development Costs: Mine development costs include engineering and metallurgical studies, drilling and other related costs to delineate an ore body, the removal of overburden to initially expose an ore body at open pit surface mines and the building of access ways, shafts, lateral access, drifts, ramps and other infrastructure at underground mines.
When proven and probable reserves as defined by Industry Guide 7 exist, development costs are capitalized and the property is a commercially minable property. Mine development costs incurred either to develop new ore deposits, expand the capacity of operating mines, or to develop mine areas substantially in advance of current production would be capitalized. Costs of start-up activities and costs incurred to maintain current production or to maintain assets on a standby basis are charged to operations as incurred. Costs of abandoned projects are charged to operations upon abandonment. All capitalized costs would be amortized using the units of production method over the estimated life of the ore body based on recoverable ounces to be mined from proven and probable reserves.
Certain costs to design and construct mining and processing facilities may be incurred prior to establishing proven and probable reserves. As no proven and probable reserves have been established
77
on any of the Company's properties except for the Company's 49% interest in the San José mine, design, construction and development costs are not capitalized at any of the Company's properties, and accordingly, substantially all costs are expensed as incurred, resulting in the Company reporting larger losses than if such expenditures had been capitalized. Additionally, the Company does not have a corresponding depreciation or amortization of these costs going forward since these expenditures were expensed as incurred as opposed to being capitalized. As a result of these and other differences, the Company's financial statements may not be comparable to the financial statements of mining companies that have established reserves.
Mineral Property Interests: Mineral property interests include acquired interests in development and exploration stage properties, which are considered tangible assets. The amount capitalized relating to a mineral property interest represents its fair value at the time of acquisition, either as an individual asset purchase or as a part of a business combination. The value of mineral property interests is primarily driven by the nature and amount of mineralized material believed to be contained in the properties. When proven and probable reserves exist, the relevant capitalized costs and mineral property interests are to be charged to expense based on the units of production method and upon commencement of production. However, when a property does not contain mineralized material that satisfies the definition of proven and probable reserves, such as with the El Gallo 1 mine, the amortization of the capitalized costs and mineral property interests are charged to expense based on the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the mine, which based on the Company's El Gallo 1 mine plan as of December 31, 2014 is estimated to end in late 2017. As a result of these and other differences, the Company's financial statements will not be comparable to the financial statements of mining companies that have established reserves as defined by Industry Guide 7.
Impairment of Assets: The Company reviews and evaluates its long-lived assets for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the related carrying amounts may not be recoverable. Mineral properties are monitored for impairment based on factors such as mineral prices, government regulation and taxation, the Company's continued right to explore the area, exploration reports, assays, technical reports, drill results and its continued plans to fund exploration programs on the property.
For operating mines, recoverability is measured by comparing the undiscounted future net cash flows to the net book value. When the net book value exceeds future net undiscounted cash flows, an impairment loss is measured and recorded based on the excess of the net book value over fair value. Fair value for operating mines is determined using a combined approach, which uses a discounted cash flow model for the existing operations and a market approach for the fair value assessment of exploration land claims. Future cash flows are estimated based on quantities of recoverable mineralized material, expected gold and silver prices (considering current and historical prices, trends and related factors), production levels, operating costs, capital requirements and reclamation costs, all based on life-of-mine plans. The term "recoverable mineralized material" refers to the estimated amount of gold or other commodities that will be obtained after taking into account losses during processing and treatment of mineralized material. In estimating future cash flows, assets are grouped at the lowest level for which there are identifiable cash flows that are largely independent of future cash flows from other asset groups. The Company's estimates of future cash flows are based on numerous assumptions and it is possible that actual future cash flows will be significantly different than the estimates, as actual future quantities of recoverable minerals, gold, silver and other commodity prices, production levels and costs and capital are each subject to significant risks and uncertainties.
For exploration properties, the Company is unable to estimate undiscounted future net cash flows from its operations due to the absence of proven and probable reserves. As a result, the Company uses the market approach to estimate the fair value of the Nevada and Argentina exploration properties by using a combination of the observed market value per square mile and an observed market value per ounce or pound of mineralized material based on comparable transactions, and uses this measure to
78
assess recoverability and impairment. For purposes of recognition and measurement of an impairment loss, the Company groups its properties by geological mineral complex, as this represents the lowest level at which the Company allocates its exploration spending independent of other assets and liabilities.
Asset Retirement Obligation: The Company records the fair value of a liability for an asset retirement obligation ("ARO") in the period that it is incurred if a reasonable estimate of fair value can be made. The associated asset retirement costs are capitalized as part of the carrying amount of the long-lived asset when proven or probable reserves exist, or if they relate to an acquired mineral property interest. Since no proven or probable reserves have been established for any of the Company's properties, other than at the San José mine, incremental asset retirement costs associated with the re-measurement of the fair value of the ARO at the El Gallo 1 mine or Tonkin property are charged to expense. Ongoing environmental and reclamation expenditures are debited against the ARO as incurred to the extent they relate to the ARO and to expense to the extent they do not. The fair value of AROs is measured by discounting the expected cash flows using a discount factor that reflects the credit-adjusted risk free rate of interest, while taking into account an inflation rate. The Company prepares estimates of the timing and amounts of expected cash flows when an ARO is incurred, which are updated to reflect changes in facts and circumstances. Changes in regulations or laws, any instances of non-compliance with laws or regulations that result in fines, or any unforeseen environmental contamination could result in a material impact to the amounts charged to operations for reclamation and remediation. Significant judgments and estimates are made when estimating the fair value of AROs. Expected cash flows relating to AROs could occur over long periods of time and the assessment of the extent of environmental remediation work is highly subjective. Considering all of these factors that go into the determination of an ARO, the fair value of the AROs can materially change over time.
Revenue Recognition: Revenue includes sales value received for the Company's principal products, gold and silver. The Company currently does not earn revenue from any products other than gold and silver. Revenue is recognized when title to gold and silver passes to the buyer and when collectability is reasonably assured. Title passes to the buyer based on terms of the sales contract. Product pricing is determined at the point revenue is recognized by reference to active and freely traded commodity markets, for example, the London Bullion Market for both gold and silver, in an identical form to the product sold.
The Company entered into a doré sales agreement with a Canadian financial institution in July 2012. Under that agreement, the Company has the option to sell to that institution approximately 90% of the gold and silver contained in doré bars produced at the El Gallo 1 mine prior to the completion of refining by the third party refiner, which normally takes approximately 15 business days. Revenue is recognized when the Company has provided irrevocable instructions to the refiner to transfer to the purchaser the refined ounces sold upon final outturn, and when payment of the purchase price for the purchased doré has been made in full by the purchaser.
Royalty Expense: The Company has a net smelter return ("NSR") royalty agreement with a third party on all metal production from the El Gallo 1 mine and a portion of expected future metal production from the El Gallo 2 project. The terms of the royalty agreement stipulate that production up to 30,000 of gold and gold equivalent ounces are subject to a 1% NSR, production between 30,001 to 380,000 of gold and gold equivalent ounces are subject to a 3.5% NSR, and 1% thereafter. Currently the Company is subject to the 3.5% NSR. Under the terms of the royalty agreement, the royalty holder has the option to settle the NSR payment in cash or gold and gold equivalent ounces. The royalty holder has indicated a preference to settle the NSR payment in gold and gold equivalent ounces which would be calculated on the day the refiner credits the Company's metals account. Cumulatively, on a life-of-mine basis through to December 31, 2014, approximately 148,000 gold and gold equivalent ounces have been produced from mineralized material within the scope of the NSR agreement. Royalty
79
expenses are included in Production Costs Applicable to Sales in the Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss.
Property Holding Costs: Holding costs to maintain a property on a care and maintenance basis are expensed in the period they are incurred. These costs include security and maintenance expenses, lease and claim fees and payments, and environmental monitoring and reporting costs.
Exploration Costs: Exploration costs include costs incurred to identify new mineral resources, evaluate potential resources, and convert mineral resources into proven and probable reserves. Exploration costs are expensed as incurred.
Income Taxes: The Company accounts for income taxes using the liability method, recognizing certain temporary differences between the financial reporting basis of liabilities and assets and the related income tax basis for such liabilities and assets. This method generates either a net deferred income tax liability or asset for the Company, as measured by the statutory tax rates in effect. The Company derives the deferred income tax charge or benefit by recording the change in either the net deferred income tax liability or asset balance for the year. The Company records a valuation allowance against any portion of those deferred income tax assets when it believes, based on the weight of available evidence, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred income tax asset will not be realized.
Forward-Looking Statements
This report contains or incorporates by reference "forward-looking statements," as that term is used in federal securities laws, about our financial condition, results of operations and business. These statements include, among others:
- •
- statements about our anticipated exploration results, cost and feasibility of production, receipt of permits or other regulatory or
government approvals and plans for the development of our properties;
- •
- statements concerning the benefits or outcomes that we expect will result from our business activities and certain transactions that
we contemplate or have completed, such as receipt of proceeds, increased revenues, decreased expenses and avoided expenses and expenditures; and
- •
- statements of our expectations, beliefs, future plans and strategies, anticipated developments and other matters that are not historical facts.
These statements may be made expressly in this document or may be incorporated by reference to other documents that we will file with the SEC. You can find many of these statements by looking for words such as "believes," "expects," "anticipates," "estimates" or similar expressions used in this report or incorporated by reference in this report.
Forward-looking statements and information are necessarily based upon a number of estimates and assumptions that, while considered reasonable by management, are inherently subject to significant business, economic and competitive uncertainties, risks and contingencies, and there can be no assurance that such statements and information will prove to be accurate. Therefore, actual results and future events could differ materially from those anticipated in such statements and information. We caution you not to put undue reliance on these statements, which speak only as of the date of this report. Further, the information contained in this document or incorporated herein by reference is a statement of our present intention and is based on present facts and assumptions, and may change at any time and without notice, based on changes in such facts or assumptions. Readers should not place undue reliance on forward-looking statements.
80
Risk Factors Impacting Forward-Looking Statements
The important factors that could prevent us from achieving our stated goals and objectives include, but are not limited to, those set forth in other reports we have filed with the SEC and the following:
- •
- our ability to raise funds required for the execution of our business strategy;
- •
- our ability to secure permits or other regulatory and government approvals needed to operate, develop or explore our mineral
properties and projects;
- •
- decisions of foreign countries and banks within those countries;
- •
- unexpected changes in business, economic, and political conditions;
- •
- operating results of MSC;
- •
- fluctuations in interest rates, currency exchange rates, or commodity prices;
- •
- timing and amount of mine production;
- •
- our ability to retain and attract key personnel;
- •
- technological changes in the mining industry;
- •
- changes in operating, exploration or overhead costs;
- •
- access and availability of materials, equipment, supplies, labor and supervision, power and water;
- •
- results of current and future exploration activities;
- •
- results of pending and future feasibility studies or the expansion or commencement of mining operations without feasibility studies
having been completed;
- •
- changes in our business strategy;
- •
- interpretation of drill hole results and the geology, grade and continuity of mineralization;
- •
- the uncertainty of reserve estimates and timing of development expenditures;
- •
- litigation or regulatory investigations and procedures affecting us;
- •
- local and community impacts and issues including criminal activity and violent crimes; and
- •
- accidents, public health issues, and labor disputes.
We undertake no responsibility or obligation to update publicly these forward-looking statements, except as required by law and may update these statements in the future in written or oral statements. Investors should take note of any future statements made by or on our behalf.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURE ABOUT MARKET RISK
Our exposure to market risks includes, but is not limited to, the following risks: changes in foreign currency exchange rates, changes in interest rates, equity price risks, commodity price fluctuations and country risk. We do not use derivative financial instruments as part of an overall strategy to manage market risk.
Foreign Currency Risk
While we transact most of our business in U.S. dollars, some expenses, labor, operating supplies and property and equipment are denominated in Canadian dollars, Mexican pesos or Argentine pesos. As a result, currency exchange fluctuations may impact our operating costs. The appreciation of non-U.S. dollar currencies against the U.S. dollar increases costs and the cost of purchasing property
81
and equipment in U.S. dollar terms in Canada, Mexico and Argentina, which can adversely impact our operating results and cash flows. Conversely, a depreciation of non-U.S. dollar currencies usually decreases operating costs and property and equipment purchases in U.S. dollar terms in foreign countries.
Since 2008, the Argentine peso has been steadily devaluing against the U.S. dollar by 10-30% on an annual basis. For the year ended December 31, 2013, the Argentine peso devalued by 29%. The Argentine peso devalued further, with a devaluation of 28% for the year ended December 31, 2014. Due to restrictions in holding other currencies, MSC holds all of their local cash balances in Argentine pesos and are therefore exposed to the effects of this continued devaluation and also the risk that there may be a sudden severe devaluation of the Argentine peso. A severe devaluation could result in material foreign exchange losses as reported in U.S. dollars.
The value of cash and cash equivalents denominated in foreign currencies also fluctuates with changes in currency exchange rates. Appreciation of non-U.S. dollar currencies results in a foreign currency gain on such investments and a depreciation in non-U.S. dollar currencies results in a loss. We have not utilized material market risk-sensitive instruments to manage our exposure to foreign currency exchange rates but may in the future actively manage our exposure to foreign currency exchange rate risk. We hold portions of our cash reserves in non-U.S. dollar currencies. Based on our Canadian dollar holdings of $1.3 million (C$ 1.6 million) at December 31, 2014, a 1% change in the Canadian dollar would result in a gain/loss of $0.01 million in the Consolidated Statement of Operations. We also hold immaterial portions of our cash reserves in Mexican and Argentine pesos.
Interest Rate Risk
We have no debt outstanding nor do we have any investment in debt instruments other than highly liquid short-term investments. Accordingly, we consider our interest rate risk exposure to be insignificant at this time.
Equity Price Risk
We have in the past sought and will likely in the future seek to acquire additional funding by sale of common stock. Movements in the price of our common stock have been volatile in the past and may also be volatile in the future. As a result, there is a risk that we may not be able to sell common stock at an acceptable price to meet future funding requirements.
Commodity Price Risk
We own a 49% interest in the San José mine, an operating silver-gold mine in Santa Cruz, Argentina, and a 100% interest in the El Gallo 1 mine, an operating gold-silver mine in Sinaloa, Mexico. As a result, changes in the price of gold and silver could significantly affect our results of operations and cash flows in the future. We have in the past and may in the future hold a portion of our treasury in gold and silver bullion, which is recorded at the lower of cost or market. Gold and silver prices may fluctuate widely from time to time. Based on our revenues from gold and silver sales of $45.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, a 10% change in the price of gold and silver would have had an impact of approximately $4.5 million on our revenues.
Credit Risk
We may be exposed to credit loss through our precious metals and doré sales agreements with Canadian financial institutions if these institutions are unable to make payment in accordance with the terms of the agreement. However, based on the history and financial condition of our counterparties, we do not anticipate any of the financial institutions to default on their obligation. As of December 31,
82
2014, we do not believe we have any significant credit exposure associated with precious metals and our doré sales agreements.
In Mexico, we are exposed to credit loss regarding our VAT taxes receivable, if the Mexican tax authorities are unable or unwilling to make payments in accordance with our monthly filings. Timing of collection on VAT receivables is uncertain as VAT refund procedures require a significant amount of information and follow-up. The risk is mitigated to the extent that the VAT receivable balance can be applied against future income taxes payable. However, at this time we are uncertain when, if ever, our Mexican operations will generate sufficient taxable operating profits to offset this receivable against taxes payable. We continue to face risk on the collection of our VAT receivables, which amount to $11.7 million as at December 31, 2014.
In Nevada, we are required to provide security to cover our projected reclamation costs. We have surety bonds of $4.8 million in place to satisfy bonding requirements for this purpose. The bonds have an annual fee of 1.5% of their value, with an upfront deposit of 10%. Although we do not believe we have any significant credit exposure associated with these bonds, we are exposed to credit loss regarding our deposit if the surety bond underwriter defaults on its coverage of the bond. There is also the risk the surety bonds may no longer be accepted by the governmental agencies as satisfactory reclamation coverage, in which case we would be required to replace the surety bonding with cash.
83
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
84
MANAGEMENT'S REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
Management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. The Securities Exchange Act of 1934 defines internal control over financial reporting in Rule 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the Company's principal executive and principal financial officers and effected by the Company's board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and includes those policies and procedures that:
- •
- Pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the
assets of the Company;
- •
- Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance
with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and the board of directors of the
Company; and
- •
- Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company's assets that could have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
The Company's management assessed the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014. In making this assessment, the Company's management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (1992).
Based upon its assessment, management concluded that, as of December 31, 2014, the Company's internal control over financial reporting was effective based upon those criteria. Commencing 2015, the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting will be assessed using the Internal Control—Integrated Framework 2013 issued by COSO. KPMG LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, has audited the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014.
85
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
The
Board of Directors and Shareholders
McEwen Mining Inc.:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of McEwen Mining Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss, changes in shareholders' equity and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2014. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of McEwen Mining Inc.'s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of McEwen Mining Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2014, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), McEwen Mining Inc.'s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, and our report dated March 9, 2015 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ KPMG LLP
Chartered
Professional Accountants, Licensed Public Accountants
Toronto, Canada
March 9, 2015
86
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
The
Board of Directors and Shareholders
McEwen Mining Inc.:
We have audited McEwen Mining Inc.'s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. McEwen Mining Inc.'s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, McEwen Mining Inc. maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014 based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of McEwen Mining Inc. as of December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss, changes in shareholders' equity and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2014, and our report dated March 9, 2015 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
/s/ KPMG LLP
Chartered
Professional Accountants, Licensed Public Accountants
Toronto, Canada
March 9, 2015
87
MCEWEN MINING INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
(in thousands of U.S. dollars, except per share amounts)
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
REVENUE: |
||||||||||
Gold and silver sales |
$ | 45,303 | $ | 45,982 | $ | 5,966 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
45,303 | 45,982 | 5,966 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
COSTS AND EXPENSES: |
||||||||||
Production costs applicable to sales |
40,608 | 34,594 | 3,861 | |||||||
Mine operating costs |
— | — | 8,507 | |||||||
Mine construction costs |
1,723 | 1,383 | 14,260 | |||||||
Mine development costs |
1,829 | 847 | — | |||||||
Exploration costs |
11,332 | 24,829 | 47,179 | |||||||
Property holding costs |
6,365 | 4,584 | 7,207 | |||||||
General and administrative expenses |
12,069 | 14,001 | 16,841 | |||||||
Acquisition costs |
— | — | 1,513 | |||||||
Depreciation |
979 | 942 | 1,033 | |||||||
Accretion of asset retirement obligation and reclamation expenses (note 6) |
407 | 461 | 447 | |||||||
Loss (income) from investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A., net of amortization (note 7) |
5,284 | (846 | ) | (20,835 | ) | |||||
Impairment of investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. (note 7) |
21,162 | 95,878 | — | |||||||
Impairment of mineral property interests and property and equipment (note 6) |
353,736 | 62,963 | 18,468 | |||||||
(Gain) loss on sale of assets |
(26 | ) | 6,743 | (1,110 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total costs and expenses |
455,468 | 246,379 | 97,371 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating loss |
(410,165 | ) | (200,397 | ) | (91,405 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE): |
||||||||||
Interest income, net of interest expense |
259 | 262 | 228 | |||||||
Loss on sale of marketable equity securities |
— | — | (70 | ) | ||||||
Other-than-temporary impairment on marketable equity securities |
— | — | (1,993 | ) | ||||||
(Loss) gain on sales of gold and silver bullion held as investments |
— | (223 | ) | 3,075 | ||||||
Unrealized loss on gold and silver bullion held as investments |
— | — | (359 | ) | ||||||
Registration taxes |
(6,788 | ) | — | — | ||||||
Gain (loss) on litigation settlement |
— | 560 | (3,830 | ) | ||||||
Foreign currency (loss) gain |
(2,419 | ) | (1,309 | ) | 456 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total other income (expense) |
(8,948 | ) | (710 | ) | (2,493 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss before income taxes |
(419,113 | ) | (201,107 | ) | (93,898 | ) | ||||
Income tax recovery (note 9) |
107,170 | 53,365 | 27,244 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss |
(311,943 | ) | (147,742 | ) | (66,654 | ) | ||||
OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS): |
||||||||||
Reclassification of unrealized gain on marketable securities disposed of during the period, net of taxes |
— | — | 1,000 | |||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on available-for-sale securities, net of taxes |
419 | (1 | ) | (5 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive loss |
$ | (311,524 | ) | $ | (147,743 | ) | $ | (65,659 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss per share (note 12): |
||||||||||
Basic |
$ | (1.05 | ) | $ | (0.50 | ) | $ | (0.26 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Diluted |
$ | (1.05 | ) | $ | (0.50 | ) | $ | (0.26 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average common shares outstanding (thousands) (note 12): |
||||||||||
Basic |
297,763 | 297,041 | 261,223 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Diluted |
297,763 | 297,041 | 261,223 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
88
MCEWEN MINING INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands of U.S. dollars)
| |
December 31, | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | |||||
ASSETS |
|||||||
Current assets: |
|||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 12,380 | $ | 24,321 | |||
Investments (note 4) |
1,082 | 2 | |||||
Value added taxes receivable |
11,739 | 11,591 | |||||
Inventories (note 5) |
12,404 | 8,800 | |||||
Other current assets |
2,096 | 2,057 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total current assets |
39,701 | 46,771 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Mineral property interests (note 6) |
287,812 | 642,968 | |||||
Restricted time deposits for reclamation bonding (note 6) |
— | 5,183 | |||||
Investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. (note 7) |
177,018 | 212,947 | |||||
Property and equipment, net (note 8) |
17,896 | 15,143 | |||||
Other assets |
531 | 54 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
TOTAL ASSETS |
$ | 522,958 | $ | 923,066 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
LIABILITIES & SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY |
|||||||
Current liabilities: |
|||||||
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
$ | 21,654 | $ | 9,797 | |||
Current portion of asset retirement obligation (note 6) |
2,427 | 1,392 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total current liabilities |
24,081 | 11,189 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Asset retirement obligation, less current portion (note 6) |
5,044 | 5,855 | |||||
Deferred income tax liability (note 9) |
51,899 | 158,855 | |||||
Deferred rent expense |
319 | — | |||||
Other liabilities |
400 | 400 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities |
$ | 81,743 | $ | 176,299 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
Shareholders' equity: |
|||||||
Common stock, no par value, 500,000 shares authorized; Common: 271,579 as of December 31, 2014 and 264,913 shares as of December 31, 2013 issued and outstanding Exchangeable: 28,521 shares as of Deceber 31, 2014 and 32,246 shares as of December 31, 2013 issued and outstanding |
1,360,668 | 1,354,696 | |||||
Accumulated deficit |
(919,577 | ) | (607,634 | ) | |||
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
124 | (295 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total shareholders' equity |
441,215 | 746,767 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
TOTAL LIABILITIES & SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY |
$ | 522,958 | $ | 923,066 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
Commitments and Contingencies (note 18) |
|||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
89
MCEWEN MINING INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY
(in thousands of U.S. dollars, except share amounts)
| |
|
|
Accumulated Other Comprehensive (Loss) Income |
|
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Common Stock | |
|
|||||||||||||
| |
Accumulated Deficit |
|
||||||||||||||
| |
Shares | Amount | Total | |||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2011 |
139,753 | $ | 613,831 | $ | (1,289 | ) | $ | (393,238 | ) | $ | 219,304 | |||||
Stock-based compensation |
— | 3,405 | — | — | 3,405 | |||||||||||
Issuance of exchangeable shares to acquire Minera Andes Inc. |
127,331 | 664,671 | — | — | 664,671 | |||||||||||
Assumption of stock options in connection with the acquisition of Minera Andes Inc. |
— | 3,175 | — | — | 3,175 | |||||||||||
Sale of shares for cash, net of issuance costs |
19,552 | 43,047 | — | — | 43,047 | |||||||||||
Sale of exchangeable shares for cash, net of issuance costs |
7,799 | 17,372 | — | — | 17,372 | |||||||||||
Exercise of stock options |
445 | 819 | — | — | 819 | |||||||||||
Exercise of stock options assumed from Minera Andes Inc. acquisition |
1,062 | 3,066 | — | — | 3,066 | |||||||||||
Shares issued for Mexico mining concessions |
83 | 391 | — | — | 391 | |||||||||||
Unrealized loss on marketable securities |
— | — | (5 | ) | — | (5 | ) | |||||||||
Reclassification of unrealized loss on marketable equity securities disposed of during the period, net of tax |
— | — | (993 | ) | — | (993 | ) | |||||||||
Other-than-temporary impairment on marketable equity securities |
— | — | 1,993 | — | 1,993 | |||||||||||
Net loss |
— | — | — | (66,654 | ) | (66,654 | ) | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2012 |
296,025 | $ | 1,349,777 | $ | (294 | ) | $ | (459,892 | ) | $ | 889,591 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2012 |
296,025 | $ | 1,349,777 | $ | (294 | ) | $ | (459,892 | ) | $ | 889,591 | |||||
Stock-based compensation |
— | 1,382 | — | — | 1,382 | |||||||||||
Exercise of stock options |
48 | 95 | — | — | 95 | |||||||||||
Exercise of stock options assumed from Minera Andes Inc. acquisition |
45 | 76 | — | — | 76 | |||||||||||
Shares issued for litigation settlement |
1,000 | 3,270 | — | — | 3,270 | |||||||||||
Shares issued for Mexico mining concessions |
41 | 96 | — | — | 96 | |||||||||||
Unrealized gain on available-for-sale securities, net of taxes |
— | — | (1 | ) | — | (1 | ) | |||||||||
Net loss |
— | — | — | (147,742 | ) | (147,742 | ) | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2013 |
297,159 | $ | 1,354,696 | $ | (295 | ) | $ | (607,634 | ) | $ | 746,767 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2013 |
297,159 | $ | 1,354,696 | $ | (295 | ) | $ | (607,634 | ) | $ | 746,767 | |||||
Stock-based compensation |
— | 1,324 | — | — | 1,324 | |||||||||||
Exercise of stock options |
1,499 | 1,932 | — | — | 1,932 | |||||||||||
Exercise of stock options assumed from Minera Andes Inc. acquisition |
198 | 360 | — | — | 360 | |||||||||||
Shares issued for settlement of accounts payable |
394 | 1,004 | — | — | 1,004 | |||||||||||
Shares issued to terminate TNR Gold Corp.'s back-in right |
850 | 1,352 | — | — | 1,352 | |||||||||||
Unrealized gain on available-for-sale securities, net of taxes |
— | — | 419 | — | 419 | |||||||||||
Net loss |
— | — | — | (311,943 | ) | (311,943 | ) | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2014 |
300,100 | $ | 1,360,668 | $ | 124 | $ | (919,577 | ) | $ | 441,215 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
90
MCEWEN MINING INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands of U.S. dollars)
| |
Year ended December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||||
Cash paid to suppliers and employees |
$ | (68,993 | ) | $ | (90,365 | ) | $ | (87,061 | ) | |
Cash received from gold and silver sales |
43,812 | 44,416 | 5,557 | |||||||
Dividends received from Minera Santa Cruz S.A. |
9,483 | 1,826 | 9,770 | |||||||
Proceeds from sale of gold and silver bullion held as investments |
— | 1,467 | 23,836 | |||||||
Lease incentive |
328 | — | — | |||||||
Interest received |
464 | 262 | 228 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash used in operating activities |
(14,906 | ) | (42,394 | ) | (47,670 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||||
Cash and short-term investments received from acquisition of Minera Andes Inc. |
— | — | 36,337 | |||||||
Short-term investments (net) |
— | — | 3,933 | |||||||
Acquisition of mineral property interests |
— | (150 | ) | (712 | ) | |||||
Additions to property and equipment |
(2,788 | ) | (4,306 | ) | (1,879 | ) | ||||
Investment in marketable equity securities |
(446 | ) | — | — | ||||||
Proceeds from sale of marketable securities |
— | — | 409 | |||||||
Decrease to restricted time deposits for reclamation bonding |
5,183 | — | 6 | |||||||
Deposit for surety bonds for reclamation bonding |
(481 | ) | — | — | ||||||
Proceeds from disposal of mineral property interests and property and equipment |
38 | 1,455 | 3,143 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
1,506 | (3,001 | ) | 41,237 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||||
Sale of common stock for cash, net of issuance costs |
— | — | 60,419 | |||||||
Exercise of stock options |
2,292 | 171 | 3,885 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash provided by financing activities |
2,292 | 171 | 64,304 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Effect of exchange rate change on cash and cash equivalents |
(833 | ) | (1,376 | ) | (366 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
(Decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents |
(11,941 | ) | (46,600 | ) | 57,505 | |||||
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period |
24,321 | 70,921 | 13,416 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents, end of period |
$ | 12,380 | $ | 24,321 | $ | 70,921 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Reconciliation of net loss to cash used in operating activities: |
||||||||||
Net loss |
$ | (311,943 | ) | $ | (147,742 | ) | $ | (66,654 | ) | |
Adjustments to reconcile net loss from operating activities: |
||||||||||
Loss (income) from investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A., net of amortization |
5,284 | (846 | ) | (20,835 | ) | |||||
Impairment of investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. |
21,162 | 95,878 | — | |||||||
Impairment of mineral property interests and property and equipment |
353,736 | 62,963 | 18,468 | |||||||
Other-than-temporary impairment on marketable equity securities |
— | — | 1,993 | |||||||
(Gain) loss on sale of assets |
(26 | ) | 6,743 | (1,110 | ) | |||||
Loss on sale of marketable securities |
— | — | 70 | |||||||
Lease incentive |
328 | — | — | |||||||
Income tax recovery |
(107,170 | ) | (53,365 | ) | (27,244 | ) | ||||
Gain on litigation settlement |
— | (560 | ) | 3,830 | ||||||
Loss (gain) on sale of gold and silver bullion held as investments |
— | 223 | (3,075 | ) | ||||||
Unrealized loss on gold and silver bullion held as investments |
— | — | 359 | |||||||
Proceeds on sale of gold and silver bullion held as investments |
— | 1,467 | 23,836 | |||||||
Stock-based compensation |
1,324 | 1,382 | 3,405 | |||||||
Shares issued to supplier for mining services |
1,004 | — | — | |||||||
Shares issued to TNR Gold Corp.'s to terminate back-in right |
1,352 | — | — | |||||||
Depreciation |
979 | 942 | 1,033 | |||||||
Accretion of asset retirement obligation |
407 | 461 | 447 | |||||||
Amortization of mineral property interests and asset retirement obligations |
1,236 | 1,530 | — | |||||||
Foreign exchange loss |
833 | 1,376 | 366 | |||||||
Change in non-cash working capital items: |
||||||||||
Increase in VAT receivable, net of collection of $5,049 (2013—$3,438; 2012—$720) |
(148 | ) | (2,441 | ) | (6,167 | ) | ||||
(Increase) in other assets related to operations |
(3,638 | ) | (703 | ) | 3,992 | |||||
Increase (decrease) in liabilities related to operations |
10,891 | (11,528 | ) | 10,253 | ||||||
Dividends received from Minera Santa Cruz S.A. |
9,483 | 1,826 | 9,363 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash used in operating activities |
$ | (14,906 | ) | $ | (42,394 | ) | $ | (47,670 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
91
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted)
NOTE 1 THE COMPANY
McEwen Mining Inc. was organized under the laws of the State of Colorado on July 24, 1979. The Company is engaged in the exploration for, development of, production and sale of gold and silver. On January 24, 2012, the Company changed its name from US Gold Corporation to McEwen Mining Inc. after the completion of the acquisition of Minera Andes Inc. by way of a statutory plan of arrangement under the laws of the Province of Alberta, Canada.
The Company operates in Argentina, Mexico, and the United States. It owns a 49% interest in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. ("MSC"), owner of the producing San José silver-gold mine in Santa Cruz, Argentina, which is operated by the majority owner of the joint venture, Hochschild Mining plc. It also owns the El Gallo 1 mine in Sinaloa, Mexico. Finally, the Company owns the Los Azules copper deposit in San Juan, Argentina, the El Gallo 2 project in Sinaloa, Mexico, the Gold Bar project in Nevada in the United States, and a large portfolio of exploration properties in Argentina, Mexico and Nevada.
NOTE 2 SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Use of Estimates: The Company's consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. The preparation of the Company's consolidated financial statements requires the Company to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of expenses during the reporting period. The more significant areas requiring the use of management estimates and assumptions relate to environmental, reclamation and closure obligations; estimates of fair value for asset impairments; estimates regarding the collectability of value added taxes receivable; valuation allowances for deferred tax assets; reserves for contingencies and litigation; and estimates with respect to assumptions regarding stock-based compensation expense. The Company bases its estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ significantly from these estimates.
Basis of Consolidation: The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. Significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated. Investments over which the Company exerts significant influence but does not control through majority ownership are accounted for using the equity method, as described in Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies—Investments, below.
Cash and Cash Equivalents: The Company considers cash in banks, deposits in transit, and highly liquid term deposits with original maturities of three months or less to be cash and cash equivalents. Because of the short maturity of these instruments, the carrying amounts approximate their fair value. Restricted cash is excluded from cash and cash equivalents and is included in long-term assets.
Business Combinations: The Company accounts for business combinations using the acquisition method of accounting pursuant to Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") Topic 805, Business Combinations. The acquisition method requires the Company to determine the fair value of all acquired assets, including identifiable intangible assets, and all assumed liabilities. The fair value of the
92
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 2 SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Continued)
consideration paid is allocated to the underlying identifiable net assets, based on their respective estimated fair values and any excess is recorded as goodwill.
Determining the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed requires management's judgment and the utilization of independent valuation experts, and often involves the use of significant estimates and assumptions, including assumptions with respect to future cash inflows and outflows, discount rates, and asset lives, among other items. Transaction costs are expensed as incurred and are reported on the acquisition costs line within the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss.
Investments: The Company accounts for investments over which the Company exerts significant influence but does not control through majority ownership using the equity method of accounting pursuant to ASC Topic 323, Investments—Equity Method and Joint Ventures. Under this method, the Company's share of earnings and losses is included in the Consolidated Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss and the balance of the investment is adjusted by the same amount. Under the equity method, dividends received from an investee are recorded as decreases in the investment account, not as income. If and when there has been a loss in value that is other than a temporary decline, the carrying value is reduced to its fair value.
The Company accounts for its investment in marketable equity securities as available for sale securities in accordance with ASC guidance on accounting for certain investments in debt and equity securities. The Company periodically evaluates whether declines in fair values of its investments below the Company's carrying value are other-than-temporary in accordance with ASC guidance. Declines in fair value below the Company's carrying value deemed to be other-than-temporary are charged to operations.
The Company accounts for its gold and silver bullion investments in accordance with ASC Topic 815. Since ASC Topic 815, Derivatives and Hedging, does not consider gold and silver to be readily convertible to cash, the Company carries these assets at the lower of cost or market.
Value Added Taxes Receivable: In Mexico, value added taxes ("VAT") are assessed on purchases of materials and services and sales of products. Businesses are generally entitled to recover the taxes they have paid related to purchases of materials and services, either as a refund or as a credit against future taxes payable. In Argentina, except at the San José mine, the Company expenses all VAT as their recoverability is uncertain.
Stockpiles, Material on Leach Pads, In-process Inventory, Precious Metals Inventory and Materials and Supplies: Stockpiles, material on leach pads, in-process inventory, precious metals inventory and materials and supplies are carried at the lower of average cost or net realizable value. Net realizable value represents the estimated future sales price of the product based on current and long-term metals prices, less the estimated costs to complete production and bring the product to sale. Write-downs of stockpiles, material on leach pads, in-process inventory, precious metals inventory and materials and supplies, resulting from net realizable value impairments, are reported as a component of production costs applicable to sales. The current portion of stockpiles, material on leach pad, in-process inventory and materials and supplies is determined based on the expected amounts to be processed
93
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 2 SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Continued)
within the next 12 months. Stockpiles, material on leach pads, in-process inventory and materials and supplies not expected to be processed within the next 12 months, if any, are classified as long-term.
Stockpiles represent mineralized material that has been extracted from the mine and is available for further processing. Stockpiles are measured by estimating the number of tonnes added and removed from the stockpile, an estimate of the contained metals (based on assay data) and the estimated metallurgical recovery rates. Costs are allocated to stockpiles based on relative values of material stockpiled and processed using current mining costs incurred up to the point of stockpiling the mineralized material. Material is removed from the stockpile at an average cost per tonne. Since the Company only achieved production for accounting purposes in September 2012, no value was allocated to stockpiles prior to then.
Mineralized material on leach pads is the ore that is placed on pads where it is treated with a chemical solution that dissolves the gold contained in the ore over a period of months. Costs are attributed to the ore on leach pads based on current mining costs incurred up to the point of placing the ore on the pad. Costs are removed from the leach pad based on the average cost per estimated recoverable ounce of gold on the leach pad as the gold is recovered. The estimates of recoverable gold on the leach pads are calculated from the quantities of ore placed on the leach pads (measured tons added to the leach pads), the grade of ore placed on the leach pads (based on assay data) and a recovery percentage. In general, leach pads recover between 50% and 95% of the recoverable ounces in the first year of leaching, declining each year thereafter until the leaching is complete. The cumulative metallurgical recovery rate for gold production at the El Gallo 1 mine from September 2012 (start of production) to December 31, 2014 was approximately 56% (2013—61%). Although the quantities of recoverable gold placed on the leach pads are reconciled by comparing the grades of ore placed on the pads to the quantities of gold actually recovered (metallurgical balancing), the nature of the leaching process inherently limits the ability to precisely monitor inventory levels. As a result, the metallurgical balancing process is constantly monitored and the engineering estimates are refined based on actual results over time.
In-process inventories represent materials that are currently in the process of being converted to a saleable product. The El Gallo 1 conversion process uses an Adsorption-Desorption-Recovery ("ADR") processing plant utilizing carbon columns for recovery. In-process material is measured based on assays of the material fed into the process and the projected recoveries of the respective plants. Costs are allocated to in-process inventories based on the costs of the material fed into the process attributable to the source material coming from the mines, stockpiles and/or leach pads plus the in-process conversion costs incurred to that point in the process.
Precious metal inventories include gold and silver bullion that is unsold and held at the Company's or the refinery's facilities. Costs are allocated to precious metal inventories based on costs of the respective in-process inventories incurred prior to the refining process plus applicable refining costs.
Materials and supplies inventories are comprised of chemicals, reagents and consumable parts used in drilling and other operating activities. They are valued at the lower of average cost or net realizable value. Cost includes applicable taxes and freight.
Proven and Probable Reserves: The definition of proven and probable reserves is set forth in Industry Guide 7. Proven reserves are reserves for which (a) quantity is computed from dimensions
94
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 2 SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Continued)
revealed in outcrops, trenches, workings or drill holes, grade and/or quality are computed from the results of detailed sampling and (b) the sites for inspection, sampling and measurement are spaced so closely and the geological character is so well defined that size, shape, depth and mineral content of the reserves are well-established. Probable reserves are reserves for which quantity and grade and/or quality are computed from information similar to that used for proven (measured) reserves, but the sites for inspection, sampling, and measurement are farther apart or are otherwise less adequately spaced. The degree of assurance, although lower than that for proven (measured) reserves, is high enough to assume continuity between points of observations.
As of December 31, 2014, except for the Company's 49% interest in the San José mine, none of the Company's properties contain resources that satisfy the definition of proven and probable reserves. The Company classifies the development of its properties, including the El Gallo 1 mine, as exploration stage projects since no proven or probable reserves have been established.
Property and Equipment: As described in Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies—Design, Construction and Development Costs below, substantially all costs, including design, engineering, construction, and installation of equipment are expensed as incurred as the Company has not established proven and probable reserves on any of its properties except for the Company's 49% interest in the San José mine. Only certain types of equipment which has alternative uses or significant salvage value, may be capitalized without proven and probable reserves. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method with the exception of mining equipment. Mining equipment is depreciated using the units-of-production method based on tonnes processed over the estimated total mine life. Office furniture, equipment and light vehicles are being depreciated over estimated economic lives ranging from 3 to 5 years. Leasehold improvements, which relate to the Company's corporate office, are being amortized over the term of the lease of 10 years. Trailers, heavy vehicles and other site equipment are being depreciated over estimated economic lives from 5 to 15 years. Buildings are being depreciated over an estimated economic life of 20 years.
Design, Construction, and Development Costs: Mine development costs include engineering and metallurgical studies, drilling and other related costs to delineate an ore body, the removal of overburden to initially expose an ore body at open pit surface mines and the building of access ways, shafts, lateral access, drifts, ramps and other infrastructure at underground mines.
When proven and probable reserves as defined by Industry Guide 7 exist, development costs are capitalized and the property is a commercially minable property. Mine development costs incurred either to develop new ore deposits, expand the capacity of operating mines, or to develop mine areas substantially in advance of current production would be capitalized. Costs of start-up activities and costs incurred to maintain current production or to maintain assets on a standby basis are charged to operations as incurred. Costs of abandoned projects are charged to operations upon abandonment. All capitalized costs would be amortized using the units of production method over the estimated life of the ore body based on recoverable ounces to be mined from proven and probable reserves.
Certain costs to design and construct mining and processing facilities may be incurred prior to establishing proven and probable reserves. As no proven and probable reserves have been established on any of the Company's properties except for the Company's 49% interest in the San José mine, design, construction and development costs are not capitalized at any of the Company's properties, and
95
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 2 SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Continued)
accordingly, substantially all costs are expensed as incurred, resulting in the Company reporting larger losses than if such expenditures had been capitalized. Additionally, the Company does not have a corresponding depreciation or amortization of these costs going forward since these expenditures were expensed as incurred as opposed to being capitalized. As a result of these and other differences, the Company's financial statements may not be comparable to the financial statements of mining companies that have established reserves.
Mineral Property Interests: Mineral property interests include acquired interests in development and exploration stage properties, which are considered tangible assets. The amount capitalized relating to a mineral property interest represents its fair value at the time of acquisition, either as an individual asset purchase or as a part of a business combination. The value of mineral property interests is primarily driven by the nature and amount of mineralized material believed to be contained in the properties. When proven and probable reserves exist, the relevant capitalized costs and mineral property interests are to be charged to expense based on the units of production method and upon commencement of production. However, when a property does not contain mineralized material that satisfies the definition of proven and probable reserves, such as with the El Gallo 1 mine, the amortization of the capitalized costs and mineral property interests are charged to expense based on the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the mine, which based on the Company's El Gallo 1 mine plan as of December 31, 2014 is estimated to end in late 2017. As a result of these and other differences, the Company's financial statements will not be comparable to the financial statements of mining companies that have established reserves as defined by Industry Guide 7.
Impairment of Assets: The Company reviews and evaluates its long-lived assets for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the related carrying amounts may not be recoverable. Mineral properties are monitored for impairment based on factors such as mineral prices, government regulation and taxation, the Company's continued right to explore the area, exploration reports, assays, technical reports, drill results and its continued plans to fund exploration programs on the property.
For operating mines, recoverability is measured by comparing the undiscounted future net cash flows to the net book value. When the net book value exceeds future net undiscounted cash flows, an impairment loss is measured and recorded based on the excess of the net book value over fair value. Fair value for operating mines is determined using a combined approach, which uses a discounted cash flow model for the existing operations and a market approach for the fair value assessment of exploration land claims. Future cash flows are estimated based on quantities of recoverable mineralized material, expected gold and silver prices (considering current and historical prices, trends and related factors), production levels, operating costs, capital requirements and reclamation costs, all based on life-of-mine plans. The term "recoverable mineralized material" refers to the estimated amount of gold or other commodities that will be obtained after taking into account losses during processing and treatment of mineralized material. In estimating future cash flows, assets are grouped at the lowest level for which there are identifiable cash flows that are largely independent of future cash flows from other asset groups. The Company's estimates of future cash flows are based on numerous assumptions and it is possible that actual future cash flows will be significantly different than the estimates, as actual future quantities of recoverable minerals, gold, silver and other commodity prices, production levels and costs and capital are each subject to significant risks and uncertainties.
96
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 2 SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Continued)
For exploration properties, the Company is unable to estimate undiscounted future net cash flows from its operations due to the absence of proven and probable reserves. As a result, the Company uses the market approach to estimate the fair value of the Nevada and Argentina exploration properties by using a combination of the observed market value per square mile and an observed market value per ounce or pound of mineralized material based on comparable transactions, and uses this measure to assess recoverability and impairment. For purposes of recognition and measurement of an impairment loss, the Company groups its properties by geological mineral complex, as this represents the lowest level at which the Company allocates its exploration spending independent of other assets and liabilities.
Asset Retirement Obligation: The Company records the fair value of a liability for an asset retirement obligation ("ARO") in the period that it is incurred if a reasonable estimate of fair value can be made. The associated asset retirement costs are capitalized as part of the carrying amount of the long-lived asset when proven or probable reserves exist, or if they relate to an acquired mineral property interest. Since no proven or probable reserves have been established for any of the Company's properties, other than at the San José mine, incremental asset retirement costs associated with the re-measurement of the fair value of the ARO at the El Gallo 1 mine or Tonkin property are charged to expense. Ongoing environmental and reclamation expenditures are debited against the ARO as incurred to the extent they relate to the ARO and to expense to the extent they do not. The fair value of AROs is measured by discounting the expected cash flows using a discount factor that reflects the credit-adjusted risk free rate of interest, while taking into account an inflation rate. The Company prepares estimates of the timing and amounts of expected cash flows when an ARO is incurred, which are updated to reflect changes in facts and circumstances. Changes in regulations or laws, any instances of non-compliance with laws or regulations that result in fines, or any unforeseen environmental contamination could result in a material impact to the amounts charged to operations for reclamation and remediation. Significant judgments and estimates are made when estimating the fair value of AROs. Expected cash flows relating to AROs could occur over long periods of time and the assessment of the extent of environmental remediation work is highly subjective. Considering all of these factors that go into the determination of an ARO, the fair value of the AROs can materially change over time.
Revenue Recognition: Revenue includes sales value received for the Company's principal products, gold and silver. The Company currently does not earn revenue from any products other than gold and silver. Revenue is recognized when title to gold and silver passes to the buyer and when collectability is reasonably assured. Title passes to the buyer based on terms of the sales contract. Product pricing is determined at the point revenue is recognized by reference to active and freely traded commodity markets, for example, the London Bullion Market for both gold and silver, in an identical form to the product sold.
The Company entered into a doré sales agreement with a Canadian financial institution in July 2012. Under that agreement, the Company has the option to sell to the institution approximately 90% of the gold and silver contained in doré bars produced at the El Gallo 1 mine prior to the completion of refining by the third party refiner, which normally takes approximately 15 business days. Revenue is recognized when the Company has provided irrevocable instructions to the refiner to transfer to the purchaser the refined ounces sold upon final outturn, and when payment of the purchase price for the purchased doré has been made in full by the purchaser.
97
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 2 SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Continued)
Royalty Expense: The Company has a net smelter return ("NSR") royalty agreement with a third party on all metal production from the El Gallo 1 mine and a portion of expected future metal production from the El Gallo 2 project. The terms of the royalty agreement stipulate that production up to 30,000 of gold and gold equivalent ounces are subject to a 1% NSR, production between 30,001 to 380,000 of gold and gold equivalent ounces are subject to a 3.5% NSR, and 1% thereafter. Currently the Company is subject to the 3.5% NSR. Under the terms of the royalty agreement, the royalty holder has the option to settle the NSR payment in cash or gold and gold equivalent ounces. The royalty holder has indicated a preference to settle the NSR payment in gold and gold equivalent ounces which would be calculated on the day the refiner credits the Company's metals account. Cumulatively, on a life-of-mine basis through to December 31, 2014, approximately 148,000 gold and gold equivalent ounces have been produced from mineralized material within the scope of the NSR agreement. Royalty expenses are included in Production Costs Applicable to Sales in the Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss.
Property Holding Costs: Holding costs to maintain a property on a care and maintenance basis are expensed in the period they are incurred. These costs include security and maintenance expenses, lease and claim fees and payments, and environmental monitoring and reporting costs.
Exploration Costs: Exploration costs include costs incurred to identify new mineral resources, evaluate potential resources, and convert mineral resources into proven and probable reserves. Exploration costs are expensed as incurred.
Foreign Currency: The functional currency for the Company's operations is the U.S. dollar. All monetary assets and liabilities denominated in a currency which is not the U.S. dollar are translated at current exchange rates at each balance sheet date and the resulting adjustments are included in a separate line item under other income (expense). Revenue and expense in foreign currencies are translated at the average exchange rates for the period.
Stock-Based Compensation: The Company accounts for stock options at fair value as prescribed in ASC 718. The Company estimates the fair value of each stock option at the grant date by using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model and provides for expense recognition over the service period, if any, of the stock option.
In 2013, the Company entered into an agreement with one of its mining contractors to pay for a portion of mining services with shares of common stock of the Company, up to a maximum of 2,500,000 shares. The number of shares to be issued is determined monthly, based on the amount payable by the Company for services rendered above a defined tonnage threshold, using the closing price of the Company's common stock quoted on active markets at the end of every month. The cost of the shares required to be issued are included in Production Costs Applicable to Sales. At every period-end, any outstanding shares owed are marked to market based on the price of the Company's stock quoted on active markets. The agreement was terminated on February 1, 2015.
Income Taxes: The Company accounts for income taxes under ASC 740 using the liability method, recognizing certain temporary differences between the financial reporting basis of liabilities and assets and the related income tax basis for such liabilities and assets. This method generates either a net deferred income tax liability or asset for the Company, as measured by the statutory tax rates in
98
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 2 SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Continued)
effect. The Company derives the deferred income tax charge or benefit by recording the change in either the net deferred income tax liability or asset balance for the year. The Company records a valuation allowance against any portion of those deferred income tax assets when it believes, based on the weight of available evidence, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred income tax asset will not be realized.
Comprehensive Loss: In addition to net loss, comprehensive loss includes all changes in equity during a period, such as cumulative unrecognized changes in fair value of marketable equity securities classified as available-for-sale or other investments.
Per Share Amounts: Basic earnings or loss per share includes no dilution and is computed by dividing income or loss available to common shareholders by the weighted average number of common and exchangeable shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings or loss per share reflect the potential dilution of securities that could share in the earnings of the Company and are computed in accordance with the treasury stock method based on the average number of common shares and dilutive common share equivalents outstanding. In these financial statements, warrants and stock options are not considered in the computation of diluted earnings or loss per share as their inclusion would be anti-dilutive for the periods presented.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments: Fair value accounting, as prescribed in ASC Section 825, utilizes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value. The hierarchy gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities (Level 1 measurements) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3 measurements). The three levels of the fair value hierarchy are described below:
| Level 1 | Unadjusted quoted prices in active markets that are accessible at the measurement date for identical, unrestricted assets or liabilities; | |
Level 2 |
Quoted prices in markets that are not active, or inputs that are observable, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the asset or liability; and |
|
Level 3 |
Prices or valuation techniques that require inputs that are both significant to the fair value measurement and unobservable (supported by little or no market activity). |
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
Presentation of an Unrecognized Tax Benefit: In July 2013, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued Accounting Standard Update ("ASU") 2013-11 related to the presentation of an unrecognized tax benefit when a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss or a tax credit carryforward exists. The updated guidance requires an entity to net its unrecognized tax benefits against the deferred tax assets for the same jurisdiction's net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss, or tax credit carryforwards. A gross presentation will be required only if such carryforwards are not available or would not be used by the entity to settle any additional income taxes resulting from disallowance of the uncertain tax position. The update was effective prospectively for the Company's fiscal year beginning January 1, 2014. The new guidance affects disclosures only and the adoption had no impact on the Company's consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
99
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 2 SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Continued)
Foreign Currency Matters: In March 2013, the FASB issued ASU 2013-05 related to Foreign Currency Matters to clarify the treatment of cumulative translation adjustments when a parent sells a part or all of its investment in a foreign entity or no longer holds a controlling financial interest in a subsidiary or group of assets that is a business within a foreign entity. The updated guidance also resolves the diversity in practice for the treatment of business combinations achieved in stages in a foreign entity. The update was effective prospectively for the Company's fiscal year beginning January 1, 2014. The updated guidance had no impact on the Company's consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
Presentation of Financial Statements—Going Concern—Disclosure of Uncertainties about an Entity's Ability to Continue as a Going Concern: In August 2014, ASC 205-40 guidance was amended to provide guidance about management's responsibility to evaluate whether there is substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern and to provide related footnote disclosures. The amendments require management to assess an entity's ability to continue as a going concern by incorporating and expanding upon certain principles that are currently in U.S. auditing standards. Specifically, the amendments (1) provide a definition of the term substantial doubt, (2) require an evaluation every reporting period including interim periods, (3) provide principles for considering the mitigating effect of management's plans, (4) require certain disclosures when substantial doubt is alleviated as a result of consideration of management's plans, (5) require an express statement and other disclosures when substantial doubt is not alleviated, and (6) require an assessment for a period of one year after the date that the financial statements are issued (or available to be issued). The amendments in this update are effective for the Company's fiscal year ending December 31, 2016 and interim periods in the fiscal year ending December 31, 2017, with early application permitted. The Company is evaluating the effect that the updated standard will have on its consolidated financial statements.
Presentation of Financial Statements and Property, Plant and Equipment—Reporting Discontinued Operations and Disclosures of Components of an Entity: In April 2014, ASC 205 and ASC 360 guidance was amended to change the requirements for reporting discontinued operations in ASC 205-20. A disposal of a component of an entity or a group of components of an entity is required to be reported in discontinued operations only if the disposal represents a strategic shift that has, or will have, a major effect on an entity's operations and financial results when any of the following occurs: (1) the component of an entity or group of components of an entity meets the criteria in ASC 205-20-45-1E to be classified as held for sale; (2) the component of an entity or group of components of an entity is disposed of by sale; or (3) the component of an entity or group of components of an entity is disposed of other than by sale. The update is effective prospectively for the Company's fiscal year beginning January 1, 2015. The new guidance is not expected to have an impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
Revenue from Contracts with Customers: In May 2014, ASC 606 was issued related to revenue from contracts with customers. Under this guidance, revenue is recognized when promised goods or services are transferred to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration that is expected to be received for those goods or services. The updated standard will replace most existing revenue
100
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 2 SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Continued)
recognition guidance under GAAP when it becomes effective and permits the use of either the retrospective or cumulative effect transition method. Early adoption is not permitted. The standard will be effective for the Company's fiscal year beginning January 1, 2017, including interim reporting periods within that year. The Company is evaluating the effect that the updated standard will have on its consolidated financial statements.
NOTE 3 BUSINESS ACQUISITION
On January 24, 2012, the Company completed the acquisition of Minera Andes through a court-approved plan of arrangement under Alberta, Canada law (the "Arrangement"), under which Minera Andes, a Canadian company, became an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company.
On the closing date of the Arrangement, holders of Minera Andes' common stock received a number of exchangeable shares of McEwen Mining—Minera Andes Acquisition Corp. ("Exchangeable Shares"), an indirect wholly-owned Canadian subsidiary of the Company, equal to the number of Minera Andes shares, multiplied by the exchange ratio of 0.45. In the aggregate, former Minera Andes shareholders received 127,331,498 Exchangeable Shares. After closing of the Arrangement, the name of the Company was changed to McEwen Mining Inc. The Company's common stock began trading on the NYSE and TSX under the symbol "MUX" and the Exchangeable Shares began trading on the TSX under the symbol "MAQ" on January 27, 2012.
The Exchangeable Shares are exchangeable for the Company's common stock on a one-for-one basis. Option holders of Minera Andes received replacement options entitling them to receive, upon exercise, shares of the Company's common stock, reflecting the exchange ratio of 0.45 with the appropriate adjustment of the exercise price per share. The option life and vesting period of the replacement options did not change from the option life granted under the Minera Andes option plan. The estimated fair value of the vested portion of the replacement options of $3.2 million was included as part of the purchase price consideration at their fair values based on the Black-Scholes option pricing model.
The acquisition was accounted for using the acquisition method in accordance with ASC Topic 805, Business Combinations, with the Company being identified as the acquirer. The measurement of the purchase consideration was based on the market price of the Company's common stock on January 24, 2012, which was $5.22 per share. The total purchase price, including the fair value of the options, amounted to $667.8 million. The total transaction costs incurred through December 31, 2012 by the Company was $5.4 million, of which $3.9 million was reported in the year ended December 31, 2011 in general and administrative expenses, and $1.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2012 in acquisition costs in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss.
101
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 3 BUSINESS ACQUISITION (Continued)
The allocation of the purchase price, based on the estimated fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed on January 24, 2012, is summarized in the following table:
| |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
|||
Purchase price: |
||||
Exchangeable shares of McEwen Mining-Minera Andes Acquisition Corp. |
$ | 664,671 | ||
Stock options of McEwen Mining Inc. |
3,175 | |||
| | | | | |
|
$ | 667,846 | ||
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
Net assets acquired: |
||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 31,385 | ||
Short-term investments |
4,952 | |||
Other current assets |
9,828 | |||
Inventories |
1,362 | |||
Mineral property interests |
539,092 | |||
Investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. |
262,883 | |||
Equipment |
1,647 | |||
Accounts payable |
(5,323 | ) | ||
Deferred income tax liability |
(177,980 | ) | ||
| | | | | |
|
$ | 667,846 | ||
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
The fair value of mineral property interests exceeded the carrying value of the underlying assets for tax purposes by approximately $508.5 million. The resulting estimated deferred income tax liability originally associated with this temporary difference was approximately $178.0 million, which was included in the allocation of purchase price above.
The purchase consideration was allocated to the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed, based on an independent valuation report and management's best estimates.
NOTE 4 INVESTMENTS
During 2014, the Company invested a portion of its cash in marketable equity securities at a cost of $0.4 million. These securities are classified as available-for-sale securities and are valued at fair value. Any resulting gain or loss is recorded to an unrealized income and loss account (accumulated other comprehensive income (loss)) that is reported as a separate line item in the shareholders' equity section of the balance sheet. The gains and losses for available-for-sale securities are not reported on the statement of operations until the securities are sold. As at December 31, 2014, the market value of these securities was $1.1 million, and as a result the Company recorded a gain, net of tax, of $0.4 million to accumulated other comprehensive income.
102
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 5 INVENTORIES
Inventories at December 31, 2014 and 2013 consist of the following:
| |
2014 | 2013 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Ore on leach pads |
$ | 6,221 | $ | 2,749 | |||
In-process inventory |
2,302 | 2,681 | |||||
Stockpiles |
— | 778 | |||||
Precious metals |
2,403 | 1,300 | |||||
Materials and supplies |
1,478 | 1,292 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Inventories |
$ | 12,404 | $ | 8,800 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
The Company recorded write-downs of $0.6 million, $1.2 million and $0.2 million on its ore on leach pads inventory, in-process inventory, and precious metals inventory, respectively, during the year ended December 31, 2014, for a total of $2.0 million (2013—nil), to reduce the carrying value of its metal inventories to net realizable value. The write-down was due to a high volume of waste material being extracted, higher operating costs and lower metal prices during the third quarter of 2014. The inventory write-downs of $2.0 million are included as a component of Production Costs Applicable to Sales.
NOTE 6 MINERAL PROPERTY INTERESTS AND ASSET RETIREMENT OBLIGATIONS
Mineral Property Interests
The Company conducts a review of potential triggering events for all its mineral projects on a quarterly basis. When events or changes in circumstances indicate that the related carrying amounts may not be recoverable, the Company carries out a review and evaluation of its long-lived assets in accordance with its accounting policy. In the year ended December 31, 2014, such triggering events were identified with respect to the Company's Los Azules, Nevada and Argentina properties.
For Los Azules, a triggering event identified in relation to an acquisition in the second quarter of 2014 of a copper project located in Argentina, which the Company believed shared similarities with the Los Azules project due to its scale, location, and stage of development. Based on the announcement day value of the similar project, the estimated market value per pound of copper equivalent mineralized material from this transaction was below the carrying value per pound of estimated copper equivalent mineralized material of Los Azules, indicating a potential significant decrease in the market price of Los Azules, and therefore a requirement to test Los Azules for recoverability. In performing a recoverability test, the Company used the observed market value per pound of copper equivalent mineralized material based on this contemporaneous and other comparable transactions to estimate the fair value of Los Azules ("In-Situ Multiple"). The carrying value of the property exceeded its estimated fair value, resulting in an impairment charge of $120.4 million, along with a resulting deferred income tax recovery of $22.5 million, being recorded in the Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss for the second quarter of 2014. Refer to Note 17, Fair Value Accounting, for further detail on the valuation of Los Azules.
Subsequently, a further decline in the observed market value of comparable transactions was noted in the fourth quarter of 2014. The Company used a similar methodology as that used in the second quarter of 2014, however, applied an additional discount of 35% to the In-Situ Multiple, to reflect the
103
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 6 MINERAL PROPERTY INTERESTS AND ASSET RETIREMENT OBLIGATIONS (Continued)
decline in the observed market value of comparable transactions from June 2014 (date of the last impairment test) to December 31, 2014. The additional impairment charge recorded in the fourth quarter of 2014 was of $107.9 million, with a deferred income tax recovery of $19.3 million. The total impairment charge for the year ended December 31, 2014 was of $228.3 million.
For the Nevada and Argentina properties, the triggering events were that the Company noted a decline in the observed market value of comparable transactions, which indicated a potential significant decrease in the market price of these properties, and the strategic review by the Company of its exploration program, pursuant to which the Company has made the decision to focus primarily on core assets, namely the Los Azules, Gold Bar, Tonkin and North Battle Mountain properties. In performing the recoverability test for these properties, the Company used the observed market value per acre and per ounce of gold equivalent mineralized material of comparable transactions to estimate the fair value of each property. The carrying value of each of the properties exceeded their estimated fair value. The total impairment charge for Nevada and Argentina properties amounted to $98.4 million and $27.0 million, respectively, along with a resulting deferred income tax recovery of $31.6 million and $3.2 million, respectively, being recorded in the Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Impairments recorded in the year ended December 31, 2013 related to the Company's exploration properties in Santa Cruz, Argentina, and Nevada, respectively. The impairment charge of $27.7 million, along with a deferred income tax recovery of $2.3 million, recorded in the second quarter of 2013 related to the Santa Cruz properties and were primarily due to an unexpected significant decline in gold and silver market prices, continued inflationary pressures and a new tax on mining reserves in the Province, resulting in a depressed market for exploration properties in Argentina. Relating to the Company's Nevada properties, an impairment charge of $6.3 million, along with a deferred income tax recovery of $2.2 million, was recorded in the third quarter of 2013 as a result of the Company selling or allowing certain claims to lapse. Finally, in the fourth quarter of 2013, an additional impairment charge of $28.9 million, along with a deferred tax recovery of $10.1 million, was recorded in relation to certain mineral property interests in Nevada, as part of the Company's annual impairment test for the year ended December 31, 2013. The Company used the market approach to estimate the fair value of the impaired properties by using the observed market value per square mile based on comparable transactions in North America. Refer to Note 17, Fair Value Accounting, for further details.
Impairments recorded in the year ended December 31, 2012 related to the Company's North Battle Mountain properties of $14.0 million. In November 2012, the Company entered into an exploration earn-in and joint venture option agreement ("Option Agreement") with a third party whereby it has the option to earn a 51% interest in the property once it incurs cumulative project related expenditures of $2.4 million on or before October 2015. The North Battle Mountain properties were acquired in 2007 and had a carrying value of $18.2 million. The Company determined that the implied value of the Option Agreement was reduced to $4.2 million, resulting in an impairment of $14.0 million, along with a deferred income tax recovery of $4.9 million. The Company used the market approach to estimate the fair value of the properties by using the observed market value per square mile based on comparable transactions in South America.
104
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 6 MINERAL PROPERTY INTERESTS AND ASSET RETIREMENT OBLIGATIONS (Continued)
Further, in 2012, the Company performed a strategic review of its property holdings in Nevada and as a result, allowed certain claims from its Other United States Properties to lapse. These mineral property interests in question were acquired in 2007 and had a carrying value of $2.9 million. As such, the Company recorded an impairment charge of $2.9 million in Impairment of Mineral Property Interests and Property and Equipment in the Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss for the year ended December 31, 2012. The Company wrote off the carrying value of $1.3 million related to lapsing of certain mineral concessions in the El Gallo 2 area. The properties were part of the "Mexico" segment, as shown below and in Note 16, Operating Segment Reporting.
Based on the above, impairment charges were recorded on the following mineral property interests for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012:
Name of Property/Complex
|
Segment | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
(in thousands) |
|
|||||||||
Los Azules Project |
Argentina | $ | 228,301 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Other San Juan Properties |
Argentina | 7,817 | — | — | ||||||||
Telken Tenements(1) |
Argentina | — | 13,792 | — | ||||||||
Este Tenements(1) |
Argentina | — | 2,784 | — | ||||||||
Piramides Tenements(1) |
Argentina | — | 5,079 | — | ||||||||
Tobias Tenements(1) |
Argentina | — | 6,074 | — | ||||||||
Cerro Mojon Tenements |
Argentina | 1,971 | — | — | ||||||||
La Merced Tenements |
Argentina | 1,891 | — | — | ||||||||
Cabeza de Vaca Tenements |
Argentina | 877 | — | — | ||||||||
El Trumai Tenements |
Argentina | 1,534 | — | — | ||||||||
Martes 13 Tenements |
Argentina | 3,568 | — | — | ||||||||
Celestina Tenements |
Argentina | 1,753 | — | — | ||||||||
Other Santa Cruz Exploration Properties |
Argentina | 7,601 | — | — | ||||||||
Tonkin Complex |
Nevada | 31,391 | — | — | ||||||||
Gold Bar Complex |
Nevada | 25,435 | — | — | ||||||||
Limo Complex |
Nevada | 23,438 | 19,450 | — | ||||||||
North Battle Mountain Complex |
Nevada | 1,921 | — | 14,044 | ||||||||
East Battle Mountain Complex |
Nevada | 4,060 | — | — | ||||||||
West Battle Mountain Complex |
Nevada | 2,567 | 6,287 | — | ||||||||
Other United States Properties |
Nevada | 9,611 | 9,497 | 2,902 | ||||||||
El Gallo 2 Properties |
Mexico | — | — | 1,343 | ||||||||
Property, plant and equipment |
Argentina | — | — | 179 | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total impairments |
$ | 353,736 | $ | 62,963 | $ | 18,468 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- In the fourth quarter of 2013, these tenements were transferred to MSC as part of the vend-in agreement described in Note 7, Investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. ("MSC")—San José Mine, and were therefore not included in the Company's mineral property interests as at December 31, 2014 and 2013.
105
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 6 MINERAL PROPERTY INTERESTS AND ASSET RETIREMENT OBLIGATIONS (Continued)
The carrying values for all of the mineral properties held by the Company as at December 31, 2014 and 2013 are noted below:
Name of Property/Complex
|
State/Province | Country | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
(in thousands) |
||||||||
Los Azules Copper Project |
San Juan | Argentina | $ | 202,889 | $ | 431,190 | |||||
Other San Juan Exploration Properties |
San Juan | Argentina | — | 7,818 | |||||||
Cerro Mojon Tenements |
Santa Cruz | Argentina | — | 1,971 | |||||||
La Merced Tenements |
Santa Cruz | Argentina | — | 1,891 | |||||||
Cabeza de Vaca Tenements |
Santa Cruz | Argentina | — | 877 | |||||||
El Trumai Tenements |
Santa Cruz | Argentina | — | 1,534 | |||||||
Martes 13 Tenements |
Santa Cruz | Argentina | — | 3,568 | |||||||
Celestina Tenements |
Santa Cruz | Argentina | — | 1,753 | |||||||
Other Santa Cruz Exploration Properties |
Santa Cruz | Argentina | — | 7,601 | |||||||
Tonkin Complex |
Nevada | United States | 20,423 | 51,946 | |||||||
Gold Bar Complex |
Nevada | United States | 51,577 | 77,012 | |||||||
Limo Complex |
Nevada | United States | — | 23,438 | |||||||
North Battle Mountain Complex |
Nevada | United States | 2,227 | 4,148 | |||||||
East Battle Mountain Complex |
Nevada | United States | — | 4,060 | |||||||
West Battle Mountain Complex |
Nevada | United States | — | 2,567 | |||||||
Other United States Properties |
Nevada | United States | — | 9,610 | |||||||
El Gallo 1 Mine |
Sinaloa | Mexico | 7,214 | 8,502 | |||||||
El Gallo 2 Properties |
Sinaloa | Mexico | 3,482 | 3,482 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Mineral Property Interests |
$ | 287,812 | $ | 642,968 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
During the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, the Company incurred $11.3 million, $24.8 million, and $47.2 million, respectively, in exploration expenses and related expenditure costs which are included in the Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss in each of the years presented.
For the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company recorded $1.3 million (2013—$1.5 million) of amortization expense related to El Gallo 1, which is included in Production Costs Applicable to Sales in the Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss for the year ended December 31, 2014. This included $0.8 million (2013—$1.0 million) in amortization expense related to its mineral properties in Mexico for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Asset Retirement Obligations
The Company is responsible for reclamation of certain past and future disturbances at its properties. The two most significant properties subject to these obligations are the historic Tonkin property in Nevada and the El Gallo 1 mine in Mexico.
The current undiscounted estimate of the reclamation costs for existing disturbances on the Tonkin property to the degree required by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management ("BLM") and the Nevada Department of Environmental Protection ("NDEP") is $2.6 million. Assumptions used to compute the
106
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 6 MINERAL PROPERTY INTERESTS AND ASSET RETIREMENT OBLIGATIONS (Continued)
asset retirement obligations for the year ended December 31, 2014 for the Tonkin property included a credit adjusted risk free rate and inflation rate of 8.7% (2013, 2012—8.7%) and 3.0% (2013, 2012—3.0%), respectively. Expenses are expected to be incurred between the years 2015 and 2040. The Company submitted a mine closure plan to the NDEP and BLM for the Tonkin property during the fourth quarter of 2010. The closure plan was approved by the NDEP in March 2012 but is still under review by the BLM pursuant to the National Environmental Policy Act. It is possible that reclamation plan cost estimates and bonding requirements may increase as a result of this review. The Company, however, is unable to meaningfully estimate possible increases at this time.
For mineral properties in the United States, the Company maintains required reclamation bonding with various governmental agencies. During the third quarter of 2014, the Company replaced its cash bonding of $4.8 million with surety bonds of the same amounts, as discussed in Note 13, Contingencies.
The current undiscounted estimate of the reclamation costs for existing disturbances at the El Gallo 1 mine is currently $4.6 million. Assumptions used to compute the asset retirement obligations for the year ended December 31, 2014 for the El Gallo 1 mine included a credit adjusted risk free rate and inflation rate of 6.4% (2013, 2012—6.4%) and 4.1% (2013, 2012—3.8%), respectively. Expenses are expected to be incurred between the years 2015 and 2019. Under Mexican regulations, surety bonding of projected reclamation costs is not required.
The Company's asset retirement obligations for years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 are as follows:
| |
2014 | 2013 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Asset retirement obligation liability, beginning balance |
$ | 7,247 | $ | 6,359 | |||
Settlements |
(52 | ) | (60 | ) | |||
Accretion of liability |
407 | 461 | |||||
Adjustment reflecting updated estimates |
(131 | ) | 487 | ||||
| | | | | | | | |
Asset retirement obligation liability, ending balance |
$ | 7,471 | $ | 7,247 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
As at December 31, 2014, the current portion of the asset retirement obligation was $2.4 million (December 31, 2012—$1.4 million).
The definition of proven and probable reserves is set forth in Industry Guide 7. If proven and probable reserves exist at the Company's properties, the relevant capitalized mineral property interests and asset retirement costs are to be charged to expense based on the units of production method and upon commencement of production. Since the Company has not completed feasibility or other studies sufficient to characterize the mineralized material at El Gallo 1 as proven or probable reserves under the SEC definition, the amortization of the capitalized mineral property interests and asset retirement costs are charged to expense based on the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the mine. For the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company recorded $1.3 million (2013—$1.5 million) of amortization expense related to El Gallo 1, which is included in Production Costs Applicable to Sales in the Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss for the year ended December 31, 2014,
107
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 6 MINERAL PROPERTY INTERESTS AND ASSET RETIREMENT OBLIGATIONS (Continued)
of which $0.5 million (2013—$0.5 million) related to the amortization of capitalized asset retirement costs.
NOTE 7 INVESTMENT IN MINERA SANTA CRUZ S.A. ("MSC")—SAN JOSÉ MINE
As noted in Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies—Investments, the Company accounts for investments over which it exerts significant influence but does not control through majority ownership using the equity method of accounting. In applying the equity method of accounting to the Company's Investment in MSC, MSC's financial statements, which are originally prepared by MSC in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board, have been adjusted to conform with U.S. GAAP. As such, the summarized financial data presented under this heading is in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
The Company's 49% attributable share of operations from its investment in MSC was a loss of $5.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to income of $0.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2013 and $20.8 million for the period between January 25, 2012 (after the closing of the acquisition of Minera Andes) and December 31, 2012. These amounts are net of the amortization of the fair value increments arising from the purchase price allocation and related income tax recovery. Included in the income tax recovery is the impact of fluctuations in the exchange rate between the Argentine peso and the U.S. dollar on the peso-denominated deferred tax liability associated with the investment in MSC recorded as part of the acquisition of Minera Andes. As a devaluation of the Argentine peso relative to the U.S. dollar results in a recovery of deferred income taxes, the impact has been a decrease to the Company's loss, or an increase to the Company's income, from its investment in MSC periods presented.
In addition to the Company's attributable loss of $5.3 million, the Company recorded an impairment charge of $21.2 million, primarily as a result of an unexpected and significant decline in silver market prices, as well as in the observed market value of comparable transactions in South America, which indicated a potential significant decrease in the market price of the exploration properties owned by MSC. To estimate the fair value of the Company's investment in MSC, the Company used a combined approach, which uses a discounted cash flow model for the operating mine and a market approach for the fair value assessment of exploration properties, and determined that the carrying value of the investment in MSC exceeded its estimated fair value. As the loss in value of the investment was considered other than temporary, an impairment of $21.2 million was recorded in the Company's Consolidated Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Refer to Note 17, Fair Value Accounting, for further detail on the valuation of MSC. In comparison, the impairment charge recorded in the year ended December 31, 2013 was $95.9 million. The impairment charge in 2013 was primarily a result of an unexpected and significant decline in gold and silver market prices, continued inflationary pressures during the year, and amendments to the Santa Cruz Provincial Tax Code and Provincial Tax Law, which imposed a new tax on mining reserves in the Province of Santa Cruz.
During the fourth quarter of 2013, the Company entered into a vend-in agreement with MSC and subsidiaries of Hochschild pursuant to which both parties agreed to contribute to MSC the mining
108
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 7 INVESTMENT IN MINERA SANTA CRUZ S.A. ("MSC")—SAN JOSÉ MINE (Continued)
rights of certain Santa Cruz exploration properties. The carrying value of the Company's properties of $35.9 million, net of the related deferred tax liability of $17.3 million, was transferred to the Company's investment in MSC, with no gain or loss recognized upon transfer, and is reflected in the Investment in MSC balance as at December 31, 2013.
During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company received $9.5 million in dividends from MSC, compared to $1.8 million in 2013.
Changes in the Company's investment in MSC for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 are as follows:
| |
2014 | 2013 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Investment in MSC, beginning balance |
$ | 212,947 | $ | 273,948 | |||
Attributable net (loss) income from MSC |
(2,597 | ) | 2,126 | ||||
Amortization of fair value increments |
(13,190 | ) | (18,425 | ) | |||
Income tax recovery |
10,503 | 17,145 | |||||
Dividend distribution received |
(9,483 | ) | (1,826 | ) | |||
Impairment of investment in MSC |
(21,162 | ) | (95,878 | ) | |||
Contribution of Santa Cruz exploration properties, net of tax |
— | 35,857 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Investment in MSC, ending balance |
$ | 177,018 | $ | 212,947 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
109
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 7 INVESTMENT IN MINERA SANTA CRUZ S.A. ("MSC")—SAN JOSÉ MINE (Continued)
A summary of the operating results from MSC for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the period from January 25, 2012 (after the closing of the acquisition of Minera Andes) to December 31, 2012 is as follows:
| |
For the year ended December 31, |
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
For the period ended December 31, 2012 |
|||||||||
| |
2014 | 2013 | ||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Minera Santa Cruz S.A. (100%) |
||||||||||
Net sales |
$ | 213,013 | $ | 240,723 | $ | 290,848 | ||||
Production costs applicable to sales |
(173,274 | ) | (190,281 | ) | (155,915 | ) | ||||
(Loss) income from operations before extraordinary items |
(5,300 | ) | 4,338 | 51,634 | ||||||
Net (loss) income |
(5,300 | ) | 4,338 | 51,634 | ||||||
Portion attributable to McEwen Mining Inc. (49%) |
||||||||||
Net (loss) income |
$ | (2,597 | ) | $ | 2,126 | $ | 25,301 | |||
Amortization of fair value increments |
(13,190 | ) | (18,425 | ) | (22,682 | ) | ||||
Income tax recovery |
10,503 | 17,145 | 18,217 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
(Loss) income from investment in MSC, net of amortization |
$ | (5,284 | ) | $ | 846 | $ | 20,835 | |||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
As at December 31, 2014, MSC had current assets of $113.3 million, total assets of $540.6 million, current liabilities of $67.0 million and total liabilities of $179.4 million. These balances include the increase in fair value and amortization of the fair value increments arising from the purchase price allocation and are net of the impairment charges. Excluding the fair value increments from the purchase price allocation and impairment charges, MSC had current assets of $111.5 million, total assets of $311.5 million, current liabilities of $67.0 million, and total liabilities of $102.7 million as at December 31, 2014.
110
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 8 PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, property and equipment consisted of the following:
| |
2014 | 2013 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Trucks and trailers |
$ | 1,012 | $ | 1,041 | |||
Office furniture and equipment |
1,404 | 1,163 | |||||
Leasehold improvements |
661 | — | |||||
Drill rigs |
998 | 998 | |||||
Building |
1,514 | 1,469 | |||||
Land |
8,699 | 8,672 | |||||
Mining equipment |
1,548 | 1,206 | |||||
Construction-in-progress |
6,286 | 3,894 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Subtotal |
$ | 22,122 | $ | 18,443 | |||
Less: accumulated depreciation |
(4,226 | ) | (3,300 | ) | |||
| | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 17,896 | $ | 15,143 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
Additions to property and equipment during the year ended December 31, 2014 are mainly in relation to leasehold improvements to the Company's corporate office, as well as construction-in-progress assets which include advances the Company made to a supplier for long-lead items for its El Gallo 2 project.
Depreciation expense for 2014 was $1.0 million (2013—$0.9 million, 2012—$1.0 million).
111
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 9 INCOME TAXES
The tax effects of temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of the deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities at December 31, 2014 and 2013 respectively are presented below:
| |
2014 | 2013 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Deferred tax assets: |
|||||||
Alternative minimum tax (AMT) credit carryforward |
$ | 41 | $ | 41 | |||
Net operating loss carryforward |
108,070 | 98,734 | |||||
Mineral properties |
14,797 | 19,884 | |||||
Other temporary differences |
6,859 | 6,302 | |||||
Capital loss carryforward |
241 | 241 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total gross deferred tax assets |
130,008 | 125,202 | |||||
Less: valuation allowance |
(129,794 | ) | (125,202 | ) | |||
| | | | | | | | |
Net deferred tax assets |
$ | 214 | $ | — | |||
| | | | | | | | |
Deferred tax liabilities: |
|||||||
Investments |
(214 | ) | — | ||||
Acquired mineral property interests |
(51,899 | ) | (158,855 | ) | |||
| | | | | | | | |
Total deferred tax liabilities |
$ | (52,113 | ) | $ | (158,855 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total net deferred tax liability |
$ | (51,899 | ) | $ | (158,855 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company estimates tax loss carry forwards to be $330.2 million and $303.3 million, respectively expiring starting in 2015 and going through 2034.
The Company believes that it is unlikely that the full amount of deferred tax assets will be realized. Therefore, a valuation allowance has been provided for most of the full amount of deferred tax assets. The change in valuation allowance of approximately $4.5 million (2013—$34.7 million) primarily reflects an increase of net operating loss carryforwards. The deferred tax liability related to the Minera Andes acquisition was $26.6 million as at December 31, 2014 (2013—$101.5 million).
On December 11, 2013, the Mexican government enacted a tax reform that increased the effective tax rate applicable to the Company's Mexican operations. The law, effective January 1, 2014, increased the future corporate income tax rate to 30%, created a 10% withholding tax on dividends paid to non-resident shareholders and created a new Extraordinary Mining duty which is equal to 0.5% of gross revenues from the sale of gold, silver and platinum. Furthermore, the reform introduced a Special Mining Duty of 7.5%. The Special Mining Duty is deductible for income tax purposes. The Special Mining Duty is generally applicable to earnings before income tax, depreciation, depletion, amortization and interest. There will be no deductions related to development type costs but exploration and prospecting costs are deductible when incurred. Certain undeducted exploration expenditures incurred prior to January 1, 2014 are also deductible in the calculation of the Special Mining Duty. For the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company had no taxes payable under the 7.5% Special Mining Duty, but accrued $0.2 million under the 0.5% gross revenue surcharge.
112
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 9 INCOME TAXES (Continued)
A reconciliation of the tax provision for 2014, 2013 and 2012 at statutory U.S. Federal and State income tax rates to the actual tax provision recorded in the financial statements is comprised of the following components:
Expected tax recovery at
|
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
US Federal and State tax recovery at statutory rate |
$ | (142,499 | ) | $ | (68,377 | ) | $ | (31,925 | ) | |
Reconciling items: |
||||||||||
Equity pickup in MSC |
1,849 | (2,924 | ) | (7,292 | ) | |||||
Impact of Mexican tax reform |
754 | (1,921 | ) | — | ||||||
Prior year true ups/acquisitions |
8,330 | (19,016 | ) | 781 | ||||||
Adjustment for foreign tax rates |
(2,557 | ) | 8,680 | 3,245 | ||||||
Tax rate changes |
— | (187 | ) | (1,869 | ) | |||||
Imputed interest |
198 | 171 | 135 | |||||||
Other permanent differences |
(7,552 | ) | 22,090 | (3,259 | ) | |||||
Unrealized foreign exchange rate (loss)/gain |
19,447 | (28,317 | ) | (21,263 | ) | |||||
NOL expired |
10,268 | 1,711 | (2,696 | ) | ||||||
Valuation allowance |
4,592 | 34,725 | 36,899 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Tax Recovery |
$ | (107,170 | ) | $ | (53,365 | ) | $ | (27,244 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
As at December 31, 2014, there are no unrecognized tax benefits. The entire income tax benefit, with the exception of $0.2 million allocated to other comprehensive income for the Company's investment in marketable securities, relates to continuing operations.
The Company or its subsidiaries file income tax returns in Canada, the United States, Mexico, and Argentina. These tax returns are subject to examination by local taxation authorities provided the tax years remain open to audit under the relevant statute of limitations. The following summarizes the open tax years by major jurisdiction:
United
States: 2011 to 2014
Canada: 2007 to 2014
Mexico: 2010 to 2014
Argentina: 2010 to 2014
NOTE 10 SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY
During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company issued approximately 1,499,300 shares (2013—48,000 shares) of common stock upon exercise of stock options under the Equity Incentive Plan at a weighted average exercise price of $1.29 per share (2013—$1.97) for proceeds of $1.9 million (2013—$0.1 million). The Company also issued 198,000 shares (2013—45,000 shares) of common stock upon exercise of certain stock options the Company assumed as part of the Minera Andes Inc. acquisition, at a weighted average exercise price of C$1.96 per share (2013—C$1.80) for proceeds of $0.4 million (2013—$0.1 million).
113
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 10 SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY (Continued)
As a result of a litigation settlement in November 2012 with TNR Gold Corp ("TNR"), the Company granted TNR an option to acquire a minority ownership position in the Los Azules project (the "Back-In Right Option"). The Back-In Right Option gave TNR the option of owning up to approximately 13% of the Los Azules deposit. On October 16, 2014, the Company terminated the Back-In Right Option. In exchange for the termination of the Back-In Right Option, the Company issued 850,000 shares of the Company's common stock to TNR, and granted a 0.4% net smelter royalty ("NSR") on Los Azules. Further, if Company sells all of its interest in the project within thirty six months of closing of the transaction on October 16, 2014, the Company will grant a bonus payment equal to 1% of the gross proceeds to TNR. The value of the 850,000 shares of $1.4 million was recorded as Exploration Costs in the Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss for the year ended December 31, 2014.
During the year ended December 31, 2014, 3.7 million (2013—51.1 million) Exchangeable Shares were converted into common stock. At December 31, 2014, total outstanding Exchangeable Shares not exchanged and not owned by the Company or its subsidiaries totaled 28.5 million (2013—32.2 million). These Exchangeable Shares were initially issued by the Company in connection with the acquisition of Minera Andes as noted in Note 3, Business Acquisition. The Exchangeable Shares, by virtue of the redemption and exchange rights attached to them and the provisions of certain voting and support agreements, provide the holders with economic and voting rights that are, as nearly as practicable, equivalent to those of a holder of shares of common stock of the Company. Accordingly, remaining Exchangeable Shares are included as part of the consolidated share capital of the Company.
NOTE 11 STOCK BASED COMPENSATION
Stock Options
The Company has a non-qualified stock option and stock grant plan, under which equity awards may be granted to employees, consultants, advisors, and directors (the "Plan"). The Plan is administered by the Board of Directors or committee, which determines the terms pursuant to which any option is granted. The Board of Directors or committee may delegate to certain officers the authority to grant awards to certain employees (other than such officers), consultants and advisors. The number of shares of common stock reserved for issuance thereunder is 13.5 million shares, with no more than 1 million shares subject to grants of options to an individual in a calendar year. The plan also provides for the grant of incentive options under Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code (the "Code"), which provide potential tax benefits to the recipients compared to non-qualified options.
114
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 11 STOCK BASED COMPENSATION (Continued)
The following table summarizes information about stock options under the Plan outstanding at December 31, 2014:
| |
Number of Shares |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) |
Intrinsic Value |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands, except per share and year data) |
||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2011 |
3,870 | $ | 3.24 | 7.3 | |||||||||
Granted |
300 | $ | 5.80 | ||||||||||
Exercised |
(445 | ) | $ | 1.84 | $ | 596 | |||||||
Forfeited |
(128 | ) | $ | 6.27 | |||||||||
Expired |
(36 | ) | $ | 7.96 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2012 |
3,561 | $ | 3.47 | 6.6 | |||||||||
Granted |
1,728 | $ | 2.26 | ||||||||||
Exercised |
(48 | ) | $ | 1.97 | $ | 47 | |||||||
Forfeited |
(400 | ) | $ | 4.57 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2013 |
4,841 | $ | 2.96 | 5.2 | |||||||||
Granted |
1,731 | $ | 2.90 | ||||||||||
Exercised |
(1,499 | ) | $ | 1.29 | $ | 438 | |||||||
Forfeited |
(422 | ) | $ | 4.39 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
4,650 | $ | 3.35 | 4.4 | $ | 11 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Exercisable at December 31, 2014 |
1,954 | $ | 4.12 | 4.5 | $ | 11 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock options have been granted to key employees, directors and others under the Plan. Options to purchase shares under the Plan were granted at or above market value as of the date of the grant. During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company granted stock options to certain employees and directors for an aggregate of 1.7 million shares of common stock (2013—1.7 million, 2012—0.3 million) at a weighted average exercise price of $2.90 per share (2013—$2.26, 2012—$5.80). The options vest equally over a three-year period if the individual remains affiliated with the Company (subject to acceleration of vesting in certain events) and are exercisable for a period of 5 years (2012—5 years, 2012—10 years) from the date of issue.
The fair value of the options granted under the Plan was estimated at the date of grant, using the Black-Scholes Option Valuation Model, with the following weighted-average assumptions:
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Risk-free interest rate |
1.01% | 0.50% to 0.86% | 0.97% | |||
Dividend yield |
n/a | n/a | n/a | |||
Volatility factor of the expected market price of common stock |
70% | 66% to 69% | 75% | |||
Weighted-average expected life of option |
3.5 years | 3.5 years | 6.0 years | |||
Weighted-average grant date fair value |
$1.45 | $1.02 | $3.80 |
During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company recorded stock option expense of $1.3 million (2013—$1.4 million, 2012—$3.4 million).
115
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 11 STOCK BASED COMPENSATION (Continued)
At December 31, 2014, there was $1.8 million (2013—$1.1 million) of unrecognized compensation expense related to 2.7 million (2013—2.0 million) unvested stock options outstanding. This cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of approximately 1.6 years (2013—1.4 years).
The following tables summarize information about stock options outstanding and exercisable at December 31, 2014 for the Company's Plan, the replacement options from the acquisition of Minera Andes in 2012, and the replacement options from the acquisition of Nevada Pacific Gold Ltd. in 2007. C$ refers to Canadian dollars.
McEwen Mining Inc.
| |
Options Outstanding | Options Exercisable | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Range of Exercise Price
|
Number Outstanding |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) |
Number Exercisable |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) |
|||||||||||||
$0.75 - $2.25 |
1,515,334 | $ | 2.18 | 3.2 | 676,665 | $ | 2.09 | 2.9 | |||||||||||
$2.26 - $2.75 |
381,800 | $ | 2.50 | 4.9 | 331,800 | $ | 2.51 | 5.0 | |||||||||||
$2.76 - $3.25 |
1,706,500 | $ | 2.90 | 4.6 | — | n/a | n/a | ||||||||||||
$3.26 - $6.50 |
516,500 | $ | 5.01 | 5.3 | 416,500 | $ | 4.82 | 4.9 | |||||||||||
$6.51 - $8.31 |
529,500 | $ | 7.16 | 6.0 | 529,500 | $ | 7.16 | 6.0 | |||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
4,649,634 | $ | 3.35 | 4.4 | 1,954,465 | $ | 4.12 | 4.5 | |||||||||||
Nevada Pacific Gold Ltd.
| |
Options Outstanding | Options Exercisable | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Range of Exercise Price
|
Number Outstanding |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) |
Number Exercisable |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) |
|||||||||||||
C$4.25 - C$4.50 |
40,500 | C$ | 4.30 | 1.2 | 40,500 | C$ | 4.30 | 1.2 | |||||||||||
C$4.51 - C$4.75 |
110,343 | C$ | 4.74 | 1.9 | 110,343 | C$ | 4.74 | 1.9 | |||||||||||
C$4.76 - C$5.00 |
2,300 | C$ | 4.91 | 2.1 | 2,300 | C$ | 4.91 | 2.1 | |||||||||||
C$5.01 - C$6.70 |
46,000 | C$ | 6.70 | 1.4 | 46,000 | C$ | 6.70 | 1.4 | |||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
199,143 | C$ | 5.11 | 1.6 | 199,143 | C$ | 5.11 | 1.6 | |||||||||||
116
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 11 STOCK BASED COMPENSATION (Continued)
Minera Andes Inc.
| |
Options Outstanding | Options Exercisable | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Range of Exercise Price
|
Number Outstanding |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) |
Number Exercisable |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) |
|||||||||||||
C$2.00 - C$2.50 |
256,650 | C$ | 2.27 | 0.4 | 256,650 | C$ | 2.27 | 0.4 | |||||||||||
C$2.51 - C$3.00 |
45,000 | C$ | 2.51 | 0.4 | 45,000 | C$ | 2.51 | 0.4 | |||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
301,650 | C$ | 2.30 | 0.4 | 301,650 | C$ | 2.30 | 0.4 | |||||||||||
Shares issued to supplier for mining services
As detailed in Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies—Stock Based Compensation, the Company entered into an agreement with one of its mining contractors to pay for a portion of mining services with shares of common stock of the Company. As at December 31, 2014, the Company was required to issue a cumulative total of approximately 712,830 common shares, of which approximately 393,190 were issued in the year ended December 31, 2014. The fair value of the remaining 319,640 outstanding common shares of $0.4 million is included in accounts payable and accrued liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheet as at December 31, 2014. The agreement was subsequently terminated on February 1, 2015.
NOTE 12 LOSS PER SHARE
Basic net loss per share is computed by dividing the net loss available to common shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted net loss per share is computed similarly except that the weighted average number of common shares is increased to reflect all dilutive instruments.
Below is a reconciliation of the basic and diluted weighted average number of common shares and the computations for basic loss per share for the year ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012:
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands, except per share amounts) |
|||||||||
Net loss |
$ | (311,943 | ) | $ | (147,742 | ) | $ | (66,654 | ) | |
Weighted average number of common shares |
297,763 | 297,001 | 261,223 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss per common share |
$ | (1.05 | ) | $ | (0.50 | ) | $ | (0.26 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Options to purchase 3.3 million shares of common stock (2013—2.1 million, 2012—1.6 million) at an average exercise price of $3.95 at December 31, 2014 (2013—$5.04, 2012—$6.32) were not included in the computation of diluted weighted average shares because their exercise price exceeded the average price of the Company's common stock for the year ended December 31, 2014, and because their effect would have been anti-dilutive. Other outstanding options to purchase 1.8 million shares of common stock (2013—3.6 million, 2012—2.9 million) were not included in the computation of diluted
117
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 12 LOSS PER SHARE (Continued)
weighted average shares in the year ended December 31, 2013 because their effect would have been anti-dilutive.
NOTE 13 RENTAL EXPENSE, COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Rental Expense
For the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company had rental expense under operating leases of $0.5 million (2013—$0.8 million; 2012—$0.7 million).
Commitments
At December 31, 2014, the Company is obligated for the next five years under purchase commitments, long term leases covering office space, exploration expenditures, option payments on properties for the following minimum amounts:
| |
2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||||||||
Lease Obligations |
$ | 928 | $ | 543 | $ | 464 | $ | 466 | $ | 472 | ||||||
Purchase Commitments |
17 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 945 | $ | 543 | $ | 464 | $ | 466 | $ | 472 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Surety Bonds
As part of its ongoing business and operations, the Company is required to provide bonding for its environmental reclamation obligations in the United States, as discussed in Note 6, Mineral Properties and Asset Retirement Obligations. These surety bonds are available for draw down in the event the Company does not perform its reclamation obligations. When the specific reclamation requirements are met, the beneficiary of the surety bonds will cancel and/or return the instrument to the issuing entity. The Company believes it is in compliance with all applicable bonding obligations and will be able to satisfy future bonding requirements, through existing or alternative means, as they arise. As at December 31, 2014 there were $4.8 million of outstanding surety bonds (2013—nil). The annual financing fees are 1.5% of the value of the surety bonds, with an upfront 10% deposit of $0.5 million which is included in Other Assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheet.
Contingencies
The Company's mining and exploration activities are subject to various laws and regulations governing the protection of the environment. These laws and regulations are continually changing and generally becoming more restrictive. The Company conducts its operations so as to protect public health and the environment, and believes its operations are materially in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations. The Company has made, and expects to make in the future, expenditures to comply with such laws and regulations.
The Company has transferred its interest in several mining properties to third parties. The Company could remain potentially liable for environmental enforcement actions related to its prior
118
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 13 RENTAL EXPENSE, COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (Continued)
ownership of such properties. However, the Company has no reasonable belief that any violation of relevant environmental laws or regulations has occurred regarding these transferred properties.
NOTE 14 RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
An aircraft owned and operated by Lexam L.P. (which is controlled by Robert R. McEwen, limited partner and beneficiary of Lexam L.P.) has been made available to the Company in order to expedite business travel. In his role as Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of the Company, Mr. McEwen must travel extensively and frequently on short notice.
Mr. McEwen is able to charter the aircraft from Lexam L.P. at a preferential rate. The Company's independent board members have approved a policy whereby only the variable expenses of operating this aircraft for business related travel are eligible for reimbursement by the Company. The hourly amount that the Company has agreed to reimburse Lexam L.P. is under half the full cost per hour of operating the aircraft or equivalent hourly charter cost and in any event less than even Mr. McEwen's preferential charter rate. Where possible, trips also include other company personnel, both executives and non-executives, to maximize efficiency. The agreement was approved by the independent members of the Company's Board of Directors.
For the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company incurred and paid $0.1 million (2013—$0.2 million; 2012—$0.3 million) to Lexam L.P. for the use of this aircraft.
NOTE 15 UNAUDITED SUPPLEMENTARY QUARTERLY INFORMATION
The following table summarizes unaudited supplementary quarterly information for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012.
| |
Three Months Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
March 31, 2014 | June 30, 2014 | September 30, 2014 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||||
| |
(unaudited) (in thousands, except per share) |
||||||||||||
Net income (loss) |
$ | 17,887 | $ | (104,022 | ) | $ | (13,033 | ) | $ | (212,775 | ) | ||
Net income (loss) per share: |
|||||||||||||
Basic |
$ | 0.06 | $ | (0.35 | ) | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.71 | ) | ||
Diluted |
$ | 0.06 | $ | (0.35 | ) | $ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.71 | ) | ||
Weighted average shares outstanding: |
|||||||||||||
Basic |
297,159 | 297,164 | 297,164 | 299,009 | |||||||||
Diluted |
298,410 | 297,164 | 297,164 | 299,009 | |||||||||
119
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 15 UNAUDITED SUPPLEMENTARY QUARTERLY INFORMATION (Continued)
| |
Three Months Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
March 31, 2013 | June 30, 2013 | September 30, 2013 | December 31, 2013 | |||||||||
| |
(unaudited) (in thousands, except per share) |
||||||||||||
Net (loss) income |
$ | (10,982 | ) | $ | (128,681 | ) | $ | 3,264 | $ | (11,343 | ) | ||
Net (loss) income per share: |
|||||||||||||
Basic |
$ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.43 | ) | $ | 0.01 | $ | (0.04 | ) | ||
Diluted |
$ | (0.04 | ) | $ | (0.43 | ) | $ | 0.01 | $ | (0.04 | ) | ||
Weighted average shares outstanding: |
|||||||||||||
Basic |
296,778 | 297,097 | 297,125 | 297,159 | |||||||||
Diluted |
296,778 | 297,097 | 297,899 | 297,159 | |||||||||
| |
Three Months Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
March 31, 2012 | June 30, 2012 | September 30, 2012 | December 31, 2012 | |||||||||
| |
(in thousands, except per share) |
||||||||||||
Net loss |
$ | (17,351 | ) | $ | (20,364 | ) | $ | (2,654 | ) | $ | (26,285 | ) | |
Net loss per share: |
|||||||||||||
Basic |
$ | (0.07 | ) | $ | (0.07 | ) | $ | (0.01 | ) | $ | (0.10 | ) | |
Diluted |
$ | (0.07 | ) | $ | (0.07 | ) | $ | (0.01 | ) | $ | (0.10 | ) | |
Weighted average shares outstanding: |
|||||||||||||
Basic |
244,640 | 278,655 | 279,019 | 274,295 | |||||||||
Diluted |
244,640 | 278,655 | 279,019 | 274,295 | |||||||||
120
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 16 OPERATING SEGMENT REPORTING
McEwen Mining is a mining and minerals exploration company focused on precious metals in Argentina, Mexico and the United States. The Company identifies its reportable segments as those consolidated operations that are currently engaged in the exploration for and production of precious metals. Operations not actively engaged in the exploration for, or production of precious metals, are aggregated at the corporate level for segment reporting purposes.
| |
For the year ended December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Argentina | Mexico | U.S. | Corporate & Other |
Total | |||||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||||||||
Gold and silver sales |
$ | — | $ | 45,303 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 45,303 | ||||||
Production costs applicable to sales |
— | (40,608 | ) | — | — | (40,608 | ) | |||||||||
Mine construction costs |
— | (1,723 | ) | — | — | (1,723 | ) | |||||||||
Mine development costs |
— | (1,829 | ) | — | — | (1,829 | ) | |||||||||
Exploration costs |
(2,453 | ) | (5,468 | ) | (3,060 | ) | (351 | ) | (11,332 | ) | ||||||
Impairment of mineral property interests and property and equipment |
(255,313 | ) | — | (98,423 | ) | — | (353,736 | ) | ||||||||
Impairment of investment in MSC |
(21,162 | ) | — | — | — | (21,162 | ) | |||||||||
Loss on investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. (net of amortization) |
(5,284 | ) | — | — | — | (5,284 | ) | |||||||||
Operating loss |
(285,800 | ) | (10,101 | ) | (105,797 | ) | (8,467 | ) | (410,165 | ) | ||||||
Income tax recovery |
74,952 | 371 | 31,632 | 215 | 107,170 | |||||||||||
As at December 31, 2014 |
||||||||||||||||
Investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. |
177,018 | — | — | — | 177,018 | |||||||||||
Mineral property interests |
202,889 | 10,696 | 74,227 | — | 287,812 | |||||||||||
Total assets |
382,637 | 58,936 | 74,806 | 6,579 | 522,958 | |||||||||||
121
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 16 OPERATING SEGMENT REPORTING (Continued)
| |
For the year ended December 31, 2013 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Argentina | Mexico | U.S. | Corporate & Other |
Total | |||||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||||||||
Gold and silver sales |
$ | — | $ | 45,982 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 45,982 | ||||||
Production costs applicable to sales |
— | (34,594 | ) | — | — | (34,594 | ) | |||||||||
Mine construction costs |
— | (1,383 | ) | — | — | (1,383 | ) | |||||||||
Mine development costs |
— | (847 | ) | — | — | (847 | ) | |||||||||
Exploration costs |
(14,776 | ) | (6,658 | ) | (2,952 | ) | (443 | ) | (24,829 | ) | ||||||
Income on investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. (net of amortization) |
846 | — | — | — | 846 | |||||||||||
Impairment of investment in MSC |
(95,878 | ) | — | — | — | (95,878 | ) | |||||||||
Impairment of mineral property interests and property and equipment |
(27,729 | ) | — | (35,234 | ) | — | (62,963 | ) | ||||||||
Gain (loss) on sale of assets |
(316 | ) | — | (6,430 | ) | 3 | (6,743 | ) | ||||||||
Operating loss |
(139,784 | ) | (2,998 | ) | (47,422 | ) | (10,193 | ) | (200,397 | ) | ||||||
Income tax recovery |
38,015 | 495 | 14,855 | — | 53,365 | |||||||||||
As at December 31, 2013 |
||||||||||||||||
Investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. |
212,947 | — | — | — | 212,947 | |||||||||||
Mineral property interests |
458,203 | 11,984 | 172,781 | — | 642,968 | |||||||||||
Total assets |
674,269 | 54,131 | 177,248 | 17,418 | 923,066 | |||||||||||
| |
For the year ended December 31, 2012 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Argentina | Mexico | U.S. | Corporate & Other |
Total | |||||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||||||||
Gold and silver sales |
$ | — | $ | 5,966 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 5,966 | ||||||
Production costs applicable to sales |
— | (3,861 | ) | — | — | (3,861 | ) | |||||||||
Mine operating costs |
— | (8,507 | ) | — | — | (8,507 | ) | |||||||||
Mine construction costs |
— | (14,260 | ) | — | — | (14,260 | ) | |||||||||
Exploration costs |
(25,091 | ) | (15,918 | ) | (5,060 | ) | (1,110 | ) | (47,179 | ) | ||||||
Income on investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. (net of amortization) (adjusted—note 15) |
20,835 | — | — | — | 20,835 | |||||||||||
Impairment of mineral property interests and property and equipment |
(179 | ) | (1,343 | ) | (16,946 | ) | — | (18,468 | ) | |||||||
Operating loss (adjusted—note 15) |
(8,156 | ) | (43,417 | ) | (25,144 | ) | (14,688 | ) | (91,405 | ) | ||||||
Income tax recovery |
21,129 | — | 6,115 | — | 27,244 | |||||||||||
As at December 31, 2012 |
||||||||||||||||
Investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. |
273,948 | — | — | — | 273,948 | |||||||||||
Mineral property interests |
539,092 | 12,707 | 215,268 | — | 767,067 | |||||||||||
Total assets |
825,047 | 47,359 | 220,148 | 58,383 | 1,150,937 | |||||||||||
122
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 17 FAIR VALUE ACCOUNTING
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis
The following tables set forth the fair value of the Company's assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis (at least annually) by level within the fair value hierarchy as at December 31, 2014 and 2013. As required by accounting guidance, assets and liabilities are classified in their entirety based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
| |
2014 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Assets: |
|||||||||||||
Investments |
$ | 1,082 | $ | 1,082 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
$ | 1,082 | $ | 1,082 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities: |
|||||||||||||
Portion of accounts payable and accrued liabilities recorded at fair value |
$ | 355 | $ | 355 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
$ | 355 | $ | 355 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
2013 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Assets: |
|||||||||||||
Investments |
$ | 2 | $ | 2 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
$ | 2 | $ | 2 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities: |
|||||||||||||
Portion of accounts payable and accrued liabilities recorded at fair value |
$ | 177 | $ | 177 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
$ | 177 | $ | 177 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The Company's investments are marketable equity securities which are exchange traded are valued using quoted market prices in active markets and as such are classified within Level 1 of the fair value hierarchy. The fair value of the investments is calculated as the quoted market price of the marketable equity security multiplied by the quantity of shares held by the Company.
As at December 31, 2014, accounts payable included an accrual of $0.4 million (2013—$0.2 million) for the fair value of accounts payable that are required to be settled with approximately 319,640 shares of common stock (2013—90,300 shares of common stock), as discussed in Note 11, Stock Based Compensation—Shares Issued to Supplier for Mining Services. The fair value of these accounts payable is assumed to approximate the fair value of the underlying shares with which they will be settled. As the Company's stock is quoted on an active market, this liability is classified within Level 1 of the fair value hierarchy.
The fair value of other financial assets and liabilities were assumed to approximate their carrying values due to their short-term nature and historically negligible credit losses.
123
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 17 FAIR VALUE ACCOUNTING (Continued)
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a non-recurring basis
As discussed in Note 6, Mineral Property Interests and Asset Retirement Obligations, and Note 7, Investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. ("MSC")—San José Mine, the Company recorded several impairment charges in the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
In the second and fourth quarter of 2014, the Company recorded an impairment charge of $120.4 million and $107.9 million, respectively, in relation to the Los Azules project. In both quarters, the estimated fair value of Los Azules was determined using an In-Situ Multiple based on the observed market value per pound of copper equivalent for recent comparable transactions, with a predominant weighting being given to a specific transaction which took place in the second quarter of 2014, as described in Note 6. In addition, in its impairment analysis for the fourth quarter of 2014, the Company applied a discount of 35% to the In-Situ Multiple, in order to reflect the decline in the observed market value of comparable transactions from June 2014 (date of the last impairment test) to December 31, 2014. Further, although McEwen owns 100% of Los Azules, a Back-In Right Option held by TNR existed on the Los Azules project as at June 30, 2014. This Back-In Right Option was subsequently replaced by a 0.4% NSR, as described in Note 10, Shareholders' Equity, as at December 31, 2014. The fair value of the Back-In Right Option and NSR, estimated using the Market Approach, were deducted from the fair value of the Company's interest in Los Azules in the impairment analyses as at June 30, 2014 and December 31, 2014, respectively.
An impairment loss of $21.2 million was also recorded with respect to the Company's investment in MSC. To estimate the fair value of the Company's investment in MSC, the Company used a combined approach, which uses a discounted cash flow model for the operating mine and a market approach for the fair value of exploration properties. Further, a discount of 20% was applied to the observable market value per acre for the Argentina exploration properties to reflect the country risk associated with early-stage exploration lands located in Argentina at the date of assessment.
The Company also recorded impairment charges totaling $31.4 million, $25.4 million and $1.9 million relating to its Gold Bar, Tonkin and North Battle Mountain properties. The fair value of these properties was determined using the observed market value per acre and per ounce of gold equivalent mineralized material.
Further, as a result of the Company's decision to focus on its core projects, the Company recorded impairments of its non-core Nevada and Argentina properties of $39.7 million and $27.0 million, respectively.
In the second and fourth quarters of 2013, the Company recorded impairment charges related to certain of its mineral property interests in Nevada and Argentina, as well as its investment in MSC, as discussed in Notes 6 and 7, respectively.
The estimated fair values of the Nevada and Argentina mineral property interests were determined using observed market values per acre in the respective regions. Further, a discount of 40% was applied to the observable market value per acre for the Argentina exploration properties to reflect the country risk associated with early-stage exploration lands located in Argentina at the date of impairment. The country risk, observed at the date of impairment, is based on the decline in observable enterprise values of publicly traded exploration companies located in Argentina compared to those of other publicly traded exploration companies located in South America.
124
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 17 FAIR VALUE ACCOUNTING (Continued)
With respect to the Company's investment in MSC, the estimated fair value as at June 30, 2013 was determined using a discounted cash flow approach. As at December 31, 2013, the Company revised its approach to estimate the fair value of its investment in MSC to take into consideration the vend in of the Company's and Hochchilds' properties in the fourth quarter of 2013. The combined approach uses a discounted cash flow to determine the fair value of the operating mine and a market approach to determine the fair value of the exploration properties.
The following table sets forth a summary of the quantitative and qualitative information related to the unobservable inputs used in the calculation of the Company's non-recurring Level 3 fair value measurements for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
| |
2014 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Date of Fair Value Measurement |
Valuation Technique |
Unobservable Input |
Range / Weighted Average |
||||
Los Azules Copper Project |
December 31, 2014 | Market value per pound of copper equivalent mineralized material | Discount to reflect decline in observed market value of comparable transactions from June 2014 (date of the last impairment test) to December 31, 2014 | 35% | ||||
Investment in MSC |
December 31, 2014 |
Discounted cash flow for operating mine |
Discount Rate |
10% |
||||
Investment in MSC |
December 31, 2014 | Market value per acre for exploration properties | Discount to observed market value pre acre to reflect Argentina country risk | 20% | ||||
| |
2013 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Date of Fair Value Measurement |
Valuation Technique |
Unobservable Input |
Range / Weighted Average |
|||||
Mineral property interests |
|||||||||
Telken Tenements |
June 30, 2013 | Market value per acre | Discount to observed market value pre acre to reflect Argentina country risk | 40% | |||||
Investment in MSC |
June 30, 2013 |
Discounted cash flow |
Discount Rate |
10.0% |
|||||
125
MCEWEN MINING INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
(tabular amounts are in thousands of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise noted) (Continued)
NOTE 17 FAIR VALUE ACCOUNTING (Continued)
The following non financial assets and the Company's investment in MSC were measured at fair values on a non-recurring basis as part of the Company's impairment assessments during the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
| |
|
2014 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Date of Fair Value Measurement |
|||||||||||||||||
| |
Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total Loss | |||||||||||||
| |
|
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||||||
Mineral property interests |
||||||||||||||||||
Los Azules Copper Project |
December 31, 2014 | $ | 202,889 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 202,889 | $ | 228,301 | |||||||
Tonkin Complex |
December 31, 2014 | 20,423 | — | — | 20,423 | 31,391 | ||||||||||||
Gold Bar Complex |
December 31, 2014 | 51,577 | — | — | 51,577 | 25,435 | ||||||||||||
North Battle Mountain Complex |
December 31, 2014 | 2,227 | — | — | 2,227 | 1,921 | ||||||||||||
Investment in MSC |
December 31, 2014 | 177,018 | — | — | 177,018 | 21,162 | ||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
$ | 454,134 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 454,134 | $ | 308,210 | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
|
2013 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Date of Fair Value Measurement | |||||||||||||||||
| |
Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total Loss | |||||||||||||
| |
|
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||||||
Mineral property interests |
||||||||||||||||||
Limo Complex |
December 31, 2013 | $ | 23,438 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 23,438 | $ | 19,450 | |||||||
Other United States Properties |
December 31, 2013 | 9,610 | — | — | 9,610 | 9,497 | ||||||||||||
Telken Tenements(1) |
June 30, 2013 | 26,442 | — | — | 26,442 | 13,792 | ||||||||||||
Este Tenements(1) |
June 30, 2013 | 5,337 | — | — | 5,337 | 2,784 | ||||||||||||
Piramides Tenements(1) |
June 30, 2013 | 9,736 | — | — | 9,736 | 5,079 | ||||||||||||
Tobias Tenements(1) |
June 30, 2013 | 11,645 | — | — | 11,645 | 6,074 | ||||||||||||
Investment in MSC |
June 30, 2013 | 176,282 | — | — | 176,282 | 95,878 | ||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
$ | 262,490 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 262,490 | $ | 152,554 | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- The fair values for the Telken, Este, Piramides and Tobias Tenements were determined prior to the transfer of these properties to MSC as part of the vend-in agreement between the Company and Hochschild, as described in Note 7, Investment in Minera Santa Cruz S.A. ("MSC")—San José Mine. In the fourth quarter of 2013, these tenements were transferred to MSC and were therefore not included in the Company's mineral property interests as at December 31, 2013.
NOTE 18 COMPARATIVE FIGURES
Certain prior year information has been reclassified to conform with the current year's presentation.
126
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
During the fiscal period covered by this report, our management, with the participation of the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer of the Company, carried out an evaluation of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) of the Exchange Act). Based on such evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, as of the end of the period covered by this report, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the required time periods specified in the Commission's rules and forms and are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our reports is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
There has been no change in our internal control over financial reporting during the most recent fiscal quarter that has materially affected, or that is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Management's report on internal control over financial reporting and the attestation report of KPMG LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, are included in Item 8 of this annual report on Form 10-K.
None.
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Pursuant to General Instruction G of Form 10-K, the information contained in this Item 10 is incorporated by reference to our Definitive Proxy Statement for our 2015 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, expected to be filed with the SEC on or before April 30, 2015.
The Company has a code of business conduct and ethics that applies to all of its employees, officers and directors. The code of business conduct and ethics is available on our website at www.mcewenmining.com and we will post any amendments to, or waivers, from, the code of ethics on that website.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The information contained in this Item 11 is incorporated by reference to our Definitive Proxy Statement for our 2015 Annual Meeting of Shareholders.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The information contained in this Item 12 is incorporated by reference to our Definitive Proxy Statement for our 2015 Annual Meeting of Shareholders.
127
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS, RELATED TRANSACTIONS AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
The information contained in this Item 13 is incorporated by reference to our Definitive Proxy Statement for our 2015 Annual Meeting of Shareholders.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
The information contained in this Item 14 is incorporated by reference to our Definitive Proxy Statement for our 2015 Annual Meeting of Shareholders.
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
The exhibits listed in the accompanying exhibit index are filed (except where otherwise indicated) as part of this report.
128
In accordance with Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act, the Company caused this Report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| MCEWEN MINING INC. | ||||
By: |
/s/ ROBERT R. MCEWEN |
|||
| Dated: March 9, 2015 | Robert R. McEwen, Chairman of the Board of Directors and Chief Executive Officer |
|||
In accordance with the Exchange Act, this Report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Company and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| /s/ ROBERT R. MCEWEN Robert R. McEwen |
Chairman of the Board of Directors and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | March 9, 2015 | ||
/s/ PERRY Y. ING Perry Y. Ing |
Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
March 9, 2015 |
||
/s/ ALLEN V. AMBROSE Allen V. Ambrose |
Director |
March 9, 2015 |
||
/s/ MICHELE L. ASHBY Michele L. Ashby |
Director |
March 9, 2015 |
||
/s/ LEANNE M. BAKER Leanne M. Baker |
Director |
March 9, 2015 |
||
/s/ RICHARD W. BRISSENDEN Richard W. Brissenden |
Director |
March 9, 2015 |
||
/s/ GREGORY P. FAUQUIER Gregory P. Fauquier |
Director |
March 9, 2015 |
||
/s/ DONALD R. M. QUICK Donald Quick |
Director |
March 9, 2015 |
||
/s/ MICHAEL L. STEIN Michael L. Stein |
Director |
March 9, 2015 |
129
| 2.1 | Arrangement Agreement, dated September 22, 2011, by and among the Company, Canadian Exchange Co. and Minera Andes (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on September, 23, 2011, Exhibit 2.1, File No. 001-33190) | ||
3.1.1 |
Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of the Company as filed with the Colorado Secretary of State on January 24, 2012 (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on January 24, 2012, Exhibit 3.1, File No. 001-33190) |
||
3.1.2 |
Articles of Amendment to the Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of the Company (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on January 24, 2012, Exhibit 3.2, File No. 001-33190) |
||
3.2 |
Amended and Restated Bylaws of the Company (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on March 12, 2012, Exhibit 3.2, File No. 001-33190) |
||
9.1 |
Voting and Exchange Trust Agreement, dated January 24, 2012, by and among the Company, Canadian Exchange Co., Callco and Computershare Trust Company of Canada, as trustee (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on January 24, 2012, Exhibit 10.2, File No. 001-33190) |
||
10.1 |
Support Agreement, dated January 24, 2012, by and among the Company, Canadian Exchange Co. and Callco (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on January 24, 2012, Exhibit 10.1, File No. 001-33190) |
||
10.2 |
Amended and Restated US Gold Corporation Equity Incentive Plan dated as of October 4, 2011 (incorporated by reference from Annex H to the Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A filed with the SEC on December 13, 2011, File No. 001-33190) |
||
10.3 |
Agreement to Pay Distributions dated February 21, 1992, by and between Tonkin Springs Gold Mining Company and French American Banking Corporation (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 8-K dated February 21, 1992, Exhibit 4, File No. 000-09137) |
||
10.4 |
Form of Indemnification Agreement between the Company and its officers and directors (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 8-K dated December 7, 2005, Exhibit 10.1, File No. 000-09137) |
||
10.5 |
Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Company and Tonkin Springs LLC, as purchasers, and Gold Standard Royalty (Nevada) Inc., and Julian E. Simpson, as Sellers, dated July 19, 2011 (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 25, 2011, Exhibit 10.1, File No. 001-33190) |
||
10.6 |
Employment Agreement between the Company and William Faust dated July 27, 2011 (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on August 2, 2011, Exhibit 10.1, File No. 001-33190) |
||
10.7 |
Settlement Agreement dated for reference purposes February 4, 2013 between TNR Gold Corp. and Solitario Argentina, S.A., plaintiffs, and MIM Argentina Exploraciones S.A. and certain subsidiaries of the Company, defendants (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on February 7, 2013, Exhibit 10.1, File No. 001-33190) |
||
10.8 |
Refining Agreement dated December 16, 2013, by and among the Company and Johnson Matthey Gold & Silver Refining Inc. (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 10-K filed with the SEC on March 10, 2014, Exhibit 10.8, File No. 001-33190) |
130
| 10.9 | Mining Production Work Agreement dated September 23, 2013, by and among the Company, and Exploraciones Mineras Del Desierto SA de CV (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 10-K filed with the SEC on March 10, 2014, Exhibit 10.9, File No. 001-33190) | ||
14 |
Code of Ethics (incorporated by reference from the Report on Form 10-K filed with the SEC on March 10, 2014, Exhibit 14, File No. 001-33190) |
||
21 |
Subsidiaries of the Company, filed herein. |
||
23.1 |
Consent of KPMG LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm, filed herein. |
||
31.1 |
Certification pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 for Robert R. McEwen, filed herein. |
||
31.2 |
Certification pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 for Perry Y. Ing, filed herein. |
||
32 |
Certification pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 for Robert R. McEwen and Perry Y. Ing, filed herein. |
||
101 |
The following materials from the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2014 are filed herewith, formatted in XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language): (i) the Audited Consolidated Statements of Operations and Other Comprehensive Loss for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, (ii) the Audited Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, (iii) the Audited Consolidated Statement of Changes in Shareholders' Equity for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, (iv) the Audited Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, and (v) the Notes to the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements, filed herein. |
131
