Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - MACOM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. | d817839dex311.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EX-21.1 - MACOM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. | d817839dex211.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - MACOM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. | d817839dex231.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - MACOM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. | d817839dex321.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - MACOM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. | d817839dex312.htm |
| EXCEL - IDEA: XBRL DOCUMENT - MACOM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. | Financial_Report.xls |
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended October 3, 2014
OR
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission file number: 001-35451
M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 27-0306875 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| 100 Chelmsford Street, Lowell, Massachusetts | 01851 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (978) 656-2500
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Each Class |
Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered | |
| Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share | NASDAQ Global Select Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer ¨ | Accelerated filer x | Non-accelerated filer ¨ | Smaller reporting company ¨ | |||
| (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | ||||||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of the registrant’s common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of April 4, 2014, the last business day of the registrant’s second fiscal quarter, was approximately $410.2 million based on the closing price of the registrant’s common stock as of such date as reported on the NASDAQ Global Select Market. For purposes of the foregoing calculations only, shares of common stock held by each executive officer and director of the registrant and their respective affiliates have been excluded, as such persons may be deemed to be affiliates. This determination of affiliate status is not necessarily a conclusive determination for other purposes.
The number of outstanding shares of the registrant’s common stock, par value $0.001 per share, as of November 15, 2014 was 47,604,204.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Part III incorporates certain information by reference from the registrant’s definitive proxy statement for the 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which will be filed no later than 120 days after the close of the registrant’s fiscal year ended October 3, 2014.
Table of Contents
M/A-COM TECHNOLOGY SOLUTIONS HOLDINGS, INC.
ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K
FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED OCTOBER 3, 2014
2
Table of Contents
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT
This Annual Report on Form 10-K (Annual Report) contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 21E of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, including statements regarding our business outlook, strategy, plans, expectations, estimates and objectives for future operations, and our future results of operations and financial position. Forward-looking statements include all statements that are not historical facts and generally may be identified by terms such as “anticipates,” “believes,” “could,” “continue,” “estimates,” “expects,” “intends,” “may,” “plans,” “potential,” “predicts,” “projects,” “seeks,” “should,” “targets,” “will,” “would,” or similar expressions or variations or the negatives of those terms, but are not the exclusive means of identifying forward-looking statements in this Annual Report.
Although forward-looking statements in this Annual Report reflect the good faith judgment of our management based on what we know at the time they are made, such statements involve inherent risks and uncertainties and actual results and outcomes may differ materially and adversely from the results and outcomes expressed or implied by our forward-looking statements. A number of important factors could cause actual results to differ materially and adversely from those in the forward-looking statements. We urge you to consider the risks and uncertainties in Item 1A. “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Annual Report and the other documents filed by us with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Except as required by law, we have no plans, and undertake no obligation, to revise or update our forward-looking statements to reflect any event or circumstance that may arise after the date of this report. We caution readers not to place undue reliance upon any such forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date made.
In this document, the words “Company,” “we,” “our,” “us,” and similar terms refer only to M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries, and not any other person or entity.
“M/A-COM” and “MACOM” are trademarks of M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. All other brands and names listed are trademarks of their respective owners.
3
Table of Contents
Overview
We are a leading provider of high-performance analog semiconductor solutions that enable next-generation internet applications, the cloud connected apps economy, and the modern, networked battlefield across the radio frequency (RF), microwave and millimeterwave spectrum. We design and manufacture differentiated, high-value products for customers who demand high performance, quality and reliability. We offer a broad portfolio of over 3,500 standard and custom devices, which include integrated circuits (IC), multi-chip modules, power pallets and transistors, diodes, switches and switch limiters, passive and active components and complete subsystems, across 42 product lines serving over 6,000 end customers in four primary markets. Our semiconductor products are electronic components that our customers incorporate into their larger electronic systems, such as point-to-point wireless backhaul radios, optical networking equipment, high density data networks, radar, automobile navigation systems, magnetic resonance imaging systems and unmanned aerial vehicles. Our primary markets are: Networks, which includes wired broadband, cellular backhaul, cellular infrastructure, enterprise networking, broadcast video transmission and optical communications applications; Aerospace and Defense (A&D), which includes military and commercial radar, RF jammers, electronic countermeasures and communication data links; Automotive, which includes global positioning (GPS) modules we sell to Ford and Ford affiliates; and Multi-market, which includes industrial, medical, test and scientific applications.
We build upon a 60-year heritage of delivering innovative solutions dating back to the founding of Microwave Associates, Inc. We utilize our system-level knowledge and our extensive capabilities in high-frequency modeling, IC design, integration, manufacturing and packaging of semiconductors to address our customers’ needs. Our specialized engineers and technologists located across eleven global design centers collaborate with our customers during the early stage of their system development process to incorporate our standard products and identify custom products we can develop to enhance their overall system performance. We intend to continue to expand our revenue opportunities through our market-facing strategy of aligning our solutions with our customers’ needs and collaborating with them during the product definition stage of their systems toward design-in of our products. We believe this approach will allow us to sell more complete semiconductor solutions that integrate more functions and incorporate more highly-valued content into our products. We believe the combination of our market-facing strategy and our engineering expertise enables us to identify profitable growth opportunities and rapidly develop and deliver new products and solutions. Many of our products have long lifecycles ranging from five to ten years, and some of our products have been shipping for over 20 years. We believe these factors create a competitive advantage. Our goal is to strengthen customer relationships and capture design wins, where a customer allows us to be a supplier of a particular component used in its system.
We believe our “fab-lite” manufacturing model provides us with a competitive advantage and an attractive financial model through a largely variable cost structure. We operate a Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) and silicon semiconductor fab at our Lowell, Massachusetts headquarters, and we are currently in the process of adding Gallium Nitride (GaN) fabrication capacity at that site as well. In the A&D market, a domestic fab can be a requirement to be a strategic supplier, and we believe our status as a “Trusted Foundry” offers us further competitive differentiation.
We also utilize external semiconductor foundries to supply us with additional capacity, lower costs, and to provide us access to additional process technologies. The ability to utilize a broad array of internal proprietary process technologies as well as commercially available foundry technologies allows us to select the most appropriate technology to solve our customers’ needs. We believe our fab-lite strategy also provides us with dependable domestic supply, control over quality, reduced capital investment requirements, faster time to market, and additional outsourced capacity when needed. In addition, the experience base cultivated through the continued operation of our internal fab provides us with the expertise to better manage our external foundry suppliers.
4
Table of Contents
We serve our broad and diverse customer base through a multi-channel sales strategy utilizing our direct sales force, a global network of independent sales representatives, distributors and an e-commerce channel. Our direct sales force and application engineers are focused on securing design wins by supporting industry-leading original equipment manufacturer (OEM) customers. Our external sales representatives, distributors and our e-commerce channel, are focused on increasing our design wins with smaller or emerging customers early in their new product development efforts.
Our Markets & Products
The growth of advanced electronic systems using analog RF, microwave and millimeterwave technologies has created demand for high-performance analog semiconductor components, modules and solutions. The terms RF, microwave and millimeterwave are used to refer to electromagnetic waves in a particular frequency range produced by applying an alternating current to an antenna or conductor. A wide variety of advanced electronic systems rely on electromagnetic waves for high-speed data transmission or reception. We offer high-performance analog semiconductor products for both wireless and wireline applications across the frequency spectrum from RF to millimeterwave. We regularly develop high-value products to serve our customers in four primary markets: Networks, A&D, Automotive and Multi-market, which represented 43.8%, 20.9%, 19.3% and 16.0%, respectively, of our revenue in fiscal year 2014.
The market demand for analog RF, microwave and millimeterwave semiconductors is driven by the growth of mobile internet devices, cloud computing and streaming video that strain existing network capacity, as well as the growth in advanced information-centric military applications. In addition, the increasing need for real-time information, sensing and imaging functions in automotive, industrial, medical, scientific and test and measurement applications is driving demand for our products.
Networks. Growth in the Networks market is driven by the proliferation of wireless and wired devices from smartphones and tablets to data centers, as well as the data rich applications and services they enable such as mobile internet, cloud computing, video-on-demand, social media, global positioning functionality and location based services. Growth in global next-generation internet and internet of things (IoT) drives demand for communications infrastructure equipment requiring amplifiers, filters, receivers, switches, synthesizers, transformers, upconverters and other components to expand and upgrade cellular backhaul, cellular infrastructure, wired broadband and fiber optic networks. Semiconductor products and solutions must continually deliver greater bandwidth and functionality as the demands of our customers and end users increase.
Our expertise in system-level architectures and advanced IC design capability allow us to offer Networks OEMs highly-integrated solutions optimized for performance and cost. We are a leader in high-frequency semiconductors used in point-to-point radios for cellular backhaul, where we provide a highly-integrated chipset solution featuring innovative IC and low cost package design capabilities. Similarly, our portfolio of opto-electronics products for clock and data recovery, optical post amplifiers, laser and modulator drivers, transimpedence amplifiers, transmitter and receiver applications in 2.5/6/10/40/100 gigabit per second (Gbps) long haul, metro and fiber-to-the-home (FTTx) fiber optic networks enable telecommunications carriers and data centers to cost-efficiently increase their network capacity by a factor of four to ten times over earlier generation solutions. For optical communications applications, we utilize a proprietary combination of GaAs, Indium Phosphide (InP) and Silicon Germanium (SiGe) technologies to obtain advantages in performance and size. For wired broadband applications, we offer OEMs the opportunity to streamline their supply chain through our broad catalog of active components such as active splitters, amplifiers, multi-function ICs and switches, as well as passive components such as transformers, diplexers, filters, power dividers and combiners.
Aerospace & Defense. In the A&D market, military applications require more advanced electronic systems, such as radar warning receivers, communications data links and tactical radios, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), RF jammers, electronic countermeasures and smart munitions. Military applications are becoming more sophisticated, favoring higher performance semiconductor ICs based on GaAs and GaN technologies due to their high power density, improved power efficiency and broadband capability. Radar systems for mapping and
5
Table of Contents
targeting missions are undergoing a major transition from existing mechanically-scanned radar products to a next-generation of active electronically-scanned array (AESA) based products. Consisting of hundreds or thousands of transmit/receive modules commonly based on GaAs and GaN technologies, AESAs deliver greater speed, range, resolution and reliability over mechanically-scanned radar products that utilize a single transmitter and receiver with mechanical steering. Military communications employing wireless infrastructure and tactical radios in the field remain critical for allowing geographically dispersed operators to exchange information quickly and efficiently. UAVs and their underlying semiconductor content require innovative designs to meet rigorous specifications for high performance, small size and low power consumption.
We believe our in-depth knowledge of critical radar system requirements, integration expertise and track record of reliability make us a valued resource for our A&D customers faced with demanding application parameters. Further, we have been accredited by the United States Department of Defense with “Trusted Foundry” status, a designation conferred on microelectronics vendors exhibiting the highest levels of process integrity and protection, which we believe differentiates us as a trusted manufacturer of ICs for U.S. military and aerospace applications. For radar applications, we offer standard and custom power transistor pallets, discrete components, switch limiters, phase shifters and integrated modules for transmit and receive functions in air traffic control, marine, weather and military radar applications. For military communications data link and tactical radio applications, we offer a family of active, passive and discrete products, such as integrated IC modules, control components, voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs), transformers, power transistors and pallets and diodes. In some cases, we design parts specifically for these applications, while in others, our reputation for quality and broad catalog allows these demanding customers to reduce the cost of their high-performance systems by designing in standard dual-use or commercial off-the-shelf parts that we have developed for other applications. We believe manufacturing many of these products in our Lowell, Massachusetts “Trusted Foundry” fab offers us a competitive advantage in the A&D market because of our proprietary process technologies and certain A&D customers’ requirements for a domestic supply chain.
Automotive. Demand for our products targeting the Automotive market is largely driven by the need for real-time access to information to support driver information, active safety and efficiency applications in vehicles which automotive OEMs have begun adopting in their vehicle designs to comply with government fuel efficiency and emission reduction requirements, increase safety, and deliver an improved driving experience to the consumer. Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) such as telematics, active cruise control, vision systems, collision avoidance and hybrid energy management systems each require highly accurate location information, time and other data as inputs to complex control systems and algorithms, as well as connectivity to global data infrastructure.
Through RF reception, signal processing, and systems engineering, we deliver stand-alone, networked embedded modules. Our automotive module products include RF reception, signal processing and other functionality enabling the delivery of the required location, time, and predictive horizon data to these ADAS system applications. Our distributed architecture approach allows multiple control systems across the vehicle (e.g. telematics, powertrain, safety) to leverage a single sensor, resulting in lower system cost and quicker time to market with next generation technologies for OEMs.
Multi-market. Multi-market encompasses industrial, medical, test and measurement and scientific applications, where analog RF, microwave and millimeterwave semiconductor solutions are gaining prevalence. In addition, evolving medical technology has increased the need for high-performance semiconductor solutions in medical imaging and patient monitoring to provide enhanced analysis and functionality.
In Multi-market, our products are used in industrial, medical, test and measurement and scientific applications. In the medical industry, our custom designed non-magnetic diode product line is a critical component for certain MRI applications. For sensing and test and measurement applications, we believe our patented heterolithic microwave integrated circuit (HMIC) process is ideal for high-performance, integrated bias networks and switches. Our catalog of general purpose GaAs ICs includes low noise amplifiers, switches and power amplifiers that address a wide range of applications such as industrial automation systems to test and measurement equipment.
6
Table of Contents
To address our target markets, we offer a broad range of standard and custom ICs, modules and complete subsystems across 42 product lines. Our product catalog currently consists of more than 3,500 products including the following key product platforms: power pallets and transistors, ICs, diodes, switches and switch limiters, passive and active components, multi-chip modules and complete subsystems. Many of our product platforms are leveraged across multiple markets and applications. For example, our application expertise with regard to power transistor technology is leveraged across both scientific laboratory equipment applications and commercial and defense radar system applications. Our diode technology is used in switch filter banks of military tactical radios as well as medical imaging systems. The table below presents the major product families and major applications in our primary target markets.
| TARGET MARKET |
MAJOR PRODUCT FAMILIES |
MAJOR APPLICATIONS | ||
| Networks | Active Splitters | 2G/3G/4G Wireless Basestations | ||
| Amplifiers | 40/100G Fiber Optics | |||
| Attenuators | Broadcast Video | |||
| Clock and Data Recovery | CATV Infrastructure | |||
| Crosspoint Switches | Enterprise Routing and Switching | |||
| Carrier Convergence Processors | GPON/FTTx | |||
| Enterprise Voice & Data Processors | Hybrid PBX | |||
| Filters/Diplexers | IP PBX | |||
| Laser Drivers | Optical Transport Networks | |||
| Modulator Driver Amplifiers | Point-to-Point Wireless Backhaul | |||
| Post Amplifiers | Session Border Controller | |||
| SDI Cable Drivers | Set Top Boxes | |||
| SDI Equalizers | Unified Communication | |||
| SDI Reclockers | Wireless Trunk Gateway | |||
| Signal Conditioners | Wireline Access Gateway | |||
| Switches | Wireline Trunk Gateway | |||
| Transformers/Baluns | ||||
| Transimpedance Amplifiers | ||||
| Upconverters/Downconverters | ||||
| VoIP Processors | ||||
| Voltage Controlled Oscillators | ||||
| Aerospace and Defense | Amplifiers | Air Traffic Control Radar | ||
| Attenuators | Weather Radar | |||
| Components | Public Safety Radios | |||
| Diodes | Tactical & Manpack Radios | |||
| Power Transistors & Modules | Satellite Communications | |||
| Mixers | Military Communications | |||
| Phase Shifters | ||||
| Switch Limiters | ||||
| Voltage Control Oscillators | ||||
| Automotive | GPS Module | Global Positioning System | ||
| Multi-Market | Amplifiers | Industrial | ||
| Attenuators | Medical | |||
| Couplers | Scientific | |||
| Diodes | Test & Measurement | |||
| Logic Drivers | ||||
| Mixers | ||||
| Power Detectors | ||||
| Power Transistors | ||||
| Switches | ||||
| Transceivers | ||||
7
Table of Contents
We believe the combination of our market-facing strategy and our engineering expertise enables us to identify profitable growth opportunities and rapidly develop and deliver new products and solutions. Many of our products have long lifecycles ranging from five to ten years, and some of our products have been shipping for over 20 years. Our goal is to strengthen customer relationships and capture design wins, where a customer allows us to be a supplier of a particular component used in its system.
Research and Development
Our research and development efforts are directed toward the rapid development of new and innovative products and solutions, process technologies and packaging techniques. The interaction of semiconductor process technology, circuit design technology and packaging technology defines the performance parameters and the customers’ acceptance of our products. We believe our core competency is the ability to model, design, integrate, manufacture and package differentiated solutions. We leverage this core competency to solve difficult and complex challenges that our customers face during their system design phases. We believe our integrated and customized solutions offer customers high performance, quality, reliability and faster time to market.
Circuit design and device modeling expertise. Our engineers are experts in the design of circuits capable of reliable, high-performance analog RF, microwave and millimeterwave signal conditioning. Our staff has decades of experience in solving complex design challenges in applications involving high frequency, high power, and environmentally-rugged operating conditions. We also develop proprietary device and electro-magnetic modeling techniques that our engineers use to generate predictive models prior to fabrication. Our predictive modeling expertise allows us to achieve faster design cycle times resulting in shorter time to market for our products.
Packaging expertise. Our extensive packaging expertise enables us to model the interaction between the semiconductor and its package. Our engineers make adjustments in the design of both the semiconductor and the package, to take account of that interaction. We offer products in a variety of different package types for specific applications, including plastic over-molded, ceramic and laminate-based.
Semiconductor process technology. We leverage our domestic semiconductor wafer fabrication capabilities and our foundry suppliers to offer customers the right process technology to meet their particular requirements. Depending on the requirements for the application, our semiconductor products may be designed using an internally developed or externally sourced process technology.
We continue to invest in proprietary processes to enable us to develop and manufacture high-value solutions. For example, we have developed innovative, patented technologies such as HMIC, which provides high integration, high power and low loss switching capabilities for our primary markets. This technology replaces mechanical switches for very high power applications such as wireless basestations. We are also in the process of transferring from an external foundry supplier an innovative, high-performance GaN process technology manufacturing capability to our Lowell, Massachusetts fabrication facility. Upon completion of the transfer and qualification process, we believe that being able to offer our customers this dual-sourced, internal and external GaN supply capability will provide us with a competitive advantage.
Our engineers’ system-level design expertise allows us to offer differentiated solutions that leverage multiple process technologies and are integrated into a single, higher-level assembly, thereby delivering our customers enhanced functionality.
Research and development expenses were $73.7 million, $44.6 million and $36.8 million for fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. We anticipate that we will continue to make significant research and development expenditures in order to drive future new product and process introductions and maintain our competitive position.
8
Table of Contents
Sales and Marketing
We employ a global multi-channel sales strategy and support model intended to facilitate our customers’ evaluations and selections of our products. We sell through our direct sales force, our application engineering staff and our global network of independent sales representatives, resellers and distributors, as well as an e-commerce channel. We have strategically positioned our direct sales and applications engineering staff in 32 locations worldwide, augmented by independent sales representatives and distributors with additional domestic and foreign locations to offer responsive local support resources to our customers and to build long-term relationships. From our global design centers, our application engineers visit customers at their engineering and manufacturing facilities, aid them in understanding our capabilities, and collaborate with them to deliver products that can optimize their system performance. Our global independent sales representatives and distributor network allows us to extend our sales capabilities to new customers in new geographies more cost effectively than we can using our direct sales force alone.
Our products are principally sold in the U.S., Asia and Europe, which is where we concentrate our direct sales force, engineering staff, independent sales representatives, and distributors. Sales to our distributors accounted for 22.5%, 18.4% and 21.3% of our revenue in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Our agreements with sales representatives, resellers and distributors may provide for an initial term of one or more years with the opportunity for subsequent renewals or for an indefinite term, and also typically provide that either party may terminate the agreement for convenience with a minimum period of prior notice to the other party, typically between 30 and 90 days.
Our sales efforts are focused on customers’ needs in our four primary markets rather than on particular product lines, facilitating product cross-selling across end markets and within key accounts. Through our website, customers can order online, request samples, as well as access our product selection guides, detailed product brochures and data sheets, application notes, suggested design block diagrams and test fixture information, technical articles and information regarding quality and reliability.
Customers
Our diversified base of over 6,000 end customers includes original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), contract manufacturers and distributors. For fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, one direct customer individually accounted for more than 10% of our revenue, Ford Motor Company (Ford) at 19.0%, 24.8% and 15.7%, respectively. In addition, our principal distributor, Richardson Electronics, an Arrow Electronics Company (Richardson), accounted for 15.0%, 15.6% and 17.5% of our revenue in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Our top 25 direct customers accounted for an aggregate of 56.5%, 59.0% and 54.0% of our revenue in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Revenue from our distributors accounted for an aggregate of 22.5%, 18.4% and 21.3% of our revenue in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 respectively.
Competition
The markets for our products are highly competitive and are characterized by rapid technological change and continuously evolving customer requirements. We believe that the principal competitive factors in our markets include:
| • | the ability to timely design and deliver products and solutions that meet customers’ performance, reliability and price requirements; |
| • | the breadth and diversity of product offerings; |
| • | the ability to provide a reliable supply of products in sufficient quantities and in a timely manner; |
| • | the ability of engineering talent to drive innovation and new product development; |
| • | the quality of customer service and technical support; and |
| • | the financial reliability, operational stability and reputation of the supplier. |
9
Table of Contents
We believe that we compete favorably with respect to these factors. We compete primarily with other suppliers of high-performance analog semiconductor solutions for use in wireless and wireline RF, microwave and millimeterwave applications, some of whom have greater financial resources and scale than us. We expect competition in our markets to intensify, as new competitors enter the RF, microwave and millimeterwave markets, existing competitors merge or form alliances, and new technologies emerge. We believe in the future there will be increased competition from companies utilizing alternative technologies, such as high-volume manufacturers using low-cost silicon process technology. Some of our competitors are also our customers, and in certain product categories we compete with semiconductor manufacturers from which we also obtain foundry services, including Sumitomo Electric Device Innovations, Inc. and RF Micro Devices, Inc. (RFMD).
We compete with Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI) across three of our primary markets, Networks, A&D and Multi-market. In the Networks market, we also compete with Avago Technologies Limited (Avago), RFMD, TriQuint Semiconductor, Inc. (Triquint) and SEMtech Corporation. In the A&D market, we also compete with Cobham Defense Electronic Systems (Cobham), Microsemi Corporation (Microsemi) and TriQuint. In the Multi-market arena, we also compete with Cobham, Avago, Microsemi and Skyworks Solutions, Inc (Skyworks).
Segment and Geographic Information
We manage our operations in one reportable segment, semiconductors and modules. Financial information about our operations, including our revenue and long-lived assets by geographic region, is included in our consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes in Item 8. “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report.
Risks attendant to our foreign operations are discussed in this Annual Report under Item 1A. “Risk Factors.”
Backlog and Inventory
Our sales are made primarily on a purchase order basis, rather than pursuant to long-term contracts where the customer commits to buy any minimum amount of product over an extended period. On occasion, we ship finished goods inventory to certain customer or third-party “hub” locations, but do not recognize revenue associated with such shipments until these customers consume the inventory from the hub. We also frequently ship products from inventory shortly after receipt of an order, which we refer to as “turns business”. Due to these arrangements and industry practice, which allows customers to cancel orders with limited advance notice prior to shipment, and with little or no penalty, we believe that backlog as of any particular date may not be a reliable indicator of our future revenue levels.
Intellectual Property
Our success depends in part upon our ability to protect our intellectual property. To accomplish this, we rely on a combination of intellectual property rights, including patents, copyrights, trademarks and trade secrets, as well as customary contractual protections with our customers, suppliers, employees and consultants.
As of October 3, 2014, we had 380 U.S. and 118 foreign patents and 45 U.S. and 25 foreign pending patent applications covering elements of circuit design, manufacturing and wafer fabrication. We do not know whether any of our pending patent applications will result in the issuance of patents or whether the examination process will require us to narrow our claims. The expiration dates of our patents range from 2014 to 2032. We do not regard any of the patents scheduled to expire in the next 12 months as material to our overall intellectual property portfolio. Notwithstanding our active pursuit of patent protection when available, we believe that our future success will be determined by the innovation, technical expertise and management abilities of our engineers and management more than by patent ownership.
The semiconductor industry is characterized by the existence of a large number of patents, copyrights, trademarks and trade secrets, and by the vigorous pursuit, protection and enforcement of intellectual property rights. Many of our customer agreements require us to indemnify our customers for third-party intellectual
10
Table of Contents
property infringement claims, which may in the future require that we defend those claims and might require that we pay damages in the case of adverse rulings. Claims of this sort could harm our relationships with our customers and might deter future customers from doing business with us. With respect to any intellectual property rights claims against us or our customers or distributors, we may be required to cease manufacture of the infringing product, pay damages or settlement amounts, expend resources to develop non-infringing technology, seek a license, which may not be available on commercially reasonable terms or at all, or relinquish patents or other intellectual property rights.
Manufacturing, Sources of Supply and Raw Materials
In any particular situation, we may choose to leverage our internal proprietary process technologies or other technologies from external fabs. We believe this ability to leverage our existing internal capabilities and external outsourcing helps us to provide optimized solutions for our customers.
All of our internal wafer fabrication, and a majority of our internal assembly and test operations, are conducted at our Lowell, Massachusetts headquarters. We believe having a U.S.-based wafer fab is a competitive advantage for us over fabless competitors, in that we have greater control over quality, a secure source of supply, and a domestic source for U.S. A&D customers. We also believe that our domestic fab allows us to better manage quality control and develop products faster with shorter fabrication lead times than we otherwise could at external foundries. We also perform internal assembly and test functions at our Long Beach, California, Nashua, New Hampshire and Hsinchu, Taiwan, locations.
We complement our internal manufacturing with outsourced foundry partners and other supply chain suppliers. Our operations staff has extensive expertise in the management of outsourced manufacturing service providers and other supply chain participants. We believe our fab-lite model of outsourcing certain of our manufacturing activities rather than investing heavily in capital-intensive production facilities, provides us with the flexibility to respond to new market opportunities, simplifies our operations, provides access to other process technologies and additional manufacturing capacity and reduces our capital requirements. We also use third-party contract manufacturers for assembly, packaging and test functions and in some cases for fully-outsourced turnkey manufacturing of our products.
The principal materials used in the production of our IC products are high purity source materials such as gallium, aluminum, arsenic, nitrite, carbon and silicon. We purchase from hundreds of suppliers worldwide, a wide variety of semiconductors, wafers, packages, metals, printed circuit boards, electromechanical components and other materials for use in our operations. These supply relationships are generally conducted on a purchase order basis. The use of external suppliers involves a number of risks, including the possibility of material disruptions in the supply of key raw materials and components, the lack of control over delivery schedules, capacity, quality and costs.
While we attempt to maintain alternative sources for our principal raw materials to reduce the risk of supply interruptions or price increases, some of the raw materials and components are not readily available from alternate suppliers due to their unique nature, design or the length of time necessary for re-design or qualification. We routinely utilize single sources of supply for various materials based on availability, performance, efficiency or cost considerations. For example, wafers procured from merchant foundries for a particular process technology are generally sourced through a single foundry, on which we rely for all of our wafers in that process. Our reliance on external suppliers puts us at risk of supply chain disruption, if the supplier does not have sufficient raw material inventory to meet our manufacturing needs, goes out of business, changes or discontinues the process in which components or wafers are manufactured, or declines to continue supplying us for competitive or other reasons, as discussed in more detail in Item 1A. “Risk Factors” herein. Where practical, we attempt to mitigate these risks by qualifying multiple sources of supply, redesigning products for alternative components and purchasing incremental inventory of raw materials and components in order to protect us against supply disruptions.
11
Table of Contents
Quality Assurance
The goal of our quality assurance program is for our products to meet our customers’ requirements, be delivered on time and function reliably throughout their useful lives. The International Organization for Standards (ISO) provides models for quality assurance for various operational disciplines, such as design, manufacturing, and testing, which comprise part of our overall quality management system. Our Lowell, Massachusetts, Long Beach, Santa Clara and Newport Beach, California, Morrisville, North Carolina, Nashua, New Hampshire, Belfast, Northern Ireland, Cork, Ireland, Sydney, Australia and Hsinchu, Taiwan locations have each received ISO 9001:2008 certifications in one or more of their principal functional areas. In addition, our Lowell facility has received an ISO 14001:2004 environmental management systems certification.
Environmental Regulation
Our operations involve the use of hazardous substances and are regulated under federal, state, and local laws governing health and safety and the environment in the U.S. and other countries. These regulations include limitations on discharge of pollutants into the air, water and soil, remediation requirements, product chemical content limitations, manufacturing chemical use and handling restrictions, pollution control requirements, waste minimization considerations, and requirements regarding the treatment, transport, storage and disposal of hazardous wastes. We are also subject to regulation by the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration and similar health and safety laws in other jurisdictions. While we are committed to compliance with applicable regulations, the risk of environmental liabilities can never be completely eliminated, and there can be no assurance that the application of environmental and health and safety laws to our business will not require us to incur material future expenditures.
We are also regulated under a number of federal, state and local laws regarding responsible sourcing, recycling, product packaging and product content requirements in the U.S. and other countries, including legislation enacted in the European Union and other foreign jurisdictions that have placed greater restrictions on the use of lead, among other chemicals, in electronic products, which affects materials composition and semiconductor packaging. These laws are becoming more stringent and may in the future cause us to incur material expenditures or otherwise cause financial harm.
Export Regulations
We market and sell our products both inside and outside the U.S. Certain products are subject to the Export Administration Regulations, administered by the Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry Security, which require that we obtain an export license before we can export certain controlled products or technology to specified countries. Additionally, some of our products are subject to the International Traffic in Arms Regulations, which restrict the export of information and material that may be used for military or intelligence applications by a foreign person. Similar controls exist in other jurisdictions. Failure to comply with these laws could result in sanctions by the government, including substantial monetary penalties, denial of export privileges, and debarment from government contracts. We maintain an export compliance program staffed by dedicated personnel under which we screen export transactions against current lists of restricted exports, destinations, and end users with the objective of managing export-related decisions, transactions and shipping logistics to ensure compliance with these requirements.
Employees
As of October 3, 2014, we employed 918 persons worldwide and none of our domestic employees were represented by a collective bargaining agreement; however, a number of our employees working in our European operations were covered by collective bargaining agreements. We consider our relations with employees to be good, and we have not experienced a work stoppage due to labor issues.
12
Table of Contents
General Development
We were incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware in March 2009. Our operations are conducted through our various subsidiaries, which are organized and operated according to the laws of their respective jurisdictions of incorporation.
M/A-COM Technology Solutions Inc., our primary operating subsidiary, which provides high-performance analog semiconductor solutions for use in wireless and wireline applications across the RF, microwave, and millimeterwave spectrum, was incorporated under the laws of the state of Delaware on July 16, 2008. M/ACOM Technology Solutions (Cork) Limited, our primary foreign operating subsidiary, was incorporated under the laws of Ireland on November 18, 2008. In September 2008, Cobham acquired certain assets from a third party, including the RF and microwave component and subsystem design and business operations that would ultimately become the operations of M/A-COM Technology Solutions Inc. and M/ACOM Technology Solutions (Cork) Limited. The heritage of some of these business operations dates back over 60 years to the founding of Microwave Associates, Inc. and the M/A-COM brand dates back over 30 years.
On March 30, 2009, we acquired 100% of the outstanding stock of M/A-COM Technology Solutions Inc. and M/ACOM Technology Solutions (Cork) Limited and the related M/A-COM brand from Cobham (MACOM Acquisition) for $22.1 million in cash net of purchase price adjustments, the issuance of $35.0 million in short- and long-term debt payable to the seller and contingent consideration of approximately $30.0 million based on our achievement of revenue targets in the 12-month periods ended September 30, 2010, 2011 and 2012.
On May 28, 2010, we acquired Mimix Holdings, Inc. (Mimix), a supplier of high-performance GaAs semiconductors, for $1.2 million in cash and 17.5 million shares of our Series A-2 convertible preferred stock (Mimix Merger). We acquired Mimix for its complementary products and technologies in our core markets, which enabled us to strengthen customer relationships.
On April 25, 2011, we acquired Optomai, Inc. (Optomai), a fabless semiconductor company that develops high-performance ICs and modules for next generation fiber optic networks, for $1.8 million in cash and potential contingent consideration based on our achievement of certain revenue, product release and contribution margin targets based on sales of products utilizing Optomai intellectual property through, as amended, September 2013. No amounts of contingent consideration have been paid nor are payable pursuant to the terms of the agreement. We acquired Optomai for technologies that accelerated our entrance into the fiber optics market.
On December 18, 2013, we acquired Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. (Mindspeed), a supplier of semiconductor solutions for communications infrastructure applications (Mindspeed Acquisition). We acquired Mindspeed to further our expansion into high-performance analog products. We funded the acquisition through the use of available cash and borrowings under our revolving credit facility (see Note 8 of our Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements). The aggregate purchase price paid by us in the Mindspeed Acquisition, net of cash acquired, was $232.0 million and we assumed $81.3 million of liabilities and incurred costs of $4.5 million expensed in fiscal year 2014. The Mindspeed Acquisition was accounted for as a purchase and the operations of Mindspeed have been included in our consolidated financial statements since December 18, 2013, the date of acquisition.
Subsequent to closing the Mindspeed Acquisition, in February 2014, we divested the wireless business of Mindspeed. The operations of the wireless business are included in discontinued operations. In May 2014, we divested the customer premise equipment communication processor (CPE) product line we acquired in the Mindspeed Acquisition. The operations of the CPE product line are included in the results of operations through the date of the sale.
On February 13, 2014, we completed the acquisition of Nitronex, LLC (Nitronex Acquisition). Nitronex designs, develops, manufactures and markets GaN semiconductors and holds an exclusive license to fundamental
13
Table of Contents
GaN patents in the RF field of use. We completed the Nitronex Acquisition through a cash payment of $26.1 million for all of the outstanding membership interests of Nitronex. We funded the Nitronex Acquisition through the use of available cash and borrowings under our revolving credit facility.
We acquired Nitronex from a party under common control with MACOM, and as a result we have accounted for the Nitronex Acquisition as a pooling of interest from the date of acquisition by the common control party in June 2012. The original acquisition of Nitronex by the common control party was accounted for as a purchase. The financial statements of MACOM have been retroactively combined to include the results of operations of Nitronex from June 2012.
On November 17, 2014, we entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger to acquire BinOptics Corporation (BinOptics Acquisition). The aggregate consideration payable for BinOptics will be approximately $230 million, subject to adjustment based on customary post-closing purchase price adjustment provisions and indemnification obligations of BinOptics equityholders after the closing of the BinOptics Acquisition. We currently expect the acquisition to close prior to the end of calendar 2014. See the risk factor titled “We may be unable to close the BinOptics Acquisition or successfully integrate the business and personnel of BinOptics, and may not realize the anticipated synergies and benefits of the BinOptics Acquisition.” in Item 1A. “Risk Factors” in this Annual Report.
We intend to continue to pursue acquisitions of technologies, design teams, products and companies that complement our strengths and help us execute our strategies. Our acquisition strategy is designed to accelerate our revenue growth, expand our technology portfolio, grow our addressable market, and create shareholder value. We believe our management team has a proven track record in identifying, acquiring and successfully integrating companies and technologies in the high-performance analog semiconductor industry.
Available Information
We maintain a website at www.macom.com, including an investors section at which we routinely post important information, such as webcasts of quarterly earnings calls and other investor events in which we participate or host, and any related materials. You may access our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports, as well as other reports relating to us that are filed with or furnished to the SEC, free of charge in the investors section of our website as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC. The public may also read and copy materials we file with the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room, which is located at 100 F Street, NE, Room 1580, Washington, DC 20549. You can obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC also maintains a website that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC at www.sec.gov. The contents of the websites mentioned above are not incorporated into and should not be considered a part of this Annual Report.
14
Table of Contents
Our business involves a high degree of risk. If any of the following risks actually occurs, our business, financial condition or results of operations could suffer. The risks described below are not the only ones facing us. Additional risks not presently known to us or that we currently consider immaterial also may adversely affect our Company.
Risks Relating to Our Business
Our revenue growth is substantially dependent on our successful development and release of new products.
Maintaining or growing our revenue will depend on our ability to timely develop new products for existing and new markets that meet customers’ performance, reliability and price requirements. The development of new products is a highly complex process, and we have in the past and may in the future experience delays and failures in completing the development and introduction of new products. Our successful product development depends on a number of factors, including the following:
| • | the accurate prediction of market requirements, changes in technology and evolving standards; |
| • | the availability of qualified product designers and process technologies needed to solve difficult design challenges in a cost-effective, reliable manner; |
| • | our ability to design products that meet customers’ cost, size and performance requirements; |
| • | our ability to manufacture new products according to customer needs with acceptable manufacturing yields; |
| • | our ability to offer new products at competitive prices; |
| • | the acceptance by customers of our new product designs; |
| • | the identification of and entry into new markets for our products; |
| • | the acceptance of our customers’ products by the market and the lifecycle of such products; |
| • | our ability to deliver products in a timely manner within our customers’ product planning and deployment cycle; and |
| • | our ability to maintain and increase our level of product content in our customers’ systems. |
A new product design effort may last 12 to 18 months or longer, and requires significant investments in engineering hours and materials, as well as sales and marketing expenses, which will not be recouped if the product launch is unsuccessful. We may not be able to design and introduce new products in a timely or cost-efficient manner, and our new products may fail to meet the requirements of the market or our customers, or may be adopted by customers slower than we expect. In that case, we may not reach our expected level of production orders and may lose market share, which could adversely affect our ability to sustain our revenue growth or maintain our current revenue levels.
Various factors may reduce our gross margin, which could negatively affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If we are unable to utilize our design, fabrication, assembly and test facilities at a high level, the significant fixed costs associated with these facilities may not be fully absorbed, resulting in higher average unit costs and lower gross margin. Our various products have different gross margin and increased sales of lower-margin products, such as our products targeted at automotive and other consumer markets, in a given period relative to sales of higher-margin products such as our optical products, may cause us to report lower overall gross margin. In our fourth quarter of fiscal year 2012 and at other times in the past, we have experienced periods where our gross margin declined due to, among other things, reduced factory utilization resulting from reduced customer demand, reduced selling prices and a change in product mix towards lower-margin products. Future market
15
Table of Contents
conditions may adversely affect our revenue and utilization rates and consequently our future gross margin, and this, in turn, could have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, increased raw material costs, changes in manufacturing yields, more complex engineering requirements and other factors may lead to lower margins for us in the future. As a result of these or other factors, we may be unable to maintain or increase our gross margin in future periods and our gross margin may fluctuate from period to period.
Our operating results may fluctuate significantly from period to period. We may not meet investors’ quarterly or annual financial expectations and, as a result, our stock price may decline.
Our quarterly and annual operating results and related expectations may vary significantly in the future based upon a number of factors, many of which are beyond our control. Factors that could cause operating results and related expectations to fluctuate include:
| • | the general economic growth or decline in the U.S. or foreign markets; |
| • | the reduction or cancellation of orders by customers, whether as a result of a loss of market share by us or our customers, changes in the design of customers’ products or slowing demand for our products or customers’ products; |
| • | the amount of new customer orders we both book and ship in any particular fiscal quarter, which accounts for a significant amount of our net revenue in any particular quarter, and which can often be weighted toward the latter part of each fiscal quarter, making the timing of recognition of the associated revenue difficult to forecast with fidelity and susceptible to slippage between quarters; |
| • | the relative linearity of our shipments within any particular fiscal quarter, in that a less linear shipment pattern within a given fiscal quarter tends to result in lower gross margin in that quarter, and a shipment pattern weighted toward the latter part of a fiscal quarter tends to reduce our cash flows from operations in that quarter, as collections of related receivables do not occur until later fiscal periods; |
| • | the gain or loss of a key customer or significant changes in the financial condition of one or more key customers; |
| • | the fluctuations in manufacturing output, yields, capacity levels, quality control or other potential problems or delays we or our subcontractors may experience in the fabrication, assembly, testing or delivery of our products; |
| • | the fluctuations in demand relating to the A&D market due to changes in government programs, budgets or procurement; |
| • | the market acceptance of our products and particularly the timing and success of new product and technology introductions by us, customers or competitors; |
| • | the amount, timing, and relative success of our investments in research and development, which impacts our ability to develop, introduce and market new products and solutions on a timely basis; |
| • | the period-to-period changes in the mix of products we sell, which can result in lower gross margin; |
| • | the availability, quality and cost of semiconductor wafers and other raw materials, equipment, components and internal or outsourced manufacturing, packaging and test capacity, particularly where we have only one qualified source of supply; |
| • | the effects of seasonal and other changes in customer purchasing cycles and component inventory levels; |
| • | the effects of competitive pricing pressures, including decreases in average selling prices of our products; |
| • | the effects of impairment charges associated with intangible assets, including goodwill and acquisition-related intangible assets; |
16
Table of Contents
| • | the loss of key personnel or the shortage of available skilled workers; |
| • | the effects of factors that could cause our reported domestic and foreign income taxes and income tax rate to increase in future periods, such as limits on our ability to utilize net operating losses or tax credits and the geographic distribution of our income, which may change from period to period; and |
| • | the effects of war, natural disasters, acts of terrorism, macroeconomic uncertainty or decline or geopolitical unrest. |
The foregoing factors are difficult to forecast, and these, as well as other factors, could materially and adversely affect our quarterly and annual operating results and related expectations for future periods. In addition, if our operating results in any period do not meet our publicly stated guidance, if any, or the expectations of investors or securities analysts, our stock price may decline. Similarly, any publicly stated guidance we provide in the future may itself fail to meet the expectations of investors or securities analysts, and our stock price may decline as a result.
If our primary markets decline or fail to grow, our revenue and profitability may suffer.
Our future growth depends to a significant extent on the continued growth in usage of advanced electronic systems in our primary markets: Networks, A&D, Automotive and Multi-market. The rate and extent to which these markets grow, if at all, is uncertain. These markets may fail to grow or decline for many reasons, including insufficient consumer demand, lack of access to capital, sequestration or other changes in the U.S. defense budget and procurement processes, changes in regulatory environments, macro-economic factors and changes in network specifications. If demand for electronic systems in which our products are incorporated declines, fails to grow, or grows more slowly than we anticipate, purchases of our products may be reduced, which may adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. In particular, our sales to Ford, which accounted for 19.0% of our revenue for fiscal year 2014 and substantially all of the revenue in our Automotive market, are dependent upon the health of the automotive industry, Ford’s ability to maintain or grow its market share, Ford’s continuing to source parts from us for its current platforms, lack of success by potential competitors in displacing us and Ford’s continuing to design our products into its automotive platforms as they evolve, none of which are assured.
We may be unable to close the BinOptics Acquisition or successfully integrate the business and personnel of BinOptics, and may not realize the anticipated synergies and benefits of the BinOptics Acquisition.
On November 17, 2014, we entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger to acquire BinOptics. The BinOptics Acquisition is subject to various conditions to closing and may not close. If the BinOptics Acquisition does not close, we will have expended significant time and resources and we will not realize the expected benefits from the transaction.
We also may not realize the expected benefits from the BinOptics Acquisition after closing because of integration difficulties or other challenges. The success of the BinOptics Acquisition will depend, in part, on our ability to realize all or some of the anticipated synergies and other benefits from integrating the BinOptics business with our existing businesses. The integration process may be complex, costly, and time-consuming. The potential difficulties we may face in integrating the operations of the BinOptics business include, among others:
| • | failure to implement our business plan for the combined business and expand BinOptics production capacity as planned; |
| • | unexpected losses of key employees, customers or suppliers of BinOptics; |
| • | unanticipated issues in conforming BinOptics standards, processes, procedures and controls with our operations; |
| • | coordinating new product and process development; |
17
Table of Contents
| • | increasing the scope, geographic diversity and complexity of our operations; |
| • | diversion of management’s attention from other business concerns; |
| • | adverse effects on our or BinOptics existing business relationships; |
| • | unanticipated changes in applicable laws and regulations; |
| • | operating risks inherent in BinOptics business and operations; |
| • | unanticipated expenses and liabilities; |
| • | unfamiliarity with BinOptics technology, products and markets, including the high-performance, high-speed laser market generally, which may place us at a competitive disadvantage; and |
| • | other difficulties in the assimilation of BinOptics operations, technologies, products and systems. |
BinOptics may have unanticipated or larger than anticipated liabilities for patent and trademark infringement claims, violations of laws, commercial disputes, taxes and other known and unknown types of liabilities. There may be liabilities that we underestimated or did not discover in the course of performing our due diligence investigation of these entities. We have limited recourse under the merger agreement to recover damages relating to the liabilities of BinOptics and its subsidiaries.
We may not be able to maintain or increase the levels of revenue, earnings or operating efficiency that each of BinOptics and us had achieved or might achieve separately. In addition, we may not accomplish the integration of the BinOptics business smoothly, successfully or within the anticipated costs or timeframe. If we experience difficulties with the integration process or if the BinOptics business deteriorates, the anticipated cost savings, growth opportunities and other synergies of the BinOptics Acquisition may not be realized fully, or at all, or may take longer to realize than expected. If any of the above risks occur, our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows may be materially and adversely impacted, we may fail to meet the expectations of investors or analysts, and our stock price may decline as a result.
We typically depend on orders from a limited number of customers for a significant percentage of our revenue.
In fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, sales to our distributor Richardson and to Ford each accounted for more than 10% of our revenue. Sales to our top 10 direct and distribution customers accounted for an aggregate of 60%, 59% and 55%, respectively, of our revenue. While the composition of our top 10 customers varies from year to year, we expect that sales to a limited number of customers will continue to account for a significant percentage of our revenue for the foreseeable future. The purchasing arrangements with our customers are typically conducted on a purchase order basis that does not require our customers to purchase any minimum amount of our products over a period of time. As a result, it is possible that any of our major customers could terminate their purchasing arrangements with us or significantly reduce or delay the amount of our products that they order, purchase products from our competitors or develop their own products internally. The loss of, or a reduction in, orders from any major customer could cause a decline in revenue and adversely affect our results of operations.
Our investment in research and development may not be successful, which may impact our profitability.
The semiconductor industry requires substantial investment in research and development in order to develop and bring to market new and enhanced technologies and products. Research and development expenses were $73.7 million, $44.6 million and $36.8 million for our fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. In each of the last three fiscal years, we invested in research and development as part of our strategy toward the development of innovative products and solutions to fuel our growth and profitability. We cannot assure you if or when the products and solutions where we have focused our research and development expenditures will become commercially successful. In addition, we may not have sufficient resources to maintain the level of investment in
18
Table of Contents
research and development required to remain competitive or succeed in our strategy. Our efforts to develop new and improved process technologies for use in our products require substantial expenditures that may not generate any return on investment, may take longer than we anticipate to generate a return or may generate a return on investment that is inadequate. In July 2013, we announced that we had licensed 0.5, 0.25 and 0.15 micron GaN process technology from Global Communications Semiconductors, LLC (GCS) and would be installing such process technology to our Lowell, Massachusetts manufacturing facility. This installation effort is expected to be a multi-year process and to involve tens of millions of dollars of investment in capital equipment, license fees and other related costs and expenses. We have in the past and may in the future experience unexpected difficulties, expenses, or delays in installing and qualifying this GaN technology, and ultimately, may not be successful in our efforts, may not realize the competitive advantage we anticipate from the license and porting effort, and may not realize customer demand for the GaN technology that meets our expectations following the installation effort, any of which could lead to reduced revenues and gross margin or otherwise harm our business. Similarly, following the Nitronex Acquisition we have announced a number of strategic plans and positive expectations concerning the future cost structure, manufacturability, market applicability and potential positive impact on our market share of another type of GaN technology called GaN-on-Silicon, which is a focus of Nitronex’s business. We may experience unexpected difficulties, expenses or delays in driving the scale manufacturing, decreased manufacturing cost structure, productization or customer adoption of GaN of any type that we are targeting, and ultimately may not be successful in our efforts, may not realize the competitive advantage or revenues or profits we anticipate from this technology, any of which could lead to reduced revenues and gross margin or otherwise harm our business.
We may incur significant risk and expense in attempting to win new business, and such efforts may never generate revenue.
To obtain new business, we often need to win a competitive selection process to develop semiconductors for use in our customers’ systems, known in the industry as a “design win”. These competitive selection processes can be lengthy and can require us to incur significant and unreimbursed design and development expenditures and dedicate scarce engineering resources in pursuit of a single customer opportunity. We may not win the competitive selection process and may never generate any revenue despite incurring significant design and development expenditures and selling, general and administrative expenses. Failure to obtain a design win sometimes prevents us from supplying components for an entire generation of a customer’s system. This can result in lost or foregone revenue and could weaken our position in future competitive selection processes.
Even when we achieve a design win, success is not assured. Customer qualification and design cycles can be lengthy, and it may take a year or more following a successful design win and product qualification for one of our products to be purchased in volume by the customer. We may experience difficulties manufacturing the part in volume, such as low yields, supply chain delays or shortages, or quality issues. Further, while the customer has successfully qualified our part for use in its system when it awards a design win to us, it may not have qualified all of the other components being sourced for its system, or qualified its system as a whole with its end customers. Any difficulties our customer may experience in completing those qualifications may delay or prevent us from translating the design win into revenue. These risks can be particularly acute in our A&D market, where we may spend material amounts and commit substantial design engineer resources to product development work in support of an OEM customer’s attempt to win business tied to a government contract award, but realize no related revenue or less than expected revenue from that investment based on failure of the OEM to win the business, government program cancellation, federal budget limitations, or otherwise. Any of these events, or any cancellation of a customer’s program or failure of our customer to successfully market its own product after our design win could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations, as we may have incurred significant expense and generated no revenue.
19
Table of Contents
We are subject to order and shipment uncertainties. Our profitability will decline if we fail to accurately forecast customer demand when managing inventory.
We generally sell our products on the basis of purchase orders rather than long-term purchase commitments from our customers. Our customers can typically cancel purchase orders or defer product shipments for some period without incurring liability to us. We typically plan production and inventory levels based on internal forecasts of customer demand, which can be highly unpredictable and can fluctuate substantially, leading to excess inventory write-downs, and resulting negative impacts on gross margin and net income. We have limited visibility into our customers’ inventories, future customer demand, and the product mix that our customers will require, which could adversely affect our production forecasts and operating margins. In a number of markets we serve, large dollar value customer orders scheduled for delivery in the current fiscal quarter may be canceled or rescheduled by the customer for delivery in a future fiscal quarter on short notice, which could cause our reported revenue to vary materially from our prior expectations. In addition, the rapid pace of innovation in our industry could render significant portions of our inventory obsolete. If we overestimate our customers’ requirements, we may have excess inventory, which could lead to obsolete inventory and unexpected costs. Conversely, if we underestimate our customers’ requirements, we may have inadequate inventory, which could lead to foregone revenue opportunities, loss of potential market share and damage to customer relationships as product deliveries may not be made on a timely basis, disrupting our customers’ production schedules. Some of our larger customers also require us to build and maintain minimum inventories and keep them available for purchase at specified locations based on non-binding demand estimates that are subject to change, which exposes us to increased inventory risk and makes it more difficult to manage our working capital. If demand from such customers decreases, we may be left with excess or obsolete inventory we are unable to sell. In response to anticipated long lead times to obtain inventory and materials from outside suppliers and foundries, we periodically order materials and build a stock of finished goods inventory in advance of customer demand. This advance ordering of raw material and building of finished goods inventory has in the past and may in the future result in excess inventory levels or unanticipated inventory write-downs if expected orders fail to materialize, or other factors make our products less saleable. In addition, any significant future cancellation or deferral of product orders could adversely affect our revenue and margins, increase inventory write-downs due to obsolete inventory, and adversely affect our operating results and stock price.
The average selling prices of our products may decrease over time, which could have a material adverse effect on our revenue and gross margin.
It is common in our industry for the average selling price of a given product to decrease over time as production volumes increase, competing products are developed, technology, industry standards and customer platforms evolve, or new technologies featuring higher performance or lower cost emerge. To combat the negative effects that erosion of average selling prices have had in the past and may in the future have on our revenue and gross margin, we attempt to actively manage the prices of our existing products and introduce new process technologies and products in the market that exhibit higher performance, new features that are in demand, or lower manufacturing cost. Despite this strategy, we may experience price erosion in select product platforms or generally in future periods. Failure to maintain our current prices or to successfully execute on our new product development strategy will cause our revenue and gross margin to decline, which could decrease the value of your investment in our common stock.
We face intense competition in our industry, and our inability to compete successfully could negatively affect our operating results.
The semiconductor industry is highly competitive. While we compete with a wide variety of companies, we compete with ADI across most of our primary markets. Our other significant competitors include, among others, Avago, Cobham, Microsemi, RFMD, Skyworks and TriQuint.
We believe future competition could also come from companies developing new alternative technologies, component suppliers based in countries with lower production costs and IC manufacturers achieving higher
20
Table of Contents
levels of integration that exceed the functionality offered by our products. Our customers and suppliers could also develop products that compete with or replace our products. A decision by any of our large customers to design and manufacture ICs internally could have an adverse effect on our operating results. Increased competition could mean lower prices for our products, reduced demand for our products, and a corresponding reduction in our ability to recover development, engineering and manufacturing costs.
Many of our existing and potential competitors have entrenched market positions, historical affiliations with original equipment manufacturers, considerable internal manufacturing capacity, established intellectual property rights, and substantial technological capabilities. Many of them may also have greater financial, technical, manufacturing or marketing resources than we do. Prospective customers may decide not to buy from us due to concerns about our relative size, financial stability or other factors. Our failure to successfully compete could result in lower revenue, decreased profitability and a lower stock price.
We operate in the semiconductor industry, which is cyclical and subject to significant downturns.
The semiconductor industry is highly cyclical and is characterized by constant and rapid technological change, price erosion, product obsolescence, evolving standards, short product lifecycles and significant fluctuations in supply and demand. The industry has historically experienced significant fluctuations in demand and product obsolescence, resulting in product overcapacity, high inventory levels and accelerated erosion of average selling prices. Downturns in many sectors of the electronic systems industry have in the past contributed to extended periods of weak demand for semiconductor products. We have experienced adverse effects on our profitability and cash flows during such downturns in the past, and our business may be similarly harmed by any downturns in the future, particularly if we are unable to effectively respond to reduced demand in a particular market.
We expect to make future acquisitions, dispositions and investments, which involve numerous risks.
We have an active corporate development program and routinely evaluate potential acquisitions of, and investments with or other strategic alliances involving, complementary technologies, design teams, products, and companies. We also may evaluate the merits of a potential divestment of one or more of our existing business lines. We expect to pursue such transactions if appropriate opportunities arise. However, we may not be able to identify suitable transactions in the future, or if we do identify such transactions, we may not be able to complete them on commercially acceptable terms, or at all. We also face intense competition for acquisitions from other acquirers in our industry. These competing acquirers may have significantly greater financial and other resources than us, which may prevent us from successfully pursuing a transaction. In the event we pursue acquisitions, we will face numerous risks including:
| • | difficulties in integrating the personnel, culture, operations, technology or products and service offerings of the acquired company; |
| • | diversion of management’s attention from normal daily operations of our business; |
| • | difficulties in entering markets where competitors have stronger market positions; |
| • | difficulties in improving and integrating the financial reporting capabilities and operating systems of any acquired operations, particularly foreign and formerly private operations, as needed to maintain effective internal control over financial reporting and disclosure controls, and procedures; |
| • | loss of any key personnel of the acquired company as well as their know-how, relationships and expertise, which is common following an acquisition; |
| • | maintaining customer, supplier or other favorable business relationships of acquired operations; |
| • | generating insufficient revenue from completed acquisitions to offset increased expenses associated with any abandoned or completed acquisitions; |
21
Table of Contents
| • | acquiring material or unknown leasehold, environmental, regulatory, infringement, contractual or other liabilities associated with any acquired operations; |
| • | litigation frequently associated with merger and acquisition transactions; and |
| • | increasing expense associated with amortization or depreciation of intangible and tangible assets we acquire. |
Our past acquisitions required or continue to require significant management time and attention relating to the transaction and integration activities. If we fail to properly integrate these acquired companies with ours, we may not receive the expected benefits of the acquisitions. Even if a proposed acquisition is successfully realized and integrated, we may not receive the expected benefits of the transaction.
Past transactions, whether completed or abandoned by us, have resulted, and in the future may result, in significant costs, expenses, liabilities and charges to earnings. The accounting treatment for any acquisition may result in significant amortizable intangible assets which, when amortized, will negatively affect our consolidated results of operations. The accounting treatment for any acquisition may result in significant goodwill, which, if impaired, will negatively affect our consolidated results of operations. Furthermore, we may incur indebtedness or issue equity securities to pay for acquisitions. The incurrence of indebtedness could limit our operating flexibility and be detrimental to our profitability, and the issuance of equity securities would be dilutive to our existing stockholders. Any or all of the above factors may differ from the investment community’s expectations in a given quarter, which could negatively affect our stock price. In addition, as a result of the foregoing, we may not be able to successfully execute acquisitions in the future to the same extent as we have the in the past, if at all.
In the event we make future investments, the investments may decline in value or fail to deliver any strategic benefits we anticipate from them, and we may lose all or part of our investment. In the event we undertake divestments, we may suffer from associated management distraction, damaged customer relationships, failure to realize the perceived strategic, or financial merits of the divestment, or we may incur material indemnity liabilities to the purchaser. Further, the investments may have unanticipated or larger than anticipated liabilities for patent and trademark infringement claims, violations of laws, commercial disputes, taxes and other known and unknown types of liabilities. There may be liabilities that we underestimate or do not discover in the course of performing our due diligence investigation of the investment. We may not have recourse under the transaction documents to recover any damages relating to potential liabilities.
We may incur liabilities for claims of intellectual property infringement relating to our products.
The semiconductor industry is generally subject to frequent litigation regarding patents and other intellectual property rights. Other companies in the industry have numerous patents that protect their intellectual property rights in these areas, and have made in the past and may make in the future, claims that we have infringed or misappropriated their intellectual property rights. Our customers may assert claims against us for indemnification if they receive claims alleging that their or our products infringe others’ intellectual property rights, and have in the past and may in the future choose not to purchase our products based on their concerns over such a pending claim. In the event of an adverse result of any intellectual property rights litigation, we could be required to pay substantial damages for infringement, expend significant resources to develop non-infringing technology, incur material liability for royalty payments or fees to obtain licenses to the technology covered by the litigation or be subjected to an injunction, which could prevent us from selling our products, and materially and adversely affect our revenue and results of operations. Negotiated settlements resolving such claims may require us to pay substantial sums, as was the case in September 2013 when we paid $7.25 million in settlement of a suit alleging intellectual property misappropriation. We cannot be sure that we will be successful in any such non-infringing development or that any such license would be available on commercially reasonable terms, if at all. Any claims relating to the infringement of third-party proprietary rights, even if not meritorious, could result in costly litigation, lost sales, or damaged customer relationships and diversion of management’s attention and resources.
22
Table of Contents
We depend on third parties for products and services required for our business, which may limit our ability to meet customer demand, assure product quality and control costs.
We purchase numerous raw materials, such as ceramic packages, precious metals, semiconductor wafers and ICs, from a limited number of external suppliers. We also currently use several external manufacturing suppliers for assembly and testing of our products, and in some cases for fully-outsourced turnkey manufacturing of our products. We currently expect to increase our use of outsourced manufacturing in the future as a strategy. The ability and willingness of our external suppliers to perform is largely outside of our control. The use of external suppliers involves a number of risks, including the possibility of material disruptions in the supply of key components, the lack of control over delivery schedules, capacity constraints, manufacturing yields, quality and fabrication costs and misappropriation of our intellectual property. If these vendors’ processes vary in reliability or quality, they could negatively affect our products and, therefore, our customer relations and results of operations. We generally purchase raw materials on a purchase order basis and we do not have significant long-term supply commitments from our vendors. Where we do have long-term supply commitments, they may result in our being obligated to purchase more material than we need, materially and negatively impacting our operating results. In terms of relative bargaining power, many of our suppliers are larger than we are, with greater resources, and many of their other customers are larger and have greater resources than we do. If these vendors experience shortages or fail to accurately predict customer demand, they may have insufficient capacity to meet our demand, creating a capacity constraint on our business. They may also choose to supply others in preference to us in times of capacity constraint or otherwise, particularly where the other customers purchase in higher volume. Third-party supplier capacity constraints have in the past and may in the future prevent us from supplying customer demand that we otherwise could have fulfilled at attractive prices. If we have a firm commitment to supply our customer but are unable to do so based on inability or unwillingness of one of our suppliers to provide related materials or services, we may be liable for resulting damages and expense incurred by our customer.
Based on superior performance features, cost parameters or other factors, we utilize sole source suppliers for certain semiconductor packages and other materials, and it is common for one of our outside semiconductor foundries to be our sole supplier for the particular semiconductor fabrication process technologies manufactured at that supplier’s facility. Such supplier concentrations involve the risk of a potential future business interruption if the supplier becomes unable or unwilling to supply us at any point. While in some cases alternate suppliers may exist, because there are limited numbers of third-party wafer suppliers that use the process technologies we select for our products and that have sufficient capacity to meet our needs, it may not be possible or may be expensive to find an alternative source of supply. Even if we are able to find an alternative source, moving production to an alternative supplier requires an extensive qualification or re-qualification process that could prevent or delay product shipments, or disrupt customer’s production schedules, which could harm our business. In addition, some of our external foundry suppliers compete against us in the market in addition to being our supplier. The loss of a supplier can also significantly harm our business and operating results. A supplier may discontinue supplying us if its business is not sufficiently profitable, for competitive reasons or otherwise. We have in the past and may in the future have our supply relationship discontinued by an external foundry, causing us to experience supply chain disruption, customer dissatisfaction, loss of business and increased cost.
If we lose key personnel or fail to attract and retain key personnel, we may be unable to pursue business opportunities or develop our products.
We believe our continued ability to recruit, hire, retain and motivate highly-skilled engineering, operations, sales, administrative and managerial personnel is key to our future success. Competition for these employees is intense, particularly with respect to qualified engineers. Our failure to retain our present employees and hire additional qualified personnel in a timely manner and on reasonable terms could harm our competitiveness and results of operations. In addition, from time to time, we may recruit and hire employees from our competitors, customers, suppliers and distributors, which could result in liability to us, and has in the past and could in the
23
Table of Contents
future, damage our business relationship with these parties. None of our senior management team is contractually bound to remain with us for a specified period, and we generally do not maintain key person life insurance covering our senior management. The loss of any member of our senior management team could strengthen a competitor or harm our ability to implement our business strategy.
Sources for certain components and materials are limited, which could result in interruptions, delays, or reductions in product shipments.
Our industry may be affected from time to time by limited supplies of certain key components and materials. We have in the past and may in the future, experience delays or reductions in supply shipments, which could reduce our revenue and profitability. If key components or materials are unavailable, our costs could increase and our revenue could decline.
In particular, our manufacturing headquarters, design facilities, assembly and test facilities, and supply chain, and those of our contract manufacturers, are subject to risk of catastrophic loss due to fire, flood, or other natural or man-made disasters. The majority of our semiconductor products are fabricated in our Lowell, Massachusetts headquarters, where our only internal wafer fab is located. The majority of the internal and outsourced assembly and test facilities we utilize are located in the Pacific Rim, and some of our internal design, assembly and test facilities are located in California regions with above average seismic and severe weather activity. In addition, our research and development personnel are concentrated in a few locations, primarily our headquarters, Santa Clara, California, Sydney, Australia, Belfast, Northern Ireland and Cork, Ireland locations, with the expertise of the personnel at each such location generally focused on one or two specific areas. Any catastrophic loss or significant damage to any of these facilities would likely disrupt our operations, delay production, shipments and revenue, and result in significant expenses to repair or replace the facility, and in some instances, could significantly curtail our research and development efforts in a particular product area or primary market, which could have a material adverse effect on our operations. For example, in October 2011, heavy monsoon rains in Thailand caused widespread flooding affecting major cities and industrial parks where there is a concentration of semiconductor manufacturing, assembly and test sites. One of our contract manufacturing suppliers located in Thailand was affected by the flooding and, as a result of the flooding of our affected contract manufacturer, $2.7 million of orders that were scheduled for shipment to our customers in the three months ended December 30, 2011 were delayed into the second quarter of fiscal year 2012, or were canceled. In particular, any catastrophic loss at our headquarters facility would materially and adversely affect our business and financial results, revenue and profitability.
Our failure to continue to keep pace with new or improved semiconductor process technologies could impair our competitive position.
Semiconductor manufacturers constantly seek to develop new and improved semiconductor process technologies. Our future success depends in part upon our ability to continue to gain access to these semiconductor process technologies, internally or externally, in order to adapt to emerging customer requirements and competitive market conditions. We may be unable to internally develop such technologies successfully, and may be unable to gain access to them from merchant foundries or other sources on commercially reasonable terms, or at all. If we fail for any reason to remain abreast of new and improved semiconductor process technologies as they emerge, we may lose market share and our revenue and gross margin may decline, which could adversely affect our operating results.
Minor deviations in the manufacturing process can cause substantial manufacturing yield loss or even cause halts in production, which could have a material adverse effect on our revenue and gross margin.
Our products involve complexities in both their design and the semiconductor process technology employed in their fabrication. In many cases, the products are also assembled in customized packages or feature high levels of integration. Our products must meet exacting customer specifications for quality, performance and reliability.
24
Table of Contents
Our manufacturing yield, or the percentage of units of a given product in a given period that is usable relative to all such units produced, is a combination of yields including wafer fabrication, assembly, and test yields. Due to the complexity of our products, we periodically experience difficulties in achieving acceptable yields as even minor deviations in the manufacturing process can cause substantial manufacturing yield loss or even cause halts in production. Our customers may also test our components once they have been assembled into their products. The number of usable products that result from our production process can fluctuate as a result of many factors, including the following:
| • | design errors; |
| • | defects in photomasks, which are used to print circuits on wafers; |
| • | minute impurities in materials used; |
| • | contamination of the manufacturing environment; |
| • | equipment failure or variations in the manufacturing processes; |
| • | losses from broken wafers or other human error; |
| • | defects in packaging; and |
| • | issues and errors in testing. |
Typically, for a given level of sales, when our yields improve, our gross margin improves. When our yields decrease, our unit costs are typically higher, our gross margin is lower and our profitability is adversely affected, any or all of which can harm our results of operations and lower our stock price.
We depend on third-party sales representatives and distributors for a material portion of our revenues.
We sell many of our products to customers through independent sales representatives and distributors, as well as through our direct sales force. We are unable to predict the extent to which our independent sales representatives and distributors will be successful in marketing and selling our products. Moreover, many of our independent sales representatives and distributors also market and sell competing products. Our relationships with our representatives and distributors typically may be terminated by either party at any time, and do not require them to buy any of our products. Sales to distributors accounted for 22.5% of our revenue in fiscal year 2014, and sales to our largest distributor, Richardson, represented 15.0% of our revenue in the same period. If our distributors cease doing business with us or fail to successfully market and sell our products, our ability to sustain and grow our revenue could be materially adversely affected.
Our internal and external manufacturing, assembly and test model subjects us to various manufacturing and supply risks.
We operate a semiconductor wafer processing and manufacturing facility at our headquarters in Lowell, Massachusetts. This facility is also our primary internal design and assembly and test facility. We maintain other internal assembly and test operation facilities as well, including leased sites in Long Beach, California and Hsinchu, Taiwan. We also use multiple external foundries for outsourced semiconductor wafer supply, as well as multiple domestic and Asian assembly and test suppliers to assemble and test our products. A number of factors will affect the future success of these internal manufacturing facilities and outsourced supply and service arrangements, including the following:
| • | the level of demand for our products; |
| • | our ability to expand and contract our facilities and purchase commitments in a timely and cost-effective manner in response to changes in demand for our products; |
| • | our ability to generate revenue in amounts that cover the significant fixed costs of operating our facilities; |
25
Table of Contents
| • | our ability to qualify our facilities for new products in a timely manner; |
| • | the availability of raw materials, including GaAs, SiGe and InP substrates and high purity source materials such as gallium, aluminum, arsenic, carbon, nitrite, indium and silicon; |
| • | our manufacturing cycle times and yields; |
| • | the political and economic risks associated with our reliance on outsourced Asian assembly and test suppliers; |
| • | the location of our facilities and those of our outsourced suppliers; |
| • | natural disasters impacting our facilities and those of our outsourced suppliers; |
| • | our ability to hire, train, manage and retain qualified production personnel; |
| • | our compliance with applicable environmental and other laws and regulations; and |
| • | our ability to avoid prolonged periods of downtime or high levels of scrap in our and our suppliers’ facilities for any reason. |
We may experience difficulties in managing any future growth.
To successfully conduct business in a rapidly evolving market, we must effectively plan and manage any current and future growth. Our ability to do so will be dependent on a number of factors, including:
| • | maintaining access to sufficient manufacturing capacity to meet customer demands; |
| • | arranging for sufficient supply of key raw materials and services to avoid shortages or supply bottlenecks; |
| • | building out our administrative infrastructure at the proper pace to support any current and future sales growth while maintaining operating efficiencies; |
| • | adhering to our high quality and process execution standards, particularly as we hire and train new employees and during periods of high volume; |
| • | managing the various components of our working capital effectively; |
| • | upgrading our operational and financial systems, procedures and controls, including improvement of our accounting and internal management systems; and |
| • | maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction. |
If we do not effectively manage any future growth, we may not be able to take advantage of attractive market opportunities, our operations may be impacted, and we may experience delays in delivering products to our customers or damaged customer relationships, and achieve lower than anticipated revenue and decreased profitability.
We may not realize the expected benefits of our recent restructuring activities and other initiatives designed to reduce costs and increase revenue across our operations.
We have pursued a number of restructuring initiatives designed to reduce costs and increase revenue across our operations. These initiatives included reductions in our number of manufacturing facilities and significant workforce reductions in certain areas as we realigned our business. Additional initiatives included establishing certain operations closer in location to our global customers and evaluating functions that may be more efficiently performed through outsourcing arrangements. These initiatives have been substantial in scope and disruptive to some of our historical operations. We may not realize the expected benefits of these new initiatives.
26
Table of Contents
As a result of these initiatives, we have incurred restructuring or other charges and we may in the future experience disruptions in our operations, loss of personnel and difficulties in delivering products in a timely fashion. In fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, we incurred restructuring charges of $14.8 million, $1.1 million and $1.9 million, respectively, consisting primarily of employee severance and related costs resulting from reductions in our workforce.
Our business could be harmed if systems manufacturers choose not to use components made of compound semiconductor materials we utilize.
Silicon semiconductor technologies are the dominant process technologies for the manufacture of ICs in high-volume, commercial markets, and the performance of silicon ICs continues to improve. While we use silicon for some applications, we also often use compound semiconductor technologies such as GaAs, InP, SiGe, or GaN to deliver reliable operation at higher power, higher frequency, or smaller form factor than a silicon solution has historically allowed. While these compound semiconductor materials offer high-performance features, it is generally more difficult to design and manufacture products with reliability and in volume using them. GaN and InP, in particular, are newer process technologies that do not have as extensive a track record of reliable performance in the field as many of the competing process technologies. Compound semiconductor technology tends to be more expensive than silicon technology due to its above-described challenges, and the generally lower volumes at which parts in those processes tend to be manufactured relative to silicon parts for high-volume consumer applications.
System designers in some markets may be reluctant to adopt our non-silicon products or may be likely to adopt silicon products in lieu of our products if silicon products meeting their demanding performance requirements are available, because of:
| • | their unfamiliarity with designing systems using our products; |
| • | their concerns related to manufacturing costs and yields; |
| • | their unfamiliarity with our design and manufacturing processes; or |
| • | the uncertainties about the relative cost effectiveness of our products compared to high-performance silicon components. |
We cannot be certain that additional systems manufacturers will design our compound semiconductor products into their systems or that the companies that have utilized our products will continue to do so in the future. Improvements in the performance of available silicon process technologies and solutions could result in a loss of market share on our part. If our products fail to achieve or maintain market acceptance for any of the above reasons, our results of operations will suffer.
We may incur material costs and our business may be interrupted in connection with consolidation and outsourcing initiatives.
We have a number of ongoing strategic initiatives aimed at reducing our long-term operating cost model, including the outsourcing of various manufacturing functions to third party suppliers and consolidation of our operations within existing facilities. While the goal of these actions is to reduce recurring fixed cost, there are associated restructuring charges and execution risks associated with these initiatives. Exiting a leased site may involve contractual or negotiated exit payments with the landlord, temporary holding over at an increased lease rate, costs to perform restoration work required by the lease, or associated environmental liability, any of which may be material in amount. Consolidation of operations and outsourcing may involve substantial capital expenses and the transfer of manufacturing processes and personnel from one site to another, with resultant startup issues at the receiving site and need for re-qualification of the transitioned operations with major customers and for ISO or other certifications. We may experience shortages of affected products, delays and higher than expected expenses. Affected employees may be distracted by the transition or may seek other employment, which could cause our overall operational efficiency to suffer.
27
Table of Contents
We are subject to risks from our international sales and operations.
We have operations in Europe, Asia and Australia, and customers around the world. As a result, we are subject to regulatory, geopolitical and other risks associated with doing business outside the U.S. Global operations involve inherent risks, including currency controls, currency exchange rate fluctuations, tariffs, required import and export licenses, associated delays and other related international trade restrictions and regulations.
The legal system in many of the regions where we conduct business can lack transparency in certain respects relative to that of the U.S. and can accord local government authorities a higher degree of control and discretion over business than is customary in the U.S. This makes the process of obtaining necessary regulatory approvals and maintaining compliance inherently more difficult and unpredictable. In addition, the protection accorded to proprietary technology and know-how under these legal systems may not be as strong as in the U.S., and, as a result, we may lose valuable trade secrets and competitive advantages. The cost of doing business in European jurisdictions can also be higher than in the U.S. due to exchange rates, local collective bargaining regimes, and local legal requirements and norms regarding employee benefits and employer-employee relations, in particular. We are also subject to U.S. legal requirements related to our foreign operations, including the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act.
Sales to customers located outside the U.S. accounted for 49.1%, 41.3% and 47.1% of our revenue for the fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. We expect that revenue from international sales will continue to be a significant part of our total revenue. Because the majority of our foreign sales are denominated in U.S. dollars, our products become less price-competitive in countries with currencies that are low or are declining in value against the U.S. dollar. Also, we cannot be sure that our international customers will continue to accept orders denominated in U.S. dollars. If they do not, our reported revenue and earnings will become more directly subject to foreign exchange fluctuations. Some of our customer purchase orders and agreements are governed by foreign laws, which may differ significantly from U.S. laws. We may be limited in our ability to enforce our rights under such agreements and to collect amounts owed to us.
The majority of our assembly, packaging, and test vendors are located in Asia. We generally do business with our foreign assemblers in U.S. dollars. Our manufacturing costs could increase in countries with currencies that are increasing in value against the U.S. dollar. Also, our international manufacturing suppliers may not continue to accept orders denominated in U.S. dollars. If they do not, our costs will become more directly subject to foreign exchange fluctuations. From time to time we may attempt to hedge our exposure to foreign currency risk by buying currency contracts or otherwise, and any such efforts involve expense and associated risk that the currencies involved may not behave as we expect, and we may lose money on such hedging strategies or not properly hedge our risk.
In addition, if terrorist activity, armed conflict, civil, economic or military unrest or political instability occurs in the U.S. or other locations, such events may disrupt our manufacturing, assembly, logistics, security and communications, and could also result in reduced demand for our products. We have in the past and, may again in the future, experience difficulties relating to employees traveling in and out of countries facing civil unrest or political instability, and with obtaining travel visas for our employees. Major health pandemics could also adversely affect our business and our customer order patterns. We could also be affected if labor issues disrupt our transportation arrangements or those of our customers or suppliers. There can be no assurance that we can mitigate all identified risks with reasonable effort. The occurrence of any of these events could have a material adverse effect on our operating results.
Our business could be adversely affected if we experience product returns, product liability and defects claims.
Our products are complex and frequently operate in high-performance, challenging environments. We may not be able to anticipate all of the possible performance or reliability problems that could arise with our products after they are released to the market. If such problems occur or become significant, we may experience reduced
28
Table of Contents
revenue and increased costs related to product recalls, inventory write-offs, warranty or damage claims, delays in, cancellations of, or returns of product orders and other expenses. The many materials and vendors used in the manufacture of our products increase the risk that some defects may escape detection in our manufacturing process and subsequently affect our customers, even in the case of long-standing product designs. Our use of newly-developed or less mature semiconductor process technologies, such as GaN and InP, which have a less extensive track record of reliability in the field than other more mature process technologies, also increases the risk of performance and reliability problems. These matters have arisen in our operations from time to time in the past, have resulted in significant expense to us per occurrence, and will likely occur again in the future. The occurrence of defects could result in product returns and liability claims, reduced product shipments, the loss of customers, the loss of or delay in market acceptance of our products, harm to our reputation, diversion of management’s time and resources, lower revenue, higher expenses and reduced profitability. Any warranty or other rights we may have against our suppliers for quality issues caused by them may be more limited than those our customers have against us, based on our relative size, bargaining power, or otherwise. In addition, even if we ultimately prevail, such claims could result in costly litigation, divert management’s time and resources and damage our customer relationships.
We also face exposure to potential liability resulting from the fact that some of our customers integrate our products into consumer products such as automobiles or mobile communication devices, which are then sold to consumers in the marketplace. We may be named in product liability claims even if there is no evidence that our products caused a loss. Product liability claims could result in significant expenses in connection with the defense of such claims and possible damages. In addition, we may be required to participate in a recall if our products prove to be defective. Any product recall or product liability claim brought against us, particularly in high-volume consumer markets, could have a material negative impact on our reputation, business, financial condition or results of operations.
The outcome of litigation in which we are involved is unpredictable and an adverse decision in any such matter could subject us to damage awards and lower the market price of our stock.
From time to time we are a party to litigation matters such as those described in Part II. Item 1, “Legal Proceedings” of this Annual Report. These and any other future disputes, litigations, investigations, administrative proceedings or enforcement actions we may be involved in may divert financial and management resources that would otherwise be used to benefit our operations, result in negative publicity and harm our customer or supplier relationships. Although we intend to contest such matters vigorously, we cannot assure you that their outcome will be favorable to us. An adverse resolution of any such matter in the future, including the results of any amicable settlement, could subject us to material damage awards or settlement payments or otherwise materially harm our business.
Our financial results may be adversely affected by increased tax rates and exposure to additional tax liabilities.
Our effective tax rate is highly dependent upon the geographic composition of our worldwide earnings and tax regulations governing each region, each of which can change from period to period. We are subject to income taxes in both the U.S. and various foreign jurisdictions, and significant judgment is required to determine our worldwide tax liabilities. Our effective tax rate as well as the actual tax ultimately payable could be adversely affected by changes in the amount of our earnings attributable to countries with differing statutory tax rates, changes in the valuation of our deferred tax assets, changes in tax laws or tax rates (particularly in the U.S. or Ireland), increases in non-deductible expenses, the availability of tax credits, material audit assessments, or repatriation of non-U.S. earnings, each of which could materially affect our profitability. Any significant increase in our effective tax rates could materially reduce our net income in future periods and decrease the value of your investment in our common stock.
Changes in tax laws are introduced from time to time to reform U.S. taxation of international business activities. Depending on the final form of legislation enacted, if any, these consequences may be significant for
29
Table of Contents
us due to the large scale of our international business activities. If any of these proposals are enacted into legislation, they could have material adverse consequences on the amount of tax we pay and, thereby, on our financial position and results of operations.
Our limited ability to protect our proprietary information and technology may adversely affect our ability to compete.
Our future success and ability to compete is dependent in part upon our protection of our proprietary information and technology through patent filings and otherwise. We cannot be certain that any patents we apply for will be issued or that any claims allowed from pending applications will be of sufficient scope or strength to provide meaningful protection or commercial advantage. Our competitors may also be able to design around our patents. The laws of some countries in which our products are or may be developed, manufactured, or sold, may not protect our products or intellectual property rights to the same extent as U.S. laws, increasing the possibility of piracy of our technology and products. Although we intend to vigorously defend our intellectual property rights, we may not be able to prevent misappropriation of our technology or may need to expend significant financial and other resources in defending our rights.
In addition, we rely on trade secrets, technical know-how and other unpatented proprietary information relating to our product development and manufacturing activities. We try to protect this information by entering into confidentiality agreements with employees and other parties. We cannot be sure that these agreements will be adequate and will not be breached, that we would have adequate remedies for any breach or that our trade secrets and proprietary know-how will not otherwise become known or independently discovered by others.
Additionally, our competitors may independently develop technologies that are substantially equivalent or superior to our technology. Despite our efforts to protect our proprietary rights, unauthorized parties may attempt to copy, or otherwise obtain or use our products or technology. Patent litigation is expensive, and our ability to enforce our patents and other intellectual property, is limited by our financial resources and is subject to general litigation risks. If we seek to enforce our rights, we may be subject to claims that the intellectual property rights are invalid, are otherwise not enforceable, or are licensed to the party against whom we assert a claim. In addition, our assertion of intellectual property rights could result in the other party seeking to assert alleged intellectual property rights of its own against us, which is a frequent occurrence in such litigations.
If we fail to comply with export control regulations we could be subject to substantial fines or other sanctions, including loss of export privileges.
Certain of our products are subject to the Export Administration Regulations, administered by the Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry Security, which require that we obtain an export license before we can export products or technology to specified countries. Other products are subject to the International Traffic in Arms Regulations, which restrict the export of information and material that may be used for military or intelligence applications by a foreign person. U.S. regulators have announced “export control reform” that is expected to change many of the rules applicable to us in this area in the future in ways we do not yet fully understand, and we could experience challenges in complying with the new rules as they become effective, or face difficulties or an inability to ship products to certain countries and customers.
We are also subject to U.S. import regulations and the import and export regimes of other countries in which we operate. Failure to comply with these laws could result in sanctions by the government, including substantial monetary penalties, denial of export privileges and debarment from government contracts. Export and import regulations may create delays in the introduction of our products in international markets, or prevent the export or import of our products to certain countries or customers altogether. Any change in export or import regulations or related legislation, shift in approach by regulators to the enforcement or scope of existing regulations, changes in the interpretation of existing regulations by regulators or change in the countries, persons or technologies targeted by such regulations, could harm our business by resulting in decreased use of our products by, or our
30
Table of Contents
decreased ability to export or sell our products to, existing or potential customers with international operations. In addition, our sale of our products to or through third-party distributors, resellers and sales representatives creates the risk that any violation of these laws they may engage in may cause disruption in our markets or otherwise bring liability on us.
We face risks associated with government contracting.
Some of our revenue is derived from contracts with agencies of the U.S. government or subcontracts with its prime contractors. Under some of our government subcontracts, we are required to maintain secure facilities and to obtain security clearances for personnel involved in performance of the contract, in compliance with applicable federal standards. If we were unable to comply with these requirements, or if personnel critical to our performance of these contracts were to lose their security clearances, we might be unable to perform these contracts or compete for other projects of this nature, which could adversely affect our revenue.
We may need to modify our activities or incur substantial costs to comply with environmental laws, and if we fail to comply with environmental laws, we could be subject to substantial fines or be required to change our operations.
We are subject to a variety of international, federal, state and local governmental regulations directed at preventing or mitigating climate change and other environmental harms, as well as to the storage, discharge, handling, generation, disposal and labeling of toxic or other hazardous substances used to manufacture our products. If we fail to comply with these regulations, substantial fines could be imposed on us, and we could be required to suspend production, alter manufacturing processes, cease operations or remediate polluted land, air or groundwater, any of which could have a negative effect on our revenue, results of operations and business. Failure to comply with environmental regulations could subject us to civil or criminal sanctions and property damage or personal injury claims. Compliance with current or future environmental laws and regulations could restrict our ability to expand our facilities or build new facilities, or require us to acquire additional expensive equipment, modify our manufacturing processes, or incur other substantial expenses which could harm our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, under some of these laws and regulations, we could be held financially responsible for remedial measures if our properties or, those nearby are contaminated, even if we did not cause the contamination. We have incurred in the past and may in the future incur environmental liability based on the actions of prior owners, lessees or neighbors of sites we have leased or may lease in the future, or sites we become associated with due to acquisitions. We cannot predict:
| • | changes in environmental or health and safety laws or regulations; |
| • | the manner in which environmental or health and safety laws or regulations will be enforced, administered or interpreted; |
| • | our ability to enforce and collect under any indemnity agreements and insurance policies relating to environmental liabilities; or |
| • | the cost of compliance with future environmental or health and safety laws or regulations or the costs associated with any future environmental claims, including the cost of clean-up of currently unknown environmental conditions. |
In addition to the costs of complying with environmental, health and safety requirements, we may in the future incur costs defending against environmental litigation brought by government agencies, lessors at sites we currently lease or have been associated with in the past and other private parties. We may be defendants in lawsuits brought by parties in the future alleging environmental damage, personal injury or property damage. A significant judgment or fine levied against us, or agreed settlement payment, could materially harm our business, financial condition and results of operations.
31
Table of Contents
Environmental regulations such as the WEEE and RoHS directives limit our flexibility and may require us to incur material expense.
Various countries require companies selling a broad range of electrical equipment to conform to regulations such as the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) and the European Directive 2002/95/Ec on Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS). New environmental standards such as these could require us to redesign our products in order to comply with the standards, require the development of compliance administration systems or otherwise limit our flexibility in running our business or require us to incur substantial compliance costs. For example, RoHS requires that certain substances be removed from most electronic components. The WEEE directive makes producers of electrical and electronic equipment financially responsible for specified collection, recycling, treatment and disposal of past and future covered products. We have already invested significant resources into complying with these regimes, and further investments may be required. Alternative designs implemented in response to regulation may be more costly to produce, resulting in an adverse effect on our gross profit margin. If we cannot develop compliant products in a timely fashion or properly administer our compliance programs, our revenue may also decline due to lower sales, which would adversely affect our operating results. Further, if we were found to be non-compliant with any rule or regulation, we could be subject to fines, penalties and/or restrictions imposed by government agencies that could adversely affect our operating results.
Customer demands and new regulations related to “conflict” minerals may force us to incur additional expenses and liabilities.
In August 2012, the SEC adopted its final rule to implement Section 1502 of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act regarding disclosure and reporting requirements for companies who use “conflict” minerals mined from the Democratic Republic of Congo and adjoining countries in their products. In the semiconductor industry, these minerals are most commonly found in metals used in the manufacture of semiconductor devices and related assemblies. These new requirements could adversely affect our ability to source related minerals and metals and increase our related cost. We will face difficulties and increased expense associated with complying with the disclosure requirements, such as costs related to determining the source of any conflict minerals used in our products. Continued timely reporting is dependent upon the improvement and implementation of new systems and processes and information supplied by our suppliers of products that contain, or potentially contain, conflict minerals. Also, our supply chain is complex, and some suppliers may be unwilling to share related confidential information regarding the source of their products, or may provide us information that is inaccurate or inadequate. If those risks arise, or if our processes in obtaining that information do not fulfill the SEC’s requirements, we may face both reputational challenges and SEC enforcement risks based on our inability to sufficiently verify the origins of the subject minerals and metals or otherwise. More recently, Executive Orders issued by the President of the U.S. have increased sanctions in this area as well, which may impact us in the scenarios described above. Moreover, we may encounter challenges to satisfy any related requirements of our customers, which may be different from or more onerous than the requirements of the related SEC rules and Executive Orders. If we cannot satisfy these customers, they may choose a competitor’s products or may choose to disqualify us as a supplier, and we may have to write off inventory in the event that it becomes unsalable as a result of these regulations.
32
Table of Contents
Our term loan and revolving credit facility could result in outstanding debt with a claim to our assets that is senior to that of our stockholders, and may have other adverse effects on our results of operations.
As of October 3, 2014, we have a term loan outstanding of $349.1 million and revolving credit facility with a syndicate of lenders with a potential future borrowing availability of up to $100.0 million, subject to compliance with financial and other covenants. As of October 3, 2014, we had no outstanding borrowings under the revolving credit facility. However, we currently intend to draw approximately $100 million on the revolving credit facility to partially fund the BinOptics Acquisition. The facility is secured by a first priority lien on all domestic subsidiaries. The amount of our indebtedness could have important consequences, including the following:
| • | our ability to obtain additional financing in the future for working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions, general corporate or other purposes may be limited; |
| • | our ability to make distributions to our stockholders in a sale or liquidation until any balance on the line is repaid in full; |
| • | we may be more vulnerable to economic downturns, less able to withstand competitive pressures and less flexible in responding to changing business and economic conditions; |
| • | our cash flow from operations will be allocated to the payment of the principal of, and interest on, any outstanding indebtedness; and |
| • | we cannot assure you that our business will generate sufficient cash flow from operations or other sources to enable us to meet our payment obligations under the facility and to fund other liquidity needs. |
Our credit facility also contains certain restrictive covenants that may limit or eliminate our ability to incur additional debt, sell, lease or transfer our assets, pay dividends, make capital expenditures, investments and loans, make acquisitions, guarantee debt or obligations, create liens, enter into transactions with our affiliates, enter into new lines of business and enter into certain merger, consolidation or other reorganizations transactions. These restrictions could limit our ability to withstand downturns in our business or the economy in general or to take advantage of business opportunities that may arise, any of which could place us at a competitive disadvantage relative to our competitors that are not subject to such restrictions. If we breach a loan covenant, the lenders could either refuse to lend funds to us or accelerate the repayment of any outstanding borrowings under the credit facility. We might not have sufficient assets to repay such indebtedness upon a default. If we are unable to repay the indebtedness, the lenders could initiate a bankruptcy proceeding against us or collection proceedings with respect to our subsidiaries securing the facility, which could materially decrease the value of our common stock.
We are a holding company and rely on dividends, distributions and other payments, advances and transfers of funds from our subsidiaries to meet our obligations.
As a holding company, we derive substantially all of our cash flow from our subsidiaries. Because we conduct our operations through our subsidiaries, we depend on those entities for dividends and other payments or distributions to meet our operating needs. Legal and contractual restrictions in any existing and future outstanding indebtedness we or our subsidiaries incur may limit our ability to obtain cash from our subsidiaries. The deterioration of the earnings from, or other available assets of, our subsidiaries for any reason could limit or impair their ability to pay dividends or other distributions to us.
Variability in self-insurance liability estimates could adversely impact our results of operations.
We self-insure for employee health insurance and workers’ compensation insurance coverage up to a predetermined level, beyond which we maintain stop-loss insurance from a third-party insurer. Our aggregate exposure varies from year to year based upon the number of participants in our insurance plans. We estimate our
33
Table of Contents
self-insurance liabilities using an analysis provided by our claims administrator and our historical claims experience. Our accruals for insurance reserves reflect these estimates and other management judgments, which are subject to a high degree of variability. If the number or severity of claims for which we self-insure increases, it could cause a material and adverse change to our reserves for self-insurance liabilities, as well as to our earnings.
We may be subject to liabilities based on alleged links between the semiconductor manufacturing process and certain illnesses and birth defects.
In recent years, there has been increased media scrutiny and associated reports regarding a potential link between working in semiconductor manufacturing clean room environments and birth defects and certain illnesses, primarily cancer. Regulatory agencies and industry associations have begun to study the issue to determine if any actual correlation exists. Because we utilize clean rooms, we may become subject to liability claims alleging personal injury. In addition, these reports may also affect our ability to recruit and retain employees. A significant judgment against us or material defense costs could harm our reputation, business, financial condition and results of operations.
We rely on third parties to provide corporate infrastructure services necessary for the operation of our business. Any failure of one or more of our vendors to provide these services could have a material adverse effect on our business.
We rely on third-party vendors to provide critical corporate infrastructure services, including, among other things, certain services related to information technology and network development and monitoring. We depend on these vendors to ensure that our corporate infrastructure will consistently meet our business requirements. The ability of these third-party vendors to successfully provide reliable, high quality services is subject to technical and operational uncertainties that are beyond our control. While we may be entitled to damages if our vendors fail to perform under their agreements with us, our agreements with these vendors limit the amount of damages we may receive. In addition, we do not know whether we will be able to collect on any award of damages or that any such damages would be sufficient to cover the actual costs we would incur as a result of any vendor’s failure to perform under its agreement with us. Any failure of our corporate infrastructure could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. Upon expiration or termination of any of our agreements with third-party vendors, we may not be able to replace the services provided to us in a timely manner or on terms and conditions, including service levels and cost, that are favorable to us, and a transition from one vendor to another vendor could subject us to operational delays and inefficiencies until the transition is complete.
Risks Relating to Ownership of our Common Stock
The market price of our common stock may be volatile, which could result in substantial losses for investors.
You should consider an investment in our common stock risky and invest only if you can withstand a significant loss and wide fluctuations in the market value of your investment. In addition to the risks described in this report, other factors that may cause the market price of our common stock to fluctuate include:
| • | changes in general economic, industry and market conditions; |
| • | domestic and international economic factors unrelated to our performance; |
| • | actual or anticipated fluctuations in our quarterly operating results; |
| • | changes in or failure to meet publicly disclosed expectations as to our future financial performance, as was the case in August 2012 when the trading price of our common stock declined approximately 21% on the day following our public announcement of lower than expected revenue, gross margin and business outlook figures; |
34
Table of Contents
| • | changes in securities analysts’ estimates of our financial performance or lack of research and reports by industry analysts; |
| • | changes in market valuations or earnings of similar companies; |
| • | addition or loss of significant customers; |
| • | announcements by us or our competitors, customers or suppliers of significant products, contracts, acquisitions, strategic partnerships or other events; |
| • | developments or disputes concerning patents or proprietary rights, including any injunction issued or material sums paid for damage awards, settlement payments, license fees, attorney’s fees or other litigation expenses associated with intellectual property lawsuits we may initiate, or in which we may be named as defendants; |
| • | failure to complete significant sales; |
| • | developments concerning current or future strategic alliances or acquisitions; |
| • | any future sales of our common stock or other securities; and |
| • | additions or departures of directors, executives or key personnel. |
Furthermore, the stock markets recently have experienced price and volume fluctuations that have affected and continue to affect the market prices of equity securities of many companies. These fluctuations often have been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of those companies. These broad market and industry fluctuations, as well as general economic, political, and market conditions such as recessions, interest rate changes or international currency fluctuations, may negatively impact the market price of our common stock. In the past, companies that have experienced volatility in the market price of their stock have been subject to securities class action litigation. We may be the target of this type of litigation in the future. Securities litigation against us could result in substantial costs and divert our management’s attention from other business concerns, which could seriously harm our business.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or reports about our business, or publish negative reports about our business, our stock price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our common stock will depend on the research and reports that securities or industry analysts publish about us or our business. We do not have any control over these analysts. If one or more of the analysts who cover us downgrade our common stock or change their opinion of our common stock, our stock price would likely decline. If one or more of these analysts cease their coverage of us or fail to regularly publish reports on us, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which could cause our stock price or trading volume to decline.
Our common stock price may decline if a substantial number of shares are sold in the market by our stockholders.
Future sales of substantial amounts of shares of our common stock by our existing stockholders in the public market, or the perception that these sales could occur, may cause the market price of our common stock to decline. Increased sales of our common stock in the market for any reason could exert significant downward pressure on our stock price. These sales also might make it more difficult for us to sell equity or equity-related securities in the future at a time and price we deem appropriate.
Some of our stockholders can exert control over us, and they may not make decisions that reflect our interests or those of other stockholders.
Our largest stockholders control a significant amount of our outstanding common stock. As of October 3, 2014, John and Susan Ocampo beneficially owned 52.6% of our common stock and certain investment funds affiliated with Summit Partners, L.P. owned 19.9% of our common stock on an as-converted basis. As a result,
35
Table of Contents
these stockholders will be able to exert a significant degree of influence over our management and affairs and control over matters requiring stockholder approval, including the election of our directors and approval of significant corporate transactions. In addition, this concentration of ownership may delay or prevent a change in control of us and might affect the market price of our securities. In addition, the interests of these stockholders may not always coincide with your interests or the interests of other stockholders.
We may engage in future capital-raising transactions that dilute our stockholders or cause us to incur debt.
We may issue additional equity, debt or convertible securities to raise capital in the future. If we do, existing stockholders may experience significant further dilution. In addition, new investors may demand rights, preferences or privileges that differ from, or are senior to, those of our existing stockholders. Our incurrence of indebtedness could limit our operating flexibility and be detrimental to our results of operations.
We are required to evaluate our internal control over financial reporting under Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, and any adverse results from such evaluation could result in a loss of investor confidence in our financial reports and have an adverse effect on our stock price.
Pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, we are required to furnish a report by our management on our internal control over financial reporting and evaluate the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of the end of each fiscal year. Such a report will contain, among other matters, an assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of the end of our fiscal year, including a statement as to whether or not our internal control over financial reporting is effective. This assessment must include disclosure of any material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting identified by management. If our management identifies one or more material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting during this process, we will be unable to assert such internal control is effective. If we are unable to assert that our internal control over financial reporting is effective, or if our independent registered public accounting firm is unable to express an opinion on the effectiveness of our internal controls, we could lose investor confidence in the accuracy and completeness of our financial reports, which could have an adverse effect on our stock price. We cannot assure you that we will not have deficiencies or weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting in the future.
We may also rely on external consultants to supplement our internal controls. For example, we may rely on external consultants to supplement our financial reporting in connection with our accounting for income taxes and other complex accounting and financial matters, some of which require significant technical accounting expertise or require significant judgment. Use of external consultants involves additional risk that our external consultants may not perform as expected, or that coordination between our internal and external resources may not be adequate, resulting in one or more procedures not being performed or reviewed as planned, or one or more errors not being identified and corrected. If we do not effectively manage our external consultants or if they fail to perform as expected or fail to provide an adequate level of expertise in certain areas, our ability to comply with our financial reporting requirements and other rules that apply to reporting companies could be impaired and the accuracy and completeness of our financial reports could be compromised, which could adversely affect our stock price.
As an emerging growth company, we have elected to delay adoption of new or revised accounting standards, and thus our financial statements may not be comparable to those of most other companies. In addition, we are entitled to utilize other reduced disclosure and governance requirements applicable to emerging growth companies.
Pursuant to the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act (JOBS Act), as an emerging growth company, we have elected to take advantage of an extended transition period for any new or revised accounting standards that may be issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) or the SEC, which means that when a standard is issued or revised and it has different application dates for public or private companies, we, as an emerging growth company, can delay adoption of the standard until it applies to private companies. This may make a
36
Table of Contents
comparison of our financial statements with any other public company that is not an emerging growth company difficult, as they may be applying different standards. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our stock price may be more volatile and could decline.
As an emerging growth company, we also intend to utilize certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies, including, but not limited to, not being required to provide the auditor attestation report otherwise required by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act with respect to our internal control over financial reporting, and reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports and proxy statements. We may utilize these reporting exemptions until we are no longer an emerging growth company. We will remain an emerging growth company for up to five years, subject to certain conditions. We cannot predict if investors will find our common stock less attractive because we rely on these exemptions.
Anti-takeover provisions in our charter documents and Delaware law could prevent or delay a change in control of our company that stockholders may consider beneficial and may adversely affect the price of our stock.
Provisions of our fourth amended and restated certificate of incorporation and second amended and restated bylaws may discourage, delay or prevent a merger, acquisition or change of control that a stockholder may consider favorable. These provisions could also discourage proxy contests and make it more difficult for stockholders to elect directors and take other corporate actions. The existence of these provisions could limit the price that investors might be willing to pay in the future for shares of our common stock. These provisions include authorizing the issuance of “blank check” preferred stock, staggered elections of directors, and establishing advance notice requirements for nominations for election to the board of directors and for proposing matters to be submitted to a stockholder vote. Provisions of Delaware law may also discourage, delay or prevent someone from acquiring or merging with our company or obtaining control of our company. Specifically, Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporate Law may prohibit business combinations with stockholders owning 15% or more of our outstanding voting stock and could reduce our value.
We do not intend to pay dividends for the foreseeable future.
We do not intend to pay any cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. The payment of cash dividends is restricted under the terms of the agreements governing our indebtedness. In addition, because we are a holding company, our ability to pay cash dividends may be limited by restrictions on our ability to obtain sufficient funds through dividends from subsidiaries, including restrictions under the terms of the agreements governing our indebtedness. We anticipate that we will retain all of our future earnings for use in the development of our business and for general corporate purposes. Any determination to pay dividends in the future will be at the discretion of our board of directors. Accordingly, investors must rely on sales of their common stock after price appreciation, which may never occur, as the only way to realize any future gains on their investments.
We are a “controlled company” within the meaning of the rules of the NASDAQ Stock Market, and, as a result, will qualify for, and will rely on, exemptions from certain corporate governance requirements. Our stockholders will not have the same protections afforded to stockholders of companies that are subject to such requirements.
John and Susan Ocampo control a majority of the voting power of our outstanding common stock. We are a “controlled company” within the meaning of the corporate governance standards of the Nasdaq Stock Market. Under these rules, a listed company of which more than 50% of the voting power is held by an individual, group or another company is a “controlled company” and may elect not to comply with certain corporate governance requirements, including:
| • | the requirement that a majority of the board of directors consist of independent directors; |
| • | the requirement that the listed company have a nominating and governance committee that is composed entirely of independent directors with a written charter addressing the committee’s purpose and responsibilities; |
37
Table of Contents
| • | the requirement that the listed company have a compensation committee that is composed entirely of independent directors with a written charter addressing the committee’s purpose and responsibilities; and, |
| • | the requirement for an annual performance evaluation of the nominating and governance and compensation committees. |
We currently are a “controlled company”, currently plan to rely on the exemption regarding the requirement that a majority of the board of directors consist of independent directors in the future, and may utilize any or all of these exemptions from time to time in the future. Accordingly, you may not have the same protections afforded to stockholders of companies that are subject to all of the corporate governance requirements of the Nasdaq Stock Market.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS.
None.
For additional information regarding property, plant and equipment by geographic region for each of the last two fiscal years, see Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8 of this Annual Report.
Our principal executive offices are located in a leased facility in Lowell, Massachusetts. We also maintain leased facilities for our design centers located in Massachusetts, California, North Carolina, New York, Ireland, Northern Ireland, France, Canada and Australia as well as for our administrative, assembly and test operations located in New Hampshire and Taiwan, and our local sales offices in Oregon, Canada, Germany, Malaysia, China, Japan, India and South Korea. We do not own any real property. We believe that our leased facilities are adequate for our present operations. The following is a list of our main facilities and their primary functions as of November 30, 2014.
| Site |
Major Activity |
Square Footage | Lease Expiration | |||
| Lowell, Massachusetts |
Administration, Wafer Fabrication, Assembly and Test, Research and Development, Sales and Marketing | 157,600 | December 2022 | |||
| Newport Beach, California |
Administration, Research and Development, Sales and Marketing | 88,160 | December 2019 | |||
| Lowell, Massachusetts |
Administration, Research and Development, Application Engineering | 60,700 | December 2022 | |||
| Long Beach, California |
Administration, Assembly and Test, Research and Development, Sales and Marketing | 25,317 | January 2018 | |||
| Cork, Ireland |
Administration, Research and Development, Sales and Marketing, Application Engineering, Reliability Testing | 21,634 | April 2017 | |||
From time to time we may be subject to commercial and employment disputes, claims by other companies in the industry that we have infringed their intellectual property rights and other similar claims and litigations. Any such claims may lead to future litigation and material damages and defense costs. Other than as set forth below, we
38
Table of Contents
were not involved in any pending legal proceedings as of the filing date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K that we believe could have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results, financial condition or cash flows.
Patent Suit Against Laird. We brought a patent infringement suit against Laird Technologies, Inc. (Laird) in the Federal District Court for the District of Delaware on February 11, 2014, seeking monetary damages and a permanent injunction. The suit alleges that Laird infringes on our United States Patent No. 6,272,349 (‘349 Patent), titled “Integrated Global Positioning System Receiver,” by making, using, selling, offering to sell or selling products incorporating an integrated global positioning receiver that include structure(s) recited in the ‘349 Patent, including global positioning system modules for automotive industry customers. Laird filed an answer and declaratory judgment claims of invalidity and noninfringement on June 30, 2014. We filed a reply to the counterclaims on July 24, 2014.
We filed a motion for preliminary injunction, seeking to enjoin Laird’s infringement pending full trial on the merits. The court granted the motion for a preliminary injunction on June 13, 2014 and required us to post a bond of $4 million to secure the injunction. In granting the injunction, the court found that we are likely to succeed on the merits of the case at a full trial and that the equities weighed in favor of preliminarily enjoining Laird from making sales of its product until trial. Trial is scheduled to begin on May 16, 2016.
Mindspeed Tender Offer Litigation in Delaware and California. Following our November 2013 announcement of the execution of a definitive agreement between us and Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. (Mindspeed) contemplating a tender offer by us for all outstanding shares of common stock of Mindspeed and thereafter a merger with Mindspeed (Merger), a number of purported class action lawsuits were filed against Mindspeed, its directors, our merger subsidiary and us in the Delaware Court of Chancery and the California Superior Court for Orange County.
The complaints alleged, generally, that the Mindspeed director defendants breached their fiduciary duties to Mindspeed stockholders, and that the other defendants aided and abetted such breaches, by seeking to sell Mindspeed through an allegedly defective process, for an unfair price, and on unfair terms. The lawsuits sought, among other things, equitable relief that would enjoin the consummation of the proposed Merger, rescission of the proposed Merger (to the extent the proposed Merger has already been consummated), damages and attorneys’ fees and costs.
Further Discussion of Delaware Tender Offer Litigation. On November 22, 2013, an amended complaint was filed in the Delaware Court of Chancery. The amended complaint included similar allegations to the original complaint, along with claims that the Mindspeed Schedule 14D-9 filed in connection with the Merger included misstatements or omissions of material facts. On November 25, 2013, a motion for preliminary injunction was filed in the Delaware Court of Chancery. On December 3, 2013, all of the complaints filed in the Delaware Court of Chancery were consolidated (Delaware Actions).
On December 6, 2013, the plaintiffs in the Delaware Actions filed their brief in support of a motion to enjoin the proposed Merger. While the Defendants denied the allegations made in the lawsuits and maintain that they have committed no wrongdoing whatsoever, to permit the timely consummation of the Merger, and without admitting the validity of any allegations made in the lawsuits, the Defendants concluded that it was desirable that the Delaware Actions be resolved.
On December 9, 2013, the Defendants’ and plaintiffs’ counsel in the Delaware Actions entered into a memorandum of understanding to settle the Delaware Actions and to resolve all allegations which were brought or could have been brought by the purported class of Mindspeed shareholder plaintiffs. The settlement provides for the release of all claims against the Defendants relating to the proposed Merger. In connection with the settlement, Mindspeed agreed to provide additional supplemental disclosures concerning the tender offer as reflected in Amendment No. 3 to the Schedule 14D-9 filed with the SEC on December 10, 2013, which supplement the information provided in the Schedule 14D-9. After the parties entered into the memorandum of
39
Table of Contents
understanding, the motion for a preliminary injunction was withdrawn and the hearing vacated in the Delaware Actions. The Merger closed on December 18, 2013. The parties submitted final settlement papers to the Delaware Court of Chancery, which ordered that notice of the settlement be issued to class members. On September 23, 2014, the Court of Chancery approved the settlement and awarded plaintiffs’ counsel the agreed-upon attorneys’ fee of $425,000.
Further Discussion of California Tender Offer Litigation. On December 5, 2013, an amended complaint was filed in one of the California actions. The amended complaint includes similar allegations to the original complaint along with claims that the Mindspeed Schedule 14D-9 filed in connection with the Merger included misstatements or omissions of material facts. Plaintiffs in the action filed a request to dismiss the case in light of the settlement approved by the Delaware Court of Chancery. On November 5, 2014, the California Court entered an order dismissing the action.
CSR Matter. In January 2013, CSR Technology Inc. (CSR) filed a complaint against us in the Massachusetts Superior Court for Suffolk County alleging breach of contract, breach of the implied covenant of good faith and fair dealing, misrepresentation, deceptive business practices and unfair competition, all relating to our purported failure to honor an alleged minimum purchase commitment contract with respect to certain semiconductor chips to be supplied by CSR for use in our automotive module product. The complaint claimed alleged damages of $2.2 million and asked for attorney’s fees and other remedies. We filed an answer to the complaint on January 28, 2013. The parties concluded fact discovery and CSR filed a motion for summary judgment, which we opposed. The parties agreed to settle the case in July 2014 without any finding of liability or judgment against us, and the compliant was dismissed by the court with prejudice in August 2014.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES.
Not applicable.
40
Table of Contents
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES.
Our common stock has been listed on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the symbol “MTSI” since March 15, 2012. The following table sets forth for the periods indicated the high and low sale prices of our common stock on the NASDAQ Global Select Market. The number of stockholders of record of our common stock as of November 15, 2014 was approximately 20.
The high and low sales prices of our common stock by quarter in fiscal year 2014 and fiscal year 2013 follows:
| High | Low | |||||||
| Fiscal Year 2014: |
||||||||
| First quarter |
$ | 18.25 | $ | 13.20 | ||||
| Second quarter |
21.70 | 15.43 | ||||||
| Third quarter |
23.44 | 15.76 | ||||||
| Fourth quarter |
25.70 | 19.04 | ||||||
| High | Low | |||||||
| Fiscal Year 2013: |
||||||||
| First quarter |
$ | 15.00 | $ | 10.01 | ||||
| Second quarter |
17.00 | 13.58 | ||||||
| Third quarter |
16.14 | 12.45 | ||||||
| Fourth quarter |
17.28 | 13.35 | ||||||
We have not paid cash dividends on our common stock since the date of our IPO and we do not anticipate paying cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Our credit facility also contains restrictions on our ability to pay cash dividends, subject to certain exceptions.
41
Table of Contents
Stock Price Performance Graph
The following graph shows a comparison from March 15, 2012 (the date our common stock commenced trading on NASDAQ) through October 3, 2014 of the total cumulative return of our common stock with the total cumulative return of the NASDAQ Composite Index and the PHLX Semiconductor Index. The amounts represented below assume an investment of $100 in our common stock at the closing price of $20.55 on March 15, 2012 and in the NASDAQ Composite Index and the PHLX Semiconductor Index on the closest month end date of February 29, 2012, and assume reinvestment of dividends. The comparisons in the graph are historical and are not intended to forecast or be indicative of possible future performance of our common stock.
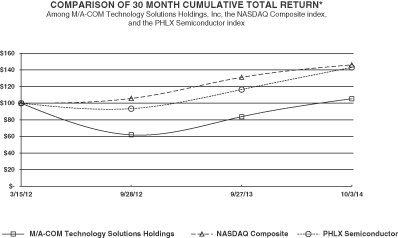
| March 15, 2012 |
September 28, 2012 |
September 27, 2013 |
October 3, 2014 |
|||||||||||||
| M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 61.80 | $ | 83.75 | $ | 105.26 | ||||||||
| NASDAQ Composite Index |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 105.67 | $ | 131.19 | $ | 146.00 | ||||||||
| PHLX Semiconductor Index |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 93.68 | $ | 116.39 | $ | 143.00 | ||||||||
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
| Period |
Total Number of Shares (or Units) Purchased (1) |
Average Price Paid per Share (or Unit) |
Total Number of Shares (or Units) Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs |
Maximum Number (or Approximate Dollar Value) of Shares (or Units) that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs |
||||||||||||
| July 5, 2014 — August 1, 2014 |
1,730 | $ | 19.91 | — | — | |||||||||||
| August 2, 2014 — August 29, 2014 |
3,790 | $ | 21.37 | — | — | |||||||||||
| August 30, 2014 — October 3, 2014 |
2,110 | $ | 23.85 | — | — | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
7,630 | $ | 21.73 | — | — | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (1) | We employ “withhold to cover” as a tax payment method for vesting of restricted stock awards for our employees, pursuant to which, outside of a publicly-announced repurchase plan, we withheld from employees the shares noted in the table above to cover tax withholding related to the vesting of their awards. The average prices listed in the above table are averages of the fair market prices at which we valued shares withheld for purposes of calculating the number of shares to be withheld. |
42
Table of Contents
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA.
You should read the following selected financial data in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes, as well as Item 1A. “Risk Factors” and Item 7. “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report.
We acquired Nitronex on February 13, 2014. Because we and Nitronex were under common control since June 25, 2012, we present combined financial statements in a manner similar to a pooling-of-interests for all periods since June 25, 2012, the earliest date of common control. Accordingly, our historical financial statements have been retroactively combined as if Nitronex was acquired on June 25, 2012. All periods from June 25, 2012, have been combined using historical amounts of each entity.
We derived (i) the statements of operations data for the fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, and (ii) the balance sheet data as of October 3, 2014 and September 27, 2013, from our audited consolidated financial statements, which appear elsewhere in this Annual Report. We derived the statements of operations data for the fiscal years 2011 and 2010 and balance sheet data as of September 28, 2012, September 30, 2011 and October 1, 2010 from our audited consolidated financial statements, which do not appear elsewhere in this Annual Report. We adopted a 52-or 53-week fiscal year ending on the Friday closest to September 30.
43
Table of Contents
The historical results presented below are not necessarily indicative of financial results to be achieved in future periods.
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Statements of Operations Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 418,662 | $ | 323,071 | $ | 303,336 | $ | 310,295 | $ | 260,297 | ||||||||||
| Cost of revenue (4)(5) |
249,674 | 186,658 | 169,213 | 178,435 | 166,554 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Gross profit |
168,988 | 136,413 | 134,123 | 131,860 | 93,743 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Research and development (5) |
73,685 | 44,588 | 36,752 | 36,121 | 25,795 | |||||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative (5) |
86,179 | 52,004 | 45,688 | 48,103 | 45,860 | |||||||||||||||
| Litigation settlement |
— | 7,250 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Contingent consideration |
— | (577 | ) | (3,922 | ) | 210 | 2,000 | |||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges |
14,823 | 1,060 | 1,862 | 1,499 | 2,234 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
174,687 | 104,325 | 80,380 | 85,933 | 75,889 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
(5,699 | ) | 32,088 | 53,743 | 45,927 | 17,854 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Other income (expense): |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant liability gain (expense) (1) |
(3,928 | ) | (4,312 | ) | 3,175 | (5,080 | ) | — | ||||||||||||
| Class B conversion liability expense (2) |
— | — | (44,119 | ) | (39,737 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(12,362 | ) | (817 | ) | (695 | ) | (1,561 | ) | (2,323 | ) | ||||||||||
| Other income |
3,217 | 372 | 185 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Other income (expense), net |
(13,073 | ) | (4,757 | ) | (41,454 | ) | (46,378 | ) | (2,323 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Income (loss) before income taxes |
(18,772 | ) | 27,331 | 12,289 | (451 | ) | 15,531 | |||||||||||||
| Income tax provision (benefit) |
(8,054 | ) | 9,135 | 15,953 | 1,319 | 8,996 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations |
(10,718 | ) | 18,196 | (3,664 | ) | (1,770 | ) | 6,535 | ||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from discontinued operations |
(4,605 | ) | — | — | 754 | 494 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
(15,323 | ) | 18,196 | (3,664 | ) | (1,016 | ) | 7,029 | ||||||||||||
| Less: net income attributable to noncontrolling interest in a subsidiary |
— | — | — | — | 195 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to controlling interest |
(15,323 | ) | 18,196 | (3,664 | ) | (1,016 | ) | 6,834 | ||||||||||||
| Accretion to redemption value of redeemable preferred stock and participating stock dividends (3) |
— | — | (2,616 | ) | (80,452 | ) | (6,298 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders |
$ | (15,323 | ) | $ | 18,196 | $ | (6,280 | ) | $ | (81,468 | ) | $ | 536 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Basic income (loss) per common share: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations |
$ | (0.23 | ) | $ | 0.40 | $ | (0.25 | ) | $ | (54.63 | ) | $ | 0.01 | |||||||
| Income from discontinued operations |
(0.10 | ) | — | — | 0.50 | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income (loss) — basic |
$ | (0.33 | ) | $ | 0.40 | $ | (0.25 | ) | $ | (54.13 | ) | $ | 0.05 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Diluted income (loss) per common share: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations |
$ | (0.23 | ) | $ | 0.39 | $ | (0.25 | ) | $ | (54.63 | ) | $ | — | |||||||
| Income from discontinued operations |
(0.10 | ) | — | — | 0.50 | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income (loss) — diluted |
$ | (0.33 | ) | $ | 0.39 | $ | (0.25 | ) | $ | (54.13 | ) | $ | 0.04 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Shares used to compute net income (loss) per common share: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
47,009 | 45,916 | 24,758 | 1,505 | 11,880 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Diluted |
47,009 | 47,137 | 24,758 | 1,505 | 12,586 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
44
Table of Contents
| As of | ||||||||||||||||||||
| October 3, 2014 |
September 27, 2013 |
September 28, 2012 |
September 30, 2011 |
October 1, 2010 |
||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated Balance Sheet Data (in thousands): |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 173,895 | $ | 110,488 | $ | 84,600 | $ | 45,668 | $ | 23,946 | ||||||||||
| Working capital |
287,703 | 194,289 | 157,029 | 89,426 | 56,955 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
682,234 | 316,635 | 281,561 | 211,268 | 164,836 | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt, less current portion |
343,178 | — | — | — | 30,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Class B conversion liability |
— | — | — | 81,378 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Convertible and redeemable preferred stock |
— | — | — | 182,018 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
228,567 | 247,141 | 210,455 | (144,837 | ) | 44,655 | ||||||||||||||
Dividends of $0.63 per share, $0.81 per share and $2.44 per share were paid to the record holders as of January 4, 2011 of our Series A-1 convertible preferred stock, Series A-2 convertible preferred stock and common stock, respectively, aggregating $80 million.
| (1) | Represents changes in the fair value of common stock warrants recorded as liabilities and adjusted each reporting period to fair value. |
| (2) | Represents changes in the fair value of certain features of our Class B convertible preferred stock that were recorded as liabilities and adjusted each reporting period to fair value. This liability was settled in connection with the IPO in March 2012. |
| (3) | In fiscal year 2011, includes $76.2 million of dividends declared and paid in January 2011 to holders of our Series A-1 and A-2 convertible preferred stock. |
| (4) | In fiscal year 2014, includes approximately $18.1 million of costs for step-up in valuation of Mindspeed’s inventory to fair value. |
| (5) | In fiscal year 2014, cost of revenue, research and development and selling, general and administrative includes approximately $1.4 million, $4.5 million and $13.9 million, respectively, of costs related to the acquisition and integration of Mindspeed. |
45
Table of Contents
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATION.
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes that appear elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. In addition to historical information, the following discussion contains forward-looking statements that are subject to risks and uncertainties. Actual results may differ substantially and adversely from those referred to herein due to a number of factors, including but not limited to those described below and in Item 1A “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
OVERVIEW
We are a leading provider of high-performance analog semiconductor solutions that enable next-generation internet applications, the cloud connected apps economy, and the modern, networked battlefield across the radio frequency (RF), microwave and millimeterwave spectrum. We design and manufacture differentiated, high-value products for customers who demand high performance, quality and reliability. We offer a broad portfolio of over 3,500 standard and custom devices, which include integrated circuits (IC), multi-chip modules, power pallets and transistors, diodes, switches and switch limiters, passive and active components and complete subsystems, across 42 product lines serving over 6,000 end customers in four primary markets. Our semiconductor products are electronic components that our customers incorporate into their larger electronic systems, such as point-to-point wireless backhaul radios, optical networking equipment, high density data networks, radar, automobile navigation systems, magnetic resonance imaging systems and unmanned aerial vehicles. Our primary markets are: Networks, which includes wired broadband, cellular backhaul, cellular infrastructure, enterprise networking, broadcast video transmission and optical communications applications; Aerospace and Defense (A&D), which includes military and commercial radar, RF jammers, electronic countermeasures, and communication data links; Automotive, which includes global positioning (GPS) modules we sell to Ford and Ford affiliates; and Multi-market, which includes industrial, medical, test and scientific applications.
History and Basis of Presentation
M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. was incorporated in the State of Delaware on March 25, 2009, and on March 30, 2009, acquired 100% of the outstanding stock of M/A-COM Technology Solutions Inc. and M/ACOM Technology Solutions (Cork) Limited and the related M/A-COM brand, which we refer to as the MACOM Acquisition. We acquired Mimix, a supplier of high-performance GaAs semiconductors, on May 28, 2010, Optomai a developer of ICs and modules for fiber optic networks, on April 25, 2011, Mindspeed, a supplier of high-performance analog products, on December 18, 2013, Nitronex, a supplier of high-performance gallium nitride (GaN) semiconductors for RF, microwave and millimeterwave applications on February 13, 2014, and other acquisitions as highlighted in Note 3 of our Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report.
Because we and Nitronex were controlled by the same majority owner since June 25, 2012, we present combined financial statements in a manner similar to a pooling-of-interests for all periods since June 25, 2012, the earliest date of common control. Accordingly, our historical financial statements have been retroactively combined as if Nitronex was acquired on June 25, 2012. All periods from June 25, 2012, have been combined using historical amounts of each entity. Since February 13, 2014, the results of Nitronex are included on a consolidated basis.
On November 17, 2014, we entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger with BinOptics, a supplier of high-performance laser products, pursuant to which, subject to the satisfaction or waiver of customary closing conditions, BinOptics will become our wholly-owned subsidiary at closing. We believe BinOptics aligns with our core growth strategy in our Networks market, and that it has a high-performance laser semiconductor business model that is consistent with our target model for higher margin products with long product lifecycles.
46
Table of Contents
Further, we believe that BinOptics complements our existing business with an established footprint and customer relationships in the Asia-Pacific region and expands our addressable market for InP high-performance laser products and technology for use in optical networks. The operations of BinOptics will be included in our consolidated financial statements from the date of acquisition.
Subsequent to closing the Mindspeed Acquisition, in February 2014, we divested the wireless business of Mindspeed. The operations of the wireless business are included in discontinued operations.
On May 9, 2014, we completed the sale of the Mindspeed customer premise equipment communication processor (CPE) product line for $12.0 million and a potential additional $2.0 million based upon the achievement of certain revenue related milestones through December 31, 2014.
We have one reportable operating segment, semiconductors and modules. We have a 52 or 53-week fiscal year ending on the Friday closest to September 30. The fiscal year 2014 includes 53 weeks. The fiscal years 2013 and 2012 included 52 weeks. To offset the effect of holidays, we include the extra week arising in our fiscal years in the first quarter.
Description of Our Revenue, Cost of Revenue and Expenses
Revenue. Substantially all of our revenue is derived from sales of high-performance analog semiconductor solutions for use in wireless and wireline applications across the RF, microwave and millimeterwave spectrum and in high-speed communications. We design, integrate, manufacture and package differentiated product solutions that we sell to customers through our direct sales organization, our network of independent sales representatives, and our distributors.
We believe the primary drivers of our future revenue growth will include:
| • | engaging early with our lead customers to develop products and solutions that can be driven across multiple growth markets; |
| • | leveraging our core strength and leadership position in standard, catalog products that service all of our end applications; |
| • | increasing content of our semiconductor solutions in our customers’ systems through cross-selling of our more than 42 product lines; |
| • | introducing new products through internal development and acquisitions with market reception that command higher prices based on the application of advanced technologies such as GaN, added features, higher levels of integration and improved performance; and |
| • | realizing growth in the market for high-performance analog semiconductors generally, and in our four primary markets in particular. |
Our core strategy is to develop innovative, high-performance products that address our customers’ most difficult technical challenges in our primary markets: Networks, A&D, Automotive and Multi-market. While sales in any or all of our primary markets may slow or decline from period to period, over the long-term we generally expect to benefit from strength in these markets.
We expect our revenue in the Networks market to be primarily driven by continued upgrades and expansion of communications equipment to support expansion in the internet of things (IoT), driven by the proliferation of mobile computing devices such as smartphones and tablets, coupled with bandwidth rich services such as video on demand and cloud computing, as well as demand for higher bandwidth wired and wireless services, the rapid adoption of cloud-based services and the migration to an application centric architecture, which we expect will drive faster adoption of higher speed, low latency optical and wireless links.
47
Table of Contents
We expect our revenue in the A&D market to be driven by the upgrading of radar applications and modern battlefield communications devices designed to improve situational awareness. Growth in this market is subject to changes in governmental programs and budget funding, which is difficult to predict.
We expect our revenue in the Automotive market to be subject to fluctuations in our largest customer’s market share and overall macroeconomic conditions.
We expect revenue in Multi-market to be driven by diverse demand for our multi-purpose catalog products.
Cost of revenue. Cost of revenue primarily consists of the cost of semiconductor wafers and other materials used in the manufacture of our products, and the cost of assembly and testing of our products, whether performed by our internal manufacturing personnel or outsourced vendors. Cost of revenue also includes costs associated with personnel engaged in our manufacturing operations, such as wages and share-based compensation expense, as well as costs and overhead related to our manufacturing operations, including lease occupancy and utility expense related to our manufacturing operations, depreciation, production computer services and equipment costs and the cost of our manufacturing quality assurance and supply chain activities. Further, cost of revenue includes the impact of warranty and inventory adjustments, including write-downs for excess and obsolete inventory, and for fair market value adjustments related to the accounting for acquisitions, as well as amortization of intangible assets related to acquired technology.
Our gross margin in any period is significantly affected by industry demand and competitive factors in the markets into which we sell our products. Gross margin is also significantly affected by our product mix, that is, the percentage of our revenue in that period that is attributable to relatively higher or lower-margin products. Additional factors affecting our gross margin include fluctuations in the cost of wafers and materials, including precious metals, utilization of our wafer fabrication operation, level of usage of outsourced manufacturing, assembly, and test services, changes in our manufacturing yields, changes in foreign currencies, and numerous other factors, some of which are not under our control. As a result of these or other factors, we may be unable to maintain or increase our gross margin in future periods, and our gross margin may fluctuate from period to period.
Research and development. R&D expense consists primarily of costs relating to our employees engaged in the design and development of our products and technologies, including wages and share-based compensation. R&D expense also includes costs for consultants, facilities, services related to supporting computer design tools used in the engineering and design process, prototype development and project materials. We expense all research and development costs as incurred. We expect to maintain or increase the dollar amount of R&D investment in future periods as we continue to invest in new product development, although amounts may increase or decrease in any individual quarter.
Selling, general and administrative. SG&A expense consists primarily of costs of our management, sales and marketing, finance, human resources and administrative organizations, including wages and share-based compensation. SG&A expense also includes costs associated with being a public company, professional fees, sales commissions paid to independent sales representatives, costs of advertising, trade shows, marketing, promotion, travel, occupancy and equipment costs, computer services costs, costs of providing customer samples, amortization of certain acquisition-related intangible assets relating to customer relationships and costs and expenses to acquire businesses.
Contingent consideration. Contingent earn-out consideration represents expense in which we have agreed to pay contingent amounts to the previous owners of acquired businesses based upon those businesses achieving contractual milestones. We record these obligations as liabilities at fair value and any changes in fair value are reflected in our earnings. As of October 3, 2014, we had approximately $0.8 million of outstanding earn-out obligations.
48
Table of Contents
Restructuring charges. Restructuring expense consists of severance and related costs incurred in connection with reductions in staff relating to initiatives designed to lower our manufacturing and operating costs and integrate acquired businesses, including restructuring actions taken following the Mindspeed and Nitronex acquisitions.
Other income (expense). Other income (expense) consists of our stock warrant liability expense and/or gain, interest expense, income from transition services provided related to sales of businesses and assets, and income from our administrative and business development services agreement with GaAs Labs, which is one of our stockholders and an affiliate of our directors and majority stockholders John and Susan Ocampo. We expect interest expense to be higher in future periods due to increased borrowing to fund the Mindspeed, Nitronex and expected BinOptics acquisitions, as well as to provide additional liquidity.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND ESTIMATES
Our discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based on our consolidated financial statements. The preparation of financial statements, in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the U.S. (GAAP), requires management to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. By their nature, these estimates and judgments are subject to an inherent degree of uncertainty. On an ongoing basis, we re-evaluate our estimates and judgments. We base our estimates and judgments on our historical experience and on other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making the judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. The accounting policies which our management believes involve the most significant application of judgment, or involve complex estimation, include revenue recognition, inventory valuation, share-based compensation, income tax expense and deferred tax accounting, fair value measurements and impairment of long-lived assets. Actual results could differ from those estimates, and material effects on our operating results and financial position may result.
As discussed in Part I, Item 1A. “Risk Factors”, as an emerging growth company and pursuant to Section 102(6)(1) of the JOBS Act, we have elected to delay adoption of new or revised accounting standards that have different effective dates for public and private companies until those standards apply to private companies, and thus our financial statements may not be comparable to those of other companies that comply with public company effective dates.
Revenue recognition. We recognize revenue when: (i) there is persuasive evidence that an arrangement exists; (ii) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; (iii) the price is fixed or determinable; and (iv) collectability is reasonably assured. In circumstances with our distribution customers where we are unable to establish that certain sales prices are fixed and determinable, we defer the recognition of revenue, and the related costs, under agreements providing for rights of return and price protection until such time as our products are sold by the distributors to their customers. As of October 3, 2014, we have deferred revenue of $17.0 million and related cost of $4.6 million. In circumstances with distributor customers where returns are reasonably estimable and the sales price is fixed and determinable, we recognize revenue with the transfer of title and risk of loss, and provide for reserves for returns and other allowances. Historically, such returns and allowances have not been material based on the terms of our arrangements. We generally do not provide customers other than distributors the right to return product, with the exception of warranty related matters. Accordingly, we do not generally maintain a reserve for sales returns for such customers.
Inventory valuations. Inventory is stated at the lower of cost or market. We use a combination of standard cost and moving weighted-average cost methodologies to determine the cost basis for inventories, approximating a first-in, first-out basis. The standard cost of finished goods and work-in-process inventory is composed of material, labor and manufacturing overhead, which approximates actual cost. In addition to stating inventory at
49
Table of Contents
the lower of cost or market, we also evaluate inventory each quarter for excess quantities and obsolescence, establishing reserves when necessary based upon historical experience, assessment of economic conditions, and expected demand. Estimating demand is inherently difficult, particularly given the cyclical nature of the semiconductor industry, and can result in excess or obsolete inventory. Once we write down inventory to its estimated net realizable value, we establish a new cost basis for that item and do not increase its carrying value due to subsequent changes in demand forecasts. Accordingly, if inventory previously written down is subsequently sold, we may realize higher than normal gross margin on these transactions. Neither inventory write-downs nor sales of previously written down inventory had a material impact on our operating results for any period presented in this Annual Report.
Share-based compensation. We provide share-based compensation awards to our directors, officers and employees as incentives in the form of options to purchase our common stock (stock options), restricted shares of our common stock (restricted stock) and units representing the right to receive common stock (restricted stock units), typically subject to a time-based or performance-based vesting restrictions. We measure compensation cost for such awards based upon fair value on the date of grant, and recognize this cost as expense over the service period the awards are expected to vest, net of estimated forfeitures. The fair value of restricted stock and restricted stock units is determined based on the excess of the estimated fair value of our common stock on the date of grant over the price paid or payable for the shares, which is generally zero. The fair value of stock options is determined using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. We recognize the compensation expense associated with share-based awards on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period of the award, which is generally the vesting period. The determination of fair value of share-based awards utilizing the Black-Scholes model is affected by the fair value of our common stock as of the time of grant and a number of assumptions, including expected volatility, expected life, risk-free interest rate, and expected dividends.
Determining the appropriate fair value model and calculating the fair value of share-based awards requires significant judgment and the use of assumptions which may differ materially from actual results. Actual results, and future changes in estimates, may differ substantially from our current estimates.
Income taxes expense and deferred tax accounting. We periodically assess the likelihood that our deferred tax assets will be recovered from our future income, and, to the extent we believe that it is more likely than not our deferred tax assets will not be recovered, we must establish a valuation allowance against our deferred tax assets. In making this assessment, we consider available positive and negative evidence. Conclusions reached are subject to significant judgments that are dependent upon changes in facts and circumstance. We acquired significant federal net operating loss (NOL) carryforwards in our acquisition of Mindspeed, approximately $307.0 million after consideration of change in control limitations within the Internal Revenue Code. We have concluded that recovery of these NOL carryforwards is more likely than not and recognized these deferred tax assets in our accounting for the business combination, without a valuation allowance. Our assessment of recovery is based in part on our assumption of generating taxable income in future periods through 2033. To the extent this assumption changes and we conclude that recovery in whole or in part is not more likely than not, we will need to provide a valuation allowance which will decrease our net income.
Fair value measurements. We measure financial assets and liabilities at fair value. Fair value is an exit price, representing the amount that would be received from the sale of an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants. As such, fair value is a market-based measurement that should be determined based on assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability. As a basis for considering such assumptions, we group financial assets and liabilities in a three-tier fair value hierarchy. This hierarchy requires us to use observable market data, when available, and to minimize the use of unobservable inputs when determining fair value. On a recurring basis, we measure certain financial assets and liabilities at fair value.
50
Table of Contents
The fair values of the contingent consideration liabilities are estimated based upon a risk-adjusted present value of the probability-weighted expected payments by us. Specifically, we consider base, upside and downside scenarios for the operating metrics upon which the contingent payments are to be based. Probabilities were assigned to each scenario and the probability-weighted payments are discounted to present value using risk-adjusted discount rates.
These estimates include significant judgments about potential future liquidity events and actual results could materially differ and have a material impact upon the values of the recorded liabilities. Any changes in the estimated fair values of the liabilities in the future will be reflected in our earnings and such changes could be material.
Impairment of long-lived assets. We evaluate long-lived assets for recoverability when events or changes in circumstances indicate that their carrying amounts may not be recoverable. In evaluating an asset for recoverability, we estimate the undiscounted cash flows expected to result from our use and eventual disposition of the asset. If the sum of the expected undiscounted cash flows is less than the carrying amount of the asset, an impairment loss, equal to the excess of the carrying amount over the fair value of the asset, is recognized. There was no impairment of long-lived assets in any period presented. As a result of our fiscal 2014 acquisitions, we had approximately $142.6 million of intangible assets as of October 3, 2014. To the extent that our assumptions about generation of future cash flows change, we could possibly be required to record a material impairment of intangible assets.
Goodwill is also subject to an annual impairment test, or more frequently, if indicators of potential impairment arise. We perform the two-step goodwill impairment test. In fiscal years 2014 and 2013, we conducted step I of the quantitative goodwill impairment test, and concluded that there was no goodwill impairment and that the performance of the step II testing was not necessary.
51
Table of Contents
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
We acquired Nitronex on February 13, 2014. Given that we and Nitronex were under common control since June 25, 2012, we present combined financial statements in a manner similar to a pooling-of-interests for all periods since June 25, 2012, the earliest date of common control. Accordingly, our historical financial statements have been retroactively combined as if Nitronex was acquired on June 25, 2012. All periods from June 25, 2012, have been combined using historical amounts of each entity. The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, our statement of operations data (in thousands):
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 418,662 | 323,071 | 303,336 | ||||||||
| Cost of revenue (1)(5)(6) |
249,674 | 186,658 | 169,213 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Gross profit |
168,988 | 136,413 | 134,123 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||
| Research and development (1)(6) |
73,685 | 44,588 | 36,752 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative (1)(4)(6) |
86,179 | 52,004 | 45,688 | |||||||||
| Litigation settlement |
— | 7,250 | — | |||||||||
| Contingent consideration |
— | (577 | ) | (3,922 | ) | |||||||
| Restructuring charges |
14,823 | 1,060 | 1,862 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total operating expenses |
174,687 | 104,325 | 80,380 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income from operations |
(5,699 | ) | 32,088 | 53,743 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Other (expense) income: |
||||||||||||
| Warrant liability (expense) income (2) |
(3,928 | ) | (4,312 | ) | 3,175 | |||||||
| Class B conversion liability expense (3) |
— | — | (44,119 | ) | ||||||||
| Interest expense (1) |
(12,362 | ) | (817 | ) | (695 | ) | ||||||
| Other income |
3,217 | 372 | 185 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Other (expense) income, net |
(13,073 | ) | (4,757 | ) | (41,454 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) before income taxes |
(18,772 | ) | 27,331 | 12,289 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income tax provision |
(8,054 | ) | 9,135 | 15,953 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations |
(10,718 | ) | 18,196 | (3,664 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Loss from discontinued operations |
(4,605 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | (15,323 | ) | $ | 18,196 | $ | (3,664 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (1) | Amortization expense related to intangible assets arising from acquisitions, non-cash compensation expense and amortization of deferred financing costs included in our consolidated statements of operations is set forth below (in thousands): |
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Amortization expense: |
||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 18,274 | $ | 2,986 | $ | 2,259 | ||||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
1,779 | 1,335 | 1,336 | |||||||||
| Non-cash compensation expense: (a) |
||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
1,771 | 1,039 | 715 | |||||||||
| Research and development |
2,818 | 1,688 | 979 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
6,688 | 3,369 | 2,068 | |||||||||
| Amortization of deferred financing costs — interest expense |
3,021 | 321 | 271 | |||||||||
| (a) | Includes (i) share-based compensation expense and (ii) incentive compensation amounts payable by the previous owner of the MACOM business to certain of our employees in connection with the sale of such business to us and recorded in our financial statements in a manner similar to share-based compensation. |
52
Table of Contents
| (2) | Represents changes in the fair value of common stock warrants recorded as liabilities and adjusted each reporting period to fair value. |
| (3) | Represents changes in the fair value of certain features of our Class B convertible preferred stock that were recorded as liabilities and adjusted each reporting period to fair value. The liabilities were settled in connection with the IPO in March 2012. |
| (4) | Includes litigation costs of $4.3 million, $2.6 million and $484,000 incurred in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. |
| (5) | In fiscal year 2014, includes approximately $18.1 million of costs for step-up in valuation of Mindspeed’s inventory to fair value. |
| (6) | In fiscal year 2014, cost of revenue, research and development, and selling, general, and administrative includes approximately $1.4 million, $4.5 million and $13.9 million, respectively, of costs related to the acquisition and integration of Mindspeed. |
The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, our statement of operations data expressed as a percentage of our revenue:
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Revenue |
100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||
| Cost of revenue |
59.6 | 57.8 | 55.8 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Gross profit |
40.4 | 42.2 | 44.2 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||
| Research and development |
17.6 | 13.8 | 12.1 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
20.6 | 16.1 | 15.1 | |||||||||
| Litigation settlement |
— | 2.2 | — | |||||||||
| Contingent consideration |
— | (0.2 | ) | (1.3 | ) | |||||||
| Restructuring charges |
3.5 | 0.3 | 0.6 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total operating expenses |
41.7 | 32.3 | 26.5 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income from operations |
(1.4 | ) | 9.9 | 17.7 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Other (expense) income: |
||||||||||||
| Warrant liability expense (income) |
(0.9 | ) | (1.3 | ) | 1.0 | |||||||
| Class B conversion liability expense |
— | — | (14.5 | ) | ||||||||
| Interest expense |
(3.0 | ) | (0.3 | ) | (0.2 | ) | ||||||
| Other income |
0.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Other (expense) income, net |
(3.1 | ) | (1.5 | ) | (13.7 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) before income taxes |
(4.5 | ) | 8.5 | 4.1 | ||||||||
| Income tax provision |
(1.9 | ) | 2.8 | 5.3 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations |
(2.6 | ) | 5.6 | (1.2 | ) | |||||||
| Income from discontinued operations |
(1.1 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) |
(3.7 | )% | 5.6 | % | (1.2 | )% | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Comparison of Fiscal Year Ended October 3, 2014 to Fiscal Year Ended September 27, 2013
Revenue. In fiscal year 2014, our revenue increased $95.6 million, or 29.6%, to $418.7 million from $323.1 million for fiscal year 2013. The increase in revenue was primarily due to the acquisition of Mindspeed, which expanded our product offerings significantly.
53
Table of Contents
Revenue from our primary markets, the percentage of change between the years, and revenue by primary markets expressed as a percentage of total revenue were (in thousands, except percentages):
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | %Change | ||||||||||
| Networks |
$ | 183,344 | $ | 83,743 | 118.9 | % | ||||||
| A&D |
87,560 | 91,338 | (4.1 | )% | ||||||||
| Multi-market |
66,925 | 63,622 | 5.2 | % | ||||||||
| Automotive |
80,833 | 84,368 | (4.2 | )% | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | 418,662 | $ | 323,071 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Networks |
43.8 | % | 25.9 | % | ||||||||
| A&D |
20.9 | % | 28.3 | % | ||||||||
| Multi-market |
16.0 | % | 19.7 | % | ||||||||
| Automotive |
19.3 | % | 26.1 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
In fiscal year 2014, our Networks market revenue increased by $99.6 million, or 118.9%, compared to fiscal year 2013. The increase in revenue was primarily from sales of our newly acquired products from our Mindspeed Acquisition addressing carrier infrastructure, fiber-to-the-home access networks, physical media devices and broadcast video, as well as increased sales of our products targeting wireless backhaul and optical applications, partly offset by continued weakness in our products targeting set top box products.
In fiscal year 2014, our A&D market revenue decreased by $3.8 million, or 4.1%, compared to fiscal year 2013. We attribute this decrease to ramp down of certain legacy radar programs as well as cyclical demand for radar applications.
In fiscal year 2014, our Multi-market revenues increased $3.3 million, or 5.2%, compared to fiscal year 2013. The modest increase in revenue in the 2014 period was primarily from sales of our newly acquired CPE products, as partly offset by softness in demand for catalog products. We divested the CPE products in May 2014.
In fiscal year 2014, our Automotive market revenues decreased by $3.5 million, or 4.2%, compared to fiscal year 2013. This modest decrease was due to lower demand by our largest automotive customer for our GPS module.
Gross profit. In fiscal year 2014, our gross profit increased by $32.6 million or 23.9%, compared to fiscal 2013. Gross margin of 40.4%, decreased 1.8%, compared to fiscal year 2013. The higher gross profit was largely the result of leveraging higher revenue against fixed costs compared to fiscal year 2013. The decline in gross margin percentage included the effect of the step-up in valuation of Mindspeed’s inventory to fair value and other acquisition and integration costs increasing costs by $19.5 million, which offset the positive impact of selling higher margin products.
Research and development. In fiscal year 2014, R&D expense increased $29.1 million, or 65.3%, to $73.7 million, or 17.6% of our revenue, compared with $44.6 million, or 13.8% of our revenue in fiscal year 2013. R&D expense increased primarily as a result of increased headcount and employee compensation related to acquired businesses, of which approximately $4.5 million related to Mindspeed acquisition and integration costs.
Selling, general and administrative. In fiscal year 2014, SG&A expense increased $34.2 million, or 65.7%, to $86.2 million, or 20.6% of our revenue, compared with $52.0 million, or 16.1% of our revenue for fiscal year 2013. The increase was primarily due to increased headcount and employee compensation expense related to acquired businesses, acquisition integration expense, and increased litigation costs, of which approximately $13.9 million related to the Mindspeed Acquisition.
54
Table of Contents
Litigation settlement. In fiscal year 2013, we incurred $7.3 million in connection with the global settlement of all claims and litigation between us and GigOptix.
Contingent consideration. In fiscal year 2013, we recorded income of $0.6 million as a result of changes in the fair value of the contingent consideration related to past acquisitions.
Restructuring charges. In fiscal year 2014, restructuring charges were $14.8 million, or 3.5% of our revenue compared with $1.1 million, or 0.3% of our revenue for fiscal year 2013. Restructuring charges were due to a reduction in headcount as part of the integration of the Mindspeed business and included severance, related benefits, and an immaterial amount of non-employee related charges.
Income (loss) from operations. In fiscal year 2014, loss from operations decreased $37.8 million to a loss of $5.7 million, or 1.4% of our revenue compared with income from operations of $32.1 million, or 9.9%, of our revenue for fiscal year 2013. The fiscal year 2014 loss was primarily driven by the incremental costs incurred related to our acquisition and integration of Mindspeed.
Warrant liability. In fiscal year 2014, we recorded an expense of $3.9 million compared to an expense of $4.3 million for fiscal year 2013. The expense relates to the change in the estimated fair value of common stock warrants we issued in December 2010, which we carry as a liability at fair value.
Interest expense. In fiscal year 2014, interest expense was $12.4 million, or 3.0% of our revenue, compared with $0.8 million, or 0.3% of our revenue for fiscal year 2013, primarily due to increased borrowings outstanding under our Credit Agreement at higher interest rates. The borrowings were primarily utilized to fund our Mindspeed and Nitronex Acquisitions.
Other income. In fiscal year 2014, other income was $3.2 million for services and fees earned under a transition services agreement related to a business sold during the fiscal year.
Provision for income taxes. In fiscal year 2014, the provision for income taxes was a benefit of $8.1 million compared to an expense of $9.1 million for fiscal year 2013. The provision for income taxes decreased primarily due to a current period taxable loss in the U.S. for which we have recorded a benefit, partially offset by income taxed in foreign jurisdictions.
The difference between the U.S. federal statutory income tax rate of 35% and the Company’s effective income tax rates for fiscal year 2014 and 2013, was primarily impacted by changes in fair values of the stock warrant liability which are not deductible nor taxable for tax purposes, as well as income taxed in foreign jurisdictions at generally lower tax rates, partly offset by U.S. state income taxes, and, for fiscal year 2014, by nondeductible expenses for tax purposes resulting from the Mindspeed Acquisition and pre-acquisition Nitronex losses.
The aggregate net deferred income tax assets acquired in the Mindspeed Acquisition were $92.9 million, net of a $9.2 million valuation allowance. A valuation allowance is required to the extent we believe that it is more likely than not our deferred tax assets will not be recovered.
At the date of the acquisition, Mindspeed had federal NOL carryforwards of approximately $668.8 million, which will expire at various dates through 2033, and federal research and development tax credit carryforwards of $19.9 million. Both the NOL and the tax credits are subject to change-in-control limitations within the Internal Revenue Code and, accordingly, these carryforwards were reduced to $307.0 million, the estimated realizable amount after consideration of the limitations. The NOL carryforwards and tax credits are included in the computation of net deferred income tax assets arising from the acquisition.
During fiscal year 2014, the Company increased its unrecognized tax benefits by $1.7 million primarily relating to positions to be taken by the Company in its US tax filings. During fiscal year 2014, the Company settled the federal audit for fiscal years 2011 and 2012 with no material impact upon the financial statements.
55
Table of Contents
Comparison of Fiscal Year Ended September 27, 2013 to Fiscal Year Ended September 28, 2012
Revenue. In fiscal year 2013, our revenue increased $19.7 million, or 6.5%, to $323.1 million from $303.3 million for fiscal year 2012. The increase in revenue was primarily due to increasing sales of GPS modules to our customer Ford, in our Automotive market.
Revenue from our primary markets, the percentage of change between the years, and revenue by primary markets expressed as a percentage of total revenue were (in thousands, except percentages):
| Fiscal Years | % Change | |||||||||||
| 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||
| Networks |
83,743 | 83,379 | 0.4 | % | ||||||||
| A&D |
91,338 | 96,143 | (5.0 | )% | ||||||||
| Multi-Market |
63,622 | 70,427 | (9.7 | )% | ||||||||
| Automotive |
84,368 | 53,387 | 58.0 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
323,071 | 303,336 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Networks |
25.9 | % | 27.5 | % | ||||||||
| A&D |
28.3 | % | 31.7 | % | ||||||||
| Multi-Market |
19.7 | % | 23.2 | % | ||||||||
| Automotive |
26.1 | % | 17.6 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
In fiscal year 2013, our Networks market revenue was essentially flat compared to fiscal year 2012. The increased revenue was due to increased sales of our optical products, partly offset by a decrease in sales of our products for wired broadband applications and cellular infrastructure and wireless backhaul applications.
In fiscal year 2013, our A&D market revenue decreased by $4.8 million compared to fiscal year 2012. This decrease was due to decreased revenue from sales of our products for satellite communications applications and for tactical and public safety radios.
In fiscal year 2013, our Multi-market revenues decreased by $6.8 million compared to fiscal year 2012. This decrease was driven by decreased sales of our products targeting certain higher volume consumer applications.
In fiscal year 2013, our Automotive market revenues increased by $31.0 million compared to fiscal year 2012. This increased revenue was due to higher adoption by Ford of our GPS modules across the majority of its domestic fleet.
Gross profit. In fiscal year 2013, our gross profit increased $2.3 million, or 1.7%, compared to fiscal year 2012. Gross margin of 42.2%, decreased 2.0% compared to fiscal year 2012. The higher gross profit was largely the result of leveraging greater revenue against fixed costs compared to fiscal year 2013. The decline in gross margin percentage included the effect of unfavorable manufacturing costs caused by lower factory utilization due to decreased sales of our products targeting certain higher volume consumer applications.
Research and development. In fiscal year 2013, R&D expense increased $7.8 million, or 21.3%, to $44.6 million, or 13.8% of our revenue, compared with $36.8 million, or 12.1% of our revenue, in fiscal year 2012. R&D expenses increased for higher compensation expense, material purchases and engineering supplies.
Selling, general and administrative. In fiscal year 2013, SG&A expense increased $6.3 million, or 13.8%, to $52.0 million, or 16.1% of our revenue, compared with $45.7 million, or 15.1% of our revenue, for fiscal year 2012. SG&A expenses increased due to increased litigation and related professional fees, a $1.3 million expense to restore a leased facility under the requirements of the lease agreement, and an increase in compensation expense.
56
Table of Contents
Litigation settlement. In fiscal year 2013, we incurred $7.3 million in connection with the global settlement of all claims and litigation between us and GigOptix.
Contingent consideration. In fiscal year 2013, we recorded income of $0.6 million, a result of changes in the fair value of the contingent consideration related to past acquisitions.
Restructuring charges. In fiscal year 2013, restructuring charges were $1.1 million, or 0.3% of our revenue, compared with $1.9 million, or 0.6% of our revenue for fiscal year 2012. Restructuring charges were due to a planned reduction in headcount and included severance and related benefits that we subsequently paid.
Income (loss) from operations. In fiscal year 2013, income from operations decreased $21.7 million, or 40.3%, to $32.1 million, or 9.9%, of our revenue, compared with $53.7 million, or 17.7%, of our revenue for fiscal year 2012.
Warrant liability. In fiscal year 2013, we recorded an expense of $4.3 million compared to a gain of $3.2 million for fiscal year 2012. The expense relates to the change in the estimated fair value of common stock warrants we issued in December 2010, which we carry as a liability at fair value.
Interest expense. In fiscal year 2013, interest expense was $0.8 million, or 0.3% of our revenue, compared with $0.7 million, or 0.2% of our revenue for fiscal year 2012.
Other income. In fiscal year 2013, other income was $0.4 million, from a related-party consulting agreement. The increase was due to higher billing rates over fiscal year 2012.
Provision for income taxes. In fiscal year 2013, the provision for income taxes was an expense of $9.1 million compared to and expense of $16.0 million for fiscal year 2012. The provision for income taxes and the effective income tax rate decreased primarily due to increases in the 2013 period in the amount of income taxed in foreign jurisdictions at generally lower tax rates as well as due to the impact of a retroactive U.S. research and development tax credit that had previously expired on December 31, 2011 and was reinstated as part of The American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 enacted on January 2, 2013, resulting in a larger benefit being recognized during fiscal year 2013.
The difference between the U.S. federal statutory income tax rate of 35% and the Company’s effective income tax rates for fiscal years 2013 and 2012 was driven primarily by changes in fair values of the warrant liability and, in fiscal year 2012, the Class B conversion liability, neither of which are deductible nor taxable for tax purposes, income taxed in foreign jurisdictions at generally lower tax rates, partially offset by U.S. state income taxes, and, in fiscal year 2013, a benefit relating to the retroactive reinstatement of the U.S. research and development tax credits, and, in fiscal year 2012, a $1.7 million deferred income tax benefit resulting from a change in the deferred income tax liability related to acquired intangible assets.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
As of October 3, 2014, we held $173.9 million of cash and cash equivalents, all deposited with financial institutions. Cash from operations was $25.3 million in fiscal 2014, of which the principal components were net loss of $15.3 million, plus non-cash expense of $57.7 million, partially offset by unfavorable changes in operating assets and liabilities of $17.0 million, net of acquired balances. Decreases in accounts receivable of $2.2 million as well as increases in deferred revenue of $7.6 million were partially offset by increases in inventory of $9.6 million and prepaid and other assets of $0.6 million and decreases in accounts payable, accrued and other liabilities and income taxes payable of $7.1 million, $6.8 million and $2.7 million, respectively.
57
Table of Contents
Cash used in investing activities was $264.2 million in fiscal year 2014, which consisted of net business acquisition expenditures of $260.9 million for the purchase of Mindspeed, Nitronex and other smaller businesses, purchases of intangibles of $5.5 million, $17.0 million of purchases of property and capital equipment, including renovation of leased facilities and purchases of production and manufacturing equipment, tooling, engineering equipment and software tools, as well as $5.3 million of purchases of investments. These expenditures were partially offset by proceeds from the sale of businesses of $12.0 million and proceeds from the sale of assets of $12.3 million for the divestiture of the wireless business of Mindspeed and the sale of our CPE product line, respectively.
Cash from financing activities was $302.4 million in fiscal year 2014, of which $337.4 million related to borrowings under our credit facility, net of financing costs. Proceeds from stock option exercises, employee stock purchases and excess tax benefits related to restricted stock awards totaled $2.7 million during the period. Payment of assumed Mindspeed debt totaled $40.9 million. We have presented payments received by Nitronex from GaAs Labs, LLC prior to our acquisition of Nitronex as capital contributions.
On May 8, 2014, we refinanced our outstanding indebtedness under our prior revolving credit facility (Prior Facility) and discharged its obligations thereunder by entering into a credit agreement (Credit Agreement) with Goldman Sachs Bank USA and a syndicate of lenders. Concurrent with the execution of the Credit Agreement, the Company terminated the Prior Facility and repaid the outstanding $245.0 million principal and interest due through draws on the Credit Agreement. The Credit Agreement provides for term loans in an aggregate principal amount of $350.0 million, which mature in May 2021 (Term Loans) and a revolving credit facility of up to $100.0 million, which matures in May 2019 (Revolving Facility). The Term Loans were issued with an original issue discount (OID) of 0.75%, which is being amortized over the term of the Term Loans using the effective interest rate method. Borrowings under both the Term Loans and the Revolving Facility bear interest at variable rates payable quarterly. The Term Loans are payable in quarterly principal installments of 0.25% of the Term Loans on the last business day of each calendar quarter, beginning on the last business day of September 2014, with the remainder due on the maturity date. At the signing of the Credit Agreement, the entire $350.0 million principal, less the OID, amount of the Term Loans, was funded and no draws were made on the Revolving Facility. The Term Loans and Revolving Facility are secured by a first priority lien on substantially all of the Company’s assets and provide that we must comply with certain financial and non-financial covenants. As of October 3, 2014, we were in compliance with all financial and non-financial covenants under the Credit Agreement.
As of October 3, 2014, we had $349.1 million of outstanding Term Loan borrowings under the Credit Agreement with $100.0 million of borrowing availability under the Revolving Facility as of that date. We expect to draw all $100.0 million of remaining borrowing availability under the Revolving Facility in connection with the closing of the BinOptics Acquisition and to fund the remainder of the purchase price from our cash on hand.
In July 2013, we announced that we had licensed GaN process technology from GCS and would be installing such process technology at our Lowell, Massachusetts manufacturing facility. This installation effort is expected to be a multi-year process and to involve tens of millions of dollars of investment in capital equipment, license fees, and other related costs and expenses. We have a long-term technology licensing and transfer commitment that calls for remaining potential payments by us, as of October 3, 2014, of up to $5.3 million through July 2016.
We currently estimate our capital expenditures for property, plant, and equipment in fiscal year 2015 to be approximately $18.5 million.
The undistributed earnings of our foreign subsidiaries are indefinitely reinvested and we do not intend to repatriate such earnings. We believe the decision to reinvest these earnings will not have a significant impact on our liquidity. As of October 3, 2014, cash held by our foreign subsidiaries was $32.9 million, which, along with cash generated from foreign operations, is expected to be used in the support of international growth and working capital requirements.
58
Table of Contents
We plan to use our available cash and cash equivalents and potential remaining borrowing capacity under our Revolving Facility for general corporate purposes, including working capital and the BinOptics Acquisition. We may also use a portion of our cash and cash equivalents and any amounts remaining under our Revolving Facility, which we may draw on from time to time, for the acquisition of, or investment in, complementary technologies, design teams, products and companies. We believe that our cash and cash equivalents, cash generated from operations, and borrowing availability under the Revolving Facility will be sufficient to meet our working capital requirements for at least the next 12 months. We may need to raise additional capital from time to time through the issuance and sale of equity or debt securities, and there is no assurance that we will be able do so on favorable terms or at all.
OFF-BALANCE SHEET ARRANGEMENTS
We do not have significant contractual obligations not fully recorded on our consolidated balance sheet or fully disclosed in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements. As of October 3, 2014, we do not have material material off-balance sheet arrangements as defined in SEC Regulation S-K Item 303(a)(4)(ii).
CONTRACTUAL OBLIGATIONS
The following is a summary of our contractual payment obligations for consolidated debt, purchase agreements, operating leases, other commitments and long-term liabilities as of October 3, 2014, (in thousands):
| Payments Due By Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Obligation |
Total | Less Than 1 Year |
1-3 Years | 3-5 Years | More Than 5 Years |
|||||||||||||||
| Long-term Debt Principal Payments |
$ | 349,125 | $ | 3,478 | $ | 6,853 | $ | 6,717 | $ | 332,077 | ||||||||||
| Estimated Interest Payments on Long-term Debt |
98,991 | 15,652 | 30,837 | 30,226 | 22,276 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating Lease Obligations (1) |
36,203 | 7,388 | 13,292 | 10,426 | 5,097 | |||||||||||||||
| Purchase Commitments (2) |
5,208 | 5,208 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| $ | 489,527 | $ | 31,726 | $ | 50,982 | $ | 47,369 | $ | 359,450 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | We have non-cancelable operating lease agreements for office, research, development, and manufacturing space in the U.S. and foreign locations. We also have operating leases for certain equipment, automobiles and services. These lease agreements expire at various dates through 2022 and certain agreements contain provisions for extension at substantially the same terms as currently in effect. |
| (2) | In the normal course of business, we enter into supply arrangements with certain of our suppliers to purchase minimum quantities of inventories. |
As of October 3, 2014, we had an estimated $1.7 million in asset retirement obligations for the restoration of leased facilities upon the termination of the related leases. Although it is reasonably possible that our estimates could materially change in the next 12 months, we are presently unable to reliably estimate when any cash settlement of these obligations may occur.
As of October 3, 2014, we had a long term technology licensing and transfer commitment that calls for potential payments of up to $5.3 million through July 2016.
As of October 3, 2014, we had recorded $1.7 million of unrecognized tax benefits. The Company is unable to make a reasonable estimate as to when and if such amounts will be paid.
OTHER MATTERS
Inflation did not have a material impact upon our results of operations during the three-year period ended October 3, 2014.
59
Table of Contents
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK.
We are exposed to market risk in the ordinary course of business, which consists primarily of interest rate risk associated with our cash and cash equivalents and our long-term debt obligations, as well as foreign exchange rate risk.
Interest rate risk. The primary objectives of our investment activity are to preserve principal, provide liquidity, and earn a money market rate of return. To minimize market risk, we maintain our portfolio in cash and diversified short-term investments, which may consist of bank deposit and money market funds. The interest rates are variable and fluctuate with current market conditions. The risk associated with fluctuating interest rates is limited to this investment portfolio. We believe that a 10% change in interest rates would not have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations.
Our exposure to interest rate risk also relates to the increase or decrease in the amount of interest expense we must pay on the outstanding debt under the Credit Agreement. The interest rates on our term loans and revolving credit facility are variable interest rates based on our lender’s prime rate or a LIBOR rate, in each case plus an applicable margin, which exposes us to market interest rate risk when we have outstanding borrowings under the Credit Agreement. As of October 3, 2014, we had $349.1 million of outstanding borrowings under the Credit Agreement. Assuming our outstanding debt remains constant under the Credit Agreement for an entire year and the applicable annual interest rate increases or decreases by 1%, our annual interest expense would increase or decrease by $3.5 million.
Foreign currency risk. To date, our international customer agreements have been denominated primarily in U.S. dollars. Accordingly, we have limited exposure to foreign currency exchange rates. The functional currency of a majority of our foreign operations is U.S. dollars with the remaining operations being local currency. The effects of exchange rate fluctuations on the net assets of the majority of our operations are accounted for as transaction gains or losses. We believe that a change of 10% in such foreign currency exchange rates would not have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations. In the future, we may enter into foreign currency exchange hedging contracts to reduce our exposure to changes in exchange rates.
60
Table of Contents
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA.
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Page | ||||
| M/A-COM TECHNOLOGY SOLUTIONS HOLDINGS, INC. |
||||
| 62 | ||||
| Consolidated Financial Statements: |
||||
| 63 | ||||
| 64 | ||||
| 65 | ||||
| 66 | ||||
| 68 | ||||
| 69 | ||||
61
Table of Contents
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc.
Lowell, Massachusetts
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of October 3, 2014 and September 27, 2013 and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for each of the three fiscal years in the period ended October 3, 2014. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of October 3, 2014 and September 27, 2013, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three fiscal years in the period ended October 3, 2014 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company and Nitronex, LLC (“Nitronex”) merged in a common control business combination on February 13, 2014. The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been presented in a manner similar to a pooling-of-interests and include the results of operations of Nitronex since June 25, 2012, which was the date common control commenced and amounts have been retroactively combined using historical amounts.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Boston, Massachusetts
December 9, 2014
62
Table of Contents
M/A-COM TECHNOLOGY SOLUTIONS HOLDINGS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except per share data)
| October 3, 2014 |
September 27, 2013 |
|||||||
| ASSETS |
||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 173,895 | $ | 110,488 | ||||
| Accounts receivable, net |
75,156 | 63,526 | ||||||
| Inventories |
73,572 | 54,908 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
35,957 | 10,404 | ||||||
| Other current assets |
14,769 | 7,121 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current assets |
373,349 | 246,447 | ||||||
| Property and equipment, net |
50,357 | 32,735 | ||||||
| Goodwill |
10,784 | 6,750 | ||||||
| Intangible assets, net |
142,633 | 24,798 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
84,629 | 404 | ||||||
| Other assets |
20,482 | 5,501 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total assets |
$ | 682,234 | $ | 316,635 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accounts payable |
29,797 | 25,986 | ||||||
| Current portion long-term debt |
3,478 | — | ||||||
| Accrued liabilities |
34,248 | 16,921 | ||||||
| Income taxes payable |
865 | 20 | ||||||
| Deferred revenue |
17,258 | 9,231 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current liabilities |
85,646 | 52,158 | ||||||
| Long-term debt, less current portion |
343,178 | — | ||||||
| Warrant liability |
15,801 | 11,873 | ||||||
| Other long-term liabilities |
9,042 | 3,478 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
— | 1,985 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities |
453,667 | 69,494 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 11) |
||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity: |
||||||||
| Preferred stock, $0.001 par value, 10,000 shares authorized, no shares issued |
— | — | ||||||
| Common stock, $0.001 par value, 300,000 shares authorized; 47,607 and 46,493 shares issued and 47,584 and 46,470 shares outstanding as of October 3, 2014 and September 27, 2013, respectively, of which 59 and 74 shares, respectively, are subject to forfeiture |
48 | 46 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(1,354 | ) | (167 | ) | ||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
377,714 | 379,780 | ||||||
| Treasury stock, 23 shares of common stock as of October 3, 2014 and September 27, 2013, respectively, at cost |
(330 | ) | (330 | ) | ||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(147,511 | ) | (132,188 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total stockholders’ equity |
228,567 | 247,141 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
$ | 682,234 | $ | 316,635 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
63
Table of Contents
M/A-COM TECHNOLOGY SOLUTIONS HOLDINGS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(In thousands, except per share data)
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 418,662 | $ | 323,071 | $ | 303,336 | ||||||
| Cost of revenue |
249,674 | 186,658 | 169,213 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Gross profit |
168,988 | 136,413 | 134,123 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||
| Research and development |
73,685 | 44,588 | 36,752 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
86,179 | 52,004 | 45,688 | |||||||||
| Litigation settlement |
— | 7,250 | — | |||||||||
| Contingent consideration |
— | (577 | ) | (3,922 | ) | |||||||
| Restructuring charges |
14,823 | 1,060 | 1,862 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total operating expenses |
174,687 | 104,325 | 80,380 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
(5,699 | ) | 32,088 | 53,743 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Other income (expense): |
||||||||||||
| Warrant liability gain (expense) |
(3,928 | ) | (4,312 | ) | 3,175 | |||||||
| Class B conversion liability expense |
— | — | (44,119 | ) | ||||||||
| Interest expense |
(12,362 | ) | (817 | ) | (695 | ) | ||||||
| Other income |
3,217 | 372 | 185 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Other income (expense), net |
(13,073 | ) | (4,757 | ) | (41,454 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) before income taxes |
(18,772 | ) | 27,331 | 12,289 | ||||||||
| Income tax provision (benefit) |
(8,054 | ) | 9,135 | 15,953 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations |
(10,718 | ) | 18,196 | (3,664 | ) | |||||||
| Loss from discontinued operations |
(4,605 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) |
(15,323 | ) | 18,196 | (3,664 | ) | |||||||
| Accretion to redemption value of redeemable preferred stock and participating stock dividends |
— | — | (2,616 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders |
$ | (15,323 | ) | $ | 18,196 | $ | (6,280 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) per share: |
||||||||||||
| Basic income (loss) per common share: |
||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations |
$ | (0.23 | ) | $ | 0.40 | $ | (0.25 | ) | ||||
| Loss from discontinued operations |
(0.10 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) — basic |
$ | (0.33 | ) | $ | 0.40 | $ | (0.25 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted income (loss) per common share: |
||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations |
$ | (0.23 | ) | $ | 0.39 | $ | (0.25 | ) | ||||
| Loss from discontinued operations |
(0.10 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) — diluted |
$ | (0.33 | ) | $ | 0.39 | $ | (0.25 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Shares used to compute net income (loss) per common share: |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
47,009 | 45,916 | 24,758 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted |
47,009 | 47,137 | 24,758 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
64
Table of Contents
M/A-COM TECHNOLOGY SOLUTIONS HOLDINGS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
(In thousands)
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
(15,323 | ) | $ | 18,196 | $ | (3,664 | ) | |||||
| Pension adjustment |
(90 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Foreign currency translation gain (loss) |
(1,097 | ) | (30 | ) | 44 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total comprehensive income (loss) |
$ | (16,510 | ) | $ | 18,166 | $ | (3,620 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
65
Table of Contents
M/A-COM TECHNOLOGY SOLUTIONS HOLDINGS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT)
(In thousands, except per share data)
| Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss |
Additional Paid-In Capital |
Accumulated Deficit |
Total Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock | Treasury Stock | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance — September 30, 2011 |
1,747 | $ | 2 | — | $ | — | $ | (181 | ) | $ | — | $ | (144,658 | ) | $ | (144,837 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock upon initial public offering, net of costs incurred |
5,556 | 5 | — | — | — | 93,681 | — | 93,686 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conversion of redeemable and convertible preferred stock and Class B conversion liability |
37,677 | 38 | — | — | — | 310,094 | — | 310,132 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Payment of Class B conversion preference |
— | — | — | — | — | (60,000 | ) | — | (60,000 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital contributions |
— | — | — | — | — | 13,645 | — | 13,645 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reclaim of escrow |
— | — | — | — | — | 247 | — | 247 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of stock options awards |
366 | — | — | — | — | 527 | — | 527 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vesting of restricted common stock |
106 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares repurchased for tax withholdings on stock awards |
— | — | 43 | (685 | ) | — | — | — | (685 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based and other incentive compensation |
— | — | — | — | — | 3,762 | — | 3,762 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accretion of preferred stock |
— | — | — | — | — | (554 | ) | (2,062 | ) | (2,616 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Excess tax benefits |
— | — | — | — | — | 214 | — | 214 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation |
— | — | — | — | 44 | — | — | 44 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (3,664 | ) | (3,664 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Balance — September 28, 2012 |
45,452 | 45 | 43 | (685 | ) | (137 | ) | 361,616 | (150,384 | ) | 210,455 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital contributions |
— | — | — | — | — | 8,435 | — | 8,435 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options |
614 | 1 | — | — | — | 604 | — | 605 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vesting of restricted common stock and units |
248 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock pursuant to employee stock purchase plan |
131 | — | — | — | — | 1,281 | — | 1,281 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares repurchased for tax withholdings on stock awards |
— | — | 6 | (77 | ) | — | — | — | (77 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Retirement of treasury stock |
(26 | ) | — | (26 | ) | 432 | — | (432 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based and other incentive compensation |
— | — | — | — | — | 6,096 | — | 6,096 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excess tax benefits |
— | — | — | — | — | 2,180 | — | 2,180 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation |
— | — | — | — | (30 | ) | — | — | (30 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 18,196 | 18,196 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Balance — September 27, 2013 |
46,419 | $ | 46 | 23 | $ | (330 | ) | $ | (167 | ) | $ | 379,780 | $ | (132,188 | ) | $ | 247,141 | |||||||||||||||
(Continued)
66
Table of Contents
M/A-COM TECHNOLOGY SOLUTIONS HOLDINGS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT)
(In thousands, except per share data)
| Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss |
Additional Paid-In Capital |
Accumulated Deficit |
Total Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock | Treasury Stock | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance — September 27, 2013 |
46,419 | $ | 46 | 23 | $ | (330 | ) | $ | (167 | ) | $ | 379,780 | $ | (132,188 | ) | $ | 247,141 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Capital contributions |
— | — | — | — | — | 3,200 | — | 3,200 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common control business combination |
— | — | — | — | — | (26,080 | ) | — | (26,080 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common control tax benefits |
— | — | — | — | — | 6,069 | — | 6,069 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options |
515 | 1 | — | — | — | 2,218 | — | 2,219 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock pursuant to employee stock purchase plan |
150 | — | — | — | — | 1,810 | — | 1,810 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vesting of restricted common stock and units |
536 | 1 | — | — | — | — | — | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares repurchased for tax withholdings on stock awards |
(72 | ) | — | — | — | — | (1,282 | ) | — | (1,282 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based and other incentive compensation |
— | — | — | — | — | 11,277 | — | 11,277 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair value of vested awards assumed in acquisition |
— | — | — | — | — | 785 | — | 785 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Excess tax benefits |
— | — | — | — | — | (63 | ) | — | (63 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation |
— | — | — | — | (1,097 | ) | — | — | (1,097 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension adjustment |
— | — | — | — | (90 | ) | — | — | (90 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (15,323 | ) | (15,323 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Balance — October 3, 2014 |
47,548 | $ | 48 | 23 | $ | (330 | ) | $ | (1,354 | ) | $ | 377,714 | $ | (147,511 | ) | $ | 228,567 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
(Concluded)
67
Table of Contents
M/A-COM TECHNOLOGY SOLUTIONS HOLDINGS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In thousands)
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: |
||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | (15,323 | ) | $ | 18,196 | $ | (3,664 | ) | ||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net (loss) income to net cash from operating activities (net of acquisition): |
||||||||||||
| Warrant liability expense (gain) |
3,928 | 4,312 | (3,175 | ) | ||||||||
| Class B conversion liability expense |
— | — | 44,119 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
52,671 | 14,822 | 12,592 | |||||||||
| Amortization and write-off of deferred financing costs |
3,021 | 321 | 271 | |||||||||
| Contingent consideration |
— | (577 | ) | (3,922 | ) | |||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
(13,328 | ) | (4,650 | ) | 1,985 | |||||||
| Loss on disposal of property and equipment |
89 | 47 | 152 | |||||||||
| Stock-based and other noncash incentive compensation |
11,277 | 6,096 | 3,762 | |||||||||
| Change in operating assets and liabilities (net of acquisition): |
||||||||||||
| Payment of contingent consideration |
— | (5,328 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Accounts receivable |
2,223 | (8,495 | ) | (8,275 | ) | |||||||
| Inventories |
(9,586 | ) | 3,368 | (5,208 | ) | |||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets |
(646 | ) | (4,753 | ) | (220 | ) | ||||||
| Accounts payable |
(7,140 | ) | (3,642 | ) | 5,998 | |||||||
| Accrued and other liabilities |
(6,811 | ) | 4,337 | (1,995 | ) | |||||||
| Income taxes |
(2,656 | ) | 3,714 | (7,017 | ) | |||||||
| Deferred revenue |
7,571 | 1,135 | (5,023 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash from operating activities |
25,290 | 28,903 | 30,380 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: |
||||||||||||
| Purchases of property and equipment |
(16,973 | ) | (12,336 | ) | (15,679 | ) | ||||||
| Strategic investments |
(5,250 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Acquisition of intellectual property |
(5,490 | ) | (897 | ) | — | |||||||
| Acquisition of businesses, net |
(260,875 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Sale of product line |
12,000 | — | — | |||||||||
| Sale of business |
12,345 | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(264,243 | ) | (13,233 | ) | (15,679 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from initial public offering, net of underwriters’ discount |
— | — | 98,175 | |||||||||
| Payment of Class B preference |
— | — | (60,000 | ) | ||||||||
| Capital contributions |
3,200 | 8,435 | 11,578 | |||||||||
| Borrowings from revolving credit facility |
245,000 | — | — | |||||||||
| Payments on revolving credit facility |
(245,000 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Proceeds from notes payable |
350,000 | — | — | |||||||||
| Payments on notes payable |
(3,500 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Payments of assumed debt |
(40,917 | ) | — | (6,532 | ) | |||||||
| Financing and offering costs |
(9,106 | ) | (1,527 | ) | (3,362 | ) | ||||||
| Excess tax benefits |
(63 | ) | 2,180 | 214 | ||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock |
(1,282 | ) | (77 | ) | (685 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from stock option exercises and employee stock purchases |
4,028 | 1,886 | 527 | |||||||||
| Payment of contingent consideration |
— | (675 | ) | (15,000 | ) | |||||||
| Payment of dividends |
— | — | (635 | ) | ||||||||
| Other |
— | (4 | ) | (49 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash from financing activities |
302,360 | 10,218 | 24,231 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| NET INCREASE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
63,407 | 25,888 | 38,932 | |||||||||
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS — Beginning of year |
110,488 | 84,600 | 45,668 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS — End of year |
$ | 173,895 | $ | 110,488 | $ | 84,600 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURES OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION: |
||||||||||||
| Cash paid for interest |
$ | 6,994 | $ | 501 | $ | 317 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash paid for income taxes |
$ | 4,668 | $ | 7,318 | $ | 19,634 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
68
Table of Contents
M/A-COM TECHNOLOGY SOLUTIONS HOLDINGS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. NATURE OF BUSINESS AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. (MACOM or the Company) was incorporated in Delaware on March 25, 2009. MACOM is a leading provider of high-performance analog semiconductor solutions that enable next-generation internet applications, the cloud connected apps economy, and the modern, networked battlefield across the radio frequency (RF), microwave and millimeterwave spectrum. Headquartered in Lowell, Massachusetts, MACOM has offices in North America, Europe, Asia and Australia.
MACOM’s fiscal year ends on the Friday closest to the last day of September. For fiscal years in which there are 53 weeks, the first quarter reporting period includes 14 weeks. The fiscal years presented in the accompanying consolidated financial statements were 53 weeks in length for fiscal year ended October 3, 2014 and 52 weeks in length for fiscal years September 27, 2013 and September 28, 2012. Unless otherwise indicated, references in the consolidated financial statements to fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, are to the Company’s fiscal years ended October 3, 2014, September 27, 2013 and September 28, 2012, respectively.
MACOM acquired Nitronex, LLC (Nitronex) in connection with a common-control business combination on February 13, 2014 (Nitronex Acquisition). Nitronex, a supplier of high-performance gallium nitride (GaN) semiconductors for RF, microwave and millimeterwave applications, was previously acquired by GaAs Labs, LLC (GaAs Labs) on June 25, 2012. GaAs Labs is a stockholder in MACOM and GaAs Labs, Nitronex, and MACOM were under common control from June 25, 2012 through February 13, 2014, due to a common controlling stockholder. The accompanying financial statements as of October 3, 2014 and September 27, 2013, and for each of the fiscal years ended October 3, 2014, September 27, 2013 and September 28, 2012 combine MACOM’s historical consolidated financial statements with the historical financial statements of Nitronex from June 25, 2012 through October 3, 2014, and have been presented in a manner similar to a pooling-of-interests to include the results of operations of each business since the date of common control. The accompanying combined and consolidated financial statements are referred to as “consolidated” for all periods presented.
On December 18, 2013, MACOM completed the acquisition of Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. (Mindspeed), a supplier of high-performance, analog semiconductor solutions for communications infrastructure applications (Mindspeed Acquisition). MACOM acquired Mindspeed to further its expansion into high-performance analog products.
MACOM completed the Mindspeed Acquisition through a cash tender offer (Offer) by Micro Merger Sub, Inc. (Merger Sub), a wholly-owned subsidiary of MACOM, for all of the outstanding shares of common stock, par value $0.01 per share, of Mindspeed (Shares) at a purchase price of $5.05 per share, net to the seller in cash, without interest, less any applicable withholding taxes (Offer Price). Immediately following the Offer, Merger Sub merged with and into Mindspeed, with Mindspeed surviving as a wholly-owned subsidiary of MACOM. At the effective time of the merger, each Share not acquired in the Offer (other than shares held by MACOM, Merger Sub, and Mindspeed, and shares of restricted stock assumed by MACOM in the merger) was converted into the right to receive the Offer Price. MACOM funded the Mindspeed Acquisition through the use of available cash and borrowings under its revolving credit facility (see Note 8). The aggregate purchase price for the Shares, net of cash acquired, was $232.0 million, and MACOM assumed $81.3 million of liabilities and incurred transaction costs of $4.5 million expensed in fiscal year 2014.
The Mindspeed Acquisition was accounted for as a purchase, and the operations of Mindspeed have been included in MACOM’s consolidated financial statements since December 18, 2013, the date of acquisition.
In connection with the Mindspeed Acquisition, MACOM assumed all of the outstanding options and all unvested restricted stock awards under Mindspeed’s equity plans and converted such options and stock awards
69
Table of Contents
into equivalent MACOM awards under the same general terms and conditions as were in existence with adjustments made to shares and exercise prices, if any, pursuant to a formula stipulated in the terms of the acquisition.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principles of Consolidation—The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its majority-owned subsidiaries. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. Prior to the Nitronex Acquisition, MACOM and Nitronex, did not have material intracompany transactions.
Use of Estimates—The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities during the reporting periods, the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting periods, and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements. On an ongoing basis, the Company bases estimates and assumptions on historical experience, currently available information, and various other factors that management believes to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ materially from these estimates and assumptions.
Discontinued Operations—In the second quarter of fiscal year 2014, the Company sold assets of the non-core wireless business of Mindspeed and presented the divested businesses as assets held for sale as of the date of the Mindspeed acquisition. The operating results of the business are reflected in discontinued operations.
Foreign Currency Translation and Remeasurement—The Company’s consolidated financial statements are presented in U.S. dollars. While the majority of the Company’s foreign operations use the U.S. dollar as the functional currency, the financial statements of the Company’s foreign operations for which the functional currency is not the U.S. dollar are translated into U.S. dollars at the exchange rates in effect at the balance sheet dates (for assets and liabilities) and at average exchange rates (for revenue and expenses). The unrealized translation gains and losses on the net investment in these foreign operations are accumulated as a component of other comprehensive income (loss).
The financial statements of the Company’s foreign operations where the functional currency is the U.S. dollar, but where the underlying transactions are transacted in a different currency, are remeasured at the exchange rate in effect at the balance sheet date with respect to monetary assets and liabilities. Nonmonetary assets and liabilities, such as inventories and property and equipment, and related statements of operations accounts, such as cost of revenue and depreciation, are remeasured at historical exchange rates. Revenue and expenses, other than cost of revenue, amortization and depreciation, are translated at the average exchange rate for the period in which the transaction occurred. The net gains (losses) on foreign currency remeasurement are reflected in selling, general and administrative expense in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations. The Company’s recognized net gains and losses on foreign exchange are included in selling, general and administrative expense and for all periods presented were immaterial.
Cash and Cash Equivalents—Cash equivalents are primarily composed of short-term, highly-liquid instruments with an original maturity of three months or less.
Accounts Receivable—Accounts receivable are stated net of an allowance for estimated uncollectible accounts, which is determined by establishing reserves for specific accounts and considering historical and estimated probable losses.
Inventories—Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market. The Company uses a combination of standard cost and moving weighted-average cost methodologies to determine the cost basis for its inventories, approximating a first-in, first-out basis. The standard cost of finished goods and work-in-process inventory is
70
Table of Contents
composed of material, labor and manufacturing overhead, which approximates actual cost. In addition to stating inventory at the lower of cost or market, the Company also evaluates inventory each reporting period for excess quantities and obsolescence, establishing reserves when necessary based upon historical experience, assessment of economic conditions and expected demand. Once recorded, these reserves are considered permanent adjustments to the carrying value of inventory.
Property and Equipment—Property and equipment are stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred, whereas major improvements that significantly extend the useful life of the assets are capitalized as additions to property and equipment.
Property and equipment are depreciated or amortized using the straight-line method over the following estimated useful lives:
| Asset Classification |
Estimated Useful Life In Years | |
| Machinery and equipment |
2 – 7 | |
| Computer equipment and software |
2 – 5 | |
| Furniture and fixtures |
7 – 10 | |
| Leasehold improvements |
Shorter of useful life or term of lease |
Goodwill and Intangible Assets—The Company has intangible assets with indefinite and definite lives. Goodwill and the “M/A-COM” trade name are indefinite-lived assets and were acquired through business combinations. Neither the goodwill nor the “M/A-COM” trade name are subject to amortization; these are reviewed for impairment annually and more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the assets may be impaired. If impairment exists, a loss would be recorded to write down the value of the indefinite-lived assets to their implied fair values. There have been no impairments of intangible assets in any period presented through October 3, 2014. The Company’s other intangible assets, including acquired technology and customer relationships, are definite-lived assets and are subject to amortization. The Company amortizes definite-lived assets over their estimated useful lives, which range from five to ten years, based on the pattern over which the Company expects to receive the economic benefit from these assets.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets—Long-lived assets include property and equipment and definite-lived intangible assets subject to amortization, which includes technology and customer relationships. The Company evaluates long-lived assets for recoverability when events or changes in circumstances indicate that their carrying amounts may not be recoverable. Circumstances which could trigger a review include, but are not limited to, significant decreases in the market price of the asset or asset group, significant adverse changes in the business climate or legal factors, the accumulation of costs significantly in excess of the amount originally expected for the acquisition or construction of the asset, current period cash flow or operating losses combined with a history of losses or a forecast of continuing losses associated with the use of the asset and a current expectation that the asset will more likely than not, be sold or disposed of significantly before the end of its previously estimated useful life.
In evaluating an asset for recoverability, the Company estimates the undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the Company’s use and eventual disposition of the asset. If the sum of the expected undiscounted cash flows is less than the carrying amount of the asset, an impairment loss, equal to the excess of the carrying amount over the fair value of the asset, is recognized. There was no impairment of long-lived assets in any period presented. Intangible assets related to in-process research and development acquired are not amortized until the underlying asset begins revenue generating activity, at which time it is amortized over its estimated useful life. Intangibles related to abandoned in-process research and development projects are expensed in the period the project is abandoned.
Revenue Recognition—The Company recognizes revenue when: (i) there is persuasive evidence that an arrangement exists; (ii) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; (iii) the price is fixed or
71
Table of Contents
determinable; and (iv) collectability is reasonably assured. In circumstances with distribution customers where the Company is unable to conclude certain sales prices are fixed and determinable, the Company defers the recognition of revenue, and the related costs, under agreements providing for rights of return and price protection until such time as the Company’s products are sold by the distributors to their customers. In circumstances with distributor customers where returns are reasonably estimable and the sales price is fixed and determinable, the Company recognizes revenue with the transfer of title and risk of loss, and provide for reserves for returns and other allowances. The Company does not generally provide customers other than distributors the right to return product, with the exception of warranty related matters. Accordingly, the Company does not generally maintain a reserve for sales returns for such customers. Shipping and handling fees billed to customers are recorded as revenue while the related costs are classified as a component of costs of revenue. The Company provides warranties for its products and accrues the estimated costs of warranty claims in the period the related revenue is recorded. As of October 3, 2014 and September 27, 2013, $4.6 million and $3.1 million, respectively, of product costs pertaining to deferred revenue was included in inventories as finished goods in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Advertising Costs—Advertising costs, which are not material, are expensed as incurred.
Research and Development Costs—Costs incurred in the research and development of products are expensed as incurred.
Income Taxes—Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized based on temporary differences between the financial reporting and income tax bases of assets and liabilities, using rates anticipated to be in effect when such temporary differences reverse. A valuation allowance against net deferred tax assets is required if, based upon the available evidence, it is more likely than not that some or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
The Company provides reserves for potential payments of tax to various tax authorities related to uncertain tax positions and other issues. Reserves are based on a determination of whether and how much of a tax benefit taken by the Company in its tax filings or positions is more likely than not to be realized following an examination by taxing authorities. The Company recognizes the financial statement benefit of an uncertain tax position only after considering the probability that a tax authority would sustain the position in an examination. For tax positions meeting a “more-likely-than-not” threshold, the amount recognized in the financial statements is the benefit expected to be realized upon settlement with the tax authority. For tax positions not meeting the threshold, no financial statement benefit is recognized. Potential interest and penalties associated with such uncertain tax positions are recorded as a component of income tax expense.
Nitronex elected, for U.S. income tax purposes, to be taxed as a limited-liability company. As such, for the periods prior to its acquisition by MACOM, Nitronex’s federal and state income taxes are the responsibility of GaAs Labs and no provision for income taxes is recorded in the financial statements for such periods.
Earnings Per Share—Basic net income (loss) per share is computed by dividing net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the period, excluding the dilutive effect of common stock equivalents. Diluted net income (loss) per share reflects the dilutive effect of common stock equivalents, such as convertible preferred stock, stock options, warrants, and restricted stock units, using the treasury stock method.
Asset Retirement Obligations—The Company recognizes the fair value of a liability for an asset retirement obligation in the period in which it is incurred when a reasonable estimate of fair value can be made. The fair value of the liability is added to the carrying amount of the associated asset and this additional carrying amount is amortized over the life of the asset.
Changes in the fair value of a liability for an asset retirement obligation due to the passage of time are measured by applying an interest method of allocation. Under this method, changes in fair value due to the
72
Table of Contents
passage of time are recognized as an increase in the liability and expense in the same expense category for which the asset relates. Changes in fair value resulting from revisions to the timing or the amount of the original estimate of undiscounted cash flows are recognized as an increase, or a decrease in the carrying amounts of the liability and associated asset.
Fair Value Measurements—Financial assets and liabilities are measured at fair value. Fair value is an exit price, representing the amount that would be received from the sale of an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants. As such, fair value is a market-based measurement that should be determined based on assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability. As a basis for considering such assumptions, the Company groups financial assets and liabilities in a three-tier fair value hierarchy, according to the inputs used in measuring fair value as follows: Level 1—observable inputs such as quoted prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities; Level 2—inputs other than quoted prices in active markets that are observable either directly or indirectly, such as quoted prices in active markets for similar assets and liabilities, quoted prices for identical assets and liabilities in markets that are not active, and model-based valuation techniques for which significant assumptions are observable in active markets; and Level 3—unobservable inputs for which there is little or no market data, requiring the Company to develop its own assumptions for model-based valuation techniques. This hierarchy requires the Company to use observable market data, when available, and to minimize the use of unobservable inputs when determining fair value.
The carrying amounts of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued liabilities approximate fair value due to the short-term nature of these assets and liabilities.
Contingent Consideration—The Company estimates and records at the acquisition date, the fair value of contingent consideration making up part of the purchase price consideration for acquisitions. Additionally, at each reporting period, the Company estimates the change in the fair value of contingent consideration, and any change in fair value is recognized in the consolidated statements of operations. The Company estimates the fair value of contingent consideration by discounting the associated expected cash flows, using a probability-weighted, discounted cash flow model. The estimate of the fair value of contingent consideration requires subjective assumptions to be made regarding future operating results, discount rates, and probabilities assigned to various potential operating result scenarios.
Share-Based Compensation—The Company accounts for all share-based compensation arrangements using the fair value method. The Company recognizes compensation expense over the requisite service period of the award, which is generally the vesting period, using the straight-line method and providing that the minimum amount of compensation recorded is equal to the vested portion of the award. The Company records the expense in the consolidated statements of operations in the same manner in which the award recipients’ costs are classified. The Company uses the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to estimate the fair value of stock options, inclusive of assumptions for risk-free interest rates, dividends, expected terms and estimated volatility. The Company records expense related to awards issued to non-employees over the related service period and periodically revalues the awards as they vest. The Company derives the risk-free interest rate assumption from the U.S. Treasury’s rates for U.S. Treasury zero-coupon bonds with maturities similar to the expected term of the award being valued. The Company based the assumed dividend yield on its expectation of not paying dividends in the foreseeable future. The Company calculated the weighted-average expected term of the options using the simplified method, which is a method of applying a formula that uses the vesting term and the contractual term to compute the expected term of a stock option. The decision to use the simplified method is based on a lack of relevant historical data, due to the Company’s limited operating experience. In addition, due to the Company’s limited historical data, the Company incorporates the historical volatility of comparable companies with publicly available share prices to determine estimated volatility. The accounting for stock options requires forfeitures to be estimated at the time of grant and revised, if necessary, in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates.
Guarantees and Indemnification Obligations—The Company enters into agreements in the ordinary course of business with, among others, customers, distributors and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs).
73
Table of Contents
Most of these agreements require the Company to indemnify the other party against third-party claims alleging that a Company product infringes a patent and/or copyright. Certain agreements in which the Company grants limited licenses to specific Company trademarks require the Company to indemnify the other party against third-party claims alleging that the use of the licensed trademark infringes a third-party trademark. Certain of these agreements require the Company to indemnify the other party against certain claims relating to property damage, personal injury, or the acts or omissions of the Company, its employees, agents or representatives. In addition, from time to time, the Company has made certain guarantees in the form of warranties regarding the performance of Company products to customers.
The Company has agreements with certain vendors, creditors, lessors, and service providers pursuant to which the Company has agreed to indemnify the other party for specified matters, such as acts and omissions of the Company, its employees, agents or representatives.
The Company has procurement or licensed agreements with respect to technology that is used in its products and agreements in which the Company obtains rights to a product from an OEM. Under some of these agreements, the Company has agreed to indemnify the supplier for certain claims that may be brought against such party with respect to the Company’s acts or omissions relating to the supplied products or technologies.
The Company’s certificate of incorporation and agreements with certain of its and its subsidiaries’ directors and officers provide them indemnification rights, to the extent legally permissible, against liabilities incurred by them in connection with legal actions in which they may become involved by reason of their service as a director or officer. As a matter of practice, the Company has maintained director and officer liability insurance coverage, including coverage for directors and officers of acquired companies.
The Company has not experienced any losses related to these indemnification obligations in any period presented, and no claims with respect thereto were outstanding as of October 3, 2014. The Company does not expect significant claims related to these indemnification obligations and, consequently, has concluded that the fair value of these obligations is negligible. No liabilities related to indemnification liabilities have been established.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements— Under the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act (JOBS Act), the Company meets the definition of an emerging growth company. The Company has elected to avail itself of the extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards pursuant to Section 107(b) of the JOBS Act.
In April 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) 2014-08, Reporting Discontinued Operations and Disclosures of Disposals of Components of an Entity, which raises the threshold for disposals to qualify as discontinued operations. A discontinued operation is defined as: (1) a component of an entity or group of components that has been disposed of or classified as held for sale and represents a strategic shift that has or will have a major effect on an entity’s operations and financial results; or (2) an acquired business that is classified as held for sale on the acquisition date. ASU 2014-08 also requires additional disclosures regarding discontinued operations, as well as material disposals that do not meet the definition of discontinued operations. The application of this guidance is prospective from the date of adoption and applies only to disposals (or new classifications to held for sale) that have not been reported as discontinued operations in our previously issued financial statements. ASU 2014-09 will be effective for the Company in our fiscal year beginning on October 4, 2014.
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. ASU 2014-09 requires revenue recognition to depict the transfer of goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. ASU 2014-09 sets forth a new revenue recognition model that requires identifying the contract, identifying the performance obligations, determining the transaction price, allocating the transaction price to performance obligations and recognizing the revenue upon satisfaction of performance obligations. The amendments in the ASU can be
74
Table of Contents
applied either retrospectively to each prior reporting period presented or retrospectively with the cumulative effect of initially applying the update recognized at the date of the initial application along with additional disclosures. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of ASU 2014-09, which is effective for the Company in our fiscal year beginning on September 30, 2017.
Evaluation of Subsequent Events—Management has evaluated subsequent events involving the Company for potential recognition or disclosure in the accompanying audited consolidated financial statements through the date of the issuance of the consolidated financial statements. Subsequent events are events or transactions that occurred after the balance sheet date but before the accompanying consolidated financial statements are issued. See Note 26 to these Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
3. ACQUISITIONS AND INVESTMENTS
Acquisition under Common Control—On February 13, 2014, MACOM acquired Nitronex, an entity under common control, through a cash payment of $26.1 million for all of the outstanding ownership interests of Nitronex. MACOM funded the Nitronex Acquisition through the use of available cash and borrowings under its revolving credit facility. The purchase price includes $3.9 million held on account by a third-party escrow agent pending any claims by MACOM in connection with general representation matters made by GaAs Labs in the transaction. The indemnification period expires in August 2015, at which point if no claims are made, all amounts will be paid to GaAs Labs.
On June 25, 2012, GaAs Labs acquired 100% of the outstanding voting stock of Nitronex in exchange for $2.1 million previously advanced by GaAs Labs as notes payable and the assumption of liabilities aggregating $11.2 million, which was accounted for as a purchase. All assets acquired and liabilities assumed were recognized based upon the fair value of such assets and liabilities measured as of the date of acquisition. The full amount of goodwill resulting from this acquisition is deductible for tax purposes. The aggregate purchase price was allocated to the tangible and identifiable intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their estimated fair values at the date of acquisition as follows (in thousands):
| Current assets |
$ | 1,184 | ||
| Other assets |
980 | |||
| Intangible assets |
8,350 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total assets acquired |
10,514 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Current liabilities |
4,219 | |||
| Debt |
6,532 | |||
| Other liabilities |
457 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total liabilities assumed |
11,208 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Net assets acquired |
(694 | ) | ||
| Consideration: |
||||
| Previously advanced notes payable |
2,066 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Goodwill |
$ | 2,760 | ||
|
|
|
The components of the acquired intangible assets were as follows (in thousands):
| Amount | Useful
Lives (Years) |
|||||||
| Technology |
$ | 7,600 | 7 | |||||
| Customer relationships |
750 | 10 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| $ | 8,350 | |||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
The overall weighted-average life of the identified intangible assets acquired in the acquisition is estimated to be seven years.
75
Table of Contents
The Company has presented payments in the form of capital contributions received by Nitronex from the majority stockholder prior to the acquisition of Nitronex of $3.2 million, $8.4 million and $11.6 million, respectively, in fiscal year 2014, 2013 and 2012, as an increase to additional paid-in capital.
Acquisition of Mindspeed Technologies, Inc.—On December 18, 2013, MACOM completed the acquisition of Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. (Mindspeed), a supplier of semiconductor solutions for communications infrastructure applications (Mindspeed Acquisition). The Company acquired Mindspeed to further its expansion into high-performance analog products.
MACOM completed the Mindspeed Acquisition through a cash tender offer (Offer) by Micro Merger Sub, Inc. (Merger Sub), a wholly-owned subsidiary of MACOM, for all of the outstanding shares of common stock, par value $0.01 per share, of Mindspeed (Shares) at a purchase price of $5.05 per share, net to the seller in cash, without interest, less any applicable withholding taxes (Offer Price). Immediately following the Offer, Merger Sub merged with and into Mindspeed, with Mindspeed surviving as a wholly-owned subsidiary of MACOM. At the effective time of the merger, each Share not acquired in the Offer (other than shares held by MACOM, Merger Sub and Mindspeed, and shares of restricted stock assumed by MACOM in the merger) was converted into the right to receive the Offer Price. MACOM funded the Mindspeed Acquisition through the use of available cash and borrowings under its revolving credit facility. The aggregate purchase price for the Shares, net of cash acquired, was $232.0 million and MACOM assumed $81.3 million of liabilities and incurred costs of $4.5 million expensed during fiscal year 2014.
The Mindspeed Acquisition was accounted for as a purchase and the operations of Mindspeed have been included in MACOM’s consolidated financial statements since the date of acquisition.
MACOM is recognizing assets acquired and liabilities assumed based upon the fair value of such assets and liabilities measured as of the date of acquisition. The aggregate purchase price for Mindspeed is being allocated to the tangible and identifiable intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their estimated fair values at the date of acquisition. None of the goodwill resulting from this acquisition is deductible for tax purposes.
The Company will finalize its allocation of purchase price during the first quarter of fiscal year 2015, upon finalization of the income tax related analysis. The preliminary allocation of purchase price as of October 3, 2014, is as follows:
| Original Allocation |
Allocation Adjustments |
October 3,
2014 Adjusted Allocation |
||||||||||
| Assets acquired: |
||||||||||||
| Current assets |
$ | 53,302 | $ | (2,690 | ) | $ | 50,612 | |||||
| Intangible assets |
146,690 | (8,027 | ) | 138,663 | ||||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
66,101 | 26,780 | 92,881 | |||||||||
| Other assets |
33,297 | (1,509 | ) | 31,788 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total assets acquired |
299,390 | 14,554 | 313,944 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Liabilities assumed: |
||||||||||||
| Current liabilities |
31,159 | 4,111 | 35,270 | |||||||||
| Debt |
39,824 | 353 | 40,177 | |||||||||
| Other long-term liabilities |
5,595 | 270 | 5,865 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total liabilities assumed |
76,578 | 4,734 | 81,312 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net assets acquired |
222,812 | 9,820 | 232,632 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Consideration: |
||||||||||||
| Cash paid upon closing, net of cash acquired |
$ | 232,028 | — | $ | 232,028 | |||||||
| Fair value of vested awards assumed in acquisition |
1,491 | (706 | ) | 785 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total consideration |
233,519 | (706 | ) | 232,813 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Goodwill |
10,707 | (10,526 | ) | 181 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
76
Table of Contents
The Allocation Adjustments were recorded during the measurement period between the December 18, 2013 acquisition and the end of fiscal year 2014 as a result of obtaining the information necessary to update preliminary estimates.
In connection with the Mindspeed Acquisition, MACOM assumed all of the outstanding options and all unvested restricted stock awards under Mindspeed’s equity plans and converted such options and stock awards into equivalent MACOM awards under the same general terms and conditions as were in existence with adjustments made to shares and exercise prices, if any, pursuant to a formula stipulated in the terms of the acquisition. The fair value of the assumed options and stock awards was $4.1 million, of which $0.8 million relates to vested stock options which has been included in the purchase consideration and the remainder relates to unvested stock options and stock awards, which will be expensed as the remaining services are provided.
The components of the acquired intangible assets were as follows (in thousands):
| Amount | Useful Lives (Years) | |||||
| Developed technology |
$ | 109,263 | 7 | |||
| Customer relationships |
11,430 | 10 | ||||
| In-process research and development |
17,970 | N/A | ||||
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | 138,663 | |||||
|
|
|
|||||
The overall weighted-average life of the identified intangible assets acquired in the acquisition is estimated to be seven years.
The following is a summary of Mindspeed revenue and earnings included in MACOM’s accompanying consolidated statements of operations for fiscal year 2014 (in thousands):
| Revenue |
94,613 | |||
| Loss from continuing operations before income taxes |
(9,266 | ) |
Unaudited Supplemental Pro Forma Data—The pro forma statements of operations data for fiscal year 2014 below give effect to the Mindspeed Acquisition, described above, as if it had occurred at September 29, 2012. These amounts have been calculated after applying MACOM’s accounting policies and adjusting the results of Mindspeed to reflect the acquisition costs of $4.4 million paid by MACOM, $14.1 million of restructuring charges and change-in-control payments, the impact of the step-up to fair value of the acquired inventory, as well as the additional depreciation and amortization that would have been charged assuming the fair value adjustments to property, plant and equipment and intangible assets and additional interest expense on acquisition-related borrowings had been applied and incurred since September 29, 2012. The supplemental pro forma earnings for fiscal year 2014 and 2013 were adjusted to exclude discontinued operations. This pro forma data is presented for informational purposes only and does not purport to be indicative of the Company’s future results of operations.
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 438,118 | $ | 460,730 | ||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes |
964 | (18,622 | ) | |||||
Other Acquisitions—In the fiscal fourth quarter of 2014 we acquired two businesses, I.K.E., Incorporated (IKE Micro) and Photonic Controls, LLC (Photonic Controls), for total cash consideration of $2.8 million. The first acquisition, IKE Micro, is a specialized build-to-print house based in Nashua, New Hampshire. The primary purpose of IKE Micro acquisition is to drive COGS reductions and further improve gross margin in our
77
Table of Contents
Optoelectronics business. The second acquisition, Photonic Controls, is a small design company based in Horseheads, New York which specializes in photonic semiconductor development and system design. Its primary focus is to design silicon photonic chips for 100G/400G optical networks.
The assets acquired and liabilities assumed were recorded at their fair values and operating results were included in the financial statements from the date of acquisition. The preliminary purchase price allocation resulted in goodwill of $3.9 million and intangible assets, including manufacturing know-how and customer relationships, of $1.6 million recorded on the date of acquisition, which will be amortized over 7-10 years. Additionally, the Company recorded a contingent consideration liability of $0.8 million related to the acquisition of Photonic Controls which is included in other long-term liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet as of October 3, 2014. The maximum possible payment of contingent purchase price is $1.3 million. Approximately $1.7 million of the goodwill resulting from these acquisitions is deductible for tax purposes. The purchase price allocation will be finalized in fiscal 2015 upon receipt of final information related to valuation of intangibles. The acquisitions were not material to the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Acquisition of the MACOM Business—In connection with the acquisition of the MACOM business in March 2009, the Company became obligated to pay the seller up to $30.0 million as contingent consideration. The amount to be paid to the seller was measured based upon the Company’s qualifying revenue, as defined in the purchase agreement, through September 2012. The Company paid $6.0 million and $15.0 million in fiscal years 2013 and 2012, respectively, in full satisfaction of all amounts owed under the arrangement.
The changes in fair value of contingent consideration resulting from acquisitions are set forth below (in thousands):
| Balance — September 30, 2011 |
25,502 | |||
| Payment — MACOM business acquisition |
(15,000 | ) | ||
| Change in fair value |
(3,922 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance — September 28, 2012 |
6,580 | |||
| Payment — MACOM business acquisition |
(6,003 | ) | ||
| Change in fair value |
(577 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance — September 27, 2013 |
— | |||
| Acquisition of Photonic Controls |
820 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance — October 3, 2014 |
$ | 820 | ||
|
|
|
Investments—The Company determines the appropriate classification of its investments at the time of acquisition and re-evaluates such determination at each balance sheet date. The Company records at cost non-marketable equity investments where it does not have the ability to exercise significant influence or control and periodically reviews such investments for impairment.
During fiscal year 2014, the Company made a minority investment of $0.3 million in the convertible debt of a privately-held U.S. based company. The Company classified this investment as trading securities. (See Note 4.)
During fiscal year 2014, the Company made a minority investment of $5.0 million in the equity of a privately-held U.S. based company. This minority equity investment is accounted for under the cost method due to ownership less than 20% and lack of significant influence and is included on the consolidated balance sheets in other long-term assets. The Company evaluated the investment for other-than-temporary impairment as of the end of fiscal year 2014 and determined that no impairment existed. Additionally, the Company determined that the equity investment contained embedded derivatives. The accounting treatment of derivative financial instruments requires that the Company record the fair value of the derivatives as of the inception date of the equity investment and to adjust the fair value as of each subsequent balance sheet date. At the inception of the equity investment and for the consolidated balance sheet date as of October 3, 2014, the Company determined the embedded derivatives did not have value.
78
Table of Contents
4. FAIR VALUE
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis consist of the following (in thousands):
| October 3, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Fair Value | Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) |
Observable Inputs (Level 2) |
Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
|||||||||||||
| Assets |
||||||||||||||||
| Trading securities |
$ | 250 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 250 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total assets measured at fair value |
$ | 250 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 250 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Liabilities |
||||||||||||||||
| Contingent consideration |
$ | 820 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 820 | ||||||||
| Common stock warrant liability |
$ | 15,801 | — | — | $ | 15,801 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total liabilities measured at fair value |
$ | 16,621 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 16,621 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| September 27, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
| Fair Value | Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) |
Observable Inputs (Level 2) |
Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
|||||||||||||
| Liabilities |
||||||||||||||||
| Warrant liability |
$ | 11,873 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 11,873 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total liabilities measured at fair value |
$ | 11,873 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 11,873 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
The changes in assets and liabilities with inputs classified within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy consist of the following (in thousands):
| Fiscal Year 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| September 27, 2013 |
Net Realized/Unrealized Losses (Gains) Included in Earnings |
Purchases and Issuances |
Sales and Settlements |
Transfers in and/or (out) of Level 3 |
October 3, 2014 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Trading securities |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 250 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 250 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Contingent consideration |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 820 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 820 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Warrant liability |
$ | 11,873 | $ | 3,928 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 15,801 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Fiscal Year 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| September 28, 2012 |
Net Realized/Unrealized Losses (Gains) Included in Earnings |
Purchases and Issuances |
Sales
and Settlements |
Transfers in and/or (out) of Level 3 |
September 27, 2013 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Contingent consideration |
$ | 6,580 | $ | (577 | ) | $ | — | $ | (6,003 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Warrant liability |
$ | 7,561 | $ | 4,312 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 11,873 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Fiscal Year 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| September 30, 2011 |
Net Realized/Unrealized Losses (Gains) Included in Earnings |
Purchases and Issuances |
Sales
and Settlements |
Transfers in and/or (out) of Level 3 |
September 28, 2012 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Contingent consideration |
$ | 25,502 | $ | (3,922 | ) | $ | — | $ | (15,000 | ) | $ | — | $ | 6,580 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Warrant liability |
$ | 10,736 | $ | (3,175 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 7,561 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Class B conversion liability |
$ | 81,378 | $ | 44,119 | $ | — | $ | (125,497 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
79
Table of Contents
The fair values of the contingent consideration liabilities were estimated based upon a risk-adjusted present value of the probability-weighted expected payments by the Company. Specifically, the Company considered base, upside and downside scenarios for the operating metrics upon which the contingent payments are to be based. Probabilities were assigned to each scenario and the probability-weighted payments were discounted to present value using risk-adjusted discount rates.
For periods prior to March 2012, the fair value of the common stock warrants was estimated based upon a present value of the probability-weighted expected investment returns to the holders. The Company weighted various scenarios of possible investment returns to the holders over the terms of the contracts, such as upon a sale of the Company and upon an initial public offering of its common stock, using a range of potential outcomes. Using the scenarios developed, management considered the likely timing and method of exercise of the warrants and investment returns to the holders. Where a settlement was considered likely in the near term, the probable settlement amounts were weighted. Where the time to exercise was expected to be longer, a Black-Scholes option pricing model was used to estimate the fair value of the warrants, giving consideration to remaining contractual life, expected volatility and risk free rates. The probability-weighted expected settlement of the warrant was discounted to the present using a risk adjusted discount rate. As of October 3, 2014 and September 27, 2013, the fair value of the common stock warrants has been estimated using a Black-Scholes option pricing model giving consideration to the quoted market price of the common stock on that date, an expected lives of 6.2 years and 7.2 years, expected volatility of 42.3% and 43.5% and risk free rates of 2.16% and 2.02%, respectively. The change in approach to estimation results from the Company’s IPO in March 2012 and the availability of a quoted market price for the common stock underlying the warrants.
The fair values of the Class B conversion liabilities were estimated based upon a consideration of the estimated fair value of the underlying common stock into which the Class B is convertible, and the expected preferential payments pursuant to the terms of the securities. The Company estimated the fair value of the common stock by using the same probability-weighted scenarios used in estimating the fair value of the warrants. For each potential scenario, the value to the Class B was estimated relative to the existing preferences. The amount in excess of the liquidation preferences, if any, was then probability-weighted and discounted to the present using a risk adjusted discount rate. The Class B conversion liabilities were settled upon the closing of the Company’s IPO in March 2012.
These estimates include significant judgments and actual results could materially differ and have a material impact upon the values of the recorded liabilities. Any changes in the estimated fair values of the liabilities in the future will be reflected in the Company’s earnings and such changes could be material.
5. ALLOWANCE FOR DOUBTFUL ACCOUNTS
The activity in the allowance for doubtful accounts related to accounts receivable is as follows (in thousands):
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Balance — beginning of year |
$ | 195 | $ | 699 | $ | 657 | ||||||
| Provision (recoveries), net |
70 | (443 | ) | 42 | ||||||||
| Charge-offs |
(39 | ) | (61 | ) | — | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Balance — end of year |
$ | 226 | $ | 195 | $ | 699 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
80
Table of Contents
6. INVENTORIES
Inventories consist of the following (in thousands):
| October 3, 2014 |
September 27, 2013 |
|||||||
| Raw materials |
$ | 34,919 | $ | 27,855 | ||||
| Work-in-process |
5,500 | 6,021 | ||||||
| Finished goods |
33,153 | 21,032 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 73,572 | $ | 54,908 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
7. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
Property and equipment consists of the following (in thousands):
| October 3, 2014 |
September 27, 2013 |
|||||||
| Machinery and equipment |
$ | 68,438 | $ | 48,050 | ||||
| Leasehold improvements |
7,998 | 5,129 | ||||||
| Furniture and fixtures |
1,017 | 782 | ||||||
| Construction in process |
12,918 | 6,234 | ||||||
| Computer equipment and software |
7,758 | 6,384 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total property and equipment |
98,129 | 66,579 | ||||||
| Less accumulated depreciation and amortization |
(47,772 | ) | (33,844 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Property and equipment — net |
$ | 50,357 | $ | 32,735 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Depreciation and amortization expense related to property and equipment for fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 was $14.0 million, $10.5 million and $9.0 million, respectively.
8. DEBT
On September 26, 2013, and as amended November 5, 2013, the Company entered into an amended and restated loan agreement with a syndicate of lenders, which provided for a revolving credit facility of up to $300.0 million that was due to mature in September 2018 (Prior Facility). Borrowings under the revolving credit facility either bore a variable interest rate based on either the lender’s prime rate or a LIBOR rate, plus an applicable margin. The revolving credit facility was secured by a first priority lien on substantially all of the Company’s assets and required compliance with certain financial and non-financial covenants. In connection with the Mindspeed and Nitronex acquisitions, MACOM drew down an aggregate of $245.0 million of indebtedness on its Prior Facility.
On May 8, 2014, the Company refinanced its outstanding indebtedness under the Prior Facility and discharged its obligations thereunder by entering into a credit agreement (Credit Agreement) with Goldman Sachs Bank USA and a syndicate of lenders. Concurrent with the execution of the Credit Agreement, the Company terminated the Prior Facility and repaid the outstanding $245.0 million principal and interest due through draws on the Credit Agreement. Upon terminating the Prior Facility, previously deferred financing costs pertaining to that facility of $2.1 million were expensed as additional interest.
The Credit Agreement provides for term loans in an aggregate principal amount of $350.0 million, which mature in May 2021 (Term Loans) and a revolving credit facility of up to $100.0 million, which matures in May 2019 (Revolving Facility). The Term Loans were issued with an original issue discount of 0.75%, which is being amortized over the term of the Term Loans using the straight-line method, which approximates the effective interest rate method. Borrowings under the Term Loans bear interest (payable quarterly) at: (i) for LIBOR loans,
81
Table of Contents
a rate per annum equal to the LIBOR rate (subject to a floor of 0.75%), plus an applicable margin of 3.75%, and (ii) for base rate loans, a rate per annum equal to the prime rate (subject to a floor of 1.75%), plus an applicable margin of 2.75%. Borrowings under the Revolving Facility bear interest (payable quarterly) at (i) for LIBOR loans, a rate per annum equal to the LIBOR rate, plus an applicable margin in the range of 2.00% to 2.50% (based on the Company’s total net leverage ratio being within certain defined ranges), and (ii) for base rate loans, a rate per annum equal to the prime rate, plus an applicable margin in the range of 1.00% to 1.50% (based on the Company’s total net leverage ratio being within certain defined ranges). The Company also pays a quarterly unused line fee for the Revolving Facility in the range of 0.25% to 0.375% (based on the Company’s total net leverage ratio being within certain defined ranges) as well as overall agency fees. The Term Loans are payable in quarterly principal installments of 0.25% of the Term Loans on the last business day of each calendar quarter, beginning on the last business day of September 2014, with the remainder due on the maturity date. At the signing of the Credit Agreement, the entire $350 million principal amount of the Term Loans was funded, and no draws were made on the Revolving Facility through October 3, 2014. The Term Loans and Revolving Facility are secured by a first priority lien on substantially all of the Company’s assets and provide that the Company must comply with certain financial and non-financial covenants. The Company incurred $8.7 million in fees for the issuance of the Credit Agreement which were recorded as deferred financing costs and are being amortized over the life of Credit Agreement as interest expense. As of October 3, 2014, approximately $8.2 million of deferred financing costs remain unamortized.
As of October 3, 2014, the following remained outstanding on the Term Loans:
| Principal balance |
$ | 349,125 | ||
| Unamortized discount |
(2,469 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| 346,656 | ||||
| Current portion |
3,478 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Long-term, less current portion |
$ | 343,178 | ||
|
|
|
As of October 3, 2014, the minimum principal payments under the Term Loans in future fiscal years was as follows (in thousands):
| 2015 |
$ | 3,478 | ||
| 2016 |
3,444 | |||
| 2017 |
3,409 | |||
| 2018 |
3,375 | |||
| 2019 |
3,342 | |||
| Thereafter |
332,077 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
$ | 349,125 | ||
|
|
|
The fair value of the Term Loans was estimated to be approximately $350.0 million as of October 3, 2014, and was determined using Level 3 inputs, including a quoted rate.
Additionally, the Company assumed $40.9 million of debt in its 2014 acquisitions. The Company paid off these assumed debt amounts of $40.9 million during fiscal year 2014.
9. EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS
The Company established a defined contribution savings plan under Section 401(k) of the Code (Section 401(k)) on October 1, 2009 (401(k) Plan). The 401(k) Plan follows a calendar year, covers substantially all U.S. employees who meet minimum age and service requirements, and allows participants to defer a portion of their annual compensation on a pretax basis, subject to legal limitations. Company contributions to the plan may be made at the discretion of the Company’s board of directors. There were no Company contributions made to the 401(k) Plan for calendar year 2014 through October 3, 2014. Contributions to the 401(k) Plan for calendar years 2013 and 2012 were $1.0 million and $1.0 million, respectively.
82
Table of Contents
The Company’s employees located in foreign jurisdictions meeting minimum age and service requirements participate in defined contribution plans whereby participants may defer a portion of their annual compensation on a pretax basis, subject to legal limitations. Company contributions to these plans are discretionary and vary per region. The Company expensed contributions of $1,045,000, $881,000 and $711,000 for fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Nitronex has an established defined contribution savings plan (Nitronex Plan) under Section 401(k) covering substantially all U.S. employees who meet minimum age and service requirements, and allows participants to defer a portion of their annual compensation on a pretax basis, subject to legal limitations. The Nitronex Plan follows a calendar year.
As a result of the Mindspeed Acquisition, the Company maintains a qualified defined benefit pension plan for its subsidiary located in Germany. The plan is unfunded with a benefit obligation of approximately $1.4 million October 3, 2014, which is included in other long-term liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet as of October 3, 2014. The assumptions used in calculating the benefit obligation for the plan are dependent on the local economic conditions and were measured as of October 3, 2014. The net periodic benefit costs were not material to the Company during fiscal year 2014.
10. ACCRUED LIABILITIES
Accrued liabilities consist of the following (in thousands):
| October 3, 2014 |
September 27, 2013 |
|||||||
| Compensation and benefits |
$ | 19,540 | $ | 9,935 | ||||
| Product warranty |
693 | 566 | ||||||
| Professional fees |
1,528 | 1,905 | ||||||
| Distribution costs |
1,757 | 672 | ||||||
| Restructuring costs |
801 | 145 | ||||||
| Interest payable |
2,447 | 131 | ||||||
| Rent and utilities |
1,658 | 546 | ||||||
| Other |
5,824 | 3,021 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 34,248 | $ | 16,921 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
11. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Operating Leases—The Company has non-cancelable operating lease agreements for office, research and development and manufacturing space in the United States and foreign locations. The Company also has operating leases for certain equipment, automobiles and services in the United States and foreign jurisdictions. These lease agreements expire at various dates through 2022 and certain agreements contain provisions for extension at substantially the same terms as currently in effect. Any lease escalation clauses, rent abatements and/or concessions, such as rent holidays and landlord or tenant incentives or allowances, are included in the determination of straight-line rent expense over the lease term.
83
Table of Contents
Future minimum lease payments for the next five fiscal years as of October 3, 2014, are as follows (in thousands):
| 2015 |
$ | 7,388 | ||
| 2016 |
6,909 | |||
| 2017 |
6,383 | |||
| 2018 |
5,362 | |||
| 2019 |
5,064 | |||
| Thereafter |
5,097 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total minimum lease payments |
$ | 36,203 | ||
|
|
|
Rent expense incurred under non-cancelable operating leases was $6.6 million, $4.5 million and $4.1 million in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Pursuant to the terms of a facility lease, the Company would be obligated to reimburse a landlord for lease incentives of up to $1.0 million should the Company default on the lease during the term, which expires in January 2018.
The Company is obligated under certain facility leases to restore those facilities to the condition in which the Company or its predecessors first occupied the facilities. The Company is required to remove leasehold improvements and equipment installed in these facilities prior to termination of the leases. The estimated costs for the removal of these assets are recorded as asset retirement obligations. A summary of the changes in the estimated fair values of the asset retirement obligations is as follows (in thousands):
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Balance — beginning of year |
$ | 994 | $ | 1,074 | $ | 913 | ||||||
| Assumed on acquisition |
900 | — | — | |||||||||
| Payments |
(442 | ) | (1,403 | ) | (41 | ) | ||||||
| Accretion expense and settlements |
223 | 1,323 | 202 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Balance — end of year |
$ | 1,675 | $ | 994 | $ | 1,074 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Purchase Commitments—As of October 3, 2014, the Company had outstanding non-cancelable purchase commitments aggregating $5.2 million pursuant to inventory supply arrangements.
Litigation—The Company is periodically subject to legal proceedings, claims and contingencies arising in the ordinary course of business.
Patent Suit Against Laird. We brought a patent infringement suit against Laird Technologies, Inc. (Laird) in the Federal District Court for the District of Delaware on February 11, 2014, seeking monetary damages and a permanent injunction. The suit alleges that Laird infringes on our United States Patent No. 6,272,349 (‘349 Patent), titled “Integrated Global Positioning System Receiver,” by making, using, selling, offering to sell or selling products incorporating an integrated global positioning receiver that include structure(s) recited in the ‘349 Patent, including global positioning system modules for automotive industry customers. Laird filed an answer and declaratory judgment claims of invalidity and noninfringement on June 30, 2014. We filed a reply to the counterclaims on July 24, 2014.
We filed a motion for preliminary injunction, seeking to enjoin Laird’s infringement pending full trial on the merits. The court granted the motion for a preliminary injunction on June 13, 2014 and required us to post a bond of $4 million to secure the injunction. In granting the injunction, the court found that we are likely to
84
Table of Contents
succeed on the merits of the case at a full trial and that the equities weighed in favor of preliminarily enjoining Laird from making sales of its product until trial. Trial is scheduled to begin on May 16, 2016.
Mindspeed Tender Offer Litigation in Delaware and California. Following our November 2013 announcement of the execution of a definitive agreement between us and Mindspeed contemplating a tender offer by us for all outstanding shares of common stock of Mindspeed and thereafter a merger with Mindspeed (Merger), a number of purported class action lawsuits were filed against Mindspeed, its directors, our merger subsidiary and us in the Delaware Court of Chancery and the California Superior Court for Orange County.
The complaints alleged, generally, that the Mindspeed director defendants breached their fiduciary duties to Mindspeed stockholders, and that the other defendants aided and abetted such breaches, by seeking to sell Mindspeed through an allegedly defective process, for an unfair price, and on unfair terms. The lawsuits sought, among other things, equitable relief that would enjoin the consummation of the proposed Merger, rescission of the proposed Merger (to the extent the proposed Merger has already been consummated), damages and attorneys’ fees and costs.
Further Discussion of Delaware Tender Offer Litigation. On November 22, 2013, an amended complaint was filed in the Delaware Court of Chancery. The amended complaint included similar allegations to the original complaint, along with claims that the Mindspeed Schedule 14D-9 filed in connection with the Merger included misstatements or omissions of material facts. On November 25, 2013, a motion for preliminary injunction was filed in the Delaware Court of Chancery. On December 3, 2013, all of the complaints filed in the Delaware Court of Chancery were consolidated (Delaware Actions).
On December 6, 2013, the plaintiffs in the Delaware Actions filed their brief in support of a motion to enjoin the proposed Merger. While the Defendants denied the allegations made in the lawsuits and maintain that they have committed no wrongdoing whatsoever, to permit the timely consummation of the Merger, and without admitting the validity of any allegations made in the lawsuits, the Defendants concluded that it was desirable that the Delaware Actions be resolved.
On December 9, 2013, the Defendants’ and plaintiffs’ counsel in the Delaware Actions entered into a memorandum of understanding to settle the Delaware Actions and to resolve all allegations which were brought or could have been brought by the purported class of Mindspeed shareholder plaintiffs. The settlement provides for the release of all claims against the Defendants relating to the proposed Merger. In connection with the settlement, Mindspeed agreed to provide additional supplemental disclosures concerning the tender offer as reflected in Amendment No. 3 to the Schedule 14D-9 filed with the SEC on December 10, 2013, which supplement the information provided in the Schedule 14D-9. After the parties entered into the memorandum of understanding, the motion for a preliminary injunction was withdrawn and the hearing vacated in the Delaware Actions. The Merger closed on December 18, 2013. The parties submitted final settlement papers to the Delaware Court of Chancery, which ordered that notice of the settlement be issued to class members. On September 23, 2014, the Court of Chancery approved the settlement and awarded plaintiffs’ counsel the agreed-upon attorneys’ fee of $425,000.
Further Discussion of California Tender Offer Litigation. On December 5, 2013, an amended complaint was filed in one of the California actions. The amended complaint includes similar allegations to the original complaint along with claims that the Mindspeed Schedule 14D-9 filed in connection with the Merger included misstatements or omissions of material facts. Plaintiffs in the action filed a request to dismiss the case in light of the settlement approved by the Delaware Court of Chancery. On November 5, 2014, the California Court entered an order dismissing the action.
CSR Matter. In January 2013, CSR Technology Inc. (CSR) filed a complaint against us in the Massachusetts Superior Court for Suffolk County alleging breach of contract, breach of the implied covenant of good faith and fair dealing, misrepresentation, deceptive business practices and unfair competition, all relating to our purported
85
Table of Contents
failure to honor an alleged minimum purchase commitment contract with respect to certain semiconductor chips to be supplied by CSR for use in our automotive module product. The complaint claimed alleged damages of $2.2 million and asked for attorney’s fees and other remedies. We filed an answer to the complaint on January 28, 2013. The parties concluded fact discovery and CSR filed a motion for summary judgment, which we opposed. The parties agreed to settle the case in July 2014 without any finding of liability or judgment against us, and the compliant was dismissed by the court with prejudice in August 2014.
With respect to the above legal proceedings, individually and in the aggregate, unless described above, we have not been able to reasonably estimate the amount or range of any possible loss, and accordingly have not accrued or disclosed any related amounts of possible loss in the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
12. RESTRUCTURINGS
The Company has periodically implemented restructuring actions in connection broader plans to reduce staffing, and, generally, reduce operating costs. The restructuring expenses are comprised of direct and incremental costs related to headcount reductions, including, change-in-control obligations, severance, and outplacement fees for the terminated employees. The following is a summary of the costs incurred and remaining balances included in accrued expenses related to restructuring actions taken (in thousands):
| Balance — September 30, 2011 |
$ | 522 | ||
| Current period charges |
1,862 | |||
| Payments |
(2,056 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance — September 28, 2012 |
328 | |||
| Current period charges |
1,060 | |||
| Payments |
(1,243 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance — September 27, 2013 |
145 | |||
| Current period charges |
14,823 | |||
| Payments |
(14,167 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance — October 3, 2014 |
$ | 801 | ||
|
|
|
The restructuring actions taken in fiscal years 2013 and 2012, which related to headcount reductions, are complete.
In fiscal year 2014, the Company implemented restructuring plans to reduce manufacturing and operating costs of the Mindspeed and Nitronex operations through a reduction of staffing. These restructuring plans resulted in a charge to continuing operations in fiscal year 2014, and the related obligations are expected to be paid through the first quarter of fiscal year 2015. No further charges are expected related to this plan. The Company’s restructuring charges are primarily employee related with non-employee related charges determined to be immaterial.
13. PRODUCT WARRANTIES
The Company establishes a product warranty liability at the time of revenue recognition. Product warranties generally have terms of between 12 months and 60 months and cover nonconformance with specifications and defects in material or workmanship. For sales to distributors, our warranty generally begins when the product is resold by the distributor. For sales to automotive customers, our warranty generally begins when the automobiles are sold to consumers and generally coincides with the automobile manufacturer’s warranty, which is typically three years or less based upon mileage limitations. The liability is based on estimated costs to fulfill customer product warranty obligations and utilizes historical product failure rates. Should actual warranty obligations differ from estimates, revisions to the warranty liability may be required.
86
Table of Contents
Product warranty liability activity is as follows (in thousands):
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Balance — beginning of year |
$ | 566 | $ | 910 | $ | 1,885 | ||||||
| Assumed on acquisition |
202 | — | 44 | |||||||||
| Provisions |
201 | 1,083 | 399 | |||||||||
| Direct charges |
(276 | ) | (1,427 | ) | (1,418 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Balance — end of year |
$ | 693 | $ | 566 | $ | 910 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
14. INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Amortization expense related to amortized intangible assets is as follows (in thousands):
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 18,787 | $ | 2,986 | $ | 2,259 | ||||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
1,806 | 1,335 | 1,336 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 20,593 | $ | 4,321 | $ | 3,595 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Intangible assets consist of the following (in thousands):
| October 3, 2014 |
September 27, 2013 |
|||||||
| Acquired technology |
$ | 131,953 | $ | 23,637 | ||||
| Customer relationships |
24,670 | 13,150 | ||||||
| In-process research and development |
17,970 | — | ||||||
| Trade name |
3,400 | 3,400 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
177,993 | 40,187 | ||||||
| Less accumulated amortization |
(35,360 | ) | (15,389 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Intangible assets — net |
$ | 142,633 | $ | 24,798 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
A summary of the activity in intangible assets and goodwill follows (in thousands):
| Total | Acquired Technology |
Customer Relationships |
In-Process Research and Development |
Trade Name |
Goodwill | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at September 28, 2012 |
$ | 44,654 | $ | 21,354 | $ | 13,150 | $ | — | $ | 3,400 | $ | 6,750 | ||||||||||||
| Net intangibles acquired |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other intangibles purchased |
2,283 | 2,283 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Balance at September 27, 2013 |
46,937 | 23,637 | 13,150 | — | 3,400 | 6,750 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net intangibles acquired |
137,405 | 103,881 | 11,520 | 17,970 | — | 4,034 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other intangibles purchased |
4,435 | 4,435 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Balance at October 3, 2014 |
$ | 188,777 | $ | 131,953 | $ | 24,670 | $ | 17,970 | $ | 3,400 | $ | 10,784 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
87
Table of Contents
As of October 3, 2014, estimated amortization of the intangible assets in future fiscal years, was as follows (in thousands):
| 2015 |
$ | 22,920 | ||
| 2016 |
20,825 | |||
| 2017 |
19,942 | |||
| 2018 |
17,055 | |||
| 2019 |
14,006 | |||
| Thereafter |
26,515 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
$ | 121,263 | ||
|
|
|
The in-process research and development and trade name are indefinite-lived intangible assets and are not subject to amortization. The Company performed its annual impairment test for the trade name and goodwill in the fourth quarter of each fiscal year presented, concluding no impairment existed.
Accumulated amortization, for the acquired technology and customer relationships, was $27.8 million and $7.6 million, respectively, as of October 3, 2014, and $9.6 million and $5.8 million, respectively, as of September 27, 2013.
In July 2013, the Company entered into a long term technology licensing and transfer agreement that calls for potential payments by the Company of up to $9.0 million through July 2016 based upon the achievement of specified milestones. Costs incurred in connection with the licensing and the transfer of the technology aggregated $4.4 million and $1.7 million in fiscal years 2014 and 2013, respectively, and were capitalized as incurred as acquired technology. Costs will be amortized to costs of sales upon completion of the transfer, which is currently expected to be completed through fiscal year 2016.
15. INCOME TAXES
Deferred income taxes reflect the net effect of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and amounts used for income tax purposes. The components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows (in thousands):
| October 3, 2014 |
September
27, 2013 |
|||||||
| Current deferred tax assets: |
||||||||
| Accrued liabilities |
$ | 9,830 | $ | 4,361 | ||||
| Inventory |
8,088 | 3,466 | ||||||
| Deferred revenue |
4,451 | 2,251 | ||||||
| Accounts receivable |
142 | 59 | ||||||
| Federal net operating loss |
15,452 | 267 | ||||||
| Other current deferred tax assets |
46 | — | ||||||
| Valuation allowance |
(2,052 | ) | — | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Current net deferred tax assets |
$ | 35,957 | $ | 10,404 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Non-current deferred tax assets (liabilities): |
||||||||
| Federal and foreign net operating losses and credits |
$ | 128,035 | $ | 4,718 | ||||
| Intangible assets |
(33,158 | ) | (2,554 | ) | ||||
| Property and equipment |
(3,072 | ) | (2,889 | ) | ||||
| Other non-current deferred tax assets |
272 | — | ||||||
| Valuation allowance |
(7,448 | ) | (856 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Non-current net deferred tax assets (liabilities) |
84,629 | (1,581 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total deferred tax asset |
$ | 120,586 | $ | 8,823 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
88
Table of Contents
As of October 3, 2014, the Company had $381.3 million of gross federal net operating loss carryforward consisting of $307.0 million attributable to the Mindspeed Acquisition, $9.9 million relating to a prior acquisition, and $64.4 million relating to the current period loss. The reported net operating loss carryforward includes any limitation under Sections 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, which applies to an ownership change as defined under Section 382.
The deferred tax assets as of October 3, 2014 were reduced by $1.7 million representing tax deductions arising from the exercise of stock options by Company employees in excess of compensation recognized for financial reporting. Additional paid-in capital will be increased by $1.7 million if and when such deferred tax assets are ultimately realized.
The domestic and foreign income (loss) from continuing operations before taxes were as follows (in thousands):
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| United States |
$ | (38,708 | ) | $ | 13,052 | $ | 7,443 | |||||
| Foreign |
19,936 | 14,279 | 4,846 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) from operations before income taxes |
$ | (18,772 | ) | $ | 27,331 | $ | 12,289 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The components of the provision for income taxes are as follows (in thousands):
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Current: |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
$ | 712 | $ | 11,287 | $ | 10,487 | ||||||
| State |
(419 | ) | 1,512 | 2,141 | ||||||||
| Foreign |
2,181 | 986 | 1,340 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Current provision |
2,474 | 13,785 | 13,968 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Deferred: |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
(8,968 | ) | (3,326 | ) | 2,569 | |||||||
| State |
(313 | ) | (1,146 | ) | 258 | |||||||
| Foreign |
(725 | ) | (273 | ) | (1,387 | ) | ||||||
| Change in valuation allowance |
(522 | ) | 95 | 545 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Deferred provision (benefit) |
(10,528 | ) | (4,650 | ) | 1,985 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total provision |
$ | (8,054 | ) | $ | 9,135 | $ | 15,953 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The Company’s net deferred tax asset relates predominantly to its operations in the United States. A valuation allowance is recorded when, based on assessment of both positive and negative evidence, management determines that it is not more likely than not that the assets are recoverable. Such assessment is required on a jurisdictional basis.
The $9.5 million of valuation allowance as of October 3, 2014 relates primarily to state net operating loss (NOL) carryforwards assumed in the Mindspeed Acquisition whose recovery is not considered more likely than not. The $0.9 million of valuation allowance as of September 27, 2013 related to a foreign jurisdiction for which the Company does not believe recovery of the deferred tax asset is more likely than not.
89
Table of Contents
The Company’s effective tax rates differ from the federal and statutory rate as follows:
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Federal statutory rate |
35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||||||
| Nitronex losses |
(5.7 | ) | 8.3 | 23.0 | ||||||||
| Foreign rate differential |
24.3 | (9.5 | ) | (28.4 | ) | |||||||
| State taxes net of federal benefit |
2.4 | 2.1 | 10.1 | |||||||||
| Change in tax status |
— | — | (9.3 | ) | ||||||||
| Class B Conversion and warrant liabilities |
(7.3 | ) | 4.1 | 95.9 | ||||||||
| Change in valuation allowance |
(0.6 | ) | 0.3 | 3.7 | ||||||||
| Research and development credits |
4.1 | (8.0 | ) | (3.7 | ) | |||||||
| Nondeductible compensation expense |
(3.4 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Nondeductible legal fees |
(4.1 | ) | 0.6 | 1.7 | ||||||||
| Other permanent differences |
(1.8 | ) | 0.5 | 1.8 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Effective income tax rate |
42.9 | % | 33.4 | % | 129.8 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
For fiscal year 2014, the effective tax rate to calculate the tax benefit on $18.8 million of pre-tax loss from continuing operations was 42.9%. For fiscal years 2013 and 2012 the effective tax rate to calculate the tax expense on pre-tax income of $27.3 million and $12.3 million, respectively, was 33.4% and 129.8%, respectively. The effective income tax rate for fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 were primarily impacted by pre-acquisition Nitronex losses and a lower income tax rate in many of the foreign jurisdictions in which the Company’s foreign subsidiaries operate. For the fiscal year ended 2012, the effective tax rate was also significantly impacted by the changes in fair values of the Class B conversion and warrant liability, which are neither taxable nor deductible for income tax purposes.
All earnings of foreign subsidiaries are considered indefinitely reinvested for the periods presented. Undistributed earnings of all foreign subsidiaries as of October 3, 2014 aggregated $54.4 million. It is not practicable to determine the U.S. federal and state deferred tax liabilities associated with such foreign earnings.
Activity related to unrecognized tax benefits is as follows (in thousands):
| Balance — September 30, 2011 |
$ | 437 | ||
| Additions based on tax positions |
597 | |||
| Reductions based on tax positions |
(437 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance — September 28, 2012 |
597 | |||
| Reductions based on tax positions |
(597 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance — September 27, 2013 |
— | |||
| Additions based on tax positions |
1,670 | |||
| Reductions based on tax positions |
— | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance — October 3, 2014 |
$ | 1,670 | ||
|
|
|
The balance of the unrecognized tax benefit as of October 3, 2014 includes a $1.4 million reduction in current deferred tax assets and $0.3 million is included in other long-term liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The entire balance of unrecognized tax benefits, if recognized, will reduce income tax expense. It is the Company’s policy to recognize any interest and penalties accrued related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense. During fiscal year 2014, the Company did not make any payment of interest and penalties. There was nothing accrued in the consolidated balance sheets for the payment of interest and penalties at October 3, 2014 as the remaining unrecognized tax benefits would only serve to reduce the Company’s current federal and state NOL carryforwards, if ultimately recognized.
90
Table of Contents
During fiscal year 2014, the Company settled the federal audit for fiscal years 2011 and 2012 with no material impact upon the financial statements. A summary of the fiscal tax years that remain subject to examination, as of October 3, 2014, for the Company’s significant tax jurisdictions are:
| Jurisdiction |
Tax Years Subject to Examination |
|||
| United States — federal |
2013 — forward | |||
| United States — various states |
2011 — forward | |||
| Ireland |
2011 — forward | |||
Generally, the Company is no longer subject to federal income tax examinations for years before 2013, except to the extent of loss and tax credit carryforwards from those years.
16. SHARE-BASED COMPENSATION PLANS
The following table presents the effects of stock-based compensation expense related to stock-based awards to employees and non-employees in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations during the periods presented (in thousands):
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 1,771 | $ | 1,068 | $ | 704 | ||||||
| Research and development |
2,818 | 1,739 | 967 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
6,688 | 3,649 | 1,989 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 11,277 | $ | 6,456 | $ | 3,660 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The Company has the following equity incentive plans: the Amended and Restated 2009 Stock Incentive Plan (2009 Plan), the 2012 Omnibus Incentive Plan (2012 Plan), the 2012 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (ESPP), the Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (Mindspeed 2013 Plan), the Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. 2003 Long-Term Incentives Plan (Mindspeed 2003 Plan) and the Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. Directors Stock Plan (Mindspeed Directors Plan).
Upon the closing of the IPO, all shares that were reserved under the 2009 Plan but not awarded were assumed by the 2012 Plan. No additional awards will be made under the 2009 Plan. Under the 2012 Plan, the Company has the ability to issue incentive stock options (ISOs), non-statutory stock options (NSOs), stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units (RSUs), performance units, performance shares and other equity-based awards to employees, directors and outside consultants. The ISOs and NSOs must be granted at a price per share not less than the fair value of our common stock on the date of grant. Options granted to date generally vest over a four-year period with 25% vesting at the end of one year and the remaining vest monthly thereafter. Certain of the share-based awards granted and outstanding as of October 3, 2014, are subject to accelerated vesting upon a sale of the Company or similar changes in control. Options granted generally are exercisable up to 10 years. In fiscal year 2012, the Company began granting RSUs, which generally vest annually over one to five years. As of October 3, 2014, the Company had 9.9 million shares available for future grants under the 2012 Plan.
The Mindspeed 2013 Plan, the Mindspeed 2003 Plan, the Mindspeed Directors Plan and certain inducement equity grants (collectively, the Mindspeed Plans) were assumed by the Company in connection with the Mindspeed Acquisitions. No additional equity awards will be made under the Mindspeed Equity Plans.
91
Table of Contents
A summary of stock option activity for fiscal year 2014 is as follows (in thousands, except per share amounts):
| Number of Shares | Weighted-Average Exercise Price per Share |
Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Term (in Years) |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
|||||||||||||
| Options outstanding — September 27, 2013 |
841 | $ | 1.60 | 6.2 | $ | 13,131 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Assumed in Mindspeed Acquisition |
439 | 24.50 | ||||||||||||||
| Granted |
405 | 17.50 | ||||||||||||||
| Exercised |
(515 | ) | 4.31 | |||||||||||||
| Forfeited, canceled or expired |
(222 | ) | 26.62 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Options outstanding — October 3, 2014 |
948 | $ | 11.73 | 6.6 | $ | 10,015 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Options vested and expected to vest — October 3, 2014 |
857 | $ | 11.11 | 6.3 | $ | 9,640 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Options exercisable — October 3, 2014 |
562 | $ | 7.86 | 4.7 | $ | 8,348 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Aggregate intrinsic value represents the difference between the Company’s closing stock price on October 3, 2014, and the exercise price of outstanding, in-the-money options. The total intrinsic value of options exercised was $7.6 million, $8.4 million and $4.6 million for fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012. As of October 3, 2014, total unrecognized compensation cost, excluding the impact of the assumed Mindspeed stock options, adjusted for estimated forfeitures, related to non-vested stock options was $2.2 million, which is expected to be recognized over the next 2.5 years.
No options were granted in fiscal years 2013 and 2012. In April 2014, the Company granted stock options as to 405,000 shares of common stock with a grant date fair value of $3.5 million that are subject to vesting only upon the market price of the Company’s underlying public stock closing above a certain price target within ten years of the grant date. Due to the market condition upon which vesting is based, the fair value of the awards was estimated using a Monte Carlo simulation model. Compensation cost is recognized regardless of the number of awards that are earned based on the market condition. Compensation cost is recognized on a straight-line basis over the estimated service period of three years. In the event that the Company’s common stock achieves the target price of $32.55 per share prior to the end of the estimated service period, any remaining unamortized compensation cost will be recognized. These options are included in the table and other information above.
The weighted-average assumptions used for calculating the fair value of stock options granted during fiscal year 2014, is as follows:
| Risk-free interest rate |
2.71 | |||
| Expected term (years) |
10 | |||
| Expected volatility |
42.6 | % | ||
| Expected dividends |
— |
92
Table of Contents
A summary of restricted stock awards and units activity for fiscal year 2014 is as follows (in thousands):
| Number of Shares |
Weighted-Average Remaining Contractual Term in Years |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
||||||||||
| Issued and unvested — September 27, 2013 |
1,129 | 2.3 | $ | 18,148 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Assumed in Mindspeed Acquisition |
285 | |||||||||||
| Granted |
1,049 | |||||||||||
| Vested |
(536 | ) | ||||||||||
| Forfeited, canceled or expired |
(207 | ) | ||||||||||
| Issued and unvested shares — October 3, 2014 |
1,720 | 2.6 | $ | 37,203 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Shares expected to vest |
1,521 | 2.6 | $ | 32,908 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The total fair value of restricted stock awards and units vesting was $9.2 million, $3.9 million and $1.7 million for fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012. As of October 3, 2014, total unrecognized compensation cost, adjusted for estimated forfeitures, related to RSUs and restricted stock was approximately $20.1 million, which is expected to be recognized over the next 2.5 years.
Concurrently with the IPO in March 2012, the ESPP became effective. The ESPP allows eligible employees to purchase shares of the Company’s common stock at a discount through payroll deductions of up to 15% of their eligible compensation, subject to any plan limitations. In administering the ESPP, the board of directors has limited discretion to set the length of the offering periods thereunder. The board of directors has provided for an initial offering period of eight months following the IPO, followed by six- month offering periods thereafter. As of October 3, 2014, total unrecognized compensation cost related to the ESPP was not material. In fiscal years 2014 and 2013, 150,000 and 131,000, respectively, of shares of common stock were issued under the ESPP.
The financial impact of any modifications to share-based awards during the periods presented was immaterial.
For the purpose of determining the exercise prices of the Company’s share-based awards prior to the IPO, fair value of the Company’s common stock was contemporaneously estimated by its board of directors as of each grant date, with input from management. Since the IPO, the Company’s quoted market price represents the fair value of the common stock.
The 2012 Plan contains an “evergreen” provision, pursuant to which the number of shares of common stock available for issuance under the 2012 Plan can be increased on the first day of each fiscal year equal to the lesser of (a) 4.0% of outstanding common stock on a fully diluted basis as of the end of the immediately preceding fiscal year, (b) 1.9 million shares of common stock, and (c) a lesser amount determined by the board of directors; provided, however, that any shares from any increases in previous years that are not actually issued will continue to be available for issuance under the 2012 Plan. The ESPP also contains an “evergreen” provision, pursuant to which the number of shares of common stock available for issuance under the ESPP can be increased on the first day of each fiscal year equal to the lesser of (a) 1.25% of outstanding common stock on a fully diluted basis as of the end of the immediately preceding fiscal year, (b) 550,000 shares of common stock, and (c) a lesser amount determined by the board of directors; provided, however, that any shares from any increases in previous years that are not actually issued will continue to be available for issuance under the ESPP. In fiscal year 2014, pursuant to the evergreen provisions, the number of shares of common stock available for issuance under the 2012 Plan and the ESPP were increased by 1.9 million shares and 550,000 shares, respectively.
17. PREFERRED STOCK
Upon completion of the IPO in March 2012, all outstanding shares of preferred stock were converted to common stock. Since that date, common stock is the only outstanding capital stock.
93
Table of Contents
In December 2010, the Company authorized 34,169,560 shares and issued 34,169,559.75 shares of Class B preferred stock (Class B) to new investors for $120.0 million in gross proceeds and net proceeds of $118.7 million. In connection with the Class B issuance, the Company also issued warrants to the new investors to purchase 1,281,358 shares of common stock for $14.05 per share. The warrants expire December 21, 2020, or earlier as per the terms of the agreement, including within 10 days following consummation of a sale of all or substantially all assets or capital stock or other equity securities of the Company, including by merger consolidation, recapitalization, or similar transactions, if not otherwise exercised.
Prior to cancellation in connection with the IPO, the Class A preferred stock (Class A) and Class B preferred stock had preferential voting, dividend, redemption, and other rights superior to common stock. Each share of Class A and Class B automatically converted into .25 shares of common stock on the completion of the IPO.
Qualified Public Offering or QPO Preference—The Class B stockholders were eligible to receive a preference payment based upon a formula that resulted in $60.0 million being paid to the Class B stockholders upon the close of the IPO on March 20, 2012.
The Class B was recorded outside of permanent stockholders’ equity as mezzanine equity due to the existence of the optional redemption rights. As a result of the amendments to the preference rights of Class A described above, the Company reclassified the Class A from stockholders’ equity to mezzanine equity in December 2010. The reclassification was made at the issuance date fair value, which aggregated $106.4 million.
The Company initially recorded the carrying value of the Class B as the total gross proceeds from the issuance less issuance costs, the fair value of the warrants (see Note 18) and the fair value of the Class B Conversion Liability discussed further below. The Company accreted the carrying value of the redeemable securities, including the Class B, to their redemption values using the effective interest method over the period from issuance to earliest redemption date. The accretion was recorded as an increase in the carrying value of the redeemable securities and a reduction to additional paid in capital, or in the absence of such, as an increase in the accumulated deficit.
A summary of the allocation of proceeds to and changes in the carrying value of the Class B follows (in thousands):
| Shares | Amount | |||||||
| Balance — September 30, 2011 |
$ | — | ||||||
| Issuance of Class B redeemable convertible preferred stock, net of allocation of proceeds |
34,170 | 75,618 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Accretion |
2,616 | |||||||
| Reclassification upon conversion of Class B to common stock |
(78,234 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Balance — September 28, 2012 |
$ | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
Class B Conversion Liability—The Class B redemption right allowed the holders to elect to receive a greater redemption amount related to the fair value of the Company’s common stock. This feature and the QPO Preference are embedded derivatives not deemed clearly and closely related to the host contract, Class B, due to, among other things, the potential cash settlement of both features. The embedded derivatives have been aggregated for financial reporting purposes. Accordingly, the embedded derivatives require separate accounting from the Class B. Upon issuance of the Class B, the estimated fair values of these embedded derivatives were bifurcated from the remainder of the Class B proceeds and recorded as long-term liabilities in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. Prior to March 2012, the carrying values of the embedded derivatives were adjusted to fair value at the end of each reporting period and the changes in fair value recognized in the statements of operations. The Class B conversion liabilities were settled upon the closing of the Company’s IPO
94
Table of Contents
in March 2012. The following is a summary of the changes in the carrying value of the Class B conversion liability (in thousands):
| Balance — September 30, 2011 |
$ | 81,378 | ||
| Change in estimated fair value |
44,119 | |||
| Payment of Class B preference |
(60,000 | ) | ||
| Reclassification upon conversion of Class B to common stock |
(65,497 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance — September 28, 2012 |
$ | — | ||
|
|
|
18. STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Outstanding shares of common stock presented in the accompanying consolidated statements of stockholders’ equity as of October 3, 2014 and September 27, 2013, exclude 59,000 and 74,000 shares, respectively, issued as compensation to employees that were subject to forfeiture, pending continued employment with the Company through stated vesting dates.
Common Stock Warrants—In connection with the Class B issuance, the Company issued warrants to purchase 1,281,358 shares of common stock for $14.05 per share. The warrants expire December 21, 2020, or earlier as per the terms of the agreement, including immediately following consummation of a sale of all or substantially all assets or capital stock or other equity securities of the Company, including by merger, consolidation, recapitalization, or similar transactions. Prior to completion of the IPO in March 2012, the number of shares issuable upon exercise of the warrants were subject to potential increases pursuant to certain antidilution rights included in the agreements. Following completion of the IPO in March 2012, and pursuant to an investor rights agreement between the Company and the holders of the warrants, the holders of the warrants have the right in certain circumstances to require the Company to register the warrants or the underlying shares of common stock for resale under the Securities Act. The Company does not have a sufficient number of shares currently registered and available to satisfy the request for registration, if such is made. As of October 3, 2014, no exercise of the warrants had occurred and no request had been made to register the warrants or any underlying securities for resale by the holders.
The inclusion of antidilution rights and the subsequent registration rights result in the warrants being recorded outside stockholders’ equity (deficit) and as a liability in accordance with authoritative accounting literature. The Company is recording the estimated fair values of the warrants as a long-term liability in the accompanying consolidated financial statements with changes in the estimated fair value being recorded in the accompanying statements of operations. The following is a summary of the activity of the warrant liability (in thousands):
| Balance — September 28, 2012 |
$ | 7,561 | ||
| Change in estimated fair value |
4,312 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance — September 27, 2013 |
11,873 | |||
| Change in estimated fair value |
3,928 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance — October 3, 2014 |
$ | 15,801 | ||
|
|
|
19. RELATED-PARTY TRANSACTIONS
GaAs Labs, LLC (GaAs Labs), a stockholder and an affiliate of directors and majority stockholders John and Susan Ocampo, was formerly engaged to provide management services pursuant to an agreement entered into in fiscal year 2008 and amended in December 2010. Selling, general and administrative expenses for fiscal year 2012 includes $360,000 for such services. The agreement terminated by its terms concurrently with the closing of the IPO in March 2012.
95
Table of Contents
In April 2012, the Company entered into an agreement with GaAs Labs whereby GaAs Labs pays the Company for administrative and business development services provided to GaAs Labs on a time and materials basis. There are no minimum service requirements or payment obligations and the agreement may be terminated by either party with 30 days’ notice. For fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, the Company billed GaAs Labs $118,000, $372,000 and $185,000, respectively, for services provided pursuant to this agreement and has recorded these amounts as other income in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
In February 2012, the Company entered into a design services agreement with Ubiquiti Networks, Inc. (Ubiquiti). Two of the Company’s directors were also directors of Ubiquiti’s at such time. Such directors resigned from Ubiquti’s board of directors in October 2013. An affiliate of one of the directors was also an Ubiquiti stockholder. The agreement provides that the Company will provide engineering services to Ubiquiti toward the development of an IC device. The agreement also provides that Ubiquiti will pay the Company up to $500,000 for such services based on milestone achievement and sets a unit price for any future production orders of such devices. Pursuant to the terms of the agreement, the Company did not record any related revenue in fiscal year 2014 and recorded related revenue of $300,000 and $200,000 in fiscal years 2013 and 2012, respectively.
In fiscal years 2014 and 2013, the Company recorded revenue of $150,000 and $242,000, respectively, from sales of product to a privately-held company with a common director.
20. DIVESTITURES
Upon closing the Mindspeed Acquisition, MACOM decided to divest the wireless business of Mindspeed. The operations of the wireless business are included in discontinued operations. There was no gain or loss on the sale, which had a selling price of $12.0 million and which closed in February 2014. The accompanying consolidated statement of operations for fiscal 2014 includes the following operating results related to the divested business (in thousands):
| Revenue |
$ | 2,440 | ||
| Loss before income taxes |
(7,381 | ) | ||
| Benefit for income taxes |
2,776 | |||
| Loss from discontinued operations |
$ | (4,605 | ) |
In fiscal year 2014, the Company sold non-core assets representing one product line, receiving cash proceeds aggregating $12.0 million. The Company has no continuing interests in these assets. There was no gain or loss on the sale, which closed in May 2014.
96
Table of Contents
21. EARNINGS PER SHARE
The following table set forth the computation for basic and diluted net income (loss) per share of common stock (in thousands, except per share data):
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Numerator: |
||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from continuing operations |
$ | (10,718 | ) | $ | 18,196 | $ | (3,664 | ) | ||||
| Loss from discontinued operations |
(4,605 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) |
(15,323 | ) | 18,196 | (3,664 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Accretion to redemption value of redeemable convertible preferred stock |
— | — | (2,616 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders |
$ | (15,323 | ) | $ | 18,196 | $ | (6,280 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Denominator: |
||||||||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding-basic |
47,009 | 45,916 | 24,758 | |||||||||
| Dilutive effect of options and warrants |
— | 1,221 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding-diluted |
47,009 | 47,137 | 24,758 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Common stock earnings per share-basic: |
||||||||||||
| Continuing operations |
$ | (0.23 | ) | 0.40 | $ | (0.25 | ) | |||||
| Discontinued operations |
(0.10 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net common stock earnings per share-basic |
$ | (0.33 | ) | $ | 0.40 | $ | (0.25 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Common stock earnings per share-diluted: |
||||||||||||
| Continuing operations |
$ | (0.23 | ) | 0.39 | $ | (0.25 | ) | |||||
| Discontinued operations |
(0.10 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net common stock earnings per share-diluted |
$ | (0.33 | ) | $ | 0.39 | $ | (0.25 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The following common equivalent shares were excluded from the calculation from net income per share as their inclusion would have been antidilutive (in thousands):
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Stock options and restricted stock |
1,079 | — | 1,821 | |||||||||
| Convertible preferred stock |
— | — | 17,733 | |||||||||
| Warrants |
329 | — | 141 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total common stock equivalent shares excluded |
1,408 | — | 19,695 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
22. SUPPLEMENTAL CASH FLOW INFORMATION
The following is supplemental cash flow information regarding noncash investing and financing activities:
| • | As of October 3, 2014 and September 27, 2013, the Company had $1.0 million and $2.4 million, respectively, in unpaid amounts related to purchases of property and equipment and intangibles included in accounts payable and accrued liabilities. These amounts have been excluded from the payments for purchases of property and equipment until paid. |
| • | Upon closing certain acquisitions in 2014, MACOM assumed $40.9 million of the seller’s indebtedness, all of which was paid in fiscal year 2014. |
| • | In June 2012, GaAs Labs contributed $2.1 million to Nitronex as a capital contribution in connection with a note payable previously executed between GaAs Labs and Nitronex. |
97
Table of Contents
| • | In March 2012, upon completion of the IPO, all shares of convertible preferred stock converted into common stock. As a result, the carrying values immediately prior to the conversion of Series A-1 convertible preferred stock ($64.0 million), Series A-2 convertible preferred stock ($42.4 million) and Class B ($78.2 million) were reclassified to stockholders’ equity, primarily as in additional paid-in capital. In addition, the carrying value of the Class B conversion liability immediately prior to conversion of the Class B ($125.5 million) was reclassified to additional paid-in capital. |
23. ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
The components of accumulated other comprehensive income, net of income taxes, are as follows (in thousands):
| Foreign currency items |
Pension items | Total | ||||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income at September 27, 2013 |
$ | (167 | ) | $ | — | $ | (167 | ) | ||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment |
(1,097 | ) | — | (1,097 | ) | |||||||
| Pension adjustment, net of tax |
— | (90 | ) | (90 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income at October 3, 2014 |
$ | (1,264 | ) | $ | (90 | ) | $ | (1,354 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
In fiscal year 2014, the Company recorded an immaterial amount in taxes related to other comprehensive income.
24. GEOGRAPHIC AND SIGNIFICANT CUSTOMER INFORMATION
The Company has one reportable operating segment which designs, develops, manufactures, and markets semiconductors and modules. The determination of the number of reportable operating segments is based on the chief operating decision maker’s use of financial information for the purposes of assessing performance and making operating decisions. In evaluating financial performance and making operating decisions, the chief operating decision maker primarily uses consolidated net revenue, gross profit and operating income (loss).
Information about the Company’s operations in different geographic regions, based upon customer locations, is presented below (in thousands):
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| Revenue by Geographic Region |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| United States |
$ | 213,180 | $ | 189,708 | $ | 160,453 | ||||||
| International (1) |
205,482 | 133,363 | 142,883 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 418,662 | $ | 323,071 | $ | 303,336 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| As Of | ||||||||
| Long-Lived Assets by Geographic Region |
October 3, 2014 |
September 27, 2013 |
||||||
| United States |
$ | 42,031 | $ | 26,226 | ||||
| International (2) |
8,326 | 6,509 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 50,357 | $ | 32,735 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1) | No international countries represented greater than 10% of total revenue during the periods presented. |
| (2) | No international country or region represented greater than 10% of the total net long-lived assets as of the dates presented, other than the Asia-Pacific region, which accounted for 11%. |
98
Table of Contents
The following is a summary of customer concentrations as a percentage of total sales and accounts receivable as of and for the periods presented:
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||
| Revenue |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Customer A |
19 | % | 25 | % | 16 | % | ||||||
| Customer B |
15 | % | 16 | % | 18 | % | ||||||
| Accounts Receivable |
October 3, 2014 |
September 27, 2013 |
||||||
| Customer A |
16 | % | 21 | % | ||||
| Customer B |
16 | % | 18 | % | ||||
No other customer represented more than 10% of revenue or accounts receivable in the periods presented in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. In fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, ten customers represented an aggregate of 60%, 59% and 55% of total revenue, respectively.
25. QUARTERLY FINANCIAL DATA (UNAUDITED)
(In thousands, except per share data)
| First Quarter |
Second Quarter |
Third Quarter |
Fourth Quarter |
Fiscal Year |
||||||||||||||||
| Fiscal Year 2014 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 84,154 | $ | 107,827 | $ | 112,364 | $ | 114,317 | $ | 418,662 | ||||||||||
| Gross profit |
35,722 | 26,863 | 50,214 | 56,189 | 168,988 | |||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
(8,921 | ) | (22,122 | ) | 1,183 | 14,537 | (15,323 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Per share data (2) |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss), basic |
$ | (0.19 | ) | $ | (0.47 | ) | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.31 | $ | (0.33 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income (loss), diluted |
$ | (0.19 | ) | $ | (0.47 | ) | $ | 0.02 | $ | 0.30 | $ | (0.33 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Fiscal Year 2013 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 76,076 | $ | 78,843 | $ | 83,477 | $ | 84,675 | $ | 323,071 | ||||||||||
| Gross profit |
31,486 | 32,833 | 35,504 | 36,590 | 136,413 | |||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) (1) |
4,056 | 5,420 | 6,980 | 1,740 | 18,196 | |||||||||||||||
| Per share data (2) |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss), basic |
$ | 0.09 | $ | 0.12 | $ | 0.15 | $ | 0.04 | $ | 0.40 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income (loss), diluted |
$ | 0.09 | $ | 0.11 | $ | 0.15 | $ | 0.04 | $ | 0.39 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | The fourth quarter of fiscal year 2013 includes a litigation settlement of $7.3 million. |
| (2) | Earnings per share calculations for each of the quarters are based on the weighted average number of shares outstanding and included common stock equivalents in each period. Therefore, the sums of the quarters do not necessarily equal the full year earnings per share. |
26. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On November 17, 2014, the Company entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger to acquire BinOptics Corporation (BinOptics Acquisition). The aggregate consideration payable for BinOptics will be approximately $230 million, subject to adjustment based on customary post-closing purchase price adjustment provisions and indemnification obligations of BinOptics equityholders after the closing of the BinOptics Acquisition. The Company currently expect the acquisition to close prior to the end of calendar 2014.
99
Table of Contents
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE.
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our President and Chief Executive Officer and Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (Exchange Act)), as of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives and management necessarily applies its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures. Based on such evaluation, our President and Chief Executive Officer and Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of October 3, 2014.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act. Our internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles of the United States (GAAP). A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of October 3, 2014, based on the framework set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (1992). Based on that assessment, management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of October 3, 2014.
Attestation Report of the Registered Public Accounting Firm
This Annual Report on Form 10-K does not include an attestation report of our registered public accounting firm on our internal control over financial reporting due to an exemption established by the JOBS Act for “emerging growth companies.”
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act) during the quarter ended October 3, 2014, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
100
Table of Contents
None.
101
Table of Contents
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE.
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive proxy statement for the 2015Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after October 3, 2014.
We have adopted a written code of business conduct and ethics that applies to our directors, officers and employees, including our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller and persons performing similar functions. We make available our code of business conduct and ethics free of charge through our website, which is located at www.macomtech.com. We intend to disclose any amendments to, or waivers from, our code of business conduct and ethics that are required to be publicly disclosed pursuant to rules of the SEC and the NASDAQ Global Select Market by posting any such amendment or waivers on our website and disclosing any such waivers in a Form 8-K filed with the SEC.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION.
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive proxy statement for the 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after October 3, 2014.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS.
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive proxy statement for the 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after October 3, 2014.
Equity Compensation Plan Information
We have two equity compensation plans under which shares are currently authorized for issuance, our 2012 Omnibus Incentive Plan (2012 Plan) and our 2012 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (2012 ESPP). We also maintain our Amended and Restated 2009 Omnibus Incentive Plan (2009 Plan), however, no additional awards may be issued under the 2009 Plan. Each of our aforementioned plans were approved by our stockholders prior to our initial public offering in March 2012. The following table provides information regarding securities authorized for issuance as of October 3, 2014 under our equity compensation plans.
| Plan Category |
(a) Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights (1)(5) |
(b) Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights (1)(5) |
(c) Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a))(2)(3)(4) |
|||||||||
| Equity Compensation Plans Approved by Security Holders |
788,717 | $ | 9.37 | 9,103,960 | ||||||||
| Equity Compensation Plans Not Approved by Security Holders |
— | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
788,717 | $ | 9.37 | 9,103,960 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 1. | Does not include 1,688,301 unvested shares outstanding as of October 3, 2014 in the form of restricted stock awards or restricted stock units under our 2012 Plan, which do not require the payment of any consideration by the recipients. |
102
Table of Contents
| 2. | Reflects 1,656,407 restricted stock units granted and outstanding as of October 3, 2014. |
| 3. | The 2012 Plan contains an “evergreen” provision, pursuant to which the number of shares of our common stock available for issuance under the 2012 Plan can be increased on the first day of each fiscal year equal to the lesser of (a) 4.0% of our outstanding common stock on a fully diluted basis as of the end of our immediately preceding fiscal year, (b) 1.9 million shares of our common stock, and (c) a lesser amount determined by our board of directors; provided, however, that any shares from any increases in previous years that are not actually issued will continue to be available for issuance under the 2012 Plan. |
| 4. | The 2012 ESPP contains an “evergreen” provision, pursuant to which the number of shares of our common stock available for issuance under the 2012 ESPP can be increased on the first day of each fiscal year equal to the lesser of (a) 1.25% of our outstanding common stock on a fully diluted basis as of the end of our immediately preceding fiscal year, (b) 550,000 shares of our common stock, and (c) a lesser amount determined by our board of directors; provided, however, that any shares from any increases in previous years that are not actually issued will continue to be available for issuance under the 2012 ESPP. |
| 5. | In connection with the Mindspeed Acquisition, we assumed the equity awards under the Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. 2013 Equity Incentive Plan, the Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. 2003 Long-Term Incentives Plan, the Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. Directors Stock Plan and certain inducement equity grants (collectively, the Mindspeed Plans). An aggregate of 159,376 shares may be issued upon the exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights under the Mindspeed Plans, at a weighted-average exercise price of $23.37 per share. No additional equity awards will be made under the Mindspeed Plans. |
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE.
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive proxy statement for the 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after October 3, 2014.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES.
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive proxy statement for the 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after October 3, 2014.
103
Table of Contents
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES.
(a) Financial Statements (included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K):
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of October 3, 2014 and September 27, 2013
Consolidated Statements of Operations for the Fiscal Years Ended October 3, 2014, September 27, 2013 and September 28, 2012
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Fiscal Years October 3, 2014, September 27, 2013 and September 28, 2012
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity and Comprehensive Income (Loss) for the Fiscal Years Ended October 3, 2014, September 27, 2013 and September 28, 2012
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(b) Exhibits
The exhibits required by Item 601 of Regulation S-K are filed herewith and incorporated by reference herein.
| Exhibit Number |
Description | |
| 2.1 | Agreement and Plan of Merger by and among M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc., Micro Merger Sub, Inc. and Mindspeed Technologies, Inc., dated November 5, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 5, 2013). | |
| 2.2 | Membership Interest Purchase Agreement by and among M/A-COM Technology Solutions Inc., Nitronex, LLC and GaAs Labs, LLC, dated February 13, 2014 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 13, 2014). | |
| 2.3 | Agreement and Plan of Merger by and among M/A-COM Technology Solutions Inc., BinOptics Corporation, Borealis Merger Sub, Inc. and Ithaca Stockholders’ Agent, LLC, as stockholders’ agent, dated November 17, 2014 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 19, 2014). | |
| 3.1 | Fourth Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 to Amendment No. 6 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on February 28, 2012). | |
| 3.2 | Second Amended and Restated Bylaws (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.4 to Amendment No. 6 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on February 28, 2012). | |
| 4.1 | Specimen of Common Stock Certificate (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Amendment No. 4 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on November 23, 2011). | |
| 4.2 | Form of Common Stock Purchase Warrant issued on December 21, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on August 1, 2011). | |
| 4.3 | Second Amended and Restated Investor Rights Agreement, dated February 28, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to Amendment No. 6 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on February 28, 2012). | |
104
Table of Contents
| 4.4 | First Amendment to the Second Amended and Restated Investor Rights Agreement, dated May 20, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.5 to our Registration Statement on Form S-3 (File No. 333-188728) filed on May 21, 2013). | |
| 10.1* | Form of Indemnification Agreement between M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. and each of its directors and executive officers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Amendment No. 3 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on October 21, 2011). | |
| 10.2* | M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. Amended and Restated 2009 Omnibus Stock Plan, as amended (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to our Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on November 28, 2012). | |
| 10.3* | Form of Incentive Stock Option Agreement under the M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. 2009 Omnibus Stock Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on August 1, 2011). | |
| 10.4* | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement under the M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. 2009 Omnibus Stock Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on August 1, 2011). | |
| 10.5* | M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. 2012 Omnibus Incentive Plan, as amended (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to our Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on November 28, 2012). | |
| 10.6* | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement Under 2012 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on May 5, 2012). | |
| 10.7* | Form of Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement under 2012 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on August 1, 2014). | |
| 10.8* | M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. 2012 Employee Stock Purchase Plan, as amended. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to our Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on December 5, 2013). | |
| 10.9* | Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed by Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. on February 12, 2013 (File No. 001-31650)). | |
| 10.10* | Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. 2003 Long-Term Incentives Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed by Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. on April 8, 2011 (File No. 001-31650)). | |
| 10.11* | M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. Change in Control Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 23, 2014). | |
| 10.12* | Offer of Employment Letter to Michael Murphy, dated September 28, 2009, as amended (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on August 1, 2011). | |
| 10.13* | Offer of Employment to John Croteau, dated September 6, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 7, 2012). | |
| 10.14* | Offer of Employment to Robert McMullan, dated December 11, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 16, 2013). | |
| 10.15* | Transition Agreement by and among Conrad Gagnon, M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. and M/A-COM Technology Solutions Inc., dated December 14, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 16, 2013). | |
105
Table of Contents
| 10.16 | Lease Agreement between Cobham Properties, Inc. and M/A-COM Technology Solutions Inc., dated October 2, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 11, 2012). | |
| 10.17 | Credit Agreement by and among M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc., Goldman Sachs Bank USA, as Administrative Agent, Collateral Agent, Swing Line Lender and an L/C Issuer, and the other agents and lenders party thereto, dated May 8, 2014 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on May 12, 2014). | |
| 21.1 | Subsidiaries of Registrant. | |
| 23.1 | Consent of Deloitte & Touche LLP. | |
| 31.1 | Certification of Principal Executive Officer Required Under Rule 13a-14(a) and 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. | |
| 31.2 | Certification of Principal Financial Officer Required Under Rule 13a-14(a) and 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. | |
| 32.1 | Certification of Principal Executive Officer and Principal Financial Officer Required Under Rule 13a-14(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and 18 U.S.C. §1350. | |
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document | |
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | |
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Calculation Linkbase Document | |
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Definition Linkbase Document | |
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Label Linkbase Document | |
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Presentation Linkbase Document | |
| * | Management contract or compensatory plan. |
106
Table of Contents
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
Date: December 9, 2014
| M/A-COM TECHNOLOGY SOLUTIONS HOLDINGS, INC. Registrant | ||||
| By: | /s/ John Croteau | |||
| John Croteau | ||||
| President and Chief Executive Officer | ||||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities indicated on December 9, 2014.
| Signature and Title |
Signature and Title | |||
| /s/ John Croteau |
/s/ John Ocampo | |||
| John Croteau | John Ocampo | |||
| President and Chief Executive Officer | Chairman of the Board | |||
| Director (principal executive officer)
/s/ Robert J. McMullan |
/s/ Susan Ocampo Susan Ocampo Director | |||
| Robert J. McMullan Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (principal accounting and financial officer) |
/s/ Peter Chung Peter Chung Director | |||
| /s/ Gil Van Lunsen | ||||
| Gil Van Lunsen Director | ||||
| /s/ Charles Bland | ||||
| Charles Bland | ||||
| Director | ||||
107
Table of Contents
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Exhibit Number |
Description | |
| 2.1 | Agreement and Plan of Merger by and among M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc., Micro Merger Sub, Inc. and Mindspeed Technologies, Inc., dated November 5, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 5, 2013). | |
| 2.2 | Membership Interest Purchase Agreement by and among M/A-COM Technology Solutions Inc., Nitronex, LLC and GaAs Labs, LLC, dated February 13, 2014 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 13, 2014). | |
| 2.3 | Agreement and Plan of Merger by and among M/A-COM Technology Solutions Inc., BinOptics Corporation, Borealis Merger Sub, Inc. and Ithaca Stockholders’ Agent, LLC, as stockholders’ agent, dated November 17, 2014 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 19, 2014). | |
| 3.1 | Fourth Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 to Amendment No. 6 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on February 28, 2012). | |
| 3.2 | Second Amended and Restated Bylaws (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.4 to Amendment No. 6 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on February 28, 2012). | |
| 4.1 | Specimen of Common Stock Certificate (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Amendment No. 4 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on November 23, 2011). | |
| 4.2 | Form of Common Stock Purchase Warrant issued on December 21, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on August 1, 2011). | |
| 4.3 | Second Amended and Restated Investor Rights Agreement, dated February 28, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to Amendment No. 6 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on February 28, 2012). | |
| 4.4 | First Amendment to the Second Amended and Restated Investor Rights Agreement, dated May 20, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.5 to our Registration Statement on Form S-3 (File No. 333-188728) filed on May 21, 2013). | |
| 10.1* | Form of Indemnification Agreement between M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. and each of its directors and executive officers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Amendment No. 3 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on October 21, 2011). | |
| 10.2* | M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. Amended and Restated 2009 Omnibus Stock Plan, as amended (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to our Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on November 28, 2012). | |
| 10.3* | Form of Incentive Stock Option Agreement under the M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. 2009 Omnibus Stock Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on August 1, 2011). | |
| 10.4* | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement under the M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. 2009 Omnibus Stock Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on August 1, 2011). | |
| 10.5* | M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. 2012 Omnibus Incentive Plan, as amended (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to our Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on November 28, 2012). | |
108
Table of Contents
| 10.6* | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement Under 2012 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on May 5, 2012). | |
| 10.7* | Form of Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement under 2012 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on August 1, 2014). | |
| 10.8* | M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. 2012 Employee Stock Purchase Plan, as amended. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to our Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on December 5, 2013). | |
| 10.9* | Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed by Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. on February 12, 2013 (File No. 001-31650)). | |
| 10.10* | Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. 2003 Long-Term Incentives Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed by Mindspeed Technologies, Inc. on April 8, 2011 (File No. 001-31650)). | |
| 10.11* | M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. Change in Control Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 23, 2014). | |
| 10.12* | Offer of Employment Letter to Michael Murphy, dated September 28, 2009, as amended (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-175934) filed on August 1, 2011). | |
| 10.13* | Offer of Employment to John Croteau, dated September 6, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 7, 2012). | |
| 10.14* | Offer of Employment to Robert McMullan, dated December 11, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 16, 2013). | |
| 10.15* | Transition Agreement by and among Conrad Gagnon, M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc. and M/A-COM Technology Solutions Inc., dated December 14, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 16, 2013). | |
| 10.16 | Lease Agreement between Cobham Properties, Inc. and M/A-COM Technology Solutions Inc., dated October 2, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 11, 2012). | |
| 10.17 | Credit Agreement by and among M/A-COM Technology Solutions Holdings, Inc., Goldman Sachs Bank USA, as Administrative Agent, Collateral Agent, Swing Line Lender and an L/C Issuer, and the other agents and lenders party thereto, dated May 8, 2014 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on May 12, 2014). | |
| 21.1 | Subsidiaries of Registrant. | |
| 23.1 | Consent of Deloitte & Touche LLP. | |
| 31.1 | Certification of Principal Executive Officer Required Under Rule 13a-14(a) and 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. | |
| 31.2 | Certification of Principal Financial Officer Required Under Rule 13a-14(a) and 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. | |
| 32.1 | Certification of Principal Executive Officer and Principal Financial Officer Required Under Rule 13a-14(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and 18 U.S.C. §1350. | |
109
Table of Contents
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document | |
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | |
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Calculation Linkbase Document | |
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Definition Linkbase Document | |
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Label Linkbase Document | |
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Presentation Linkbase Document | |
| * | Management contract or compensatory plan. |
110
