Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - GREENBRIER COMPANIES INC | d774171dex311.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EX-32.2 - GREENBRIER COMPANIES INC | d774171dex322.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - GREENBRIER COMPANIES INC | d774171dex312.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - GREENBRIER COMPANIES INC | d774171dex321.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - GREENBRIER COMPANIES INC | d774171dex231.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EX-21.1 - GREENBRIER COMPANIES INC | d774171dex211.htm |
| EXCEL - IDEA: XBRL DOCUMENT - GREENBRIER COMPANIES INC | Financial_Report.xls |
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549-1004
FORM 10-K
x ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d)
OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended August 31, 2014
or
¨ Transition Report Pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d)
of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934
for the transition period from to
Commission File No. 1-13146
THE GREENBRIER COMPANIES, INC.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
| Oregon | 93-0816972 | |
| (State of Incorporation) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
One Centerpointe Drive, Suite 200, Lake Oswego, OR 97035
(Address of principal executive offices)
(503) 684-7000
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| (Title of Each Class) | (Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered) | |||
| Common Stock without par value | New York Stock Exchange | |||
| Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: | ||||
| None | ||||
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes X No
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15 (d) of the Act. Yes No X
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes X No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes X No
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of Registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. [ ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definition of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one)
Large accelerated filer X Accelerated filer Non-accelerated filer Smaller reporting company
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes No X
Aggregate market value of the Registrant’s Common Stock held by non-affiliates as of February 28, 2014 (based on the closing price of such shares on such date) was $1,065,956,913.
The number of shares outstanding of the Registrant’s Common Stock on October 23, 2014 was 27,375,514, without par value.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Certain portions of the Registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement prepared in connection with the Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on January 7, 2015 are incorporated by reference into Parts II and III of this Report.
Table of Contents
THE GREENBRIER COMPANIES, INC.
FORM 10-K
| PAGE |
||||||
| 1 | ||||||
| Item 1. |
3 | |||||
| Item 1A. |
10 | |||||
| Item 1B. |
24 | |||||
| Item 2. |
24 | |||||
| Item 3. |
25 | |||||
| Item 4. |
25 | |||||
| Item 5. |
MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES | 26 | ||||
| Item 6. |
SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA | 28 | ||||
| Item 7. |
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS | 29 | ||||
| Item 7A. |
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK | 41 | ||||
| Item 8. |
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA | 43 | ||||
| Item 9. |
CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE | 85 | ||||
| Item 9A. |
CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES | 85 | ||||
| Item 9B. |
OTHER INFORMATION | 88 | ||||
| Item 10. |
DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE | 88 | ||||
| Item 11. |
EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION | 88 | ||||
| Item 12. |
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS | 88 | ||||
| Item 13. |
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE | 88 | ||||
| Item 14. |
PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES | 88 | ||||
| Item 15. |
89 | |||||
| 94 | ||||||
| 95 | ||||||
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
From time to time, The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. and its subsidiaries (“Greenbrier” or the “Company”) or their representatives have made or may make forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, including, without limitation, statements as to expectations, beliefs and strategies regarding the future. Such forward-looking statements may be included in, but not limited to, press releases, oral statements made with the approval of an authorized executive officer or in various filings made by us with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including this filing on Form 10-K and in the Company’s President’s letter to stockholders that is typically distributed to the stockholders in conjunction with this Form 10-K and the Company’s Proxy Statement. These statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other important factors that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements rely on a number of assumptions concerning future events and include statements relating to:
| • | availability of financing sources and borrowing base for working capital, other business development activities, capital spending and leased railcars for syndication (sale of railcars with lease attached); |
| • | ability to renew, maintain or obtain sufficient credit facilities and financial guarantees on acceptable terms; |
| • | ability to utilize beneficial tax strategies; |
| • | ability to grow our businesses; |
| • | ability to obtain lease and sales contracts which provide adequate protection against changes in interest rates and increased costs of materials and components; |
| • | ability to obtain adequate insurance coverage at acceptable rates; |
| • | ability to obtain adequate certification and licensing of products; and |
| • | short-term and long-term revenue and earnings effects of the above items. |
The following factors, among others, could cause actual results or outcomes to differ materially from the forward-looking statements:
| • | fluctuations in demand for newly manufactured railcars or marine barges; |
| • | fluctuations in demand for wheels, repair & parts; |
| • | delays in receipt of orders, risks that contracts may be canceled during their term or not renewed and that customers may not purchase the amount of products or services under the contracts as anticipated; |
| • | ability to maintain sufficient availability of credit facilities and to maintain compliance with or to obtain appropriate amendments to covenants under various credit agreements; |
| • | domestic and global economic conditions including such matters as embargoes or quotas; |
| • | U.S., Mexican and other global political or security conditions including such matters as terrorism, war, civil disruption and crime; |
| • | growth or reduction in the surface transportation industry; |
| • | ability to maintain good relationships with our labor force, third party labor providers and collective bargaining units representing our direct and indirect labor force; |
| • | steel and specialty component price fluctuations and availability, scrap surcharges, steel scrap prices and other commodity price fluctuations and availability and their impact on product demand and margin; |
| • | delay or failure of acquired businesses or joint ventures, assets, start-up operations, or new products or services to compete successfully; |
| • | changes in product mix and the mix of revenue levels among reporting segments; |
| • | labor disputes, energy shortages or operating difficulties that might disrupt operations or the flow of cargo; |
| • | production difficulties and product delivery delays as a result of, among other matters, inefficiencies associated with expansion or the start-up of production lines and new facilities or increased production rates, changing technologies, transfer of production between facilities or non-performance of alliance partners, subcontractors or suppliers; |
| • | interruption of our manufacturing operations as a result of lease termination or expiration; |
| • | ability to renew or replace expiring customer contracts on satisfactory terms; |
| • | ability to obtain and execute suitable contracts for leased railcars for syndication; |
| • | lower than anticipated lease renewal rates, earnings on utilization based leases or residual values for leased equipment; |
| • | discovery of defects in railcars or services resulting in increased warranty costs or litigation; |
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 1 |
Table of Contents
| • | physical damage, business interruption or product or service liability claims that exceed our insurance coverage; |
| • | commencement of and ultimate resolution or outcome of pending or future litigation and investigations; |
| • | natural disasters or severe weather patterns that may affect either us, our suppliers or our customers; |
| • | loss of business from, or a decline in the financial condition of, any of the principal customers that represent a significant portion of our total revenues; |
| • | competitive factors, including introduction of competitive products, new entrants into certain of our markets, price pressures, limited customer base, and competitiveness of our manufacturing facilities and products; |
| • | industry overcapacity and our manufacturing capacity utilization; |
| • | decreases or write-downs in carrying value of inventory, goodwill, intangibles or other assets due to impairment; |
| • | severance or other costs or charges associated with lay-offs, shutdowns, or reducing the size and scope of operations; |
| • | changes in future maintenance or warranty requirements; |
| • | ability to adjust to the cyclical nature of the industries in which we operate; |
| • | changes in interest rates and financial impacts from interest rates; |
| • | ability and cost to maintain and renew operating permits; |
| • | actions or failures to act by various regulatory agencies including potential environmental remediation obligations or changing tank car or other rail car regulation; |
| • | changes in fuel and/or energy prices; |
| • | risks associated with our intellectual property rights or those of third parties, including infringement, maintenance, protection, validity, enforcement and continued use of such rights; |
| • | expansion of warranty and product support terms beyond those which have traditionally prevailed in the rail supply industry; |
| • | availability of a trained work force at a reasonable cost and with reasonable terms of employment; |
| • | availability and/or price of essential raw materials, specialties or components, including steel castings, to permit manufacture of units on order; |
| • | failure to successfully integrate joint ventures or acquired businesses; |
| • | discovery of previously unknown liabilities associated with acquired businesses; |
| • | failure of or delay in implementing and using new software or other technologies; |
| • | the impact of cybersecurity risks and the costs of mitigating and responding to a data security breach; |
| • | ability to replace maturing lease and management services revenue and earnings with revenue and earnings from new commercial transactions, including new railcar leases, additions to the lease fleet and new management services contracts; |
| • | credit limitations upon our ability to maintain effective hedging programs; |
| • | financial impacts from currency fluctuations and currency hedging activities in our worldwide operations; |
| • | changes in legislation and increased costs related to health care; and |
| • | misconduct by employees, including the outcome of the internal investigation into allegations raised by whistleblower complaints concerning a senior employee at our Concarril facility. |
Any forward-looking statements should be considered in light of these factors. Words such as “anticipates,” “believes,” “forecast,” “potential,” “goal,” “contemplates,” “expects,” “intends,” “plans,” “projects,” “hopes,” “seeks,” “estimates,” “could,” “would,” “will,” “may,” “can,” “designed to,” “foreseeable future” and similar expressions identify forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from the results contemplated by the forward-looking statements. Many of the important factors that will determine these results and values are beyond our ability to control or predict. You are cautioned not to put undue reliance on any forward-looking statements. Except as otherwise required by law, we do not assume any obligation to update any forward-looking statements.
In assessing forward-looking statements contained herein, readers are urged to read carefully all cautionary statements contained in this Form 10-K, including, without limitation, those contained under the heading, “Risk Factors,” contained in Part I, Item 1A of this Form 10-K.
All references to years refer to the fiscal years ended August 31st unless otherwise noted.
The Greenbrier Companies is a registered trademark of The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. Gunderson, Maxi-Stack, Auto-Max and YSD are registered trademarks of Gunderson LLC.
| 2 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
| Item 1. | BUSINESS |
Introduction
We are one of the leading designers, manufacturers and marketers of railroad freight car equipment in North America and Europe, a manufacturer and marketer of marine barges in North America and a leading provider of wheel services, parts, leasing and other services to the railroad and related transportation industries in North America. In addition, we provide railcar repair, refurbishment and retrofitting services in North America through a joint venture partnership.
We operate an integrated business model in North America that combines freight car manufacturing, wheel services, repair, refurbishment, retrofitting, component parts reconditioning, leasing and fleet management services. Our model is designed to provide customers with a comprehensive set of freight car solutions utilizing our substantial engineering, mechanical and technical capabilities as well as our experienced commercial personnel. This model allows us to develop cross-selling opportunities and synergies among our various business segments and to enhance our margins. We believe our integrated model is difficult to duplicate and provides greater value for our customers.
Through July 18, 2014, we operated in three reportable segments: Manufacturing; Wheels, Repair & Parts; and Leasing & Services. On July 18, 2014, we and Watco Companies, LLC (“Watco”), our joint venture partner, contributed our respective repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations to GBW Railcar Services LLC (“GBW”), an unconsolidated 50/50 joint venture which became our fourth reportable segment (GBW Joint Venture) upon formation. Financial information about our business segments as well as geographic information for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 is located in Note 19 Segment Information to our Consolidated Financial Statements. The Wheels, Repair & Parts segment included the results of operations for our railcar repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations through July 18, 2014. After July 18, 2014, the results of operations are included as part of Earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates as we account for our interest in GBW under the equity method of accounting.
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc., which was incorporated in Delaware in 1981, consummated a merger on February 28, 2006 with its affiliate, Greenbrier Oregon, Inc., an Oregon corporation, for the sole purpose of changing its state of incorporation from Delaware to Oregon. Greenbrier Oregon survived the merger and assumed the name, The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. Our principal executive offices are located at One Centerpointe Drive, Suite 200, Lake Oswego, Oregon 97035, our telephone number is (503) 684-7000 and our Internet website is located at http://www.gbrx.com.
Products and Services
Manufacturing
North American Railcar Manufacturing - We manufacture a broad array of railcar types in North America, which includes most railcar types other than coal cars. We have demonstrated an ability to capture high market shares in many of the car types we produce. The primary products we produce for the North American market are:
Intermodal Railcars - We manufacture a comprehensive range of intermodal railcars. Our most important intermodal product is our articulated double-stack railcar. The double-stack railcar is designed to transport containers stacked two-high on a single platform. An articulated double-stack railcar is composed of up to five platforms, each of which is linked by a common set of wheels and axles. Our comprehensive line of articulated and non-articulated double-stack intermodal railcars offers varying load capacities and configurations. The double-stack railcar provides significant operating and capital savings over other types of intermodal railcars.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 3 |
Table of Contents
Tank Cars - We produce a variety of tank cars, including both general and certain pressurized tank cars, which are designed for the transportation of products such as crude oil, ethanol, liquefied petroleum gas, caustic soda, urea ammonium nitrate, vegetable oils, bio-diesel and various other products for the North American market. We continue to expand our product lines and production rates.
Automotive - We manufacture a full line of railcar equipment specifically designed for the transportation of automotive products. Our automotive offerings include our proprietary Auto-Max railcar, Multi-Max auto rack and flat cars for automotive transportation.
Conventional Railcars - We produce a wide range of boxcars, which are used in the transport of forest products, perishables, general merchandise and commodities. We also produce a variety of covered hopper cars for the grain, fertilizer, sand, cement and petrochemical industries as well as gondolas for the steel and metals markets and various other conventional railcar types. Our flat car products include center partition cars for the forest products industry, bulkhead flat cars and solid waste service flat cars.
European Railcar Manufacturing - Our European manufacturing operation produces a variety of railcar (wagon) types, including a comprehensive line of pressurized tank cars for liquid petroleum gas and ammonia and non-pressurized tank cars for light oil, chemicals and other products. In addition, we produce flat cars, coil cars for the steel and metals market, coal cars for both the continental European and United Kingdom markets, gondolas, sliding wall cars and automobile transporter cars.
Marine Vessel Fabrication - Our Portland, Oregon manufacturing facility, located on a deep-water port on the Willamette River, includes marine vessel fabrication capabilities. The marine facilities also increase utilization of steel plate burning and fabrication capacity providing flexibility for railcar production. United States (U.S.) coastwise law, commonly referred to as the Jones Act, requires all commercial vessels transporting merchandise between ports in the U.S. to be built, owned, operated and manned by U.S. citizens and to be registered under the U.S. flag. We manufacture a broad range of Jones Act ocean-going and river barges for transporting merchandise between ports within the U.S. including conventional deck barges, double-hull tank barges, railcar/deck barges, barges for aggregates and other heavy industrial products and dump barges. Our primary focus is on the larger ocean-going vessels although the facility has the capability to compete in other marine-related products.
Wheels, Repair & Parts
Wheel Services and Component Parts Manufacturing - We operate a large wheel services and component parts network in North America. Our wheel shops, operating in nine locations, provide complete wheel services including reconditioning of wheels and axles in addition to new axle machining and finishing and axle downsizing. Our component parts facilities, operating in four locations, recondition and manufacture railcar cushioning units, couplers, yokes, side frames, bolsters and various other parts. We also produce roofs, doors and associated parts for boxcars.
Railcar Repair, Refurbishment and Retrofitting - Prior to the formation of GBW on July 28, 2014, we operated 23 railcar repair, refurbishment and retrofitting shops, and the results of these operations were included in our Wheels, Repair & Parts segment. On July 18, 2014, we and Watco, our joint venture partner, contributed our railcar repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations to GBW, an unconsolidated 50/50 joint venture which became our fourth reportable segment (GBW Joint Venture) upon formation. The results of the GBW Joint Venture’s operations are included as part of Earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates as we account for our interest in GBW under the equity method of accounting. This joint venture operates the largest independent railcar repair shop network in North America consisting of 39 railcar repair, refurbishment, retrofitting and maintenance shops including 14 tank car repair shops certified by the Association of American Railroads (“AAR”) and one location operated exclusively by our company for GBW. This network of railcar repair, refurbishment, retrofitting and maintenance shops performs heavy railcar repair and refurbishment, as well as routine railcar maintenance. GBW is actively engaged in the repair, refurbishment and retrofitting of railcars for third parties, as well as for our leased and managed fleet.
| 4 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Leasing & Services
Leasing - Our relationships with financial institutions, combined with our ownership of a lease fleet of approximately 8,600 railcars, enables us to offer flexible financing programs including operating leases and “by the mile” leases to our customers. As an equipment owner, we participate principally in the operating lease segment of the market. The majority of our leases are “full service” leases whereby we are responsible for maintenance and administration. Maintenance of the fleet is provided, in part, through our GBW joint venture. Assets from our owned lease fleet are periodically sold to take advantage of market conditions, manage risk and maintain liquidity.
Management Services - Our management services business offers a broad array of software and services that include railcar maintenance management, railcar accounting services (such as billing and revenue collection, car hire receivable and payable administration), total fleet management (including railcar tracking using proprietary software), administration and railcar remarketing. Frequently, we originate leases of railcars, which are either newly built or refurbished by us, with railroads or shippers, and sell the railcars and attached leases to financial institutions and subsequently provide management services under multi-year agreements. We currently own or provide management services for a fleet of approximately 246,000 railcars for railroads, shippers, carriers, institutional investors and other leasing and transportation companies in North America.
| Fleet Profile (1) As of August 31, 2014 |
||||||||||||
| Owned Units(2) |
Managed Units |
Total Units |
||||||||||
| Customer Profile: |
||||||||||||
| Leasing Companies |
228 | 109,488 | 109,716 | |||||||||
| Class I Railroads |
2,912 | 94,225 | 97,137 | |||||||||
| Shipping Companies |
3,972 | 21,652 | 25,624 | |||||||||
| Non-Class I Railroads |
834 | 12,387 | 13,221 | |||||||||
| En route to Customer Location |
454 | 97 | 551 | |||||||||
| Off-lease |
150 | – | 150 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Total Units |
8,550 | 237,849 | 246,399 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| (1) | Each platform of a railcar is treated as a separate unit. |
| (2) | Percent of owned units on lease is 98.2% with an average remaining lease term of 2.1 years. The average age of owned units is 15 years. |
Backlog
Multi-year supply agreements are a part of rail industry practice. The following table depicts our reported third party railcar backlog in number of railcars and estimated future revenue value attributable to such backlog, at the dates shown:
| August 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| New railcar backlog units (1) |
31,500 | 14,400 | 10,700 | |||||||||
| Estimated future revenue value (in millions) (2) |
$ | 3,330 | $ | 1,520 | $ | 1,200 | ||||||
| (1) | Each platform of a railcar is treated as a separate unit. |
| (2) | Subject to change based on finalization of product mix. |
Based on current production plans, at least 17,000 units in the August 31, 2014 backlog are scheduled for delivery in 2015. The balance of the production is scheduled for delivery into 2018. A portion of the orders included in backlog reflects an assumed product mix. Under terms of the orders, the exact mix will be determined in the future which may impact the dollar amount of backlog. Subsequent to year end we received new railcar orders for 11,400 units valued at nearly $1 billion. The new orders referenced are subject to customary documentation and completion of terms.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 5 |
Table of Contents
Marine backlog as of August 31, 2014 was approximately $112 million compared to $10 million as of August 31, 2013.
Customer orders may be subject to cancellations or modifications and contain terms and conditions customary in the industry. In most cases, little variation has been experienced between the quantity ordered and the quantity actually delivered. Our railcar and marine backlogs are not necessarily indicative of future results of operations.
Customers
Our customers include railroads, leasing companies, financial institutions, shippers, carriers and transportation companies. We have strong, long-term relationships with many of our customers. We believe that our customers’ preference for high quality products, our technological leadership in developing innovative products and competitive pricing of our railcars have helped us maintain our long-standing relationships with our customers.
In 2014, revenue from two customers, CIT Company (CIT) and TTX Company (TTX), accounted for approximately 41% of total revenue, 21% of Wheels, Repair & Parts revenue and 49% of Manufacturing revenue. No other customers accounted for greater than 10% of total revenue.
Raw Materials and Components
Our products require a supply of materials including steel and specialty components such as brakes, wheels and axles. Specialty components purchased from third parties represent a significant amount of the cost of most freight cars. Our customers often specify particular components and suppliers of such components. Although the number of alternative suppliers of certain specialty components has declined in recent years, there are at least two suppliers for most such components.
Certain materials and components are periodically in short supply which could potentially impact production at our new railcar and refurbishment facilities. In an effort to mitigate shortages and reduce supply chain costs, we have entered into strategic alliances and multi-year arrangements for the global sourcing of certain materials and components, we operate a replacement parts business and we continue to pursue strategic opportunities to protect and enhance our supply chain. We periodically make advance purchases to avoid possible shortages of material due to capacity limitations of component suppliers and possible price increases.
In 2014, the top ten suppliers for all inventory purchases accounted for approximately 45% of total purchases. Amsted Rail Company, Inc. accounted for 19% of total inventory purchases in 2014. No other suppliers accounted for more than 10% of total inventory purchases. The Company believes it maintains good relationships with its suppliers.
Competition
There are currently six major railcar manufacturers competing in North America. In addition, a number of small manufacturers have recently entered the market. We compete on the basis of quality, price, reliability of delivery, product design and innovation, reputation and customer service and support.
Competition in the marine industry is dependent on the type of product produced. There are two principal competitors, located in the Gulf States, which build product types similar to ours. We compete on the basis of experienced labor, launch ways capacity, quality, price and reliability of delivery.
We believe that we are among the top three European railcar manufacturers, which maintain a combined market share of approximately 80%. European freight car manufacturers are largely located in central and eastern Europe where labor rates are lower and work rules are more flexible.
Competition in the wheels, repair and parts business is dependent on the type of product or service provided. There are many competitors in the railcar repair and refurbishment business and an increasing number of competitors in the wheel services and other parts businesses. We compete primarily on the basis of quality, timeliness of delivery, customer service, location of shops, price and engineering expertise.
| 6 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
There are at least twenty institutions that provide railcar leasing and services similar to ours. Many of them are also customers that buy new railcars from our manufacturing facilities and used railcars from our lease fleet, as well as utilize our management services. Many of these institutions may have greater resources than we do on our own balance sheet. We compete primarily on the basis of quality, price, delivery, reputation, service offerings and deal structuring and syndication ability. We believe our strong servicing capability and our ability to sell railcars with a lease attached (syndicate railcars), integrated with our manufacturing, repair shops, railcar specialization and expertise in particular lease structures provide a strong competitive position.
Marketing and Product Development
In North America, we use an integrated marketing and sales effort to coordinate relationships in our various segments. We provide our customers with a diverse range of equipment and financing alternatives designed to satisfy each customer’s unique needs, whether the customer is buying new equipment, refurbishing existing equipment or seeking to outsource the maintenance or management of equipment. These custom programs may involve a combination of railcar products, leasing, refurbishing and remarketing services. In addition, we provide customized maintenance management, equipment management, accounting services and proprietary software solutions.
In Europe, we maintain relationships with customers through a network of country-specific sales representatives. Our engineering and technical staff works closely with their customer counterparts on the design and certification of railcars. Many European railroads are state-owned and are subject to European Union regulations covering the tender of government contracts.
Through our customer relationships, insights are derived into the potential need for new products and services. Marketing and engineering personnel collaborate to evaluate opportunities and identify and develop new products. For example, we continue to expand our tank car, automotive and covered hopper product offerings in North America. Research and development costs incurred during the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 were $3.6 million, $2.0 million and $2.0 million.
Patents and Trademarks
We have a number of U.S. and non-U.S. patents of varying duration, and pending patent applications, registered trademarks, copyrights and trade names that are important to our products and product development efforts. The protection of our intellectual property is important to our business and we have a proactive program aimed at protecting our intellectual property and the results from our research and development.
Environmental Matters
We are subject to national, state and local environmental laws and regulations concerning, among other matters, air emissions, wastewater discharge, solid and hazardous waste disposal and employee health and safety. Prior to acquiring facilities, we usually conduct investigations to evaluate the environmental condition of subject properties and may negotiate contractual terms for allocation of environmental exposure arising from prior uses. We operate our facilities in a manner designed to maintain compliance with applicable environmental laws and regulations. Environmental studies have been conducted on certain of our owned and leased properties that indicate additional investigation and some remediation on certain properties may be necessary.
Our Portland, Oregon manufacturing facility is located adjacent to the Willamette River. We have entered into a Voluntary Clean-up Agreement with the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality (“DEQ”) in which we agreed to conduct an investigation of whether, and to what extent, past or present operations at the Portland property may have released hazardous substances to the environment. We are also conducting groundwater remediation relating to a historical spill on the property that preceded our ownership.
Portland Harbor Site
In December 2000, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (“EPA”) classified portions of the Willamette River bed known as the Portland Harbor, including the portion fronting our manufacturing facility, as a federal
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 7 |
Table of Contents
“National Priority List” or “Superfund” site due to sediment contamination (the “Portland Harbor Site”). We, along with more than 140 other parties, have received a “General Notice” of potential liability from the EPA relating to the Portland Harbor Site. The letter advised us that we may be liable for the costs of investigation and remediation (which liability may be joint and several with other potentially responsible parties) as well as for natural resource damages resulting from releases of hazardous substances to the site. At this time, ten private and public entities, including us (the “Lower Willamette Group” or “LWG”), have signed an Administrative Order on Consent (“AOC”) to perform a remedial investigation/feasibility study (“RI/FS”) of the Portland Harbor Site under EPA oversight, and several additional entities have not signed such consent, but are nevertheless contributing money to the effort. The EPA-mandated RI/FS is being conducted by the LWG and has cost over $110 million during a 14-year period. We have agreed to initially bear a percentage of the total costs incurred by the LWG in connection with the investigation. Our aggregate expenditure has not been material during the 14-year period. Some or all of any such outlay may be recoverable from other responsible parties. EPA expects the investigation to continue until 2017.
Eighty-three parties, including the State of Oregon and the federal government, have entered into a non-judicial mediation process to try to allocate costs associated with the Portland Harbor site. Approximately 110 additional parties have signed tolling agreements related to such allocations. On April 23, 2009, the Company and the other AOC signatories filed suit against 69 other parties due to a possible limitations period for some such claims; Arkema Inc. et al v. A & C Foundry Products, Inc.et al, US District Court, District of Oregon, Case #3:09-cv-453-PK. All but 12 of these parties elected to sign tolling agreements and be dismissed without prejudice, and the case has now been stayed by the court, pending completion of the RI/FS. Although, as described below, the draft feasibility study has been submitted, the RI/FS will not be complete until the EPA approves it, which is not likely to occur until at least 2016.
A draft of the remedial investigation study was submitted to the EPA on October 27, 2009. The draft feasibility study was submitted to the EPA on March 30, 2012. The draft feasibility study evaluates several alternative cleanup approaches. The approaches submitted would take from 2 to 28 years with costs ranging from $169 million to $1.8 billion for cleanup of the entire Portland Harbor Site, depending primarily on the selected remedial action levels. The draft feasibility study suggests costs ranging from $9 million to $163 million for cleanup of the area of the Willamette River adjacent to our Portland, Oregon manufacturing facility, depending primarily on the selected remedial action level.
The draft feasibility study does not address responsibility for the costs of clean-up or allocate such costs among the potentially responsible parties, or define precise boundaries for the cleanup. Responsibility for funding and implementing the EPA’s selected cleanup will be determined after the issuance of the Record of Decision, currently scheduled by EPA for 2017. Based on the investigation to date, we believe that we did not contribute in any material way to contamination in the river sediments or the damage of natural resources in the Portland Harbor Site and that the damage in the area of the Portland Harbor Site adjacent to our property precedes our ownership of the Portland, Oregon manufacturing facility. Because these environmental investigations are still underway, sufficient information is currently not available to determine our liability, if any, for the cost of any required remediation or restoration of the Portland Harbor Site or to estimate a range of potential loss. Based on the results of the pending investigations and future assessments of natural resource damages, we may be required to incur costs associated with additional phases of investigation or remedial action, and may be liable for damages to natural resources. In addition, we may be required to perform periodic maintenance dredging in order to continue to launch vessels from our launch ways in Portland, Oregon, on the Willamette River, and the river’s classification as a Superfund site could result in some limitations on future dredging and launch activities. Any of these matters could adversely affect our business and Consolidated Financial Statements, or the value of our Portland property.
We have also signed an Order on Consent with DEQ to finalize the investigation of potential onsite sources of contamination that may have a release pathway to the Willamette River. Interim precautionary measures are also required in the order and we are currently discussing with the DEQ potential remedial actions which may be required. Our aggregate expenditure has not been material during the 14-year period, however we could incur significant expenses for remediation. Some or all of any such outlay may be recoverable from other responsible parties.
| 8 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Regulation
The Federal Railroad Administration in the U.S. and Transport Canada in Canada administer and enforce laws and regulations relating to railroad safety. These regulations govern equipment and safety appliance standards for freight cars and other rail equipment used in interstate commerce. The AAR promulgates a wide variety of rules and regulations governing the safety and design of equipment, relationships among railroads and other railcar owners with respect to railcars in interchange, and other matters. The AAR also certifies railcar builders and component manufacturers that provide equipment for use on North American railroads. These regulations require us to maintain our certifications with the AAR as a railcar builder and component manufacturer, and products sold and leased by us in North America must meet AAR, Transport Canada, and Federal Railroad Administration standards.
The primary regulatory and industry authorities involved in the regulation of the ocean-going barge industry are the U.S. Coast Guard, the Maritime Administration of the U.S. Department of Transportation, and private industry organizations such as the American Bureau of Shipping.
The regulatory environment in Europe consists of a combination of European Union (“EU”) regulations and country specific regulations, including a harmonized set of Technical Standards for Interoperability of freight wagons throughout the EU.
U.S., Canadian and railroad industry regulatory authorities are considering various proposals that mandate enhanced safety features for newly manufactured tank cars, and may also require a range of safety retrofitting to be performed on existing tank cars, in certain hazardous materials service. In addition, these authorities are considering stricter operating regulations for trains hauling tank cars that contain certain hazardous materials. We are unable to predict what regulatory changes may be made, how these changes will be implemented or over what time period any changes may become effective.
Employees
As of August 31, 2014, we had 9,244 full-time employees, consisting of 7,251 employees in Manufacturing, 594 in Wheels, Repair & Parts, 182 employees in Leasing & Services and corporate and 1,217 employees who were seconded to our GBW joint venture and who are expected to become employees of the joint venture on January 1, 2015. At our Wheels, Repair & Parts locations, 44 employees are represented by unions and in Manufacturing, 4,065 employees are represented by unions. In addition to our own employees, as of August 31, 2014, 635 union employees worked at our Sahagun, Mexico railcar manufacturing facility under our services agreement with Bombardier Transportation, Inc. This service agreement will expire November 30, 2014. We believe that our relations with our employees are generally good.
Additional Information
We are a reporting company and file annual, quarterly, current and special reports, proxy statements and other information with the Securities and Exchange Committee (“SEC”). Through a link on the Investor Relations section of our website, http://www.gbrx.com, we make available the following filings as soon as reasonably practicable after they are electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC: our Annual Report on Form 10-K; Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q; Current Reports on Form 8-K; and any amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. All such filings are available free of charge. Copies of our Audit Committee Charter, Compensation Committee Charter, Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee Charter and the Company’s Corporate Governance Guidelines are also available on our web site at http://www.gbrx.com. In addition, each of the reports and documents listed above are available free of charge by contacting our Investor Relations Department at The Greenbrier Companies, Inc., One Centerpointe Drive, Suite 200, Lake Oswego, Oregon 97035.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 9 |
Table of Contents
| Item 1A. | RISK FACTORS |
In addition to the risks outlined in this annual report under the heading “Forward-Looking Statements,” as well as other comments included herein regarding risks and uncertainties, the following risk factors should be carefully considered when evaluating our company. Our business, financial condition or financial results could be materially and adversely affected by any of these risks.
During economic downturns or a rising interest rate environment, the cyclical nature of our business results in lower demand for our products and services and reduced revenue.
Our business is cyclical. Overall economic conditions and the purchasing practices of buyers have a significant effect upon our business due to the impact on demand for our products and services. As a result, during downturns, we could operate with a lower level of backlog and may temporarily slow down or halt production at some or all of our facilities. Economic conditions that result in higher interest rates increase the cost of new leasing arrangements, which could cause some of our leasing customers to lease fewer of our railcars or demand shorter lease terms. An economic downturn or increase in interest rates may reduce demand for our products and services, resulting in lower sales volumes, lower prices, lower lease utilization rates and decreased profits.
Changes in the credit markets and the financial services industry could negatively impact our business, results of operations, financial condition or liquidity.
The credit markets and the financial services industry continue to experience volatility which may result in tighter availability of credit on more restrictive terms and limit our ability to sell railcar assets. Our liquidity, financial condition and results of operations could be negatively impacted if our ability to borrow money to finance operations, obtain credit from trade creditors, offer leasing products to our customers or sell railcar assets were to be impaired. In addition, scarcity of capital could also adversely affect our customers’ ability to purchase or pay for products from us or our suppliers’ ability to provide us with product, either of which could negatively affect our business and results of operations.
Currently, interest rates remain at historically low levels. Higher interest rates could increase the cost of, or potentially deter, new leasing arrangements with our customers or reduce our ability to syndicate railcars under lease to financial institutions, either of which could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Volatility in the global financial markets may adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operation.
During periods of volatility in the global financial markets, certain of our customers could delay or otherwise reduce their purchases of railcars and other products and services. If volatile conditions in the global credit markets impact our customers’ access to credit, product order volumes may decrease or customers may default on payments owed to us.
Likewise, if our suppliers face challenges obtaining credit, or otherwise operating their businesses, the supply of materials we purchase from them to manufacture our products may be interrupted. Any of these conditions or events could result in reductions in our revenues, increased price competition, or increased operating costs, which could adversely affect our business, financial conditions and results of operations.
| 10 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
We face aggressive competition by a concentrated group of competitors and a number of factors may influence our performance. If we are unable to compete successfully, our market share, margin and results of operations may be adversely affected.
We face aggressive competition by a concentrated group of competitors in all geographic markets and in each area of our business. The railcar manufacturing and repair industry is intensely competitive and we expect it to remain so in the foreseeable future. Competitive factors, including introduction of competitive products, new entrants into certain of our markets, price pressures, limited customer base and the relative competitiveness of our manufacturing facilities and products affect our ability to compete effectively. In addition, new technologies or the introduction of new railcars or other product offerings by our competitors could render our products obsolete or less competitive. If we do not compete successfully, our market share, margin and results of operation may be adversely affected.
A number of factors may influence our performance, including without limitation: fluctuations in the demand for newly manufactured railcars or marine barges; fluctuations in demand for wheels, repair and parts; our ability to adjust to the cyclical nature of the industries in which we operate; delays in receipt of orders, risks that contracts may be canceled during their term or not renewed and that customers may not purchase the amount of products or services under the contracts as anticipated; our customers may be financially unable to pay for products and services already provided; domestic and global economic conditions including such matters as embargoes or quotas; growth or reduction in the surface transportation industry; steel and specialty component price fluctuations and availability, scrap surcharges, steel scrap prices and other commodity price fluctuations and their impact on product demand and margin; loss of business from, or a decline in the financial condition of, any of the principal customers that represent a significant portion of our total revenues; industry overcapacity and our manufacturing capacity utilization; and other risks, uncertainties and factors. If we are unfavorably affected by any of these factors, our market share, margin and results of operation may be adversely affected.
Our actual results may differ significantly from our announced strategic initiatives.
From time to time, we have released, and may continue to release information in our quarterly earnings releases, quarterly earnings conference calls, or otherwise, regarding our anticipated future performance and goals. Our actual results may differ significantly and we may not be successful in achieving the objectives outlined in our announced strategic initiatives. Failure to meet these goals could have a material adverse effect on our trading price or volume of our stock.
A change in our product mix due to shifts in demand could have an adverse effect on our profitability.
We manufacture and, through our GBW joint venture, repair a variety of railcars. The demand for specific types of these railcars and mix of refurbishment work varies from time to time. These shifts in demand could affect our margins and could have an adverse effect on our profitability. Currently a portion of our backlog and railcar demand includes a concentrated product mix of covered hoppers and tank cars used in energy related transportation. A sudden change in these markets could have an adverse effect on our profitability. For example, a change in environmental and governmental regulations, competitive pricing, pipeline capacity, the price of crude oil and related products and other factors could reduce demand for railcars in the energy transportation industry.
Our backlog is not necessarily indicative of the level of our future revenues.
Our manufacturing backlog represents future production for which we have written orders from our customers in various periods, and estimated potential revenue attributable to those orders. Some of this backlog is subject to our fulfillment of certain competitive conditions. Our reported backlog may not be converted to revenue in any particular period and some of our contracts permit cancellations without financial penalties or with limited compensation that would not replace lost revenue or margins. Actual revenue from such contracts may not equal
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 11 |
Table of Contents
our anticipated revenues based on our backlog, and therefore, our backlog is not necessarily indicative of the level of our future revenues.
We rely on limited suppliers for certain components and services needed in our production. If we are not able to procure specialty components or services on commercially reasonable terms or on a timely basis, our business, financial condition and results of operations would be adversely affected.
Our manufacturing operations depend in part on our ability to obtain timely deliveries of materials, components and services in acceptable quantities and quality from our suppliers. In 2014, the top ten suppliers for all inventory purchases accounted for approximately 45% of total purchases. Amsted Rail Company, Inc. accounted for 19% of total inventory purchases in 2014. No other suppliers accounted for more than 10% of total inventory purchases. Certain components of our products, particularly specialized components like castings, bolsters, trucks, wheels and axles, and certain services, such as lining capabilities, are currently available from only a limited number of suppliers. Increases in the number of railcars manufactured have increased the demand for such components and services and strong demand may cause industry-wide shortages if suppliers are in the process of ramping up production or reach capacity production. Our dependence on a limited number of suppliers involves risks, including limited control over pricing, availability and delivery schedules. If any one or more of our suppliers cease to provide us with sufficient quantities of our components or services in a timely manner or on terms acceptable to us, or cease to provide services or manufacture components of acceptable quality, we could incur disruptions or be limited in our production of our products and we could have to seek alternative sources for these components or services. We could also incur delays while we attempt to locate and engage alternative qualified suppliers and we might be unable to engage acceptable alternative suppliers on favorable terms, if at all. In addition, we are increasing the number of components and services we manufacture or provide ourselves, directly or through joint ventures. If we are not successful at manufacturing such components or providing such services or have production problems after transitioning to self-produced supplies, we may not be able to replace such components or services from third party suppliers in a timely manner. Any such disruption in our supply of specialized components and services or increased costs of those components or services could harm our business and adversely affect our results of operations.
U.S., Canadian and railroad industry regulatory authorities are considering various proposals concerning tank railcar manufacturing standards. We cannot predict what regulatory changes may be made in this regard, if any, or when any such regulatory changes may become effective. If adopted, new regulations could materially affect the tank railcar manufacturing process industry-wide, which could negatively affect the potential availability of certain critical components and raw materials including, in particular, steel. If we are unable to source critical components and raw materials like steel in a timely manner and at reasonable cost, we may be unable to manufacture railcars that comply with any new regulations or take advantage of any increase in demand for our products and services as a result of any such new regulations, and our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
We derive a significant amount of our revenue from a limited number of customers, the loss of or reduction of business from one or more of which could have an adverse effect on our business.
A significant portion of our revenue is generated from a few major customers. Although we have some long-term contractual relationships with our major customers, we cannot be assured that our customers will continue to use our products or services or that they will continue to do so at historical levels. A reduction in the purchase or leasing of our products or a termination of our services by one or more of our major customers could have an adverse effect on our business and operating results.
| 12 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Train derailments or other accidents or claims could subject us to legal claims and/or result in regulatory changes that adversely impact our business, financial condition and our results of operations.
We provide a number of services which include the manufacture and supply of wheels, components and parts and lease of railcars for our customers that transport a variety of commodities, including tank railcars that transport hazardous materials such as crude oil, ethanol and other products. We could be subject to various legal claims, including claims for negligence, personal injury, physical damage and product or service liability, as well as potential penalties and liability under environmental laws and regulations, in the event of a derailment or other accident involving railcars, including tank railcars. If we become subject to any such claims and are unable successfully to resolve them or have inadequate insurance for such claims, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
On July 6, 2013, a train carrying crude oil and operated by Montreal, Main & Atlantic Railway, Inc. derailed in the town of Lac-Mégantic, Quebec, causing severe damage and resulting in a number of human fatalities. Some of our competitors and a number of other parties, have been named as a defendant in a class action lawsuit regarding this derailment alleging wrongful death and negligence claims. While we are not currently aware of circumstances that would indicate we are likely to have liability in this matter, the amount of potential damages at issue in the class action could be extremely large. If we were to be found liable for significant damages with respect to this claim, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
In addition, U.S., Canadian and railroad industry regulatory authorities are considering various proposals that would restrict or even eliminate the use of DOT 111 cars for the transportation of certain hazardous materials. We have 312 tank railcars in our lease fleet with a net book value of approximately $26.4 million as of August 31, 2014 which could be negatively impacted in the event of regulatory changes and any refurbishment requirements. We are unable to predict what regulatory changes may be made in this regard or even what time period such regulatory changes may become effective.
While certain regulatory changes could result in increased levels of repair or refurbishment work for our GBW Railcar Services joint venture and/or new tank car manufacturing activity, if we are unable to manage to adapt our business successfully to changing regulations, our business and results of operations could be adversely affected. Delays in issuing definitive regulations or other factors which could prolong or exacerbate uncertainty in the marketplace could adversely impact orders for new railcars, including orders currently in our backlog. Any such reduction or delay in orders for new railcars could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, certain proposals restrict the operation of trains carrying hazardous materials or reduce train speeds on an already congested rail network. Further congestion on the railroads could lead to reduced velocity. This could also lead to an increase in the cost of rail freight transportation and impact availability making it less competitive compared to alternative modes of freight transportation. It could also lead to reduced demand for our products as railroads limit additional equipment on their lines.
Any failure by us to comply with regulations imposed by federal and foreign agencies could negatively affect our financial results.
Our operations and the industry we serve, including our customers, are subject to extensive regulation by governmental, regulatory and industry authorities and by federal and foreign agencies. These organizations establish rules and regulations for the railcar industry, including construction specifications and standards for the design and manufacture of railcars; mechanical, maintenance and related standards; and railroad safety. New regulatory rulings and regulations from these entities could impact our financial results, demand for our products and the economic value of our assets. In addition, if we fail to comply with the requirements and regulations of these entities, we could face sanctions and penalties that could negatively affect our financial results.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 13 |
Table of Contents
Risks related to our operations outside of the U.S. could adversely affect our operating results.
Our current operations outside of the U.S. and any future expansion of our international operations are subject to the risks associated with cross-border business transactions and activities. Political, legal, trade, financial market or economic changes or instability could limit or curtail our foreign business activities and operations. Some foreign countries in which we operate or may operate have regulatory authorities that regulate railroad safety, railcar design and railcar component part design, performance and manufacturing. If we fail to obtain and maintain certifications of our railcars and railcar parts within the various foreign countries where we operate or may operate, we may be unable to market and sell our railcars in those countries. In addition, unexpected changes in regulatory requirements, tariffs and other trade barriers, more stringent rules relating to labor or the environment, adverse tax consequences, currency and price exchange controls could limit operations and make the manufacture and distribution of our products difficult. The uncertainty of the legal environment or geo-political risks in these and other areas could limit our ability to enforce our rights effectively. Because we have operations outside the U.S., we could be adversely affected by violations of the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and similar worldwide anti-corruption laws. We operate in parts of the world that have experienced governmental corruption to some degree, and in certain circumstances, strict compliance with anti-corruption laws may conflict with local customs and practices. The failure to comply with laws governing international business practices may result in substantial penalties and fines. Any international expansion or acquisition that we undertake could amplify these risks related to operating outside of the U.S.
Risks related to potential misconduct by employees may adversely impact us.
We recently received various complaints through our whistleblower hotline concerning alleged misconduct involving a senior employee at our Concarril manufacturing facility in Sahagun, Mexico. While an independent investigation is underway, and in its early stages, we currently believe that the alleged misconduct did not have a material adverse impact on our financial condition or results of operations. However, there can be no assurance that such material adverse impact will not occur, or that we will succeed in preventing misconduct by employees in the future. Any such events in the future may materially and adversely impact us.
If we or our joint ventures fail to complete capital expenditure projects on time and within budget, or if these projects, once completed, fail to operate as anticipated, such failure could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
From time-to-time, we, or our joint ventures, undertake strategic capital projects in order to enhance, expand and/or upgrade facilities and operational capabilities. We are currently enhancing our manufacturing facilities in Mexico to both replace and increase our production capacity and become more vertically integrated. Our ability, and our joint ventures’ ability, to complete these projects on time and within budget, and for us to realize the anticipated increased revenues or otherwise realize acceptable returns on these investments or other strategic capital projects that may be undertaken is subject to a number of risks. Many of these risks are beyond our control, including a variety of market, operational, permitting, and labor related factors. In addition, the cost to implement any given strategic capital project ultimately may prove to be greater than originally anticipated. If we, or our joint ventures, are not able to achieve the anticipated results from the implementation of any of these strategic capital projects, or if unanticipated implementation costs are incurred, our business, financial condition and results of operations may be adversely affected.
We operate two manufacturing facilities in Sahagun, Mexico, one of which we own and one which is leased. Our lease of the Sahagun, Mexico manufacturing facility expires in November 2014. We are in the process of replacing this leased capacity with an alternative site in Tlaxcala, Mexico which was purchased during 2014. If we are unable to fully vacate the leased manufacturing facility by the expiration of the lease, we may be subject to penalties for overstaying the lease. In addition, if we are unable to move equipment, startup or produce railcars at our new facility at Tlaxcala on time or on budget this could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations. Any interruption or decrease in our manufacturing operations or penalties in connection with overstaying our lease could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
| 14 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Our relationships with our joint venture and alliance partners could be unsuccessful, which could adversely affect our business.
We have entered into several joint venture agreements and other alliances with other companies to increase our sourcing alternatives, reduce costs, to produce new railcars and repair and retrofit railcars for the North American marketplace. We may seek to expand our relationships or enter into new agreements with other companies. If our joint venture or alliance partners are unable to fulfill their contractual obligations or if these relationships are otherwise not successful in the future, our manufacturing and other costs could increase, we could encounter production disruptions, growth opportunities could fail to materialize, or we could be required to fund such joint venture or alliances in amounts significantly greater than initially anticipated, any of which could adversely affect our business.
If any of our joint ventures generate significant losses, including future potential goodwill impairment charges, it could adversely affect our results of operations. For example, if our joint venture with Watco is unable to operate as anticipated, incurs significant losses or otherwise is unable to honor its obligation to us under the GBW joint venture agreements, our financial results could be materially adversely affected.
Shortages of skilled labor could adversely affect our operations.
We depend on skilled labor in the manufacture of railcars and marine barges, repair, refurbishment, retrofitting and maintenance of railcars and provision of wheel services and supply of parts. Some of our facilities are located in areas where demand for skilled laborers often exceeds supply. Shortages of some types of skilled laborers such as welders and machine operators could restrict our ability to maintain or increase production rates, lead to production inefficiencies and increase our labor costs.
A failure to design or manufacture products or technologies or to achieve timely certification or market acceptance of new products or technologies could have an adverse effect on our profitability.
We continue to introduce new railcar products and technologies, and we periodically accept orders prior to receipt of railcar certification or proof of ability to manufacture a quality product that meets customer standards. We could be unable to successfully design or manufacture these new railcar products and technologies. Our inability to develop and manufacture such new products and technologies in a timely fashion and profitable manner, obtain timely certification, or achieve market acceptance, or the existence of quality problems in our new products, could have a material adverse effect on our revenue and results of operations and subject us to penalties, cancellation of orders and/or other damages.
We could be unable to remarket leased railcars on favorable terms upon lease termination or realize the expected residual values, which could reduce our revenue and decrease our overall return.
We re-lease or sell railcars we own or manage upon the expiration of existing lease terms. The total rental payments we receive under our operating leases do not fully amortize the acquisition costs of the leased equipment, which exposes us to risks associated with remarketing the railcars. Our ability to remarket leased railcars profitably is dependent upon several factors, including, but not limited to, market and industry conditions, cost of and demand for newer models, costs associated with the refurbishment of the railcars and interest rates. Our inability to re-lease or sell leased railcars on favorable terms could result in reduced revenues and margins or net gain on disposition of equipment and decrease our overall returns and affect our ability to syndicate railcars to investors.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 15 |
Table of Contents
We could have difficulty integrating the operations of any companies that we acquire or joint ventures we enter into, which could adversely affect our results of operations.
The success of our acquisition and joint venture strategy depends upon our ability to successfully complete acquisitions, to enter into joint ventures and integrate any businesses that we acquire into our existing business. The integration of acquired business operations could disrupt our business by causing unforeseen operating difficulties, diverting management’s attention from day-to-day operations and requiring significant financial resources that would otherwise be used for the ongoing development of our business. The difficulties of integration could be increased by the necessity of coordinating geographically dispersed organizations, integrating personnel with disparate business backgrounds and combining different corporate cultures. Each of these circumstances could be more likely to occur or more severe in consequence in the case of an acquisition or joint venture involving a business that is outside of our core areas of expertise. In addition, we could be unable to retain key employees or customers of the combined businesses. We could face integration issues pertaining to the internal controls, information systems and operational functions of the acquired companies and we also could fail to realize cost efficiencies or synergies that we anticipated when selecting our acquisition candidates and joint ventures. Any of these items could adversely affect our results of operations.
We depend on our senior management team and other key employees, and significant attrition within our management team or unsuccessful succession planning could adversely affect our business.
Our success depends in part on our ability to attract, retain and motivate senior management and other key employees. Achieving this objective may be difficult due to many factors, including fluctuations in global economic and industry conditions, competitors’ hiring practices, cost reduction activities, and the effectiveness of our compensation programs. Competition for qualified personnel can be very intense. We must continue to recruit, retain and motivate senior management and other key employees sufficient to maintain our current business and support our future projects. We are vulnerable to attrition among our current senior management team and other key employees. A loss of any such personnel, or the inability to recruit and retain qualified personnel in the future, could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, certain key members of our senior management team are at or nearing retirement age. If we are unsuccessful in our succession planning efforts, the continuity of our business and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Our product and service warranties could expose us to potentially significant claims.
We offer our customers limited warranties for many of our products and services. Accordingly, we may be subject to significant warranty claims in the future, such as multiple claims based on one defect repeated throughout our production or servicing process or claims for which the cost of repairing the defective part is highly disproportionate to the original cost of the part. These types of warranty claims could result in costly product recalls, customers seeking monetary damages, significant repair costs and damage to our reputation.
If warranty claims attributable to actions of third party component manufacturers are not recoverable from such parties due to their poor financial condition or other reasons, we could be liable for warranty claims and other risks for using these materials on our products.
The timing of our asset sales and related revenue recognition could cause significant differences in our quarterly results and liquidity.
We may build railcars or marine barges in anticipation of a customer order, or that are leased to a customer and ultimately planned to be sold to a third party. The difference in timing of production and the ultimate sale is subject to risk. In addition, we periodically sell railcars from our own lease fleet and the timing and volume of such sales is difficult to predict. As a result, comparisons of our manufacturing revenue, deliveries, quarterly net gain on disposition of equipment, income and liquidity between quarterly periods within one year and between
| 16 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
comparable periods in different years may not be meaningful and should not be relied upon as indicators of our future performance.
Our financial performance and market value could cause future write-downs of goodwill or intangibles in future periods.
We, and our joint ventures accounted for under the equity method of accounting, are required to perform an annual impairment review of goodwill and indefinite lived assets which could result in an impairment charge if it is determined that the carrying value of the asset is in excess of the fair value. We perform a goodwill impairment test annually during our third fiscal quarter. Goodwill is also tested more frequently if changes in circumstances or the occurrence of events indicates that a potential impairment exists. When changes in circumstances, such as a decline in the market price of our common stock, changes in demand or in the numerous variables associated with the judgments, assumptions and estimates made in assessing the appropriate valuation of goodwill indicate the carrying amount of certain indefinite lived assets may not be recoverable, the assets are evaluated for impairment. Among other things, our assumptions used in the valuation of goodwill, which relate to our Wheels, Repair & Parts segment, include growth of revenue and margins and increased cash flows over time. If actual operating results were to differ from these assumptions, it may result in an impairment of our goodwill. A non-cash impairment charge of $76.9 million ($71.8 million, net of tax) was recorded for the year ended August 31, 2013 which relates to our Wheels, Repair & Parts segment. As of August 31, 2014, we had $43.3 million of goodwill in our Wheels, Repair & Parts segment, relating to our wheels and parts business. Future write-downs of goodwill and intangibles could affect certain of the financial covenants under debt instruments and could restrict our financial flexibility. In the event of goodwill impairment, we may have to test other intangible assets for impairment. Impairment charges to our or our joint venture’s goodwill or our indefinite lived assets would impact our results of operations.
We have potential exposure to environmental liabilities, which could increase costs or have an adverse effect on results of operations.
We are subject to extensive national, state, provincial and local environmental laws and regulations concerning, among other things, air emissions, water discharge, solid waste and hazardous substances handling and disposal and employee health and safety. These laws and regulations are complex and frequently change. We could incur unexpected costs, penalties and other civil and criminal liability if we fail to comply with environmental laws or permits issued to us pursuant to those laws. We also could incur costs or liabilities related to off-site waste disposal or remediating soil or groundwater contamination at our properties, including these set forth below and in the “Environmental Matters” section of this Report. In addition, future environmental laws and regulations may require significant capital expenditures or changes to our operations.
In addition to environmental, health and safety laws, the transportation of commodities by railcar raises potential risks in the event of a derailment or other accident. Generally, liability under existing law in the U.S. and Canada for accidents such as derailments depends on the negligence of the party. However, for certain hazardous commodities being shipped, strict liability concepts may apply.
Our Portland, Oregon manufacturing facility is located adjacent to the Willamette River. We have entered into a Voluntary Cleanup Agreement with the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality (“DEQ”) in which we agreed to conduct an investigation of whether, and to what extent, past or present operations at the Portland property may have released hazardous substances to the environment. We are also conducting groundwater remediation relating to a historical spill on the property which preceded our ownership.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has classified portions of the river bed of the Portland Harbor, including the portion fronting the Company’s manufacturing facility, as a federal “National Priority List” or “Superfund” site due to sediment contamination (the “Portland Harbor Site”). We, along with more than 140 other parties, have received a “General Notice” of potential liability from the EPA relating to the Portland Harbor Site. The letter advised us that we may be liable for the costs of investigation and remediation (which liability
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 17 |
Table of Contents
may be joint and several with other potentially responsible parties) as well as for natural resource damages resulting from releases of hazardous substances to the site. We are part of a group that signed an Administrative Order on Consent (“AOC”) to perform a remedial investigation/feasibility study (“RI/FS”) of the Portland Harbor Site under EPA oversight, and several additional entities have not signed such consent, but are nevertheless contributing money to the effort. We have agreed to initially bear a percentage of the total costs incurred in connection with the investigation. EPA expects the investigation to continue until 2017. We cannot assure that any such costs will be recoverable from third parties.
A draft of the remedial investigation study was submitted to the EPA on October 27, 2009. The draft feasibility study was submitted to the EPA on March 30, 2012. The draft feasibility study evaluates several alternative cleanup approaches. The approaches submitted would take from 2 to 28 years with costs ranging from $9 million to $163 million for cleanup of the area of the Willamette River adjacent to our Portland, Oregon manufacturing facility, depending primarily on the selected remedial action level. The draft feasibility study does not address responsibility for the costs of clean-up or allocate such costs among potentially responsible parties, or define precise boundaries for the cleanup. Responsibility for funding and implementing the EPA’s selected cleanup will be determined after the issuance of the Record of Decision.
We have also signed an Order on Consent with DEQ to finalize the investigation of potential onsite sources of contamination that may have a release pathway to the Willamette River. Interim precautionary measures are also required in the order and we are currently discussing with the DEQ potential remedial actions which may be required. Our aggregate expenditure has not been material during the 14-year period, however, we could incur significant expenses for remediation. Some or all of any such outlay may be recoverable from other responsible parties. However, we cannot assure that any such costs will be recoverable from third parties.
Because these environmental investigations are still underway, sufficient information is currently not available to determine our liability, if any, for the cost of any required remediation of the Portland Harbor Site on our adjacent land or to estimate a range of potential loss. Based on the results of the pending investigations and future assessments of natural resource damages, we may be required to incur costs associated with additional phases of investigation or remedial action, and may be liable for damages to natural resources. In addition, we may be required to perform periodic maintenance dredging in order to continue to launch vessels from our launch ways in Portland, Oregon, on the Willamette River, and the river’s classification as a Superfund site could result in some limitations on future dredging and launch activities. Any of these matters could adversely affect our business and Consolidated Financial Statements, or the value of our Portland property.
We are subject to cybersecurity risks and may incur increasing costs in an effort to minimize those risks.
Our business employs systems and websites that allow for the storage and transmission of proprietary or confidential information regarding our customers, employees, job applicants and other parties, including financial information, intellectual property and personal identification information. Security breaches and other disruptions could compromise our information, expose us to liability and harm our reputation and business. The steps we take to deter and mitigate these risks may not be successful. We may not have the resources or technical sophistication to anticipate or prevent current or rapidly evolving types of cyber-attacks. Attacks may be targeted at us, our customers, or others who have entrusted us with information. Actual or anticipated attacks may cause us to incur increasing costs, including costs to deploy additional personnel and protection technologies, train employees, and engage third-party experts or consultants. Advances in computer capabilities, or other technological developments may result in the technology and security measures used by us to protect transaction or other data being breached or compromised. In addition, data and security breaches can also occur as a result of non-technical issues, including intentional or inadvertent breach by our employees or by persons with whom we have commercial relationships. Any compromise or breach of our security could result in a violation of applicable privacy and other laws, legal and financial exposure, negative impacts on our customers’ willingness to transact business with us and a loss of confidence in our security measures, which could have an adverse effect on our results of operations and our reputation.
| 18 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
We have indebtedness, which could have negative consequences to our business or results of operations.
As of August 31, 2014, our total debt was approximately $458.2 million, consisting of borrowings under our convertible notes, credit facilities and term loans. Our significant indebtedness could have negative consequences to us, and could place us at a competitive disadvantage compared to our less leveraged competitors. It may be difficult for us to satisfy our repayment and other obligations with respect to such indebtedness, and we may not be able to refinance our existing indebtedness as it matures. Significant indebtedness may also increase our vulnerability to adverse general economic, industry or competitive developments or conditions and limit our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and the industry in which we operate. We may be limited in our ability to raise additional capital or obtain additional financing to fund our operations, capital expenditures or other growth initiatives, and other general corporate requirements and may be required to dedicate a significant portion of our cash flow from operations to interest and principal payments on our indebtedness. We are more exposed to the risk of increased interest rates as certain of our borrowings are at variable rates of interest. As a consequence of our level of indebtedness, a significant portion of our cash flow from operations may be dedicated to debt service requirements. In addition, the terms of our revolving credit facility limit our ability to incur additional indebtedness. If we fail to comply with these covenants, a default may occur, in which case the lender could accelerate the debt. We cannot be assured that we would be able to renegotiate, refinance, restructure or otherwise obtain the necessary funds to satisfy the indebtedness or these obligations.
Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates could lead to increased costs and lower profitability.
Outside of the U.S., we operate in Mexico, Germany and Poland, and our non-U.S. businesses conduct their operations in local currencies and other regional currencies. We also source materials worldwide. Fluctuations in exchange rates may affect demand for our products in foreign markets or our cost competitiveness and may adversely affect our profitability. Although we attempt to mitigate a portion of our exposure to changes in currency rates through currency rate hedge contracts and other activities, these efforts cannot fully eliminate the risks associated with the foreign currencies. In addition, some of our borrowings are in foreign currency, giving rise to risk from fluctuations in exchange rates. A material or adverse change in exchange rates could result in significant deterioration of profits or in losses for us.
Fluctuations in the availability and price of energy, freight transportation, steel and other raw materials, and our fixed price contracts could have an adverse effect on our ability to manufacture and sell our products on a cost-effective basis and could adversely affect our margins and revenue of our Manufacturing and Wheels, Repair & Parts businesses.
A significant portion of our business depends upon the adequate supply of steel, components and other raw materials at competitive prices and a small number of suppliers provide a substantial amount of our requirements. The cost of steel and all other materials used in the production of our railcars represents more than half of our direct manufacturing costs per railcar and in the production of our marine barges represents more than 30% of our direct manufacturing costs per marine barge.
Our businesses also depend upon the adequate supply of energy at competitive prices. When the price of energy increases, it adversely impacts our operating costs and could have an adverse effect upon our ability to conduct our businesses on a cost-effective basis. We cannot be assured that we will continue to have access to supplies of energy or necessary components for manufacturing railcars and marine barges. Our ability to meet demand for our products could be adversely affected by the loss of access to any of these supplies, the inability to arrange alternative access to any materials, or suppliers limiting allocation of materials to us.
In some instances, we have fixed price contracts which anticipate material price increases and surcharges, or contracts that contain actual or formulaic pass-through of material price increases and surcharges. However, if the price of steel or other raw materials were to fluctuate in excess of anticipated increases on which we have based our fixed price contracts, or if we were unable to adjust our selling prices or have adequate protection in
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 19 |
Table of Contents
our contracts against changes in material prices, or if we are unable to reduce operating costs to offset any price increases, our margins would be adversely affected. The loss of suppliers or their inability to meet our price, quality, quantity and delivery requirements could have an adverse effect on our ability to manufacture and sell our products on a cost-effective basis.
Decreases in the price of scrap adversely impact our Wheels, Repair & Parts margin and revenue. A portion of our Wheels, Repair & Parts business involves scrapping steel parts and the resulting revenue from such scrap steel increases our margins and revenues. When the price of scrap steel declines, our margins and revenues in such business therefore decrease.
Some of our employees belong to labor unions and strikes or work stoppages could adversely affect our operations.
We are a party to collective bargaining agreements with various labor unions at some of our operations. Disputes with regard to the terms of these agreements or our potential inability to negotiate acceptable contracts with these unions in the future could result in, among other things, strikes, work stoppages or other slowdowns by the affected workers. We cannot be assured that our relations with our workforce will remain positive. Union organizers are actively working to organize at some of our other facilities. If our workers were to engage in a strike, work stoppage or other slowdown, or other employees were to become unionized or the terms and conditions in future labor agreements were renegotiated, or if union representation is implemented at such sites and we are unable to agree with the union on reasonable employment terms, including wages, benefits, and work rules, we could experience a significant disruption of our operations and higher ongoing labor costs. In addition, we could face higher labor costs in the future as a result of severance or other charges associated with lay-offs, shutdowns or reductions in the size and scope of our operations or due to the difficulties of restarting our operations that have been temporarily shuttered.
A prolonged decline in performance of the rail freight industry would have an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our future success depends in part upon the performance of the rail freight industry, which in turn depends on the health of the economy. If railcar loadings, railcar and railcar components replacement rates or refurbishment rates or industry demand for our railcar products weaken or otherwise do not materialize, our financial condition and results of operations would be adversely affected.
Updates or changes to our information technology systems may result in problems that could negatively impact our business.
We have information technology systems, comprising hardware, network, software, people, processes and other infrastructure that are important to the operation of our businesses. We continue to evaluate and implement upgrades and changes to information technology systems that support substantially all of our operating and financial functions. We could experience problems in connection with such implementations, including compatibility issues, training requirements, higher than expected implementation costs and other integration challenges and delays. A significant problem with an implementation, integration with other systems or ongoing management and operation of our systems could negatively impact our business by disrupting operations. Such a problem could also have an adverse effect on our ability to generate and interpret accurate management and financial reports and other information on a timely basis, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial reporting system and internal controls and adversely affect our ability to manage our business.
| 20 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
An adverse outcome in any pending or future litigation could negatively impact our business and results of operations.
We are a defendant in several pending cases in various jurisdictions. If we are unsuccessful in resolving these claims, our business and results of operations could be adversely affected. In addition, future claims that may arise relating to any pending or new matters, whether brought against us or initiated by us against third parties, could distract management’s attention from business operations and increase our legal and related costs, which could also negatively impact our business and results of operations.
We could be liable for physical damage, business interruption or product liability claims that exceed our insurance coverage.
The nature of our business subjects us to physical damage, business interruption and product liability claims, especially in connection with the repair and manufacture of products that carry hazardous or volatile materials. Although we maintain liability insurance coverage at commercially reasonable levels compared to similarly-sized heavy equipment manufacturers, an unusually large physical damage, business interruption or product liability claim or a series of claims based on a failure repeated throughout our production process could exceed our insurance coverage or result in damage to our reputation.
We could be unable to procure adequate insurance on a cost-effective basis in the future.
The ability to insure our businesses, facilities and rail assets is an important aspect of our ability to manage risk. As there are only limited providers of this insurance to the railcar industry, there is no guarantee that such insurance will be available on a cost-effective basis in the future. In addition, we cannot assure that our insurance carriers will be able to pay current or future claims.
Changes in accounting standards or inaccurate estimates or assumptions in the application of accounting policies could adversely affect our financial results.
Our accounting policies and methods are fundamental to how we record and report our financial condition and results of operations. Some of these policies require use of estimates and assumptions that may affect the reported value of our assets or liabilities and financial results and are critical because they require management to make difficult, subjective, and complex judgments about matters that are inherently uncertain. Accounting standard setters and those who interpret the accounting standards (such as the Financial Accounting Standards Board, the SEC, and our independent registered public accounting firm) may amend or even reverse their previous interpretations or positions on how these standards should be applied. In some cases, we could be required to apply a new or revised standard retrospectively, resulting in the revision of prior period financial statements. Changes in accounting standards can be hard to predict and can materially impact how we record and report our financial condition and results of operations.
From time to time we may take tax positions that the Internal Revenue Service may contest.
We have in the past and may in the future take tax positions that the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) may contest. We are required by an IRS regulation to disclose particular tax positions to the IRS as part of our tax returns for that year and future years. If the IRS successfully contests a tax position that we take, we may be required to pay additional taxes, interest or fines that may adversely affect our results of operation and financial position.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 21 |
Table of Contents
Fires, natural disasters, severe weather conditions or public health crisis could disrupt our business and result in loss of revenue or higher expenses.
Any serious disruption at any of our facilities due to fire, hurricane, earthquake, flood, or any other natural disaster, or an epidemic or other public health crisis, or a panic reaction to a perceived health risk, could impair our ability to use our facilities and have a material adverse impact on our revenues and increase our costs and expenses. If there is a natural disaster or other serious disruption at any of our facilities, particularly any of our Mexican facilities, it could impair our ability to adequately supply our customers, cause a significant disruption to our operations, cause us to incur significant costs to relocate or reestablish these functions and negatively impact our operating results. While we insure against certain business interruption risks, such insurance may not adequately compensate us for any losses incurred as a result of natural or other disasters.
Repercussions from terrorist activities or armed conflict could harm our business.
Terrorist activities, anti-terrorist efforts, and other armed conflict involving the U.S. or its interests abroad may adversely affect the U.S. and global economies, potentially preventing us from meeting our financial and other obligations. In particular, the negative impacts of these events may affect the industries in which we operate. This could result in delays in or cancellations of the purchase of our products or shortages in raw materials, parts, or components. Any of these occurrences could have a material adverse impact on our financial results.
Compliance with recently passed health care legislation and increases in the cost of providing health care plans to our employees may adversely affect our business.
In March 2010, Congress passed the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and the Health Care and Education Affordability Reconciliation Act (collectively, the “Acts”). Among other things, the Acts contain provisions that affect employer-sponsored health care plans, impose excise taxes on certain plans, and reduce the tax benefits available to employers that receive the Medicare Part D subsidy. Nationally, the cost of providing health care plans to a company’s employees has increased at annual rates in excess of inflation. There continues to be uncertainty whether the Acts will increase the cost of employee health plan coverage. Continued significant annual increases in the cost of providing employee health coverage may adversely affect our business and results of operations.
Unanticipated changes in our tax provisions or exposure to additional income tax liabilities could affect our financial condition and profitability.
We are subject to income taxes in both the United States and foreign jurisdictions. Significant judgment is required in determining our worldwide provision for income taxes. Changes in estimates of projected future operating results, loss of deductibility of items, recapture of prior deductions (including related to interest on convertible notes), or changes in assumptions regarding our ability to generate future taxable income could result in significant increases to our tax expense and liabilities that could adversely affect our financial condition and profitability.
| 22 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
If we are unable to protect our intellectual property and prevent its improper use by third parties or if third parties assert that our products or services infringe their intellectual property rights, our ability to compete in the market may be harmed, and our business and financial condition may be adversely affected.
The protection of our intellectual property is important to our business. We rely on a combination of trademarks, copyrights, patents and trade secrets to protect our intellectual property. However, these protections might be inadequate. Our pending or future trademark, copyright and patent applications might not be approved or, if allowed, might not be sufficiently broad. If our intellectual property rights are not adequately protected we may not be able to commercialize our technologies, products or services and our competitors could commercialize our technologies, which could result in a decrease in our sales and market share and could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. Conversely, third parties might assert that our products, services, or other business activities infringe their patents or other intellectual property rights. Infringement and other intellectual property claims and proceedings brought against us, whether successful or not, could result in substantial costs and harm our reputation. Such claims and proceedings can also distract and divert our management and key personnel from other tasks important to the success of our business. In addition, intellectual property litigation or claims could force us to cease selling or using products that incorporate the asserted intellectual property, which would adversely affect our revenues, pay substantial damages for past use of the asserted intellectual property or pay substantial fees to obtain a license from the holder of the asserted intellectual property, which license may not be available on reasonable terms, if at all. In the event of an adverse determination in an intellectual property suit or proceeding, or our failure to license essential technology or redesign our products so as not to infringe third party intellectual property rights, our sales could be harmed and our costs could increase, which could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 23 |
Table of Contents
| Item 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
| Item 2. | PROPERTIES |
We operate at the following primary facilities as of August 31, 2014:
| Description | Location | Status | ||
| Manufacturing Segment |
||||
| Manufacturing facilities1: |
Portland, Oregon | Owned | ||
| 2 locations in Sahagun, Mexico | Leased — 1 location Owned — 1 location | |||
| Tlaxcala, Mexico | Owned — 1 location | |||
| Frontera, Mexico | Leased | |||
| 3 locations in Poland | Owned | |||
| Administrative offices: |
Colleyville, Texas | Leased | ||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts Segment | ||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts facilities: |
13 locations in the U.S. | Leased — 7 locations Owned — 6 locations | ||
| Repair facilities leased to our GBW joint venture: |
21 locations in the U.S.
2 locations in Canada |
Leased — 9 locations Owned — 5 locations Customer premises —7 locations Customer premises | ||
| Administrative offices: |
1 location in the U.S. | Leased | ||
| Leasing & Services Segment |
||||
| Corporate offices, railcar marketing and leasing activities: |
Lake Oswego, Oregon | Leased | ||
1 We operate two manufacturing facilities in Sahagun, Mexico, one of which we own and one of which is leased with a lease expiration date of November 2014. We are in the process of replacing this leased capacity with an alternative site in Tlaxcala, Mexico that was purchased during 2014 and began production in October 2014.
We believe that our facilities are in good condition and that the facilities, together with anticipated capital improvements and additions, are adequate to meet our operating needs for the foreseeable future. We continually evaluate our Manufacturing and Wheels, Repair & Parts facilities in order to remain competitive and to take advantage of market opportunities.
| 24 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
| Item 3. | LEGAL PROCEEDINGS |
There is hereby incorporated by reference the information disclosed in Note 22 to Consolidated Financial Statements, Part II, Item 8 of this Form 10-K.
| Item 4. | MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES |
Not applicable.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 25 |
Table of Contents
| PART | II |
| Item 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Our common stock has been traded on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol GBX since July 14, 1994. There were approximately 403 holders of record of common stock as of October 23, 2014. The following table shows the reported high and low sales prices of our common stock on the New York Stock Exchange for the fiscal periods indicated.
| High | Low | |||||||
| 2014 |
||||||||
| Fourth quarter |
$ | 72.79 | $ | 54.00 | ||||
| Third quarter |
$ | 56.65 | $ | 41.40 | ||||
| Second quarter |
$ | 43.20 | $ | 30.46 | ||||
| First quarter |
$ | 33.20 | $ | 22.57 | ||||
| 2013 |
||||||||
| Fourth quarter |
$ | 25.33 | $ | 21.10 | ||||
| Third quarter |
$ | 25.24 | $ | 19.85 | ||||
| Second quarter |
$ | 22.51 | $ | 15.41 | ||||
| First quarter |
$ | 19.19 | $ | 13.25 | ||||
Dividends
In July 2014, the Board of Directors authorized the reinstatement of our company’s dividend program. Quarterly dividends of $0.15 per share were declared on July 1, 2014 and October 29, 2014. No other dividends were declared during 2013 or 2014. There is no assurance as to the payment of future dividends as they are dependent upon future earnings, capital requirements, customary debt covenant restrictions and our financial condition.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
In October 2013, the Board of Directors authorized our company to repurchase up to $50 million of our company’s common stock. Under the share repurchase program, shares of common stock could be purchased on the open market or through privately negotiated transactions from time-to-time. The timing and amount of purchases was based upon market conditions, securities law limitations and other factors. The share repurchase program did not obligate our company to acquire any specific number of shares in any period.
Under this program, as of August 31, 2014, we repurchased a total of 764,546 shares for approximately $34.4 million at an average price per share of $45.04. Shares repurchased under our share repurchase program during the three months ended August 31, 2014 were as follows:
| Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased |
Average Price Paid Per Share (Including Commissions) |
Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publically Announced Plans or Programs |
Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs |
||||||||||||
| June 1, 2014 – June 30, 2014 |
– | – | – | $ | 23,706,605 | |||||||||||
| July 1, 2014 – July 31, 2014 |
5,000 | $ | 66.40 | 5,000 | $ | 23,374,608 | ||||||||||
| August 1, 2014 – August 31, 2014 |
118,219 | $ | 66.09 | 118,219 | $ | 15,561,626 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| 123,219 | 123,219 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| 26 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Subsequent to August 31, 2014 and through October 23, 2014, we purchased an additional 253,016 shares for approximately $15.6 million. We completed our $50 million share repurchase program in October 2014.
In October 2014, the Board of Directors authorized a new share repurchase program for our company to repurchase up to $50 million of our company’s common stock. Under the share repurchase program, shares of common stock may be purchased on the open market or through privately negotiated transactions from time-to-time. The timing and amount of purchases will be based upon market conditions, securities law limitations and other factors. The share repurchase program does not obligate our company to acquire any specific number of shares in any period. The share repurchase program expires June 30, 2016, but may be modified, suspended or discontinued at any time without prior notice.
Performance Graph
The following graph demonstrates a comparison of cumulative total returns for the Company’s Common Stock, the Dow Jones US Industrial Transportation Index and the Standard & Poor’s (S&P) 500 Index. The graph assumes an investment of $100 on August 31, 2009 in each of the Company’s Common Stock and the stocks comprising the indices. Each of the indices assumes that all dividends were reinvested and that the investment was maintained to and including August 31, 2014, the end of the Company’s 2014 fiscal year.
The comparisons in this table are required by the SEC, and therefore, are not intended to forecast or be indicative of possible future performance of our Common Stock.
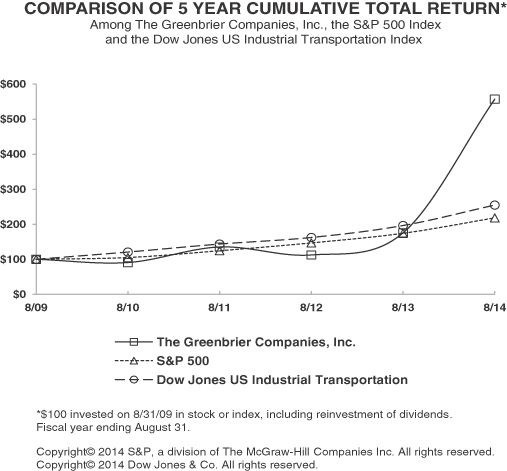
Equity Compensation Plan Information
Equity Compensation Plan Information is hereby incorporated by reference to the “Equity Compensation Plan Information” table in Registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A, which Proxy Statement is anticipated to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of the Registrant’s year ended August 31, 2014.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 27 |
Table of Contents
| Item 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
YEARS ENDED AUGUST 31,
| (In thousands, except unit and per share data) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||||||||||||||
| Statement of Operations Data |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | 1,624,916 | $ | 1,215,734 | $ | 1,253,964 | $ | 721,102 | $ | 295,566 | ||||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
495,627 | 469,222 | 481,865 | 452,865 | 388,434 | |||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
83,419 | 71,462 | 71,887 | 69,323 | 72,280 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 2,203,962 | $ | 1,756,418 | $ | 1,807,716 | $ | 1,243,290 | $ | 756,280 | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings from operations |
$ | 239,520 | $ | 41,651 | $ | 118,788 | $ | 67,574 | $ | 52,107 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to Greenbrier |
$ | 111,919 | (1) | $ | (11,048 | )(2) | $ | 58,708 | $ | 6,466 | (3) | $ | 4,277 | (4) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic earnings (loss) per common share attributable to Greenbrier: |
$ | 3.97 | $ | (0.41 | ) | $ | 2.21 | $ | 0.27 | $ | 0.23 | |||||||||
| Diluted earnings (loss) per common share attributable to Greenbrier: |
$ | 3.44 | $ | (0.41 | ) | $ | 1.91 | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.21 | |||||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
28,164 | 26,678 | 26,572 | 24,100 | 18,585 | |||||||||||||||
| Diluted |
34,209 | 26,678 | 33,718 | 26,501 | 20,213 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends paid per share |
$ | .15 | $ | .00 | $ | .00 | $ | .00 | $ | .00 | ||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 1,517,168 | $ | 1,289,741 | $ | 1,384,544 | $ | 1,301,655 | $ | 1,072,888 | ||||||||||
| Revolving notes and notes payable |
$ | 458,172 | $ | 422,098 | $ | 488,834 | $ | 519,479 | $ | 501,330 | ||||||||||
| Total equity |
$ | 573,721 | $ | 456,827 | $ | 453,645 | $ | 375,901 | $ | 297,407 | ||||||||||
| Other Operating Data |
||||||||||||||||||||
| New railcar units delivered |
16,200 | 11,600 | 15,000 | 9,400 | 2,500 | |||||||||||||||
| New railcar backlog (units) |
31,500 | 14,400 | 10,700 | 15,400 | 5,300 | |||||||||||||||
| New railcar backlog (value in millions) |
$ | 3,330 | $ | 1,520 | $ | 1,200 | $ | 1,230 | $ | 420 | ||||||||||
| Lease fleet: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Units managed |
237,849 | 223,911 | 219,020 | 215,843 | 225,223 | |||||||||||||||
| Units owned |
8,550 | 8,581 | 10,841 | 8,684 | 8,156 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash Flow Data |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | 55,979 | $ | 37,017 | $ | 33,313 | $ | 20,016 | $ | 8,715 | ||||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
8,774 | 7,492 | 11,248 | 20,087 | 12,215 | |||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
5,474 | 16,318 | 73,324 | 44,199 | 18,059 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 70,227 | $ | 60,827 | $ | 117,885 | $ | 84,302 | $ | 38,989 | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of assets |
$ | 54,235 | $ | 75,338 | $ | 33,560 | $ | 18,730 | $ | 22,978 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | 15,341 | $ | 13,469 | $ | 11,754 | $ | 9,853 | $ | 11,061 | ||||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
12,582 | 12,843 | 13,265 | 11,853 | 11,435 | |||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
12,499 | 15,135 | 17,352 | 16,587 | 15,015 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 40,422 | $ | 41,447 | $ | 42,371 | $ | 38,293 | $ | 37,511 | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | 2014 includes a non-cash gain on contribution to joint venture of $13.6 million net of tax and a restructuring charge of $1.0 million net of tax. The gain related to the Company contributing its repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations to the GBW joint venture. |
| (2) | 2013 includes a non-cash goodwill impairment charge of $71.8 million net of tax and a restructuring charge of $1.8 million net of tax. |
| (3) | 2011 includes a loss on extinguishment of debt of $9.4 million net of tax for the write-off of unamortized debt issuance costs, prepayment premiums, debt discount and other costs associated with the repayment of senior unsecured notes and certain term loans. |
| (4) | 2010 includes non-cash income of $11.9 million net of tax for a special item related to the release of the liability associated with the 2008 de-consolidation of our former Canadian subsidiary and includes a gain on extinguishment of debt of $1.3 million net of tax for the gain associated with the early retirement of a portion of the convertible senior notes, partially offset by the write-off of loan fees and debt discount. |
| 28 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
| Item 7. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
Executive Summary
Through July 18, 2014, we operated in three reportable segments: Manufacturing; Wheels, Repair & Parts; and Leasing & Services. Our segments are operationally integrated. On July 18, 2014, we and Watco Companies, LLC (“Watco”), our joint venture partner, contributed our respective repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations to GBW Railcar Services LLC (“GBW”), an unconsolidated 50/50 joint venture which became our fourth reportable segment (GBW Joint Venture) upon formation. The Manufacturing segment, operating from facilities in the United States, Mexico and Poland, produces double-stack intermodal railcars, tank cars, conventional railcars, automotive railcar products and marine vessels. The Wheels, Repair & Parts segment performs wheel and axle servicing, as well as production and reconditioning of a variety of parts for the railroad industry in North America. The Leasing & Services segment owns approximately 8,600 railcars and provides management services for approximately 238,000 railcars for railroads, shippers, carriers, institutional investors and other leasing and transportation companies in North America. Our GBW joint venture provides railcar repair, refurbishment, retrofitting and maintenance services through 39 shops throughout North America, 14 of which are currently tank car certified by the Association of American Railroads (“AAR”) and one location operated exclusively by our company for GBW. We also produce rail castings through an unconsolidated joint venture.
Multi-year supply agreements are a part of rail industry practice. Customer orders may be subject to cancellations or modifications and contain terms and conditions customary in the industry. In most cases, little variation has been experienced between the quantity ordered and the quantity actually delivered.
Our total manufacturing backlog of railcar units as of August 31, 2014 was approximately 31,500 units with an estimated value of $3.33 billion compared to 14,400 units with an estimated value of $1.52 billion as of August 31, 2013. Currently, the entire backlog is expected to be sold to third parties, therefore no orders in our backlog are expected to be placed into our owned lease fleet. A portion of the orders included in backlog reflects an assumed product mix. Under terms of the orders, the exact mix will be determined in the future which may impact the dollar amount of backlog. Marine backlog as of August 31, 2014 was approximately $112 million compared to $10 million as of August 31, 2013. Our backlog of railcar units and marine vessels is not necessarily indicative of future results of operations. Subsequent to year end we received new railcar orders for 11,400 units valued at nearly $1 billion. The new orders referenced are subject to customary documentation and completion of terms.
We operate two manufacturing facilities in Sahagun, Mexico, one of which we own and one of which is leased with a lease expiration date in November 2014. We are replacing this leased capacity with an alternative site in Tlaxcala, Mexico which was purchased during 2014 and began production in October 2014. We expect to incur costs during the first quarter of 2015 related to relocating equipment and startup of lines in the new facility. We are also expanding capacity, particularly for tank car production, at our manufacturing facilities in Mexico including our joint venture facility in northern Mexico. In conjunction with these activities, we and our joint venture partner have extended the term of our joint venture through 2029.
On July 18, 2014, we completed the formation of GBW, an unconsolidated 50/50 joint venture with Watco. As of August 31, 2014, the GBW joint venture operates 38 shops previously part of our company’s and Watco’s networks. The Wheels, Repair & Parts segment included the results of operations for our repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations through July 18, 2014. After July 18, 2014, the results of operations were included as part of Earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates as we account for our interest in GBW under the equity method of accounting. Upon the formation of GBW, we recognized a pre-tax non-cash gain of $29.0 million for the year ended August 31, 2014 attributed to the operations we contributed to GBW.
During 2013, we implemented a restructuring plan to sell or close certain Wheels, Repair & Parts facilities to enhance margins and improve capital efficiency. Restructuring charges related to this plan were $1.5 million ($1.0 million, net of tax) and $2.7 million ($1.8 million, net of tax) for the years ended August 31, 2014 and 2013. The restructuring plan was completed prior to the formation of GBW.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 29 |
Table of Contents
Results of Operations
Revenue, margin and operating profit, presented below, include amounts from external parties and exclude intersegment activity that is eliminated in consolidation. Performance for our segments is evaluated based on operating profit. Corporate includes selling and administrative costs not directly related to goods and services and certain costs that are intertwined among segments due to our integrated business. Management does not allocate Interest and foreign exchange or Income tax expense for either external or internal reporting purposes.
Overview
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Revenue: |
||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | 1,624,916 | $ | 1,215,734 | $ | 1,253,964 | ||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
495,627 | 469,222 | 481,865 | |||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
83,419 | 71,462 | 71,887 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| 2,203,962 | 1,756,418 | 1,807,716 | ||||||||||
| Margin: |
||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
250,908 | 132,845 | 131,580 | |||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
31,689 | 37,721 | 48,324 | |||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
39,623 | 35,807 | 34,516 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| 322,220 | 206,373 | 214,420 | ||||||||||
| Operating profit: |
||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
202,555 | 88,822 | 87,880 | |||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
40,597 | (60,966 | ) | 31,455 | ||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
41,055 | 42,411 | 31,055 | |||||||||
| Corporate |
(44,687 | ) | (28,616 | ) | (31,602 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Earnings from operations |
239,520 | 41,651 | 118,788 | |||||||||
| Interest and foreign exchange |
18,695 | 22,158 | 24,809 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Earnings before income tax and earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
220,825 | 19,493 | 93,979 | |||||||||
| Income tax expense |
(72,401 | ) | (25,060 | ) | (32,393 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) before earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
148,424 | (5,567 | ) | 61,586 | ||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
1,355 | 186 | (416 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
149,779 | (5,381 | ) | 61,170 | ||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interest |
(37,860 | ) | (5,667 | ) | (2,462 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to Greenbrier |
$ | 111,919 | $ | (11,048 | ) | $ | 58,708 | |||||
| Diluted earnings (loss) per common share |
$ | 3.44 | $ | (0.41 | ) | $ | 1.91 | |||||
|
|
||||||||||||
The increase in revenue for the year ended August 31, 2014 was primarily the result of a higher volume of deliveries in the Manufacturing segment of our business. The decrease in revenue for the year ended August 31, 2013 was primarily the result of a lower volume of deliveries in the Manufacturing segment of our business.
The increase in earnings for the year ended August 31, 2014 was primarily attributable to an increase in manufacturing gross margin and a non-cash Gain on contribution to joint venture of $13.6 million, net of tax. In addition, the prior year included a non-cash goodwill impairment charge of $71.8 million, net of tax. The decrease in net earnings for the year ended August 31, 2013 as compared to the year ended August 31, 2012 was primarily attributable to a non-cash goodwill impairment charge of $71.8 million, net of tax and restructuring charges of $1.8 million, net of tax. These were partially offset by an increase in gain on disposition of equipment.
| 30 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Manufacturing Segment
Manufacturing revenue was $1.625 billion, $1.216 billion and $1.254 billion for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. Railcar deliveries, which are the primary source of manufacturing revenue, were 16,200 units in 2014 compared to 11,600 units in 2013 and 15,000 units in 2012. Manufacturing revenue increased $409.2 million in 2014 compared to 2013 primarily due to a higher volume of deliveries as compared to the prior year. These higher deliveries were a result of improved efficiencies and an increase in capacity in response to higher demand. Manufacturing revenue decreased $38.2 million in 2013 compared to 2012 primarily due to a lower volume of deliveries as compared to the prior year. These lower deliveries were a result of a change in product mix to more labor intensive railcar types and lower demand for certain of our products.
Manufacturing margin as a percentage of revenue was 15.4% in 2014, 10.9% in 2013 and 10.5% in 2012. The increase in 2014 compared to 2013 was primarily the result of a favorable change in product mix and pricing, higher volumes of new railcars syndicated with leases attached and improved production efficiencies and overhead absorption. The increase in 2013 compared to 2012 was primarily the result of a favorable change in product mix and an increase in marine revenue. These factors were partially offset by certain inefficiencies with ramping up tank car production.
Manufacturing operating profit was $202.6 million and 12.5% of revenue for the year ended August 31, 2014, $88.8 million and 7.3% of revenue for the year ended August 31, 2013 and $87.9 million and 7.0% of revenue for the year ended August 31, 2012. The increase in operating profit in 2014 and 2013 compared to the prior comparable period was primarily attributed to higher margins.
Wheels, Repair & Parts Segment
The Wheels, Repair & Parts segment included the results of operations for our repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations (“Repair”) through July 18, 2014. On July 18, 2014 we and Watco, our joint venture partner, contributed our respective Repair operations to GBW, an unconsolidated 50/50 joint venture. After July 18, 2014, the results of GBW were included as part of Earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates as we account for our interest in GBW under the equity method of accounting.
Wheels, Repair & Parts revenue was $495.6 million, $469.2 million and $481.9 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. The $26.4 million increase in revenue in 2014 compared to 2013 was primarily the result of an increase in wheel set and component volumes as a result of increased demand and a change in wheel set and component product mix, resulting in a higher average selling price. These were partially offset by a decrease in repair revenue primarily due to the closure of facilities as part of our previously disclosed restructuring plan to sell or close certain Wheels, Repair & Parts facilities to enhance margins and improve capital efficiency. The $12.7 million decrease in revenue in 2013 compared to 2012 was primarily the result of lower demand for wheel set replacements and a decrease in scrap metal pricing and volume. These were partially offset by an increase in demand for repair work.
Wheels, Repair & Parts margin as a percentage of revenue was 6.4% for 2014, 8.0% for 2013 and 10.0% for 2012. The decrease in margin as a percentage of revenue in 2014 compared to 2013 was primarily the result of operating inefficiencies at certain of our repair facilities and a less favorable parts product mix. The decrease in margin as a percentage of revenue in 2013 compared to 2012 was primarily the result of inefficiencies from operating at lower wheel volumes and inefficiencies at certain underperforming facilities. These were partially offset by a favorable change in parts product mix.
Wheels, Repair & Parts operating profit was $40.6 million and 8.2% of revenue for the year ended August 31, 2014, an operating loss of $61.0 million for the year ended August 31, 2013 and an operating profit of $31.5 million and 6.5% of revenue for the year ended August 31, 2012. The increase in operating profit in 2014 compared to 2013 was primarily attributed to a $29.0 million pre-tax non-cash gain on contribution to joint venture in 2014 and a pre-tax non-cash goodwill impairment charge of $76.9 million in 2013. The decrease in operating profit in 2013 compared to 2012 was primarily attributed to a pre-tax non-cash goodwill impairment charge of $76.9 million in 2013.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 31 |
Table of Contents
Leasing & Services Segment
Leasing & Services revenue was $83.4 million, $71.5 million and $71.9 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. The $11.9 million increase in revenue in 2014 compared to 2013 was primarily the result of a syndication of railcars purchased from a third party. These railcars were not manufactured by our company, but rather purchased from a third party with a lease attached, with the intent to resell them. The gross proceeds from the sale of these railcars with leases attached were recorded as revenue and the cost of purchasing these railcars from a third party was recorded in cost of sales. The increase in revenue as compared to the prior year was also a result of an increase in management services revenue due to the addition of new management service agreements and higher average volumes of rent-producing leased railcars for syndication. These were partially offset by a decline in leasing revenue resulting from a smaller average owned lease fleet as compared to the prior year. The $0.4 million decrease in revenue in 2013 compared to 2012 was primarily the result of lower average volumes of rent-producing leased railcars for syndication and a decrease in earnings on mileage utilization leases. These were partially offset by an increase in management services revenue primarily due to the addition of new management services agreements.
Leasing & Services margin as a percentage of revenue was 47.5% in 2014 compared to 50.1% in 2013 and 48.0% in 2012. The decrease in 2014 compared to 2013 was primarily the result of a lower margin syndication of railcars purchased from a third party and the reduction in the maintenance accrual on terminated maintenance management agreements during the prior year. These were partially offset by higher average volumes of rent-producing leased railcars for syndication as compared to the prior year. The increase in 2013 compared to 2012 was primarily the result of a reduction in the maintenance accrual on terminated maintenance management agreements and a receipt of a settlement on a terminated railcar lease agreement, both in 2013. These were partially offset by lower average volumes of rent-producing leased railcars for syndication.
Leasing & Services operating profit was $41.1 million and 49.2% of revenue for the year ended August 31, 2014, $42.4 million and 59.3% of revenue for the year ended August 31, 2013 and $31.1 million and 43.2% of revenue for the year ended August 31, 2012. The decrease in operating profit in 2014 compared to 2013 was primarily attributed to a decrease in Net gain on disposition of equipment. The increase in operating profit in 2013 compared to 2012 was primarily attributed to an increase in Net gain on disposition of equipment.
The percentage of owned units on lease as of August 31, 2014 was 98.2% compared to 97.4% at August 31, 2013 and 93.5% at August 31, 2012.
Selling and Administrative
Selling and administrative expense was $125.3 million, or 5.7% of revenue for the year ended August 31, 2014, $103.2 million, or 5.9% of revenue for the year ended August 31, 2013 and $104.6 million, or 5.8% of revenue, for the year ended August 31, 2012. The $22.1 million increase in 2014 compared to 2013 was primarily due to increased levels of activity resulting in an increase in employee related costs, including incentive compensation associated with increased levels of profitability. The increase was also attributed to an increase in legal and consulting costs associated with the formation of the new GBW joint venture. The $1.4 million decrease in 2013 compared to 2012 was primarily due to a decrease in incentive compensation costs.
Net Gain on Disposition of Equipment
Net gain on disposition of equipment was $15.0 million, $18.1 million and $9.0 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
The gain for the year ended August 31, 2014 consists of $14.6 million in gains realized on the disposition of leased assets and $0.4 million on the disposition of equipment related to our restructuring plan to sell or close certain Wheels, Repair & Parts facilities to enhance margins and improve capital efficiency. The gain for the year ended August 31, 2013 consists of $19.0 million in gains realized on the disposition of leased assets, a $0.6 million other gain and a $1.5 million loss related to the sale of certain assets from our roller bearing operation in Elizabethtown, Kentucky. The entire gain for the year ended August 31, 2012 was realized on the disposition of leased assets.
| 32 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Assets from Greenbrier’s lease fleet are periodically sold in the normal course of business in order to take advantage of market conditions and manage risk and liquidity.
Gain on Contribution to Joint Venture
On July 18, 2014, we and Watco contributed our respective Repair operations to a newly formed entity, GBW, an unconsolidated 50/50 joint venture with Watco. As of August 31, 2014, the GBW joint venture operated 38 shops previously part of our company’s and Watco’s networks. As a result of the formation of GBW, we recognized a pre-tax non-cash gain of $29.0 million for the year ended August 31, 2014 which was calculated as the fair value of our 50% share in GBW, less cash and intangibles contributed to GBW and an allocation in goodwill attributed to the repair, refurbishment and retrofitting business contributed to GBW.
Goodwill Impairment
The results of our annual goodwill impairment test during the third quarter of 2013 indicated that the carrying amount related to Wheels, Repair & Parts was in excess of fair value. As a result, a non-cash impairment loss was recorded to the extent that the carrying amount of the reporting unit’s goodwill exceeded the implied fair value of that goodwill. A non-cash impairment charge of $76.9 million ($71.8 million, net of tax) was recorded for the year ended August 31, 2013. The primary drivers of the impairment charge were lower than expected operating results and changes in forecasted future results, accompanied by a reduction in observed market multiples.
Restructuring Charges
During 2013, we implemented a restructuring plan to sell or close certain Wheels, Repair & Parts facilities to enhance margins and improve capital efficiency. Restructuring charges related to this plan totaled $1.5 million and $2.7 million for the years ended August 31, 2014 and 2013 and consisted of employee related termination costs, contract termination expenses and other costs.
Interest and Foreign Exchange
Interest and foreign exchange expense was composed of the following:
| (In thousands) | Years ended August 31, | Increase (decrease) |
||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||
| Interest and foreign exchange: |
||||||||||||
| Interest and other expense |
$ | 18,306 | $ | 19,203 | $ | (897 | ) | |||||
| Accretion of convertible debt discount |
– | 2,455 | (2,455 | ) | ||||||||
| Foreign exchange loss |
389 | 500 | (111 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| $ | 18,695 | $ | 22,158 | $ | (3,463 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Interest and other expense decreased in 2014 from 2013 primarily due to lower interest expense on reduced levels of average borrowings and the convertible note debt discount being fully amortized in the prior year.
Interest and foreign exchange expense was composed of the following:
| (In thousands) | Years ended August 31, | Increase (decrease) |
||||||||||
| 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||
| Interest and foreign exchange: |
||||||||||||
| Interest and other expense |
$ | 19,203 | $ | 22,474 | $ | (3,271 | ) | |||||
| Accretion of convertible debt discount |
2,455 | 3,259 | (804 | ) | ||||||||
| Foreign exchange (gain) loss |
500 | (924 | ) | 1,424 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| $ | 22,158 | $ | 24,809 | $ | (2,651 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 33 |
Table of Contents
Interest and other expense decreased in 2013 from 2012 primarily due to lower interest expense on reduced levels of average borrowings and a benefit from interest accruals associated with uncertain tax positions that expired during the year. This was partially offset by a foreign exchange gain in 2012 and a foreign exchange loss in 2013.
Income Tax
Our effective tax rate is generally decreased by foreign earnings taxed at rates below the domestic 35% rate and by domestic partnership earnings taxed to noncontrolling interest in a consolidated subsidiary. Our rate can also be increased or decreased by discrete items that may occur in any given year, but are not consistent from one year to the next. Significant discrete items in recent years have included reductions in nondeductible goodwill and reversals of uncertain tax positions.
In 2014 our tax expense was $72.4 million on $220.8 million of pre-tax earnings for an effective tax rate of 32.8%. The rate would have been 29.5% had nondeductible goodwill not reduced the gain recognized on the contribution of our repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations to the GBW joint venture.
In 2013 our tax expense was $25.1 million on $19.5 million of pre-tax earnings that had been reduced by a goodwill impairment charge of $76.9 million that was largely nondeductible. The rate would have been 30.4% without the impairment charge. The rate also benefited from the reversal of uncertain tax positions.
In 2012 our tax expense was $32.4 million on $94.0 million of pre-tax earnings for an effective tax rate of 34.5%. The rate benefitted from the recognition of deferred tax assets in certain foreign jurisdictions and from the restructuring of a foreign subsidiary.
Earnings (Loss) from Unconsolidated Affiliates
Earnings from unconsolidated affiliates were $1.4 million for the year ended August 31, 2014 and primarily included the results of operations from our castings joint venture and our GBW joint venture. Earnings from unconsolidated affiliates were $0.2 million for the year ended August 31, 2013 and primarily included the results of operations from our castings joint venture. Loss from unconsolidated affiliates was $0.4 million for the year ended August 31, 2012 and included the results of operations from our castings joint venture and from WLR–Greenbrier Rail Inc.
Net Earnings Attributable to Noncontrolling Interest
The years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 include net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interest of $37.9 million, $5.7 million and $2.5 million which primarily represents our joint venture partner’s share in the results of operations of our Mexican railcar manufacturing joint venture, adjusted for intercompany sales. The change in 2014 compared to 2013 is primarily a result of operating at higher production rates, improved manufacturing efficiencies and lower intercompany activity in the current year. The change in 2013 compared to 2012 was due to the result of increased sales to third parties and lower intercompany activity.
| 34 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Liquidity and Capital Resources
| Years Ended August 31, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
$ | 135,907 | $ | 104,592 | $ | 116,056 | ||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
(30,078 | ) | 6,159 | (88,947 | ) | |||||||
| Net cash used in financing activities |
(17,561 | ) | (65,732 | ) | (28,794 | ) | ||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes |
(787 | ) | (1,155 | ) | 5,034 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 87,481 | $ | 43,864 | $ | 3,349 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
We have been financed through cash generated from operations and borrowings. At August 31, 2014 cash and cash equivalents was $184.9 million, an increase of $87.5 million from $97.4 million at the prior year end.
Cash provided by operating activities was $135.9 million, $104.6 million and $116.1 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. The increase in 2014 was primarily due to higher earnings, a change in the timing of working capital needs, the timing of sales of leased railcars for syndication as well as billings in excess of costs, which are recorded in deferred revenue, for our marine barges recorded under the percentage of completion method. The decrease in 2013 was primarily due to a change in the timing of working capital needs and the timing of sales of leased railcars for syndication.
Cash provided by (used in) investing activities primarily related to capital expenditures less proceeds from the sale of assets. Cash used in investing activities was $30.1 million for the year ended August 31, 2014 compared to cash provided by investing activities of $6.2 million for the year ended August 31, 2013. Cash used in investing activities was $88.9 million in 2012.
Capital expenditures totaled $70.2 million, $60.8 million and $117.9 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. Proceeds from the sale of assets, which primarily related to sales of railcars from our lease fleet within Leasing & Services, were approximately $54.2 million, $75.3 million and $33.6 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
Approximately $56.0 million, $37.0 million and $33.3 million of capital expenditures for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 were attributable to Manufacturing operations. Capital expenditures for Manufacturing are expected to be approximately $95.0 million in 2015 and primarily relate to enhancements to our manufacturing facilities and replacement of certain leased manufacturing capacity in Mexico with an alternative site and expansion of capacity, particularly for tank car production, at our manufacturing facilities in Mexico.
Approximately $5.4 million, $16.3 million and $73.3 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 of capital expenditures were attributable to Leasing & Services operations and corporate. Leasing & Services and corporate capital expenditures for 2015 are expected to be approximately $35.0 million. Proceeds from sales of leased railcar equipment are expected to be approximately $10.0 million for 2015. We regularly buy and sell assets from our lease fleet.
Wheels, Repair & Parts capital expenditures for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 were $8.8 million, $7.5 million and $11.2 million and are expected to be approximately $10.0 million in 2015 for maintenance and improvement of existing facilities.
Cash used in financing activities was $17.6 million, $65.7 million and $28.8 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. Cash used in financing activities primarily related to repurchase of stock and repayments of debt, net of debt proceeds.
In October 2013, the Board of Directors authorized our company to repurchase up to $50 million of our common stock. Under the share repurchase program, shares of common stock could be purchased on the open market or through privately negotiated transactions from time-to-time. The timing and amount of purchases was based
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 35 |
Table of Contents
upon market conditions, securities law limitations and other factors. The share repurchase program did not obligate us to acquire any specific number of shares in any period. During the year ended August 31, 2014, we repurchased a total of 764,546 shares for approximately $34.4 million. Subsequent to August 31, 2014 and through October 23, 2014, we purchased an additional 253,016 shares for approximately $15.6 million. We completed our $50 million share repurchase program in October 2014.
In October 2014, the Board of Directors authorized a new share repurchase program for our company to repurchase up to $50 million of our company’s common stock. Under the share repurchase program, shares of common stock may be purchased on the open market or through privately negotiated transactions from time-to-time. The timing and amount of purchases will be based upon market conditions, securities law limitations and other factors. The share repurchase program does not obligate our company to acquire any specific number of shares in any period. The share repurchase program expires June 30, 2016, but may be modified, suspended or discontinued at any time without prior notice.
In March 2014, we refinanced approximately $125 million of existing senior term debt, due in March 2014 and May 2015, secured by a pool of leased railcars with new 6-year $200 million senior term debt also secured by a pool of leased railcars and cash. The new debt bears a floating interest rate of LIBOR plus 1.75% with principal of $1.75 million paid quarterly in arrears and a balloon payment of $159.8 million due at maturity. An interest rate swap agreement was entered into on 50% of the initial balance to swap the floating interest rate of LIBOR plus 1.75% to a fixed rate of 3.7375%.
In July 2014, the Board of Directors authorized the reinstatement of our company’s dividend program. Quarterly dividends of $0.15 per share were declared on July 1, 2014 and October 29, 2014.
Senior secured credit facilities, consisting of three components, aggregated to $359.1 million as of August 31, 2014. We had an aggregate of $321.0 million available to draw down under the committed credit facilities as of August 31, 2014. This amount consists of $265.0 million available on the North American credit facility, $19.1 million on the European credit facilities and $36.9 million on the Mexican joint venture credit facilities as of August 31, 2014.
As of August 31, 2014 a $290.0 million revolving line of credit, maturing June 2016 and secured by substantially all of our assets in the U.S. not otherwise pledged as security for term loans, was available to provide working capital and interim financing of equipment, principally for the U.S. and Mexican operations. Advances under this facility bear interest at LIBOR plus 2.25% or Prime plus 1.25% depending on the type of borrowing. Available borrowings under the credit facility are generally based on defined levels of inventory, receivables, property, plant and equipment and leased equipment, as well as total debt to consolidated capitalization and fixed charges coverage ratios.
As of August 31, 2014, lines of credit totaling $19.1 million secured by certain of our European assets, with various variable rates that range from Warsaw Interbank Offered Rate (“WIBOR”) plus 1.2% to WIBOR plus 1.5%, were available for working capital needs of the European manufacturing operation. European credit facilities are continually being renewed. Currently these European credit facilities have maturities that range from December 2014 through June 2015.
As of August 31, 2014, our Mexican joint venture had two lines of credit totaling $50.0 million. The first line of credit provides up to $20.0 million and is secured by certain of the joint venture’s accounts receivable and inventory. Advances under this facility bear interest at LIBOR plus 2.5%. The Mexican joint venture will be able to draw amounts available under this facility through January 2015. The second line of credit provides up to $30.0 million and is fully guaranteed by each of the joint venture partners, including our Company. Advances under this facility bear interest at LIBOR plus 2.0%. The Mexican joint venture will be able to draw against this facility through January 2015.
As of August 31, 2014 outstanding borrowings under the senior secured credit facilities consisted of $9.6 million in letters of credit under the North American credit facility and $13.1 million outstanding under the Mexican joint venture credit facilities.
| 36 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
The revolving and operating lines of credit, along with notes payable, contain covenants with respect to us and our various subsidiaries, the most restrictive of which, among other things, limit our ability to: incur additional indebtedness or guarantees; pay dividends or repurchase stock; enter into sale leaseback transactions; create liens; sell assets; engage in transactions with affiliates, including joint ventures and non U.S. subsidiaries, including but not limited to loans, advances, equity investments and guarantees; enter into mergers, consolidations or sales of substantially all our assets; and enter into new lines of business. The covenants also require certain maximum ratios of debt to total capitalization and minimum levels of fixed charges (interest plus rent) coverage.
We may from time to time seek to repurchase or otherwise retire or exchange securities, including outstanding borrowings and equity securities, and take other steps to reduce our debt or otherwise enhance our balance sheet. These actions may include open market repurchases, unsolicited or solicited privately negotiated transactions or other retirements, repurchases or exchanges. Such repurchases or exchanges, if any, will depend on a number of factors, including, but not limited to, prevailing market conditions, trading levels of our debt, our liquidity requirements and contractual restrictions, if applicable.
We have operations in Mexico and Poland that conduct business in their local currencies as well as other regional currencies. To mitigate the exposure to transactions denominated in currencies other than the functional currency, we enter into foreign currency forward exchange contracts with established financial institutions to protect the margin on a portion of foreign currency sales in firm backlog primarily in Euro. No provision has been made for credit loss due to counterparty non-performance.
As of August 31, 2014, the Mexican joint venture had $14.6 million of third party debt, of which we and our joint venture partner have each guaranteed approximately $10.8 million.
In accordance with customary business practices in Europe, we have $4.0 million in bank and third party warranty and performance guarantee facilities as of August 31, 2014. To date no amounts have been drawn under these guarantee facilities.
On July 18, 2014, we and Watco contributed our respective repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations to GBW, an unconsolidated 50/50 joint venture. We made a $10 million cash contribution at closing and an additional $2.5 million cash contribution in August 2014. We are likely to make additional capital contributions or loans to GBW in the future including an additional $2.5 million capital contribution which has already been committed.
We expect existing funds and cash generated from operations, together with proceeds from financing activities including borrowings under existing credit facilities and long-term financings, to be sufficient to fund dividends, working capital needs, planned capital expenditures and expected debt repayments for the next twelve months.
The following table shows our estimated future contractual cash obligations as of August 31, 2014:
| Years Ending August 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | Total | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | Thereafter | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Notes payable |
$ | 445,091 | $ | 7,720 | $ | 22,465 | $ | 7,437 | $ | 237,219 | $ | 7,000 | $ | 163,250 | ||||||||||||||
| Interest (1) |
61,541 | 14,129 | 13,856 | 13,229 | 13,015 | 4,749 | 2,563 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Revolving notes |
13,081 | 13,081 | – | – | – | – | – | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating leases |
16,799 | 4,928 | 2,951 | 2,835 | 2,170 | 1,610 | 2,305 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Railcar leases |
10,721 | 6,007 | 2,093 | 1,569 | 1,052 | – | – | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other |
2,908 | 2,793 | 90 | 25 | – | – | – | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 550,141 | $ | 48,658 | $ | 41,455 | $ | 25,095 | $ | 253,456 | $ | 13,359 | $ | 168,118 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | A portion of the estimated future cash obligation relates to interest on variable rate borrowings. |
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 37 |
Table of Contents
Due to uncertainty with respect to the timing of future cash flows associated with our unrecognized tax benefits at August 31, 2014, we are unable to estimate the period of cash settlement with the respective taxing authority. Therefore, approximately $0.2 million in uncertain tax positions have been excluded from the contractual table above. See Note 18 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion on income taxes.
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not currently have off balance sheet arrangements that have or are likely to have a material current or future effect on our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. requires judgment on the part of management to arrive at estimates and assumptions on matters that are inherently uncertain. These estimates may affect the amount of assets, liabilities, revenue and expenses reported in the financial statements and accompanying notes and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities within the financial statements. Estimates and assumptions are periodically evaluated and may be adjusted in future periods. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Income taxes - For financial reporting purposes, income tax expense is estimated based on amounts anticipated to be reported on tax return filings. Those anticipated amounts may change from when the financial statements are prepared to when the tax returns are filed. Further, because tax filings are subject to review by taxing authorities, there is risk that a position taken in preparation of a tax return may be challenged by a taxing authority. If a challenge is successful, differences in tax expense or between current and deferred tax items may arise in future periods. Any material effect of such differences would be reflected in the financial statements when management considers the effect probable of occurring and the amount reasonably estimable. Valuation allowances reduce deferred tax assets to amounts more likely than not be realized based on information available when the financial statements are prepared. This information may include estimates of future income and other assumptions that are inherently uncertain.
Maintenance obligations - We are responsible for maintenance on a portion of the managed and owned lease fleet under the terms of maintenance obligations defined in the underlying lease or management agreement. The estimated maintenance liability is based on maintenance histories for each type and age of railcar. These estimates involve judgment as to the future costs of repairs and the types and timing of repairs required over the lease term. As we cannot predict with certainty the prices, timing and volume of maintenance needed in the future on railcars under long-term leases, this estimate is uncertain and could be materially different from maintenance requirements. The liability is periodically reviewed and updated based on maintenance trends and known future repair or refurbishment requirements. These adjustments could be material due to the inherent uncertainty in predicting future maintenance requirements.
Warranty accruals - Warranty costs to cover a defined warranty period are estimated and charged to operations. The estimated warranty cost is based on historical warranty claims for each particular product type. For new product types without a warranty history, preliminary estimates are based on historical information for similar product types. These estimates are inherently uncertain as they are based on historical data for existing products and judgment for new products. If warranty claims are made in the current period for issues that have not historically been the subject of warranty claims and were not taken into consideration in establishing the accrual or if claims for issues already considered in establishing the accrual exceed expectations, warranty expense may exceed the accrual for that particular product. Conversely, there is the possibility that claims may be lower than estimates. The warranty accrual is periodically reviewed and updated based on warranty trends. However, as we cannot predict future claims, the potential exists for the difference in any one reporting period to be material.
Environmental costs - At times we may be involved in various proceedings related to environmental matters. We estimate future costs for known environmental remediation requirements and accrue for them when it is probable that we have incurred a liability and the related costs can be reasonably estimated based on currently available information. If further developments or resolution of an environmental matter result in facts and circumstances
| 38 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
that are significantly different than the assumptions used to develop these reserves, the accrual for environmental remediation could be materially understated or overstated. Adjustments to these liabilities are made when additional information becomes available that affects the estimated costs to study or remediate any environmental issues or when expenditures for which reserves are established are made. Due to the uncertain nature of estimating potential environmental matters, there can be no assurance that we will not become involved in future litigation or other proceedings or, if we were found to be responsible or liable in any litigation or proceeding, that such costs would not be material to us.
Revenue recognition - Revenue is recognized when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, delivery has occurred or services have been rendered, the price is fixed or determinable and collectability is reasonably assured.
Railcars are generally manufactured, repaired or refurbished and wheels and parts produced under firm orders from third parties. Revenue is recognized when these products or services are completed, accepted by an unaffiliated customer and contractual contingencies removed. Certain leases are operated under car hire arrangements whereby revenue is earned based on utilization, car hire rates and terms specified in the lease agreement. Car hire revenue is reported from a third party source two months in arrears; however, such revenue is accrued in the month earned based on estimates of use from historical activity and is adjusted to actual as reported. These estimates are inherently uncertain as they involve judgment as to the estimated use of each railcar. Adjustments to actual have historically not been significant. Revenues from construction of marine barges are either recognized on the percentage of completion method during the construction period or on the completed contract method based on the terms of the contract. Under the percentage of completion method, judgment is used to determine a definitive threshold against which progress towards completion can be measured to determine timing of revenue recognition.
We will periodically sell railcars with leases attached to financial investors. In addition we will often perform management or maintenance services at market rates for these railcars. Pursuant to the guidance in ASC 840-20-40, we evaluate the terms of any remarketing agreements and any contractual provisions that represent retained risk and the level of retained risk based on those provisions. We determine whether the level of retained risk exceeds 10% of the individual fair value of the railcars with leases attached that are delivered. For any contracts with multiple elements (i.e. railcars, maintenance, management services, etc.) we allocate revenue among the deliverables primarily based upon objective and reliable evidence of the fair value of each element in the arrangement. If objective and reliable evidence of fair value of any element is not available, we will use the element’s estimated selling price for purposes of allocating the total arrangement consideration among the elements.
Impairment of long-lived assets - When changes in circumstances indicate the carrying amount of certain long-lived assets may not be recoverable, the assets are evaluated for impairment. If the forecast undiscounted future cash flows are less than the carrying amount of the assets, an impairment charge to reduce the carrying value of the assets to fair value is recognized in the current period. These estimates are based on the best information available at the time of the impairment and could be materially different if circumstances change. If the forecast undiscounted future cash flows exceeded the carrying amount of the assets it would indicate that the assets were not impaired.
Goodwill and acquired intangible assets - We periodically acquire businesses in purchase transactions in which the allocation of the purchase price may result in the recognition of goodwill and other intangible assets. The determination of the value of such intangible assets requires management to make estimates and assumptions. These estimates affect the amount of future period amortization and possible impairment charges.
Goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets are tested for impairment annually during the third quarter. Goodwill is also tested more frequently if changes in circumstances or the occurrence of events indicates that a potential impairment exists. When changes in circumstances, such as a decline in the market price of our common stock, changes in demand or in the numerous variables associated with the judgments, assumptions and estimates made in assessing the appropriate valuation of goodwill indicate the carrying amount of certain indefinite lived assets may not be recoverable, the assets are evaluated for impairment. Among other things, our
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 39 |
Table of Contents
assumptions used in the valuation of goodwill include growth of revenue and margins, market multiples, discount rates and increased cash flows over time. If actual operating results were to differ from these assumptions, it may result in an impairment of our goodwill.
The provisions of Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 350, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other, require that we perform a two-step impairment test on goodwill. In the first step, we compare the fair value of each reporting unit with its carrying value. We determine the fair value of our reporting units based on a weighting of income and market approaches. Under the income approach, we calculate the fair value of a reporting unit based on the present value of estimated future cash flows. Under the market approach, we estimate the fair value based on observed market multiples for comparable businesses. The second step of the goodwill impairment test is required only in situations where the carrying value of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value as determined in the first step. In the second step we would compare the implied fair value of goodwill to its carrying value. The implied fair value of goodwill is determined by allocating the fair value of a reporting unit to all of the assets and liabilities of that unit as if the reporting unit had been acquired in a business combination and the fair value of the reporting unit was the price paid to acquire the reporting unit. The excess of the fair value of a reporting unit over the amounts assigned to its assets and liabilities is the implied fair value of goodwill. An impairment loss is recorded to the extent that the carrying amount of the reporting unit goodwill exceeds the implied fair value of that goodwill. The goodwill balance relates to the Wheels, Repair & Parts segment.
New Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 2 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| 40 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
| Item 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
Foreign Currency Exchange Risk
We have operations in Mexico and Poland that conduct business in their local currencies as well as other regional currencies. To mitigate the exposure to transactions denominated in currencies other than the functional currency of each entity, we enter into foreign currency forward exchange contracts to protect the margin on a portion of forecast foreign currency sales. At August 31, 2014, $91.0 million of forecast sales in Europe were hedged by foreign exchange contracts. Because of the variety of currencies in which purchases and sales are transacted and the interaction between currency rates, it is not possible to predict the impact a movement in a single foreign currency exchange rate would have on future operating results.
In addition to exposure to transaction gains or losses, we are also exposed to foreign currency exchange risk related to the net asset position of our foreign subsidiaries. At August 31, 2014, net assets of foreign subsidiaries aggregated $59.4 million and a 10% strengthening of the U.S. dollar relative to the foreign currencies would result in a decrease in equity of $5.9 million, or 1.2% of Total equity Greenbrier. This calculation assumes that each exchange rate would change in the same direction relative to the U.S. dollar.
Interest Rate Risk
We have managed a portion of our variable rate debt with interest rate swap agreements, effectively converting $99.1 million of variable rate debt to fixed rate debt. As a result, we are exposed to interest rate risk relating to our revolving debt and a portion of term debt, which are at variable rates. At August 31, 2014, 75% of our outstanding debt has fixed rates and 25% has variable rates. At August 31, 2014, a uniform 10% increase in interest rates would result in approximately $0.2 million of additional annual interest expense.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 41 |
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of August 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), equity and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended August 31, 2014. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. and subsidiaries as of August 31, 2014 and 2013, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended August 31, 2014, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of August 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO), and our report dated October 30, 2014 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ KPMG LLP
Portland, Oregon
October 30, 2014
| 42 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
| Item 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
Consolidated Balance Sheets
AS OF AUGUST 31,
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||
| Assets |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 184,916 | $ | 97,435 | ||||
| Restricted cash |
20,140 | 8,807 | ||||||
| Accounts receivable, net |
199,679 | 154,848 | ||||||
| Inventories |
305,656 | 316,783 | ||||||
| Leased railcars for syndication |
125,850 | 68,480 | ||||||
| Equipment on operating leases, net |
258,848 | 305,468 | ||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net |
243,698 | 201,533 | ||||||
| Investment in unconsolidated affiliates |
69,359 | 10,739 | ||||||
| Goodwill |
43,265 | 57,416 | ||||||
| Intangibles and other assets, net |
65,757 | 68,232 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| $ | 1,517,168 | $ | 1,289,741 | |||||
|
|
||||||||
| Liabilities and Equity |
||||||||
| Revolving notes |
$ | 13,081 | $ | 48,209 | ||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
383,289 | 315,938 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
81,383 | 86,040 | ||||||
| Deferred revenue |
20,603 | 8,838 | ||||||
| Notes payable |
445,091 | 373,889 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Notes 21 & 22) |
||||||||
| Equity: Greenbrier |
||||||||
| Preferred stock - without par value; 25,000 shares authorized; none outstanding |
– | – | ||||||
| Common stock - without par value; 50,000 shares authorized; 27,364 and 28,084 outstanding at August 31, 2014 and 2013 |
– | – | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
235,763 | 259,864 | ||||||
| Retained earnings |
282,559 | 174,842 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(6,932 | ) | (6,504 | ) | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Total equity Greenbrier |
511,390 | 428,202 | ||||||
| Noncontrolling interest |
62,331 | 28,625 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Total equity |
573,721 | 456,827 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| $ | 1,517,168 | $ | 1,289,741 | |||||
|
|
||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 43 |
Table of Contents
Consolidated Statements of Operations
YEARS ENDED AUGUST 31,
| (In thousands, except per share amounts) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | 1,624,916 | $ | 1,215,734 | $ | 1,253,964 | ||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
495,627 | 469,222 | 481,865 | |||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
83,419 | 71,462 | 71,887 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| 2,203,962 | 1,756,418 | 1,807,716 | ||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
1,374,008 | 1,082,889 | 1,122,384 | |||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
463,938 | 431,501 | 433,541 | |||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
43,796 | 35,655 | 37,371 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| 1,881,742 | 1,550,045 | 1,593,296 | ||||||||||
| Margin |
322,220 | 206,373 | 214,420 | |||||||||
| Selling and administrative |
125,270 | 103,175 | 104,596 | |||||||||
| Net gain on disposition of equipment |
(15,039 | ) | (18,072 | ) | (8,964 | ) | ||||||
| Gain on contribution to joint venture |
(29,006 | ) | – | – | ||||||||
| Goodwill impairment |
– | 76,900 | – | |||||||||
| Restructuring charges |
1,475 | 2,719 | – | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Earnings from operations |
239,520 | 41,651 | 118,788 | |||||||||
| Other costs |
||||||||||||
| Interest and foreign exchange |
18,695 | 22,158 | 24,809 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Earnings before income tax and earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
220,825 | 19,493 | 93,979 | |||||||||
| Income tax expense |
(72,401 | ) | (25,060 | ) | (32,393 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) before earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
148,424 | (5,567 | ) | 61,586 | ||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
1,355 | 186 | (416 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
149,779 | (5,381 | ) | 61,170 | ||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interest |
(37,860 | ) | (5,667 | ) | (2,462 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to Greenbrier |
$ | 111,919 | $ | (11,048 | ) | $ | 58,708 | |||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Basic earnings (loss) per common share: |
$ | 3.97 | $ | (0.41 | ) | $ | 2.21 | |||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Diluted earnings (loss) per common share: |
$ | 3.44 | $ | (0.41 | ) | $ | 1.91 | |||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Weighted average common shares: |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
28,164 | 26,678 | 26,572 | |||||||||
| Diluted |
34,209 | 26,678 | 33,718 | |||||||||
| Dividends declared per common share |
$ | 0.15 | $ | – | $ | – | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| 44 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
YEARS ENDED AUGUST 31,
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
$ | 149,779 | $ | (5,381 | ) | $ | 61,170 | |||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) |
||||||||||||
| Translation adjustment |
116 | 1,056 | (4,168 | ) | ||||||||
| Reclassification of derivative financial instruments recognized in net earnings (loss) 1 |
471 | (561 | ) | 4,988 | ||||||||
| Unrealized gain (loss) on derivative financial instruments 2 |
(1,019 | ) | (399 | ) | 708 | |||||||
| Other (net of tax effect) |
10 | (203 | ) | (130 | ) | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| (422 | ) | (107 | ) | 1,398 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
149,357 | (5,488 | ) | 62,568 | ||||||||
| Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest |
(37,866 | ) | (5,695 | ) | (2,334 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to Greenbrier |
$ | 111,491 | $ | (11,183 | ) | $ | 60,234 | |||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| 1 | Net of tax of effect of $0.5 million, $0.3 million and $1.3 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. |
| 2 | Net of tax of effect of $0.7 million, $0.2 million and $0.3 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 45 |
Table of Contents
Consolidated Statements of Equity
| Attributable to Greenbrier | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | Common Stock |
Additional Paid-in Capital |
Retained Earnings |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
Total Attributable to Greenbrier |
Attributable to Noncontrolling Interest |
Total Equity |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance September 1, 2011 |
25,186 | $ | 242,286 | $ | 127,182 | $ | (7,895 | ) | $ | 361,573 | $ | 14,328 | $ | 375,901 | ||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
– | – | 58,708 | – | 58,708 | 2,462 | 61,170 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net |
– | – | – | 1,526 | 1,526 | (128 | ) | 1,398 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Investment by joint venture partner |
– | – | – | – | – | 1,362 | 1,362 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest adjustments |
– | – | – | – | – | 3,844 | 3,844 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock awards (net of cancellations and expense) |
461 | 9,392 | – | – | 9,392 | – | 9,392 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Unamortized restricted stock |
– | (9,392 | ) | – | – | (9,392 | ) | – | (9,392 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock amortization |
– | 8,343 | – | – | 8,343 | – | 8,343 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrants exercised |
1,496 | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Excess tax benefit from restricted stock awards |
– | 1,627 | – | – | 1,627 | – | 1,627 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance August 31, 2012 |
27,143 | $ | 252,256 | $ | 185,890 | $ | (6,369 | ) | $ | 431,777 | $ | 21,868 | $ | 453,645 | ||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
– | – | (11,048 | ) | – | (11,048 | ) | 5,667 | (5,381 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net |
– | – | – | (135 | ) | (135 | ) | 28 | (107 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest adjustments |
– | – | – | – | – | (2,144 | ) | (2,144 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Investment by joint venture partner |
– | – | – | – | – | 3,206 | 3,206 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock awards (net of cancellations and expense) |
27 | 8,913 | – | – | 8,913 | – | 8,913 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Unamortized restricted stock |
– | (8,921 | ) | – | – | (8,921 | ) | – | (8,921 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock amortization |
– | 6,716 | – | – | 6,716 | – | 6,716 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Excess tax benefit from restricted stock awards |
– | 900 | – | – | 900 | – | 900 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrants exercised |
914 | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance August 31, 2013 |
28,084 | $ | 259,864 | $ | 174,842 | $ | (6,504 | ) | $ | 428,202 | $ | 28,625 | $ | 456,827 | ||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
– | – | 111,919 | – | 111,919 | 37,860 | 149,779 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income, net |
– | – | – | (428 | ) | (428 | ) | 6 | (422 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest adjustments |
– | – | – | – | – | 2,774 | 2,774 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Investment by joint venture partner |
– | – | – | – | – | 419 | 419 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Joint venture partner distribution declared |
– | – | – | – | – | (7,353 | ) | (7,353 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock awards (net of cancellations and expense) |
44 | 11,303 | – | – | 11,303 | – | 11,303 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Unamortized restricted stock |
– | (12,360 | ) | – | – | (12,360 | ) | – | (12,360 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock amortization |
– | 11,285 | – | – | 11,285 | – | 11,285 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Excess tax benefit from restricted stock awards |
– | 109 | – | – | 109 | – | 109 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends |
– | – | (4,202 | ) | – | (4,202 | ) | – | (4,202 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase of stock |
(764 | ) | (34,438 | ) | – | – | (34,438 | ) | – | (34,438 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance August 31, 2014 |
27,364 | $ | 235,763 | $ | 282,559 | $ | (6,932 | ) | $ | 511,390 | $ | 62,331 | $ | 573,721 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| 46 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
YEARS ENDED AUGUST 31,
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
$ | 149,779 | $ | (5,381 | ) | $ | 61,170 | |||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
(4,687 | ) | (9,662 | ) | 11,617 | |||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
40,422 | 41,447 | 42,371 | |||||||||
| Net gain on disposition of equipment |
(15,039 | ) | (18,072 | ) | (8,964 | ) | ||||||
| Accretion of debt discount |
– | 2,455 | 3,259 | |||||||||
| Stock based compensation expense |
11,285 | 6,302 | 8,757 | |||||||||
| Gain on contribution to joint venture |
(29,006 | ) | – | – | ||||||||
| Goodwill impairment |
– | 76,900 | – | |||||||||
| Other |
3,350 | (1,055 | ) | 4,905 | ||||||||
| Decrease (increase) in assets: |
||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net |
(23,749 | ) | (7,323 | ) | 37,763 | |||||||
| Inventories |
(9,675 | ) | 19,045 | 3,709 | ||||||||
| Leased railcars for syndication |
(57,779 | ) | 22,881 | (76,071 | ) | |||||||
| Other |
(4,069 | ) | 969 | – | ||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
63,362 | (15,429 | ) | 16,236 | ||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
11,713 | (8,485 | ) | 11,304 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
135,907 | 104,592 | 116,056 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from sales of assets |
54,235 | 75,338 | 33,560 | |||||||||
| Capital expenditures |
(70,227 | ) | (60,827 | ) | (117,885 | ) | ||||||
| Increase in restricted cash |
(333 | ) | (2,530 | ) | (4,164 | ) | ||||||
| Investment in and advances to unconsolidated affiliates |
(13,753 | ) | (2,240 | ) | (506 | ) | ||||||
| Other |
– | (3,582 | ) | 48 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
(30,078 | ) | 6,159 | (88,947 | ) | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net changes in revolving notes with maturities of 90 days or less |
– | (16,396 | ) | (57,302 | ) | |||||||
| Proceeds from revolving notes with maturities longer than 90 days |
37,819 | 38,177 | 63,773 | |||||||||
| Repayments of revolving notes with maturities longer than 90 days |
(72,947 | ) | (34,966 | ) | (33,934 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of notes payable |
200,000 | 2,186 | 2,750 | |||||||||
| Repayments of notes payable |
(128,797 | ) | (58,831 | ) | (7,070 | ) | ||||||
| Debt issuance costs |
(382 | ) | – | – | ||||||||
| Increase in restricted cash |
(11,000 | ) | – | – | ||||||||
| Repurchase of stock |
(33,583 | ) | – | – | ||||||||
| Dividends |
(4,123 | ) | ||||||||||
| Cash distribution to joint venture partner |
(5,076 | ) | – | – | ||||||||
| Investment by joint venture partner |
419 | 3,206 | 1,362 | |||||||||
| Excess tax benefit from restricted stock awards |
109 | 900 | 1,627 | |||||||||
| Other |
– | (8 | ) | – | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Net cash used in financing activities |
(17,561 | ) | (65,732 | ) | (28,794 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes |
(787 | ) | (1,155 | ) | 5,034 | |||||||
| Increase in cash and cash equivalents |
87,481 | 43,864 | 3,349 | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
||||||||||||
| Beginning of period |
97,435 | 53,571 | 50,222 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| End of period |
$ | 184,916 | $ | 97,435 | $ | 53,571 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Cash paid during the period for: |
||||||||||||
| Interest |
$ | 14,347 | $ | 14,964 | $ | 12,737 | ||||||
| Income taxes, net |
$ | 69,263 | $ | 29,680 | $ | 8,601 | ||||||
| Non-cash activity |
||||||||||||
| Transfer of Inventories to Accounts receivable, net |
$ | 20,986 | $ | – | $ | – | ||||||
| Dividends declared and accrued in Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
$ | 79 | $ | – | $ | – | ||||||
| Capital expenditures accrued in Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
$ | 3,349 | $ | – | $ | – | ||||||
| Transfer of Equipment on operating leases to Inventories |
$ | – | $ | 17,826 | $ | – | ||||||
| Transfer of Leased railcars for syndication to Equipment on operating leases |
$ | – | $ | 6,437 | $ | 8,963 | ||||||
| Transfer of Property, plant and equipment, net to Intangibles and other assets, net |
$ | – | $ | 1,856 | $ | – | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 47 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Note 1 - Nature of Operations
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. and its subsidiaries (“Greenbrier” or the “Company”) through July 18, 2014 operated in three reportable segments: Manufacturing; Wheels, Repair & Parts; and Leasing & Services. The three segments are operationally integrated. On July 18, 2014, the Company and Watco Companies, LLC (“Watco”), its joint venture partner, contributed its respective repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations to GBW Railcar Services LLC (“GBW”), an unconsolidated 50/50 joint venture which became the Company’s fourth reportable segment (GBW Joint Venture) upon formation. The Manufacturing segment, operating from facilities in the United States, Mexico and Poland, produces double-stack intermodal railcars, tank cars, conventional railcars, automotive railcar products and marine vessels. The Wheels, Repair & Parts segment performs wheel and axle servicing in North America and production of a variety of parts for the railroad industry. The Leasing & Services segment owns approximately 8,600 railcars and provides management services for approximately 238,000 railcars for railroads, shippers, carriers, institutional investors and other leasing and transportation companies in North America. The Company’s GBW joint venture provides railcar repair, refurbishment, retrofitting and maintenance services through 39 shops throughout North America, 14 of which are currently tank car certified by the Association of American Railroads (“AAR”) and one location operated exclusively by the Company for GBW. Greenbrier also produces rail castings through an unconsolidated joint venture.
The Wheels, Repair & Parts segment included the results of operations for the Company’s repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations (“Repair”) through July 18, 2014. On July 18, 2014 the Company and Watco, its joint venture partner, contributed its respective Repair operations to GBW, an unconsolidated 50/50 joint venture. After July 18, 2014, the results of GBW were included as part of Earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates as the Company accounts for its interest in GBW under the equity method of accounting. See Note 3 – Gain on Contribution to Joint Venture for additional information.
Note 2 - Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of consolidation - The financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiaries in which it has a controlling interest. All intercompany transactions and balances are eliminated upon consolidation.
Unclassified Balance Sheet - The balance sheets of the Company are presented in an unclassified format as a result of significant leasing activities for which the current or non-current distinction is not relevant. In addition, the activities of the Manufacturing; Wheels, Repair & Parts; and Leasing & Services segments are so intertwined that in the opinion of management, any attempt to separate the respective balance sheet categories would not be meaningful and may lead to the development of misleading conclusions by the reader.
Foreign currency translation - Certain operations outside the U.S., primarily in Poland, prepare financial statements in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. Revenues and expenses are translated at average exchange rates for the year, while assets and liabilities are translated at year-end exchange rates. Translation adjustments are accumulated as a separate component of equity in other comprehensive income (loss). The foreign currency translation adjustment balances were $4.8 million, $4.9 million and $6.0 million as of August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
Cash and cash equivalents - Cash may temporarily be invested primarily in money market funds. All highly-liquid investments with a maturity of three months or less at the date of acquisition are considered cash equivalents.
Restricted cash - Restricted cash relates to amounts held in restricted accounts to support a target minimum rate of return on certain agreements and a pass through account for activity related to management services provided for certain third party customers. In addition, restricted cash relates to cash collateral associated with a term loan.
| 48 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Accounts receivable - Accounts receivable includes receivables from related parties (see Note 17 – Related Party Transactions) and is stated net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $2.0 million and $3.9 million as of August 31, 2014 and 2013.
| As of August 31, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
||||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of period |
$ | 3,894 | $ | 3,525 | $ | 3,913 | ||||||
| Additions, net of reversals |
604 | 543 | 641 | |||||||||
| Usage |
(2,524 | ) | (285 | ) | (663 | ) | ||||||
| Currency translation effect |
59 | 111 | (366 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Balance at end of period |
$ | 2,033 | $ | 3,894 | $ | 3,525 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Inventories - Inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market using the first-in first-out method. Work-in-process includes material, labor and overhead.
Leased railcars for syndication - Leased railcars for syndication consist of newly-built railcars manufactured at one of the Company’s facilities or railcars purchased from a third party, which have been placed on lease to a customer and which the Company intends to sell to an investor with the lease attached. These railcars are generally anticipated to be sold within six months of delivery of the last railcar or six months from when the Company acquires the railcar from a third party and are not depreciated during that period. The Company does not believe any economic value of a railcar is lost in the first six months; therefore the Company does not depreciate these assets. In the event the railcars are not sold in the first six months, the railcars are either held in Leased railcars for syndication and are depreciated or are transferred to Equipment on operating leases and are depreciated. As of August 31, 2014, Leased railcars for syndication was $125.9 million compared to $68.5 million as of August 31, 2013.
Equipment on operating leases, net - Equipment on operating leases is stated net of accumulated depreciation. Depreciation to estimated salvage value is provided on the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of up to thirty-five years. Management periodically reviews salvage value estimates based on current scrap prices and what the Company expects to receive upon disposal.
Property, plant and equipment - Property, plant and equipment is stated at cost net of accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is provided on the straight-line method over estimated useful lives which are as follows:
| Depreciable Life | ||||
| Buildings and improvements |
10 – 25 years | |||
| Machinery and equipment |
3 – 15 years | |||
| Other |
3 – 7 years | |||
Goodwill - Goodwill is recorded when the purchase price of an acquisition exceeds the fair market value of the net assets acquired. Goodwill is not amortized and is tested for impairment at least annually and more frequently if material changes in events or circumstances arise. The provisions of ASC 350, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other, require the Company to perform a two-step impairment test on goodwill. In the first step, the Company compares the fair value of each reporting unit with its carrying value. The second step of the goodwill impairment test is required only in situations where the carrying value of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value as determined in the first step. In the second step, the Company compares the implied fair value of goodwill to its carrying value. An impairment loss is recorded to the extent that the carrying amount of the reporting unit goodwill exceeded the implied fair value of that goodwill.
Intangible and other assets, net - Intangible assets are recorded when a portion of the purchase price of an acquisition is allocated to assets such as customer contracts and relationships, trade names, certifications and backlog. Intangible assets with finite lives are amortized using the straight line method over their estimated
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 49 |
Table of Contents
useful lives and primarily include long-term customer agreements which are amortized over 5 to 20 years. Other assets include loan fees and debt acquisition costs which are capitalized and amortized as interest expense over the life of the related borrowings.
Impairment of long-lived assets - When changes in circumstances indicate the carrying amount of certain long-lived assets may not be recoverable, the assets are evaluated for impairment. If the forecasted undiscounted future cash flows are less than the carrying amount of the assets, an impairment charge to reduce the carrying value of the assets to estimated realizable value is recognized in the current period. No impairment was recorded in the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
Maintenance obligations - The Company is responsible for maintenance on a portion of the managed and owned lease fleet under the terms of maintenance obligations defined in the underlying lease or management agreement. The estimated liability is based on maintenance histories for each type and age of railcar. The liability, included in Accounts payable and accrued liabilities, is reviewed periodically and updated based on maintenance trends and known future repair or refurbishment requirements.
Warranty accruals - Warranty costs are estimated and charged to operations to cover a defined warranty period. The estimated warranty cost is based on history of warranty claims for each particular product type. For new product types without a warranty history, preliminary estimates are based on historical information for similar product types. The warranty accruals, included in Accounts payable and accrued liabilities, are reviewed periodically and updated based on warranty trends.
Income taxes - The liability method is used to account for income taxes. Deferred income taxes are provided for the temporary effects of differences between assets and liabilities recognized for financial statement and income tax reporting purposes. Valuation allowances reduce deferred tax assets to an amount that will more likely than not be realized. As a result, we recognize liabilities for uncertain tax positions based on whether evidence indicates that it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained on audit. It is inherently difficult and subjective to estimate such amounts, as this requires us to estimate the probability of various possible outcomes. The Company reevaluates these uncertain tax positions on a quarterly basis. Changes in assumptions may result in the recognition of a tax benefit or an additional charge to the tax provision.
Noncontrolling interest - The Company has a joint venture with Grupo Industrial Monclova, S.A. (“GIMSA”) that manufactures new railroad freight cars for the North American marketplace at GIMSA’s existing manufacturing facility located in Frontera, Mexico. Each party owns a 50% interest in the joint venture. The financial results of this operation are consolidated for financial reporting purposes as the Company maintains a controlling interest as evidenced by the right to appoint the majority of the board of directors, control over accounting, financing, marketing and engineering, and approval and design of products. The noncontrolling interest reflected in the Company’s consolidated financial statements primarily represents the joint venture partner’s equity in this venture.
Accumulated other comprehensive loss – Accumulated other comprehensive loss, net of tax as appropriate, consisted of the following:
| (In thousands) | Unrealized Loss on Derivative Financial Instruments |
Foreign Currency Translation Adjustment |
Other | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss |
||||||||||||
| Balance, August 31, 2013 |
$ | (1,053 | ) | $ | (4,923 | ) | $ | (528 | ) | $ | (6,504 | ) | ||||
| 2014 activity |
(548 | ) | 110 | 10 | (428 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Balance, August 31, 2014 |
$ | (1,601 | ) | $ | (4,813 | ) | $ | (518 | ) | $ | (6,932 | ) | ||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Revenue recognition - Revenue is recognized when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, delivery has occurred or services have been rendered, the price is fixed or determinable and collectability is reasonably assured.
| 50 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Railcars are generally manufactured, repaired or refurbished under firm orders from third parties. Revenue is recognized when new, refurbished or repaired railcars are completed, accepted by an unaffiliated customer and contractual contingencies removed. Marine revenues are either recognized on the percentage of completion method during the construction period or on the completed contract method based on the terms of the contract. Cash payments received prior to meeting revenue recognition criteria are accounted for in Deferred revenue. Operating lease revenue is recognized as earned under the lease terms. Certain leases are operated under car hire arrangements whereby revenue is earned based on utilization, car hire rates and terms specified in the lease agreement.
The Company sells railcars with leases attached to financial investors. In addition the Company will often perform management or maintenance services at market rates for these railcars. The Company evaluates the terms of any remarketing agreements and any contractual provisions that represent retained risk and the level of retained risk based on those provisions. The Company applies a 10% threshold to determine whether the level of retained risk exceeds 10% of the individual fair value of the rail cars delivered. For any contracts with multiple elements (i.e. railcars, maintenance, management services, etc) the Company allocates revenue among the deliverables primarily based upon objective and reliable evidence of the fair value of each element in the arrangement. If objective and reliable evidence of fair value of any element is not available, the company will use its estimated selling price for purposes of allocating the total arrangement consideration among the elements.
Interest and foreign exchange - Includes foreign exchange gains and losses, amortization of loan fee expense, accretion of debt discounts and external interest expense.
| Years ended August 31, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Interest and foreign exchange: |
||||||||||||
| Interest and other expense |
$ | 18,306 | $ | 19,203 | $ | 22,474 | ||||||
| Accretion of convertible debt discount |
– | 2,455 | 3,259 | |||||||||
| Foreign exchange (gain) loss |
389 | 500 | (924 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| $ | 18,695 | $ | 22,158 | $ | 24,809 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Research and development - Research and development costs are expensed as incurred. Research and development costs incurred for new product development during the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 were $3.6 million, $2.0 million and $2.0 million.
Forward exchange contracts - Foreign operations give rise to risks from changes in foreign currency exchange rates. Forward exchange contracts with established financial institutions are used to hedge a portion of such risk. Realized and unrealized gains and losses are deferred in other comprehensive income (loss) and recognized in earnings concurrent with the hedged transaction or when the occurrence of the hedged transaction is no longer considered probable. Ineffectiveness is measured and any gain or loss is recognized in foreign exchange gain or loss. Even though forward exchange contracts are entered into to mitigate the impact of currency fluctuations, certain exposure remains, which may affect operating results. In addition, there is risk for counterparty non-performance.
Interest rate instruments - Interest rate swap agreements are used to reduce the impact of changes in interest rates on certain debt. The net cash amounts paid or received under the agreements are accrued and recognized as an adjustment to interest expense.
Net earnings per share - Basic earnings per common share (EPS) excludes the potential dilution that would occur if additional shares were issued upon exercise of outstanding warrants or conversion of bonds. Restricted share grants are treated as outstanding when issued and restricted stock units are not treated as outstanding when issued. Restricted share grants and restricted stock units are included in weighted average basic common shares outstanding when calculating EPS when the Company is in a net earnings position.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 51 |
Table of Contents
Diluted EPS is calculated using the more dilutive of two approaches. The first approach includes the dilutive effect of outstanding warrants and shares underlying the 2026 Convertible notes in the share count using the treasury stock method. The second approach supplements the first by including the “if converted” effect of the 2018 Convertible notes. Under the “if converted method”, debt issuance and interest costs, both net of tax, associated with the convertible notes are added back to net earnings and the share count is increased by the shares underlying the convertible notes. The 2026 Convertible notes would only be included in the calculation of both approaches if the current average stock price is greater than the initial conversion price using the treasury stock method.
Stock-based compensation - The value, at the date of grant, of stock awarded under restricted share grants and restricted stock unit grants is amortized as compensation expense over the vesting period of one to five years or to the recipients eligible retirement date. Compensation expense recognized related to restricted stock for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 was $11.3 million, $6.3 million and $8.8 million and was recorded in Selling and administrative on the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Management estimates - The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. requires judgment on the part of management to arrive at estimates and assumptions on matters that are inherently uncertain. These estimates may affect the amount of assets, liabilities, revenue and expenses reported in the financial statements and accompanying notes and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities within the financial statements. Estimates and assumptions are periodically evaluated and may be adjusted in future periods. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Initial Adoption of Accounting Policies - In the first quarter of 2014, the Company adopted an accounting standard update regarding the testing of indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment. This update was intended to reduce the cost and complexity of testing indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment by providing entities with an option to perform a qualitative assessment to determine whether further impairment testing is necessary. This update impacted testing steps only and therefore the adoption did not have an impact on the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements.
In the first quarter of 2014, the Company adopted an accounting standard update that amended prior reporting requirements with respect to comprehensive income by requiring additional disclosures by component about the amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive loss. The adoption of this accounting standard update did require additional disclosures, but did not have an impact on the Company’s financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Prospective Accounting Changes - In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) and International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”) issued a jointly converged standard on the recognition of revenue from contracts with customers. The issued guidance converges the criteria for reporting revenue, as well as requiring disclosures sufficient to describe the nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from these contracts. Companies can transition to the standard either retrospectively or as a cumulative effective adjustment as of the date of adoption. The new standard is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2016. The Company plans to adopt this guidance beginning September 1, 2017. The Company is evaluating the impact of this standard on its consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
Note 3 - Gain on Contribution to Joint Venture
On July 18, 2014 the Company and Watco (Greenbrier and Watco are referred to collectively as the “Members”) contributed its respective railcar repair, refurbishment, retrofitting and maintenance operations to a newly formed entity, GBW, a 50/50 unconsolidated joint venture. The Company accounts for its interest in GBW under the equity method of accounting. As of August 31, 2014, the GBW joint venture operates 38 railcar repair, refurbishment and retrofitting shops previously part of the Company’s and Watco’s networks.
Each Member contributed its respective operations, $10 million cash at closing and other assets, including intangible assets, to GBW and agreed to lease to GBW real and personal properties which had been previously
| 52 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
used by the Member in its railcar repair businesses in exchange for membership interests in GBW. Each Member also sold its repair inventory to GBW at its book value. Each Member retained its pre-closing accounts receivable, accounts payable, and other pre-closing liabilities and obligations. In addition, each Member made an additional $2.5 million capital contribution to GBW during 2014. In addition to the initial contributions described above, each Member is required to fund GBW through additional capital contributions and/or loans to GBW as provided for in the annual business plan.
GBW is managed by a four member board of managers composed of two managers appointed by Watco and two managers appointed by the Company. The voting power of the managers is based on the Members’ relative sharing ratios which is 50/50 as of August 31, 2014. The managers of GBW approve the annual business plan, which is to provide for GBW’s anticipated funding needs for operations and capital expenditures and other matters.
Upon formation of GBW, the Company recognized a pre-tax non-cash gain of $29.0 million for the year ended August 31, 2014 which was calculated as the fair value of the Company’s 50% share in GBW, less cash and intangibles contributed to GBW and an allocation of goodwill attributed to the repair business the Company contributed to GBW. The gain was included as Gain on Contribution to Joint Venture in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The Company also recorded an investment in unconsolidated affiliates on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The investment in unconsolidated affiliates attributed the Company’s interest in GBW was $56.3 million as of August 31, 2014.
Note 4 - Restructuring
During 2013, the Company implemented a restructuring plan to sell or close certain Wheels, Repair & Parts facilities to enhance margins and improve capital efficiency and completed the restructuring plan during 2014. Restructuring charges related to this plan totaled $1.5 million and $2.7 million for the years ended August 31, 2014 and 2013 and were included in the Consolidated Statement of Operations. All of the restructuring charges for the years ended August 31, 2014 and 2013 and the restructuring reserve related to the Company’s Wheels, Repair & Parts segment.
| (In thousands) | Accrual at 2013 |
Charged to Expense |
Paid or Settled |
Accrual at August 31, 2014 |
||||||||||||
| Employee termination costs |
$ | 1,409 | $ | 1,290 | $ | 2,699 | $ | – | ||||||||
| Other costs |
299 | 185 | 484 | – | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Balance, August 31, 2014 |
$ | 1,708 | $ | 1,475 | $ | 3,183 | $ | – | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | Accrual at 2012 |
Charged to Expense |
Paid or Settled |
Accrual at 2013 |
||||||||||||
| Employee termination costs |
$ | – | $ | 1,610 | $ | 201 | $ | 1,409 | ||||||||
| Contract termination costs |
– | 50 | 50 | – | ||||||||||||
| Other costs |
– | 1,059 | 760 | 299 | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Balance, August 31, 2013 |
$ | – | $ | 2,719 | $ | 1,011 | $ | 1,708 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Note 5 - Inventories
| As of August 31, | ||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||
| Manufacturing supplies and raw materials |
$ | 235,903 | $ | 217,182 | ||||
| Work-in-process |
48,853 | 48,990 | ||||||
| Finished goods |
23,766 | 54,839 | ||||||
| Excess and obsolete adjustment |
(2,866 | ) | (4,228 | ) | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| $ | 305,656 | $ | 316,783 | |||||
|
|
||||||||
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 53 |
Table of Contents
| As of August 31, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Excess and obsolete adjustment |
||||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of period |
$ | 4,228 | $ | 5,132 | $ | 4,450 | ||||||
| Charge to cost of revenue |
1,945 | 2,661 | 3,042 | |||||||||
| Disposition of inventory |
(3,307 | ) | (3,614 | ) | (2,210 | ) | ||||||
| Currency translation effect |
– | 49 | (150 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Balance at end of period |
$ | 2,866 | $ | 4,228 | $ | 5,132 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Note 6 - Equipment on Operating Leases, net
Equipment on operating leases is reported net of accumulated depreciation of $93.9 million and $97.8 million as of August 31, 2014 and 2013. Depreciation expense was $9.8 million, $12.0 million and $13.6 million as of August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. In addition, certain railcar equipment leased-in by the Company on operating leases (see Note 21 Lease Commitments) is subleased to customers under non-cancelable operating leases. Aggregate minimum future amounts receivable under all non-cancelable operating leases and subleases are as follows:
| (In thousands) | ||||
| Year ending August 31, |
||||
| 2015 |
$ | 19,272 | ||
| 2016 |
10,158 | |||
| 2017 |
6,766 | |||
| 2018 |
4,013 | |||
| 2019 |
1,907 | |||
| Thereafter |
941 | |||
|
|
||||
| $ | 43,057 | |||
|
|
||||
Certain equipment is also operated under daily, monthly or car hire utilization arrangements. Associated revenue amounted to $24.8 million, $24.3 million and $23.4 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
Note 7 - Property, Plant and Equipment, net
| As of August 31, | ||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||
| Land and improvements |
$ | 38,356 | $ | 36,132 | ||||
| Machinery and equipment |
242,911 | 233,737 | ||||||
| Buildings and improvements |
118,795 | 110,030 | ||||||
| Construction in progress |
58,164 | 19,206 | ||||||
| Other |
38,636 | 32,888 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| 496,862 | 431,993 | |||||||
| Accumulated depreciation |
(253,164 | ) | (230,460 | ) | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| $ | 243,698 | $ | 201,533 | |||||
|
|
||||||||
Depreciation expense was $25.8 million, $25.1 million and $23.3 million as of August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
Note 8 - Goodwill
The Company’s goodwill balance as of August 31, 2014 and 2013 related to our Wheels, Repair & Parts segment. The gross goodwill balance before accumulated goodwill impairment losses and other reductions was $195.8 million as of August 31, 2014. The total accumulated goodwill impairment losses were $128.2 million and other reductions of $24.3 million as of August 31, 2014.
| 54 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Changes in the carrying value of goodwill are as follows:
| (In thousands) | Manufacturing | Wheels, Repair & Parts |
Leasing & Services |
Total | ||||||||||||
| Balance August 31, 2013 |
$ | – | $ | 57,416 | $ | – | $ | 57,416 | ||||||||
| Reductions (1) |
– | (14,151 | ) | – | (14,151 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Balance August 31, 2014 |
$ | – | $ | 43,265 | $ | – | $ | 43,265 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Relates to the reduction in goodwill associated with the Company’s repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations contributed to the GBW joint venture in July 2014. |
The Company performs a goodwill impairment test annually during the third quarter. Goodwill is also tested more frequently if changes in circumstances or the occurrence of events indicates that a potential impairment exists. The provisions of ASC 350, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other, require the Company to perform a two-step impairment test on goodwill.
In the first step, the Company compares the fair value of each reporting unit with its carrying value. The Company determines the fair value of the reporting unit based on a weighting of income and market approaches. Under the income approach, the Company calculates the fair value of a reporting unit based on the present value of estimated future cash flows. Under the market approach, the Company estimates the fair value based on observed market multiples for comparable businesses.
In the second step, the Company compares the implied fair value of goodwill to its carrying value. The implied fair value of goodwill is determined by allocating the fair value of the reporting unit to all of the assets and liabilities of that unit as if the reporting unit had been acquired in a business combination and the fair value of the reporting unit was the price paid to acquire the reporting unit. The excess of the fair value of a reporting unit over the amounts assigned to its assets and liabilities is considered the implied fair value of goodwill. An impairment loss is recorded to the extent that the carrying amount of the reporting unit goodwill exceeded the implied fair value of that goodwill.
The Company completed its annual goodwill impairment test during the third quarter of 2014 and an interim goodwill impairment test during the fourth quarter of 2014 as a result of contributing its repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations to the GBW joint venture. See Note 3 – Gain on Contribution to Joint Venture for additional information. The Company concluded in both tests that goodwill was not impaired.
The Company completed its annual goodwill impairment test during the third quarter of 2013 and a pre-tax non-cash impairment charge of $76.9 million was recorded for the year ended August 31, 2013, related to the Wheels, Repair & Parts segment, as the carrying amount exceeded the implied fair value of goodwill.
In July 2014, the Company and Watco formed GBW, a 50/50 joint venture. The Company contributed cash at closing and other assets to GBW. As a result, the Company reduced goodwill by $14.2 million during the year ended August 31, 2014, which relates to goodwill associated with the Company’s repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations contributed to GBW.
Note 9 - Intangibles and Other Assets, net
Intangible assets that are determined to have finite lives are amortized over their useful lives. Intangible assets with indefinite useful lives are not amortized and are periodically evaluated for impairment.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 55 |
Table of Contents
The following table summarizes the Company’s identifiable intangible and other assets balance:
| As of August 31, | ||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||
| Intangible assets subject to amortization: |
||||||||
| Customer relationships |
$ | 65,023 | $ | 66,288 | ||||
| Accumulated amortization |
(30,282 | ) | (26,964 | ) | ||||
| Other intangibles |
3,699 | 4,967 | ||||||
| Accumulated amortization |
(3,156 | ) | (4,162 | ) | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| 35,284 | 40,129 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Intangible assets not subject to amortization |
912 | 912 | ||||||
| Prepaid and other assets |
11,347 | 10,601 | ||||||
| Nonqualified savings plan investments |
10,223 | 7,687 | ||||||
| Debt issuance costs, net |
7,602 | 7,802 | ||||||
| Assets held for sale |
389 | 1,101 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| $ | 65,757 | $ | 68,232 | |||||
|
|
||||||||
Amortization expense for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 was $4.5 million, $4.3 million and $5.6 million. Amortization expense for the years ending August 31, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018 and 2019 is expected to be $3.7 million, $3.7 million, $3.6 million, $3.4 million and $3.4 million.
Note 10 - Revolving Notes
Senior secured credit facilities, consisting of three components, aggregated to $359.1 million as of August 31, 2014.
As of August 31, 2014, a $290.0 million revolving line of credit, maturing June 2016, secured by substantially all the Company’s assets in the U.S. not otherwise pledged as security for term loans, was available to provide working capital and interim financing of equipment, principally for the U.S. and Mexican operations. Advances under this facility bear interest at LIBOR plus 2.25% or Prime plus 1.25% depending on the type of borrowing. Available borrowings under the credit facility are generally based on defined levels of inventory, receivables, property, plant and equipment and leased equipment, as well as total debt to consolidated capitalization and fixed charges coverage ratios.
As of August 31, 2014, lines of credit totaling $19.1 million secured by certain of the Company’s European assets, with various variable rates that range from Warsaw Interbank Offered Rate (“WIBOR”) plus 1.2% to WIBOR plus 1.5%, were available for working capital needs of the European manufacturing operation. European credit facilities are continually being renewed. Currently these European credit facilities have maturities that range from December 2014 through June 2015.
As of August 31, 2014, the Company’s Mexican joint venture had two lines of credit totaling $50.0 million. The first line of credit provides up to $20.0 million and is secured by certain of the joint venture’s accounts receivable and inventory. Advances under this facility bear interest at LIBOR plus 2.5%. The Mexican joint venture will be able to draw amounts available under this facility through January 2015. The second line of credit provides up to $30.0 million and is fully guaranteed by each of the joint venture partners, including the Company. Advances under this facility bear interest at LIBOR plus 2.0%. The Mexican joint venture will be able to draw against this facility through January 2015.
As of August 31, 2014, outstanding borrowings under the senior secured credit facilities consisted of $9.6 million in letters of credit under the North American credit facility and $13.1 million outstanding under the Mexican joint venture credit facilities.
| 56 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
As of August 31, 2013, outstanding borrowings under the senior secured credit facilities consisted of $6.8 million in letters of credit under the North American credit facility and $48.2 million outstanding under the Mexican joint venture credit facilities.
Note 11 - Accounts Payable and Accrued Liabilities
| As of August 31, | ||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||
| Trade payables |
$ | 204,744 | $ | 163,490 | ||||
| Other accrued liabilities |
66,421 | 70,691 | ||||||
| Accrued payroll and related liabilities |
64,959 | 42,047 | ||||||
| Income taxes payable |
19,709 | 13,094 | ||||||
| Accrued maintenance |
14,329 | 11,420 | ||||||
| Accrued warranty |
9,340 | 12,128 | ||||||
| Other |
3,787 | 3,068 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| $ | 383,289 | $ | 315,938 | |||||
|
|
||||||||
Note 12 - Maintenance and Warranty Accruals
| As of August 31, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Accrued maintenance |
||||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of period |
$ | 11,420 | $ | 11,475 | $ | 10,865 | ||||||
| Charged to cost of revenue |
11,423 | 9,003 | 10,750 | |||||||||
| Payments |
(8,514 | ) | (9,058 | ) | (10,140 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Balance at end of period |
$ | 14,329 | $ | 11,420 | $ | 11,475 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Accrued warranty |
||||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of period |
$ | 12,128 | $ | 9,221 | $ | 8,645 | ||||||
| Charged to cost of revenue |
2,205 | 6,157 | 2,496 | |||||||||
| Payments |
(5,122 | ) | (3,315 | ) | (1,746 | ) | ||||||
| Currency translation effect |
129 | 65 | (174 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Balance at end of period |
$ | 9,340 | $ | 12,128 | $ | 9,221 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Note 13 - Notes Payable
| As of August 31, | ||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||
| Convertible senior notes, due 2018 |
$ | 230,000 | $ | 230,000 | ||||
| Convertible senior notes, due 2026 |
14,856 | 14,856 | ||||||
| Term loans |
199,985 | 128,783 | ||||||
| Other notes payable |
250 | 250 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| $ | 445,091 | $ | 373,889 | |||||
|
|
||||||||
Convertible senior notes, due 2018, bear interest at a fixed rate of 3.5%, paid semi-annually in arrears on April 1st and October 1st. The convertible notes will mature on April 1, 2018, unless earlier repurchased by the Company or converted in accordance with their terms. Holders may convert at their option at any time prior to the business day immediately preceding the stated maturity date. The convertible notes are senior unsecured obligations and rank equally with other senior unsecured debt. The convertible notes are convertible into shares of the Company’s common stock, at an initial conversion rate of 26.2838 shares per $1,000 principal amount of the notes (which is equal to an initial conversion price of $38.05 per share). The initial conversion rate and conversion price are subject to adjustment upon the occurrence of certain events, such as distributions, dividends or stock splits. There were $7.9
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 57 |
Table of Contents
million in original debt issuance costs, included in Intangibles and other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets, which are being amortized using the effective interest method. The amortization expense is being included in Interest and foreign exchange on the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Convertible senior notes, due 2026, bear interest at a fixed rate of 2.375%, paid semi-annually in arrears on May 15th and November 15th. In May 2013, the Company retired $52.9 million of its outstanding notes pursuant to a scheduled put option. The Company may be required to also pay contingent interest of 0.375% on the notes in certain circumstances. Greenbrier may redeem all or a portion of the notes at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the notes plus accrued and unpaid interest. On May 15, 2016 and May 15, 2021 or in the event of certain circumstances or fundamental changes, holders can require the Company to repurchase all or a portion of their notes at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the notes plus accrued and unpaid interest. Payment on the convertible notes is guaranteed by substantially all of the Company’s material domestic subsidiaries. The convertible senior notes are convertible upon the occurrence of specified events into cash and shares, if any, of Greenbrier’s common stock at an initial conversion rate of 20.8125 shares per $1,000 principal amount of the notes (which is equal to an initial conversion price of $48.05 per share). The initial conversion rate and conversion price are subject to adjustment upon the occurrence of certain events, such as distributions, dividends or stock splits. The value of the equity component was $14.9 million as of August 31, 2014 and 2013. The debt discount associated with the convertible senior notes was fully accreted using the effective interest rate method through May 2013 and the accretion expense was included in Interest and foreign exchange on the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The pre-tax accretion of the debt discount was $2.5 and $3.2 million for the years ended August 31, 2013 and 2012.
Term loans are primarily composed of:
| • | In March 2014, the Company refinanced approximately $125 million of existing senior term debt, due in March 2014 and May 2015, secured by a pool of leased railcars with new 6-year $200 million senior term debt also secured by a pool of leased railcars and cash. The new debt bears a floating interest rate of LIBOR plus 1.75% with principal of $1.75 million paid quarterly in arrears and a balloon payment of $159.8 million due at maturity. An interest rate swap agreement was entered into on 50% of the initial balance to swap the floating interest rate of LIBOR plus 1.75% to a fixed rate of 3.7375%. The principal balance as of August 31, 2014 was $198.3 million. |
| • | Other term loans with an aggregate balance of $1.7 million as of August 31, 2014 and maturity dates ranging from June 2015 to February 2018. |
The notes payable, along with the revolving and operating lines of credit, contain certain covenants with respect to the Company and various subsidiaries, the most restrictive of which, among other things, limit the ability to: incur additional indebtedness or guarantees; pay dividends or repurchase stock; enter into sale leaseback transactions; create liens; sell assets; engage in transactions with affiliates, including joint ventures and non-U.S. subsidiaries, including but not limited to loans, advances, equity investments and guarantees; enter into mergers, consolidations or sales of substantially all the Company’s assets; and enter into new lines of business. The covenants also require certain maximum ratios of debt to total capitalization and minimum levels of fixed charges (interest and rent) coverage.
Principal payments on the notes payable are expected as follows:
| (In thousands) |
||||
| Year ending August 31, |
||||
| 2015 |
$ | 7,720 | ||
|
2016(1) |
22,465 | |||
| 2017 |
7,437 | |||
| 2018 |
237,219 | |||
| 2019 |
7,000 | |||
| Thereafter |
163,250 | |||
| $ | 445,091 | |||
| (1) | The repayment of the $14.9 million of Convertible senior notes due 2026 is assumed to occur in 2016, which is the next date holders can require the Company to repurchase all or a portion of the notes. |
| 58 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Note 14 - Derivative Instruments
Foreign operations give rise to market risks from changes in foreign currency exchange rates. Foreign currency forward exchange contracts with established financial institutions are utilized to hedge a portion of that risk in Euro. Interest rate swap agreements are used to reduce the impact of changes in interest rates on certain debt. The Company’s foreign currency forward exchange contracts and interest rate swap agreements are designated as cash flow hedges, and therefore the effective portion of unrealized gains and losses is recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income or loss.
At August 31, 2014 exchange rates, forward exchange contracts for the purchase of Polish Zloty and the sale of Euro aggregated $91.0 million. The fair value of the contracts is included in Accounts payable and accrued liabilities when there is a loss, or Accounts receivable when there is a gain, on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. As the contracts mature at various dates through December 2015, any such gain or loss remaining will be recognized in manufacturing revenue along with the related transactions. In the event that the underlying sales transaction does not occur or does not occur in the period designated at the inception of the hedge, the amount classified in accumulated other comprehensive loss would be reclassified to the current year’s results of operations in Interest and foreign exchange.
At August 31, 2014, an interest rate swap agreement had a notional amount of $99.1 million and matures March 2020. The fair value of the contract is included in Accounts payable and accrued liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. As interest expense on the underlying debt is recognized, amounts corresponding to the interest rate swap are reclassified from Accumulated other comprehensive loss and charged or credited to interest expense. At August 31, 2014 interest rates, approximately $1.8 million would be reclassified to interest expense in the next 12 months.
Fair Values of Derivative Instruments
| Asset Derivatives | Liability Derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||
| August 31, | August 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | Balance sheet location |
Fair Value |
Fair Value |
Balance sheet location |
Fair Value |
Fair Value |
||||||||||||||
| Derivatives designated as hedging instruments |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign forward exchange contracts |
Accounts receivable | $ | 129 | $ | 819 | Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | $ | 704 | $ | 342 | ||||||||||
| Interest rate swap contracts |
Other assets | – | – | Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 1,286 | 1,250 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 129 | $ | 819 | $ | 1,990 | $ | 1,592 | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign forward exchange contracts |
Accounts receivable | $ | 71 | $ | 223 | Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | $ | 5 | $ | 40 | ||||||||||
The Effect of Derivative Instruments on the Statement of Operations
| Derivatives in cash flow hedging relationships |
Location of gain (loss) recognized in income on derivative |
Gain (loss) recognized in income on derivative Years ended |
||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
| Foreign forward exchange contract |
Interest and foreign exchange | $ | 87 | $ | (204 | ) | ||||
| Interest rate swap contracts |
Interest and foreign exchange | 17 | – | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| $ | 104 | $ | (204 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 59 |
Table of Contents
| Derivatives in cash flow hedging relationships |
Gain
(loss) Years |
Location of gain (loss) from accumulated OCI into income |
Gain (loss) reclassified from portion) Years |
Location of gain (loss) in income
on portion and amount excluded from |
Gain portion and amount excluded from Years |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign forward exchange contracts |
$ | 108 | $ | (570 | ) | Revenue |
$ | 741 | $ | 1,917 | Interest and foreign exchange | $ | 1,029 | $ | 2,410 | |||||||||||||
| Interest rate swap contracts |
(1,790 | ) | (68 | ) | Interest and foreign exchange | (1,737 | ) | (1,679 | ) | Interest and foreign exchange | – | – | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | (1,682 | ) | $ | (638 | ) | $ | (996 | ) | $ | 238 | $ | 1,029 | $ | 2,410 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Note 15 - Equity
In January 2011, the stockholders approved the 2010 Amended and Restated Stock Incentive Plan (formerly known as the 2005 Stock Incentive Plan as amended). This plan provides for the grant of incentive stock options, non-statutory stock options, restricted shares, restricted stock units and stock appreciation rights. There are no stock options or stock appreciation rights outstanding as of August 31, 2014. The Company currently grants restricted shares and restricted stock units. Restricted share grants are considered outstanding shares of common stock at the time they are issued. The holders of unvested restricted shares are entitled to voting rights and participation in dividends. The dividends are not forfeitable if the awards are later forfeited prior to vesting. The Company began granting restricted stock units during the year ended August 31, 2013. Shares associated with restricted stock unit awards are not considered legally outstanding shares of common stock until vested. Restricted stock unit awards, including performance-based awards, are entitled to participate in dividends and these awards are considered participating securities and are considered outstanding for earnings per share purposes when the effect is dilutive.
In January 2013, the stockholders approved an amendment to the 2010 Amended and Restated Stock Incentive Plan to increase the total number of shares reserved for issuance by 1,500,000 shares. As a result, the maximum aggregate number of the Company’s common shares authorized for issuance is 4,325,000. On August 31, 2014 there were 1,144,143 shares available for grant compared to 1,384,997 and 259,650 shares available for grant as of the years ended August 31, 2013 and 2012.
During the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, the Company awarded restricted share and restricted stock unit grants totaling 269,665, 387,986 and 466,680 shares which include performance-based grants. As of August 31, 2014, there were a total of 495,776 shares associated with unvested performance-based grants. The actual number of shares that will vest associated with performance-based grants will vary depending on the Company’s performance. Approximately 490,752 additional shares may be granted if performance-based restricted share and restricted stock unit awards vest at stretch levels of performance. These additional shares are associated with restricted share and restricted stock unit awards granted during the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. The fair value of awards granted was $13.1 million, $9.2 million and $9.5 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
The value, at the date of grant, of stock awarded under restricted share grants and restricted stock unit grants is amortized as compensation expense over the lesser of the vesting period of one to three years or to the recipients eligible retirement date. Compensation expense recognized related to restricted share grants and restricted stock unit grants for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 was $11.3 million, $6.3 million and $8.8 million and was recorded in Selling and administrative on the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Unamortized compensation cost related to restricted stock grants was $13.6 million as of August 31, 2014.
| 60 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
The unvested restricted share and restricted stock unit grants were 816,090 and 913,918 as of August 31, 2014 and 2013. The following table summarizes restricted share and restricted stock unit grant transactions for shares, both vested and unvested, under the 2010 Amended and Restated Stock Incentive Plan:
| Shares | ||||
| Balance at August 31, 2011 (1) |
2,104,953 | |||
| Granted |
466,680 | |||
| Forfeited |
(6,283 | ) | ||
|
|
||||
| Balance at August 31, 2012 (1) |
2,565,350 | |||
| Granted |
387,986 | |||
| Forfeited |
(13,333 | ) | ||
|
|
||||
| Balance at August 31, 2013 (1) |
2,940,003 | |||
| Granted |
269,665 | |||
| Forfeited |
(28,811 | ) | ||
|
|
||||
| Balance at August 31, 2014 (1) |
3,180,857 | |||
|
|
||||
| (1) | Balance represents cumulative grants net of forfeitures. |
Share Repurchase Program
In October 2013, the Board of Directors authorized the Company to repurchase up to $50 million of the Company’s common stock. Under the share repurchase program, shares of common stock could be purchased on the open market or through privately negotiated transactions from time-to-time. The timing and amount of purchases was based upon market conditions, securities law limitations and other factors. The share repurchase program did not obligate the Company to acquire any specific number of shares in any period. During the year ended August 31, 2014, the Company repurchased a total of 764,546 shares for approximately $34.4 million. Subsequent to August 31, 2014 and through October 23, 2014, the Company purchased an additional 253,016 shares for approximately $15.6 million. The Company completed its $50 million share repurchase program in October 2014.
In October 2014, the Board of Directors authorized a new share repurchase program for the Company to repurchase up to $50 million of the Company’s common stock. Under the share repurchase program, shares of common stock may be purchased on the open market or through privately negotiated transactions from time-to-time. The timing and amount of purchases will be based upon market conditions, securities law limitations and other factors. The share repurchase program does not obligate the Company to acquire any specific number of shares in any period. The share repurchase program expires June 30, 2016, but may be modified, suspended or discontinued at any time without prior notice.
Note 16 - Earnings (Loss) per Share
The shares used in the computation of the Company’s basic and diluted earnings (loss) per common share are reconciled as follows:
| Years ended August 31, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Weighted average basic common shares outstanding (1) |
28,164 | 26,678 | 26,572 | |||||||||
| Dilutive effect of warrants (2) |
– | – | 1,101 | |||||||||
| Dilutive effect of convertible notes (2)(3) |
6,045 | – | 6,045 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Weighted average diluted common shares outstanding |
34,209 | 26,678 | 33,718 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| (1) | Restricted stock grants and restricted stock units, including some grants subject to certain performance criteria, are included in weighted average basic common shares outstanding when the Company is in a net earnings position. Weighted average basic common shares outstanding exclude 0.9 million shares of unvested restricted stock and restricted stock units for the year ended August 31, 2013 as they are anti-dilutive due to a net loss. No restricted stock, restricted stock units or warrants were anti-dilutive for the years ended August 31, 2014 and 2012. |
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 61 |
Table of Contents
| (2) | The dilutive effect of common stock equivalents is excluded from the share calculations for the year ended August 31, 2013 due to a net loss. |
| (3) | In 2014 and 2012, the dilutive effect of the 2018 Convertible notes are included as they were considered dilutive under the “if converted” method. The dilutive effect of the 2026 Convertible notes was excluded from the share calculations as the average stock price for each year presented was less than the initial conversion price of $48.05 and therefore considered anti-dilutive. |
Dilutive EPS for the years ended August 31, 2014 and 2012 was calculated using the more dilutive of two approaches. The first approach includes the dilutive effect of outstanding warrants and shares underlying the 2026 Convertible notes in the share count using the treasury stock method. The second approach supplements the first by including the “if converted” effect of the 2018 Convertible notes issued in March 2011. Under the “if converted method” debt issuance and interest costs, both net of tax, associated with the convertible notes are added back to net earnings and the share count is increased by the shares underlying the convertible notes. The 2026 Convertible notes would only be included in the calculation of both approaches if the average stock price is greater than the initial conversion price of $48.05 using the treasury stock method.
| Years ended August 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2012 | |||||||
| Net earnings attributable to Greenbrier |
$ | 111,919 | $ | 58,708 | ||||
| Add back: |
||||||||
| Interest and debt issuance costs on the 2018 Convertible notes, net of tax |
5,664 | 5,677 | ||||||
| Earnings before interest and debt issuance costs on convertible notes |
$ | 117,583 | $ | 64,385 | ||||
| Weighted average diluted common shares outstanding |
34,209 | 33,718 | ||||||
| Diluted earnings per share (1) |
$ | 3.44 | $ | 1.91 | ||||
| (1) | Diluted earnings per share was calculated as follows: |
| Earnings | before interest and debt issuance costs on convertible notes |
| Weighted | average diluted common shares outstanding |
Note 17 - Related Party Transactions
In July 2014, the Company and Watco completed the formation of GBW, an unconsolidated 50/50 joint venture. The Company accounts for its interest in GBW under the equity method of accounting. The Company leases real and personal property to GBW with lease revenue totaling $0.6 million for the year ended August 31, 2014. The Company sold wheel sets and components to GBW which totaled $1.3 million for the year ended August 31, 2014. GBW provided repair, refurbishment and retrofitting services to the Company which totaled $0.1 million for the year ended August 31, 2014. The Company had a net receivable of $22.7 million as of August 31, 2014 which consisted primarily of a $21.0 million receivable for the initial sale of inventory to GBW. Under employee secondment agreements, GBW paid the Company $7.8 million for the year ended August 31, 2014, for reimbursement of employee related costs.
In May 2013, the Company purchased an 8% interest in an entity that owns a portfolio of railcar assets that it leases to third parties. The Company accounts for this investment under the equity method of accounting. The Company sold railcars for a total of $16.0 million and $23.2 million to this entity for the year ended August 31, 2014 and 2013.
In March 2012, the Company purchased a 1% interest in three trusts (the “Trusts”). The Company accounts for this investment under the equity method of accounting. The Company sold railcars for a total of $38.5 million and $61.1 million to the Trusts for the years ended August 31, 2013 and 2012.
In April 2010, WLR–Greenbrier Rail Inc. (“WLR-GBX”) was formed and acquired a lease fleet of nearly 4,000 railcars valued at approximately $256.0 million. WLR-GBX is wholly owned by affiliates of WL Ross & Co,, LLC “WL Ross”). The Company performs certain management and advisory services and in exchange receives management and other fee income and incentive compensation tied to the performance of WLR-GBX. The Company has also paid certain incidental fees and agreed to indemnify WLR-GBX and its affiliates against certain liabilities in connection with such advisory services. Under the management agreement the Company
| 62 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
received $0.9 million in fees for each of the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. The Company also leases approximately 400 railcars from the WLR-GBX lease fleet. The Company has paid $3.3 million, $3.2 million and $3.1 million in lease expense for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively and has future lease commitments totaling $2.9 million. In addition, Wendy Teramoto, Senior Vice President at WL Ross, is currently a director of the Company.
William Furman, Director, President and Chief Executive Officer of the Company, also serves as director of Schnitzer Steel Industries, Inc. (“Schnitzer”). In the normal course of business, the Company sells scrap metal to Schnitzer. During the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, the Company sold scrap metal to Schnitzer totaling $3.0 million, $8.0 million and $9.2 million, respectively.
Mr. Furman is the owner of a private aircraft managed by a private independent management company. From time to time, the Company’s business requires charter use of privately-owned aircraft. In such instances, it is possible that charters may be placed on Mr. Furman’s aircraft. The Company placed charters on Mr. Furman’s aircraft aggregating $0.5 million, $0.2 million and $0.2 million for each of the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
Note 18 - Income Taxes
Components of income tax expense of continuing operations were as follows:
| Years ended August 31, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Current |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
$ | 49,795 | $ | 20,162 | $ | 10,750 | ||||||
| State |
3,791 | 2,491 | 2,783 | |||||||||
| Foreign |
23,229 | 11,465 | 8,548 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| 76,815 | 34,118 | 22,081 | ||||||||||
| Deferred |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
(79 | ) | (6,597 | ) | 19,426 | |||||||
| State |
(1,142 | ) | (2,357 | ) | (3,399 | ) | ||||||
| Foreign |
(3,148 | ) | (134 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| (4,369 | ) | (9,088 | ) | 16,021 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Change in valuation allowance |
(45 | ) | 30 | (5,710 | ) | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| $ | 72,401 | $ | 25,060 | $ | 32,392 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Income tax expense is computed at rates different from statutory rates. The reconciliation between effective and statutory tax rates on operations is as follows:
| Years ended August 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Federal statutory rate |
35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||||||
| State income taxes, net of federal benefit |
1.3 | (1.2 | ) | (1.9 | ) | |||||||
| Impact of foreign operations |
(0.8 | ) | (19.1 | ) | (2.1 | ) | ||||||
| Change in valuation allowance related to deferred tax asset |
– | 1.3 | (6.1 | ) | ||||||||
| Change in income tax reserve for uncertain tax positions |
– | (7.1 | ) | (0.1 | ) | |||||||
| Reversal of net deferred tax assets related to foreign restructuring |
– | – | 1.9 | |||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest in flow through entity |
(5.3 | ) | (1.2 | ) | (0.4 | ) | ||||||
| Permanent differences and other |
0.7 | 1.9 | 8.2 | |||||||||
| Non-deductible goodwill |
1.9 | 119.0 | – | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| 32.8 | % | 128.6 | % | 34.5 | % | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 63 |
Table of Contents
The tax effects of temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities were as follows:
| As of August 31, | ||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||
| Deferred tax assets: |
||||||||
| Contract placement |
$ | 1,938 | $ | 2,051 | ||||
| Maintenance and warranty accruals |
8,254 | 7,963 | ||||||
| Accrued payroll and related liabilities |
12,737 | 8,616 | ||||||
| Deferred revenue |
4,496 | 4,072 | ||||||
| Inventories and other |
10,709 | 8,708 | ||||||
| Derivative instruments and translation adjustment |
413 | 478 | ||||||
| Investment and asset tax credits |
1,388 | 1,324 | ||||||
| Net operating loss |
1,695 | 2,168 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| 41,630 | 35,380 | |||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities: |
||||||||
| Fixed assets |
94,424 | 107,725 | ||||||
| Investment in GBW joint venture |
16,497 | – | ||||||
| Original issue discount |
3,481 | 2,962 | ||||||
| Intangibles |
2,719 | 4,792 | ||||||
| Deferred gain on redemption of debt |
3,511 | 4,430 | ||||||
| Other |
1,056 | 31 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| 121,688 | 119,940 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Valuation allowance |
1,325 | 1,480 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Net deferred tax liability |
$ | 81,383 | $ | 86,040 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
As of August 31, 2014 the Company had $15.8 million of state net operating loss (“NOL”) carryforwards that will begin to expire in 2015, $1.4 million of state credit carryforwards that will begin to expire in 2017, and $5.8 million of foreign NOL carryforwards that will begin to expire in 2018. The Company uses tax law ordering for purposes of determining when excess tax benefits have been realized. During the current year the Company also recognized excess tax benefits of $0.1 million from the vesting of restricted stock awards.
The net decrease in the valuation allowance on deferred taxes for which no benefit is anticipated was approximately $0.1 million for the year ended August 31, 2014.
No provision has been made for U.S. income taxes on approximately $80.9 million of cumulative undistributed earnings of certain foreign subsidiaries because the Company plans to reinvest these earnings indefinitely in operations outside the U.S. Generally, such amounts become subject to U.S. taxation upon the remittance of dividends and under certain other circumstances. It is not practicable to estimate the amount of deferred tax liability related to investments in foreign subsidiaries.
The following is a tabular reconciliation of the total amounts of unrecognized tax benefits for the years presented:
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Unrecognized Tax Benefit – Opening Balance |
$ | 1,289 | $ | 3,720 | $ | 3,053 | ||||||
| Gross increases – tax positions in prior period |
18 | 511 | 878 | |||||||||
| Gross decreases – tax positions in prior period |
– | (2,942 | ) | (211 | ) | |||||||
| Settlements |
– | – | – | |||||||||
| Lapse of statute of limitations |
(39 | ) | – | – | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Unrecognized Tax Benefit – Ending Balance |
$ | 1,268 | $ | 1,289 | $ | 3,720 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| 64 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
The Company is subject to taxation in the U.S., various states and foreign jurisdictions. The Company is no longer subject to U.S. Federal examination for fiscal years ending before 2011, to state and local examinations before 2010, or to foreign examinations before 2008.
Unrecognized tax benefits, excluding interest, at August 31, 2014 were $1.0 million of which $0.3 million, if recognized, would affect the effective tax rate. The unrecognized tax benefits at August 31, 2013 were $1.1 million. Accrued interest on reserves for uncertain tax positions as of August 31, 2014 and 2013 were $0.2 million and $0.2 million, respectively. The Company recorded an interest benefit of $0.2 million and $0.8 million for changes in the reserves during the years ended August 31, 2014 and 2013. The Company had not accrued any penalties on the reserves. Interest and penalties related to income taxes are not classified as a component of income tax expense. Benefits from the realization of unrecognized tax benefits for deductible differences attributable to ordinary operations will be recognized as a reduction of income tax expense. The Company does not anticipate a significant decrease in the reserves for uncertain tax positions during the next twelve months.
Note 19 - Segment Information
Through July 18, 2014, Greenbrier operated in three reportable segments: Manufacturing; Wheels, Repair & Parts; and Leasing & Services. On July 18, 2014, the Company completed the formation of GBW, an unconsolidated 50/50 joint venture with Watco which became the Company’s fourth reportable segment (GBW Joint Venture) upon formation of the joint venture. The accounting policies of the segments are the same as those described in the summary of significant accounting policies. Performance is evaluated based on Earnings from operations. Corporate includes selling and administrative costs not directly related to goods and services and certain costs that are intertwined among segments due to our integrated business. The Company does not allocate Interest and foreign exchange or Income tax expense for either external or internal reporting purposes. Intersegment sales and transfers are valued as if the sales or transfers were to third parties. Related revenue and margin is eliminated in consolidation and therefore are not included in consolidated results in the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements.
The Wheels, Repair & Parts segment included the results of operations for its Repair operations through July 18, 2014. On July 18, 2014, the Company and Watco, its joint venture partner, contributed its respective Repair operations to GBW, an unconsolidated 50/50 joint venture. After July 18, 2014, the results of GBW were included as part of Earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates as the Company accounts for its interest in GBW under the equity method of accounting. Certain assets including real property, personal property and working capital were not contributed to GBW and remain as part of Wheels, Repair & Parts segment as of August 31, 2014.
The results of operations for the GBW joint venture are not reflected in the tables below as the investment is accounted for under the equity method of accounting. For the period from July 18, 2014 to August 31, 2014, GBW generated total revenue of $38.5 million and operating income of $0.6 million and had total assets as of August 31, 2014 of $210.6 million. The Company recognized $0.3 million for the period from July 18, 2014 to August 31, 2014 representing the Company’s share of earnings in the joint venture.
The information in the following table is derived directly from the segments’ internal financial reports used for corporate management purposes.
For the year ended August 31, 2014:
| Revenue | Earnings (loss) from operations | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| External | Intersegment | Total | External | Intersegment | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | 1,624,916 | $ | 790 | $ | 1,625,706 | $ | 202,555 | $ | 61 | $ | 202,616 | ||||||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
495,627 | 11,833 | 507,460 | 40,597 | 442 | 41,039 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
83,419 | 25,973 | 109,392 | 41,055 | 25,973 | 67,028 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Eliminations |
– | (38,596 | ) | (38,596 | ) | – | (26,476 | ) | (26,476 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Corporate |
– | – | – | (44,687 | ) | – | (44,687 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 2,203,962 | $ | – | $ | 2,203,962 | $ | 239,520 | $ | – | $ | 239,520 | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 65 |
Table of Contents
For the year ended August 31, 2013:
| Revenue | Earnings (loss) from operations | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| External | Intersegment | Total | External | Intersegment | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | 1,215,734 | $ | 7,244 | $ | 1,222,978 | $ | 88,822 | $ | (30 | ) | $ | 88,792 | |||||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
469,222 | 14,958 | 484,180 | (60,966 | ) | (291 | ) | (61,257 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
71,462 | 18,740 | 90,202 | 42,411 | 18,737 | 61,148 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Eliminations |
– | (40,942 | ) | (40,942 | ) | – | (18,416 | ) | (18,416 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Corporate |
– | – | – | (28,616 | ) | – | (28,616 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 1,756,418 | $ | – | $ | 1,756,418 | $ | 41,651 | $ | – | $ | 41,651 | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
For the year ended August 31, 2012:
| Revenue | Earnings (loss) from operations | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| External | Intersegment | Total | External | Intersegment | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | 1,253,964 | $ | 47,941 | $ | 1,301,905 | $ | 87,880 | $ | 3,603 | $ | 91,483 | ||||||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
481,865 | 16,406 | 498,271 | 31,455 | 316 | 31,771 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
71,887 | 18,651 | 90,538 | 31,055 | 18,651 | 49,706 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Eliminations |
– | (82,998 | ) | (82,998 | ) | – | (22,570 | ) | (22,570 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Corporate |
– | – | – | (31,602 | ) | – | (31,602 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 1,807,716 | $ | – | $ | 1,807,716 | $ | 118,788 | $ | – | $ | 118,788 | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Years ended August 31, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | 521,711 | $ | 401,630 | $ | 402,976 | ||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
298,009 | 318,483 | 413,013 | |||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
436,075 | 463,381 | 508,539 | |||||||||
| Unallocated |
261,373 | 106,247 | 60,016 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
| $ | 1,517,168 | $ | 1,289,741 | $ | 1,384,544 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
| Depreciation and amortization: |
||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | 15,341 | $ | 13,469 | $ | 11,754 | ||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
12,582 | 12,843 | 13,265 | |||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
12,499 | 15,135 | 17,352 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| $ | 40,422 | $ | 41,447 | $ | 42,371 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures: |
||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | 55,979 | $ | 37,017 | $ | 33,313 | ||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
8,774 | 7,492 | 11,248 | |||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
5,474 | 16,318 | 73,324 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| $ | 70,227 | $ | 60,827 | $ | 117,885 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| 66 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
The following table summarizes selected geographic information.
| Years ended August 31, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Revenue (1): |
||||||||||||
| U.S. |
$ | 1,998,579 | $ | 1,544,775 | $ | 1,642,348 | ||||||
| Foreign |
205,383 | 211,643 | 165,368 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| $ | 2,203,962 | $ | 1,756,418 | $ | 1,807,716 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Identifiable assets: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. |
$ | 1,115,473 | $ | 865,294 | $ | 982,078 | ||||||
| Canada |
– | 756 | 718 | |||||||||
| Mexico |
321,391 | 348,144 | 323,318 | |||||||||
| Europe |
80,304 | 75,547 | 78,430 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| $ | 1,517,168 | $ | 1,289,741 | $ | 1,384,544 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| (1) | Revenue is presented on the basis of geographic location of customers. |
Reconciliation of earnings from operations to earnings before income tax and earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates:
| Years ended August 31, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
| Earnings from operations |
$ | 239,520 | $ | 41,651 | $ | 118,788 | ||||||
| Interest and foreign exchange |
18,695 | 22,158 | 24,809 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
| Earnings before income tax and earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
$ | 220,825 | $ | 19,493 | $ | 93,979 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Note 20 - Customer Concentration
Customer concentration is defined as a single customer that accounts for more than 10% of total revenues or accounts receivable. In 2014, revenue from two customers represented 24% and 17% of total revenue, respectively. In 2013, revenue from two customers represented 17% and 10% of total revenue, respectively. In 2012, revenue from three customers represented 26%, 16% and 11% of total revenue, respectively. No other customers accounted for more than 10% of total revenues for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013, or 2012. Two customers had balances that individually equaled or exceeded 10% of accounts receivable and represented 19% and 12% of the consolidated accounts receivable balance at August 31, 2014. One customer had balances that individually equaled or exceeded 10% of accounts receivable and in total represented 18% of the consolidated accounts receivable balance at August 31, 2013.
Note 21 - Lease Commitments
Lease expense for railcar equipment leased-in under non-cancelable leases was $6.8 million, $6.7 million and $6.0 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. Aggregate minimum future amounts payable under these non-cancelable railcar equipment leases are as follows:
| (In thousands) | ||||
| Year ending August 31, |
||||
| 2015 |
$ | 6,007 | ||
| 2016 |
2,093 | |||
| 2017 |
1,569 | |||
| 2018 |
1,052 | |||
| 2019 |
– | |||
| Thereafter |
– | |||
|
|
||||
| $ | 10,721 | |||
|
|
||||
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 67 |
Table of Contents
Operating leases for domestic railcar repair facilities, office space and certain manufacturing and office equipment expire at various dates through September 2022. Rental expense for facilities, office space and equipment was $12.3 million, $13.1 million and $14.1 million for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. Aggregate minimum future amounts payable under these non-cancelable operating leases are as follows:
| (In thousands) | ||||
| Year ending August 31, |
||||
| 2015 |
$ | 4,928 | ||
| 2016 |
2,951 | |||
| 2017 |
2,835 | |||
| 2018 |
2,170 | |||
| 2019 |
1,610 | |||
| Thereafter |
2,305 | |||
|
|
||||
| $ | 16,799 | |||
|
|
||||
Note 22 - Commitments and Contingencies
The Company’s Portland, Oregon manufacturing facility is located adjacent to the Willamette River. The Company has entered into a Voluntary Cleanup Agreement with the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality (“DEQ”) in which the Company agreed to conduct an investigation of whether, and to what extent, past or present operations at the Portland property may have released hazardous substances into the environment. The Company is also conducting groundwater remediation relating to a historical spill on the property which preceded its ownership.
In December 2000, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) classified portions of the Willamette River bed known as the Portland Harbor, including the portion fronting the Company’s manufacturing facility, as a federal “National Priority List” or “Superfund” site due to sediment contamination (the “Portland Harbor Site”). The Company and more than 140 other parties, have received a “General Notice” of potential liability from the EPA relating to the Portland Harbor Site. The letter advised the Company that it may be liable for the costs of investigation and remediation (which liability may be joint and several with other potentially responsible parties) as well as for natural resource damages resulting from releases of hazardous substances to the site. At this time, ten private and public entities, including the Company (the “Lower Willamette Group” or “LWG”), have signed an Administrative Order on Consent (“AOC”) to perform a remedial investigation/feasibility study (“RI/FS”) of the Portland Harbor Site under EPA oversight, and several additional entities have not signed such consent, but are nevertheless contributing money to the effort. The EPA-mandated RI/FS is being conducted by the LWG and has cost over $110 million during a 14-year period. The Company has agreed to initially bear a percentage of the total costs incurred by the LWG in connection with the investigation. The Company’s aggregate expenditure has not been material during the 14-year period. Some or all of any such outlay may be recoverable from other responsible parties. EPA expects the investigation to continue until 2017.
Eighty-three parties, including the State of Oregon and the federal government, have entered into a non-judicial mediation process to try to allocate costs associated with the Portland Harbor site. Approximately 110 additional parties have signed tolling agreements related to such allocations. On April 23, 2009, the Company and the other AOC signatories filed suit against 69 other parties due to a possible limitations period for some such claims; Arkema Inc. et al v. A & C Foundry Products, Inc.et al, US District Court, District of Oregon, Case #3:09-cv-453-PK. All but 12 of these parties elected to sign tolling agreements and be dismissed without prejudice, and the case has now been stayed by the court, pending completion of the RI/FS. Although, as described below, the draft feasibility study has been submitted, the RI/FS will not be complete until the EPA approves it, which is not likely to occur until at least 2016.
A draft of the remedial investigation study was submitted to the EPA on October 27, 2009. The draft feasibility study was submitted to the EPA on March 30, 2012. The draft feasibility study evaluates several alternative cleanup approaches. The approaches submitted would take from 2 to 28 years with costs ranging from
| 68 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
$169 million to $1.8 billion for cleanup of the entire Portland Harbor Site, depending primarily on the selected remedial action levels. The draft feasibility study suggests costs ranging from $9 million to $163 million for cleanup of the area of the Willamette River adjacent to the Company’s Portland, Oregon manufacturing facility, depending primarily on the selected remedial action level.
The draft feasibility study does not address responsibility for the costs of clean-up or allocate such costs among the potentially responsible parties, or define precise boundaries for the cleanup. Responsibility for funding and implementing the EPA’s selected cleanup will be determined after the issuance of the Record of Decision, currently scheduled by EPA for 2017. Based on the investigation to date, the Company believes that it did not contribute in any material way to contamination in the river sediments or the damage of natural resources in the Portland Harbor Site and that the damage in the area of the Portland Harbor Site adjacent to its property precedes its ownership of the Portland, Oregon manufacturing facility. Because these environmental investigations are still underway, sufficient information is currently not available to determine the Company’s liability, if any, for the cost of any required remediation or restoration of the Portland Harbor Site or to estimate a range of potential loss. Based on the results of the pending investigations and future assessments of natural resource damages, the Company may be required to incur costs associated with additional phases of investigation or remedial action, and may be liable for damages to natural resources. In addition, the Company may be required to perform periodic maintenance dredging in order to continue to launch vessels from its launch ways in Portland, Oregon, on the Willamette River, and the river’s classification as a Superfund site could result in some limitations on future dredging and launch activities. Any of these matters could adversely affect the Company’s business and Consolidated Financial Statements, or the value of its Portland property.
The Company has also signed an Order on Consent with DEQ to finalize the investigation of potential onsite sources of contamination that may have a release pathway to the Willamette River. Interim precautionary measures are also required in the order and the Company is currently discussing with the DEQ potential remedial actions which may be required. Our aggregate expenditure has not been material during the 14-year period, however the Company could incur significant expenses for remediation. Some or all of any such outlay may be recoverable from other responsible parties.
On October 13, 2014, the Company disclosed that during September 2014, it received various complaints through its whistleblower hotline concerning alleged misconduct involving a senior employee at its Concarril manufacturing facility in Sahagun, Mexico. The Company has retained outside counsel to conduct an independent investigation of the matter, and has placed the employee on a paid leave of absence. In addition, the Company voluntarily contacted the United States Securities and Exchange Commission and the United States Department of Justice to advise both agencies that an independent investigation was underway. The investigation is at an early stage, but information developed to date suggests that there may have been conflicts of interest in connection with procurement of supplies and materials at the Concarril facility, and inappropriate personal use of Company assets and resources. Although the investigation is at an early stage, based on information developed to date, the Company believes that the alleged misconduct does not involve its other operations, or executive officers or other senior managers and that the alleged misconduct did not have a material impact on its financial condition or results of operations.
From time to time, Greenbrier is involved as a defendant in litigation in the ordinary course of business, the outcome of which cannot be predicted with certainty. While the ultimate outcome of such legal proceedings cannot be determined at this time, management believes that the resolution of these actions will not have a material adverse effect on the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements.
In accordance with customary business practices in Europe, the Company has $4.0 million in bank and third party warranty and performance guarantee facilities, all of which have been utilized as of August 31, 2014. To date no amounts have been drawn under these guarantee facilities.
As of August 31, 2014, the Mexican joint venture had $14.6 million of third party debt outstanding, for which the Company and its joint venture partner had each guaranteed approximately $10.8 million.
As of August 31, 2014, the Company had outstanding letters of credit aggregating $9.6 million associated with performance guarantees, facility leases and workers compensation insurance.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 69 |
Table of Contents
On July 18, 2014, the Company and Watco contributed its respective repair, refurbishment and retrofitting operations to GBW, an unconsolidated 50/50 joint venture. The Company made a $10 million cash contribution at closing and an additional $2.5 million cash contribution in August 2014. The Company is likely to make additional capital contributions or loans to GBW in the future including an additional $2.5 million capital contribution which has already been committed.
Note 23 - Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The estimated fair values of financial instruments and the methods and assumptions used to estimate such fair values are as follows:
| (In thousands) | Carrying Amount |
Estimated Fair Value |
||||||
| Notes payable as of August 31, 2014 |
$ | 445,091 | $ | 654,458 | ||||
| Notes payable as of August 31, 2013 |
$ | 373,889 | $ | 324,631 | ||||
The carrying amount of cash and cash equivalents, accounts and notes receivable, revolving notes, accounts payable and accrued liabilities, foreign currency forward contracts and interest rate swaps is a reasonable estimate of fair value of these financial instruments. Estimated rates currently available to the Company for debt with similar terms and remaining maturities are used to estimate the fair value of notes payable.
Note 24 - Fair Value Measures
Certain assets and liabilities are reported at fair value on either a recurring or nonrecurring basis. Fair value, for this disclosure, is defined as an exit price, representing the amount that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants, under a three-tier fair value hierarchy which prioritizes the inputs used in measuring a fair value as follows:
| Level 1 - |
observable inputs such as unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical instruments; | |
| Level 2 - |
inputs, other than the quoted market prices in active markets for similar instruments, which are observable, either directly or indirectly; and | |
| Level 3 - |
unobservable inputs for which there is little or no market data available, which require the reporting entity to develop its own assumptions. |
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of August 31, 2014 are:
| (In thousands) | Total | Level 1 | Level 2(1) | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial instruments |
$ | 200 | $ | – | $ | 200 | $ | – | ||||||||
| Nonqualified savings plan investments |
10,223 | 10,223 | – | – | ||||||||||||
| Cash equivalents |
35,036 | 35,036 | – | – | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| $ | 45,459 | $ | 45,259 | $ | 200 | $ | – | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial instruments |
$ | 1,995 | $ | – | $ | 1,995 | $ | – | ||||||||
| (1) | Level 2 assets include derivative financial instruments which are valued based on significant observable inputs. See Note 14 Derivative Instruments for further discussion. |
Assets or liabilities measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis as of August 31, 2014 are:
| (In thousands) | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Goodwill |
$ | 43,265 | $ | – | $ | – | $ | 43,265 | ||||||||
| 70 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of August 31, 2013 are:
| (In thousands) | Total | Level 1 | Level 2(1) | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial instruments |
$ | 1,042 | $ | – | $ | 1,042 | $ | – | ||||||||
| Nonqualified savings plan investments |
7,687 | 7,687 | – | – | ||||||||||||
| Cash equivalents |
1,004 | 1,004 | – | – | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| $ | 9,733 | $ | 8,691 | $ | 1,042 | $ | – | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial instruments |
$ | 1,632 | $ | – | $ | 1,632 | $ | – | ||||||||
| (1) | Level 2 assets include derivative financial instruments which are valued based on significant observable inputs. See Note 14 Derivative Instruments for further discussion. |
Assets or liabilities measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis as of August 31, 2013 are:
| (In thousands) | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Goodwill |
$ | 57,416 | $ | – | $ | – | $ | 57,416 | ||||||||
Note 25 - Variable Interest Entities
In May 2013, the Company purchased an 8% interest in an entity that owns a portfolio of railcar assets that are leased to third parties; the remaining 92% is owned by a third party. During the year ended August 31, 2014, the Company sold 204 railcars to this entity for $16.0 million resulting in a total of 468 railcars manufactured by the Company and subject to operating leases sold for $39.2 million to this entity as of August 31, 2014.
As of August 31, 2014 and 2013, the carrying amount of the Company’s investment in this entity is $3.1 million and $1.9 million which is recorded in Intangibles and other assets, net on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Note 26 - Guarantor/Non Guarantor
The convertible senior notes due 2026 (the “Notes”) issued on May 22, 2006 are fully and unconditionally and jointly and severally guaranteed by substantially all of Greenbrier’s material 100% owned U.S. subsidiaries: Autostack Company LLC, Greenbrier-Concarril, LLC, Greenbrier Leasing Company LLC, Greenbrier Leasing Limited Partner, LLC, Greenbrier Management Services, LLC, Greenbrier Leasing, L.P., Greenbrier Railcar LLC, Gunderson LLC, Gunderson Marine LLC, Gunderson Rail Services LLC, Meridian Rail Holding Corp., Meridian Rail Acquisition Corp., Meridian Rail Mexico City Corp., Brandon Railroad LLC, Gunderson Specialty Products, LLC, Greenbrier Railcar Leasing, Inc and GBW Railcar Holdings, LLC. No other subsidiaries guarantee the Notes including Greenbrier Union Holdings I LLC, Greenbrier MUL Holdings I LLC, Greenbrier Leasing Limited, Greenbrier Europe B.V., Greenbrier Germany GmbH, WagonySwidnica S.A., Zaklad Naprawczy Taboru Kolejowego Olawa sp. z o.o., Zaklad Transportu Kolejowego SIARKOPOL sp. z o.o., Gunderson-Concarril, S.A. de C.V., Greenbrier Rail Services Canada, Inc., Mexico Meridianrail Services, S.A. de C.V., Greenbrier Railcar Services – Tierra Blanca S.A. de C.V., YSD Doors, S.A. de C.V., Gunderson-Gimsa S.A. de C.V., Greenbrier, S.A. de C.V. and Greenbrier-Gimsa, LLC.
The following represents the supplemental consolidating condensed financial information of Greenbrier and its guarantor and non guarantor subsidiaries, as of August 31, 2014 and 2013 and for the years ended August 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. The information is presented on the basis of Greenbrier accounting for its ownership of its wholly owned subsidiaries using the equity method of accounting. The equity method investment for each subsidiary is recorded by the parent in intangibles and other assets. Intercompany transactions of goods and services between the guarantor and non guarantor subsidiaries are presented as if the sales or transfers were at fair value to third parties and eliminated in consolidation.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 71 |
Table of Contents
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc.
Condensed Consolidating Balance Sheet
As of August 31, 2014
| Parent | Combined Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Combined Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Eliminations | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| Assets |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 149,747 | $ | 112 | $ | 35,057 | $ | – | $ | 184,916 | ||||||||||
| Restricted cash |
– | 13,238 | 6,902 | – | 20,140 | |||||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net |
626 | 474,409 | 62,421 | (337,777 | ) | 199,679 | ||||||||||||||
| Inventories |
– | 113,117 | 192,634 | (95 | ) | 305,656 | ||||||||||||||
| Leased railcars for syndication |
– | 128,965 | – | (3,115 | ) | 125,850 | ||||||||||||||
| Equipment on operating leases, net |
– | 257,415 | 3,613 | (2,180 | ) | 258,848 | ||||||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net |
6,220 | 102,972 | 134,506 | – | 243,698 | |||||||||||||||
| Investment in unconsolidated affiliates |
910,732 | 143,768 | 3,961 | (989,102 | ) | 69,359 | ||||||||||||||
| Goodwill |
– | 43,265 | – | – | 43,265 | |||||||||||||||
| Intangibles and other assets, net |
17,031 | 45,013 | 14,221 | (10,508 | ) | 65,757 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 1,084,356 | $ | 1,322,274 | $ | 453,315 | $ | (1,342,777 | ) | $ | 1,517,168 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities and Equity |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revolving notes |
$ | – | $ | – | $ | 13,081 | $ | – | $ | 13,081 | ||||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
315,879 | 221,863 | 185,335 | (339,788 | ) | 383,289 | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
12,109 | 80,489 | – | (11,215 | ) | 81,383 | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
122 | 19,950 | 487 | 44 | 20,603 | |||||||||||||||
| Notes payable |
244,856 | 198,705 | 1,530 | – | 445,091 | |||||||||||||||
| Total equity Greenbrier |
511,390 | 801,267 | 190,861 | (992,128 | ) | 511,390 | ||||||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest |
– | – | 62,021 | 310 | 62,331 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total equity |
511,390 | 801,267 | 252,882 | (991,818 | ) | 573,721 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 1,084,356 | $ | 1,322,274 | $ | 453,315 | $ | (1,342,777 | ) | $ | 1,517,168 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 72 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc.
Condensed Consolidating Statement of Operations
For the year ended August 31, 2014
| Parent | Combined Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Combined Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Eliminations | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | – | $ | 887,252 | $ | 1,419,143 | $ | (681,479 | ) | $ | 1,624,916 | |||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
– | 502,210 | – | (6,583 | ) | 495,627 | ||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
1,256 | 81,546 | 2 | 615 | 83,419 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,256 | 1,471,008 | 1,419,145 | (687,447 | ) | 2,203,962 | |||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
– | 792,267 | 1,257,953 | (676,212 | ) | 1,374,008 | ||||||||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
– | 470,521 | – | (6,583 | ) | 463,938 | ||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
– | 43,878 | – | (82 | ) | 43,796 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| – | 1,306,666 | 1,257,953 | (682,877 | ) | 1,881,742 | |||||||||||||||
| Margin |
1,256 | 164,342 | 161,192 | (4,570 | ) | 322,220 | ||||||||||||||
| Selling and administrative |
45,621 | 41,001 | 38,063 | 585 | 125,270 | |||||||||||||||
| Net gain on disposition of equipment |
– | (13,905 | ) | (820 | ) | (314 | ) | (15,039 | ) | |||||||||||
| Gain on contribution to joint venture |
– | (29,006 | ) | – | – | (29,006 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges |
– | 1,475 | – | – | 1,475 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from operations |
(44,365 | ) | 164,777 | 123,949 | (4,841 | ) | 239,520 | |||||||||||||
| Other costs |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest and foreign exchange |
11,654 | 4,774 | 2,267 | – | 18,695 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) before income taxes and earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
(56,019 | ) | 160,003 | 121,682 | (4,841 | ) | 220,825 | |||||||||||||
| Income tax (expense) benefit |
7,563 | (55,382 | ) | (26,170 | ) | 1,588 | (72,401 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) before earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
(48,456 | ) | 104,621 | 95,512 | (3,253 | ) | 148,424 | |||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
160,375 | 18,739 | 166 | (177,925 | ) | 1,355 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
111,919 | 123,360 | 95,678 | (181,178 | ) | 149,779 | ||||||||||||||
| Net (earnings) loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
– | – | (40,634 | ) | 2,774 | (37,860 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to Greenbrier |
$ | 111,919 | $ | 123,360 | $ | 55,044 | $ | (178,404 | ) | $ | 111,919 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 73 |
Table of Contents
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc.
Consolidating Statement of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
For the year ended August 31, 2014
| (In thousands) | Parent | Combined Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Combined Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Eliminations | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
$ | 111,919 | $ | 123,360 | $ | 95,678 | $ | (181,178 | ) | $ | 149,779 | |||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Translation adjustment |
– | – | 116 | – | 116 | |||||||||||||||
| Reclassification of derivative financial instruments recognized in net earnings (loss) |
– | 1,071 | (600 | ) | – | 471 | ||||||||||||||
| Unrealized gain (loss) on derivative financial instruments |
– | (1,105 | ) | 86 | – | (1,019 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Other (net of tax effect) |
– | – | 10 | – | 10 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| – | (34 | ) | (388 | ) | – | (422 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
111,919 | 123,326 | 95,290 | (181,178 | ) | 149,357 | ||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
– | – | (40,640 | ) | 2,774 | (37,866 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to Greenbrier |
$ | 111,919 | $ | 123,326 | $ | 54,650 | $ | (178,404 | ) | $ | 111,491 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 74 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc.
Condensed Consolidating Statement of Cash Flows
For the year ended August 31, 2014
| (In thousands) | Parent | Combined Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Combined Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Eliminations | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
$ | 111,919 | $ | 123,360 | $ | 95,678 | $ | (181,178 | ) | $ | 149,779 | |||||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings (loss) to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
4,016 | (6,121 | ) | (2,582 | ) | – | (4,687 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
1,875 | 27,259 | 11,370 | (82 | ) | 40,422 | ||||||||||||||
| Net gain on disposition of equipment |
– | (13,905 | ) | (820 | ) | (314 | ) | (15,039 | ) | |||||||||||
| Stock based compensation expense |
11,285 | – | – | – | 11,285 | |||||||||||||||
| Gain on contribution to joint venture |
– | (29,006 | ) | – | – | (29,006 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Other |
– | 388 | 189 | 2,773 | 3,350 | |||||||||||||||
| Decrease (increase) in assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net |
36,996 | (11,493 | ) | (11,679 | ) | (37,573 | ) | (23,749 | ) | |||||||||||
| Inventories |
– | 16,920 | (26,595 | ) | – | (9,675 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Leased railcars for syndication |
– | (60,547 | ) | – | 2,768 | (57,779 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Other |
(935 | ) | 53,889 | (4,424 | ) | (52,599 | ) | (4,069 | ) | |||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
(44,631 | ) | 45,953 | 26,483 | 35,557 | 63,362 | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
(33 | ) | 11,355 | 389 | 2 | 11,713 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities |
120,492 | 158,052 | 88,009 | (230,646 | ) | 135,907 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from sales of assets |
– | 53,229 | 1,006 | – | 54,235 | |||||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures |
(4,125 | ) | (16,636 | ) | (49,470 | ) | 4 | (70,227 | ) | |||||||||||
| Increase in restricted cash |
– | (331 | ) | (2 | ) | – | (333 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Investment in and net advances to unconsolidated affiliates |
(169,584 | ) | (73,558 | ) | (1,253 | ) | 230,642 | (13,753 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
(173,709 | ) | (37,296 | ) | (49,719 | ) | 230,646 | (30,078 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from revolving notes with maturities longer than 90 days |
– | – | 37,819 | – | 37,819 | |||||||||||||||
| Repayment of revolving notes with maturities longer than 90 days |
– | – | (72,947 | ) | – | (72,947 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of notes payable |
– | 200,000 | – | – | 200,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Repayments of notes payable |
– | (128,157 | ) | (640 | ) | – | (128,797 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Debt issuance costs |
– | (382 | ) | – | – | (382 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Increase in restricted cash |
– | (11,000 | ) | – | – | (11,000 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Intercompany advances |
177,395 | (181,161 | ) | 3,766 | – | – | ||||||||||||||
| Repurchase of stock |
(33,583 | ) | – | – | – | (33,583 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Dividends |
(4,123 | ) | – | – | – | (4,123 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Cash distribution to joint venture partner |
– | – | (5,076 | ) | (5,076 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Investment by joint venture partner |
419 | 419 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Excess tax benefit from restricted stock awards |
109 | – | – | – | 109 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
139,798 | (120,700 | ) | (36,659 | ) | – | (17,561 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes |
(7 | ) | 31 | (811 | ) | – | (787 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Increase in cash and cash equivalents |
86,574 | 87 | 820 | – | 87,481 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Beginning of period |
63,173 | 25 | 34,237 | – | 97,435 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| End of period |
$ | 149,747 | $ | 112 | $ | 35,057 | $ | – | $ | 184,916 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 75 |
Table of Contents
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc.
Condensed Consolidating Balance Sheet
As of August 31, 2013
| Parent | Combined Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Combined Non-Guarantor |
Eliminations | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| Assets |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 63,173 | $ | 25 | $ | 34,237 | $ | – | $ | 97,435 | ||||||||||
| Restricted cash |
– | 1,907 | 6,900 | – | 8,807 | |||||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net |
37,623 | 217,268 | 54,412 | (154,455 | ) | 154,848 | ||||||||||||||
| Inventories |
– | 151,023 | 165,855 | (95 | ) | 316,783 | ||||||||||||||
| Leased railcars for syndication |
– | 68,827 | – | (347 | ) | 68,480 | ||||||||||||||
| Equipment on operating leases, net |
– | 304,234 | 3,809 | (2,575 | ) | 305,468 | ||||||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net |
2,112 | 103,315 | 96,106 | – | 201,533 | |||||||||||||||
| Investment in unconsolidated affiliates |
700,344 | 68,728 | 2,824 | (761,157 | ) | 10,739 | ||||||||||||||
| Goodwill |
– | 57,416 | – | – | 57,416 | |||||||||||||||
| Intangibles and other assets, net |
15,685 | 49,813 | 10,691 | (7,957 | ) | 68,232 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 818,937 | $ | 1,022,556 | $ | 374,834 | $ | (926,586 | ) | $ | 1,289,741 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities and Equity |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revolving notes |
$ | – | $ | – | $ | 48,209 | $ | – | $ | 48,209 | ||||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
137,631 | 178,662 | 154,096 | (154,451 | ) | 315,938 | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
8,093 | 86,610 | – | (8,663 | ) | 86,040 | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
155 | 8,546 | 98 | 39 | 8,838 | |||||||||||||||
| Notes payable |
244,856 | 126,863 | 2,170 | – | 373,889 | |||||||||||||||
| Total equity Greenbrier |
428,202 | 621,875 | 141,945 | (763,820 | ) | 428,202 | ||||||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest |
– | – | 28,316 | 309 | 28,625 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total equity |
428,202 | 621,875 | 170,261 | (763,511 | ) | 456,827 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 818,937 | $ | 1,022,556 | $ | 374,834 | $ | (926,586 | ) | $ | 1,289,741 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 76 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc.
Condensed Consolidating Statement of Operations
For the year ended August 31, 2013
| Parent | Combined Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Combined Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Eliminations | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | – | $ | 666,171 | $ | 1,001,017 | $ | (451,454 | ) | $ | 1,215,734 | |||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
– | 480,849 | – | (11,627 | ) | 469,222 | ||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
806 | 70,672 | 1 | (17 | ) | 71,462 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 806 | 1,217,692 | 1,001,018 | (463,098 | ) | 1,756,418 | |||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
– | 610,379 | 928,461 | (455,951 | ) | 1,082,889 | ||||||||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
– | 443,337 | – | (11,836 | ) | 431,501 | ||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
– | 35,754 | – | (99 | ) | 35,655 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| – | 1,089,470 | 928,461 | (467,886 | ) | 1,550,045 | |||||||||||||||
| Margin |
806 | 128,222 | 72,557 | 4,788 | 206,373 | |||||||||||||||
| Selling and administrative |
38,636 | 30,937 | 33,602 | – | 103,175 | |||||||||||||||
| Net gain on disposition of equipment |
– | (16,238 | ) | (1,276 | ) | (558 | ) | (18,072 | ) | |||||||||||
| Goodwill impairment |
– | 76,900 | – | – | 76,900 | |||||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges |
– | 2,719 | – | – | 2,719 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from operations |
(37,830 | ) | 33,904 | 40,231 | 5,346 | 41,651 | ||||||||||||||
| Other costs |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest and foreign exchange |
15,358 | 3,901 | 3,100 | (201 | ) | 22,158 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) before income taxes and earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
(53,188 | ) | 30,003 | 37,131 | 5,547 | 19,493 | ||||||||||||||
| Income tax (expense) benefit |
21,367 | (36,202 | ) | (9,067 | ) | (1,158 | ) | (25,060 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) before earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
(31,821 | ) | (6,199 | ) | 28,064 | 4,389 | (5,567 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
20,773 | 11,532 | 45 | (32,164 | ) | 186 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
(11,048 | ) | 5,333 | 28,109 | (27,775 | ) | (5,381 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net (earnings) loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
– | – | (3,946 | ) | (1,721 | ) | (5,667 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to Greenbrier |
$ | (11,048 | ) | $ | 5,333 | $ | 24,163 | $ | (29,496 | ) | $ | (11,048 | ) | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 77 |
Table of Contents
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc.
Consolidating Statement of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
For the year ended August 31, 2013
| (In thousands) | Parent | Combined Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Combined Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Eliminations | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
$ | (11,048 | ) | $ | 5,333 | $ | 28,109 | $ | (27,775 | ) | $ | (5,381 | ) | |||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Translation adjustment |
– | (34 | ) | 1,090 | – | 1,056 | ||||||||||||||
| Reclassification of derivative financial instruments recognized in net earnings (loss) |
– | 1,197 | (1,758 | ) | – | (561 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on derivative financial instruments |
– | (202 | ) | (197 | ) | – | (399 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Other (net of tax effect) |
– | – | (203 | ) | – | (203 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| – | 961 | (1,068 | ) | – | (107 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
(11,048 | ) | 6,294 | 27,041 | (27,775 | ) | (5,488 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Comprehensive (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
– | – | (3,974 | ) | (1,721 | ) | (5,695 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to Greenbrier |
$ | (11,048 | ) | $ | 6,294 | $ | 23,067 | $ | (29,496 | ) | $ | (11,183 | ) | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 78 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc.
Condensed Consolidating Statement of Cash Flows
For the year ended August 31, 2013
| (In thousands) | Parent | Combined Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Combined Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Eliminations | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
$ | (11,048 | ) | $ | 5,333 | $ | 28,109 | $ | (27,775 | ) | $ | (5,381 | ) | |||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings (loss) to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
(1,005 | ) | (9,983 | ) | (611 | ) | 1,937 | (9,662 | ) | |||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
2,124 | 29,688 | 9,734 | (99 | ) | 41,447 | ||||||||||||||
| Net gain on disposition of equipment |
– | (16,238 | ) | (1,276 | ) | (558 | ) | (18,072 | ) | |||||||||||
| Accretion of debt discount |
2,455 | – | – | – | 2,455 | |||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation expense |
6,196 | 106 | – | – | 6,302 | |||||||||||||||
| Goodwill impairment |
– | 76,900 | – | – | 76,900 | |||||||||||||||
| Other |
– | 1,160 | (70 | ) | (2,145 | ) | (1,055 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Decrease (increase) in assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net |
15,704 | (360 | ) | (6,140 | ) | (16,527 | ) | (7,323 | ) | |||||||||||
| Inventories |
– | 4,975 | 14,280 | (210 | ) | 19,045 | ||||||||||||||
| Leased railcars for syndication |
– | 25,325 | – | (2,444 | ) | 22,881 | ||||||||||||||
| Other |
272 | 416 | 28,400 | (28,119 | ) | 969 | ||||||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
(626 | ) | (27,742 | ) | (3,200 | ) | 16,139 | (15,429 | ) | |||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
(154 | ) | (7,505 | ) | (836 | ) | 10 | (8,485 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities |
13,918 | 82,075 | 68,390 | (59,791 | ) | 104,592 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from sales of assets |
– | 74,545 | 793 | – | 75,338 | |||||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures |
(515 | ) | (28,586 | ) | (32,017 | ) | 291 | (60,827 | ) | |||||||||||
| Decrease (increase) in restricted cash |
– | 139 | (2,669 | ) | – | (2,530 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Investment in and advances to unconsolidated affiliates |
(28,175 | ) | (31,325 | ) | (2,240 | ) | 59,500 | (2,240 | ) | |||||||||||
| Other |
– | – | (3,582 | ) | – | (3,582 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
(28,690 | ) | 14,773 | (39,715 | ) | 59,791 | 6,159 | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net changes in revolving notes with maturities of 90 days or less |
– | – | (16,396 | ) | – | (16,396 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Proceeds from revolving notes with maturities longer than 90 days |
– | – | 38,177 | – | 38,177 | |||||||||||||||
| Repayment of revolving notes with maturities longer than 90 days |
– | – | (34,966 | ) | – | (34,966 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Intercompany advances |
95,598 | (93,991 | ) | (1,607 | ) | – | – | |||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of notes payable |
– | – | 2,186 | – | 2,186 | |||||||||||||||
| Repayments of notes payable |
(52,868 | ) | (4,090 | ) | (1,873 | ) | – | (58,831 | ) | |||||||||||
| Investment by joint venture partner |
– | – | 3,206 | – | 3,206 | |||||||||||||||
| Excess tax benefit from restricted stock awards |
900 | – | – | – | 900 | |||||||||||||||
| Other |
(8 | ) | – | – | – | (8 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
43,622 | (98,081 | ) | (11,273 | ) | – | (65,732 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes |
– | 964 | (2,119 | ) | – | (1,155 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
28,850 | (269 | ) | 15,283 | – | 43,864 | ||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Beginning of period |
34,323 | 294 | 18,954 | – | 53,571 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| End of period |
$ | 63,173 | $ | 25 | $ | 34,237 | $ | – | $ | 97,435 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 79 |
Table of Contents
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc.
Condensed Consolidating Statement of Operations
For the year ended August 31, 2012
| (In thousands) | Parent | Combined Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Combined Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Eliminations | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | – | $ | 809,629 | $ | 1,057,996 | $ | (613,661 | ) | $ | 1,253,964 | |||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
– | 494,359 | – | (12,494 | ) | 481,865 | ||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
1,102 | 71,382 | – | (597 | ) | 71,887 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,102 | 1,375,370 | 1,057,996 | (626,752 | ) | 1,807,716 | |||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
– | 730,850 | 996,591 | (605,057 | ) | 1,122,384 | ||||||||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
– | 446,034 | – | (12,493 | ) | 433,541 | ||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
– | 37,450 | – | (79 | ) | 37,371 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| – | 1,214,334 | 996,591 | (617,629 | ) | 1,593,296 | |||||||||||||||
| Margin |
1,102 | 161,036 | 61,405 | (9,123 | ) | 214,420 | ||||||||||||||
| Selling and administrative |
42,486 | 29,383 | 32,727 | – | 104,596 | |||||||||||||||
| Net gain on disposition of equipment |
– | (8,963 | ) | – | (1 | ) | (8,964 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from operations |
(41,384 | ) | 140,616 | 28,678 | (9,122 | ) | 118,788 | |||||||||||||
| Other costs |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest and foreign exchange |
18,839 | 3,754 | 3,336 | (1,120 | ) | 24,809 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) before income taxes and earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
(60,223 | ) | 136,862 | 25,342 | (8,002 | ) | 93,979 | |||||||||||||
| Income tax (expense) benefit |
21,560 | (51,655 | ) | (4,362 | ) | 2,064 | (32,393 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (38,663 | ) | 85,207 | 20,980 | (5,938 | ) | 61,586 | ||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
97,371 | (537 | ) | (1 | ) | (97,249 | ) | (416 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
58,708 | 84,670 | 20,979 | (103,187 | ) | 61,170 | ||||||||||||||
| Net loss (earnings) attributable to noncontrolling interest |
– | – | (5,574 | ) | 3,112 | (2,462 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to Greenbrier |
$ | 58,708 | $ | 84,670 | $ | 15,405 | $ | (100,075 | ) | $ | 58,708 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 80 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc.
Consolidating Statement of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
For the year ended August 31, 2012
| (In thousands) | Parent | Combined Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Combined Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Eliminations | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
$ | 58,708 | $ | 84,670 | $ | 20,979 | $ | (103,187 | ) | $ | 61,170 | |||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Translation adjustment |
11 | (367 | ) | (3,812 | ) | – | (4,168 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Reclassification of derivative financial instruments recognized in net earnings (loss) |
– | 1,025 | 3,963 | – | 4,988 | |||||||||||||||
| Unrealized gain (loss) on derivative financial instruments |
– | (122 | ) | 830 | – | 708 | ||||||||||||||
| Other (net of tax effect) |
– | – | (130 | ) | – | (130 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | 536 | 851 | – | 1,398 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
58,719 | 85,206 | 21,830 | (103,187 | ) | 62,568 | ||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
– | – | (5,446 | ) | 3,112 | (2,334 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to Greenbrier |
$ | 58,719 | $ | 85,206 | $ | 16,384 | $ | (100,075 | ) | $ | 60,234 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 81 |
Table of Contents
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc.
Condensed Consolidating Statement of Cash Flows
For the year ended August 31, 2012
| (In thousands) | Parent | Combined Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Combined Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries |
Eliminations | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
$ | 58,708 | $ | 84,670 | $ | 20,979 | $ | (103,187 | ) | $ | 61,170 | |||||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings (loss) to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
23,749 | (7,548 | ) | (2,520 | ) | (2,064 | ) | 11,617 | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
2,596 | 31,618 | 8,236 | (79 | ) | 42,371 | ||||||||||||||
| Net gain on disposition of equipment |
– | (8,963 | ) | – | (1 | ) | (8,964 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Accretion of debt discount |
3,259 | – | – | – | 3,259 | |||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation expense |
8,757 | – | – | – | 8,757 | |||||||||||||||
| Other |
– | 1,024 | 37 | 3,844 | 4,905 | |||||||||||||||
| Decrease (increase) in assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net |
13,197 | 44,373 | (20,223 | ) | 416 | 37,763 | ||||||||||||||
| Inventories |
– | 3,395 | 313 | 1 | 3,709 | |||||||||||||||
| Leased railcars for syndication |
– | (78,863 | ) | – | 2,792 | (76,071 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Other |
1,847 | (393 | ) | 4,878 | (6,332 | ) | – | |||||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
(43,798 | ) | 55,609 | 4,448 | (23 | ) | 16,236 | |||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
(155 | ) | 10,711 | 735 | 13 | 11,304 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities |
68,160 | 135,633 | 16,883 | (104,620 | ) | 116,056 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from sales of equipment |
– | 33,560 | – | – | 33,560 | |||||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures |
(709 | ) | (89,531 | ) | (28,684 | ) | 1,039 | (117,885 | ) | |||||||||||
| Decrease (increase) in restricted cash |
– | 66 | (4,230 | ) | – | (4,164 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Investment in and net advances to unconsolidated affiliates |
(103,703 | ) | 230 | (614 | ) | 103,581 | (506 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Intercompany advances |
19,092 | – | – | (19,092 | ) | – | ||||||||||||||
| Other |
– | 48 | – | – | 48 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing Activities |
(85,320 | ) | (55,627 | ) | (33,528 | ) | 85,528 | (88,947 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net changes in revolving notes with maturities of 90 days or less |
(60,000 | ) | – | 2,698 | – | (57,302 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Proceeds from revolving notes with maturities longer than 90 days |
– | – | 63,773 | – | 63,773 | |||||||||||||||
| Repayment of revolving notes with maturities longer than 90 days |
– | – | (33,934 | ) | – | (33,934 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Intercompany advances |
76,476 | (76,936 | ) | (18,632 | ) | 19,092 | – | |||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of notes Payable |
– | 250 | 2,500 | – | 2,750 | |||||||||||||||
| Repayments of notes payable |
– | (4,166 | ) | (2,904 | ) | – | (7,070 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Investment by joint venture partner |
– | – | 1,362 | – | 1,362 | |||||||||||||||
| Excess tax benefit from restricted stock awards |
1,627 | – | – | – | 1,627 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
18,103 | (80,852 | ) | 14,863 | 19,092 | (28,794 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes |
12 | 611 | 4,411 | – | 5,034 | |||||||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
955 | (235 | ) | 2,629 | – | 3,349 | ||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Beginning of period |
33,368 | 529 | 16,325 | – | 50,222 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
| End of period |
$ | 34,323 | $ | 294 | $ | 18,954 | $ | – | $ | 53,571 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
| 82 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
Quarterly Results of Operations (Unaudited)
| (In thousands, except per share amount) | First | Second | Third | Fourth | Total | |||||||||||||||
| 2014 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | 359,473 | $ | 347,755 | $ | 425,583 | $ | 492,105 | $ | 1,624,916 | ||||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
113,401 | 136,540 | 140,663 | 105,023 | 495,627 | |||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
17,481 | 17,921 | 27,039 | 20,978 | 83,419 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 490,355 | 502,216 | 593,285 | 618,106 | 2,203,962 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
311,440 | 306,572 | 351,829 | 404,167 | 1,374,008 | |||||||||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
107,975 | 127,940 | 129,825 | 98,198 | 463,938 | |||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
9,381 | 9,853 | 14,856 | 9,706 | 43,796 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 428,796 | 444,365 | 496,510 | 512,071 | 1,881,742 | ||||||||||||||||
| Margin |
61,559 | 57,851 | 96,775 | 106,035 | 322,220 | |||||||||||||||
| Selling and administrative |
26,109 | 28,125 | 34,800 | 36,236 | 125,270 | |||||||||||||||
| Net gain on disposition of equipment |
(3,651 | ) | (5,416 | ) | (5,619 | ) | (353 | ) | (15,039 | ) | ||||||||||
| Gain on contribution to joint venture |
– | – | – | (29,006 | ) | (29,006 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges |
879 | 540 | 56 | – | 1,475 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings from operations |
38,222 | 34,602 | 67,538 | 99,158 | 239,520 | |||||||||||||||
| Other costs |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest and foreign exchange |
4,744 | 4,099 | 5,437 | 4,415 | 18,695 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings before income tax and earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
33,478 | 30,503 | 62,101 | 94,743 | 220,825 | |||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
(10,522 | ) | (9,883 | ) | (16,303 | ) | (35,693 | ) | (72,401 | ) | ||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
41 | (67 | ) | 298 | 1,083 | 1,355 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
22,997 | 20,553 | 46,096 | 60,133 | 149,779 | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interest |
(7,609 | ) | (4,966 | ) | (12,508 | ) | (12,777 | ) | (37,860 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to Greenbrier |
$ | 15,388 | $ | 15,587 | $ | 33,588 | $ | 47,356 | $ | 111,919 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic earnings per common share: (1) |
$ | 0.54 | $ | 0.55 | $ | 1.20 | $ | 1.69 | $ | 3.97 | ||||||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share: (1) |
$ | 0.49 | $ | 0.50 | $ | 1.03 | $ | 1.43 | $ | 3.44 | ||||||||||
| (1) | Quarterly amounts do not total to the year to date amount as each period is calculated discretely. Diluted earnings per common share includes the dilutive effect of the 2026 Convertible Notes using the treasury stock method when dilutive and the dilutive effect of shares underlying the 2018 Convertible Notes using the “if converted” method in which debt issuance and interest costs, net of tax, were added back to net earnings. |
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 83 |
Table of Contents
Quarterly Results of Operations (Unaudited)
| (In thousands, except per share amount) | First | Second | Third | Fourth | Total | |||||||||||||||
| 2013 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
$ | 285,368 | $ | 294,047 | $ | 284,591 | $ | 351,728 | $ | 1,215,734 | ||||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
112,100 | 111,952 | 131,167 | 114,003 | 469,222 | |||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
17,906 | 17,167 | 17,905 | 18,484 | 71,462 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 415,374 | 423,166 | 433,663 | 484,215 | 1,756,418 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
258,492 | 262,650 | 253,360 | 308,387 | 1,082,889 | |||||||||||||||
| Wheels, Repair & Parts |
101,476 | 103,134 | 120,476 | 106,415 | 431,501 | |||||||||||||||
| Leasing & Services |
7,627 | 9,107 | 9,808 | 9,113 | 35,655 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 367,595 | 374,891 | 383,644 | 423,915 | 1,550,045 | ||||||||||||||||
| Margin |
47,779 | 48,275 | 50,019 | 60,300 | 206,373 | |||||||||||||||
| Selling and administrative |
26,100 | 24,942 | 25,322 | 26,811 | 103,175 | |||||||||||||||
| Net gain on disposition of equipment |
(1,408 | ) | (3,076 | ) | (5,131 | ) | (8,457 | ) | (18,072 | ) | ||||||||||
| Goodwill impairment |
– | – | 76,900 | – | 76,900 | |||||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges |
– | – | – | 2,719 | 2,719 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from operations |
23,087 | 26,409 | (47,072 | ) | 39,227 | 41,651 | ||||||||||||||
| Other costs |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest and foreign exchange |
5,900 | 6,322 | 5,905 | 4,031 | 22,158 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) before income tax and earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
17,187 | 20,087 | (52,977 | ) | 35,196 | 19,493 | ||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
(4,586 | ) | (5,590 | ) | (2,729 | ) | (12,155 | ) | (25,060 | ) | ||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from unconsolidated affiliates |
(40 | ) | (105 | ) | 82 | 249 | 186 | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
12,561 | 14,392 | (55,624 | ) | 23,290 | (5,381 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interest |
(2,134 | ) | (553 | ) | (406 | ) | (2,574 | ) | (5,667 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) attributable to Greenbrier |
$ | 10,427 | $ | 13,839 | $ | (56,030 | ) | $ | 20,716 | $ | (11,048 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic earnings (loss) per common share: (1) |
$ | 0.38 | $ | 0.51 | $ | (2.10 | ) | $ | 0.74 | $ | (0.41 | ) | ||||||||
| Diluted earnings (loss) per common share: (1) |
$ | 0.35 | $ | 0.45 | $ | (2.10 | ) | $ | 0.64 | $ | (0.41 | ) | ||||||||
| (1) | Quarterly amounts do not total to the year to date amount as each period is calculated discretely. For the first, second and fourth quarters, diluted earnings per common share includes the outstanding warrants using the treasury stock method and the dilutive effect of shares underlying the 2018 Convertible Notes using the “if converted” method in which debt issuance and interest costs, net of tax, were added back to net earnings. |
| 84 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
| Item 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
None.
| Item 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management has evaluated, under the supervision and with the participation of our President and Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the period covered by this report pursuant to Rule 13a-15(b) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the Exchange Act). Based on that evaluation, our President and Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, as of the end of the period covered by this report, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective in ensuring that information required to be disclosed in our Exchange Act reports is (1) recorded, processed, summarized and reported in a timely manner, and (2) accumulated and communicated to our management, including our President and Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Changes in Internal Controls
There have been no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended August 31, 2014 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management of The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. together with its consolidated subsidiaries (the “Company”), is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed under the supervision of the Company’s principal executive and principal financial officers to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of the Company’s financial statements for external reporting purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
As of the end of the Company’s 2014 fiscal year, management conducted an assessment of the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on the framework established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). Based on this assessment, management has determined that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of August 31, 2014 is effective.
Our independent registered public accounting firm, KPMG LLP, independently assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting, as stated in their attestation report, which is included at the end of Part II, Item 9A of this Form 10-K.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 85 |
Table of Contents
Inherent Limitations on Effectiveness of Controls
The Company’s management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, does not expect that our disclosure controls and procedures or our internal control over financial reporting will prevent or detect all error and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the control system’s objectives will be met. The design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints, and the benefits of controls must be considered relative to their costs. Further, because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that misstatements due to error or fraud will not occur or that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within the Company have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision-making can be faulty and that breakdowns can occur because of simple error or mistake. Controls can also be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people, or by management override of the controls. The design of any system of controls is based in part on certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions. Projections of any evaluation of controls effectiveness to future periods are subject to risks. Over time, controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or deterioration in the degree of compliance with policies or procedures.
| 86 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
The Greenbrier Companies, Inc.
We have audited The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) internal control over financial reporting as of August 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of August 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of August 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), equity and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended August 31, 2014, and our report dated October 30, 2014 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
/s/ KPMG LLP
Portland, Oregon
October 30, 2014
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 87 |
Table of Contents
| Item 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION |
None
| Item 10. | DIRECTORS AND EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
There is hereby incorporated by reference the information under the captions “Election of Directors,” “Board Committees, Meetings and Charters,” “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” and “Executive Officers of the Company” in the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A, which Proxy Statement is anticipated to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of Registrant’s year ended August 31, 2014.
| Item 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
There is hereby incorporated by reference the information under the caption “Executive Compensation” and “Compensation Committee Report” in Registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A, which Proxy Statement is anticipated to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of Registrant’s year ended August 31, 2014.
| Item 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDERS MATTERS |
There is hereby incorporated by reference the information under the captions “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” and “Equity Compensation Plan Information” in Registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A, which Proxy Statement is anticipated to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of Registrant’s year ended August 31, 2014.
| Item 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
There is hereby incorporated by reference the information under the caption “Transactions with Related Persons” and “Independence of Directors” in Registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A, which Proxy Statement is anticipated to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of Registrant’s year ended August 31, 2014.
| Item 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES |
There is hereby incorporated by reference the information under the caption “Ratification of Appointment of Auditors” in Registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A, which Proxy Statement is anticipated to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of the Registrant’s year ended August 31, 2014.
| 88 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
| Item 15. | EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
| (1) | Financial Statements |
See Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8
| (a) | (2) Financial Statements Schedule* |
| * | All other schedules have been omitted because they are inapplicable, not required or because the information is given in the Consolidated Financial Statements or notes thereto. This supplemental schedule should be read in conjunction with the Consolidated Financial Statements and notes thereto included in this report. |
| (a) | (3) The following exhibits are filed herewith and this list is intended to constitute the exhibit index: |
| 3.1 | Registrant’s Articles of Incorporation are incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed April 5, 2006. |
| 3.2 | Articles of Merger amending the Registrant’s Articles of Incorporation are incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed April 5, 2006. |
| 3.3 | Registrant’s Bylaws, as amended January 11, 2006, are incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.3 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed April 5, 2006. |
| 3.4 | Amendment to the Registrant’s Bylaws, dated October 31, 2006, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed November 6, 2006. |
| 3.5 | Amendment to the Registrant’s Bylaws, dated January 8, 2008, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed November 8, 2007. |
| 3.6 | Amendment to the Registrant’s Bylaws, dated April 8, 2008, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed April 11, 2008. |
| 3.7 | Amendment to the Registrant’s Bylaws, dated April 7, 2009, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed April 13, 2009. |
| 3.8 | Amendment to the Registrant’s Bylaws, dated June 8, 2009, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed June 10, 2009. |
| 3.9 | Amendment to the Registrant’s Bylaws, dated June 10, 2009, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed June 12, 2009. |
| 3.10 | Amendment to the Registrant’s Bylaws, dated October 30, 2012, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed November 5, 2012. |
| 3.11 | Amendment to the Registrant’s Bylaws, dated January 9, 2013, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed January 15, 2013. |
| 3.12 | Amendment to the Registrant’s Bylaws, dated October 29, 2013, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed October 31, 2013. |
| 4.1 | Specimen Common Stock Certificate of Registrant is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-3 filed April 7, 2010 (SEC File Number 333-165924). |
| 4.2 | Indenture between the Registrant, the Guarantors named therein and U.S. Bank National Association as Trustee, dated May 22, 2006, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed May 25, 2006. |
| 4.3 | Investor Rights and Restrictions Agreement among the Registrant, WLR Recovery Fund IV, L.P., WLR IV Parallel ESC, L.P., WL Ross & Co. LLC and the other holders from time to time party thereto, dated June 10, 2009, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed June 12, 2009. |
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 89 |
Table of Contents
| 4.4 | Indenture between the Registrant and U.S. Bank National Association, as Trustee, including the form of Global Note attached as Exhibit A thereto, dated April 5, 2011, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed April 5, 2011. |
| 10.1 | Registration Rights Agreement among the Registrant, the Guarantors named therein, Bear, Stearns & Co. Inc. and Banc of America Securities LLC, dated May 22, 2006, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed May 25, 2006. |
| 10.2 | Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement among the Registrant, Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Union Bank, National Association, as Syndication Agent, Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as Sole Lead Arranger and Sole Book Manager, and the lenders identified therein, dated June 30, 2011, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed July 7, 2011. |
| 10.3 | Lender Joinder Agreement by and among The Private Bank and Trust Company, the Registrant and Bank Of America, N.A., dated as of November 2, 2011, to the Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of June 30, 2011 by and among the Registrant, the lenders party thereto and Bank of America, N.A., is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed January 6, 2012. |
| 10.4 | Lender Joinder Agreement by and among Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, the Registrant and Bank Of America, N.A., dated as of December 12, 2011, to the Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of June 30, 2011 by and among the Registrant, the lenders party thereto and Bank of America, N.A., is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed January 6, 2012. |
| 10.5 | Amendment No. 1, dated October 7, 2010 [sic], to the Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement among the Registrant, Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Union Bank, National Association, as Syndication Agent, Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as Sole Lead Arranger and Sole Book Manager, and the lenders identified therein, dated as of June 30, 2011, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed April 4, 2013. |
| 10.6 | Amendment No. 2, dated February 8, 2013, to the Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement among the Registrant, Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Union Bank, National Association, as Syndication Agent, Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as Sole Lead Arranger and Sole Book Manager, and the lenders identified therein, dated as of June 30, 2011, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed April 4, 2013. |
| 10.7 | Amendment No. 3, dated March 20, 2014, to the Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement among the Registrant, Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Union Bank, National Association, as Syndication Agent, Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as Sole Lead Arranger and Sole Book Manager, and the lenders identified therein, dated as of June 30, 2011, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed April 3, 2014. |
| 10.8 | Amendment No. 4, dated July 18, 2014, to the Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement among the Registrant, Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Union Bank, National Association, as Syndication Agent, Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as Sole Lead Arranger and Sole Book Manager, and the lenders identified therein, dated as of June 30, 2011, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed July 24, 2014. |
| 10.9* | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between the Registrant and Mr. William A. Furman, dated August 28, 2012, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed January 9, 2013. |
| 10.10* | Form of Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between the Registrant and certain of its executive officers, as amended and restated on August 28, 2012, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to the Registrant’s Form 10-K filed November 1, 2012. |
| 90 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
| 10.11* | Amendment No. 1 to Form of Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between the Registrant and certain of its executive officers, as amended and restated on August 28, 2012, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed January 8, 2014. |
| 10.12* | Form of Agreement concerning Indemnification and Related Matters (Directors) between Registrant and its directors is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to the Registrant’s Form 10-K filed November 10, 2008. |
| 10.13* | Form of Agreement concerning Indemnification and Related Matters (Officers) between Registrant and its officers is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed April 4, 2013. |
| 10.14* | Consulting Agreement between A. Daniel O’Neal Jr. and Greenbrier Leasing Company LLC, dated December 31, 2010, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed April 7, 2011. |
| 10.15* | Consulting Agreement between C. Bruce Ward and Greenbrier Leasing Corporation, dated March 31, 2005 and as amended on January 1, 2007, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed December 13, 2010. |
| 10.16* | Consulting Agreement between Timothy A. Stuckey and the Registrant, dated June 30, 2013, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to the Registrant’s Form 10-K filed October 31, 2013. |
| 10.17* | Form of Change of Control Agreement is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.26 to the Registrant’s Form 10-K filed November 10, 2008. |
| 10.18* | Form of Change of Control Agreement is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed April 4, 2013. |
| 10.19* | The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. Form of Amendment to Change of Control Agreement, approved on May 28, 2013, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed June 6, 2013. |
| 10.20* | Second Amended and Restated Change of Control Agreement between the Registrant and William Glenn, dated August 28, 2012, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.17 to the Registrant’s Form 10-K filed November 1, 2012. |
| 10.21* | The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. 2010 Amended and Restated Stock Incentive Plan is incorporated herein by reference to Appendix B to the Registrant’s Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A filed November 24, 2010. |
| 10.22* | Amendment No. 1 to The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. 2010 Amended and Restated Stock Incentive Plan is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed April 4, 2013. |
| 10.23* | Amendment No. 2 to the Greenbrier Companies, Inc. 2010 Amended and Restated Stock Incentive Plan is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed January 8, 2014. |
| 10.24* | Form of Director Restricted Share Agreement related to the 2010 Amended and Restated Stock Incentive Plan is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed April 7, 2011. |
| 10.25* | Form of Director Restricted Share Agreement related to the 2010 Amended and Restated Stock Incentive Plan is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed April 3, 2014. |
| 10.26* | Form of Director Restricted Share Agreement (2014 Discretionary Director Grants Subject to Shareholder Approval) related to the 2010 Amended and Restated Stock Incentive Plan is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed April 3, 2014. |
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 91 |
Table of Contents
| 10.27* | Form of Employee Restricted Share Agreement (time and performance vesting) related to the 2010 Amended and Restated Stock Incentive Plan is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed July 8, 2011. |
| 10.28* | Form of Employee Restricted Share Agreement as amended on April 2, 2012 (time and performance vesting) related to the 2010 Amended and Restated Stock Incentive Plan is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed June 29, 2012. |
| 10.29* | The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plan Basic Plan Document is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.38 to the Registrant’s Form 10-K filed November 4, 2011. |
| 10.30* | The Greenbrier Companies Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plan Adoption Agreement is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.39 to the Registrant’s Form 10-K filed November 4, 2011. |
| 10.31* | Amendment No. 1 to the Greenbrier Companies Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plan Adoption Agreement, dated May 25, 2011, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed July 8, 2011. |
| 10.32* | Amendment No. 2 to the Greenbrier Companies Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plan Adoption Agreement, dated August 28, 2012, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.27 to the Registrant’s Form 10-K filed November 1, 2012. |
| 10.33* | Updated Rabbi Trust Agreements, dated October 1, 2012, related to The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plan, are incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed January 9, 2013. |
| 10.34* | The Greenbrier Companies Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plan Adoption Agreement for Directors, dated July 1, 2012, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.28 to the Registrant’s Form 10-K filed November 1, 2012. |
| 10.35* | Updated Rabbi Trust Agreements, dated October 1, 2012, related to the Greenbrier Companies, Inc. Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plan for Directors, are incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q filed January 9, 2013. |
| 10.36* | The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement, approved on May 28, 2013, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed June 3, 2013. |
| 10.37* | The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement, approved on May 5, 2014, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed May 9, 2014. |
| 10.38 | Railcar Remarketing and Management Agreement between Greenbrier Management Services, LLC and WL Ross-Greenbrier Rail I LLC, dated as of April 29, 2010, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed May 3, 2010.** |
| 10.39 | Advisory Services Agreement between Greenbrier Leasing Company LLC and WLR-Greenbrier Rail Inc., dated as of April 29, 2010, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed May 3, 2010.** |
| 10.40 | Contract Placement Agreement between Greenbrier Leasing Company LLC and WLR-Greenbrier Rail Inc., dated as of April 29, 2010, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed May 3, 2010.** |
| 10.41 | Syndication Agreement between Greenbrier Leasing Company LLC and WLR-Greenbrier Rail Inc., dated as of April 29, 2010, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed May 3, 2010.** |
| 10.42 | Amendment to Syndication Agreement between Greenbrier Leasing Company LLC and WLR-Greenbrier Rail Inc., dated as of August 18, 2010, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed August 20, 2010. |
| 92 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
| 10.43 | Line of Credit Participation Letter Agreement between Greenbrier Leasing Company LLC and WLR-Greenbrier Rail Inc., dated as of April 29, 2010, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed May 3, 2010.** |
| 10.44 | Guaranty of Greenbrier Leasing Company LLC, dated as of April 29, 2010, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed May 3, 2010.** |
| 10.45 | Guaranty of the Greenbrier Companies, Inc., dated as of August 18, 2010, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed August 20, 2010. |
| 10.46 | Purchase Agreement among The Greenbrier Companies, Inc., Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated and Goldman, Sachs & Co., dated March 30, 2011, is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed April 5, 2011. |
| 10.47 | The Greenbrier Companies, Inc. Executive Stock Ownership Guidelines, adopted as of August 28, 2012, are incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.39 to the Registrant’s Form 10-K filed November 1, 2012. |
| 10.48 | Contribution Agreement, dated July 18, 2014, by and among Watco Companies, L.L.C., the Registrant, and with respect to Article III and Article IX only, GBW Railcar Services Holdings, L.L.C., is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed July 24, 2014. |
| 10.49 | Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of GBW Railcar Services Holdings, L.L.C., dated July 18, 2014, by and among the Registrant, Watco Mechanical Services, L.L.C., and Millennium Rail, Inc., is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed July 24, 2014. |
| 10.50 | Credit Agreement, dated March 20, 2014, by and among Greenbrier Leasing Company LLC, an Oregon limited liability company, Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Union Bank, N.A., as Syndication Agent, Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as Sole Lead Arranger and Sole Book Manager, and the lenders identified therein is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed March 26, 2014. |
| 14.1 | Code of Business Conduct and Ethics is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 14.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed January 11, 2012. |
| 21.1 | List of the subsidiaries of the Registrant. |
| 23.1 | Consent of KPMG LLP, independent auditors. |
| 31.1 | Certification pursuant to Rule 13(a) – 14(a). |
| 31.2 | Certification pursuant to Rule 13(a) – 14(a). |
| 32.1 | Certification pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350 as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
| 32.2 | Certification pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350 as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
| 101 | The following financial information from the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended August 31, 2014, formatted in XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language) and furnished electronically herewith: (i) the Consolidated Balance Sheets; (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Operations; (iii) Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss) (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Equity (v) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows; (vi) the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
| * | Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement |
| ** | Certain confidential information contained in these Exhibits was omitted by means of redacting a portion of the text and replacing it with brackets and asterisks ([***]). These Exhibits have been filed separately with the SEC without the redaction and have been granted confidential treatment by the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to a Confidential Treatment Request under Rule 24b-2 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. |
Note: For all exhibits incorporated by reference, unless otherwise noted above, the SEC file number is 001-13146.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 93 |
Table of Contents
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
THE GREENBRIER COMPANIES, INC.
| Dated: October 30, 2014 | By: | /s/ William A. Furman | ||||
| William A. Furman | ||||||
| President and Chief Executive Officer | ||||||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Date | |
| /s/ William A. Furman William A. Furman, President, Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board |
October 30, 2014 | |
| /s/ Duane C. McDougall Duane McDougall, Director |
October 30, 2014 | |
| /s/ Graeme A. Jack Graeme A. Jack, Director |
October 30, 2014 | |
| /s/ Victoria McManus Victoria McManus, Director |
October 30, 2014 | |
| /s/ A. Daniel O’Neal, Jr. A. Daniel O’Neal, Jr., Director |
October 30, 2014 | |
| /s/ Charles J. Swindells Charles J. Swindells, Director |
October 30, 2014 | |
| /s/ Wendy L. Teramoto Wendy L. Teramoto, Director |
October 30, 2014 | |
| /s/ C. Bruce Ward C. Bruce Ward, Director |
October 30, 2014 | |
| /s/ Donald A. Washburn Donald A. Washburn, Director |
October 30, 2014 | |
| /s/ Mark J. Rittenbaum Mark J. Rittenbaum, Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) |
October 30, 2014 | |
| /s/ Adrian J. Downes Adrian J. Downes, Senior Vice President and Chief Accounting Officer (Principal Accounting Officer) |
October 30, 2014 | |
| 94 | The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report |
Table of Contents
The Company filed the required 303A.12(a) New York Stock Exchange Certification of its Chief Financial Officer with the New York Stock Exchange with no qualifications following the 2014 Annual Meeting of Shareholders and the Company filed as an exhibit to its Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended August 31, 2013, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, a Certification of the Chief Executive Officer and a Certification of the Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
| The Greenbrier Companies 2014 Annual Report | 95 |
