Attached files
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-Q
(Mark One)
xQUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the Quarterly Period Ended February 28, 2013
or
rTRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the Transition Period from ___________ to _____________
Commission File Number: 333-175483
China Xuefeng Environmental Engineering Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
Nevada
|
99-0364975
|
|
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization)
|
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.
|
|
C214. Fitting Integration Building,
Fazhan Road to Sugian Gate Section
Jiangsu Province, China
|
223800
|
|
(Address of principal executive offices)
|
(Zip Code)
|
+86 (527) 8437-0508
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Not Applicable
(Former name, former address and former fiscal year, if changed since last report)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
Large accelerated filer
|
o
|
Accelerated filer
|
o
|
|
|
Non-accelerated filer
|
o
|
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company)
|
Smaller reporting company
|
x
|
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act).Yes o No x
As of April 18, 2013, there were 55,200,000 outstanding shares of common stock of the registrant, par value $.001 per share.
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC.
QUARTERLY REPORT ON FORM 10-Q
February 28, 2013
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
PART I—FINANCIAL INFORMATION
|
Page | |
|
Item 1.
|
Financial Statements.
|
1
|
|
Item 2.
|
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
|
25
|
|
Item 3.
|
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
|
33
|
|
Item 4.
|
Controls and Procedures.
|
34
|
|
PART II—OTHER INFORMATION
|
||
|
Item 1.
|
Legal Proceedings.
|
34
|
|
Item 1A.
|
Risk Factors.
|
34
|
|
Item 2.
|
Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds.
|
34
|
|
Item 3.
|
Defaults Upon Senior Securities.
|
35
|
|
Item 4.
|
Mine Safety Disclosures.
|
35
|
|
Item 5.
|
Other Information.
|
35
|
|
Item 6.
|
Exhibits.
|
35
|
|
Signatures
|
36
|
|
CERTAIN USAGE OF TERMS
Except as otherwise indicated by the context, references in this report to “we,” “us,” “our,” “our Company,” or “the Company” are to the combined business of China Xuefeng Environmental Engineering Inc. (formerly known as NYC Moda Inc.).
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT ON FORWARD-LOOKING INFORMATION
This Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q contains “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Act, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). Forward-looking statements discuss matters that are not historical facts. Because they discuss future events or conditions, forward-looking statements may include words such as “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “intend,” “could,” “should,” “would,” “may,” “seek,” “plan,” “might,” “will,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “predict,” “project,” “forecast,” “potential,” “continue” negatives thereof or similar expressions. Forward-looking statements speak only as of the date they are made, are based on various underlying assumptions and current expectations about the future and are not guarantees. Such statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause our actual results, level of activity, performance or achievement to be materially different from the results of operations or plans expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements.
We cannot predict all of the risks and uncertainties. Accordingly, such information should not be regarded as representations that the results or conditions described in such statements or that our objectives and plans will be achieved and we do not assume any responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of any of these forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements are found at various places throughout this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q and include information concerning possible or assumed future results of our operations, including statements about potential acquisition or merger targets; business strategies; future cash flows; financing plans; plans and objectives of management; any other statements regarding future acquisitions, future cash needs, future operations, business plans and future financial results, and any other statements that are not historical facts.
These forward-looking statements represent our intentions, plans, expectations, assumptions and beliefs about future events and are subject to risks, uncertainties and other factors. Many of those factors are outside of our control and could cause actual results to differ materially from the results expressed or implied by those forward-looking statements. In light of these risks, uncertainties and assumptions, the events described in the forward-looking statements might not occur or might occur to a different extent or at a different time than we have described. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date of the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q. All subsequent written and oral forward-looking statements concerning other matters addressed in this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q and attributable to us or any person acting on our behalf are expressly qualified in their entirety by the cautionary statements contained or referred to in this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q.
Except to the extent required by law, we undertake no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events, a change in events, conditions, circumstances or assumptions underlying such statements, or otherwise.
PART I—FINANCIAL INFORMATION
Item 1. Financial Statements.
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Financial Statements for the
Three and Nine Months Ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012
1
|
CONTENTS
|
PAGE
|
|
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS:
|
|
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets
|
3
|
|
Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income
|
5
|
|
Consolidated Statement of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity
|
7
|
|
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
|
8
|
|
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
9
|
2
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(IN U.S. $)
|
February 28,
|
May 31,
|
|||||||
|
ASSETS
|
2013
|
2012
|
||||||
|
(Unaudited)
|
||||||||
|
Current assets:
|
||||||||
|
Cash
|
$ | 7,985,488 | $ | 4,139,165 | ||||
|
Prepaid expenses
|
128,777 | 6,855 | ||||||
|
Total current assets
|
8,114,265 | 4,146,020 | ||||||
|
Fixed assets, net
|
24,299 | 27,365 | ||||||
|
Other assets:
|
||||||||
|
Prepayment for acquisition of land use right
|
795,000 | 788,532 | ||||||
|
Deferred income taxes
|
435,263 | 2,632 | ||||||
|
Total other assets
|
1,230,263 | 791,164 | ||||||
|
TOTAL ASSETS
|
$ | 9,368,827 | $ | 4,964,549 | ||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
3
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(IN U.S. $)
|
February 28,
|
May, 31
|
|||||||
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
2013
|
2012
|
||||||
|
(Unaudited)
|
||||||||
|
Current liabilities:
|
||||||||
|
Deferred revenue
|
$ | 1,741,050 | $ | - | ||||
|
Income taxes payable
|
522,673 | - | ||||||
|
Loan from stockholder
|
125,907 | - | ||||||
|
Accrued liabilities
|
27,138 | 81,321 | ||||||
|
Total current liabilities
|
2,416,768 | 81,321 | ||||||
|
Stockholders’ equity:
|
||||||||
|
Common stock, $0.001 par value per share, 75,000,000 shares authorized, and 41,200,000 shares issued and outstanding
|
41,200 | 41,200 | ||||||
|
Additional paid in capital
|
4,403,049 | 4,421,426 | ||||||
|
Statutory reserve fund
|
193,656 | - | ||||||
|
Retained earnings (deficit)
|
1,740,611 | (18,177 | ) | |||||
|
Other comprehensive income
|
239,642 | 195,585 | ||||||
|
Stockholders’ equity before noncontrolling interests
|
6,618,158 | 4,640,034 | ||||||
|
Noncontrolling interests
|
333,901 | 243,194 | ||||||
|
Total stockholders’ equity
|
6,952,059 | 4,883,228 | ||||||
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
$ | 9,368,827 | $ | 4,964,549 | ||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
4
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013 AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
| Three Months Ended | Nine Months Ended | |||||||||||||||
|
February 28,
|
February 29,
|
February 28,
|
February 29,
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
2013
|
2012
|
2013
|
2012
|
||||||||||||
|
Revenue
|
$ | 1,311,705 | $ | - | $ | 3,463,225 | $ | - | ||||||||
|
Cost of revenue
|
(114,941 | ) | - | (400,174 | ) | - | ||||||||||
|
Gross profit
|
1,196,764 | - | 3,063,051 | - | ||||||||||||
|
Operating expenses
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Selling and marketing
|
28,405 | 3,660 | 37,612 | 6,620 | ||||||||||||
|
General and administrative
|
154,248 | 21,248 | 335,782 | 75,180 | ||||||||||||
|
Total operating expenses
|
182,653 | 24,908 | 373,394 | 81,800 | ||||||||||||
|
Income (loss) from operations
|
1,014,111 | (24,908 | ) | 2,689,657 | (81,800 | ) | ||||||||||
|
Interest income
|
2,074 | 1,454 | 5,087 | 4,487 | ||||||||||||
|
Income (loss) before provision for (benefit from) income taxes
|
1,016,185 | (23,454 | ) | 2,694,744 | (77,313 | ) | ||||||||||
|
Provision for (benefit from) income taxes
|
242,144 | (5,863 | ) | 653,898 | (19,328 | ) | ||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
5
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013 AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
| Three Months Ended | Nine Months Ended | |||||||||||||||
|
February 28,
|
February 29,
|
February 28,
|
February 29,
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
2013
|
2012
|
2013
|
2012
|
||||||||||||
|
Net income (loss) before noncontrolling interests
|
774,041 | (17,591 | ) | 2,040,846 | (57,985 | ) | ||||||||||
|
Noncontrolling interests
|
(36,322 | ) | 880 | (88,402 | ) | 2,899 | ||||||||||
|
Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders
|
737,719 | (16,711 | ) | 1,952,444 | (55,086 | ) | ||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment
|
(11,017 | ) | 51,518 | 44,057 | 127,370 | |||||||||||
|
Total comprehensive income (loss)
|
$ | 726,702 | $ | 34,807 | $ | 1,996,501 | $ | 72,284 | ||||||||
|
Earnings (loss) per common share, basic and diluted
|
$ | 0.02 | $ | (0.00 | ) | $ | 0.05 | $ | (0.00 | ) | ||||||
|
Weighted average shares outstanding, basic and diluted
|
41,200,000 | 41,200,000 | 41,200,000 | 41,200,000 | ||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
6
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
FOR THE NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013 (UNAUDITED) (IN U.S.$)
|
Common
Stock
|
Additional
Paid-in Capital
|
Retained
Earnings
|
Noncontrolling
Interests
|
Statutory
Reserve Fund
|
Other
Comprehensive
Income
|
Total
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance, May 31, 2012
|
$ | 41,200 | $ | 4,421,426 | $ | (18,177 | ) | $ | 243,194 | $ | - | $ | 195,585 | $ | 4,883,228 | |||||||||||||
|
Reverse merger adjustment
|
- | (18,377 | ) | - | - | - | - | (18,377 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
|
Net Income
|
- | - | 1,952,444 | 88,402 | - | - | 2,040,846 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Appropriation to statutory reserve
|
- | - | (193,656 | ) | - | 193,656 | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment
|
- | - | - | 2,305 | - | 44,057 | 46,362 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance, February 28, 2013 (unaudited)
|
$ | 41,200 | $ | 4,403,049 | $ | 1,740,611 | $ | 333,901 | $ | 193,656 | $ | 239,642 | $ | 6,952,059 | ||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
7
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
FOR THE NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013 AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
|
Nine Months Ended
|
||||||||
|
February 28,
|
February 29,
|
|||||||
|
2013
|
2012
|
|||||||
|
(U.S. $)
|
(U.S. $)
|
|||||||
|
Cash flows from operating activities:
|
||||||||
|
Net income (loss)
|
$ | 2,040,846 | $ | (57,985 | ) | |||
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash
|
||||||||
|
provided by (used in) operating activities:
|
||||||||
|
Depreciation
|
7,937 | 3,956 | ||||||
|
Deferred income taxes
|
(431,248 | ) | (19,328 | ) | ||||
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities:
|
||||||||
|
(Increase) decrease in prepaid expenses
|
(121,922 | ) | 4,163 | |||||
|
Increase in deferred revenue
|
1,741,050 | - | ||||||
|
Increase in income taxes payable
|
522,673 | - | ||||||
|
(Decrease) increase in accrued liabilities
|
(54,183 | ) | 5,678 | |||||
|
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities
|
3,705,153 | (63,516 | ) | |||||
|
Cash flows from investing activities:
|
||||||||
|
Purchase of equipment
|
(4,657 | ) | (30,535 | ) | ||||
|
Cash flows from financing activities:
|
||||||||
|
Repayment of stockholder loan
|
(47,994 | ) | - | |||||
|
Proceeds from stockholder loan
|
175,031 | - | ||||||
|
Net cash provided by financing activities
|
127,037 | - | ||||||
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash
|
18,790 | 136,202 | ||||||
|
Net change in cash
|
3,846,323 | 42,151 | ||||||
|
Cash, beginning
|
4,139,165 | 4,644,191 | ||||||
|
Cash, end
|
$ | 7,985,488 | $ | 4,686,342 | ||||
|
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information
|
||||||||
|
Cash paid for:
|
||||||||
|
Interest
|
$ | - | $ | - | ||||
|
Income taxes
|
$ | 564,536 | $ | - | ||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
8
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 1. ORGANIZATION
China Xuefeng Environmental Engineering Inc. (the “Company”), formerly known as NYC Moda Inc., was incorporated under the laws of the State of Nevada on March 30, 2011. Since its inception until the closing of the Exchange Agreement, the Company was a development-stage company in the business of distributing designer clothing and footwear from established brands to customers around the world.
On November 27, 2012, the Company filed a certificate of amendment to its articles of incorporation to change its name from “NYC Moda, Inc.” to “China Xuefeng Environmental Engineering Inc.” (the “Name Change”) and to initiate a 4-for-1 forward stock split (the “Forward Split”) of its outstanding shares of common stock. The effective dates of the Name Change and the Forward Split were December 14, 2012 and December 17, 2012, respectively. Upon the effectiveness of the Forward Split, the number of outstanding shares of the Company’s common stock increased from 10,300,000 to 41,200,000 shares. The effect of the stock split was applied retroactively to all the periods’ consolidated financial statements as if the current structure existed since the inception of the periods presented. The number of authorized shares of common stock remains at 75,000,000 shares.
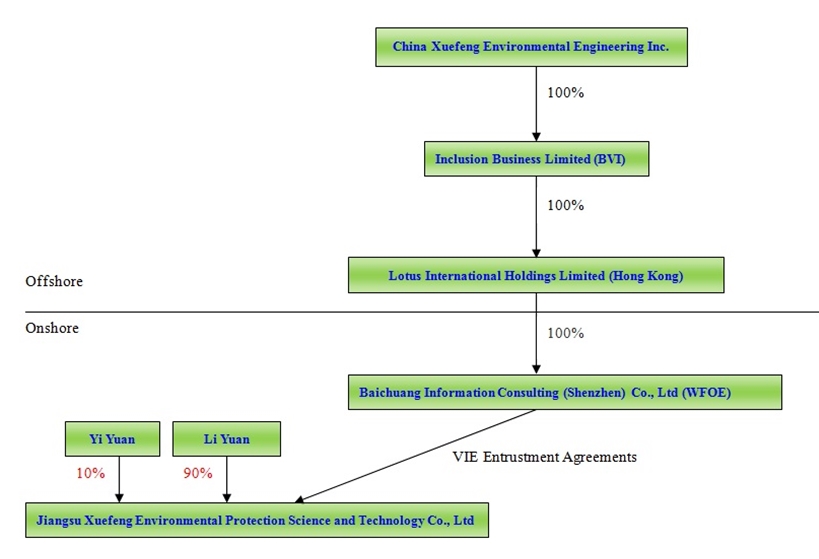
On November 27, 2012, the Company completed a reverse acquisition transaction through a share exchange with the stockholders of Inclusion Business Limited (“Inclusion”), whereby the Company acquired 100% of the outstanding shares of Inclusion in exchange for a total of 7,895,000 shares of its common stock, representing 76.65% of the issued and outstanding shares of common stock. As a result of the reverse acquisition, Inclusion became the Company’s wholly-owned subsidiary and the former Inclusion Stockholders became controlling stockholders. The share exchange transaction was treated as a reverse acquisition, with Inclusion as the acquirer and the Company as the acquired party for accounting purposes. Unless the context suggests otherwise, when being referred in this report to business and financial information for periods prior to the consummation of the reverse acquisition, the reference is to the business and financial information of Inclusion and its consolidated subsidiaries and variable interest entities.
As a result of the transaction with Inclusion, the Company owns all of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Lotus International Holdings Limited (“Lotus”), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Inclusion, which in turn owns all of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Baichuang Information Consulting (Shenzhen) Co. Ltd (“Baichuang Consulting”). In addition, the Company effectively and substantially controls Jiangsu Xuefeng Environmental Protection Science and Technology Co., Ltd. (“Jiangsu Xuefeng”) through a series of captive agreements with Baichuang Consulting.
Subsequent to the closing of the Exchange Agreement, the Company conducts its operations through its controlled consolidated affiliate Jiangsu Xuefeng. Jiangsu Xuefeng, incorporated under the laws of the People’s Republic of China (“PRC”) on December 14, 2007, is primarily engaged in providing improvement and upgrading services of garbage recycling processing technology and equipment.
On October 17, 2012, Baichuang Consulting (the “WFOE”), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Lotus, entered into a series of contractual arrangements (“VIE agreements”). The VIE agreements include (i) an Exclusive Technical Service and Business Consulting Agreement; (ii) a Proxy Agreement, (iii) Share Pledge Agreement and, (iv) Call Option Agreement with the stockholders of Jiangsu Xuefeng.
9
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 1. ORGANIZATION (CONTINUED)
Exclusive Technical Service and Business Consulting Agreement: Pursuant to the Exclusive Technical Service and Business Consulting Agreement, the WFOE provides technical support, consulting, training, marketing and operation consulting services to Jiangsu Xuefeng. In consideration for such services, Jiangsu Xuefeng has agreed to pay an annual service fee to the WFOE of 95% of Jiangsu Xuefeng’s annual net income with an additional payment of approximately US$15,800 (RMB 100,000) each month. The Agreement has an unlimited term and only can be terminated upon written notice agreed to by both parties.
Proxy Agreement: Pursuant to the Proxy Agreement, the stockholders of Jiangsu Xuefeng agreed to irrevocably entrust the WFOE to designate a qualified person acceptable under PRC law and foreign investment policies, all of the equity interests in Jiangsu Xuefeng held by the stockholders of Jiangsu Xuefeng. The Agreement has an unlimited term and only can be terminated upon written notice agreed to by both parties.
Share Pledge Agreement: Pursuant to the Share Pledge agreement, each of the stockholders pledged their shares in Jiangsu Xuefeng, to the WFOE, to secure their obligations under the Exclusive Technical Service and Business Consulting Agreement. In addition, the stockholders of Jiangsu Xuefeng agreed not to transfer, sell, pledge, dispose of or create any encumbrance on their interests in Jiangsu Xuefeng that would affect the WFOE’s interests. This Agreement remains effective until the obligations under the Exclusive Technical Service and Business Consulting Agreement, Call Option Agreement and Proxy Agreement have been fulfilled or terminated.
Call Option Agreement: Pursuant to the Call Option agreement, the WFOE has an exclusive option to purchase, or to designate a purchaser, to the extent permitted by PRC law and foreign investment policies, part or all of the equity interests in Jiangsu Xuefeng held by each of the stockholders. To the extent permitted by PRC laws, the purchase price for the entire equity interest is approximately US$0.16 (RMB1.00) or the minimum amount required by PRC law or government practice. This Agreement remains effective until all the call options under the Agreement have been transferred to Baichuang Consulting or its designated entities or natural persons.
As a result of the entry into the foregoing agreements, the Company has a corporate structure which is set forth below:
10
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 1. ORGANIZATION (CONTINUED)
NOTE 2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
BASIS OF ACCOUNTING AND PRESENTATION
Pursuant to Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 810, “Consolidation” (“ASC 810”), the Company is required to include in its consolidated financial statements the financial statements of its variable interest entities (“VIEs”). ASC 810 requires a VIE to be consolidated by a company if that company is subject to a majority of the risk of loss for the VIE or is entitled to receive a majority of the VIE’s residual returns. VIEs are those entities in which a company, through contractual arrangements, bears the risk of, and enjoys the rewards normally associated with ownership of the entity, and therefore the company is the primary beneficiary of the entity.
Through the VIE agreements disclosed in Note 1, the Company is deemed the primary beneficiary of Jiangsu Xuefeng. Accordingly, the results of Jiangsu Xuefeng have been included in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. The following financial statement amounts and balances of Jiangsu Xuefeng have been included in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. Jiangsu Xuefeng has no assets that are collateral for or restricted solely to settle their obligations. The creditors of Jiangsu Xuefeng do not have recourse to the Company’s general credit.
11
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
BASIS OF ACCOUNTING AND PRESENTATION (CONTINUED)
|
ASSETS
|
February 28,
2013
|
May 31,
2012
|
||||||
|
(Unaudited, in U.S. $)
|
(In U.S. $)
|
|||||||
|
Current assets:
|
||||||||
|
Cash
|
$ | 7,956,386 | $ | 4,120,811 | ||||
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets
|
127,792 | 5,870 | ||||||
|
Total current assets
|
8,084,178 | 4,126,681 | ||||||
|
Fixed assets
|
38,748 | 33,799 | ||||||
|
Less: accumulated depreciation
|
14,449 | 6,434 | ||||||
|
Fixed assets, net
|
24,299 | 27,365 | ||||||
|
Other assets:
|
||||||||
|
Prepayment for acquisition of land use right
|
795,000 | 788,532 | ||||||
|
Deferred income taxes
|
435,263 | 2,632 | ||||||
|
Total other assets
|
1,230,263 | 791,164 | ||||||
|
TOTAL ASSETS
|
$ | 9,338,740 | $ | 4,945,210 | ||||
|
LIABILITIES
|
||||||||
|
Current liabilities:
|
||||||||
|
Payable to WFOE(1)
|
1,086,984 | - | ||||||
|
Deferred revenue
|
1,741,050 | - | ||||||
|
Income taxes payable
|
522,673 | - | ||||||
|
Loan from stockholder
|
96,706 | - | ||||||
|
Accrued liabilities
|
27,138 | 81,321 | ||||||
|
Total current liabilities
|
3,474,551 | 81,321 | ||||||
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES
|
$ | 3,474,551 | $ | 81,321 | ||||
|
(1)
|
Payable to WFOE represents outstanding amounts due to Baichuang Information Consulting (Shenzhen) Co. Ltd. under the Exclusive Technical Service and Business Consulting Agreement for consulting services provided to Jiangsu Xuefeng in exchange for 95% of Jiangsu Xuefeng’s net income and additional monthly payments of RMB 100,000 (approximately US$15,800).
|
12
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
BASIS OF ACCOUNTING AND PRESENTATION (CONTINUED)
| For the three months ended
(Unaudited)
|
For the nine months ended
(Unaudited)
|
|||||||||||||||
| February 28, | February 29, | February 28, | February 29, | |||||||||||||
| 2013 | 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Revenue
|
$ | 1,311,705 | $ | - | $ | 3,463,225 | $ | - | ||||||||
|
Net income (2)
|
653,793 | (17,591 | ) | 1,768,039 | (57,985 | ) | ||||||||||
|
(2)
|
Under the Exclusive Technical Service and Business Consulting Agreement, 95% of the net income is to be remitted to WFOE.
|
|
For the nine months ended
(Unaudited)
|
||||||||
|
February 28,
|
February 29,
|
|||||||
|
2013
|
2012
|
|||||||
|
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities
|
$ | 3,704,199 | $ | (63,519 | ) | |||
|
Net cash (used in) investing activities
|
(4,657 | ) | (30,535 | ) | ||||
|
Net cash provided by financing activities
|
96,131 | - | ||||||
The unaudited financial statements for the three and nine months ended February 28, 2013, include China Xuefeng Environmental Engineering Inc., Inclusion, Lotus and its wholly owned subsidiary, Baichuang Consulting and its VIE, Jiangsu Xuefeng. The unaudited financial statements for the three and nine months ended February 29, 2012, include Lotus and its wholly owned subsidiary, Baichuang Consulting and its VIE, Jiangsu Xuefeng for comparative purpose only, as Inclusion was not in existence at that time. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation when applicable.
The Company believes that Baichuang Consulting’s contractual agreements with Jiangsu Xuefeng are in compliance with PRC law and are legally enforceable. The stockholders of Jiangsu Xuefeng are also the senior management of the Company and therefore the Company believes that they have no current interest in seeking to act contrary to the contractual arrangements. However, Jiangsu Xuefeng and its stockholders may fail to take certain actions required for the Company’s business or to follow the Company’s instructions despite their contractual obligations to do so. Furthermore, if Jiangsu Xuefeng or its stockholders do not act in the best interests of the Company under the contractual arrangements and any dispute relating to these contractual arrangements remains unresolved, the Company will have to enforce its rights under these contractual arraignments through PRC law and courts and therefore will be subject to uncertainties in the PRC legal system. All of these contractual arrangements are governed by PRC law and provide for the resolution of disputes through arbitration in the PRC. Accordingly, these contracts would be interpreted in accordance with PRC law and any disputes would be resolved in accordance with PRC legal procedures.
13
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
BASIS OF ACCOUNTING AND PRESENTATION (CONTINUED)
As a result, uncertainties in the PRC legal system could limit the Company’s ability to enforce these contractual arrangements, which may make it difficult to exert effective control over Jiangsu Xuefeng, and its ability to conduct the Company’s business may be adversely affected.
Under ASC 810, an enterprise has a controlling financial interest in a VIE, and must consolidate that VIE, if the enterprise has both of the following characteristics: (a) the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly affect the VIE’s economic performance; and (b) the obligation to absorb losses, or the right to receive benefits, that could potentially be significant to the VIE. The enterprise’s determination of whether it has this power is not affected by the existence of kick-out rights or participating rights. Jiangsu Xuefeng’s actual stockholders do not hold any kick-out rights that will affect the consolidation determination.
The unaudited interim consolidated financial statements of the Company as of February 28, 2013 and for the three and nine month periods ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012, have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America and the rules and regulations of the SEC which apply to interim financial statements. Accordingly, they do not include all of the information and footnotes normally required by accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America for annual financial statements. In the opinion of management, such information contains all adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments, necessary for a fair presentation of the results for the periods presented. The interim consolidated financial information should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto, included in the Company’s Form 8-K filed with the SEC. The results of operations for the three and nine months ended February 28, 2013 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for future quarters or for the year ending May 31, 2013.
All consolidated financial statements and notes to the consolidated financial statements are presented in United States dollars (“US Dollar” or “US$” or “$”).
USE OF ESTIMATES
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect certain reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSLATION
Almost all Company assets are located in the PRC. The functional currency for the majority of the Company’s operations is the Renminbi (“RMB”). The Company uses the United States dollar (“US Dollar” or “US$” or “$”) for financial reporting purposes. The financial statements of the Company have been translated into US dollars in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 830, “Foreign Currency Matters.”
14
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSLATION (CONTINUED)
All asset and liability accounts have been translated using the exchange rate in effect at the balance sheet date. Equity accounts have been translated at their historical exchange rates when the capital transactions occurred. Statements of operations amounts have been translated using the average exchange rate for the periods presented. Adjustments resulting from the translation of the Company’s financial statements are recorded as other comprehensive income (loss).
The exchange rates used to translate amounts in RMB into US dollars for the purposes of preparing the financial statements are as follows:
|
February 28,
2013
|
May 31,
2012
|
February 29,
2012
|
||||||||||
|
Balance sheet items, except for stockholders’ equity, as of year or period end
|
0.1590 | 0.1577 | N/A | |||||||||
|
Amounts included in the statements of operations, statements of changes in stockholders’ equity and statements of cash flows for the period
|
0.1585 | N/A | 0.1565 | |||||||||
For the three months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012, foreign currency translation adjustments of ($11,017) and $51,518 have been reported as other comprehensive income (loss). For the nine months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012, foreign currency translation adjustments of $44,057 and $127,370 have been reported as other comprehensive income.
Although government regulations now allow convertibility of the RMB for current account transactions, significant restrictions still remain. Hence, such translations should not be construed as representations that the RMB could be converted into US dollars at that rate or any other rate.
The value of the RMB against the US dollar and other currencies may fluctuate and is affected by, among other things, changes in the PRC’s political and economic conditions. Any significant revaluation of the RMB may materially affect the Company’s financial condition in terms of US dollar reporting.
REVENUE RECOGNITION
Revenues are primarily derived from providing garbage recycling processing system technology support, renovation and upgrade services and patent licensing to its customers. The Company’s revenue recognition policies comply with FASB ASC 605 “Revenue Recognition.” In general, the Company recognizes revenue when there is persuasive evidence of an arrangement, the fee is fixed or determinable, the products or services have been delivered or performed and collectability of the resulting receivable is reasonably assured.
15
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
REVENUE RECOGNITION (CONTINUED)
Multiple-Element Arrangements
In October 2009, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2009-13, “Multiple Deliverable Revenue Arrangements.” ASU No. 2009-13 amended the guidance on arrangements with multiple deliverables under ASC 605-25, “Revenue Recognition—Multiple-Element Arrangements.”
To qualify as a separate unit of accounting under ASC 605-25, the delivered item must have value to the customer on a standalone basis. The significant deliverables under the Company’s multiple-element arrangements are improvement and upgrade services and patent licensing.
Improvement and Upgrade Service
The improvement and upgrade service is a one-time service. An inspection is conducted by the customer according to industry standards within three days of the completion of the improvement and upgrade. An acceptance form is provided by the customer if the inspection is satisfactory. Performance testing is conducted on the upgraded equipment for no more than one month. Testing can be done in less than a month period. A final evaluation report is provided within five days of the completion of the performance testing. The fee for improvement and upgrade services is fixed and becomes due within 30 days, upon the signing of the contract and is not subject to refund, forfeiture or any other concession if patent licensing is not completed. No warranty is provided by the Company.
Patent Licensing
Patent licensing is limited to 5 years with payments due annually in advance. The Company is responsible for the repair services when they are necessary. The out of pocket expenses for the repair services will be charged separately to the customer by the Company. The patent technology of “harmless and comprehensive garbage processing equipment” provided by the Company to its customers has high garbage processing capacity and stable operation capacity. It is the first modern system equipment in China to use DCS (Distributed Control System) centralized control, by which mechanical automation will be realized for the comprehensive treatment of life garbage. Its core technology is to organically integrate the anaerobic digestion and aerobic fermentation garbage process, degrade and transform the organic matter of domestic waste, effectively sort out the garbage and recycle all kinds of materials, to eventually realize the true waste resource utilization and harmless utilization, with its resource utilization and harmless utilization rate approximate 100%. The resource recovery products, biogas, not only can be used for meeting the needs of the plant itself, but also can be sold as a separate product, which greatly improves the efficiency of garbage processing of customer’s equipment, decreases production cost, and increases the recovery return of garbage processing.
16
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
REVENUE RECOGNITION (CONTINUED)
Patent Licensing (Continued)
The Company’s customer who pays for an upgrade and improvement fee is not required to enter into a licensing agreement to continue to use the patented technology. If the customer does not require the garbage process equipment to reach the level of the patented technology which can process 500 tons to 1,000 tons of garbage per day, then the customer does not need to enter into the patent licensing agreement.
The Company determined that its improvement and upgrade service is individually a separate unit of accounting. In determining whether the improvement and upgrade service has a standalone value, the Company considered factors including the availability of similar services from other vendors, its fee structure based on inclusion and exclusion of the service, and its marketing and delivery of the service. The Company uses the vendor-specific objective evidence to determine the selling price for its improvement and upgrade service when sold in multiple-element arrangements. Although not yet being sold separately, the price established by the management has the relevant authority.
The Company also determined that the patent licensing has standalone value because the patent can be leased separately. The Company uses the vendor-specific objective evidence to determine the selling price for patent licensing when sold in multiple-element arrangements. Although not yet being leased separately, the price established by the management has the relevant authority.
The Company allocates the arrangement consideration based on their relative selling prices. Revenues for deliverables under improvement and upgrade service are recognized by the end of the improvement and upgrade period at the time the performance testing is passed and the final evaluation report is provided by the customer, which generally is within 30 days, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met. Revenues for deliverables under patent licensing are recognized monthly over the leasing period.
The Company believes the effect of changes in the selling price for improvement and upgrade services and patent licensing will not have significant effect on the allocation of the arrangement.
VULNERABILITY DUE TO OPERATIONS IN PRC
The Company’s operations may be adversely affected by significant political, economic and social uncertainties in the PRC. Although the PRC government has been pursuing economic reform policies for more than twenty years, no assurance can be given that the PRC government will continue to pursue such policies or that such policies may not be significantly altered, especially in the event of a change in leadership, social or political disruption or unforeseen circumstances affecting the PRC’s political, economic and social conditions. There is also no guarantee that the PRC government’s pursuit of economic reforms will be consistent, effective or continue.
17
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
FASB ASC 820, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures,” specifies a hierarchy of valuation techniques based upon whether the inputs to those valuation techniques reflect assumptions other market participants would use based upon market data obtained from independent sources (observable inputs). In accordance with ASC 820, the following summarizes the fair value hierarchy:
|
|
Level 1 Inputs – Unadjusted quoted market prices for identical assets and liabilities in an active market that the Company has the ability to access.
|
|
|
Level 2 Inputs – Inputs other than the quoted prices in active markets that are observable either directly or indirectly.
|
|
|
Level 3 Inputs – Inputs based on prices or valuation techniques that are both unobservable and significant to the overall fair value measurements.
|
ASC 820 requires the use of observable market data, when available, in making fair value measurements. When inputs used to measure fair value fall within different levels of the hierarchy, the level within which the fair value measurement is categorized is based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurements. Valuation techniques used need to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs.
The Company did not identify any assets or liabilities that are required to be presented at fair value on a recurring basis. Non-derivative financial instruments include cash, payables and accrued liabilities. As of February 28, 2013 and May 31, 2012, the carrying values of these financial instruments approximated their fair values due to their short term nature.
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS
The Company considers all demand and time deposits and all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE
Accounts receivable are recorded at the contract amount after deduction of trade discounts, allowances, if any, and do not bear interest. The allowance for doubtful accounts, when necessary, is the Company’s best estimate of the amount of probable credit losses of accounts receivable. The Company determines the allowance based on historical write-off experience, customer specific facts and economic conditions.
Account balances are charged off against the allowance after all means of collection have been exhausted and the potential for recovery is considered remote. The Company does not have any off-balance-sheet credit exposure related to its customers. As of February 28, 2013 and May 31, 2012, the Company did not have any accounts receivable. For the periods presented, the Company did not write off any accounts receivable as bad debts.
18
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
FIXED ASSETS
Fixed assets are recorded at cost, less accumulated depreciation. Cost includes the prices paid to acquire the assets, and any expenditure that substantially increase the asset’s value or extends the useful life of an existing asset. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Major repairs and betterments that significantly extend original useful lives or improve productivity are capitalized and depreciated over the periods benefited. Maintenance and repairs are generally expensed as incurred.
The estimated useful lives for fixed assets categories are as follows:
|
Computers and equipment
|
3 years
|
|
Fixtures and furniture
|
5 years |
DEFERRED REVENUE
Deferred revenue includes payments received for a) improvement and upgrade services and b) patent licensing fees. These payments received but not yet earned are recognized as deferred revenue on the consolidated balance sheets.
INCOME TAXES
The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with FASB ASC 740, “Income Taxes” (“ASC 740”), which requires the recognition of deferred income taxes for differences between the basis of assets and liabilities for financial statement and income tax purposes. Deferred tax assets and liabilities represent the future tax consequences for those differences, which will either be taxable or deductible when the assets and liabilities are recovered or settled. At February 28, 2013, the differences relate entirely to revenue deferred for financial statement purpose. Deferred taxes are also recognized for operating losses that are available to offset future taxable income. Deferred tax assets at May 31, 2012 consisted entirely of the tax benefit of net operating losses that were available to offset future taxable income. A valuation allowance is established when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
ASC 740 addresses the determination of whether tax benefits claimed or expected to be claimed on a tax return should be recorded in the financial statements. Under ASC 740, the Company may recognize the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position only if it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position. The tax benefits recognized in the financial statements from such a position would be measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. ASC 740 also provides guidance on de-recognition of income tax assets and liabilities, classification of current and deferred income tax assets and liabilities, and accounting for interest and penalties associated with tax positions. As of February 28, 2013 and May 31, 2012, the Company does not have a liability for any unrecognized tax benefits.
19
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
ADVERTISING COSTS
Advertising costs are charged to operations when incurred. For the three and nine months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012, advertising expense was $23,775 and $0, respectively.
STATUTORY RESERVE FUND
Pursuant to corporate law of the PRC, the Company is required to transfer 10% of its net income, as determined under PRC accounting rules and regulations, to a statutory reserve fund until such reserve balance reaches 50% of the Company’s registered capital. The statutory reserve fund is non-distributable other than during liquidation and can be used to fund previous years’ losses, if any, and may be utilized for business expansion or used to increase registered capital, provided that the remaining reserve balance after such use is not less than 25% of the registered capital. For the nine months ended February 29, 2012, the Company was not required to fund the statutory reserve fund as the Company had an accumulated deficit. For the nine months ended February 28, 2013, a statutory reserve of $193,656 was required to be funded by the Company.
NOTE 3. RECENTLY ISSUED ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
In July 2012, The FASB has issued ASU No. 2012-02, “Intangibles--Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Testing Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets for Impairment.” This ASU states that an entity has the option first to assess qualitative factors to determine whether the existence of events and circumstances indicates that it is more likely than not that the indefinite-lived intangible asset is impaired. If, after assessing the totality of events and circumstances, an entity concludes that it is not more likely than not that the indefinite-lived intangible asset is impaired, then the entity is not required to take further action. However, if an entity concludes otherwise, then it is required to determine the fair value of the indefinite-lived intangible asset and perform the quantitative impairment test by comparing the fair value with the carrying amount in accordance with Codification Subtopic 350-30, “Intangibles--Goodwill and Other, General Intangibles Other than Goodwill.”
Under the guidance in this ASU, an entity also has the option to bypass the qualitative assessment for any indefinite-lived intangible asset in any period and proceed directly to performing the quantitative impairment test. An entity will be able to resume performing the qualitative assessment in any subsequent period.
The amendments in this ASU are effective for annual and interim impairment tests performed for fiscal years beginning after September 15, 2012. Early adoption is permitted, including for annual and interim impairment tests performed as of a date before July 27, 2012, if a public entity’s financial statements for the most recent annual or interim period have not yet been issued or, for nonpublic entities, have not yet been made available for issuance. The Company does not believe that the adoption of this pronouncement will have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
20
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 3. RECENTLY ISSUED ACCOUNTING STANDARDS (CONTINUED)
In October 2012, the FASB issued ASU 2012-04, “Technical Corrections and Improvements.” ASU 2012-04 contains amendments to clarify the ASC, correct unintended application of guidance, or make minor improvements to the ASC that are not expected to have a significant effect on current accounting practice or create a significant administrative cost to most entities. Additionally, the amendments are intended to make the ASC easier to understand and the fair value measurement guidance easier to apply by eliminating inconsistencies and providing needed clarifications. The amendments that do not have transition guidance were effective upon issuance. The amendments that are subject to the transition guidance will be effective for fiscal periods beginning after December 15, 2012. The Company does not believe that the adoption of this pronouncement will have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
In February 2013, the FASB issued ASU 2013-02, “Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reporting of Amounts Reclassified out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income.” ASU 2013-02 requires an entity to report the effect of significant reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive income on the respective line items in net income if the amount being reclassified is required to be reclassified in its entirety to net income. For other amounts that are not required to be reclassified in their entirety to net income in the same reporting period, an entity is required to cross-reference other disclosures that provide additional detail about those amounts. The amendments do not change the current requirements for reporting net income or other comprehensive income in financial statements. For public entities, the amendments are effective prospectively for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2012. Early adoption is permitted. The Company does not believe that the adoption of this pronouncement will have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
NOTE 4. FIXED ASSETS
Fixed assets are summarized as follows:
|
February 28,
2013
|
May 31,
2012
|
|||||||
|
(U.S. $)
|
(U.S. $)
|
|||||||
|
Computers and equipment
|
$ | 25,883 | $ | 21,039 | ||||
|
Fixtures and furniture
|
12,865 | 12,760 | ||||||
| 38,748 | 33,799 | |||||||
|
Less: Accumulated depreciation
|
(14,449 | ) | (6,434 | ) | ||||
| $ | 24,299 | $ | 27,365 | |||||
For the three months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012, depreciation expense was $2,796 and $2,380, respectively. For the nine months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012, depreciation expense was $7,937 and $3,956, respectively.
21
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 5. PREPAYMENT FOR ACQUISITION OF LAND USE RIGHT
On March 23, 2012, the Company entered into an agreement with a PRC owned third party to acquire a 50-year land use right for construction of a factory facility for cash consideration of US$858,600, equivalent to RMB 5,400,000, of which US$ 795,000, equivalent to RMB 5,000,000 was paid before February 28, 2013. As of February 28, 2013, the land used right had not been obtained and no certificate for the use of land had been issued to the Company.
The agreement provides terms that under certain circumstances, such as delay in construction, the Company may be subject to a penalty of up to 20% of the payment for the land use right, or forfeiture of the land use right.
NOTE 6. ACCRUED LIABILITIES
Accrued liabilities consisted of the following:
|
February 28,
2013
|
May 31,
2012
|
|||||||
|
(U.S. $)
|
(U.S. $)
|
|||||||
|
Payroll
|
$ | 14,138 | $ | 10,995 | ||||
|
Professional fees
|
13,000 | 70,000 | ||||||
|
Other
|
- | 326 | ||||||
| $ | 27,138 | $ | 81,321 | |||||
NOTE 7. INCOME TAXES
The provision for (benefit from) income taxes consisted of the following:
|
For the three months ended
|
For the nine months ended
|
|||||||||||||||
|
February 28
|
February 29
|
February 28
|
February 29
|
|||||||||||||
|
2013
|
2012
|
2013
|
2012
|
|||||||||||||
|
(U.S. $)
|
(U.S. $)
|
(U.S. $)
|
(U.S. $)
|
|||||||||||||
|
Current
|
$ | 676,003 | $ | - | $ | 1,085,146 | $ | - | ||||||||
|
Deferred
|
(433,889 | ) | (5,863 | ) | (431,248 | ) | (19,328 | ) | ||||||||
| $ | 242,144 | $ | (5,863 | ) | $ | 653,898 | $ | (19,328 | ) | |||||||
The Company’s tax filings are subject to examination by the tax authorities in the PRC. Tax filings for the tax year ended December 31, 2011 were examined by the tax authorities in April 2012. The tax filings were accepted and no adjustments were proposed by the tax authorities.
22
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 8. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTION
On August 5, 2012, the Company entered into an agreement to lease the rights of patent on garbage recycling processing technology from Li Yuan, one of the Company’s officers/stockholders. Under the current terms, the Company is required to pay a fee of $12,680 (RMB 80,000) each month for five years from September 2012 to August 2017. As of February 28, 2013, a prepaid patent leasing fee of $127,200 is included in prepaid expenses on the consolidated balance sheets.
The remaining payments for the patent rights not paid as of February 28, 2013 are as follows:
|
Period Ending
|
Annual
|
|||
|
May 31,
|
Amount
|
|||
|
2013
|
$ | - | ||
|
2014
|
63,400 | |||
|
2015
|
152,160 | |||
|
2016
|
152,160 | |||
|
2017
|
152,160 | |||
|
Thereafter
|
38,040 | |||
|
|
||||
| $ | 557,920 | |||
The Company obtained a demand loan from the above officer/stockholder which is non-interest bearing. The loan of approximately $96,000 representing expenses paid by the above officer/stockholder and approximately $79,000 representing the registered capital and operating expenses of Baichuang Information Consulting (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd. (“Baichuang Consulting”) for the nine months ended February 28, 2013. As of February 28, 2013, Baichuang Consulting repaid approximate $48,000 to the above officer/stockholder. The net balance is reflected as loan from stockholder as of February 28, 2013.
NOTE 9. LEASES
The Company leases office space under a one-year operating lease from an unrelated third party, which expired on March 31, 2013 and was extended to March 31, 2016. The lease requires the Company to prepay the rental for one year of $7,048 (RMB44,664). The related prepayments of $592 and $5,870 are included in the prepaid expenses on the consolidated balance sheets as of February 28, 2013 and May 31, 2012, respectively. The lease provides for renewal options. Rent expense charged to operations for the three and nine months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012 was $1,762 and $5,286, respectively. The minimum future rentals under the lease as February 28, 2013 are as follows:
23
CHINA XUEFENG ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE AND NINE MONTHS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2013
AND FEBRUARY 29, 2012 (UNAUDITED)
NOTE 9. LEASES (CONTUNUED)
|
Period Ending
|
Annual
|
|||
|
May 31,
|
Amount
|
|||
|
2013
|
$ | 21,252 | ||
|
2014
|
85,008 | |||
|
2015
|
85,008 | |||
|
2016
|
70,840 | |||
|
|
||||
| $ | 262,108 | |||
NOTE 10. CONCENTRATION OF CREDIT RISK
Substantially all of the Company’s assets and bank accounts are in banks located in the PRC and are not covered by protection similar to that provided by the FDIC on funds held in United States banks.
The following table represents certain information about the Company’s customers which individually accounted for more than 10% of the Company’s gross revenue during the periods indicated:
|
For the three months ended
|
For the nine months ended
|
|||||||||||||||
|
February 28, 2013
|
February 28, 2013
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Amount
|
%
|
Amount
|
%
|
|||||||||||||
|
CUSTOMER 1
|
500,850 | 28.02 | % | 499,275 | 12.68 | % | ||||||||||
|
CUSTOMER 2
|
524,700 | 29.36 | % | 523,050 | 13.28 | % | ||||||||||
|
CUSTOMER 3
|
548,550 | 30.69 | % | 546,825 | 13.88 | % | ||||||||||
|
CUSTOMER 4
|
548,550 | 30.69 | % | 546,825 | 13.88 | % | ||||||||||
|
CUSTOMER 5
|
* | 618,150 | 15.69 | % | ||||||||||||
|
CUSTOMER 6
|
* | 570,600 | 14.49 | % | ||||||||||||
*Less than 10% of total sales for the three months ended February 28, 2013.
NOTE 11. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On March 19, 2013, the Company completed a closing of a private offering (the “Offering”) of shares of the Company’s common stock, par value $0.001 per share (the “Shares”), at a price of $0.50 per share, for an aggregate purchase price of $7,000,000. Upon the closing, the Company issued 14,000,000 shares of its common stock pursuant to the Offering. The Shares were offered and sold to the subscribers in the Offering pursuant to a subscription agreement dated March 18, 2013.
24
Item 2. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
The following discussion of our financial condition and results of operations should also be read in conjunction with our unaudited consolidated financial statements and the notes to those financial statements appearing elsewhere in this Form 10-Q. The following discussion contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933 and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 relating to future events or our future performance. Actual results may materially differ from those projected in the forward-looking statements as a result of certain risks and uncertainties set forth in this Form 10-Q. Although management believes that the assumptions made and expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, there is no assurance that the underlying assumptions will, in fact, prove to be correct or that actual results will not be different from expectations expressed in this report.
Overview
We are in the business of providing services to optimize garbage-recycling processes. We utilize our patented technology of “comprehensive and harmless garbage-processing equipment”, to upgrade software systems and reconstruct hardware for our clients, and therefore expand the sorting scope and capacity of our clients’ garbage recycling equipment. We conduct our operations through our controlled consolidated affiliate Jiangsu Xuefeng Environmental Protection Science and Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as “Jiangsu Xuefeng”). Jiangsu Xuefeng was incorporated under the laws of the People’s Republic of China (“PRC”) on December 14, 2007.
Our Services
With the development of the urbanization in China, the amount of household garbage is growing, whereas the processing capability of garbage processing equipment cannot satisfy the demand. In order to resolve the defects of the processing equipment of other garbage processing plants, we provide upgrades and improvement to the software systems and hardware equipment by installing the various systems of patented technology “comprehensive and harmless garbage-processing equipment” into customers’ equipment, and reconstructing the hardware to expand the garbage sorting scope and capacity of our clients’ equipment.
The Patent technology of “harmless and comprehensive garbage processing equipment” provided by Jiangsu Xuefeng to its customers has high garbage processing capacity and stable operation capacity. It is the first modern system equipment in China to use DCS (Distributed Control System) centralized control, by which mechanical automation will be realized for the comprehensive treatment of life garbage. Its core technology is to organically integrate the anaerobic digestion and aerobic fermentation garbage process, degrade and transform the organic matter of domestic waste, effectively sort out the garbage and recycle all kinds of materials, to eventually realize the true waste resource utilization and harmless utilization, with its resource utilization and harmless utilization rate approximate 100%. The resource recovery products, biogas, can not only be used for meeting the needs of the plant itself, but also for outer supply, which greatly improves the efficiency of garbage processing of customer’s equipment, decreases production cost, and increases the recovery return of garbage processing.
The comprehensive and harmless garbage processing equipment is comprised of waste digestion pretreatment system, methane gas power generation system, sorting processing system, bricklaying building system, leachate treatment system, DCS (distribution control system), XFET-5 ecological and water-saving toilets and excrement comprehensive processing system and various material collection systems. The equipment technology is designed and manufactured based on the complicated situation of the household garbage in China. According to the features of various garbage, the equipment utilizes the wind-force, gravity, magnetic, shape and etc to process the garbage by the combined way of machine selecting, winnowing, magnetic separation, automatic cutting, smashing and other technological processes. The equipment has large processing capacity and could run whole day. The stand-alone equipment can process 500 tons to 1000 tons of garbage per day. It can sort and process complicated municipal solid waste, leaving no pollution and no residue, reaching the"3 without" standard of no waste gas, no waste water and no waste residue.
25
After we complete the internal system upgrade and hardware equipment improvement of the garbage equipment, we deliver the upgraded equipment to the customers. The customers will conduct inspection and performance testing to the upgraded equipment no more than one month pursuant to the contract to inspect whether the internal control system and the hardware structure can operate steadily and reach the garbage process features. The inspecting items including the following: whether the quality of the equipment and accessories after improvement can match the patented technology and process various kinds of garbage, whether the various garbage systems can process automatically, and whether the daily garbage processing capacity reaches the standard of the contract. If during the performance testing period, all the performance index can fulfill the requirements of the contract, it would be deemed that we have fully executed the agreements.
Prior to the first service agreement in April 2012, we did not conduct any business activities except for the preparation of the business and the development of the clients, etc. When we complete the upgrading service for the client, we go through the acceptance check and commissioning of the company in accordance with the contract, to make sure that the service provided met the demand of the clients. After that, we are not subject to any additional service. The revenue we generated belongs to the service class income, with the main cost being the salaries of the staff and the leasing fees for the patent, whereas the hardware and software equipment, as well as the material used in the upgrading are the responsibility of the clients.
Recent Developments
Acquisition of Inclusion Business Limited (“Inclusion”)
The Company was organized in the state of Nevada on March 30, 2011. The Company was initially created to engage in the business of clothing distribution. Since its inception, the Company was a development stage company and has not earned any revenue.
On November 27, 2012, we completed a reverse acquisition transaction through a share exchange with Inclusion and its stockholders, or the “Inclusion Stockholders”, whereby we acquired 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Inclusion in exchange for our issuance of 7,895,000 shares of our common stock (pre-Forward Split), which constituted 76.65% of our issued and outstanding capital stock as of and immediately after the consummation of the reverse acquisition. As a result of the reverse acquisition, Inclusion became our wholly-owned subsidiary and the former Inclusion Stockholders became our controlling stockholders. The share exchange transaction has been treated as a reverse acquisition, with Inclusion as the acquirer and the Company as the acquired party for accounting purposes.
Prior to the closing of the reverse acquisition, the Company’s prior shareholder, Mr. Zhenxing Liu, surrendered 7,895,000 shares of the common stock of the Company. Mr. Zhenxing Liu did not receive any consideration from the Company for accounting purposes. However, Mr. Zhenxing Liu may be deemed to have received consideration from the increase in the value of 250,000 shares held by Mr. Zhenxing Liu as a result of the reverse acquisition. Mr. Zhenxing Liu purchased 8,145,000 shares at approximately $0.007 per share at the time when the Company was considered a shell and kept 250,000 shares after the surrender. On November 30, 2012, at the closing of the reverse acquisition, the stockholder’s equity increased to $5,194,728. Accordingly, the value of the 250,000 shares held by Mr. Zhenxing Liu appreciated to approximately $124,673. Other than such appreciation in the value of his shares, Mr. Zhenxing Liu did not receive any other consideration in connection with the reverse acquisition.
As a result of our acquisition of Inclusion, we now own all of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Lotus International Holdings Limited (“Lotus”), which in turn owns all of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Baichuang Information Consulting (Shenzhen) Co. Ltd (“Baichuang Consulting”). In addition, we effectively and substantially control Jiangsu Xuefeng through a series of captive agreements with Baichuang Consulting.
26
Subsequent to the closing of the Exchange Agreement, we conduct our operations through our controlled consolidated affiliate Jiangsu Xuefeng. Jiangsu Xuefeng is primarily engaged in providing improvement and upgrading services of garbage recycling processing technology and equipment.
Name Change and Forward Stock Split
In connection with the acquisition of Inclusion, on November 27, 2012, the Company filed a certificate of amendment to its articles of incorporation to change its name from “NYC Moda, Inc.” to “China Xuefeng Environmental Engineering Inc.” (the “Name Change”) and effectuate a 4-for-1 forward stock split (the “Forward Split”) of its outstanding shares of common stock. The effective dates of the Name Change and the Forward Split were December 14, 2012 and December 17, 2012, respectively. Upon the effectiveness of the Forward Split, the number of outstanding shares of the Company’s common stock increased from 10,300,000 to 41,200,000 shares. The effect of the stock split was applied retroactively to all the periods’ consolidated financial statements as if the current structure existed since inception of the periods presented. The number of authorized shares of common stock remains at 75,000,000 shares.
Private Offering
On March 19, 2013, we completed a closing of a private offering (the “Offering”) of shares of the Company’s common stock, par value $0.001 per share (the “Shares”), at a price of $0.50 per share, for an aggregate purchase price of $7,000,000 (the “Purchase Price”). Upon the closing, the Company issued 14,000,000 shares of its common stock pursuant to the Offering.
Results of Operations
Comparison of Three Months and Nine Months Ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012
The following table sets forth in U.S. dollars key components of our unaudited results of operations during the three-month and nine-month periods ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012, and the percentage change between 2013 and 2012.
Three months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012
|
2013
|
2012
|
Percentage
|
||||||||||
|
(U.S. $)
|
(U.S. $)
|
Change
|
||||||||||
|
Revenue
|
$
|
1,311,705
|
$
|
-
|
100
|
%
|
||||||
|
Cost of revenue
|
(114,941
|
)
|
-
|
100
|
%
|
|||||||
|
Gross profit
|
1,196,764
|
-
|
100
|
%
|
||||||||
|
Selling expenses
|
28,405
|
3,660
|
676
|
%
|
||||||||
|
General and administrative expenses
|
154,248
|
21,248
|
626
|
%
|
||||||||
|
Total operating expenses
|
182,653
|
24,908
|
633
|
%
|
||||||||
|
Operating income (loss)
|
1,014,111
|
(24,908
|
)
|
4171
|
%
|
|||||||
|
Interest income
|
2,074
|
1,454
|
43
|
%
|
||||||||
|
Income (loss) before provision for (benefit from) income taxes
|
1,016,185
|
(23,454
|
)
|
4433
|
%
|
|||||||
|
Provision for (benefit from) income taxes
|
242,144
|
(5,863
|
)
|
4230
|
%
|
|||||||
|
Net income (loss) before non controlling interests
|
774,041
|
(17,591
|
)
|
4500
|
%
|
|||||||
|
Noncontrolling interests
|
(36,322
|
)
|
880
|
(4228
|
%)
|
|||||||
|
Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders
|
737,719
|
(16,711
|
)
|
4515
|
%
|
|||||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment
|
(11,017)
|
51,518
|
(121
|
%)
|
||||||||
|
Total comprehensive income
|
$
|
726,702
|
$
|
34,807
|
1988
|
%
|
||||||
27
Nine months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012
|
2013
|
2012
|
Percentage
|
||||||||||
|
(U.S. $)
|
(U.S. $)
|
Change
|
||||||||||
|
Revenue
|
$
|
3,463,225
|
$
|
-
|
100
|
%
|
||||||
|
Cost of revenue
|
(400,174
|
)
|
-
|
(100
|
%)
|
|||||||
|
Gross profit
|
3,063,051
|
-
|
100
|
%
|
||||||||
|
Selling expenses
|
37,612
|
6,620
|
468
|
%
|
||||||||
|
General and administrative expenses
|
335,782
|
75,180
|
347
|
%
|
||||||||
|
Total operating expenses
|
373,394
|
81,800
|
356
|
%
|
||||||||
|
Operating income (loss)
|
2,689,657
|
(81,800
|
)
|
3388
|
%
|
|||||||
|
Interest income
|
5,087
|
4,487
|
13
|
%
|
||||||||
|
Income (loss) before provision for (benefit from) income taxes
|
2,694,744
|
(77,313
|
)
|
3585
|
%
|
|||||||
|
Provision for (benefit from) income taxes
|
653,898
|
(19,328
|
)
|
3483
|
%
|
|||||||
|
Net income (loss) before non controlling interests
|
2,040,846
|
(57,985
|
)
|
3620
|
%
|
|||||||
|
Noncontrolling interests
|
(88,402
|
)
|
2,899
|
(2858
|
%)
|
|||||||
|
Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders
|
1,952,444
|
(55,086
|
)
|
3149
|
%
|
|||||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment
|
44,057
|
127,370
|
(65
|
%)
|
||||||||
|
Total comprehensive income
|
$
|
1,996,501
|
$
|
72,284
|
2662
|
%
|
||||||
Revenue. We provide improvement and upgrading service for the garbage processing equipment to our customers. This is a one-time service. We also lease the patent to our customers. The patent licensing is limited to 5 years with payments due annually in advance.
For the three months ended February 28, 2013, sales related to improvement and upgrading services provided to garbage recycling processing systems of two unrelated third parties in accordance with contracts for a total of $954,900. The services were completed and accepted by the customers and the payment was received in full as of February 28, 2013. For the three months ended February 28, 2013, the patent licensing revenue was generated from six unrelated third parties in accordance with the contracts for a total of $356,805.
For the nine months ended February 28, 2013, sales related to improvement and upgrading services provided to garbage recycling processing systems of seven unrelated third parties in accordance with contracts for a total of $3,011,500. The services were completed and accepted by the customers and the payment was received in full as of February 28, 2013. For the nine months ended February 28, 2013, the patent licensing revenue was generated from six unrelated third parties in accordance with the contracts for a total of $451,725.
28
Both for the three and nine months ended February 29, 2012, there was no revenue generated.
Cost of Revenues. Our cost of revenues increased to $114,941 and $400,174 for the three and nine months ended February 28, 2013, respectively, from $0 for the three and nine months ended February 29, 2012. The increase in cost of revenues is attributable to the increase in revenues. Our costs of revenues primarily consist of leasing fees of the related party for the patent, employees’ salaries, insurance, training expenses and other daily operating expenses. In addition, business taxes were classified as cost of sales as well before December 1, 2012. Under China tax law, our business tax should be changed to value added tax after December 1, 2012 but we are exempt from the VAT under the authorization from local tax bureau.
Gross Profit. Our gross profit increased to $1,196,764 and 3,063,051 for the three and nine months ended February 28, 2013, respectively, which represented a gross profit ratio at 91% and 88%, respectively. The reason the increase in gross profit ratio is because of the exemption from VAT as we mentioned above.
There was no gross profit for the three and nine months ended February 29, 2012 as our operations had not commenced yet.
Selling and Marketing Expenses. Our selling and marketing expenses increased to $28,405 and $37,612 for the three and nine months ended February 28, 2013, respectively, from $3,660 and $6,620 for the three and nine months ended February 29, 2012, respectively, which represented an increase by 676% and 468%, respectively. Our selling and marketing expenses were primarily comprised of sales employees’ salary and insurance and advertising expenses. The increase in selling and marketing expenses was mainly due to the increase in number of sales employees.
General and Administrative Expenses. Our general and administrative (“G&A”) expenses increased to $154,248 and $335,782 for the three and nine months ended February 28, 2013, respectively, from $21,248 and $75,180 for the three and nine months ended February 29, 2012, respectively, representing a 626% and 347% increase, respectively. Our G&A expenses were primarily comprised of G&A employees’ salaries, insurance, rent and professional fees incurred for G&A functions. As we are listed in the United States, expenses incurred for attorneys, auditors and financial advisors increased as well.
Provision for (benefit from) Income Taxes. Our provision for income taxes increased to $242,144 and $653,898 for the three and nine months ended February 28, 2013, respectively, from a tax benefit of $5,863 and $19,328 for the three and nine months ended February 29, 2012, respectively. Our effective tax rate was the same as the statutory rate of 25% for the three and nine months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012. Our tax filings for the year ended December 31, 2011 were examined by the tax authorities in April 2012. The tax filings were accepted and no adjustments were proposed by the tax authorities. The increase in the provision for income taxes was primarily due to the increase in our income.
Net Income. For the three months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012, we generated net income (loss) of $774,041 and ($17,591), respectively. This represented an increase in net income of $791,632 or 4,500%. For the nine months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012, we generated net income (loss) of $2,040,846 and ($57,985), respectively. This represented an increase in net income of $2,098,831 or 3,620%. The entrusted management agreements assign to Baichuang Consulting only 95% of the income generated from Jiangsu Xuefeng. For that reason, we reflected a “non-controlling interest” of $36,322 and ($800) for the three months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012, respectively, and $88,402 and ($2,899) for the nine months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012, respectively, before recognizing net income attributable to the Company on our Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income. After that deduction and taking into account the income and expenses incurred by the parent corporation, our net income (loss) attributable to the Company for the three and nine months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012 was $737,791 and ($16,711), representing $0.02 and ($0.00) per share, respectively, and $1,952,444 and ($55,086), representing $0.05 and ($0.00) per share, respectively.
29
Foreign Currency Translation Adjustment. Our reporting currency is the U.S. dollar. Our local currency, Renminbi (RMB), is our functional currency. Results of operations and cash flows are translated at average exchange rates during the period, and assets and liabilities are translated at the unified exchange rate as quoted by the People’s Bank of China at the end of the period. Translation adjustments resulting from this process are included in accumulated other comprehensive income in the statement of stockholders’ equity. Transaction gains and losses that arise from exchange rate fluctuations on transactions denominated in a currency other than the functional currency are included in the results of operations as incurred. For the three and nine months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012, a foreign currency gain (loss) of ($11,017) and $51,518, respectively, and $44,057 and $127,370, respectively, have been reported as other comprehensive income in the consolidated statements of income and other comprehensive income.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of February 28, 2013, we had cash and cash equivalents of $7,985,488, primarily consisting of cash on hand and demand deposits. The cash balance was principally derived from Jiangsu Xuefeng’s capital contributions received of $4,541,532 since January 2011 and cash collection of our revenue. Despite our large cash balances, the interest income generated for the period are nominal for principally two reasons: the bank’s current deposit interest is very low, the annual interest rates float up or down at 0.35%; The interest income reported on the statement is the net interest which was deducted bank services charges, legal person overdraft fees. The legal person overdraft fee was calculated as 2% of overdraft limit. For the nine months ended February 28, 2013, the total legal person overdraft fee was $8,559. As the amount involved is nominal, there is no separate disclosure.
To date, we have financed our operations primarily through cash flows from operations and equity contributions by our stockholders.
Operating activities
Net cash provided by operating activities was $3,705,153 for the nine months ended February 28, 2013 as compared to net cash used for $63,516 for the nine months ended February 29, 2012. The changes are mainly due to the increase in our net profit, cash received in advance from customers and an increase in income tax payable.
Investing activities
Net cash used for investing activities represented the purchase of equipment. For the nine months ended February 28, 2013 and February 29, 2012, the purchase of equipment was $4,657 and $30,535, respectively.
Financing activities
For the nine months ended February 28, 2013, the net cash provided by financing activities consists of the repayment of the stockholder loan of $47,994 and proceeds from the stockholder loan of $175,031. The proceeds from the stockholder loan were paid for overseas professional services and the register of Baichuang Consulting due to Chinese banks’ restriction of cash transfers.
We believe that our cash on hand and cash flows from operations will meet our present cash needs for the next 12 months.
We may, however, in the near future, require additional cash resources due to changed business conditions, implementation of our strategy to ramp up our marketing efforts and increase brand awareness, or acquisitions we may decide to pursue. If our own financial resources are insufficient to satisfy our capital requirements, we currently may seek to sell additional equity or debt securities or obtain additional credit facilities. The sale of additional equity securities could result in dilution to our stockholders. New indebtedness would result in increased debt service obligations and could require us to agree to operating and financial covenants that could restrict our operations. Financing may not be available in amounts or on terms acceptable to us, if at all. Any failure by us to raise additional funds on terms favorable to us, or at all, could limit our ability to expand our business operations and could harm our overall business prospects.
30
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not have any off-balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
Transfer of Cash
All of our business operations are carried out by Jiangsu Xuefeng, our variable interest entity in China. PRC regulations restrict the ability to make dividends and other payments to its offshore parent company. In the future, in order for the U.S. parent corporation to pay dividends to our shareholders from the earnings obtained in China, we will have to transfer funds from Jiangsu Xuefeng to Baichuang Consulting, our Chinese subsidiary, and then to China Xuefeng Environmental Engineering, our U.S. parent corporation. Any limitations on the ability of our PRC subsidiary to transfer funds could materially and adversely limit our ability to grow, make investments or acquisitions that could be beneficial to our business, pay dividends and otherwise fund and conduct our business. Our ability to transfer funds from Baichuang Consulting to China Xuefeng Environmental Engineering Inc. will be limited by two factors as follows:
Statutory Reserves. The Company Law of the PRC applicable to Chinese companies with foreign ownership provides that net income can be distributed as dividends only after: (i) cumulative prior years’ losses have been recouped; (ii) 10% of after tax income has been allocated to a statutory surplus reserve until the reserve amounts to 50% of the company’s registered capital; and (iii) allocations have been made to the discretionary surplus reserve, if such a reserve is approved at the meeting of the equity owners. Allocations to this statutory reserve fund can only be used for specific purposes and are not transferable to us in the form of loans, advances or cash dividends.
Currency Conversion. The Chinese Yuan (Renminbi) is not freely convertible into US Dollars. The State Administration of Foreign Exchange (“SAFE”) administers foreign exchange dealings and requires that they shall be conducted though designated financial institutions. Foreign Invested Enterprises, such as Baichuang Consulting, may purchase foreign currency from designated financial institutions in connection with current account transactions, including profit repatriation. However, the procedures required in order to effect such purchases can significantly delay a transfer of funds to the U.S.
These factors will limit the amount of funds that we can transfer from Baichuang Consulting to our U.S. parent company and may delay any such transfer, with resulting effect on the ability of the U.S. parent to pay dividends to its shareholders.
Lotus International Holdings Limited, a Hong Kong corporation and Baichuang Information Consulting (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd, a WFOE, is a bridge to transfer funds inside and outside the PRC. There are three ways for foreign cash to be transferred into Chinese subsidiaries:
31
(1) Capital funds: At the establishment of the WFOE, (Baichuang Consulting), in accordance with the provisions of PRC Foreign-Owned Enterprise Law, funds were injected as capital by Lotus International into its wholly foreign owned enterprise established in mainland China, Baichuang Consulting.
(2) Raised capital - acquisition: if the Company raised sufficient capital, it could transfer the capital to Jiangsu Xuefeng by causing Lotus International (HK company) to apply to the Chinese Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM) for approval of an acquisition of Jiangsu Xuefeng by Lotus International. MOFCOM would approve such an acquisition only after a lengthy review process, and only if it determined that the price paid by Lotus International for Jiangsu Xuefeng represented a commercially fair price.
(3) Raised capital - joint venture: If the Company obtained capital that was less than the purchase price for Jiangsu Xuefeng deemed acceptable by MOFCOM, Lotus International could still inject the funds into Jiangsu Xuefeng by complying with the provisions of the PRC Sino-Foreign Equity Joint Venture Law. To accomplish this capital transfer, we would be required to apply to the Chinese government for approval to convert Jiangsu Xuefeng into an equity joint venture, in which Lotus International (HK company) would be its equity joint venturer. If approved, Lotus International would then own a portion of the equity in Jiangsu Xuefeng, and the VIE agreements between Jiangsu Xuefeng and Baichuang Consulting (WFOE) would be modified accordingly to reduce the portion of net income payable by Jiangsu Xuefeng to Baichuang Consulting.
We have no current plans for the Company to fund Jiangsu Xuefeng, and expect the VIE structure to remain in place for the foreseeable future.
Pursuant to the Exclusive Technical Service and Business Consulting Agreement between Baichuang Consulting (WFOE) and Jiangsu Xuefeng, Baichuang Consulting is to provide technical support and consulting services to Jiangsu Xuefeng in exchange for (i) 95% of the total annual net income of Jiangsu Xuefeng and (ii) RMB100,000 per month (US$15,870). As a result, there are also two ways to transfer the funds from inside the PRC to outside the PRC:
(1) According to the provisions of the Service Fee in Article 3 of the Exclusive Technology Service and Business Consulting Agreement, 95% of the net income of Jiangsu Xuefeng will be paid to Baichuang Consulting as a service fee, and in turn Baichuang Consulting will in compliance with the provisions of PRC Foreign-Owned Enterprise Law transfer this income to Lotus International (HK company) for the purpose of profit distribution.
(2) According to the provisions of the Service Fee in Article 3 of the Exclusive Technology Service and Business Consulting Agreement, a management fee of $15,870 will be paid to Baichuang Consulting each month, and in turn Baichuang Consulting will be in compliance with the provisions of the PRC Foreign-Owned Enterprise Law and transfer this income to Lotus International (HK company) for the purpose of profit distribution.
The earnings and cash transfer procedures are all designed to comply with PRC regulations. As a result, there will be no government regulations which will impact our transactions to transfer cash within our corporate structure. It should be noted, however, that to date Jiangsu Xuefeng has not made any payment to Baichuang Consulting, despite the provisions of the VIE agreements that promise 95% of net profits to Baichuang Consulting. The amount due from Jiangsu Xuefeng to Baichuang Consulting has been recorded on their inter-company accounts as a payable due to Baichuang Consulting; however no interest or penalty or other compensation is being accrued as a result of the failure of Jiangsu Xuefeng to make the payments due. Rather, it is management’s plan for the foreseeable future that Jiangsu Xuefeng will make payments to Baichuang Consulting to the extent necessary for Baichuang Consulting to pay its ongoing expenses, and may also make payment to Baichuang Consulting to pay the expenses of our U.S. parent company if we find that procedure more convenient than borrowing dollars from related parties. Jiangsu Xuefeng will retain all other income to fund the growth of Jiangsu Xuefeng.
When the funds are transferred to outside the PRC, all transferred amounts will be reported to the national tax bureau to examine whether the local and national taxes have been fully paid by Jiangsu Xuefeng and Baichuang Consulting. If Baichuang Consulting obtained the revenue from Jiangsu Xuefeng, then Baichuang Consulting has to be subject to 5% business tax and 25% income tax.
Finally, it should be noted that, upon repatriation of earnings of Baichuang Consulting to the United States, those earnings may become subject to United States federal and state income taxes. We have not accrued any U.S. federal or state tax liability on the undistributed earnings of our foreign subsidiary because those funds are intended to be indefinitely reinvested in our international operations. Accordingly, taxes imposed upon repatriation of those earnings to the U.S. may reduce the net worth of the Company.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In July 2012, The FASB issued ASU No. 2012-02, “Intangibles--Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Testing Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets for Impairment.” This ASU states that an entity has the option first to assess qualitative factors to determine whether the existence of events and circumstances indicates that it is more likely than not that the indefinite-lived intangible asset is impaired. If, after assessing the totality of events and circumstances, an entity concludes that it is not more likely than not that the indefinite-lived intangible asset is impaired, then the entity is not required to take further action. However, if an entity concludes otherwise, then it is required to determine the fair value of the indefinite-lived intangible asset and perform the quantitative impairment test by comparing the fair value with the carrying amount in accordance with Codification Subtopic 350-30, “Intangibles--Goodwill and Other, General Intangibles Other than Goodwill.”
32
Under the guidance in this ASU, an entity also has the option to bypass the qualitative assessment for any indefinite-lived intangible asset in any period and proceed directly to performing the quantitative impairment test. An entity will be able to resume performing the qualitative assessment in any subsequent period.
The amendments in this ASU are effective for annual and interim impairment tests performed for fiscal years beginning after September 15, 2012. Early adoption is permitted, including for annual and interim impairment tests performed as of a date before July 27, 2012, if a public entity’s financial statements for the most recent annual or interim period have not yet been issued or, for nonpublic entities, have not yet been made available for issuance. The Company does not believe that the adoption of this pronouncement will have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
In October 2012, the FASB issued ASU 2012-04, “Technical Corrections and Improvements.” ASU 2012-04 contains amendments to clarify the ASC, correct unintended application of guidance, or make minor improvements to the ASC that are not expected to have a significant effect on current accounting practice or create a significant administrative cost to most entities. Additionally, the amendments are intended to make the ASC easier to understand and the fair value measurement guidance easier to apply by eliminating inconsistencies and providing needed clarifications. The amendments that do not have transition guidance were effective upon issuance. The amendments that are subject to the transition guidance will be effective for fiscal periods beginning after December 15, 2012. The Company does not believe that the adoption of this pronouncement will have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
In February 2013, the FASB issued ASU 2013-02, “Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reporting of Amounts Reclassified out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income.” ASU 2013-02 requires an entity to report the effect of significant reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive income on the respective line items in net income if the amount being reclassified is required to be reclassified in its entirety to net income. For other amounts that are not required to be reclassified in their entirety to net income in the same reporting period, an entity is required to cross-reference other disclosures that provide additional detail about those amounts. The amendments do not change the current requirements for reporting net income or other comprehensive income in financial statements. For public entities, the amendments are effective prospectively for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2012. Early adoption is permitted. The Company does not believe that the adoption of this pronouncement will have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012
On April 5, 2012, the JOBS Act was signed into law. The JOBS Act contains provisions that, among other things, reduce certain reporting requirements for qualifying public companies. As an “emerging growth company,” we may, under Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act, delay adoption of new or revised accounting standards applicable to public companies until such standards would otherwise apply to private companies. We may take advantage of this extended transition period until the first to occur of the date that we (i) are no longer an "emerging growth company" or (ii) affirmatively and irrevocably opt out of this extended transition period. We have elected to take advantage of the benefits of this extended transition period. Our financial statements may therefore not be comparable to those of companies that comply with such new or revised accounting standards. Until the date that we are no longer an "emerging growth company" or affirmatively and irrevocably opt out of the exemption provided by Securities Act Section 7(a)(2)(B), upon issuance of a new or revised accounting standard that applies to our financial statements and that has a different effective date for public and private companies, we will disclose the date on which adoption is required for non-emerging growth companies and the date on which we will adopt the recently issued accounting standard.
Item 3. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
Smaller reporting companies are not required to provide the information required by this item.
33
Item 4. Controls and Procedures.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Pursuant to Rule 13a-15(b) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (“Exchange Act”), the Company carried out an evaluation, with the participation of the Company’s management, including the Company’s Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”) (the Company’s principal financial and accounting officer), of the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as defined under Rule 13a-15(e) under the Exchange Act) as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based upon that evaluation, for the reasons set forth below, the Company’s CEO and CFO concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures are not effective as of February 28, 2013to ensure that information required to be disclosed by the Company in the reports that the Company files or submits under the Exchange Act, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to the Company’s management, including the Company’s CEO and CFO, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the Company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. In its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of February 28, 2013, the Company determined that there were control deficiencies that constituted the following material weaknesses:
|
●
|
The Company does not have a sufficient number of accounting personnel, which would provide segregation of duties within our internal control procedures to support the accurate and timely reporting of our financial results.
|
|
●
|
The Company’s current accounting personnel lack experience and knowledge in identifying and resolving complex accounting issues under U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
|
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
No change in our system of internal control over financial reporting occurred during the period covered by this report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
From time to time, we may become involved in litigation relating to claims arising out of its operations in the normal course of business. We are not involved in any pending legal proceeding or litigation and, to the best of our knowledge, no governmental authority is contemplating any proceeding to which we are a party or to which any of our properties is subject, which would reasonably be likely to have a material adverse effect on us.
None.
34
None.
Not applicable.
None.
|
Exhibit No.
|
Description
|
|
| 2.1 | Share Exchange Agreement dated as of November 27, 2012, by and among NYC Moda Inc., Inclusion Business Limited, the shareholders of Inclusion Business Limited, and Zhenxing LIU, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 3, 2013. | |
|
10.1
|
Subscription Agreement dated March 19, 2013, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 21, 2013.
|
|
|
31.1
|
Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 *
|
|
|
31.2
|
Certification of Principal Financial Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 *
|
|
|
32.1
|
Certification of Principal Executive Officer of the Company, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 **
|
|
|
32.2
|
Certification of Principal Financial Officer of the Company, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 **
|
|
|
101.INS
|
XBRL Instance Document †
|
|
|
101.SCH
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document †
|
|
|
101.CAL
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document †
|
|
|
101.DEF
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document †
|
|
|
101.LAB
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document †
|
|
|
101.PRE
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document †
|
|
|
*
|
Filed herewith.
|
|
|
**
|
In accordance with SEC Release 33-8238, Exhibits 32.1 and 32.2 are furnished and not filed.
|
|
|
†
|
Furnished herewith. XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language) information is furnished and not filed or a part of a registration statement or prospectus for purposes of Sections 11 or 12 of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, is deemed not filed for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and otherwise is not subject to liability under these sections.
|
35
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, there unto duly authorized.
|
China Xuefeng Environmental Engineering Inc.
|
|||
|
Date: April 22, 2013
|
By:
|
/s/ Li Yuan
|
|
|
Li Yuan
|
|||
|
Chief Executive Officer
|
|||
|
(Duly Authorized Officer and Principal Executive Officer)
|
|||
|
Date: April 22, 2013
|
By:
|
/s/ Kuanfu Fan
|
|
|
Kuanfu Fan
|
|||
|
Chief Financial Officer
(Duly Authorized Officer and Principal Financial Officer)
|
|||
36
