Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 - Integrity Applications, Inc. | v238113_ex23-1.htm |
| EX-10.12 - EXHIBIT 10.12 - Integrity Applications, Inc. | v238113_ex10-12.htm |
As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on October 26, 2011
Registration No. 333-176415
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, DC 20549
AMENDMENT NO. 2
TO
FORM S-1/A
REGISTRATION STATEMENT
UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
Integrity Applications, Inc.
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in Its Charter)
|
Delaware
|
3841
|
98-0668934
|
||
|
(State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation
|
(Primary Standard Industrial Classification
|
(I.R.S. Employer Identification
|
||
|
or Organization)
|
Code Number)
|
Number)
|
|
Integrity Applications, Inc.
102 Ha’Avoda St.
Ashkelon, Israel
972 (8) 675-7878
|
|
(Address, Including Zip Code, and Telephone Number, Including Area Code, of Registrant’s Principal Executive Offices)
|
|
Avner Gal
Chief Executive Officer
Integrity Applications, Inc.
P.O. Box 432
Ashkelon 78100, Israel
972 (8) 675-7878
972 (8) 675-7850 (facsimile)
|
|
(Name, Address, Including Zip Code, and Telephone Number, Including Area Code, of Agent For Service)
|
|
Copies to :
Robert L. Grossman, Esq.
Greenberg Traurig, P.A.
333 Avenue of the Americas, Suite 4400
Miami, FL 33131
(305) 579-0500
(305) 579-0717 (facsimile)
|
Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale to the public: From time to time after the effective date of this registration statement.
If any of the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933 check the following box: x
If this Form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, please check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
|
¨ Large accelerated filer
|
¨ Accelerated filer
|
|
¨ Non-accelerated filer (Do not check if a smaller reporting company)
|
x Smaller reporting company
|
CALCULATION OF REGISTRATION FEE
|
Title of Each Class of Securities To Be Registered
|
Amount To Be
Registered(1)
|
Proposed
Maximum Offering
Price Per Share
|
Proposed Maximum
Aggregate Offering
Price
|
Amount Of
Registration Fee
|
||||||||||||
|
Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share
|
1,295,545
|
$
|
6.25
|
(2)
|
$
|
8,097,156.25
|
$
|
940.08
|
(3)
|
|||||||
|
(1)
|
Pursuant to Rule 416 of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, this Registration Statement also registers such additional shares of common stock as may become issuable to prevent dilution as a result of stock splits, stock dividends or similar transactions.
|
|
(2)
|
The selling stockholders may sell their shares of the registrant’s common stock at a fixed price of $6.25 per share (the offering price per share of common stock in the registrant’s most recent private placement completed in July 2011) until shares of the registrant’s common stock are quoted on the OTC Bulletin Board, and thereafter at prevailing market prices or privately negotiated prices. The registrant’s common stock is presently not traded on any market or securities exchange, and the registrant has not applied for listing or quotation on any public market.
|
|
(3)
|
Estimated solely for the purpose of calculating the amount of the registration fee in accordance with Rule 457(o) under the Securities Act.
|
The registrant hereby amends this Registration Statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the Registrant shall file a further amendment which specifically states that this Registration Statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or until the Registration Statement shall become effective on such date as the Securities and Exchange Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may determine.
The information in this prospectus is not complete and may be changed. The selling stockholders may not sell these securities until the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities and it is not soliciting offers to buy these securities in any state where the offer or sale is not permitted.
Subject to Completion, dated October 26, 2011
1,295,545 Shares

Common Stock
This prospectus relates to the resale by selling stockholders named herein of up to an aggregate of 1,295,545 shares of common stock, par value $0.001 per share, of Integrity Applications, Inc. The shares of common stock being offered by the selling stockholders hereunder were acquired by the selling stockholders in a private placement, which was commenced on July 26, 2010 and consisted of seven closings held on December 16, 2010, December 30, 2010, January 31, 2011, March 31, 2011, April 29, 2011, May 31, 2011 and July 29, 2011, respectively. There is no relationship between Integrity Applications, Inc., the registrant under the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part, and Integrity Applications, Incorporated, the engineering and software services company based in Chantilly, Virginia.
There is no public market for our common stock. We intend to seek a qualification for our common stock to be quoted on the Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board; however, no assurance can be given as to our success in qualifying for quotation on the OTCBB. The selling stockholders may sell their shares of our common stock at a fixed price of $6.25 per share (the offering price per share of common stock in our most recent private placement completed in July 2011) until our common stock is quoted on the OTCBB, and thereafter in a variety of transactions as described under the heading “Plan of Distribution” beginning on page 76, including transactions on any stock exchange, market or facility on which our common stock may be traded, in privately negotiated transactions or otherwise at market prices prevailing at the time of sale, at prices related to such market prices or at negotiated prices. We have no basis for estimating either the number of shares of our common stock that will ultimately be sold by the selling stockholders or the prices at which such shares will be sold (unless sold at a fixed price, as described above).
All of the shares of common stock are being sold by the selling stockholders named in this prospectus. We will not receive any of the proceeds from the sale of the shares of common stock being sold by the selling stockholders. We are bearing all of the expenses in connection with the registration of the shares of common stock, but all selling and other expenses incurred by the selling stockholders, including commissions and discounts, if any, attributable to the sale or disposition of the shares will be borne by them.
You should read this prospectus, the applicable prospectus supplement, if any, and other offering materials carefully before you invest.
An investment in our common stock involves substantial risks. See “Risk Factors” beginning on page 7 of this prospectus.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any other regulatory body has approved or disapproved of these securities or passed upon the accuracy or adequacy of this prospectus. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
The date of this prospectus is , 2011.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Prospectus
|
Page
|
||||
|
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
|
1 | |||
|
SUMMARY
|
2 | |||
|
RISK FACTORS
|
7 | |||
|
USE OF PROCEEDS
|
25 | |||
|
DIVIDEND POLICY
|
25 | |||
|
DETERMINATION OF OFFERING PRICE
|
25 | |||
|
DILUTION
|
25 | |||
|
CAPITALIZATION
|
26 | |||
|
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
|
27 | |||
|
BUSINESS
|
33 | |||
|
PRINCIPAL AND SELLING STOCKHOLDERS
|
55 | |||
|
MANAGEMENT
|
61 | |||
|
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS
|
66 | |||
|
DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES
|
68 | |||
|
FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSEQUENCES
|
72 | |||
|
PLAN OF DISTRIBUTION
|
76 | |||
|
LEGAL MATTERS
|
77 | |||
|
EXPERTS
|
77 | |||
|
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
|
78 | |||
|
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
F-1 | |||
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This prospectus includes forward-looking statements. These forward looking statements include statements about our expectations, beliefs or intentions regarding our product development efforts, business, financial condition, results of operations, strategies or prospects. All statements other than statements of historical fact included in this prospectus, including statements regarding our future activities, events or developments, including such things as future revenues, product development, market acceptance, responses from competitors, capital expenditures (including the amount and nature thereof), business strategy and measures to implement strategy, competitive strengths, goals, expansion and growth of our business and operations, plans, references to future success, projected performance and trends, and other such matters, are forward-looking statements. The words “believe,” “expect,” “intend,” “anticipates,” or “propose,” and other similar words and phrases, are intended to identify forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements made in this prospectus are based on certain historical trends, current conditions and expected future developments as well as other factors we believe are appropriate in the circumstances. These statements relate only to events as of the date on which the statements are made and we undertake no obligation to update publicly any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law. All of the forward-looking statements made in this prospectus are qualified by these cautionary statements and there can be no assurance that the actual results anticipated by us will be realized or, even if substantially realized, that they will have the expected consequences to or effects on us or our business or operations. Whether actual results will conform to our expectations and predictions is subject to a number of risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially. Risks and uncertainties, the occurrence of which could adversely affect our business, include the risks identified in this prospectus under the caption “Risk Factors” beginning on page 7.
1
SUMMARY
This summary highlights information contained elsewhere in this prospectus. This summary is not complete and does not contain all of the information that you should consider before deciding to invest in our common stock. You should read this entire prospectus, including the section entitled “Risk Factors,” and our financial statements and the notes thereto before deciding to invest in our common stock. Unless the context otherwise requires, the terms “we”, “our”, “ours” and “us”, refer to A.D. Integrity Applications, Ltd., an Israeli corporation, which we refer to as Integrity Israel, for all periods prior to July 15, 2010 and to Integrity Israel and Integrity Applications, Inc., a Delaware corporation, which we refer to as Integrity U.S., on a combined basis, for all periods from and including July 15, 2010.
Our Company
Overview
We are a development stage medical device company focused on the design, development and commercialization of non-invasive glucose monitoring devices for use by persons suffering from diabetes. Our wholly-owned subsidiary, Integrity Israel, was founded in 2001 with a mission to develop, produce and market non-invasive glucose monitors for home use by diabetics. We have developed a non-invasive blood glucose monitor, the GlucoTrack® glucose monitoring device, which is designed to help people with diabetes obtain blood glucose level readings without the pain, inconvenience, cost and difficulty of conventional (invasive) spot finger stick devices. The GlucoTrack DF-F utilizes a patented combination of ultrasound, electromagnetic and thermal technologies to obtain blood glucose measurements in less than one minute via a small sensor that is clipped onto one’s earlobe and connected to a small, handheld control and display unit, all without drawing blood. Integrity Israel conducted pre-clinical trials involving over 5,000 readings from approximately 350 patients over the last seven years. Clinical data collected during 2009 at the Soroka University Medical Center in Be’er Sheva, Israel indicate a positive correlation between GlucoTrack DF-F readings and those obtained from conventional invasive devices. More specifically, a set of pre-clinical trials conducted on 89 patients of various weights, ages, diabetes types and genders involved 1,772 measurements, of which 96% were within the clinically acceptable zones (zones A and B) of the Clarke Error Grid, which we refer to as the CEG. Similarly, approximately 90% of the measurements in an at home study of four participants were within clinically acceptable zones A and B of the CEG. Measurements are clinically acceptable, as compared to a referenced invasive device, when the variance, if any, between the devices would have no worse than a benign effect on the patients. These pre-clinical trials involved small patient populations. Because of the small sample size, the results of these pre-clinical trials may not be indicative of future results. Analyses from the at home study show that there are a few parameters that reduce accuracy, such as the learning curve, the use of a home use device as a reference, failure to properly follow instructions for use, including use of the reference (invasive) device, and the variability of the ambient temperature in a given testing environment. We have already made some modifications to the GlucoTrack DF-F to limit the effect of these parameters and further modifications are in process, including the addition of a sensor to gauge the ambient temperature in the testing environment, and modifications to the software utilized by the GlucoTrack device to take the ambient temperature into account in determining the patient’s blood glucose level. While we believe that these modifications will improve the results of the GlucoTrack device, no assurance can be given as to the extent (if any) to which these modifications will improve the effectiveness of the device. We believe that the results of the home study show that with some modifications to the GlucoTrack DF-F, we will be able to improve the accuracy and reliability measurements of glucose levels in the home and home-like environments. We expect to begin the performance and safety stage of formal clinical trials in Israel and Europe by the second quarter of 2012 and, expect to begin clinical trials in the United States by late 2012, if our clinical trial protocol is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The GlucoTrack DF-F has not yet been approved for commercial sale in the United States, the European Union or any other jurisdiction. See “Business - Government Regulation - Regulation of the Design, Manufacture and Distribution of Medical Devices” below for a discussion of the approval process for commercial sale. There can be no assurance that approval for commercial sale in any jurisdiction will be obtained. We have not yet generated any revenues from our operations and have incurred losses of $2,788,446 during the year ended December 31, 2010 and $516,657 during the six months ended June 30, 2011.
Recent Developments
Reorganization
On July 15, 2010, Integrity U.S., Integrity Israel, and Integrity Acquisition Corp. Ltd., an Israeli corporation, completed a reverse triangular merger, which we refer to as the reorganization, pursuant to which Integrity Acquisition merged with and into Integrity Israel and all of the stockholders and option holders of Integrity Israel became entitled to receive shares and options in Integrity U.S. in exchange for their shares and options in Integrity Israel. Following the reorganization, the former equity holders of Integrity Israel received the same proportional ownership in Integrity U.S. as they had in Integrity Israel prior to the reorganization. As a result of the reorganization, Integrity Israel became a wholly owned subsidiary of Integrity U.S. Pursuant to a tax ruling from the Israeli Tax Authorities, the former stockholders and options holders of Integrity Israel will be exempt from tax liability with respect to the reorganization until they sell their holdings in Integrity U.S. so long as they deposit all their shares and options with a trustee for a period of two years from the issuance of such shares or options, as applicable, in connection with the reorganization, give their written consent to the tax ruling and satisfy certain additional conditions detailed in the ruling. As a result, any of our stockholders that complies with this tax ruling will be unable to sell any of its shares of common stock of Integrity U.S. for such two year period (unless decided otherwise by the Israeli Tax Authorities). Approximately 82% of our stockholders at the time of the reorganization (holding 3,280,000 of 3,999,998 shares then outstanding) complied with the ruling.
2
Private Placement
On July 26, 2010, we commenced an offering of up to 2,000,000 shares of our common stock to accredited investors at a price of $6.25 per share in a private placement transaction. The private placement resulted in the sale by us of an aggregate of 1,295,545 shares of common stock in seven closings held on December 16, 2010, December 30, 2010, January 31, 2011, March 31, 2011, April 29, 2011, May 31, 2011 and July 29, 2011, respectively. Purchasers of common stock in the private placement are entitled to anti-dilution protection until September 1, 2012 for certain issuances of common stock by us for less than $6.25 per share. See “Description of Securities.”
In connection with the private placement, we agreed to issue to Andrew Garrett, Inc., the placement agent for the private placement, in partial consideration for its services as such, warrants to purchase a number of shares of common stock equal to 10% of the number of shares sold at such closing. In total, we issued to Andrew Garrett, Inc. warrants to purchase up to an aggregate of 129,556 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $6.25 per share in connection with each closing of the private placement. The warrants have a five year term expiring on the fifth anniversary of the date of effectiveness of this registration statement.
On December 16, 2010, we issued 259,185 shares of common stock to the holders of certain Senior Secured Promissory Notes issued by Integrity Israel in April 2010. Such issuance was made in accordance with the terms of the notes and was made in partial repayment of the aggregate outstanding principal amount thereof. Upon the issuance of the shares described above and the payment of any additional principal amount outstanding in cash, all of the Senior Notes were retired on December 16, 2010. Also on December 16, 2010, we issued 54,792 shares of common stock to the holders of certain Junior Promissory Notes issued by Integrity Israel in November 2010 in accordance with, and in full repayment of, such notes.
Stockholder Dispute
Integrity Israel is party to a loan and investment agreement dated February 18, 2003 with Y.H. Dimri Holdings, pursuant to which Dimri loaned Integrity Israel a principal amount of NIS 1,440,000 subject to linkage differences in Israel ($421,669 based on an exchange rate of $3.415 NIS/dollar as of June 30, 2011), which we refer to as the first phase loan. Upon completion of the development of the prototype of Integrity Israel’s monitoring device, Dimri could have advanced an additional loan to Integrity Israel in the amount of NIS 1,248,000 ($365,446 based on the same exchange rate), which we refer to as the second phase loan. In connection with the first phase loan, Dimri received shares of common stock representing 25% of Integrity Israel’s ordinary shares at such time. Under the investment agreement, certain rights in Integrity Israel were granted to Dimri, including an anti-dilution provision that provided that Dimri’s holdings in Integrity Israel would not be diluted below 18% of Integrity Israel’s issued capital shares as a result of any investment in Integrity Israel, subject to the fulfillment of certain requirements. On the date of the reorganization, Dimri owned 18% of Integrity Israel’s ordinary shares and, therefore, upon the completion of the reorganization, Dimri was entitled to receive 18% of the shares of common stock of the Company outstanding on such date in exchange for his shares in Integrity Israel, subject to the fulfillment of certain requirements. We believe, based on the advice of Israeli counsel, that, given Dimri no longer owns shares in Integrity Israel as a result of the reorganization, rights attached to the shares in Integrity Israel no longer exist in Integrity Israel and do not and have never existed in us. However, Dimri has refused to acknowledge or agree to the termination of these rights and has challenged our position. See “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” on page 66 for a further description of the Dimri agreement.
On June 23, 2011, Mr. Dimri appealed to the District Court of HaMerkaz District in Petah Tikva, Israel, requesting the court to appoint an arbitrator to decide the dispute between Integrity Israel, the founders of Integrity Israel and Dimri (HPB 40754-06-11). On September 25, 2011, Integrity Israel's counsel filed an answer with the Court, disputing the facts and allegation raised in Dimri's motion and suggesting choosing an arbitrator with certain capacities, experience and skills. At a hearing held on October 11, 2011, the court appointed an arbitrator in this matter. The proposed arbitrator is required to inform the court no later than November 1, 2011 if there is anything that will preclude his service as an arbitrator in this matter. If there is, an alternate arbitrator will be appointed by the court. It should be noted that, in accordance with Israeli law, Mr. Dimri was not required to, and he did not, specify in his request for the appointment of an arbitrator the relief to be sought by him in the arbitration. As a result, we do not yet know the relief to be sought by Mr. Dimri in the arbitration. We anticipate that Mr. Dimri will specify the relief sought by him after the commencement of the arbitration proceedings.
We do not know what other actions Mr. Dimri will ultimately bring, if any, and against whom they will brought. Nevertheless, we, our counsel and Integrity Israel’s counsel believe that we and Integrity Israel have defenses to any such claims and appropriate claims and counterclaims of our own and we intend to strongly defend against any such action by Mr. Dimri and to assert our own claims and counterclaims as we deem necessary.
3
Going Concern
We have not yet generated any revenues from our operations and have incurred accumulated losses and cumulative negative operating cash flow of $ 11,210,101 and $ 8,238,555, respectively, since September 30, 2001 (inception). We currently have no sources of recurring revenue and are therefore dependent upon external sources for financing our operations. There can be no assurance that we will succeed in obtaining the necessary financing to continue our operations. As a result, our independent registered public accounting firm has expressed substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans concerning these matters are described in Note 1 to our financial statements; however management cannot assure you that its plans will be successful in addressing these issues. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty. If we cannot successfully continue as a going concern, our stockholders may lose their entire investment in the common stock.
Market Opportunity
Diabetes is a chronic, life-threatening disease for which there is no known cure. Diabetes is caused by the body’s inability to produce or effectively utilize the hormone insulin. This inability prevents the body from adequately regulating blood glucose levels. Glucose, the primary source of energy for cells, must be maintained at certain concentrations in the blood in order to permit optimal cell function and health. Normally, the pancreas provides control of blood glucose levels by secreting the hormone insulin to decrease blood glucose levels when concentrations are too high. In people with diabetes, blood glucose levels fluctuate between very high levels, a condition known as hyperglycemia, and very low levels, a condition known as hypoglycemia. Hyperglycemia can lead to serious long-term complications, such as blindness, kidney disease, nervous system disease, amputations, stroke and cardiovascular disease and, in certain cases, can result in death. Hypoglycemia can lead to confusion, loss of consciousness or death.
According to the Diabetes Atlas (Fourth Edition) published by the International Diabetes Federation in 2009, an estimated 285 million adults aged from 20 to 79 worldwide, or 6.4% of the world’s adult population, would suffer from diabetes in 2010, not including those persons who suffer from Impaired Glucose Tolerance or Gestational Diabetes. The International Diabetes Federation estimates that this number will grow to approximately 438 million adults worldwide, or 7.7% of the world’s adult population, in 2030, and that by 2030 the number of adults suffering from diabetes will have increased by 98.1% in Africa, 93.9% in the Middle East and North Africa, 72.1% in Southeast Asia, 65.1% in South and Central America, 47.0% in the Western Pacific, 42.4% in North America and the Caribbean and 20.0% in Europe, over such regions’ respective 2010 levels. According to a statement made by the President of the International Diabetes Federation at a press briefing at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes in September 2011, an estimated 366 million people currently suffer from diabetes, and approximately 4.6 million deaths are attributable to diabetes annually.
According to the National Diabetes Education Program, about 75% of all newly diagnosed cases of Type 1 diabetes in the United States occur in juveniles younger than 18 years of age. In addition, Type 2 diabetes is occurring with increasing frequency in juveniles. The increase in prevalence is related to an increase in obesity amongst children. According to the 2007-2008 National Health and Examination Survey, approximately 16% - 17% of children and teens were overweight, about double the number of overweight teens two decades earlier.
In its 2011 National Diabetes Fact Sheet, the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated that the direct medical costs and indirect expenditures attributable to diabetes in the United States were $174 billion in 2007, an increase of $42 billion from 2002. Of this amount, the CDC estimated that approximately $116 billion were direct medical costs. According to International Diabetes Federation estimates published in 2009, worldwide healthcare expenditures to treat and prevent diabetes and its complications will total $490 billion in 2030.
The outcome of clinical data supports the recommendation that frequent monitoring of blood glucose levels is an important component of effective diabetes management. The landmark 1993 Diabetes Control and Complications Trial, consisting of patients with Type 1 diabetes, and the 1998 UK Prospective Diabetes Study, consisting of patients with Type 2 diabetes, demonstrated that patients who intensely managed blood glucose levels delayed the onset and slowed the progression of diabetes-related complications. In the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial, a major component of intensive management was monitoring blood glucose levels at least four times per day using conventional spot finger stick blood glucose meters. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial demonstrated that intensive management reduced the risk of complications by 76% for eye disease, 60% for nerve disease and 50% for kidney disease. However, the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial also found that intensive management led to a two- to three-fold increase in the frequency of hypoglycemic events. In the December 2005 edition of the New England Journal of Medicine, the authors of a peer-reviewed study concluded that intensive diabetes therapy has long-term beneficial effects on the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with Type 1 diabetes. The study showed that intensive diabetes therapy reduced the risk of cardiovascular disease by 42% and the risk of non-fatal heart attack, stroke or death from cardiovascular disease by 57%. However, despite evidence that intensive glucose management reduces the long-term complications associated with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association reported in a 2001 issue of its publication Diabetes Care that up to 67% of patients with diabetes fail to routinely monitor their glucose levels. The December 2005 issue of Pharmacy and Therapeutics magazine indicates that only 14% of American diabetics (about 2.5 million people out of 18.2 million Americans with diabetes) practice self monitoring of blood glucose regularly.
Spot finger stick devices are the most prevalent devices for blood glucose monitoring. These devices require inserting a strip into a glucose meter, taking a blood sample with a finger stick and placing a drop of blood on the test strip that yields a single point in time blood glucose measurement. Despite continued developments in the field of blood glucose monitors, the routine measurement of glucose levels remains invasive, painful, inconvenient, difficult and costly.
4
The FDA has approved the use of invasive continuous glucose monitoring systems for blood glucose monitoring when prescribed by a doctor. Continuous glucose monitoring systems use a sensor inserted under the skin to check glucose levels in interstitial fluid. The sensor stays in place for several days to a week and then must be replaced. A transmitter sends information about glucose levels via radio waves from the sensor to a pager-like wireless monitor. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases at the National Institutes of Health, continuous glucose monitoring device users must check blood samples with a conventional glucose meter to calibrate the continuous glucose monitoring systems devices. In addition, because currently approved continuous glucose monitoring systems are not as accurate as standard blood glucose meters, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases recommends that continuous glucose monitoring device users confirm glucose levels with a meter before changing treatment. We believe that a significant market opportunity exists for a reliable, inexpensive, non-invasive blood glucose measurement device and that such a device could greatly increase compliance with blood glucose measurement recommendations and help many diabetics better manage their disease, providing significant benefits to both patients and health care payors.
Competitive Advantage
Our non-invasive blood glucose monitor, the GlucoTrack DF-F, utilizes a combination of ultrasound, electromagnetic and thermal technologies to obtain blood glucose measurements in less than one minute via a small sensor that is clipped onto one’s earlobe and connected to a handheld control and display unit.
We believe that the GlucoTrack DF-F addresses the expressed, currently unmet needs of the diabetic market as it removes or diminishes two of the most significant barriers to the recommended frequent monitoring of blood glucose by diabetics:
|
·
|
pain, as the GlucoTrack DF-F is a truly non-invasive device; and
|
|
·
|
cost, as, despite the relatively high upfront cost of purchasing a GlucoTrack DF-F, we anticipate that the total cost of purchasing a device and purchasing replacement ear clips every six months (anticipated to be the only recurring cost, other than recalibration costs, which are expected to be minimal) over the useful life of the device will be significantly lower than the cost of purchasing single use glucose sticks over that same period. See Figure B on page 37 and the accompanying footnotes for a direct cost comparison of the GlocoTrack DF-F and conventional (invasive) spot finger stick devices
|
Despite the fact that the overall costs associated with owning and using a GlucoTrack DF-F device are expected to be substantially lower than the cost of purchasing and using single use invasive devices over an extended period of time, as demonstrated in Figure B below, the significant initial purchase price of a GlucoTrack device might present a barrier to adoption of the GlucoTrack system by patients. In light of this fact, we are considering options to lessen the initial financial burden associated with purchasing a GlucoTrack device, including leasing devices to users. In addition, we intend to seek reimbursement approval for the GlucoTrack device from third-party payors, including government payors, such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs, managed care organizations and other third-party payors. There can be no assurance that such third party-payors will provide reimbursement coverage for the GlucoTrack or, if so, whether such reimbursement coverage will be adequate. See “Risk Factors - If GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, fail to achieve market acceptance, we may not be able to generate significant revenue or achieve or sustain profitability.” on page 15 of this prospectus.
We believe that the GlucoTrack DF-F will only require calibration once every few months; although, in informal discussions with the FDA, the FDA has indicated that initially it would require recalibration of the GlucoTrack DF-F every month. Monthly (or perhaps less frequent) recalibration presents an advantage as compared to other non-invasive devices under different stages of development, as they generally require more frequent recalibration (although one company claims that its device under development does not require any calibration or recalibration). Furthermore, the GlucoTrack DF-F does not use any optical method (either Infra Red (IR) or Near Infra Red (NIR) technology), which we understand are being used by other developers of noninvasive blood glucose measurement devices. We believe that optical technologies are less reliable than the GlucoTrack DF-F’s combination of ultrasound, electromagnetic and thermal technologies due to inherent physiological limitations with optical technology.
We expect that the initial calibration and the first one or two recalibrations would be completed by experienced clinicians in a clinical setting, and all other recalibrations after the initial one or two recalibrations would be completed by the patient in his or her home or another location of his or her choosing. As with all other non-invasive glucose monitoring devices that require recalibration, in order to recalibrate the GlucoTrack DF-F a clinician or patient will need to obtaining a measurement of the patient’s blood glucose levels using an invasive device, which measurement is used as a reference point in the recalibration process.
To our knowledge, there are currently no devices approved for use in either the United States or the European Union for spot or continuous non-invasive blood glucose measurement. The FDA has previously approved a single non-invasive product for glucose trend analysis, the GlucoWatch®, so long as the device was used with conventional finger stick glucose monitoring devices. However, the device is no longer available commercially.
Corporate Information
Our principal executive offices are located at 102 Ha’Avoda Street, Ashkelon Israel and our telephone number is 972 (8) 675-7850. Our website address is www.integrity-app.com . Information contained on our website or that can be accessed through our website does not constitute a part of this prospectus and is not incorporated herein by reference. There is no relationship between Integrity Applications, Inc., the registrant under the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part, and Integrity Applications, Incorporated, the engineering and software services company based in Chantilly, Virginia.
GlucoTrack® is a registered trademark of Integrity Applications, Inc.
5
|
Common stock offered by the selling stockholders:
|
1,295,545 shares
|
|
Common stock outstanding:
|
5,295,543 shares as of August 19, 2011, excluding shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of outstanding warrants and stock options.
|
|
Trading market:
|
There is currently no market for our common stock and we can offer no assurances that a market for our shares of common stock will develop in the future. We intend to seek a qualification for our common stock to be quoted on the OTCBB; however, no assurance can be given as to our success in qualifying for quotation on the OTCBB.
|
|
Price per share:
|
The selling stockholders may sell their shares of our common stock at a fixed price of $6.25 per share (the offering price per share of common stock in our most recent private placement completed in July 2011) until our common stock is quoted on the OTCBB, and thereafter at prevailing market prices or privately negotiated prices.
|
|
Use of proceeds:
|
We will not receive any of the proceeds from the sale or other disposition of the shares of common stock offered hereby.
|
|
Risk factors:
|
We are subject to a number of risks that you should be aware of before you decide to purchase our common stock. These risks are discussed more fully in the section captioned “Risk Factors,” beginning on page 7 of this prospectus.
|
6
An investment in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. Before making an investment decision, you should carefully consider the following risk factors. If any of these risks actually occur, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially harmed. In addition, risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial may also materially harm our business, financial condition and results of operations. If this were to happen, the value of our common stock could decline significantly and you could lose all or part of your investment.
A former stockholder of Integrity Israel who is entitled to receive shares in our company, subject to the fulfillment of certain requirements, has challenged our and Integrity Israel’s position that certain rights he had in Integrity Israel terminated upon the Reorganization.
Integrity Israel is party to an investment agreement with Dimri, pursuant to which Dimri loaned Integrity Israel a principal amount of NIS 1,440,000, subject to linkage differences in Israel ($421,669 based on an exchange rate of 3.415 NIS/dollar). In connection with such loan, Dimri received shares of common stock representing 25% of Integrity Israel’s ordinary shares at such time. Under the Dimri agreement, certain rights in Integrity Israel were granted to Dimri, including an anti-dilution provision that provided that Dimri’s holdings in Integrity Israel would not be diluted below 18% of Integrity Israel’s issued capital shares as a result of any investment in Integrity Israel, subject to the fulfillment of certain requirements. On the date of the reorganization, Dimri owned 18% of Integrity Israel’s ordinary shares and, therefore, upon the completion of the reorganization Dimri was entitled to receive 18% of the shares of common stock of the Company outstanding on such date in exchange for his shares in Integrity Israel, subject to the fulfillment of certain requirements. We believe, based on the advice of Israeli counsel, that, given Dimri no longer owns shares in Integrity Israel as a result of the reorganization, rights attached to the shares in Integrity Israel no longer exist in Integrity Israel and do not and have never existed in us. However, Dimri has refused to acknowledge or agree to the termination of these rights and has challenged our position. On June 23, 2011, Mr. Dimri appealed to the District Court of HaMerkaz District in Petah Tikva, Israel, requesting the court to appoint an arbitrator to decide the dispute between Integrity Israel, the founders of Integrity Israel and Dimri (HPB 40754-06-11). On September 25, 2011, Integrity Israel's counsel filed an answer with the Court, disputing the facts and allegation raised in Dimri's motion and suggesting choosing an arbitrator with certain capacities, experience and skills. At a hearing held on October 11, 2011, the court appointed an arbitrator in this matter. The proposed arbitrator is required to inform the court no later than November 1, 2011 if there is anything that will preclude his service as an arbitrator in this matter. If there is, an alternate arbitrator will be appointed by the court. It should be noted that, in accordance with Israeli law, Mr. Dimri was not required to, and he did not, specify in his request for the appointment of an arbitrator the relief to be sought by him in the arbitration. As a result, we do not yet know the relief to be sought by Mr. Dimri in the arbitration. We anticipate that Mr. Dimri will specify the relief sought by him after the commencement of the arbitration proceedings.
As a condition to the private placement, our founders, Avner Gal, Zvi Cohen, David Malka, Ilana Freger and Alex Reikhman, entered into an Irrevocable Undertaking of Indemnification with us pursuant to which, among other things, the founders agreed to indemnify us and hold us harmless from any adverse consequences (excluding the fees and costs of defending us) that result from Dimri’s, or Dimri’s successors’ or assigns’, enforcement of the anti-dilution rights granted to Dimri as described above. The founders’ obligations under the Irrevocable Undertaking of Indemnification only obligate each founder to transfer up to such number of shares of our common stock that he or she owned as of the date of the reorganization to Dimri or to us. The term of the Irrevocable Undertaking of Indemnification is three years (subject to extension if there is a pending action), provided that, after two years, any founder may sell or transfer up to twenty percent (20%) of his or her shares of common stock covered by the Irrevocable Undertaking of Indemnification so long as no action is pending by Dimri against us at the time of such sale and the sale price of the common stock is at least $6.25 per share. No assurances can be made that the Irrevocable Undertaking of Indemnification will fully protect us or our stockholders from any adverse consequences of an action by Dimri to enforce its anti-dilution rights. In addition, Dimri may assert other rights that it had under the Investment Agreement, for which we are not indemnified.
Notwithstanding the indemnification by our founders, any such challenge by Dimri, or any other legal action, if any, brought by Dimri against us, Integrity Israel and/or the founders, could have a material adverse effect on us and our stockholders, including (i) significant costs and expenses that may be incurred in connection with any action, suit or other proceeding, (ii) potential dilution of the interests of our other stockholders (including purchasers in this offering) if Dimri is successful in such challenge and either (a) the founders cannot transfer their shares until the end of the two-year lock-up imposed by the Israeli Tax Authorities or (b) the founders otherwise exhaust all of their shares in satisfaction of their indemnification obligations, (iii) the impact that the loss of shares of common stock owned by Messrs. Gal and Malka, who are key employees of ours, as a result of their indemnification obligation would have on their commitment to us given the loss of a portion of their economic interests in us and (iv) if a court were to order Integrity Israel to issue shares to Dimri as part of a successful challenge, we would not wholly own Integrity Israel.
7
We have a history of operating losses and do not expect to generate revenues or become profitable in the near future.
We are a pre-clinical stage medical device company with a limited operating history. We are not profitable and have incurred losses since our inception. We do not anticipate that we will generate revenue from the sale of products until at least 2012. Our initial product, the GlucoTrack DF-F, has not been approved for marketing in the United States, the European Union or any other jurisdiction and may not be sold or marketed without FDA clearance or approval in the United States, the receipt of a CE Mark in the European Union or the receipt of regulatory approval in accordance with the applicable requirements of any other jurisdiction. We continue to incur research and development and general and administrative expenses related to our operations and the development of our first product. Our net losses for the years ended December 31, 2010 and 2009 were approximately $2.8 million and $1.2 million, respectively, and we had an accumulated deficit of approximately $11.2 million as of June 30, 2011. We expect to continue to incur losses for the foreseeable future, and these losses will likely increase as we prepare for and begin to commercialize GlucoTrack DF-F, if it is approved. If the GlucoTrack DF-F and possibly other products fail in clinical trials or do not gain regulatory clearance or approval, or if the GlucoTrack DF-F does not achieve market acceptance, we may never become profitable. Even if we achieve profitability in the future, we may not be able to sustain profitability in subsequent periods.
Our independent registered public accounting firm has expressed substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
Our independent registered public accounting firm noted in its report accompanying our financial statements for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2010 that we had suffered significant losses during the development stage, had a negative operating cash flow since inception and that the development and commercialization of our product is expected to require substantial expenditures. We have not yet generated any revenues from our operations to fund our activities, and are therefore dependent upon external sources for financing our operations. There can be no assurance that we will succeed in obtaining the necessary financing to continue our operations. As a result, our independent registered public accounting firm has expressed substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans concerning these matters are described in Note 1 to our financial statements; however management cannot assure you that its plans will be successful in addressing these issues. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty. If we cannot successfully continue as a going concern, our stockholders may lose their entire investment in the common stock.
We may require substantial additional funding, which may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
We may need to raise additional capital to engage in our planned clinical and pre-clinical development and commercialization activities. Our future funding requirements will depend on many factors, including but not limited to:
|
·
|
our need to expand research and development activities;
|
|
·
|
the need and ability to hire additional management and scientific and medical personnel;
|
|
·
|
the effect of competing technological and market developments;
|
|
·
|
the need to implement additional internal systems and infrastructure, including financial and reporting systems;
|
|
·
|
the rate of progress and cost of our clinical trials;
|
|
·
|
the costs associated with establishing commercialization capabilities, including a sales force if we distribute our product other than through distributors;
|
8
|
|
·
|
the costs and timing of seeking and obtaining FDA and other non-U.S. regulatory clearances and approvals; and
|
|
|
·
|
the ability to maintain, expand and defend the scope of our intellectual property portfolio.
|
Until we can generate a sufficient amount of product revenue to finance our cash requirements, which we may never do, we expect to finance future cash needs primarily through public or private equity offerings, debt financings or strategic collaborations. We do not know whether additional funding will be available on acceptable terms, or at all. If we are not able to secure additional funding when needed, or at all, we may have to delay, reduce the scope of or eliminate clinical trials or research and development programs. To the extent that we raise additional funds by issuing equity securities, our stockholders may experience significant dilution, and debt financing, if available, may involve restrictive covenants. In addition to the dilution normally attendant to an equity offering, holders of our shares of common stock may experience additional dilution, in the event that we complete an equity offering prior to September 1, 2012, as a result of the anti-dilution protections afforded to the investors in the private placement.
The recent worldwide economic crisis and market instability may materially and adversely affect the demand for our products, if and when approved, as well as our ability to obtain credit or secure funds through sales of our stock, which may materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and ability to fund our operations.
The current worldwide economic crisis may reduce the demand for new and innovative medical devices, resulting in delayed market acceptance of our products, if and when they are approved. Such a delay could have a material adverse impact on our business, expected cash flows, results of operations and financial condition. Additionally, we have funded our operations to date primarily through private sales of common stock. The recent economic turmoil and instability in the world’s equity and credit markets may materially adversely affect our ability to sell additional shares of common stock and/or borrow cash. There can be no assurance that we will be able to raise additional working capital on acceptable terms or at all, and any failure to do so may materially adversely affect our ability to continue operations.
Healthcare reforms, changes in healthcare policies, including recently enacted legislation reforming the U.S. healthcare system, and changes to third-party reimbursements for diabetes-related products may affect demand for our products and have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
The United States government has in the past considered and may in the future consider healthcare policies and proposals intended to curb rising healthcare costs, including those that could significantly affect reimbursement for healthcare products such as the GlucoTrack DF-F. These policies have included, and may in the future include: basing reimbursement policies and rates on clinical outcomes, the comparative effectiveness and costs of different treatment technologies and modalities; imposing price controls and taxes on medical device providers; and other measures.
Congress recently passed health care reform legislation that the President signed into law on March 23, 2010. The package signed into law by the President is considered by some to be the most dramatic change to the country’s health care system in decades. The principal aim of the law currently enacted is to expand health insurance coverage to approximately 32 million Americans who are currently uninsured. The law’s most far-reaching changes do not take effect until 2014, including a requirement that most Americans carry health insurance. The consequences of these significant coverage expansions on the sale of our products is unknown and speculative at this point.
The enacted legislation contains many provisions designed to generate the revenues necessary to fund the coverage expansions. The most relevant of these provisions are those that impose fees or taxes on certain health-related industries, including medical device manufacturers like us. The legislation signed into law on March 23, 2010 and March 30, 2010 imposes an annual excise tax (or sales tax) on medical devices like ours, beginning with calendar year 2013. The taxes would be allocated based on our proportionate share of the prior-year’s aggregate domestic gross receipts from medical device sales.
9
In addition to the new legislation discussed above, the effect of which cannot presently be quantified given its recent enactment, various healthcare reform proposals have also emerged at the state level. Future significant changes in the healthcare systems in the United States or elsewhere could also have a negative impact on the demand for the GlucoTrack DF-F or other GlucoTrack products, if approved for sale, or our future products, if any. These include changes that may lower reimbursement rates for such products from what we might otherwise have obtained and changes that may be proposed or implemented by the current administration or Congress.
We cannot predict what healthcare initiatives, if any, will be implemented at the federal or state level, or the effect any future legislation or regulation will have on us. In addition to the taxes imposed by the new federal legislation, any further expansion in government’s role in the U.S. healthcare industry may lower reimbursements for our products, reduce medical procedure volumes and materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our product research and development activities may not result in commercially viable products.
Our current product candidate, the GlucoTrack DF-F, is in the early stages of development and, therefore, is prone to the risks of failure inherent in medical device product development. We will likely be required to undertake significant clinical trials to demonstrate to the FDA that the GlucoTrack DF-F is either safe and effective for its intended use or is substantially equivalent in terms of safety and effectiveness to an existing, lawfully marketed non-Section 515 premarket approval device. We may also be required to undertake clinical trials by non-U.S. regulatory agencies. Clinical trials are expensive and uncertain processes that may take years to complete. Failure can occur at any point in the process and early positive results do not ensure that the entire clinical trial will be successful. Product candidates in clinical trials may fail to show desired efficacy and safety traits despite early promising results. A number of companies in the medical device industry have suffered significant setbacks in advanced clinical trials, even after their product candidates demonstrated promising results at earlier points.
The results of limited pre-clinical trials may not be indicative of future results, and our planned clinical trials may not satisfy the requirements of the FDA or other non-U.S. regulatory authorities.
Positive results from limited pre-clinical trials that we have conducted should not be relied upon as evidence that later-stage or large-scale clinical trials will succeed. These pre-clinical trials involved small patient populations. Because of the small sample size, the results of these pre-clinical trials may not be indicative of future results. We will be required to demonstrate with substantial evidence through well-controlled clinical trials that the GlucoTrack DF-F or future product candidates, if any, either (i) are safe and effective for their intended uses or (ii) are substantially equivalent in terms of safety and effectiveness to devices that are already marketed under Section 510(k).
Further, the GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, may not be cleared or approved, as the case may be, even if the clinical data are satisfactory and support, in our view, its or their clearance or approval. The FDA or other non-U.S. regulatory authorities may disagree with our trial design or interpretation of the clinical data. In addition, any of these regulatory authorities may change requirements for the clearance or approval of a product candidate even after reviewing and providing comment on a protocol for a pivotal clinical trial that has the potential to result in FDA approval. In addition, any of these regulatory authorities may also clear or approve a product candidate for fewer or more limited uses than we request or may grant clearance or approval contingent on the performance of costly post-marketing clinical trials. In addition, the FDA or other non-U.S. regulatory authorities may not approve the labeling claims necessary or desirable for the successful commercialization of the GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any.
We are highly dependent on the success of our initial product candidate, GlucoTrack DF-F, and cannot give any assurance that it will receive regulatory clearance or be successfully commercialized.
We are highly dependent on the success of our initial product candidate, GlucoTrack DF-F. We cannot give any assurance that the FDA will permit us to clinically test the device, nor can we give any assurance that GlucoTrack DF-F will receive regulatory clearance or approval or be successfully commercialized, for a number of reasons, including, without limitation, the potential introduction by our competitors of more clinically-effective or cost-effective alternatives, failure in our sales and marketing efforts, or the failure to obtain positive coverage determinations or reimbursement. Any failure to obtain clearance or approval of or to successfully commercialize GlucoTrack DF-F would have a material and adverse effect on our business.
10
If our competitors develop and market products that are more effective, safer or less expensive than GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, our commercial opportunities will be negatively impacted .
The life sciences industry is highly competitive and we face significant competition from many medical device companies that are researching and marketing products designed to address the needs of persons suffering from diabetes. We are currently developing medical devices that will compete with other medical devices that currently exist or are being developed. Products that we may develop in the future are also likely to face competition from other medical devices and therapies. Some of our competitors have significantly greater financial, manufacturing, marketing and product development resources than we do. Large medical device companies, in particular, have extensive experience in clinical testing and in obtaining regulatory clearances or approvals for medical devices. These companies also have significantly greater research and marketing capabilities than us. Some of the medical device companies that we expect to compete with include Roche Disetronic, a division of Roche Diagnostics; LifeScan, Inc., a division of Johnson & Johnson; the MediSense and TheraSense divisions of Abbott Laboratories; Bayer Corporation; Echo Therapeutics, Inc.; GlucoLight; Grove Instruments; and Medtronic, Inc. In addition, many other universities and private and public research institutions are or may become active in research involving blood glucose measurement devices.
We believe that our ability to successfully compete will depend on, among other things:
|
|
·
|
the results of our clinical trials;
|
|
|
·
|
our ability to recruit and enroll patients for our clinical trials;
|
|
|
·
|
the efficacy, safety, performance and reliability of our product candidates;
|
|
|
·
|
the speed at which we develop product candidates;
|
|
|
·
|
our ability to commercialize and market any of our product candidates that may receive regulatory clearance or approval;
|
|
|
·
|
our ability to design and successfully execute appropriate clinical trials;
|
|
|
·
|
the timing and scope of regulatory clearances or approvals;
|
|
|
·
|
appropriate coverage and adequate levels of reimbursement under private and governmental health insurance plans, including Medicare;
|
|
|
·
|
our ability to protect intellectual property rights related to our products;
|
|
|
·
|
our ability to have partners manufacture and sell commercial quantities of any approved products to the market; and
|
|
|
·
|
acceptance of product candidates by physicians and other health care providers.
|
If our competitors market products that are more effective, safer, easier to use or less expensive than GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, or that reach the market sooner than GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, we may not achieve commercial success. In addition, the medical device industry is characterized by rapid technological change. It may be difficult for us to stay abreast of the rapid changes in each technology. If we fail to stay at the forefront of technological change, we may be unable to compete effectively. Technological advances or products developed by our competitors may render our technologies or product candidates obsolete or less competitive.
11
Our product development activities could be delayed or stopped.
We do not know whether our planned clinical trials will begin on time, or at all, or be completed on schedule, or at all. The commencement of our planned clinical trials could be substantially delayed or prevented by several factors, including:
|
|
·
|
the failure to obtain sufficient funding to pay for all necessary clinical trials;
|
|
|
·
|
limited number of, and competition for, suitable patients that meet the protocol’s inclusion criteria and do not meet any of the exclusion criteria;
|
|
|
·
|
limited number of, and competition for, suitable sites to conduct the clinical trials, and delay or failure to obtain FDA approval, if necessary, to commence a clinical trial;
|
|
|
·
|
delay or failure to obtain sufficient supplies of the product candidate for clinical trials;
|
|
|
·
|
requirements to provide the medical device required in clinical trials at cost, which may require significant expenditures that we are unable or unwilling to make;
|
|
|
·
|
delay or failure to reach agreement on acceptable clinical trial agreement terms or clinical trial protocols with prospective sites or investigators; and
|
|
|
·
|
delay or failure to obtain institutional review board approval or renewal of such approval to conduct a clinical trial at a prospective or accruing site, respectively.
|
The completion of clinical trials could also be substantially delayed or prevented by several factors, including:
|
|
·
|
slower than expected rates of patient recruitment and enrollment;
|
|
|
·
|
failure of patients to complete the clinical trial;
|
|
|
·
|
unforeseen safety issues;
|
|
|
·
|
lack of efficacy evidenced during clinical trials;
|
|
|
·
|
termination of clinical trials by one or more clinical trial sites;
|
|
|
·
|
inability or unwillingness of patients or medical investigators to follow clinical trial protocols; and
|
|
|
·
|
inability to monitor patients adequately during or after treatment.
|
Our clinical trials may be suspended or terminated at any time by the FDA, other regulatory authorities, the Institutional review board for any given site, or us. Any failure or significant delay in completing clinical trials for GlucoTrack or future product candidates, if any, could materially harm our financial results and the commercial prospects for our product candidates.
12
The regulatory approval process is expensive, time-consuming and uncertain and may prevent us from obtaining approvals for the commercialization of GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any.
The research, testing, manufacturing, labeling, approval, selling, marketing and distribution of medical devices are subject to extensive regulation by the FDA and other non-U.S. regulatory authorities, which regulations differ from country to country. We are not permitted to market our product candidates in the United States until we receive a clearance letter under the 510(k) premarket notification process or approval of a Section 515 premarket approval, from the FDA, depending on the nature of the device. We have not submitted an application or premarket notification for or received marketing clearance or approval for any of our product candidates. Obtaining approval of any premarket approval can be a lengthy, expensive and uncertain process. While the FDA normally reviews and clears a premarket notification in three months, there is no guarantee that our products will qualify for this more expeditious regulatory process, which is reserved for Class I and II devices, nor is there any assurance that, even if a device is reviewed under the 510(k) premarket notification process, the FDA will review it expeditiously or determine that the device is substantially equivalent to a lawfully marketed non-premarket approval device. If the FDA fails to make this finding, then we cannot market the device. In lieu of acting on a premarket notification, the FDA may seek additional information or additional data which would further delay our ability to market the product. In addition, failure to comply with FDA, non-U.S. regulatory authorities or other applicable U.S. and non-U.S. regulatory requirements may, either before or after product clearance or approval, if any, subject us to administrative or judicially imposed sanctions, including:
|
|
·
|
restrictions on the products, manufacturers or manufacturing process;
|
|
|
·
|
adverse inspectional observations (Form 483), warning letters or non-warning letters incorporating inspectional observations;
|
|
|
·
|
civil and criminal penalties;
|
|
|
·
|
injunctions;
|
|
|
·
|
suspension or withdrawal of regulatory clearances or approvals;
|
|
|
·
|
product seizures, detentions or import bans;
|
|
|
·
|
voluntary or mandatory product recalls and publicity requirements;
|
|
|
·
|
total or partial suspension of production;
|
|
|
·
|
imposition of restrictions on operations, including costly new manufacturing requirements; and
|
|
|
·
|
refusal to clear or approve pending applications or premarket notifications.
|
Regulatory approval of a premarket approval application, premarket approval application supplement or clearance pursuant to a 510(k) premarket notification is not guaranteed, and the approval or clearance process, as the case may be, is expensive and may, especially in the case of the premarket approval application, take several years. The FDA also has substantial discretion in the medical device clearance or approval processes. Despite the time and expense exerted, failure can occur at any stage and we could encounter problems that cause us to abandon clinical trials or to repeat or perform additional pre-clinical studies and clinical trials. The number of pre-clinical studies and clinical trials that will be required for FDA clearance or approval varies depending on the medical device candidate, the disease or condition that the medical device candidate is designed to address, and the regulations applicable to any particular medical device candidate. The FDA can delay, limit or deny clearance or approval of a medical device candidate for many reasons, including:
|
|
·
|
a medical device candidate may not be deemed safe or effective, in the case of a premarket approval application;
|
|
|
·
|
a medical device candidate may not be deemed to be substantially equivalent to a lawfully marketed non-premarket approval device in the case of a 510(k) premarket notification;
|
|
|
·
|
FDA officials may not find the data from pre-clinical studies and clinical trials sufficient;
|
|
|
·
|
the FDA might not approve our third-party manufacturer’s processes or facilities; or
|
|
|
·
|
the FDA may change its clearance or approval policies or adopt new regulations.
|
13
Failure to recruit and enroll patients for clinical trials may cause the development of our product candidates to be delayed.
We may encounter delays if we are unable to recruit and enroll and retain enough patients to complete clinical trials. Patient enrollment depends on many factors, including the size of the patient population, the nature of the protocol, the proximity of patients to clinical sites and the eligibility criteria for the trial. Delays in patient enrollment are not unusual. Any such delays in planned patient enrollment may result in increased costs, which could harm our ability to develop products.
Even if we obtain regulatory clearances or approvals for the GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, the terms of clearances or approvals and ongoing regulation of our products may limit how we manufacture and market our product candidates, which could materially impair our ability to generate anticipated revenues.
Once regulatory clearance or approval has been granted, the cleared or approved product and its manufacturer are subject to continual review. Any cleared or approved product may only be promoted for its indicated uses. In addition, if the FDA or other non-U.S. regulatory authorities clear or approve GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, the labeling, packaging, adverse event reporting, storage, advertising and promotion for the product will be subject to extensive regulatory requirements. We, and the manufacturers of our products, if other than us, also will be required to comply with the FDA’s Quality System Regulation, which includes requirements relating to quality control and quality assurance, as well as the corresponding maintenance of records and documentation. Moreover, device manufacturers are required to report adverse events by filing Medical Device Reports with the FDA, which are publicly available. Further, regulatory agencies must approve our manufacturing facilities before they can be used to manufacture products, and these facilities are subject to ongoing regulatory inspection. If we fail to comply with the regulatory requirements of the FDA and other non-U.S. regulatory authorities, or if previously unknown problems with our products, manufacturers or manufacturing processes are discovered, we could be subject to administrative or judicially imposed sanctions, including:
|
|
·
|
restrictions on the products, manufacturers or manufacturing process;
|
|
|
·
|
adverse inspectional observations (Form 483), warning letters, or non-warning letters incorporating inspectional observations;
|
|
|
·
|
civil or criminal penalties or fines;
|
|
|
·
|
injunctions;
|
|
|
·
|
product seizures, detentions or import bans;
|
|
|
·
|
voluntary or mandatory product recalls and publicity requirements;
|
|
|
·
|
suspension or withdrawal of regulatory clearances or approvals;
|
|
|
·
|
total or partial suspension of production;
|
|
|
·
|
imposition of restrictions on operations, including costly new manufacturing requirements; and
|
|
|
·
|
refusal to clear or approve pending applications or premarket notifications.
|
In addition, the FDA and other non-U.S. regulatory authorities may change their policies and additional regulations may be enacted that could prevent or delay regulatory clearance or approval of our product candidates. We cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of government regulation that may arise from future legislation or administrative action, either in the United States or abroad. If we are not able to maintain regulatory compliance, we will likely not be permitted to market future product candidates and may not achieve or sustain profitability.
14
Even if we receive regulatory clearance or approval to market the GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, the market may not be receptive to our products.
Even if GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, obtain regulatory clearance or approval, resulting products may not gain market acceptance among physicians, patients, health care payors or the medical community. We believe that the degree of market acceptance will depend on a number of factors, including:
|
|
·
|
timing of market introduction of competitive products;
|
|
|
·
|
safety and efficacy of our product;
|
|
|
·
|
prevalence and severity of any side effects;
|
|
|
·
|
potential advantages or disadvantages over alternative treatments;
|
|
|
·
|
strength of marketing and distribution support;
|
|
|
·
|
price of our product candidates, both in absolute terms and relative to alternative treatments; and
|
|
|
·
|
availability of coverage and reimbursement from government and other third-party payors.
|
If GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, fail to achieve market acceptance, we may not be able to generate significant revenue or achieve or sustain profitability.
The coverage and reimbursement status of newly cleared or approved medical devices is uncertain, and failure to obtain adequate coverage and adequate reimbursement could limit our ability to market GlucoTrack DF-F or future product candidates, if any, and may inhibit our ability to generate revenue from GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, that may be cleared or approved.
There is significant uncertainty related to the third-party coverage and reimbursement of newly cleared or approved medical devices. The commercial success of GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, in both domestic and international markets will depend in part on the availability of coverage and adequate reimbursement from third-party payors, including government payors, such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs, managed care organizations and other third-party payors. Government and other third-party payors are increasingly attempting to contain health care costs by limiting both coverage and the level of reimbursement for new products and, as a result, they may not cover or provide adequate payment for GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any. These payors may conclude that our products are not as safe or effective as existing devices or that the overall cost of using one of our devices exceeds the overall cost of the competing device, and third-party payors may not approve GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, for coverage and adequate reimbursement. Furthermore, deficit reduction and austerity measures in the United States and abroad may put further pressure on governments to limit coverage of, and reimbursement for, our products. The failure to obtain coverage and adequate reimbursement for GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, or health care cost containment initiatives that limit or restrict reimbursement for such products may reduce any future product revenue.
If we fail to attract and retain key management and scientific personnel, we may be unable to successfully develop or commercialize GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any.
We will need to expand and effectively manage our managerial, operational, financial, development and other resources in order to successfully pursue our research, development and commercialization efforts for GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any. Our success depends on our continued ability to attract, retain and motivate highly qualified management and pre-clinical and clinical personnel. The loss of the services of any of our senior management, particularly Avner Gal, could delay or prevent the development or commercialization of GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any. We do not maintain key man insurance on Mr. Gal or any of our other employees, although we intend to seek key man life insurance on Mr. Gal immediately upon the initial closing of this offering. We will need to hire additional personnel as we continue to expand our research and development activities and build a sales and marketing function. Although we currently have employment agreements with each of Messrs. Gal and Malka, those agreements provide that they may be terminated by Mr. Gal or Mr. Malka, as applicable, upon 180 days or 90 days written notice to the company, respectively.
15
We may not be able to attract or retain qualified management and scientific personnel in the future due to the intense competition for qualified personnel among medical device and other businesses. If we are not able to attract and retain the necessary personnel to accomplish our business objectives, we may experience constraints that will significantly impede the achievement of our research and development objectives, our ability to raise additional capital and our ability to implement our business strategy. In particular, if we lose any members of our senior management team, we may not be able to find suitable replacements in a timely fashion or at all and our business may be harmed as a result.
If and when we evolve from a company primarily involved in development to a company also involved in commercialization, we may encounter difficulties in managing our growth and expanding our operations successfully.
As we advance GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, through research and development, we will need to expand our development, regulatory, manufacturing, marketing and sales capabilities or contract with third parties to provide these capabilities. We anticipate that, as our operations expand, we will need to manage additional relationships with such third parties. Maintaining these relationships and managing our future growth will impose significant added responsibilities on members of our management. We must be able to manage our development efforts effectively; manage our clinical trials effectively; hire, train and integrate additional management, development, administrative and sales and marketing personnel; improve managerial, development, operational and finance systems; and expand our facilities, all of which may impose a strain on our administrative and operational infrastructure.
We likely will rely on third parties to manufacture and supply our product candidates.
We do not own or operate manufacturing facilities for clinical or commercial production of GlucoTrack DF-F, other than a prototype lab. We have no experience in medical device manufacturing, and lack the resources and the capability to manufacture GlucoTrack DF-F on a commercial scale. If our future manufacturing partners are unable to produce our products in the amounts that we require, we may not be able to establish a contract and obtain a sufficient alternative supply from another supplier on a timely basis and in the quantities we require. We expect to depend on third-party contract manufacturers for the foreseeable future.
GlucoTrack DF-F does, and our future product candidates, if any, likely will require precise, high quality manufacturing. Any of our contract manufacturers will be subject to ongoing periodic unannounced inspection by the FDA and other non-U.S. regulatory authorities to ensure strict compliance with quality system regulations, including current good manufacturing practices and other applicable government regulations and corresponding standards. If our contract manufacturers fail to achieve and maintain high manufacturing standards in compliance with quality system regulations, we may experience manufacturing errors resulting in patient injury or death, product recalls or withdrawals, delays or interruptions of production or failures in product testing or delivery, delay or prevention of filing or approval of marketing applications for our products, cost overruns or other problems that could seriously harm our business.
Any performance failure on the part of our contract manufacturers could delay clinical development or regulatory clearance or approval of our product candidates or commercialization of our future product candidates, depriving us of potential product revenue and resulting in additional losses. In addition, our dependence on a third-party for manufacturing may adversely affect our future profit margins. Our ability to replace an existing manufacturer may be difficult because the number of potential manufacturers is limited and the FDA must approve any replacement manufacturer before it can begin manufacturing our product candidates. Such approval would require additional non-clinical testing and compliance inspections. It may be difficult or impossible for us to identify and engage a replacement manufacturer on acceptable terms in a timely manner, or at all.
16
We currently have no marketing staff and no sales or distribution organization. If we are unable to develop our sales, marketing and distribution capability on our own or through collaborations with marketing partners, we will not be successful in commercializing our product candidates.
We currently have no marketing, sales or distribution capabilities. If our product candidates are approved, we intend to establish a sales and marketing organization with technical expertise and supporting distribution capabilities to commercialize our product candidates, which will be expensive and time-consuming. Any failure or delay in the development of our internal sales, marketing and distribution capabilities would adversely impact the commercialization of these products. With respect to GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, we may choose to collaborate with third parties that have direct sales forces and established distribution systems, either to augment our own sales force and distribution systems or in lieu of our own sales force and distribution systems. To the extent that we enter into co-promotion or other licensing arrangements, our product revenue is likely to be lower than if we directly marketed or sold our products. In addition, any revenue we receive will depend in whole or in part upon the efforts of such third parties, which may not be successful and are generally not within our control. If we are unable to enter into such arrangements on acceptable terms or at all, we may not be able to successfully commercialize GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any. If we are not successful in commercializing GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, either on our own or through collaborations with one or more third parties, our future product revenue will suffer and we may incur significant additional losses.
Independent clinical investigators and contract research organizations that we engage to conduct our clinical trials may not be diligent, careful or timely.
We will depend on independent clinical investigators to conduct our clinical trials. Contract research organizations may also assist us in the collection and analysis of data. These investigators and contract research organizations will not be our employees and we will not be able to control, other than by contract, the amount of resources, including time, that they devote to products that we develop. If independent investigators fail to devote sufficient resources to the clinical trials, or if their performance is substandard, it will delay the approval or clearance and commercialization of any products that we develop. Further, the FDA requires that we comply with standards, commonly referred to as good clinical practice, for conducting, recording and reporting clinical trials to assure that data and reported results are credible and accurate and that the rights, integrity and confidentiality of trial subjects are protected. If our independent clinical investigators and contract research organizations fail to comply with good clinical practice, the results of our clinical trials could be called into question and the clinical development of our product candidates could be delayed. Failure of clinical investigators or contract research organizations to meet their obligations to us or comply with federal regulations could adversely affect the clinical development of our product candidates and harm our business.
If we are unable to obtain and enforce patent protection for our products, our business could be materially harmed.
Our success depends, in part, on our ability to protect proprietary methods and technologies that we develop under the patent and other intellectual property laws of the United States and other countries, so that we can prevent others from unlawfully using our inventions and proprietary information. However, we may not hold proprietary rights to some patents required for us to commercialize proposed products. For this and other reasons, we may be unable to secure desired patent rights, thereby losing desired exclusivity. Although we do not believe that we need any licenses for the GlucoTrack DF-F, we may need to obtain licenses in the future for other products or in certain circumstances, such as if one of our patents were declared invalid in the future. If such licenses are not available to us on acceptable terms, we will not be able to market the affected products or conduct the desired activities, unless we successfully challenge the validity, enforceability or infringement of the third-party patent or otherwise circumvent the third-party patent.
Our strategy depends on our ability to rapidly identify and seek patent protection for our discoveries. The process of obtaining patent protection is expensive and time-consuming. Despite our efforts to protect our proprietary rights, unauthorized parties may be able to obtain and use information that we regard as proprietary.
17
The issuance of a patent does not guarantee that it is valid or enforceable. Any patents we have obtained, or which we may obtain in the future, may be challenged, invalidated, unenforceable or circumvented. Moreover, the United States Patent and Trademark Office may commence interference proceedings involving our patents or patent applications. Any challenge to, finding of unenforceability or invalidation or circumvention of our patents or patent applications would be costly, would require significant time and attention of our management and could have a material adverse effect on our business. In addition, court decisions may introduce uncertainty in the enforceability or scope of patents owned by medical device companies.
Our pending patent applications may not result in issued patents. The patent position of medical device companies, including us, is generally uncertain and involves complex legal and factual considerations. The standards that the USPTO and its foreign counterparts use to grant patents are not always applied predictably or uniformly and can change. There is also no uniform, worldwide policy regarding the subject matter and scope of claims granted or allowable in medical device patents. Accordingly, we do not know the degree of future protection for our proprietary rights or the breadth of claims that will be allowed in any patents issued to us or to others. The legal systems of certain countries do not favor the aggressive enforcement of patents, and the laws of foreign countries may not protect our rights to the same extent as the laws of the United States. Therefore, the enforceability or scope of our patents in the United States or in foreign countries cannot be predicted with certainty, and, as a result, any patents that we own may not provide sufficient protection against competitors. We may not be able to obtain or maintain patent protection for our pending patent applications or those we may file in the future.
We cannot assure you that any patents that will issue, that may issue or that may be licensed to us will be enforceable or valid or will not expire prior to the commercialization of our product candidates, thus allowing others to more effectively compete with us. Therefore, any patents that we own may not adequately protect our product candidates or our future products.
If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our proprietary information and know-how, the value of our technology and products could be adversely affected.
In addition to patent protection, we also rely on other proprietary rights, including protection of trade secrets, know-how and confidential and proprietary information. To maintain the confidentiality of trade secrets and proprietary information, we will seek to enter into confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants and collaborators upon the commencement of their relationships with us. These agreements generally require that all confidential information developed by the individual or made known to the individual by us during the course of the individual’s relationship with us be kept confidential and not disclosed to third parties. Our agreements with employees also generally provide and will generally provide that any inventions conceived by the individual in the course of rendering services to us shall be our exclusive property. However, we may not obtain these agreements in all circumstances, and individuals with whom we have these agreements may not comply with their terms. In the event of unauthorized use or disclosure of our trade secrets or proprietary information, these agreements, even if obtained, may not provide meaningful protection, particularly for trade secrets or other confidential information. To the extent that our employees, consultants or contractors use technology or know-how owned by third parties in their work for us, disputes may arise between us and those third parties as to the rights in related inventions.
Adequate remedies may not exist in the event of unauthorized use or disclosure of our confidential information. The disclosure of trade secrets would impair our competitive position and may materially harm our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Some jurisdictions may require us to grant licenses to third parties. Such compulsory licenses could be extended to include some of our product candidates, which may limit potential revenue opportunities.
Many countries, including certain countries in Europe, have compulsory licensing laws under which a patent owner may be compelled to grant licenses to third parties. In addition, most countries limit the enforceability of patents against government agencies or government contractors. In these countries, the patent owner may be limited to monetary relief and may be unable to enjoin infringement, which could materially diminish the value of the patent. Compulsory licensing of life-saving products is also becoming increasingly popular in developing countries, either through direct legislation or international initiatives. Such compulsory licenses could be extended to include some of our product candidates, which may limit our potential revenue opportunities.
18
Our commercial success depends significantly on our ability to operate without infringing the patents and other proprietary rights of third parties.
Other entities may have or obtain patents or proprietary rights that could limit our ability to manufacture, use, sell, offer for sale or import products or impair our competitive position. In addition, to the extent that a third-party develops new technology that covers our products, we may be required to obtain licenses to that technology, which licenses may not be available on commercially reasonable terms, if at all. If licenses are not available on acceptable terms, we will not be able to market the affected products or conduct the desired activities unless we successfully challenge the validity, enforceability or infringement of the third-party patent or circumvent the third-party patent, which would be costly and would require significant time and attention of our management. Third parties may have or obtain valid and enforceable patents or proprietary rights that could block us from developing products using our technology. Our failure to obtain a license to any technology that we require may materially harm our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If we become involved in patent litigation or other proceedings related to a determination of rights, we could incur substantial costs and expenses, substantial liability for damages or be required to stop our product development and commercialization efforts.
Third parties may sue us for infringing their patent rights. Likewise, we may need to resort to litigation to enforce a patent issued or licensed to us or to determine the scope and validity of proprietary rights of others. In addition, a third-party may claim that we have improperly obtained or used our confidential or proprietary information. The cost to us of any litigation or other proceeding relating to intellectual property rights, even if resolved in our favor, could be substantial, and the litigation would divert management’s efforts. Some of our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of complex patent litigation more effectively than we can because they have substantially greater resources. Uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of any litigation could limit our ability to continue our operations.
If any parties successfully claim that our creation or use of proprietary technologies infringes upon their intellectual property rights, we might be forced to pay damages, potentially including treble damages, if we are found to have willfully infringed on such parties’ patent rights. In addition to any damages we might have to pay, a court could require us to stop the infringing activity or obtain a license. Any license required under any patent may not be made available on commercially acceptable terms, if at all. In addition, such licenses are likely to be non-exclusive and, therefore, our competitors may have access to the same technology. If we fail to obtain a required license and are unable to design around a patent, we may be unable to effectively market some of our technology and products, which could limit our ability to generate revenues or achieve profitability and possibly prevent us from generating revenue sufficient to sustain operations.
Failure to obtain regulatory approval outside the United States will prevent us from marketing our product candidates abroad.
We intend to market our product candidates in non-U.S. markets. In order to market product candidates in the European Union and many other non-U.S. jurisdictions, we must obtain separate regulatory approvals. We have had limited interactions with non-U.S. regulatory authorities, the approval procedures vary among countries and can involve additional testing, and the time required to obtain approval may differ from that required to obtain FDA approval. Approval or clearance by the FDA does not ensure approval by regulatory authorities in other countries, and approval by one or more non-U.S. regulatory authorities does not ensure approval by regulatory authorities in other countries or by the FDA. The non-U.S. regulatory approval process may include all of the risks associated with obtaining FDA approval or clearance. We may not obtain non-U.S. regulatory approvals on a timely basis, if at all. We may not be able to file for non-U.S. regulatory approvals and may not receive necessary approvals to commercialize our product candidates in any market.
19
Non-U.S. governments often impose strict price controls, which may adversely affect our future profitability.
We intend to seek approval to market GlucoTrack DF-F and our future product candidates, if any, in both the U.S. and in non-U.S. jurisdictions. If we obtain approval in one or more non-U.S. jurisdictions, we will be subject to rules and regulations in those jurisdictions relating to our products. In some countries, particularly countries of the European Union, each of which has developed its own rules and regulations, pricing may be subject to governmental control under certain circumstances. In these countries, pricing negotiations with governmental authorities can take considerable time after the receipt of marketing approval for a medical device candidate. To obtain reimbursement or pricing approval in some countries, we may be required to conduct a clinical trial that compares the cost-effectiveness of our product to other available products. If reimbursement of our product candidates is unavailable or limited in scope or amount, or if pricing is set at unsatisfactory levels, we may be unable to achieve or sustain profitability.
Our business may become subject to economic, political, regulatory and other risks associated with international operations, which could harm our business.
Our business is subject to risks associated with conducting business internationally. Accordingly, our future results could be harmed by a variety of factors, including:
|
|
·
|
difficulties in compliance with non-U.S. laws and regulations;
|
|
|
·
|
changes in non-U.S. regulations and customs;
|
|
|
·
|
changes in non-U.S. currency exchange rates and currency controls;
|
|
|
·
|
changes in a specific country’s or region’s political or economic environment;
|
|
|
·
|
trade protection measures, import or export licensing requirements or other restrictive actions by U.S. or non-U.S. governments;
|
|
|
·
|
negative consequences from changes in tax laws; and
|
|
|
·
|
difficulties associated with staffing and managing foreign operations, including differing labor relations.
|
Conditions in Israel may harm our ability to produce and sell our products and may adversely affect our business.
Our principal executive offices and research and development facilities, as well as some of our suppliers, are located in Israel. Political, economic and military conditions in Israel directly affect our operations. Specifically, we could be materially adversely affected by:
|
|
·
|
any major hostilities involving Israel;
|
|
|
·
|
a full or partial mobilization of the reserve forces of the Israeli army;
|
|
|
·
|
the interruption or curtailment of trade between Israel and its present trading partners; and
|
|
|
·
|
a significant downturn in the economic or financial conditions in Israel.
|
Since the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948, a number of armed conflicts have taken place between Israel and its neighbors. A state of hostility, varying in degree and intensity, has led to security and economic problems for Israel.
20
Despite the progress towards peace between Israel and its neighbors, the future of these peace efforts remains uncertain. Since October 2000, there has been a substantial deterioration in the relationship between Israel and the Palestinian Authority and a significant increase in violence, civil unrest and hostility, including armed clashes between the State of Israel and the Palestinians, and acts of terror have been committed inside Israel and against Israeli targets in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Moreover, since December 2010, there has been a wave of protests and civil resistance demonstrations in several countries in the Middle East and North Africa, including Egypt and Syria, which share a border with Israel. The demonstrations and acts of civil resistance in Egypt led to the resignation of the former Egyptian president Hosni Mubarak and to extensive revisions in the Egyptian governmental structure. It is not clear how this revolutionary wave, also known as the Arab Spring, will develop and how it will affect the political and security situation in the Middle East. It is also not clear how it will affect Israel and its relationship with its Arab neighbors. Any hostilities involving Israel or any future armed conflicts, political instability or continued violence in the region would likely have a negative effect on our business condition and harm our results of operations.
In addition, Israel’s economy has been subject to numerous destabilizing factors, including a period of rampant inflation in the early to middle 1980s, low foreign exchange reserves, fluctuations in world commodity prices, military conflicts and civil unrest. Furthermore, several countries restrict business with Israel and Israeli companies, which may limit our ability to make sales in those countries. These restrictions, continuing or escalating hostilities in the region or curtailment of trade between Israel and its present trading partners may have an adverse affect on our operating results and financial condition, including our ability to develop, manufacture and market our products.
Our operations could be disrupted as a result of the obligations of key personnel to perform Israeli military service.
Some of our executive officers and employees in Israel are obligated to perform at least 30 days, and up to 40 days, depending on rank and position, of military reserve duty annually and are subject to being called for active duty under emergency circumstances. Moreover, in light of escalating hostilities and threats of armed conflict in the Middle East since October 2000, our executive officers and employees may be called for active military duty for an unlimited period of time. Increased military activity could also result in a reduction of prospective qualified employees available to work for us to increase our business or replace employees on active military duty. Our operations could be disrupted by the absence for a significant period of our executive officers or key employees as a result of military service. Any disruption in our operations could adversely affect our ability to develop and market products.
It may be difficult to enforce a United States judgment against us or our officers and directors to the extent they are located in Israel based upon asserted United States securities law claims.
Most of our executive officers and directors are non-residents of the United States and a substantial portion of our assets and the assets of these persons will be located outside of the United States. Therefore, it may be difficult for an investor, or any other person or entity, to enforce a United States court judgment, including a judgment based upon the civil liability provisions of the Securities Act and the Exchange Act, in original actions instituted in an Israeli court against any of these persons. Furthermore, service of process upon these persons may be difficult to obtain within the United States.
We may not be able to enforce covenants not-to-compete under current Israeli law, which might result in added competition for our products.
We have non-competition agreements or provisions with all of our employees and executive officers, all of which are governed by Israeli law. These agreements or provisions prohibit our employees from competing with us or working for our competitors, generally during, and for up to 9 months after termination of, their employment with us. However, Israeli courts are reluctant to enforce non-compete undertakings of former employees and tend, if at all, to enforce those provisions for only relatively brief periods of time or in restricted geographical areas. In addition, Israeli courts typically require the presence of additional circumstances, such as a demonstration of an employer’s legitimate interest which was damaged; breach of fiduciary duties, loyalty and acting not in good faith; a payment of a special consideration for employee’s non compete obligation; material concern for disclosing employer's trade secrets; or a demonstration that an employee has unique value to the employer specific to that employer’s business, before enforcing a non-competition undertaking against such employee.
21
The funding that we received through the Office of the Chief Scientist, which we refer to as the OCS, for research and development activities restricts our ability to manufacture products or to transfer technology outside of Israel.
On March 4, 2004, the OCS agreed to provide us with a grant of 420,000 New Israeli Shekels, or approximately $93,462, for our plan to develop a non-invasive blood glucose monitor, which we refer to as the development plan. This grant constituted 60% of our research and development budget for the development plan. Due to our acceptance of this grant, we are subject to the provisions of the Israeli Law for the Encouragement of Industrial Research and Development, 1984, which we refer to as the R&D Law. Among other things, the R&D Law restricts our ability to sell or transfer rights in technology or know-how developed with OCS funding or transfer any Means of Control (as defined in the R&D Law) of us to non-Israeli entities. The Industrial Research and Development Committee at the OCS, which we refer to as the research committee, may, under special circumstances, approve the transfer outside of Israel of rights in technology or know-how developed with OCS funding subject to certain conditions, including the condition that certain payments be made to the OCS. Additionally, we may not manufacture products developed with OCS funding outside of Israel without the approval of the research committee. The restrictions regarding the sale or transfer of technology or manufacturing rights out of Israel could have a material adverse effect on our ability to enter into strategic alliances or enter into merger or acquisition transactions in the future that provide for the sale or transfer of our technology or manufacturing rights.
If we are successful in bringing the GlucoTrack DF-F to market, we will be required to use a portion of our net sales to repay certain loans and to pay royalties to the OCS, which will have a negative impact on our net revenues and profitability.
Integrity Israel is required to pay royalties to the OCS on the proceeds from the sale of our systems resulting from research and development projects for which the OCS provided a grant. During the first three years of sales, we are required to pay royalties of 3% of the sales of such products. In the fourth, fifth and sixth years of sales, we are required to pay royalties of 4% of such sales and from the seventh year on we are required to pay royalties of 5% of such sales, in all cases, up to 100% of the amount of grants received by us from the OCS plus interest at the London Interbank Offered Rate, which we refer to as LIBOR. We do not have any other future performance obligations related to the OCS grants. As of June 30, 2011, the contingent liabilities with respect to OCS grants subject to repayment under these royalty agreements equaled $93,462 (NIS 420,000), not including interest.
Messrs. Avner Gal and Zvika Cohen collectively loaned us $48,735 in May 2002 pursuant to an oral agreement. Messrs. Nir Tarlovsky, Yitzhak Fisher and Asher Kugler loaned us $75,000 on March 16, 2004. These loans, in addition to the loan from Dimri mentioned above, are not to be repaid until the first year in which we realize profits in our annual income statement (accounting profit). At such time, the loans are to be repaid on a quarterly basis in an amount equal to 10% of our total sales after deduction of VAT in the relevant quarter, begining the quarter following the first year in which we realize profits in our annual income statement. The total amount to be repaid by the Company to each lender shall be an amount equal to the aggregate principal amount lent by such lender to the Company, plus an amount equal to the product of the amount of each payment made by the Company in respect of such loan multiplied by the difference between the Israeli Consumer Price Index on the date on which the loan was made and the Israeli Consumer Price Index on the date of such payment. However, notwithstanding the abovementioned mechanism, we will not be required to repay the loans during any time when such repayment would cause a deficit in our working capital. Our board of directors is entitled to modify the repayment terms of these loans, so long as such modification does not discriminate against any particular lender, and provided that all payments must be allocated among the lenders on a pro-rata basis.
To the extent that the Company is required to pay royalties to the OCS and repay the loans described above, such payments will reduce the net revenues of the Company for the year(s) in which such payment(s) are made, and, as a result, will reduce the profits of the Company (or increase the losses of the Company, as applicable) for such periods.
We are subject to certain employee severance obligations, which may result in an increase in our expenditures.
Under Israeli law, employers are required to make severance payments to dismissed employees and employees leaving employment in certain other circumstances, on the basis of the latest monthly salary for each year of service. This obligation results in an increase in our expenses, including accrued expenses. Integrity Israel currently makes monthly deposits to insurance policies and severance pay funds in order to provide for this liability.
There is currently no public trading market for our common stock and a trading market may not develop, making it difficult for our stockholders to sell their shares.
There is currently no public trading market for our common stock. We intend to seek a qualification for our common stock to be quoted on the OTCBB, which is administered by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority. In order to have our common stock qualified for quotation on the OTCBB, a FINRA-registered market maker must file an application on Form 211 with FINRA and receive clearance to make a market in the common stock. We will request a FINRA-registered market maker to file an application on Form 211 with FINRA to quote the common stock on the OTCBB once this registration statement on Form S-1 is declared effective by the United States Securities and Exchange Commission. In any event, the application on Form 211 will not be approved until after our registration statement on Form S-1 is declared effective by the SEC. No assurance can be made that a market maker will file an application on Form 211 with FINRA to make a market in the common stock, that an application, if filed, will be approved by FINRA, or that a ticker symbol will be assigned by FINRA for the common stock or that the registration statement will be declared effective in a timely or prompt manner, if at all.
In the absence of an active public trading market, an investor may be unable to liquidate an investment in our common stock. As a result, investors: (i) may be precluded from transferring their shares of common stock; (ii) may have to hold their shares of common stock for an indefinite period of time; and (iii) must be able to bear the complete economic risk of losing their investment in us. In the event a market should develop for the common stock, there can be no assurance that the market price will equal or exceed the price paid for any of the shares offered herein.
22
The market price of our common stock may fluctuate significantly.
If our common stock becomes quoted on the OTCBB or a national securities exchange, the market price of the common stock may fluctuate significantly in response to numerous factors, some of which are beyond our control, such as:
|
|
·
|
the announcement of new products or product enhancements by us or our competitors;
|
|
|
·
|
developments concerning intellectual property rights and regulatory approvals;
|
|
|
·
|
variations in our and our competitors’ results of operations;
|
|
|
·
|
changes in earnings estimates or recommendations by securities analysts, if the common stock is covered by analysts;
|
|
|
·
|
developments in the medical device industry;
|
|
|
·
|
the results of product liability or intellectual property lawsuits;
|
|
|
·
|
future issuances of common stock or other securities;
|
|
|
·
|
the addition or departure of key personnel;
|
|
|
·
|
announcements by us or our competitors of acquisitions, investments or strategic alliances; and
|
|
|
·
|
general market conditions and other factors, including factors unrelated to our operating performance.
|
Further, the stock market in general, and the market for medical device companies in particular, has recently experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations. Continued market fluctuations could result in extreme volatility in the price of our common stock, which could cause a decline in the value of the common stock. Price volatility of our common stock might be significant if the trading volume of the common stock is low, which often occurs with respect to newly traded securities on the OTCBB.
Future sales of common stock could reduce our stock price.
Sales by stockholders of substantial amounts of shares of common stock, the issuance of new shares of common stock by us or the perception that these sales may occur in the future, could materially and adversely affect the market price of the common stock.
Because our common stock may be a “penny stock,” it may be more difficult for investors to sell shares of the common stock, and the market price of the common stock may be adversely affected.
Our common stock may be a penny stock if, among other things, the stock price is below $5.00 per share, it is not listed on a national securities exchange or approved for quotation on the Nasdaq Stock Market or any other national stock exchange or it has not met certain net tangible asset or average revenue requirements. Broker-dealers who sell penny stocks must provide purchasers of these stocks with a standardized risk-disclosure document prepared by the SEC. This document provides information about penny stocks and the nature and level of risks involved in investing in the penny-stock market. A broker must also give a purchaser, orally or in writing, bid and offer quotations and information regarding broker and salesperson compensation, make a written determination that the penny stock is a suitable investment for the purchaser and obtain the purchaser’s written agreement to the purchase. Broker-dealers must also provide customers that hold penny stock in their accounts with such broker-dealer a monthly statement containing price and market information relating to the penny stock. If a penny stock is sold to an investor in violation of the penny stock rules, the investor may be able to cancel its purchase and get its money back.
If applicable, the penny stock rules may make it difficult for investors to sell their shares of common stock. Because of the rules and restrictions applicable to a penny stock, there is less trading in penny stocks and the market price of the common stock may be adversely affected. Also, many brokers choose not to participate in penny stock transactions. Accordingly, investors may not always be able to resell their shares of common stock publicly at times and prices that they feel are appropriate.
23
Compliance with changing regulations concerning corporate governance and public disclosure may result in additional expenses.
There have been changing laws, regulations and standards relating to corporate governance and public disclosure, including the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, new regulations promulgated by the SEC and rules promulgated by the national securities exchanges. These new or changed laws, regulations and standards are subject to varying interpretations in many cases due to their lack of specificity, and, as a result, their application in practice may evolve over time as new guidance is provided by regulatory and governing bodies, which could result in continuing uncertainty regarding compliance matters and higher costs necessitated by ongoing revisions to disclosure and governance practices. As a result, our efforts to comply with evolving laws, regulations and standards are likely to continue to result in increased general and administrative expenses and a diversion of management time and attention from revenue-generating activities to compliance activities. Our directors, Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer could face an increased risk of personal liability in connection with the performance of their duties. As a result, we may have difficulty attracting and retaining qualified directors and executive officers, which could harm our business. If our efforts to comply with new or changed laws, regulations and standards differ from the activities intended by regulatory or governing bodies, we could be subject to liability under applicable laws or our reputation may be harmed.
24
We will not receive any of the proceeds from the sale or other disposition of the shares of common stock offered hereby.
DIVIDEND POLICY
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock and do not anticipate paying any dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. Any cash that might be available for payment of dividends will be used to expand our business. Payments of any cash dividends in the future will depend on our financial condition, results of operation and capital requirements, as well as other factors deemed relevant to our board of directors.
DETERMINATION OF OFFERING PRICE
Until our common stock is quoted on the OTCBB, the selling stockholders may sell their shares of our common stock at a fixed price of $6.25 per share. This offering price was determined on the basis of the offering price per share of common stock in our most recent private placement completed in July 2011. If our common stock becomes quoted on the OTCBB, the selling shareholders will sell their shares of our common stock at prevailing market prices or privately negotiated prices. There is currently no public market for our common stock. Although we intend to seek a qualification for our common stock to be quoted on the OTCBB; no assurance can be given as to our success in qualifying for quotation on the OTCBB.
DILUTION
The common stock to be sold by the selling stockholders is common stock that is currently issued and outstanding. Accordingly, there will be no dilution to our existing stockholders.
25
CAPITALIZATION
The table below sets forth our capitalization on an unaudited basis as of June 30, 2011:
|
|
·
|
on an actual basis; and
|
|
|
·
|
on a pro forma as adjusted basis to reflect the sale by us of 269,680 shares of common stock in the private placement since June 30, 2011.
|
You should read this table together with the section entitled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our financial statements and the related notes appearing elsewhere in this prospectus.
|
As of June 30,
2011 (unaudited)
Actual Adjusted
|
Pro Forma
|
|||||||
|
Debt
|
||||||||
|
Credit Facility
|
-
|
-
|
||||||
|
Long-Term Loans from Stockholder
|
641,428
|
|
641,428
|
|
||||
|
Total Debt
|
641,428
|
641,428
|
|
|||||
|
Stockholders’ Equity
|
||||||||
|
Common Stock
|
5,026
|
|
5,296
|
|
||||
|
Additional Paid-In Capital
|
11,886,895
|
|
13,351,180
|
|
||||
|
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income
|
(16,394
|
)
|
(16,394
|
)
|
||||
|
Deficit Accumulated during the Development Stage
|
(11,210,101
|
)
|
(11,210,101
|
)
|
||||
|
Total Stockholders’ Equity
|
665,426
|
|
2,129,980
|
|
||||
|
Total Capitalization
|
1,306,854
|
|
2,771,408
|
|
||||
26
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Prospective investors should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations together with our financial statements and the related notes and other financial information included elsewhere in this prospectus. Some of the information contained in this discussion and analysis or set forth elsewhere in this prospectus, including information with respect to our plans and strategy for our business and related financing, includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. You should review the “Risk Factors” section of this prospectus for a discussion of important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from the results described in or implied by the forward-looking statements contained in the following discussion and analysis .
Overview
We are a development stage medical device company focused on the design, development and commercialization of non-invasive glucose monitoring devices for use by persons suffering from diabetes. Our wholly-owned subsidiary, Integrity Israel, was founded in 2001 with a mission to develop, produce and market non-invasive glucose monitors for home use by diabetics. We have developed a non-invasive blood glucose monitor, the GlucoTrack DF-F glucose monitoring device, which is designed to help people with diabetes obtain blood glucose level readings without the pain, inconvenience, cost and difficulty of conventional (invasive) spot finger stick devices. The GlucoTrack DF-F utilizes a patented combination of ultrasound, electromagnetic and thermal technologies to obtain blood glucose measurements in less than one minute via a small sensor that is clipped onto one’s earlobe and connected to a small, handheld control and display unit, all without drawing blood. Integrity Israel conducted pre-clinical trials involving over 5,000 readings from approximately 350 patients over the last five years. Clinical data collected during 2009 at the Soroka University Medical Center in Be’er Sheva, Israel indicate a positive correlation between GlucoTrack DF-F readings and those obtained from conventional invasive devices. More specifically, a set of pre- clinical trials conducted on 89 patients of various weights, ages, diabetes types and genders involved 1,772 measurements, of which 96% were within the clinically acceptable zones of the CEG (zones A and B). Similarly, approximately 90% of the measurements in an at home study of four participants were within clinically acceptable zones A and B of the CEG. Measurements are clinically acceptable, compared to a referenced invasive device, when the variance, if any, between the devices would have no worse than a benign effect on the patients. These pre-clinical trials involved small patient populations. Because of the small sample size, the results of these pre-clinical trials may not be indicative of future results. We expect to begin the performance and safety stage of formal clinical trials in Israel and Europe by the second quarter of 2012 and to begin clinical trials in the United States by late 2012, if our clinical trial protocol is approved by the FDA.
Recent Developments
On July 15, 2010, Integrity U.S., Integrity Israel, and Integrity Acquisition completed a reorganization, pursuant to which Integrity Acquisition merged with and into Integrity Israel and all of the stockholders and option holders of Integrity Israel became entitled to receive shares and options in Integrity U.S. in exchange for their shares and options in Integrity Israel. Following the reorganization, the former equity holders of Integrity Israel received the same proportional ownership in Integrity U.S. as they had in Integrity Israel prior to the reorganization. As a result of the reorganization, Integrity Israel became a wholly owned subsidiary of Integrity U.S. Pursuant to a tax ruling from the Israeli Tax Authorities, the former stockholders and options holders of Integrity Israel will be exempted from tax liability with respect to the reorganization until they sell their holdings in Integrity U.S. so long as they deposit all their shares and options with a trustee for a period of two years from the issuance of such shares or options, as applicable, in connection with the reorganization, give their written consent to the tax ruling and satisfy certain additional conditions detailed in the ruling. As a result, any of our stockholders that complies with this tax ruling will be unable to sell any of its shares of common stock of Integrity U.S. for such two year period. Approximately 82% of our stockholders at the time of the reorganization (holding 3,280,000 of 3,999,998 shares then outstanding) complied with the ruling.
On July 26, 2010, we commenced an offering of up to 2,000,000 shares of our common stock to accredited investors at a price of $6.25 per share in the private placement. The private placement resulted in the sale by us of an aggregate of 1,295,545 shares of common stock in seven closings held on December 16, 2010, December 30, 2010, January 31, 2011, March 31, 2011, April 29, 2011, May 31, 2011 and July 29, 2011, respectively. Purchasers of common stock in the private placement are entitled to anti-dilution protection until September 1, 2012 for certain issuances of common stock by us for less than $6.25 per share. See “Description of Securities.”
27
In connection with the private placement, we agreed to issue to Andrew Garrett, Inc. at each closing of the private placement, in partial consideration for its services as placement agent, warrants to purchase a number of shares of common stock equal to 10% of the number of shares sold at such closing. In total, we issued to the placement agent warrants to purchase up to an aggregate of 129,556 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $6.25 per share in connection with each closing of the private placement. The warrants have a five year term expiring on the fifth anniversary of the date of effectiveness of this registration statement.
On December 16, 2010, we issued 259,185 shares of common stock to the holders of certain Senior Secured Promissory Notes issued by Integrity Israel in April 2010. Such issuance was made in accordance with the terms of the notes and was made in partial repayment of the aggregate outstanding principal amount thereof. Upon the issuance of the shares described above and the payment of any additional principal amount outstanding in cash, all of the Senior Notes were retired on December 16, 2010. Also on December 16, 2010, we issued 54,792 shares of common stock to the holders of certain Junior Promissory Notes issued by Integrity Israel in November 2010 in accordance with, and in full repayment of, such notes.
We have not generated any revenues from operations to fund our activities and are therefore dependent upon external sources for financing our operations. There can be no assurance that we will succeed in obtaining the necessary financing to continue our operations. Since the inception of Integrity Israel in 2001, we have suffered accumulated losses of approximately $11.2 million and have a cumulative negative operating cash flow of approximately $8.2 million. These factors raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern without the proceeds of this offering. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Integrity Israel is committed to pay royalties to the OCS on the proceeds from the sale of our systems resulting from research and development projects for which the OCS provided a grant. During the first three years of sales, we are required to pay royalties of 3% of the sales of such products. In the fourth, fifth and sixth years of sales, we are required to pay royalties of 4% of such sales and from the seventh year on we are required to pay royalties of 5% of such sales, in all cases, up to 100% of the amount of grants received by us from the OCS plus interest at LIBOR. We do not have any other future performance obligations related to the OCS grants. As of June 30, 2011, the contingent liabilities with respect to OCS grants subject to repayment under these royalty agreements equaled $93,462 (NIS 420,000), not including interest.
Critical Accounting Policies
This Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations discusses our financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. The preparation of these financial statements requires making estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, as well as the reported revenues and expenses for the reporting periods. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate such estimates and judgments, including those described in greater detail below. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other factors that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. A more detailed discussion on the application of these and other accounting policies can be found in Note 2 in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in this prospectus. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
While all the accounting policies impact the financial statements, certain policies may be viewed to be critical. Our management believes that the accounting policies which involve more significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of our consolidated financial statement include stock-based compensation.
Stock-based compensation, including grants of stock options and grants of shares, are recognized in the consolidated statements of operations as an operating expense, based on an estimate of the fair value of each award on the date of grant. The fair value of stock options is estimated using the Black Scholes option-pricing model and the fair value of share grants is estimated using recent transaction prices.
The fair value of the portion of the award that is ultimately expected to vest, is recognized as an expense over the requisite service period or over the implicit service period when performance condition affects the vesting, if it is probable that the performance condition will be achieved.
Compensation costs are expensed, net of estimated forfeitures, applying the accelerated vesting method (graded vesting).
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
ASC Topic 220, "Comprehensive Income"
In June 2011, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issued Accounting Standard Update No. 2011-05, “Comprehensive Income (Topic 220) - Presentation of Comprehensive Income,” which we refer to as ASU 2011-05. ASU 2011-05 eliminates the option to present the components of other comprehensive income as part of the statement of equity and requires an entity to present the total of comprehensive income, the components of net income, and the components of other comprehensive income either in a single continuous statement of comprehensive income or in two separate but consecutive statements.
28
ASU 2011-05 will be effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2011 (fiscal year 2012 for the Company) and should be applied retrospectively.
Results of Operations
The following discussion of the our operating results explains material changes in our results of operations for the six and three months ended June 30, 2011 and the fiscal year ended December 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009 compared to their respective prior periods. The discussion should be read in conjunction with the section entitled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the financial statements and related notes included in the prospectus.
Six Months Ended June 30, 2011 Compared to Six Months Ended June 30, 2010
Revenues
We had no revenue during the six months ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 as we had not yet commercialized the GlucoTrack product candidate.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses were $781,114 for the six months ended June 30, 2011, as compared to $489,096 for the prior-year period. The increase is primarily attributable to an increase in stock based compensation as well as an increase in employees’ salaries, development of a new model of the main unit for GlucoTrack DF-F and costs involved in expediting product readiness for clinical trials. Research and development expenses consist primarily of salaries and other personnel-related expenses, including stock-based compensation expenses, materials, travel expenses, clinical trials and other expenses. We expect research and development expenses to increase in the second half of 2011 and beyond as we enter into more advanced stages of development for GlucoTrack DF-F, including the commencement of multicenter, formal clinical trials, as well as commencement of the development of other products in the GlucoTrack family.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses were $254,736 for the six months ended June 30, 2011, as compared to $226,352 for the prior-year period. The increase is primarily attributable to an increase in stock based compensation. General and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and other related expenses for executive, finance and administrative personnel, including stock-based compensation expense. Other general and administrative costs and expenses include facility-related costs not otherwise included in research and development costs and expenses, and professional fees for legal and accounting services. We expect that our general and administrative costs and expenses will increase during the second half of 2011 and beyond as we prepare for and later commence clinical trial activities for the GlucoTrack DF-F and incur increased costs to comply with the reporting and other compliance obligations applicable to public reporting companies.
Financing Expenses, net
Financing expenses, net was 21,071 for the six months ended June 30, 2011, as compared to expenses of $757,003 for the prior-year period. The decrease is primarily attributable to decrease in stock-based interest compensation to holders of convertible notes, the changes in exchange rates, which impact the principal of loans from stockholders that are denominated in NIS, and the decrease in other interest expenses.
Net Loss
Net loss was $1,056,921 for the six months ended June 30, 2011, as compared to $1,472,451 for the prior-year period.
29
Three Months Ended June 30, 2011 Compared to Three Months Ended June 30, 2010
Revenues
We had no revenue during the three months ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 as we had not yet commercialized the GlucoTrack product candidate.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses were $407,631 for the three months ended June 30, 2011, as compared to $272,483 for the prior-year period. The increase is primarily attributable to an increase in stock based compensation as well as an increase in employees’ salaries, development of a new model of the main unit for GlucoTrack DF-F and costs involved in expediting product readiness for clinical trials. Research and development expenses consist primarily of salaries and other personnel-related expenses, including stock-based compensation expenses, materials, travel expenses, clinical trials and other expenses. We expect research and development expenses to increase in the second half of 2011 and beyond as we enter into more advanced stages of development for GlucoTrack DF-F, including the commencement of multicenter, formal clinical trials, as well as commencement of the development of other products in the GlucoTrack family.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses were $89,098 for the three months ended June 30, 2011, as compared to $83,293 for the prior-year period. The increase is primarily attributable to an increase in stock based compensation as well as an increase in employees’ salaries. General and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and other related expenses for executive, finance and administrative personnel, including stock-based compensation expense. Other general and administrative costs and expenses include facility-related costs not otherwise included in research and development costs and expenses, and professional fees for legal and accounting services. We expect that our general and administrative costs and expenses will increase during the second half of 2011 and beyond as we prepare for and later commence clinical trial activities for the GlucoTrack DF-F and incur increased costs to comply with the reporting and other compliance obligations applicable to public reporting companies.
Financing Expenses, net
Financing expense, net was $19,928 for the three months ended June 30, 2011, as compared to $753,670 for the prior-year period. The decrease is primarily attributable to decrease in stock-based interest compensation to holders of convertible notes, the changes in exchange rates, which impact the principal of loans from stockholders that are denominated in NIS, and the decrease in other interest expenses.
Net Loss
Net loss was $516,657 for the three months ended June 30, 2011, as compared to $1,109,446 for the prior-year period.
Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2010 Compared to the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2009
Revenues
We had no revenue during the years ended December 31, 2010 and 2009 as we had not yet commercialized the GlucoTrack product candidate.
30
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses were $934,056 for the year ended December 31, 2010, as compared to $1,005,108 for the prior-year period. The decrease is primarily attributable to a decrease in professional fees associated with subcontractors and related expenses associated with pre-clinical trials. Research and development expenses consist primarily of salaries and other personnel-related expenses, including stock-based compensation expenses, materials, travel expenses and other expenses. We expect research and development expenses to increase in the second half of 2011 and beyond as we enter into more advanced stages of development for GlucoTrack DF-F, including the commencement of multicenter, formal clinical trials, as well as commencement of the development of other products in the GlucoTrack family.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses were $457,495 for the year ended December 31, 2010, as compared to $165,156 for the prior-year period. The increase is primarily attributable to an increase in professional fees associated with our capital raising efforts, including costs associated with the reorganization, the private placement and the offering of the Senior Subordinated Notes. General and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and other related expenses for executive, finance and administrative personnel, including stock-based compensation expense. Other general and administrative costs and expenses include facility-related costs not otherwise included in research and development costs and expenses, and professional fees for legal and accounting services. We expect that our general and administrative costs and expenses will increase during the second half of 2011 and beyond as we prepare for and later commence clinical trial activities for the GlucoTrack DF-F and incur increased costs to comply with the reporting and other compliance obligations applicable to public reporting companies.
Financing Expenses, net
Financing expense, net was $1,397,807 for the year ended December 31, 2010, as compared to approximately $32,032 for the prior-year period. The increase is primarily attributable to an increase in costs related to the issuance of common stock to the holders of convertible notes.
Net Loss
Net loss was $2,788,446 for the year ended December 31, 2010, as compared to approximately $1,202,296 for the prior-year period.
Year Ended December 31, 2009 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2008
Revenues
We had no revenue during the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 as we had not yet commercialized the GlucoTrack product candidate.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses were $1,005,108 for the year ended December 31, 2009, as compared to $1,242,410 for the year ended December 31, 2008. The decrease is primarily attributable to a decrease in professional fees associated with subcontractors.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses were $165,156 for the year ended December 31, 2009, as compared to $156,632 for the year ended December 31, 2008. The increase is primarily attributable to an increase in fundraising expenses. General and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and other related expenses, including stock-based compensation expense. Other general and administrative costs and expenses include facility-related costs not otherwise included in research and development costs and expenses, and professional fees for legal and accounting services.
31
Financing Expenses, net
Financing expense, net was $32,032 for the year ended December 31, 2009, as compared to $129,939 for the year ended December 31, 2008. The decrease is primarily attributable to a decrease in foreign exchange loss for balances denominated in New Israeli Shekels and linkage difference on principal of loans from stockholders, partially offset by other.
Net Loss
Net loss was $1,202,296 for the year ended December 31, 2009, as compared to $1,528,981 for the year ended December 31, 2008.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We currently have extremely limited liquidity. As of September 30, 2011, cash on hand was approximately NIS 8.9 million (approximately $2.4 million per the same day exchange rate). Our credit line availability was NIS 300,000 (approximately $81,000 at the same rate). Based on our current strategy and operating plan, we believe that this sum (approximately $2.4 million) will enable us to operate for a period of at least 12 months. If we change our current strategy or operating plan, we may need to raise additional capital prior to the end of such 12 month period.
Integrity Israel is party to a loan and investment agreement dated February 18, 2003 with Dimri pursuant to which Dimri loaned us a principal amount of NIS 1,440,000, subject to linkage differences in Israel ($421,669 based on an exchange rate of $3.415 NIS/dollar as of June 30, 2011). In addition, Messrs. Avner Gal and Zvika Cohen collectively loaned us $48,735 in May 2002 pursuant to an oral agreement. Messrs. Nir Tarlovsky, Yitzhak Fisher and Asher Kugler loaned us $75,000 on March 16, 2004. These loans, in addition to the loan from Dimri mentioned above, are not to be repaid until the first year in which we realize profits in our annual income statement (accounting profit). At such time, the loans are to be repaid on a quarterly basis in an amount equal to 10% of our total sales after deduction of VAT in the relevant quarter, begining on the quarter following the first year in which we realize profits in our annual income statement. The total amount to be repaid by the Company to each lender shall be an amount equal to the aggregate principal amount lent by such lender to the Company, plus an amount equal to the product of the amount of each payment made by the Company in respect of such loan multiplied by the difference between the Israeli Consumer Price Index on the date on which the loan was made and the Israeli Consumer Price Index on the date of such payment. However, notwithstanding the abovementioned mechanism, we will not be required to repay the loans during any time when such repayment would cause a deficit in our working capital. Our board of directors is entitled to modify the repayment terms of these loans, so long as such modification does not discriminate against any particular lender, and provided that all payments must be allocated among the lenders on a pro-rata basis.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of June 30, 2010, we did not have any off-balance sheet arrangements as defined in Item 303(a)(4) of Regulation S-K.
32
BUSINESS
Overview
On July 15, 2010, Integrity U.S., Integrity Israel, and Integrity Acquisition completed a reorganization, pursuant to which Integrity Acquisition merged with and into Integrity Israel and all of the stockholders and option holders of Integrity Israel became entitled to receive shares and options in us, in exchange for their shares and options in Integrity Israel. Following the reorganization, the former equity holders of Integrity Israel were entitled to the same proportional ownership in us as they had in Integrity Israel prior to the reorganization. As a result of the reorganization, Integrity Israel became our wholly-owned subsidiary.
On April 29, 2010, Integrity Israel received a tax ruling from the Israeli Tax Authorities pursuant to which the former stockholders and options holders of Integrity Israel will be exempt from tax liability with respect to the reorganization until they sell their holdings in our Company, provided that they deposit all their shares and options with a trustee for a period of two years from the issuance of shares in connection with the reorganization, give their written consent to the tax ruling and satisfy additional conditions detailed in the ruling. As a result, none of such stockholders will be entitled to sell any of their shares of common stock for such two year period. Approximately 82% of our stockholders at the time of the reorganization (holding 3,280,000 of 3,999,998 shares then outstanding) complied with the ruling.
We are a development stage medical device company focused on the design, development and commercialization of non-invasive glucose monitoring devices for use by persons suffering from diabetes. Integrity Israel was founded in 2001 with a mission to develop, produce and market non-invasive glucose monitors for home use by diabetics. We have developed a non-invasive blood glucose monitor, the GlucoTrack DF-F, which is designed to help people with diabetes obtain blood glucose level readings without the pain, inconvenience, cost and difficulty of conventional (invasive) spot finger stick devices. The GlucoTrack DF-F utilizes a patented combination of ultrasound, electromagnetic and thermal technologies to obtain blood glucose measurements in less than one minute via a small sensor that is clipped onto one’s earlobe and connected to a small, handheld control and display unit, all without drawing blood. We have developed four generations of prototypes of the GlucoTrack DF-F, completed in 2003, 2005, 2006 and 2008 respectively. The GlucoTrack DF-F currently in pre-clinical trials is the GlucoTrack DF-F prototype completed in 2008. Integrity Israel has conducted pre-clinical trials involving over 5,000 readings from approximately 350 patients over the last seven years. Clinical data collected during 2009 at the Soroka University Medical Center in Be’er Sheva, Israel indicate a positive correlation between GlucoTrack DF-F readings and those obtained from conventional invasive devices. More specifically, a set of pre-clinical trials conducted on 89 patients of various weights, age, diabetes type and gender involved 1,772 measurements, of which 96% were within the clinically acceptable zones of the CEG, (zones A and B). Similarly, an at home study of four participants conducted in early 2010 resulted in approximately 90% of the measurements within clinically acceptable zones A and B of the CEG. Measurements are clinically acceptable, as compared to a referenced invasive device, when the variance, if any, between the devices would have little or no effect on the patients. These pre-clinical trials involved small patient populations. Because of the small sample size, the results of these pre-clinical trials may not be indicative of future results. Analyses from the at home study show that there are a few parameters that reduce accuracy, such as the learning curve, the use of a home use device as a reference, failure to properly follow instructions for use, including use of the reference (invasive) device, and the variability of the ambient temperature in a given testing environment. We have already made some modifications to the GlucoTrack DF-F to limit the effect of these parameters and additional modifications are in process, including the addition of a sensor to gauge the ambient temperature in the testing environment, and modifications to the software utilized by the GlucoTrack device to take the ambient temperature into account in determining the patient’s blood glucose level. While we believe that these modifications will improve the results of the GlucoTrack device, no assurance can be given as to the extent (if any) to which these modifications will improve the effectiveness of the device. We believe that the results of the home study show that with some modifications to the GlucoTrack DF-F, we will be able to improve the accuracy and reliability measurements of glucose levels in the home and home-like environments. We expect to begin the performance and safety stage of formal clinical trials in Israel and Europe by the second quarter of 2012 and, expect to begin clinical trials in the United States by late 2012, if our clinical trial protocol is approved by the FDA. The GlucoTrack DF-F has not yet been approved for commercial sale in the United States, the European Union or any other jurisdiction. See “Business - Government Regulation - Regulation of the Design, Manufacture and Distribution of Medical Devices” below for a discussion of the approval process for commercial sale. There can be no assurance that approval for commercial sale in any jurisdiction will be obtained.
To our knowledge, there are currently no devices approved for use in either the United States or the European Union for spot or continuous non-invasive blood glucose measurement.
We were incorporated in Delaware and Integrity Acquisition was incorporated in Israel, in May 2010. Integrity Israel was incorporated on September 30, 2001. On July 15, 2010, Integrity Israel conducted the reorganization pursuant to which, through a reverse triangular merger, Integrity Israel’s stockholders received newly issued shares of our common stock for their shares in Integrity Israel. We operate primarily through Integrity Israel. Our principal offices are located at 102 Ha’Avoda St., Ashkelon, Israel 78100 and our telephone number is 972-8-675-7878. There is no relationship between Integrity Applications, Inc., the registrant under the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part, and Integrity Applications, Incorporated, the engineering and software services company based in Chantilly, Virginia.
Our website address is http://www.integrity-app.com; the reference to such website address does not constitute incorporation by reference of the information contained on the website and such information should not be considered part of this prospectus.
33
Market Opportunity
Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic, life-threatening disease for which there is no known cure. Diabetes is caused by the body’s inability to produce or effectively utilize the hormone insulin. This inability prevents the body from adequately regulating blood glucose levels. Glucose, the primary source of energy for cells, must be maintained at certain concentrations in the blood in order to permit optimal cell function and health. Normally, the pancreas provides control of blood glucose levels by secreting the hormone insulin to decrease blood glucose levels when concentrations are too high. In people with diabetes, blood glucose levels fluctuate between very high levels, a condition known as hyperglycemia, and very low levels, a condition called hypoglycemia. Hyperglycemia can lead to serious long-term complications, such as blindness, kidney disease, nervous system disease, amputations, stroke and cardiovascular disease. Hypoglycemia can lead to confusion, loss of consciousness or death.
Diabetes is typically classified into two major groups: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes is characterized by the body’s inability to produce insulin, resulting from destruction of the insulin producing cells of the pancreas. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes must rely on frequent insulin injections in order to regulate and maintain blood glucose levels. Type 1 diabetes is frequently diagnosed during childhood or adolescence, although disease onset can occur at any age. Type 2 diabetes, the more common form of diabetes, is characterized by the body’s inability to either properly utilize insulin or produce enough insulin. Type 2 diabetes is associated with older age, obesity, family history of diabetes, history of gestational diabetes, impaired glucose metabolism, physical inactivity and race or ethnicity. Depending on the severity of Type 2 diabetes, individuals may require diet and nutrition management, exercise, oral medications or insulin injections to regulate blood glucose levels.
According to the Diabetes Atlas (Fourth Edition) published by the International Diabetes Federation in 2009, an estimated 285 million adults aged from 20 to 79 worldwide, or 6.4% of the world’s adult population, will suffer from diabetes in 2010, not including those persons who suffer from IGT or Gestational Diabetes. The International Diabetes Federation estimates that this number will grow to approximately 438 million adults worldwide, or 7.7% of the world’s adult population, in 2030, and that by 2030 the number of adults suffering from diabetes will have increased by 98.1% in Africa, 93.9% in the Middle East and North Africa, 72.1% in Southeast Asia, 65.1% in South and Central America, 47.0% in the Western Pacific, 42.4% in North America and the Caribbean and 20.0% in Europe, over such regions’ respective 2010 levels. According to a statement made by the President of the International Diabetes Federation at a press briefing at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes in September 2011, an estimated 366 million people currently suffer from diabetes, and approximately 4.6 million deaths are attributable to diabetes annually.
We believe that individuals with IGT generally do not take glucose level measurements because they do not find the pain and cost of monitoring to outweigh the risk they take by not monitoring their glucose level. Having knowledge about the glucose level can postpone, or even, to some extent prevent the development of diabetes. A simple to use, painless device may encourage this population to monitor themselves more frequently. We believe that a device like GlucoTrack (not necessarily the DF-F) may be attractive to the IGT community, given that the device is expected to be less expensive than conventional (invasive) spot finger stick devices, easy to use and painless.
The CDC, in its 2011 National Diabetes Fact Sheet, estimated that in the United States alone, more than 25.8 million people, or 8.3% of the U.S. population, suffered from diabetes in 2010. According to the National Diabetes Education Program, approximately 5-10% of the diabetes population had Type 1 diabetes at the time of measurement.
According to the National Diabetes Education Program, about 75% of all newly diagnosed cases of Type 1 diabetes in the United States occur in juveniles younger than 18 years of age. In addition, according to the National Diabetes Education Program, Type 2 diabetes is occurring with increasing frequency in young people. The increase in prevalence is related to an increase in obesity amongst children. According to the 2007-2008 National Health and Examination Survey, approximately 16% of children and teens were overweight, about double the number two decades before.
The CDC, in its 2011 National Diabetes Fact Sheet, estimates that the direct medical costs and indirect expenditures attributable to diabetes in the United States were $174 billion in 2007, an increase of $42 billion since 2002. Of this amount, the CDC estimates that approximately $116 billion were direct medical costs. The International Diabetes Federation estimates that worldwide healthcare expenditures to treat and prevent diabetes and its complications will total at least $376 billion in 2010, $198 billion in the United States alone, and $490 billion worldwide in 2030. According to a May 2010 special report by Pharmalive.com, a leading publisher of market research in medical markets, the market for self-monitoring glucose tests is estimated to be approximately $8 billion in 2010.
34
Glucose Monitoring
Blood glucose levels can be affected by many factors, including the carbohydrate and fat content of meals, exercise, stress, illness or impending illness, hormonal releases, variability in insulin absorption and changes in the effects of insulin in the body. Given the many factors that affect blood glucose levels, maintaining glucose within a normal range can be difficult. Diabetics generally manage their blood glucose levels by administering insulin or ingesting carbohydrates throughout the day to maintain blood glucose within normal ranges. Normal ranges in diabetics vary from person to person. In order to maintain blood glucose levels within normal ranges, diabetics must first measure their blood glucose levels so that they can make the proper therapeutic adjustments. As adjustments are made, additional blood glucose measurements may be necessary to gauge the individual’s response to the adjustments. More frequent testing of blood glucose levels provides patients with information that can be used to better understand and manage their diabetes. Testing of blood glucose levels is usually done before meals, after meals and before going to sleep. Diabetics who take insulin usually need to test more often than those who do not take insulin.
The outcome of clinical data supports the recommendation that frequent monitoring of blood glucose levels is an important component of effective diabetes management. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial, consisting of patients with Type 1 diabetes, and the 1998 UK Prospective Diabetes Study, consisting of patients with Type 2 diabetes, demonstrated that patients who intensely managed blood glucose levels delayed the onset and slowed the progression of diabetes-related complications. In the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial, a major component of intensive management was monitoring blood glucose levels at least four times per day using conventional spot finger stick blood glucose meters. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial demonstrated that intensive management reduced the risk of complications by 76% for eye disease, 60% for nerve disease and 50% for kidney disease. However, the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial also found that intensive management led to a two- to three-fold increase in the frequency of hypoglycemic events. In the December 2005 edition of the New England Journal of Medicine, the authors of a peer-reviewed study concluded that intensive diabetes therapy has long-term beneficial effects on the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with Type 1 diabetes. The study showed that intensive diabetes therapy reduced the risk of cardiovascular disease by 42% and the risk of non-fatal heart attack, stroke or death from cardiovascular disease by 57%. However, despite evidence that intensive glucose management reduces the long-term complications associated with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association reported in a 2001 issue of its publication Diabetes Care that up to 67% of patients with diabetes fail to routinely monitor their glucose levels.
Spot finger stick devices are the most prevalent devices for blood glucose monitoring. These devices require inserting a strip into a glucose meter, taking a blood sample with a finger stick and placing a drop of blood on the test strip that yields a single point in time blood glucose measurement. Despite continued developments in the field of blood glucose monitors, the routine measurement of glucose levels remains invasive, painful, inconvenient, difficult and costly. This has resulted in a sub-optimal measurement regimen for many diabetics.
The FDA, has also recently approved continuous glucose monitoring systems for blood glucose monitoring, when prescribed by a doctor. Continuous glucose monitoring systems use sensors inserted under the skin to check glucose levels in interstitial fluid. The sensor stays in place for several days to a week and then must be replaced. A transmitter sends information about glucose levels via radio waves from the sensor to a pager-like wireless monitor. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases at the National Institutes of Health, continuous glucose monitoring device users must check blood samples with a conventional glucose meter to calibrate the continuous glucose monitoring systems devices, and because currently approved continuous glucose monitoring systems are not as accurate as standard blood glucose meters, users should confirm glucose levels with a meter before changing treatment.
To our knowledge, there are currently no devices approved for use in either the United States or the European Union for spot or continuous non-invasive blood glucose measurement. The FDA has previously approved a single non-invasive product for glucose trend analysis, the GlucoWatch®, so long as the device was used with conventional finger stick glucose monitoring devices. However, the device is no longer available commercially.
35
We believe that a significant market opportunity exists for a reliable, inexpensive, non-invasive blood glucose measurement device and that such a device could greatly increase compliance with blood glucose measurement recommendations and help many diabetics better manage their disease, providing significant benefits to both patients and payors.
The Product
Our non-invasive blood glucose monitor, the GlucoTrack DF-F, utilizes a combination of ultrasound, electromagnetic and thermal technologies to obtain blood glucose measurements in less than one minute via a small sensor that is clipped onto one’s earlobe and connected to a handheld control and display unit. See Figure A, below.
Figure A

We believe that the GlucoTrack DF-F addresses the expressed, currently unmet needs of the diabetic market as it removes or diminishes two of the most significant barriers to the recommended frequent monitoring of blood glucose by diabetics:
|
|
·
|
pain, as the GlucoTrack DF-F is a truly non-invasive device; and
|
|
|
·
|
cost, as, despite the relatively high upfront cost of purchasing a GlucoTrack DF-F, we anticipate that the total cost of purchasing a device and purchasing replacement ear clips every six months (anticipated to be the only recurring cost, other than recalibration costs, which are expected to be minimal) over the useful life of the device will be significantly lower than the cost of purchasing single use glucose sticks over that same period. See Figure B on page 37 and the accompanying footnotes for a direct cost comparison of the GlocoTrack DF-F and conventional (invasive) spot finger stick devices.
|
36
Integrity estimates that over a five-year period, a GlucoTrack DF-F user could save an average of $6,405 when compared to the cost of a conventional invasive blood glucose monitoring system, while also taking advantage of the benefits of more frequent blood glucose testing. See Figure B, below.
Figure B
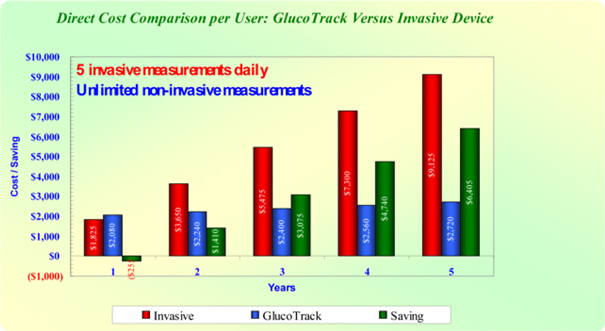
The direct cost comparison assumes (i) a single invasive measurement costs $1.00; (ii) the average user of an invasive device takes five measurements daily; (iii) the average retail price for the GlucoTrack DF-F is $2,000 (including one personal ear clip); and (iv) the personal ear clip is replaced every six months at a cost of $80. The direct cost comparison excludes recalibration costs, which are expected to be approximately $70, in total, over a five year period.
Despite the fact that the overall costs associated with owning and using a GlucoTrack DF-F device are expected to be substantially lower than the cost of purchasing and using single use invasive devices over an extended period of time, as demonstrated in Figure B above, the significant initial purchase price of a GlucoTrack device might present a barrier to adoption of the GlucoTrack system by patients. In light of this fact, we are considering options to lessen the initial financial burden associated with purchasing a GlucoTrack device, including leasing devices to users. In addition, we intend to seek reimbursement approval for the GlucoTrack device from third-party payors, including government payors, such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs, managed care organizations and other third-party payors. There can be no assurance that such third party-payors will provide reimbursement coverage for the GlucoTrack or, if so, whether such reimbursement coverage will be adequate. See “Risk Factors - If GlucoTrack DF-F or our future product candidates, if any, fail to achieve market acceptance, we may not be able to generate significant revenue or achieve or sustain profitability.” on page 15 of this prospectus.
37
Instead of using blood as conventional spot finger stick devices do, the GlucoTrack DF-F uses a small, non-invasive sensor that is clipped onto a user’s earlobe to obtain certain body measurements using three technologies, which are then analyzed using a proprietary algorithm on a small, handheld control and display unit. Within one minute, the GlucoTrack DF-F will produce a blood glucose measurement that can be simultaneously audibly announced and displayed on the control unit, as well as recorded on internal flash memory. A conceptual block diagram of the GlucoTrack DF-F is set forth below as Figure C.
Figure C
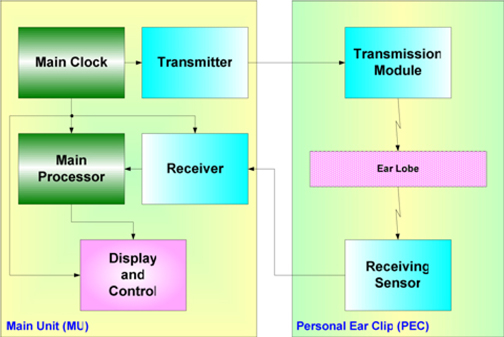
As shown in Figure C, the GlucoTrack DF-F contains two units: the main unit, which contains the triggers that produce the signals to obtain the necessary measurements utilizing three distinct technologies, which the main unit signals to the transmission module, which is located in the second unit, the personal ear clip. The personal ear clip is attached to the user’s earlobe. The transmission module in the personal ear clip transmits the signal through the earlobe. The receiving sensor in the personal ear clip receives signals from the earlobe with modified characteristics, impacted by the glucose concentration in the earlobe. The receiving sensor in the personal ear clip converts the signals into digital data and transmits the data to the receiver in the main unit. The data is then analyzed and compared to the transmitted signals based on the calibration data by the main processor and the result is displayed on the large screen of the main unit, as well as recorded for further analysis. The entire process is synchronized by the main clock, located in the main unit. The main unit and the personal ear clip are connected through a multi-wire flexible cable. When and if we develop our continuous measurement model, we plan for this connection to be wireless.
Although we have not yet commenced the clinical trials that we will use for our regulatory clearances and approvals, in 2009, Integrity Israel completed its initial hospital pilot study at Soroka University Medical Center in Be’er Sheva, Israel using the GlucoTrack DF-F on 89 patients of varying weights, age, diabetes type and gender for a total of two discrete, non-successive days each. The study produced a total of 1,772 reference blood glucose measurements. The primary statistical tools used to evaluate the performance of GlucoTrack DF-F were CEG analysis and Mean Absolute Relative Difference, which we refer to as MARD mean . The CEG analysis was developed by Dr. William Clarke and his team from the University of Virginia as a universal tool for assessing the accuracy of glucose monitors and is currently used (and has been used for the last two decades) widely all over the world as the industry-standard analytical tool to assess such accuracy. The purpose of the CEG is to assess measurement error from a clinical point of view, i.e. the statistical difference in the readings and the impact of any error on the patient. The CEG is a plot of all data pairs categorized into five discrete zones: A (clinically accurate reading), B (the decision based on the reading is benign or no treatment is given), C (the decision based on the reading leads to normal glucose levels being overcorrected), D (the decision based on the reading results in a failure to treat high and low levels) and E (the decision based on the reading results in an erroneous treatment decision). The A and B zones are the most clinically desirable zones and the D and E zones are the least clinically desirable zones. For example, a pair of data points at 200 mg/dl for the reference device compared to 280 mg/dl for the unit under testing are within zone B despite the significant difference between the two while measurements of 50 mg/dl for the reference device compared to 110 for the unit under testing are in zone D because of the possible failure to treat a low level of glucose. Devices with a higher combined A and B percentage (closer to 100%) and lower combined D and E percentage (closer to 0) are considered to have better performance. MARD mean is an error calculation tool that measures the average relative difference between the unit under testing and the reference measurements, on a percentage basis. While CEG is a specific tool to evaluate clinical risk due to errors in measuring glucose, MARD mean is a common statistical tool, subtracting the measurement value of a measurement of a specific subject with respect to a tested device from the measurement value of that subject’s measurement from a reference device and then taking the absolute value of the result. The last step is to calculate the mean of these absolute values to obtain MARD mean . MARD mean is a common statistical index that is used to compare a set of paired measurements coming from two devices or systems in order to evaluate the bias between the two.
38
CEG analysis of data from the study conducted by Integrity Israel during 2009 at Soroka University Medical Center showed that GlucoTrack DF-F had 96% of the data in the combined A and B zones, with approximately 60% in the A zone, 36% in the B zone, 2% in each of the C and D zones and 0% in the E zone. MARD mean for the study was approximately 22%. We believe that the results of the Soroka University study show that GlucoTrack DF-F accurately and reliably measured blood glucose readings using the same calibration set. See also the home measurement study below.
In plotting the CEG analysis, the horizontal axis represents the reference device, while the vertical axis represents the unit under testing. See Figure D below. The relevant range of glucose measurements (generally 40-500 mg/dl) is measured on each axis. The CEG is split into two halves by a line of full correlation which represents where the measurements obtained from the reference device and the unit under testing are identical. This line forms a 45° angle from both the vertical and horizontal axes. Zones A, B, C, D and E are on each side of the 45° line.
Each measurement is taken simultaneously by the reference device and the unit under testing. A point in the CEG is plotted at the intersection of the two readings. The location within the CEG is checked against the various zones to determine which zone the data pair falls within. Figure E sets forth an example of an A zone case. The error between the unit under testing and the reference device of 16.7% is considered clinically accurate as no risk is involved due to this particular error.
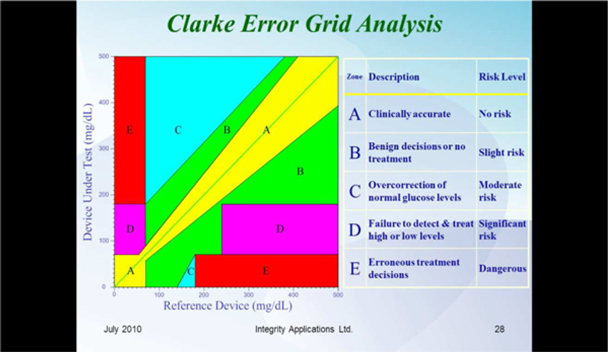
39
Figure E
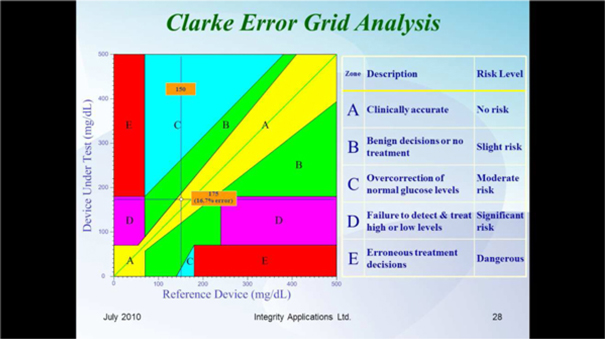
An even more extreme example is set forth in Figure F. The deviation between the unit under testing and the reference device is 60%, but since the CEG point falls within zone B, which suggests benign decisions (as in this particular example) or no treatment due to the error, the result is clinically accepted, as the risk is slight.
Figure F

40
A full explanation of the different CEG zones is set forth below in Figure G:
Figure G
|
Zone
|
Description
|
Definition of Risk
|
Risk
|
|||
|
A
|
Clinically accurate, would lead to correct treatment decisions
|
No effect on clinical action
|
None
|
|||
|
B
|
Would lead to benign decisions or no treatment
|
Altered clinical action, little or no effect on clinical outcome
|
Slight
|
|||
|
C
|
Would lead to overcorrection of normal glucose levels
|
Altered clinical action, likely to affect clinical outcome
|
Moderate
|
|||
|
D
|
Would lead to failure to detect & treat high or low glucose levels
|
Altered clinical action, could have significant medical risk
|
Significant
|
|||
|
E
|
|
Would lead to erroneous treatment decisions
|
|
Altered clinical action, could have dangerous consequences
|
|
Dangerous
|
41
The CEG analysis from the testing of the GlucoTrack DFF-F in the clinic is set forth below in Figure H:
Figure H
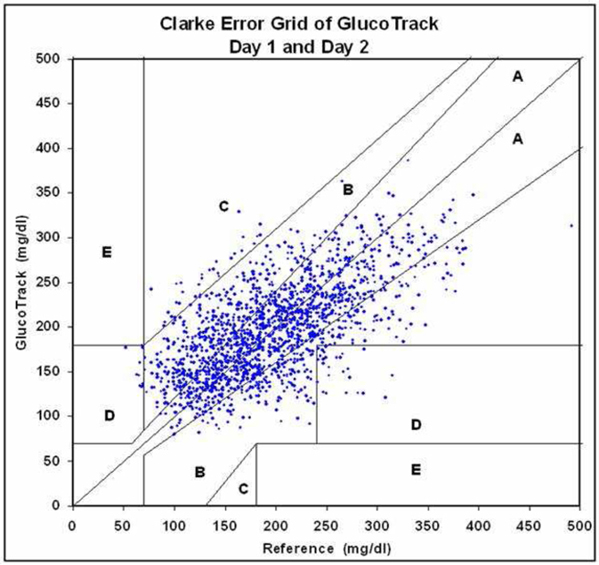
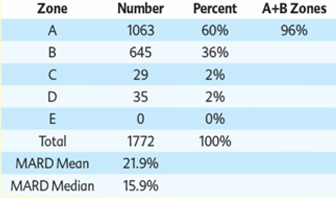
42
Since the GlucoTrack DF-F non-invasive measurement does not directly measure glucose levels, but rather measures a series of physiological characteristics that correlate with glucose levels, each patient must be calibrated by using a reference to a measurement obtained from an invasive device. Calibration consists of comparing each individual patient’s physiological measurements by GlucoTrack DF-F to the measurements from the invasive device under different circumstances over a defined period (such as fasting and after eating). Pre-clinical trials indicate that recalibration is necessary every few months, while to our knowledge, competing products require recalibration significantly more frequently. However, to date, in informal discussions with the FDA, the FDA has indicated that initially it would require recalibration of the GlucoTrack DF-F every month. Recalibration of the device would be accomplished in the same manner as the initial calibration of the device, as described above, by using a reference to a measurement obtained from an invasive device. We expect that the initial calibration and the first one or two recalibrations would be completed by experienced clinicians in a clinical setting, and all other recalibrations after the first one or two recalibrations would be completed by the patient in his or her home or another location of his or her choosing. As with all other non-invasive glucose monitoring devices that require recalibration, in order to recalibrate the GlucoTrack DF-F a clinician or patient will need to obtaining a measurement of the patient’s blood glucose levels using an invasive device, which measurement is used as a reference point in the recalibration process.
The following results for the GlucoTrack DF-F set forth below in Figure I measured between 1 to 22 days after calibration, but without re-calibration for each patient, demonstrates that calibration of the GlucoTrack DF-F remains valid for the period tested without degredation in the accuracy level.
Figure I

43
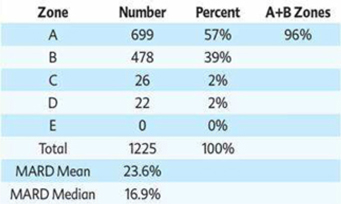
We conducted an initial study of home users to test the performance of the GlucoTrack DF-F outside of the clinic environment while the device is being operated by the patients themselves, without being monitored by professionals at the clinic. In this study, the performance of the GlucoTrack DF-F was monitored under normal home or home-like use conditions for four participants and 222 data points, with each subject performing the measurement procedure him or herself in the home or home-like environment for at least seven days. In this group, GlucoTrack readings were compared with each participant’s own invasive glucose monitoring device, which served as the reference for calibration and comparison of measurements. Each participant was monitored according to his or her own routine of glucose monitoring, but no less than five measurements per day were taken. In the home study, GlucoTrack DF-F had 90% of the data in the combined A and B C E G zones, with approximately 54% in the A zone, 36% in the B zone, 1% in the C zone, 9% in the D zone and 0% in the E zone. The MARD mean for the study was approximately 23.6%.
Within the last three years a new type of device, the continuous glucose monitoring system device, was introduced into the market. Currently, three different brands have obtained FDA clearance to market, and are selling, continuous glucose monitoring system devices in the US and EU markets. These brands are sold by Medtronic-MiniMed, Abbott and Dexcom. Continuous glucose monitoring system devices are invasive devices in which a needle is inserted under the skin (either in the abdomen or the upper arm) and measures Interstitual Fluid. Although we cannot predict what standards will be employed by applicable regulatory authorities as we seek a CE mark and FDA clearance, the average results, to date, in our pre-clinical trials of the GlucoTrack DF-F are similar to the results obtained from the continuous glucose monitoring devices that have been introduced to the market, as of the time of their introduction.
Analyses of our at home tests show that there are a few parameters that reduce accuracy of the measurements obtained from the GlucoTrack DF-F, such as the learning curve, the use of a home use device as a reference, failure to properly follow instructions for use, including use of the reference (invasive) device, and the variability of the ambient temperature in a given testing environment. We have already made some modifications to the GlucoTrack DF-F to limit the effect of these parameters and further modifications are in process, including the addition of a sensor to gauge the ambient temperature in the testing environment, and modifications to the software utilized by the GlucoTrack device to take the ambient temperature into account in determining the patient’s blood glucose level. While we believe that these modifications will improve the results of the GlucoTrack device, no assurance can be given as to the extent (if any) to which these modifications will improve the effectiveness of the device.
The three different technologies used by GlucoTrack DF-F, ultrasound, electromagnetic and thermal, simultaneously measure three independent criteria. As indicated in the Soroka University study, these three criteria are correlated to produce an acceptable measurement of a user’s blood glucose level. Additional development and wider studies will be necessary in order to demonstrate that GlucoTrack DF-F produces an acceptable measurement of a user’s blood glucose level outside of the clinic setting prior to our beginning formal clinical trials of the device.
The technologies operate as follows:
|
|
·
|
Ultrasound: The GlucoTrack DF-F uses ultrasound technology to measure the change of speed of sound through the earlobe, which is impacted by the glucose concentration in the capillary blood vessels.
|
|
|
·
|
Electromagnetic: The GlucoTrack’s DF-F’s electromagnetic technology uses a measurement of conductivity to measure the change in tissue impedance, which is a function of glucose concentration. The GlucoTrack DF-F’s electromagnetic technology analyzes criteria similar to those analyzed by conventional invasive devices, such as spot finger stick devices, but does so in a non-invasive manner.
|
44
|
|
·
|
Thermal: The GlucoTrack DF-F’s thermal technology uses heat transfer characteristics of the tissue, which are influenced by glucose concentration.
|
The GlucoTrack DF-F does not directly measure the glucose level concentration in the blood. Rather, it measures several physiological phenomena which are correlated with the glucose level. In order to correlate between the measured signal and the glucose level, a translation is needed. This translation is accomplished through the calibration of the device by reference to a measurement obtained from an invasive device.
Non-invasive devices (under different stages of development) generally require frequent recalibration. The former GlucoWatch required recalibrations approximately every 13 hours. The main reasons for calibration are that tissue parameters generally fluctuate in the area of the measurement, and are sensitive to the location of the sensor and the impact of potential disturbances. For various reasons, we believe that the GlucoTrack DF-F will have significantly less need for recalibration initially, just once a month and hopefully less later. Disturbances are less frequent in the earlobes, where the GlucoTrack DF-F takes its measurements. Utilizing three channels simultaneously reduces the noise contribution in the measurement. In addition, the personal ear clip also contains sensors that help locate it in the right place. In informal clinical trials to date, the measurements were conducted between one and 22 days post-calibration, with a median duration of six days. Although these measurements were based on the same calibration, no degradation in accuracy was observed.
The GlucoTrack does not use any optical method (either Infra Red (IR) or Near Infra Red (NIR) technology), which we understand are being used by other developers of noninvasive blood glucose measurement devices. Integrity believes that optical technologies are less reliable than the GlucoTrack’s combination of ultrasound, electromagnetic and thermal technologies due to inherent physiological limitations with optical technology. More specifically, optical technology is based on dispersion of a beam that is analyzed by spectrometric methods. As such devices are non-invasive, the beam passes through other components in the finger tip, such as skin, bone, muscle and fat tissue, which interfere with the measurements. Generally, most of these interferences have been overcome, but not the epidermis, primarily due to roughness, pigmentation and perspiration, which act like lenses in optical wavelengths.
Unlike conventional spot finger stick devices, which require single-use glucose test strips, the GlucoTrack DF-F requires no short term disposables. We believe that the personal ear clip which accompanies each GlucoTrack DF-F will need to be replaced only every six months. Since there is no additional cost or pain involved with each blood glucose measurement using the GlucoTrack DF-F, we believe that users of the device would be encouraged to take multiple blood glucose measurements per day, significantly increasing compliance with blood glucose measurement recommendations and helping diabetics better manage their disease. More frequent testing of blood glucose levels may provide a patient with information that can be used to determine optimal timing and dosage for corrective treatments such as insulin, and can also direct a patient to seek a clinical analysis or detailed testing and diagnosis. We believe that the GlucoTrack DF-F’s non-invasive advantages will particularly appeal to diabetic markets which require special care, including the premature infant (through a separate GlucoTrack device to be developed later), pediatric and elderly care markets.
We intend to eventually develop a family of GlucoTrack devices, including devices for night time usage, devices which would provide advance warnings of potential hypoglycemic episodes, continuous measurement devices, driver alert devices, a basic model to be used in poorer countries, a device for use in pediatric incubators, and a device for people with pre-diabetes. The current GlucoTrack device, or DF-F, measures glucose levels at discrete times as desired by the user, known as spot measurement. We intend that next generation models of GlucoTrack will include both spot and continuous measurements of glucose levels. We also intend to develop accessories for GlucoTrack, including colored ear clips for use with those models of GlucoTrack where a single main unit supports up to three different users, belt holders, desktop stands and software applications for data processing and analysis. Certain models of the device will include a USB port to allow for offline analysis of downloaded data. All of the above models will be derivative of the current DF-F model. The modifications involve mostly engineering changes as opposed to development. Notwithstanding the foregoing, there is no assurance that we will be successful in developing or engineering any of these models or accessories. We are currently replacing the display in the Main Unit with a color touch-screen.
45
The GlucoTrack DF-F has not yet been approved for commercial sale in the United States, the European Union or any other jurisdiction. See “Government Regulation - Regulation of the Design, Manufacture and Distribution of Medical Devices” below for a discussion of the approval process for commercial sale. There can be no assurance that approval for commercial sale in any jurisdiction will be obtained.
Manufacturing
We do not have commercial manufacturing facilities and do not intend to build commercial manufacturing facilities of our own in the foreseeable future. We intend to enter into agreements with various third parties for the formulation and manufacture of our products. We make prototypes of GlucoTrack devices for testing, including for limited use in clinical testing, in the prototype laboratory located at our Ashkelon, Israel offices. We intend to enter into agreements with third-party manufacturers for the manufacture of prototypes for certain GlucoTrack devices. These suppliers and their manufacturing facilities must comply with FDA regulations, current quality system regulations, which include current good manufacturing practices, and to the extent laboratory analysis is involved, current good laboratory practices.
Sales & Marketing
We do not have dedicated sales or marketing personnel yet, because neither the GlucoTrack DF-F nor other GlucoTrack devices are approved for commercial sale. In order to commercialize the GlucoTrack DF-F, if it is approved for commercial sale, we intend to collaborate with third parties with established sales and marketing operations in the medical device industry to market and sell the GlucoTrack DF-F to end users or for personal use. However, there can be no assurance that we will be able to enter into distribution agreements on terms acceptable to it or at all. We have signed an agreement with a leading chain of private diabetes clinics to purchase GlucoTrack DF-F devices, pending approval for commercial sale by that chain’s headquarters, which will depend on performance of the device in upcoming clinical trials. The agreement requires tests of a few devices by the clinics (no FDA or CE Mark approval is required in this particular country) as a prerequisite for sales. If the device is approved by the chain, then it will purchase devices directly from us for sale directly to its patients, without the need for third-party marketing or sales. If the device is approved by the chain’s headquarters, this chain will have an annual obligation during the first year to purchase a minimum of 10,000 units at a price of $835 per unit. Minimum obligations for the second and following years are subject to mutual agreement. There is no assurance that any sales will be made pursuant to this agreement. We anticipate that we will begin sales efforts in various jurisdictions as the GlucoTrack DF-F receives commercial approval in such jurisdictions.
Government Regulatory
Healthcare is heavily regulated in the United States by federal, state and local governments, and by similar authorities in other countries. Any product that we develop must receive all relevant regulatory approvals or clearances, as the case may be, before it may be marketed in a particular country. The laws and regulations affecting healthcare change regularly thereby increasing the uncertainty and risk associated with any healthcare-related venture. The United States government has in the past considered, is currently considering and may in the future consider healthcare policies and proposals intended to curb rising healthcare costs, including those that could significantly and adversely affect reimbursement for healthcare products such as GlucoTrack DF-F devices. These policies have included, and may in the future include: basing reimbursement policies and rates on clinical outcomes, the comparative effectiveness and costs of different treatment technologies and modalities; imposing price controls and taxes on medical device providers; and other measures. Future significant changes in the healthcare systems in the United States or elsewhere could also have a negative impact on the demand for GlucoTrack, if it is approved or cleared for sale, or our future products, if any. These include changes that may reduce reimbursement rates for such products and changes that may be proposed or implemented by the current administration or Congress. We cannot predict, however, if any proposal that has been or will be considered will be adopted or what effect any such legislation will have on us.
46
In the United States, the federal government regulates healthcare through various agencies, including but not limited to the following: (i) the FDA which administers the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, as well as other relevant laws; (ii) the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, which administers the Medicare and Medicaid programs; (iii) the Office of Inspector General, which enforces various laws aimed at curtailing fraudulent or abusive practices including, by way of example, the Anti-Kickback Law, the Anti-Physician Referral Law, commonly referred to as Stark, the Anti-Inducement Law, the Civil Money Penalty Law, and the laws that authorize the OIG to exclude health care providers and others from participating in federal healthcare programs; and (iv) the Office of Civil Rights which administers the privacy aspects of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996. All of the aforementioned are agencies within the Department of Health and Human Services. Healthcare is also provided or regulated, as the case may be, by the Department of Defense through its TriCare program, the Department of Veterans Affairs under, among other laws, the Veterans Health Care Act of 1992, the Public Health Service within HHS under the Public Health Service Act, the Department of Justice through the Federal False Claims Act and various criminal statutes, and state governments under the Medicaid program and their internal laws regulating all healthcare activities.
Regulation of the Design, Manufacture and Distribution of Medical Devices
Any product that we develop must receive all relevant regulatory clearances or approvals, as the case may be, before it may be marketed in a particular country. In the United States, under Section 201(h) of the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, a medical device is an article, which, among other things, is intended for use in the diagnosis of disease or other conditions, or in the cure, mitigation, treatment or prevention of disease, in man or other animals. We believe that GlucoTrack devices will be classified as medical devices and subject to regulation by numerous agencies and legislative bodies, including the FDA and its foreign counterparts. Devices are subject to varying levels of regulatory control, the most comprehensive of which requires that a clinical evaluation be conducted before a device receives approval for commercial distribution. The FDA classifies medical devices into one of three classes. Class I devices are relatively simple and can be manufactured and distributed with general controls. Class II devices are somewhat more complex and require greater scrutiny. Class III devices are new and frequently help sustain life.
In the United States, a company generally can obtain permission to distribute a new device in two ways – through a Section 510(k) premarket notification application or through a Section 515 premarket approval application. The 510(k) submission applies to any device that is substantially equivalent to a device first marketed prior to May 1976 or to another device marketed after that date, but which was substantially equivalent to a pre-May 1976 device. These devices are either Class I or Class II devices. Under the 510(k) submission process, the FDA will issue an order finding substantial equivalence to a predicate device (pre-May 1976 or post-May 1976 device that was substantially equivalent to a pre-May 1976 device) and permitting commercial distribution of that device for its intended use. A 510(k) submission must provide information supporting its claim of substantial equivalence to the predicate device. The FDA permits certain low risk medical devices to be marketed without requiring the manufacturer to submit a premarket notification. In other instances, the FDA may require that a premarket notification not only be submitted, but also be accompanied by clinical data. If clinical data from human experience is required to support the 510(k) submission, this data must be gathered in compliance with investigational device exemption regulations for investigations performed in the United States. The FDA review process for premarket notifications submitted pursuant to section 510(k) should take about 90 days, but it can take substantially longer if the agency has concerns, and there is no guarantee that the agency will clear the device for marketing, in which case the device cannot be distributed in the United States. Nor is there any guarantee that the agency will deem the device subject to the 510(k) process, as opposed to the more time-consuming, resource intensive and problematic PMA process described below.
47
The more comprehensive premarket approval process applies to a new device that is not substantially equivalent to a pre-May 28, 1976 product or to one that is to be used in supporting or sustaining life or preventing impairment. These devices are normally Class III devices and can only be marketed following approval of a premarket approval application. For example, most implantable devices are subject to the premarket approval application approval process. Two steps of FDA approval generally are required before a company can market a product in the U.S. that is subject to Section 515 premarket approval application approval, as compared to a Section 510(k) clearance. First, a company must comply with investigational device exemption regulations in connection with any human clinical investigation of the device; however those regulations permit a company to undertake a clinical study of a “non-significant risk” device without formal FDA approval. Prior express FDA approval is required if the device is a significant risk device. If there is any doubt as to whether a device is a “non-significant risk” device, companies normally seek prior approval from the FDA. Normally, clinical studies of new diagnostic products are conducted in tandem with a cleared or approved device and treatment decisions are based on the results from the existing diagnostic device. In such a setting, the FDA may well consider the clinical trial as one not posing a significant risk. However, FDA action is always uncertain and dependent on the contours of the design of the clinical trial and the device and there is no assurance that the FDA would consider any proposed clinical trial as one posing a non-significant risk. Moreover, before undertaking any clinical trial, the company sponsoring the trial and the investigator conducting the trial are required by federal law to seek and obtain the approval of institutional review boards. An institutional review board weighs the risks and benefits of a proposed trial to ensure the human subjects are not exposed to unnecessary risk. University medical centers as well as other entities maintain and operate institutional review boards. The GlucoTrack DF-F will be classified as a significant risk device, although that may not be true with other products mentioned in this prospectus. Second, the FDA must review a company’s PMA application, which contains, among other things, clinical information acquired under the investigational device exemption. The FDA will approve the premarket approval application if it finds there is reasonable assurance the device is safe and effective for its intended use. The premarket approval process takes substantially longer than the 510(k) process.
We believe that the GlucoTrack DF-F device will be classified as a Class III device that will be subject to the premarket approval application approval process and require human clinical trials, although that may not be true with other products mentioned in this prospectus. We currently anticipate that we will submit the protocol for U.S. clinical trials of the GlucoTrack DF-F to the FDA by mid-2012. Following approval of the clinical trial protocol for the GlucoTrack DF-F by the FDA, we intend to conduct clinical trials of the GlucoTrack DF-F device at two locations in the U.S. We have commenced negotiations for these locations.
Sales of medical devices outside the United States are subject to foreign regulatory requirements that vary widely from country to country. These laws and regulations range from simple product registration requirements in some countries to complex clearance and production controls in others. As a result, the processes and time periods required to obtain foreign marketing approval may be longer or shorter than those necessary to obtain FDA approval. These differences may affect the efficiency and timeliness of international market introduction of GlucoTrack DF-F. For countries in the European Union, or EU, medical devices must display a CE mark before they may be imported or sold and must comply with the requirements of the European Medical Device Directive, which we refer to as the MDD, or the Active Implantable Medical Device Directive. Integrity anticipates that the GlucoTrack devices will be subject to the MDD. Compliance with the MDD and obtaining a CE Mark involve obtaining International Organization for Standardization, or ISO, 13485 certification, an internationally recognized quality system, and approval of the product’s technical file by a notified body that is recognized by applicable authorities of an EU Member State. We have selected Kema, a Dutch company, as the notified body with which we will seek approval of GlucoTrack. Kema has approved the clinical protocol for the GlucoTrack DF-F device and the protocol has been approved by the ethical committee of Soroka University Medical Center in Be’er Sheva, Israel, enabling the commencement of clinical trials at the center. We have also had an initial meeting with a Spanish medical center with respect to conducting clinical trials in that center as well. We currently anticipate that clinical trials of the GlucoTrack DF-F at Soroka University Medical Center and in the Spanish medical center (assuming agreement is reached) by late 2011. The Soroka University Medical Center and Spanish center trials are anticipated to last for approximately four months each, following which the results of such trials will be analyzed and submitted to Kema for review and audit. Further, we currently anticipate receiving the CE Mark no earlier than the fourth quarter of 2012 and FDA approval approximately one year thereafter, however, there can be no assurance that either such approval will be obtained within such time frames, or at all. We may also seek regulatory approval to market the GlucoTrack devices in foreign countries that do not rely on the CE Mark. To date, the only non-CE Mark jurisdiction which we have identified as an intended target market for our products is South Africa. Based on guidance published by the South African Ministry of Health, we do not believe that regulatory approval is required to market the GlucoTrack DF-F in South Africa. To the extent that we seek to market our devices in other non-CE Mark countries in the future, we will be required to comply with the applicable regulatory requirements in each such country. Such regulatory requirements vary by country and may be onerous. As a result, no assurance can be given that we will be able to satisfy the regulatory requirements to sell our products in any such country.
Even when a clinical study has been approved or cleared by the FDA or a notified body or deemed approved, the study is subject to factors beyond a manufacturer’s control, including, but not limited to the fact that the institutional review board at a given clinical site might not approve the study, might decline to renew approval which is required annually, or might suspend or terminate the study before the study has been completed. Also, the interim results of a study may not be satisfactory, leading the sponsor to terminate or suspend the study on its own initiative or the FDA or a notified body may terminate or suspend the study. There is no assurance that a clinical study at any given site will progress as anticipated; there may be an insufficient number of patients who qualify for the study or who agree to participate in the study, or the investigator at the site may have priorities other than the study. Also, there can be no assurance that the clinical study will provide sufficient evidence to assure the FDA or a notified body that the product is safe and effective, a prerequisite for FDA approval of a PMA, or substantially equivalent in terms of safety and effectiveness to a predicate device, a prerequisite for clearance under 510(k). Even if the FDA or a notified body approves or clears a device, it may limit its intended uses in such a way that manufacturing and distributing the device may not be commercially feasible.
48
After clearance or approval to market is given, the FDA and foreign regulatory agencies, upon the occurrence of certain events, are authorized under various circumstances to withdraw the clearance or approval or require changes to a device, its manufacturing process or its labeling or additional proof that regulatory requirements have been met.
A manufacturer of a device approved through the premarket approval application process is not permitted to make changes to the device which affect its safety or effectiveness without first submitting a supplement application to its premarket approval application and obtaining FDA approval for that supplement. In some instances, the FDA may require clinical trials to support a supplement application. A manufacturer of a device cleared through a 510(k) submission must submit another premarket notification if it intends to make a change or modification in the device that could significantly affect the safety or effectiveness of the device, such as a significant change or modification in design, material, chemical composition, energy source or manufacturing process. Any change in the intended uses of a premarket approval application device or a 510(k) device requires an approval supplement or cleared premarket notification. Exported devices are subject to the regulatory requirements of each country to which the device is exported, as well as certain FDA export requirements.
Recently Enacted Health Care Reform Legislation
Congress recently passed health care reform legislation. The President signed the measure into law on March 23, 2010 and on March 30, 2010, the President signed into law a reconciliation bill that modifies certain provisions of the same.
The principal aim of the law as currently enacted is to expand health insurance coverage to approximately 32 million Americans who are currently uninsured. The law’s most far-reaching changes do not take effect until 2014, including a requirement that most Americans carry health insurance. The consequences of these significant coverage expansions on the sales of our products is unknown and speculative at this point.
The enacted legislation contains many provisions designed to generate the revenues necessary to fund the coverage expansions. The most relevant of these provisions are those that impose fees or taxes on certain health-related industries, including medical device manufacturers.
Beginning in 2013, each medical device manufacturer will have to pay an excise tax (or sales tax) in an amount equal to 2.3% of the price for which such manufacturer sells its medical devices. The tax applies to all medical devices, including our products and product candidates.
Additionally, the legislation as enacted also provides for increased enforcement of the fraud and abuse regulations previously mentioned.
Reimbursement
We anticipate that sales volumes and prices of the GlucoTrack DF-F and any other products we commercialize will depend in large part on the availability of reimbursement from third-party payors. Third-party payors include governmental programs such as Medicare and Medicaid, private insurance plans and workers’ compensation plans. These third-party payors may deny reimbursement for a product or therapy if they determine that the product was not medically appropriate or necessary. Also, third-party payors are increasingly challenging the prices charged for medical products and services. Some third-party payors must also approve coverage for new or innovative devices before they will reimburse health care providers who use the products. Even though a new product may have been cleared for commercial distribution, it may find limited demand for the device until reimbursement approval has been obtained from governmental and private third-party payors.
49
Inasmuch as a percentage of the projected patient population that could potentially benefit from the GlucoTrack DF-F is elderly, Medicare would likely be a potential source of reimbursement. Medicare is a federal program that provides certain hospital and medical insurance benefits to persons age 65 and over, certain disabled persons, persons with end-stage renal disease and those suffering from Lou Gehrig’s Disease. In contrast, Medicaid is a medical assistance program jointly funded by federal and state governments and administered by each state pursuant to which benefits are available to certain indigent patients. The Medicare and Medicaid statutory framework is subject to administrative rulings, interpretations and discretion that affect the amount and timing of reimbursement made under Medicare and Medicaid.
Medicare reimburses for medical devices in a variety of ways depending on where and how the device is used. However, Medicare only provides reimbursement if CMS determines that the device should be covered and that the use of the device is consistent with the coverage criteria. A coverage determination can be made at the local level, known as a Local Coverage Determination, by the Medicare administrative contractor (formerly called carriers and fiscal intermediaries), a private contractor that processes and pays claims on behalf of CMS for the geographic area where the services were rendered, or at the national level by CMS through a National Coverage Determination. There are new statutory provisions intended to facilitate coverage determinations for new technologies under the Medicare Prescription Drug Improvement and Modernization Act of 2003, or MMA, §§ 731 and 942, but it is unclear how these new provisions will be implemented. Coverage presupposes that the device has been cleared or approved by the FDA and, further, that the coverage will be no broader than the approved intended uses of the device (i.e., the device’s label) as cleared or approved by the FDA, but coverage can be narrower. In that regard, a narrow Medicare coverage determination may undermine the commercial viability of a device.
Obtaining a coverage determination, whether local or national, is a time-consuming, expensive and highly uncertain proposition, especially for a new technology, and inconsistent local determinations are possible. On average, according to an industry report, Medicare coverage determinations for medical devices lag 15 months to five years or more behind FDA approval for respective devices. Moreover, Medicaid programs and private insurers are frequently influenced by Medicare coverage determinations. A key component in the reimbursement decision by most private insurers will be whether the GlucoTrack DF-F is reimbursed by virtue of a National Coverage Determination by CMS. We may negotiate contracted rates for the GlucoTrack DF-F with private insurance providers for the purchase of the GlucoTrack DF-F by their members pending a coverage determination by CMS. Our inability to obtain a favorable coverage determination for the GlucoTrack DF-F may adversely affect our ability to market the GlucoTrack DF-F and thus, the commercial viability of the product. In international markets, reimbursement and healthcare payment systems vary significantly by country and many countries have instituted price ceilings on specific product lines. Distributors expressly support the reimbursement process and, depending on the distribution agreement and geographic area, may assume responsibility for the process.
We believe that the overall escalating cost of medical products and services has led to, and will continue to lead to, increased pressures on the healthcare industry to reduce the costs of products and services. Furthermore, deficit reduction and austerity measures in the United States and abroad may put further pressure on governments to limit coverage of, and reimbursement for, our products. There can be no assurance that third-party reimbursement and coverage will be available or adequate, or that future legislation, regulation, or reimbursement policies of third-party payors will not adversely affect the demand for our products or our ability to sell these products on a profitable basis. The unavailability or inadequacy of third-party payor coverage or reimbursement could have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results and financial condition. Until reimbursement or insurance coverage is established, patients will have to bear the financial cost of GlucoTrack. Third-party coverage may be particularly difficult to obtain while the GlucoTrack DF-F is not approved by the FDA as a replacement for existing single-point finger stick devices.
Until a reimbursement code is achieved, in order to reduce out of pocket money for users and increase the number of devices sold, a leasing program is planned (Europe and USA). Leases for a period of one, two or three years may be offered for the end-users of the device. The pay per month will then be similar to the current monthly payment for the invasive measurement, although there will be no limitation on the number of measurements per day a patient can perform. In this approach, the device will pay for itself in a shorter time.
50
Anti-Fraud and Abuse Rule
There are extensive federal and state laws and regulations prohibiting fraud and abuse in the healthcare industry that can result in significant criminal and civil penalties that can materially affect us. These federal laws include, by way of example, the following:
|
|
·
|
The anti-kickback statute (Section 1128B(b) of the Social Security Act) prohibits certain business practices and relationships that might affect the provision and cost of healthcare services reimbursable under Medicare, Medicaid and other federal healthcare programs, including the payment or receipt of remuneration for the referral of patients whose care will be paid by Medicare or other governmental programs;
|
|
|
·
|
The physician self-referral prohibition (Ethics in Patient Referral Act of 1989, as amended, commonly referred to as the Stark Law, Section 1877 of the Social Security Act), which prohibits referrals by physicians of Medicare or Medicaid patients to providers of a broad range of designated healthcare services in which the physicians (or their immediate family members) have ownership interests or with which they have certain other financial arrangements;
|
|
|
·
|
The anti-inducement law (Section 1128A(a)(5) of the Social Security Act), which prohibits providers from offering anything to a Medicare or Medicaid beneficiary to induce that beneficiary to use items or services covered by either program;
|
|
|
·
|
The False Claims Act (31 U.S.C. § 3729 et seq.), which prohibits any person from knowingly presenting or causing to be presented false or fraudulent claims for payment to the federal government (including the Medicare and Medicaid programs); and
|
|
|
·
|
The Civil Monetary Penalties Law (Section 1128A of the Social Security Act), which authorizes the United States Department of Health and Human Services to impose civil penalties administratively for fraudulent or abusive acts.
|
Sanctions for violating these federal laws include criminal and civil penalties that range from punitive sanctions, damage assessments, monetary penalties, imprisonment and/or denial of Medicare and Medicaid payments or exclusion from the Medicare and Medicaid programs, or both. These laws also impose an affirmative duty on those receiving Medicare or Medicaid funding to ensure that they do not employ or contract with persons excluded from the Medicare and other government programs.
Many states have adopted or are considering legislative proposals similar to the federal fraud and abuse laws, some of which extend beyond the Medicare and Medicaid programs, to prohibit the payment or receipt of remuneration for the referral of patients and physician self-referrals regardless of whether the service was reimbursed by Medicare or Medicaid. Many states have also adopted or are considering legislative proposals to increase patient protections, such as limiting the use and disclosure of patient specific health information. These state laws also impose criminal and civil penalties similar to the federal laws.
In the ordinary course of their business, medical device manufacturers and suppliers have been and are subject regularly to inquiries, investigations and audits by federal and state agencies that oversee these laws and regulations. Recent federal and state legislation has greatly increased funding for investigations and enforcement actions, which have increased dramatically over the past several years. This trend is expected to continue. Private enforcement of healthcare fraud also has increased due in large part to amendments to the civil False Claims Act in 1986 that were designed to encourage private persons to sue on behalf of the government. These whistleblower suits by private persons, known as qui tam relators, may be filed by almost anyone, including present and former patients or nurses and other employees, as well as competitors. HIPAA, in addition to its privacy provisions, created a series of new healthcare-related crimes.
51
As federal and state budget pressures continue, federal and state administrative agencies may also continue to escalate investigation and enforcement efforts to root out waste and to control fraud and abuse in governmental healthcare programs. A violation of any of these federal and state fraud and abuse laws and regulations could have a material adverse effect on a supplier’s liquidity and financial condition. An investigation into the use of a device by physicians may dissuade physicians from recommending that their patients use the device. This could have a material adverse effect on our ability to commercialize the GlucoTrack DF-F.
The Privacy Provisions of HIPAA
HIPAA, among other things, protects the privacy and security of individually identifiable health information by limiting its use and disclosure. HIPAA directly regulates “covered entities,” such as healthcare providers, insurers and clearinghouses, and regulates “business associates,” with respect to the privacy of patients’ medical information. All entities that receive and process protected health information are required to adopt certain procedures to safeguard the security of that information. It is uncertain whether we would be deemed to be a covered entity under HIPAA and it is unlikely that, based on its current business model, we would be a business associate. Nevertheless, we will likely be contractually required to physically safeguard the integrity and security of any patient information that we receive, store, create or transmit. If we fail to adhere to our contractual commitments, then our physician, hospital or insurance customers may be subject to civil monetary penalties, which could adversely affect our ability to market our devices. Recent changes in the law wrought by the HITECH Act provisions of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 increase the duties of business associates and covered entities with respect to protected health information that thereby subject them to direct government regulation, increasing its compliance costs and exposure to civil monetary penalties and other government sanctions. While the new law does not alter the definition of a business associate, it makes it more likely that covered entities with whom we are likely to do business will require us to enter into business associate agreements.
Intellectual Property
We believe that intellectual property is important to our business and to the medical device industry overall. We rely on a combination of patent, copyright and other intellectual property laws, trade secrets, nondisclosure agreements and other measures to protect our intellectual property and proprietary rights.
We understand the importance of obtaining patent and trade secret protection for new technologies, products and processes. Our success will depend in large part on our ability to file for and obtain patent protection of our principal products and procedures, to defend existing or future patents, to maintain trade secrets and to operate without infringing upon the proprietary rights of others.
We have obtained an issued patent for “A Method of Monitoring Glucose Level” in the United States, Europe, Australia, Canada, China, Israel, Japan, Mexico, the Philippines, Russia, South Africa and South Korea. This patent expires in April 2024 in the United States, and in August 2023 in all other jurisdictions. Additional patent applications are pending in various stages of review in Brazil and India.
We have filed patent applications in the United States, Taiwan and the PCT for an invention entitled “Device For Non-Invasively Measuring Glucose.”
We have obtained a registered trademark for GlucoTrack in the United States, Europe and fifteen other countries, including Australia, Brazil, Canada, Israel Japan, South Korea, Russia and South Africa, and have trademark applications for GlucoTrack in various stages of approval in two other countries. We have two additional trademark applications filed in the United States and Israel.
Patent protection is highly uncertain and involves complex legal and factual questions and issues. The patent application and issuance process can be expected to take several years and entail considerable expense. There can be no assurance that patents will issue as a result of any applications or that our existing patents, or any patents resulting from such applications, will be sufficiently broad to afford protection against competitors with similar or competing technology. Patents that we obtain may be challenged, invalidated or circumvented, or the rights granted under such patents may not provide us with any competitive advantages.
52
We believe that our patents and products do not and will not infringe patents or violate proprietary rights of others, although it is possible that our existing patent rights may not be valid or that infringement of existing or future patents or proprietary rights may occur. Litigation may be necessary to defend or enforce our patent rights or to determine the scope and validity of the proprietary rights of others. Defense and enforcement of patent claims can be expensive and time consuming, even in those instances in which the outcome is favorable, and could result in the diversion of substantial resources and management time and attention from our other activities. An adverse outcome could subject us to significant liability to third parties, require us to obtain licenses from third parties, alter our products or processes, or require that we cease altogether any related research and development activities or product sales.
We are currently pursuing further patents covering the technologies related to GlucoTrack’s particular measurements, as well as the combination of the three technologies used by GlucoTrack. A provisional patent has recently been filed and final application(s) will be made later.
Competition
The market for blood glucose monitoring devices is intensely competitive, subject to rapid change and significantly affected by new product introductions. Four companies, Roche Disetronic, a division of Roche Diagnostics; LifeScan, Inc., a division of Johnson & Johnson; the MediSense and TheraSense divisions of Abbott Laboratories; and Bayer Corporation, currently account for substantially all of the worldwide sales of self-monitored glucose testing systems. These competitors’ products use a meter and disposable test strips to test blood obtained by pricking the finger or, in some cases, the forearm.
In addition, other companies are developing or marketing minimally invasive or noninvasive glucose testing devices and technologies that could compete with our devices. There are also a number of academic and other institutions involved in various phases of technology development regarding blood glucose monitoring devices. We believe that the majority of noninvasive blood glucose monitors in development monitor glucose via trend analysis, rather than spot or continuous measurement. Trend analysis devices do not provide specific glucose measurements, as do spot or continuous testing devices, rather they alert a patient that their blood glucose levels are increasing or decreasing, and require frequent calibrations (from a few hours to a few days, compared to initially once a month for GlucoTrack and less frequently as the device is used). Accordingly, patients using such devices must also use conventional spot finger stick devices in order to determine optimal timing and dosage for corrective treatments such as insulin, whereas GlucoTrack provides patients with noninvasive spot blood glucose measurements that can be used for this purpose without the need for trend analysis. Among the companies developing noninvasive glucose testing devices are Echo Therapeutics, Inc., GlucoLight, C8 and Grove Instruments. Cygnus, a company subsequently acquired by Johnson & Johnson, obtained FDA approval and a CE Mark in 2001 for a noninvasive trend analysis device that was marketed under the name GlucoWatch, however, the device is no longer commercially available. Other companies developing continuous measurement devices, based on minimally invasive methods, such as implants or subdermal needles include Medtronic, Inc., Abbot Laboratories and Dexcom, Inc.
Some of our competitors are either publicly traded or are divisions of publicly-traded companies, and they enjoy several competitive advantages, including:
|
|
·
|
significantly greater name recognition;
|
|
|
·
|
established relations with healthcare professionals, customers and third-party payors;
|
|
|
·
|
established distribution networks;
|
|
|
·
|
additional lines of products, and the ability to offer rebates or bundle products to offer higher discounts or incentives to gain a competitive advantage;
|
|
|
·
|
greater experience in conducting research and development, manufacturing, clinical trials, obtaining regulatory approval for products and marketing approved products; and
|
|
|
·
|
greater financial and human resources for product development, sales and marketing, and patent litigation.
|
53
Some of our other competitors also enjoy these competitive advantages. As a result, we cannot assure that we will be able to compete effectively against these companies or their products.
To our knowledge, a summary of potential competitors with non-invasive products in development is set forth below:
Figure J
|
Company
|
Product
|
Technology
|
Calibration
|
Type of
Measurement
|
Technology Description
|
|||||||
|
1
|
Echo Therapeutics
(MA, USA)
|
Symphony
|
UltraSound
|
Daily calibration
|
Continuous
|
Needle-free skin permeation and non-invasive, continuous transdermal glucose biosensor (device attached to skin).
|
||||||
|
2
|
Freedom Meditech
(MA, USA)
|
Optical Polarimetry (in front of the eye)
|
Spot; Screening
|
Non-invase direct measurement of glucose levels in front of the eye via optical polarimetry.
|
||||||||
|
3
|
C-8 MediSensors
(CA, USA)
|
HG1-c
|
Raman spectroscopy
|
"No calibration"
|
Continuous
|
Through a device strapped to a patient’s abdomen, continuously measures glucose levels by measuring the “Raman” effect of the permeation of light through glucose cells in the body.
|
||||||
|
4
|
GlucoLight
(PA, USA)
|
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
|
Continuous
|
Hospital-based monitor monitors blood glucose level using Optical Coherence Tomography, a form of imaging technology which uses a disposable patch affixed to the patient’s skin to measure the presence of glucose.
|
||||||||
|
5
|
AiMedics
(Australia)
|
HypoMon
|
Skin Bio-Sensors
|
Continuous
|
Uses skin sensors strapped to a patient’s chest to continuously measure the patient’s glucose levels as they sleep. Used for Type 1 patients aged 10 to 25 years.
|
|||||||
|
6
|
|
Cybiocare
(Quebec, Canada)
|
|
OHD
|
|
Optical
|
|
|
Continuous
|
|
Through a device strapped to a patient’s arm, continuously measures glucose levels by using infrared light to detect hypoglycemia in the patient.
|
As of September 30, 2011, we had twelve full-time employees and ten part-time employees. None of our employees are represented by a collective bargaining agreement.
Property
We currently lease approximately 3,100 square feet of office space in Ashkelon, Israel for our principal offices and prototype laboratory on a month-to-month basis at a cost of 11,500 NIS ($3,368 based on the exchange rate on June 30, 2011) plus VAT per month. We believe that we could easily find similar space at comparable rent if necessary.
Legal Proceedings
We are not presently a party to any material litigation, other than Integrity Israel’s matters with Dimri discussed under “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions - Agreement with Y. H. Dimri Ltd.” We may, however, become involved in other litigation from time to time relating to claims arising in the ordinary course of our business. These claims, even if not meritorious, could result in the expenditure of significant financial and managerial resources.
54
PRINCIPAL AND SELLING STOCKHOLDERS
The following table sets forth certain information known to us regarding beneficial ownership of our common stock as of August 19, 2011 by our executive officers and directors (individually and as a group) and each person who is known by us to beneficially own more than five percent of our common stock. In addition, the following table sets forth the name of each selling stockholder and the number of shares of common stock that each selling stockholder may offer pursuant to this prospectus. The shares of common stock being offered by the selling stockholders hereunder were acquired by the selling stockholders in the private placement, which was commenced on July 26, 2010 and consisted of seven closings held on December 16, 2010, December 30, 2010, January 31, 2011, March 31, 2011, April 29, 2011, May 31, 2011 and July 29, 2011, respectively. Except as otherwise indicated, we believe that each of the beneficial owners and selling stockholders listed below has sole voting and investment power with respect to such shares, subject to community property laws, where applicable. Unless otherwise noted, the address of each stockholder is c/o Integrity Applications, Inc., P.O. Box 432, Ashkelon 78100, Israel.
None of the selling stockholders has had a material relationship with us other than as a stockholder at any time within the past three years or has ever been one of our officers or directors.
Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with the rules of the SEC, and includes any shares of common stock as to which a person has sole or shared voting power or investment power and any shares of common stock which the person has the right to acquire within 60 days through the exercise of any option, warrant or right, through conversion of any security or pursuant to the automatic termination of a power of attorney or revocation of a trust, discretionary account or similar arrangement.
|
Shares Owned Prior to the
Offering
|
Number of
Shares Being
Offered
|
Shares Owned After
the Offering
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Name of Beneficial Owner
|
Number 1
|
Percent 2
|
Shares
|
Number 1
|
Percent 2
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Executive Officers and Directors:
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Jacob Bar-Shalom
|
0 | — | 0 | — | ||||||||||||||||
|
Zvi Cohen
|
361,702 | 6.8 | % | — | 361,702 | 6.8 | % | |||||||||||||
|
Dr. Robert Fischell
|
48,000 | * | — | 48,000 | * | |||||||||||||||
|
Avner Gal
|
410,151 | 7.8 | % | — | 410,151 | 7.8 | % | |||||||||||||
|
Joel Gold 3
|
318,432 | 6.0 | % | — | 318,432 | 6.0 | % | |||||||||||||
|
David Malka
|
185,166 | 3.5 | % | — | 185,166 | 3.5 | % | |||||||||||||
|
All Executive Officers and Directors As A Group (6 Persons)
|
1,323,451 | 25.0 | % | — | 1,323,451 | 25.0 | % | |||||||||||||
|
Principal Stockholders:
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Amos and Daughters Investments and Properties Ltd. 4
|
393,714 | 7.4 | % | — | 393,714 | 7.4 | % | |||||||||||||
|
Vayikra Capital, LLC 5
|
398,467 | 7.5 | % | — | 398,467 | 7.5 | % | |||||||||||||
|
*
|
Less than one percent.
|
|
1
|
In determining beneficial ownership, a beneficial owner of a security includes any person who, directly or indirectly, through any contract, arrangement, understanding, relationship or otherwise has or shares (1) voting power which includes the power to vote, or to direct the voting of, such securities and/or (2) investment power which includes the power to dispose, or to direct the disposition, of such security. In addition, for the purposes of this chart, a person is deemed to be the beneficial owner of a security if that person has the right to acquire beneficial ownership of such security within 60 days, including, but not limited to, any right to acquire: (a) through exercise of an option, warrant or right; (b) through the conversion of security; (c) pursuant to the power to revoke a trust, discretionary account or similar arrangement; or (d) pursuant to the automatic termination of a trust, discretionary account or similar arrangement.
|
|
The address of Amos and Daughters Investments and Properties Ltd. is Shekel House, 111 Arlozorov St. Tel-Aviv 61216 Israel. Eri Steimatzky has voting and investment control over the shares held by Amos and Daughters Investments and Properties Ltd..
|
|
5
|
The address of Vayikra Capital, LLC is 1 Farmstead Road, Short Hills 07078 NJ, USA. Philip M. Darivoff has voting and investment control over the shares held by Vayikra Capital, LLC.
|
55
|
Shares Owned Prior to the
Offering
|
Number of
Shares Being
Offered
|
Shares Owned After
the Offering
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Name of Beneficial Owner
|
Number 1
|
Percent 2
|
Shares
|
Number 1
|
Percent 2
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Y.H. Dimri Holdings 6
|
719,998 | 13.6 | % | — | 719,998 | 13.6 | % | |||||||||||||
|
Selling Stockholders:
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Accredited Members Inc. 7
|
6,855 | * | 6,855 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Charles Abramovitz 8
|
24,173 | * | 24,173 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
H Applebaum Family Trust U/A DTD 07/17/92 9
|
24,000 | * | 24,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Alan Armbrust
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Ronald C. Astrup
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Scott E. Bennett
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Howard Berg 10
|
80,000 | 1.51 | % | 80,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||||
|
Kimberly L. Blake-Dotson
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Adam Boris DDS
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Rodney and Lorie Bourne JT TEN/WROS 11
|
1,600 | * | 1,600 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Rodney Bourne Roth IRA 12
|
2,400 | * | 2,400 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Sam Buck Jr.
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Daniel C. Cadle
|
4,768 | * | 4,768 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Dave Carson
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Bryan W. Chetelat 13
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Ernest J. Chornyei
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Chung Family Trust DTD 07/11/1999 14
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
John W. Clingman
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
William Conklin
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Brian Dahl
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Mark S. Devan
|
64,000 | 1.21 | % | 64,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||||
|
Michael H. Diamant
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Gary J. Faden
|
3,520 | * | 3,520 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Seth Farbman
|
2,400 | * | 2,400 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Dr Robert and Susan Fischell JT TEN/WROS 15
|
40,000 | * | 40,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
6
|
The address of Y.H. Dimri Holdings is 1 Jerusalem St. Netivot, 87710 Israel. Y.H. Dimri is entitled to these subject to the fulfillment of certain requirements. Yigal Dimri has voting and investment control over the shares held by Y.H. Dimri Holdings.
|
|
Includes 11,603 shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Charles Abramovitz CPA SEP-IRA.
|
|
Howard Applebaum has voting and investment control over the shares held by the H Applebaum Family Trust U/A Dtd 07/17/92.
|
|
Includes 35,984 shares held by the Specialists In Otolaryngology Defined Benefit Plan U/A Dtd 01/01/2009 of which Howard Berg has voting and investment control.
|
|
11
|
Rodney and Lorie Bourne have shared voting and investment control held by them as joint tenants.
|
|
12
|
Rodney Bourne has investment and voting control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Rodney Bourne Roth IRA.
|
|
14
|
Aubrey Chung Jr. has voting and investment control over the shares held by the Chung Family Trust Dtd 07/11/1999.
|
|
15
|
Dr. Robert and Susan Fischell have shared voting and investment control over shares held by them as joint tenants.
|
56
|
Shares Owned Prior to the
Offering
|
Number of
Shares Being
Offered
|
Shares Owned After
the Offering
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Name of Beneficial Owner
|
Number 1
|
Percent 2
|
Shares
|
Number
1
|
Percent 2
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Peter Flannary
|
24,000 | * | 24,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Morris E. Franklin Jr. Trust DTD 04/24/1988 16
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Aaron Fricke IRA 17
|
17,137 | * | 17,137 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Kenneth John Fricke IRA 18
|
8,569 | * | 8,569 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Gary A. Gelbfish
|
24,058 | * | 24,058 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Gh Downie Holdings LLC 19
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Jerry L. Gilmore IRA 20
|
21,137 | * | 21,137 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Alfred Gollomp
|
2,000 | * | 2,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Aron Green
|
3,200 | * | 3,200 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Estate of Harry Gruszecki 21
|
4,800 | * | 4,800 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Subhash and Harbans Gulati JT TEN/WROS 22
|
3,428 | * | 3,428 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Dan R. and Marianne Hamby JT TEN/WROS 23
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO William E. Harnish IRA 24
|
7,200 | * | 7,200 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO John Harrison IRA 25
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Chad Heimsoth
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Michael Herman
|
19,737 | * | 19,737 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Patricia C. Holmes IRA 26
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
JAG Multi Investments LLC 27
|
34,273 | * | 34,273 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
JAM 123 LLC 28
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
JAM Capital Associates LLC 29
|
8,569 | * | 8,569 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Sylvia S. Johe Revocable Trust U/A DTD 11/07/2008 30
|
7,800 | * | 7,800 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
16
|
Morris Franklin has voting and investment control over the shares held by the Morris E. Franklin Jr. Trust DTD 04/24/1988.
|
|
17
|
Aaron Fricke has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Aaron Fricke IRA.
|
|
18
|
Kenneth John Fricke has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Kenneth John Fricke IRA.
|
|
20
|
Jerry L. Gilmore has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Jerry L. Gilmore IRA.
|
|
Tobi D’Andrea, executor, has voting and investment control over the shares held by The Estate of Harry Gruszeki.
|
|
22
|
Subhash and Harbans Gulati have shared voting and investment control over shares held by them as joint tenants.
|
|
23
|
Dan R. and Marianne Hamby have shared voting and investment control over shares held by them as joint tenants.
|
|
24
|
William E. Harnish has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO William E. Harnish IRA.
|
|
25
|
John Harrison has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO John Harrison IRA.
|
|
26
|
Patricia C. Holmes has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Patricia C. Holmes IRA.
|
|
Alexander M. Goren and James G. Goren have voting and investment control over the shares held by JAG Multi Investments LLC.
|
|
29
|
Leonard Pearlman has voting and investment control over the shares held by Jam Capital Associates LLC.
|
|
Sylvia S Johe has Voting and Investment Control Over the shares held by the Sylvia S Johe Revocable Trust U/A DTD 11/07/2008.
|
57
|
Shares Owned Prior to the
Offering
|
Number of
Shares Being
Offered
|
Shares Owned After
the Offering
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Name of Beneficial Owner
|
Number 1
|
Percent 2
|
Shares
|
Number
1
|
Percent 2
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Larry Kaibel
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Robert G. Kammann
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Rami Kanzen-Longbeach
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
James Karanfilian
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Michael Katz
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Nadine Kirk RA 31
|
2,400 | * | 2,400 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Helen M Kreisler Revoc Trust U/A DTD 06/01/2001 32
|
8,569 | * | 8,569 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Jimmy and Loyce Kulbeth JT TEN/WROS 33
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Dennis K. Larson
|
32,000 | * | 32,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Jan J. and Sofia M. Laskowski JT TEN/WROS 34
|
8,569 | * | 8,569 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Ira F. Levy
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Emily Mays IRA 35
|
2,400 | * | 2,400 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Dr. Daniel Mccollum
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Joseph C. Mcnay
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
George Melas-Kyriazi
|
24,000 | * | 24,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Francine D. Merenghi Liv Trust U/A Td 07/30/1999 36
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO E. Ward Merrell Segregated Rollover IRA 37
|
17,569 | * | 17,569 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Jonathan Meyers IRA 38
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Eileen Minte
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO James Mitchell IRA 39
|
3,428 | * | 3,428 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Christine A.. Mittman
|
16,569 | * | 16,569 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Seaview Orthopaedics 401k U/A DTD 06/30/1986 Self Directed Account FBO Roy D. Mittman 40
|
19,315 | * | 19,315 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
31
|
Nadine Kirk has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Nadine Kirk IRA.
|
|
32
|
Helen M. Kreisler has voting and investment control over the shares held by the Helen M. Kreisler Revoc Trust U/A DTD 06/01/2001.
|
|
33
|
Jimmy and Joyce Kulberth share voting and investment control over shares held by them as joint tenants.
|
|
34
|
Jan J. and Sofia M. Laskowski share voting and investment control over shared held by them as joint tenants.
|
|
35
|
Emily Mays has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Emily Mays IRA.
|
|
36
|
Francine D. Merenghi has voting and investment control over the shares held by the Francine D. Merenghi Liv Trust U/A Td 07/30/1999.
|
|
37
|
E. Ward Merrell has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO E. Ward Merrell Segregated Rollover IRA.
|
|
38
|
Jonathan Meyers has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Jonathan Meyers IRA.
|
|
39
|
James Mitchell has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO James Mitchell IRA.
|
|
Harry Wolfmuller and Arthur Vasen have voting and investment control over the shares held by the Seaview Orthopaedics 401k U/A DTD 06/30/1986 FBO Roy D. Mittman.
|
58
|
Shares Owned Prior to the
Offering
|
Number of
Shares Being
Offered
|
Shares Owned After
the Offering
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Name of Beneficial Owner
|
Number 1
|
Percent 2
|
Shares
|
Number
1
|
Percent 2
|
|||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Steven Morgan IRA 41
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Damon Mungo
|
6,446 | * | 6,446 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO George Mungo IRA 42
|
2,571 | * | 2,571 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Anthony Musto
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Gregory B. Pepus 43
|
32,000 | * | 32,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Roger D. Plackemeier
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Profit Sharing Plan and Trust Of Pruitt&Pruitt Att At Law DTD 2/5/2002 44
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
The Royal W Ranney Rev Trust U/A DTD 03/22/1999 45
|
8,569 | * | 8,569 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Robert S. Rau
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Howard Rhine
|
2,000 | * | 2,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Michael C. Robert and Patricia R. Ochoa JT TEN/WROS 46
|
32,000 | * | 32,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Larry Roher
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Alvin Rush
|
2,000 | * | 2,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Jonathan Sack 47
|
20,000 | * | 20,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Albert M. Scholten
|
5,000 | * | 5,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
John T. Sheridan 48
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Steven and Judy Slaybaugh JT TEN/WROS 49
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Thomas Smith
|
8,569 | * | 8,569 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Jay R. Solan 50
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
41
|
Steven Morgan has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Steven Morgan IRA.
|
|
42
|
George Mungo has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO George Mungo IRA.
|
|
43
|
Includes 21,440 shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Gregory B. Pepus IRA. Gregory B. Pepus has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Gregory B. Pepus.
|
|
J Calhoun Pruitt Jr. has voting and investment control over the shares held by The Profit Sharing Plan and Trust Of Pruitt&Pruitt Att At Law DTD 2/5/2002.
|
|
Royal W. Ranney and Merle Jean Ranney have voting and investment control over the shares held by The Royal W. Ranney Rev Trust U/A DTD 03/22/1999.
|
|
46
|
Michael C. Robert and Patricia R. Ochoa share voting and investment control over shares held by them as joint tenants.
|
|
47
|
Includes 3,900 shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Jonathan S. Sack SEP IRA and 14,100 shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Jonathan Sack PSP over which the selling stockholder has voting or investment control.
|
|
48
|
Includes 8,000 shares held in a joint account with the selling stockholder's spouse, 2,880 shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO John T. Sheridan IRA over which the selling stockholder has voting or investment control, and 5,120 shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO John T. Sheridan SEP-IRA over which the selling stockholder has voting or investment control.
|
|
49
|
Steven and Judy Slaybaugh share voting and investment control over shares held by them as joint tenants.
|
59
|
Shares Owned Prior to the
Offering
|
Number of
Shares Being
Offered
|
Shares Owned After
the Offering
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Name of Beneficial Owner
|
Number 1
|
Percent 2
|
Shares
|
Number
1
|
Percent 2
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Southern Investment Trust DTD 4/10/08 51
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Karen Wendy Spence
|
25,137 | * | 25,137 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Robert M. Sterling
|
4,800 | * | 4,800 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Theodore Stortz
|
17,137 | * | 17,137 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Alan R. Sycoff
|
30,846 | * | 30,846 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
JMS Diversified Holdings LLC 52
|
6,855 | * | 6,855 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Joyce M. Sycoff IRA 53
|
10,282 | * | 10,282 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Tom D. Todd
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Anthony Towell
|
4,000 | * | 4,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Steven M .Wagner 54
|
16,000 | * | 16,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO C. Glen Wensley IRA 55
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Seaview Orthopedics 401(k) U/A dated 6/30/86 Self Directed Account FBO Harry Wolfmuller 56
|
2,880 | * | 2,880 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Thomas Wollschlager
|
32,000 | * | 32,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Donald E. Womeldorph Jr.
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
Zoion Inc. 57
|
8,000 | * | 8,000 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
51
|
Gary Southern has voting and investment control over the shares held by The Southern Investment Trust DTD 4/10/08.
|
|
Joyce M. Sycoff has voting and investment control over the shares held by JMS Diversified Holdings LLC.
|
|
53
|
Joyce M. Sycoff has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Joyce M. Sycoff IRA.
|
|
54
|
Includes 8,000 shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Steven Wagner IRA. Steven Wagner has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO Steven Wagner IRA.
|
|
55
|
C. Glen Wensley has voting and investment control over shares held by RBC Capital Markets LLC Custodian FBO C. Glen Wensley IRA.
|
|
Harry Wolfmuller and Arthur Vasen have voting and investment control over the shares held by The Seaview Orthopedics 401(K) Uad 6/30/86 Self Directed Account FBO Harry Wolfmuller.
|
|
James Hughes and Sofia Gitis have voting and investment control over the shares held by Zoion Inc.
|
60
MANAGEMENT
The following is a list of the names, ages and positions of our directors and executive officers as well as one significant employee, Eugene Naidis. The directors hold office for one year terms and until their successors have been elected and qualified. The executive officers hold office for one year terms or until their successors are elected by the board of directors. The executive officers and directors of Integrity Israel are the same as our executive officers and directors, except that Elazar Sonnenschein, a designee of Dimri pursuant to the Investment Agreement with Dimri, serves as a director of Integrity Israel.
|
Name
|
Age
|
Position with Integrity
|
||
|
Avner Gal
|
57
|
Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer
|
||
|
Zvi Cohen
|
57
|
Director
|
||
|
Dr. Robert Fischell
|
81
|
Director
|
||
|
Joel L. Gold
|
69
|
Director
|
||
|
David Malka
|
46
|
Director and Vice President of Operations
|
||
|
Jacob Bar-Shalom
|
45
|
Chief Financial Officer
|
||
|
Eugene Naidis
|
|
43
|
|
Project Manager
|
Directors and Executive Officers
Avner Gal has served as our Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer since our founding in 2001. Prior to founding us, Mr. Gal served as a managing director of Solid Systems, an Israeli start-up company engaged in the development of radar and ultra-sound technologies, from 2000 to 2001. From 1999 to 2000, Mr. Gal served as an engineering department manager with Comverse Network Systems. From 1996 to 1999, Mr. Gal was a section head at MTI Engineering Ltd., a consulting company and electronic systems provider in the communications, aerospace and military industries. Prior to entering the private sector, Mr. Gal served for twenty-three years in various field and headquarters positions in the Israeli Navy and retired as Naval Commander. Mr. Gal received a Bachelor of Science degree in electrical engineering from the Technion - Israeli Institute of Technology in Haifa, Israel, a Master of Science degree in electrical engineering from the Naval Postgraduate School in Monterey, California and a Master of Business Administration in marketing management from the University of Derby, Israeli Branch, Ramat-Efaal, Israel. As an Israeli Naval Officer, Avner spent the majority of his duty as a development engineer. Among other projects, he initiated, characterized and managed the development of a full Electronic Warfare, which we refer to as EW, suite (interception and deception), which is still operational on board all missile patrol boats of the Israeli Navy. Another EW system which Avner was in charge of developing is operational on board Israeli submarines. Avner was also the head of the Israeli Navy’s technical intelligence branch and served as the managing integrator for the electronic combat suite on board Dolphin submarines. During the last 25 years Avner has been the primary instructor in the Naval Projects’ Officers Course. Mr. Gal’s scientific and business education and experience, as well as his knowledge of the Company and its product candidate gained through his role as the Company’s chief executive officer, are all factors that led to the conclusion that he should serve as a member of our board of directors.
Zvi Cohen has served as one of our directors since our founding in 2001. Mr. Cohen founded Zicon Ltd., an Israeli company engaged in the businesses of assembling, manufacturing and engineering electronic components, in 1985 and served as a managing director of the company from 1985 until February 2001, and as President from February 2011 until September 2011. Zicon focuses on full turnkey projects, such as personal computer board assemblies, harnesses, wiring, system assembly and integration, ICT and functional testing, for commercial, military and medical devices. Zicon has been in the medical device business for approximately ten years and is one of the leading manufacturers of medical devices (particularly MRI and ultrasound machines) in Israel and qualifies for ISO 13485 and with the FDA. On September 19, 2011, in connection with insolvency proceedings initiated by Zicon in respect of a proposed restructuring of Zicon, the District Court of HaMerkaz District in Petah Tikva, Israel, sitting in its capacity as a bankruptcy court (PRK 24929-09-11), appointed Adv. Israel Bachar and Mr. Uriel Alfasi, CPA as joint trustees for Zicon, and ordered that all proceedings initiated against Zicon will be stayed until October 31, 2011. Prior to founding Zicon, Mr. Cohen served in various operations capacities with Electrical Industries Manufacturing. Mr. Cohen received a Bachelor of Science degree in industrial management and a Master of Business Administration degree, both from Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv, Israel. Mr. Cohen’s experience in the medical device industry, including as founder and managing director of Zicon, are all factors that led to the conclusion that he should serve as a member of our board of directors.
61
Dr. Robert Fischell has served as one of our directors since 2010. Dr. Fischell is an inventor and serial entrepreneur with over 130 issued U.S. patents. Dr. Fischell spent 36 years with the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, which resulted in 53 patents in both aerospace and biomedical technology. His interests at Johns Hopkins then turned to the invention of new medical devices such as pacemakers and implantable heart defibrillators. Starting in 1969, Dr. Fischell began the formation of 14 private companies that licensed his patents on medical devices. These companies include Pacesetter Systems, Inc. (purchased by Siemens and St. Jude Medical), IsoStent, Inc. (merged with Cordis Company, a Johnson and Johnson Company), NeuroPace, Inc., Neuralieve, Inc., Angel Medical Systems, Inc, and Svelte Medical Systems, Inc. As it relates to diabetes management devices, he was the inventor of the first implantable insulin pump (which became Minimed, which sold to Medtronic). Dr. Fischell’s honors include Inventor of the Year for the USA in 1984, election to the National Academy of Engineering in 1989, the Distinguished Physics Alumnus Award of the University of Maryland, and several medals for distinguished accomplishments in science, engineering and innovation. In 2004, Discover magazine gave Dr. Fischell their annual Technology for Humanity award. In 2008, Dr. Fischell received the honorary degree of Doctor of Humane Letters from the Johns Hopkins University in recognition of his many life saving inventions. Dr. Fischell received his BSME degree from Duke University and MS and Sc.D. degrees from the University of Maryland. Dr. Fischell’s extensive experience in the medical device industry, including inventing and commercializing numerous medical devices, are all factors that led to the conclusion that he should serve as a member of our board of directors.
Joel L. Gold has served as one of our directors since 2005. Mr. Gold is an Investment Banker at Buckman Buckman & Reid, Inc, an investment-banking firm located in New Jersey. From November 2004 until June 2010, he was an investment banker at Andrew Garrett, Inc., the placement agent for our recently completed private placement. From January 1999 until December 1999, he was an Executive Vice President of Solid Capital Markets, an investment-banking firm also located in New York City. From September 1997 to January 1999, he served as a Senior Managing Director of Interbank Capital Group, LLC, an investment banking firm also located in New York City. From April 1996 to September 1997, Mr. Gold was an Executive Vice President of LT Lawrence & Co., and from March 1995 to April 1996, Managing Director of Fechtor Detwiler & Co., Inc. Mr. Gold was a Managing Director of Furman Selz Incorporated from January 1992 until March 1995. From April 1990 until January 1992, Mr. Gold was a Managing Director of Bear Stearns and Co., Inc. For approximately 20 years before he became affiliated with Bear Stearns, he held various positions with Drexel Burnham Lambert, Inc. He is currently a director of Food Innovations, a specialty food company, and Best Energy Services. From 1995 until the company’s sale in April 2011, Mr. Gold served as a director of Emerging Vision, a formerly publicly held retail eye care company. Mr. Gold also served as a director of BlastGard International, a publicly held developer of blast mitigation materials, until his resignation from the board on February 2010. Mr. Gold has a B.S. in accounting from Brooklyn College, an M.B.A. from Columbia Graduate School of Business, and a Juris Doctorate from New York University Law School. Mr. Gold is the President and Founder of Just One Life, a charitable organization that assists women with difficult childbirth conditions. Mr. Gold’s extensive knowledge and experience in the area of finance, as well as his experience as a director of a publicly held company, are all factors that led to the conclusion that he should serve as a member of our board of directors.
David Malka has served as one of our directors and our Vice President of Operations since 2003. Prior to joining us, Mr. Malka served as a vice president of operations for Solid Systems from 2000 to 2003. From 1994 to 2000, Mr. Malka served as a manager of production and purchasing at Kollmorgen-Servotronix, an Israeli company specializing in the design, development and manufacture of digital servo control systems. From 1991 to 1993, Mr. Malka was a production design and inspection worker at TFL Time & Frequency Systems Ltd. Mr. Malka has a degree in practical engineering - industrial management from the Institute of Work & Production Productivity, Tel-Aviv and a B.A. in management from the Open University in Israel. Mr. Malka’s extensive executive experience in the medical device industry led to the conclusion that he should serve as a member of our board of directors.
Jacob Bar-Shalom has served as our Chief Financial Officer since January 2011. Since December 2008, Mr. Bar-Shalom has served as a principal of XplanIT Financial Consulting and Outsourcing, a company that provides financial services to private and publicly-held high-tech companies. In this capacity, he also currently serves as the Chief Financial Officer of ForexManage Ltd. Prior to joining XplanIT, Mr. Bar-Shalom served as the Group Chief Financial Officer of Veolia Israel, a subsidiary of Veolia Environment (NYSE: VE), a worldwide provider of environmental services from February 2007 to November 2008. From January 2006 to January 2007, Mr. Bar-Shalom served as the outsourced Chief Financial Officer of Acro, Inc. (OTCBB: ACRI), a provider of detection devices for the homeland security market. Mr. Bar-Shalom also previously served as the Chief Financial Officer of Digital Fuel Technologies, an international software company, from 2002 until 2005, and as a Senior Manager at the accounting firms BDO Seidman and Ernst & Young. Mr. Bar-Shalom holds a Masters of Business Administration from the Hebrew University in Jerusalem and is a Certified Public Accountant in the U.S. Mr. Bar-Shalom serves as Chairman of the Board of MicroFinance Israel, a non-governmental organization that he founded.
62
Significant Employee
Eugene Naidis joined us in 2002 as a software engineer and since 2005 has served as the project manager. Prior to joining us, Mr. Naidis served as a software team manager at Solid Systems from 1996 to 2002. From 1999 to 2002, Mr. Naidis also served as a software engineer at INESA East, an Israeli company engaged in the development, design and manufacturing of specialty measurement devices. Prior to joining Solid Systems, Mr. Naidis served as a programmer at Luck-Scan, a technological incubator in Ashkelon, Israel and at Magnitogorsk Iron & Steel Works, Magnitogorsk, Russian Federation. Mr. Naidis received a Bachelor of Science degree in metallurgy engineering and a Master of Science degree in metallurgy and computer engineering from the Metallurgical Institute, Magnitogorsk, Russian Federation, and an authorization in systems programming from the Institute for Labor and Productivity, Tel Aviv, Israel.
Advisory Board
Our Advisory Board is set forth below. None of the members of our Advisory Board has entered into any written agreements with us other than MedicSense, the company of which Mr. Adi Ickowicz is a principal. MedicSense is assisting us in obtaining its FDA clearance and CE mark in consideration for being paid a monthly fee and options in our company.
Dr. Ilana Harman-Boehm, M.D. heads the Department of Internal Medicine and is the Director of the Diabetes Unit at Soroka University Medical Center in Beer-Sheba, Israel. Dr. Harman served as deputy Chairman for the Israeli Diabetes Association and serves as Director of Educational Programs.
Professor Yariv Malimovka, M.D. is a leading expert in vascular surgery. He currently serves as a senior scientific advisor to major medical centers (such as Clinica Tara Tenerife España) in Spain, as well as in Eastern Europe. In addition, Professor Malimovka also manages Internacional Clinic Arterial Disease, an institute for research and treatment of arteriosclerosis in Madrid, Spain.
Mr. Adi Ickowicz, Bsc. ME serves as Director of MedicSense, a consulting firm which specializes in helping companies navigating the international regulatory maze. With more than 20 years of experience, Mr. Ickowicz has helped many companies meet regulatory demands for their products, guiding them through specific technological requirements and best practices for the collection of clinical data.
Director Compensation
Directors and members of the Advisory Board receive no compensation from us other than their compensation as our employees, for those that are employees, which compensation is described below under Executive Compensation.
Executive Compensation
Summary Compensation Table
The following table sets forth the 2010 and 2009 compensation for our Mr. Gal, our principal executive officer, and Mr. Malka, our other executive officer for the years ended December 31, 2010 and 2009. Mr. Bar-Shalom was not appointed as an officer of ours until 2011.
|
Name and Principal Position
|
Year
|
Salary
|
All Other
Compensation
|
Total
Compensation
|
||||||||||
|
Avner Gal
|
2010
|
(1) | $ | 106,542 | $ | 27,012 | (2) | $ | 133,554 | |||||
|
Chief Executive Officer
|
2009
|
(3) | $ | 103,334 | $ | 25,451 | (4) | $ | 128,785 | |||||
|
David Malka
|
2010
|
(1) | $ | 55,674 | $ | 20,092 | (5) | $ | 75,766 | |||||
|
Vice President of Operations
|
2009
|
(3) | $ | 54,573 | $ | 18,568 | (6) | $ | 73,141 | |||||
|
(1)
|
Calculated based on the average exchange rate for the year of New Israeli Shekels for U.S. Dollars of NIS 3.72 = U.S. $1.00.
|
|
(2)
|
Includes $21,586 in automobile expenses paid by us, including leasing costs, insurance premiums, gasoline and/or repairs incurred in connection with the executive’s automobile and $5,155 in cellular communications expenses paid by us, representing the estimated costs of our cellular communications expenses attributable to the executive.
|
63
|
(3)
|
Calculated based on the average exchange rate for the year of New Israeli Shekels for U.S. Dollars of NIS 3.92 = U.S. $1.00.
|
|
(4)
|
Includes $19,924 in automobile expenses paid by us, including leasing costs, insurance premiums, gasoline and/or repairs incurred in connection with the executive’s automobile and $5,527 in cellular communications expenses paid by us, representing the estimated costs of our cellular communications expenses attributable to the executive.
|
|
(5)
|
Includes $17,514 in automobile expenses paid by us, including leasing costs, insurance premiums, gasoline and/or repairs incurred in connection with the executive’s automobile and $2,578 in cellular communications expenses paid by us, representing the estimated costs of our cellular communications expenses attributable to the executive.
|
|
(6)
|
Includes $15,804 in automobile expenses paid by us, including leasing costs, insurance premiums, gasoline and/or repairs incurred in connection with the executive’s automobile and $2,764 in cellular communications expenses paid by us, representing the estimated costs of our cellular communications expenses attributable to the executive.
|
Outstanding Equity Awards At Fiscal Year End
We did not have any outstanding equity awards held by any of our named executive officers as of December 31, 2010.
Avner Gal
Avner Gal entered into an employment agreement with Integrity Israel in July 2010 pursuant to which Mr. Gal agreed to continue to serve as the chief executive officer and managing director of Integrity Israel. Mr. Gal’s employment agreement provides for an annual salary of NIS 480,000, or $140,566 based on the exchange rate on June 30, 2011, an annual bonus to be determined by the board of directors, an additional sum payable in the event that Mr. Gal meets certain milestones approved by the board, as well as the payment of certain social and insurance benefits and the use of a company car. The agreement also provides for a renegotiation of Mr. Gal’s annual salary on the one-year anniversary thereof and the renegotiation of Mr. Gal’s bonus formula once Integrity Israel has begun commercialization of its products. The agreement is terminable by either party on 180 days notice, immediately by Integrity Israel with the payment of an amount equal to 180 days of annual salary, or immediately by Integrity Israel for cause (as defined in the agreement) without the payment of severance. Mr. Gal received options to purchase 264,778 shares of our common stock, which represents 5% of the shares of our common stock outstanding following the private placement. The options will be exercisable at $6.25 per share and will vest in one-third increments upon (i) submission of clinical trials’ results to the Notified Body; (ii) CE mark approval; (iii) FDA approval, subject to immediate vesting in the event of a change of control. Mr. Gal is subject to non-compete and a confidentiality agreement during the term of the agreement and for one year thereafter.
Jacob Bar-Shalom
On January 1, 2011, we appointed Jacob Bar-Shalom as Chief Financial Officer. Mr. Bar-Shalom is providing services to us pursuant to an agreement between us and XplanIT Ltd., of which Mr. Bar-Shalom serves as a principal. Pursuant to its agreement with XplanIT, we will pay XplanIT a monthly retainer of NIS 11,000 plus VAT for the preparation of our annual and three quarterly reports in accordance with US GAAP and general accounting and financial reporting services, with additional work, if any, to be performed at a rate of NIS 400 per hour plus VAT, as well as reimbursement of business expenses commensurate with our expense reimbursement policies. Presently, Mr. Bar-Shalom provides services to us on a part-time basis.
David Malka
David Malka entered into an employment agreement with Integrity Israel in July 2010 pursuant to which Mr. Malka agreed to continue to serve as the vice president of operations of Integrity Israel. Mr. Malka’s employment agreement provides for an annual salary of NIS 240,000, or $70,278 based on the exchange rate on June 30, 2011, and an annual bonus to be determined by the board of directors and an additional sum provided that Mr. Malka reaches certain milestones approved by the board, as well as the payment of certain social and insurance benefits and the use of a company car. The agreement also provides for a renegotiation of Mr. Malka’s annual salary on the one-year anniversary thereof and the renegotiation of Mr. Malka’s bonus formula once Integrity Israel has begun commercialization of its products. The agreement is terminable by either party on 90 days notice, immediately by Integrity Israel with the payment of an amount equal to 90 days of annual salary, or immediately by Integrity Israel for cause (as defined in the agreement) without the payment of severance. Mr. Malka received options to purchase 79,434 shares of our common stock, which represents 1.5% of the shares of our common stock outstanding following the private placement. The options will be exercisable at $6.25 per share and will vest in one-third increments upon (i) submission of clinical trials’ results to the Notified Body; (ii) CE mark approval; and (iii) FDA approval, subject to immediate vesting in the event of a change of control. Mr. Malka is subject to non-compete and confidentiality agreement during the term of the agreement and for one year thereafter.
64
Eugene Naidis
We entered into an employment agreement with Eugene Naidis on December 1, 2004. Pursuant to this agreement, Mr. Naidis is engaged by us as a project manager and software engineer pursuant to the following terms and conditions: (i) Mr. Naidis is entitled to paid annual leave of 1.5 days for every full month of employment by us and to a standard pension plan; (ii) as we consider Mr. Naidis’ position to be one that requires a special degree of personal trust, Mr. Naidis is not entitled to compensation for working overtime; and (iii) Mr. Naidis is subject to non-competition and non-solicitation restrictions during the term of his employment and for six months thereafter and to standard non-disclosure obligations and protection of our intellectual property rights. If it is determined that Mr. Naidis’ position is not one that requires a special degree of personal trust, he would be entitled to overtime. Mr. Naidis also receives a cellular phone from us.
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
No member of our board of directors during 2010 had any relationship that would be considered a compensation committee interlock.
65
Agreement with Y. H. Dimri Ltd.
Integrity Israel is party to a loan and investment agreement dated February 18, 2003 with Dimri pursuant to which Dimri loaned us a principal amount of NIS 1,440,000, subject to linkage differences in Israel ($421,669 based on an exchange rate of $3.415 NIS/dollar as of June 30, 2011). Upon completion of the development of the prototype of Integrity Israel’s monitoring device, Dimri could have advanced an additional loan to Integrity Israel in the amount of NIS 1,248,000 ($365,446 based on the same exchange rate). In connection with the first phase loan, Dimri received shares of common stock representing 25% of Integrity Israel’s ordinary shares at such time. Under the Dimri agreement, certain rights in Integrity Israel were granted to Dimri, including an anti-dilution provision that provided that Dimri’s holdings in Integrity Israel would not be diluted below 18% of Integrity Israel’s issued capital shares as a result of any investment in Integrity Israel subject to the fulfillment of certain requirements. On the date of the reorganization, Dimri owned 18% of Integrity Israel’s ordinary shares and, therefore, upon the completion of the reorganization, Dimri was entitled to receive 18% of the shares of common stock of the Company outstanding on such date in exchange for his shares in Integrity Israel, subject to the fulfillment of certain requirements. We believe, based on the advice of Israeli counsel, that, given Dimri no longer owns shares in Integrity Israel as a result of the reorganization, rights attached to the shares in Integrity Israel no longer exist in Integrity Israel and do not and have never existed in us. However, Dimri has refused to acknowledge or agree to the termination of these rights and has challenged our position.
As a condition to the private placement, our founders entered into an Irrevocable Undertaking of Indemnification with us pursuant to which, among other things, the founders agreed to indemnify us and hold us harmless from any adverse consequences (excluding the fees and costs of defending us) that result from Dimri’s, or Dimri’s successors’ or assigns’, enforcement of the anti-dilution rights granted to Dimri as described above. The founders’ obligations under the Irrevocable Undertaking of Indemnification only obligate each founder to transfer up to such number of shares of our common stock that he or she owned as of July 26, 2010 to Dimri or to us. The term of the Irrevocable Undertaking of Indemnification is three years (subject to extension if there is a pending action), provided that after two years, any founder may sell or transfer up to twenty percent (20%) of his or her shares of common stock covered by the Irrevocable Undertaking of Indemnification so long as no action is pending by Dimri against us at the time of such sale and the sale price of the common stock is at least $6.25 per share. No assurances can be made that the Irrevocable Undertaking of Indemnification will fully protect us or our stockholders from any adverse consequences of an action by Dimri to enforce its anti-dilution rights. In addition, Dimri may assert other rights that it had under the Investment Agreement, for which we are not indemnified.
All of the individuals who are a party to the Irrevocable Undertaking of Indemnification have agreed to refrain from any competition with us and our activities during the term in which they own any shares of common stock and for a period of ten years thereafter.
Finally, each of such individuals had a right of first refusal (i) with respect to any transfer of Integrity Israel’s shares; and (ii) to participate in any future capital raise by Integrity Israel.
Following the commencement of the private placement, Mr. Dimri’s former representative on the board of directors of Integrity Israel, Zeev Mintus, resigned, and Mr. Dimri replaced him with Elazar Sonnenschein. In connection with his resignation, on September 11, 2010, Mr. Mintus also claimed in an email sent to Mr. Gal and placement agent representatives that “Dimri’s rights can only be waived with its written consent, and Dimri has made it absolutely clear that it does not give consent.” He also claimed that the previous day and other times in the past, Mr. Gal had told him that Mr. Dimri’s rights would continue in full with respect to the new corporate parent and would not be adversely affected by the reorganization. Finally, he alleged that the fact that Integrity Israel and its shareholders would consider evading their contractual obligations “—let alone work to effect a scheme to defraud both Dimri and investors in a planned IPO is untenable.” We deny these allegations and consider them to be defamatory. Mr. Gal responded indicating, among other things, that although we have continually indicated that we are willing to constructively discuss existing matters with Mr. Dimri, we disagreed with Mr. Mintus’ assertions relating to Mr. Dimri’s rights and contested Mr. Mintus’ allegations about statements allegedly made by Mr. Gal.
66
Integrity Israel and Andrew Garrett, Inc. subsequently received an email from separate counsel to Mr. Dimri alleging that Integrity Israel and Mr. Gal breached the agreement with Mr. Dimri, demanding that the “IPO process” cease until the matter is resolved and indicating that Mr. Dimri was prepared to seek injunctive relief to stop “the IPO” from proceeding and that he was prepared to seek all other legal recourse that he deemed appropriate. Such counsel also indicated that Mr. Dimri has been willing to discuss a proposal to compensate him for the elimination of his rights.
Counsel to Integrity Israel responded on October 5, 2010 rejecting and denying Mr. Dimri’s demands, arguments, positions and allegations and indicating that Integrity Israel would be willing to meet and discuss a reasonable and amicable solution, indicating that the private placement would continue, explaining that the reorganization had received all required approvals, including by the government, and had not been opposed by anyone, including Mr. Dimri, that as a result, no one had a right to shares in Integrity Israel, but only in us, and that Mr. Dimri has no more rights in us than any other stockholder. This response also indicated that the rights attached to the Integrity Israel shares do not continue in us and that we would fight any challenge to our position, which we intend to do. Integrity Israel’s counsel warned against interfering with the private placement process and warned against future defamatory remarks against us or our officers and directors.
On November 9, 2010, Integrity Israel and the founders received a letter from other counsel representing Mr. Dimri in his claims against Integrity Israel and the founders. The letter (i) reiterated the aforesaid arguments in greater detail, alleging, amongst other things, that Integrity Israel and the founders breached the agreement with Mr. Dimri and failed to act in good faith; (ii) added a claim that Mr. Dimri’s rights followed the transfer of the founders’ shares to us pursuant to the reorganization and that Mr. Dimri’s rights of first refusal should have been triggered by such transfer; (iii) demanded that Integrity Israel, the founders and us ensure that Mr. Dimri will be issued anti-dilution shares in our company so that he will maintain a stockholding of 18%; and (iv) requested that Mr. Dimri’s rights be committed to written agreements. The letter from Mr. Dimri’s counsel also suggested that Mr. Dimri is willing to seek a solution with Integrity Israel, us and the founders.
Counsel to Integrity Israel responded on February 6, 2011, rejecting and denying Mr. Dimri’s demands, arguments and allegations and indicating that Integrity Israel would be willing to meet to discuss an amicable solution. Integrity Israel’s counsel and founders’ counsel have met with Mr. Dimri’s counsel twice since then to discuss these issues, but no solution has been agreed to.
On May 11, 2011, Mr. Dimri’s counsel sent a letter requesting the appointment of an arbitrator pursuant to Mr. Dimri’s Loan and Investment Agreement, suggesting that one of three lawyers will be appointed as an arbitrator. On June 9, 2011, Integrity Israel’s counsel responded rejecting the names offered by Mr. Dimri’s counsel and suggesting three other lawyers.
On June 23, 2011, Mr. Dimri appealed to the District Court of HaMerkaz District in Petah Tikva, Israel, requesting the court to appoint an arbitrator to decide the dispute between Integrity Israel, the founders and Dimri (HPB 40754-06-11). On September 25, 2011, Integrity Israel's counsel filed an answer with the Court, disputing the facts and allegation raised in Dimri's motion and suggesting choosing an arbitrator with certain capacities, experience and skills. At a hearing held on October 11, 2011, the court appointed an arbitrator in this matter. The proposed arbitrator is required to inform the court no later than November 1, 2011 if there is anything that will preclude his service as an arbitrator in this matter. If there is, an alternate arbitrator will be appointed by the court. It should be noted that, in accordance with Israeli law, Mr. Dimri was not required to, and he did not, specify in his request for the appointment of an arbitrator the relief to be sought by him in the arbitration. As a result, we do not yet know the relief to be sought by Mr. Dimri in the arbitration. We anticipate that Mr. Dimri will specify the relief sought by him after the commencement of the arbitration proceedings.
We do not know what other actions Mr. Dimri will ultimately bring, if any, and against whom they will be brought. Nevertheless, we, our counsel and Integrity Israel’s counsel believe that we have substantial defenses to any such claims and appropriate claims and counterclaims of our own and we intend to strongly defend against any such action by Mr. Dimri and to assert our own claims and counterclaims as we deem necessary.
Other Loans to Us
Messrs. Avner Gal and Zvika Cohen collectively loaned us $48,735 in May 2002 pursuant to an oral agreement. Messrs. Nir Tarlovski, Yitzhak Fisher and Asher Kugler loaned us $75,000 on March 16, 2004. These loans, in addition to the loan from Dimri mentioned above, are not to be repaid until the first year in which we realize profits in our annual income statement (accounting profit). At such time, the loans are to be repaid on a quarterly basis in an amount equal to 10% of our total sales after deduction of VAT in the relevant quarter, begining on the quarter following the first year in which we realize profits in our annual income statement. The total amount to be repaid by the Company to each lender shall be an amount equal to the aggregate principal amount lent by such lender to the Company, plus an amount equal to the product of the amount of each payment made by the Company in respect of such loan multiplied by the difference between the Israeli Consumer Price Index on the date on which the loan was made and the Israeli Consumer Price Index on the date of such payment. However, notwithstanding the abovementioned mechanism, the Company will not be required to repay the loans during any time when such repayment would cause a deficit in the Company's working capital. The Gal and Cohen loan has priority over the Dimri loan. The terms of the repayment provisions of the foregoing loans can be modified by our board of directors, if such modification is applied equally to all loans. Our board of directors is entitled to modify the repayment terms of these loans, so long as such modification does not discriminate against any particular lender, and provided that all payments must be allocated among the lenders on a pro-rata basis.
67
DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES
General
The following description of our capital stock and provisions of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws are summaries and are qualified by reference to our certificate of incorporation, bylaws and, with respect to the anti-dilution provision described under “—Common Stock”, the form of subscription agreement between us and the investors in the private placement.
Reorganization
On July 15, 2010, Integrity U.S., Integrity Israel, and Integrity Acquisition completed a reorganization, pursuant to which Integrity Acquisition merged with and into Integrity Israel and all of the stockholders and option holders of Integrity Israel became entitled to receive shares and options in us in exchange for their shares and options in Integrity Israel. Following the reorganization, the former equity holders of Integrity Israel received the same proportional ownership in us as they had in Integrity Israel prior to the reorganization. As a result of the reorganization, Integrity Israel became our wholly-owned subsidiary.
Common Stock
Holders of our common stock who acquired shares in our recently completed private placement have anti-dilution protection with respect to such shares until September 1, 2012 for certain issuances of common stock by us for less than $6.25 per share, subject to certain exceptions described below. As a result, in the event that we issue shares for less than $6.25 per share prior to September 1, 2012, each investor in the private placement will be entitled to purchase a number of additional shares of common stock equal to: (a) the total purchase price paid by such purchaser in the private placement divided by the per share purchase price offered by the Company in the dilutive issuance less (b) the number of shares of common stock acquired by such purchaser in the private placement. Such anti-dilution protections are not transferable, and will be subject to a pro rata reduction to the extent the investor sells any common stock prior to the dilutive issuance. For example, if (i) an investor purchased 16,000 shares of common stock for $100,000, and (ii) we later issue shares at a price of $5.00 per share in a transaction that triggers the anti-dilution protection provisions (and such investor has not sold any common stock since the closing of the offering), then such investor would be entitled to receive an additional 4,000 shares of common stock as a result of such dilutive issuance. The foregoing anti-dilution protections do not apply to: (i) issuances made to our employees, consultants, officers and/or directors in return for their services to us, provided that, in the case of an issuance of shares of common stock, such issuance is not made at a price less than the market price on the date of issuance, and in the case of an issuance of common stock equivalents, the exercise or conversion price thereof is not less than the market price on the date of issuance, (ii) issuance of shares pursuant to such anti-dilution provision, (iii) issuances made upon the conversion or exercise of any of our securities outstanding as of the date each respective subscription was entered into, (iv) issuances made pursuant to a bona fide firm commitment underwritten public offering, (v) issuances made in connection with any strategic acquisition, merger, business combination or similar transaction, the primary purpose of which is not to raise equity capital, and (vi) issuances made to former stockholders of Integrity Israel pursuant to (A) any obligation or commitment arising under applicable law or under any contract, agreement, or settlement to which we or Integrity Israel are bound, or (B) any injunction or other binding order of any court or other tribunal having jurisdiction over us or any of our subsidiaries.
As of August 19, 2011, 40,000,000 shares of common stock were authorized and 5,295,543 shares of common stock were issued and outstanding, held of record by 174 stockholders.
The holders of common stock are entitled to one vote for each share held on all matters submitted to a vote of the stockholders and do not have any cumulative voting rights. Holders of common stock are entitled to receive proportionally any dividends declared by the board of directors out of funds legally available therefor, subject to any preferential dividend or other rights of any then outstanding preferred stock.
In the event of our liquidation or dissolution, holders of common stock are entitled to share ratably in all assets remaining after payment of all debts and other liabilities, subject to the prior rights of any then outstanding preferred stock. Holders of common stock have no preemptive, subscription, redemption or conversion rights. All outstanding shares of common stock are validly issued, fully paid and nonassessable.
68
The rights, preferences and privileges of holders of common stock are subject to, and may be adversely affected by, the rights of holders of shares of any series of preferred stock that we may designate and issue in the future.
We believe that given Mr. Dimri no longer owns shares in Integrity Israel as a result of the reorganization, any rights attached to the shares in Integrity Israel no longer exist in Integrity Israel and do not and have never existed in us.
Preferred Stock
Under the terms of our certificate of incorporation, the board of directors is authorized to issue shares of preferred stock in one or more series without stockholder approval. The board of directors has the discretion to determine the rights, preferences, privileges and restrictions, including voting rights, dividend rights, conversion rights, redemption privileges and liquidation preferences, of each series of preferred stock, any or all of which may be greater than or senior to the rights of the common stock. The issuance of preferred stock could adversely affect the voting power of holders of common stock and reduce the likelihood that such holders will receive dividend payments or payments on liquidation. In certain circumstances, an issuance of preferred stock could have the effect of decreasing the market price of the common stock.
Authorizing the board of directors to issue preferred stock and determine its rights and preferences has the effect of eliminating delays associated with a stockholder vote on specific issuances. The issuance of preferred stock, while providing flexibility in connection with possible acquisitions, future financings and other corporate purposes, could have the effect of making it more difficult for a third-party to acquire, or could discourage a third-party from seeking to acquire, a majority of our outstanding stock. Upon the closing of the offering, there will be no shares of preferred stock outstanding, and we have no present plans to issue any shares of preferred stock.
Stock Options
We maintain the Integrity Applications, Inc. 2010 Incentive Compensation Plan, which we refer to as the plan, to provide a means for us and our related entities to attract key personnel to provide services to us and our related entities, as well as to provide a means by which those key persons can acquire and maintain stock ownership, resulting in a strengthening of their commitment to our welfare and the welfare of our related entities and promoting the mutuality of interests between participants and our stockholders. The plan provides participants with additional incentive and reward opportunities designed to enhance our profitable growth and provide the participants with annual and long term performance incentives to expend their maximum efforts in the creation of stockholder value. The plan provides for the issuance of stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock awards, deferred stock awards, shares granted as a bonus or in lieu of another award, dividend equivalents, other stock-based awards or performance awards. We have reserved 529,555 shares of common stock for issuance under the plan.
69
The following table sets forth information as of August 19, 2011 about securities authorized for issuance under the our 2010 Incentive Compensation Plan, which has been approved by our stockholders.
|
Number of securities to be
issued upon exercise of
outstanding options, warrants
and rights
|
Weighted-average exercise
price of outstanding options,
warrants and rights
|
Number of securities remaining
available for future issuance
under equity compensation
plans (excluding securities
reflected in column (a))
|
||||||||||
|
(a)
|
(b)
|
(c)
|
||||||||||
|
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders(1)
|
454,354 | $ | 5.55 | 75,201 | ||||||||
|
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders
|
— | — | — | |||||||||
|
Total
|
454,354 | $ | 5.55 | 75,201 | ||||||||
|
(1)
|
Represents the 2010 Incentive Compensation Plan.
|
The total number of shares of common stock subject to outstanding options to purchase common stock as of August 19, 2011 was 454,354 shares.
Warrants
Pursuant to the placement agent agreement that we entered into with Andrew Garrett, Inc. in connection with the private placement, we have issued to Andrew Garrett, Inc. warrants to purchase up to an aggregate of 129,556 shares at a an exercise price of $6.25 per share. The warrants have a five year term expiring on the fifth anniversary of the date of effectiveness of this registration statement. Other than the warrants issued to Andrew Garrett, Inc., there are no outstanding warrants to purchase shares of our common stock.
Limitations on Resales by FINRA Members
Pursuant to FINRA Rule 5110(g)(1), holders of shares who purchased shares of our common stock in the private placement during the 180 day period prior to the filing of this Registration Statement who are affiliated with members of FINRA and who elect, pursuant to the Registration Rights Agreement, to include their shares for resale pursuant to the registration statement, are required to refrain, during the period commencing on the effective date of the registration statement and ending on the date that is 180 days after such effective date, from selling, transferring, assigning, pledging or hypothecating or otherwise entering into any hedging, short sale, derivative, put or call transaction that would result in the effective economic disposition of such holder’s shares.
Anti-Takeover Effects of Delaware Law and Our Charter and Bylaws
Certificate of Incorporation and Bylaws
Blank Check Preferred Stock . Our board of directors, without stockholder approval, has the authority under our certificate of incorporation to issue preferred stock with rights superior to the rights of the holders of common stock. As a result, preferred stock could be issued quickly and easily, could impair the rights of holders of common stock and could be issued with terms calculated to delay or prevent a change of control or make removal of management more difficult.
Election of Directors . Our certificate of incorporation provides that a majority of directors then in office may fill any vacancy occurring on the board of directors, even though less than a quorum may then be in office. These provisions may discourage a third-party from voting to remove incumbent directors and simultaneously gaining control of the board of directors by filling the vacancies created by that removal with its own nominees.
Stockholder Action . Our certificate of incorporation provides that stockholders may act at meetings of stockholders or by written consent in lieu of a stockholders’ meeting.
70
Stockholder Meetings . Our bylaws provide that the only business that may be conducted at a special meeting of stockholders is such business as was specified in the notice of the meeting. These provisions may discourage another person or entity from making a tender offer, even if it acquired a majority of our outstanding voting stock, because the person or entity could only take action at a duly called stockholders’ meeting relating to the business specified in the notice of meeting and not by written consent.
Requirements for Advance Notification of Stockholder Nominations and Proposals . Our bylaws provide that a stockholder seeking to bring business before an annual meeting of stockholders, or to nominate candidates for election as directors at an annual meeting of stockholders, must provide timely notice of this intention in writing. To be timely, a stockholder must deliver or mail the notice and we must receive the notice at our principal executive offices not less than five days prior to the date our directors determine for proposals to be received. The bylaws also include a similar requirement for making director nominations and specify requirements as to the form and content of the stockholder’s notice. These provisions could delay stockholder actions that are favored by the holders of a majority of our outstanding stock until the next stockholders’ meeting.
Delaware Anti-Takeover Statute
We are a Delaware corporation subject to Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, or the DGCL. Under Section 203, some business combinations between a Delaware corporation whose stock generally is publicly-traded or held of record by more than 2,000 stockholders and an interested stockholder are prohibited for a three-year period following the date that the stockholder became an interested stockholder, unless:
|
|
·
|
the corporation has elected in its restated certificate of incorporation not to be governed by Section 203;
|
|
|
·
|
the board of directors of the corporation approved the transaction which resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder before the stockholder became an interested stockholder;
|
|
|
·
|
upon consummation of the transaction which resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder, the interested stockholder owned at least 85% of the voting stock of the corporation outstanding at the commencement of the transaction, excluding voting stock owned by directors who are also officers or held in employee benefit plans in which the employees do not have a confidential right to tender stock held by the plan in a tender or exchange offer; or
|
|
|
·
|
the board of directors approves the business combination and holders of two-thirds of the voting stock which the interested stockholder did not own authorize the business combination at a meeting.
|
We have not made an election in our certificate of incorporation to opt out of Section 203. In addition to the above exceptions to Section 203, the three-year prohibition does not apply to some business combinations proposed by an interested stockholder following the announcement or notification of an extraordinary transaction involving the corporation and a person who was not an interested stockholder during the previous three years or who became an interested stockholder with the approval of a majority of the corporation’s directors. For the purposes of Section 203, a business combination generally includes mergers or consolidations, transactions involving the assets or stock of the corporation or its majority-owned subsidiaries and transactions which increase an interested stockholder’s percentage ownership of stock. Also, an interested stockholder generally includes a stockholder who becomes beneficial owner of 15% or more of a Delaware corporation’s voting stock, together with the affiliates or associates of that stockholder.
Transfer Agent and Registrar
American Stock Transfer and Trust Company, LLC serves as transfer agent and registrar for our common stock.
71
The following discussion summarizes certain U.S. federal income tax consequences to a purchaser of a share of common stock. This discussion is based on the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code, the applicable Treasury regulations promulgated or proposed thereunder, administrative pronouncements of the Internal Revenue Service, or IRS, and judicial decisions, in each case as of the date hereof, all of which are subject to change at any time, possibly retroactively. There can be no assurance that the IRS will not take a view contrary to that set forth herein which may be upheld by a court. No ruling from the IRS or opinion of counsel has been or will be sought as to any of the matters discussed below.
This summary is for general information purposes only and does not constitute tax advice. This summary applies only to an initial purchaser who acquires shares of common stock as a capital asset within the meaning of section 1221 of the Code. It does not purport to address all tax consequences that may be relevant to any particular investor or to an investor subject to special tax rules (including, for example, a financial institution, dealer or trader in stocks or securities, insurance company, regulated investment company, personal holding company, S corporation, tax-exempt organization, a person who holds common shares in a hedging transaction or as part of a “straddle”, “conversion transaction” or other risk reduction transaction, a person subject to the alternative minimum tax, an individual subject to the U.S. expatriation tax regime, a “controlled foreign corporation,” or a “passive foreign investment company”). In addition, this summary does not address any aspect of state, local or foreign taxation.
EACH PROSPECTIVE PURCHASER OF COMMON STOCK IS URGED TO CONSULT THE PURCHASER’S TAX ADVISER CONCERNING THE U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSEQUENCES TO THE PURCHASER OF ACQUIRING, OWNING AND DISPOSING OF SHARES OF COMMON STOCK, AS WELL AS THE APPLICATION OF STATE, LOCAL AND FOREIGN INCOME AND OTHER TAX LAWS. As used herein, the term “U.S. Holder” means a beneficial owner of a share of common stock that for U.S. federal income tax purposes is:
|
|
·
|
an individual who is a citizen or individual resident of the United States;
|
|
|
·
|
a corporation, or other entity taxable as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, created or organized in or under the law of the United States or of any political subdivision thereof;
|
|
|
·
|
an estate the income of which is subject to U.S. federal income taxation regardless of its source; or
|
|
|
·
|
a trust if (i) a court within the United States is able to exercise primary supervision over the administration of the trust, and one or more United States persons have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust, or (ii) the trust was in existence on August 20, 1996 and properly elected to continue to be treated as a United States person.
|
The term “non-U.S. Holder” means a beneficial owner of a share of common stock that is not a U.S. Holder.
If a partnership holds shares of our common stock, the tax treatment of a partner will generally depend upon the status of the partner and the activities of the partnership. A partner of a partnership holding shares of our common stock should consult his, her, or its own tax advisors.
U.S. Holders
Distributions
A distribution on a share of common stock will be includible in the gross income of a U.S. Holder as ordinary income to the extent the distribution is out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits (as computed for U.S. federal income tax purposes). To the extent distributions with respect to a share of common stock in any taxable year are not paid out of current or accumulated earnings and profits, they will be treated as a non-taxable return (and reduction) of basis in that share of common stock to the extent thereof, and if and to the extent they exceed earnings and profits and basis, they will be treated as gain from the sale of the share of common stock (see “—Disposition of Shares of Common Stock”).
72
The rate of federal income tax that a non-corporate taxpayor generally pays on dividends, provided certain conditions and requirements are satisfied, such as minimum holding period requirements, is 15% for taxable years beginning before January 1, 2013, after which dividends are taxable as ordinary income. To qualify for the reduced rate, the non-corporate stockholder must satisfy certain holding period and other requirements. Dividends received by a corporation are generally eligible for the dividends received deduction, subject to the limitations under section 1059 of the Code relating to extraordinary dividends.
Disposition of Shares of Common Stock
Upon a sale or other taxable disposition of a share of common stock, a U.S. Holder generally will recognize capital gain or loss equal to the difference between the amount realized and the U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the share of common stock. A U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in its common stock generally would equal the amount paid for such common stock. That gain or loss will be long-term capital gain or loss if the holding period for that share of common stock was more than one year on the date of sale or other disposition. The maximum rate of federal income tax applicable to a long-term capital gain of a non-corporate taxpayor in a taxable year beginning before January 1, 2013 is generally 15%. In later taxable years, that 15% reverts to 20%. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations.
Newly enacted legislation requires certain U.S. Holders who are individuals, estates or trusts to pay an additional 3.8% tax on, among other things, dividends and capital gains from the sale or other disposition of common stock for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2012. U.S. Holders should consult their tax advisors regarding the effect, if any, of this legislation on their ownership and disposition of our common stock.
Backup Withholding
A U.S. Holder may be subject to backup withholding in respect of dividends on common stock and the proceeds from a sale, exchange or redemption of common stock unless the holder (a) is a corporation or other exempt recipient or (b) provides, when required, the U.S. Holder’s taxpayor identification number to the payor, certifies that the U.S. Holder is not subject to backup withholding and otherwise complies with the backup withholding rules. Backup withholding is not an additional tax; any amount so withheld is creditable against the U.S. Holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability or is refundable, provided the required information is furnished to the IRS.
Non-U.S. Holders
Distributions
A distribution on a share of our common stock made to a non-U.S. Holder out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits generally will constitute a dividend for U.S. tax purposes. Dividends paid to a non-U.S. Holder generally will be subject to withholding of United States federal income tax at a 30% rate or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty. A non-U.S. Holder who wishes to claim the benefit of an applicable treaty rate is required to satisfy applicable certification and other requirements. Dividends that are effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business within the United States and, if certain tax treaties apply, are attributable to a permanent establishment in the United States, are not subject to the withholding tax, but instead are subject to U.S. federal income tax on a net income basis at applicable graduated individual or corporate rates. Certain certification requirements and disclosure requirements must be complied with in order for effectively connected income to be exempt from withholding. Any such effectively connected income received by a foreign corporation may, under certain circumstances, be subject to an additional branch profits tax at a 30% rate (or lower applicable income tax treaty rate).
73
To the extent distributions exceed our current and accumulated earnings and profits, they will generally constitute a return of capital and will first reduce the non-U.S. Holder’s basis in our common stock, but not below zero, and then will be treated as gain from the sale of stock as discussed below under “—Disposition of Shares of Common Stock.”
Disposition of Shares of Common Stock
A non-U.S. Holder generally will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax or withholding with respect to any gain recognized on a sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of our common stock unless:
|
|
·
|
certain circumstances exist under which the gain is treated as effectively connected with the conduct by the non-U.S. Holder of a trade or business in the United States, and, if certain tax treaties apply, is attributable to a permanent establishment maintained by the non-U.S. Holder in the United States;
|
|
|
·
|
the non-U.S. Holder is an individual and is present in the United States for 183 or more days in the taxable year of the sale, exchange or other taxable disposition, and meets certain other requirements; or
|
|
|
·
|
our common stock constitutes a “United States real property interest” by reason of our status as a U.S. real property holding corporation, or USRPHC, for U.S. federal income tax purposes at any time within the shorter of the five-year period preceding the disposition or the non-U.S. Holder’s holding period for our common stock.
|
If the first exception applies, the non-U.S. Holder generally will be subject to U.S. federal income tax with respect to such item on a net basis in the same manner as a U.S. Holder unless otherwise provided in an applicable income tax treaty; a non-U.S. Holder that is a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes may also be subject to a branch profits tax with respect to such item at a rate of 30% (or at a reduced rate under an applicable income tax treaty). If the second exception applies, the non-U.S. Holder generally will be subject to U.S. federal income tax at a rate of 30% (or at a reduced rate under an applicable income tax treaty) on the amount by which such non-U.S. Holder’s capital gains allocable to U.S. sources exceed capital losses allocable to U.S. sources during the taxable year of disposition of the common shares.
With respect to the third exception, we believe we are not currently and do not anticipate becoming a USRPHC for United States federal income tax purposes. However, because the determination of whether we are a USRPHC depends on the fair market value of our United States real property interests relative to the fair market value of our other trade or business assets and our non-United States real property interests, there can be no assurance that we are not a USRPHC or will not become one in the future. Even if we are or were to become a USRPHC, gain arising from the sale, exchange or other taxable disposition by a non-U.S. Holder of our common stock will not be subject to tax if such class of stock is “regularly traded,” as defined by applicable Treasury Regulations, on an established securities market, and such non-U.S. Holder owned, actually or constructively, 5% or less of such class of our stock throughout the shorter of the five-year period ending on the date of the sale or exchange or the non-U.S. Holder’s holding period for such stock. If gain on the sale, exchange, or other taxable disposition of our stock were subject to taxation under the third exception above, the non-U.S. Holder would be subject to regular United States federal income tax with respect to such gain in generally the same manner as a United States person.
Federal Estate Tax
Our common stock held by an individual non-U.S. Holder at the time of death, or by certain entities (for example, certain trusts) will be included in such holder’s gross estate for United States federal estate tax purposes, unless an applicable estate tax treaty provides otherwise.
74
Information Reporting and Backup Withholding
Generally, we must report to the IRS and to the non-U.S. Holder the amount of dividends paid to a non-U.S. Holder and the amount of tax, if any, withheld with respect to those payments. Copies of the information returns reporting such dividend payments and any withholding may also be made available to the tax authorities in the country in which the non-U.S. Holder resides under the provisions of an applicable treaty. No information reporting or backup withholding will be required regarding the proceeds of the sale of shares of our common stock made within the United States or conducted through certain U.S.-related financial intermediaries, if the payor receives the certification that the holder is not a U.S. person, as defined under the Code, and does not have actual knowledge or reason to know the holder is a U.S. person, as defined under the Code, who is not an exempt recipient, or the holder otherwise establishes an exemption. Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Any amounts withheld under the backup withholding rules will be allowed as a refund or a credit against the holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability provided the required information is timely furnished to the IRS.
Recently Enacted Legislation Relating to Foreign Accounts
Under recently enacted legislation, a relevant withholding agent may be required to withhold 30% of any dividends and the proceeds of a sale of our common stock paid after December 31, 2012 (subject to certain delayed effective dates established by the U.S. Treasury or IRS) to (i) a foreign financial institution (as specially defined for this purpose) unless such foreign financial institution agrees to verify, report and disclose its U.S. accountholders and meets certain other specified requirements, or (ii) a non-financial foreign entity that is the beneficial owner of the payment unless such entity certifies that it does not have any substantial U.S. owners or provides the name, address and taxpayor identification number of each substantial U.S. owner and such entity meets certain other specified requirements. Holders of our common stock should consult their tax advisors regarding the effect, if any, of this legislation on their ownership of our common stock.
75
Until our common stock is quoted on the OTCBB, the selling stockholders, which as used herein includes donees, pledgees, transferees or other successors-in-interest selling shares of common stock or interests in shares of common stock received after the date of this prospectus from a selling stockholder as a gift, pledge, partnership distribution or other transfer, may sell their shares of our common stock at a fixed price of $6.25 per share. This offering price was determined on the basis of the offering price per share of common stock in our most recent private placement completed in July 2011.
Thereafter, the selling stockholders may, from time to time, sell, transfer or otherwise dispose of any or all of their shares of common stock or interests in shares of common stock on any stock exchange, market or trading facility on which the shares are traded or in private transactions. These dispositions may be at fixed prices, at prevailing market prices at the time of sale, at prices related to the prevailing market price, at varying prices determined at the time of sale, or at negotiated prices.
The selling stockholders may use any one or more of the following methods when disposing of shares or interests therein:
|
|
block trades in which the broker-dealer will attempt to sell the shares as agent, but may position and resell a portion of the block as principal to facilitate the transaction;
|
|
|
short sales effected after the date the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part is declared effective by the SEC;
|
|
|
through the writing or settlement of options or other hedging transactions, whether through an options exchange or otherwise;
|
|
|
broker-dealers may agree with the selling stockholders to sell a specified number of such shares at a stipulated price per share;
|
The selling stockholders may, from time to time, pledge or grant a security interest in some or all of the shares of common stock owned by them and, if they default in the performance of their secured obligations, the pledgees or secured parties may offer and sell the shares of common stock, from time to time, under this prospectus, or under an amendment to this prospectus under Rule 424(b)(3) or other applicable provision of the Securities Act amending the list of selling stockholders to include the pledgee, transferee or other successors in interest as selling stockholders under this prospectus. The selling stockholders also may transfer the shares of common stock in other circumstances, in which case the transferees, pledgees or other successors in interest will be the selling beneficial owners for purposes of this prospectus.
In connection with the sale of our common stock or interests therein, the selling stockholders may enter into hedging transactions with broker-dealers or other financial institutions, which may in turn engage in short sales of the common stock in the course of hedging the positions they assume. The selling stockholders may also sell shares of our common stock short and deliver these securities to close out their short positions, or loan or pledge the common stock to broker-dealers that in turn may sell these securities. The selling stockholders may also enter into option or other transactions with broker-dealers or other financial institutions or the creation of one or more derivative securities which require the delivery to such broker-dealer or other financial institution of shares offered by this prospectus, which shares such broker-dealer or other financial institution may resell pursuant to this prospectus (as supplemented or amended to reflect such transaction).
76
The aggregate proceeds to the selling stockholders from the sale of the common stock offered by them will be the purchase price of the common stock less discounts or commissions, if any. Each of the selling stockholders reserves the right to accept and, together with their agents from time to time, to reject, in whole or in part, any proposed purchase of common stock to be made directly or through agents. We will not receive any of the proceeds from this offering.
The selling stockholders also may resell all or a portion of the shares in open market transactions in reliance upon Rule 144 under the Securities Act of 1933, provided that they meet the criteria and conform to the requirements of that rule.
The selling stockholders and any underwriters, broker-dealers or agents that participate in the sale of the common stock or interests therein may be underwriters within the meaning of Section 2(11) of the Securities Act. Any discounts, commissions, concessions or profit they earn on any resale of the shares may be underwriting discounts and commissions under the Securities Act. Selling stockholders who are underwriters within the meaning of Section 2(11) of the Securities Act will be subject to the prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act.
To the extent required, the shares of our common stock to be sold, the names of the selling stockholders, the respective purchase prices and public offering prices, the names of any agents, dealer or underwriter, any applicable commissions or discounts with respect to a particular offer will be set forth in an accompanying prospectus supplement or, if appropriate, a post-effective amendment to the registration statement that includes this prospectus.
In order to comply with the securities laws of some states, if applicable, the common stock may be sold in these jurisdictions only through registered or licensed brokers or dealers. In addition, in some states the common stock may not be sold unless it has been registered or qualified for sale or an exemption from registration or qualification requirements is available and is complied with.
We have advised the selling stockholders that the anti-manipulation rules of Regulation M under the Exchange Act may apply to sales of shares in the market and to the activities of the selling stockholders and their affiliates. In addition, to the extent applicable we will make copies of this prospectus (as it may be supplemented or amended from time to time) available to the selling stockholders for the purpose of satisfying the prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act. The selling stockholders may indemnify any broker-dealer that participates in transactions involving the sale of the shares against certain liabilities, including liabilities arising under the Securities Act.
We have agreed to indemnify the selling stockholders against liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act and state securities laws, relating to the registration of the shares offered by this prospectus.
We have agreed with the selling stockholders to keep the registration statement of which this prospectus constitutes a part effective until the earlier of (1) such time as all of the shares covered by this prospectus have been disposed of pursuant to and in accordance with the registration statement or (2) the date on which the shares may be sold without restriction pursuant to Rule 144 of the Securities Act.
LEGAL MATTERS
The legality of the securities offered by this prospectus is being passed upon by Greenberg Traurig, LLP, Miami, Florida.
EXPERTS
The audited consolidated financial statements of Integrity Applications, Inc. included in this prospectus and elsewhere in the registration statement have been so included in reliance upon the report of Fahn Kanne & Co., independent registered public accountants, upon the authority of said firm as experts in accounting and auditing in giving said report.
77
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
We have filed with the SEC a registration statement on Form S-1 under the Securities Act with respect to the common stock. This prospectus, which constitutes a part of the registration statement, does not contain all of the information set forth in the registration statement, some items of which are contained in exhibits to the registration statement as permitted by the rules and regulations of the SEC. For further information with respect to us and our common stock, we refer you to the registration statement, including the exhibits and the consolidated financial statements and notes filed as a part of the registration statement. Statements contained in this prospectus concerning the contents of any contract or any other document are not necessarily complete. If a contract or document has been filed as an exhibit to the registration statement, please see the copy of the contract or document that has been filed. Each statement in this prospectus relating to a contract or document filed as an exhibit is qualified in all respects by the filed exhibit. The exhibits to the registration statement should be reviewed for the complete contents of these contracts and documents. A copy of the registration statement, including the exhibits and the financial statements and notes filed as a part of the registration statement, may be inspected without charge at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549, and copies of all or any part of the registration statement may be obtained from the SEC upon the payment of fees prescribed by it. You may call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 for more information on the operation of the public reference facilities. The SEC maintains a website at http://www.sec.gov that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding companies that file electronically with it.
As a result of this offering, we will become subject to the information and reporting requirements of the Exchange Act and, in accordance therewith, will file periodic reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC. These periodic reports, proxy statements and other information will be available for inspection and copying at the SEC’s public reference facilities and the website of the SEC referred to above.
78
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
Consolidated Financial Statements
as of June 30, 2011 (unaudited) and
as of December 31, 2010 (audited)
F-1
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC .
(A Development Stage Company)
Consolidated Financial Statements
as of June 30, 2011 (unaudited) and
as of December 31, 2010 (audited)
Table of Contents
|
|
Page
|
|
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
|
F-3
|
|
Consolidated Financial Statements
|
|
|
Balance Sheets
|
F-4
|
|
Statements of Operations
|
F-5
|
|
Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
|
F-6 – F-10
|
|
Statements of Cash Flows
|
F-11 – F-12
|
|
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
|
F-13 – F-34
|
F-2

|
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders of
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
|
Head Office
23 Menachem Begin Road
Tel-Aviv 66184, ISRAEL
P.O.B. 36172, 61361
|
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Integrity Applications, Inc. (a development stage company) (hereinafter: the "Company") and subsidiary as of December 31, 2010 and 2009, and the related consolidated statements of operations, changes in stockholders’ equity (deficit) and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2010. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Board of Directors and management of the Company. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audit included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of Integrity Applications, Inc. and subsidiary as of December 31, 2010 and 2009, and the consolidated results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2010, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1, the Company is in the development stage as defined in FASB Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) Topic 915, " Development Stage Entities ". It has not yet generated any revenues from its operations to fund its activities and is therefore dependent upon external sources for financing its operations. As of December 31, 2010, the Company has incurred accumulated losses of US$ 10,153,180 and cumulative negative operating cash flow of US$ 7,360,722. These factors among others, as discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans in regards to these matters are also described in Note 1. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
|
FAHN KANNE & CO.
|
|
Certified Public Accountants (Isr.)
|
|
Tel-Aviv, Israel
|
|
October 7, 2011 (Except with respect to Note 9D, as to which the date is October 26, 2011.)
|
F-3
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
|
US dollars (except share data)
|
||||||||||||
|
June 30,
|
December 31,
|
|||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010
|
2009 (*)
|
||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
|||||||||||
|
ASSETS
|
||||||||||||
|
Current Assets
|
||||||||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents
|
1,501,275
|
1,494,248
|
62,032
|
|||||||||
|
Other current assets (Note 3)
|
61,409
|
85,704
|
34,530
|
|||||||||
|
Total current assets
|
1,562,684
|
1,579,952
|
96,562
|
|||||||||
|
Property and Equipment, Net (Note 4)
|
98,146
|
57,350
|
68,065
|
|||||||||
|
Funds in Respect of Employee Rights Upon Retirement
|
150,639
|
133,335
|
100,249
|
|||||||||
|
Total assets
|
1,811,469
|
1,770,637
|
264,876
|
|||||||||
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT)
|
||||||||||||
|
Current Liabilities
|
||||||||||||
|
Credit from banking institutions
|
-
|
18,843
|
92,715
|
|||||||||
|
Accounts payable (Note 5)
|
43,616
|
10,666
|
23,990
|
|||||||||
|
Other current liabilities (Note 6)
|
182,476
|
258,586
|
123,226
|
|||||||||
|
Total current liabilities
|
226,092
|
288,095
|
239,931
|
|||||||||
|
Long-Term Loans from Stockholders (Note 8)
|
641,428
|
625,881
|
573,746
|
|||||||||
|
Liability for Employee Rights Upon Retirement
|
278,523
|
258,522
|
226,941
|
|||||||||
|
Total liabilities
|
1,146,043
|
1,172,498
|
1,040,618
|
|||||||||
|
Commitments and Contingent Liabilities (Note 9)
|
||||||||||||
|
Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) (Note 10)
|
||||||||||||
|
Common Stock of US$ 0.001 par value ("Common Stock"):
|
||||||||||||
|
40,000,000 shares authorized as of June 30, 2011, December 31, 2010 and 2009; issued and outstanding 5,025,863; 4,844,575; 3,999,998 shares as of June 30, 2011, December 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively
|
5,026
|
4,845
|
4,000
|
|||||||||
|
Additional paid in capital
|
11,886,895
|
10,762,892
|
6,482,391
|
|||||||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss)
|
(16,394
|
)
|
(16,418
|
)
|
102,601
|
|||||||
|
Deficit accumulated during developmental stage
|
(11,210,101
|
)
|
(10,153,180
|
)
|
(7,364,734
|
)
|
||||||
|
Total stockholders' equity (deficit)
|
665,426
|
598,139
|
(775,742
|
)
|
||||||||
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity (deficit)
|
1,811,469
|
1,770,637
|
264,876
|
|||||||||
|
(*)
|
As described in Note 1A, the financial statements were retroactively restated to reflect the historical financial statements of the subsidiary A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd., which merged with a subsidiary of the Company on July 15, 2010 as part of a structural reorganization of the group.
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-4
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
|
|
US dollars (except share data)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Three month period
ended June 30,
|
Six month period
ended June 30,
|
Year ended
December 31,
|
Cumulative period
from September 30,
2001 (date of
inception) through
June 30,
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010 (*)
|
2011
|
2010 (*)
|
2010 (*)
|
2009 (*)
|
2008 (*)
|
2011 (*)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
(unaudited)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Research and development expenses, net (Note 11)
|
407,631
|
272,483
|
781,114
|
489,096
|
934,056
|
1,005,108
|
1,242,410
|
7,547,527
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
General and administrative expenses (Note 12)
|
89,098
|
83,293
|
254,736
|
226,352
|
457,495
|
165,156
|
156,632
|
1,872,325
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Other income
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(912
|
)
|
-
|
-
|
(912
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Operating loss
|
496,729
|
355,776
|
1,035,850
|
715,448
|
1,390,639
|
1,170,264
|
1,399,042
|
9,418,940
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Financing expenses, net (Note 13)
|
19,928
|
753,670
|
21,071
|
757,003
|
1,397,807
|
32,032
|
129,939
|
1,791,161
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Loss for the period
|
516,657
|
1,109,446
|
1,056,921
|
1,472,451
|
2,788,446
|
1,202,296
|
1,528,981
|
11,210,101
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Loss per share (basic and diluted) (Note 15)
|
0.10
|
0.28
|
0.22
|
0.37
|
0.70
|
0.30
|
0.40
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Weighted average number of shares outstanding (basic and diluted) (Note 15)
|
4,989,720
|
3,999,998
|
4,922,582
|
3,999,998
|
4,034,706
|
3,995,805
|
3,816,314
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(*)
|
As described in Note 1A, the financial statements were retroactively restated to reflect the historical financial statements of the subsidiary A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd., which merged with a subsidiary of the Company on July 15, 2010 as part of a structural reorganization of the group.
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-5
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) (*)
|
US Dollars (except share data)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Common Stock
|
Accumulated
other
|
Deficit
accumulated
during
|
Total
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Number
of shares
|
Amount
|
Additional
paid in capital
|
comprehensive
loss
|
developmental
stage
|
stockholders ’
equity (deficit)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
September 30, 2001 (date of inception)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2,136,307 Common Stock of US$ 0.001 per share issued for cash
|
2,136,307
|
2,136
|
38,306
|
-
|
-
|
40,442
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Loss for the period
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(63,293
|
)
|
(63,293
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Loss on translation of subsidiary's financial statements from its functional currency to the reporting currency
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(5
|
)
|
-
|
(5
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive loss
|
(63,298
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2002
|
2,136,307
|
2,136
|
38,306
|
(5
|
)
|
(63,293
|
)
|
(22,856
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Loss for the year
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(350,290
|
)
|
(350,290
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Loss on translation of subsidiary's financial statements from its functional currency to the reporting currency
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(15,035
|
)
|
-
|
(15,035
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive loss
|
(365,325
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2003
|
2,136,307
|
2,136
|
38,306
|
(15,040
|
)
|
(413,583
|
)
|
(388,181
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Loss for the year
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(288,233
|
)
|
(288,233
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Loss on translation of subsidiary's financial statements from its functional currency to the reporting currency
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(15,069
|
)
|
-
|
(15,069
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive loss
|
(303,302
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 42,727 Common Stock for cash of US$ 1.76 per share on March 16, 2004
|
42,727
|
43
|
74,957
|
-
|
-
|
75,000
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 72,773 Common Stock for cash of US$ 1.72 per share on November 25, 2004
|
72,773
|
73
|
128,783
|
-
|
-
|
128,856
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2004
|
2,251,807
|
2,252
|
242,046
|
(30,109
|
)
|
(701,816
|
)
|
(487,627
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||
|
(*)
|
As described in Note 1A, the financial statements were retroactively restated to reflect the historical financial statements of the subsidiary A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd., which merged with a subsidiary of the Company on July 15, 2010 as part of a structural reorganization of the group.
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-6
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) (*) (cont.)
|
US Dollars (except share data)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Common Stock
|
Accumulated
other
|
Deficit
accumulated
during
|
Total
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Number
of shares
|
Amount
|
Additional
paid in capital
|
comprehensive
loss
|
developmental
stage
|
stockholders ’
equity (deficit)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of January 1, 2005
|
2,251,807
|
2,252
|
242,046
|
(30,109
|
)
|
(701,816
|
)
|
(487,627
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Loss for the year
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(1,055,594
|
)
|
(1,055,594
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Gain on translation of subsidiary's financial statements from its functional currency to the reporting currency
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
8,542
|
-
|
8,542
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive loss
|
(1,047,052
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 218,281 Common Stock for cash of US$ 1.72 per share on January 14, 2005
|
218,281
|
218
|
374,782
|
-
|
-
|
375,000
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 291,051 Common Stock for cash of US$ 1.72 per share on April 5, 2005
|
291,051
|
291
|
499,709
|
-
|
-
|
500,000
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 59,389 Common Stock for cash of US$ 3.37 per share on May 31, 2005
|
59,389
|
60
|
199,940
|
-
|
-
|
200,000
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation
|
52,147
|
52
|
189,564
|
-
|
-
|
189,616
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2005
|
2,872,675
|
2,873
|
1,506,041
|
(21,567
|
)
|
(1,757,410
|
)
|
(270,063
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Loss for the year
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(1,282,842
|
)
|
(1,282,842
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Loss on translation of subsidiary's financial statements from its functional currency to the reporting currency
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(57,127
|
)
|
-
|
(57,127
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive loss
|
(1,339,969
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 87,315 Common Stock for cash of US$ 1.47 per share on January 26, 2006
|
87,315
|
87
|
128,118
|
-
|
-
|
128,205
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 1,899 Common Stock for cash of US$ 3.63 per share on March 31, 2006
|
1,899
|
2
|
6,888
|
-
|
-
|
6,890
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 13,786 Common Stock for cash of US$ 3.63 per share on June 16, 2006
|
13,786
|
14
|
49,986
|
-
|
-
|
50,000
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 14,113 Common Stock for cash of US$ 3.63 per share on June 30, 2006
|
14,113
|
14
|
51,166
|
-
|
-
|
51,180
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 51,207 Common Stock for cash of US$ 3.91 per share on August 15, 2006
|
51,207
|
51
|
199,949
|
-
|
-
|
200,000
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 301,948 Common Stock for cash of US$ 4.31 per share on October 5, 2006
|
301,948
|
302
|
1,299,698
|
-
|
-
|
1,300,000
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 348,402 Common Stock for cash of US$ 4.31 per share on December 14, 2006
|
348,402
|
349
|
1,372,146
|
-
|
-
|
1,372,495
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation
|
63,395
|
63
|
277,434
|
-
|
-
|
277,497
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2006
|
3,754,740
|
3,755
|
4,891,426
|
(78,694
|
)
|
(3,040,252
|
)
|
1,776,235
|
||||||||||||||||
|
(*)
|
As described in Note 1A, the financial statements were retroactively restated to reflect the historical financial statements of the subsidiary A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd., which merged with a subsidiary of the Company on July 15, 2010 as part of a structural reorganization of the group.
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-7
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) (*) (cont.)
|
US Dollars (except share data)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Common Stock
|
Accumulated
other
|
Receivable in
|
Deficit
accumulated
during
|
Total
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Number
of shares
|
Amount
|
Additional paid
in capital
|
comprehensive
income (loss)
|
respect of stock
issuance
|
developmental
stage
|
stockholders ’
equity (deficit)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of January 1, 2007
|
3,754,740
|
3,755
|
4,891,426
|
(78,694
|
)
|
-
|
(3,040,252
|
)
|
1,776,235
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Loss for the year
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(1,593,205
|
)
|
(1,593,205
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Gain on translation of subsidiary's financial statements from its functional currency to the reporting currency
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
84,528
|
-
|
-
|
84,528
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive loss
|
(1,508,677
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation
|
28,707
|
29
|
274,630
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
274,659
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2007
|
3,783,447
|
3,784
|
5,166,056
|
5,834
|
-
|
(4,633,457
|
)
|
542,217
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Loss for the year
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(1,528,981
|
)
|
(1,528,981
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Gain on translation of subsidiary's financial statements from its functional currency to the reporting currency
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
110,134
|
-
|
-
|
110,134
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive loss
|
(1,418,847
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 61,989 Common Stock for cash of US$ 5.52 per share on September 27, 2008
|
61,989
|
62
|
341,938
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
342,000
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 104,220 Common Stock for cash of US$ 5.52 per share on October 7, 2008
|
104,220
|
104
|
574,896
|
-
|
(75,000
|
)
|
-
|
500,000
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation
|
-
|
-
|
84,380
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
84,380
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2008
|
3,949,656
|
3,950
|
6,167,270
|
115,968
|
(75,000
|
)
|
(6,162,438
|
)
|
49,750
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
(*)
|
As described in Note 1A, the financial statements were retroactively restated to reflect the historical financial statements of the subsidiary A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd., which merged with a subsidiary of the Company on July 15, 2010 as part of a structural reorganization of the group.
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-8
(A Development Stage Company)
STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) (*) (cont.)
|
US Dollars (except share data)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Common Stock
|
Accumulated
other
|
Receivable in
|
Deficit
accumulated
during
|
Total
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Number
of shares
|
Amount
|
Additional paid
in capital
|
comprehensive
income (loss)
|
respect of stock
issuance
|
developmental
stage
|
stockholders ’
equity (deficit)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of January 1, 2009
|
3,949,656
|
3,950
|
6,167,270
|
115,968
|
(75,000
|
)
|
(6,162,438
|
)
|
49,750
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Loss for the year
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(1,202,296
|
)
|
(1,202,296
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Loss on translation of subsidiary's financial statements from its functional currency to the reporting currency
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(13,367
|
)
|
-
|
-
|
(13,367
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive loss
|
(1,215,663
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 50,342 Common Stock for cash of US$ 6.02 per share in January 2009
|
50,342
|
50
|
302,950
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
303,000
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Repayment of receivable in respect of stock issuance
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
75,000
|
-
|
75,000
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation
|
-
|
-
|
12,171
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
12,171
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2009
|
3,999,998
|
4,000
|
6,482,391
|
102,601
|
-
|
(7,364,734
|
)
|
(775,742
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Loss for the year
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(2,788,446
|
)
|
(2,788,446
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Loss on translation of subsidiary's financial statements from its functional currency to the reporting currency
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(119,019
|
)
|
-
|
-
|
(119,019
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive loss
|
(2,907,465
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 530,600 Common Stock for cash of US$ 6.25 per share in December 2010, net of related expenses
|
530,600
|
531
|
2,356,501
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
2,357,032
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based interest compensation to convertible notes holders
|
194,391
|
194
|
1,214,749
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
1,214,943
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Conversion of convertible notes
|
119,586
|
120
|
694,676
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
694,796
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation
|
-
|
-
|
14,575
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
14,575
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2010
|
4,844,575
|
4,845
|
10,762,892
|
(16,418
|
)
|
-
|
(10,153,180
|
)
|
598,139
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
(*)
|
As described in Note 1A, the financial statements were retroactively restated to reflect the historical financial statements of the subsidiary A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd., which merged with a subsidiary of the Company on July 15, 2010 as part of a structural reorganization of the group.
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-9
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (*) (cont.)
|
US Dollars (except share data)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Common Stock
|
Accumulated
other
|
Receivable in
|
Deficit
accumulated
during
|
Total
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Number
of shares
|
Amount
|
Additional paid
in capital
|
comprehensive
loss
|
respect of stock
issuance
|
developmental
stage
|
stockholders ’
equity (deficit)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of January 1, 2011
|
4,844,575
|
4,845
|
10,762,892
|
(16,418
|
)
|
-
|
(10,153,180
|
)
|
598,139
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Loss for the period of six months
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(1,056,921
|
)
|
(1,056,921
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Gain on translation of subsidiary's financial statements from its functional currency to the reporting currency
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
24
|
-
|
-
|
24
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive loss
|
(1,056,897
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 16,320 Common Stock for cash of US$ 6.25 per share in January 31, 2011, net of related expenses
|
16,320
|
16
|
83,164
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
83,180
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 90,768 Common Stock for cash of US$ 6.25 per share in March 31, 2011, net of related expenses
|
90,768
|
91
|
479,810
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
479,901
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 40,000 Common Stock for cash of US$ 6.25 per share in April 29, 2011, net of related expenses
|
40,000
|
40
|
191,682
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
191,722
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of 34,200 Common Stock for cash of US$ 6.25 per share in May 31, 2011, net of related expenses
|
34,200
|
34
|
179,992
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
180,026
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation
|
-
|
-
|
189,355
|
-
|
-
|
189,355
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance as of June 30, 2011 (unaudited)
|
5,025,863
|
5,026
|
11,886,895
|
(16,394
|
)
|
-
|
(11,210,101
|
)
|
665,426
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
(*)
|
As described in Note 1A, the financial statements were retroactively restated to reflect the historical financial statements of the subsidiary A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd., which merged with a subsidiary of the Company on July 15, 2010 as part of a structural reorganization of the group.
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-10
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
|
US dollars (except share data)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Six month period
ended June 30,
|
Year ended
December 31,
|
Cumulative period
from September 30,
2001 (date of inception)
through June 30,
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010 (*)
|
2010 (*)
|
2009 (*)
|
2008 (*)
|
2011 (*)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
(unaudited)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cash flows from operating activities:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Loss for the period
|
(1,056,921
|
)
|
(1,472,451
|
)
|
(2,788,446
|
)
|
(1,202,296
|
)
|
(1,528,981
|
)
|
(11,210,101
|
)
|
||||||||||||
|
Adjustments to reconcile loss for the period to net cash used in operating activities:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Depreciation
|
10,398
|
9,471
|
19,153
|
20,837
|
24,229
|
119,839
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Increase in liability for employee rights upon retirement
|
9,553
|
13,647
|
16,284
|
34,485
|
46,844
|
232,128
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation
|
189,355
|
10,611
|
14,575
|
12,171
|
84,380
|
1,042,186
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based interest compensation to convertible notes holders
|
-
|
651,835
|
1,214,943
|
-
|
-
|
1,214,943
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Linkage difference on principal of loans from stockholders (**)
|
(8,733
|
)
|
3,088
|
15,909
|
10,617
|
21,193
|
143,382
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Interest on convertible notes
|
-
|
27,835
|
78,192
|
-
|
-
|
78,192
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Gain on sale of property and equipment
|
-
|
-
|
(912
|
)
|
-
|
-
|
(912
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Gain from trading marketable securities
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(756
|
)
|
(7,030
|
)
|
(12,920
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Changes in assets and liabilities:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Decrease (increase) in other current assets
|
27,658
|
(9,280
|
)
|
(46,562
|
)
|
577
|
4,816
|
(31,661
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Increase (decrease) in accounts payable
|
31,671
|
(29,849
|
)
|
(14,120
|
)
|
(8,530
|
)
|
21,494
|
40,116
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Increase (decrease) in other current liabilities
|
(80,814
|
)
|
134,974
|
123,147
|
(29,835
|
)
|
35,791
|
146,253
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Net cash used in operating activities
|
(877,833
|
)
|
(660,119
|
)
|
(1,367,837
|
)
|
(1,162,730
|
)
|
(1,297,264
|
)
|
(8,238,555
|
)
|
||||||||||||
|
Cash flows from investment activities:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Increase in funds in respect of employee rights upon retirement
|
(11,699
|
)
|
(12,170
|
)
|
(25,387
|
)
|
(28,819
|
)
|
(12,281
|
)
|
(128,939
|
)
|
||||||||||||
|
Purchase of property and equipment
|
(47,750
|
)
|
(1,134
|
)
|
(8,725
|
)
|
(5,007
|
)
|
(11,932
|
)
|
(201,904
|
)
|
||||||||||||
|
Proceeds from sale of property and equipment
|
-
|
-
|
4,791
|
-
|
-
|
4,791
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Investment in marketable securities
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
(145,168
|
)
|
(388,732
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Proceeds from sale of marketable securities
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
135,195
|
145,368
|
406,995
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Short-term loan granted to related party, net of repayments
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
127,551
|
(55,768
|
)
|
(14,252
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Net cash provided by (used in) investment activities
|
(59,449
|
)
|
(13,304
|
)
|
(29,321
|
)
|
228,920
|
(79,781
|
)
|
(322,041
|
)
|
|||||||||||||
|
(*)
|
As described in Note 1A, the financial statements were retroactively restated to reflect the historical financial statements of the subsidiary A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd., which merged with a subsidiary of the Company on July 15, 2010 as part of a structural reorganization of the group.
|
|
(**)
|
Represents charges taken to reflect changes in the Israeli Consumer Price Index with respect to loans from stockholders that are denominated in New Israeli Shekels and linked to the Israeli Consumer Price Index.
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-11
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS (cont.)
|
US dollars (except share data)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Six month period
ended June 30,
|
Year ended
December 31,
|
Cumulative period
from September 30,
2001 (date of inception)
through June 30,
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010 (*)
|
2010 (*)
|
2009 (*)
|
2008 (*)
|
2011 (*)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
(unaudited)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cash flows from financing activities
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Credit from banking institutions
|
(18,977
|
)
|
(94,263
|
)
|
(75,845
|
)
|
88,265
|
1,115
|
(6,526
|
)
|
||||||||||||||
|
Proceeds from issuance of convertible notes
|
-
|
869,130
|
1,144,000
|
-
|
-
|
1,144,000
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Repayment of convertible notes
|
-
|
-
|
(527,396
|
)
|
-
|
-
|
(527,396
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Proceeds from issuance of Common Stock, net of issuance expenses
|
934,829
|
-
|
2,357,032
|
378,000
|
842,000
|
8,939,996
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Deferred offering cost
|
-
|
(77,292
|
)
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Proceeds from stockholders loans
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
347,742
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Net cash provided by financing activities
|
915,852
|
697,575
|
2,897,791
|
466,265
|
843,115
|
9,897,816
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents
|
28,457
|
56,980
|
(68,417
|
)
|
3,275
|
110,949
|
164,055
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents
|
7,027
|
81,132
|
1,432,216
|
(464,270
|
)
|
(422,981
|
)
|
1,501,275
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the period
|
1,494,248
|
62,032
|
62,032
|
526,302
|
949,283
|
-
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents at end of the period
|
1,501,275
|
143,164
|
1,494,248
|
62,032
|
526,302
|
1,501,275
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Supplementary information on financing activities not involving cash flows:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Conversion of convertible notes to Common Stock (see Notes 10C)
|
-
|
-
|
694,796
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
(*)
|
As described in Note 1A, the financial statements were retroactively restated to reflect the historical financial statements of the subsidiary A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd., which merged with a subsidiary of the Company on July 15, 2010 as part of a structural reorganization of the group.
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-12
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 1 –
|
GENERAL
|
|
A.
|
Integrity Applications, Inc. (the "Company") was incorporated on May 18, 2010, under the laws of the State of Delaware. On July 15, 2010, Integrity Acquisition Corp. Ltd. (hereinafter: "Integrity Acquisition"), a wholly owned Israeli subsidiary of the Company which was established on May 23, 2010, completed a merger with A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd. (hereinafter: "Integrity Israel"), an Israeli corporation which was previously held by the stockholders of the Company. Pursuant to the merger, all stockholders, option holders and warrant holders of Integrity Israel received an equal number of shares, options and warrants of the Company, as applicable in exchange for their shares, options and/or warrants in Integrity Israel. Following the merger, Integrity Israel remained a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company. As the merger transaction constitutes a structural reorganization, the merger has been accounted for at historical cost in a manner similar to a pooling of interests. On this basis, stockholders’ equity has been retroactively restated such that each ordinary share of Integrity Israel is reflected in stockholders' equity as a share of Common Stock of the Company as of the date of the issuance thereof by Integrity Israel. In addition, the historical financial statements of the Company for all dates prior to May 18, 2010 have been retroactively restated to reflect the activities of Integrity Israel.
|
Integrity Israel was incorporated in 2001 and commenced its operations in 2002. Integrity Israel, a medical device company, focuses on the design, development and commercialization of non-invasive glucose monitoring devices for home use by persons suffering with diabetes.
Since its inception, Integrity Israel has devoted substantially all of its efforts to business planning, research and development and raising capital, and has not yet generated any revenues. Accordingly, Integrity Israel (and therefore the Company) is considered to be in the development stage as defined in Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) Topic 915, " Development Stage Entities ".
|
B.
|
Going concern uncertainty
|
Since its incorporation (May 18, 2010), the Company has not had any operations other than those carried out by Integrity Israel. The development and commercialization of Integrity Israel's product is expected to require substantial expenditures. Integrity Israel has not yet generated any revenues from its operations to fund its activities, and therefore is dependent upon external sources for financing its operations. There can be no assurance that Integrity Israel will succeed in obtaining the necessary financing to continue its operations. Since inception, Integrity Israel has incurred accumulated losses of US$ 11,210,101 and cumulative negative operating cash flow of US$ 8,238,555. These factors raise substantial doubt about Integrity Israel and the Company's ability to continue as a going concern. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty. During 2010, the Company raised funds via the issuance of Common Stock (including via the conversion of convertible notes), in a total amount of approximately US$ 4 million. During the six months ended June 30, 2011, the Company raised funds via the issuance of Common Stock in a total amount of approximately US$ 1.1 million. The Company may need to secure additional capital in the future in order to meet its anticipated liquidity needs. The Company would expect to secure additional capital primarily through the sale of additional common stock or other equity securities and/or debt financing. Funds from these sources may not be available to us on acceptable terms, if at all, and we cannot give any assurance that we will be successful in securing such additional capital.
|
C.
|
Stock split
|
The Board of Directors and stockholders of the Company approved in July 2010 a stock split of the outstanding shares and options of the Company's Common Stock, pursuant to which each share and option was spilt into 2.1363 shares and options (the "split"), as applicable. The split became effective as of July 23, 2010. Unless otherwise noted, all shares, per share amounts and options for all periods presented have been retroactively restated to give effect to the split.
F-13
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 1 –
|
GENERAL (cont.)
|
|
D.
|
Risk factors
|
The Company and Integrity Israel (collectively, the "Group") have a limited operating history and faces a number of risks, including uncertainties regarding finalization of the development process, demand and market acceptance of the Group's products, the effects of technological changes, competition and the development of other new products by competitors. Additionally, other risk factors also exist, such as the ability to manage growth and the effect of planned expansion of operations on the Group's future results.
In addition, the Group expects to continue incurring significant operating costs and losses in connection with the development of its product and increased marketing efforts.
As mentioned above, the Group has not yet generated any revenues from its operations to fund its activities and therefore the Group is dependent on the receipt of additional funding from its stockholders and investors in order to continue as a going concern.
|
E.
|
Unaudited Interim Financial Statements
|
The accompanying unaudited financial statements as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 were prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In the opinion of management, the unaudited financial statements presented herein include all adjustments necessary for a fair presentation of the Company’s financial position at June 30, 2011 and the results of its operations for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 and its cash flows for the six month period ended June 30, 2011 and 2010. All such adjustments are of a normal recurring nature. Interim financial statements are prepared on a basis consistent with the Company’s annual financial statements. Results of operations for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 are not necessarily indicative of the operating results that may be expected for the entire year ending December 31, 2011.
|
NOTE 2 –
|
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
|
The consolidated financial statements were prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (US GAAP).
|
A.
|
Functional currency
|
The functional currency of the Company is the US dollar (“US$”), which is the currency of the primary economic environment in which the operations of the Company are conducted and is also the reporting currency of the Group. The functional currency of Integrity Israel is the New Israeli Shekel ("NIS").
The financial statements of the subsidiary were translated into US dollars in accordance with the relevant standards of the FASB. Accordingly, assets and liabilities were translated from NIS to US dollars using year-end exchange rates, and income and expense items were translated at average exchange rates during the year.
Gains or losses resulting from translation adjustments are reflected in stockholders' equity (deficit), under “accumulated other comprehensive income (loss)”.
Balances denominated in or linked to foreign currency are stated on the basis of the exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet date. For foreign currency transactions included in the statement of operations, the exchange rates applicable on the relevant transaction dates are used. Transaction gains or losses arising from changes in the exchange rates used in the translation of such balances are carried to financing income or expenses.
|
June 30,
|
December 31,
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010
|
2010
|
2009
|
2008
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Official exchange rate of NIS 1
|
0.293
|
0.258
|
0.282
|
0.265
|
0.263
|
|||||||||||||||
F-14
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 2 –
|
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (cont.)
|
|
B.
|
Principles of consolidation
|
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiary. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated on consolidation.
As described in Note 1A above, the merger of Integrity Israel has been accounted for in a manner similar to a pooling of interests at historical cost.
|
C.
|
Use of estimates in the preparation of financial statements
|
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with US GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
As applicable to these consolidated financial statements, the most significant estimates and assumptions relate to stock based compensation.
|
D.
|
Cash and cash equivalents
|
The Group considers all short-term investments, which are highly liquid with original maturities of three months or less at the date of purchase, to be cash equivalents.
|
E.
|
Property and equipment, net
|
|
1.
|
Property and equipment are stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. When an asset is retired or otherwise disposed of, the related carrying value and accumulated depreciation are removed from the respective accounts and the net difference less any amount realized from disposition is reflected in the statements of operations.
|
|
2.
|
Rates of depreciation:
|
|
%
|
|||
|
Computers
|
33
|
||
|
Furniture and office equipment
|
7-15
|
||
|
Leasehold improvements
|
Shorter of lease
term
and 10 years
|
|
F.
|
Impairment of long-lived assets
|
The Group's long-lived assets are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to the future undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds its fair value. The Group has not recorded any impairment losses in the reported periods.
F-15
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 2 –
|
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (cont.)
|
|
G.
|
Deferred income taxes
|
Deferred income taxes are determined utilizing the asset and liability method based on the estimated future tax effects of differences between the financial accounting and the tax bases of assets and liabilities under the applicable tax law. Deferred tax balances are computed using the tax rates expected to be in effect when these differences reverse. Valuation allowances in respect of deferred tax assets are provided for if, based upon the weight of available evidence, it is more likely than not that all or a portion of the deferred income tax assets will not be realized.
|
H.
|
Liability for employee rights upon retirement
|
Integrity Israel's liability for employee rights upon retirement with respect to its Israeli employees is calculated, pursuant to Israeli severance pay law, based on the most recent salary of each employee multiplied by the number of years of employment, as of the balance sheet date. Employees are entitled to one month's salary for each year of employment, or a portion thereof. Integrity Israel makes monthly deposits to insurance policies and severance pay funds. The liability of the Company is fully provided for.
The deposited funds include profits accumulated up to the balance sheet date. The deposited funds may be withdrawn upon the fulfillment of Integrity Israel's severance obligations pursuant to Israeli severance pay laws or labor agreements with its employees. The value of the deposited funds is based on the cash surrender value of these policies, and includes immaterial profits/losses.
Severance expenses for the six month period ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 and for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008 amounted to US$ 9,553, US$ 13,647, US$ 16,284, US$ 34,485 and US$ 46,844, respectively.
|
I.
|
Research and development expenses
|
Research and development expenses are charged to operations as incurred. Grants received from the Government of Israel for development of approved projects were recognized as a reduction of expenses when the related costs were incurred (see also J. below).
|
J.
|
Royalty-bearing grants
|
Royalty-bearing grants from the Office of the Chief Scientist of the Ministry of Industry, Trade and Labor (the "OCS") for funding approved research and development projects are recognized at the time Integrity Israel is entitled to such grants, on the basis of the costs incurred and reduce research and development costs. The cumulative research and development grants received by Integrity Israel from inception through December 2004 amount to US$ 93,462 (NIS 420,000). Integrity Israel has not received any research and development grants since December 2004.
As of June 30, 2011, 2010 and December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008, the Company has not accrued any royalties, since no revenues were recognized in respect of the funded project.
|
K.
|
Loss per share
|
Basic loss per share is computed by dividing loss during the period by the weighted average number of shares outstanding during the period.
In computing diluted earnings per share, basic earnings per share are adjusted to reflect the potential dilution that could occur upon the exercise of options issued or granted using the “treasury stock method” and upon the conversion of convertible notes using the “if-converted method,” if their effect is dilutive.
F-16
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 2 –
|
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (cont.)
|
|
L.
|
Stock-based compensation
|
Share-based payments including grants of stock options and shares are recognized in the statement of operations as an operating expense, based on the fair value of the award on the date of grant. The fair value of options is estimated using the Black Scholes option-pricing model and the fair value of share grants is estimated using recent transaction prices. The Group has expensed compensation costs, net of estimated forfeitures, applying the accelerated vesting method, over the requisite service period or over the implicit service period when a performance condition affects the vesting, and it is considered probable that the performance condition will be achieved.
Share-based payments awarded to consultants (non-employees) are accounted for in accordance with ASC Topic 505-50, " Equity-Based Payments to Non-Employees ".
|
M.
|
Other comprehensive income (loss)
|
Other comprehensive income (loss), presented in stockholders' equity (deficit), includes, gains (losses) from the translation of the subsidiary's financial statements from its functional currency to the reporting currency of the group.
|
N.
|
Fair value of financial instruments
|
ASC Topic 825-10, " Financial Instruments " defines financial instruments and requires disclosure of the fair value of financial instruments held by the Company. The Company considers the carrying amount of cash and cash equivalents, other current assets, credit from banking institutions, accounts payable and other current liabilities balances, to approximate their fair values because of the short period of time between the origination of such instruments and their expected realization. The Company did not estimate the fair value of the long-term loans from stockholders which do not bear any interest, since the repayment schedule has not been determined.
|
O.
|
Convertible notes
|
The Company has considered the provisions of ASC Topic 815, " Derivatives and Hedging ", and determined that the conversion feature should not be separated from the host instrument because it did not meet the definition of a derivative due to the lack of a net settlement feature. Furthermore, the Company applied ASC Topic 470-20, " Debt - Debt with Conversion and Other Options " which clarifies the accounting for instruments with beneficial conversion features or contingency adjustable conversion ratios. As described in Note 10C, the Company has determined that the convertible notes did not provide beneficial conversion feature.
As of December 31, 2010, the entire balance of convertible notes (which were issued during fiscal year 2010) was either repaid in cash or converted into Common Stock (see also Note 10C).
|
P.
|
Concentrations of credit risk
|
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist principally of cash and cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents are deposited with major banks in Israel and the United States of America. Management believes that such financial institutions are financially sound and, accordingly, minimal credit risk exists with respect to these financial instruments.
The Company has no significant off-balance-sheet concentration of credit risk, such as foreign exchange contracts, option contracts or other foreign hedging arrangements.
|
Q.
|
Contingencies
|
The Company records accruals for loss contingencies arising from claims, litigation and other sources when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount can be reasonably estimated. These accruals are adjusted periodically as assessments change or additional information becomes available. As of June 30, 2011, the Company has not recorded an expense related to the outstanding litigation because it has not yet been determined if a liability has incurred and if so, if the liability can be reasonably estimated (see Note 9D). Legal costs incurred in connection with loss contingencies are expensed as incurred.
F-17
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 2 –
|
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (cont.)
|
|
R.
|
Recently issued accounting pronouncements
|
ASC Topic 220, "Comprehensive Income"
In June 2011, the FASB issued Accounting Standard Update No. 2011-05, “Comprehensive Income (Topic 220) - Presentation of Comprehensive Income” (“ASU 2011-05”). ASU 2011-05 eliminates the option to present the components of other comprehensive income as part of the statement of equity and requires an entity to present the total of comprehensive income, the components of net income, and the components of other comprehensive income either in a single continuous statement of comprehensive income or in two separate but consecutive statements.
ASU 2011-05 will be effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2011 (fiscal year 2012 for the Company) and should be applied retrospectively.
|
NOTE 3 –
|
OTHER CURRENT ASSETS
|
|
US dollars
|
||||||||||||
|
June 30,
|
December 31,
|
|||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010
|
2009
|
||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
|||||||||||
|
Related parties
|
12,033
|
11,578
|
13,343
|
|||||||||
|
Prepaid expenses
|
14,566
|
14,391
|
9,343
|
|||||||||
|
Government Institution (*)
|
33,832
|
53,363
|
11,844
|
|||||||||
|
Other
|
978
|
6,372
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
61,409
|
85,704
|
34,530
|
||||||||||
|
Represents amounts prepaid by Integrity Israel to the Israeli tax authorities or amounts owed to Integrity Israel by the Israeli Value Added Tax authorities
|
|
NOTE 4 –
|
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
|
|
US dollars
|
||||||||||||
|
June 30,
|
December 31,
|
|||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010
|
2009
|
||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
|||||||||||
|
Computers
|
78,272 | 68,704 | 56,700 | |||||||||
|
Furniture and office equipment
|
120,220 | 74,879 | 84,137 | |||||||||
|
Leasehold improvements
|
26,184 | 25,195 | 23,687 | |||||||||
| 224,676 | 168,778 | 164,524 | ||||||||||
|
Less – accumulated depreciation
|
(126,530 | ) | (111,428 | ) | (96,459 | ) | ||||||
| 98,146 | 57,350 | 68,065 | ||||||||||
In the six month period ended June 30, 2011 and 2010, and for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008, depreciation was US$ 10,398 US$ 9,471, US$ 19,153, US$ 20,837 and US$ 24,229, respectively, and additional equipment was purchased in an amount of US$ 47,750, US$ 1,134, US$ 8,725 US$ 5,007 and US$ 11,932, respectively.
F-18
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 5 –
|
ACCOUNTS PAYABLE
|
|
US dollars
|
||||||||||||
|
June 30,
|
December 31,
|
|||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010
|
2009
|
||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
|||||||||||
|
Open accounts
|
43,616
|
8,354
|
21,098
|
|||||||||
|
Checks payable
|
-
|
2,312
|
2,892
|
|||||||||
|
43,616
|
10,666
|
23,990
|
||||||||||
|
NOTE 6 –
|
OTHER CURRENT LIABILITIES
|
|
US dollars
|
||||||||||||
|
June 30,
|
December 31,
|
|||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010
|
2009
|
||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
|||||||||||
|
Related parties
|
30,870
|
50,133
|
10,526
|
|||||||||
|
Employees and related institutions
|
95,331
|
110,436
|
63,963
|
|||||||||
|
Accrued expenses and other
|
56,275
|
98,017
|
48,737
|
|||||||||
|
182,476
|
258,586
|
123,226
|
||||||||||
|
NOTE 7 –
|
LINE OF CREDIT
|
As of June 30, 2011, the Company did not use any of its credit facilities with its Israeli banks. As of June 30, 2011, the Company has an unutilized credit line of US$ 87,847 (NIS 300,000).
|
NOTE 8 –
|
LONG-TERM LOANS FROM STOCKHOLDERS
|
During the years 2003-2004, Integrity Israel received loans from stockholders. The loans are indexed to the Israeli Consumer Price Index from their origination date and bear no interest.
These loans are not required to be repaid until the first year in which the Company reports profits in its annual statements of operations (accounting profit). Such financial statements will not be published before January 1, 2013 and accordingly, the loans have been presented as long-term liabilities. At such time, repayment of the stockholder loans is to be made from cash flows that will be received from sales, such that 10% of the total sales of the Company after deduction of VAT in every quarter, starting with the quarter following the first year in which the Company realizes profits in its annual statement of operations, will be transferred to each lender or group of lenders, until full repayment of the loans. However, notwithstanding the abovementioned mechanism, the Company will not be required to repay the loans during any time when such repayment would cause a deficit in the Company's working capital.
As of June 30, 2011, no repayments of the stockholders loans have been made.
F-19
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 9 –
|
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENT LIABILITIES
|
|
A.
|
On March 4, 2004, the Office of the Chief Scientist of the Ministry of Industry, Trade and Labor (the “OCS”) agreed to provide Integrity Israel with a grant of NIS 420,000, or approximately US$ 93,462, for its plan to develop a non-invasive blood glucose monitor (the “development plan”). This grant constituted 60% of Integrity Israel’s research and development budget for the development plan. Due to Integrity Israel’s acceptance of this grant, it is subject to the provisions of the Israeli Law for the Encouragement of Industrial Research and Development of 1984 (the “R&D Law”). Integrity Israel is required to pay royalties to the OCS on the proceeds from the sale of the Company's systems resulting from research and development projects for which the OCS provided a grant. The maximum royalties payable by Integrity Israeli will be an amount equal to NIS 420,000 (US$93,462 based on the current exchange rate), plus interest from the date of grant at LIBOR. In the first 3 years of sales, Integrity Israel will be required to pay a 3% royalty on the sale of any product developed under the research and development projects. In the fourth, fifth and sixth years of sales, Integrity Israel will be required to pay a 4% royalty on sales of such products and from the seventh year onward Integrity Israel will be required to pay a 5% royalty. Integrity Israel was entitled to the grants only upon incurring research and development expenditures. There were no future performance obligations related to the grants received from the OCS. As of June 30, 2011, the contingent liabilities with respect to grants received from the OCS subject to repayment under these royalty agreements on future sales equal an amount of US$ 93,462 (NIS 420,000), not including interest. There is no expiration date with respect to Integrity Israel’s obligations to pay royalties to the OCS in respect of products resulting from research and development projects for which the OCS provided a grant to Integrity Israel.
|
|
B.
|
Integrity Israel currently leases approximately 3,100 sq. ft. of office space in the city located in Ashkelon, Israel for its principal offices and prototype laboratory. The lease term began on February 1, 2006 and was extended until January 31, 2009. Pursuant to a verbal agreement with the landlord, Integrity Israel currently leases these facilities on a month to month basis at a cost of NIS 11,500 plus VAT per month (US$ 3,367).
|
|
C.
|
In 2010, the Company engaged Andrew Garrett, Inc. as its exclusive placement agent (the "Placement Agent") in connection with the offering on a “best efforts” basis of a minimum 560,000 shares (US$ 3,500,000) of the Company's Common Stock and a maximum of 2,000,000 shares of the Company’s Common Stock (US$ 12,500,000) (the "Offerings"). Pursuant to a placement agent agreement with the Placement Agent, the Placement Agent (or its sub-agents) was entitled to receive, as a commission, an amount equal to 7% of the funds raised in the Offerings, such amounts to be paid in cash, plus 3% of the funds as a management fee plus a 3% non-accountable expense allowance (13% in the aggregate). In addition, the placement agent agreement required the Company to issue to the Placement Agent (or its sub-agents) warrants to purchase up to 10% of the shares of Common Stock issued to investors (or underlying convertible securities issued to investors) in connection with the Offerings at a price per share that will be equal to the offering price.
|
In connection with the Offerings described in Note 10, the Company paid to the Placement Agent US$ 753,850 and US$ 147,297 in cash during 2010 and the six month period ended June 30, 2011, respectively. In addition, the Company issued to the Placement Agent warrants to purchase 83,281 and 18,129 shares, respectively, of the Company's Common Stock with an exercise price of US$ 6.25, exercisable for a period of 5 years.
|
D.
|
Y.H. Dimri Holdings, which was a shareholder of Integrity Israel prior to the reorganization and merger described in Note 1 ("Dimri"), has alleged (post the reorganization) that, in connection with such reorganization, certain of Dimri's rights in Integrity Israel were violated. Under Dimri's investment agreement, certain rights in Integrity Israel were granted to the Dimri including an anti-dilution provision that provided that Dimri’s holdings in Integrity Israel would not be diluted below 18% of Integrity Israel’s issued capital shares as a result of any investment in Integrity Israel. On the date of the reorganization, Dimri owned 18% of Integrity Israel’s ordinary shares and, therefore, upon the completion of the reorganization, Dimri was entitled to receive 18% of the shares of common stock of the Company outstanding on such date in exchange for his shares in Integrity Israel, subject to the fulfillment of certain requirements. The Company's management, considering the legal advice of its Israeli counsel, believes that, given Dimri no longer owns shares in Integrity Israel as a result of the reorganization, rights attached to the shares in Integrity Israel no longer exist in Integrity Israel and do not and have never existed in the Company. However, Dimri has refused to acknowledge or agree to the termination of these rights and has challenged Company's position.
|
On June 23, 2011, Mr. Dimri appealed to the District Court of HaMerkaz District in Petah Tikva, Israel, requesting the court to appoint an arbitrator to decide the dispute between Integrity Israel, the founders of Integrity Israel and Mr. Dimri (HPB 40754-06-11). On September 25, 2011, Integrity Israel's counsel filed an answer with the Court, disputing the facts and allegation raised in Dimri's motion and suggesting choosing an arbitrator with certain capacities, experience and skills. At a hearing held on October 11, 2011, the court appointed an arbitrator in this matter. The proposed arbitrator is required to inform the court no later than November 1, 2011 if there is anything that will preclude his service as an arbitrator in this matter. If there is, an alternate arbitrator will be appointed by the court. It should be noted that, in accordance with Israeli law, Mr. Dimri was not required to, and he did not, specify in his request for the appointment of an arbitrator the relief to be sought by him in the arbitration. As a result, we do not yet know the relief to be sought by Mr. Dimri in the arbitration. We anticipate that Mr. Dimri will specify the relief sought by him after the commencement of the arbitration proceedings.
The Company does not know what other actions Mr. Dimri will ultimately bring, if any, and against whom they will be brought. Nevertheless, the Company’s management, considering the advice of its counsel and Integrity Israel’s counsel, believes that the Company and Integrity Israel have defenses to any such claims and appropriate claims and counterclaims of their own and they intend to strongly defend against any such action by Mr. Dimri and to assert their own claims and counterclaims as they deem necessary.
Notwithstanding the aforesaid, the Company, considering the advice of its Israeli counsel, is unable to assess or make any estimate of the amount of potential loss, if any. Accordingly, no provision has been made for this claim.
F-20
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 10 –
|
SHARE CAPITAL
|
|
A.
|
Description of the rights attached to the Shares in the Company
|
Each share of Common Stock entitles the holder to one vote, either in person or by proxy, at meetings of stockholders. The holders are not permitted to vote their shares cumulatively. Accordingly, the stockholders of the Company's Common Stock who hold, in the aggregate, more than fifty percent of the total voting rights can elect all of the directors and, in such event, the holders of the remaining minority shares will not be able to elect any of such directors. The vote of the holders of a majority of the issued and outstanding shares of Common Stock entitled to vote thereon is sufficient to authorize, affirm, ratify or consent to such act or action, except as otherwise provided by law.
|
B.
|
Stock-based compensation
|
|
1.
|
Grants to non-employees
|
|
a.
|
During 2005, Integrity Israel granted to three consultants an aggregate sum of 144,250 of its ordinary shares of NIS 0.01 par value as consideration for consulting services. The compensation expense was recorded as an expense over the consulting service period (varying from 2 months to 2 years).
|
The non-cash compensation recorded with respect to such grants was US$ 123,625, US$ 229,564 and US$ 175,516 for the years 2007, 2006 and 2005, respectively. The fair value of the shares was based on the recent share price applicable.
Following the merger with Integrity Israel, the shares were replaced with shares of the Company.
|
b.
|
In October 2006, the Company granted 45,531 options with an exercise price of US$ 4.305 per share in consideration of investor finders. In November 2008, the Company granted 8,989 options with an exercise price of US$ 5.517 per share in consideration of investor finders. The fair value of the grant was based on the most recent share price with respect to the relevant grant date.
|
Following the merger with Integrity Israel, the options were replaced with options to purchase shares of the Company.
|
c.
|
See Note 9C.
|
|
2.
|
Grants to employees
|
|
a.
|
During 2005-2006, Integrity Israel granted to two individuals (an officer and a director), options exercisable into 24,394 options of NIS 0.01 par value of Integrity Israel. The exercise price of each option was US$ 3.49 (with respect to 4,486 options) and US$ 3.84 (with respect to 19,908 options). The vesting period was three years with respect to the 4,486 options and two months with respect to the 19,908 options.
|
The total non-cash compensation recorded with respect to such grants was US$ 45,291, US$ 2,435 and US$ 203 for the years 2007, 2006 and 2005, respectively. The fair value of the grants was based on the most recent share price with respect to the relevant grant date.
Following the merger with Integrity Israel, the options were replaced with options of the Company.
F-21
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 10 –
|
SHARE CAPITAL (cont.)
|
|
B.
|
Stock-based compensation (cont.)
|
|
2.
|
Grants to employees (cont.)
|
|
b.
|
In August 2007, Integrity Israel’s Board of Directors ( "Integrity Israel's Board ") approved a stock option plan (" Integrity Israel's plan ") for the grant, without consideration of options exercisable into ordinary shares of NIS 0.01 par value of Integrity Israel to employees, officers and directors of Integrity Israel. The exercise price and vesting period for each grantee of options was determined by Integrity Israel's Board and specified in such grantee's option agreement. The options were to vest over a period of 1-12 quarters based on each grantee's option agreements. Any option not exercised within 10 years after the date of grant thereof will expire.
|
In July 2010, following the merger with Integrity Israel, the Company adopted the 2010 Share Incentive Plan (the "2010 Share Incentive Plan"), pursuant to which the Company's Board of Directors is authorized to grant options exercisable into Common Stock of the Company. The Company has reserved 529,555 shares of common stock for issuance under the plan. The purpose of the 2010 Share Incentive Plan is to offer an incentive to employees, directors, officers, consultants, advisors, suppliers and any other person or entity whose services are considered valuable to the Company, as well as to replace the Integrity Israel Plan and to replace all options granted in the past by Integrity Israel.
Upon the adoption of the 2010 Share Incentive Plan, all options granted under the Integrity Israel Plan were replaced by options subject to the 2010 Share Incentive Plan on a 1 for 1 basis.
As of June 30, 2011, 91,829 options have been granted to employees and 21,641 options to non-employees. All options granted in the Integrity Israel Plan were replaced with options of the Company and are subject to the 2010 Share Incentive Plan. The non-cash compensation relating to options granted to employees and directors was US$ 320 and US$ 10,611 during the six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010, respectively, and US$ 14,575, US$ 12,171 and US$ 84,380 during the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
|
c.
|
See Note 16A, 16B.
|
The following tables present a summary of the status of the grants to employees, officers and directors as of June 30, 2011 and December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008:
|
Number
|
Weighted average
exercise price (US$)
|
|||||||
|
Six month period ended June 30, 2011
(unaudited)
|
||||||||
|
Balance outstanding at beginning of period
|
428,367
|
5.49
|
||||||
|
Granted (*)
|
29,315
|
6.25
|
||||||
|
Exercised
|
-
|
-
|
||||||
|
Forfeited
|
(3,328
|
)
|
3.84
|
|||||
|
Balance outstanding at end of the period
|
454,354
|
5.55
|
||||||
|
Balance exercisable at the end of the period
|
110,142
|
3.27
|
||||||
(*) Represents the minimum number of options, as of the date indicated, to be issued to Messrs. Gal and Malka following the completion of the Offering, the number of which was finalized in August 2011 upon the completion of the Offering. See Note 16 for a discussion regarding the total number of options to be issued in connection with the Offering.
F-22
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 10 –
|
SHARE CAPITAL (cont.)
|
|
B.
|
Stock-based compensation (cont.)
|
|
2.
|
Grants to employees (cont.)
|
|
Number
|
Weighted average
exercise price (US$)
|
|||||||
|
Year ended December 31, 2010
|
||||||||
|
Balance outstanding at beginning of year
|
109,197
|
3.27
|
||||||
|
Granted (*)
|
314,897
|
6.25
|
||||||
| Granted | 4,273 | 6.02 | ||||||
|
Exercised
|
-
|
-
|
||||||
|
Forfeited
|
-
|
-
|
||||||
|
Balance outstanding at end of the year
|
428,367
|
5.49
|
||||||
|
Balance exercisable at the end of the year
|
109,197
|
3.27
|
||||||
(*) Represents the minimum number of options, as of the date indicated, to be issued to Messrs. Gal and Malka following the completion of the Offering, the number of which was finalized in August 2011 upon the completion of the Offering. See Note 16 for a discussion regarding the total number of options to be issued in connection with the Offering.
|
Number
|
Weighted average
exercise price (US$)
|
|||||||
|
Year ended December 31, 2009
|
||||||||
|
Balance outstanding at beginning of year
|
106,213
|
2.76
|
||||||
|
Granted
|
2,984
|
5.52
|
||||||
|
Exercised
|
-
|
-
|
||||||
|
Forfeited
|
-
|
-
|
||||||
|
Balance outstanding at end of the year
|
109,197
|
3.27
|
||||||
|
Balance exercisable at the end of the year
|
106,213
|
2.76
|
||||||
|
Number
|
Weighted average
exercise price (US$)
|
|||||||
|
Year ended December 31, 2008
|
||||||||
|
Balance outstanding at beginning of year
|
106,213
|
2.76
|
||||||
|
Granted
|
-
|
-
|
||||||
|
Exercised
|
-
|
-
|
||||||
|
Forfeited
|
-
|
-
|
||||||
|
Balance outstanding at end of the year
|
106,213
|
2.76
|
||||||
|
Balance exercisable at the end of the year
|
82,239
|
2.71
|
||||||
The aggregate intrinsic value of the balances exercisable as of June 30, 2011, December 31, 2010 and 2009 is US$ 328,223, US$ 325,407 and US$ 370,683, respectively. The aggregate intrinsic value of the balances outstanding as of June 30, 2011, December 31, 2010 and 2009 is US$ 318,048, US$ 325,559 and US$ 325,407, respectively. This amount represents the total intrinsic value, based on management's estimate of the Company's stock price of US$ 6.25 as of June 30, 2011 and December 31, 2010 and US$6.02 as of December 31, 2009, less the weighted average exercise price. This represents the potential amount received by the option holders had all option holders exercised their options as of that date.
F-23
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 10 –
|
SHARE CAPITAL (cont.)
|
|
B.
|
Stock-based compensation (cont.)
|
|
2.
|
Grants to employees (cont.)
|
The following tables summarize information about options outstanding at June 30, 2011 and December 31, 2010:
|
Exercise
prices
|
Outstanding at
June 30, 2011
|
Weighted average
remaining
contractual life years
|
Weighted
average
exercise price
|
Exercisable at
June 30, 2011
|
Weighted
average
exercise price
|
|||||||||||||||
|
US$
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
1.72
|
46,004
|
6.1
|
1.72
|
46,004
|
1.72
|
|||||||||||||||
|
3.27
|
30,966
|
4.4
|
3.27
|
30,966
|
3.27
|
|||||||||||||||
|
3.48
|
4,486
|
4.4
|
3.48
|
4,486
|
3.48
|
|||||||||||||||
|
3.63
|
4,849
|
6.1
|
3.63
|
4,849
|
3.63
|
|||||||||||||||
|
3.84
|
16,580
|
5.5
|
3.84
|
16,580
|
3.84
|
|||||||||||||||
|
5.52
|
2,984
|
8.1
|
5.52
|
2,984
|
5.52
|
|||||||||||||||
|
6.02
|
4,273
|
5.62
|
6.02
|
4,273
|
6.02
|
|||||||||||||||
|
6.25
|
344,212
|
(*)
|
9.5
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
||||||||||||||
|
454,354
|
110,142
|
|||||||||||||||||||
(*) Represents the minimum number of options, as of the date indicated, to be issued to Messrs. Gal and Malka following the completion of the Offering, the number of which was finalized in August 2011 upon the completion of the Offering. See Note 16 for a discussion regarding the total number of options to be issued in connection with the Offering.
|
Exercise
prices
|
Outstanding at
December 31,
2010
|
Weighted average
remaining
contractual life years
|
Weighted
average
exercise price
|
Exercisable at
December 31,
2010
|
Weighted
average
exercise price
|
|||||||||||||||
|
US$
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
1.72
|
46,004
|
6.6
|
1.72
|
46,004
|
1.72
|
|||||||||||||||
|
3.27
|
30,966
|
4.9
|
3.27
|
30,966
|
3.27
|
|||||||||||||||
|
3.48
|
4,486
|
4.9
|
3.48
|
4,486
|
3.48
|
|||||||||||||||
|
3.63
|
4,849
|
6.6
|
3.63
|
4,849
|
3.63
|
|||||||||||||||
|
3.84
|
19,908
|
6.0
|
3.84
|
19,908
|
3.84
|
|||||||||||||||
|
5.52
|
2,984
|
8.6
|
5.52
|
1,493
|
5.52
|
|||||||||||||||
|
6.02
|
4,273
|
6.12
|
6.02
|
1,491
|
6.02
|
|||||||||||||||
|
6.25
|
314,897
|
(*)
|
10.0
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
||||||||||||||
|
428,367
|
109,197
|
|||||||||||||||||||
(*) Represents the minimum number of options, as of the date indicated, to be issued to Messrs. Gal and Malka following the completion of the Offering, the number of which was finalized in August 2011 upon the completion of the Offering. See Note 16 for a discussion regarding the total number of options to be issued in connection with the Offering.
The fair value of options granted was estimated at the dates of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The following are the data and assumptions used:
|
2011
|
2010
|
2009
|
||||||||||
|
Dividend yield (%)
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|||||||||
|
Expected volatility (%) (*)
|
50
|
50
|
50
|
|||||||||
|
Risk free interest rate (%)
|
2
|
2
|
2
|
|||||||||
|
Expected term of options (years) (**)
|
5-6
|
5-6
|
5-6
|
|||||||||
|
Exercise price (US dollars)
|
6.25
|
6.02/6.25
|
5.52
|
|||||||||
|
Share price (US dollars) (***)
|
6.25
|
6.02/6.25
|
5.52
|
|||||||||
|
Fair value (US dollars)
|
3.08
|
2.81/3.08
|
1.42
|
|||||||||
|
(*)
|
Due to the fact that the Company is a nonpublic entity, the expected volatility was based on the historic volatility of public companies which operate in the same industry sector.
|
|
(**)
|
Due to the fact that the Company does not have historical exercise data, the expected term was determined based on the "simplified method" in accordance with Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 110.
|
|
(***)
|
The fair value of the share was based on the most recent share prices, as applicable to each grant.
|
|
(****)
|
There were no grants to employees during 2008.
|
F-24
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 10 –
|
SHARE CAPITAL (cont.)
|
|
C.
|
Convertible notes
|
|
|
1.
|
In April 2010, the Company issued Secured Notes (“Senior Notes”) in the aggregate initial principal amount of US$ 999,000 together with rights to acquire Common Stock following the reorganization and merger described in Note 1. The principal amount of the notes, together with any interest accrued but unpaid thereon, and any fees and charges, are referred to collectively as the “Outstanding Amount” of such Senior Notes.
|
The Senior Notes provided for an interest rate of 9% per annum and were due and payable on the first to occur of (a) the date of the closing of the Company’s next Qualified Financing (as defined therein); or (b) August 9, 2010, provided that the holders of Senior Notes were permitted to extend the date in clause (b) by up to 60 days with respect to all of the Senior Notes (the “Maturity Date”). Interest on the Senior Notes was to be paid on the Maturity Date if such interest was not exchanged for Common Stock in the manner described above.
Immediately after the initial closing of the Offering, each purchaser of Senior Note (a “Senior Note Purchaser”) was entitled to receive Common Stock issued and sold at the closing of the Offering in accordance with the following:
|
|
(i)
|
If the Senior Note Purchaser elected, to be repaid under its Senior Note in shares of Common Stock in lieu of any cash, such Senior Note Purchaser received the number of shares of Common Stock equal to the quotient obtained by dividing (i) 200% of the unpaid portion of the Outstanding Amount of such Senior Note Purchaser’s Senior Note by (ii) the offering price per share of the Common Stock, rounded to the nearest whole share; or
|
|
|
(ii)
|
If the Senior Note Purchaser did not make the election in clause (i) above, such Senior Note Purchaser instead received the number of shares of Common Stock equal to the quotient obtained by dividing (i) 100% of the unpaid portion of the Outstanding Amount of such Senior Note Purchaser’s Senior Note by (ii) the offering price per share of the Common Stock, rounded to the nearest whole share, in addition to a cash payment equal to the Outstanding Amount of such Senior Note Purchaser’s Senior Note pursuant to the terms thereof.
|
The Senior Notes bear interest of 9% per annum and are due and payable on the first to occur of (a) the date of the closing of the Company’s next Qualified Financing; or (b) August 9, 2010, provided that the holders of Senior Notes were permitted to extend the date in clause (b) by up to 60 days with respect to all of the Senior Notes (the “Maturity Date”). Interest on the Senior Notes was to be paid on the Maturity Date if such interest was not exchanged for Common Stock in the manner described above.
The original amount of the Senior Notes (US$ 999,000), which entitled the holders of the Senior Notes to an either cash or stock settlement at a price per share equal to the fair value of the share that would be determined at the offering, represents stock-settled debt under the provisions of ASC Topic 47-20, " Debt-Debt with Conversion and Other Options ". Due to the conversion price, the Company has determined that this component did not provide an active beneficial conversion feature. However, the entitlement of the Senior Note holders to receive a fixed value of Common Stock in an amount equal to 100% of the original amount of the Senior Notes (in addition to the stock settled debt described above), which represented an obligation to issue a variable number of shares under the provisions of ASC Topic 480, " Distinguishing Liabilities for Equity " (totaling US$ 999,000), was recognized as a stock-based interest compensation (which was included among financing expenses, net) over the term of the Senior Notes (April 2010 - August 2010).
F-25
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 10 –
|
SHARE CAPITAL (cont.)
|
|
C.
|
Convertible notes (cont.)
|
|
1.
|
(cont.)
|
On December 16, 2010, the Company completed an initial closing of the Offering, at which the Company issued 87,977 shares of Common Stock to certain holders of Senior Notes, who held an amount of US$ 549,797 (including unpaid interest) and which elected to be repaid in shares. The remaining amount of the Senior Notes, US$ 527,396 (including unpaid interest), was settled in cash.
In addition, the Company issued 171,208 shares of Common Stock to the holders of Senior Notes as a repayment of the obligation to issue a variable number of shares. The fair value of the shares (US$ 1,069,244) represents 100% of the original amount of the Senior Notes and interest accumulated up to the Offering date.
The Company issued to the Placement Agent, warrants to purchase an aggregate of 25,919 shares of Common Stock with an exercise price of US$ 6.25 and in addition was required to pay US$ 129,870 in cash (see Note 9C).
|
2.
|
In November 2010, Integrity Israel issued Unsecured Junior Promissory Notes ("Junior Notes") in the aggregate initial principal amount of US$ 170,000 (of which US$ 25,000 was received in 2011). The Junior Promissory Notes were substantially similar to the Senior Notes, except that immediately after the initial closing of the Offering, each holder of Junior Promissory Notes was entitled to receive the number of shares of Common Stock equal to the quotient obtained by dividing (i) 200% of the Outstanding Amount of such holder’s Junior Promissory Note by (ii) the price per share of the Common Stock in the Offering, rounded to the nearest whole share. The entitlement to receive a fixed value of Common Stock sold at the closing of the Offering in an amount equal to 200% of the original amount of the Junior Notes was recognized as an obligation to issue a variable number of shares under the provisions of ASC Topic 480, " Distinguishing Liabilities for Equity ", accordingly an amount equal to 100% of the original amount of the Junior Notes was recognized as stock-based interest compensation (which was included among financing expenses, net).
|
On December 16, 2010, the Company completed an initial closing of the Offering, at which, 54,792 shares of Common Stock were issued to the purchasers of the Junior Promissory Notes pursuant to the terms and in full repayment of such Junior Promissory Notes. The fair value of the shares (US$ 345,100) represents 200% of the original amount of the Senior Notes and interest accumulated up to the Offering date.
The Company issued to the Placement Agent, warrants to purchase an aggregate of 5,480 shares of Common Stock with an exercise price of US$ 6.25 and in addition was required to pay US$ 77,292 in cash (see Note 9C).
|
D.
|
On December 16, 2010, the Company completed an initial closing of the Offering at which the Company received an amount of US$ 3,016,250 for 482,600 shares of Common Stock issued to investors in the Offering representing a price share of US$ 6.25. The Company issued to the Placement Agent, warrants to purchase an aggregate of 48,260 shares of Common Stock at the third closing with an exercise price of US$ 6.25 and in addition was required to pay US$ 392,112 in cash (see Note 9C).
|
F-26
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 10 –
|
SHARE CAPITAL (cont.)
|
|
E.
|
On December 30, 2010, the Company completed a second closing of the Offering at which the Company received an amount of US$ 300,000 for 48,000 shares of Common Stock issued to investors in the Offering representing a price per share of US$ 6.25. The Company issued to the Placement Agent, warrants to purchase an aggregate of 4,800 shares of Common Stock at the third closing with an exercise price of US$ 6.25 and in addition was required to pay US$ 39,942 in cash (see Note 9C).
|
|
F.
|
On January 31, 2011, the Company completed a third closing of the Offering at which the Company received an amount of US$ 102,000 for 16,320 shares of Common Stock issued to investors in the Offering representing a price per share of US$ 6.25. The Company issued to the Placement Agent, warrants to purchase an aggregate of 1,632 shares of Common Stock at the third closing with an exercise price of US$ 6.25 and in addition was required to pay US$ 13,260 in cash (see Note 9C).
|
|
G.
|
On March 31, 2011, the Company completed a fourth closing of the Offering at which the Company received an amount of US$ 567,300 for 90,768 shares of Common Stock issued to investors in the Offering representing a price per share of US$ 6.25. The Company issued to the Placement Agent, warrants to purchase an aggregate of 9,077 shares of Common Stock at the fourth closing with an exercise price of US$ 6.25 and in addition was required to pay US$ 73,749 in cash (see Note 9C).
|
|
H.
|
On April 29, 2011, the Company completed a fifth closing of the Offering at which the Company received an amount of US$ 250,000 for 40,000 shares of common stock issued to investors in the Offering representing a price per share of US$ 6.25. The Company issued to the Placement Agent, warrants to purchase an aggregate of 4,000 shares of common-stock at the fifth closing with an exercise price of US$ 6.25 and in addition was required to pay US$ 32,500 in cash (see Note 9C).
|
|
I.
|
On May 31, 2011, the Company completed a sixth closing of the Offering at which the Company received an amount of US$ 213,750 for 34,200 shares of common stock issued to investors in the Offering representing a price per share of US$ 6.25. The Company issued to the Placement Agent, warrants to purchase an aggregate of 3,420 shares of common-stock at the sixth closing with an exercise price of US$ 6.25 and in addition was required to pay US$ 27,788 in cash (see Note 9C).
|
F-27
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 11 –
|
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT EXPENSES, NET
|
|
US dollars
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Three month period
ended June 30,
|
Six month period
ended June 30,
|
Year ended
December 31,
|
Cumulative period
from September 30,
2001 (date of
inception) through
June 30,
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010
|
2011
|
2010
|
2010
|
2009
|
2008
|
2011
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
(unaudited)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Salaries and related expenses
|
289,116 | 127,554 | 550,095 | 264,703 | 557,042 | 482,662 | 679,149 | 4,202,947 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Professional fees
|
57,654 | 70,260 | 85,611 | 95,242 | 94,711 | 205,903 | 251,235 | 1,357,607 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Materials
|
14,171 | 3,428 | 32,329 | 16,163 | 19,114 | 56,791 | 43,499 | 411,767 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Depreciation
|
6,103 | 12,925 | 10,398 | 25,571 | 53,219 | 44,948 | 42,105 | 213,238 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Travel expenses
|
8,385 | 10,142 | 23,818 | 15,804 | 58,215 | 25,195 | 49,634 | 248,387 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Vehicle maintenance
|
8,087 | 8,079 | 15,135 | 16,795 | 33,697 | 30,411 | 33,656 | 222,699 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Other
|
24,115 | 40,095 | 63,728 | 54,818 | 118,058 | 159,198 | 143,132 | 984,344 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 407,631 | 272,483 | 781,114 | 489,096 | 934,056 | 1,005,108 | 1,242,410 | 7,640,989 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Less: Grants from the OCS (*)
|
- | - | - | - | - | - | - | (93,462 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 407,631 | 272,483 | 781,114 | 489,096 | 934,056 | 1,005,108 | 1,242,410 | 7,547,527 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
(*)
|
See Note 9A.
|
F-28
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 12 –
|
GENERAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE EXPENSES
|
|
US dollars
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Three month period
ended June 30,
|
Six month period
ended June 30,
|
Year ended
December 31,
|
Cumulative period
from September 30,
2001 (date of
inception) through
June 30,
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010
|
2011
|
2010
|
2010
|
2009
|
2008
|
2011
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
(unaudited)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Salaries and related expenses
|
41,192 | 13,811 | 84,161 | 27,804 | 55,995 | 55,131 | 36,925 | 352,696 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Professional fees
|
26,035 | 55,051 | 96,962 | 174,957 | 365,398 | 52,270 | 83,095 | 1,251,677 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Other
|
21,871 | 14,431 | 73,613 | 23,591 | 36,102 | 57,755 | 36,612 | 267,952 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 89,098 | 83,293 | 254,736 | 226,352 | 457,495 | 165,156 | 156,632 | 1,872,325 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NOTE 13 –
|
FINANCING EXPENSES, NET
|
|
US dollars
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Three month period
ended June 30,
|
Six month period
ended June 30,
|
Year ended
December 31,
|
Cumulative period
from September 30,
2001 (date of
inception) through
June 30,
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010
|
2011
|
2010
|
2010
|
2009
|
2008
|
2011
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
(unaudited)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Linkage difference on principal of loans from stockholders
|
4,628 | 4,004 | 8,579 | 3,591 | 15,909 | 10,617 | 21,193 | 160,694 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Exchange rate differences
|
14,915 | 44,392 | 8,728 | 45,879 | (51,844 | ) | 18,210 | 120,457 | 247,263 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based interest compensation to holders of convertible notes (see Note 10C)
|
- | 651,835 | - | 651,835 | 1,214,943 | - | - | 1,214,943 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Interest expenses on credit from banks and other
|
385 | 3,959 | 3,764 | 6,218 | 17,987 | 3,205 | (11,711 | ) | (32,551 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Interest expenses and other, related to convertible notes
|
- | 49,480 | - | 49,480 | 200,812 | - | - | 200,812 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19,928 | 753,670 | 21,071 | 757,003 | 1,397,807 | 32,032 | 129,939 | 1,791,161 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
F-29
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 14 –
|
INCOME TAX
|
|
A.
|
Measurement of results for tax purposes under the Israeli Income Tax (Inflationary Adjustments) Law, 1985 (the “Inflationary Adjustment Law”)
|
Until December 31, 2007, Integrity Israel reported for tax purposes in accordance with the provisions of the Inflationary Adjustments Law, whereby taxable income was measured in NIS, adjusted for changes in the Israeli Consumer Price Index. Results of operations for tax purposes were measured in terms of earnings in NIS after adjustments for changes in the Israeli Consumer Price Index ("CPI"). Commencing January 1, 2008, the Inflationary Adjustment Law became void and in its place there are transition provisions, whereby the results of operations for tax purposes are to be measured on a nominal basis.
|
B.
|
Reduction in Israeli corporate tax rates
|
On July 25, 2005, the Israeli Parliament passed an amendment to the Income Tax Ordinance (No. 147) – 2005, gradually reducing the tax rate applicable to the Company as follows: in 2006 – 31%, in 2007 – 29%, in 2008 – 27%, in 2009 – 26% and in 2010 and thereafter – 25%.
On July 23, 2009, as part of the Economic Efficiency Law (Legislative Amendments for the Implementation of the Economic Plan for the years 2009 and 2010) – 2009 (the “Arrangements Law”), article 126 of the Income Tax Ordinance (New Version) – 1961 was amended, whereby the corporate tax rate would be gradually reduced commencing in the 2011 tax year and thereafter, as follows: 2011 – 24%, 2012 – 23%, 2013 – 22%, 2014 – 21%, 2015 – 20% and 2016 and thereafter – 18%.
|
C.
|
Tax assessments
|
The Company and Integrity Israel have not received final tax assessments since their inception.
|
D.
|
Carryforward tax losses
|
As of December 31, 2010, Integrity Israel has loss carry forward balances for income tax purposes of US$ 10.6 million that are available to offset future taxable income, if any.
F-30
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 14 –
|
INCOME TAX (cont.)
|
|
E.
|
The following is a reconciliation between the theoretical tax on pre-tax income, at the tax rate applicable to the Company (federal tax rate) and the tax expense reported in the financial statements:
|
|
US dollars
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Three month period
ended June 30,
|
Six month period
ended June 30,
|
Year ended
December 31,
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010
|
2011
|
2010
|
2010
|
2009
|
2008
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Pretax loss
|
(516,657 | ) | (1,109,446 | ) | (1,056,921 | ) | (1,472,451 | ) | (2,788,446 | ) | (1,202,296 | ) | (1,528,981 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
Federal tax rate
|
15 | % | 15 | % | 15 | % | 15 | % | 15 | % | 15 | % | 15 | % | ||||||||||||||
|
Income tax benefit computed at the ordinary tax rate
|
(77,499 | ) | (166,417 | ) | (158,538 | ) | (220,868 | ) | (418,267 | ) | (180,344 | ) | (229,347 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
Non-deductible expenses
|
543 | 505 | 1,064 | 1,010 | 2,009 | 1,913 | 2,091 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation
|
28,355 | 747 | 28,403 | 1,592 | 2,186 | 1,826 | 12,657 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based interest compensation to holders of convertible notes
|
- | 97,775 | - | 97,775 | 182,241 | - | - | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Tax in respect of differences in corporate tax rates
|
(28,749 | ) | (148,445 | ) | (68,837 | ) | (184,745 | ) | (278,845 | ) | (132,253 | ) | (183,478 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
Losses and timing differences in respect of which no deferred taxes were generated
|
77,350 | 215,835 | 197,908 | 305,236 | 510,676 | 308,858 | 398,077 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
F.
|
Deferred taxes result principally from temporary differences in the recognition of certain revenue and expense items for financial and income tax reporting purposes. Significant components of the Group's future tax assets are as follows:
|
|
US dollars
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
June 30,
|
December 31,
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010
|
2010
|
2009
|
2008
|
||||||||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Composition of deferred tax assets:
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Provision for employee-related obligation
|
39,183 | 35,673 | 36,568 | 37,561 | 37,509 | |||||||||||||||
|
Non-capital loss carry forwards
|
2,551,746 | 2,159,610 | 2,393,919 | 1,768,416 | 1,515,096 | |||||||||||||||
|
Valuation allowance
|
(2,590,929 | ) | (2,195,283 | ) | (2,430,487 | ) | (1,805,977 | ) | (1,552,605 | ) | ||||||||||
| - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||
F-31
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 15 –
|
LOSS PER SHARE
|
The loss and the weighted average number of shares used in computing basic and diluted loss per share for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010, and for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008, are as follows:
|
US dollars
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Three month period
ended June 30,
|
Six month period
ended June 30,
|
Year ended
December 31,
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010
|
2011
|
2010
|
2010
|
2009
|
2008
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 516,657 | 1,109,446 | 1,056,921 | 1,472,451 | 2,788,446 | 1,202,296 | 1,528,981 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Number of shares
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Three month period
ended June 30,
|
Six month period
ended June 30,
|
Year ended
December 31,
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2011
|
2010
|
2011
|
2010
|
2010
|
2009
|
2008
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Weighted average number of shares used in the computation of basic and diluted earnings per share
|
4,989,720 | 3,999,998 | 4,922,582 | 3,999,998 | 4,034,706 | 3,995,805 | 3,816,314 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Total weighted average number of ordinary shares related to outstanding options and warrants excluded from the calculations of diluted loss per share (*)
|
555,764 | 113,470 | 555,764 | 113,470 | 511,648 | 109,197 | 106,213 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
(*)
|
All stock issuable upon the exercise of all outstanding stock options and warrants and conversion of convertible notes have been excluded from the calculation of the diluted net loss per share for all the reported periods, since the effect of the shares issuable with respect of these instruments was anti-dilutive.
|
F-32
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 16 –
|
RELATED PARTIES
|
|
A.
|
Avner Gal, the owner of approximately 8.16% of the Company's outstanding Common Stock entered into an employment agreement with Integrity Israel in July 2010 pursuant to which Mr. Gal agreed to continue to serve as the chief executive officer and managing director of Integrity Israel. The agreement was approved by the board of directors and stockholders of Integrity Israel. Mr. Gal’s employment agreement provides for an annual salary of NIS 480,000 (US$ 140,556) and an annual bonus to be determined by the Board of Directors and an additional sum provided that Mr. Gal reaches certain milestones approved by the Board, as well as the payment of certain social and insurance benefits and the use of a group four car. The agreement also provides for a renegotiation of Mr. Gal’s annual salary on the one-year anniversary thereof and the renegotiation of Mr. Gal’s bonus formula once Integrity Israel has begun commercialization of its products. The agreement is terminable by either party on 180 days notice, immediately by Integrity Israel with the payment of an amount equal to 180 days of annual salary, or immediately by Integrity Israel for cause (as defined in the agreement) without the payment of severance.
|
In connection with the Offering, Mr. Gal was entitled to receive options to purchase 5% of all issued and outstanding Common Stock of the Company after the Offering for sale of a minimum 560,000 shares ($3,500,000) of the Company's Common Stock and a maximum of 2,000,000 shares of the Company's Common Stock ($12,500,000). The offering (which commenced in December 2010) was completed in July 2011 and, as a result, Mr. Gal became entitled to receive a grant of 264,778 options. The options shall be deemed vested, in 3 equal parts, in accordance with the achievement of the following milestones: (i) submission of clinical trials’ results to the Notified Body; (ii) CE mark approval; (iii) FDA approval. The options will be exercisable at $6.25 per share. In the event of a merger and/or acquisition in which one or more of the abovementioned milestones have not yet been met, the Options shall be deemed vested on the date of the merger and/or acquisition. Mr. Gal is subject to non-compete and a confidentiality agreement during the term of the agreement and for one year thereafter. All options granted as described above are subject to the terms of the 2010 share incentive plan.
The total non-cash compensation recorded with respect to such grants was US$ 145,412 for the six month period ended June 30, 2011. The fair value of the shares was based on the recent share price applicable.
|
B.
|
David Malka, the owner of 3.68% of the Company's outstanding Common Stock entered into an employment agreement with Integrity Israel in July 2010 pursuant to which Mr. Malka agreed to continue to serve as the vice president of operations of Integrity Israel. The agreement is subject to approval by the board of directors and stockholders of Integrity Israel. Mr. Malka’s employment agreement provides for an annual salary of NIS 240,000 (US$ 70,278) and an annual bonus to be determined by the Board of Directors in its sole discretion and an additional sum provided that Mr. Malka reaches certain milestones approved by the Board, as well as the payment of certain social and insurance benefits and the use of a group three car. The agreement also provides for a renegotiation of Mr. Malka’s annual salary on the one-year anniversary thereof and the renegotiation of Mr. Malka’s bonus formula once Integrity Israel has begun commercialization of its products. The agreement is terminable by either party on 90 days notice, immediately by Integrity Israel with the payment of an amount equal to 90 days of annual salary, or immediately by Integrity Israel for cause (as defined in the agreement) without the payment of severance.
|
F-33
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (cont.)
(Information as of June 30, 2011 and for the three and six month periods ended June 30, 2011 and 2010 is unaudited)
|
NOTE 16 –
|
RELATED PARTIES (cont.)
|
|
B.
|
(cont.)
|
In connection with the Offering, Mr. Malka was entitled to receive options to purchase 1.5% of all issued and outstanding Common Stock of the Company after the Offering for sale of a minimum 560,000 shares ($3,500,000) of the Company's Common Stock and a maximum of 2,000,000 shares of the Company's common stock ($12,500,000). The offering (which commenced in December 2010) was completed in July 2011 and, as a result, Mr. Malka became entitled to receive a grant of 79,434 options. The options shall be deemed vested, in equal parts, in accordance with the achievement of the following milestones: (i) Submission of clinical trials’ results to the Notified Body; (ii) CE mark approval; (iii) FDA approval. The options will be exercisable at $6.25 per share. In the event of a merger and/or acquisition in which one or more of the abovementioned milestones have not yet been met, the options shall be deemed vested on the date of the merger and/or acquisition. Mr. Malka is subject to non-compete and confidentiality agreement during the term of the agreement and for one year thereafter. All options granted as described above are subject to the terms of the 2010 share incentive plan.
The total non-cash compensation recorded with respect to such grants was US$ 43,623 for the six month period ended June 30, 2011. The fair value of the shares was based on the recent share price applicable.
|
C.
|
Zicon Ltd., a company of which Zvi Cohen, a director of the Company, is a principal stockholder, officer and director, has manufactured certain pc boards for Integrity Israel over the last four years. In the years 2008-2010, total compensation paid by the Company to Zicon has been less than US$ 20,000, each year.
|
|
D.
|
See Notes 3, 6, 8 and 9.D.
|
|
NOTE 17 –
|
SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
|
On July 29, 2011, the Company completed a seventh closing of the Offering at which the Company received an amount of US$ 1,685,500 for 269,680 shares of Common Stock. The Company issued to the Placement Agent warrants to purchase an aggregate of 26,968 shares of common-stock at the seventh closing with an exercise price of US$ 6.25 and in addition was required to pay US$ 219,115 in cash (see Note 9C).
|
|
||||
F-34
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS INC.

Common Stock
PROSPECTUS
, 2011
PART TWO
INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
Item 13. Other Expenses of Issuance and Distribution.
The following table sets forth an estimate of the fees and expenses payable by us in connection with the registration of our securities offered hereby. All of such fees and expenses, except for the SEC Registration Fee, are estimated:
|
SEC Registration and Filing Fee
|
$ | 1,000 | ||
|
Legal Fees and Expenses
|
$ | 110,000 | ||
|
Accounting Fees and Expenses
|
$ | 15,000 | ||
|
Printing Fees and Expenses
|
$ | 5,000 | ||
|
Miscellaneous
|
$ | 5,000 | ||
|
TOTAL
|
$ | 136,000 |
Item 14. Indemnification of Directors and Officers.
Integrity Applications, Inc. was incorporated in the State of Delaware and is subject to the Delaware General Corporation Law (the “DGCL”). Section 145 of the DGCL empowers a Delaware corporation to indemnify any person who was or is a party or is threatened to be made a party to any threatened, pending or completed action, suit or proceeding, whether civil, criminal, administrative or investigative (other than an action by or in the right of such corporation) by reason of the fact that such person is or was a director, officer, employee or agent of such corporation, or is or was serving at the request of such corporation as a director, officer, employee or agent of another corporation or enterprise. A corporation may, in advance of the final action of any civil, criminal, administrative or investigative action, suit or proceeding, pay the expenses (including attorneys’ fees) incurred by any officer, director, employee or agent in defending such action, provided that the director or officer undertakes to repay such amount if it shall ultimately be determined that he or she is not entitled to be indemnified by the corporation. A corporation may indemnify such person against expenses (including attorneys’ fees), judgments, fines and amounts paid in settlement actually and reasonably incurred by such person in connection with such action, suit or proceeding if he or she acted in good faith and in a manner he or she reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interests of the corporation, and, with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, had no reasonable cause to believe his or her conduct was unlawful.
A Delaware corporation may indemnify officers and directors in an action by or in the right of the corporation to procure a judgment in its favor under the same conditions, except that no indemnification is permitted without judicial approval if the officer or director is adjudged to be liable to the corporation. Where an officer or director is successful on the merits or otherwise in the defense of any action referred to above, the corporation must indemnify him or her against the expenses (including attorneys’ fees) which he or she actually and reasonably incurred in connection therewith. The indemnification provided is not deemed to be exclusive of any other rights to which an officer or director may be entitled under any corporation’s by-law, agreement, vote or otherwise.
Our bylaws provide that we will indemnify any person who was or is a party or is threatened to be made a party to any threatened, pending or completed action, suit or proceeding, whether civil, criminal, administrative or investigative (other than an action by or in the right of our company) by reason of the fact that he is or was a director, officer, employee or agent of ours, or is or was serving at our request as a director, officer, employee, trustee or agent of one of our subsidiaries or another corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust or other enterprise (all such persons being referred to hereinafter as an agent), against expenses (including attorneys’ fees), judgments, fines and amounts paid in settlement actually and reasonably incurred by him or her in connection with such action, suit or proceeding if he or she acted in good faith and in a manner he or she reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to our best interests, and with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, had no reasonable cause to believe his or her conduct was unlawful.
Additionally, our bylaws provide that we will indemnify any person who was or is a party or is threatened to be made a party to any threatened, pending or completed action or suit by or in the right of our company to procure a judgment in our favor by reason of the fact that he is or was an agent against expenses (including attorneys’ fees) actually and reasonably incurred by him or her in connection with the defense or settlement of such action or suit if he or she acted in good faith and in a manner he or she reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to our best interests, except that no indemnification will be made in respect of any claim, issue or matter as to which such person shall have been adjudged to be liable to us by a court of competent jurisdiction, after exhaustion of all appeals therefrom, unless and only to the extent that the court in which such action or suit was brought shall determine upon application that, despite the adjudication of liability but in view of all the circumstances of the case, such person is fairly and reasonably entitled to indemnity for such expenses which such court shall deem proper.
II-1
Our certificate of incorporation provides that none of its directors shall be liable to us or our stockholders for monetary damages for breach of fiduciary duty as a director, except for liability (a) for any breach of the director’s duty of loyalty to us or our stockholders, (b) for acts or omissions not in good faith or which involve intentional misconduct or a knowing violation of law, (c) under Section 174 of the DGCL, or (d) for any transaction from which the director derived an improper personal benefit. To the extent the DGCL is amended to authorize the further elimination or limitation of the liability of directors, then the liability of one of our directors, in addition to the limitation on personal liability provided by our certificate of incorporation, shall be limited to the fullest extent permitted by the amended DGCL.
We have obtained and maintains insurance policies insuring our directors and officers and the directors and officers of our subsidiaries against certain liabilities they may incur in their capacity as directors and officers. Under such policies, the insurer, on our behalf, may also pay amounts for which we have granted indemnification to the directors or officers.
Additionally, we have entered into indemnification agreements with all of our directors and officers to provide them with the maximum indemnification allowed under our bylaws and applicable law, including indemnification for all judgments and expenses incurred as the result of any lawsuit in which such person is named as a defendant by reason of being a director, officer or employee of our company, to the extent indemnification is permitted by the laws of the State of Delaware.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers or persons controlling us pursuant to the foregoing provisions, we understand that in the opinion of the SEC such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is therefore unenforceable.
Item 15. Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
In the three years preceding August 22, 2011, we issued the following securities that were not registered under the Securities Act:
On July 26, 2010, we commenced a private placement of up to 2,000,000 shares of our common stock to accredited investors at a price of $6.25 per share pursuant to Section 4(2) of the Securities Act and Regulation D promulgated thereunder. Andrew Garrett, Inc. acted as placement agent for us in connection with the private placement and received, as a commission, an amount equal to 7% of the funds raised in the private placement, plus 3% of the funds as a management fee, plus a 3% non-accountable expense allowance and warrants to purchase up to 10% of the shares of common stock issued to investors in the private placement. We issued and sold an aggregate of 1,295,545 shares of common stock in the private placement in seven closings, as follows:
(a) On December 16, 2010, we completed an initial closing of the private placement, at which we issued approximately $3,566,000, or 570,577 shares, of common stock to investors in the offering, including approximately $550,000, or 87,977 shares, of common stock issued to holders of our Senior Secured Promissory Notes who elected to receive only shares of common stock for their Senior Secured Promissory Notes and not repayment in cash of such notes. We issued an additional 171,208 shares of common stock to holders of Senior Secured Promissory Notes pursuant to the terms of the notes and an additional 54,792 shares of common stock to purchasers of the Junior Promissory Notes issued by Integrity Israel in November 2010 pursuant to the terms and in full repayment of such Junior Promissory Notes.
(b) On December 30, 2010, we completed a second closing of the private placement at which we issued an additional $300,000, or 48,000 shares, of common stock. We issued to the placement agent warrants to purchase an aggregate of 84,459 shares of common stock at the initial and second closings.
II-2
(c) On January 31, 2011, we completed a third closing of the private placement at which we issued an additional $102,000, or 16,320 shares, of common stock. We issued to the placement agent warrants to purchase an aggregate of 1,632 shares of common stock at the third closing.
(d) On March 31, 2011, we completed a fourth closing of the private placement at which we issued 90,768 shares of common-stock for an amount of $567,300. We issued to the placement agent warrants to purchase an aggregate of 9,077 shares of common stock at the fourth closing.
(e) On April 29, 2011, we completed a fifth closing of the private placement at which we issued 40,000 shares of common-stock for an amount of $250,000. We issued to the placement agent warrants to purchase an aggregate of 4,000 shares of common stock at the fifth closing.
(f) On May 31, 2011, we completed a sixth closing of the private placement at which we issued 34,200 shares of common-stock for an amount of $213,750. We issued to the placement agent warrants to purchase an aggregate of 3,420 shares of common stock at the sixth closing.
(g) On July 29, 2011, we completed a seventh closing of the private placement at which we issued 269,680 shares of common stock for an amount of $1,685,500. We issued to the placement agent warrants to purchase an aggregate of 26,968 shares of common stock at the seventh closing.
Item 16. Exhibits
|
Exhibit
Number
|
Description
|
|
|
2.1
|
Merger Agreement and Plan of Reorganization, dated as of May 25, 2010, by and among Integrity Applications, Inc., Integrity Acquisition Ltd. and A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd. *
|
|
|
3.1
|
Certificate of Incorporation of Integrity Applications, Inc. *
|
|
|
3.2
|
Certificate of Amendment to Certificate of Incorporation of Integrity Applications, Inc. *
|
|
|
3.3
|
Bylaws of Integrity Applications, Inc. *
|
|
|
4.1
|
Specimen Certificate Evidencing Shares of Common Stock *
|
|
|
4.2
|
Form of Common Stock Purchase Warrant *
|
|
|
5.1
|
Opinion of Greenberg Traurig, LLP **
|
|
|
10.1
|
Integrity Applications, Inc. 2010 Incentive Compensation Plan *
|
|
|
10.2
|
Form of Subscription Agreement between Integrity Applications, Inc. and the investor signatory thereto *
|
|
|
10.3
|
Registration Rights Agreement, dated December 16, 2010, by and among Integrity Applications, Inc., Andrew Garrett, Inc. and each investor signatory thereto *
|
|
|
10.4
|
Form of Director and Officer Indemnification Agreement *
|
|
|
10.5
|
Exclusive Placement Agent Agreement, dated as of September 1, 2009, by and between Andrew Garrett, Inc. and A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd. *
|
|
|
10.6
|
Amendment No. 1 to Exclusive Placement Agent Agreement, effective as of December 16th, 2010, by and between Andrew Garrett, Inc., Integrity Applications, Inc. and A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd. *
|
|
|
10.7
|
Personal Employment Agreement, dated as of July 22, 2009, between A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd. and Avner Gal *
|
|
|
10.8
|
Personal Employment Agreement, dated as of July 22, 2010, between A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd. and David Malka *
|
|
|
10.9
|
Letter Agreement, dated November 10, 2010, by and among Integrity Applications Inc., Integrity Applications Ltd. and Xplanit Ltd. *
|
|
|
10.10
|
Irrevocable Undertaking of Indemnification, dated as of July 26, 2010, by and among Integrity Applications, Inc., Avner Gal, Zvi Cohen, Ilana Freger, David Malka and Alexander Raykhman *
|
|
|
10.11
|
Investment Agreement, dated February 18, 2003, between A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd., Avner Gal, Zvi Cohen, David Freger and David Malka and Yigal Dimri *
|
|
|
10.12
|
Agreement, dated as of November 1, 2005 by and between A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd. and Diabeasy Diabeasy cc.
|
|
|
10.13
|
Agreement, dated as of October 2, 2005, by and between Technology Transfer Group and Integrity Applications Ltd. *
|
|
|
10.14
|
Form of Stock Option Agreement *
|
|
|
10.15
|
Form of Stock Option Agreement (ESOP) *
|
|
|
10.16
|
Letter of Approval, addressed to Integrity Applications Ltd. from the Ministry of Industry, Trade and Employment of the State of Israel ***
|
|
|
10.17
|
Letter of Undertaking, addressed to the Ministry of Industry, Trade and Employment of the State of Israel - Office of the Chief Scientist from Integrity Applications Ltd. **
|
|
|
10.18
|
Investment Agreement, dated March 16, 2004, by and among A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd., Yitzhak Fisher, Asher Kugler and Nir Tarlovsky.
|
|
|
21.1
|
Subsidiaries of Integrity Applications, Inc. *
|
II-3
|
23.1
|
Consent of Fahn Kanne & Co.
|
|
|
23.2
|
Consent of Greenberg Traurig, LLP (included in Exhibit 5.1) **
|
|
|
24.1
|
Power of Attorney *
|
|
*
|
Previously filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1, as filed with the SEC on August 22, 2011.
|
|
**
|
Previously filed as an exhibit to Amendment No. 1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1, as filed with the SEC on October 7, 2011.
|
|
***
|
To be re-filed by amendment to this Registration Statement on Form S-1.
|
II-4
Item 17. Undertakings
(a) The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes:
(1) To file, during any period in which offers or sales are being made, a post-effective amendment to this registration statement:
(i) To include any prospectus required by Section 10(a)(3) of the Securities Act of 1933;
(ii) To reflect in the prospectus any facts or events arising after the effective date of the registration statement (or the most recent post-effective amendment thereof) which, individually or in the aggregate, represent a fundamental change in the information set forth in the registration statement. Notwithstanding the foregoing, any increase or decrease in volume of securities offered (if the total dollar value of securities offered would not exceed that which was registered) and any deviation from the low or high end of the estimated maximum offering range may be reflected in the form of prospectus filed with the Commission pursuant to Rule 424(b) if, in the aggregate, the changes in volume and price represent no more than 20 percent change in the maximum aggregate offering price set forth in the “Calculation of Registration Fee” table in the effective registration statement;
(iii) To include any material information with respect to the plan of distribution not previously disclosed in the registration statement or any material change to such information in the registration statement.
(2) That, for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each such post-effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
(3) To remove from registration by means of a post-effective amendment any of the securities being registered which remain unsold at the termination of the offering.
(4) That, for the purpose of determining liability under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser, each prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b) as part of a registration statement relating to an offering, other than registration statements relying on Rule 430B or other than prospectuses filed in reliance on Rule 430A, shall be deemed to be part of and included in the registration statement as of the date it is first used after effectiveness. Provided, however, that no statement made in a registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into the registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract of sale prior to such first use, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or prospectus that was part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately prior to such date of first use.
(5) That, for the purpose of determining liability of the registrant under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser in the initial distribution of the securities, the registrant undertakes that in a primary offering of securities of the registrant pursuant to this registration statement, regardless of the underwriting method used to sell the securities to the purchaser, if the securities are offered or sold to such purchaser by means of any of the following communications, the registrant will be a seller to the purchaser and will be considered to offer or sell such securities to such purchaser:
(i) Any preliminary prospectus or prospectus of the registrant relating to the offering required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424;
II-5
(ii) Any free writing prospectus relating to the offering prepared by or on behalf of the registrant or used or referred to by the undersigned registrant;
(iii) The portion of any other free writing prospectus relating to the offering containing material information about the registrant or its securities provided by or on behalf of the registrant; and
(iv) Any other communication that is an offer in the offering made by the registrant to the purchaser.
(b) Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the registrant pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, the registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy expressed in the Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
II-6
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, the registrant certifies that it has reasonable grounds to believe that it meets all of the requirements for filing on Form S-1 and has duly caused this registration statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the City of Tel Aviv, State of Israel on October 26, 2011.
|
INTEGRITY APPLICATIONS, INC.
|
||
|
(Registrant)
|
||
|
By:
|
/s/ AVNER GAL
|
|
|
Name:
|
Avner Gal
|
|
|
Title:
|
Chief Executive Officer
|
|
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this registration statement has been signed below by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
Signature
|
Title
|
Date
|
||
|
/s/ AVNER GAL
|
Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer
|
October 26, 2011
|
||
|
Avner Gal
|
(Principal Executive Officer)
|
|||
|
/s/ JACOB BAR-SHALOM
|
Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer
|
October 26, 2011
|
||
|
Jacob Bar-Shalom
|
and Principal Accounting Officer)
|
|||
|
*
|
Director
|
October 26, 2011
|
||
|
Zvi Cohen
|
||||
|
*
|
Director
|
October 26, 2011
|
||
|
Dr. Robert Fischell
|
||||
|
*
|
Director
|
October 26, 2011
|
||
|
Joel L. Gold
|
||||
|
/s/ David Malka
|
Director and Vice President of Operations
|
October 26, 2011
|
||
|
David Malka
|
* Signed by Avner Gal, as attorney in fact.
II-7
EXHIBIT INDEX
|
Exhibit
Number
|
Description
|
|
|
2.1
|
Merger Agreement and Plan of Reorganization, dated as of May 25, 2010, by and among Integrity Applications, Inc., Integrity Acquisition Ltd. and A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd. *
|
|
|
3.1
|
Certificate of Incorporation of Integrity Applications, Inc. *
|
|
|
3.2
|
Certificate of Amendment to Certificate of Incorporation of Integrity Applications, Inc. *
|
|
|
3.3
|
Bylaws of Integrity Applications, Inc. *
|
|
|
4.1
|
Specimen Certificate Evidencing Shares of Common Stock *
|
|
|
4.2
|
Form of Common Stock Purchase Warrant *
|
|
|
5.1
|
Opinion of Greenberg Traurig, LLP **
|
|
|
10.1
|
Integrity Applications, Inc. 2010 Incentive Compensation Plan *
|
|
|
10.2
|
Form of Subscription Agreement between Integrity Applications, Inc. and the investor signatory thereto *
|
|
|
10.3
|
Registration Rights Agreement, dated December 16, 2010, by and among Integrity Applications, Inc., Andrew Garrett, Inc. and each investor signatory thereto *
|
|
|
10.4
|
Form of Director and Officer Indemnification Agreement *
|
|
|
10.5
|
Exclusive Placement Agent Agreement, dated as of September 1, 2009, by and between Andrew Garrett, Inc. and A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd. *
|
|
|
10.6
|
Amendment No. 1 to Exclusive Placement Agent Agreement, effective as of December 16th, 2010, by and between Andrew Garrett, Inc., Integrity Applications, Inc. and A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd. *
|
|
|
10.7
|
Personal Employment Agreement, dated as of July 22, 2009, between A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd. and Avner Gal *
|
|
|
10.8
|
Personal Employment Agreement, dated as of July 22, 2010, between A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd. and David Malka *
|
|
|
10.9
|
Letter Agreement, dated November 10, 2010, by and among Integrity Applications Inc., Integrity Applications Ltd. and Xplanit Ltd. *
|
|
|
10.10
|
Irrevocable Undertaking of Indemnification, dated as of July 26, 2010, by and among Integrity Applications, Inc., Avner Gal, Zvi Cohen, Ilana Freger, David Malka and Alexander Raykhman *
|
|
|
10.11
|
Investment Agreement, dated February 18, 2003, between A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd., Avner Gal, Zvi Cohen, David Freger and David Malka and Yigal Dimri *
|
|
|
10.12
|
Agreement, dated as of November 1, 2005 by and between A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd. and Diabeasy Diabeasy cc.
|
|
|
10.13
|
Agreement, dated as of October 2, 2005, by and between Technology Transfer Group and Integrity Applications Ltd. *
|
|
|
10.14
|
Form of Stock Option Agreement *
|
|
|
10.15
|
Form of Stock Option Agreement (ESOP) *
|
|
|
10.16
|
Letter of Approval, addressed to Integrity Applications Ltd. from the Ministry of Industry, Trade and Employment of the State of Israel ***
|
|
|
10.17
|
Letter of Undertaking, addressed to the Ministry of Industry, Trade and Employment of the State of Israel - Office of the Chief Scientist from Integrity Applications Ltd. **
|
|
|
10.18
|
Investment Agreement, dated March 16, 2004, by and among A.D. Integrity Applications Ltd., Yitzhak Fisher, Asher Kugler and Nir Tarlovsky.
|
|
|
21.1
|
Subsidiaries of Integrity Applications, Inc. *
|
|
|
23.1
|
Consent of Fahn Kanne & Co.
|
|
|
23.2
|
Consent of Greenberg Traurig, LLP (included in Exhibit 5.1) **
|
|
|
24.1
|
Power of Attorney *
|
|
*
|
Previously filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1, as filed with the SEC on August 22, 2011.
|
|
**
|
Previously filed as an exhibit to Amendment No. 1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1, as filed with the SEC on October 7, 2011.
|
|
***
|
To be re-filed by amendment to this Registration Statement on Form S-1.
|
