Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8 K - BIOVEST INTERNATIONAL INC | d240190d8k.htm |
| EX-99.1 - PRESS RELEASE - BIOVEST INTERNATIONAL INC | d240190dex991.htm |
 Redefining Immunity for Life
Carlos F. Santos,
Ph.D.
Chief Science Officer, Accentia
SVP, Dev & Regulatory, Biovest
OTCQB: BVTI
www.Biovest.com
MD Becker
Cancer
Immunotherapy
Conference 2011
Late-Stage Clinical
Development
of
BiovaxID®
Active Immunotherapy for
Non-Hodgkin’s
Lymphoma
Exhibit 99.2 |
 Autologus Active Immunotherapy for the
Treatment of B-cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
|
 Discuss how vaccination fits standards in treatment of
Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Discuss randomized, controlled data from Phase 3 trial
and supporting data from multiple Phase 2 studies
High vaccine immune response rates
DFS benefit observed
Isotype impact on outcomes
Conclusions:
Numerous clinical trials suggest vaccines ideally suited as first-
line consolidation
Accuracy matters: successful hybridoma vaccine vs recombinant
fragment vaccines
Presentation Agenda |
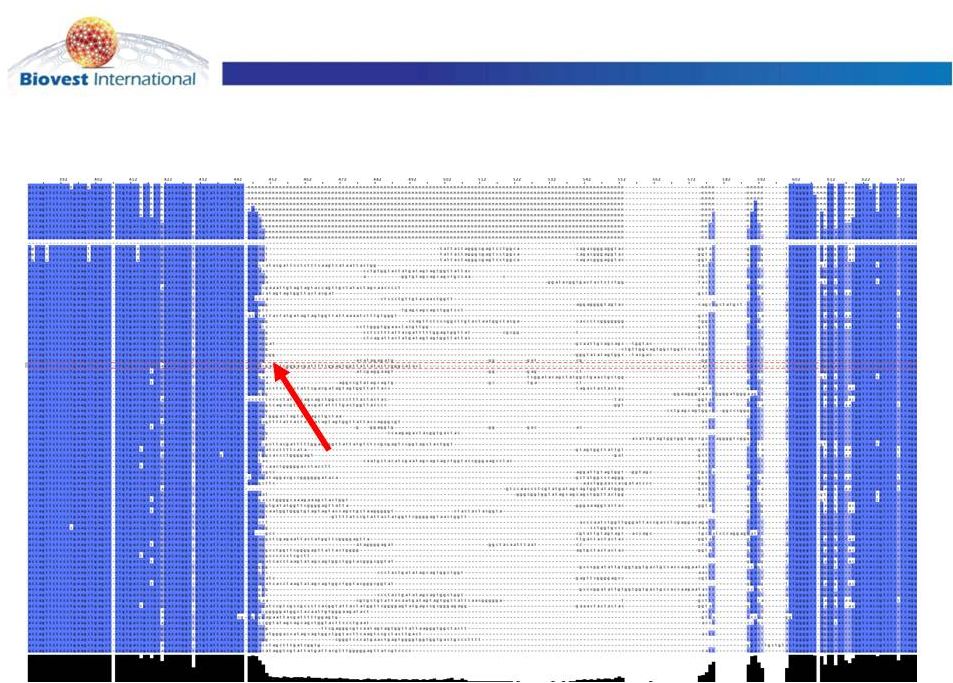 Id’s are Unique Amongst Tumor Antigens
IgM variability in humans (1 line = 1 subject)
Each B-cell
provides unique Id sequence
and unique vaccine |
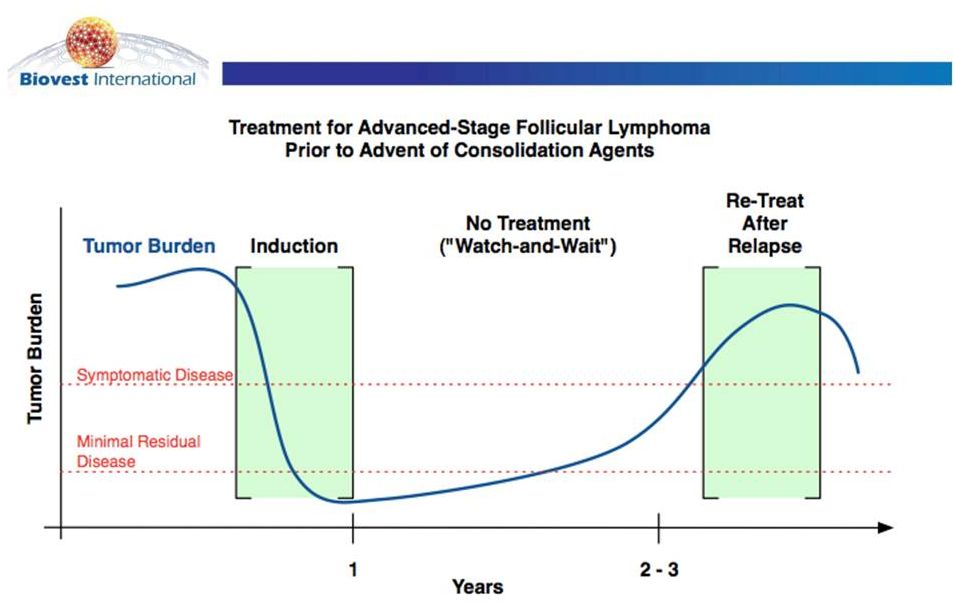 Cancer’s
Ultimate
Success:
Minimal
Residual
Disease |
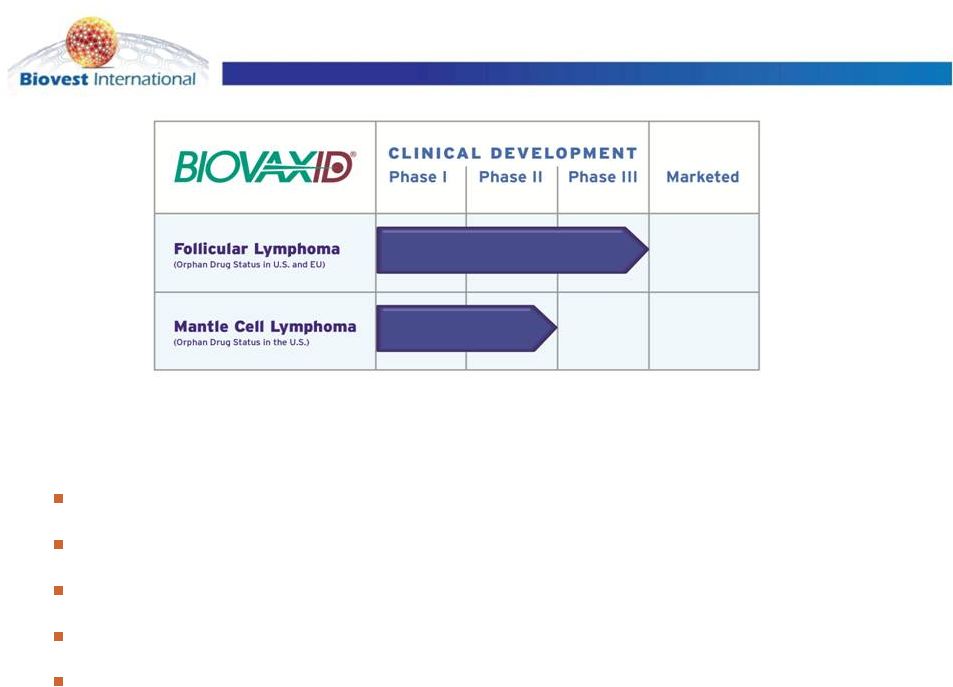 BiovaxID: Id-KLH + GMCSF
Multiple Phase 2 and Successful Phase 3 Clinical Trial Provides
Evidence of Vaccine Safety/Efficacy:
First successful vaccine to treat Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
First non-immunosuppressive consolidation therapy
Plenary presentation (ASCO 2009)
ASH oral presentation (ASH 2010)
Data published in Journal of Clinical Oncology (June 2011)
|
 1971-2:
Immunization with myeloma-Id induces host to reject tumor cells
with Id antigens
Sirisinha et al. PNAS 68:3130, 1971; Lynch et al.
PNAS 69:1540, 1972 1992:
Immunogenicity of Id vaccines in lymphoma patients using
hybridoma- produced Id
Kwak, Levy et al. N Engl J Med 327:1209, 1992
1996:
Use of GM-CSF as an adjuvant enhances T cell responses
Kwak et al. PNAS 93:10972, 1996
1999:
NCI phase II study of autologous hybridoma-derived Id-vaccine
in first CR: lymphoma-specific CD8+ T cell responses
correlated with molecular remissions (Bendandi et al.
Nat Med 5:1171, 1999)
Hypothesis:
Id-vaccine
prolongs
DFS
in
patients
with
FL
in
CR/CRu
after
PACE
2000:
NCI phase III trial to test treatment effect of Id-vaccine in
first CR/CRu on DFS
2004:
NCI transfers IND to Biovest
2008:
Biovest/NCI phase III trial (BV301) closed
2009:
BV301 Phase III results: vaccination with Id-vaccine in first
CR/CRu improves DFS.
BV301 Investigators, J Clin Oncol 27:18s, 2009 (abstr 2)
Idiotype Vaccination Development History |
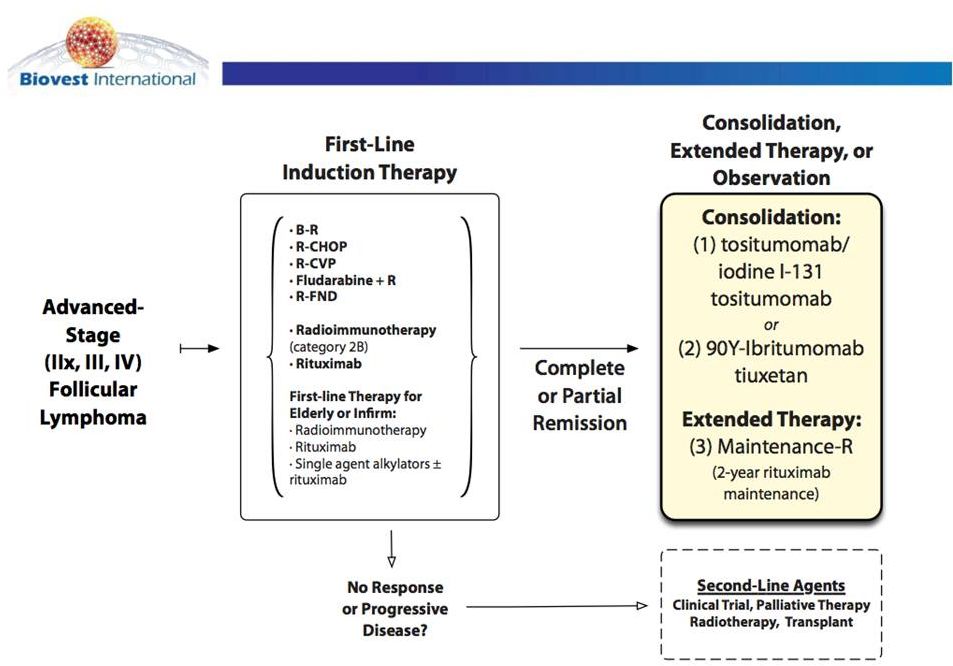 2011 NCCN Follicular Lymphoma Treatment Guidelines |
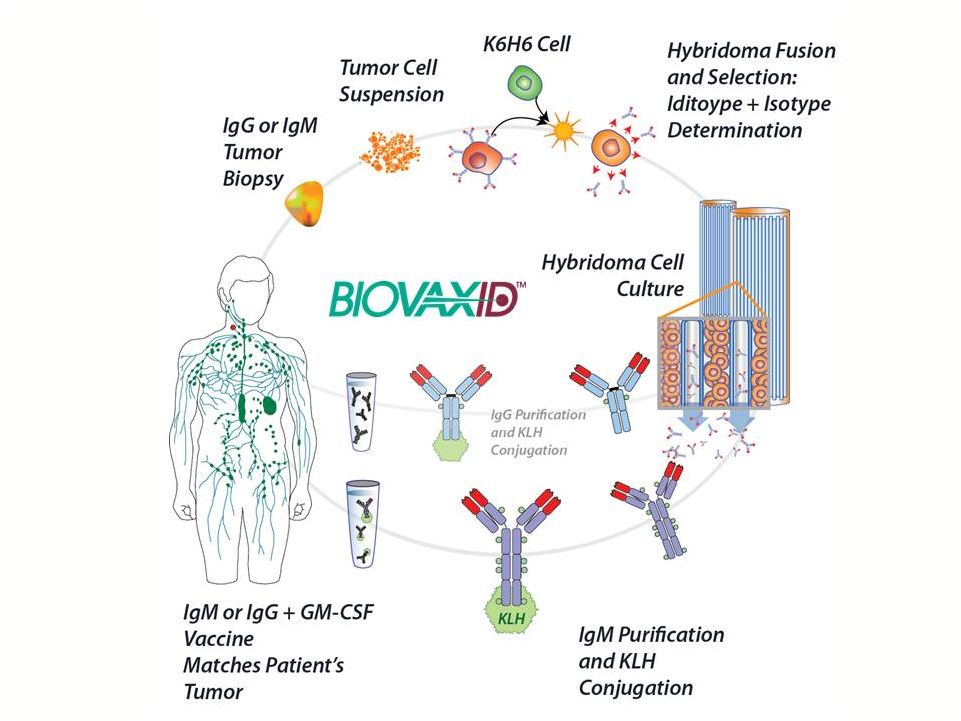 |
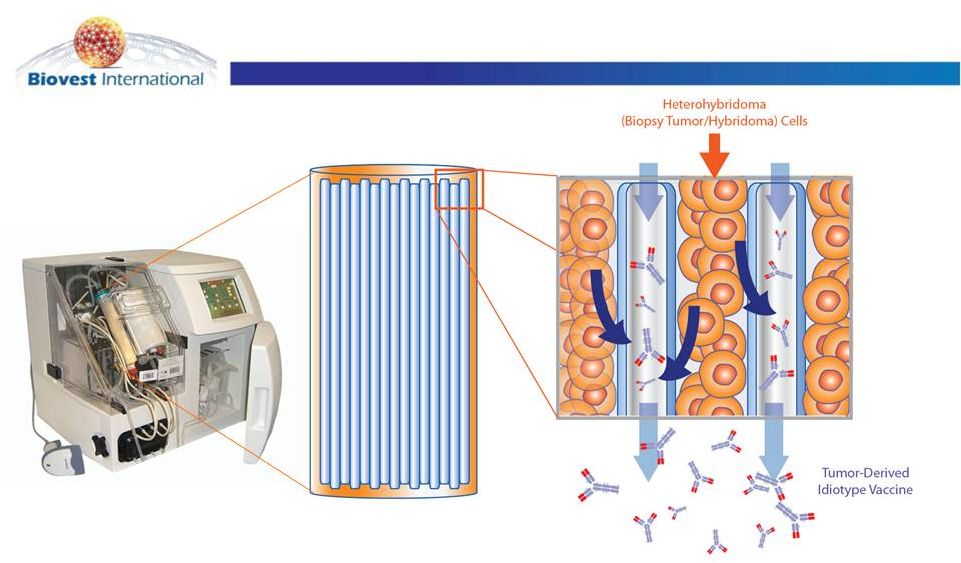 Hybridoma
Autologous
Production
Preserves
Isotype
Hollow-Fiber Bioreactor
Cultures Tumor Derived Cells
(Heterohybridoma)
for Id Protein Production
Isotype-Matched Id Protein
Secreted and
Purified |
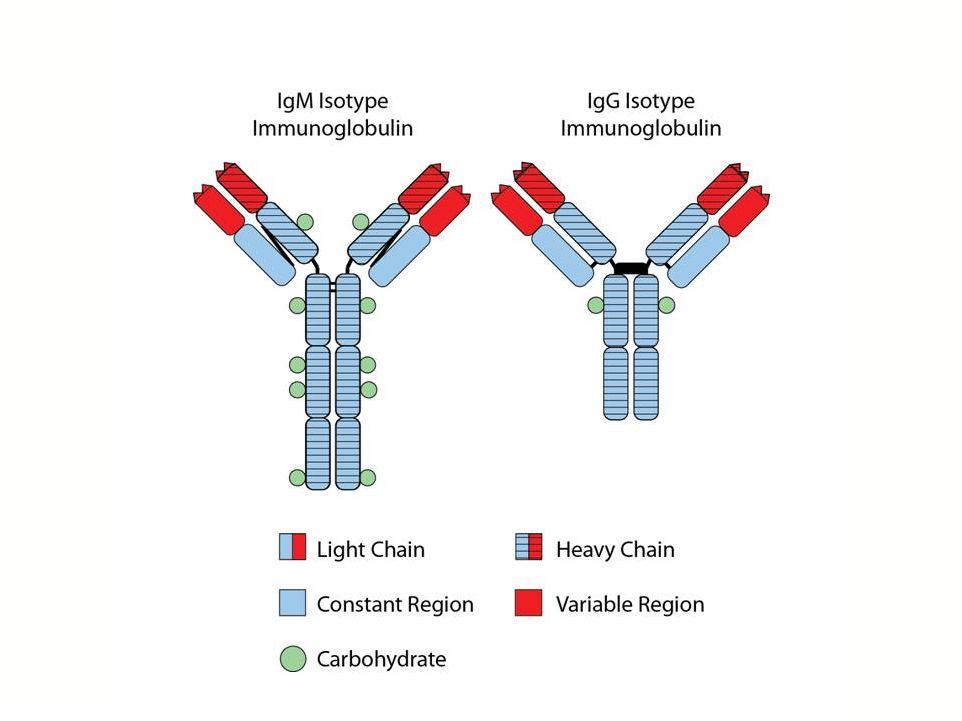 FL
Tumor Cell sIg’s are Generally IgG or IgM Isotype |
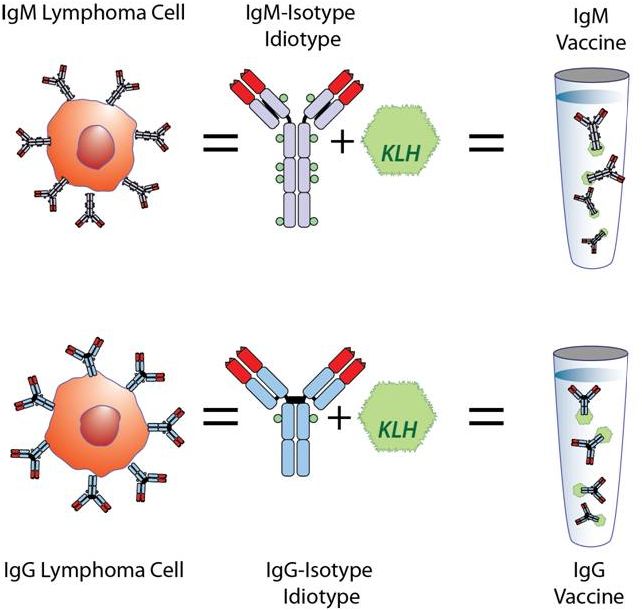 IgM
Biopsy
Cells
IgG
Biopsy
Cells
Personalized Vaccine Preserves Tumor Isotype |
 NCI/Biovest Phase III Study Objectives
Primary
Objectives
To determine whether Id-Vaccine (Id-KLH; Id-vaccine;
BiovaxID) + GM-CSF prolongs disease-free survival (DFS)
compared to control vaccine (KLH) + GM-CSF in patients with
follicular lymphoma in CR/CRu after PACE
Secondary
Objectives
Evaluate safety of Id-vaccine + GM-CSF
Compare overall survival of subjects in both treatment arms
Evaluate immunologic and molecular responses |
 Primary Objective:
To determine whether Id-vaccine prolongs DFS compared to control
vaccine in patients with follicular lymphoma in CR/CRu after PACE
Prospective Efficacy Analyses:
(1) DFS for all randomized patients
(2) DFS for randomized, vaccinated patients receiving Id-vaccine or
control
Vaccine Isotype Subset Analysis:
DFS by vaccine isotype (IgM or IgG) for patients receiving Id-
vaccines
IgG isotype can induce idiotype-specific tolerance
-
Reitan et al. PNAS 99:7588, 2002;
-
De Groot et al. Blood 112(8): 3303, 2008
BiovaxID Phase III: Prospective and Subset Analyses |
 NCI/Biovest Phase III Study Protocol
BiovaxID
Phase 3
Clinical
Trial |
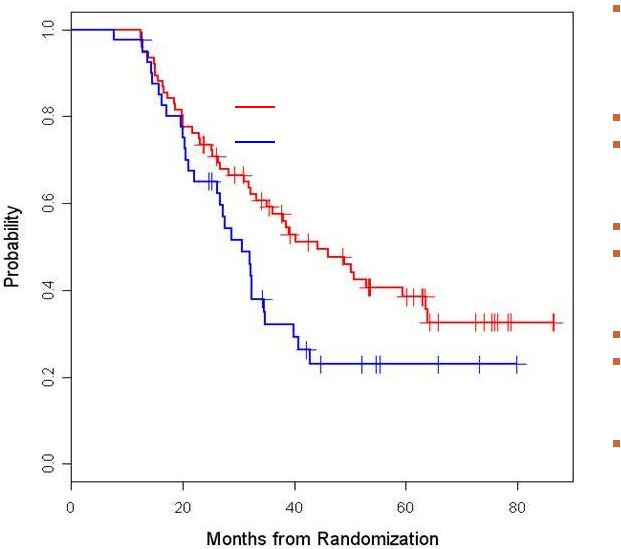 Modified ITT Disease
Free Survival from Randomization: Id-vaccine vs. Control (n=117)
Median Follow-up
56.6 mo (range 12.6 –
89.3)
Median DFS
Id-vaccine = 44.2 mo
Control = 30.6 mo
N = 117
Id-vaccine N = 76
Control N = 41
Events
Id-vaccine = 44
Control = 29
Cox PH Model
HR = 0.62; [95% CI:
0.39,0.99] (p=0.047)
log-rank
p=0.045
Control arm
Id-vaccine arm |
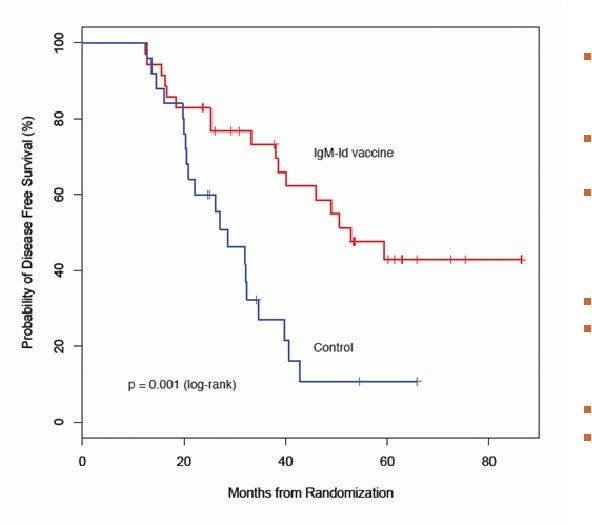 Disease-Free Survival for Patients with IgM-isotype
lymphomas: IgM-Id Vaccine vs. Control Vaccine
Median Follow-up
56.6 mo (range 12.6 –
89.3)
Median DFS
IgM-Id vaccine =
52.9 mo [95% CI:40.2,NA
Control =
28.7 mo [95% CI:21.0,39.8]
N = 60
IgM-Id vaccine N = 35
Control
N = 25
Events
IgM-Id vaccine = 17
Control = 20
|
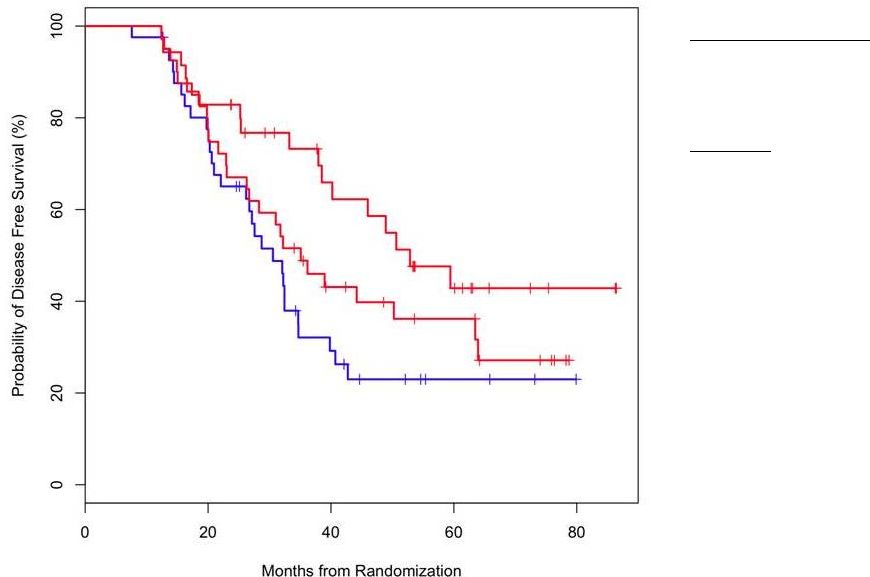 Disease Free Survival for Patients receiving IgM-Id or IgG-Id
Vaccine vs. All Patients Receiving Control Vaccine
Median Follow-up
56.6 mo (range 12.6 –
89.3)
N = 115
IgG-Id vaccine N = 40
IgM-Id vaccine N = 35
Control N = 40
IgM-Id Vaccine vs All
Controls:
p=0.01
IgG-Id Vaccine vs All
Controls:
p=0.30
IgM-Id Vaccine
IgG-Id Vaccine
All Controls |
 Study
Results
Vaccine Prod.
Method
Vaccine
Isotype
NCI Phase 2
Study
(n=20)
45% remain in CR after 9.2
years
Murine/Human
Hybridoma Rescue
Fusion
Preserves
Tumor
Isotype
(IgG and IgM)
Biovest
BV301
Phase
(n=117)
DFS for cohorts:
mITT: 44.2 vs 30.6m (p=0.046)
IgM: 52.9 vs 28.7m (p=0.001)
IgG: 35.1 vs 32.4m (p=0.8)
Genitope
(n=278)
No difference in PFS
Murine
Recombinant
IgG
regardless of
tumor isotype
Favrille
(n=315)
No difference in TTP
Sf9 (Insect)
Recombinant
Comparison of Prior Phase 3 FL Id Clinical Trials by Isotype
1.
Bendandi
et
al.
Nat
Med
5:1171,
1999.
2.
BV301
Investigators,
J
Clin
Oncol
27:18s,
2009
(abstr
2),
3.
Genitope
Corp.
4.Freedman,
et
al.
J
Clin
Oncol.
2009
Jun
20;27(18):3036-43.
1
3
3
4
2 |
| Conclusions
Vaccination with IgM but not IgG idiotype prolongs remission duration in
follicular lymphoma patients.
The reasons why IgM-Id is effective but not IgG-Id is unclear but has
been suggested previously by mouse studies.
Ids that have switched to IgG were shown to be tolerogenic whereas
Ids of their IgM progenitors were highly immunogenic (Reitan et al. Proc
Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2002).
Fc fragment of IgG has been shown to have highly promiscuous MHC
Class II T-cell epitopes that specifically activate regulatory T cells and
tip the immune responses towards tolerance rather than
immunogenicity (De Groot et al, Blood, 2008).
Positive outcome of our study may reflect the use of hybridomas to
produce Id protein with variable and constant regions identical to patient
tumor Ig.
These findings may have profound implications on Id vaccine
production strategies and clinical development. |
 Regulatory Strategy: Follicular Lymphoma
Request Pre-filing Meetings with US FDA , EU
EMA and
‘Health Canada’ Regulatory Authorities (4Q 2011)
First meeting request submitted & scheduled
Deliver comprehensive clinical package
Analysis ongoing at MD Anderson (secondary endpoint)
Finalize CMC package
Validation of new BiovaxID manufacturing site at
Biovest MN Cell Culture Center
Conduct Pre-filing Clinical Meetings with FDA, EMA
and ‘Health Canada’
Regulatory Authorities
(Q4 2011 & 1H 2012)
Separate clinical meetings & CMC meetings with each
agency (clinical meetings to occur first) |
 Redefining Immunity for Life
OTCQB: BVTI
www.Biovest.com
Corporate Contact:
Douglas W.
Calder
Vice President, Strategic
Planning & Capital Markets
324 South Hyde Park Ave. #350
Tampa, FL 33606
Phone:
813-864-2558
Email: dwcalder@Biovest.com
|
