Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - DYNAVAX TECHNOLOGIES CORP | d234560d8k.htm |
| EX-99.1 - PRESS RELEASE - DYNAVAX TECHNOLOGIES CORP | d234560dex991.htm |
 Sunday, September 18, 2011
ICAAC
Chicago, IL
An Observer-Blinded, Randomized, Parallel-Group, Multi-
Center Study Comparing the Safety and Immunogenicity of
HEPLISAV to Licensed Vaccine (Engerix-B®) among
Healthy Subjects 40 to 70 Years of Age
Exhibit 99.2 |
 Background: HBV in older adults
HBV Vaccination for adults is recommended for persons at
increased risk of infection
Current HBV vaccines are less immunogenic in healthy
adults age 40+ (Averhoff, AJPrevMed, 1998)
There has been no decrease in the rate of HBV infection in
adults age 40-59 in the US from 1988-2008 (McQuillan,
NCHS Data Brief, 2010)
>40% of reported acute HBV infections in the US occur in
adults age 40+ (MMWR, 2009)
>50% of reported acute HBV infections in Germany occur in
adults age 40+ (RKI, 2011) |
 Introduction: HBV Vaccine
Current licensed Hepatitis B virus (HBV) vaccine
Contains
20
µg
HBsAg
adjuvanted
with
aluminum
hydroxide
Administered in 3 doses on a 0,1, 6 month schedule
HBsAg+ISS (HEPLISAV)
Contains a new class of adjuvant (1018 ISS)
Toll-like Receptor 9 (TLR9) agonist
20 µg HBsAg mixed with 3000 µg 1018 ISS
Administered in 2 doses on 0,1 month schedule |
 TLR
Overview TLR3
TLR7
TLR8
TLR9
TLR1
TLR2
TLR4
TLR5
TLR6
TLR10
TLR2
ssRNA
CpG DNA
(ISS)
dsRNA
ssRNA
Endosome
Cytosol
Diacyl
lipopeptides
Triacyl
lipopeptides
LPS
Flagellin
?
4 of these TLR recognize nucleic acids
TIRAP
MyD88
TIRAP
MyD88
MyD88
TIRAP
TRAM
TRIF
MyD88
MyD88
MyD88
MyD88
TRIF
MyD88 |
 HBV-16: Study Design
Healthy adults, 40 to 70 years of age
Two doses of HEPLISAV (0, 4 weeks) + 1 dose placebo (24 weeks)
compared to 3 doses of Engerix-B (0, 4, 24 weeks)
Immunogenicity
assessed
by
Ortho
Vitros
ECi
assay
Seroprotection
defined
as
anti-HBsAg
10
miU/ml
Randomization –
HEPLISAV to Engerix-B 4:1
Randomization stratified by age, by site (ages 40 to 49 years, 50 to 59
years, 60 years and over)
SEAC and DSMB oversight
3793 screened, 2452 randomized, 2449 treated, 2269 completed all
visits |
 HBV-16: Visit Schedule
Week 0
Week 4
Week 8
Week 12
Week 18
Week 24
Week 28
Week 36
Week 44
Week 52
Screen and
Randomize
Active
Active
Placebo
Active
Active
Active
Injection Period
Follow-up Period
HEPLISAV
ENGERIX-B
Week 32 |
 HBV-16:
Objectives
-
Immunogenicity
Primary
Demonstrate non-inferiority to Engerix-B at 8 weeks after the last
injection
(week 12 for HEPLISAV vs.
week 32 for Engerix-B)
Non-inferiority
(week
12
HEPLISAV
vs.
week
32
Engerix-B)
HEPLISAV will be considered non-inferior to Engerix-B if the lower limit of
the
95%
confidence
interval
of
the
difference
in
seroprotection
rates
(SPR) (HEPLISAV SPR for the 3 new lots combined minus the Engerix-B
SPR) is greater than -10%.
Superiority
(week
12
HEPLISAV
vs.
week
32
Engerix-B)
If HEPLISAV is found to be non-inferior, then and only then will it be
declared to be superior if the lower limit of this 95% confidence interval is
greater than zero |
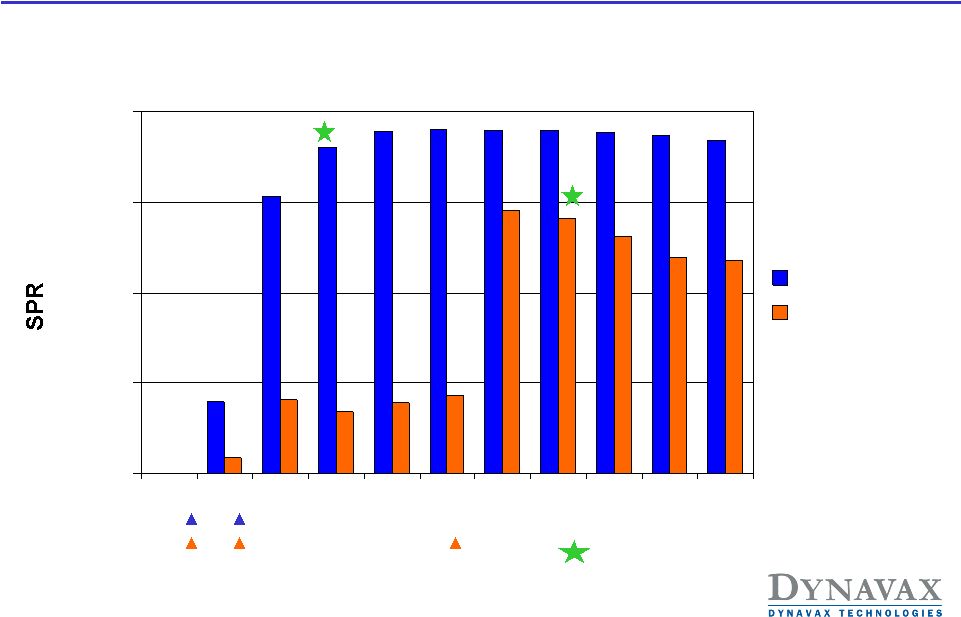 HBV-16: Seroprotection
Rates (Primary Endpoint)
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Baseline
4
8
12
18
24
28
32
36
44
52
Weeks
HEPLISAV
Engerix-B
Engerix-B Injections
HEPLISAV Injections
Non-inferiority Per-Protocol Population
Primary Endpoint
% Difference in SPR at 8 weeks after last active dose: 19.6% (95% CI 14.7%,
24.7%) (N=1123 for HEPLISAV, 359 for Engerix-B)
90%
70.5%
95%
73%
92%
59% |
 HBV-16: Anti-HBsAg
Geometric Mean Concentration
1
10
100
1000
Baseline
4
8
12
18
24
28
32
36
44
52
Weeks
HEPLISAV
Engerix-B
Engerix-B Injections
HEPLISAV Injections
Non-inferiority Per-Protocol Population |
 HBV-16 Anti-HBsAg
Geometric Mean Concentration:
HEPLISAV Lot Consistency (Primary Endpoint)
1
10
100
1000
Baseline
4
8
12
18
24
28
32
36
44
52
Lot 8
Lot 9
Lot 10
Engerix-B
HEPLISAV
Engerix-B
Primary Endpoint
(N= 428 for Lot 8; 438 for Lot 9; 424 for Lot 10) |
 Upper bound
Lower bound
Consistency
Criteria
HBV-16: Ratio of GMCs for Lot Consistency
Adjusted Ratios
Lot 10/Lot 8
Lot 10/Lot 9
Lot 8/Lot 9 |
 HBV-16:
Results
-
Safety
Post Injection Reactions
Incidence similar in HEPLISAV (51.0%) vs.
Engerix (49.4%)
Severe reactions were uncommon and slightly lower in HEPLISAV (2.8%
vs. 4.2%)
Pain was more frequent in HEPLISAV (34.8% vs.
31.8%)
Systemic post immunization reactions were less frequent in HEPLISAV (33.4% vs.
34.7%)
Incidence decreased with subsequent injections
AEs
Subjects experiencing at least 1 AE; HEPLISAV (50.5%) vs.
Engerix-B (53.0%) -
most common was nasopharyngitis (4.0% vs.
5.2%)
Most AEs were mild to moderate in intensity –
severe AEs (4.5% vs.
5.4%)
AEs considered by PI to be treatment related (7.2% vs.
6.0%) –
most common was
injection site erythema (1.5% vs.
0.8%) |
 HBV-16: Results -
Safety
SAEs
123 SAEs reported
in 99 subjects –
3.4% of subjects in HEPLISAV vs.
4.8% in
Engerix-B
Most common was in SOC of Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue (1.1%
HEPLISAV vs.
1.0% Engerix-B)
1 SAE
was
considered
by
PI
to
be
treatment
related
–
bronchial
hyper-reactivity
after 3rd injection (Engerix-B)
2 deaths –
pulmonary embolism (HEPLISAV) and myocardial infarction (Engerix-B)
AIAEs
3 new onset autoimmune adverse events occurred during the trial
2 cases of hypothyroidism and 1 case of vitiligo
all were in the HEPLISAV group (3/1968 vs 0/481, P=1.00)
|
 HBV-16: Conclusions
In healthy adults aged 40 to 70 years:
HEPLISAV
provided
superior
peak
seroprotection
with
fewer
doses than Engerix-B
HEPLISAV
provided
earlier
seroprotection
compared
to
Engerix-B
HEPLISAV
provided
superior
duration
of
seroprotection
with
fewer doses than Engerix-B
The clinical consistency of HEPLISAV was demonstrated
The safety profile of HEPLISAV was similar to Engerix-B
|
 The
HBV-16 Study Team Site
Principle
Investigators
Michael Kyle
Joe Blumenau
Matthew Davis
Martin Kabongo
Reinaldo Tirado-Bernardini
Dennis O’Keefe
Tami Helmer
Donald Sislen
Ben Lasko
Nancy Campbell
Lunde Canas
William Jennings
Stephan Sharp
Duane Wombolt
Randle Middleton
Eric Ross
Maureen Ziboh
Eugene DuBoff
John Ervin
Daniel Brune
Michael Noss
Martin Throne
Harry Geisberg
Keith Reisinger
Mahashweta Ghosh
William Travis Ellison
John Murray, Jr.
Gerasimos Zaharatos
Dynavax
HBV-16
Team
Elizabeth Fung
Liezl Boehnlein
Kim Erby
Lani Ibarra
Connie Louis-Tse
JoAnn Dyangko
Stacy Maryannis
Tanya Cope
Elsa Guzman-Bonilla
Leslie de la Cruz
Hamid Namini
Fang Xie
Dr. Jeff Enejosa
Dr. Sean Bennett
Dr. William L. Heyward
Dr. J. Tyler Martin
Clinical
Research
Organizations
Axio, Inc.
Accelovance, Inc.
Parexel, Inc.
BARC USA
Almac-US |
