Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - VIVUS INC | a11-12998_18k.htm |
Exhibit 99.1
|
|
Suzanne Oparil, MD Dept of Medicine-Cardiovascular Disease, University of Alabama, Birmingham, AL, USA, 35294 Wesley W. Day, PhD Charles Bowden, MD Vivus Inc, Mountain View, CA, USA, 94040 Evaluation of Cardiovascular Effects in Three Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials with Controlled-Release Phentermine/Topiramate (PHEN/TPM CR) |
|
|
Author Disclosure Past 12 months Suzanne Oparil, MD Grant/Research Support: Amgen Inc., and Merck and Co. Consultant/Advisory Board: Boehringer-Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo Inc., Eli Lilly, Forest Laboratories, NicOx, Novartis, Vivus, and Omron Healthcare Speakers Bureau: Daiichi Sankyo Inc., and Novartis Wesley W. Day, PhD Employee of Vivus, Inc. Charles Bowden, MD Employee of Vivus, Inc. |
|
|
Introduction Data represents a pooled evaluation of cardiovascular effects from three 56-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials for weight loss with controlled-release phentermine/topiramate (PHEN/TPM CR) Pre-specified evaluations: Weight loss over time Blood pressure and heart rate over time Subgroup analyses of blood pressure Change in heart rate by baseline heart rate Categorical changes in blood pressure and heart rate Rate pressure product (RPP) over time - defined as: Heart rate (bpm) X (SBP in mmHg) / 1000 |
|
|
PHEN/TPM CR PHEN/TPM CR is a fixed-dose combination under investigation for the treatment of weight loss1 PHEN (Phentermine hydrochloride) is a sympathomimetic amine, an anorectic agent, approved by the FDA at 37.5 mg/day as a short-term therapeutic adjunct to a weight loss regimen2 TPM (Topiramate) is approved by the FDA for treatment of epilepsy (200-400 mg/day) and migraine headache prophylaxis (100-200 mg/day), and has demonstrated weight loss and cardiometabolic benefits in clinical trials3-9 1. Gadde, K, et al. 2011,The Lancet, 377: 1341-1352. 2. Adipex-P [package insert]; 2005. 3.Topamax [package insert]; 2011 4. Bray GA et al. Obes Res. 2003. 11, 722-733 5. Wilding J, et al.Int J Obes. 2004. 28, 1399-1410 28; 1399-1410 6. Tonstad S, et al. Am J Cardiol. 2005.96 (2); 243-251. 7. Stenlöf K, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007. 9(3); 360–368 8. Toplak H et al. Int J Obes, 2007 31; 138-146. 9. Rosenstock J et al., Diabetes Care. 2007 30:1480-1486 |
|
|
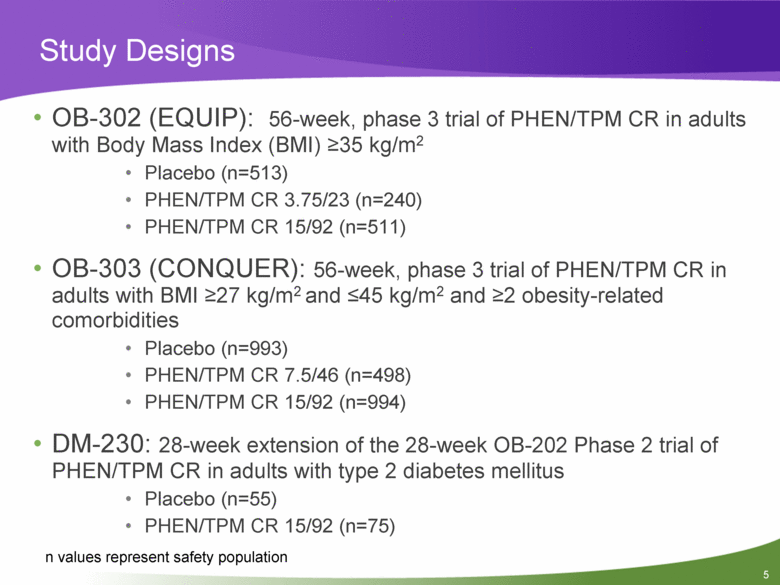
Study Designs OB-302 (EQUIP): 56-week, phase 3 trial of PHEN/TPM CR in adults with Body Mass Index (BMI) >35 kg/m2 Placebo (n=513) PHEN/TPM CR 3.75/23 (n=240) PHEN/TPM CR 15/92 (n=511) OB-303 (CONQUER): 56-week, phase 3 trial of PHEN/TPM CR in adults with BMI >27 kg/m2 and <45 kg/m2 and >2 obesity-related comorbidities Placebo (n=993) PHEN/TPM CR 7.5/46 (n=498) PHEN/TPM CR 15/92 (n=994) DM-230: 28-week extension of the 28-week OB-202 Phase 2 trial of PHEN/TPM CR in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus Placebo (n=55) PHEN/TPM CR 15/92 (n=75) n values represent safety population |
|
|
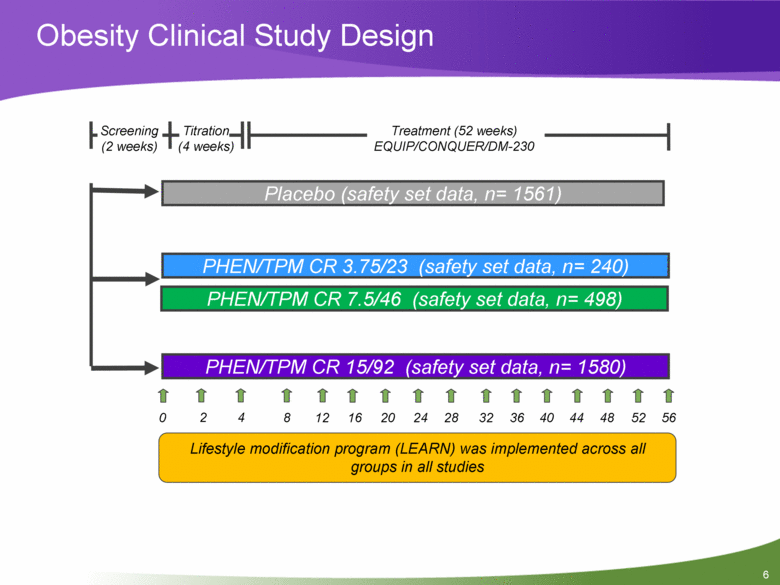
Obesity Clinical Study Design Titration (4 weeks) Treatment (52 weeks) EQUIP/CONQUER/DM-230 PHEN/TPM CR 15/92 (safety set data, n= 1580) PHEN/TPM CR 3.75/23 (safety set data, n= 240) Placebo (safety set data, n= 1561) 0 2 4 12 8 16 20 24 32 28 36 40 44 48 56 52 Screening (2 weeks) PHEN/TPM CR 7.5/46 (safety set data, n= 498) Lifestyle modification program (LEARN) was implemented across all groups in all studies |
|
|
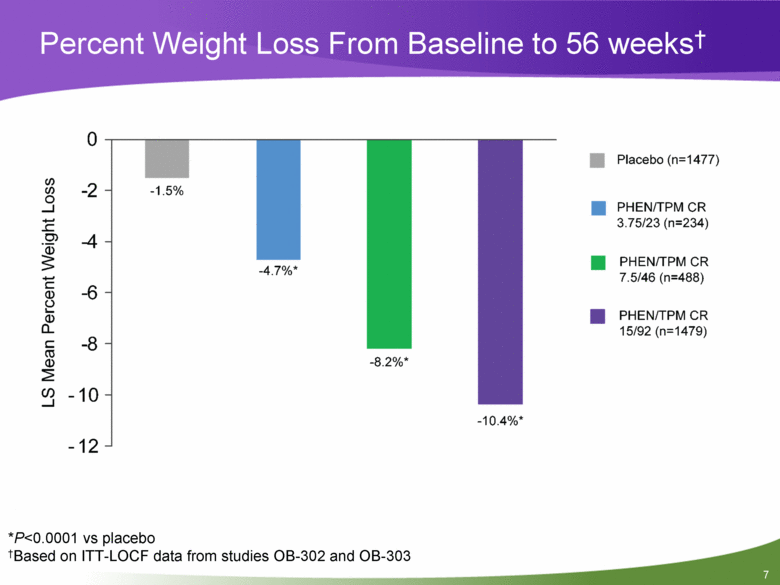
Percent Weight Loss From Baseline to 56 weeks† *P<0.0001 vs placebo †Based on ITT-LOCF data from studies OB-302 and OB-303 |
|
|
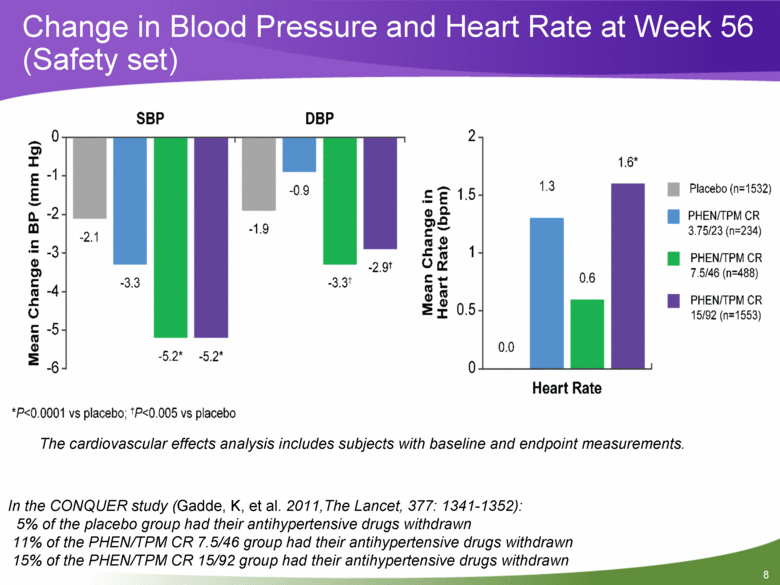
Change in Blood Pressure and Heart Rate at Week 56 (Safety set) The cardiovascular effects analysis includes subjects with baseline and endpoint measurements. In the CONQUER study (Gadde, K, et al. 2011,The Lancet, 377: 1341-1352): 5% of the placebo group had their antihypertensive drugs withdrawn 11% of the PHEN/TPM CR 7.5/46 group had their antihypertensive drugs withdrawn 15% of the PHEN/TPM CR 15/92 group had their antihypertensive drugs withdrawn |
|
|
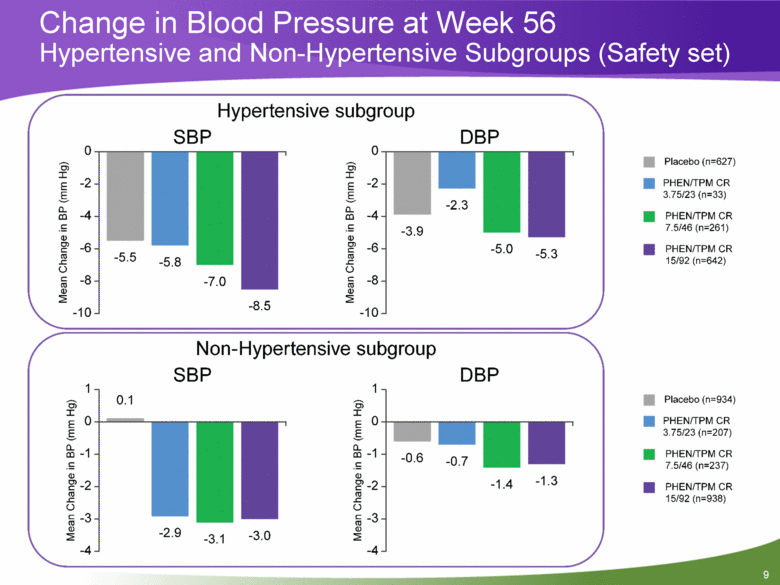
Change in Blood Pressure at Week 56 Hypertensive and Non-Hypertensive Subgroups (Safety set) |
|
|
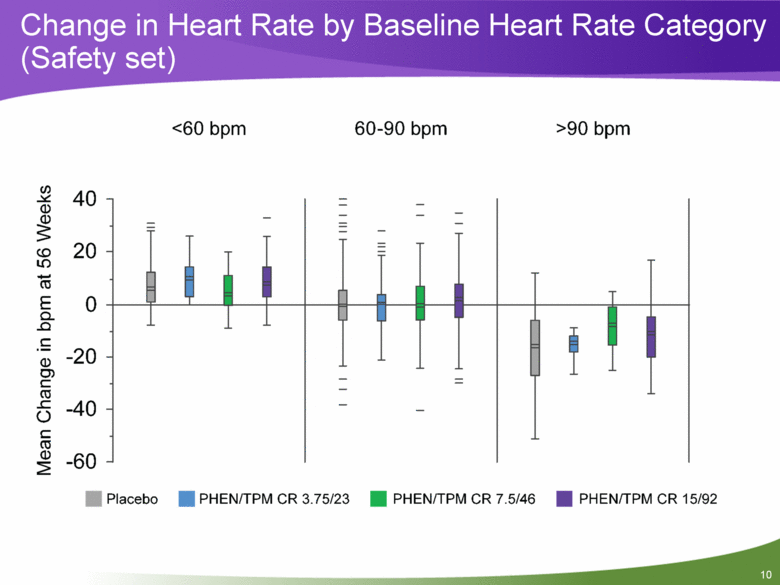
Change in Heart Rate by Baseline Heart Rate Category (Safety set) |
|
|
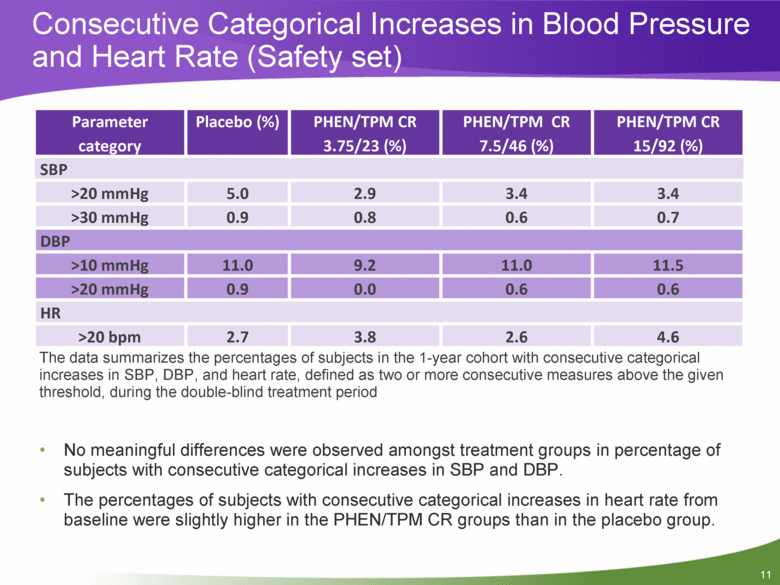
Consecutive Categorical Increases in Blood Pressure and Heart Rate (Safety set) The data summarizes the percentages of subjects in the 1-year cohort with consecutive categorical increases in SBP, DBP, and heart rate, defined as two or more consecutive measures above the given threshold, during the double-blind treatment period No meaningful differences were observed amongst treatment groups in percentage of subjects with consecutive categorical increases in SBP and DBP. The percentages of subjects with consecutive categorical increases in heart rate from baseline were slightly higher in the PHEN/TPM CR groups than in the placebo group. Parameter category Placebo (%) PHEN/TPM CR 3.75/23 (%) PHEN/TPM CR 7.5/46 (%) PHEN/TPM CR 15/92 (%) SBP >20 mmHg 5.0 2.9 3.4 3.4 >30 mmHg 0.9 0.8 0.6 0.7 DBP >10 mmHg 11.0 9.2 11.0 11.5 >20 mmHg 0.9 0.0 0.6 0.6 HR >20 bpm 2.7 3.8 2.6 4.6 |
|
|
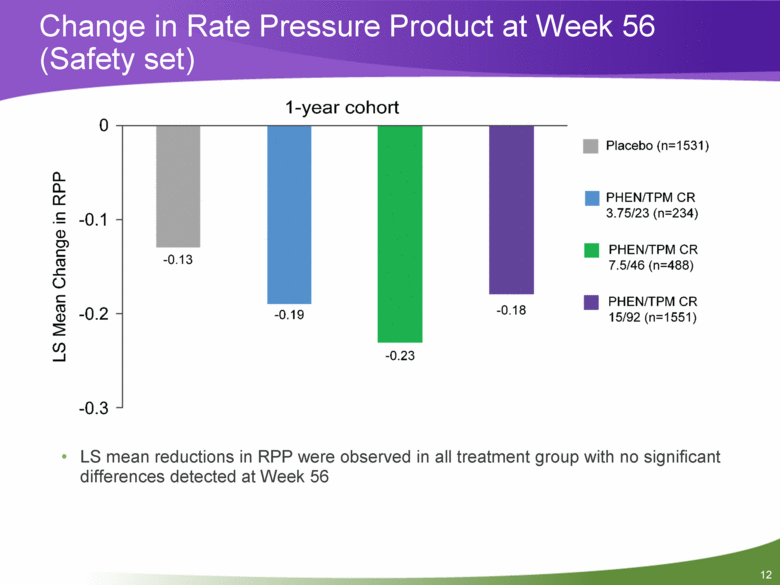
Change in Rate Pressure Product at Week 56 (Safety set) LS mean reductions in RPP were observed in all treatment group with no significant differences detected at Week 56 |
|
|
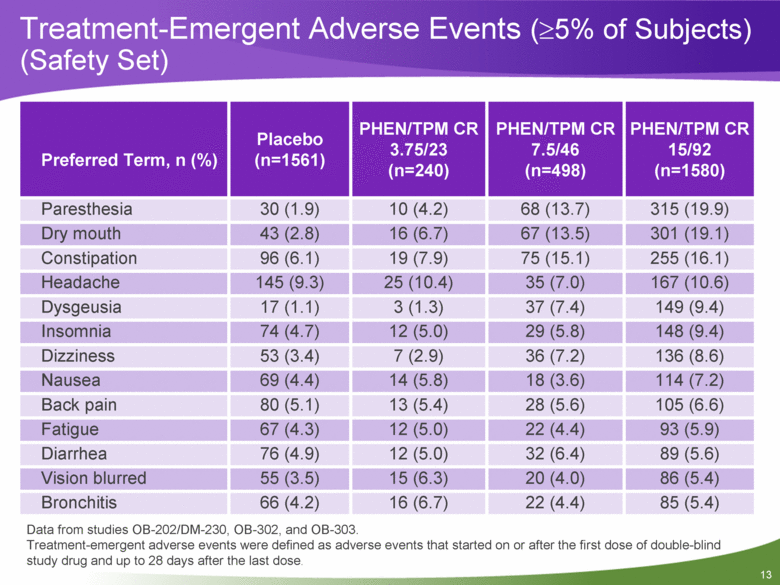
Preferred Term, n (%) Placebo (n=1561) PHEN/TPM CR 3.75/23 (n=240) PHEN/TPM CR 7.5/46 (n=498) PHEN/TPM CR 15/92 (n=1580) Paresthesia 30 (1.9) 10 (4.2) 68 (13.7) 315 (19.9) Dry mouth 43 (2.8) 16 (6.7) 67 (13.5) 301 (19.1) Constipation 96 (6.1) 19 (7.9) 75 (15.1) 255 (16.1) Headache 145 (9.3) 25 (10.4) 35 (7.0) 167 (10.6) Dysgeusia 17 (1.1) 3 (1.3) 37 (7.4) 149 (9.4) Insomnia 74 (4.7) 12 (5.0) 29 (5.8) 148 (9.4) Dizziness 53 (3.4) 7 (2.9) 36 (7.2) 136 (8.6) Nausea 69 (4.4) 14 (5.8) 18 (3.6) 114 (7.2) Back pain 80 (5.1) 13 (5.4) 28 (5.6) 105 (6.6) Fatigue 67 (4.3) 12 (5.0) 22 (4.4) 93 (5.9) Diarrhea 76 (4.9) 12 (5.0) 32 (6.4) 89 (5.6) Vision blurred 55 (3.5) 15 (6.3) 20 (4.0) 86 (5.4) Bronchitis 66 (4.2) 16 (6.7) 22 (4.4) 85 (5.4) Data from studies OB-202/DM-230, OB-302, and OB-303. Treatment-emergent adverse events were defined as adverse events that started on or after the first dose of double-blind study drug and up to 28 days after the last dose. Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events (>5% of Subjects) (Safety Set) |
|
|
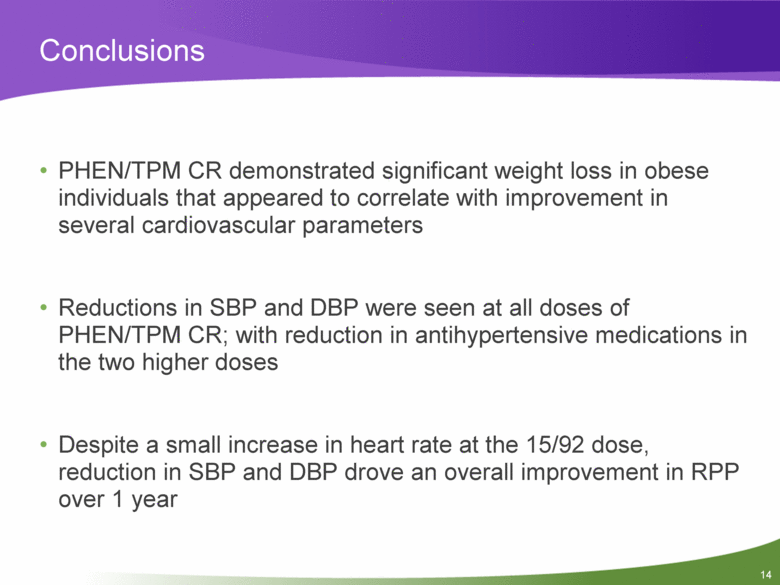
Conclusions PHEN/TPM CR demonstrated significant weight loss in obese individuals that appeared to correlate with improvement in several cardiovascular parameters Reductions in SBP and DBP were seen at all doses of PHEN/TPM CR; with reduction in antihypertensive medications in the two higher doses Despite a small increase in heart rate at the 15/92 dose, reduction in SBP and DBP drove an overall improvement in RPP over 1 year |
|
|
Acknowledgements We would like to thank the PHEN/TPM CR study participants, the site staff and investigators We acknowledge assistance developing the slides from Peter Hughes, PhD and Barbara Troupin, MD, from Vivus; and graphics development assistance from the Lockwood Group |