Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - China Biologic Products Holdings, Inc. | exhibit31-1.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - China Biologic Products Holdings, Inc. | exhibit31-2.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - China Biologic Products Holdings, Inc. | exhibit32-2.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - China Biologic Products Holdings, Inc. | exhibit32-1.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-Q/A
(Amendment No. 1)
(Mark One)
x QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the quarterly period ended: March 31, 2010
o TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from ____________ to
_____________
Commission File Number: 001-34566
| CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS, INC. |
| (Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) |
| Delaware | 75-2308816 | |||
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |||
| or organization) |
| No. 14 East Hushan Road |
| Tai’an City, Shandong 271000 |
| People’s Republic of China |
| (Address of principal executive offices) |
| (+86) 538-620-2306 |
| (Registrant’s telephone number, including area code) |
| (Former name, former address and former fiscal year, if changed since last report) |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
Yes o No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer o | Accelerated filer o |
| Non-accelerated filer o (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company x |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No x
The number of shares outstanding of each of the issuer’s classes of common stock, as of May 12, 2010 is as follows:
| Class of Securities | Shares Outstanding | |
| Common Stock, $0.0001 par value | 23,520,803 |
EXPLANATORY NOTE
China Biologic Products, Inc. (the "Company") is filing this Amendment No. 1 to its Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (the "Amendment") to restate its consolidated financial statements for the three months ended March 31, 2010 included in its Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2010, previously filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on May 14, 2010 (the "the Original Filing"). This Amendment is being filed to amend the recognition of fair value of the callable feature for the warrants issued in 2006 and recognition of deferred tax liabilities in connection with business combination of Guiyang Dalin Biologic Technologies Co. Ltd. ("Dalin").
Recognition of fair value of the callable feature for the warrants issued in 2006
In 2006, the Company issued 1,070,000 warrants (the "2006 Warrants") to certain accredited investors. According to the terms of the 2006 Warrants, the Company may, in its sole discretion, elect to require the 2006 Warrants holders to exercise up to all of the unexercised portion of the 2006 Warrants ("Callable Feature"). The Company inadvertently omitted the fair value of the Callable Features embedded in the 2006 Warrants when reclassifying the fair value of 2006 Warrants from equity to derivative liabilities as of January 1, 2009 in adopting EITF 07-5, "Determining Whether an Instrument (or Embedded Feature) Is Indexed to an Entity's Own Stock" (FASB ASC 815-40-15-5) ("EITF 07-05"). As a result, the retained earnings and additional paid-in capital should have been increased by $535,615 and $138,160, respectively, and the derivative liabilities should have been decreased by $673,775 as of January 1, 2009. The retained earnings and additional paid-in capital should have been increased by $1,246,476 and decreased by $1,246,476, respectively, as of March 31, 2010.
Recognition of deferred tax liabilities in connection with the business combination of Dalin
In connection with the business combination of Dalin in 2009, the Company misinterpreted the US GAAP regarding the accounting for the business combination. As a result, the Company did not recognize deferred tax liabilities for differences between the assigned values and the tax bases of the intangible assets and certain property, plant and equipment acquired in the business combination as in accordance with ASC Topic 740, Income Taxes. As of January 1, 2009, deferred tax liabilities of $4,749,099 should have been recognized with a corresponding increase in goodwill of $4,749,099. During the three months ended March 31, 2010, the Company also should have recorded deferred tax benefit representing the tax effect of the amortization of intangible assets and the depreciation of property, plant and equipment for the three months ended March 31, 2010. As a result, the goodwill, deferred tax liabilities, retained earnings and noncontrolling interest should have been increased by $4,775,139, $4,150,333, $290,477 and $334,143, respectively, as of March 31, 2010. The net income, net income attributable to noncontrolling interest and other comprehensive income of the Company should have been increased by $124,919, $66,810 and $43, for the three months ended March 31, 2010, respectively.
For the purposes of the Amendment, and in accordance with Rule 12b-15 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, each item of the Original Filing that was affected by the restatement has been amended and restated in its entirety. Unless otherwise indicated, this report speaks only as of the date that the Original Report was filed. No attempt has been made in this Amendment to update other disclosures presented in the Original Filing. This Amendment does not reflect events occurring after the filing of the Original Filing or modify or update those disclosures, including the exhibits to the Original Filing affected by subsequent events, except that this Amendment includes as exhibits 31.1, 31.2, 32.1 and 32.2 new certifications by the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer as required by Rule 12b-15.
| TABLE OF CONTENTS | ||
| PART I | FINANCIAL INFORMATION | |
| ITEM 1. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS. | 2 |
| ITEM 2. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS. | 45 |
| ITEM 3. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK | 56 |
| ITEM 4 | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES. | 56 |
| . | ||
| PART II | OTHER INFORMATION | |
| ITEM 1. | LEGAL PROCEEDINGS. | 57 |
| ITEM 1A. | RISK FACTORS. | 59 |
| ITEM 2. | UNREGISTERED SALES OF EQUITY SECURITIES AND USE OF PROCEEDS. | 59 |
| ITEM 3. | DEFAULTS UPON SENIOR SECURITIES. | 59 |
| ITEM 4. | (REMOVED AND RESERVED). | 59 |
| ITEM 5. | OTHER INFORMATION. | 59 |
| ITEM 6. | EXHIBITS. | 60 |
PART I
FINANCIAL INFORMATION
ITEM 1. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS.
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS,
INC.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010 AND
2009
| Contents | Page(s) |
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of March 31, 2010 (unaudited) and December 31, 2009 |
3 |
|
Consolidated Statements of Income and Other Comprehensive Income for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009 (unaudited) |
4 |
|
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity |
5 |
|
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009 (unaudited) |
6 |
|
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (unaudited) |
7 |
-2-
| CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS, INC. AND
SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS |
||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||
| March 31, | December 31, | |||||
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||
|
|
(Unaudited) |
|||||
| (As Restated - Note 2) | ||||||
|
CURRENT ASSETS: |
||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 51,190,425 | $ | 53,843,951 | ||
|
Notes receivable |
550,125 | - | ||||
|
Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $1,255,629 and $1,254,955 as of March 31,2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively |
3,764,123 | 1,767,076 | ||||
|
Accounts receivable - related party |
270,086 | 222,617 | ||||
|
Other receivables |
2,177,594 | 2,186,441 | ||||
|
Inventories, net of allowance for obsolete of $717,960 and $519,333 as of March 31,2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively |
39,175,405 | 35,132,724 | ||||
|
Prepayments and deferred expense |
1,672,261 | 1,299,125 | ||||
|
Deferred tax assets |
785,081 | 1,053,771 | ||||
|
Total current assets |
99,585,100 | 95,505,705 | ||||
|
|
||||||
|
PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, net |
31,867,690 | 28,873,413 | ||||
|
|
||||||
|
OTHER ASSETS: |
||||||
|
Investment in unconsolidated affiliate |
6,815,961 | 6,627,355 | ||||
|
Prepayments - non-current |
3,362,943 | 3,223,960 | ||||
|
Intangible assets, net |
20,335,295 | 21,180,322 | ||||
|
Goodwill |
17,200,728 | 17,200,728 | ||||
|
Total other assets |
47,714,927 | 48,232,365 | ||||
|
|
||||||
|
Total assets |
$ | 179,167,717 | $ | 172,611,483 | ||
|
|
||||||
|
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES: |
||||||
|
Accounts payable |
$ | 3,520,975 | $ | 3,701,843 | ||
|
Notes payable |
- |
48,598 | ||||
|
Short term loans - bank |
7,408,350 | 4,474,350 | ||||
|
Short term loans - holder of noncontrolling interest |
3,652,500 | 3,652,500 | ||||
|
Other payables and accrued liabilities |
17,282,264 | 19,246,814 | ||||
|
Other payable - related parties |
3,087,527 | 3,087,527 | ||||
|
Accrued interest - holder of noncontrolling interest |
1,154,687 | 2,068,526 | ||||
|
Customer deposits |
4,553,560 | 3,868,577 | ||||
|
Taxes payable |
7,519,268 | 8,774,079 | ||||
|
Investment payable |
2,195,365 | 2,195,365 | ||||
|
Total current liabilities |
50,374,496 | 51,118,179 | ||||
|
|
||||||
|
OTHER LIABILITIES: |
||||||
|
Other payable - land use right |
323,390 | 323,687 | ||||
|
Notes payable, net of discount of $7,325,349 and $8,464,380 as of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively |
174,651 | 89,760 | ||||
|
Derivative liability - conversion option |
15,275,245 | 19,960,145 | ||||
|
Fair value of derivative instruments |
9,177,262 | 12,701,262 | ||||
| Deferred tax liabilities | 4,150,333 | 4,275,295 | ||||
|
Total other liabilities |
29,100,881 | 37,350,149 | ||||
|
|
||||||
|
Total liabilities |
79,475,377 | 88,468,328 | ||||
|
|
||||||
|
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
EQUITY: |
||||||
|
Common stock, $0.0001 par value, 100,000,000 shares authorized, |
||||||
|
23,500,803 and 23,056,442 shares issued and outstanding at March 31 ,2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively |
2,349 | 2,305 | ||||
|
Additional paid-in-capital |
26,778,332 | 21,270,601 | ||||
|
Statutory reserves |
19,831,853 | 17,414,769 | ||||
|
Retained earnings |
15,028,114 | 6,781,449 | ||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income |
4,246,881 | 4,227,537 | ||||
|
Total shareholders' equity |
65,887,529 | 49,696,661 | ||||
|
|
||||||
|
NONCONTROLLING INTEREST |
33,804,811 | 34,446,494 | ||||
|
Total equity |
99,692,340 | 84,143,155 | ||||
|
|
||||||
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 179,167,717 | $ | 172,611,483 | ||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated statements.
- 3 -
| CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS, INC. AND
SUBSIDIARIES CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME AND OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010 AND 2009 (Unaudited) | ||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||
|
(As Restated - Note 2) |
||||||
| REVENUES: | ||||||
| Revenues | $ | 26,861,522 | $ | 20,905,869 | ||
| Revenues - related party | 237,031 | 242,729 | ||||
| Total revenues | 27,098,553 | 21,148,598 | ||||
| COST OF REVENUES: | ||||||
| Cost of revenues | 6,798,854 | 6,214,930 | ||||
| GROSS PROFIT | 20,299,699 | 14,933,668 | ||||
| OPERATING EXPENSES: | ||||||
| Selling expenses | 942,908 | 579,496 | ||||
| General and administrative expenses | 4,962,252 | 3,822,907 | ||||
| Research and development expenses | 1,168,655 | 467,727 | ||||
| Total operating expenses | 7,073,815 | 4,870,130 | ||||
| INCOME FROM OPERATIONS | 13,225,884 | 10,063,538 | ||||
| OTHER (INCOME) EXPENSE: | ||||||
| Equity in income of unconsolidated affiliate | (188,541 | ) | (40,247 | ) | ||
| Change in fair value of derivative liabilities | (3,833,577 | ) | 409,292 | |||
| Interest expense, net | 181,053 | 370,853 | ||||
| Other income - related party | (914,289 | ) |
- |
|||
| Other expense, net | 94,320 | 51,315 | ||||
| Total other (income) expense, net | (4,661,034 | ) | 791,213 | |||
| INCOME BEFORE PROVISION FOR INCOME TAXES AND NONCONTROLLING INTEREST | 17,886,918 | 9,272,325 | ||||
| PROVISION FOR INCOME TAXES | 3,071,147 | 1,905,395 | ||||
| NET INCOME BEFORE NONCONTROLLING INTEREST | 14,815,771 | 7,366,930 | ||||
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest | 4,152,022 | 3,058,134 | ||||
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO CONTROLLING INTEREST | 10,663,749 | 4,308,796 | ||||
| OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME: | ||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | 19,344 | 18,633 | ||||
| Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest | (23,955 | ) | 427,298 | |||
| COMPREHENSIVE INCOME | $ | 10,659,138 | $ | 4,754,727 | ||
| BASIC EARNINGS PER SHARE: | ||||||
| Weighted average number of shares | 23,386,893 | 21,434,942 | ||||
| Earnings per share | $ | 0.46 | $ | 0.20 | ||
| DILUTED EARNINGS PER SHARE: | ||||||
| Weighted average number of shares | 26,471,425 | 21,434,942 | ||||
| Earnings per share | $ | 0.26 | $ | 0.20 | ||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated statements.
-4-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
| Retained earnings | Accumulated | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| other | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common stock | Additional | Statutory | comprehensive | Noncontrolling | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Par value | paid in capital | reserves | Unrestricted | income | interest | Total | |||||||||||||||||
|
BALANCE, December 31, 2008 |
21,434,942 | $ | 2,143 | $ | 10,700,032 | $ | 6,989,801 | $ | 15,392,253 | $ | 4,159,298 | $ | 4,805,381 | $ | 42,048,908 | |||||||||
| Cumulative effect of reclassification of 2006 warrants | (600,289 | ) | (393,962 | ) | (994,251 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation | 27,373 | 27,373 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | 4,308,796 | 3,058,134 | 7,366,930 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividend declared to noncontrolling interest shareholders | (4,633,987 | ) | (4,633,987 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest acquired from acquisition | 21,501,712 | 21,501,712 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjustment to statutory reserve | 2,760,836 | (2,760,836 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | 18,633 | 427,298 | 445,931 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BALANCE, March 31, 2009 (unaudited) | 21,434,942 | $ | 2,143 | $ | 10,127,116 | $ | 9,750,637 | $ | 16,546,251 | $ | 4,177,931 | $ | 25,158,538 | $ | 65,762,616 | |||||||||
| Stock based compensation | 34,908 | 34,908 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrants exercised | 1,284,000 | 128 | 8,571,281 | 8,571,409 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Convertible notes exercised | 250,000 | 25 | 2,187,305 | 2,187,330 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock option exercised | 87,500 | 9 | 349,991 | 350,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | (2,100,670 | ) | 13,557,524 | 11,456,854 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividend declared to noncontrolling interest shareholders | (4,321,405 | ) | (4,321,405 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest acquired from acquisition | 23,347 | 23,347 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjustment to statutory reserve | 7,664,132 | (7,664,132 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | 49,606 | 28,490 | 78,096 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BALANCE, December 31, 2009 | 23,056,442 | $ | 2,305 | $ | 21,270,601 | $ | 17,414,769 | $ | 6,781,449 | $ | 4,227,537 | $ | 34,446,494 | $ | 84,143,155 | |||||||||
| Stock based compensation | 571,893 | 571,893 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of Warrants | 180,826 | 18 | 2,436,907 | 2,436,925 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock upon conversion of Convertible Note | 263,535 | 26 | 2,498,931 | 2,498,957 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income, as restated (Note 2) | 10,663,749 | 4,152,022 | 14,815,771 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividend declared to noncontrolling interest shareholders | (4,782,420 | ) | (4,782,420 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjustment to statutory reserve | 2,417,084 | (2,417,084 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-control Interest transfer per equity transferred in Fangcheng | 12,670 | 12,670 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments, as restated (Note 2) | 19,344 | (23,955 | ) | (4,611 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
|
BALANCE, March 31, 2010 (unaudited), as restated (Note 2) |
23,500,803 | $ | 2,349 | $ | 26,778,332 | $ | 19,831,853 | $ | 15,028,114 | $ | 4,246,881 | $ | 33,804,811 | $ | 99,692,340 | |||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated statements.
- 5 -
| CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS, INC. AND
SUBSIDIARIES CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010 AND 2009 (Unaudited) | ||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: |
(As Restated - Note 2) |
|||||
| Net income attributable to controlling interest | $ | 10,663,749 | $ | 4,308,796 | ||
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest | 4,152,022 | 3,058,134 | ||||
| Consolidated net income | 14,815,771 | 7,366,930 | ||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||
| Depreciation | 793,657 | 759,072 | ||||
| Amortization | 869,251 | 838,459 | ||||
| Loss (gain) on disposal of equipment | 3,019 | (276 | ) | |||
| Allowance for bad debt - accounts receivables | 23,329 | 26,581 | ||||
| Allowance for obsolete inventories | 198,559 | - | ||||
| Deferred tax benefit, net | 89,664 | (124,799 | ) | |||
| Stock based compensation | 571,893 | 27,373 | ||||
| Change in fair value of derivative liabilities | (3,833,577 | ) | 409,292 | |||
| Amortization of deferred note issuance cost | 86,790 | - | ||||
| Amortization of discount on convertible notes | 99,318 | - | ||||
| Equity in income of unconsolidated affiliate | (188,541 | ) | (40,246 | ) | ||
| Change in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||
| Notes receivable | (549,938 | ) | (468,832 | ) | ||
| Accounts receivable | (1,997,040 | ) | (97,007 | ) | ||
| Accounts receivable - related party | (47,452 | ) | (212,367 | ) | ||
| Other receivables | 8,847 | (18,487 | ) | |||
| Inventories | (4,283,720 | ) | (3,513,011 | ) | ||
| Prepayments and deferred expenses | (512,690 | ) | (124,944 | ) | ||
| Accounts payable | (180,806 | ) | (252,850 | ) | ||
| Other payables and accrued liabilities | (2,383,690 | ) | 307,916 | |||
| Accrued interest - holder of noncontrolling interest | (913,840 | ) | 305,966 | |||
| Customer deposits | 684,750 | 2,872,712 | ||||
| Taxes payable | (1,260,708 | ) | (979,190 | ) | ||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 2,092,846 | 7,082,292 | ||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | ||||||
| Cash acquired through acquisition | 334 | 11,938,784 | ||||
| Payments made for acquisition | (1,476,781 | ) | - | |||
| Purchase of plant and equipment | (1,443,043 | ) | (986,640 | ) | ||
| Additions to intangible assets | (24,484 | ) | (88,845 | ) | ||
| Advances on non-current assets | (569,626 | ) | (474,736 | ) | ||
| Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities | (3,513,600 | ) | 10,388,563 | |||
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | ||||||
| Proceeds from warrants conversion | 689,160 | - | ||||
| Proceeds from short term loans - bank | 5,924,660 | 7,647,822 | ||||
| Payments on short term loans - bank | (2,962,330 | ) | - | |||
| Payments on notes payables | (48,582 | ) | - | |||
| Distribution paid to noncontrolling interest shareholders | (4,780,790 | ) | - | |||
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (1,177,882 | ) | 7,647,822 | |||
| EFFECTS OF EXCHANGE RATE CHANGE IN CASH | (54,890 | ) | 72,655 | |||
| (DECREASE) INCREASE IN CASH | (2,653,526 | ) | 25,191,332 | |||
| CASH and CASH EQUIVALENTS, beginning of year | 53,843,951 | 8,814,616 | ||||
| CASH and CASH EQUIVALENTS, end of year | $ | 51,190,425 | $ | 34,005,948 | ||
| SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION | ||||||
| Income taxes paid | $ | 3,806,691 | $ | 1,783,619 | ||
| Interest paid (net of capitalized interest) | $ | 62,286 | $ | 236,649 | ||
| Non-cash investing and financing activities: | ||||||
| Reclassification of derivative liability to equity related to conversion of convertible notes | $ | 1,809,771 | $ | - | ||
| Reclassification of derivative liability to equity related to exercise of warrants | $ | 2,436,907 | $ | - | ||
| Distribution paid by offsetting accounts receivable - related party | $ | - | $ | 3,735,243 | ||
| Net assets acquired with prepayments made in prior periods | $ | - | $ | 14,240,772 | ||
| Net assets addition with unpaid commitment | $ | 395,540 | $ | 14,240,772 | ||
| Plant and equipment acquired with prepayments made in prior periods | $ | 424,858 | $ | 87,305 | ||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated statements.
-6-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Note 1 – Organization background and principal activities
Principal Activities and Reorganization
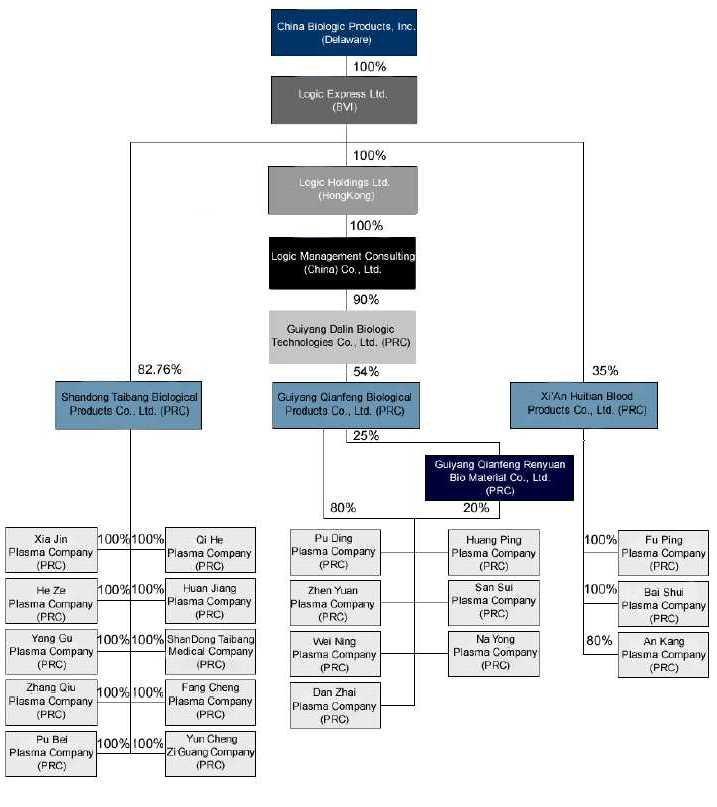
China Biologic Products, Inc. (the “Company” or “CBP”) was originally incorporated in 1992 under the laws of the state of Texas. After it completed the acquisition with Logic Express Limited, it converted to a Delaware corporation. The Company through its direct and indirect subsidiaries is principally engaged in the research, development, commercialization, manufacture and sale of human blood products to customers in the People’s Republic of China (the “PRC”) and to some extent in India.
Current Development
Dalin Acquisition and Entrustment Agreement
Logic Express Ltd. (“Logic Express”), CBP’s wholly owned subsidiary, through Logic Holdings(Hong Kong) Ltd. (“Logic Holdings”) completed the acquisition of 90% interest in Guiyang Dalin Biologic Technologies Co. Ltd. (“Dalin”), previously known as Chongqing Dalin Biologic Technologies Co. Ltd., in April 2009 upon payment of 90% of the total purchase price of approximately RMB 194,400,000 ($28,479,600). The Company is obligated to pay the remaining 10% of the purchase price, RMB 19,440,000 (approximately $2,847,960), on or before April 9, 2010, the one-year anniversary of the local Administration for Industry and Commerce’s approval of the equity transfer. On April 9, 2010, the Company paid the final 10% of the total purchase price according to the equity transfer agreement.
In accordance with the terms of the equity transfer agreement, Logic Holdings effectively became a 90% shareholder in Dalin, including the right to receive its pro rata share of the profits on January 1, 2009.
On April 6, 2009, Logic Express entered into an equity transfer and entrustment agreement, or Entrustment Agreement, among Logic Express, Shandong Taibang Biological Products Co. Ltd (“Shandong Taibang”), and the Shandong Institute of Biological Products (“the Shandong Institute”), the holder of the minority interests in Shandong Taibang, pursuant to which, Logic Express agreed to permit Shandong Taibang and the Shandong Institute to participate in the indirect purchase of Qianfeng’s equity interests. Under the terms of the Entrustment Agreement, Shandong Taibang agreed to contribute 18% or RMB 35,000,000 (approximately $5,116,184) of the Dalin purchase price and the Shandong Institute agreed to contribute 12.86% or RMB 25,000,000 (approximately $3,654,917) of the Dalin purchase price. Logic Express is obligated to repay to Shandong Taibang and the Shandong Institute their respective investment amounts on or before April 6th, 2010, along with their pro rata share, based on their percentage of the Dalin purchase price contributed, of any distribution on the indirect equity investment in Qianfeng payable to Logic Express during 2009. Logic Express has agreed that if these investment amounts are not repaid within five days of the payment due date, then Logic Express is obligated to pay Shandong Taibang and the Shandong Institute liquidated damages equal to 0.03% of the overdue portion of the amount due until such time as it is paid. Logic Express has also agreed to pledge 30% of its ownership in Shandong Taibang to the Shandong Institute as security for nonpayment. If failure to repay continues for longer than three months after the payment due date, then the Shandong Institute will be entitled to any rights associated with the pledged interests, including but not limited to rights of disposition and profit distribution, until such time as the investment amount has been repaid. Logic Express also provided a guarantee that Shandong Taibang and the Shandong Institute will receive no less than a 6% return based on their original investment amount. On April 12, 2010, the Company fully paid Shandong Institute and Shandong Taibang on the respective investment amounts, as well as the interest, according to the Entrustment Agreement, as described in more detail in Note 3 below.
Formation of PRC Subsidiary
On December 21, 2009, the Company established Logic Management and Consulting (China) Co., Ltd. (“Logic China”), wholly-owned by the Hong Kong subsidiary, for the purpose of being a holding company for the majority interest in Dalin and to facilitate our Chinese operation at the holding company level. On December 28, 2009, the Company transferred the 90% equity interest in Guiyang Dalin from Logic Holding to Logic China to better situate the Company in PRC operations.
Acquisition of 20% of equity interest in Fangcheng Plasma Co.
On January 13, 2010, the 20% title of Fangcheng Plasma Company was transferred from former non-controlling interest to Taibang, who is now the 100% owner of Fangcheng Plasma Company.
Acquisition of Ziguang Bio-Technology Co.
On January 22, 2010, Shandong Taibang entered into an Equity Transfer Agreement with Yuncheng Ziguang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. which is located in Yuncheng, Shandong Province. Under the terms of the Equity Transfer Agreement, Shandong Taibang agreed to purchase 100% of Yuncheng Ziguang’s equity interest at a purchase price of RMB 10,066,672 (approximately $1,476,781), which was paid on February 24, 2010.
-7-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Note 2 – Restatement of March 31, 2010 consolidated financial statements
This financial statements contain restatements related to the recognition of fair value of the callable feature for the warrants issued in 2006 and recognition of deferred tax liabilities in connection with business combination of Dalin for the three months ended and as of March 31, 2010.
Recognition of fair value of the callable feature for the warrants issued in 2006
In 2006, the Company issued 1,070,000 warrants (the “2006 Warrants”) to certain accredited investors. According to the terms of the 2006 Warrants, the Company may, in its sole discretion, elect to require the 2006 Warrants holders to exercise up to all of the unexercised portion of the 2006 Warrants (“Callable Feature”). The Company inadvertently omitted the fair value of the Callable Features embedded in the 2006 Warrants when reclassifying the fair value of 2006 Warrants from equity to derivative liabilities as of January 1, 2009 in adopting EITF 07-5, “Determining Whether an Instrument (or Embedded Feature) Is Indexed to an Entity's Own Stock” (FASB ASC 815-40-15-5) (“EITF 07-05”). As a result, the retained earnings and additional paid-in capital should have been increased by $535,615 and $138,160, respectively, and the derivative liabilities should have been decreased by $673,775 as of January 1, 2009. The retained earnings and additional paid-in capital should have been increased by $1,246,476 and decreased by $1,246,476, respectively, as of March 31, 2010.
Recognition of deferred tax liabilities in connection with the business combination of Dalin
In connection with the business combination of Dalin in 2009 (see Note 1), the Company misinterpreted US GAAP regarding the accounting for business combination. As a result, the Company did not recognize deferred tax liabilities for differences between the assigned values and the tax bases of the intangible assets and certain property, plant and equipment acquired in the business combination as in accordance with ASC Topic 740, Income Taxes. As of January 1, 2009, deferred tax liabilities of $4,749,099 should have been recognized with a corresponding increase in goodwill of $4,749,099. During the three months ended March 31, 2010, the Company also should have recorded deferred tax benefit representing the tax effect of the amortization of intangible assets and the depreciation of property, plant and equipment for the three months ended March 31, 2010. As a result, the goodwill, deferred tax liabilities, retained earnings, accumulated other comprehensive income and noncontrolling interest should have been increased by $4,775,139, $4,150,333, $290,477, $186 and $334,143, respectively, as of March 31, 2010. The net income, net income attributable to noncontrolling interest and other comprehensive income of the Company should have been increased by $124,919, $66,810 and $43, for the three months ended March 31, 2010, respectively.
Reclassification of accumulated other comprehensive income
to noncontrolling interest
As required by ASC 810-10-50-1 Aa2, the Company reclassify $1,025,442 of
accumulated other comprehensive income to noncontrolling interest as of March
31, 2010 to separately disclose the amounts of comprehensive income attributable
to both the Company and noncontrolling interests. As a result of this
reclassification, the accumulated other comprehensive income decreased by
$1,025,442 and noncontrolling interests increased by $1,025,442 as of March 31,
2010. This reclassification has no effect on previously reported financial
position or results.
The impact of these restatements and reclassificication on the March 31, 2010 financial statements is reflected in the following tables:
| Balance Sheet Amounts | As Previously Reported | Restatement | Reclassification | As Restated | ||||||||
| Goodwill | $ | 12,425,589 | $ | 4,775,139 | $ |
- |
$ | 17,200,728 | ||||
| Total assets | 174,392,578 | 4,775,139 | - | 179,167,717 | ||||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities (note 14) | - | 4,150,333 | - | 4,150,333 | ||||||||
| Total liabilities | 75,325,044 | 4,150,333 | - | 79,475,377 | ||||||||
| Additional paid-in-capital | 28,024,808 | (1,246,476 | ) | - | 26,778,332 | |||||||
| Retained earnings | 13,491,161 | 1,536,953 | - | 15,028,114 | ||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income | 5,272,137 | 186 |
(1,025,442 |
) | 4,246,881 | |||||||
| Noncontrolling interest (note 21) | 32,445,226 | 334,143 |
1,025,442 |
33,804,811 | ||||||||
| Total equity | 99,067,534 | 624,806 | 99,692,340 | |||||||||
| Statement of Operations and Other Comprehensive Income Amounts | As Previously Reported | Restatement | Reclassification | As Restated | ||||||||
| Provision for income taxes (note 14) | $ | 3,196,066 | $ | (124,919 | ) | $ |
- |
$ | 3,071,147 | |||
| Net income | 14,690,852 | 124,919 |
- |
14,815,771 | ||||||||
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest (note 21) | 4,085,212 | 66,810 |
- |
4,152,022 | ||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | (4,654 | ) | 43 |
- |
(4,611 | ) | ||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | (4,654 | ) | 23,998 |
- |
19,344 | |||||||
| Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest | - | (23,955 | ) |
- |
(23,955 | ) | ||||||
| Comprehensive income attributed to controlling interest | 10,600,986 | 82,107 |
- |
10,683,093 | ||||||||
| Basic earnings per share (note 13) | $ | 0.45 | $ | 0.01 |
- |
$ | 0.46 | |||||
| Diluted earnings per share (note 13) | $ | 0.41 | $ | (0.15 | ) |
- |
$ | 0.26 | ||||
| Statement of Cash Flow | As Previously Reported | Restatement |
|
Reclassification | As Restated | |||||||
| Net income | $ | 14,690,852 | $ | 124,919 | $ |
- |
$ | 14,815,771 | ||||
| Deferred tax benefit, net | 214,583 | (124,919 | ) |
- |
89,664 |
-8-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Note 3 – Summary of significant accounting policies
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. The Company’s functional currency is the Chinese Renminbi (“RMB”); however, the Company’s reporting currency is the United States Dollar (“USD”); therefore, the accompanying consolidated financial statements have been translated and presented in USD. All material inter-company transactions and balances have been eliminated in the consolidation.
While management has included all normal recurring adjustments considered necessary to give a fair presentation of the operating results for the periods presented, interim results are not necessarily indicative of results for a full year. The information included in this Form 10-Q should be read in conjunction with information included in the 2009 annual report filed on Form 10-K.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. For example, management estimates the fair value of stock based compensation as well as potential losses on outstanding receivables. Management believes that the estimates utilized in preparing its financial statements are reasonable and prudent. Actual results could differ from these estimates.
Foreign Currency Translation
The reporting currency of the Company is the US dollar. The Company’s functional currency is the Chinese Renminbi (“RMB”), also the local currency of the Company’s principal operating subsidiaries. Results of operations and cash flows are translated at average exchange rates during the period. Assets and liabilities are translated at the unified exchange rate as quoted by the People’s Bank of China at the end of the period. Translation adjustments resulting from this process are included in accumulated other comprehensive income in the consolidated statements of changes in equity. Transaction gains and losses that arise from exchange rate fluctuations on transactions denominated in a currency other than the functional currency are included in the results of operations as incurred.
In accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board’s (FASB) accounting standard, cash flows from the Company's operations is calculated based upon the local currencies. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the consolidated statement of cash flows will not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the consolidated balance sheet.
The consolidated balance sheet amounts, with the exception of equity, at March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009 were translated at RMB 6.82 to $1.00 and RMB 6.82 to $1.00, respectively. The equity accounts were stated at their historical rate. The average translation rates applied to consolidated statements of income and cash flow for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009 were RMB 6.82 and RMB 6.83 to $1.00, respectively.
-9-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue when products are delivered and the customer takes ownership and assumes risk of loss, collection of the relevant receivable is probable, persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists and the sales price is fixed or determinable, which are generally considered to be met upon delivery and acceptance of products at the customer site. Sales are presented net of any discounts given to customers. As a policy, the Company does not accept any product returns and based on the Company’s records, product returns, if any, are immaterial. Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of goods, net of a value-added tax (“VAT”).
Shipping and Handling
Shipping and handling costs related to costs of goods sold are included in selling expenses and totaled $68,435 and $44,180 for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
Financial Instruments
On January 1, 2008, the Company adopted FASB’s accounting standard related to fair value measurements and began recording financial assets and liabilities subject to recurring fair value measurement at the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants. These fair value principles prioritize valuation inputs across three broad levels. Receivables, payables, short and long term loans, and derivative liabilities qualify as financial instruments. Management concluded the carrying values of the receivables, payables and short term loans approximate their fair values because of the short period of time between the origination of such instruments and their expected realization, and if applicable, their stated rates of interest are equivalent to interest rates currently available. The fair values of the long term debt and derivative liabilities are measured pursuant to the three levels defined by the FASB’s accounting standard as follow:
-
Level 1: inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
-
Level 2: inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, and inputs that are observable for the assets or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instruments.
-
Level 3: inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and significant to the fair value.
As required by FASB’s accounting standard, financial assets and liabilities are classified in their entirety based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. Depending on the product and the terms of the transaction, the fair value of the derivative liabilities were modeled using a series of techniques, including closed-form analytic formula, such as the Black-Scholes Option Pricing Model, which does not entail material subjectivity because the methodology employed does not necessitate significant judgment, and the pricing inputs are observed from actively quoted markets. Derivative liabilities related to warrants issued by the Company and the liability related to derivative instruments (including the conversion option) embedded in the Company’s Senior Secured Convertible Notes are carried at fair value, with changes in the fair value charged or credited to income. The fair values are determined using the Black-Scholes Model or a binomial model, defined in FASB’s accounting standard related to fair value measurements as level 2 inputs.
-10-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO
CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
| Carrying Value as of March 31, 2010 |
Fair Value Measurements at March
31, 2010 using Fair Value Hierarchy |
|||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||
| Derivative liabilities-Conversion option | $ | 15,275,245 | $ | - | $ | 15,275,245 | $ | - | ||||
| Warrants liabilities | $ | 9,177,262 | $ | - | $ | 9,177,262 | $ | - | ||||
The assumptions used in calculating the fair value of the derivative liabilities as of March 31, 2010 using the Black-Scholes option pricing model are as follows:
| Conversion | Warrants | |||||
| Options | ||||||
| Expected dividend yield | 0% | 0% | ||||
| Risk-free interest rate | 0.52% | 1.13% | ||||
| Expected life (in years) | 1.2 | 2.2 | ||||
| Weighted average expected volatility | 130% | 130.0% |
The Company did not identify any other assets or liabilities that are required to be presented on the balance sheet at fair value in accordance with FASB’s accounting standard.
Concentration Risks
The Company's operations are carried out in the PRC and are subject to specific considerations and significant risks not typically associated with companies in North America and Western Europe. Accordingly, the Company's business, financial condition and results of operations may be influenced by the political, economic and legal environments in the PRC, and by the general state of the PRC economy. The Company's results may be adversely affected by changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, currency conversion and remittance abroad, and rates and methods of taxation, among other things.
The Company maintains balances at financial institutions which, from time to time, may exceed Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation insured limits for the banks located in the United States or may exceed Hong Kong Deposit Protection Board insured limits for the banks located in Hong Kong. Balances at financial institutions or state-owned banks within the PRC are not covered by insurance. Total cash in banks as of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009 amounted to $50,943,464 and $53,576,495, respectively, $1,268,701 and $1,009,053 of which are covered by insurance, respectively. The Company has not experienced any losses in such accounts and believes it is not exposed to any risks on its cash in bank accounts.
-11-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
The Company’s major product, human albumin: 20%/10ml, 20%/25ml and 20%/50ml, and 10%/10ml, 10%/25ml and 10%/50ml, accounted for 46.9% and 58.4% of total revenues, for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively. If the market demands for human albumin cannot be sustained in the future or if the price of human albumin decreases, it would adversely affect the Company’s operating results.
All of the Company’s customers are located in the PRC and India. As of March 31, 2010 and 2009, the Company had no significant concentration of credit risk. There were no customers that individually comprised 10% or more of the revenue during the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009. Only one customer represented more than 10% of trade receivables at March 31, 2010 and no individual customer represented more than 10% of trade receivables at December 31, 2009. The Company performs ongoing credit evaluations of its customers’ financial condition and, generally, requires no collateral from its customers.
There was one vendor that individually comprised 10% or more of the purchase and account payables during the three months ended March 31, 2010 and no vendor that individually comprised 10% or more of the purchase or account payables during the same period in 2009.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand and demand deposits in accounts maintained with state-owned banks within the PRC, Hong Kong and the United States. The Company considers all highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less at the time of purchase to be cash equivalents.
Accounts Receivable
During the normal course of business, the Company extends unsecured credit to its customers. Management reviews its accounts receivable on a regular basis to determine if the allowance for doubtful accounts is adequate. An estimate for doubtful accounts is made when collection of the full amount is no longer probable. Account balances are written-off after management has exhausted all efforts of collection.
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market using the weighted average method. The cost of finished goods included direct costs of raw materials as well as direct labor used in production. Indirect production costs such as utilities and indirect labor related to production such as assembling, shipping and handling for raw material costs are also included in the cost of inventories.
-12-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
The Company reviews its inventory periodically for possible obsolete goods and cost in excess of net realizable value to determine if any reserves are necessary. As of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, the Company reserved $717,960 and $519,333, respectively, as allowance for obsolete inventory for raw material plasma that may not qualify for production due to the 90-day quarantine period rules implemented by SFDA on July 1, 2008.
Plant and Equipment
Plant and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets with 5% residual value.
| Estimated useful lives of the assets are as follows: | |
| Estimated Useful Life | |
| Buildings and improvement | 30 years |
| Machinery and equipment | 10 years |
| Furniture, fixtures and office equipment | 5-10 years |
Construction in progress represents the costs incurred in connection with the construction of buildings, new additions, and capitalized interest incurred in connection with the Company’s plant facilities. In accordance with the provisions of FASB’s accounting standard related to capitalization of interest, interest incurred on borrowings is capitalized to the extent that borrowings do not exceed construction in progress. The credit is a reduction of interest expense. No depreciation is provided for construction in progress until such time as the assets are completed and placed into service. Maintenance, repairs and minor renewals are charged directly to expenses as incurred. Major additions and betterment to property and equipment are capitalized.
The Company periodically evaluates the carrying value of long-lived assets in accordance with FASB’s accounting standard related to accounting for impairment and disposal of long-lived assets. When estimated cash flows generated by those assets are less than the carrying amounts of the asset, the Company recognizes an impairment loss. Based on its review, the Company believes that, as of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, there were no impairments of its long-lived assets.
-13-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Investment in Unconsolidated Affiliate
Equity method investments are recorded at original cost and adjusted to recognize the Company’s proportionate share of the investee’s net income or losses and additional contributions made and distributions received. The Company recognizes a loss if it is determined that other than temporary decline in the value of the investment exists. Subsidiaries in which the Company has the ability to exercise significant influence, but does not have a controlling interest is accounted for using the equity method. Significant influence is generally considered to exist when the Company has an ownership interest in the voting stock between 20% and 50%, and other factors, such as representation on the Board of Directors, voting rights and the impact of commercial arrangements, are considered in determining whether the equity method of accounting is appropriate. The Company accounts for investments with ownership less than 20% using cost method.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets are stated at cost (estimated fair value upon contribution or acquisition), less accumulated amortization. Amortization expense is recognized on the straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the assets as follows:
| Intangible assets | Estimated useful lives | |
| Land use rights | 50 years | |
| Permits and licenses | 5-10 years | |
| Blood donor network | 10 years | |
| Software | 3.8 years | |
| Good Manufacturing Practice certificate | 5-10 years | |
| Long-term customer-relationship intangible assets | 4 years |
All land in the PRC is owned by the government; however, the government grants “land use rights.” The Company has obtained rights to use various parcels of land for 50 years. The Company amortizes the cost of the land use rights over their useful life using the straight-line method.
Other intangible assets represent permits, licenses, blood donor network, software, Good Manufacturing Practice (“GMP”) certificate and long-term customer-relationship intangible assets. The Company amortized the cost of these intangible assets over their useful life using the straight-line method.
Intangible assets of the Company are reviewed at least annually or more often if circumstances dictate, to determine whether their carrying value has become impaired. The Company considers assets to be impaired if the carrying value exceeds the future projected cash flows from related operations. The Company also re-evaluates the years of amortization to determine whether subsequent events and circumstances warrant revised estimates of useful lives. As of March 31, 2010, the Company expects these assets to be fully recoverable.
-14-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the cost of an acquisition over the fair value of the Company’s share of the net identifiable assets of the acquired subsidiary at the date of acquisition. Goodwill is tested annually for impairment and carried at cost less accumulated impairment losses. Impairment losses on goodwill are not reversed. Gains and losses on the disposal of an entity include the carrying amount of goodwill relating to the entity sold.
Revenues and Customer Deposits
Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are recorded as customer deposits.
The Company’s revenues are primarily derived from the manufacture and sale of human blood products. The Company’s revenues by significant types of product for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009 are as follows:
| Three months ended March 31, | ||||||
| (Unaudited) | ||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||
| Human Albumin – 20%/10% in 10ml, 25ml and 50ml | $ | 12,699,407 | $ | 12,351,699 | ||
| Human Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin | 3,332,307 | 60,099 | ||||
| Human Immunoglobulin for Intravenous Injection | 5,395,465 | 5,372,502 | ||||
| Human Rabies Immunoglobulin | 3,778,122 | 1,629,011 | ||||
| Human Tetanus Immunoglobulin | 687,315 | 1,029,686 | ||||
| Human Immunoglobulin | 649,973 | 213,877 | ||||
| Others | 555,964 | 491,724 | ||||
| Total | $ | 27,098,553 | $ | 21,148,598 | ||
The Company is engaged in sale of human blood products to customers in China and India. The amount sold in India was less than 10% of total sales for the three months ended March 31, 2010.
Research and Development Costs
Research and development costs composed of salary, material used and other expense as incurred.
Retirement and Other Post Retirement Benefits
Contributions to retirement schemes (which are defined contribution plans) are charged to the statement of operations as and when the related employee service is provided.
-15-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Product Liability
The Company’s products are covered by two product liability insurance of approximately $2,934,000 (RMB 20,000,000) each for Shandong Taibang and Qianfeng. As of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, no claim on the insurance policy was filed. However, there is one pre-existing potential claim against Qianfeng’s products outstanding, which are still pending and the Company believes to be immaterial to the consolidated financial statements for the period ended March 31, 2010.
Government Grants
The Company’s subsidiary, Shandong Taibang, is entitled to receive grants from the Tai’an municipal government due to its operation in the high and new technology business sector. For the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, no non-refundable grants were received from the Tai’an municipal government. Grants received from the Tai’an municipal government can be used for enterprise development and technology innovation purposes.
Income Taxes
The Company reports income taxes pursuant to FASB’s accounting standard for income taxes. Under the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes as required by this accounting standard, deferred income tax liabilities and assets are determined based on the temporary differences between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities using tax rates expected to be in effect during the years in which the basis differences reverse. A valuation allowance is recorded when it is more likely than not that some of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. FASB’s accounting standard for accounting for uncertainty in income taxes requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Income tax positions must meet a more-likely-than-not recognition threshold to be recognized. A tax position is recognized as a benefit only if it is “more likely than not” that the tax position would be sustained in a tax examination, with a tax examination being presumed to occur. The amount recognized is the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than 50% likely of being realized on examination. For tax positions not meeting the “more likely than not” test, no tax benefit is recorded.
Deferred tax is accounted for using the balance sheet liability method in respect of temporary differences arising from differences between the carrying amount of assets and liabilities in the financial statements and the corresponding tax basis used in the computation of assessable tax profit. In principle, deferred tax liabilities are recognized for all taxable temporary differences, and deferred tax assets are recognized to the extent that it is probable that taxable profit will be available against which deductible temporary differences can be utilized.
Deferred tax is calculated using tax rates that are expected to apply to the period when the asset is realized or the liability is settled. Deferred tax is charged or credited in the income statement, except when it is related to items credited or charged directly to equity, in which case the deferred tax is also dealt with in equity.
-16-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are offset when they related to income taxes levied by the same taxation authority and the Company intends to settle its current tax assets and liabilities on a net basis.
Provision for income taxes consist of taxes currently due plus deferred taxes. Penalties and interest incurred related to underpayment of income tax are classified as income tax expense in the year incurred. No significant penalties or interest relating to income taxes have been incurred during the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009. GAAP also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification, interest and penalties, accounting in interim periods, disclosures and transition.
Value Added Tax
Enterprises or individuals, who sell products, engage in repair and maintenance or import and export goods in the PRC are subject to a VAT in accordance with Chinese laws. The VAT rate applicable to the Company is 6% of the gross sales price. Products distributed by Shandong Medical are subjected to a 17% VAT. No credit is available for VAT paid on purchases.
Stock-based Compensation
The Company accounts and reports stock-based compensation pursuant to FASB’s accounting standard related to accounting for stock-based compensation which defines a fair-value-based method of accounting for stock based employee compensation and transactions in which an entity issues its equity instruments to acquire goods and services from non-employees. Stock compensation for stock granted to non-employees has been determined in accordance with this standard as the fair value of the consideration received or the fair value of equity instruments issued, whichever is more reliably measured.
Noncontrolling Interest
Effective January 1, 2009, the Company adopted FASB’s accounting standard regarding non-controlling interest in consolidated financial statements. Certain provisions of this statement are required to be adopted retrospectively for all periods presented. Such provisions include a requirement that the carrying value of noncontrolling interests (previously referred to as minority interests) be removed from the mezzanine section of the balance sheet and reclassified as equity.
-17-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Further, as a result of adoption this accounting standard, net income attributable to noncontrolling interests is now excluded from the determination of consolidated net income.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In December 2009, FASB issued ASU No. 2009-16, Accounting for Transfers of Financial Assets. This Accounting Standards Update amends the FASB Accounting Standards Codification for the issuance of FASB Statement No. 166, Accounting for Transfers of Financial Assets—an amendment of FASB Statement No. 140.The amendments in this Accounting Standards Update improve financial reporting by eliminating the exceptions for qualifying special-purpose entities from the consolidation guidance and the exception that permitted sale accounting for certain mortgage securitizations when a transferor has not surrendered control over the transferred financial assets. In addition, the amendments require enhanced disclosures about the risks that a transferor continues to be exposed to because of its continuing involvement in transferred financial assets. Comparability and consistency in accounting for transferred financial assets will also be improved through clarifications of the requirements for isolation and limitations on portions of financial assets that are eligible for sale accounting. The effective date of this amended pronouncement was as of the beginning of a reporting entity’s first annual reporting period that begins after November 15, 2009, for interim periods within that first annual reporting period, and for interim and annual reporting periods thereafter. The Company adopted this standard and the adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In December 2009, FASB issued ASU No. 2009-17, Improvements to Financial Reporting by Enterprises Involved with Variable Interest Entities. This Accounting Standards Update amends the FASB Accounting Standards Codification for the issuance of FASB Statement No. 167, Amendments to FASB Interpretation No. 46(R). The amendments in this Accounting Standards Update replace the quantitative-based risks and rewards calculation for determining which reporting entity, if any, has a controlling financial interest in a variable interest entity with an approach focused on identifying which reporting entity has the power to direct the activities of a variable interest entity that most significantly impact the entity’s economic performance and (1) the obligation to absorb losses of the entity or (2) the right to receive benefits from the entity. An approach that is expected to be primarily qualitative will be more effective for identifying which reporting entity has a controlling financial interest in a variable interest entity. The amendments in this Update also require additional disclosures about a reporting entity’s involvement in variable interest entities, which will enhance the information provided to users of financial statements. The effective date of this amended pronouncement was as of the beginning of a reporting entity’s first annual reporting period that begins after November 15, 2009, for interim periods within that first annual reporting period. The Company adopted this standard and the adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
-18-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
In January 2010, FASB issued ASU No. 2010-01- Accounting for Distributions to Shareholders with Components of Stock and Cash. The amendments in this Update clarify that the stock portion of a distribution to shareholders that allows them to elect to receive cash or stock with a potential limitation on the total amount of cash that all shareholders can elect to receive in the aggregate is considered a share issuance that is reflected in EPS prospectively and is not a stock dividend for purposes of applying Topics 505 and 260 (Equity and Earnings Per Share). The amendments in this update are effective for interim and annual periods ending on or after December 15, 2009, and should be applied on a retrospective basis. The Company adopted this standard and the adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In January 2010, FASB issued ASU No. 2010-02 – Accounting and Reporting for Decreases in Ownership of a Subsidiary – a Scope Clarification. The amendments in this Update affect accounting and reporting by an entity that experiences a decrease in ownership in a subsidiary that is a business or nonprofit activity. The amendments also affect accounting and reporting by an entity that exchanges a group of assets that constitutes a business or nonprofit activity for an equity interest in another entity. The amendments in this update are effective beginning in the period that an entity adopts SFAS No. 160, “Non-controlling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements – An Amendment of ARB No. 51.” If an entity has previously adopted SFAS No. 160 as of the date the amendments in this update are included in the Accounting Standards Codification, the amendments in this update are effective beginning in the first interim or annual reporting period ending on or after December 15, 2009. The amendments in this update should be applied retrospectively to the first period that an entity adopted SFAS No. 160. The Company adopted this standard and the adoption of this standard did not have material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In January 2010, FASB issued ASU No. 2010-06 – Improving Disclosures about Fair Value Measurements. This update provides amendments to Subtopic 820-10 that requires new disclosure as follows: 1) Transfers in and out of Levels 1 and 2. A reporting entity should disclose separately the amounts of significant transfers in and out of Level 1 and Level 2 fair value measurements and describe the reasons for the transfers. 2) Activity in Level 3 fair value measurements. In the reconciliation for fair value measurements using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3), a reporting entity should present separately information about purchases, sales, issuances, and settlements (that is, on a gross basis rather than as one net number).This update provides amendments to Subtopic 820-10 that clarify existing disclosures as follows: 1) Level of disaggregation. A reporting entity should provide fair value measurement disclosures for each class of assets and liabilities. A class is often a subset of assets or liabilities within a line item in the statement of financial position. A reporting entity needs to use judgment in determining the appropriate classes of assets and liabilities. 2) Disclosures about inputs and valuation techniques. A reporting entity should provide disclosures about the valuation techniques and inputs used to measure fair value for both recurring and nonrecurring fair value measurements. Those disclosures are required for fair value measurements that fall in either Level 2 or Level 3.The new disclosures and clarifications of existing disclosures are effective for interim and annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2009, except for the disclosures about purchases, sales, issuances, and settlements in the roll forward of activity in Level 3 fair value measurements. Those disclosures are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2010, and for interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this ASU, however, the Company does not expect the adoption of this ASU to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
-19-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
In February 2010, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update 2010-09, “Subsequent Events (Topic 855): Amendments to Certain Recognition and Disclosure Requirements,” or ASU 2010-09. ASU 2010-09 primarily rescinds the requirement that, for listed companies, financial statements clearly disclose the date through which subsequent events have been evaluated. Subsequent events must still be evaluated through the date of financial statement issuance; however, the disclosure requirement has been removed to avoid conflicts with other SEC guidelines. ASU 2010-09 was effective immediately upon issuance and was adopted in February 2010.
Reclassifications
Certain prior period amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current period presentation. These reclassifications have no effect on net income or cash flows.
Note 4 – Related party transactions
The material related party transactions undertaken by the Company with related parties as of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009 are presented as follows:
| March 31, 2010 | December 31, | ||||||||
| Assets | Purpose | (unaudited) | 2009 | ||||||
| Accounts receivable – related party(1) | Processing fees | $ | 270,086 | $ | 222,617 | ||||
| March 31, 2010 | December 31, | ||||||||
| Liabilities | Purpose | (unaudited) | 2009 | ||||||
| Short term loans – holder of noncontrolling interest(2) | Loan | $ | 3,652,500 | $ | 3,652,500 | ||||
| Accrued interest – holder of noncontrolling interest(2) | Interest payable | $ | 1,154,687 | $ | 2,068,526 | ||||
| Other payable – related parties(3) | Loan | $ | 2,122,772 | $ | 2,122,772 | ||||
| Other payable – related parties(4) | Contribution | 964,168 | 964,168 | ||||||
| Distribution payable - holder of noncontrolling interest | Distribution | 587 | 587 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 3,087,527 | $ | 3,087,527 |
(1) Qianfeng provides processing services for Guizhou Eakan, one of the Qianfeng’s non-controlling shareholders. The total processing services income amounted to $237,031 and $242,729 for the three months period ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively. As of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, Guizhou Eakan owes Qianfeng processing fees in an amount of $270,086 and $222,617, respectively. The outstanding balance as of March 31, 2010 has been paid in cash at the beginning of April 2010.
-20-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
(2) On April 6, 2009, Logic Express entered into an
equity transfer and entrustment agreement, or Entrustment Agreement, among Logic
Express, Shandong Taibang, and the Shandong Institute of Biological Products, or
the Shandong Institute, the holder of the noncontrolling interests in Shandong
Taibang, pursuant to which, Logic Express agreed to permit Shandong Taibang and
the Shandong Institute to participate in the indirect purchase of Qianfeng's
equity interests. Under the terms of the Entrustment Agreement, Shandong
Institute agreed to contribute 12.86% or $3,652,500 (RMB 25,000,000) of the
Dalin purchase price. Logic express is obligated to repay to the Shandong
Institute their investment amount on or before April 6th, 2010, along with their
pro rata share, based on their percentage of the Dalin purchase price
contributed, of any distribution on the indirect equity investment in Qianfeng
payable to Logic Express during 2009. As of March 31, 2010, the Company was able
to settle the interest liability with Shandong Institute for $1,154,687
therefore recognizing an other income of $913,839. On April 12, 2010, the
Company fully paid the Shandong Institute and Shandong Taibang on the respective
investment amounts, as well as the interest, according the Entrustment
Agreement. The interest paid to the Shandong Institute is approximately
$1,154,687.
(3) Qianfeng has payables to Guizhou Eakan Investing Corp. in the amount of approximately $2,122,772 (RMB14, 470,160). Guizhou Eakan Investing Corp. is one of the shareholders of Guizhou Eakan, one of the Qianfeng’s minority shareholders. The Company borrowed this non-interest bearing amount for working capital purposes. The balance is due on demand in the form of cash.
(4) Qianfeng has payables to Guizhou Jie’an, a holder of noncontrolling interest, in amount of approximately $964,168 (RMB 6,569,840). In 2007, Qianfeng received additional contributions from Guizhou Jie’an in the amount of $962,853 to maintain Jie’an ownership interest in the Company at 9%. However, due to legal dispute among Shareholders over Raising Additional Capital as stated in legal proceeding section, commitment and contingent liabilities, the money may be returned to Jie’an.
| Note 5 – Accounts receivable | ||||||
| Trade accounts receivable consist of the following: | ||||||
| March 31, 2010 | December 31, 2009 | |||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||
| Trade accounts receivable | $ | 5,019,752 | $ | 3,022,031 | ||
| Less: Allowance for doubtful accounts | (1,255,629 | ) | (1,254,955 | ) | ||
| Total | $ | 3,764,123 | $ | 1,767,076 |
-21-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
The activity in the allowance for doubtful accounts for trade accounts receivable for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and the year ended December 31, 2009 is as follows:
| March 31, 2010 | December 31, 2009 | |||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||
| Beginning allowance for doubtful accounts | $ | 1,254,955 | $ | 1,268,052 | ||
| Additional charged to bad debt expense | 2,883 | 18,737 | ||||
| Recovery of amount previously reserved | (2,210 | ) | (31,826 | ) | ||
| Write-off charged against the allowance | - | - | ||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | 1 | (8 | ) | |||
| Ending allowance for doubtful accounts | $ | 1,255,629 | $ | 1,254,955 | ||
| Note 6 – Inventories | ||||||
| Inventories consisted of the following: | ||||||
| March 31, 2010 | December 31, 2009 | |||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||
| Raw materials | $ | 21,671,903 | $ | 19,720,420 | ||
| Work-in-process | 8,938,701 | 8,407,319 | ||||
| Finished goods | 9,282,761 | 7,524,318 | ||||
| Total | 39,893,365 | 35,652,057 | ||||
| Less: Allowance for obsolete inventories | (717,960 | ) | (519,333 | ) | ||
| Inventories, net | $ | 39,175,405 | $ | 35,132,724 |
Note 7 – Other receivables, prepayments and deferred expense
Other receivables represent deposits the Company paid to suppliers or service providers, as well as receivables from employees amounting to $2,177,594 and $2,186,441 as of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively. In 2009, the Shandong Taibang sponsored two separate housing projects with local developers to assist 107 of its employees to purchase houses to be constructed. Developers required deposits of at least 80% of the total purchase price before the commencement of the project. Employees are required to deposit at least 30% and up to 80% of the total purchase prices and Shandong Taibang advanced $1,512,583 in total, which represents the difference between the required deposits by the developer and the actual deposits made by the employees, on behalf of the employees to the developer. The advances to the employees are expected to be re-paid within one year.
Prepayments and deferred expense represent partial payments for deposits on material purchases, prepaid leases and prepayment for insurance expenses and amounted to $1,672,261 and $1,299,125 as of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively.
Long term prepayments represent partial payments or deposits on plant and equipment and intangible assets purchases and amounted to $3,362,943 and $3,223,960 as of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively.
-22-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Note 8 – Plant and equipment, net
Plant and equipment consist of the following:
| March 31, 2010 | December 31, 2009 | |||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||
| Buildings and improvements | $ | 14,593,694 | $ | 12,901,205 | ||
| Machinery and equipment | 23,957,008 | 23,428,848 | ||||
| Furniture, fixtures, office equipment and vehicle | 4,000,773 | 3,862,385 | ||||
| Total depreciable assets | 42,551,475 | 40,192,438 | ||||
| Accumulated depreciation | (14,747,707 | ) | (13,953,793 | ) | ||
| Plant and equipment, net | 27,803,768 | 26,238,645 | ||||
| Construction in progress | 4,063,922 | 2,634,768 | ||||
| Total | $ | 31,867,690 | $ | 28,873,413 |
Depreciation expense for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009 amounted to $793,657 and $759,072, respectively. No interest was capitalized into construction in progress in the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009. Construction in progress summary as below:
| CIP balance as of | ||||||||||
| March 31, 2010 | Expected date of | Estimated additional | ||||||||
| Projects | (unaudited) | completion | cost to input | |||||||
| Danzhan Plasma Co. | $ | 599,094 | June 2010 | $ | 203,089 | |||||
| Huangping Plasma Co. | 850,448 | June 2010 | 221,890 | |||||||
| Puding Plasma Co. | 521,748 | June 2010 | 72 | |||||||
| Nayong Plasma Co. | 590,403 | June 2010 | 436,556 | |||||||
| Weining Plasma Co. | 703,288 | June 2010 | 31,425 | |||||||
| Qiangfeng | 8,069 | June 2010 | 254,821 | |||||||
| Taibang | 790,872 | June 2010 | 427,427 | |||||||
| Total | $ | 4,063,922 | $ | 1,575,280 |
Note 9 – Investment in unconsolidated affiliate
On October 10, 2008, Shandong Taibang entered into an Equity Transfer Agreement (the "Huitian Agreement") with Mr. Fan Qingchun (the "Transferor"), a PRC citizen holding 35% of the equity interest in Huitian, a PRC limited liability company. Pursuant to the Huitian Agreement, the Transferor agrees to sell to Shandong Taibang, and Shandong Taibang agrees to purchase from the Transferor, 35% equity interest in Huitian for an aggregate purchase price of $6,502,901 (or RMB 44,327,890) including interest of $48,101 (RMB 327,890).
-23-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Logic Express also entered into an investment entrustment agreement (the "Investment Agreement") with the minority shareholder in Shandong Taibang, Shandong Institute, pursuant to which Logic Express agrees to provide the investment amount for the acquisition and the Shandong Institute agree to entrust Shandong Taibang to acquire the 35% equity interest of Huitian in its name. In exchange Logic Express is also obligated to pay Shandong Taibang approximately $17,604 (or RMB120,000) per year as consideration for Shandong Taibang's performance under this agreement. Under the Investment Agreement, after the acquisition, Logic Express will be in charge of Huitian's daily operation and management, will bear the costs, expenses, liabilities and losses incurred in its operation, and will enjoy its profits. Shandong Taibang will perform relevant tasks according to Logic Express's instruction, and will not exercise any management right over Huitian or derive any financial return from Huitian. Logic Express agreed to indemnify Shandong Taibang for any loss in connection with the investment and pledged its equity interest in Shandong Taibang as collateral against such losses.
Summarized unaudited financial information of Huitian is as follows:
| March 31, 2010 | December 31, 2009 | |||||
| Current assets | $ | 7,612,869 | $ | 9,912,775 | ||
| Non-current assets | 9,964,191 | 10,195,357 | ||||
| Total assets | $ | 17,577,060 | $ | 20,108,132 | ||
| Current liabilities | 983,021 | 4,031,033 | ||||
| Non-current liabilities | 308,070 | 308,070 | ||||
| Shareholders' equity | 16,285,969 | 15,769,029 | ||||
| Total liabilities and shareholders' equity | $ | 17,577,060 | $ | 20,108,132 |
The portion of the difference between the cost of an investment and the amount of underlying equity in net assets of Huitian that is recognized as goodwill shall not be amortized, but instead should continue to be reviewed for impairment in accordance with FASB’s accounting standard.
| Summarized unaudited financial information of Huitian is as follows: | ||||||
| Three months ended | Three months ended | |||||
| March 31, 2010 | March 31, 2009 | |||||
| Net sales | $ | 2,402,751 | $ | 1,159,285 | ||
| Gross profit | $ | 1,335,319 | $ | 389,530 | ||
| Income before taxes | $ | 647,420 | $ | 135,281 | ||
| Net income | $ | 538,689 | $ | 114,989 | ||
| Company’s share of net income | $ | 188,541 | $ | 40,247 | ||
The roll forward of investment in Huitian in the balance sheet is shown below:
-24-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
| Huitian - 35% | |||
| Ownership | |||
| December 31, 2008 | $ | - | |
| Investment made | 6,533,977 | ||
| Net income from 2009 | 566,984 | ||
| Dividend declared | (473,952 | ) | |
| Foreign currency translation gain | 346 | ||
| December 31, 2009 | 6,627,355 | ||
| Net income from the three months ended March 31, 2010 | 188,541 | ||
| Dividend declared | - | ||
| Foreign currency translation gain | 65 | ||
| March 31, 2010 (unaudited) | $ | 6,815,961 |
Note 10 – Intangible assets, net
Intangible assets consisted of the following:
| March 31, 2010 | December 31, 2009 | |||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||
| Land use rights | $ | 4,184,039 | $ | 4,163,140 | ||
| Permits and licenses | 11,261,611 | 11,261,611 | ||||
| Blood donor network | 2,347 | 2,347 | ||||
| Software | 149,492 | 145,897 | ||||
| GMP certificate | 2,327,885 | 2,327,885 | ||||
| Long-term customer-relationship | 6,941,170 | 6,941,170 | ||||
| Totals | 24,886,544 | 24,842,050 | ||||
| Accumulated amortization | (4,531,249 | ) | (3,661,728 | ) | ||
| Intangible assets, net | $ | 20,335,295 | $ | 21,180,322 |
Total amortization expense for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009 amounted to $869,251 and $838,459 respectively.
The amortization expense related to purchased and other intangible assets due to the consolidation of Dalin is $793,386 and $792,629 for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
Amortization expense for intangible assets for the next five fiscal years is as follows:
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | Thereafter | |||||||||||||
| Amortization expense | $ | 3,353,442 | $ | 3,346,893 | $ | 1,583,503 | $ | 1,485,798 | $ | 1,164,382 | $ | 9,401,277 |
-25-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
| Note 11 – Debt | ||||||||||||
| Short term loans and current maturities of long term loan | ||||||||||||
| Short term loans represent renewable loans due to various banks which are normally due within one year. | ||||||||||||
| The Company’s bank loans consisted of the following: | ||||||||||||
| Loans | Due by | Annual interest rates |
March 31, 2010 (Unaudited) |
December 31, 2009 |
||||||||
| Short term loans: | ||||||||||||
| Short term bank loan, secured(1) | June 1, 2010 | 5.40% | $ |
1,467,000 |
$ | 1,467,000 | ||||||
| Short term bank loan, un-secured | January 7, 2010 | 5.31% | 2,934,000 | 2,934,000 | ||||||||
| Short term loan, un-secured | On demand | 0.00% | 73,350 | 73,350 | ||||||||
| Short term bank loan, secured(2) | March 22, 2010 | 5.84% | 2,934,000 | - | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 7,408,350 | $ | 4,474,350 | ||||||||
Interest expense related to the bank loans totaling $62,286 and $622,449 were incurred during the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
(1) The loan in the amount of $1,467,000 is secured by Shandong Taibang’s land use rights and buildings located in Taian, Shandong Province, PRC with the carrying net value as follows:
| March 31, 2010 | December 31, 2009 | |||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||
| Buildings in Taian, Shandong | $ | 1,238,010 | $ | 1,238,010 | ||
| Land use rights in Taian, Shandong | 433,793 | 433,793 | ||||
| Total | $ | 1,671,803 | $ | 1,671,803 |
(2) The loan in the amount of $2,934,000 is secured by Qianfeng’s buildings located in Guiyang, Guizhou Province, PRC, with carrying net values of RMB 28,933,927 as of March 31, 2010.
Other payables and accruals
Other payables and accruals consist of the following:
-26-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
| March 31, 2010 | December 31, 2009 | |||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||
| Other payables (1) | $ | 8,722,680 | $ | 7,465,640 | ||
| Accruals for promotion costs and others (2) | 3,502,207 | 5,281,843 | ||||
| Accruals for salaries and welfare | 1,552,363 | 2,341,874 | ||||
| Accruals for RTO expenses | 245,657 | 245,657 | ||||
| Accruals for selling commission and promotion fee | 749,451 | 691,858 | ||||
| Other Payable - government grant | 95,077 | 143,488 | ||||
| Other payable - deposit received | 336,348 | 160,683 | ||||
| Other payable - funds | 1,627,475 | 2,383,501 | ||||
| Accrued interest | - | 81,264 | ||||
| Others(3) | 451,006 | 451,006 | ||||
| Total | $ | 17,282,264 | $ | 19,246,814 |
| (1) |
The other payables mainly comprise of deposits by potential strategic investors with the amount of $7,465,640. As of March 31, 2010, Qianfeng has received in an aggregate amount of $7,465,640 from potential private strategic investors in connection with subscribing shares from Qianfeng pursuant to Equity Purchase Agreement. The registration of the new investors as Qianfeng’s shareholders and the related increase in registered capital of Qianfeng with the Administration for Industry and Commerce (“AIC”) is incomplete due to share holders dispute as disclosed in below legal proceedings section below (Note 14). Additional interest of $1.2millions was accrued for the year from 2007 to current quarter based on average market interest rate around 5.9%. |
| (2) |
Accruals for promotions and others mainly represent the payables for donors promoting expenses, accrual for audit fee, payables to employees and payables to vendors or subcontractors for construction in plasma stations in Qianfeng. |
| (3) |
Others mainly comprise of the contingent liability due to the pending, outcome of the preceding of Qianfeng’s Guarantee to a Third Party as disclosed in below legal proceedings section below, Qianfeng provisioned a loss contingency reserve during its third quarter of 2009 for approximately $451,006 (RMB 3,074,342) to cover its share of the enforcement of this judgment. |
Other payable - land use rights
In July 2003, Shandong Taibang obtained certain land use rights from the Tai’an municipal government. Shandong Taibang is required to make payments totaling approximately $20,369 (RMB 138,848) per year to the local state-owned entity, for the 50-year life of the rights or until Biological Institute completes its privatization process. The Company recorded “land use rights” equal to “other payable – land use rights” totaling $ 323,390 and $323,687 as of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively, determined using present value of annual payments over 50 years.
-27-
| CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND
SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS March 31, 2010 (Unaudited) | ||||||
| Note 12 – Convertible Notes | ||||||
| March 31, 2010 | December 31, | |||||
| (unaudited) | 2009 | |||||
| $9,554,140, 3.8% Senior Secured Convertible Notes, due June 5, 2011 | $ | 9,554,140 | $ | 9,554,140 | ||
| Less: converted | (2,054,140 | ) | (1,000,000 | ) | ||
| Total convertible notes outstanding | 7,500,000 | 8,554,140 | ||||
| Less: unamortized discount | (7,325,349 | ) | (8,464,380 | ) | ||
| Notes payables, net | $ | 174,651 | $ | 89,760 | ||
On June 5, 2009, the Company entered into a securities purchase agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with certain accredited investors (collectively, the “Investors”), pursuant to which the Company agreed to issue to the Investors, 3.8% Senior Secured Convertible Notes in the aggregate principal amount of $9,554,140 (the “Notes”) and warrants (the “Warrants” and together with the Notes, the “Subscribed Securities”) to purchase up to 1,194,268 shares of common stock of the Company (the “Warrant Shares” and together with the Conversion Shares, the “Underlying Securities”). The transaction closed on June 10, 2009. Other than with respect to this transaction, none of the Investors have had a material relationship with the Company or any of the Company’s officers, directors or affiliates or any associate of any such officer or director.
The Notes accrue interest at 3.8% per annum (the “Interest Rate”), from the closing until repayment, whether on maturity on June 5, 2011, by acceleration or otherwise. Interest on the Notes is due and payable in cash semi-annually on September 30 and March 31 of each year, commencing September 30, 2009, but the Company has the option to pay the interest due through the issuance of its common stock at a conversion price of $4.00 per share. If the Company defaults in the payment of the principal of or interest on the Notes when due, then upon the Investors’ election, the Company is obligated to either (a) redeem all or a portion of the Notes pursuant to the redemption rights discussed below or (b) pay interest on such defaulted amount at a rate equal to the Interest Rate plus 2.0%. The Notes are convertible at any time before maturity into shares of our common stock at a conversion price of $4.00 per share, subject to certain adjustments as specified in the Notes.
The Company’s obligations under the Notes are secured by the pledge by Siu Ling Chan, our board chair and a principal shareholder, of 3,000,000 shares of common stock held by her, pursuant to the terms of a Guarantee and Pledge Agreement among the Company, the investors and Ms. Chan. To induce Ms. Chan to enter into the Guarantee and Pledge Agreement with the Investors, the Company has agreed to indemnify her for all damages, liabilities, losses and expenses of any kind (“losses”), which may be sustained or suffered by her, arising out of or in connection with any enforcement action instituted by the Investors pursuant to the Guarantee and Pledge Agreement. The Company’s indemnification obligation is limited to losses that arise as the result of any negligent or unlawful conduct of the Company that is caused unilaterally by the Company and is beyond Ms. Chan’s control in her capacity as a director of the Company, and will not exceed the fair market value of the pledged shares as of the closing of the transaction.
-28-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
The Warrants have a term of 3 years, an exercise price of $4.80 per share, subject to adjustments as provided in the Warrants, from time to time pursuant to anti-dilution and other customary provisions, and are exercisable by the Investors at any time after the date on which their related Notes are converted, except that if any of the Notes is converted in part, the Investors may only exercise a corresponding portion of the related Warrant.
The Company has granted the Investors demand and piggy-back registration rights with respect to the Underlying Securities, pursuant to a registration rights agreement among the Company and the Investors.
The Company paid its placement agent a cash fee of 6.1% of the proceeds received in connection with the issuance of the Notes and also issued to the placement agent a 3-year warrant to purchase 93,750 shares of the Company’s common stock at an exercise price of $6.00 per share, expiring after 3 years. The aggregate $870,417 fees paid to the placement agent, including the fair value of the warrant issued to them was deferred and is being amortized over the life of the Notes.
On December 22, 2009, two of the Company’s Note holders exercised their rights to convert $1,000,000 of their Notes into an aggregate of 250,000 shares of the Company’s common stock. On January 13, 2010, two Note holders continued to exercise their rights to convert $1,054,140 of their remaining Notes into an aggregate of 263,535 shares of the Company’s common stock. The fair value market of conversion options of $2,627,558, carrying value of $14,428 and accrued interest of $8,550 were included in additional paid-in-capital upon conversion of the convertible notes. As a result, Notes in the principal amount of $7,500,000 is outstanding as of March 31, 2010.
Note 13 - Earnings (loss) per share (Restated)
Basic earnings/(loss) per share is computed by dividing net income by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings/(loss) per share is calculated by dividing net income by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding and dilutive potential common shares outstanding during the period.
| Earnings (loss) per share is as follows for the three months ended March 31, | ||||||
| Basic earnings per share | ||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||
| Net income attributable to controlling interest for basic earnings per share | $ | 10,663,749 | $ | 4,308,796 | ||
| Weighted average shares used in basic computation | 23,386,893 | 21,434,942 | ||||
| Earnings per share - Basic | $ | 0.46 | $ | 0.20 |
-29-
| CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND
SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS March 31, 2010 (Unaudited) | ||||||
| Diluted earnings per share | ||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||
| Net income attributable to controlling interest for basic earnings per share | $ | 10,663,749 | $ | 4,308,796 | ||
| Add: interest of convertible notes | 172,121 |
- |
||||
| Subtract: Gain from changes in Fair value of derivative liabilities and warrants | (3,833,576 | ) | - | |||
| Net income attributable to controlling interest for diluted earnings per share | $ | 7,002,294 | $ | 4,308,796 | ||
| Weighted average shares used in basic computation | 23,386,893 | 21,434,942 | ||||
| Diluted effect of convertible debentures, warrants and options | 3,084,532 | - | ||||
| Weighted average shares used in diluted computation | 26,471,425 | 21,434,942 | ||||
| Earnings per share - Diluted | $ | 0.26 | $ | 0.20 | ||
For the three months ended March 31, 2010, 50,000 shares of stock option were excluded from the calculation because of anti-diluted nature. All other warrants, stock options and conversion options were included in the calculation of diluted earnings per share because of their dilutive nature.
For the three months ended March 31, 2009, all outstanding warrants and options were excluded in the calculation of diluted earnings per share because of their anti-dilutive nature.
Note 14 – Taxes (Restated)
Income taxes
Starting from January 1, 2008, all of the Company’s Chinese subsidiaries, except plasma companies, became subject to 25% income tax rate according to the newly issued Income Tax Laws of PRC. According to PRC’s central government policy, certain new technology or high technology companies will enjoy preferential tax treatment of 15%, instead of 25%.
On February 12, 2009, Shandong Taibang received the new technology or high technology certification from Shandong provincial government. The Certification allows the Company to receive the 15% preferential income tax rate, for a period of three years starting from January 1, 2008.
Qianfeng is currently enjoying the preferential income tax rate of 15% also under the 10-year Western Development Tax Concession, which started on January 2001 and ends on December 2010. The PRC tax authority is studying the possibility of extending the concession, especially for those industries that encouraged by the PRC government, such as ours. In the event that PRC tax authorities discontinue the concession, Qianfeng will apply for the new or high technology preferential tax treatment of 15% like Shandong Taibang.
-30-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
All of the Company plasma companies are qualified as small scale taxpayers and are subject to a tax rate of 6% in 2010.
Starting from January 1, 2008, all dividends paid to foreign parents are subject to a 10% income tax. As a result, Logic Holdings recorded $0 and $218,238 income tax expense for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively, for dividends Dalin paid to its foreign parent, Logic Holdings. Logic Express recorded $582,763 and $218,089 income tax expense during the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively, for dividends Taibang distributed to its foreign parent, Logic Express.
The following table reconciles the U.S. statutory rates to the Company’s effective tax rate for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009:
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||
| U.S. Statutory rates | 34.0% | 34.0% | ||||
| Foreign Income | (34.0 | ) | (34.0 | ) | ||
| China Tax rates | 25.0 | 25.0 | ||||
| China income tax exemption | (10.0 | ) | (10.0 | ) | ||
| Temporary differences (China) (1) | 0.8 | (1.4 | ) | |||
| Other items (2) | 1.4 | 6.9 | ||||
| Effective income tax rates | 17.2% | 20.5% |
(1) The 0.8% represents the effect of realization of temporary difference of $143,771 for the three months ended March 31, 2010. The -1.4% represents the effect of realization of temporary difference of -$124,799 for the three months ended March 31, 2010.
(2) The other items represent $0.6 million of income tax expense for dividends that Shandong Taibang distributed to Logic Express, its foreign parent and $3.1 million of expense incurred by CBP, Logic Express and Logic Holding that are not deductible in PRC offset by $3.8 million gains (not taxable) from fair value changes of derivative liabilities for the three months ended March 31, 2010. The 6.9% represents the $0.2 million income tax expense for dividends Shandong Taibang paid to Logic Express, its foreign parent and $1.3 million expenses incurred by CBP, Logic Express and Logic Holding that are not deductible in PRC for the three months ended March 31, 2009.
The estimated tax savings due to the tax exemption for the three months ending March 31, 2010 and 2009 amounted to $1,742,291 and $763,331, respectively. The net effect on earnings per share if the income tax had been applied would decrease basic earnings per share for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009 by $0.07 and $0.04, respectively. The net effect on earnings per share if the income tax had been applied would decrease diluted earnings per share for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009 by $0.07 and $0.01, respectively.
The provision for income taxes consists of the following for the unaudited three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009:
-31-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||
| Current | ||||||
| U.S. | $ | - | $ | - | ||
| Foreign (China) | 2,927,376 | 2,030,194 | ||||
| Total current | 2,927,376 | 2,030,194 | ||||
| Deferred | ||||||
| U.S. | - | - | ||||
| Foreign (China) | 143,771 | (124,799 | ) | |||
| Total deferred | 143,771 | (124,799 | ) | |||
| Provision for income taxes | $ | 3,071,147 | $ | 1,905,395 |
Deferred taxes
In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, the Company considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the future operation during the periods in which those temporary differences are utilized. Based upon an assessment of the historical operations and factors, the Company believes that it will be able to realize the deferred tax assets.
As of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, significant temporary differences between the tax basis and financial statement basis of accounting for assets and liabilities that gave rise to deferred taxes were principally related to the following:
| March 31, 2010 | December 31, 2009 | |||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||
| Deferred tax assets arising from: | ||||||
| -Accrued expenses | $ | 785,081 | $ | 1,053,771 | ||
| -Tax loss carryforwards | 1,707,840 | 1,618,630 | ||||
| Gross deferred tax assets | 2,492,921 | 2,672,401 | ||||
| Less: valuation allowance | (1,707,840 | ) | (1,618,630 | ) | ||
| Net deferred tax assets | $ | 785,081 | $ | 1,053,771 | ||
| Deferred tax liabilities arising from: | ||||||
| - Intangible assets | 3,702,044 | 3,821,093 | ||||
| - Property, plant and equipment | 448,289 | 454,202 | ||||
| Deferred tax liabilities | $ | 4,150,333 | $ | 4,275,295 | ||
| Classification on consolidated balance sheets: | ||||||
| Deferred tax assets - current | $ | 785,081 | $ | 1,053,771 | ||
| Deferred tax liabilities - non-current | $ | 4,150,333 | $ | 4,275,295 |
-32-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
CBP was incorporated in the United States and has incurred net operating losses for income tax purposes for the three months ended March 31, 2010. The estimated net operating loss carry forwards for United States income taxes amounted to $5,023,058 and $4,760,677 as of as of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively, which may be available to reduce future years’ taxable income. These carry forwards will expire, if not utilized, from 2026 through 2029. Management believes that the realization of the benefits from these losses appears uncertain due to the Company’s limited operating history and continuing losses for United States income tax purposes. Accordingly, the Company has provided a 100% valuation allowance on the deferred tax asset benefit from CBP to reduce the asset to zero. Management reviews this valuation allowance periodically and makes adjustments as warranted. The following table represents the rollforward of the deferred tax valuation allowance:
| For the three months | For the year ended | |||||
| ended March 31, 2010 | December 31, 2009 | |||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||
| Balance of January 1, | $ | 1,618,630 | $ | 1,018,941 | ||
| Increase | 89,210 | 599,689 | ||||
| Balance as of December 31, | $ | 1,707,840 | $ | 1,618,630 |
The Company has cumulative undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries of approximately $58 million as of March 31, 2010, which is included in consolidated retained earnings and will continue to be indefinitely reinvested in international operations. Accordingly, no provision has been made for U.S. deferred taxes related to future repatriation of these earnings, nor is it practicable to estimate the amount of income taxes that would have to be provided if we concluded that such earnings will be remitted in the future.
Value added tax
VAT on sales amounted to $1,928,948 and $1,578,403 for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Sales are recorded net of VAT collected and paid as the Company acts as an agent for the government. VAT taxes are not impacted by the income tax holiday.
| Taxes payable consisted of the following: | ||||||
| March 31, 2010 | December 31, 2009 | |||||
|
(unaudited) |
||||||
| VAT tax payable | $ | 911,348 | $ | 1,110,216 | ||
| Income tax payable | 6,471,237 | 7,479,279 | ||||
| Other miscellaneous tax payable | 136,683 | 184,584 | ||||
| $ | 7,519,268 | $ | 8,774,079 |
-33-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Note 15 – Commitments and contingent liabilities
Capital and lease commitments
The Company’s 82.76% owned subsidiary, He Ze Plasma Company, entered into a lease agreement on January 13, 2005, with the Yun Cheng Lan Tian Transportation Company in Yun Cheng County, Shandong Province, to lease land use rights for a period of 10 years. The annual lease amount is approximately $1,751 (RMB 12,000) with no early termination penalty. The Company has the right of first refusal to renew the lease after the ten year lease term.
The Company’s 82.76% owned subsidiary, Qi He Plasma Company, entered into a lease agreement on April 26, 2007, with the Zhang Bo Shi Village in Qi He County, Shandong Province, to lease land use rights for a period of 50 years. The annual lease amount is approximately $4,566 (RMB 31,144) with no early termination penalty.
The Company’s 82.76% owned subsidiary, Zhang Qiu Plasma Company, leased land use right and the use of building and equipment for a period of 10 year from January 1, 2007 with annual lease payment of $43,977 (RMB300,000). The lease was terminated in March 2008. The Company entered into a lease agreement on April 1, 2008, with the Zhang Qiu Red Cross Blood Center, to lease land use rights and the use building and equipment for a period of 10 years. The annual lease payment is approximately $1,466 (RMB 10,000) with no early termination penalty.
The Company’s 48.6% indirectly owned subsidiary, Qianfeng, entered into a lease agreement on June 1, 2006 with a group of individuals in an area located next to its production facility, to lease and use the space for processing industrial waste for 10 years. The annual lease amount is approximately $1,530 (RMB 10,438).
The Company’s indirectly owned subsidiary, Huang Ping Plasma Company, entered into a lease with Huang Ping County Finance Department on April 28, 2007, Guizhou Province, to lease land use rights and use a building and equipment for a period of 3 years. The annual lease payment is approximately $10,261 (RMB 70,000).
The Company’s indirectly owned subsidiary, Wei Ning Plasma Company, entered into a lease with Wei Ning County Health Department, Guizhou Province on April 9, 2007, to lease land use rights and use building and equipment for a period of 3 years. The annual lease payment is approximately $11,727 (RMB 80,000).
The Company recognizes lease expense on a straight line basis over the term of the lease in accordance to FASB’s accounting standard related to leases. Total contractual commitments for construction in progress and operating lease commitments outstanding as of March 31, 2010:
-34-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | Thereafter | |||||||||||||
| Commitments for construction projects | $ | 1,575,280 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||
| Operating Lease | 224,825 | 250,839 | 198,740 | 9,327 | 8,951 | 192,518 | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 1,800,105 | $ | 250,839 | $ | 198,740 | $ | 9,327 | $ | 8,951 | $ | 192,518 | ||||||
| For the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, total rent expense amounted to $20,348 and $33,134, respectively. | ||||||||||||||||||
Legal proceedings
Bobai County Collection
Station
In January 2007, the Company's PRC subsidiary, Shandong Taibang, advanced $413,697 (RMB3.0 million) to Feng Lin, the 20% minority shareholder in Fang Cheng Plasma Company, the Company's majority owned subsidiary, for the purpose of establishing or acquiring a plasma collection station. Mr. Lin and Shandong Taibang intended to establish the Bobai Kangan Plasma Collection Co., Ltd. (“Bobai”) in Bobai County, Guangxi and on January 18, 2007, Shandong Taibang signed a letter of intent to acquire the assets of the Bobai Plasma Collection Station, which was co-owned by Mr. Lin and Mr. Keliang Huang. However, in January 2007, Hua Lan Biological Engineering Co., Ltd. (“Hua Lan”) filed suit in the District Court of Hong Qi District, Xin Xiang City, Henan Province, alleging that Feng Lin, Keliang Huang and Shandong Taibang established and/or sought to operate the Bobai Plasma Collection Station using a permit for collecting and supplying human plasma in Bobai County, that was originally granted to Hua Lan by the government of the Guangxi region, without Hua Lan's permission. The establishment and registration of Bobai was never realized as a result of this law suit. On January 29, 2007, on Hua Lan's motion, the District Court entered an order to freeze funds in the amount of approximately $386,100 (RMB3,000,000) held by the defendants in the case, including approximately $65,750 (RMB500,000) in funds held in Shandong Taibang's bank account in Tai'an City. A hearing was held on June 25, 2007 and judgment was entered against the defendants along with a $226,780 (RMB1,700,000) joint financial judgment. The Company appealed the District Court judgment to the Xinxiang City Intermediate Court. In November 2007, the Intermediate Court affirmed the judgment against the three defendants and increased the amount of the joint financial judgment to approximately $405,954 (RMB3,000,000).
In January 2008, Hua Lan enforced the judgment granted by the Intermediate Court to freeze the Company's bank accounts. Shandong Taibang has filed a separate action against Hua Lan before the Tai'an City District Court to seek recovery of any losses in connection with Hua Lan's claim and to request that the Tai'an City District Court preserve Hua Lan's property or freeze up to approximately $411,300 (RMB 3 million) of Hua Lan's assets to secure the return of such funds to the Company. The intermediate court in Tai'an City accepted the application on February 14, 2008 but the matter is still pending. Pending the outcome of the proceedings, Shandong Taibang increased its loss contingency reserve during its fourth quarter of 2007 from approximately $75,593 (RMB566,667) to $133,400 (RMB1,000,000) to cover its share of the enforcement of this judgment. During the fourth quarter of 2008, full amount of the judgment, including Feng Lin and Keliang Huang's portions of the judgment and the related fees, approximately $456,222 (RMB 3,109,900) has been withdrawn from Shandong Taibang's account. The Company recorded Feng Lin and Keliang Huang's portion of the judgment, approximately $304,143 (RMB2,073,234), as receivable as a result of the withdrawal. As of December 31, 2008, the Company determined that it is unlikely that the Company will be able to recover such receivable from those two individuals and wrote off the receivable as bad debt expense. In January 2010, Feng Lin transferred his 20% equity in Fang Cheng Plasma Company as a repayment to such receivable. As a result, the Company is now the 100% owner of the Fang Cheng Plasma Company.
-35-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
In October 2009, Shandong Taibang appealed to the High Court of Henan Province requesting the court to reverse judgments from the Hong Qi District Court based on Shandong Taibang's belief that Hua Lan’s involvement in Bobai was in violation of PRC Blood Products Regulations as Hua Lan did not invest, as Shandong Taibang did, in Bobai as required by the Regulation. The Company was awaiting the judgment of the Henan High Court as of the date of this report. In light of the foregoing, it is unlikely that the Company's planned acquisition of the assets of Bobai will go forward.
Dispute among Qianfeng Shareholders over Raising Additional Capital
On May 28, 2007, a 91% majority of Qianfeng's shareholders approved a plan to raise additional capital from private strategic investors through the issuance of an additional 20,000,000 shares of Qianfeng equity interests at RMB 2.80 per share. The plan required all existing Qianfeng shareholders to waive their rights of first refusal to subscribe for the additional shares. The remaining 9% minority holder of Qianfeng's shares, the Guizhou Jie'an Company, or Jie'an, did not support the plan and did not agree to waive its right of first refusal. On May 29, 2007, the majority shareholders caused Qianfeng to sign an Equity Purchase Agreement with certain investors, pursuant to which the investors agreed to invest an aggregate of RMB 50,960,000 (approximately $7,475,832) in exchange for 18,200,000 shares, or 21.4%, of Qianfeng's equity interests. At the same time, Jie'an also subscribed for 1,800,000 shares, representing its 9% pro rata share of the 20,000,000 shares being offered. The proceeds from all parties were received by Qianfeng in accordance with the agreement.
In June 2007, Jie'an brought suit in the High Court of Guizhou province, China, against Qianfeng and the three other original Qianfeng shareholders, alleging the illegality of the Equity Purchase Agreement. In its complaint, Jie'an alleged that it had a right to acquire the shares waived by the original Qianfeng shareholders and offered to the investors in connection with the Equity Purchase Agreement. On September 12, 2008, the Guizhou High Court ruled against Jie'an and sustained the Equity Purchase Agreement, but on November 2008, Jie'an appealed the Guizhou High Court judgment to the People's Supreme Court in Beijing. On May 13, 2009, the People's Supreme Court sustained the original ruling and denied the rights of first refusal of Jie'an over the additional shares waived by the original Qianfeng's shareholders. The registration of the new investors as Qianfeng's shareholders and the related increase in registered capital of Qianfeng with the Administration for Industry and Commerce are still pending. On January 27, 2010, the strategic investors brought suit in the High Court of Guizhou Province against Qianfeng alleging Qianfeng’s failure to register their equity interest in Qianfeng with the local AIC and requesting the distribution of their share of Qianfeng’s dividends. Dalin was also joined as a co-defendant as it is the majority shareholder and exercises control over Qianfeng’s day-to-day operations. The Company does not expect the strategic investors to prevail because, upon evaluation of the Equity Purchase Agreement, the Company believes that the Equity Purchase Agreement is void due to certain invalid pre-conditions and the absence of shareholder authorization of the initial investment. In the event that Qianfeng is required to return their original investment amount to the strategic investors, Qianfeng has set aside the strategic investors’ fund along with RMB 7,313,387 (approximately $1,072,216) in accrued interests, and RMB 519,600 (approximately $74,712) for the 1% penalty imposed by the agreement for any breach. If strategic investors prevail in their suit, Dalin's interests in Qianfeng may be reduced to approximately 41.3% . The High Court of Guizhou heard the case on April 8, 2010 and encouraged, and accepted by both parties, to settle the dispute outside the court. As of the date of this report, the Company is still negotiating with the strategic investors for a term that is acceptable to the Company.
-36-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Administration Interference
Qianfeng is party to an administrative proceeding against the government of the Qiandongnan Autonomous Region, or the Qiandongnan Authorities, in Guizhou Province, China, in connection with the ownership of three of Qianfeng's entitled eight plasma stations in Guizhou Province. Qianfeng was authorized to acquire a total of eight plasma stations in Guizhou Province based on several national and provincial administrative authorizations issued by the PRC State Council and the Guizhou Ministry of Health between 2006 and 2007, but to date, the governmental authorizations have not been fully implemented by the Qiandongnan Authorities. In early 2007, Qianfeng submitted RMB 8,010,000 (approximately $1,173,465) to the local finance department of Sansui County, Qiandongnan, for acquiring the Sansui Plasma Collection Station (“Sansui”), but the local finance department refused to honor the purchase and returned the full consideration to Qianfeng. Furthermore, subsequent local rulings published by the Qiandongnan Authorities February 28, 2008 appear to authorize another private company to acquire the Sansui and two other stations, the Zhengyuan Plasma Collection Station and the Shibing Plasma Collection Station. In December 2008 Qianfeng filed an administrative review application with the People's Government of Guizhou Province, or the Guizhou Provincial Government, but the Guizhou Provincial Government has delayed making a final decision pending further review of regulations regarding administrative authorizations. Qianfeng has received verbal notification from staff in the Guizhou Provincial Government that the Qiandongnan Authorities have withdrawn the local rulings. As a result, Qianfeng has withdrawn its application with the Guizhou Provincial Government to facilitate further negotiation with Qiandongnan Authorities on its right to acquire all eight plasma stations in Guizhou Province. In addition, Qianfeng has set aside the funds necessary to purchase Sansui pending the outcome of the administrative review. There have been no further developments on this case as of the date of this report.
-37-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
Qianfeng's Guarantee to a Third Party
In 2007, as a condition to purchase Huang Ping Plasma Station, Qianfeng entered into an agreement with Guizhou Zhongxin Investment Company (“Zhongxin”) in which Qianfeng agreed to repay Zhongxin's debt out of Qianfeng's payables to Zhongxin arising from plasma purchased from Zhongxin. In the same agreement, Qianfeng also guaranteed to the Huang Ping County Hospital (“Huang Ping Hospital”), which was the co-owner with Zhongxin of the Huang Ping Plasma Station, for the amount of RMB3,074,342 (approximately, $451,006) of debt that Zhongxin owed to Huang Ping Hospital. On June 1, 2009, Huang Ping Hospital brought suit, in Huang Ping County People's Court of Guizhou Province, against Zhongxin for non-payment of its payables and debt due to Huang Ping Hospital and Qianfeng as the guarantor. On November 2, 2009, the court ruled in favor of the plaintiff and Qianfeng will need to repay the Zhongxin’s debt to Huang Ping Hospital on behalf of Zhongxin as the guarantor. In October 2009, Qianfeng appealed to the Middle Court of Kaili District in Guizhou Province and was accepted by the court in January 2010. On April 8, 2010, the Middle Court of Kaili District ruled to sustain the original judgment. As a result, Qianfeng is in the process of filing suit against Zhongxin in the attempt to recover the RMB 3,074,342 debt that was under the guarantee. The Equity Transfer Agreement pursuant to which we acquired a 90% interest in Dalin, Qianfeng's majority shareholder, provides that the sellers will be responsible, in accordance with their equity proportion in Qianfeng, for damages incurred by Qianfeng from Zhongxin's debt and shall repay Dalin the sellers' proportionate share of payments made by Qianfeng to creditors in connection with Zhongxin's debt within 10 days after payment by Qianfeng. The RMB 3,074,342 contingent liability and proportionate share of the liability to be recovered from the sellers were properly reflected in the financials as of March 31, 2010.
Note 16 – Warrants and options
Warrants
On June 5, 2009, the Company entered into a securities purchase agreement with certain accredited investors pursuant to which the Company issued 3.8% Senior Secured Convertible Notes in the aggregate principal amount of $9,554,140 and Warrants to purchase up to 1,194,268 shares of common stock of the Company. The Warrants have a term of 3 years, an exercise price of $4.80 per share, as adjusted from time to time pursuant to anti-dilution and other customary provisions, and are exercisable by the Investors at any time after the date on which their related Notes are converted, except that if any of the Notes is converted in part, the Investors may only exercise a corresponding portion of the related Warrant. The Company also issued to the placement agents 93,750 Warrants to purchase common stock at an exercise price of $6.00 per share, expiring after 3 years. During the first quarter of 2010, 143,575 shares of the Investor’s Warrants and all of the placement agents Warrants were converted into the Company’s common stock and the related derivative liabilities amounted to $2,436,907 were transferred to additional paid-in capital accordingly.
-38-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
These common stock purchase warrants were not issued with the intent of effectively hedging any future cash flow, fair value of any asset, liability or any net investment in a foreign operation. The warrants do not qualify for hedge accounting, and as such, all future changes in the fair value of these warrants will be recognized currently in earnings until such time as the warrants are exercised or expire.
| The summary of warrant activity is as follows: | |||||||||
| Weighted | Average | ||||||||
| Warrants | Average | Remaining | |||||||
| Outstanding | Exercise Price | Contractual Life | |||||||
| December 31, 2008 | 1,284,000 | $ | 2.84 | 2.55 | |||||
| Granted | - | - | - | ||||||
| Forfeited | - | - | - | ||||||
| Exercised | - | - | - | ||||||
| March 31, 2009 (unaudited) | 1,284,000 | $ | 2.84 | 2.30 | |||||
| Granted | 1,288,018 | 4.89 | 2.44 | ||||||
| Forfeited | - | - |
- |
||||||
| Exercised | (1,284,000 | ) | 2.84 | 1.80 | |||||
| December 31, 2009 | 1,288,018 | $ | 4.89 | 2.44 | |||||
| Granted | - | - | - | ||||||
| Forfeited | - | - | - | ||||||
| Exercised | (237,325 | ) | 4.80 | 3.17 | |||||
| March 31, 2010 (unaudited) | 1,050,693 | $ | 4.80 | 2.20 | |||||
| Options |
On May 9, 2008, the Company adopted the 2008 Equity Incentive Plan, which provides up to 5,000,000 shares of Company’s Common Stock to be made available to employees and directors at various prices as established by the Board of Directors of the Company. On January 7, 2010, our board of directors granted to one of the employee options to purchase 50,000 shares of our common stock, with an exercise price of $12.60 and vested immediately with the expiration date of January 7, 2020, under the 2008 plan, in accordance with his employment agreement with the company. On February 4, 2010, the board of directors granted to a newly appointed director options to purchase 20,000 shares of our common stock, with an exercise price of $10.66; 10,000 shares of which will be vested on August 4, 2010 and the remaining 10,000 shares will be vested on February 4, 2011. As of March 31, 2010, there were 3,932,500 shares available under the plan.
The fair value of each option granted on May 9, 2008, July 24, 2008, January 7, 2010 and February 4, 2010 are estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
-39-
| CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND
SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS March 31, 2010 (Unaudited) | ||||||||||||
| May 9, | July 24, | January 7, | February 4, | |||||||||
| Granted on | 2008 | 2008 | 2010 | 2010 | ||||||||
| Expected dividend yield | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | ||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate | 3.56% | 3.56% | 2.62% | 2,29% | ||||||||
| Expected life (in years) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| Weighted average expected volatility | 59.4% | 81.2% | 130.0% | 130.0% | ||||||||
The volatility of the Company’s common stock was estimated by management based on the historical volatility of the Company’s common stock, the risk free interest rate was based on Treasury Constant Maturity Rates published by the U.S. Federal Reserve for periods applicable to the estimated life of the options, and the expected dividend yield was based on the Company’s current and expected dividend policy. The value of the options was based on the Company’s common stock price on the date the options were granted. Because the Company does not have a history of employee stock options, the Company utilized the simplified method to estimate the life of the options which is the same as assuming that the options are exercised at the mid-point between the vesting date and expiration date. For the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, the Company expensed $571,893 and $27,373 in compensation expense. The options are accounted for as equity under FASB’s accounting standard related to derivative instruments and hedging activities. The options activity is as follows:
| Weighted | Average | |||||||||||
| Average | Remaining | |||||||||||
| Options | Options | Exercise | Contractual | |||||||||
| Outstanding | Exercisable | Price | Life | |||||||||
| December 31, 2008 | 997,500 | 937,500 | $ | 4.00 | 9.43 | |||||||
| Granted | - | 30,000 | 4.00 | 9.31 | ||||||||
| Forfeited | - | - | - | - | ||||||||
| Exercised | - | - | - | - | ||||||||
| March 31, 2009 (unaudited) | 997,500 | 967,500 | $ | 4.00 | 9.18 | |||||||
| Granted | - | 30,000 | 4.00 | 9.06 | ||||||||
| Forfeited | - | - | - | - | ||||||||
| Exercised | (87,500 | ) | (87,500 | ) | 4.00 | 8.42 | ||||||
| December 31, 2009 | 910,000 | 910,000 | $ | 4.00 | 8.43 | |||||||
| Granted | 70,000 | 50,000 | 12.05 | 9.80 | ||||||||
| Forfeited | - | - | - | - | ||||||||
| Exercised | - | - | - | - | ||||||||
| March 31, 2010 (unaudited) | 980,000 | 960,000 | $ | 4.57 | 8.53 |
Note 17 – Change in fair value of derivative
liabilities
Loss (gain) on change in fair value of derivative liabilities for the three months ended March 31, 2010 comprised as following:
-40-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
| Fair value at | Fair value at | Change in fair | |||||||||||||
| January 1, | dates of | Fair value at | Fair value at | value at | |||||||||||
| 2010 or | warrants | date of notes | March 31, | March 31, | |||||||||||
| Change in fair value of derivative liabilities of: | issuance date | exercised | conversion | 2010 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| Conversion option of convertible notes | $ | 19,960,145 | $ | - | $ | 2,627,558 | $ | 15,275,245 | $ | (2,057,342 | ) | ||||
| Warrants attached to convertible notes | 11,804,252 | 1,078,788 | - | 9,177,262 | (1,548,202 | ) | |||||||||
| Warrants issued to placement agent | 897,010 | 668,977 | - | - | (228,033 | ) | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 32,661,407 | $ | 1,747,765 | $ | 2,627,558 | $ | 24,452,507 | $ | (3,833,577 | ) | ||||
Note 18 – Interest expense (income), net
Interest expense (income), net for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009 comprised as following:
| Interest expense (income), net | 2010 | 2009 | ||||
| Interest expense – bank and other loans | $ | 62,286 | $ | 622,449 | ||
| Interest expense – due to strategic investors | 99,182 | - | ||||
| Interest expense – convertible notes | 172,121 | - | ||||
| Interest income | (152,536 | ) | (251,596 | ) | ||
| Total | $ | 181,053 | $ | 370,853 |
Note 19 – Statutory reserves
In accordance with the “Law of the PRC on Joint Ventures Using Chinese and Foreign Investment” and the Company’s Articles of Association, appropriations from net profit should be made to the Reserve Fund and the Enterprise Expansion Fund, after offsetting accumulated losses from prior years, and before profit distributions to the investors. The percentages to be appropriated to the Reserve Fund and the Enterprise Expansion Fund are determined by the Board of Directors of the Company.
Reserve fund
10% of the net income determined in accordance with PRC accounting rules and regulations are transferred to a statutory surplus reserve fund until such reserve balance reaches 50% of the Company’s registered capital. As of March 31, 2010, approximately $19.8 million were reserved and have met 50% of the Company’s registered capital. The transfer to this reserve must be made before distribution of any dividend to shareholders. The surplus reserve fund is non-distributable other than during liquidation and can be used to fund previous years’ losses, if any, and may be utilized for business expansion or converted into share capital by issuing new shares to existing stockholders in proportion to their shareholding or by increasing the par value of the shares currently held by them, provided that the remaining reserve balance after such issue is not less than 25% of the registered capital.
-41-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS March 31, 2010 (Unaudited)
Enterprise expansion fund
The enterprise fund may be used to acquire plant and equipment or to increase the working capital to expend on production and operation of the business. The Company’s policy is to transfer 5% of the Shandong Taibang’s net income to this fund determined in accordance with the Company’s policy.
Note 20 – Retirement benefit plans
Regulations in the PRC require the Company to contribute to a defined contribution retirement plan for the benefit of all permanent employees. All permanent employees are entitled to an annual pension equal to their basic salaries at retirement. The PRC government is responsible for the benefit liability to these retired employees. The Company is required to make contributions to the state retirement plan at 20% of the monthly base salaries of the current employees. For the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, the Company made pension contributions in the amount of $109,033 and $220,493, respectively.
Note 21 - Noncontrolling interest and
distribution (Restated)
The roll forward of noncontrolling interest in the balance sheet is shown below:
| Fang Cheng | Shandong | Guizhou | Guiyang | Guiyang | ||||||||||||||
| Plasma Co. | Taibang | Renyuan | Qianfeng | Dalin | ||||||||||||||
| Minority | Minority | Minority | Minority | Minority | Total | |||||||||||||
| Owner | Owner | Owners | Owners | Owner | Noncontrolling | |||||||||||||
| (20%) | (17.24%) | (75%) | (46%) | (10%) | interest | |||||||||||||
| December 31, 2008 | $ | - | $ | 4,805,381 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 4,805,381 | ||||||
| Dalin acquisition | - | - | 2,444,203 | 17,317,241 | 1,763,615 | 21,525,059 | ||||||||||||
| Net income(loss) | (12,670 | ) | 5,321,061 | (111,753 | ) | 9,884,220 | 1,534,800 | 16,615,658 | ||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation gain/(loss) | - | (186 | ) | 115,238 | 330,316 | 10,420 | 455,788 | |||||||||||
| Dividend declared | - | (1,212,834 | ) | - | (7,327,205 | ) | (415,353 | ) | (8,955,392 | ) | ||||||||
| December 31, 2009 | $ | (12,670 | ) | $ | 8,913,422 | $ | 2,447,688 | $ | 20,204,572 | $ | 2,893,482 | $ | 34,446,494 | |||||
| Net income(loss) | 1,514,990 | (59,708 | ) | 2,359,885 | 336,855 | 4,152,022 | ||||||||||||
| Reverse for 20% acquisition | 12,670 | - | - |
- |
- | 12,670 | ||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation gain/(loss) | - | 93,941 | 25,115 | (93,962) | (49,049) | (23,955) | ||||||||||||
| Dividend declared | - | - | - | (4,048,920 | ) | (733,500 | ) | (4,782,420 | ) | |||||||||
| March 31, 2010 (unaudited) | $ | - | $ | 10,522,353 | $ | 2,413,095 | $ | 18,421,575 | $ | 2,447,788 | $ | 33,804,811 |
Dividends declared are split pro rata between the shareholders according to their ownership interest. The payment of the dividends may occur at different times to the shareholders resulting in distributions which do not appear to be reflective of the minority ownership percentages. As of March 31, 2010, minority shareholders owned 17.24% of the Shandong Taibang, 10% of Dalin and 46% of Qianfeng. The table below shows the minority shareholder and dividends outstanding.
-42-
| CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES | ||||||||||||
| NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS | ||||||||||||
| March 31, 2010 | ||||||||||||
| (Unaudited) | ||||||||||||
| Shandong | Guiyang | Guiyang | ||||||||||
| Taibang | Qianfeng | Dalin | Total | |||||||||
| Noncontrolling | Noncontrolling | Noncontrollin | Noncontrolling | |||||||||
|
|
shareholder | shareholder | g shareholder | shareholder | ||||||||
| Distribution payable, December 31, 2008 | $ | 3,252,354 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 3,252,354 | ||||
| Dividend declared | 1,212,834 | 7,327,205 | 415,353 | 8,955,392 | ||||||||
| Dividend paid | (4,479,381 | ) | (7,330,671 | ) | (415,353 | ) | (12,225,405 | ) | ||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | 14,780 | 3,466 | - | 18,246 | ||||||||
| Distribution payable, December 31, 2009 | $ | 587 | - | - | $ | 587 | ||||||
| Dividend declared | - | 4,048,920 | 733,500 | 4,782,420 | ||||||||
| Dividend paid | - | (4,048,920 | ) | (733,500 | ) | (4,782,420 | ) | |||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | - | - | - | - | ||||||||
| Distribution payable, March 31, 2010 (unaudited) | $ | 587 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 587 | ||||
Note 22 – Business combinations
Acquisition of Ziguang Bio-Technology Co.
On January 22, 2010, Shandong Taibang entered into an Equity Transfer Agreement with Yuncheng Ziguang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. which is located in Yuncheng, Shandong Province. Under the terms of the Equity Transfer Agreement, Shandong Taibang agreed to purchase 100% of Yuncheng Ziguang’s equity interest at a purchase price of RMB 10,066,672 (approximately $1,476,781), which was paid on February 24, 2010. Yuncheng Ziguang’s main business is manufacturing, packing and selling of health drinks and foods. Among its assets, Yuncheng Ziguang owns six buildings and a right to acquire a land use right with approximately 323,000 square feet in size. The purpose of this acquisition is mainly for relocation of Shandong Taibang’s Yun Cheng plasma station, which is adjacent to Yuncheng Ziguang, into the existing building and the land that Yuncheng Ziguang currently owns or entitled to own. Yun Cheng plasma station is the oldest and smallest among the Company's five stations in Shandong. Shandong Taibang expects that the relocation of the plasma station into the new facility will increase its plasma collection capacity with a low investment cost.
The following table summarizes the fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of acquisition, which represents the purchase price allocation at the date of the acquisition of Ziguang based on an independent third party appraiser. The appraiser conducted an on-site visit, inspected each item, conducted market research and investigation, followed some asset evaluation policies and regulations issued by the Chinese government, and provided an evaluation report.
-43-
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
March 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
|
Fair Value |
|||
| Current assets | $ | 334 | |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 1,613,370 | ||
| Total assets | 1,613,704 | ||
| Total liabilities | (136,924 |
) |
|
| Net assets | $ | 1,476,780 |
No material acquisition-related costs were incurred and recognized in the Company’s income statement for the three months ended March 31, 2010.
No supplemental pro forma information was disclosed as Ziguang had not commenced operations for the period ended March 31, 2010.
Note 23 – Subsequent Events
The Company paid the final 10% of Dalin acquisition purchase price on April 9, 2010 according to the equity transfer agreement as described under the Current Development in the Note 1.
-44-
| ITEM 2. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS. |
Special Note Regarding Forward Looking
Statements
This Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q, including the following “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. Such statements include, among others, those concerning our expected financial performance and strategic and operational plans, as well as all assumptions, expectations, predictions, intentions or beliefs about future events. You are cautioned that any such forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and that a number of risks and uncertainties could cause actual results of the Company to differ materially from those anticipated, expressed or implied in the forward-looking statements. The words “believe,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “project,” “targets,” “optimistic,” “intend,” “aim,” “will” or similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. All statements other than statements of historical fact are statements that could be deemed forward-looking statements. Risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those anticipated include risks related to, among others: our potential inability to raise additional capital that is necessary to fund our operations and our expansion, including our intended acquisitions; the possibility that third parties hold proprietary rights that preclude us from marketing our products; the emergence of additional competing technologies; changes in domestic and foreign laws, regulations and taxes; changes in economic conditions; uncertainties related to China’s legal system and economic, political and social events in China; a general economic downturn; a downturn in the securities markets. Additional disclosures regarding factors that could cause our results and performance to differ from results or performance anticipated by this Report are discussed in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2009 at Item 1A. “Risk Factors.”
Readers are urged to carefully review and consider the various disclosures made by us in this Report and our other filings with the SEC. These reports attempt to advise interested parties of the risks and factors that may affect our business, financial condition and results of operations and prospects. The forward-looking statements made in this Report speak only as of the date hereof and, except to the extent required by federal securities law, we disclaim any obligation to provide updates, revisions or amendments to any forward-looking statements to reflect changes in our expectations or future events.
Use of Terms
Except as otherwise indicated by the context, all references in this report to:
-
“BVI” are to the British Virgin Islands;
-
“China Biologic,” the “Company,” “we,” “us,” or “our,” are to the combined business of China Biologic Products, Inc., a Delaware corporation, and its direct and indirect subsidiaries;
-
“Dalin” are to our majority owned subsidiary, Guiyang Dalin Biologic Technologies Co., Ltd., a PRC limited company;
-
“Exchange Act” are to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended;
-
“Hong Kong” are to the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China;
-
“China” or “PRC” are to the People's Republic of China;
-
“Huitian” are to Xi'an Huitian Blood Products Co., Ltd., our minority owned PRC operating subsidiary;
-
"Logic China" are to our wholly owned indirect PRC subsidiary Logic Management and Consulting (China) Co., Ltd.
-
“Logic Express” are to our wholly owned subsidiary Logic Express Limited, a BVI company;
-
“Logic Holdings” a to Logic Holdings (Hong Kong) Limited, our wholly-owned Hong Kong subsidiary;
-
“Qianfeng” are to Qianfeng Biological Products Co., Ltd., Dalin's majority owned PRC operating subsidiary;
-
“RMB” are to Renminbi, the legal currency of China;
- 45 -
-
“Securities Act” are to the Securities Act of 1933, as amended;
-
“Taibang Medical” are to Shandong Taibang's wholly owned PRC subsidiary, Shandong Taibang Medical Company;
-
“Shandong Taibang” are to our subsidiary Shandong Taibang Biological Products Co. Ltd., a sino-foreign joint venture incorporated in China; and
-
“U.S. dollar,” “$,” “USD” and “US$” are to the legal currency of the United States.
| Throughout this report, we have converted RMB to USD as follows: | |
| March 31, 2010 | |
| Balance sheet | RMB 6.82 to US$1.00 |
| Statement of income and comprehensive income | RMB 6.82 to US$1.00 |
| March 31, 2009 | |
| Balance sheet | RMB 6.83 to US$1.00 |
| Statement of income and comprehensive income | RMB 6.83 to US$1.00 |
Overview of Our Business
We are a biopharmaceutical company and through our indirect majority-owned Chinese subsidiaries, Shandong Taibang and Qianfeng, and minority-owned Chinese subsidiary, Huitian, we are principally engaged in the research, development and manufacturing of plasma-based pharmaceutical products in China. Shandong Taibang operates from our manufacturing facility located in Tai'an City, Shandong Province and Qianfeng operates in Guizhou Province. Our minority owned subsidiary, Huitian, operates from facilities in Shaanxi Province. The plasma-based biopharmaceutical manufacturing industry in China is highly regulated by both the provincial and central governments. Accordingly, the manufacturing process of our products is strictly monitored from the initial collection of plasma from human donors to finished products. Our principal products include our approved human albumin and immunoglobulin products.
We are approved to sell human albumin 20%/10ml, 20%/25ml, 20%/50m, 10%/10ml, 10%/25ml, 10%/50ml and 25%/50ml. Human albumin is our top-selling product. Sales of these human albumin products represented approximately 46.9% and 58.4% of our total revenues, respectively, for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Human albumin is principally used to increase blood volume while immunoglobulin, one of our other major products, is used for certain disease preventions and cures. The Company’s approved human albumin and immunoglobulin products use human plasma as the basic raw material. Albumin has been used for almost 50 years to treat critically ill patients by replacing lost fluid and maintaining adequate blood volume and pressure. All of our products are prescription medicines administered in the form of injections.
We sell our products to customers in the PRC, mainly hospitals and inoculation centers. Our sales have historically been made on the basis of short-term arrangements and our largest customers have changed over the years. For the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, our top 5 customers accounted for approximately 20.7% and 20.5%, respectively, of our total revenue. For the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, our largest customer accounted for approximately 6.8% and 7.8% of our revenue, respectively. As we continue to diversify our geographic presence, customer base and product mix, we expect that our largest customers will continue to change from year to year.
We operate and manage our business as a single segment. We do not account for the results of our operations on a geographic or other basis.
All our business has been conducted in Renminbi, the official currency of China. Renminbi is still not a free floating currency. The value of Renminbi is subject to changes in the Chinese government's policies and depends to a large extent on China's domestic and international economic and political developments, as well as supply and demand in the local market. Since 1994, the official exchange rate for the conversion of Renminbi to U.S. dollars has generally been stable, and Renminbi has appreciated against the U.S. dollar since July 2005.
- 46 -
On November 25, 2009, we received approval to list our securities on The NASDAQ Global Market. The symbol for our common stock is “CBPO.” We began trading on NASDAQ under this symbol on December 2, 2009.
Our principal executive offices are located at No. 14 East Hushan Road, Tai’an City, Shandong, People’s Republic of China 271000. Our corporate telephone number is (+86) 538-620-2306 and our fax number is (+86) 538-620-3895. We maintain a website at http://www.chinabiologic.com that contains information about our operating company, but that information is not part of this report.
During the quarter ended March 31, 2010, our revenues were derived primarily from the sale of our approved human albumin and immunoglobulin products. Our revenue during the fiscal quarter ended March 31, 2010 increased 28.1%, or $5,949,955, to $27,098,553 compared with $21,148,598 over the same period in 2009. The increase in revenue is mainly due to the general increase in prices of our products. All of our approved products recorded price increases ranging from 3.1% to 118.3% .
First Quarter of 2010 Financial Performance Highlights
We continued to experience strong demand for our products and services during the three months ended March 31, 2010, which resulted in growth in our revenue and net income. The following are some financial highlights for the three months ended March 31, 2010:
-
Revenue : Revenue increased $5,949,955, or 28.1%, to $27,098,553 for the three months ended March 31, 2010, from $21,148,598 for the same period in 2009.
- Gross Profit: Gross profit increased $5,366,031, or 35.9%, to $20,299,699 for the three months ended March 31, 2010, from $14,933,668 for the same period in 2009.
- Income from operations : Income from operations increased $3,162,346, or 31.4%, to $13,225,884 for the three months ended March 31, 2010, from $10,063,538 for the same period in 2009.
- Net income : Net income increased $6,354,953, or 147.5%, to $10,663,749 for the three months ended March 31, 2010, from $4,308,796 for the same period in 2009.
- Fully diluted net income per share: Fully diluted net income per share was $0.26 for the three months ended March 31, 2010, as compared to $0.20 for the same period in 2009.
Our net income, as reported in our result of operations for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, was $10,663,749 and $4,308,796, respectively. Our results of operations in the first quarter of 2010, as compared to the same period in 2009, was materially impacted by the price increase in our products and the income reflected from change in derivative liabilities.
Results of Operations
The following tables set forth key components of our results of operations for the periods indicated, both in dollars and as a percentage of sales revenue and key components of our revenue for the periods indicated in dollars. The financial data for the three months ended March 31, 2010 reflect the operating results of the Company and its subsidiaries, including Yuncheng Ziguang, while the financial data for the same period in 2009 reflect the operating results of the Company and its subsidiaries excluding Yuncheng Ziguang, which was acquired January 21, 2010.
- 47 -
For the Three-Month Periods Ended March 31, 2010 and 2009 (Unaudited)
| Three Months | $ | % | ||||||||||
| Ended March 31, | Increase | Increase | ||||||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | (Decrease) | (Decrease) | |||||||||
| Revenue | $ | 27,098,553 | $ | 21,148,598 | $ | 5,949,955 | 28.1% | |||||
| Cost of revenue | 6,798,854 | 6,214,930 | 583,924 | 9.4% | ||||||||
| Gross profit | 20,299,699 | 14,933,668 | 5,366,031 | 35.9% | ||||||||
| Gross profit as a percentage of revenue | 74.9% | 70.6% | 4.3% | |||||||||
| Operating expenses | 7,073,815 | 4,870,130 | 2,203,685 | 45.2% | ||||||||
| Other (income) expense | (4,661,034 | ) | 791,213 | (5,452,247 | ) | (689.1% | ) | |||||
| Income before taxes and noncontrolling interest | 17,886,918 | 9,272,325 | 8,614,593 | 92.9% | ||||||||
| Income taxes | 3,071,147 | 1,905,395 | 1,165,752 | 61.2% | ||||||||
| Net income before noncontrolling interests | $ | 14,815,771 | $ | 7,366,930 | $ | 7,448,841 | 101.1% | |||||
Revenues. Our revenues are derived primarily from the sales of our human albumin and immunoglobulin products. Our revenues increased 28.1%, or $5,949,955, to $27,098,553 for the three months ended March 31, 2010, compared to revenues of $21,148,598 for the three months ended March 31, 2009. The growth in revenue is mainly due to the general price increase of our products, as well as the 0.1% increase in foreign exchange translation. All of our approved products recorded price increases ranging from 3.1% to 118.3% . For the quarter ended March 31, 2010, the average price for our approved human albumin products, which contributed 46.9% to our total revenues, increased 3.1%, the average price for our approved human hepatitis B immunoglobulin products, which contributed 12.3% to our total revenues, increased 65.8%, the average price for our approved human immunoglobulin for intravenous injection products, which contributed 19.9% to our revenues, increased 34.2%, the average price for our approved human rabies immunoglobulin products, which contributed 13.9% to our revenues, increased 24.3%, the average price for our approved human tetanus immunoglobulin products, which contributed 2.5% to our revenue, increased 19.7%, and the average price for our approved human immunoglobulin products, which contributed 2.4% to our revenue, increased 118.3%, as compared to the same period in 2009. The general price increase in our products is mainly due to the continuing supply shortage in the industry. However, increased imports of human albumin products are alleviating the previous imbalance of supply and demand.
Cost of Revenues. Our cost of sales increased $583,924, or 9.4%, to $6,798,854 for the quarter ended March 31, 2010, from $6,214,930 during the same period in 2009. This increase was mainly due to a 9.3% actual increase in cost of revenues as a result of the increased sales, as well as a 0.1% increase due to foreign exchange translation. Cost of revenues as a percentage of sales was 25.1% for the quarter ended March 31, 2010, as compared to 29.4% during the same period in 2009. The decrease in cost of revenues as a percentage of sales is primarily due to the increase in selling price of our products.
Gross Profit. Gross profit increased by $5,366,031, or 35.9%, to $20,299,699 for the quarter ended March 31, 2010, from $14,933,668 for the same period in 2009. As a percentage of sales revenue, our gross profit margin increased by 4.3% to 74.9% for the quarter ended March 31, 2010, from 70.6% for the same period in 2009. The increase in gross profit margin is due primarily to the general price increase of our products for the first quarter of 2010 as compared to the same period in 2009.
Operating Expenses. Our total operating expenses increased by $2,203,685, or 45.2%, to $7,073,815 for the quarter ended March 31, 2010, from $4,870,130 for the same period in 2009. The increase was primarily attributable to the 149.9% increase in our research and development expenses during the 2010 period, as well as the 62.7% increase in selling expense and the 29.8% increase in our general and administrative expenses. As a percentage of sales revenue, total operating expenses increased by 3.1% to 26.1% for the quarter ended March 31, 2010, from 23.0% for the same period in 2009
Selling Expenses. For the quarter ended March 31, 2010, our selling expenses increased to $942,908, from $579,496 for the quarter ended March 31, 2009, an increase of $363,412, or 62.7% . As a percentage of sales, our selling expenses for the quarter ended March 31, 2010 increased by 0.8%, to 3.5%, from 2.7% for first quarter 2009. The increase in selling expenses is due primarily to the increase in salary and employee benefit and selling and promotion expenses as the Company continues its efforts in selling directly to hospitals and inoculation centers.
- 48 -
General and Administrative Expenses. For the three months ended March 31, 2010, our general and administrative expenses increased $1,139,345, or 29.8%, to $4,962,252, from $3,822,907 for the quarter ended March 31, 2009. General and administrative expenses as a percentage of sales increased by 0.2% to18.3% for the first quarter of 2010, from 18.1% for the same period in 2009. The increase in general and administrative expenses, as compared to the same period in 2009, is due primarily to the increase in travel, meal and entertainment and conference expenses as the result of integrating multiple sites after the acquisition of Dalin. The increase was offset by the decrease in legal and accounting expenses related to the acquisition of Dalin in the first quarter of 2009. Non-cash employee compensation for the three months ended March 31, 2010 increased to $571,893, from $27,373 for the same period in 2009, as a result of granting employee stock options to one of the Company’s officers and to its newly appointed independent director.
Research and Development Expenses. For the quarter ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, our research and development expenses were $1,168,655 and $467,727, respectively, an increase of $700,928 or 149.9% . As a percentage of revenues, our research and development expenses for the quarter ended March 31, 2010 and 2009 were 4.3% and 2.2%, respectively. The increase in research and development expenses is due to the allocation of cost associated with the development of two new products that are at the end of developing stages.
Change in Fair Value of Derivative Liabilities. The embedded derivatives (including the conversion option) in our senior secured convertible notes and warrants that were issued in June 2009 are classified as derivative liabilities carried at fair value. For the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, the Company recognized an income from the change in fair value of derivative liabilities in the amounts of $3,833,577 and a loss of $409,292, respectively. The recognized income from the change in the fair value of derivative liabilities in the first quarter of 2010 is mainly due to the Company’s stock price decrease from $12.08 to $11.04 as of December 31, 2009 and March 31, 2010, respectively. Future changes in the market price of our common stock could cause the fair value of these derivative financial instruments to change significantly in future periods.
Interest (Income) Expense, net. Our net of interest (income) expense decreased by $189,800, or 51.2%, to an expense of $181,053 for the quarter ended March 31, 2010, from an interest expense of $370,853 for the same period in 2009. The decrease of interest expense was mainly due to the interest income increased by $0.3 million in the first quarter of 2010 from the Company’s short term deposits with financing institute.
Other income- related party. The other income from related party was due to the Company was able to finally settle with $0.9 million less in interest expenses accrued in accordance with the Entrustment Agreement, dated April 6, 2009, among Logic Express, Shandong Taibang and the Shandong Institute of Biological Products, the holder of the minority interests in Shandong Taibang.
Income Tax Expense. Our provision for income taxes increased $1,165,752, or 61.2%, to $3,071,147 for the quarter ended March 31, 2010, from $1,905,395 for the same period in 2009. Our effective tax rate for the quarter ended March 31, 2010 and 2009 was 17.2% and 20.5%, respectively.
Net Income before Non-Controlling Interest. Our net income before non-controlling interest increased $7,448,841, or 101.1%, to $14,815,771 for the quarter ended March 31, 2010, from $7,366,930 for the same period in 2009. Income before non-controlling interest as a percentage of revenues was 54.7% and 34.8% for the quarter ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
To date, we have financed our operations primarily through cash flows from operations, augmented by short-term bank borrowings and equity contributions by our stockholders. As of March 31, 2010, we had $51,190,425 in cash and cash equivalents, primarily consisting of cash on hand and demand deposits.
The following table provides the statements of net cash flows for the three months ended March 31, 2010 compared to March 31, 2009 (Unaudited):
- 49 -
| Three Months Ended March 31, | ||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||
| Net Cash Provided by Operating Activities | $ | 2,092,846 | $ | 7,082,292 | ||
| Net Cash (Used in) Provided by Investing Activities | $ | (3,513,600 | ) | $ | 10,388,563 | |
| Net Cash (Used in) Provided by Financing Activities | $ | (1,177,882 | ) | $ | 7,647,822 | |
| Effect of Exchange Rate Change on Cash | $ | (54,890 | ) | $ | 72,655 | |
| Net Decrease in Cash and Cash Equivalents | $ | (2,653,526 | ) | $ | 25,191,332 | |
| Cash and Cash Equivalents, Beginning | $ | 53,843,951 | $ | 8,814,616 | ||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents, Ending | $ | 51,190,425 | $ | 34,005,948 | ||
Operating activities
Net cash provided by operating activities was $2.1 million for the quarter ended March 31, 2010, as compared to $7.1 million net cash provided by operating activities for the same period in 2009. The decrease in net cash provided by operating activities was mainly due to the increase in inventory and accounts receivable of $4.3 million and $2.0 million, respectively, as well as the decrease in other payables and taxes payable of $2.4 million and $1.3 million, respectively, offset by the increase in cash related consolidated net income of $7.4 million, to $14.8 million for the quarter ended March 31, 2010, as compared to $7.4 million in the same period of 2009.
Investing activities
Net cash used in investing activities for the quarter ended March 31, 2010 was $3.5 million, as compared to $10.4 million net cash provided by in the same period of 2009. Yuncheng Ziguang acquisition and construction in progress addition used in $1.5 million and $1.4 million of cash, respectively, during the quarter ended March 31, 2010.
On January 22, 2010, Shandong Taibang entered into an Equity Transfer Agreement with Yuncheng Ziguang Biotechnology Co., Ltd., which is located in Yuncheng, Shandong Province. Under the terms of the Equity Transfer Agreement, Shandong Taibang agreed to purchase 100% of Yuncheng Ziguang's equity interest at a purchase price of RMB 10,066,672 (approximately $1,476,781), which was subsequently paid as of February 24, 2010. Yuncheng Ziguang's main business is manufacturing, packing and selling of health drinks and foods. Among its assets, Yuncheng Ziguang owns six buildings and a right to acquire a land use right with approximately 323,000 square feet in size. The purpose of this acquisition is mainly for the relocation of Shandong Taibang's Yun Cheng plasma station, which is adjacent to Yuncheng Ziguang, into the existing building and the land that Yuncheng Ziguang currently owns or entitled to own. Yun Cheng plasma station is the oldest and smallest among the Company's five stations in Shandong. Shandong Taibang expects that the relocation of the plasma station into the new facility will increase its plasma collection capacity with a low investment cost.
The following chart reflects our new corporate organizational structure:
- 50 -
- 51 -
Financing activities
Net cash used in financing activities for the quarter ended March 31, 2010 totaled $1.2 million as compared to $7.6 million provided by financing activities in the same period of 2009. The increase of the cash used in financing activities was mainly attributable to the dividend paid to minority shareholder of $4.8 million and repayment of short-term bank loan of $3.0 million, while short-term bank loans and proceeds from warrants conversion provided $5.9 million and $0.7 million.
Management believes that the Company has sufficient cash on hand and continuing positive cash inflow, from the sale of its plasma-based products in the PRC market. Our management expects continued growth in revenues throughout the term of the convertible notes, largely due to the ongoing limited supply of plasma-based products in the PRC market due to the introduction of more stringent health and safety measures which we already meet. In light of the foregoing, we believe that the Company will have the financial ability to fulfill its payment obligations under the convertible notes when they come due.
Obligations under Material Contracts
The following table sets forth our material contractual obligations as of March 31, 2010:
| Payment due by period | |||||||||||||||
| Less than | More than | ||||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligations | Total | 1 year | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | 5 years | ||||||||||
| Short-Term Obligations | $ | 12,215,537 | $ | 12,215,537 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||
| Long-Term Debt Obligations | 7,500,000 | - | 7,500,000 | - | - | ||||||||||
| Due to Related Companies | 3,086,940 | 3,086,940 | - | - | - | ||||||||||
| Operating Lease Obligations | 885,201 | 224,825 | 449,579 | 18,279 | 192,518 | ||||||||||
| Purchase Obligations | 1,575,280 | 1,575,280 | - | - | - | ||||||||||
| Total | $ | 25,626,958 | $ | 17,102,582 | $ | 7,949,579 | $ | 18,279 | $ | 192,518 | |||||
Below is a summary of our current obligations under material contracts:
- On September 26, 2008, Logic Express entered into an equity transfer agreement with Dalin, and Fan Shaowen, Chen Aimin, Chen Aiguo and Yang Gang, the shareholders of Dalin, relating to the purchase of an aggregate 90% equity interest in Dalin, for a total purchase price of RMB194,400,000 (approximately, $28,479,600), due in four installments. The parties agreed that (i) if Logic will have paid 90% of the purchase price (or RMB 174,960,000) on or before April 7, 2009, then Logic will be entitled to its share of Dalin's portion of the profit generated by Qianfeng starting from January 1, 2009, and (ii) if Logic fails to pay the said amount, the profit generated by Qianfeng from January 1, 2009 until the day of payment of said amount will be shared by the selling shareholders and Logic (i.e., Logic will be entitled to its share of Dalin's portion of the profit generated by Qianfeng calculated according to the proportion of the purchase price paid by it, and the selling shareholders will be entitled to the rest of Dalin's portion of the profit generated by Qianfeng). We timely initiated the third installment payment to achieve 90% of the purchase price on April 7, 2009, in accordance with the instructions provided by the Dalin shareholders, however, due to erroneous account information provided by the selling shareholders, RMB3,865,400 (approximately, $566,281) in funds were initially withheld by the bank, which was subsequently corrected and paid on April 8, 2009. In addition, the proper account information for the payment of RMB4,500,000 (approximately, $657,425) was not provided to the Company until April 14, 2009, upon receipt of which the funds were immediately delivered. Because the error resulted from an omission on the part of the selling shareholders themselves, we were deemed by the parties to have still fulfilled its obligations under the agreement. As of January 1, 2009, Logic Holdings became entitled to all the rights and privileges of a 90% shareholder in Dalin, including the right to receive its pro rata share of the profits generated by Dalin's 54% majority-owned operating subsidiary, Qianfeng, subject to a possible dilution to as low as 41.3%, if certain strategic investors’ purchase of Qianfeng’s equity in May 2007 is found to be valid. However, we did not exercise any control over Qianfeng until January 16, 2009, when our four nominees were elected to Qianfeng’s seven-member board of directors in a special meeting of Qianfeng’s board of directors on that date, and our management took control of Qianfeng’s operations as of the same date. We are obligated to pay the fourth and final installment, representing the remaining 10% of the purchase price, on or before April 9, 2010, the one-year anniversary of the local Administration for Industry and Commerce's approval of the equity transfer. On April 9, 2010, the Company paid the remaining 10% of the purchase price to the selling shareholders, except for the withholding of approximately $299,000 related to the contingent liabilities to be settled upon the completion of two legal proceedings according to the Equity Transfer Agreement.
- 52 -
- On April 6, 2009, Logic Express entered into an equity transfer and entrustment agreement, or Entrustment Agreement, among Logic Express, Shandong Taibang, and the Shandong Institute, the holder of the minority interests in Shandong Taibang, pursuant to which Logic Express agreed to permit Shandong Taibang and the Shandong Institute to participate in the indirect purchase of Qianfeng's equity interests. Under the terms of the Entrustment Agreement, Shandong Taibang agreed to contribute 18%, or RMB35,000,000 (approximately, $5,116,184), of the purchase price for Dalin and the Shandong Institute agreed to contribute 12.86%, or RMB25,000,000 (approximately, $3,654,917), of the purchase price. Logic Express is obligated to repay to Shandong Taibang and the Shandong Institute their respective investment amounts on or before April 6th, 2010, along with their pro rata share, based on their percentage of the purchase price contributed, of any distribution on the indirect equity investment in Qianfeng payable to Logic Express during 2009. Logic Express has agreed that if these investment amounts are not repaid within 5 days of the payment due date, then Logic Express is obligated to pay Shandong Taibang and the Shandong Institute liquidated damages equal to 0.03% of the overdue portion of the amount due until such time as it is paid. Logic Express has also agreed to pledge 30% of its ownership in Shandong Taibang to the Shandong Institute as security for nonpayment. If failure to repay continues for longer than 3 months after the payment due date, then the Shandong Institute will be entitled to any rights associated with the pledged interests, including but not limited to rights of disposition and profit distribution, until such time as the investment amount has been repaid. Logic Express also provided a guarantee that Shandong Taibang and the Shandong Institute will receive no less than a 6% return based on their original investment amount. On April 12, 2010, the Company fully paid the Shandong Institute and Shandong Taibang on the respective investment amounts, as well as the interest, according the Entrust Agreement. The interest paid to the Shandong Institute is approximately $1,154,687.
Critical Accounting Policies
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires our management to make assumptions, estimates and judgments that affect the amounts reported, including the notes thereto, and related disclosures of commitments and contingencies, if any. We have identified certain accounting policies that are significant to the preparation of our financial statements. These accounting policies are important for an understanding of our financial condition and results of operation. Critical accounting policies are those that are most important to the portrayal of our financial conditions and results of operations and require management's difficult, subjective, or complex judgment, often as a result of the need to make estimates about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain and may change in subsequent periods. Certain accounting estimates are particularly sensitive because of their significance to financial statements and because of the possibility that future events affecting the estimate may differ significantly from management's current judgments. We believe the following critical accounting policies involve the most significant estimates and judgments used in the preparation of our financial statements.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
On January 1, 2008, the Company adopted FASB's accounting standard related to fair value measurements and began recording financial assets and liabilities subject to recurring fair value measurement at the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants. These fair value principles prioritize valuation inputs across three broad levels. The Company considers the carrying amount of cash, receivables, payables including accrued liabilities and short term loans to approximate their fair values because of the short period of time between the origination of such instruments and their expected realization and if applicable, their stated rates of interest are equivalent to interest rates currently available. The fair values are measured pursuant to the three levels defined by the FASB's accounting standard as follow:
- Level 1: inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
- Level 2: inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, and inputs that are observable for the assets or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instruments.
- Level 3: inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and significant to the fair value.
- 53 -
Revenue Recognition
We recognize revenue when products are delivered and the customer takes ownership and assumes risk of loss, collection of the relevant receivable is probable, persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists and the sales price is fixed or determinable, which are generally considered to be met upon delivery and acceptance of products at the customer site. Sales are presented net of any discounts given to customers. As a policy, we do not accept any product returns and based on our records, product returns, if any, are immaterial. Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of goods, net of a value-added tax, or VAT. All products produced by us and sold in the PRC are subject to a Chinese VAT at a rate of 6% of the gross sales price or at a rate approved by the Chinese local government. Products distributed by Taibang Medical are subjected to a 17% VAT.
Inventories
Due to its unique nature, our principal raw material, human blood plasma is subject to various quality and safety control issues which include, but are not limited to, contaminations and blood born diseases. In addition, limitations of current technology pose biological hazards inherent in plasma that have yet to be discovered, which could result in a widespread epidemic due to blood infusion. In the event that human plasma is discovered to contain pathogens or infectious agents or other bio-hazards, we would be required to write down our inventory to net realizable value. We determine the net realizable value of our inventories on the basis of anticipated sales proceeds less estimated selling expenses. At each balance sheet date, we evaluate inventories that may be worth less than current carrying amounts. Total inventories amounted to $39.2 million as of March 31, 2010. In order to ensure that the growing demand for our products is met, as well as the 90-day quarantine period requirement on plasma raw material implemented by the PRC government, we have been gradually increasing our inventory level of raw materials. We strictly follow the production processes required by government regulations resulting in the relatively high level of work-in-progress customary to our industry.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
We review periodically the carrying amounts of long-lived assets including property, plant and equipment, and intangible assets with finite useful lives, to assess whether they are impaired. We evaluate these assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that their carrying amounts may not be recoverable such as a change of business plan, technical obsolescence, or a period of continuous losses. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to the estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its estimated future cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset. In determining estimates of future cash flows, significant judgment in terms of projection of future cash flows and assumptions is required.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP requires us to make a number of estimates and assumptions relating to the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates. On an ongoing basis, we review our estimates and assumptions, including those related to the recoverability of the carrying amount and the estimated useful lives of long-lived assets, valuation allowances for accounts receivable and realizable values for inventories. Changes in facts and circumstances may result in revised estimates.
Contingencies
In the normal course of business, we are subject to contingencies, including, legal proceedings and claims arising out of the business that relate to a wide range of matters, including among others, product liability. We recognize a liability for such contingency if we determine that it is probable that a loss has occurred and a reasonable estimate of the loss can be made. We may consider many factors in making these assessments, including past history and the specifics of each matter. As we have not become aware of any product liability claim since operations commenced, we have not recognized a liability for any product liability claims.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In December 2009, FASB issued ASU No. 2009-16, Accounting for Transfers of Financial Assets. This Accounting Standards Update amends the FASB Accounting Standards Codification for the issuance of FASB Statement No. 166, Accounting for Transfers of Financial Assets—an amendment of FASB Statement No. 140.The amendments in this Accounting Standards Update improve financial reporting by eliminating the exceptions for qualifying special-purpose entities from the consolidation guidance and the exception that permitted sale accounting for certain mortgage securitizations when a transferor has not surrendered control over the transferred financial assets. In addition, the amendments require enhanced disclosures about the risks that a transferor continues to be exposed to because of its continuing involvement in transferred financial assets. Comparability and consistency in accounting for transferred financial assets will also be improved through clarifications of the requirements for isolation and limitations on portions of financial assets that are eligible for sale accounting. The effective date of this amended pronouncement was as of the beginning of a reporting entity’s first annual reporting period that begins after November 15, 2009, for interim periods within that first annual reporting period, and for interim and annual reporting periods thereafter. The Company adopted this standard and the adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
- 54 -
In December 2009, FASB issued ASU No. 2009-17, Improvements to Financial Reporting by Enterprises Involved with Variable Interest Entities. This Accounting Standards Update amends the FASB Accounting Standards Codification for the issuance of FASB Statement No. 167, Amendments to FASB Interpretation No. 46(R). The amendments in this Accounting Standards Update replace the quantitative-based risks and rewards calculation for determining which reporting entity, if any, has a controlling financial interest in a variable interest entity with an approach focused on identifying which reporting entity has the power to direct the activities of a variable interest entity that most significantly impact the entity’s economic performance and (1) the obligation to absorb losses of the entity or (2) the right to receive benefits from the entity. An approach that is expected to be primarily qualitative will be more effective for identifying which reporting entity has a controlling financial interest in a variable interest entity. The amendments in this Update also require additional disclosures about a reporting entity’s involvement in variable interest entities, which will enhance the information provided to users of financial statements. The effective date of this amended pronouncement was as of the beginning of a reporting entity’s first annual reporting period that begins after November 15, 2009, for interim periods within that first annual reporting period. The Company adopted this standard and the adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements..
In January 2010, FASB issued ASU No. 2010-01– Accounting for Distributions to Shareholders with Components of Stock and Cash. The amendments in this Update clarify that the stock portion of a distribution to shareholders that allows them to elect to receive cash or stock with a potential limitation on the total amount of cash that all shareholders can elect to receive in the aggregate is considered a share issuance that is reflected in EPS prospectively and is not a stock dividend for purposes of applying Topics 505 and 260 (Equity and Earnings Per Share). The amendments in this update are effective for interim and annual periods ending on or after December 15, 2009, and should be applied on a retrospective basis. The Company adopted this standard and the adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In January 2010, FASB issued ASU No. 2010-02 – Accounting and Reporting for Decreases in Ownership of a Subsidiary – a Scope Clarification. The amendments in this Update affect accounting and reporting by an entity that experiences a decrease in ownership in a subsidiary that is a business or nonprofit activity. The amendments also affect accounting and reporting by an entity that exchanges a group of assets that constitutes a business or nonprofit activity for an equity interest in another entity. The amendments in this update are effective beginning in the period that an entity adopts SFAS No. 160, “Non-controlling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements – An Amendment of ARB No. 51.” If an entity has previously adopted SFAS No. 160 as of the date the amendments in this update are included in the Accounting Standards Codification, the amendments in this update are effective beginning in the first interim or annual reporting period ending on or after December 15, 2009. The amendments in this update should be applied retrospectively to the first period that an entity adopted SFAS No. 160. The Company adopted this standard and the adoption of this standard did not have material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In January 2010, FASB issued ASU No. 2010-06 – Improving Disclosures about Fair Value Measurements. This update provides amendments to Subtopic 820-10 that requires new disclosure as follows: 1) Transfers in and out of Levels 1 and 2. A reporting entity should disclose separately the amounts of significant transfers in and out of Level 1 and Level 2 fair value measurements and describe the reasons for the transfers. 2) Activity in Level 3 fair value measurements. In the reconciliation for fair value measurements using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3), a reporting entity should present separately information about purchases, sales, issuances, and settlements (that is, on a gross basis rather than as one net number).This update provides amendments to Subtopic 820-10 that clarify existing disclosures as follows: 1) Level of disaggregation. A reporting entity should provide fair value measurement disclosures for each class of assets and liabilities. A class is often a subset of assets or liabilities within a line item in the statement of financial position. A reporting entity needs to use judgment in determining the appropriate classes of assets and liabilities. 2) Disclosures about inputs and valuation techniques. A reporting entity should provide disclosures about the valuation techniques and inputs used to measure fair value for both recurring and nonrecurring fair value measurements. Those disclosures are required for fair value measurements that fall in either Level 2 or Level 3.The new disclosures and clarifications of existing disclosures are effective for interim and annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2009, except for the disclosures about purchases, sales, issuances, and settlements in the roll forward of activity in Level 3 fair value measurements. Those disclosures are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2010, and for interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this ASU, however, the Company does not expect the adoption of this ASU to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
- 55 -
In February 2010, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update 2010-09, “Subsequent Events (Topic 855): Amendments to Certain Recognition and Disclosure Requirements,” or ASU 2010-09. ASU 2010-09 primarily rescinds the requirement that, for listed companies, financial statements clearly disclose the date through which subsequent events have been evaluated. Subsequent events must still be evaluated through the date of financial statement issuance; however, the disclosure requirement has been removed to avoid conflicts with other SEC guidelines. ASU 2010-09 was effective immediately upon issuance and was adopted in February 2010.
Seasonality of our Sales
Our operating results and operating cash flows historically have not been subject to seasonal variations. This pattern may change, however, as a result of new market opportunities or new product introductions.
Inflation
Inflation does not materially affect our business or the results of our operations.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not have any off-balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our financial condition, changes in financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures or capital resources that are material to our investors.
ITEM 3. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Not Applicable.
ITEMS 4 AND 4A(T). CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Exchange Act). Disclosure controls and procedures refer to controls and other procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the reports we file or submit under the Securities Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the rules and forms of the SEC and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
As required by Rule 13a-15(e), our management has carried out an evaluation, with the participation and under the supervision of our Chief Executive Officer, Mr. Chao Ming Zhao and our Chief Financial Officer, Mr. Y. Tristan Kuo, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures, as of March 31, 2010. Based upon, and as of the date of this evaluation, Messrs. Zhao and Kuo, determined that, because of the material weaknesses described in Item 9A. “Controls and Procedures” on our annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009, which we are still in the process of remediating, as of March 31, 2010, our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective. Investors are directed to Item 9A of annual report on Form 10-K, as amended on March 31, 2011, for the year ended December 31, 2009 for the description of these weaknesses.
- 56 -
Changes in Internal Controls over Financial Reporting
We regularly review our system of internal control over financial reporting and make changes to our processes and systems to improve controls and increase efficiency, while ensuring that we maintain an effective internal control environment. Changes may include such activities as implementing new, more efficient systems, consolidating activities, and migrating processes.
During its evaluation of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, the management concluded that, after adding two qualified accountants, the Company still needs to increase its qualified accounting personnel and enhance the supervision, monitoring and reviewing of financial statements preparation processes. The Company has already taken measures to remediate these material weaknesses by seeking an additional financial reporting and accounting staff member with relevant accounting experience, skills and knowledge in the preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP and financial reporting disclosure requirements under SEC rules. In addition, the Company is working closely with its outside consultant in reinforcing the rigorous process for collecting and reviewing information required for the preparation of the financial statements including footnotes.
Other than the foregoing changes, there were no changes in our internal controls over financial reporting during the first quarter of fiscal 2010 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect our internal control over financial reporting.
PART II
OTHER INFORMATION
ITEM 1. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS.
From time to time, we may become involved in various lawsuits and legal proceedings, which arise, in the ordinary course of business. However, litigation is subject to inherent uncertainties, and an adverse result in these, or other matters, may arise from time to time that may harm our business. Other than the legal proceedings set forth below, we are currently not aware of any such legal proceedings or claims that we believe will have a material adverse affect on our business, financial condition or operating results.
Bobai County Collection Station
In January 2007, the Company's PRC subsidiary, Shandong Taibang, advanced $413,697 (RMB3.0 million) to Feng Lin, the 20% minority shareholder in Fang Cheng Plasma Company, the Company's majority owned subsidiary, for the purpose of establishing or acquiring a plasma collection station. Mr. Lin and Shandong Taibang intended to establish the Bobai Kangan Plasma Collection Co., Ltd. (“Bobai”) in Bobai County, Guangxi and on January 18, 2007, Shandong Taibang signed a letter of intent to acquire the assets of the Bobai Plasma Collection Station, which was co-owned by Mr. Lin and Mr. Keliang Huang. However, in January 2007, Hua Lan Biological Engineering Co., Ltd. (“Hua Lan”) filed suit in the District Court of Hong Qi District, Xin Xiang City, Henan Province, alleging that Feng Lin, Keliang Huang and Shandong Taibang established and/or sought to operate the Bobai Plasma Collection Station using a permit for collecting and supplying human plasma in Bobai County, that was originally granted to Hua Lan by the government of the Guangxi region, without Hua Lan's permission. The establishment and registration of Bobai was never realized as a result of this law suit. On January 29, 2007, on Hua Lan's motion, the District Court entered an order to freeze funds in the amount of approximately $386,100 (RMB3,000,000) held by the defendants in the case, including approximately $65,750 (RMB500,000) in funds held in Shandong Taibang's bank account in Tai'an City. A hearing was held on June 25, 2007 and judgment was entered against the defendants along with a $226,780 (RMB1,700,000) joint financial judgment. The Company appealed the District Court judgment to the Xinxiang City Intermediate Court. In November 2007, the Intermediate Court affirmed the judgment against the three defendants and increased the amount of the joint financial judgment to approximately $405,954 (RMB3,000,000).
In January 2008, Hua Lan enforced the judgment granted by the Intermediate Court to freeze the Company's bank accounts. Shandong Taibang has filed a separate action against Hua Lan before the Tai'an City District Court to seek recovery of any losses in connection with Hua Lan's claim and to request that the Tai'an City District Court preserve Hua Lan's property or freeze up to approximately $411,300 (RMB 3 million) of Hua Lan's assets to secure the return of such funds to the Company. The intermediate court in Tai'an City accepted the application on February 14, 2008 but the matter is still pending. Pending the outcome of the proceedings, Shandong Taibang increased its loss contingency reserve during its fourth quarter of 2007 from approximately $75,593 (RMB566,667) to $133,400 (RMB1,000,000) to cover its share of the enforcement of this judgment. During the fourth quarter of 2008, full amount of the judgment, including Feng Lin and Keliang Huang's portions of the judgment and the related fees, approximately $456,222 (RMB 3,109,900) has been withdrawn from Shandong Taibang's account. The Company recorded Feng Lin and Keliang Huang's portion of the judgment, approximately $304,143 (RMB2,073,234), as receivable as a result of the withdrawal. As of December 31, 2008, the Company determined that it is unlikely that the Company will be able to recover such receivable from those two individuals and wrote off the receivable as bad debt expense. In January 2010, Feng Lin transferred his 20% equity in Fang Cheng Plasma Company as a repayment to such receivable. As a result, the Company is now the 100% owner of the Fang Cheng Plasma Company.
- 57 -
In October 2009, Shandong Taibang appealed to the High Court of Henan Province requesting the court to reverse judgments from the Hong Qi District Court based on Shandong Taibang's belief that Hua Lan’s involvement in Bobai was in violation of PRC Blood Products Regulations as Hua Lan did not invest, as Shandong Taibang did, in Bobai as required by the Regulation. The Company was awaiting the judgment of the Henan High Court as of the date of this report. In light of the foregoing, it is unlikely that the Company's planned acquisition of the assets of Bobai will go forward.
Dispute among Qianfeng Shareholders over Raising Additional Capital
On May 28, 2007, a 91% majority of Qianfeng's shareholders approved a plan to raise additional capital from private strategic investors through the issuance of an additional 20,000,000 shares of Qianfeng equity interests at RMB 2.80 per share. The plan required all existing Qianfeng shareholders to waive their rights of first refusal to subscribe for the additional shares. The remaining 9% minority holder of Qianfeng's shares, the Guizhou Jie'an Company, or Jie'an, did not support the plan and did not agree to waive its right of first refusal. On May 29, 2007, the majority shareholders caused Qianfeng to sign an Equity Purchase Agreement with certain investors, pursuant to which the investors agreed to invest an aggregate of RMB 50,960,000 (approximately $7,475,832) in exchange for 18,200,000 shares, or 21.4%, of Qianfeng's equity interests. At the same time, Jie'an also subscribed for 1,800,000 shares, representing its 9% pro rata share of the 20,000,000 shares being offered. The proceeds from all parties were received by Qianfeng in accordance with the agreement.
In June 2007, Jie'an brought suit in the High Court of Guizhou province, China, against Qianfeng and the three other original Qianfeng shareholders, alleging the illegality of the Equity Purchase Agreement. In its complaint, Jie'an alleged that it had a right to acquire the shares waived by the original Qianfeng shareholders and offered to the investors in connection with the Equity Purchase Agreement. On September 12, 2008, the Guizhou High Court ruled against Jie'an and sustained the Equity Purchase Agreement, but on November 2008, Jie'an appealed the Guizhou High Court judgment to the People's Supreme Court in Beijing. On May 13, 2009, the People's Supreme Court sustained the original ruling and denied the rights of first refusal of Jie'an over the additional shares waived by the original Qianfeng's shareholders. The registration of the new investors as Qianfeng's shareholders and the related increase in registered capital of Qianfeng with the Administration for Industry and Commerce are still pending. On January 27, 2010, the strategic investors brought suit in the High Court of Guizhou Province against Qianfeng alleging Qianfeng’s failure to register their equity interest in Qianfeng with the local AIC and requesting the distribution of their share of Qianfeng’s dividends. Dalin was also joined as a co-defendant as it is the majority shareholder and exercises control over Qianfeng’s day-to-day operations. The Company does not expect the strategic investors to prevail because, upon evaluation of the Equity Purchase Agreement, the Company believes that the Equity Purchase Agreement is void due to certain invalid pre-conditions and the absence of shareholder authorization of the initial investment. In the event that Qianfeng is required to return their original investment amount to the strategic investors, Qianfeng has set aside the strategic investors’ fund along with RMB 7,313,387 (approximately $1,072,216) in accrued interests, and RMB 519,600 (approximately $74,712) for the 1% penalty imposed by the agreement for any breach. If strategic investors prevail in their suit, Dalin's interests in Qianfeng may be reduced to approximately 41.3% . The High Court of Guizhou heard the case on April 8, 2010 and encouraged, and accepted by both parties, to settle the dispute outside the court. As of the date of this report, the Company is still negotiating with the strategic investors for a term that is acceptable to the Company.
Administration Interference
Qianfeng is party to an administrative proceeding against the government of the Qiandongnan Autonomous Region, or the Qiandongnan Authorities, in Guizhou Province, China, in connection with the ownership of three of Qianfeng's entitled eight plasma stations in Guizhou Province. Qianfeng was authorized to acquire a total of eight plasma stations in Guizhou Province based on several national and provincial administrative authorizations issued by the PRC State Council and the Guizhou Ministry of Health between 2006 and 2007, but to date, the governmental authorizations have not been fully implemented by the Qiandongnan Authorities. In early 2007, Qianfeng submitted RMB 8,010,000 (approximately $1,173,465) to the local finance department of Sansui County, Qiandongnan, for acquiring the Sansui Plasma Collection Station (“Sansui”), but the local finance department refused to honor the purchase and returned the full consideration to Qianfeng. Furthermore, subsequent local rulings published by the Qiandongnan Authorities February 28, 2008 appear to authorize another private company to acquire the Sansui and two other stations, the Zhengyuan Plasma Collection Station and the Shibing Plasma Collection Station. In December 2008 Qianfeng filed an administrative review application with the People's Government of Guizhou Province, or the Guizhou Provincial Government, but the Guizhou Provincial Government has delayed making a final decision pending further review of regulations regarding administrative authorizations. Qianfeng has received verbal notification from staff in the Guizhou Provincial Government that the Qiandongnan Authorities have withdrawn the local rulings. As a result, Qianfeng has withdrawn its application with the Guizhou Provincial Government to facilitate further negotiation with Qiandongnan Authorities on its right to acquire all eight plasma stations in Guizhou Province. In addition, Qianfeng has set aside the funds necessary to purchase Sansui pending the outcome of the administrative review. There have been no further developments on this case as of the date of this report.
- 58 -
Qianfeng's Guarantee to a Third Party
In 2007, as a condition to purchase Huang Ping Plasma Station, Qianfeng entered into an agreement with Guizhou Zhongxin Investment Company (“Zhongxin”) in which Qianfeng agreed to repay Zhongxin's debt out of Qianfeng's payables to Zhongxin arising from plasma purchased from Zhongxin. In the same agreement, Qianfeng also guaranteed to the Huang Ping County Hospital (“Huang Ping Hospital”), which was the co-owner with Zhongxin of the Huang Ping Plasma Station, for the amount of RMB3,074,342 (approximately, $451,006) of debt that Zhongxin owed to Huang Ping Hospital. On June 1, 2009, Huang Ping Hospital brought suit, in Huang Ping County People's Court of Guizhou Province, against Zhongxin for non-payment of its payables and debt due to Huang Ping Hospital and Qianfeng as the guarantor. On November 2, 2009, the court ruled in favor of the plaintiff and Qianfeng will need to repay the Zhongxin’s debt to Huang Ping Hospital on behalf of Zhongxin as the guarantor. In October 2009, Qianfeng appealed to the Middle Court of Kaili District in Guizhou Province and was accepted by the court in January 2010. On April 8, 2010, the Middle Court of Kaili District ruled to sustain the original judgment. As a result, Qianfeng is in the process of filing suit against Zhongxin in the attempt to recover the RMB 3,074,342 debt that was under the guarantee. The Equity Transfer Agreement pursuant to which we acquired a 90% interest in Dalin, Qianfeng's majority shareholder, provides that the sellers will be responsible, in accordance with their equity proportion in Qianfeng, for damages incurred by Qianfeng from Zhongxin's debt and shall repay Dalin the sellers' proportionate share of payments made by Qianfeng to creditors in connection with Zhongxin's debt within 10 days after payment by Qianfeng. The RMB 3,074,342 contingent liability and proportionate share of the liability to be recovered from the sellers were properly reflected in the financials as of December 31, 2009.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS.
Not applicable.
ITEM 2. UNREGISTERED SALES OF EQUITY SECURITIES AND USE OF PROCEEDS.
We have not sold any equity securities during the quarter ended March 31, 2010 which sale was not previously disclosed in a current report on Form 8-K filed during that period.
ITEM 3. DEFAULTS UPON SENIOR SECURITIES.
None.
ITEM 4. (REMOVED AND RESERVED).
ITEM 5. OTHER INFORMATION.
We have no information to include that was required to be but was not disclosed in a report on Form 8-K during the period covered by this Form 10-Q. There have been no material changes to the procedures by which security holders may recommend nominees to our board of directors.
- 59 -
ITEM 6. EXHIBITS.
The following exhibits are filed as part of this report or incorporated by reference:
* previously filed.
60
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
CHINA BIOLOGIC PRODUCTS, INC.
Dated: May 6, 2011
/s/ Chao Ming Zhao
Chao Ming Zhao
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer
(Principal Executive Officer)
Dated: May 6, 2011
/s/ Y. Tristan Kuo
Y. Tristan Kuo
Chief Financial Officer
(Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer)
61
EXHIBIT INDEX
* previously filed.
62