
Sustainability Approach
At Alcoa, sustainability is defined as using our values to build financial success, environmental excellence, and social responsibility in partnership with all stakeholders in order to deliver net
long-term benefits to our shareholders, employees, customers, suppliers, and the communities in which we operate.
We approach sustainability
through three different but interdependent lenses: sustainability of our products, sustainability of our resources, and sustainability of our operations.
In 2010, we appointed our first chief sustainability officer to develop a comprehensive strategy that integrates all of our sustainability efforts. We also implemented a new set of strategic
sustainability targets to drive progress in our businesses to 2020 and, for some areas, to 2030. In addition, we developed a Sustainability Scorecard to align our sustainability targets with business strategy across every business.
Following is a summary of our progress in 2010. More in-depth information can be found in our online sustainability report at
www.alcoa.com/sustainability.
Sustainability of Products
LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT
In response to increasing use of life cycle assessments by
regulatory agencies, customers, and external stakeholders,
we established a Life Cycle Center of Excellence (COE) in 2010 to enhance awareness and assessments of our
processes and products. Alcoa and Alcoa Foundation also became founding members of The Sustainability Consortium, which will drive sustainability in products through all life cycle stages.
PRODUCT DESIGN
In 2009, we piloted a “design for sustainability” product
strategy for consumer electronics and conducted product pilots for a laptop and a cell phone. We expanded our product pilots in 2010, including significantly increasing furniture’s recyclable material content and reducing its end-of-life
land-filling by nearly 75% and weight by 50%.
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
During 2010, we initiated supplier sustainability pilot programs in Canada, Latin America, and the United States to better understand the potential alignment of our supply base to our key sustainability
objectives. The information gained has been critical in the development of our Global Supplier Sustainability Program, which will be implemented in 2011.
Sustainability of Resources
MINING RECLAMATION
We adopted a long-term strategic target to significantly reduce our legacy inventory of disturbed mine lands. Our goal is to achieve a five-year rolling
average mine land disturbance/mine

Visit www.alcoa.com/sustainability for more in-depth information and performance data.
rehabilitation ratio of 0.75:1 by 2020 and 1:1 by 2030. The 2020 goal equates to rehabilitating four
hectares (9.9 acres) of land for every three hectares (7.4 acres) that we disturb. This will ensure we substantially reduce legacy disturbance.
Alcoa Strategic Target
Mine
Rehabilitation
Five-year rolling average ratio of area disturbed to area rehabilitated
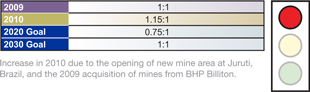
BIODIVERSITY
By 2015, all of our locations with substantive land holdings are to develop biodiversity management plans. We began piloting plans at two locations during 2010.
Sustainability of Operations
CLIMATE CHANGE
In 2010, we established a new goal to reduce 2005 levels of total carbon dioxide (CO2 ) intensity in our Global Primary Products business (refining and
smelting) by 20% by 2020 and 30% by 2030. We achieved a 22% reduction through 2010.
We obtained from PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP limited
assurance on our 2010 consolidated greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions data. Our total GHG emissions in 2010 were 44.5 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalents.
Alcoa Strategic Target
Global Primary Products
Greenhouse Gas Emission Intensity
Metric tons of CO2
equivalents (CO2e ) per ton of production
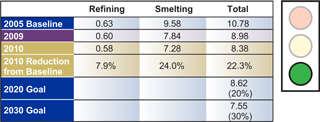
The Global Primary Products total represents the combined impact of refining and smelting operations indexed to tons of
primary metal production (refining is included at a ratio of 1.9 tons of alumina to smelted metal). These two processes and their associated power supply represent approximately 95% of Alcoa’s total emissions.
ENERGY
We are committed to reducing the
energy requirements for all of our operations and have set the following long-term
strategic targets:
| |
• |
|
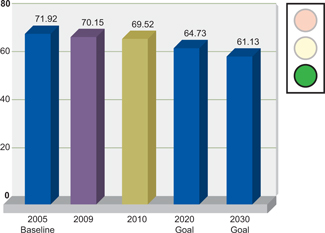
From a 2005 baseline, 10% reduction in the energy intensity of Global Primary Products by 2020;15% by 2030; and |
| |
• |
|
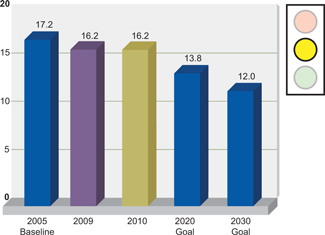
From a 2005 baseline, 20% reduction in the energy intensity of all other businesses by 2020; 30% by 2030. |
Global Primary Products achieved a 3% improvement in energy intensity for 2010 against the 2005 baseline. Global Rolled Products remained at the 2009
intensity level but was 6% below the 2005 baseline.
Alcoa Strategic Target
Energy Intensity—Global Primary Products
Gigajoules per metric ton of aluminum
produced
Alcoa Strategic Target
Energy Intensity—Global Rolled Products
Gigajoules per metric ton of aluminum
produced
WATER
Our
total use of freshwater decreased in 2010 (100.0 cubic meters) versus 2009 (109.5 cubic meters), despite an increase in total production. We also reduced our
|
|
|
| Visit www.alcoa.com/sustainability for more in-depth information and performance data. |
|
2 |
freshwater-use intensity (consumption per unit of production) by 19% versus 2005 levels, exceeding our 2020 goal of 10%.
Alcoa Strategic Target
Freshwater-Use Intensity
Cubic meters of water per metric ton of production
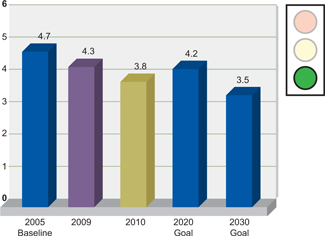
Because of the variability in the basis for measuring production in our businesses, these values represent a metric
calculated by taking each business intensity measurement indexed to production. Smelting production is indexed to metric tons of aluminum produced. Refining production is calculated at 1.9 times smelting production in metric tons of aluminum
produced. Fabrication production is indexed to metric tons of product rolled. Engineered Products and Solutions data are not included.
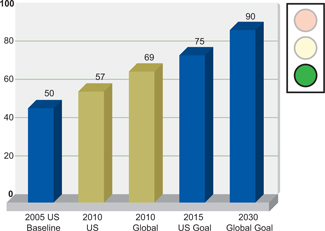
RECYCLING
In 2008, we announced an
aggressive goal to raise the U.S. used beverage can recycling rate to 75% by 2015. Later that year, this objective was adopted by the Aluminum Association. In 2010, we extended our internal goal to reach a 90% global recycling rate by 2030.
Alcoa Strategic Target
Can Recycling Rate
Percent recycled
EMISSIONS & WASTE
We are focusing our emission and waste efforts on landfilled waste, mercury emissions, and bauxite residue.
Landfilled Waste
Building on our early success in waste reduction, our new
strategic target is to recycle or reuse 75% of landfilled waste by 2020 and 100% by 2030 from a 2005 baseline.
Alcoa Strategic Target
Landfilled Waste
Thousands of metric tons
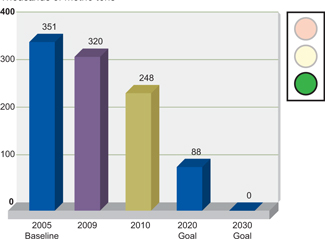
Excludes certain process waste streams from refining and power generation, including bauxite residue and fly ash.
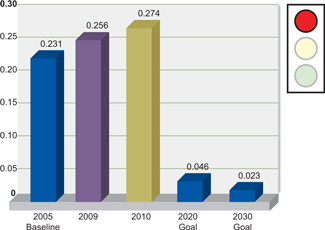
Mercury Emissions
Our strategic target for mercury is an 80% reduction in mercury emission intensity by 2020 and 90% by 2030 from a 2005 baseline. In 2010, our intensity
increased versus 2009, primarily due to increased production at refineries where reduction efforts remain a greater challenge.
Alcoa
Strategic Target
Mercury Emission Intensity
Grams per metric ton of alumina produced
|
|
|
| Visit www.alcoa.com/sustainability for more in-depth information and performance data. |
|
3 |
Bauxite Residue
Our long-term strategic targets for bauxite residue are aimed at reducing the overall footprint associated with our management of the material. These goals and our progress against them through 2010 are:
| |
• |
|
From a 2005 baseline, 20% reduction in bauxite residue land requirements per million metric tons of alumina produced by 2020; 40% by 2030. Achieved 3%.
|
| |
• |
|
Rehabilitate 30% of total residue storage area by 2020; 40% by 2030. Achieved 18%. |
| |
• |
|
Recycle or reuse 15% of residue generated by 2020; 30% by 2030. Achieved 0%. |
Alcoa Strategic Target
Bauxite
Residue Storage Efficiency
Square meters of land required per million metric tons of alumina produced
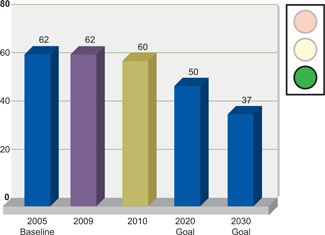
HEALTH & SAFETY
Our global 12-month rolling average for total days away (lost time and restricted days) at the end of 2010 was 57% lower than 2009 and 76% lower than 2008. Despite this achievement, we regrettably
experienced three employee fatalities and one contractor death during the year.
Alcoa Strategic Target
Incident Rates
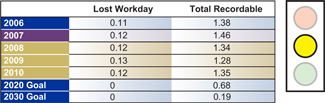
Lost workday incident rate represents the number of injuries and illnesses resulting in one or more days away from work with
or without days of job transfer or restrictions per 100 full-time workers. Total recordable incident rate represents the number of injuries and illnesses resulting in days away from work, job transfer or restriction, medical treatment, or other
recordables per 100 full-time workers.
COMMUNITY & STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT
We understand the importance of having transparent and regular dialogue with all of our stakeholders to ensure that we both understand their issues and
concerns and provide them with information.
Some of the key community and stakeholder issues that have been raised during 2010 are
highlighted in the following table. A more complete list is available in our online reporting.
2010 Stakeholder Issues
|
|
|
|
|
| Stakeholder |
|
Issue |
|
Resolution |
|
|
|
| Ethical Research Investment Services (EIRIS) |
|
In August 2010, EIRIS submitted a request for information that contained a number of allegations about the bauxite ore extraction operation at Alcoa’s new Juruti Mine in
Brazil. |
|
Alcoa responded to EIRIS in October 2010 via a nine-page document that provided a detailed response for each allegation. |
|
|
|
| Australia Environmental Protection Agency and Wildlife Victoria |
|
A portion of kangaroos living near Alcoa’s Portland smelter in Australia have been affected by fluorosis, causing arthritic conditions and lameness. |
|
We held one-on-one briefings with key government and community stakeholders and developed a kangaroo management plan in conjunction with external fauna and flora
experts. |
|
|
|
| Residents, county officials, and non-governmental organizations |
|
Relicensing of Alcoa’s three power dams in Badin, North Carolina, USA. |
|
We have provided information to media and stakeholders and dispatched our chief sustainability officer to ensure a more open and transparent dialogue with all
stakeholders. |
|
|
|
| Community members |
|
PCB contamination of the Grasse River downstream from Alcoa’s Massena, New York (USA), facility. |
|
We have developed a diverse community advisory panel, and we have openly shared all environmental data collected in the river over the last 20 years. |
Forward-Looking Statements: This report contains, in addition to historical information, statements concerning Alcoa’s
expectations, goals, targets, strategies, or future performance. These “forward-looking statements” are subject to a number of known and unknown risks and uncertainties. Some of the important factors that may cause Alcoa’s actual
results to differ materially from those expressed or implied in the forward-looking statements include changes in aluminum industry conditions generally, factors affecting Alcoa’s operations, such as equipment outages, failure of equipment or
processes to meet specifications, natural disasters, or other unexpected events, changes in the regulatory environment, the impact of reductions in Alcoa’s capital expenditures, Alcoa’s inability to realize expected benefits from its
productivity improvement, sustainability, or other initiatives, and the other risk factors summarized in Alcoa’s Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010 and other SEC reports.
4












