UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND
EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C.
20549
Form 10-K
| |
|
|
|
þ
|
|
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE
SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
|
|
|
|
For the fiscal
year ended April 30,
2010
|
|
or
|
|
o
|
|
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE
SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
|
|
|
|
For the transition period
from to .
|
Commission File Number
001-33417
| |
|
|
Delaware
(State or other jurisdiction
of
incorporation or organization)
|
|
22-2535818
(I.R.S. Employer
Identification No.)
|
1590 REED
ROAD
PENNINGTON, NJ 08534
(Address of principal executive
offices, including zip code)
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code:
(609) 730-0400
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the
Act:
| |
|
|
|
Title of Each Class
|
|
Name of Exchange on Which Registered
|
|
|
|
Common Stock, par value $0.001
|
|
The Nasdaq Global Market
|
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the
Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known
seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities
Act. Yes o No þ
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file
reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the
Act. Yes o No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed
all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of
the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding
12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant
was required to file such reports), and (2) has been
subject to such filing requirements for the past
90 days. Yes þ No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted
electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any,
every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted
pursuant to Rule 405 of
Regulation S-T
during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period
that the registrant was required to submit and post such
files). Yes o No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers
pursuant to Item 405 of
Regulation S-K
is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best
of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or
information statements incorporated by reference in
Part III of this
Form 10-K
or any amendment to this
Form 10-K. þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large
accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated
filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of
“large accelerated filer,” “accelerated
filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule
12b-2 of the
Exchange Act. (Check one):
|
|
|
|
| Large
accelerated
filer o
|
Accelerated
filer þ
|
Non-accelerated
filer o
|
Smaller
reporting
company o
|
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company
(as defined in
Rule 12b-2
of the Exchange
Act). Yes o No þ
The aggregate market value of the common stock of the registrant
held by non-affiliates as of October 31, 2009, the last
business day of the registrant’s most recently completed
second fiscal quarter, was $57.8 million based on the
closing sale price of the registrant’s common stock on that
date as reported on the Nasdaq Global Market.
The number of shares outstanding of the registrant’s common
stock as of June 30, 2010 was 10,390,563.
DOCUMENTS
INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
| |
|
|
|
Document
|
|
Part of the Form 10-K into Which Incorporated
|
|
|
|
Proxy Statement for the registrant’s 2010 Annual Meeting of
Stockholders
|
|
III
|
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
INDEX TO
REPORT ON
FORM 10-K
PowerBuoy®
is a registered trademark of Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. The
Ocean Power Technologies logo,
CellBuoytm,
Talk on
Watertm
and Making Waves in Power
SM are
trademarks or service marks of Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.
All other trademarks appearing in this annual report are the
property of their respective holders.
2
Special
Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
We have made statements in this Annual Report on
Form 10-K
(the “Annual Report”) in, among other sections,
Item 1 — “Business,”
Item 1A — “Risk Factors,”
Item 3 — “Legal Proceedings,” and
Item 7 — “Management’s Discussion and
Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations”
that are forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements
convey our current expectations or forecasts of future events.
Forward-looking statements include statements regarding our
future financial position, business strategy, budgets, projected
costs, plans and objectives of management for future operations.
The words “may,” “continue,”
“estimate,” “intend,” “plan,”
“will,” “believe,” “project,”
“expect,” “anticipate” and similar
expressions may identify forward-looking statements, but the
absence of these words does not necessarily mean that a
statement is not forward-looking.
Any or all of our forward-looking statements in this Annual
Report may turn out to be inaccurate. We have based these
forward-looking statements on our current expectations and
projections about future events and financial trends that we
believe may affect our financial condition, results of
operations, business strategy and financial needs. They may be
affected by inaccurate assumptions we might make or unknown
risks and uncertainties, including the risks, uncertainties and
assumptions described in Item 1A — “Risk
Factors.” In light of these risks, uncertainties and
assumptions, the forward-looking events and circumstances
discussed in this report may not occur as contemplated, and
actual results could differ materially from those anticipated or
implied by the forward-looking statements.
You should not unduly rely on these forward-looking statements,
which speak only as of the date of this filing. Unless required
by law, we undertake no obligation to publicly update or revise
any forward-looking statements to reflect new information or
future events or otherwise.
3
PART I
Overview
We develop and are commercializing proprietary systems that
generate electricity by harnessing the renewable energy of ocean
waves. The energy in ocean waves is predictable, and electricity
from wave energy can be produced on a consistent basis at
numerous sites located near major population centers worldwide.
Wave energy is an emerging segment of the renewable energy
market. Based on our proprietary technology, considerable ocean
experience, existing products and expanding commercial
relationships, we believe we are a leading wave energy company.
We currently offer two products as part of our line of
PowerBuoy®
systems: a utility PowerBuoy system and an autonomous PowerBuoy
system. Our PowerBuoy system is based on modular, ocean-going
buoys, which we have been ocean testing for over a decade. The
rising and falling of the waves moves the buoy-like structure
creating mechanical energy that our proprietary technologies
convert into electricity. We have tested and developed wave
power generation and control technology using proven equipment
and processes in novel applications and have deployed and
maintained our systems in the ocean. The PowerBuoy technology
has the unique, patented capability to electronically
“tune” itself automatically as wave characteristics
change. This enables the PowerBuoy to optimize its efficiency
and resulting power output in dynamic ocean wave conditions. Our
two PowerBuoy products are designed for the following
applications:
|
|
|
| |
•
|
Our utility PowerBuoy system is capable of supplying
electricity to a local or regional electric power grid. Our wave
power stations will be comprised of a single PowerBuoy system or
an integrated array of PowerBuoy systems, plus the remaining
components required to deliver electricity to a power grid. We
intend to sell our utility PowerBuoy system to utilities and
other electrical power producers seeking to add electricity
generated by wave energy to their existing electricity supply.
In July 2007, our PowerBuoy interface with the electrical
utility power grid was certified as compliant with international
standards. An independent laboratory provided testing and
evaluation services to certify that our systems comply with
designated national and international standards. The PowerBuoy
grid interface bears the Electrical Testing Laboratories (ETL)
listing mark, and can be connected to the utility grid.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Our autonomous PowerBuoy system is designed to generate
power for use independent of the power grid in remote locations.
There are a variety of potential applications for this system,
including sonar and radar surveillance, tsunami warning,
oceanographic data collection, offshore platforms and offshore
aquaculture.
|
Our product development and engineering efforts currently are
focused on increasing the reliability and peak-rated output of
our utility PowerBuoy system to 150 kilowatts (kW), and, to a
lesser extent increasing the peak rated output of the system to
500kW. In addition, we are researching and developing new
products, product applications and complementary technologies.
We believe that, by increasing the maximum rated output of our
utility PowerBuoy system, we will be able to decrease the cost
per kW of our PowerBuoy system and the cost per kilowatt hour of
the energy generated.
We expect to market our undersea substation pod and undersea
power connection infrastructure services to other companies in
the marine energy sector. We completed the successful in-ocean
trials of our undersea substation pod (“USP”) in 2009.
The USP, based on our proprietary design, has been developed to
facilitate the collection, networking and transforming of power
and data generated by multiple offshore energy devices. The USP
has been built as an open platform, and can provide connectivity
for the PowerBuoy as well as other offshore energy systems
developed by other companies. The required switching and
protection circuits for the individual PowerBuoys are also
included in the USP.
In addition, we are focusing on expanding our key commercial
opportunities for both the utility and the autonomous PowerBuoy
systems. We currently have commercial relationships with the
following:
|
|
|
| |
•
|
To develop and build wave power systems at the US Marine Corps
base in Hawaii.
|
4
|
|
|
| |
•
|
To provide PowerBuoy technology to a unique program for ocean
data gathering. Under this program, the Navy will conduct an
ocean test of an advanced design of our autonomous PowerBuoy as
the power source for the Navy’s Deep Water Active Detection
System.
|
| |
| |
•
|
To provide our PowerBuoy wave conversion system to the
Navy’s Littoral Expeditionary Autonomous PowerBuoy (LEAP)
Program.
|
|
|
|
| |
•
|
Pacific Northwest Generating Cooperative (PNGC Power) and the US
Department of Energy, both of which are providing funding toward
the fabrication and ocean installation of a 150kW PowerBuoy near
Reedsport, Oregon.
|
| |
| |
•
|
The Scottish Government, to develop a 150kW PowerBuoy for
deployment in Scotland.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Iberdrola S.A., or Iberdrola, which is a large electric utility
company located in Spain and one of the largest renewable energy
producers in the world, Total S.A., or Total, which is one of
the world’s largest oil and gas companies, and two Spanish
governmental agencies, for the first phase of the construction
of a wave power station off the coast of Santoña, Spain.
|
| |
| |
•
|
The US Department of Energy (DOE) to help fund the
scale-up of
the power output per PowerBuoy from the current level of 150kW
to 500kW.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Mitsui Engineering and Shipbuilding, with which we are working
to develop a wave power project in Japan.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Leighton Contractors, a major Australian construction and
infrastructure company, for the development of a wave power
station in Victoria, Australia.
|
We were incorporated under the laws of the State of New Jersey
in April 1984 and began commercial operations in 1994. On
April 23, 2007, we reincorporated in Delaware. Our
principal executive offices are located at 1590 Reed Road,
Pennington, New Jersey 08534, and our telephone number is
(609) 730-0400.
Our website address is www.oceanpowertechnologies.com. We
make available free of charge on our website our annual reports
on
Form 10-K,
quarterly reports on
Form 10-Q,
current reports on
Form 8-K
and all amendments to those reports as soon as reasonably
practicable after such material is filed electronically with the
Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC. The information on
our website is not a part of this Annual Report. Our common
stock has been listed on the AIM market of the London Stock
Exchange plc since October 2003 and on the NASDAQ Global Market
since April 24, 2007, the date on which we commenced our
initial public offering in the United States.
Our
Market
Global demand for electric power is expected to increase from
18.8 trillion kilowatt hours in 2007 to 35.2 trillion kilowatt
hours by 2035, according to the Energy Information
Administration, or the EIA. To meet this demand, the
International Energy Agency, or the IEA, estimates that
investments in new generating capacity will be $6.8 trillion in
the period from 2007 to 2030, of which new renewable energy
generation equipment is expected to account for approximately
half of the total projected investment in electricity generation.
According to the EIA, fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural
gas generated over 67% of the world’s electricity in 2007.
However, a variety of factors are contributing to the increasing
development of renewable energy systems that capture energy from
replenishable natural resources, including ocean waves, flowing
water, wind and sunlight, and convert it into electricity.
|
|
|
| |
•
|
Rising cost of fossil fuels. Although subject
to short-term fluctuations, the cost of fossil fuel used to
generate electricity has been generally rising and is likely to
continue to rise in the future.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Dependence on energy from foreign
sources. Many countries, including the United
States, Japan and much of Europe, depend on foreign resources
for a majority of their domestic energy needs. Concerns over
political and economic instability in some of the leading fossil
fuel producing regions of the world are encouraging consuming
countries to diversify their sources of energy.
|
5
|
|
|
| |
•
|
Environmental concerns. Environmental concerns
regarding the contamination, pollution and by-products from
fossil fuels have led many countries and several US states to
agree to reduce emissions of carbon dioxide and other gases
associated with the use of fossil fuels and to adopt policies
promoting the development of cleaner technologies.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Government incentives. Many countries have
adopted policies to provide incentives for the development and
use of renewable energy sources, such as subsidies to encourage
the commercialization of renewable energy power generation.
|
As a result of these and other factors, the EIA projects that
grid-connected renewable generating capacity will continue to
grow over the next 25 years.
Wave
Energy
The energy in ocean waves is a form of renewable energy that can
be harnessed to generate electricity. Ocean waves are created
when wind moves across the ocean surface. The interaction
between the wind and the ocean surface causes energy to be
exchanged. At first, small waves occur on the ocean surface. As
this process continues, the waves become larger and the distance
between the tops of the waves becomes longer. The size of the
waves, and the amount of energy contained in the waves, depends
on the wind speed, the time the wind blows over the waves and
the distance covered. The rising and falling of the waves move
our PowerBuoy system creating mechanical energy that our
proprietary technologies convert into usable electricity.
There are a variety of benefits to using wave energy for
electricity generation.
|
|
|
| |
•
|
Scalability within a small site area. Due to
the tremendous energy in ocean waves, wave power stations with
high capacity — 50 MegaWatts (MW) and
above — can be installed in a relatively small area.
We estimate that, upon completion of the development of our
500kW PowerBuoy system, we would be able to construct a wave
power station that would occupy approximately one-tenth of the
ocean surface occupied by an offshore wind power station of
equivalent capacity.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Predictability. The supply of electricity from
wave energy can be forecasted in advance. The amount of energy a
wave hundreds of miles away will have when it arrives at a wave
power station days later can be calculated based on satellite
images and meteorological data with a high degree of accuracy.
Power producers can use this information to develop sourcing
plans to meet their short-term electricity needs.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Constant source of energy. The annual flow of
waves at specific sites can be relatively constant. Based on our
studies and analysis of our target sites, we believe our wave
power stations will be able to produce usable electricity for
approximately 90% of all hours during a year.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Close to population centers. The proximity of
wave energy resources to large population areas means that power
transmission infrastructure is often already in place and may be
utilized for wave energy generation projects.
|
There are currently several approaches, in different stages of
development, for capturing wave energy and converting it into
electricity. Methods for generating electricity from wave energy
can be divided into two general categories: onshore systems and
offshore systems. Our PowerBuoy system is an offshore system.
Offshore systems are typically located one to five miles
offshore and in water depths of between 100 and 200 feet.
The system can be above, on or below the ocean surface. Many
offshore systems utilize a floatation device to harness wave
energy. The heaving or pitching of the floatation device due to
the force of the waves creates mechanical energy, which is
converted into electricity by various technologies. Onshore
systems are located at the edge of the shore, often on a sea
cliff or a breakwater, and typically must concentrate the wave
energy first before using it to drive an electrical generator.
Although maintenance costs of onshore systems may be less than
those associated with offshore systems, there are a variety of
disadvantages with these systems. As waves approach the shore,
the energy in the waves decreases; therefore, onshore wave power
stations do not take full advantage of the amount of energy that
waves in deeper water produce. In addition, there are a limited
number of suitable sites for onshore systems and there are
environmental and possible aesthetic issues with these wave
power stations due to their size and location on the seashore.
6
Our
Products
We offer two types of PowerBuoy systems: our utility PowerBuoy
system, which is designed to supply electricity to a local or
regional electric power grid, and our autonomous PowerBuoy
system, which is designed to generate power for use independent
of the power grid in remote locations. Both products use the
same PowerBuoy technology.
Pictured below is our 40kW-rated PowerBuoy system installed
during fiscal year 2010 and in operation off Oahu, Hawaii:
Our PowerBuoy system consists of a floating buoy-like device
that is loosely moored to the seabed so that it can freely move
up and down in response to the rising and falling of the waves,
as well as a power take-off device, an electrical generator, a
power electronics system and our control system, all of which
are sealed in the unit.
The power take-off device converts the mechanical stroking
created by the movement of the unit caused by ocean waves into
rotational mechanical energy, which, in turn, drives the
electrical generator. The power electronics system then
conditions the output from the generator into usable
electricity. The operation of the PowerBuoy system is controlled
by our customized control system.
The control system uses sophisticated sensors and an onboard
computer to continuously monitor the PowerBuoy subsystems as
well as the height, frequency and shape of the waves interacting
with the PowerBuoy system. The control system collects data from
the sensors and uses proprietary algorithms to electronically
adjust the performance of the PowerBuoy system in real-time and
on a
wave-by-wave
basis. By making these electrical adjustments automatically, the
PowerBuoy system is able to maximize the amount of usable
electricity generated from each wave. We believe that this
ability to optimize the performance of the PowerBuoy system in
real-time is a significant advantage of our product.
In the event of storm waves larger than 23 feet, the
control system for the PowerBuoy automatically locks down the
PowerBuoy system and electricity generation is suspended. When
the wave heights return to a normal operating range of
23 feet or less, the control system automatically unlocks
the PowerBuoy system and electricity generation and transmission
recommence. This safety feature prevents the PowerBuoy system
from being damaged by the increased amount of energy in storm
waves.
Our 150kW PowerBuoy system has a maximum diameter of
36 feet near the surface, and is 135 feet long, with
approximately 30 feet of the PowerBuoy system protruding
above the surface of the ocean.
Utility
PowerBuoy System
The utility PowerBuoy system is designed to transmit electricity
to shore by an underwater power cable, which would then be
connected to a power grid. Our current utility PowerBuoy systems
presently being marketed to customers have rated capacities of
40kW and 150kW. The utility PowerBuoy system is designed to be
positioned in
7
water with a depth of 100 to 200 feet, which can usually be
found one to five miles offshore. This depth allows the system
to capture meaningful amounts of energy from the waves, since
decreasing water depth depletes the energy in the waves.
The mooring system for keeping a utility PowerBuoy system in
position connects it by lines to three floats that, in turn, are
connected by lines to three anchors. This is a well-established
mooring system, referred to as three-point mooring, which we
have improved upon with various techniques that reduce cost and
deployment time.
We refer to the entire utility power generation system at one
location as a wave power station, which can either be comprised
of a single PowerBuoy system or an integrated array of PowerBuoy
systems connected by our USP to an underwater cable to transmit
the electricity to shore. Our system is designed to be scalable,
as multiple PowerBuoy units can be integrated to create a wave
power station with a larger output capacity. An array of
PowerBuoy systems would likely be configured in three staggered
rows parallel to the incoming wave front to form a long
rectangle. This staggered arrangement would maximize the level
of wave energy that the wave power station can capture.
We are also exploring the use of our utility PowerBuoy system
for applications that include generating electricity for
desalination of water, hydrogen production, water treatment and
natural resource processing. In these instances, the power
generated by the utility PowerBuoy system would bypass the grid
and be delivered directly to the point of electricity
consumption for these special applications.
Status of
Utility PowerBuoy System
We expect that our first 150kW PowerBuoy will be ready for
deployment during the second half of calendar year 2010. We have
also initiated product development efforts in connection with
our 500kW PowerBuoy.
We completed the successful in-ocean trials of our USP in
October 2009. The USP, based on our proprietary design, has been
developed to facilitate the collection, networking and
transforming of power and data generated by multiple offshore
energy devices. The USP has been built as an open platform, and
can provide connectivity for the PowerBuoy as well as other
offshore energy systems developed by other companies.
The following is a picture of the USP being lowered into the
water for ocean trials:
Our PowerBuoy interface with the electrical utility power grid
has been certified as compliant with international standards. An
independent laboratory provided testing and evaluation services
to certify that our systems comply with designated national and
international standards. The PowerBuoy grid interface bears the
ETL listing mark, and can be connected to the utility grid.
Autonomous
PowerBuoy System
The autonomous PowerBuoy system is based on similar technology
to the utility PowerBuoy system, but is designed for electricity
generation of relatively low amounts of power for use
independent of the power grid in
8
remote locations. The autonomous PowerBuoy system currently has
a maximum rated output ranging from 300 Watts to 40kW, depending
on the application. Our autonomous PowerBuoy system is designed
to operate anywhere in the ocean and in any depth of water.
We believe that the autonomous PowerBuoy system is suitable for
use on a stand-alone basis for providing power for a variety of
applications in deep ocean conditions, such as sonar and radar
surveillance, tsunami warning, offshore data collection,
offshore platforms and offshore aquaculture.
Status of
Autonomous PowerBuoy System
We have received several contracts from the US Navy to provide
our PowerBuoy technology to a unique program for ocean data
gathering. Under this program, the Navy has conducted an ocean
test of our autonomous PowerBuoy as the power source for the
Navy’s Deep Water Active Detection System and we are
performing work under a new contract for the next phase of work
under this program. This new contract is for ocean testing by
the Navy of an advanced version of the autonomous PowerBuoy for
the Navy’s operational requirements.
We also received a contract from the US Navy to provide our
PowerBuoy to the Navy’s Littoral Expeditionary Autonomous
PowerBuoy (LEAP) program. The LEAP program has been established
to enhance the US Navy’s anti-terrorism and force
protection capability by providing persistent power at sea for
port maritime surveillance in the near coast, harbors, piers and
offshore areas.
Our
Competitive Advantages
We believe that our technology for generating electricity from
wave energy and our commercial relationships give us several
potential competitive advantages in the renewable energy market.
Our PowerBuoy system uses an ocean-tested technology to
generate electricity.
|
|
|
| |
•
|
We have been conducting ocean tests for over a decade in order
to demonstrate the viability of our technology. We initiated our
first ocean installation in 1997 and have had several
deployments of our systems for testing and operation since then,
the longest of which has had continuous operation of
12 months. Our PowerBuoy systems have survived several
hurricanes and winter storms while installed in the ocean. Since
its installation in Hawaii in December 2009, our 40kW-rated
PowerBuoy has produced power consistent with our predictive
models.
|
Our PowerBuoy system’s grid connection has been
certified.
|
|
|
| |
•
|
In July 2007, we announced that our PowerBuoy grid connection
system had been certified as compliant with designated national
and international standards. This qualifies our technology for
integration into utility grid systems.
|
Our PowerBuoy system design is efficient in harnessing wave
energy.
|
|
|
| |
•
|
Our PowerBuoy system is designed to efficiently convert wave
energy into electricity by using onboard sensors to detect
actual wave conditions and then to automatically adjust, or
“tune”, the performance of the generator using our
proprietary electrical and electronics-based control systems in
response to that information.
|
| |
| |
•
|
One measure of the efficiency of an electric power generation
system is capacity factor. The capacity factor is the percent of
kilowatt hours produced by a specific system in a given period
as compared to the maximum kilowatt hours that could be produced
by the system in that period. A high capacity factor indicates a
high degree of utilization of the capacity of the system and
provides a means to compare the effectiveness of different
energy sources. Since we have not yet operated a complete wave
power station, we do not have a measured capacity factor.
However, based on our research and analysis, we believe the
design capacity factor for a PowerBuoy wave power station
located at many of our targeted sites would be favorably
positioned in the range of 30% to 45%.
|
9
Numerous potential sites for our wave power stations are
located near major population centers worldwide.
|
|
|
| |
•
|
Our systems are designed to work in sites with average annual
wave energy of at least 20kW per meter of wave front, which can
be found in many coastal locations around the world. In
particular, we are currently targeting the west coast of North
America, the west coast of Europe, the coasts of Australia and
the east coast of Japan. These potential sites not only have
appropriate natural resources for harnessing wave energy, but
they are also located near large population centers with
significant and increasing electricity requirements and access
to existing power transmission infrastructure.
|
We have significant commercial relationships.
|
|
|
| |
•
|
Our current projects with PNGC Power, the US Department of
Energy, the US Navy, the Scottish Government, and Iberdrola
provide us with an initial opportunity to sell our wave power
stations for utility applications. By collaborating with leaders
in renewable energy development, we believe we are able to
accelerate both our in-house knowledge of the utility power
generation market and our reputation as a credible renewable
energy equipment supplier. If these projects are successful, we
intend to leverage our experiences with our projects to add wave
power stations, new customers and complementary revenue streams
from operations and maintenance contracts.
|
| |
| |
•
|
With the funding from the US Navy, we have been able to refine
our PowerBuoy system while simultaneously preparing for
commercial deployment to address a particular customer need. We
believe that the successful deployment of our PowerBuoy system
for the US Navy will significantly enhance market visibility.
|
Our PowerBuoy system has the potential to offer a cost
competitive renewable energy power generation solution.
|
|
|
| |
•
|
Our product development and engineering efforts are focused on
increasing the maximum rated output and reliability of the
design of our utility PowerBuoy system. Currently we are
marketing PowerBuoys rated at 40kW and 150kW. Assuming we are
able to reach manufacturing levels of at least 300 units of
500kW PowerBuoy systems per year, we believe, based upon our
research and analysis, that the economies of scale we would have
with our fabricators would allow us to offer a renewable
electricity solution that competes with other existing renewable
energy systems and, in certain cases, with existing fossil fuel
systems in key markets.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Prior to achieving full production levels of the 500kW PowerBuoy
system, if we achieve economies of scale for our 150kW PowerBuoy
systems, we expect to be able to offer a renewable electricity
solution that competes with the price of electricity in certain
local markets where the current retail price of electricity is
relatively high or where sufficient subsidies are available.
|
Our systems are environmentally benign and aesthetically
non-intrusive.
|
|
|
| |
•
|
We believe that our PowerBuoy system does not present
significant risks to marine life and does not emit significant
levels of pollutants. In connection with our project at the US
Marine Corps Base in Hawaii, our customer, the US Navy, obtained
an independent environmental assessment of our PowerBuoy system
prior to installation, as required by the National Environmental
Policy Act. This assessment resulted in a Finding of No
Significant Impact, the highest such level of approval. Although
our project for the US Navy only contemplates an array of up to
six PowerBuoy systems in Hawaii, we believe that PowerBuoy
systems deployed in other geographic locations, including larger
PowerBuoy systems under development and multiple- buoy wave
power stations, would have minimal environmental impact due to
the physical similarities with the tested system.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Since our PowerBuoy systems are typically located one to five
miles offshore, PowerBuoy wave power stations are usually not
visible from the shore. Visual impact is often cited as one of
the reasons that many communities have opposed plans to develop
power stations, in particular wind power stations. Our PowerBuoy
system has the distinct advantage of having only a minimal
visual profile. Only a small portion of the unit is visible at
close range, with the bulk of the unit hidden below the water.
|
10
Customers/Projects
The table below shows the percentage of our revenue we derived
from significant customers for the periods indicated:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fiscal
|
|
Fiscal
|
|
Fiscal
|
|
Customer
|
|
2010
|
|
2009
|
|
2008
|
|
|
|
US Navy
|
|
|
80
|
%
|
|
|
67
|
%
|
|
|
58
|
%
|
|
Iberdrola and Total
|
|
|
4
|
%
|
|
|
18
|
%
|
|
|
31
|
%
|
|
Scottish Government
|
|
|
5
|
%
|
|
|
8
|
%
|
|
|
10
|
%
|
We expect an increasing proportion of our future revenues to be
contributed by commercial customers.
Our potential customer base for our utility PowerBuoy systems
consists of public utilities, independent power producers and
other governmental entities and agencies. Our potential customer
base for our autonomous PowerBuoy systems consists of different
public and private entities who use electricity in and near the
ocean. Our efforts to identify new customers are concentrated on
four geographic markets: the west coast of North America, the
west coast of Europe, the coasts of Australia and the east coast
of Japan. Our efforts to identify new customers are currently
led and coordinated by our Executive Chairman and our Vice
President of North America Business Development and Marketing.
We also use consultants and other personnel to assist us in
locating potential customers.
US
Navy
Since September 2001, we have entered into a series of contracts
with the United States Office of Naval Research for the
development and construction of wave power systems at the Marine
Corps base in Oahu, Hawaii. Under the contract for the current
phase of the project, which was entered into in September 2005
and expires in September 2010, we are reimbursed for costs and
paid a fixed fee, and over this period have been awarded
contracts for total potential revenue of $5.9 million. The
current PowerBuoy now in operation at the Marine Corps base was
deployed in December 2009 and has produced power consistent with
our predictive models.
Pictured below are views of our 40kW-rated PowerBuoy system
being lowered into the ocean in Oahu, and after deployment.
In June 2007, we received a $1.7 million contract from the
US Navy to provide our PowerBuoy technology to a unique program
for data gathering in the ocean. Under this
18-month
program, the US Navy conducted an ocean test in October 2008 of
our autonomous PowerBuoy as the power source for the Navy’s
Deep Water Active Detection System. In October 2008, we received
a $3.0 million contract from the US Navy to expand the
program and ocean-test an advanced version of our autonomous
PowerBuoy.
In September 2009, we received a $2.4 million contract from
the US Navy to provide our PowerBuoy to the Navy’s LEAP
program. The LEAP program is being developed to enhance the US
Navy’s anti-terrorism and force
11
protection capability by providing persistent power at sea for
port maritime surveillance in the near coast, harbors, piers and
offshore areas.
Reedsport,
Oregon Project
In February 2007, the US Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
(FERC) granted us a preliminary permit to evaluate the
feasibility of a location off the coast of Reedsport, Oregon for
the proposed construction and operation of a wave power station
with a total potential maximum rated output of up to 50MW, of
which up to the first 2MW would be a demonstration wave power
station. In February 2007, we signed a cooperative agreement
with PNGC Power, an Oregon-based electric power cooperative, as
our utility partner for the development of a wave power station.
In July 2007, we filed a Pre-Application Document and Notice of
Intent with FERC for the Reedsport project, which provides
notice of our intent to seek a license for the Reedsport power
station and information regarding the project. We believe this
was the first Pre-Application Document and Notice of Intent
filed by a wave power company, and is an important step in the
full licensing process for the Reedsport project. We will need
additional authorization from FERC to sell electric power
generated from the Reedsport wave power station into the
wholesale or retail markets. In February 2010, we filed with
FERC a full application to build, deploy and connect to the grid
a 10-PowerBuoy array (1.5MW).
In August 2007, we announced the award of a $0.5 million
contract from PNGC Power, providing funding toward the
fabrication and installation of a 150kW PowerBuoy system for the
Reedsport project. In October 2008, we received a
$2.0 million award from the DOE in support of the project.
The DOE grant will be used to help fund the fabrication and
factory testing of the first PowerBuoy to be installed at the
Reedsport site. This is the first award for the building of
ocean wave energy systems by the DOE, and we believe it is
indicative of the growing recognition and support of wave energy
in the US federal and state governments.
This project remains on schedule, with the PB150 construction
expected to be completed by the end of 2010, and ocean testing
is expected to commence in 2011.
12
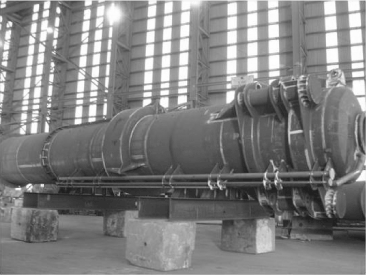
The following photographs show manufacturing activity associated
with our PB150 PowerBuoy being built in Oregon:
We continue to make progress on the overall permitting and
licensing process while working extensively with interested
stakeholder groups at local, county, state and federal agency
levels.
Next
Generation PowerBuoy
In April 2010, we won a $1.5 million award from the DOE for
the development of our next generation PowerBuoy wave power
system. The DOE grant will be used to help fund the
scale-up of
the power output per PowerBuoy from the current level of 150kW
to 500kW. In addition, the technology development effort will
focus on increasing the power extraction efficiency and
reliability.
Scotland
Project
In 2007, we received a $1.8 million contract from the
Scottish Executive for the construction of a 150kW
grid-connected PowerBuoy system at the European Marine Energy
Centre (EMEC) in Orkney, Scotland. EMEC is a test facility for
marine energy technologies, for which the Scottish Government
has built the infrastructure for grid connection. In 2008, we
signed a Berth Agreement with EMEC. This agreement provides for
the deployment and operation of PowerBuoys as well as their
connection to the wave energy berth’s dedicated 2MW subsea
cable already installed and connected to the Scottish grid. The
Berth Agreement also enables us to sell power to the grid up to
the 2MW capacity limit. The construction phase of the buoy has
been completed and we expect the buoy to be ready for deployment
during the second half of calendar year 2010. This deployment
will be for the conduct of in-ocean trials of the PB150
PowerBuoy at a location in Scotland following which a decision
will be made regarding deployment at EMEC.
13
The following pictures show manufacturing activity in Scotland
associated with our PB150 PowerBuoy:
Spain
In July 2004, we entered into a development agreement, which we
refer to as the Spain development agreement, with Iberdrola
Energias Renovables II, S.A. (Iberdrola Energias), an affiliate
of Iberdrola, Sociedad para el Desarrollo Regional de Cantabria,
S.A., or SODERCAN, which is the industrial development agency of
the Spanish region of Cantabria, and Instituto para la
Diversificacion y Ahorro de la Energia, S.A., or IDAE, a Spanish
government agency dedicated to energy conservation and
diversification efforts, to jointly study the possibility of
developing a wave power station off the coast of Santoña
located in the Cantabria region in northern Spain. Total Eolica
S.A., an affiliate of Total, joined the development agreement in
June 2005. In January 2006, we completed
14
the assessment phase of the project, which included an
assessment of wave energy resources at the site, a feasibility
analysis for deployment at the site, a determination of capacity
and design, and an estimation of investments needed for the
project as well as anticipated costs for operation, maintenance
and repairs. Expenses associated with this phase were shared
among the parties to the agreement based on agreed upon
percentages.
In July 2006, Iberdrola Energias Marinas de Cantabria, S.A., or
Iberdrola Cantabria, was formed for the purpose of constructing
and operating a wave power station off the coast of
Santoña, Spain. Iberdrola Energias is the largest
shareholder of Iberdrola Cantabria. Total Eolica, SODERCAN, IDAE
and we each have minority ownership positions. Funding is shared
among the parties to the agreement based on agreed upon
percentages that reflect the parties’ anticipated ownership
interest in the wave power station. We own 10% of Iberdrola
Cantabria.
In July 2006, we entered into an agreement for the first phase
of the construction of a wave power station off the coast of
Santoña, Spain, with our customer, Iberdrola Cantabria. We
refer to this agreement as the Spain construction agreement.
Iberdrola Cantabria was formed by affiliates of Iberdrola and
Total, two Spanish governmental agencies and us for the purpose
of constructing and operating a wave power station off the coast
of Spain. Under the Spain construction agreement, we agreed to
manufacture and deploy one 40kW PowerBuoy system and the
ocean-based substation and infrastructure required to connect
nine additional 150kW PowerBuoy systems that together are
contemplated to constitute a 1.39MW wave power station by no
later than December 31, 2009. We are currently in
discussions with Iberdrola Cantabria regarding the timing and
completion of this project. In February 2008, the Spain
construction agreement was amended to provide for the current
phase of the construction of the PowerBuoy system plus the
fabrication of the underwater power transmission cable and
underwater substation pod for all ten PowerBuoy systems. The
terms of the installation of the underwater transmission cable
and underwater substation pod will be separately negotiated and,
if so agreed, could provide for additional funding for the
installation work. Because the amended Spain construction
agreement does not cover the terms for deployment of the
underwater transmission cable and substation pod and the
manufacture and deployment of the nine additional PowerBuoy
units, we would need to enter into a subsequent contract with
Iberdrola Cantabria before we complete these elements of
construction of the full wave power station.
The initial PB40 PowerBuoy system for this project was deployed
in September 2008. After a short testing period, the buoy was
removed from the water for work on improvements to the power
take-off and control systems. We are currently in discussions
with Iberdrola Cantabria regarding the nature and costs of these
improvements and their effects on plans for the redeployment of
the buoy and the next phases of the project. If no modification
is agreed to by the parties, the customer may, subject to
certain conditions in the agreement, terminate the agreement and
would not be obligated to make any more milestone payments. In
addition, if we and Iberdrola Cantabria decide not to redeploy
the PB40 PowerBuoy, the total contract value for the current
phase of the contract may be reduced. If we are unable to
successfully meet the terms of the Spain construction agreement,
or if we are not able to successfully negotiate a subsequent
contract or contracts with Iberdrola Cantabria for the
manufacture and deployment of the nine additional PowerBuoy
units, or if Iberdrola Cantabria were to terminate the Spain
construction agreement for any of these reasons, we may lose a
component of our current and anticipated revenue stream. If we
are unable to agree to the necessary contract modifications,
Iberdrola Cantabria will have the right to terminate the
agreement if the first phase of construction is not completed on
time for reasons attributable to us, or if we interrupt our
services for more than 180 days and do not resume within a
30-day
period, or for a serious and repeated breach of a major
obligation that is not cured within a
30-day
period after we receive notice of the breach. In addition, we
have made guarantees to Iberdrola Cantabria associated with the
current phase of construction in respect of the quality, repair
and replacement of the 40kW PowerBuoy system and ocean-based
substation and the level of power output of the 40kW PowerBuoy
system. If we are found to be in default of our obligations
under the Spain construction agreement, Iberdrola Cantabria will
have the right to seek reimbursement for direct damages only,
limited to amounts specified in the contract.
We are paid under the Spain construction agreement as we
complete certain milestones for a total potential payment for
the current phase of construction of approximately
€2.7 million. From inception to April 30, 2010,
we had recognized revenue of approximately $3.0 million and
a recognized loss of $3.9 million under the Spain
construction agreement. The anticipated loss at completion of
the contract also reflects our decision made in the fourth
quarter of fiscal year 2008 to absorb $1.9 million of
additional costs of the project beyond our obligation for the
initial cost overruns and certain other costs as set forth in
the agreement. This decision was based on the progress
15
of the project up to that point, the benefits to be derived from
a successful initial project and the prospect of incremental
contract value to be received in connection with additional work
under this contract.
In March 2010, we announced the award of €2.2 million
under the European Commission’s Seventh Framework Programme
(FP7) by the European Commission’s Directorate responsible
for new and renewable sources of energy, energy efficiency and
innovation. This grant is part of a total award of
€4.5 million to a consortium of companies, including
us, to deliver a PowerBuoy wave energy device under a project
entitled WavePort, with an innovative wave prediction capability
and a
“wave-by-wave”
tuning system. It is anticipated that the PowerBuoy will be
deployed at the Santoña site in Spain. Our work under the
award is conditional on our obtaining significant additional
funding to enable completion of the WavePort project.
Pictured below are views of our 40kW-rated PowerBuoy system
during tow-out to the deployment site off Santoña, Spain,
and after deployment.
Other
Projects
In February 2006, we received approval from the South West of
England Regional Development Agency (SWRDA) to install a 5MW
demonstration wave power station off the coast of Cornwall,
England as part of SWRDA’s “Wave Hub” project, a
planned offshore facility for demonstrating and testing wave
energy generation devices. SWRDA has obtained the necessary
permits for this Wave Hub project, and the project has been
approved for over £40 million of funding for
construction of the Wave Hub infrastructure by SWRDA.
Construction contracts have been awarded and SWRDA expects
installation during 2010. We are in the planning and development
stage for our part of the project, and we are seeking funding
for the 5MW power station.
In October 2008, we signed an exclusive agreement with a
consortium of three Japanese companies to develop a
demonstration wave power station in Japan. The Japanese
consortium comprises Idemitsu Kosan Co., Mitsui
Engineering & Shipbuilding Co. (MES), and Japan Wind
Development Co. We are presently working with MES to identify
prospective sites for the wave power station.
In December 2008, we announced a Joint Development Agreement
with Leighton Contractors Pty. Ltd. (Leighton) for the
development of wave power projects off the east and south coasts
of Australia. Over the past 50 years, Leighton has played
an active role in building Australia’s ports and marine
facilities, transportation infrastructure, and energy projects
including projects within the wind and offshore oil and gas
sectors. Under the terms of the agreement, Ocean Power
Technologies (Australasia) Pty. Ltd. (OPTA), our subsidiary
based in Australia, will identify potential project sites and
assess their commercial prospects, under contract from Leighton.
Upon identification of projects to be developed, Leighton would
obtain approvals, negotiate power purchase agreements, structure
project financing, and oversee project delivery and operation of
the power stations. If these projects are undertaken, OPTA would
sell the PowerBuoy wave power stations to Victorian Wave
Partners Pty. Ltd., a special purpose company formed by Leighton
for the projects. In November 2009, we announced that OPTA was
awarded, in partnership with Leighton, an A$66.46 million
grant from the Federal Government of Australia to build a 19MW
wave power project off the coast of Victoria, Australia. The
grant is conditional on the signing of a Funding
16
Deed which will set out the terms of the grant, including
funding milestones. Victorian Wave Partners is currently seeking
the significant additional funding required to enable the
completion of the 19MW wave power station.
Over the period October 2005 to December 2009, we operated, at
intervals, a demonstration PowerBuoy system off the coast of New
Jersey, which allowed continuous monitoring of the system and
evaluation of its performance in actual wave conditions.
Periodically, the buoy was removed from the ocean for
maintenance, testing and upgrades, and was redeployed. The buoy
was deployed continuously for 12 months between October
2005 and October 2006, and survived hurricane-generated storm
waves during this period and in a later period of ocean
deployment. We have conducted extensive diagnostic tests on the
system, providing us with information about the effects of ocean
deployments that will help us implement improvements in future
PowerBuoy systems. This system was not designed to supply
electricity to the power grid, but rather to provide us with
operational data and marketing opportunities. We were partially
funded, which funds we recognized as revenue, for the
construction of this PowerBuoy system by the New Jersey Board of
Public Utilities. We do not anticipate any additional funding or
recognizing any additional revenue in connection with this
project.
Backlog
Our contract backlog consists of the aggregate anticipated
revenue remaining to be earned at a given time from the
uncompleted portions of our existing customer contracts. As of
April 30, 2010, our contract backlog was $5.7 million
as compared to $7.5 million as of April 30, 2009. We
anticipate that a majority of our backlog will be recognized as
revenue over the next 12 months.
The amount of contract backlog is not necessarily indicative of
future revenue because modifications to or terminations of
present contracts and production delays can provide additional
revenue or reduce anticipated revenue. A substantial majority of
our revenue is recognized using the
percentage-of-completion
method, and changes in estimates from time to time may have a
significant effect on revenue and backlog. Our backlog is also
typically subject to large variations from time to time due to
the timing of new awards.
Our
Business Strategy
Our goal is to strengthen our leadership in developing wave
energy technologies and commercializing wave power stations and
related services. In order to achieve this goal, we are pursuing
the following business strategies:
|
|
|
| |
•
|
Sell turn-key power stations and operating and maintenance
contracts. Our fundamental business plan is to
sell turn-key power stations, rather than to take on the capital
requirements of building and owning power stations and selling
the energy generated. In addition, in order to create recurring
revenue streams, we seek to sell operating and maintenance
(O&M) contracts over the life-cycle of the plants.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Outsource most of the plant construction and
deployment. We outsource all metal fabrication,
anchoring, mooring, cabling supply and deployment in order to
minimize our capital requirements as we scale up production
volumes. The high value-added “smart part” of the
system is assembled and tested at our facilities and shipped to
project sites for integration into the PowerBuoys.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Concentrate sales and marketing efforts on four geographic
markets. We are currently focusing our sales and
marketing efforts on the west coast of North America, the west
coast of Europe, the coasts of Australia and the east coast of
Japan. We believe that each of these areas represents a strong
potential market for our PowerBuoy wave power stations because
they combine appropriate wave conditions, political and economic
stability, large population centers, high levels of
industrialization and significant and increasing electricity
requirements.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Continue to increase PowerBuoy system
output. Our product development and engineering
efforts are focused on increasing the rated output of the design
of our PowerBuoy systems from 40kW to 150kW, and thereafter to
500kW. If we increase the size of a PowerBuoy system, we will be
able to increase the amount of wave energy the system can
capture and, in turn, increase the output of the system. For
example, if we double the size of the unit’s float
diameter, we will approximately quadruple its power capacity. We
believe that by increasing system output of the individual
PowerBuoy, and also by increasing volume production of
|
17
|
|
|
| |
|
the PowerBuoys, we will be able to decrease the cost per kW of
our PowerBuoy system and the cost per kilowatt hour of the
energy generated.
|
|
|
|
| |
•
|
Leverage customer relationships to enhance the commercial
acceptance of our utility PowerBuoy system. We
believe that our projects at the US Marine Corps base in Oahu,
Hawaii will serve as a prototype wave power station for the
installation of wave power stations at other US Navy bases. Our
relationship with PNGC Power regarding our Reedsport, Oregon
project is the first such utility relationship on the west coast
of the United States. We intend to build on these existing
commercial relationships both by expanding the number and size
of projects we have with our current customers and by entering
into new alliances and commercial relationships with other
utilities and independent power producers.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Expand revenue streams from our autonomous PowerBuoy
system. The autonomous PowerBuoy system addresses
specific power generation needs of customers requiring off-grid
electricity generation in remote locations in the open ocean.
Since our PowerBuoy systems are well suited for many of these
uses, we do not expect that they will require subsidies or other
price incentives for commercial acceptance. This equipment might
be used for powering sonar and radar surveillance, tsunami
warning, oceanographic data collection, offshore platforms and
offshore aquaculture. We have entered into contracts with the US
Navy for the testing of our autonomous PowerBuoy in connection
with a unique program for ocean data gathering, as well as for
the LEAP program for homeland security. We believe that
successful testing of our autonomous PowerBuoy System under
these contracts may result in additional revenues from the US
Navy and other prospective customers.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Maximize customer funding of technology
development. We actively seek to obtain external
funding for the development of our technology, including the
scale-up of
power capacity per PowerBuoy. In April 2010, we were awarded
$1.5 million from the US Department of Energy for the
development of our PB500 product.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Expand our partnerships in key market
areas. We believe that an important element of
our business strategy is to collaborate with other organizations
to leverage our combined expertise, market presence and core
competences. We have formed such partnerships more recently with
Leighton Contractors in Australia, Mitsui Engineering and
Shipbuilding in Japan, and Lockheed Martin in the US.
|
Marketing
and Sales
We are developing our sales capabilities and have begun
commercial marketing and selling of our PowerBuoy systems.
Because our products use a new commercial technology, the
decision process of a customer requires substantial educational
efforts, in which many of our employees may participate.
In addition to our own direct sales, we will continue to enter
into development agreements and strategic alliances with
regional utility and energy companies committed to providing
electricity from renewable energy sources. We plan to leverage
these relationships to sell and market our PowerBuoy wave power
stations to these companies and their affiliates and to other
customers in the region. We plan to expand our relationships by
entering into long-term operations and maintenance contracts to
support completed wave power stations. In order to penetrate
certain international markets, we plan to implement marketing
strategies that respond to local market demands. In particular
markets, we may grant licenses to local businesses to sell,
manufacture or operate PowerBuoy wave power stations.
Utility
PowerBuoy System Marketing
We plan to market our utility PowerBuoy systems to utilities and
independent power producers interested in adding electricity
generated from renewable sources to their existing electricity
supply. We are currently targeting customers on the west coast
of North America, the west coast of Europe, the coasts of
Australia and the east coast of Japan. In addition, we are
exploring the use of our utility PowerBuoy systems for
applications that include desalination of water, hydrogen
production, water treatment and natural resource processing. In
these instances, the power generated by the utility PowerBuoy
system would bypass the grid and be delivered directly to the
point of electricity consumption for these special applications.
18
We expect to be able to use the availability of subsidies and
other incentives to market the electricity generated by wave
power stations as an alternative to fossil fuel generated
electricity. We plan to educate potential customers on the
availability of these incentives and, where appropriate, work
with them to prepare and file the necessary applications, select
sites to meet program requirements and take advantage of these
incentives.
Autonomous
PowerBuoy System Marketing
There are a variety of potential customers, such as companies
within the offshore oil and gas industry, the US Department of
Homeland Security and US Department of Defense, that have
specific needs for off-grid power generation that can be
supplied by our autonomous PowerBuoy system. Potential
applications for off-grid power supply include sonar and radar
surveillance, tsunami warning, oceanographic data collection,
offshore platforms and offshore aquaculture.
Manufacturing
and Deployment
Manufacturing
and Raw Materials
We engage in two types of manufacturing activities: the
manufacturing of the high value-added components, or “smart
part” modules, for systems control, power generation and
power conversion for each PowerBuoy system, and the contracting
to outside companies for the fabrication of the buoy-like
structure, anchoring and mooring, and cabling.
Our core in-house manufacturing activity is the assembly and
testing of the power generation and control modules at our
Pennington, New Jersey facility. The power generation and
control modules include the critical electrical and electronic
systems that convert the mechanical energy into usable
electrical energy. The sensors and control systems use
sophisticated technology to monitor ocean conditions and
automatically optimize the performance of the PowerBuoy system
in response to those changing conditions. We have a portfolio of
patents, including those that cover our power generation, power
conversion and control technologies. Due to the critical and
proprietary nature of these systems, we do not outsource their
assembly and testing. After a generator and control module
passes our rigorous quality control procedures, it is
transported as a
ready-to-install
subsystem to the project site.
We purchase the remaining components of, and raw materials for,
each PowerBuoy system from various vendors. Currently, we
contract for these components on a
project-by-project
basis. We conduct a bidding process to select a supplier with
the optimal combination of price, delivery terms and quality.
Our goal is to develop ongoing relationships with select vendors
centrally located in different regions, which will allow us to
reduce unit costs as our volume increases. We provide
specifications to each vendor, and they are responsible for
performing quality analysis and quality control over the course
of construction, subject to our review of the quality test
procedures and results. After each vendor completes testing of
the component, it is transported
ready-to-install
to the project site.
Upon arrival at the project site, the generator and control
modules are integrated with the balance of the components of the
PowerBuoy system. We are highly dependent on our third-party
suppliers; however, we actively manage key steps in the supply
chain. We act as the general contractor, and retain the ultimate
responsibility for building the PowerBuoy wave power station,
and installing, testing and deploying the complete wave power
station at the project site. This process requires significant
project and contract management by us. We currently employ
individuals who have experience with all aspects of both the
manufacturing and engineering contracting processes, and
demonstrated organizational capabilities in these critical areas.
In January 2009, we announced that we signed a letter of intent
with Lockheed Martin Corporation to collaborate in the delivery
of a utility-scale wave power generation project in North
America. We intend to enter into an agreement under which we
would provide our project and site development expertise, build
the power take-off and control systems of the plant, and provide
our proprietary PowerBuoy technology. Lockheed Martin would
undertake construction, systems integration and deployment of
the plant, as well as operations and maintenance services. This
would be the first agreement between our two companies for a
utility-scale renewable energy project and would build on our
previous work together on systems for US homeland security and
maritime surveillance consisting of our autonomous PowerBuoy
integrated with Lockheed Martin’s advanced acoustic
sensors, signal
19
processing and communications systems. Our prospective wave
power project with Lockheed Martin is expected to be off the
coast of North America.
Deployment
For our existing and currently planned deployments, we purchase
from subcontractors the mooring system and cables needed to
install the PowerBuoy system and connect it to either the power
grid or a remote power site. The vendor usually transports these
components to the project site.
Each step in the deployment process for our existing and
currently planned deployments is outsourced to subcontractors
located near the project site. First the mooring system,
consisting of floats, anchors and chains, is brought to the wave
power station’s ultimate ocean location by workboats or
barges. At the same time, the cable to transmit the generated
electricity is laid by a subcontractor. Next, the PowerBuoy
system is towed to the ocean location and fixed to the mooring
system. The PowerBuoy system would then be connected to the
transmission cable, which would then be connected to the grid or
the distributed power site. At this point, we would have a fully
assembled PowerBuoy wave power station, which, subject to final
testing, would be ready for operation. An array of PowerBuoy
systems would be installed using a similar approach.
We expect that the subcontractor services required for
deployment of a wave power station will be readily available in
the locations where we currently plan to deploy our systems,
although we are dependent on third parties for the entire
process. We actively manage each step with personnel who have
significant project management and deployment experience.
The following are pictures showing the PowerBuoy deployment
process:
20
Research
and Development
Our research and development team consists of employees with a
broad range of experience in mechanical engineering, electrical
engineering, hydrodynamics and systems engineering. We engage in
extensive research and development efforts to improve PowerBuoy
efficiency, reliability and power output and to reduce
manufacturing cost and complexity. Our research and development
efforts are currently focused on product development, in
particular increasing the output and reliability of our utility
PowerBuoy system. We are also conducting research on
improvements to our current technology.
Research and development expenses are reflected on our
consolidated statements of operations as product development
costs. Research and development expenses were $13.0 million
for fiscal 2010, $8.4 million for fiscal 2009 and
$8.3 million for fiscal 2008.
We are currently working on the design for our 500kW PowerBuoy.
The key to increasing the rated output of the PowerBuoy system
is to increase the system’s efficiency as well as its
diameter. If we increase the size and efficiency of the wave
capture portion of the PowerBuoy system, we will be able to
increase the amount of wave energy the system can capture and,
in turn, increase the output of the system. For example, if we
double the float’s diameter, we will approximately
quadruple its power capacity. We believe that we will be able to
increase the output capacity of the PowerBuoy system using
technology that we have already developed, so our focus is on
the design, manufacture, testing and deployment of the higher
capacity systems. We are exploring design and construction
techniques that will enable the larger PowerBuoy systems to be
deployed cost effectively and safely without damage. For
example, our 40kW PowerBuoy systems are transported to the
onshore deployment sites using standard flatbed trucks. However,
the assembled 150kW PowerBuoy systems are too large for these
trucks and need to be transported in modules and assembled
on-site. In
addition, we will need to adjust the mooring system to account
for the larger-sized PowerBuoy systems.
We completed the successful in-ocean trials of our USP in
October 2009. The USP, based on our proprietary design, has been
developed to facilitate the collection, networking and
transforming of power and data generated by multiple offshore
energy devices. The USP has been built as an open platform, and
can provide connectivity for the PowerBuoy as well as other
offshore energy systems developed by other companies. The power
conversion and controls system is complete for the first 150kW
PowerBuoy system, and we expect to conduct in-ocean trials in
the second half of calendar 2010 in Scotland.
We also plan to continue our technology development of specific
applications for our PowerBuoy systems to expand our growth
opportunities. For example, we are exploring applications that
include desalination of water, hydrogen production, water
treatment and natural resource processing.
It is our intent to fund the majority of our research and
development expenses over the next several years with sources of
external funding. If we are unable to obtain external funding,
we may curtail our research and development expenses or we may
decide to self-fund significant research and development
expenses, in which case our product development costs may
continue to increase.
Intellectual
Property
We believe that our technology differentiates us from other
providers of wave and other renewable energy technologies. As a
result, our success depends in part on our ability to obtain and
maintain proprietary protection for our products, technology and
know-how, to operate without infringing the proprietary rights
of others and to prevent others from infringing our proprietary
rights. Our policy is to seek to protect our proprietary
position by, among other methods, filing United States and
foreign patent applications related to our proprietary
technology, inventions and improvements that are important to
the development of our business. We also rely on trade secrets,
know-how, and continuing technological innovation and may rely
on licensing opportunities to develop and maintain our
proprietary position.
As of April 30, 2010, we owned a total of 42 issued United
States patents and 14 United States patent applications. We have
pending foreign counterparts to 16 of our issued patents and
nine of our pending non-provisional patent applications.
21
Our patent portfolio includes patents and patent applications
with claims directed to:
|
|
|
| |
•
|
system design;
|
| |
| |
•
|
control systems;
|
| |
| |
•
|
power conversion;
|
| |
| |
•
|
anchoring and mooring; and
|
| |
| |
•
|
wave farm architecture.
|
The expiration dates for our issued United States patents range
from 2015 to 2027. We do not consider any single patent or
patent application that we hold to be material to our business.
The patent positions of companies like ours are generally
uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions. Our
ability to maintain and solidify our proprietary position for
our technology will depend on our success in continuing to
obtain effective patent claims and enforcing those claims once
granted. In addition, certain technologies that we developed
with US federal government funding are subject to certain
government rights as described in “Risk Factors —
Risks Relating to Intellectual Property.”
We use trademarks on nearly all of our products and believe that
having distinctive marks is an important factor in marketing our
products. We have registered our PowerBuoy
®,
Talk on
Watertm
and
CellBuoytm
marks and our Making Waves in
Powersm
service mark, and we have filed applications to register our
PowerTower mark in the United States.
Competition
We compete and will compete with power generation equipment
suppliers in all segments of the electric power industry,
including wave energy, other forms of renewable energy and
traditional fossil fuel. The renewable energy industry is both
highly competitive and continually evolving as participants
strive to differentiate themselves within their markets and
compete within the larger electric power industry. Many of our
competitors in certain of these segments have established a
stronger market position than ours and have greater resources
and name recognition than we have. In addition, there are many
companies, including some of the largest multinational energy
companies, that are developing or sponsoring innovative
technologies for renewable energy production. Accordingly, our
success depends in part on developing and demonstrating the
commercial viability of wave energy solutions and identifying
markets for and applications of our PowerBuoy systems and
technology.
Although the market for equipment that generates electricity
from wave energy is in its early stage of commercial
development, there are a number of private companies, some with
institutional funding, developing technologies to generate
electricity from wave energy, and we compete or will compete
with them. We believe there are over 75 companies worldwide
developing wave energy technologies. Most of these companies are
located in the United Kingdom, continental Europe, the United
States and Australia, and almost all are focused on offshore
systems. Only a few of these companies, like ourselves, have
conducted ocean testing of their systems, which is the critical
factor in proving the survivability and performance of any wave
energy system.
Sixteen companies expressed an interest to SWRDA in
participating in the development of a new Wave Hub power station
project off the coast of Cornwall, England. Two companies are
currently participating in the project: Fred Olsen Ltd. and us.
Additional competitors may enter the market, and we are likely
to compete with new companies in the future.
To compete effectively, we have to demonstrate that our
PowerBuoy systems are attractive, compared to other wave energy
systems and other renewable energy systems, by differentiating
our systems on the basis of performance, survivability in
operation and storm wave conditions, cost effectiveness and the
operations and maintenance services that we provide. We believe
that we compare favorably to our competition with respect to
each of these factors.
22
Government
Regulation
The electric power industry is subject to extensive regulation,
which varies by jurisdiction. For example, the electricity
industry in the United States is governed by both federal and
state laws and regulations, with the federal government having
jurisdiction over the sale and transmission of electricity at
the wholesale level in interstate commerce, and the states
having jurisdiction over the sale and distribution of
electricity at the retail level. The electricity industry in the
European Union, or the EU, is primarily governed by national
law, but a number of
EU-level
regulations impose obligations on member states, notably with
respect to the liberalization of the electricity markets.
The renewable energy industry has also been subject to
increasing regulation, however none of the countries in which we
are currently marketing our PowerBuoy systems have comprehensive
regulatory schemes tailored to wave energy. As the renewable
energy industry continues to evolve and as the wave energy
industry in particular develops, we anticipate that wave energy
technology and our PowerBuoy systems and their deployment will
be subject to increased oversight and regulation in accordance
with international, national and local regulations relating to
safety, sites, environmental protection, utility interconnection
and metering and related matters.
Our PowerBuoy wave power stations currently face regulation in
the US and in foreign jurisdictions concerning, among other
areas, the sale and transmission of electricity, site approval
and environmental approval and compliance. In order to encourage
the adoption of renewable energy systems, many governments offer
subsidies and other financial incentives and have mandated
renewable energy targets. These subsidies, incentives and
targets may not be applicable to our wave energy technology and
therefore may not be available to us or our customers.
Sale
and Transmission of Electricity
The US government regulates the electricity wholesale and
transmission business through FERC. FERC regulates the rates and
terms for sales of electricity at the wholesale level, and the
organization, governance and financing of the companies engaged
in electricity sales. As a result, FERC regulates the rates
charged for sales of electric power from a wave power station
into the wholesale market, although it is possible to obtain an
exemption from FERC that would allow those sales to occur at
market-based rates. FERC also regulates the construction,
operation and maintenance of any dam, water conduit, reservoir
or powerhouse along or in any of the navigable waters of the
United States for the purpose of generating electric power. As a
result, the construction and operation of a wave power station
in the United States requires the issuance of a license by FERC.
We have been granted a preliminary permit by FERC to evaluate
the feasibility of a 50MW wave power station off Reedsport,
Oregon and a 100MW wave power station off Coos Bay, Oregon.
Further, we have filed with FERC the required applications for
these two wave power station projects to provide our notice of
intent to seek licenses for the projects and to provide required
information regarding the projects. An application to FERC was
not required for our system that was installed off New Jersey
because the system was not grid-connected and was for
demonstration purposes.
Under Spanish law, each of the Spanish Autonomous Regions,
including the Cantabria region, has the power to issue
administrative authorizations for the construction and
exploitation of installations for the production of renewable
energy, including installations that use the energy of waves.
Iberdrola Energias has applied for and received the necessary
authorizations for installation of the first PowerBuoy at our
Santoña, Spain wave power project.
Site
Approval
Generally, we expect that we will deploy our PowerBuoy systems
in the range of one to five miles from the shore, subject to
water depth and overall wave heights. Although regulations
regarding the use of ocean space vary around the world, we
generally do not expect significant delay in obtaining site
approvals, as governments have to date encouraged the use of
renewable energy sources. Our customers for the Spain project
and SWRDA for the Cornwall, England project are responsible for
obtaining the necessary siting permits for their projects.
In the United States, federal agencies regulate the siting of
renewable energy and related-uses located on the outer
continental shelf, which is generally more than three miles
offshore. For projects located within three miles of
23
the US shore, the adjacent state would be responsible for
issuing a lease and other required authorizations for the
location of the project. In either case, an assessment of the
potential environmental impact of the project would be conducted
in addition to other requirements.
Environmental
Approval and Compliance
We are subject to various foreign, federal, state and local
environmental protection and health and safety laws and
regulations governing, among other things: the generation,
storage, handling, use and transportation of hazardous
materials; the emission and discharge of hazardous materials
into the ground, air or water; and the health and safety of our
employees. In addition, in the United States, the construction
and operation of a power system offshore would require permits
and approvals from FERC, the Coast Guard, the Army Corps of
Engineers and other governmental authorities. These required
permits and approvals evaluate, among other things, whether the
proposed project is in the public interest and ensure that the
project would not create a hazard to navigation. Other foreign
and international laws may require similar approvals.
We believe that a significant advantage of our PowerBuoy systems
is that they do not present significant environmental risks when
compared to traditional power generation technologies, as there
is no significant visual or audible impact and such systems have
not been shown to have a significant negative effect on fish or
sea mammals. We are not aware of any liabilities in connection
with compliance with such laws, regulations, permits and
approvals that would have a material adverse effect on our
financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Subsidies
and Incentives
Several governments have enacted subsidies and incentives
designed to encourage the development of renewable energy
resources. Because of the relative novelty of wave energy
generation, these government programs often do not apply
specifically to wave energy generation, and so these programs
may not be available to our customers or us in all cases.
Under a tariff subsidy, the government sets price subsidies to
be paid to electricity producers for renewable electricity
generated by them. The prices are set above market rates and may
be differentiated based on system size or application. Under a
renewable portfolio standard, the government requires regulated
utilities to supply a portion of their total electricity in the
form of renewable electricity. Some programs further specify
that a portion of the renewable energy quota must be from a
particular renewable energy source, although none have specific
quotas for wave energy. Several governments also facilitate low
interest loans for renewable energy systems, either through
direct lending, credit enhancement or other programs.
Countries in Europe and Asia and several states in the United
States have adopted a variety of government subsidies to allow
renewable sources of electricity to compete with conventional
sources of electricity, such as fossil fuels. Government
subsidies and incentives generally focus on grid-connected
systems and take several forms, including tariff subsidies,
renewable portfolio standards, rebates, tax incentives and low
interest loans. In addition, the adoption by governments of
limits on carbon dioxide emissions and targets for renewable
energy production has spurred a market for trading of surplus
carbon credits and renewable energy certificates.
In 2008, the US enacted the Energy Improvement and Extension Act
of 2008, which enables owners of wave power projects in the US
to receive federal tax credits, thereby improving the long-term
economics of wave power as a renewable energy source. The Act
expands the definition of qualifying facilities for the
Production Tax Credit (PTC) to include those that generate power
from marine renewables (including wave and tidal). As a result,
the PTC is now allowed for electricity produced and sold after
October 3, 2008 from marine renewable energy facilities
with a “nameplate capacity” of at least 150kWs, and
that are placed in service anytime between October 3, 2008
and December 31, 2011. The credit rate for marine
renewables is $0.01 per kilowatt hour, and the duration of the
credit will be ten years after the facility is placed in service.
Further, it is expected that the US federal and state
governments will increase their investments in the renewable
energy sector under various economic stimulus measures. The
American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 provides
significant grants, tax incentives and policy initiatives to
stimulate investment and innovation in the “cleantech”
sector. The DOE has also issued requests for proposal to be
funded under programs it has
24
established to further investment in marine energy technologies.
We have devoted additional resources to develop proposals
seeking government funding to support existing projects and
technology enhancements. Consequently, while our selling,
general and administrative costs related to such efforts may
increase over the next year, we believe that these governmental
initiatives may result in additional revenues for us over the
next several years. Given the recent announcement of the
government programs and the uncertainties surrounding their
scope and size, there can be no assurances as to whether we will
be successful in obtaining significant additional government
funding or as to the terms and conditions of any such funding.
Further, the State of Oregon has enacted the Business Energy Tax
Credit program that allows companies that invest in renewable
energy capital projects an Oregon State income tax credit of up
to 50% of the first $20.0 million of capital costs.
Each of the member states of the EU has a country-specific
target for the level of consumption of electricity from
renewable sources that it should attain by 2010. The United
Kingdom Renewables Obligation of April 2002 included a target of
10% of electricity generation to come from renewable sources by
2010 and 15% by 2015, which will continue until 2027.
Electricity suppliers that are unable to otherwise meet their
renewables obligation have to pay a buy-out price (currently
£0.033 per kilowatt hour) or purchase Renewables Obligation
Certificates from companies that generate electricity from
renewable resources. The United Kingdom Department of Trade and
Industry has established a £50 million Marine
Renewables Deployment Fund, of which £42 million is
allocated to provide a maximum seven-year benefit to any one
marine power company of £9 million, in the form of a
25% capital grant and a tariff supplement of £0.10 per
kilowatt-hour
generated.
Many countries and other local jurisdictions have established
limits on carbon dioxide emissions. In particular, a key
component of the Kyoto Protocol is the commitments made by
certain countries to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. The
country, locality or companies within the jurisdiction are given
carbon emission allowances, or carbon credits, which represent
the right to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide. A
country, locality or company having emissions that exceed its
allocated carbon credits may purchase unused carbon credits from
a country, locality or company that has reduced its emissions
beyond its requirements to do so. The carbon dioxide emissions
from a PowerBuoy wave power station are zero, and, therefore, a
PowerBuoy wave power station may generate carbon credits that
could be used and sold.
Employees
As of April 30, 2010, we had 54 employees, including
19 employees in manufacturing, 19 in research, development
and engineering functions and 16 employees in selling,
general and administrative functions. Of these employees, 41 are
located in Pennington, New Jersey and 13 are located in Warwick,
UK. We believe that our future success will depend in part on
our continued ability to attract, hire and retain qualified
personnel. None of our employees is represented by a labor
union, and we believe our employee relations are good.
By the end of fiscal 2012, we expect to increase our staff in
order to meet our current manufacturing and revenue growth
goals. We expect that the majority of our new hires will be
engineers, project managers and manufacturing personnel with
varying levels and areas of expertise.
Product
Insurance
We currently have a property and liability insurance policy
underwritten by Lloyd’s Underwriters that covers our
PowerBuoy systems currently deployed, and that can be expanded
to cover our PowerBuoy systems to be deployed in the future. We
have not claimed any losses under this policy.
You should carefully consider the risks described below with all
of the other information included in this Annual Report before
deciding to invest in our common stock. If any of the following
risks actually occur, they may materially harm our business and
our financial condition and results of operations. In this
event, the market price of our common stock could decline and
your investment could be lost.
25
Risks
Relating to Our Business
We
have a history of operating losses and may never achieve or
maintain profitability.
We have incurred net losses since we began operations in 1994,
including net losses attributable to Ocean Power Technologies,
Inc. of $19.2 million in fiscal 2010, $18.3 million in
fiscal 2009 and $14.7 million in fiscal 2008. As of
April 30, 2010, we had an accumulated deficit of
$90.4 million. These losses have resulted primarily from
costs incurred in our research and development programs and from
our selling, general and administrative costs. We expect to
increase certain of our operating expenses significantly as we
continue to expand our infrastructure and commercialization
activities. As a result, we will need to generate significant
revenues to cover these costs and achieve profitability.
We do not know whether or when we will become profitable because
of the significant uncertainties with respect to our ability to
successfully commercialize our PowerBuoy systems in the emerging
renewable energy market. Even if we do achieve profitability, we
may not be able to sustain or increase profitability on a
quarterly or annual basis. If we are unable to achieve and then
maintain profitability, the market value of our common stock may
decline.
Wave
energy technology may not gain broad commercial acceptance, and
therefore our revenues may not increase, and we may be unable to
achieve and then sustain profitability.
Wave energy technology is at an early stage of development, and
the extent to which wave energy power generation will be
commercially viable is uncertain. Many factors may affect the
commercial acceptance of wave energy technology, including the
following:
|
|
|
| |
•
|
performance, reliability and cost-effectiveness of wave energy
technology compared to conventional and other renewable energy
sources and products;
|
| |
| |
•
|
developments relating to other renewable energy generation
technologies;
|
| |
| |
•
|
fluctuations in economic and market conditions that affect the
cost or viability of conventional and renewable energy sources,
such as increases or decreases in the prices of oil and other
fossil fuels;
|
| |
| |
•
|
overall growth in the renewable energy equipment market;
|
| |
| |
•
|
availability and terms of government subsidies and incentives to
support the development of renewable energy sources, including
wave energy;
|
| |
| |
•
|
fluctuations in capital expenditures by utilities and
independent power producers, which tend to decrease when the
economy slows and interest rates increase; and
|
| |
| |
•
|
the development of new and profitable applications requiring the
type of remote electric power provided by our autonomous wave
energy systems.
|
If wave energy technology does not gain broad commercial
acceptance, our business will be materially harmed and we may
need to curtail or cease operations.
If
sufficient demand for our PowerBuoy systems does not develop or
takes longer to develop than we anticipate, our revenues may
decline, and we may be unable to achieve and then sustain
profitability.
Even if wave energy technology achieves broad commercial
acceptance, our PowerBuoy systems may not prove to be a
commercially viable technology for generating electricity from
ocean waves. We have invested a significant portion of our time
and financial resources since our inception in the development
of our PowerBuoy systems. To date, we have not yet manufactured
and deployed any PowerBuoy systems that have been
grid-connected. As we begin to manufacture, market, sell and
deploy our PowerBuoy systems in greater quantities, unforeseen
hurdles may be encountered that would limit the commercial
viability of our PowerBuoy systems, including unanticipated
manufacturing, deployment, operating, maintenance and other
costs. Our target customers and we may also encounter technical
obstacles to deploying, operating and maintaining PowerBuoy
systems in quantities necessary to generate competitively-priced
electricity.
26
If demand for our PowerBuoy systems fails to develop
sufficiently, we may be unable to grow our business or generate
sufficient revenues to achieve and then sustain profitability.
In addition, demand for PowerBuoy systems in our presently
targeted markets, including coastal North America, the west
coast of Europe, the coasts of Australia and the east coast of
Japan, may not develop or may develop to a lesser extent than we
anticipate.
If we are not successful in commercializing our PowerBuoy
system, or are significantly delayed in doing so, our business,
financial condition and results of operations could be adversely
affected.
The
reduction or elimination of government subsidies and economic
incentives for renewable energy sources could prevent demand for
our PowerBuoy systems from developing, which in turn would
adversely affect our business, financial condition and results
of operations.
Federal, state and local governmental bodies in many countries,
most notably Spain, the United Kingdom, Australia, Japan and the
United States, have provided subsidies in the form of tariff
subsidies, rebates, tax credits and other incentives to
utilities, power generators and distributors using renewable
energy. However, these incentives and subsidies generally
decline over time, and many incentive and subsidy programs have
specific expiration dates. Moreover, because the market for
electricity generated from wave energy is at an early stage of
development, some of the programs may not include wave energy as
a renewable energy source eligible for the incentives and
subsidies.
Currently, the cost of electricity generated from wave energy,
without the benefit of subsidies or other economic incentives,
substantially exceeds the price of electricity in most
significant markets in the world. As a result, the near-term
growth of the market for our utility PowerBuoy systems, which
are designed to feed electricity into a local or regional power
grid, depends significantly on the availability and size of
government incentives and subsidies for wave energy. As
renewable energy becomes more of a competitive threat to
conventional energy providers, companies active in the
conventional energy business may increase their lobbying efforts
in order to encourage governments to stop providing subsidies
for renewable energy, including wave energy. We cannot predict
the level of any such efforts, or how governments may react to
such efforts. The reduction, elimination or expiration of
government incentives and subsidies, or the exclusion of wave
energy technology from those incentives and subsidies, may
result in the diminished competitiveness of wave energy relative
to conventional and non-wave energy renewable sources of energy.
Such diminished competitiveness could materially and adversely
affect the growth of the wave energy industry, which could in
turn adversely affect our business, financial condition and
results of operations.
Our
product development costs have been steadily increasing and may
continue to increase.
Our product development costs primarily relate to our efforts to
increase the maximum rated output of our utility PowerBuoy
system to 150kW and to 500kW. Our product development costs were
$13.0 million in fiscal 2010 as compared to
$8.4 million in fiscal 2009 and $8.3 million in fiscal
2008. It is our intent to fund the majority of our research and
development expenses over the next several years with sources of
external funding. If we are unable to obtain external funding,
we may curtail our research and development expenses or we may
decide to self-fund significant research and development
expenses, in which case our product development costs may
continue to increase.
We
have invested, and will continue to invest, funds to construct
demonstration wave power stations that may generate little or no
direct revenue.
We have constructed, and plan to construct in the future,
demonstration wave power stations to establish the feasibility
of wave energy technology and to encourage the market adoption
of our wave power stations. Demonstration wave power stations
allow potential customers to see first-hand the viability of
wave energy technology as a source of electricity. We incur
significant costs in constructing and maintaining these
demonstration wave power stations, and we may generate little or
no direct revenue from them.
27
Our
PowerBuoy systems do not have a sufficient operating history to
confirm how they will perform over their estimated
30-year
useful life.
We began developing and testing wave energy technology
13 years ago. However, to date we have only manufactured 12
PowerBuoy systems for use in ocean testing and development. The
longest continuous in-ocean deployment of our PowerBuoy system
has been for 12 months. As a result, our PowerBuoy systems
do not have a sufficient operating history to confirm how they
will perform over their estimated
30-year
useful life. Our technology has not yet demonstrated that our
engineering and test results can be duplicated in volume
commercial production. We have conducted and plan to continue to
conduct practical testing of our PowerBuoy system. If our
PowerBuoy system ultimately proves ineffective or unfeasible, we
may not be able to engage in commercialproduction of our
products or we may become liable to our customers for quantities
we are obligated but are unable to produce. If our PowerBuoy
systems perform below expectations, we could lose customers and
face substantial repair and replacement expense which could in
turn adversely affect our business, financial condition and
results of operations.
Our
future success in the utility power markets depends on our
ability to increase the maximum rated power output of our
utility PowerBuoy system. If we are unable to increase the
maximum rated output of our utility PowerBuoy system, the
commercial prospects for our utility PowerBuoy system would be
adversely affected.
One of our goals is to increase the maximum rated output of our
utility PowerBuoy system, which is currently 40kW, to 150kW and
ultimately to 500kW. Our success in meeting this objective
depends on our ability to significantly increase the power
output of our PowerBuoy system in a cost-effective and timely
manner and our ability to overcome the engineering and
deployment hurdles that we face, including developing design and
construction techniques that will enable the larger PowerBuoy
systems to be deployed cost effectively and without damage, and
developing adjustments to the mooring system to account for the
larger-sized PowerBuoy systems. We have experienced problems and
delays in the development and deployment of our PowerBuoy system
in the past, and could experience similar delays or other
difficulties in the future. If we cannot increase the power
output of the utility PowerBuoy system, or if it takes us longer
to do so than we anticipate, we may be unable to expand our
utility business, maintain our competitive position, satisfy our
contractual obligations or become profitable. In addition, if
the cost associated with these development efforts exceeds our
projections, our results of operations will be adversely
affected.
If we
do not reach full commercial scale, we may not be able to offer
a cost competitive power station and the commercial prospects of
our utility PowerBuoy system would be adversely
affected.
Unless we reach full commercial scale, which we estimate to be
manufacturing levels of at least 300 units of 500kW
PowerBuoy systems per year, we may not be able to offer an
electricity solution that competes on a non-subsidized basis
with today’s price of wholesale electricity in key markets
in certain parts in the world. If we do not reach full
commercial scale, the commercial prospects for our utility
PowerBuoy system would be adversely affected.
We
have not yet deployed a wave power station consisting of an
array of two or more PowerBuoy systems. If we are unable to
deploy a multiple-system wave power station, our revenues may
not increase, and we may be unable to achieve and then maintain
profitability.
We have not yet deployed a wave power station consisting of an
array of two or more PowerBuoy systems. Our success in
developing and deploying a wave power station consisting of an
array of two or more PowerBuoy systems is contingent upon, among
other things, receipt of required governmental permits,
obtaining adequate financing, successful array design
implementation and finally, successful deployment and connection
of the PowerBuoy systems.
We have not conducted ocean testing or otherwise installed in
the ocean a multiple-system wave power station. In particular,
unlike single-system wave power stations, multiple-system wave
power stations require use of an underwater substation to
connect the power transmission cables from, and collect the
electricity generated by, each
28
PowerBuoy system in the array. If our underwater substation does
not work as we anticipate, we will need to design an alternative
system, which could delay our business plans. In addition,
unanticipated issues may arise with the logistics and mechanics
of deploying and maintaining multiple PowerBuoy systems at a
single site and the additional equipment associated with these
multiple-system wave power stations.
We may be unsuccessful in accomplishing any of these tasks or
doing so on a timely basis. The development and deployment of an
array of PowerBuoy systems may require us to incur significant
expenses for preliminary engineering, permitting and legal and
other expenses before we can determine whether a project is
feasible, economically attractive or capable of being financed.
If we
are unable to deploy larger PowerBuoy systems cost effectively
and without damage to the systems, we may be unable to compete
effectively.
We will need to build larger buoys in order to increase the
output of our current PowerBuoy systems. The larger buoys will
be more difficult than our current buoys to deploy cost
effectively and without damage. Our current deployment
methodologies, including transportation to the installation site
and the mooring of the PowerBuoy systems, will need to be
revised for PowerBuoy systems with greater output. If we cannot
develop cost effective methodologies for deployment of the
larger PowerBuoy systems, or if it takes us longer to do so than
we anticipate, we may not be able to deploy such systems in the
time we anticipate or at all. Therefore, even if we succeed in
increasing the output of our PowerBuoy systems to 150kW or
greater, if we are unable to deploy these larger PowerBuoy
systems or encounter problems in doing so, we may be unable to
expand our business, maintain our competitive position, satisfy
our contractual obligations or become profitable.
If we
are not successful in completing the development of wave power
stations in Spain, it could adversely affect our business,
financial condition and results of operations.
The initial PB40 PowerBuoy system for our Spain project was
deployed in September 2008. After a short testing period, the
buoy was removed from the water for work on improvements to the
power take-off and control systems. We are currently in
discussions with Iberdrola Cantabria regarding the nature and
costs of these improvements and their effects on plans for the
redeployment of the buoy and the next phases of the project. If
no modification to the Spain construction agreement is agreed to
by the parties, the customer may, subject to certain conditions
in the agreement, terminate the agreement and would not be
obligated to make any more milestone payments. In addition, if
we and Iberdrola Cantabria decide not to redeploy the PB40
PowerBuoy, the total contract value for the current phase of the
contract may be reduced. If we are unable to successfully meet
the terms of the Spain construction agreement, or if we are not
able to successfully negotiate a subsequent contract or
contracts with Iberdrola Cantabria for the manufacture and
deployment of the nine additional PowerBuoy units, or if
Iberdrola Cantabria were to terminate the Spain construction
agreement for any of these reasons, we may lose a component of
our current and anticipated revenue stream. If we are unable to
agree to the necessary contract modifications, Iberdrola
Cantabria will have the right to terminate the agreement if the
first phase of construction is not completed on time for reasons
attributable to us, or if we interrupt our services for more
than 180 days and do not resume within a
30-day
period, or for a serious and repeated breach of a major
obligation that is not cured within a
30-day
period after we receive notice of the breach. In addition, we
have made guarantees to Iberdrola Cantabria associated with the
current phase of construction in respect of the quality, repair
and replacement of the 40kW PowerBuoy system and ocean-based
substation and the level of power output of the 40kW PowerBuoy
system. If we are found to be in default of our obligations
under the Spain construction agreement, Iberdrola Cantabria will
have the right to seek reimbursement for direct damages only,
limited to amounts specified in the contract.
We are paid under the Spain construction agreement as we
complete certain milestones for a total potential payment for
the current phase of construction of approximately
€2.7 million. As of April 30, 2010, we had
recognized revenue of approximately $3.0 million and a
recognized loss of $3.9 million under the Spain
construction agreement. The anticipated loss at completion of
the contract also reflects our decision made in the fourth
quarter of fiscal year 2008 to absorb $1.9 million of
additional costs of the project beyond our obligation for the
initial cost overruns and certain other costs as set forth in
the agreement. This decision was based on the progress of the
project up to that time, the benefits to be derived from a
successful initial project and the prospect of incremental
contract value to be received in connection with additional work
under this contract.
29
If the Spain project were cancelled or otherwise interrupted, it
could adversely affect our business, financial condition and
results of operations.
If we
are unable to successfully negotiate and enter into operations
and maintenance contracts with our customers on terms that are
acceptable to us, our ability to diversify our revenue stream
will be impaired.
An important element of our business strategy is to maximize our
revenue opportunities with our existing and future customers by
seeking to enter into operations and maintenance contracts with
them under which we would be paid fees for operating and
maintaining wave power stations that they have purchased from
us. Even if customers purchase our PowerBuoy systems, they may
not enter into operations and maintenance contracts with us. We
may not be able to negotiate operations and maintenance
contracts that provide us with any profit opportunities. Even if
we successfully negotiate and enter into such operations and
maintenance contracts, our customers may terminate them
prematurely or they may not be profitable for a variety of
reasons, including the presence of unforeseen hurdles or costs.
In addition, our inability to perform adequately under such
operations and maintenance contracts could impair our efforts to
successfully market the PowerBuoy systems. Any one of these
outcomes could have a material adverse effect on our business,
financial condition and results of operations.
If we
are unable to fulfill our obligations under our current
operations and maintenance contract in a cost effective manner,
our financial condition and results of operations could be
adversely affected.
In January 2007, we entered into an agreement with Iberdrola
Cantabria for the monitoring, operation and maintenance of the
40kW PowerBuoy system and the ocean-based substation and
infrastructure to be manufactured and deployed under the
original Spain construction agreement. Under this operations and
maintenance agreement, we would be required to provide services
for two years following provisional acceptance of the PowerBuoy
system and substation and infrastructure. We would be paid a
fixed fee for scheduled maintenance, ongoing operations and
other routine services. In connection with any unscheduled
repairs we perform under the operations and maintenance
agreement, Iberdrola Cantabria and we will agree on the fees, if
any, and timing, for those services. To the extent we would
otherwise have profits from the fixed fee at the end of the
two-year initial term of the agreement, we would be obligated to
reimburse Iberdrola Cantabria for any fees paid to us for
unscheduled repairs. If the costs we actually incur in
connection with providing services under the operations and
maintenance agreement exceed the fees we receive, we would incur
a loss in connection with these services, which could adversely
affect our financial condition and results of operations. The
operations and maintenance agreement is subject to the
redeployment of the buoy and an agreement of the parties
regarding the deployment of the pod and cable.
Our
inability to effectively manage our growth could adversely
affect our business and operations.
The scope of our operations to date has been limited, and we do
not have experience operating on the scale that we believe will
be necessary to achieve profitable operations. Our current
personnel, facilities, systems and internal procedures and
controls are not adequate to support our projected future
growth. We plan to add sales, marketing and engineering offices
in additional locations, including Australia, Japan, continental
Europe and the west coast of the United States.
To manage the expansion of our operations, we will be required
to improve our operational and financial systems, procedures and
controls, increase our manufacturing capacity and throughput and
expand, train and manage our employee base, which must increase
significantly if we are to be able to fulfill our current
manufacturing and growth plans. Our management will also be
required to maintain and expand our relationships with
customers, suppliers and other third parties, as well as attract
new customers and suppliers. If we do not meet these challenges,
we may be unable to take advantage of market opportunities,
execute our business strategies or respond to competitive
pressures.
Problems
with the quality or performance of our PowerBuoy systems could
adversely affect our business, financial condition and results
of operations.
Our agreements with customers will generally include guarantees
with respect to the quality and performance of our PowerBuoy
systems. Because of the limited operating history of our
PowerBuoy systems, we have been
30
required to make assumptions regarding the durability,
reliability and performance of the systems, and we cannot
predict whether and to what extent we may be required to perform
under the guarantees that we expect to give our customers. Our
assumptions could prove to be materially different from the
actual performance of our PowerBuoy systems, causing us to incur
substantial expense to repair or replace defective systems in
the future. We will bear the risk of claims long after we have
sold our PowerBuoy systems and recognized revenue. Moreover, any
widespread product failures could adversely affect our business,
financial condition and results of operations.
We
currently depend on a limited number of customers for
substantially all of our revenues. The loss of, or a significant
reduction in revenues from, any of these customers could
significantly reduce our revenues and harm our operating
results.
The US Navy, our largest customer, accounted for 80% of our
revenues during fiscal 2010. In fiscal 2009, revenues from the
US Navy accounted for 67% of our total revenues while Iberdrola
and Total accounted for 18% of our revenues. Our current
contract for our project in Hawaii with the US Navy expires in
September 2010. We will be required to enter into additional
contracts with the US Navy for this project, which will require
appropriation by the US Congress and the US Navy in order to
receive additional funding. Additional funding for our project
with the US Navy may not be approved or we may not be able to
negotiate future agreements with the US Navy on acceptable
terms, if at all.
Generally, we recognize revenue using the
percentage-of-completion
method based on the ratio of costs incurred to total estimated
costs at completion. In certain circumstances, revenue under
contracts that have specified milestones or other performance
criteria may be recognized only when our customer acknowledges
that such criteria have been satisfied. In addition, recognition
of revenue (and the related costs) may be deferred for
fixed-price contracts until contract completion if we are unable
to reasonably estimate the total costs of the project prior to
completion. Because we currently have a small number of
customers and contracts, problems with a single contract can
adversely affect our business, financial condition and results
of operations.
Historically, we have relied on a small group of customers for
substantially all of our revenue, and such concentration will
continue for the foreseeable future. The loss of any of our
customers or their default in payment could adversely affect our
business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our
relationships with our alliance partners may not be successful
and we may not be successful in establishing additional
relationships, which could adversely affect our ability to
commercialize our products and services.
An important element of our business strategy is to enter into
development agreements and strategic alliances with regional
utilities, and energy and other companies committed to providing
electricity from renewable energy sources. If we are unable to
reach agreements with suitable alliance partners, we may fail to
meet our business objectives for the commercialization of our
PowerBuoy system. We may face significant competition in seeking
appropriate alliance partners. Moreover, these development
agreements and strategic alliances are complex to negotiate and
time consuming to document. We may not be successful in our
efforts to establish additional strategic relationships or other
alternative arrangements. The terms of any additional strategic
relationships or other arrangements that we establish may not be
favorable to us. Furthermore, even if we are able to find,
negotiate and enter into these relationships, such arrangements
may be conditional upon our receipt of additional funding. For
example, our projects with Leighton and the European Commission
are conditional upon our receipt of significant additional
funds. There can be no assurance that we will receive such
additional funding. In addition, these relationships may not be
successful, and we may be unable to sell and market our
PowerBuoy systems to these companies and their affiliates and
customers in the future, or growth opportunities may not
materialize, any of which could adversely affect our business,
financial condition and results of operations.
31
Our
investments in joint ventures could be adversely affected by our
lack of sole decision-making authority, our reliance on a
co-venturer’s financial condition and disputes between us
and our
co-venturers.
It is part of our strategy to co-invest in some of our wave
power projects with third parties through joint ventures by
acquiring non-controlling interests in special purpose entities.
In these situations, we will not be in a position to exercise
sole decision-making authority regarding the joint venture.
Investments in joint ventures involve risks that would not be
present were a third party not involved, including the
possibility that our co-venturers might become bankrupt or fail
to fund their share of required capital contributions. Our
co-venturers may have economic or other business interests or
goals that are inconsistent with our business interests or
goals, and may be in a position to take actions that are
contrary to our policies or objectives. Disputes between us and
our co-venturers may result in litigation or arbitration that
would increase our expenses and prevent our officers
and/or
directors from focusing their time and effort on our business.
Consequently, actions by, or disputes with, partners or
co-venturers might result in additional risk to wave power
projects undertaken by the joint venture.
Our
targeted markets are highly competitive. We compete with other
renewable energy companies and may have to compete with larger
companies that enter into the renewable energy business. If we
are unable to compete effectively, we may be unable to increase
our revenues and achieve or maintain
profitability.
The renewable energy industry, particularly in our targeted
markets of the west coast of North America, the west coast of
Europe, the coasts of Australia and the east coast of Japan, is
highly competitive and continually evolving as participants
strive to distinguish themselves and compete with the larger
electric power industry. Competition in the renewable energy
industry is likely to continue to increase with the advent of
several renewable energy technologies, including tidal and ocean
current technologies. If we are not successful in manufacturing
systems that generate competitively priced electricity, we will
not be able to respond effectively to competitive pressures from
other renewable energy technologies.
Moreover, the success of renewable energy generation
technologies may cause larger electric utility and other energy
companies with substantial financial resources to enter into the
renewable energy industry. These companies, due to their greater
capital resources and substantial technical expertise, may be
better positioned to develop new technologies.
Our inability to respond effectively to such competition could
adversely affect our business, financial condition and results
of operations.
We
have limited manufacturing experience. If we are unable to
increase our manufacturing capacity in a cost-effective manner,
our business will be materially harmed.
We plan to manufacture key components of our PowerBuoy systems,
including the advanced control and generation systems. However,
we have only manufactured our PowerBuoy systems in limited
quantities for use in development and testing and have little
commercial manufacturing experience. Our future success depends
on our ability to significantly increase both our manufacturing
capacity and production throughput in a cost-effective and
efficient manner. In order to meet our growth objectives, we
will need to increase our engineering and manufacturing staff by
the end of fiscal 2012. There is intense competition for hiring
qualified technical and engineering personnel, and we may not be
able to hire a sufficient number of qualified personnel to allow
us to meet our growth objectives.
We may be unable to develop efficient, low-cost manufacturing
capabilities and processes that will enable us to meet the
quality, price, engineering, design and production standards or
production volumes necessary to successfully commercialize our
PowerBuoy systems. If we cannot do so, we may be unable to
expand our business, satisfy our contractual obligations or
become profitable. Even if we are successful in developing our
manufacturing capabilities and processes, we may not be able to
do so in time to meet our commercialization schedule or satisfy
the requirements of our customers.
32
Failure
by third parties to supply or manufacture components of our
products or to deploy our systems timely or properly could
adversely affect our business, financial condition and results
of operations.
We are highly dependent on third parties to supply or
manufacture components of our PowerBuoy systems. If, for any
reason, our third-party manufacturers or vendors are not willing
or able to provide us with components or supplies in a timely
fashion, or at all, our ability to manufacture and sell many of
our products could be impaired.
We do not have long-term contracts with our third-party
manufacturers or vendors. If we do not develop ongoing
relationships with vendors located in different regions, we may
not be successful at controlling unit costs as our manufacturing
volume increases. We may not be able to negotiate new
arrangements with these third parties on acceptable terms, or at
all.
In addition, we rely on third parties, under our oversight, for
the deployment and mooring of our PowerBuoy systems. We have
utilized several different deployment methods, including towing
the PowerBuoy system to the deployment location, and
transporting the PowerBuoy system to the deployment location by
barge or ocean workboat. If these third parties do not properly
deploy our systems, cannot effectively deploy the PowerBuoy
system on a large, commercial scale or otherwise do not perform
adequately, or if we fail to recruit and retain third parties to
deploy our systems in particular geographic areas, our business,
financial condition and results of operations could be adversely
affected.
Business
activities conducted by our third-party contractors and us
involve the use of hazardous materials, which require compliance
with environmental and occupational safety laws regulating the
use of such materials. If we violate these laws, we could be
subject to significant fines, liabilities or other adverse
consequences.
Our manufacturing operations, in particular some of the
activities undertaken by our third-party suppliers and
manufacturers, involve the controlled use of hazardous
materials. Accordingly, our third-party contractors and we are
subject to foreign, federal, state and local laws governing the
protection of the environment and human health and safety,
including those relating to the use, handling and disposal of
these materials. We cannot completely eliminate the risk of
accidental contamination or injury from these hazardous
materials. In the event of an accident or failure to comply with
environmental or health and safety laws and regulations, we
could be held liable for resulting damages, including damages to
natural resources, fines and penalties, and any such liability
could adversely affect our business, financial condition and
results of operations.
Environmental laws and regulations are complex, change
frequently and have tended to become more stringent over time.
While we have budgeted for future capital and operating
expenditures to maintain compliance, we cannot assure you that
environmental laws and regulations will not change or become
more stringent in the future. Therefore, we cannot assure you
that our costs of complying with current and future
environmental and health and safety laws, and any liabilities
arising from past or future releases of, or exposure to,
hazardous substances will not adversely affect our business,
financial condition or results of operations.
If we
become ineligible for or are otherwise unable to replace any
contract with the US federal government that is not extended or
is terminated, our business, financial condition and results of
operations will be adversely affected.
We derive a significant portion of our revenue from US federal
government contracts, which are subject to special funding
restrictions, regulatory requirements and eligibility standards
and which the government may terminate at any time or determine
not to extend after their scheduled expiration. During fiscal
2010 and fiscal 2009, we derived 80% and 67%, respectively, of
our total revenue from contracts with the US Navy.
US federal government contracts are also subject to contractual
and regulatory requirements that may increase our costs of doing
business and could expose us to substantial contractual damages,
civil fines and criminal penalties for noncompliance. These
requirements include business ethics, equal employment
opportunity, environmental, foreign purchasing, most-favored
pricing and accounting provisions, among others. Payments that
we receive under US federal government contracts are subject to
audit and potential refunds for at least three years after the
final contract payment is received.
33
We
market and plan to market our products in numerous international
markets. If we are unable to manage our international operations
effectively, our business, financial condition and results of
operations could be adversely affected.
We market and plan to market our products in a number of foreign
countries, including the United Kingdom, Spain, Australia and
Japan, and we are therefore subject to risks associated with
having international operations. International customers
accounted for 11% of our revenues in fiscal 2010, 27% of our
revenues in fiscal 2009 and 41% of our revenues in fiscal 2008.
Risks inherent in international operations include, but are not
limited to, the following:
|
|
|
| |
•
|
changes in general economic and political conditions in the
countries in which we operate;
|
| |
| |
•
|
unexpected adverse changes in foreign laws or regulatory
requirements, including those with respect to renewable energy,
environmental protection, permitting, export duties and quotas;
|
| |
| |
•
|
trade barriers such as export requirements, tariffs, taxes and
other restrictions and expenses, which could increase the prices
of our PowerBuoy systems and make us less competitive in some
countries;
|
| |
| |
•
|
fluctuations in exchange rates may affect demand for our
PowerBuoy systems and may adversely affect our profitability in
US dollars to the extent the price of our PowerBuoy systems and
cost of raw materials and labor are denominated in a foreign
currency;
|
| |
| |
•
|
difficulty with staffing and managing widespread operations;
|
| |
| |
•
|
complexity of, and costs relating to compliance with, the
different commercial and legal requirements of the overseas
markets in which we offer and sell our PowerBuoy systems;
|
| |
| |
•
|
inability to obtain, maintain or enforce intellectual property
rights; and
|
| |
| |
•
|
difficulty in enforcing agreements in foreign legal systems.
|
Our business in foreign markets requires us to respond to rapid
changes in market conditions in these countries. Our overall
success as a global business depends, in part, on our ability to
succeed in differing legal, regulatory, economic, social and
political conditions. We may not be able to develop and
implement policies and strategies that will be effective in each
location where we do business, which in turn could adversely
affect our business, financial condition and results of
operations.
We may
not be able to raise sufficient capital to grow our
business.
We have in the past needed to raise funds to operate our
business, and we may need to raise additional funds to support
development of our products or to manufacture our PowerBuoy
systems in commercial quantities. If we are unable to raise
additional funds when needed, our ability to operate and grow
our business could be impaired. We do not know whether we will
be able to secure additional funding or funding on terms
favorable to us. Our ability to obtain additional funding will
be subject to a number of factors, including market conditions,
our operating performance and investor sentiment. These factors
may make the timing, amount, terms and conditions of additional
funding unattractive. If we issue additional equity securities,
our existing stockholders would experience dilution or may be
subordinated to any rights, preferences or privileges granted to
the new equity holders.
Our
financial results may fluctuate from quarter to quarter, which
may make it difficult to predict our future
performance.
Our financial results may fluctuate as a result of a number of
factors, many of which are outside of our control. For these
reasons, comparing our financial results on a
period-to-period
basis may not be meaningful, and our past results should not be
relied on as an indication of our future performance. Our future
quarterly and annual expenses as a percentage of our revenues
may be significantly different from those we have recorded in
the past or which we expect for the future. Our financial
results in some quarters may fall below expectations. Any of
these events could
34
cause our stock price to fall. Each of the risk factors listed
in this “Risk Factors” section, including the
following factors, may adversely affect our business, financial
condition and results of operations:
|
|
|
| |
•
|
delays in permitting or acquiring necessary regulatory consents;
|
| |
| |
•
|
delays in the timing of contract awards and determinations of
work scope;
|
| |
| |
•
|
delays in funding for or deployment of wave energy projects;
|
| |
| |
•
|
changes in cost estimates relating to wave energy project
completion, which under percentage of completion accounting
principles could lead to significant fluctuations in revenue or
to changes in the timing of our recognition of revenue from
those projects;
|
| |
| |
•
|
delays in meeting specified contractual milestones or other
performance criteria under project contracts or in completing
project contracts that could delay the recognition of revenue
that would otherwise be earned;
|
| |
| |
•
|
reductions in the availability or level of subsidies and
incentives for renewable energy sources;
|
| |
| |
•
|
decisions made by parties with whom we have commercial
relationships not to proceed with anticipated projects;
|
| |
| |
•
|
increases in the length of our sales cycle; and
|
| |
| |
•
|
reductions in the efficiency of our manufacturing processes.
|
Currency
translation and transaction risk may adversely affect our
business, financial condition and results of
operations.
Our reporting currency is the US dollar, and we conduct our
business and incur costs in the local currency of most countries
in which we operate. As a result, we are subject to currency
translation risk. In fiscal 2010, 3% of our revenues were
generated from customers outside the United States and
denominated in Euros, 5% of our revenues were generated from
customers outside the United States and denominated in British
pounds sterling and 2% of our revenues were generated from
customers outside the United States and denominated in
Australian dollars. In fiscal 2009, 17% of our revenues were
generated from customers outside the United States and
denominated in Euros, 8% of our revenues were generated from
outside the United States and denominated in British pounds
sterling and 2% of our revenues were generated from customers
outside the United States and denominated in Australian dollars.
We expect a large percentage of our revenues to be generated
outside the United States and denominated in foreign currencies
in the future. Changes in exchange rates between foreign
currencies and the US dollar could affect our revenues and cost
of revenues, and could result in exchange losses. In addition,
we incur currency transaction risk whenever one of our operating
subsidiaries enters into either a purchase or a sales
transaction using a different currency from our reporting
currency. We cannot accurately predict the impact of future
exchange rate fluctuations on our results of operations.
Currently, we do not engage in any exchange rate hedging
activities and, as a result, any volatility in currency exchange
rates may have an immediate adverse effect on our business,
results of operations and financial condition.
Existing
regulations and policies and changes to these or new regulations
and policies may present technical, regulatory and economic
barriers to the use of wave energy technology, which may
significantly reduce demand for our PowerBuoy
systems.
The market for electricity generation equipment is heavily
influenced by foreign, federal, state and local government
regulations and policies concerning the electric utility
industry, as well as policies promulgated by electric utilities.
These regulations and policies often relate to electricity
pricing and connection to the power grid. In the United States
and in a number of other countries, these regulations and
policies currently are being modified and may be modified again
in the future. Utility company and independent power producer
purchases of, or further investment in the research and
development of, alternative energy sources, including wave
energy technology, could be deterred by these regulations and
policies, which could result in a significant reduction in the
potential demand for our PowerBuoy systems.
As the renewable energy industry continues to develop and as the
generation of power from wave energy in particular achieves
commercial acceptance, we anticipate that wave energy technology
and our PowerBuoy systems
35
and their deployment will be subject to increased oversight and
regulation. We are unable to predict the nature or extent of
regulations that may be imposed or adopted. Any new government
regulations or utility policies pertaining to wave energy or our
PowerBuoy systems may result in significant additional expenses
to us and our customers and, as a result, could adversely affect
our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If we
are unable to obtain all necessary regulatory permits and
approvals, we will not be able to implement our planned
projects.
Offshore development of electric power generating facilities is
heavily regulated. Each of our planned projects is subject to
multiple permitting and approval requirements. With respect to
our projects in Spain, we are dependent upon our customer to
obtain any necessary permits and approvals, and with respect to
our projects in Oregon and Cornwall, England, we are dependent
on state, federal and regional government agencies for such
permits and approvals. Due to the unique nature of large scale
commercial wave power stations, we would expect our projects to
receive close scrutiny by permitting agencies, approval
authorities and the public, which could result in substantial
delay in the permitting process. Successful challenges by any
parties opposed to our planned projects could result in
conditions limiting the project size or in the denial of
necessary permits and approvals.
If we are unable to obtain necessary permits and approvals in
connection with any or all of our projects, those projects would
not be implemented and our business, financial condition and
results of operations would be adversely affected. Further, we
cannot assure you that we have been or will be at all times in
complete compliance with all such permits and approvals. If we
violate or fail to comply with these permits and approvals, we
could be fined or otherwise sanctioned by regulators.
We
face hurricane- and storm-related risks and other risks typical
of a marine environment which could adversely affect our
business, financial condition and results of
operations.
Our PowerBuoy systems are deployed in the ocean where they are
subject to many hazards including severe storms and hurricanes,
which could damage them and result in service interruptions. Our
systems are also subject to more frequent lock-downs caused by
higher waves during winter storm and hurricane seasons, which
will reduce annual energy output. We cannot predict whether we
will be able to recover from our insurance providers the
additional costs that we may incur due to damage caused to our
PowerBuoy systems, or whether we will continue to be able to
obtain insurance for hurricane- and storm-related damages or, if
obtainable and carried, whether this insurance will be adequate
to cover our liabilities. Any future hurricane-or storm-related
costs could adversely affect our business, financial condition
and results of operations.
Since
our PowerBuoy systems can only be deployed in certain geographic
locations, our ability to grow our business could be adversely
affected.
Our systems are designed to work in sites with average annual
wave energy of at least 20kW per meter of wave front. Not all
coastal areas worldwide have appropriate natural resources for
our PowerBuoy systems to harness wave energy. Seasonal and local
variations, water depth and the effect of particular locations
of islands and other geographical features may limit our ability
to deploy our PowerBuoy systems in coastal areas. If we are
unable to identify and deploy PowerBuoy systems at sufficient
sites near major population centers, our ability to grow our
business could be adversely affected.
We
face numerous accident and safety risks and hazards that are
inherent in offshore energy operations.
Portions of our operations are subject to many hazards and risks
inherent in the building, testing, deploying and maintenance of
our PowerBuoy systems. These hazards and risks could result in
personal injuries, loss of life, and other damages, which may
include damage to our properties and the properties of others
and other consequential damages, and could lead to the
suspension of certain of our operations, large damage claims,
damage to our safety reputation and a loss of business. Some of
these risks may be uninsurable and some claims may exceed our
insurance coverage. Therefore, the occurrence of a significant
accident or other risk event or hazard that is not fully covered
by insurance could materially and adversely affect our business
and financial results and, even if fully covered by insurance,
could materially and adversely affect our business due to the
impact on our reputation for
36
safety. In addition, the risks inherent in our business are such
that we cannot assure you that we will be able to maintain
adequate insurance in the future at reasonable rates.
If we
are unable to attract and retain management and other qualified
personnel, we may not be able to achieve our business
objectives.
Our success depends on the skills, experience and efforts of our
senior management and other key product development,
manufacturing, and sales and marketing employees. We cannot be
certain that we will be able to attract, retain and motivate
such employees. The loss of the services of one or more of these
employees could have a material adverse effect on our business.
There is a risk that we will not be able to retain or replace
these key employees. We have entered into employment agreements
with Dr. George Taylor, our executive chairman, and Charles
Dunleavy, our chief executive officer; however, the agreements
permit the employees to terminate their employment with little
notice. Implementation of our expansion plans will be highly
dependent upon our ability to hire and retain senior executives
as well as talented staff in various fields of expertise.
In addition, our anticipated growth will require us to hire a
significant number of qualified technical, commercial and
administrative personnel. By the end of fiscal 2012, we expect
to increase our staff in order to meet our current manufacturing
and revenue goals. The majority of our new hires will be
engineers with varying levels and areas of expertise, project
managers and manufacturing personnel. There is intense
competition from other companies and research and academic
institutions for qualified personnel in the areas of our
activities. If we cannot continue to attract and retain, on
acceptable terms, the qualified personnel necessary for the
continued development of our business, we may not be able to
sustain our operations or grow at a competitive pace.
Any
acquisitions that we make or joint venture agreements that we
enter into, or any failure to identify appropriate acquisition
or joint venture candidates, could adversely affect our
business, financial condition and results of
operations.
From time to time, we evaluate potential strategic acquisitions
of complementary businesses, products or technologies, as well
as consider joint ventures and other collaborative projects. We
may not be able to identify appropriate acquisition candidates
or strategic partners, or successfully negotiate, finance or
integrate any businesses, products or technologies that we
acquire. We do not have any experience with acquiring companies
or products. Any acquisition we pursue could diminish the
capital resources otherwise available to us for other uses or be
dilutive to our stockholders, and could divert management’s
time and resources from our core operations.
Strategic acquisitions, investments and alliances with third
parties could subject us to a number of risks, including risks
associated with sharing proprietary information and loss of
control of operations that are material to our business. In
addition, strategic acquisitions, investments and alliances may
be expensive to implement. Moreover, strategic acquisitions,
investments and alliances subject us to the risk of
non-performance by a counterparty, which may in turn lead to
monetary losses that materially and adversely affect our
business, financial condition and results of operations.
In the
event we are unable to satisfy regulatory requirements relating
to internal control over financial reporting, or if our internal
controls are not effective, our business and financial results
may suffer.
Effective internal controls are necessary for us to provide
reasonable assurance with respect to our financial reports and
to effectively prevent fraud. If we cannot provide reasonable
assurance with respect to our financial reports and effectively
prevent fraud, our business and operating results could be
harmed. Pursuant to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, we are
required to furnish a report by management on internal control
over financial reporting, including management’s assessment
of the effectiveness of such control. Internal control over
financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements
because of its inherent limitations, including the possibility
of human error, the circumvention or overriding of controls, or
fraud. Therefore, even effective internal controls can provide
only reasonable assurance with respect to the preparation and
fair presentation of financial statements. In addition,
projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of internal
control over financial reporting to future periods are subject
to the risk that the control may become inadequate because of
changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the
policies or procedures may deteriorate. If we fail to maintain
the adequacy of our internal
37
controls, including any failure to implement new or improved
controls, or if we experience difficulties in their
implementation, our business and operating results could be
harmed, we could fail to meet our reporting obligations, and
there could also be a material adverse effect on our stock price.
Risks
Related to Intellectual Property
If we
are unable to obtain or maintain intellectual property rights
relating to our technology and products, the commercial value of
our technology and products may be adversely affected, which
could in turn adversely affect our business, financial condition
and results of operations.
Our success and ability to compete depends in part upon our
ability to obtain protection in the United States and other
countries for our products by establishing and maintaining
intellectual property rights relating to or incorporated into
our technology and products. We own a variety of patents and
patent applications in the United States and corresponding
patents and patent applications in several foreign
jurisdictions. However, we have not obtained patent protection
in each market in which we plan to compete. In addition, we do
not know how successful we would be should we choose to assert
our patents against suspected infringers. Our pending and future
patent applications may not issue as patents or, if issued, may
not issue in a form that will be advantageous to us. Even if
issued, patents may be challenged, narrowed, invalidated or
circumvented, which could limit our ability to stop competitors
from marketing similar products or limit the length of term of
patent protection we may have for our products. Changes in
either patent laws or in interpretations of patent laws in the
United States and other countries may diminish the value of our
intellectual property or narrow the scope of our patent
protection, which could in turn adversely affect our business,
financial condition and results of operations.
Our
contracts with the government could negatively affect our
intellectual property rights, and our ability to commercialize
our products could be impaired.
Our agreements with the US Navy help fund research and
development of our PowerBuoy system. When new technologies are
developed with US federal government funding, the government
obtains certain rights in any resulting patents, technical data
and software, generally including, at a minimum, a nonexclusive
license authorizing the government to use the invention,
technical data or software for non-commercial purposes. These
rights may permit the government to disclose our confidential
information to third parties and to exercise
“march-in” rights. March-in rights refer to the right
of the US government to require us to grant a license to the
technology to a responsible applicant or, if we refuse, the
government may grant the license itself. US government-funded
inventions must be reported to the government. US government
funding must be disclosed in any resulting patent applications,
and our rights in such inventions will normally be subject to
government license rights, periodic post-contract utilization
reporting, foreign manufacturing restrictions and march-in
rights.
The government can exercise its march-in rights if it determines
that action is necessary because we fail to achieve practical
application of the technology or because action is necessary to
alleviate health or safety needs, to meet requirements of
federal regulations or to give preference to US industry. Our
government-sponsored research contracts are subject to audit and
require that we provide regular written technical updates on a
monthly, quarterly or annual basis, and, at the conclusion of
the research contract, a final report on the results of our
technical research. Because these reports are generally
available to the public, third parties may obtain some aspects
of our sensitive confidential information. Moreover, if we fail
to provide these reports or to provide accurate or complete
reports, the government may obtain rights to any intellectual
property arising from the related research. Funding from
government contracts also may limit when and how we can deploy
our technology developed under those contracts.
If we
are unable to protect the confidentiality of our proprietary
information and know-how, the value of our technology and
products could be adversely affected, which could in turn
adversely affect our business, financial condition and results
of operations.
In addition to patented technology, we rely upon unpatented
proprietary technology, processes and know-how, particularly
with respect to our PowerBuoy control and electricity generating
systems. We generally seek to protect this information in part
by confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants
and third parties. These
38
agreements may be breached, and we may not have adequate
remedies for any such breach. In addition, our trade secrets may
otherwise become known or be independently developed by
competitors.
If we
infringe or are alleged to infringe intellectual property rights
of third parties, our business, financial condition and results
of operations could be adversely affected.
Our products may infringe, or be claimed to infringe, patents or
patent applications under which we do not hold licenses or other
rights. Third parties may own or control these patents and
patent applications in the United States and abroad. From time
to time, we receive correspondence from third parties offering
to license patents to us. Correspondence of this nature might be
used to establish that we received notice of certain patents in
the event of subsequent patent infringement litigation. Third
parties could bring claims against us that would cause us to
incur substantial expenses and, if successfully asserted against
us, could cause us to pay substantial damages. Further, if a
patent infringement suit were brought against us, we could be
forced to stop or delay manufacturing or sales of the product or
component that is the subject of the suit.
As a result of patent infringement claims, or in order to avoid
potential claims, we may choose or be required to seek a license
from the third party and be required to pay license fees,
royalties or both. These licenses may not be available on
acceptable terms, or at all. Even if we were able to obtain a
license, the rights may be nonexclusive, which could result in
our competitors gaining access to the same intellectual
property. Ultimately, we could be forced to cease some aspect of
our business operations if, as a result of actual or threatened
patent infringement claims, we are unable to enter into licenses
on acceptable terms. This could significantly and adversely
affect our business, financial condition and results of
operations.
In addition to infringement claims against us, we may become a
party to other types of patent litigation and other proceedings,
including interference proceedings declared by the United States
Patent and Trademark Office and opposition proceedings in the
European Patent Office, regarding intellectual property rights
with respect to our products and technology. The cost to us of
any patent litigation or other proceeding, even if resolved in
our favor, could be substantial. Some of our competitors may be
able to sustain the costs of such litigation or proceedings more
effectively than we can because of their greater financial
resources. Uncertainties resulting from the initiation and
continuation of patent litigation or other proceedings could
have a material adverse effect on our ability to compete in the
marketplace. Patent litigation and other proceedings may also
absorb significant management time.
Risks
Related to our Common Stock
Provisions
in our corporate charter documents and under Delaware law may
delay or prevent attempts by our stockholders to change our
management and hinder efforts to acquire a controlling interest
in us.
As a result of our reincorporation in Delaware in April 2007,
provisions of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws may
discourage, delay or prevent a merger, acquisition or other
change in control that stockholders may consider favorable,
including transactions in which our stockholders might otherwise
receive a premium for their shares. These provisions may also
prevent or frustrate attempts by our stockholders to replace or
remove our management. These provisions include:
|
|
|
| |
•
|
advance notice requirements for stockholder proposals and
nominations;
|
| |
| |
•
|
the inability of stockholders to act by written consent or to
call special meetings; and
|
| |
| |
•
|
the ability of our board of directors to designate the terms of
and issue new series of preferred stock without stockholder
approval, which could be used to institute a “poison
pill” that would work to dilute the stock ownership of a
potential hostile acquirer, effectively preventing acquisitions
that have not been approved by our board of directors.
|
The affirmative vote of the holders of at least 75% of our
shares of capital stock entitled to vote is necessary to amend
or repeal the above provisions of our certificate of
incorporation. In addition, absent approval of our board of
directors, our bylaws may only be amended or repealed by the
affirmative vote of the holders of at least 75% of our shares of
capital stock entitled to vote.
39
In addition, Section 203 of the Delaware General
Corporation Law prohibits a publicly held Delaware corporation
from engaging in a business combination with an interested
stockholder, which is generally a person who together with its
affiliates owns or within the last three years has owned 15% of
our voting stock, for a period of three years after the date of
the transaction in which the person became an interested
stockholder, unless the business combination is approved in a
prescribed manner. Accordingly, Section 203 may discourage,
delay or prevent a change in control of our company.
We
have never paid cash dividends on our common stock, and we do
not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable
future.
We have not paid any cash dividends on our common stock to date.
We currently intend to retain our future earnings, if any, to
fund the development and growth of our business. In addition,
the terms of any future debt agreements may preclude us from
paying dividends. As a result, capital appreciation, if any, of
our common stock will be the sole source of gain for our
stockholders for the foreseeable future.
Our
stock price is likely to be volatile, and purchasers of our
common stock could incur substantial losses.
The market price of our common stock may fluctuate significantly
in response to factors that are beyond our control. For the
period ended April 30, 2010, the 52-week high and low
prices for our common stock were $11.22 and $3.81, respectively.
The stock market in general has recently experienced extreme
volatility that has often been unrelated or disproportionate to
the operating performance of particular companies. These broad
market fluctuations could result in fluctuations in the price of
our common stock, which could cause purchasers of our common
stock to incur substantial losses. The market price for our
common stock may be influenced by many factors, including:
|
|
|
| |
•
|
the success of competitive products or technologies;
|
| |
| |
•
|
regulatory developments in the United States and foreign
countries;
|
| |
| |
•
|
developments or disputes concerning patents or other proprietary
rights;
|
| |
| |
•
|
the recruitment or departure of key personnel;
|
| |
| |
•
|
quarterly or annual variations in our financial results or those
of companies that are perceived to be similar to us;
|
| |
| |
•
|
market conditions in the conventional and renewable energy
industries and issuance of new or changed securities
analysts’ reports or recommendations;
|
| |
| |
•
|
the failure of securities analysts to cover our common stock or
changes in financial estimates by analysts;
|
| |
| |
•
|
the inability to meet the financial estimates of analysts who
follow our common stock;
|
| |
| |
•
|
investor perception of our company and of the renewable energy
industry; and
|
| |
| |
•
|
general economic, political and market conditions.
|
Provisions
in our bylaws will require disclosure of information by
shareholders that would not otherwise be required to be
disclosed under applicable US state or US federal
laws.
In accordance with the rules of the AIM market of the London
Stock Exchange, we are required to disclose information
regarding beneficial owners of three percent or more of our
outstanding common stock to the AIM market. In order to allow us
to comply with the AIM rules, our bylaws contain a provision
requiring any beneficial owner of three percent or more of our
outstanding common stock to notify us of his or her
shareholdings, as well as of any change in his or her beneficial
ownership of one percent or more of our outstanding common
stock. Comparatively, none of the US state or US federal laws
that are applicable to us or the rules of the SEC or the Nasdaq
Global Market require stockholders to report this beneficial
ownership information to us or us to disclose
40
this information to the public or a regulatory body. We do not
intend to make any such information public, unless required by
law or the rules of the AIM market, the SEC or the Nasdaq Global
Market.
|
|
|
ITEM 1B.
|
UNRESOLVED
STAFF COMMENTS
|
Not applicable.
Our corporate headquarters are located in Pennington, New
Jersey, where we occupy approximately 22,000 square feet
under a lease expiring on April 30, 2013. We use these
facilities for administration, research and development, as well
as assembly and testing of the generators and control models for
our PowerBuoy systems.
We also have an office and warehouse facilities in Warwick,
United Kingdom, where we occupy 4,685 square feet under
leases expiring on January 1, 2011 and December 18,
2011, respectively. Thirteen employees, all members of the
executive, engineering, administration and business development
teams, operate out of this office, which serves as a hub for our
European presence.
We may add sales, marketing and engineering offices in
additional locations, including Australia, Japan, continental
Europe and the west coast of the United States.
|
|
|
ITEM 3.
|
LEGAL
PROCEEDINGS
|
We are subject to legal proceedings, claims and litigation
arising in the ordinary course of business. While the outcome of
these matters is currently not determinable, we do not expect
that the ultimate costs to resolve these matters will have a
material adverse effect on our financial position, results of
operations or cash flows.
|
|
| ITEM 4. |
(REMOVED AND RESERVED)
|
41
PART II
|
|
|
ITEM 5.
|
MARKET
FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
|
Stock
Price Information and Stockholders
Our common stock has been listed on the Nasdaq Global Market
since April 24, 2007 under the symbol “OPTT” and
on the AIM market of the London Stock Exchange since October
2003 under the symbol “OPT.” As of June 30, 2010,
there were 252 holders of record for shares of our common stock.
Since a portion of our common stock is held in
“street” or nominee name, we are unable to determine
the exact number of beneficial holders.
The following table sets forth the high and the low sale prices
of our common stock as quoted by the Nasdaq Global Market for
the period indicated.
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nasdaq Global Market
|
|
|
|
|
High
|
|
|
Low
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended April 30, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First quarter
|
|
$
|
7.72
|
|
|
$
|
4.73
|
|
|
Second quarter
|
|
|
9.50
|
|
|
|
3.81
|
|
|
Third quarter
|
|
|
11.22
|
|
|
|
6.00
|
|
|
Fourth quarter
|
|
|
7.69
|
|
|
|
6.00
|
|
|
Year Ended April 30, 2009
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First quarter
|
|
$
|
12.44
|
|
|
$
|
7.82
|
|
|
Second quarter
|
|
|
9.34
|
|
|
|
4.61
|
|
|
Third quarter
|
|
|
9.84
|
|
|
|
4.60
|
|
|
Fourth quarter
|
|
|
7.20
|
|
|
|
3.78
|
|
Dividend
Policy
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our common
stock, and we do not currently anticipate declaring or paying
cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. We
currently intend to retain all of our future earnings, if any,
to finance the growth and development of our business. Any
future determination relating to our dividend policy will be
made at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend
on a number of factors, including future earnings, capital
requirements, financial conditions, future prospects,
contractual restrictions and covenants and other factors that
our board of directors may deem relevant.
UNREGISTERED
SALES OF EQUITY SECURITIES AND USE OF PROCEEDS
Use of
Proceeds
On April 30, 2007, we sold 5,000,000 shares of our
common stock in our initial public offering in the United States
at a price of $20.00 per share, pursuant to a registration
statement on
Form S-1
(File
No. 333-138595),
which was declared effective by the SEC on April 24, 2007.
The managing underwriters in the offering were UBS Securities
LLC, Banc of America Securities LLC, and Bear,
Stearns & Co., Inc. The underwriting discounts and
commissions and offering expenses payable by us aggregated
$10.1 million, resulting in net proceeds to us of
$89.9 million. None of the underwriting discounts and
commissions or offering costs were incurred or paid to directors
or officers of ours or their associates or to persons owning ten
percent or more of our common stock or to any affiliates of ours.
From the effective date of the registration statement through
April 30, 2010, we used $3.2 million to construct
demonstration wave power stations, $18.6 million to fund
the continued development and commercialization of our PowerBuoy
system, $4.1 million to expand our sales and marketing
capabilities and $0.7 million to fund the expansion of
assembly, test and field service facilities. We have invested
the balance of the net proceeds from the offering in short- and
long-term, investment grade, interest-bearing instruments, in
accordance with our investment
42
policy. We have not used any of the net proceeds from the
offering to make payments, directly or indirectly, to any
director or officer of ours, except in connection with normal
annual officer and director compensation, or any of their
associates, to any person owning ten percent or more of our
common stock or to any affiliate of ours. There has been no
material change in our planned use of the balance of the net
proceeds from the offering as described in our final prospectus
filed with the SEC pursuant to Rule 424(b) under the
Securities Act of 1933.
|
|
|
ITEM 6.
|
SELECTED
FINANCIAL DATA
|
You should read the following selected consolidated financial
data in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements
and the related notes appearing at the end of this Annual Report
and the “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations” section of
this Annual Report. The selected consolidated financial data
have been derived from our audited consolidated financial
statements which are included elsewhere in this Annual Report,
or from audited consolidated financial statements not included
in this Annual Report.
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fiscal Years Ended April 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
2008
|
|
|
2007
|
|
|
2006
|
|
|
|
|
Consolidated Statement of Operations Data:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
5,101,311
|
|
|
$
|
4,049,445
|
|
|
$
|
4,772,017
|
|
|
$
|
2,531,315
|
|
|
$
|
1,747,715
|
|
|
Cost of revenues
|
|
|
4,298,955
|
|
|
|
4,840,403
|
|
|
|
7,960,042
|
|
|
|
3,983,742
|
|
|
|
2,059,318
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross profit (loss)
|
|
|
802,356
|
|
|
|
(790,958
|
)
|
|
|
(3,188,025
|
)
|
|
|
(1,452,427
|
)
|
|
|
(311,603
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating expenses:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Product development costs
|
|
|
13,001,550
|
|
|
|
8,372,244
|
|
|
|
8,255,123
|
|
|
|
6,219,893
|
|
|
|
4,224,997
|
|
|
Selling, general and administrative costs
|
|
|
9,063,482
|
|
|
|
9,529,071
|
|
|
|
7,732,577
|
|
|
|
4,893,580
|
|
|
|
3,190,687
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total operating expenses
|
|
|
22,065,032
|
|
|
|
17,901,315
|
|
|
|
15,987,700
|
|
|
|
11,113,473
|
|
|
|
7,415,684
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating loss
|
|
|
(21,262,676
|
)
|
|
|
(18,692,273
|
)
|
|
|
(19,175,725
|
)
|
|
|
(12,565,900
|
)
|
|
|
(7,727,287
|
)
|
|
Interest income, net
|
|
|
1,032,484
|
|
|
|
1,672,350
|
|
|
|
4,434,844
|
|
|
|
1,389,702
|
|
|
|
1,408,361
|
|
|
Other income
|
|
|
557,540
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
13,906
|
|
|
|
74,294
|
|
|
Foreign exchange gain (loss)
|
|
|
540,644
|
|
|
|
(1,295,227
|
)
|
|
|
84,158
|
|
|
|
1,523,527
|
|
|
|
(978,242
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss before income taxes
|
|
|
(19,132,008
|
)
|
|
|
(18,315,150
|
)
|
|
|
(14,656,723
|
)
|
|
|
(9,638,765
|
)
|
|
|
(7,222,874
|
)
|
|
Income tax benefit
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
143,963
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
(19,132,008
|
)
|
|
|
(18,315,150
|
)
|
|
|
(14,656,723
|
)
|
|
|
(9,638,765
|
)
|
|
|
(7,078,911
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less: Net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest in
Ocean Power Technologies (Australasia) Pty Ltd.
|
|
|
(38,299
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss attributable to Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.
|
|
$
|
(19,170,307
|
)
|
|
$
|
(18,315,150
|
)
|
|
$
|
(14,656,723
|
)
|
|
$
|
(9,638,765
|
)
|
|
$
|
(7,078,911
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic and diluted net loss per share
|
|
$
|
(1.88
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1.79
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1.44
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1.83
|
)
|
|
$
|
(1.37
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic and diluted weighted average shares outstanding
|
|
|
10,217,003
|
|
|
|
10,210,354
|
|
|
|
10,200,729
|
|
|
|
5,260,794
|
|
|
|
5,162,340
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of April 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009(2)
|
|
|
2008
|
|
|
2007
|
|
|
2006
|
|
|
|
|
Consolidated Balance Sheet Data:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments
|
|
$
|
36,772,598
|
|
|
$
|
53,117,566
|
|
|
$
|
88,836,304
|
|
|
$
|
115,895,619
|
(1)
|
|
$
|
32,439,365
|
|
|
Working capital
|
|
|
32,569,351
|
|
|
|
51,129,985
|
|
|
|
85,870,307
|
|
|
|
111,187,195
|
|
|
|
30,886,029
|
|
|
Long-term investments
|
|
|
28,865,046
|
|
|
|
28,619,528
|
|
|
|
12,233,437
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Total assets
|
|
|
72,978,193
|
|
|
|
88,793,906
|
|
|
|
107,550,965
|
|
|
|
119,711,546
|
|
|
|
33,996,138
|
|
|
Long-term debt, net of current portion
|
|
|
250,000
|
|
|
|
345,386
|
|
|
|
188,784
|
|
|
|
231,585
|
|
|
|
233,959
|
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(90,413,098
|
)
|
|
|
(71,242,791
|
)
|
|
|
(52,927,641
|
)
|
|
|
(38,270,918
|
)
|
|
|
(28,632,153
|
)
|
|
Total Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. stockholders’ equity
|
|
|
64,814,200
|
|
|
|
82,783,027
|
|
|
|
100,098,609
|
|
|
|
112,541,209
|
|
|
|
31,066,704
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
(1) |
|
On April 30, 2007, we completed our initial public offering
in the United States resulting in net proceeds to us of
$89.9 million. |
| |
|
(2) |
|
The April 30, 2009 balance of marketable securities was
changed to increase the current portion and decrease the
non-current portion by $12,009,337 to reflect the maturities of
the securities as of such date. |
|
|
|
ITEM 7.
|
MANAGEMENT’S
DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF
OPERATIONS
|
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our
financial condition and results of operations together with our
consolidated financial statements and the related notes and
other financial information included elsewhere in this Annual
Report. Some of the information contained in this discussion and
analysis or set forth elsewhere in this Annual Report, including
information with respect to our plans and strategy for our
business and related financing, includes forward-looking
statements that involve risks and uncertainties. You should
review the “Risk Factors” section of this Annual
Report for a discussion of important factors that could cause
actual results to differ materially from the results described
in or implied by the forward-looking statements contained in the
following discussion and analysis.
Overview
We develop and are commercializing proprietary systems that
generate electricity by harnessing the renewable energy of ocean
waves. Our PowerBuoy
®
systems use proprietary technologies to convert the mechanical
energy created by the rising and falling of ocean waves into
electricity. We currently market two PowerBuoy products, which
consist of our utility PowerBuoy system and our autonomous
PowerBuoy system. We also market operations and maintenance
services for our PowerBuoy systems to our customers, which are
expected to provide a source of recurring revenues. In addition,
we expect to market our undersea substation pod and undersea
power connection infrastructure services to other companies in
the marine energy sector.
We market our utility PowerBuoy system, which is designed to
supply electricity to a local or regional power grid, to
utilities and other electrical power producers seeking to add
electricity generated by wave energy to their existing
electricity supply. We market our autonomous PowerBuoy system,
which is designed to generate power for use independent of the
power grid, to customers that require electricity in remote
locations. We believe there are a variety of potential
applications for our autonomous PowerBuoy system, including
sonar and radar surveillance, tsunami warning, oceanographic
data collection, offshore platforms and offshore aquaculture.
We were incorporated in New Jersey in April 1984, began
commercial operations in 1994, and were re-incorporated in
Delaware in 2007. We currently have three wholly-owned
subsidiaries, which include Ocean Power Technologies Ltd.,
Reedsport OPT Wave Park LLC, and Oregon Wave Energy
Partners I, LLC, and we own approximately 88% of the
ordinary shares of Ocean Power Technologies (Australasia) Pty
Ltd.
The development of our technology has been funded by capital we
raised and by development engineering contracts we received
starting in fiscal 1995. In fiscal 1996, we received the first
of several research contracts with
44
the US Navy to study the feasibility of wave energy. As a result
of those research contracts, we entered into our first
development and construction contract with the US Navy in fiscal
2002 under a still on-going project for the development and
testing of our wave power systems at the US Marine Corps base in
Oahu, Hawaii. We generated our first revenue relating to our
autonomous PowerBuoy system from contracts with Lockheed Martin
Corporation in fiscal 2003, and we entered into our first
development and construction contract with Lockheed Martin in
fiscal 2004 for the development and construction of a prototype
demonstration autonomous PowerBuoy system.
As of April 30, 2010, our backlog was $5.7 million, a
decrease of $1.8 million from April 30, 2009.
Our fiscal year ends on April 30. For fiscal 2010, we
generated revenues of $5.1 million and incurred a net loss
attributable to Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. of
$19.2 million, and for fiscal 2009, we generated revenues
of $4.0 million and incurred a net loss attributable to
Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. of $18.3 million. As of
April 30, 2010, our accumulated deficit was
$90.4 million. We have not been profitable since inception,
and we do not know whether or when we will become profitable
because of the significant uncertainties with respect to our
ability to successfully commercialize our PowerBuoy systems in
the emerging renewable energy market. Since fiscal 2002, the US
Navy has accounted for a significant portion of our revenues. We
expect that over time, revenues derived from utilities and other
non-government commercial customers will increase more rapidly
than sales to government customers and may, over time, represent
the majority of our revenues.
The marine energy industry, including wave, tidal and ocean
current energy technologies, is expected to benefit from various
legislative initiatives that have been undertaken or are planned
by state and federal agencies. For example, the production tax
credit was expanded to include marine energy, as part of the
Energy Improvement and Extension Act of 2008, signed into law in
October 2008. Production tax credit provisions that were
previously in place served only to benefit other renewable
energy sources such as wind and solar. This new legislation
will, for the first time, enable owners of wave power projects
in the US to receive federal production tax credits, which, by
their prospective effect of lowering income taxes for our
customers based on energy produced, should improve the
comparative economics of wave power as a renewable energy source.
Further, it is expected that the US federal and state
governments will increase their investments in the renewable
energy sector under various economic stimulus measures. The
American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 provides
significant grants, tax incentives and policy initiatives to
stimulate investment and innovation in the “cleantech”
sector. The DOE has also issued requests for proposal to be
funded under programs it has established to further investment
in marine energy technologies. We have devoted additional
resources to develop proposals seeking government funding to
support existing projects and technology enhancements.
Consequently, while our selling, general and administrative
costs related to such efforts may increase over the next year,
we believe that these governmental initiatives may result in
additional revenues for us over the next several years. Given
the recent announcement of the government programs and the
uncertainties surrounding their scope and size, there can be no
assurances as to whether we will be successful in obtaining
significant additional government funding or as to the terms and
conditions of any such funding.
The recent global economic downturn may have a negative effect
on our business, financial condition and results of operations
because the utility companies with which we contract or propose
to contract may decrease their investment in new power
generation equipment in response to the downturn. However, the
various legislative initiatives described above may diminish the
effect of any decrease in such capital expenditures by these
utility companies insofar as they may relate to renewable energy
generation equipment. As discussed above, the timing, scope and
size of these new government programs for renewable energy is
uncertain, and there can be no assurances that we or our
customers will be successful in obtaining any additional
government funding. In addition, we do not believe the recent
global economic downturn will have a material negative impact on
our sources of supply, as our products incorporate what are
substantially non-custom, standard parts found in many regions
of the world.
According to the International Energy Agency, $3.4 trillion is
expected to be spent for new renewable energy generation
equipment in the period from 2007 to 2030. This equates to
annual global expenditures of approximately $150 billion.
We plan to take advantage of these global drivers of demand for
renewable energy, as we continue to refine and expand our
proprietary technology.
45
Financial
Operations Overview
The following describes certain line items in our statement of
operations and some of the factors that affect our operating
results.
Revenues
Generally, we recognize revenue using the
percentage-of-completion
method based on the ratio of costs incurred to total estimated
costs at completion. In certain circumstances, revenue under
contracts that have specified milestones or other performance
criteria may be recognized only when our customer acknowledges
that such criteria have been satisfied. In addition, recognition
of revenue (and the related costs) may be deferred for
fixed-price contracts until contract completion if we are unable
to reasonably estimate the total costs of the project prior to
completion. Because we have a small number of contracts,
revisions to the percentage of completion determination or
delays in meeting performance criteria or in completing projects
may have a significant effect on our revenue for the periods
involved. Upon anticipating a loss on a contract, we recognize
the full amount of the anticipated loss in the current period.
Generally our contracts are either cost plus or fixed price
contracts. Under cost plus contracts we bill the customer for
actual expenses incurred plus an agreed upon fee. Revenue is
typically recorded using
percentage-of-completion
based on the maximum awarded contract amount. In certain cases
we may choose to incur costs in excess of the maximum awarded
contract amount resulting in a loss on the contract. Currently,
we have two types of fixed price contracts, firm fixed price and
cost sharing. Under firm fixed price contracts we receive an
agreed upon amount for providing products and services which are
specified in the contract. Revenue is typically recorded using
percentage-of-completion
based on the contract amount. Depending on whether actual costs
are more or less than the agreed upon amount, there is a profit
or loss on the project. Under cost sharing contracts the fixed
amount agreed upon with the customer is only intended to fund a
portion of the costs on a specific project. We fund the
remainder of the costs as part of our product development
efforts. Revenue is typically recorded using
percentage-of-completion
based on the amount agreed upon with the customer. An amount
corresponding to the revenue is recorded in cost of revenues
resulting in gross profit on these contracts of zero. Our share
of the costs is recorded as product development expense.
The following table provides information regarding the breakdown
of our revenues by customer for fiscal years 2010, 2009 and 2008:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Years Ended April 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
2008
|
|
|
|
|
($ millions)
|
|
|
|
|
US Navy
|
|
$
|
4.1
|
|
|
$
|
2.7
|
|
|
$
|
2.8
|
|
|
Iberdrola and Total (Spain)
|
|
|
0.2
|
|
|
|
0.7
|
|
|
|
1.4
|
|
|
Scottish Government
|
|
|
0.3
|
|
|
|
0.3
|
|
|
|
0.5
|
|
|
Other
|
|
|
0.5
|
|
|
|
0.3
|
|
|
|
0.1
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
5.1
|
|
|
$
|
4.0
|
|
|
$
|
4.8
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The revenue increase for fiscal 2010 reflected a significant
increase in revenue from the US Navy related to autonomous
PowerBuoy projects and also an increase in revenue related to
our project off the coast of Reedsport, Oregon (included in
“Other” in the above table). The increased revenue was
partially offset by a decrease in revenue from our construction
project in Spain and our Hawaii project for the US Navy. The
revenue decrease for fiscal 2009 primarily reflected a lower
level of billable activity in connection with our construction
contracts in Spain and at the European Marine Energy Centre
(EMEC) at Orkney, Scotland. In 2009, we also reduced the total
expected contract value related to the Spain contract by
approximately $0.5 million, reflecting an expected
reduction in scope of the then-current phase of this project.
These decreases in revenue during fiscal 2009 were partially
offset by an increase in revenue from the Department of Energy
(DOE) related to our project off the coast of Reedsport, Oregon.
The US Navy has been our largest customer since fiscal 2002. The
US Navy accounted for 80% of our revenues in fiscal 2010, 67% of
our revenues in fiscal 2009 and 58% of our revenues in fiscal
2008. We anticipate that, if our
46
commercialization efforts are successful, the relative
contribution of the US Navy to our revenue may decline in the
future.
We currently focus our sales and marketing efforts on North
America, the west coast of Europe, Australia and the east coast
of Japan. The following table provides information regarding the
breakdown of our revenues by geographical location of our
customers for fiscal years 2010, 2009 and 2008:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Percentage of Revenues
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended
|
|
|
Year Ended
|
|
|
Year Ended
|
|
|
|
|
April 30,
|
|
|
April 30,
|
|
|
April 30,
|
|
|
Customer Location
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
2008
|
|
|
|
|
United States
|
|
|
89
|
%
|
|
|
73
|
%
|
|
|
59
|
%
|
|
Europe
|
|
|
9
|
|
|
|
25
|
|
|
|
41
|
|
|
Australia
|
|
|
2
|
|
|
|
2
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
100
|
%
|
|
|
100
|
%
|
|
|
100
|
%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost
of revenues
Our cost of revenues consists primarily of incurred material,
labor and manufacturing overhead expenses, such as engineering
expense, equipment depreciation and maintenance and facility
related expenses, and includes the cost of PowerBuoy parts and
services supplied by third-party suppliers. Cost of revenues
also includes PowerBuoy system delivery and deployment expenses
and anticipated losses at completion on some contracts.
We operated at a gross profit of $0.8 million in fiscal
2010 and a gross loss of $0.8 million in fiscal 2009 and
$3.2 million in fiscal 2008. Our ability to generate a
gross profit will depend on the nature of future contracts, our
success at increasing sales of our PowerBuoy systems and on our
ability to manage costs incurred on fixed price commercial
contracts. Additionally, approximately $0.4 million of
costs related to revenue activity during fiscal 2009 had been
previously anticipated and accrued as contract loss reserves as
of April 30, 2009. These loss reserves were no longer
necessary and, accordingly, reversed in fiscal year 2010,
contributing to the increase in gross profit.
Product
development costs
Our product development costs consist of salaries and other
personnel-related costs and the costs of products, materials and
outside services used in our product development and unfunded
research activities. Our product development costs primarily
relate to our efforts to increase the output and reliability of
our utility PowerBuoy system, including the 150kW PowerBuoy
system and to our research and development of new products,
product applications and complementary technologies. We expense
all of our product development costs as incurred, except for
external patent costs, which we capitalize and amortize over a
17-year
period commencing with the issuance date of each patent. Patents
are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in
circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the patent
may not be recoverable.
From October 2005 to December 2009, we operated, at intervals, a
40kW system off the coast of New Jersey. The system was
periodically removed from the ocean for maintenance during that
time. Other 40kW systems were deployed and tested in Hawaii for
the US Navy project during the months of June 2007 and October
2008, and in late 2009. Work is currently in progress on the
design, construction and installation of two 150kW PowerBuoy
systems in connection with projects off the coasts of Scotland
and Oregon. We completed the successful in-ocean trials of our
USP in October 2009.
Selling,
general and administrative costs
Our selling, general and administrative costs consist primarily
of professional fees, salaries and other personnel-related costs
for employees and consultants engaged in sales and marketing and
support of our PowerBuoy systems and costs for executive,
accounting and administrative personnel, professional fees and
other general corporate expenses.
47
Interest
income, net
Interest income consists of interest received on cash and cash
equivalents, investments in commercial bank-issued certificates
of deposit and US Treasury bills and notes. Total cash, cash
equivalents, restricted cash, and marketable securities were
$66.8 million as of April 30, 2010, $82.7 million
as of April 30, 2009 and $102.2 million as of
April 30, 2008. Interest income decreased due to a decline
in interest rates and a decline in cash, cash equivalents and
marketable securities.
Foreign
exchange gain (loss)
We transact business in various countries and have exposure to
fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates. Foreign
exchange gains and losses arise in the translation of
foreign-denominated assets and liabilities, which may result in
realized and unrealized gains or losses from exchange rate
fluctuations. Since we conduct our business in US dollars and
our functional currency is the US dollar, our main foreign
exchange exposure, if any, results from changes in the exchange
rate between the US dollar and the British pounds sterling, the
Euro and the Australian dollar.
We invest in certificates of deposit and maintain cash accounts
that are denominated in British pounds sterling, Euros and
Australian dollars. These foreign denominated certificates of
deposit and cash accounts had a balance of $4.1 million as
of April 30, 2010 and $8.5 million as of
April 30, 2009, compared to our total cash, cash
equivalents, restricted cash, and marketable securities balances
of $66.8 million as of April 30, 2010 and
$82.7 million as of April 30, 2009.
In addition, a portion of our operations is conducted through
our subsidiaries in countries other than the United States,
specifically Ocean Power Technologies Ltd. in the United
Kingdom, the functional currency of which is the British pounds
sterling, and Ocean Power Technologies (Australasia) Pty Ltd. in
Australia, the functional currency of which is the Australian
dollar. Both of these subsidiaries have foreign exchange
exposure that results from changes in the exchange rate between
their functional currency and other foreign currencies in which
they conduct business. All of our international revenues for the
years ended April 30, 2010, 2009, and 2008 were recorded in
Euros, British pounds sterling or Australian dollars.
We currently do not hedge our exchange rate exposure. However,
we assess the anticipated foreign currency working capital
requirements and capital asset acquisitions of our foreign
operations and attempt to maintain a portion of our cash and
cash equivalents denominated in foreign currencies sufficient to
satisfy these anticipated requirements. We also assess the need
and cost to utilize financial instruments to hedge currency
exposures on an ongoing basis and may hedge against exchange
rate exposure in the future.
Income
taxes
As of April 30, 2010, we had federal and foreign net
operating loss carryforwards of $74.6 million and federal
and foreign research and development tax credits of
$2.2 million to offset future taxable income. As of
April 30, 2010, we had state net operating loss
carryforwards of $49.1 million. If not utilized, the net
operating loss carryforwards and credit carryforwards will
expire at various dates through 2030. We may not achieve
profitability in time to utilize the tax credit and net
operating loss carryforwards in full or at all. In addition, we
have determined that the future utilization of our net operating
loss carryforwards is subject to limitations based upon changes
in ownership including changes resulting from our initial public
offering in April 2007, pursuant to regulations promulgated
under the Internal Revenue Code. We do not expect these
limitations to have a significant impact on our ability to
utilize net operating loss and credit carryforwards. As
discussed in Note 12 to our consolidated financial
statements included in this Annual Report, we have established a
valuation allowance for our net deferred tax assets, which were
$33.1 million as of April 30, 2010 and
$25.5 million as of April 30, 2009.
Outlook
We have incurred net losses since we began operations in 1994,
including net losses attributable to Ocean Power Technologies,
Inc. of $19.2 million in fiscal 2010, $18.3 million in
fiscal 2009 and $14.7 million in fiscal 2008. As of
April 30, 2010, we had an accumulated deficit of
$90.4 million. These losses have resulted primarily
48
from costs incurred in our research and development programs and
from our selling, general and administrative costs. We expect to
increase our operating expenses as we continue to expand our
infrastructure, research and development programs and
commercialization activities. As a result, we will need to
generate significant revenues to cover these costs and achieve
profitability.
We do not know whether or when we will become profitable because
of the significant uncertainties with respect to our ability to
successfully commercialize our PowerBuoy systems in the emerging
renewable energy market. Even if we do achieve profitability, we
may not be able to sustain or increase profitability on a
quarterly or annual basis.
Results
of Operations
Fiscal
Years Ended April 30, 2010 and 2009
The following table contains statement of operations
information, which serves as the basis of the discussion of our
results of operations for the years ended April 30, 2010
and 2009:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fiscal Year Ended
|
|
|
Fiscal Year Ended
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
April 30, 2010
|
|
|
April 30, 2009
|
|
|
% Change
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As a % of
|
|
|
|
|
|
As a % of
|
|
|
2010 Period to
|
|
|
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
Revenues(1)
|
|
|
2009 Period
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
5,101,311
|
|
|
|
100
|
%
|
|
$
|
4,049,445
|
|
|
|
100
|
%
|
|
|
26
|
%
|
|
Cost of revenues
|
|
|
4,298,955
|
|
|
|
84
|
|
|
|
4,840,403
|
|
|
|
120
|
|
|
|
(11
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross profit (loss)
|
|
|
802,356
|
|
|
|
16
|
|
|
|
(790,958
|
)
|
|
|
(20
|
)
|
|
|
201
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating expenses:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Product development costs
|
|
|
13,001,550
|
|
|
|
255
|
|
|
|
8,372,244
|
|
|
|
207
|
|
|
|
55
|
|
|
Selling, general and administrative costs
|
|
|
9,063,482
|
|
|
|
178
|
|
|
|
9,529,071
|
|
|
|
235
|
|
|
|
(5
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total operating expenses
|
|
|
22,065,032
|
|
|
|
433
|
|
|
|
17,901,315
|
|
|
|
442
|
|
|
|
23
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating loss
|
|
|
(21,262,676
|
)
|
|
|
(417
|
)
|
|
|
(18,692,273
|
)
|
|
|
(462
|
)
|
|
|
14
|
|
|
Interest income, net
|
|
|
1,032,484
|
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
|
1,672,350
|
|
|
|
41
|
|
|
|
(38
|
)
|
|
Other income
|
|
|
557,540
|
|
|
|
11
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Foreign exchange gain (loss)
|
|
|
540,644
|
|
|
|
11
|
|
|
|
(1,295,227
|
)
|
|
|
(32
|
)
|
|
|
142
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
(19,132,008
|
)
|
|
|
(375
|
)
|
|
|
(18,315,150
|
)
|
|
|
(452
|
)
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
Less: Net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest in
Ocean Power Technologies (Australasia) Pty Ltd
|
|
|
(38,299
|
)
|
|
|
(1
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss attributable to Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.
|
|
$
|
(19,170,307
|
)
|
|
|
(376
|
)%
|
|
$
|
(18,315,150
|
)
|
|
|
(452
|
)%
|
|
|
5
|
%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1) |
|
Certain subtotals may not add due to rounding. |
Revenues
Revenues increased by $1.1 million in fiscal 2010, or 26%,
to $5.1 million as compared to $4.0 million in fiscal
2009. The change in revenues was primarily attributable to the
following factors:
|
|
|
| |
•
|
Revenues relating to our autonomous PowerBuoy system increased
by $1.8 million as a result of work on projects with the US
Navy to provide our PowerBuoy technology to the US Navy’s
Deep Water Active Detection System and Littoral Expeditionary
Autonomous PowerBuoy program.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Revenues relating to our utility PowerBuoy system decreased by
$0.7 million due primarily to a decrease in billable work
on our wave power station off the coast of Spain, as work under
this phase of the project neared
|
49
|
|
|
| |
|
completion, coupled with a reduction in the expected contract
value of this project in late fiscal 2009. Also, a decrease in
revenue related to our Hawaii project for the US Navy, partially
offset by an increase in revenue related to our project off the
coast of Reedsport, Oregon.
|
Cost of
revenues
Cost of revenues decreased by $0.5 million, or 11%, to
$4.3 million in fiscal 2010, as compared to
$4.8 million in fiscal 2009. This decrease in cost of
revenues reflected the lower level of activity on our project
off the coast of Spain, offset by increased activity related to
our autonomous PowerBuoy projects for the US Navy.
We operated at a gross profit of $0.8 million in fiscal
2010 and a gross loss of $0.8 million in fiscal 2009.
Certain of our projects in fiscal 2010 and 2009 were under cost
sharing contracts. Under cost sharing contracts we receive a
fixed amount agreed upon with the customer that is only intended
to fund a portion of the costs on a specific project. We fund
the remainder of the costs as part of our product development
efforts. Revenue is typically recorded using
percentage-of-completion
based on the amount agreed upon with the customer. An equal
amount corresponding to the revenue is recorded in cost of
revenues resulting in gross profit on these contracts of zero.
Our share of the costs is considered to be product development
expense. Approximately $0.4 million of costs related to
revenue activity during fiscal 2009 had been previously
anticipated and accrued as contract loss reserves as of
April 30, 2009. These loss reserves were no longer
necessary and, accordingly, reversed in fiscal year 2010
contributing to the increase in a gross profit. Our ability to
generate a gross profit will depend on the nature of future
contracts, our success at increasing sales of our PowerBuoy
systems and on our ability to manage costs incurred on fixed
price commercial contracts.
Product
development costs
Product development costs increased by $4.6 million, or 55%
to $13.0 million in fiscal 2010, as compared to
$8.4 million in fiscal 2009. Product development costs were
primarily attributable to our efforts to increase the power
output and reliability of our utility PowerBuoy system,
especially the 150kW PowerBuoy system. It is our intent to fund
the majority of our research and development expenses over the
next several years with sources of external funding. If we are
unable to obtain external funding, we may curtail our research
and development expenses or we may decide to self-fund
significant research and development expenses, in which case our
product development costs may continue to increase.
Selling,
general and administrative costs
Selling, general and administrative costs decreased
$0.4 million, or 5%, to $9.1 million in fiscal 2010,
as compared to $9.5 million in fiscal 2009. The decrease
was primarily attributable to a decrease in consulting, legal,
accounting and investor relations expenses partially offset by
increased personnel-related expenses.
Interest
income
Interest income decreased by $0.7 million, or 38%, to
$1.0 million in fiscal 2010, compared to $1.7 million
in fiscal 2009, due to a decrease in cash, cash equivalents and
marketable securities. In addition, the average yield decreased
to approximately 1.40% during fiscal 2010 from approximately
1.86% during fiscal 2009.
Other
income
Other income was $0.6 million in fiscal 2010, compared to
none for fiscal 2009. During the first quarter of fiscal 2010,
we settled a claim which we had against a supplier of
engineering services, which resulted in a settlement in our
favor.
Foreign
exchange gain (loss)
Foreign exchange gain was $0.5 million in fiscal 2010,
compared to a foreign exchange loss of $1.3 million in
fiscal 2009. The difference was primarily attributable to the
relative change in value of the British pound sterling, Euro and
Australian dollar compared to the US dollar during the two
periods.
50
Fiscal
Years Ended April 30, 2009 and 2008
The following table contains statement of operations
information, which serves as the basis of the discussion of our
results of operations for the years ended April 30, 2009
and 2008:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fiscal Year Ended
|
|
|
Fiscal Year Ended
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
April 30, 2009
|
|
|
April 30, 2008
|
|
|
% Change
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As a % of
|
|
|
|
|
|
As a % of
|
|
|
2009 Period to
|
|
|
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
Revenues(1)
|
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
Revenues(1)
|
|
|
2008 Period
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
4,049,445
|
|
|
|
100
|
%
|
|
$
|
4,772,017
|
|
|
|
100
|
%
|
|
|
(15
|
)%
|
|
Cost of revenues
|
|
|
4,840,403
|
|
|
|
120
|
|
|
|
7,960,042
|
|
|
|
167
|
|
|
|
(39
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross loss
|
|
|
(790,958
|
)
|
|
|
(20
|
)
|
|
|
(3,188,025
|
)
|
|
|
(67
|
)
|
|
|
(75
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating expenses:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Product development costs
|
|
|
8,372,244
|
|
|
|
207
|
|
|
|
8,255,123
|
|
|
|
173
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
Selling, general and administrative costs
|
|
|
9,529,071
|
|
|
|
235
|
|
|
|
7,732,577
|
|
|
|
162
|
|
|
|
23
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total operating expenses
|
|
|
17,901,315
|
|
|
|
442
|
|
|
|
15,987,700
|
|
|
|
335
|
|
|
|
12
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating loss
|
|
|
(18,692,273
|
)
|
|
|
(462
|
)
|
|
|
(19,175,725
|
)
|
|
|
(402
|
)
|
|
|
(3
|
)
|
|
Interest income, net
|
|
|
1,672,350
|
|
|
|
41
|
|
|
|
4,434,844
|
|
|
|
93
|
|
|
|
(62
|
)
|
|
Foreign exchange gain (loss)
|
|
|
(1,295,227
|
)
|
|
|
(32
|
)
|
|
|
84,158
|
|
|
|
2
|
|
|
|
1639
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
$
|
(18,315,150
|
)
|
|
|
(452
|
)%
|
|
$
|
(14,656,723
|
)
|
|
|
(307
|
)%
|
|
|
25
|
%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
(1) |
|
Certain subtotals may not add due to rounding. |
Revenues
Revenues decreased by $0.8 million in fiscal 2009, or 15%,
to $4.0 million as compared to $4.8 million in fiscal
2008. The change in revenues was primarily attributable to the
following factors:
|
|
|
| |
•
|
Revenues relating to our utility PowerBuoy system decreased by
$0.8 million due primarily to a decrease in billable work
on our wave power station off the coast of Spain, as this phase
of the project neared completion, and also a reduction in the
expected contract value related to the project. Also, decreases
in revenue related to our Hawaii project for the US Navy and our
EMEC project in Orkney, Scotland were offset by an increase in
revenue related to our project off the coast of Reedsport,
Oregon.
|
| |
| |
•
|
Revenues relating to our autonomous PowerBuoy system increased
by $0.1 million as a result of work on projects with the US
Navy to provide our PowerBuoy technology to a program for data
gathering in the ocean.
|
Cost of
revenues
Cost of revenues decreased by $3.2 million, or 39%, to
$4.8 million in fiscal 2009, as compared to
$8.0 million in fiscal 2008. This decrease in cost of
revenues reflected the lower level of activity on
revenue-bearing contracts, and the recognition, in fiscal 2008,
of an additional $2.4 million of anticipated loss at
completion on our contract for a wave power station off the
coast of Spain. The additional anticipated loss was recognized
based on a change in estimated costs associated with this
contract and our decision in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2008
to absorb an additional $1.9 million in costs beyond our
contractual obligation for initial cost overruns and certain
other costs as set forth in the agreement for the Spain project.
Product
development costs
Product development costs increased $0.1 million, or 1%, to
$8.4 million in fiscal 2009, as compared to
$8.3 million in fiscal 2008. Product development costs were
primarily attributable to our efforts to increase the power
output of our utility PowerBuoy system, including the 150kW
PowerBuoy system.
51
Selling,
general and administrative costs
Selling, general and administrative costs increased
$1.8 million, or 23%, to $9.5 million in fiscal 2009,
as compared to $7.7 million in fiscal 2008. The increase
was primarily attributable to an increase of $1.8 million
in additional payroll and incentive-based costs related to
company growth.
Interest
income
Interest income decreased by $2.7 million, or 62%, to
$1.7 million in fiscal 2009, compared to $4.4 million
in fiscal 2008, due to a decrease in cash, cash equivalents and
investments. In addition, the average yield decreased from
approximately 4.05% in fiscal 2008 to approximately 1.86% in
fiscal 2009.
Foreign
exchange gain (loss)
Foreign exchange loss was $1.3 million in fiscal 2009,
compared to a foreign exchange gain of $0.1 million in
fiscal 2008. The difference was primarily attributable to the
relative change in value of the British pounds sterling compared
to the US dollar during the two periods.
Liquidity
and Capital Resources
Since our inception, the cash flows from customer revenues have
not been sufficient to fund our operations and provide the
capital resources for the planned growth of our business. For
the three years ended April 30, 2010, our revenues were
$13.9 million, our net losses were $52.1 million and
our net cash used in operating activities was $46.1 million.
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended April 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
$
|
(19,132,008
|
)
|
|
$
|
(18,315,150
|
)
|
|
Adjustments for noncash operating items
|
|
|
1,181,318
|
|
|
|
3,669,017
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash operating loss
|
|
|
(17,950,690
|
)
|
|
|
(14,646,133
|
)
|
|
Net change in assets and liabilities
|
|
|
2,180,006
|
|
|
|
(2,061,794
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash used in operating activities
|
|
$
|
(15,770,684
|
)
|
|
$
|
(16,707,927
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash provided by (used in ) investing activities
|
|
$
|
7,309,086
|
|
|
$
|
(58,579,591
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities
|
|
$
|
(99,841
|
)
|
|
$
|
207,199
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of exchange rates on cash and cash equivalents
|
|
$
|
530,206
|
|
|
$
|
(1,488,155
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash
used in operating activities
Net cash used in operating activities was $15.8 million for
fiscal 2010 and $16.7 million for fiscal 2009. The change
was the result of an increase in cash provided by operating
assets and liabilities of $4.2 million, offset by an
increase in net loss of $0.8 million, and a decrease in
non-cash charges of $2.5 million.
The change in non-cash charges was primarily due to a change in
foreign exchange gains (losses) of $1.8 million due to the
relative change in the value of the British pound against the US
dollar, a decrease in stock compensation expense of
$0.4 million, a decrease in loss on disposal of equipment
of $0.2 million and a decrease in Treasury note
amortization of $0.1 million.
The increase in cash provided by operating assets and
liabilities was primarily the result of an increase in cash
provided by accounts payable of $1.3 million, an increase
in cash provided by unearned revenues of $1.2 million, an
increase in cash provided by unbilled receivables of
$1.2 million and an increase in cash provided by other
assets and liabilities of $1.4 million, partially offset by
a decrease in cash provided by accounts receivable of
$0.9 million. The change in accounts payable reflects a net
increase in payables to the steel fabricator for our Reedsport,
Oregon project due to timing of receipt of vendor invoices. The
changes in unearned revenue and receivables were primarily due
to the timing of billings to customers.
52
Net cash
provided by (used in) investing activities
Net cash provided by investing activities was $7.3 million
for fiscal 2010 and net cash used in investing activities was
$58.6 million for fiscal 2009. The change was primarily the
result of a net decrease in purchases of securities during
fiscal 2010. Also, there was a $0.6 million decrease in
purchases of equipment and a $0.3 million increase in
restricted cash for fiscal 2010.
Net cash
(used in) provided by financing activities
Net cash used in financing activities was $0.1 million in
fiscal 2010 and net cash provided by financing activities was
$0.2 million in fiscal 2009, reflecting a net change in our
loans from the State of New Jersey. During fiscal 2009, we
received a $0.25 million loan under the New Jersey Board of
Public Utilities Renewable Energy Business Venture Assistance
Program.
Effect of
exchange rates on cash and cash equivalents
Effect of exchange rates on cash and cash equivalents was a gain
of $0.5 million in fiscal 2010 and a loss of
$1.5 million in fiscal 2009. The change was primarily the
result of gains on consolidation of foreign subsidiaries and
foreign denominated cash and cash equivalents.
Liquidity
Outlook
We expect to devote substantial resources to continue our
development efforts for our PowerBuoy systems and to expand our
sales, marketing and manufacturing programs associated with the
commercialization of the PowerBuoy system. Our future capital
requirements will depend on a number of factors, including:
|
|
|
| |
•
|
the cost of development efforts for our PowerBuoy systems;
|
| |
| |
•
|
the success of our commercial relationships with major customers;
|
| |
| |
•
|
the cost of manufacturing activities;
|
| |
| |
•
|
the cost of commercialization activities, including
demonstration projects, product marketing and sales;
|
| |
| |
•
|
our ability to establish and maintain additional commercial
relationships;
|
| |
| |
•
|
the implementation of our expansion plans, including the hiring
of new employees;
|
| |
| |
•
|
potential acquisitions of other products or
technologies; and
|
| |
| |
•
|
the costs involved in preparing, filing, prosecuting,
maintaining and enforcing patent claims and other patent-related
costs.
|
We believe that our current cash, cash equivalents and
investments will be sufficient to meet our anticipated cash
needs for working capital and capital expenditures at least
through fiscal 2012. If existing resources are insufficient to
satisfy our liquidity requirements or if we acquire or license
rights to additional product technologies, we may seek to sell
additional equity or debt securities or obtain a credit
facility. The sale of additional equity or convertible
securities could result in dilution to our stockholders. If
additional funds are raised through the issuance of debt
securities, these securities could have rights senior to those
associated with our common stock and could contain covenants
that would restrict our operations. Financing may not be
available in amounts or on terms acceptable to us. If we are
unable to obtain required financing, we may be required to
reduce the scope of our planned product development and
marketing efforts, which could harm our financial condition and
operating results.
53
Contractual
Obligations
Our major outstanding contractual obligations primarily relate
to our facilities leases. We have summarized in the table below
our fixed contractual cash obligations as of April 30, 2010.
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Payments Due by Period
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less than
|
|
|
One to
|
|
|
Three to
|
|
|
More than
|
|
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
One Year
|
|
|
Three Years
|
|
|
Five Years
|
|
|
Five Years
|
|
|
|
|
Long-term debt
|
|
$
|
345,000
|
|
|
$
|
95,000
|
|
|
$
|
100,000
|
|
|
$
|
150,000
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
Operating leases
|
|
|
842,000
|
|
|
|
331,000
|
|
|
|
511,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total
|
|
$
|
1,187,000
|
|
|
$
|
426,000
|
|
|
$
|
611,000
|
|
|
$
|
150,000
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Our long-term debt consists of an interest-free loan from the
New Jersey Economic Development Authority and a recoverable
grant award from the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities. Under
the interest-free loan, the amounts to be repaid each year are
determined as a percentage of revenues we receive in that year
from our customer contracts that meet criteria specified in the
loan agreement, with any remaining amount due on
January 15, 2012. Under the recoverable grant award, the
amount to be repaid is a fixed monthly amount of principal only,
repayable over a five-year period beginning in May 2012.
Off-Balance
Sheet Arrangements
Since inception, we have not engaged in any off-balance sheet
financing activities.
Critical
Accounting Policies and Estimates
The discussion and analysis of our financial condition and
results of operations set forth above are based on our
consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in
accordance with US generally accepted accounting principles. The
preparation of these consolidated financial statements requires
us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported
amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses. On an
ongoing basis, we evaluate our estimates and judgments,
including those described below. We base our estimates on
historical experience and on various other assumptions that we
believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. These
estimates and assumptions form the basis for making judgments
about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not
readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ
from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
We believe the following accounting policies require significant
judgment and estimates by us in the preparation of our
consolidated financial statements.
Revenue
recognition and unearned revenues
Generally, we recognize revenue using the
percentage-of-completion
method based on the ratio of costs incurred to total estimated
costs at completion. In certain circumstances, revenue under
contracts that have specified milestones or other performance
criteria may be recognized only when our customer acknowledges
that such criteria have been satisfied. In addition, recognition
of revenue (and the related costs) may be deferred for
fixed-price contracts until contract completion if we are unable
to reasonably estimate the total costs of the project prior to
completion. Because we have a small number of contracts,
revisions to the percentage of completion estimate or delays in
meeting performance criteria or in completing projects may have
a significant effect on our revenue for the periods involved.
Upon anticipating a loss on a contract, we recognize the full
amount of the anticipated loss in the current period. We had
loss reserves of $0.8 million as of April 30, 2010
related to one contract and $1.2 million as of
April 30, 2009 related to two contracts. In fiscal 2009, we
recognized a loss of $0.8 million on our contract for a
wave power station off the coast of Spain. The additional
anticipated loss in 2009 was recognized based on changes in
estimated costs associated with this contract, a reduction in
the expected contract value, and our decision in the fourth
quarter of fiscal 2008 to absorb an additional $1.9 million
in costs beyond our obligation for initial cost overruns and
certain other costs as set forth in the agreement. Approximately
$0.4 million of loss reserves related to
54
the Spanish contract were no longer necessary and, accordingly,
were reversed in fiscal 2010, contributing to the increase in
gross profit. Modifications to contract provisions, such as
those in connection with the Company’s Spain construction
agreement, as well as modifications in contract loss estimates,
may require changes in reserves established for anticipated
contract losses.
Unbilled receivables represent expenditures on contracts, plus
applicable profit margin, not yet billed. Unbilled receivables
are normally billed and collected within one year. Billings made
on contracts are recorded as a reduction in unbilled
receivables, and to the extent that those billings exceed costs
incurred plus applicable profit margin, they are recorded as
unearned revenues.
Stock-based
compensation
Costs resulting from all share-based payment transactions are
recognized in the consolidated financial statements at their
fair values. Compensation cost for the portion of the awards for
which the requisite service had not been rendered that were
outstanding as of May 1, 2006 is being recognized in the
consolidated statements of operations over the remaining service
period after such date based on the award’s original
estimated fair value.
Determining the appropriate fair-value model and calculating the
fair value of stock-based awards at the date of grant using any
valuation model requires judgment. We use the Black-Scholes
option pricing model to estimate the fair value of employee
stock options. Option pricing models, including the
Black-Scholes model, require the use of input assumptions,
including expected volatility, expected term and the expected
dividend rate. Because our stock has been publicly traded in the
United States only since April 2007, we do not have a
significant observable share-price volatility for the United
States capital markets; therefore, we estimate our expected
volatility based on that of what we consider to be similar
publicly-traded companies and expect to continue to do so until
such time as we have adequate historical data from our traded
share price in the United States. We did not estimate our
expected volatility based on the price of our common stock on
the AIM market of the London Stock Exchange on which our shares
have traded since October 2003, because we do not believe, based
on the historically low trading volume of our shares on that
market, that the volatility of our common stock on the AIM
market is an appropriate indicator of the expected volatility of
our common stock. Prior to fiscal 2007, we estimated the
expected term of our options using our best estimate of the
period of time from the grant date that we expect the options to
remain outstanding. Beginning in fiscal 2007, we estimate the
expected term using the average midpoint between the vesting
terms and the contractual terms of our options as permitted by
the Securities and Exchange Commission’s Staff Accounting
Bulletin No. 107, Share-Based Payment. If we
determine another method to estimate expected volatility or
expected term is more reasonable than our current methods, or if
another method for calculating these input assumptions is
prescribed by authoritative guidance, the fair value calculated
for future stock-based awards could change significantly. Higher
volatility and longer expected terms have a significant impact
on the value of stock-based compensation determined at the date
of grant. The expected dividend rate is not as significant to
the calculation of the fair value of our stock-based awards.
In addition, we are required to develop an estimate of the
number of stock-based awards that will be forfeited due to
employee turnover. Quarterly changes in the estimated forfeiture
rate can have a significant effect on reported stock-based
compensation. If the actual forfeiture rate is higher than the
estimated forfeiture rate, then an adjustment is made to
increase the estimated forfeiture rate, which will result in a
decrease to the expense recognized in the consolidated financial
statements during the quarter of the change. If the actual
forfeiture rate is lower than the estimated forfeiture rate,
then an adjustment is made to decrease the estimated forfeiture
rate, which will result in an increase to the expense recognized
in the consolidated financial statements. These adjustments
affect our cost of revenues, product development costs and
selling, general and administrative costs. To date, the effect
of forfeiture adjustments on our consolidated financial
statements has been insignificant. The expense we recognize in
future periods could differ significantly from the current
period
and/or our
forecasts due to adjustments in the assumed forfeiture rates.
The aggregate share-based compensation expense, related to all
share-based transactions related to employees was approximately
$1.1 million, $1.5 million and $1.8 million in
fiscal 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
55
Income
taxes
We account for income taxes under the asset and liability
method. Under this method, we determine deferred tax assets and
liabilities based upon the differences between the financial
statement carrying amounts and the tax bases of assets and
liabilities, as well as net operating loss and tax credit
carryforwards, using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in
which such items are expected to affect taxable income. The tax
consequences of most events recognized in the current
year’s financial statements are included in determining
income taxes currently payable. However, because tax laws and
financial accounting standards differ in their recognition and
measurement of assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, expenses,
gains and losses, differences arise between the amount of
taxable income and pretax financial income for a year and
between the tax bases of assets or liabilities and their
reported amounts in the financial statements. Because we assume
that the reported amounts of assets and liabilities will be
recovered and settled, respectively, a difference between the
tax basis of an asset or a liability and its reported amount in
the balance sheet will result in a taxable or a deductible
amount in some future years when the related liabilities are
settled or the reported amounts of the assets are recovered,
giving rise to a deferred tax asset or deferred tax liability.
We then assess the likelihood that our deferred tax assets will
be recovered from future taxable income and, to the extent we
believe that recovery is not likely, we establish a valuation
allowance. As discussed in Note 12 to our consolidated
financial statements included in this Annual Report, we have
established a valuation allowance for our net deferred tax
assets, which was $33.1 million as of April 30, 2010
and $25.5 million as of April 30, 2009.
Recent
Accounting Pronouncements
In December 2007, the Financial Accounting Standards Board
(“FASB”) issued guidance on business combinations,
which establishes the principles and requirements for how an
acquirer recognizes the assets acquired, the liabilities
assumed, and any noncontrolling interest in the acquirer at the
acquisition date, measured at their fair values as of that date,
with limited exceptions. This new guidance applies to business
combinations for which the acquisition date is after the
beginning of the first annual reporting period beginning after
December 15, 2008. Accordingly, the Company applied the new
guidance to business combinations occurring on or after
May 1, 2009. As of April 30, 2010, the Company has not
had any such transactions.
In December 2007, the FASB issued guidance which establishes
accounting and reporting standards for the noncontrolling
interest in a subsidiary and for the deconsolidation of a
subsidiary. It clarifies that a noncontrolling interest in a
subsidiary is an ownership interest in the consolidated entity
that should be recorded as a component of equity in the
consolidated financial statements. This statement also requires
that consolidated net income shall be adjusted to include the
net income attributed to the noncontrolling interest. It also
requires that net losses be attributed to the noncontrolling
interest even if they exceed the noncontrolling interest’s
equity balance. Disclosure on the face of the statement of
operations of the amounts of consolidated net income
attributable to the parent and to the noncontrolling interest is
required. The provisions of the new guidance are effective for
the Company for interim periods and the fiscal year beginning
May 1, 2009. Adoption of the new guidance did not have a
material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial
statements other than the presentation of a noncontrolling
interest in Ocean Power Technologies (Australasia) Pty Ltd. in
the Company’s consolidated financial statements. Net income
attributable to the noncontrolling interest in OPTA was $38,299
for the year ended April 30, 2010. For the years ended
April 30, 2009 and 2008, the Company recorded 100% of the
losses associated with OPTA. Had this current guidance been in
place for fiscal 2009 and 2008, the Company would have recorded
a net loss that was lower by $42,049 and $25,971, respectively.
In April 2009, the FASB issued additional guidance for fair
value measurement, which provides guidance on how to determine
the fair value of assets and liabilities when the volume and
level of activity for the asset/liability has significantly
decreased. This guidance also identifies circumstances that
indicate a transaction is not orderly. In addition, this
guidance requires disclosure in interim and annual periods of
the inputs and valuation techniques used to measure fair value
and a discussion of changes in valuation techniques. The new
guidance is effective for interim and annual reporting periods
ending after June 15, 2009. Adoption of the new guidance
did not have any impact on the Company’s financial position
or results of operations.
In April 2009, the FASB issued new guidance which changes
existing guidance for determining whether debt securities are
other-than-temporarily
impaired and replaces the existing requirement that the
entity’s management
56
assert it has both the intent and ability to hold an impaired
security until recovery with a requirement that management
assert: (a) it does not have the intent to sell the
security; and (b) it is more likely than not it will not
have to sell the security before recovery of its cost basis. The
new guidance requires entities to separate an
other-than-temporary
impairment of a debt security into two components when there are
credit related losses associated with the impaired debt security
for which management asserts that it does not have the intent to
sell the security, and it is more likely than not that it will
not be required to sell the security before recovery of its cost
basis. The amount of the
other-than-temporary
impairment related to a credit loss is recognized in earnings,
and the amount of the
other-than-temporary
impairment related to other factors is recorded in other
comprehensive income (loss). The new guidance is effective for
interim and annual reporting periods ended after June 15,
2009. Adoption of the new guidance did not have any impact on
the Company’s financial position or results of operations.
In April 2009, the FASB issued guidance revising disclosures
about fair values of financial instruments in interim and annual
financial statements. Prior to this guidance, disclosures about
fair values of financial instruments were only required to be
disclosed annually. The new guidance requires disclosures about
fair value of financial instruments in interim and annual
financial statements. Adoption of the new guidance did not
affect the Company’s financial position or results of
operations.
In May 2009 (amended February 2010), the FASB issued guidance
which establishes general standards of accounting for and
disclosure of events that occur after the balance sheet date but
before financial statements are issued or available to be
issued. It sets forth the period after the balance sheet date
during which management shall evaluate events or transactions
that may occur for potential recognition or disclosure in the
financial statements, the circumstances under which an entity
shall recognize events or transactions occurring after the
balance sheet date in its financial statements and the
disclosures that an entity shall make about events or
transactions that occurred after the balance sheet date. The new
guidance is effective for interim and annual periods ended after
June 15, 2009.
In June 2009, the FASB issued additional guidance that amended
the existing accounting and disclosure guidance for the
consolidation of variable interest entities. The amended
guidance requires enhanced disclosures intended to provide users
of financial statements with more transparent information about
an enterprise’s involvement in a variable interest entity.
This guidance became effective for the Company beginning on
January 1, 2010. Adoption of the new guidance did not have
any impact on the Company’s financial position or results
of operations.
|
|
|
ITEM 7A.
|
QUANTITATIVE
AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
|
We generally place our investments in money market funds,
Treasury notes, Treasury bills and certificates of deposit with
maturities of less than one year. We actively manage our
portfolio of cash equivalents and investments, but in order to
ensure liquidity, we will only invest in instruments with high
credit quality where a secondary market exists. We have not held
and do not hold any derivatives related to our interest rate
exposure. Due to the average maturity and conservative nature of
our investment portfolio, a change in interest rates would not
have a material effect on the value of the portfolio. We do not
have market risk exposure on our long-term debt because it
consists of an interest-free loan from the New Jersey Economic
Development Authority and a recoverable grant award from the New
Jersey Board of Public Utilities.
Management estimates that had the average yield on our cash,
cash equivalents, and investments decreased by 100 basis
points, our interest income for the year ended April 30,
2010 would have decreased by $0.7 million. This estimate
assumes that the decrease occurred on the first day of fiscal
2009 and reduced the yield of each investment by 100 basis
points. The impact on our future interest income of future
changes in investment yields will depend largely on the gross
amount of our cash, cash equivalents, and investments.
We transact business in various countries and have exposure to
fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates. Foreign
exchange gains and losses arise in the translation of
foreign-denominated assets and liabilities, which may result in
realized and unrealized gains or losses from exchange rate
fluctuations. Since we conduct our business in US dollars and
our functional currency is the US dollar, our main foreign
exchange exposure, if any, results from changes in the exchange
rate between the US dollar and the British pounds sterling, the
Euro and the Australian dollar.
We invest in certificates of deposit and maintain cash accounts
that are denominated in British pounds sterling, Euros and
Australian dollars. These foreign denominated certificates of
deposit and cash accounts had a balance of
57
$4.1 million as of April 30, 2010 and
$8.5 million as of April 30, 2009, compared to our
short-term and long-term investments and cash account balances
of $66.8 million as of April 30, 2010 and
$81.7 million as of April 30, 2009. These foreign
currency balances are translated at each month end to our
functional currency, the US dollar, and any resulting gain or
loss is recognized in our results of operations. If the foreign
currency exchange rates had fluctuated by 10% as of
April 30, 2010, the impact on our foreign exchange gains
and losses would have been $0.4 million.
In addition, a portion of our operations is conducted through
our subsidiaries in countries other than the United States,
specifically Ocean Power Technologies Ltd. in the United
Kingdom, the functional currency of which is the British pounds
sterling, and Ocean Power Technologies (Australasia) Pty Ltd. in
Australia, the functional currency of which is the Australian
dollar. Both of these subsidiaries have foreign exchange
exposure that results from changes in the exchange rate between
their functional currency and other foreign currencies in which
they conduct business. All of our international revenues for the
year ended April 30, 2010 were recorded in Euros, British
pounds sterling or Australian dollars.
We currently do not hedge exchange rate exposure. However, we
assess the anticipated foreign currency working capital
requirements and capital asset acquisitions of our foreign
operations and attempt to maintain a portion of our cash and
cash equivalents denominated in foreign currencies sufficient to
satisfy these anticipated requirements. We also assess the need
and cost to utilize financial instruments to hedge currency
exposures on an ongoing basis and may hedge against exchange
rate exposure in the future.
|
|
|
ITEM 8.
|
FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
|
The financial statements and supplementary data required by this
item are listed in Item 15 — “Exhibits and
Financial Statement Schedules” of this Annual Report.
|
|
|
ITEM 9.
|
CHANGES
IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
|
Not applicable.
|
|
|
ITEM 9A.
|
CONTROLS
AND PROCEDURES
|
An evaluation of the effectiveness of the design and operation
of our disclosure controls and procedures was performed as of
the end of the period covered by this report. This evaluation
was performed under the supervision and with the participation
of management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief
Financial Officer. Based upon that evaluation, our Chief
Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our
disclosure controls and procedures are effective in providing
reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed
by the Company in the reports that it files or submits under the
Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, is accumulated and
communicated to management, including our Chief Executive
Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow
timely decisions regarding required disclosure and are effective
in providing reasonable assurance that such information is
recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time
periods specified by the SEC’s rules and forms.
The annual report of management on the Company’s internal
control over financial reporting is provided under “Reports
of Management” on
page F-2.
The attestation report of KPMG LLP, the Company’s
independent registered public accounting firm, regarding the
Company’s internal control over financial reporting is
provided under “Report of Independent Registered Public
Accounting Firm” on
page F-3.
During the quarter ended April 30, 2010, there were no
changes in the Company’s internal control over financial
reporting that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to
materially affect, such internal control over financial
reporting.
|
|
|
ITEM 9B.
|
OTHER
INFORMATION
|
Not applicable.
58
PART III
|
|
|
ITEM 10.
|
DIRECTORS,
EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
|
Information with respect to this item is set forth in the Proxy
Statement for the 2010 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (the
“Proxy Statement”) under the headings “Election
of Directors,” “Executive Officers,”
“Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting
Compliance,” “Code of Ethics and Business
Conduct” and “Corporate Governance and Board
Matters,” and is incorporated herein by reference. The
Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC within 120 days
after the end of the fiscal year covered by this
Form 10-K.
|
|
|
ITEM 11.
|
EXECUTIVE
COMPENSATION
|
Information with respect to this item is set forth in the Proxy
Statement under the headings “Executive Compensation”
and “Director Compensation,” and is incorporated
herein by reference. The Proxy Statement will be filed with the
SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year
covered by this
Form 10-K.
|
|
|
ITEM 12.
|
SECURITY
OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND
RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
|
Information with respect to this item is set forth in the Proxy
Statement under the headings “Security Ownership of Certain
Beneficial Owners and Management” and “Executive
Compensation,” and is incorporated herein by reference. The
Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC within 120 days
after the end of the fiscal year covered by this
Form 10-K.
|
|
|
ITEM 13.
|
CERTAIN
RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR
INDEPENDENCE
|
Information with respect to this item is set forth in the Proxy
Statement under the headings “Certain Relationships and
Related Party Transactions” and “Corporate Governance
and Board Matters,” and is incorporated herein by
reference. The Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC within
120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this
Form 10-K.
|
|
|
ITEM 14.
|
PRINCIPAL
ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
|
Information with respect to this item is set forth in the Proxy
Statement under the heading “Ratification of the Selection
of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm,” and is
incorporated herein by reference. The Proxy Statement will be
filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the
fiscal year covered by this
Form 10-K.
PART IV
|
|
|
ITEM 15.
|
EXHIBITS AND
FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
|
(a) (1) Financial Statements: See Index to
Consolidated Financial Statements on
page F-1.
(3) Exhibits: See Exhibits Index on pages 61 to 62.
59
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the
Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused
this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned,
thereunto duly authorized.
OCEAN POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
Date: July 14, 2010
|
|
|
| |
By:
|
/s/ Charles
F. Dunleavy
|
Charles F. Dunleavy
Chief Executive Officer
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of
1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons
on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the
dates indicated:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Signature
|
|
Title
|
|
Date
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Charles
F. Dunleavy
Charles
F. Dunleavy
|
|
Director, Chief Executive Officer
(Principal Executive Officer)
|
|
July 14, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ George
W. Taylor
George
W. Taylor
|
|
Executive Chairman of the Board of Directors
|
|
July 14, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Brian
M. Posner
Brian
M. Posner
|
|
Chief Financial Officer,
Secretary and Treasurer
(Principal Financial Officer
and Principal Accounting Officer)
|
|
July 14, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Seymour
S. Preston III
Seymour
S. Preston III
|
|
Director
|
|
July 14, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Thomas
J. Meaney
Thomas
J. Meaney
|
|
Director
|
|
July 14, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Paul
F. Lozier
Paul
F. Lozier
|
|
Director
|
|
July 14, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ J.
Victor Chatigny
J.
Victor Chatigny
|
|
Director
|
|
July 14, 2010
|
60
Exhibits Index
| |
|
|
|
|
Exhibit
|
|
|
|
Number
|
|
Description
|
|
|
|
|
3
|
.1
|
|
Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the registrant
(incorporated by reference from Exhibit 3.1 to
Form 10-Q
filed September 14, 2007)
|
|
|
3
|
.2
|
|
Amended and Restated Bylaws of the registrant (incorporated by
reference from Exhibit 3.2 to
Form 10-Q
filed September 14, 2007)
|
|
|
4
|
.1
|
|
Specimen certificate of common stock (incorporated by reference
from Exhibit 4.1 to
Form S-1/A
filed March 19, 2007)
|
|
|
10
|
.1+
|
|
Engineering, Procurement and Construction of a Wave Energy Power
Plant at “Punta del Pescador” (Santoña, Spain),
dated July 27, 2006, between Iberdrola Energias Marinas de
Cantabria, S.A. and Ocean Power Technologies Limited
(incorporated by reference from Exhibit 10.1 to
Form S-1
filed November 13, 2006)
|
|
|
10
|
.2+
|
|
Contract Number N00014-05-C-0384, dated September 20, 2005,
between the Office of Naval Research, U.S. Navy and Ocean Power
Technologies, Inc., as amended by the Amendment of
Solicitation/Modification of Contract dated March 22, 2007
(incorporated by reference from Exhibit 10.2 to
Form S-1
filed November 13, 2006)
|
|
|
10
|
.3+
|
|
Contract Number N00014-02-C-0053, dated February 8, 2002,
between the Office of Naval Research, U.S. Navy and Ocean Power
Technologies Inc., as modified (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 10.3 to
Form S-1
filed November 13, 2006)
|
|
|
10
|
.4
|
|
Option Agreement for Purchase of Emissions Credits, dated
November 24, 2000 between Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.
and its affiliates and Woodside Sustainable Energy Solutions
Pty. Ltd. (incorporated by reference from Exhibit 10.4 to
Form S-1
filed November 13, 2006)
|
|
|
10
|
.5
|
|
1994 Stock Option Plan (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 10.5 to
Form S-1
filed November 13, 2006)*
|
|
|
10
|
.6
|
|
Incentive Stock Option Plan (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 10.6 to
Form S-1
filed November 13, 2006)*
|
|
|
10
|
.7
|
|
2001 Stock Plan (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 10.7 to
Form S-1
filed November 13, 2006)*
|
|
|
10
|
.8
|
|
2006 Stock Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 10.8 to
Form S-1/A
filed March 19, 2007)*
|
|
|
10
|
.9
|
|
Amended and Restated Voting and Right of First Refusal
Agreement, dated April 18, 2005, between Ocean Power
Technologies, Inc., George W. Taylor and JoAnne E. Burns
(incorporated by reference from Exhibit 10.9 to
Form S-1
filed November 13, 2006)
|
|
|
10
|
.10
|
|
Agreement to Refinance, dated November 14, 1993 between
Joseph R. Burns, Michael Y. Epstein, George W. Taylor and Ocean
Power Technologies, Inc. (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 10.10 to
Form S-1
filed November 13, 2006)
|
|
|
10
|
.11
|
|
Amended and Restated Employment Agreement, dated April 8,
2009, between Charles F. Dunleavy and Ocean Power Technologies,
Inc. (incorporated by reference from Exhibit 10.2 to
Form 8-K
filed April 13, 2009)*
|
|
|
10
|
.12
|
|
Amended and Restated Employment Agreement, dated April 8,
2009, between George W. Taylor and Ocean Power Technologies,
Inc. (incorporated by reference from Exhibit 10.1 to
Form 8-K
filed April 13, 2009)*
|
|
|
10
|
.13
|
|
Consultant Agreement, dated August 1, 1999, between Thomas
J. Meaney and Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. (incorporated by
reference from Exhibit 10.13 to
Form S-1
filed November 13, 2006)
|
|
|
10
|
.14
|
|
Employment Agreement, dated September 9, 2004, between Mark
R. Draper and Ocean Power Technologies Ltd. (incorporated by
reference from Exhibit 10.14 to
Form S-1
filed November 13, 2006)*
|
|
|
10
|
.15
|
|
Lease Agreement, dated August 30, 2005 between Ocean Power
Technologies, Inc. and Reed Road Industrial Park LLC #1, as
amended on January 27, 2006 (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 10.16 to
Form S-1
filed November 13, 2006)
|
|
|
10
|
.16
|
|
Lease, dated January 15, 2007, between University of
Warwick Science Park Innovation Centre Limited and Ocean Power
Technologies Ltd. (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 10.17 to
Form S-1/A
filed March 19, 2007)
|
61
| |
|
|
|
|
Exhibit
|
|
|
|
Number
|
|
Description
|
|
|
|
|
10
|
.17
|
|
Agreement for Renewable Energy Economic Development Grants,
dated November 3, 2003, between State of New Jersey Board
of Public Utilities and Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.
(incorporated by reference from Exhibit 10.18 to
Form S-1/A
filed March 19, 2007)
|
|
|
10
|
.18
|
|
Contract Number DM259735, dated September 17, 2005 between
Lockheed Martin Corporation Maritime Systems and Sensors (MS2)
and Ocean Power Technologies, Inc., as modified (incorporated by
reference from Exhibit 10.20 to
Form S-1/A
filed March 19, 2007)
|
|
|
10
|
.19
|
|
Marketing Cooperation Agreement, dated September 9, 2006,
between Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. and Lockheed Martin
Corporation through its Maritime Systems and Sensors business
unit (incorporated by reference from Exhibit 10.21 to
Form S-1/A
filed April 10, 2007)
|
|
|
10
|
.20
|
|
Contract Number N00014-07-C-0617, dated May 24, 2007,
between the Office of Naval Research, U.S. Navy and Ocean Power
Technologies, Inc. (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 99.1 to
Form 8-K
filed June 8, 2007)
|
|
|
10
|
.21
|
|
Modification of Contract, dated September 13, 2007,
modifying Contract Number N00014-02-C-0053, between the Office
of Naval Research, U.S. Navy and Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.,
as modified (incorporated by reference from Exhibit 10.1 to
Form 10-Q
filed December 17, 2007)
|
|
|
10
|
.22
|
|
Modification of Contract, dated September 26, 2007,
modifying Contract Number N00014-05-C-0384, between the Office
of Naval Research, U.S. Navy and Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.,
as modified. (incorporated by reference from Exhibit 10.2
to
Form 10-Q
filed December 17, 2007
|
|
|
10
|
.23
|
|
Addendum to the Agreement for the Engineering, Procurement and
Construction of a Wave Energy Power Plant at “Punta del
Pescador” (Santoña, Spain), between Iberdrola Energias
Marinas de Cantabria, S.A. and Ocean Power Technologies Limited,
dated February 18, 2008 (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 10.27 to
Form 10-K
filed July 14, 2008)
|
|
|
10
|
.24
|
|
Lease, dated February 1, 2008, between KUC Properties
Limited and Ocean Power Technologies Ltd. (incorporated by
reference from Exhibit 10.28 to
Form 10-K
filed July 14, 2008)
|
|
|
10
|
.25
|
|
Financial Assistance Award agreement between Ocean Power
Technologies, Inc. and US Department of Energy date
September 23, 2008 (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 10.1 to
Form 10-Q
filed December 10, 2008)
|
|
|
10
|
.26
|
|
Modification of Financial Assistance Award agreement between
Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. and US Department of Energy dated
October 16, 2008 (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 10.2 to
Form 10-Q
filed December 10, 2008)
|
|
|
10
|
.27
|
|
Agreement between Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. and the Office
of Naval Research of the US Navy dated October 31, 2008
(incorporated by reference from Exhibit 10.3 to
Form 10-Q
filed December 10, 2008)
|
|
|
10
|
.28
|
|
Employment Agreement, dated May 19, 2010, between Brian M.
Posner and Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.
|
|
|
21
|
.1
|
|
Subsidiaries of the registrant
|
|
|
23
|
.1
|
|
Consent of KPMG LLP
|
|
|
31
|
.1
|
|
Certification of Chief Executive Officer
|
|
|
31
|
.2
|
|
Certification of Chief Financial Officer
|
|
|
32
|
.1
|
|
Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to
Section 906 of Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
|
|
|
32
|
.2
|
|
Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to
Section 906 of Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
Confidential treatment requested as to certain portions, which
portions have been omitted and filed separately with the SEC. |
| |
|
* |
|
Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement |
62
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Index to
Consolidated Financial Statements
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Page
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F-2
|
|
|
|
|
|
F-3
|
|
|
|
|
|
F-5
|
|
|
|
|
|
F-6
|
|
|
|
|
|
F-7
|
|
|
|
|
|
F-8
|
|
|
|
|
|
F-9
|
|
F-1
Reports
of Management
Management’s
Report on Consolidated Financial Statements
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been
prepared by the Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.’s (the
Company) management in conformity with generally accepted
accounting principles to reflect the financial position of the
Company and its operating results. The financial information
appearing throughout this Annual Report is consistent with the
consolidated financial statements. Management is responsible for
the information and representations in such consolidated
financial statements, including the estimates and judgments
required for their preparation. The consolidated financial
statements have been audited by KPMG LLP, an independent
registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report,
which appears herein.
The Audit Committee of the Board of Directors, which is composed
entirely of directors who are not officers or employees of the
Company, meets regularly with management and the independent
registered public accounting firm. The independent registered
public accounting firm has had, and continues to have, direct
access to the Audit Committee without the presence of other
management personnel, and have been directed to discuss the
results of their audit work and any matters they believe should
be brought to the Committee’s attention. The independent
registered public accounting firm reports directly to the Audit
Committee.
Management’s
Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The Company’s management is responsible for establishing
and maintaining adequate internal control over financial
reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is a
process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the
reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of
financial statements for external purposes in accordance with
generally accepted accounting principles in the United States.
The Company’s internal control over financial reporting
includes those policies and procedures that:
|
|
|
| |
•
|
pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable
detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and
dispositions of the assets of the Company;
|
| |
| |
•
|
provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as
necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in
accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and
that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made
only in accordance with authorizations of management and
directors of the Company; and
|
| |
| |
•
|
provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely
detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the
Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the
financial statements.
|
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over
financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements.
Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future
periods are subject to the risk that controls may become
inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree
of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
The Company’s management assessed the effectiveness of the
Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of
April 30, 2010. In making this assessment, management used
the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring
Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal
Control — Integrated Framework. Based on this
assessment using those criteria, management concluded that the
Company’s internal control over financial reporting was
effective as of April 30, 2010.
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over
financial reporting as of April 30, 2010 has been audited
by KPMG LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm,
as stated in their report, which appears herein.
Charles F. Dunleavy
Chief Executive Officer
Brian M. Posner
Chief Financial Officer
F-2
Report of
Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.:
We have audited Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.’s internal
control over financial reporting as of April 30, 2010,
based on criteria established in Internal Control —
Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring
Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Ocean Power
Technologies, Inc.’s management is responsible for
maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting
and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control
over financial reporting, included in the accompanying
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial
Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the
Company’s internal control over financial reporting based
on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the
Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those
standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain
reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control
over financial reporting was maintained in all material
respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of
internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk
that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the
design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on
the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other
procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We
believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our
opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a
process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the
reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of
financial statements for external purposes in accordance with
generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s
internal control over financial reporting includes those
policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance
of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly
reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the
company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions
are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial
statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting
principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company
are being made only in accordance with authorizations of
management and directors of the company; and (3) provide
reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of
unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the
company’s assets that could have a material effect on the
financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over
financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements.
Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future
periods are subject to the risk that controls may become
inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree
of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. maintained, in
all material respects, effective internal control over financial
reporting as of April 30, 2010, based on criteria
established in Internal Control — Integrated
Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring
Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the
Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the
consolidated balance sheets of Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.
and subsidiaries as of April 30, 2010 and 2009, and the
related consolidated statements of operations,
stockholders’ equity and comprehensive loss, and cash flows
for each of the years in the three-year period ended
April 30, 2010, and our report dated July 14, 2010
expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial
statements.
/s/ KPMG LLP
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
July 14, 2010
F-3
Report of
Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of
Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. and subsidiaries as of
April 30, 2010 and 2009, and the related consolidated
statements of operations, stockholders’ equity and
comprehensive loss, and cash flows for each of the years in the
three-year period ended April 30, 2010. These consolidated
financial statements are the responsibility of the
Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an
opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our
audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the
Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those
standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain
reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are
free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a
test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in
the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the
accounting principles used and significant estimates made by
management, as well as evaluating the overall financial
statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a
reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred
to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial
position of Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. and subsidiaries as
of April 30, 2010 and 2009, and the results of their
operations and their cash flows for each of the years in the
three-year period ended April 30, 2010, in conformity with
U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the
Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), Ocean
Power Technologies, Inc.’s internal control over financial
reporting as of April 30, 2010, based on criteria
established in Internal Control — Integrated
Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring
Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO), and our report
dated July 14, 2010 expressed an unqualified opinion on the
effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over
financial reporting.
/s/ KPMG LLP
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
July 14, 2010
F-4
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
April 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
|
|
ASSETS
|
|
Current assets:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents
|
|
$
|
4,236,597
|
|
|
|
12,267,830
|
|
|
Marketable securities
|
|
|
32,536,001
|
|
|
|
40,849,736
|
|
|
Accounts receivable
|
|
|
1,474,600
|
|
|
|
985,149
|
|
|
Unbilled receivables
|
|
|
448,686
|
|
|
|
988,418
|
|
|
Other current assets
|
|
|
1,005,885
|
|
|
|
1,082,696
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total current assets
|
|
|
39,701,769
|
|
|
|
56,173,829
|
|
|
Property and equipment, net
|
|
|
710,563
|
|
|
|
897,718
|
|
|
Patents, net
|
|
|
1,036,881
|
|
|
|
909,727
|
|
|
Restricted cash
|
|
|
1,205,288
|
|
|
|
951,552
|
|
|
Marketable securities
|
|
|
28,865,046
|
|
|
|
28,619,528
|
|
|
Other noncurrent assets
|
|
|
1,458,646
|
|
|
|
1,241,552
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total assets
|
|
$
|
72,978,193
|
|
|
|
88,793,906
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
|
Current liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable
|
|
$
|
1,843,378
|
|
|
|
908,837
|
|
|
Accrued expenses
|
|
|
4,092,113
|
|
|
|
3,760,039
|
|
|
Unearned revenues
|
|
|
1,101,541
|
|
|
|
281,570
|
|
|
Current portion of long-term debt
|
|
|
95,386
|
|
|
|
93,398
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total current liabilities
|
|
|
7,132,418
|
|
|
|
5,043,844
|
|
|
Long-term debt
|
|
|
250,000
|
|
|
|
345,386
|
|
|
Deferred rent
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
21,649
|
|
|
Deferred credits
|
|
|
600,000
|
|
|
|
600,000
|
|
|
Other noncurrent liabilities
|
|
|
140,685
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities
|
|
|
8,123,103
|
|
|
|
6,010,879
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commitments and contingencies (note 13)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. Stockholders’ equity:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred stock, $0.001 par value; authorized
5,000,000 shares, none issued or outstanding
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Common stock, $0.001 par value; authorized
105,000,000 shares, issued and outstanding 10,390,563 and
10,210,354 shares, respectively
|
|
|
10,391
|
|
|
|
10,210
|
|
|
Treasury stock, 1,072 and 0 shares at cost, respectively
|
|
|
(6,443
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
|
|
155,726,672
|
|
|
|
154,568,931
|
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(90,413,098
|
)
|
|
|
(71,242,791
|
)
|
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss
|
|
|
(503,322
|
)
|
|
|
(553,323
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. stockholders’ equity
|
|
|
64,814,200
|
|
|
|
82,783,027
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Noncontrolling interest in Ocean Power Technologies
(Australasia) Pty Ltd.
|
|
|
40,890
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total equity
|
|
|
64,855,090
|
|
|
|
82,783,027
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity
|
|
$
|
72,978,193
|
|
|
|
88,793,906
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-5
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended April 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
2008
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
5,101,311
|
|
|
|
4,049,445
|
|
|
|
4,772,017
|
|
|
Cost of revenues
|
|
|
4,298,955
|
|
|
|
4,840,403
|
|
|
|
7,960,042
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross profit (loss)
|
|
|
802,356
|
|
|
|
(790,958
|
)
|
|
|
(3,188,025
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating expenses:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Product development costs
|
|
|
13,001,550
|
|
|
|
8,372,244
|
|
|
|
8,255,123
|
|
|
Selling, general and administrative costs
|
|
|
9,063,482
|
|
|
|
9,529,071
|
|
|
|
7,732,577
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total operating expenses
|
|
|
22,065,032
|
|
|
|
17,901,315
|
|
|
|
15,987,700
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating loss
|
|
|
(21,262,676
|
)
|
|
|
(18,692,273
|
)
|
|
|
(19,175,725
|
)
|
|
Interest income, net
|
|
|
1,032,484
|
|
|
|
1,672,350
|
|
|
|
4,434,844
|
|
|
Other income
|
|
|
557,540
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Foreign exchange gain (loss)
|
|
|
540,644
|
|
|
|
(1,295,227
|
)
|
|
|
84,158
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
(19,132,008
|
)
|
|
|
(18,315,150
|
)
|
|
|
(14,656,723
|
)
|
|
Less: Net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest in
Ocean Power Technologies (Australasia) Pty Ltd
|
|
|
(38,299
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss attributable to Ocean Power Technologies, Inc
|
|
$
|
(19,170,307
|
)
|
|
|
(18,315,150
|
)
|
|
|
(14,656,723
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic and diluted net loss per share
|
|
$
|
(1.88
|
)
|
|
|
(1.79
|
)
|
|
|
(1.44
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average shares used to compute basic and diluted net
loss per share
|
|
|
10,217,003
|
|
|
|
10,210,354
|
|
|
|
10,200,729
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-6
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Ocean
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated
|
|
|
Power
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other
|
|
|
Technologies, Inc,
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common Shares
|
|
|
Treasury Shares
|
|
|
Paid-In
|
|
|
Accumulated
|
|
|
Comprehensive
|
|
|
Stockholders
|
|
|
Noncontrolling
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
Capital
|
|
|
Deficit
|
|
|
Loss
|
|
|
Equity
|
|
|
Interest
|
|
|
Equity
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, May 1, 2007
|
|
|
10,186,254
|
|
|
$
|
10,186
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
150,842,671
|
|
|
|
(38,270,918
|
)
|
|
|
(40,730
|
)
|
|
|
112,541,209
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
112,541,209
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(14,656,723
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(14,656,723
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(14,656,723
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(495
|
)
|
|
|
(495
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(495
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total comprehensive loss
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(14,657,218
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(14,657,218
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation related to stock option grants issued to employees
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
1,788,841
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
1,788,841
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
1,788,841
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation related to stock option grants issued for services
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
137,982
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
137,982
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
137,982
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from exercise of stock options
|
|
|
24,100
|
|
|
|
24
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
287,771
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
287,795
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
287,795
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, April 30, 2008
|
|
|
10,210,354
|
|
|
|
10,210
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
153,057,265
|
|
|
|
(52,927,641
|
)
|
|
|
(41,225
|
)
|
|
|
100,098,609
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
100,098,609
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(18,315,150
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(18,315,150
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(18,315,150
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(512,098
|
)
|
|
|
(512,098
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(512,098
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total comprehensive loss
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(18,827,248
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(18,827,248
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation related to stock option grants and restricted stock
issued to employees
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
1,475,215
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
1,475,215
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
1,475,215
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation related to stock option grants and restricted stock
issued for services
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
36,451
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
36,451
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
36,451
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, April 30, 2009
|
|
|
10,210,354
|
|
|
|
10,210
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
154,568,931
|
|
|
|
(71,242,791
|
)
|
|
|
(553,323
|
)
|
|
|
82,783,027
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
82,783,027
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss attributable to Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(19,170,307
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(19,170,307
|
)
|
|
|
38,299
|
|
|
|
(19,132,008
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
50,001
|
|
|
|
50,001
|
|
|
|
2,591
|
|
|
|
52,592
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total comprehensive loss
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(19,120,306
|
)
|
|
|
40,890
|
|
|
|
(19,079,416
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation related to stock option grants and restricted stock
issued to employees
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
1,072,935
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
1,072,935
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
1,072,935
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation related to stock option grants and restricted stock
issued to non-employees
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
45,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
45,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
45,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issuance of vested and unvested restricted stock to employees
|
|
|
168,000
|
|
|
|
168
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(168
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issuance of vested and unvested restricted stock to non-employees
|
|
|
12,209
|
|
|
|
13
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
39,974
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
39,987
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
39,987
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acquisition of treasury stock
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(1,072
|
)
|
|
|
(6,443
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(6,443
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(6,443
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, April 30, 2010
|
|
|
10,390,563
|
|
|
$
|
10,391
|
|
|
|
(1,072
|
)
|
|
|
(6,443
|
)
|
|
|
155,726,672
|
|
|
|
(90,413,098
|
)
|
|
|
(503,322
|
)
|
|
|
64,814,200
|
|
|
|
40,890
|
|
|
|
64,855,090
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-7
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended April 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
2008
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from operating activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
$
|
(19,132,008
|
)
|
|
|
(18,315,150
|
)
|
|
|
(14,656,723
|
)
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating
activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign exchange (gain) loss
|
|
|
(540,644
|
)
|
|
|
1,295,227
|
|
|
|
(84,158
|
)
|
|
Depreciation and amortization
|
|
|
365,755
|
|
|
|
299,405
|
|
|
|
241,721
|
|
|
Loss on disposal of equipment
|
|
|
113,087
|
|
|
|
268,976
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Treasury note premium amortization
|
|
|
146,834
|
|
|
|
288,331
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Compensation expense related to stock option grants and
restricted stock
|
|
|
1,117,935
|
|
|
|
1,511,666
|
|
|
|
1,926,823
|
|
|
Deferred rent
|
|
|
(21,649
|
)
|
|
|
5,412
|
|
|
|
5,412
|
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable
|
|
|
(474,407
|
)
|
|
|
472,422
|
|
|
|
(878,643
|
)
|
|
Unbilled receivables
|
|
|
603,765
|
|
|
|
(589,970
|
)
|
|
|
(270,136
|
)
|
|
Other current assets
|
|
|
77,278
|
|
|
|
140,418
|
|
|
|
(918,380
|
)
|
|
Other noncurrent assets
|
|
|
(202,731
|
)
|
|
|
(857,060
|
)
|
|
|
(76,571
|
)
|
|
Accounts payable
|
|
|
953,815
|
|
|
|
(354,740
|
)
|
|
|
(122,323
|
)
|
|
Accrued expenses
|
|
|
246,816
|
|
|
|
(454,682
|
)
|
|
|
496,838
|
|
|
Unearned revenues
|
|
|
827,786
|
|
|
|
(418,182
|
)
|
|
|
699,752
|
|
|
Other current liabilities
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(26,106
|
)
|
|
Other noncurrent liabilities
|
|
|
147,684
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash used in operating activities
|
|
|
(15,770,684
|
)
|
|
|
(16,707,927
|
)
|
|
|
(13,662,494
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from investing activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchases of marketable securities
|
|
|
(33,884,604
|
)
|
|
|
(124,675,859
|
)
|
|
|
(21,201,607
|
)
|
|
Maturities of marketable securities
|
|
|
41,838,886
|
|
|
|
67,151,702
|
|
|
|
17,358,316
|
|
|
Restricted cash
|
|
|
(252,080
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Purchases of equipment
|
|
|
(239,449
|
)
|
|
|
(811,493
|
)
|
|
|
(419,835
|
)
|
|
Payments of patent costs
|
|
|
(153,667
|
)
|
|
|
(243,941
|
)
|
|
|
(112,705
|
)
|
|
Investments in joint ventures and other noncurrent assets
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(27,714
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities
|
|
|
7,309,086
|
|
|
|
(58,579,591
|
)
|
|
|
(4,403,545
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from financing activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from long-term debt
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
250,000
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Repayment of long-term debt
|
|
|
(93,398
|
)
|
|
|
(42,801
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Sale of common stock, net of issuance costs
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(870,116
|
)
|
|
Proceeds from exercise of stock options
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
287,795
|
|
|
Acquisition of treasury stock
|
|
|
(6,443
|
)
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities
|
|
|
(99,841
|
)
|
|
|
207,199
|
|
|
|
(582,321
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents
|
|
|
530,206
|
|
|
|
(1,488,155
|
)
|
|
|
(20,809
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents
|
|
|
(8,031,233
|
)
|
|
|
(76,568,474
|
)
|
|
|
(18,669,169
|
)
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period
|
|
|
12,267,830
|
|
|
|
88,836,304
|
|
|
|
107,505,473
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents, end of period
|
|
$
|
4,236,597
|
|
|
|
12,267,830
|
|
|
|
88,836,304
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental disclosure of noncash investing and financing
activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Capitalized patent costs financed through accounts payable and
accrued expenses
|
|
$
|
66,513
|
|
|
|
23,255
|
|
|
|
35,048
|
|
|
Capitalized purchases of equipment financed through accounts
payable
|
|
|
6,360
|
|
|
|
96,304
|
|
|
|
36,964
|
|
|
Capitalized investment in joint ventures financed through
accrued expenses
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
175,803
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-8
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. (the Company) was incorporated on
April 19, 1984 in the State of New Jersey, commenced active
operations in 1994 and re-incorporated in the State of Delaware
in April 2007. The Company develops and is commercializing
proprietary systems that generate electricity by harnessing the
renewable energy of ocean waves. The Company markets and sells
its products in the United States and internationally.
During the second quarter of fiscal 2010, the Company adopted
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) Accounting
Standards Codification (ASC or Codification) and the Hierarchy
of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), which
establishes the Codification as the sole source for
authoritative US GAAP and has superseded all accounting
standards in US GAAP, aside from those issued by the Securities
and Exchange Commission (SEC). The adoption of the Codification
did not have an impact on the Company’s results of
operations, cash flows or financial position. As a result of the
adoption of the Accounting Standards Codification (ASC), the
Company’s notes to the consolidated financial statements
will no longer make reference to Statement of Financial
Accounting Standards (SFAS) or other US GAAP pronouncements.
|
|
|
(2)
|
Summary
of Significant Accounting Policies
|
|
|
|
(a)
|
Consolidation
and Cost Method Investment
|
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the
accounts of the Company and its majority-owned subsidiaries. All
significant intercompany balances and transactions have been
eliminated in consolidation. Participation of stockholders other
than the Company in the net assets and in the earnings or losses
of a consolidated subsidiary is reflected in the caption
“Noncontrolling interest” in the Company’s
Consolidated Balance Sheets and Statements of Operations.
Noncontrolling interest adjusts the Company’s consolidated
results of operations to reflect only the Company’s share
of the earnings or losses of the consolidated subsidiary. As of
April 30, 2010, there was one noncontrolling interest,
consisting of 11.8% of the Company’s Australian subsidiary.
In addition, the Company evaluates its relationships with other
entities to identify whether they are variable interest
entities, and to assess whether it is the primary beneficiary of
such entities. If the determination is made that the Company is
the primary beneficiary, then that entity is included in the
consolidated financial statements. As of April 30, 2010,
there are no such entities.
The Company has a 10% investment in Iberdrola Energias
Renovables II, S.A. (Iberdrola Energias). Revenues to Iberdrola
Energias for the years ended April 30, 2010, 2009 and 2008
were $178,215, $601,736, and $1,431,983, respectively.
Additionally, aggregate accounts receivable and unbilled
receivables from Iberdrola Energias were $556,491 and $288,203
as of April 30, 2010 and 2009, respectively. See
Note 13(c).
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements
requires management of the Company to make a number of estimates
and assumptions relating to the reported amounts of assets and
liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and
liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements
and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the
period. Significant items subject to such estimates and
assumptions include the recoverability of the carrying amount of
property and equipment and patents; valuation allowances for
receivables and deferred income tax assets; and percentage of
completion of customer contracts for purposes of revenue
recognition. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
The current economic environment has increased the degree of
uncertainty inherent in those estimates and assumptions.
The Company primarily recognizes revenue under the
percentage-of-completion
method. The percentage of completion is determined by relating
the costs incurred to date to the estimated total costs. The
cumulative effects
F-9
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
resulting from revisions of estimated total contract costs and
revenues are recorded in the period in which the facts requiring
revision become known. Upon anticipating a loss on a contract,
the Company recognizes the full amount of the anticipated loss
in the current period. During the years ended April 30,
2009 and 2008, the Company recorded provisions of approximately
$810,000 and $2,370,000, respectively, related to anticipated
losses on contracts. During the year ended April 30, 2010,
the Company reversed approximately $400,000 of the loss reserves
established in fiscal year 2009 as these loss reserves were no
longer necessary as of April 30, 2010. During the years
ended April 30, 2009 and 2008 the Company recorded
reductions in the contract loss reserves of $1,728,000 and
$2,080,000, respectively. Reserves related to loss contracts in
the amounts of approximately $785,000 and $1,152,000 are
included in accrued expenses in the accompanying consolidated
balance sheets as of April 30, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
Modifications to contract provisions, such as those currently
being discussed in connection with the Company’s Spain
construction agreement (see Note 13), as well as
modifications in contract loss estimates, may require changes in
reserves established for anticipated contract losses.
Unbilled receivables represent expenditures on contracts, plus
applicable profit margin, not yet billed. Unbilled receivables
are normally billed and collected within one year. Billings made
on contracts are recorded as a reduction of unbilled
receivables, and to the extent that such billings exceed costs
incurred plus applicable profit margin, they are recorded as
unearned revenues.
|
|
|
(d)
|
Cash
and Cash Equivalents
|
Cash equivalents consist of investments in short-term financial
instruments with initial maturities of three months or less from
the date of purchase. Cash and cash equivalents include
$1,590,000 and $4,337,000 of certificates of deposit with
initial maturities of less than three months at April 30,
2010 and 2009, respectively, and $192,000 and $6,530,000
invested in a money market fund as of April 30, 2010 and
2009, respectively.
|
|
|
(e)
|
Marketable
Securities
|
Marketable securities with original maturities longer than three
months but that mature in less than one year from the balance
sheet date are classified as current assets. Marketable
securities that mature more than one year from the balance sheet
date are classified as noncurrent assets. Marketable securities
that the Company has the intent and ability to hold to maturity
are classified as investments
held-to-maturity
and are reported at amortized cost. The difference between the
acquisition cost and face values of
held-to-maturity
investments is amortized over the remaining term of the
investments and added to or subtracted from the acquisition cost
and interest income. As of April 30, 2010 and 2009, all of
the Company’s investments were classified as
held-to-maturity.
|
|
|
(f)
|
Restricted
Cash and Credit Facility
|
The Company had $1,205,288 and $951,552 of restricted cash as of
April 30, 2010 and April 30, 2009, respectively. The
cash is restricted under the terms of two security agreements.
One agreement is between Ocean Power Technologies, Inc. and
Barclays Bank. Under this agreement, the cash is on deposit at
Barclays Bank and serves as security for letters of credit that
are expected to be issued by Barclays Bank on behalf of Ocean
Power Technologies Ltd., one of the Company’s subsidiaries,
under a €800,000 credit facility established by Barclays
Bank for Ocean Power Technologies Ltd. The credit facility is
for the issuance of letters of credit and bank guarantees, and
carries a fee of 1% per annum of the amount of any such
obligations issued by Barclays Bank. The credit facility does
not have an expiration date, but is cancelable at the discretion
of the bank. As of April 30, 2010, approximately
€720,000 is included in restricted cash.
The other agreement is between Ocean Power Technologies, Inc.
and the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities (NJBPU). During the
year ended April 30, 2009, the Company received a
recoverable grant award from the NJBPU. Under this agreement,
the Company was required to assign to the NJBPU a certificate of
deposit in an amount equal
F-10
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
to the outstanding grant balance. In July 2009, the Company
assigned a certificate of deposit in the amount of $250,000 to
the NJBPU, which is outstanding as of April 30, 2010.
|
|
|
(g)
|
Property
and Equipment
|
Property and equipment is stated at cost, less accumulated
depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization is
calculated using the straight-line method over the estimated
useful lives (three to seven years) of the assets. Leasehold
improvements are amortized using the straight-line method over
the shorter of the estimated useful life of the asset or the
remaining lease term. Expenses for maintenance and repairs are
charged to operations as incurred. Depreciation was $324,596,
$259,696 and $213,977 for the years ended April 30, 2010,
2009 and 2008, respectively.
Other income consists of transactions that the Company considers
to be outside the normal scope of its operations and operating
activities. The Company recognized other income of $557,540
during the year ended April 30, 2010, primarily in
connection with the settlement of a claim that it had against a
supplier that provided engineering services to the Company.
|
|
|
(i)
|
Foreign
Exchange Gains and Losses
|
The Company has invested in certain certificates of deposit and
has maintained cash accounts that are denominated in British
pounds sterling, Euros and Australian dollars. Such certificates
of deposit and cash accounts had a balance of approximately
$4,131,000 and $8,541,000 as of April 30, 2010 and 2009,
respectively. These amounts are included in cash, cash
equivalents, restricted cash and marketable securities on the
accompanying balance sheets. Such positions may result in
realized and unrealized foreign exchange gains or losses from
exchange rate fluctuations, which are included in foreign
exchange gain (loss) in the accompanying consolidated statements
of operations. Foreign exchange gain (loss) was $540,644,
($1,295,227) and $84,158 for the years ended April 30,
2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
External costs related to the filing of patents, including legal
and filing fees, are capitalized. Amortization is calculated
using the straight-line method over the life of the patents
(17 years). Expenses for the development of technology are
charged to operations as incurred. Amortization expense was
$41,064, $39,613 and $27,744 for the years ended April 30,
2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively. Amortization expense for the
next five fiscal years related to amounts capitalized for
patents as of April 30, 2010 is estimated to be
approximately $60,000 per year.
Long-lived assets, such as property and equipment and purchased
intangible assets subject to amortization, are reviewed for
impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate
that the carrying amount of the asset may not be recoverable.
Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a
comparison of the carrying amount of the asset to estimated
undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the
asset. If the carrying amount of the asset exceeds its estimated
future cash flows, then an impairment charge is recognized by
the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the
fair value of the asset. The Company reviewed its long-lived
assets for impairment and determined there was no impairment for
the years ended April 30, 2010, and 2009.
F-11
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
|
|
|
(l)
|
Concentration
of Credit Risk
|
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to
concentration of credit risk consist principally of cash
balances, bank certificates of deposit and trade receivables.
The Company invests its excess cash in highly liquid investments
(principally short-term bank deposits, Treasury bills, Treasury
notes and a money market fund) and does not believe that it is
exposed to any significant risks related to its cash accounts,
money market fund or certificates of deposit.
The table below shows the percentage of the Company’s
revenues derived from customers whose revenues accounted for at
least 10% of the Company’s consolidated revenues for at
least one of the periods indicated:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Years Ended April 30,
|
|
|
Customer
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
2008
|
|
|
|
|
US Navy
|
|
|
80
|
%
|
|
|
67
|
%
|
|
|
58
|
%
|
|
Iberdrola and Total
|
|
|
4
|
%
|
|
|
18
|
%
|
|
|
31
|
%
|
|
Scottish Government
|
|
|
5
|
%
|
|
|
8
|
%
|
|
|
10
|
%
|
The loss of, or a significant reduction in revenues from, any of
the current customers could significantly impact the
Company’s financial position or results of operations. The
Company does not require collateral from its customers.
|
|
|
(m)
|
Net
Loss per Common Share
|
Basic and diluted net loss per share for all periods presented
is computed by dividing net loss by the weighted average number
of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Due to
the Company’s net losses, potentially dilutive securities,
consisting of outstanding stock options and non-vested
performance-based shares, were excluded from the diluted loss
per share calculation due to their anti-dilutive effect.
In computing diluted net loss per share, 1,528,453, 1,672,263
and 1,445,302 options to purchase shares of common stock,
non-vested restricted stock and shares to be issued to
non-employee directors were excluded from the computations for
the years ended April 30, 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
|
|
|
(n)
|
Stock-Based
Compensation
|
Costs resulting from all share-based payment transactions are
recognized in the consolidated financial statements at their
fair values. Compensation cost for the portion of the awards for
which the requisite service had not been rendered that were
outstanding as of May 1, 2006 is being recognized in the
consolidated statements of operations over the remaining service
period after such date based on the award’s original
estimated fair value. The aggregate share-based compensation
expense recorded in the consolidated statements of operations
for the years ended April 30, 2010, 2009 and 2008 under
SFAS No. 123R was approximately $1,073,000, $1,475,000
and $1,789,000 respectively.
Valuation
Assumptions for Options Granted During the Years Ended
April 30, 2010, 2009 and 2008
The fair value of each stock option granted during the years
ended April 30, 2010, 2009 and 2008 were estimated at the
date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model,
assuming no dividends and using the weighted average valuation
assumptions noted in the following table. The risk-free rate is
based on the US Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of
grant. The expected life (estimated period of time outstanding)
of the stock options granted was estimated using the
“simplified” method as permitted by the Securities and
Exchange Commission’s Staff Accounting
Bulletin No. 107, Share-Based Payment. Expected
volatility was based on
F-12
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
historical volatility for a peer group of companies for a period
equal to the stock option’s expected life, calculated on a
daily basis.
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Years Ended April 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
2008
|
|
|
|
|
Risk-free interest rate
|
|
|
2.98
|
%
|
|
|
3.36
|
%
|
|
|
4.69
|
%
|
|
Expected dividend yield
|
|
|
0.0
|
%
|
|
|
0.0
|
%
|
|
|
0.0
|
%
|
|
Expected life
|
|
|
6.42 years
|
|
|
|
6.29 years
|
|
|
|
5.99 years
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
|
81.8
|
%
|
|
|
79.3
|
%
|
|
|
77.9
|
%
|
The above assumptions were used to determine the weighted
average per share fair value of $4.42, $6.33 and $10.87 for
stock options granted during the years ended April 30,
2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability
method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for
the future tax consequences attributable to differences between
the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and
liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss
and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and
liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to
apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary
differences and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards are
expected to be recovered, settled or utilized. The effect on
deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is
recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment
date.
|
|
|
(p)
|
Accumulated
Other Comprehensive Loss
|
The functional currency for the Company’s foreign
operations is the applicable local currency. The translation
from the applicable foreign currencies to US dollars is
performed for balance sheet accounts using the exchange rates in
effect at the balance sheet date and for revenue and expense
accounts using an average exchange rate during the period. The
unrealized gains or losses resulting from such translation are
included in accumulated other comprehensive loss within
stockholders’ equity.
|
|
|
(q)
|
Recent
Accounting Pronouncements
|
In December 2007, the Financial Accounting Standards Board
(“FASB”) issued guidance on business combinations,
which establishes the principles and requirements for how an
acquirer recognizes the assets acquired, the liabilities
assumed, and any noncontrolling interest in the acquirer at the
acquisition date, measured at their fair values as of that date,
with limited exceptions. This new guidance applies to business
combinations for which the acquisition date is after the
beginning of the first annual reporting period beginning after
December 15, 2008. Accordingly, the Company applied the new
guidance to business combinations occurring on or after
May 1, 2009. As of April 30, 2010, the Company has not
had any such transactions.
In December 2007, the FASB issued guidance which establishes
accounting and reporting standards for the noncontrolling
interest in a subsidiary and for the deconsolidation of a
subsidiary. It clarifies that a noncontrolling interest in a
subsidiary is an ownership interest in the consolidated entity
that should be recorded as a component of equity in the
consolidated financial statements. This statement also requires
that consolidated net income shall be adjusted to include the
net income attributed to the noncontrolling interest. It also
requires that net losses be attributed to the noncontrolling
interest even if they exceed the noncontrolling interest’s
equity balance. Disclosure on the face of the statement of
operations of the amounts of consolidated net income
attributable to the parent and to the noncontrolling interest is
required. The provisions of the new guidance became effective
for the Company for interim periods and fiscal years beginning
May 1, 2009. Adoption of the new guidance did not have a
material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial
statements other than the presentation of a noncontrolling
interest in Ocean Power Technologies (Australasia) Pty Ltd. in
the Company’s consolidated financial statements. Net
F-13
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
income attributable to the noncontrolling interest in Ocean
Power Technologies (Australasia) Pty Ltd. was $38,299 for the
year ended April 30, 2010. For the years ended
April 30, 2009 and 2008, the Company recorded 100% of the
losses associated with Ocean Power Technologies (Australasia)
Pty Ltd. Had this current guidance been in place for fiscal 2009
and 2008, the Company would have recorded a net loss which was
lower by $42,049 and $25,971, respectively.
In April 2009, the FASB issued additional guidance for fair
value measurement, which provides guidance on how to determine
the fair value of assets and liabilities when the volume and
level of activity for the asset/liability has significantly
decreased. This guidance also identifies circumstances that
indicate a transaction is not orderly. In addition, this
guidance requires disclosure in interim and annual periods of
the inputs and valuation techniques used to measure fair value
and a discussion of changes in valuation techniques. The new
guidance became effective for interim and annual reporting
periods ending after June 15, 2009. Adoption of the new
guidance did not have any impact on the Company’s financial
position or results of operations.
In April 2009, the FASB issued new guidance which changes
existing guidance for determining whether debt securities are
other-than-temporarily
impaired and replaces the existing requirement that the
entity’s management assert it has both the intent and
ability to hold an impaired security until recovery with a
requirement that management assert: (a) it does not have
the intent to sell the security; and (b) it is more likely
than not it will not have to sell the security before recovery
of its cost basis. The new guidance requires entities to
separate an
other-than-temporary
impairment of a debt security into two components when there are
credit related losses associated with the impaired debt security
for which management asserts that it does not have the intent to
sell the security, and it is more likely than not that it will
not be required to sell the security before recovery of its cost
basis. The amount of the
other-than-temporary
impairment related to a credit loss is recognized in earnings,
and the amount of the
other-than-temporary
impairment related to other factors is recorded in other
comprehensive income (loss). The new guidance became effective
for interim and annual reporting periods ended after
June 15, 2009. Adoption of the new guidance did not have
any impact on the Company’s financial position or results
of operations.
In April 2009, the FASB issued guidance revising disclosures
about fair values of financial instruments in interim and annual
financial statements. Prior to this guidance, disclosures about
fair values of financial instruments were only required to be
disclosed annually. The new guidance requires disclosures about
fair value of financial instruments in interim and annual
financial statements. Adoption of the new guidance did not
affect the Company’s financial position or results of
operations.
In May 2009 (amended February 2010), the FASB issued guidance
which establishes general standards of accounting for and
disclosure of events that occur after the balance sheet date but
before financial statements are issued or available to be
issued. It sets forth the period after the balance sheet date
during which management shall evaluate events or transactions
that may occur for potential recognition or disclosure in the
financial statements, the circumstances under which an entity
shall recognize events or transactions occurring after the
balance sheet date in its financial statements and the
disclosures that an entity shall make about events or
transactions that occurred after the balance sheet date. The new
guidance is effective for interim and annual periods ended after
June 15, 2009.
In June 2009, the FASB issued additional guidance that amended
the existing accounting and disclosure guidance for the
consolidation of variable interest entities. The amended
guidance requires enhanced disclosures intended to provide users
of financial statements with more transparent information about
an enterprise’s involvement in a variable interest entity.
This guidance became effective for the Company beginning on
January 1, 2010. Adoption of the new guidance did not have
any impact on the Company’s financial position or results
of operations.
F-14
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
|
|
|
(3)
|
Marketable
Securities
|
Marketable securities with initial maturities longer than three
months but that mature in less than one year from the balance
sheet date are classified as current assets and are summarized
as follows:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
April 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
|
|
Certificates of deposit denominated in USD
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
|
3,685,370
|
|
|
Certificates of deposit denominated in GBP
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
3,217,152
|
|
|
Certificates of deposit denominated in AUD
|
|
|
519,232
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
US Treasury obligations
|
|
|
32,016,769
|
|
|
|
33,947,214
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
32,536,001
|
|
|
|
40,849,736
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Company’s marketable securities that mature more than
one year from the balance sheet date are classified as
noncurrent assets and are all classified as
held-to-maturity,
carried at amortized cost and are summarized as follows. All
non-current marketable securities mature within three years from
April 30, 2010.
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross
|
|
|
Gross
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortized
|
|
|
Unrealized
|
|
|
Unrealized
|
|
|
Market
|
|
|
|
|
Cost
|
|
|
Gains
|
|
|
Losses
|
|
|
Value
|
|
|
|
|
April 30, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US Treasury obligations
|
|
$
|
25,058,238
|
|
|
|
158,672
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
25,216,910
|
|
|
Certificate of deposit
|
|
|
3,806,808
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
3,806,808
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
28,865,046
|
|
|
|
158,672
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
29,023,718
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
April 30, 2009
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US Treasury obligations
|
|
$
|
28,619,528
|
|
|
|
423,095
|
|
|
|
(20,963
|
)
|
|
|
29,021,660
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The April 30, 2009 balance of marketable securities was
changed to increase the current portion and decrease the
noncurrent portion by $12,009,000 to reflect the maturities of
the securities as of such date.
|
|
|
(4)
|
Property
and Equipment
|
The components of property and equipment are as follows:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
April 30,
|
|
|
|
|
Life
|
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
|
|
Computers and software
|
|
|
3 years
|
|
|
$
|
654,400
|
|
|
|
581,790
|
|
|
Equipment
|
|
|
3 to 7 years
|
|
|
|
661,120
|
|
|
|
699,838
|
|
|
Office furniture and equipment
|
|
|
3 to 7 years
|
|
|
|
303,918
|
|
|
|
290,812
|
|
|
Leasehold improvements
|
|
|
3 to 8 years
|
|
|
|
147,640
|
|
|
|
141,129
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,767,078
|
|
|
|
1,713,569
|
|
|
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1,056,515
|
)
|
|
|
(815,851
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
710,563
|
|
|
|
897,718
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F-15
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
The components of accrued expenses are as follows:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
April 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
|
|
Project costs
|
|
$
|
1,072,635
|
|
|
|
262,166
|
|
|
Contract loss reserves
|
|
|
785,000
|
|
|
|
1,152,216
|
|
|
Employee incentive payments
|
|
|
682,400
|
|
|
|
672,286
|
|
|
Other
|
|
|
308,514
|
|
|
|
227,739
|
|
|
Employee-related costs
|
|
|
491,621
|
|
|
|
150,786
|
|
|
Payroll tax withholdings
|
|
|
374,208
|
|
|
|
306,228
|
|
|
Investment in joint venture
|
|
|
176,121
|
|
|
|
175,803
|
|
|
Legal and accounting fees
|
|
|
154,567
|
|
|
|
484,459
|
|
|
Value-added tax
|
|
|
47,047
|
|
|
|
328,356
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
4,092,113
|
|
|
|
3,760,039
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(6)
|
Related
Party Transactions
|
In August 1999, the Company entered into a consulting agreement
with an individual for marketing services. Currently, this
agreement is at a rate of $950 per day of services provided. The
individual became a member of the board of directors in June
2006. Under this consulting agreement, the Company expensed
approximately $72,000, $61,000 and $62,000 during the years
ended April 30, 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively. In
addition, this individual is also the chief executive officer of
a company that provided engineering and technical services to
the Company. For the year ended April 30, 2010, the Company
incurred expense of approximately $213,000 for such services.
There was no such expense incurred for the years ended
April 30, 2009 and 2008.
During the year ended April 30, 2000, the Company received
an award of $250,000 from the State of New Jersey Commission on
Science and Technology for the development of a wave power
system that was deployed off the coast of New Jersey. The award
contract was assigned to the New Jersey Economic Development
Authority in fiscal 2008. Under the terms of this award, the
Company must repay the amount funded, without interest, by
January 15, 2012. The amounts to be repaid each year are
determined as a percentage of revenues (as defined in the loan
agreement) the Company receives that year from its customer
contracts that meet criteria specified in the loan agreement,
with any remaining amount due on January 15, 2012. Based
upon the terms of the award, the Company has repaid
approximately $154,614, and the remaining $95,386 due has been
classified as current portion of long-term debt on the
accompanying balance sheet as of April 30, 2010.
During the year ended April 30, 2009, the Company received
$250,000 representing the first half of a recoverable grant
award from the NJBPU under the Renewable Energy Business Venture
Assistance Program. Under the terms of this agreement, the
amount to be repaid is a fixed monthly amount of principal only,
repayable over a five-year period beginning in May 2012. The
terms also required the Company to assign to the NJBPU a
certificate of deposit in an amount equal to the outstanding
grant balance. The Company received the remaining $250,000 under
the grant award in June 2010.
During the year ended April 30, 2001, in connection with
the sale of common stock to an investor, the Company received
$600,000 from the investor in exchange for an option to purchase
up to 500,000 metric tons of
F-16
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
carbon emissions credits generated by the Company during the
years 2008 through 2012, at a 30% discount from the
then-prevailing market rate. This amount has been recorded as
deferred credits in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets
as of April 30, 2010 and 2009. If the Company does not
become entitled under applicable laws to the full amount of
emission credits covered by the option by December 31,
2012, the Company is obligated to return the option fee of
$600,000, less the aggregate discount on any emission credits
sold to the investor prior to such date. If the Company receives
emission credits under applicable laws and fails to sell to the
investor the credits up to the full amount of emission credits
covered by the option, the investor is entitled to liquidated
damages equal to 30% of the aggregate market value of the
shortfall in emission credits (subject to a limit on the market
price of emission credits).
On April 30, 2007, the Company completed an initial public
offering in the United States on the NASDAQ Global Market by
issuing 5,000,000 shares of its common stock for a purchase
price of $20.00 per share, resulting in net proceeds to the
Company of approximately $89,900,000.
The Company has authorized 5,000,000 shares of undesignated
preferred stock with a par value of $0.001 per share. At
April 30, 2010 and 2009, no shares of preferred stock had
been issued.
|
|
|
(11)
|
Share-Based
Compensation
|
Prior to August 2001, the Company maintained qualified and
nonqualified stock option plans. As of April 30, 2010, the
Company had 264,000 shares remaining of common stock for
issuance under these plans. There are no options available for
future grant under these plans as of April 30, 2010.
In August 2001, the Company approved the 2001 Stock Plan, which
provides for the grant of incentive stock options and
nonqualified stock options. A total of 1,000,000 shares
were authorized for issuance under the 2001 Stock Plan. As of
April 30, 2010, the Company had issued or reserved
468,878 shares for issuance under the 2001 Stock Plan.
After the effectiveness of the 2006 Stock Incentive Plan, no
further options or other awards have been or will be granted
under the 2001 Stock Plan.
On April 24, 2007, the Company’s 2006 Stock Incentive
Plan became effective. A total of 803,215 shares were
authorized for issuance under the 2006 Stock Incentive Plan. On
October 2, 2009, an amendment to the 2006 Stock Incentive
Plan was approved, increasing the aggregate number of shares
authorized for issuance by 850,000 shares to 1,653,215. As
of April 30, 2010, the Company had issued share-based
awards for 822,784 shares of common stock and had reserved
an additional 830,431 shares of common stock for future
issuance under the 2006 Stock Incentive Plan. The Company’s
employees, officers, directors, consultants and advisors are
eligible to receive awards under the 2006 Stock Incentive Plan;
however, incentive stock options may only be granted to
employees. The maximum number of shares of common stock with
respect to which awards may be granted to any participant under
the 2006 Stock Incentive Plan is 200,000 per calendar year.
Members of the board of directors who are not full-time
employees receive, as part of their annual compensation, a
choice of either (a) an option to purchase
2,000 shares of common stock that is fully vested at the
time of grant, or (b) shares of common stock worth $10,000,
which vest 50% at the time of grant and 50% one year later.
Vesting provisions of stock options are determined by the board
of directors. The contractual term of these stock options is up
to ten years. The 2006 Stock Incentive Plan is administered by
the Company’s board of directors who may delegate authority
to one or more committees or subcommittees of the board of
directors or to the Company’s officers. If the board of
directors delegates authority to an officer, the officer has the
power to make awards to all of the Company’s employees,
except to executive officers. The board of directors will fix
the terms of the awards to be granted by such officer. No award
may be granted under the 2006 Stock Incentive Plan after
December 7, 2016, but the vesting and effectiveness of
awards granted before that date may extend beyond that date.
F-17
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
A summary of stock options under the plans is as follows:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted
|
|
|
Remaining
|
|
|
|
|
Shares Under
|
|
|
Average
|
|
|
Contractual
|
|
|
|
|
Option
|
|
|
Exercise Price
|
|
|
Term
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(In Years)
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding May 1, 2007
|
|
|
1,303,574
|
|
|
$
|
14.49
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited
|
|
|
(154,214
|
)
|
|
|
16.01
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
|
(24,100
|
)
|
|
|
11.94
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
320,042
|
|
|
|
15.59
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding April 30, 2008
|
|
|
1,445,302
|
|
|
|
14.61
|
|
|
|
5.2
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited
|
|
|
(130,510
|
)
|
|
|
15.40
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
317,471
|
|
|
|
8.88
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding April 30, 2009
|
|
|
1,632,263
|
|
|
|
13.43
|
|
|
|
5.1
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited
|
|
|
(588,018
|
)
|
|
|
13.21
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
331,208
|
|
|
|
6.10
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding April 30, 2010
|
|
|
1,375,453
|
|
|
|
11.87
|
|
|
|
5.2
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercisable April 30, 2010
|
|
|
892,115
|
|
|
|
13.64
|
|
|
|
3.4
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The total intrinsic value of outstanding and exercisable options
as of April 30, 2010 was $202,000. As of April 30,
2010, approximately 483,000 additional options were expected to
vest, which had $173,000 of intrinsic value and a weighted
average remaining contractual term of 8.5 years. There was
approximately $913,000, $1,417,000 and $1,709,000 of total
recognized compensation cost during the years ended
April 30, 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively. As of
April 30, 2010, there was approximately $2,040,000 of total
unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested stock
options granted under the plans. This cost is expected to be
recognized over a weighted-average period of 3.3 years. The
Company normally issues new shares to satisfy option exercises
under these plans.
Certain options were granted to consultants during the years
ended April 30, 2010, 2009 and 2008. The Company has
charged compensation expense of $45,000, $36,451 and $137,982
related to these option grants, which has been included in
selling, general and administrative costs in the accompanying
consolidated statements of operations for the years ended
April 30, 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
Compensation expense for restricted stock was historically
recorded based on its market value on the date of grant and
recognized ratably over the associated service and performance
period. There were 150,000 and 40,000 shares of restricted
stock granted to employees with service
and/or
performance-based vesting requirements during the years ended
April 30, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
F-18
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
A summary of restricted stock under the plans is as follows:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average
|
|
|
|
|
Number
|
|
|
Price per
|
|
|
|
|
of Shares
|
|
|
Share
|
|
|
|
|
Issued and unvested at May 1, 2008
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
40,000
|
|
|
|
6.48
|
|
|
Forfeited
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Vested
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issued and unvested at April 30, 2009
|
|
|
40,000
|
|
|
|
6.48
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
|
150,000
|
|
|
|
6.36
|
|
|
Forfeited
|
|
|
(22,000
|
)
|
|
|
6.27
|
|
|
Vested
|
|
|
(15,000
|
)
|
|
|
6.48
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issued and unvested at April 30, 2010
|
|
|
153,000
|
|
|
|
6.39
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
There was approximately $160,000 and $58,000 of total recognized
compensation cost during the year ended April 30, 2010 and
2009, respectively. As of April 30, 2010, there was
approximately $825,000 of total unrecognized compensation cost
related to non-vested restricted stock granted under the plans.
This cost is expected to be recognized under a weighted average
period of 2.6 years.
During the year ended April 30, 2009, 4,992 shares of
common stock were awarded to non-employee directors pursuant to
annual retainer arrangements. The aggregate share-based
compensation expense recorded in the consolidated statement of
operations for the year ended April 30, 2009 related to the
shares was approximately $40,000, which represents the fair
value on the date of grant. The shares were not issued as of
April 30, 2009 but were issued during the year ended
April 30, 2010.
During the year ended April 30, 2010, 7,217 shares of
common stock were awarded to non-employee directors pursuant to
annual retainer arrangements. The aggregate share-based
compensation expense recorded in the consolidated statement of
operations for the year ended April 30, 2010 related to the
shares was approximately $40,000, which represents the fair
value on the date of grant.
During the year ended April 30, 2010, 1,072 shares of
common stock were purchased by the Company.
F-19
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
The tax effects of temporary differences and carryforwards that
give rise to the Company’s deferred tax assets and deferred
tax liabilities are presented below.
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
April 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred tax assets:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal net operating loss carryforwards
|
|
$
|
20,818,000
|
|
|
|
15,519,000
|
|
|
Foreign net operating loss carryforwards
|
|
|
3,777,000
|
|
|
|
3,380,000
|
|
|
New Jersey state operating loss carryforwards
|
|
|
3,035,000
|
|
|
|
1,792,000
|
|
|
Federal research and development tax credits
|
|
|
1,562,000
|
|
|
|
1,089,000
|
|
|
Foreign research and development tax credits
|
|
|
670,000
|
|
|
|
646,000
|
|
|
Stock compensation
|
|
|
2,307,000
|
|
|
|
2,151,000
|
|
|
Unrealized foreign exchange loss
|
|
|
231,000
|
|
|
|
224,000
|
|
|
Accrued expenses
|
|
|
428,000
|
|
|
|
515,000
|
|
|
Other
|
|
|
271,000
|
|
|
|
233,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross deferred tax assets
|
|
|
33,099,000
|
|
|
|
25,549,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Valuation allowance
|
|
|
(33,099,000
|
)
|
|
|
(25,549,000
|
)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net deferred tax assets
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The effective income tax rate differed from the percentages
computed by applying the US Federal income tax rate of 34% to
loss before income taxes as a result of the following:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Years Ended April 30,
|
|
|
|
|
2010
|
|
|
2009
|
|
|
2008
|
|
|
|
|
Computed “expected” tax benefit
|
|
|
(34
|
)%
|
|
|
(34
|
)%
|
|
|
(34
|
)%
|
|
Increase (reduction) in income taxes resulting from:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
State income taxes, net of federal benefit
|
|
|
(5
|
)
|
|
|
(5
|
)
|
|
|
(6
|
)
|
|
Stock-based compensation expense
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
5
|
|
|
Federal research and development tax credits
|
|
|
(2
|
)
|
|
|
(1
|
)
|
|
|
(1
|
)
|
|
Foreign research and development tax credits
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
(6
|
)
|
|
Foreign rate differential
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Other non-deductible expenses
|
|
|
2
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Other
|
|
|
(1
|
)
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Increase in valuation allowance
|
|
|
39
|
|
|
|
33
|
|
|
|
42
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
—
|
%
|
|
|
—
|
%
|
|
|
—
|
%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets,
management considers whether it is more likely than not that
some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be
realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is
dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during
the periods in which those temporary differences and
carryforwards become deductible or utilized. As of
April 30, 2010 and 2009, based upon the level of historical
taxable losses, valuation allowances of $33,099,000 and
$25,549,000, respectively, were recorded. The valuation
allowance increased $7,550,000, $6,097,000 and $6,249,000 during
the years ended April 30, 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
F-20
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
As of April 30, 2010, the Company had net operating loss
carryforwards for Federal income tax purposes of approximately
$61,200,000, which begin to expire in 2011. The Company also had
Federal research and development tax credit carryforwards of
approximately $1,562,000 as of April 30, 2010, which begin
to expire in 2012. The Tax Reform Act of 1986 contains
provisions that limit the utilization of net operating loss and
tax credit carryforwards if there has been an ownership change,
as defined. The Company has determined that such an ownership
change, as described in Section 382 of the Internal Revenue
Code, occurred in conjunction with the Company’s US initial
public offering in April 2007. The Company’s annual
Section 382 limitation is approximately $3,300,000. The
Section 382 limitation is cumulative from year to year, and
thus, to the extent net operating loss or other credit
carryforwards are not utilized up to the amount of the available
annual limitation, the limitation is carried forward and added
to the following year’s available limitation. As of
April 30, 2010, the Company had state net operating loss
carryforwards of approximately $49,100,000, which begin to
expire in 2026. As of April 30, 2010, the Company had
foreign net operating loss carryforwards of approximately
$13,400,000, which begin to expire in 2024. The ability to
utilize these carryforwards may be limited in the event of an
ownership change.
On May 1, 2007, the Company adopted new authoritative
guidance issued by the FASB, for the accounting and reporting of
uncertain tax positions. The guidance requires the Company to
recognize in its consolidated financial statements the impact of
a tax position if that position is more likely than not to be
sustained upon examination, based on the technical merits of the
position. At April 30, 2010, 2009 and 2008, the Company had
no unrecognized tax positions requiring recognition. The Company
does not expect any material increase or decrease in its income
tax expense, in the next twelve months, related to examinations
or changes in uncertain tax positions. The Company files federal
and state income tax returns. US federal and state income tax
returns were audited through fiscal 2007. Years subsequent to
fiscal 2007 remain open to tax examinations.
The Company does not have any interest or penalties accrued
related to uncertain tax positions as it does not have any
unrecognized tax benefits. In the event the Company determines
that accrual of interest or penalties is necessary in the
future, the amount will be presented as a component of income
taxes.
|
|
|
(13)
|
Commitments
and Contingencies
|
|
|
|
(a)
|
Operating
Lease Commitments
|
The Company leases office, laboratory, manufacturing and other
space in New Jersey, Warwick, United Kingdom and Santander,
Spain under operating leases that expire on various dates
through April 30, 2013. Rent expense under operating leases
was approximately $579,000, $606,000 and $438,000 for the years
ended April 30, 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively. Future
minimum lease payments under operating leases as of
April 30, 2010 are as follows:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Year ending April 30:
|
|
|
|
|
|
2011
|
|
$
|
331,000
|
|
|
2012
|
|
|
263,000
|
|
|
2013
|
|
|
248,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
842,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Company is involved from time to time in certain legal
actions arising in the ordinary course of business. Management
believes that the outcome of such actions will not have a
material adverse effect on the Company’s financial position
or results of operations.
F-21
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
|
|
|
(c)
|
Spain
Construction Agreement
|
The Company is currently engaged in discussions with Iberdrola
Energias (see Note 2(a)) regarding modifications to its
agreement for the first phase of the construction of a wave
power station off the coast of Spain. This first phase was due
to be completed by December 31, 2009. If no modification is
agreed to by the parties, the customer may, subject to certain
conditions in the agreement, terminate the agreement and would
not be obligated to make any more milestone payments. The
agreement also provides that the customer may seek reimbursement
for direct damages only, limited to amounts specified in the
agreement, if the Company is in default of its obligations under
the agreement. As of April 30, 2010, the Company does not
believe that the outcome of this matter will have a material
adverse effect on the Company’s financial position or
results of operations.
|
|
|
(14)
|
Quarterly
Financial Data (Unaudited)
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Three Months Ended
|
|
|
Fiscal Year 2010
|
|
Jul 31
|
|
|
Oct 31
|
|
|
Jan 31
|
|
|
Apr 30
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
1,310,937
|
|
|
|
581,875
|
|
|
|
856,482
|
|
|
|
2,352,017
|
|
|
Gross profit
|
|
|
286,710
|
|
|
|
53,727
|
|
|
|
165,392
|
|
|
|
296,527
|
|
|
Operating loss
|
|
|
(3,240,961
|
)
|
|
|
(5,562,854
|
)
|
|
|
(6,073,657
|
)
|
|
|
(6,385,204
|
)
|
|
Net loss attributable to Ocean Power Technologies, Inc
|
|
|
(2,098,477
|
)
|
|
|
(5,191,771
|
)
|
|
|
(5,649,496
|
)
|
|
|
(6,230,563
|
)
|
|
Basic and diluted net loss per share
|
|
$
|
(0.21
|
)
|
|
|
(0.51
|
)
|
|
|
(0.55
|
)
|
|
|
(0.61
|
)
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Three Months Ended
|
|
|
Fiscal Year 2009
|
|
Jul 31
|
|
|
Oct 31
|
|
|
Jan 31
|
|
|
Apr 30
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
1,786,628
|
|
|
|
667,124
|
|
|
|
964,803
|
|
|
|
630,890
|
|
|
Gross (loss) profit
|
|
|
(161,518
|
)
|
|
|
(702,454
|
)
|
|
|
326,211
|
|
|
|
(253,197
|
)
|
|
Operating loss
|
|
|
(4,416,283
|
)
|
|
|
(5,426,265
|
)
|
|
|
(3,882,472
|
)
|
|
|
(4,967,253
|
)
|
|
Net loss attributable to Ocean Power Technologies, Inc
|
|
|
(3,893,164
|
)
|
|
|
(6,115,701
|
)
|
|
|
(3,597,665
|
)
|
|
|
(4,708,620
|
)
|
|
Basic and diluted net loss per share
|
|
$
|
(0.38
|
)
|
|
|
(0.60
|
)
|
|
|
(0.35
|
)
|
|
|
(0.46
|
)
|
|
|
|
(15)
|
Operating
Segments and Geographic Information
|
The Company’s business consists of one segment as this
represents management’s view of the Company’s
operations. The Company operates on a worldwide basis with one
operating company in the US, one subsidiary in the UK and one
subsidiary in Australia, which are categorized below as North
America, Europe and Australia, respectively. Revenues are
generally attributed to the operating unit which bills the
customers.
Geographic information is as follows:
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended April 30, 2010
|
|
|
|
|
North America
|
|
|
Europe
|
|
|
Australia
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues from external customers
|
|
$
|
4,580,872
|
|
|
|
431,801
|
|
|
|
88,638
|
|
|
|
5,101,311
|
|
|
Operating loss
|
|
|
(20,068,920
|
)
|
|
|
(934,638
|
)
|
|
|
(259,118
|
)
|
|
|
(21,262,676
|
)
|
|
Long-lived assets
|
|
|
448,022
|
|
|
|
262,541
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
710,563
|
|
|
Total assets
|
|
$
|
67,424,387
|
|
|
|
4,684,104
|
|
|
|
869,702
|
|
|
|
72,978,193
|
|
F-22
OCEAN
POWER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to
Consolidated Financial
Statements — (Continued)
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended April 30, 2009
|
|
|
|
|
North America
|
|
|
Europe
|
|
|
Australia
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues from external customers
|
|
$
|
2,944,361
|
|
|
|
1,016,223
|
|
|
|
88,861
|
|
|
|
4,049,445
|
|
|
Operating loss
|
|
|
(15,870,696
|
)
|
|
|
(2,475,659
|
)
|
|
|
(345,918
|
)
|
|
|
(18,692,273
|
)
|
|
Long-lived assets
|
|
|
524,231
|
|
|
|
373,429
|
|
|
|
58
|
|
|
|
897,718
|
|
|
Total assets
|
|
$
|
81,006,430
|
|
|
|
7,677,316
|
|
|
|
110,160
|
|
|
|
88,793,906
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended April 30, 2008
|
|
|
|
|
North America
|
|
|
Europe
|
|
|
Australia
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues from external customers
|
|
$
|
2,831,122
|
|
|
|
1,940,895
|
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
4,772,017
|
|
|
Operating loss
|
|
|
(15,695,543
|
)
|
|
|
(3,221,882
|
)
|
|
|
(258,300
|
)
|
|
|
(19,175,725
|
)
|
|
Long-lived assets
|
|
|
392,980
|
|
|
|
234,497
|
|
|
|
977
|
|
|
|
628,454
|
|
|
Total assets
|
|
$
|
103,873,654
|
|
|
|
3,624,686
|
|
|
|
52,625
|
|
|
|
107,550,965
|
|
F-23