Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-23.2 - CONSENT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM - Everest Resources Corp. | fs12010a2ex23ii_covchina.htm |
| EX-10.15 - BRIDGE LOAN AGREEMENT - Everest Resources Corp. | fs12010a2ex10xv_covchina.htm |
As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on July 2, 2010
Registration No. 333-165819
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
Amendment No. 2
to
FORM S-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
|
Covenant Group of China Inc.
|
|
(Name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
|
|
Nevada
|
000-53463
|
27-051555191
|
||
|
(State or other jurisdiction
of incorporation)
|
(Commission File Number)
|
(IRS Employer
Identification No.)
|
Two Bala Plaza, Suite 300
Bala Cynwyd, PA 19004
(610) 660-7828
(Address and telephone number of principal executive offices and principal place of business)
Mr. Kenneth Wong
President
Covenant Group of China Inc.
Two Bala Plaza, Suite 300
Bala Cynwyd, PA 19004
(610) 660-7828
(Name, address and telephone number of agent for service)
Copies to:
|
William Uchimoto, Esq.
Stevens & Lee, PC
1818 Market St.
Philadelphia, PA 19103
(215) 751-2876
|
Wesley R. Kelso, Esq.
Stevens & Lee, PC
51 South Duke St.
Lancaster, PA 17602
(717) 399-6632
|
If any of the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, check the following box: x
If this Form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. o
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. o
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
|
Large accelerated filer
|
o
|
Accelerated Filer
|
o
|
|
Non-accelerated filer
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company)
|
o
|
Smaller reporting company
|
x
|
The registrant hereby amends this registration statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the registrant shall file a further amendment which specifically states that this registration statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or until the registration statement shall become effective on such date as the United States Securities and Exchange Commission, acting pursuant to said section 8(a), may determine.
The information in this prospectus is not complete and may be changed. We may not sell these securities until the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities, and we are not soliciting offers to buy, these securities in any state where the offer or sale is not permitted.
PRELIMINARY PROSPECTUS
SUBJECT TO COMPLETION, DATED JULY , 2010
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC.
$20,600,000
of Common Stock and Warrants
On January 31, 2010, we entered into an equity credit agreement with Southridge Partners II, LP, or Southridge, pursuant to which we may from time to time sell to Southridge shares of our common stock for aggregate gross proceeds of up to $20,000,000 (the “Equity Credit Agreement”).
In connection with the Equity Credit Agreement, we are issuing to Southridge a warrant to purchase 300,000 shares of common stock for a five year period at an initial purchase price of $2.00 per share, subject to adjustment.
To the extent that Southridge resells any of the shares covered by this prospectus, it may be required to provide you with this prospectus and a prospectus supplement identifying and containing specific information about the shares being offered. You should carefully read this prospectus and the applicable prospectus supplement before deciding to buy any of these securities.
THIS PROSPECTUS MAY NOT BE USED TO OFFER OR SELL ANY SECURITIES UNLESS ACCOMPANIED BY A PROSPECTUS SUPPLEMENT.
We will describe the terms of any such offering in a supplement to this prospectus. Any prospectus supplement may also add, update, or change information contained in this prospectus. Such prospectus supplement will contain the following information about the offered securities:
|
·
|
title and amount;
|
|
·
|
offering price, any underwriting discounts and commissions or agency fees, and our net proceeds;
|
|
·
|
any market listing and trading symbol; and
|
|
·
|
names of lead or managing underwriters or agents and description of underwriting or agency arrangements.
|
Our shares of common stock trade on the Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board (“OTC.BB”) under the symbol “CVGC.” On June 24, 2010, the last reported sale price for our common stock was $2.80 per share. You are urged to obtain current market quotations for our common stock.
You should consider carefully the risk factors beginning on page 8 of this prospectus. You should carefully review the risks and uncertainties described under the heading “Risk Factors” contained in the applicable prospectus supplement.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or determined that this prospectus is accurate or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
The date of this preliminary prospectus is July , 2010.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| Page | |
|
2
|
|
|
3
|
|
|
8
|
|
|
22
|
|
|
24
|
|
|
24
|
|
|
25
|
|
|
40
|
|
|
55
|
|
|
55
|
|
|
56
|
|
|
60
|
|
|
61
|
|
|
65
|
|
|
67
|
|
|
67
|
|
|
67
|
|
|
67
|
|
|
68
|
You may only rely on the information contained in this prospectus or that we have referred you to. We have not authorized anyone to provide you with different information. This prospectus does not constitute an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any securities other than the common stock offered by this prospectus. This prospectus does not constitute an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any common stock in any circumstances in which such offer or solicitation is unlawful. Neither the delivery of this prospectus nor any sale made in connection with this prospectus shall, under any circumstances, create any implication that there has been no change in our affairs since the date of this prospectus or that the information contained by reference to this prospectus is correct as of any time after its date.
This prospectus is part of a registration statement on Form S-1 that we filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC. We may, from time to time, sell common stock or warrants to purchase common stock to Southridge under the Equity Credit Agreement for total gross proceeds of up to $20,600,000.
Each time we offer securities under this prospectus, we will provide a prospectus supplement that will contain specific information about the terms of that offering and securities offered. We may also add, update, or change in the prospectus supplement any of the information contained in this prospectus. To the extent that any statement that we make in a prospectus supplement is inconsistent with statements made in this prospectus, the statements made in this prospectus will be deemed modified or superseded by those made in the prospectus supplement. We urge you to carefully read this prospectus and any applicable prospectus supplement before deciding to buy any of these securities.
We are offering to sell, and seeking offers to buy, shares of common stock only in jurisdictions where offers and sales are permitted. The information in this prospectus is accurate only as of the date of this prospectus, regardless of the time of delivery of this prospectus or of any sale of common stock. The rules of the SEC may require us to update this prospectus in the future.
This summary highlights selected information contained elsewhere in this prospectus and does not contain all of the information you should consider in making your investment decision. Before investing in the securities offered hereby, you should read the entire prospectus, including our financial statements and related notes included in this prospectus and the information set forth under the headings “Risk Factors” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” In this prospectus, the terms “Covenant,” “the Company,” “we,” “us,” and “our” refer to Covenant Group of China, Inc.
Our Company
We are a holding company primarily engaged in the business of acquiring equity interests in private companies based and operating in the People’s Republic of China (“PRC” or “China”) and providing these companies with support, including administrative, legal, accounting and marketing assistance, and an infusion of capital with the long term goal of preparing them to become public companies in their own right. As described below, during 2009 we completed the acquisition of two privately held companies based and operating in China. On April 30, 2010, we terminated our agreements with one of our Chinese subsidiaries and rescinded the exchange of shares of our capital stock for the capital stock of that company. See “Rescission of Acquisition of Chongqing Sysway.”
We intend to continue to seek to acquire other privately held companies in China. We believe that equity investments in China present one of the most attractive global investment opportunities available in the coming four to seven years. We plan to focus on growth company acquisitions located in China. As with our current China subsidiary, we intend to have at least two members of our board of directors and management elected to serve on the board of each such company that we acquire. The management and board of directors of the Company intends to take an active role in monitoring the performance of our operating subsidiaries.
We were incorporated in the State of Nevada on November 8, 2006 under the name Everest Resources Corp. (“Everest”) as a development stage corporation that intended to engage in the exploration of gold. On December 24, 2009, we changed our name to Covenant Group of China Inc. and acquired all of the capital stock of Covenant Group Holdings Inc. (“Covenant Holdings”), a privately held company incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware and engaged in the business of acquiring equity interests in private Chinese operating companies and providing these companies with strategic support. The acquisition of the capital stock of Covenant Holdings was accomplished on December 24, 2009, pursuant to the terms of a Share Exchange Agreement by and among the Company, Covenant Holdings and all of the shareholders of Covenant Holdings. Upon the closing of the share exchange, each of the Covenant Holdings shareholders exchanged their respective shares of Covenant Holdings, on a one-for-one basis, for 9,380,909 shares of the Company’s common stock. As a result of the share exchange, Covenant Holdings became a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company.
Prior to our acquisition of Covenant Holdings, we were in the development stage and had minimal business operations. We had no interest in any property, but had the right to conduct mineral exploration activities on 471 acres located in southern British Columbia, Canada pursuant to an agreement with the former majority shareholder of the Company, Gary Sidhu. In connection with the acquisition of Covenant Holdings, Mr. Sidhu terminated the Company’s mineral exploration rights, and he agreed to surrender 5,000,000 shares of the Company’s common stock in exchange for $100,000 and a promissory note from the Company in the principal amount of $190,000, $90,000 of which the Company has prepaid. Mr. Sidhu surrendered 4,500,000 shares of our common stock and agreed to surrender his remaining 500,000 shares upon full payment of the promissory note by the Company. On March 25, 2010, Mr. Sidhu and the Company entered into an agreement pursuant to which Mr. Sidhu agreed to cancel the promissory note and surrender his remaining 500,000 shares in exchange for the Company issuing to him 300,000 shares of common stock of the Company. On May 13, 2010, Mr. Sidhu and the Company entered into an agreement pursuant to which Mr. Sidhu agreed to reduce the number of shares that he will receive from 300,000 to 70,000.
Acquisition of our Chinese Subsidiaries
There was no significant activity from June 10, 2009 through December 31, 2009, except for the acquisitions of our two operating subsidiaries, Hainan Jien Intelligent Engineering Co. Ltd., which we refer to in this prospectus as “Hainan Jien” or “Jien”, and Chongqing Sysway Information Technology Co. Ltd., which we refer to in this prospectus as “Chongqing Sysway” or “Sysway”. On June 24, 2009, Covenant Holdings entered into a stock acquisition and reorganization agreement with Hainan Jien and its stockholders. Pursuant to the terms of this agreement, Covenant Holdings acquired 100% of the capital stock of Jien, representing 100% of the company’s outstanding equity interests, in exchange for 1,350,000 shares of a public shell’s common stock. For purposes of this acquisition, the common stock of the shell company that would acquire all of the rights and obligations of Covenant Holdings was valued at $1.76 per share, which was determined by the volume weighted average stock price for the first day of trading of the Company’s common stock plus all private sales of Covenant Holdings’ common stock prior to the completion of the reverse merger with the Company. Jien was incorporated in Hainan Province, China in 1999. Jien specializes in the design and installation of security and surveillance infrastructure to protect financial institutions and government agencies, and it also implements “intelligent construction” projects for commercial customers.
On June 24, 2009, Covenant Holdings entered into a stock acquisition and reorganization agreement with Chongqing Sysway and its stockholders. Pursuant to the terms of this agreement, Covenant Holdings acquired 100% of the capital stock of Sysway, representing 100% of the company’s outstanding equity interests, in exchange for 1,400,000 shares of a public shell’s common stock. For purposes of this acquisition, the common stock of the shell company that would acquire all of the rights and obligations of Covenant Holdings was valued at $1.76 per share, which was determined in the same manner as in the acquisition of Hainan Jien. Chongqing Sysway was incorporated in 1999 in Chongqing City, Sichuan Province, PRC, as a state owned enterprise. Since 2005 Chongqing Sysway has operated as a private enterprise mainly engaged in systems integration services, including computer systems installation, website design, and system firewall setup, particularly for the tobacco industry.
Under the stock acquisition and reorganization agreements with Chongqing Sysway and Hainan Jien, we agreed to contribute $2,500,000 in capital to each of these companies. Because the government of China would not permit the ownership of the stock of Chongqing Sysway and Hainan Jien to be registered in the name of the Company until these capital contributions were made, the Company entered into share entrustment agreements with each of these companies and their former shareholders pursuant to which the shares of stock of such company and the shares of common stock of the Company to be issued in exchange for such shares are held in trust until the ownership of the stock of such company is registered in the name of the Company on the records of the Chinese government.
Rescission of our Acquisition of Chongqing Sysway
On April 30, 2010, the Board of Directors of the Company voted to terminate and rescind the stock acquisition and reorganization agreement with Chongqing Sysway due to several breaches of such agreement by Chongqing Sysway, including the failure of the prior owners of Chongqing Sysway to repay a dividend paid to them by Chongqing Sysway in excess of that permitted under the agreement and under China law and the failure of Chongqing Sysway and its prior owners to cooperate with the Company in the preparation of the financial statement disclosures required under United States securities laws.
As a result of the termination and rescission of the agreement, the Company has transferred all of the shares of capital stock of Chongqing Sysway to the prior owners of Chongqing Sysway and the 1,400,000 shares of common stock of the Company issued in exchange for the shares of capital stock of Chongqing Sysway have been returned to the Company and treated as treasury shares. The intent of this transaction is to return the Company, Chongqing Sysway, and the prior owners of the capital stock of Chongqing Sysway to their status prior to the completion of the acquisition by the Company of the capital stock of Chongqing Sysway on December 24, 2009.
Our principal offices are located at Two Bala Plaza, Suite 300, Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania 19004. Our telephone number is (610) 660-7828.
The Offering
This prospectus is part of a registration statement on Form S-1 that we filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Under this registration statement, we may, from time to time, sell to Southridge any combination of common stock or warrants to purchase common stock in one or more offerings for total gross proceeds of up to $20,600,000. This prospectus provides a general description of the securities we may offer.
Each time we sell securities, we will provide a prospectus supplement that will contain specific information about the terms of the securities being offered. The prospectus supplement may add, update or change information contained in this prospectus and may include a discussion of any risk factors or other special considerations that apply to the offered securities. If there is any inconsistency between the information in this prospectus and a prospectus supplement, you should rely on the information in that prospectus supplement. Southridge may be required to deliver a copy of this prospectus and any prospectus supplement in connection with any resale of such securities by Southridge. Before making an investment decision, it is important for you to read and consider the information contained in this prospectus and any prospectus supplement, together with the additional information described under the heading “Available Information.”
Equity Credit Agreement
On January 31, 2010, we entered into the Equity Credit Agreement with Southridge. We may sell shares of our common stock to Southridge from time to time under the Equity Credit Agreement for aggregate gross proceeds of up to $20,000,000. We have no obligation to sell any shares under the Equity Credit Agreement. Any shares of our common stock we do sell under the Equity Credit Agreement will be covered by a prospectus supplement specifying, among other things, the number of shares sold and the price per share. The Equity Credit Agreement expires on the earlier of twenty-four months after the date of this prospectus and the purchase by Southridge under such agreement of shares of our common stock having an aggregate purchase price of $20,000,000. There is no limit on the number of times or how frequently we may sell shares to Southridge under the Equity Credit Agreement.
We agreed in the Equity Credit Agreement to issue to Southbridge a warrant to purchase up to 300,000 shares of our common stock for a five year period at a purchase price of $2.00 per share (the “Southridge Warrant”). This prospectus supplement covers those warrants and the shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of those warrants.
The following is a brief summary of certain provisions of the Equity Credit Agreement, does not purport to be complete, and is qualified by reference in its entirety to the Equity Credit Agreement, which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement on Form S-1 of which this prospectus is a part.
Terms of Sale
We may require Southridge to purchase shares of our common stock from time to time under the equity credit agreement by delivering a put notice specifying the total purchase price for the shares to be purchased (the “Investment Amount”). The Investment Amount may not be greater than the lesser of (a) $1,000,000 or (b) 300% of the average dollar volume (closing bid price times the volume on the OTC.BB for a trading day) for the 20 trading days preceding the put notice.
The purchase price per share for the shares to be purchased by Southridge will be 94% of the lowest closing bid price on the OTC.BB during the five trading days following the put notice (the “Valuation Period”).
If within 15 trading days after the closing of any purchase and sale of shares under the equity credit agreement (a “Closing”) the Company delivers a notice (a “Blackout Notice”) to Southridge that the Company’s Board of Directors has determined in good faith that (a) either (i) the Company possesses material information not ripe for disclosure in a registration statement or (ii) the Company is engaged in a material activity that would be adversely affected by disclosure in a registration statement and (b) the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part would be materially misleading absent the inclusion of such information and Southridge still holds shares of common stock purchased at such Closing and the Company suspends the right of Southridge to sell the common stock for a period (a “Blackout Period”), the Company may be required to issue additional shares of common stock to Southridge if the closing bid price for the common stock on the first trading day following the Blackout Period (the “New Bid Price”) is less than the closing bid price for the common stock on the trading day immediately preceding the Blackout Period (the “Old Bid Price”). The number of additional shares to be issued, if any, will be equal to the difference between (a) the number of shares purchased at such Closing still held by Southridge (the “Remaining Shares”) multiplied by the Old Bid Price, divided by the New Bid Price and (b) the Remaining Shares.
Conditions to Obligation to Purchase Stock
The obligation of the Southridge to purchase shares of common stock at any Closing is subject to the satisfaction of the following conditions:
|
·
|
a registration statement must be in effect;
|
|
·
|
the representations and warranties made by the Company must be true and correct in all material respects;
|
|
·
|
the Company must have performed all covenants, agreements and conditions required by the equity credit agreement and by a registration rights agreement entered into by the Company in connection with the equity credit agreement;
|
|
·
|
no statute, rule, regulation, executive order, decree, ruling, or injunction has been entered that prohibits or has a direct material adverse effect on the transactions under the equity credit agreement;
|
|
·
|
no material adverse development with respect to the business, operations, properties, or financial condition of the Company has occurred;
|
|
·
|
the Company must have delivered an opinion of the Company’s legal counsel prior to the first Closing;
|
|
·
|
the shares to be purchased by Southridge must not result in Southridge owning more than 4.99% of the Company’s outstanding common stock;
|
|
·
|
the shares to be purchased by Southridge must not exceed the amount that may be issued by the Company under the rules of the principal market in which the shares of common stock are traded;
|
|
·
|
the Company must have no knowledge of any event more likely than not to cause the registration statement pursuant to which the applicable prospectus supplement is delivered to be suspended or otherwise ineffective; and
|
|
·
|
since the date of the put notice for such Closing, there shall not have occurred a subdivision or combination of the Company’s common stock, a common stock dividend or distribution, the issuance of options or rights to purchase shares of common stock for a purchase price less than the closing bid price immediately prior to such issuance, the issuance of securities convertible into or exchangeable for shares of common stock for consideration less than the closing bid price in effect immediately prior to such issuance, any other issuance of shares of common stock for consideration lower than the closing bid price in effect immediately prior to such issuance, or certain distributions of assets or indebtedness or distributions in respect of the sale of all or substantially all of the Company’s assets.
|
In addition, we may not deliver a put notice at any time during the continuance of any of the following events:
|
·
|
the receipt of any request for additional information by the SEC or any other federal or state governmental authority for additional information or amendments or supplements to the registration statement or related prospectus;
|
|
·
|
the issuance of a stop order or the initiation of any proceedings for that purpose;
|
|
·
|
receipt of any notification with respect to the suspension of the qualification or exemption from qualification of the securities covered by this prospectus supplement for sale in any jurisdiction or the initiation or threatening of any proceedings for that purpose;
|
|
·
|
the occurrence of any event that makes any statement made in the registration statement or related prospectus or document incorporated by reference therein untrue in any material respect or that requires changes to such registration statement, prospectus, or document so that, in the case of the registration statement or prospectus it will not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact required to be stated therein or necessary to make the statements therein not misleading, in light of the circumstances under which they were made; and
|
|
·
|
the Company determines that a post-effective amendment to the registration statement would be appropriate.
|
Our business and an investment in our securities are subject to a variety of risks. The following risk factors describe the most significant events, facts or circumstances that could have a material adverse effect upon our business, financial condition, results of operations, ability to implement our business plan, and the market price for our securities. Many of these events are outside of our control. The risks described below are not the only ones facing our company.
Risks Related to Our Business.
Our operating subsidiaries may not be able to adapt to rapid changes in the dynamic Chinese IT industry, thereby losing market share and revenue opportunities. The Chinese IT industry is extremely dynamic, characterized by rapid changes in technology and the frequent introduction of new and more advanced equipment and software applications. Our subsidiaries and the growth companies that we may acquire will be subject to the general risks, uncertainties and problems frequently encountered by similar companies operating in the Chinese IT industry. These include, among others, the following:
|
·
|
the failure to anticipate and adapt to developing market trends;
|
|
·
|
the failure to identify, develop and market services and products that respond to changing client needs and changing technological standards;
|
|
·
|
the inability to maintain, upgrade and improve our current services and products;
|
|
·
|
the inability to attract and retain skilled personnel, relevant to our companies’ service and product offerings; and
|
|
·
|
the failure to manage our currently rapidly expanding operations.
|
If our subsidiaries are unable to meet these challenges and any others that they may encounter, it is possible that they will lose market share and revenue opportunities and that our growth will be slowed.
We depend on the financial services industry, and changes within that industry could reduce demand for products and services. Unfavorable economic conditions adversely impacting the financial services industry could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. For example, depository financial institutions have experienced, and may continue to experience, cyclical fluctuations in profitability as well as increasing challenges to improve their operating efficiencies. Due to the entrance of foreign global players, non-traditional competitors and the global financial crises, the profit margins of depository financial institutions have narrowed. As a result, some financial institutions have slowed, and may continue to slow, their capital spending, including spending on web-based products and solutions, which can negatively impact sales to new and existing clients. Decreases in, or reallocation of, capital expenditures by our current and potential clients, unfavorable economic conditions and new or persisting competitive pressures affecting the financial services industry could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our customer base includes commercial banks and financial institutions in the PRC. Any economic downturn or regional financial upheavals disrupting growth and developments in the PRC banking and the financial services sector would presumably result in the reduction of IT expenditures or the postponement of major IT upgrading projects. If that should occur, there would be a detrimental impact on our growth opportunities if banks and financial institutions in the PRC are less prepared to incur expenditures to purchase or upgrade IT infrastructure and security surveillance systems. Our financial performance and overall investor value may therefore be adversely affected.
There exists substantial and increasing competition with which our businesses must compete in service offerings and pricing, and if our subsidiaries are not successful in addressing those issues, they may lose market share and revenue potential. In general, the level of competition in the PRC market for IT services and solutions to the financial services sector is intense. We face competition from both local and international companies. Some of our competitors have longer operating histories, larger clientele, more varied service and product offerings and more extensive personnel and financial resources which place them in a better position than our subsidiaries to develop and expand their range of services and market share. It is also expected that there will be competition from new entrants into the industry. Current or future competitors may develop or offer services that are comparable or superior to ours at a lower price. In addition, only some of the products and services of our companies are protected by intellectual property rights, therefore competitors would not be prevented from copying our business techniques. If we fail to successfully compete against our current and future competitors, our business, financial condition and operating results will be adversely affected.
In some service areas of the IT business, prices are decreasing and adversely affecting margins in those areas; if our subsidiaries do not meet the resulting pricing structure or shift away from those areas of business to more profitable services, they may lose business opportunities and may experience losses. There has been increasing competition in some areas of IT consulting services, resulting in more competitive pricing and falling margins. Customers may elect to engage competitors who offer better pricing rather than use our subsidiaries. If our subsidiaries do not successfully manage their businesses and compete in these areas for engagements, they will suffer financial losses. Our subsidiaries may also address the competitive situation by shifting to other service areas where margins are better or they may provide extra services or enhancements that result in different pricing. If they are not successful in implementing new or differentiating services, they may suffer losses in particular segments of their businesses.
The failure to retain existing customers or changes in their continued use of our services will adversely affect operating results. Our subsidiaries, in part, compete using service and product fee structures designed to establish solid, long term client relationships and recurring revenues through ongoing usage by customers. Some of their revenues are dependent on recurring revenues and the continued acceptance of their services by customers in areas such as account presentation, payments and other financial services. The failure to retain the existing customers or a change in spending patterns and budgetary aspects of competing products would adversely affect our companies’ business model. Also, competitors may compete directly with our businesses by adopting a similar business model or through the acquisition of companies, such as resellers, who provide complementary products or services.
As a holding company, our business plan calls for cross selling, development of new offerings and expanded marketing by our subsidiaries; if they are unable to achieve these goals, our subsidiaries will not grow as expected and the future value of our stock to investors may be less than expected. The expansion of our subsidiaries’ businesses is dependent, in part, on developing, marketing, selling and supporting new financial products and services to the financial industry and cross selling to expand their customer base. If any new products developed prove defective or if the companies fail to properly market these products to the financial industry or sell these products to their customers, the businesses of our subsidiaries may not expand and grow. In such a circumstance, the value of these companies may remain stagnant or decline, which would adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
IT infrastructure components are obtained from selected suppliers; if the ability to obtain needed items is disrupted, our subsidiaries’ businesses would be adversely affected. Many of the IT consulting services and system infrastructure installations conducted by our subsidiaries depend on the availability of the necessary hardware equipment and software applications from third parties. Our subsidiaries have established relations with selected suppliers. There is no assurance that these vendors/distributors will continue to offer needed items or not terminate their relationship with our subsidiaries. Although there are alternative suppliers for most of the needs, if our subsidiaries are unable to obtain the necessary IT infrastructure components from these or comparable vendors/distributors on a timely basis, our business, financial condition and results of operation would be adversely affected.
If the senior management team and critical staff are not retained, our subsidiaries would suffer a loss of reputation and an inability to manage their commitments and expand their operations as planned. In a service-oriented business, personal relationships, goodwill and networks are critical in obtaining and maintaining customer engagements. The ability to successfully complete engagements depends on a trained, knowledgeable and stable staff. The success of our subsidiaries depends on the continued efforts of the senior management teams in building good relationships with existing and potential customers and in the implementation of their growth and business strategy and their company’s ability to retain and replace its staff. Each senior management team has substantial experience in the services offered by the company and has been instrumental in their past growth and expansion. The loss of any member of the senior management team and critical staff could, without adequate replacement, result in an adverse impact on their businesses, financial conditions and results of operations.
If our subsidiaries are unable to protect their proprietary technology and other rights, they may be unable to effectively compete. Our subsidiaries rely on a combination of patent, copyright, trademark and anti-competition laws, as well as licensing agreements, third-party nondisclosure agreements, internal confidentiality policies and other contractual provisions and technical measures to protect their intellectual property rights. There can be no assurance that these protections will be adequate to prevent competitors from copying or reverse-engineering our subsidiaries’ products, or that competitors will not independently develop technologies that are substantially equivalent or superior to our technology. To protect our subsidiaries’ trade secrets and other proprietary information, employees, consultants, advisors and collaborators are required to enter into non-disclosure confidentiality agreements. There can be no assurance that these agreements will provide meaningful protection for the trade secrets, know-how or other proprietary information in the event of any unauthorized use, misappropriation or disclosure of such trade secrets, know-how or other proprietary information. Although our subsidiaries hold registered rights covering certain aspects of their technology, there can be no assurance of the level of protection that these registrations will provide. Our subsidiaries may have to resort to litigation to enforce the intellectual property rights, to protect the trade secrets or know-how, or to determine their scope, validity or enforceability. Enforcing or defending intellectual property rights is expensive, could cause diversion of our resources and may not prove successful.
If our subsidiaries’ proprietary rights infringe on those of other persons, they could be required to redesign those products, pay royalties or enter into license agreements with third parties or cease offering the infringing products or services, any of which could have an adverse impact on the business and revenues and profits of our subsidiaries and us. There can be no assurance that a third party will not assert that the intellectual property rights and services of our subsidiaries violates such third party’s intellectual property rights. To some extent, the law of the PRC is not extensively developed in the area of enforcement. As the number of products offered by our subsidiaries and competitors increases and the functionality of these products further overlap, the provision of web-based financial services technology may become increasingly subject to infringement claims. Any claims, whether with or without merit, could:
|
·
|
be expensive and time consuming to defend or prosecute;
|
|
·
|
cause our companies to cease making, licensing or using products that incorporate the challenged intellectual property;
|
|
·
|
require our companies to redesign our products, if feasible;
|
|
·
|
divert management’s attention and resources; and
|
|
·
|
require our companies to pay royalties or enter into licensing agreements in order to obtain the right to use necessary technologies.
|
System failures could hurt our business reputation, and our subsidiaries could be liable for some types of failures, the extent or amount of which cannot be predicted. The operations of our subsidiaries depend on their ability to protect their systems from interruption caused by damage from fire, earthquake, power loss, telecommunications failure, unauthorized entry or other events beyond our control. Our subsidiaries, in the future, plan to maintain their own offsite disaster recovery facility if it is necessary to their business strategies. In the event of major disasters, both primary and backup locations could be adversely impacted. Our subsidiaries do not currently have sufficient backup facilities to provide full Internet services if their primary facility is not functioning. They could also experience system interruptions due to the failure of their systems to function as intended or the failure of the systems relied upon to deliver services such as the Internet, certain services specific to the financial industry, processors that integrate with other systems and networks, and systems of third parties. Loss of all or part of the systems for a period of time could have a material adverse effect on our subsidiaries’ businesses and reputation. Our subsidiaries may be liable to their clients for breach of contract for interruptions in service. Due to the numerous variables surrounding system disruptions, the extent or amount of any potential liability cannot be predicted.
Security breaches could have a material adverse effect on our business and the business reputations of our subsidiaries. Computer systems may be vulnerable to computer viruses, hackers, and other disruptive problems caused by unauthorized access to, or improper use of, systems by third parties or employees. Although our subsidiaries intend to continue to implement state-of-the-art security measures, computer attacks or disruptions may jeopardize the security of information stored in and transmitted through computer systems of the clients and their end-users. Actual or perceived concerns that company systems may be vulnerable to such attacks or disruptions may deter financial services providers and consumers from using the company’s services.
Data networks are also vulnerable to attacks, unauthorized access and disruptions. For example, in a number of public networks, hackers have bypassed firewalls and misappropriated confidential information. It is possible that, despite existing safeguards, an employee could divert end-user funds while these funds are in company control, exposing the subsidiaries to a risk of loss or litigation and possible liability. In dealing with numerous end-users, it is possible that some level of fraud or error will occur, which may result in erroneous external payments. Losses or liabilities that are incurred as a result of any of the foregoing could have a material adverse effect on the business of our subsidiaries.
The potential obsolescence of our subsidiaries’ technology or the offering of new, more efficient means of conducting business could negatively impact our business. The industry for account presentation and payments services is relatively new and subject to rapid change. Success will depend substantially upon an ability to enhance existing products and to develop and introduce, on a timely and cost-effective basis, new products and features that meet the changing financial industry requirements and incorporate technological advancements. If our individual subsidiaries are unable to develop new products and enhanced functionalities or technologies to adapt to these changes, or if they cannot offset a decline in revenues of existing products by sales of new products, their business would suffer.
Our subsidiaries’ businesses use internally developed software and systems as well as third-party products, any of which may contain errors and bugs, the effect of which could cause our subsidiaries to spend additional money and time to correct, cause a breach of services agreements and/or pay damages. Our subsidiaries’ products may contain undetected errors, defects or bugs that may or may not be correctable. The products involve integration with products and systems developed by third parties. Complex software programs of third parties may contain undetected errors or bugs when they are first introduced or as new versions are released. There can be no assurance that errors will not be found in existing or future products or third-party products upon which our subsidiaries’ products are dependent, which could result in delays, loss of market acceptance of their products, diversion of resources, injury to their reputation, and increased expenses and potentially the payment of damages.
Our subsidiaries could be sued for contract or product liability claims, and those lawsuits may disrupt our business, divert management’s attention or have an adverse effect on our financial results. The financial industry uses our products and services to provide web-based account presentation, customer service and other financial services to their end-users. Failures in a client’s system could result in an increase in service and warranty costs or a claim for substantial damages. There can be no assurance that the limitations of liability set forth in company contracts would be enforceable or would otherwise protect us from liability for damages. The successful assertion of one or more large claims could result in substantial cost to the company and divert management’s attention from operations. Any contract liability claim or litigation against the company could, therefore, have a material adverse effect on the business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, because many of our subsidiaries projects are business-critical projects for financial services providers, a failure or inability to meet a client’s expectations could seriously damage the company’s reputation and affect its ability to attract new business.
Part of the business plan in the future is to seek additional services and clients and business opportunities through the acquisition of related service and product providers; in such acquisitions, we will have to manage the integration of the acquired business operations, systems and personnel, which may be disruptive to ongoing business, not successful, or more costly than estimated. Part of our business plan for our individual subsidiaries is to acquire additional businesses. To achieve the anticipated benefits of these acquisitions, our subsidiaries will need to successfully integrate the acquired employees, products and services, data and business methods of operations. In addition, our subsidiaries may also have to consolidate certain functions and integrate procedures, personnel, product lines and operations in an efficient and effective manner. The integration process may be disruptive to, and may cause an interruption of, business as a result of a number of potential obstacles, such as:
|
·
|
the loss of key employees or customers;
|
|
·
|
the need to coordinate diverse organizations;
|
|
·
|
difficulties in integrating administrative and other functions;
|
|
·
|
the loss of key members of management following the acquisition; and
|
|
·
|
the diversion of management’s attention from our day-to-day operations.
|
We have not entered into definitive negotiations with any other target Chinese operating companies at this time, and therefore we cannot provide further specific information to you. In this regard, we are not dissimilar from a blank check company whereby the success of the Company will be predicated upon finding suitable acquisition target companies, successfully purchasing them at a fair and economical price, and integrating them into the business culture of the Company.
If our subsidiaries are not successful in integrating these businesses or if the integrations take longer than expected, there could be significant costs and our businesses could be adversely affected.
The acquisition of our Chinese subsidiaries will increase the costs of satisfying the requirements of being a public company and may divert management’s attention from our business and adversely affect our financial results. As a public company, we are subject to a number of requirements, including the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act, Sarbanes-Oxley and eventually the listing standards of the NASDAQ Capital Market. Prior to our acquisition of Chongqing Sysway and Hainan Jien, complying with these requirements was relatively simple and inexpensive. As a result of acquiring these companies, compliance with such requirements will cause us to incur substantially higher costs and might place a strain on our systems and resources. The Exchange Act requires, among other things, that we file annual, quarterly and current reports with respect to our business and financial condition. Sarbanes-Oxley requires, among other things, that we maintain effective disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting. In order to maintain and improve the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting, significant resources and management oversight will be required. As a result, our management’s attention might be diverted from other business concerns, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. Furthermore, we might not be able to retain our independent directors or attract new independent directors for our committees.
If we fail to establish and maintain an effective system of internal control, we may not be able to report our financial results accurately or to prevent fraud. Any inability to report and file our financial results accurately and timely could harm our business and adversely impact the trading price of our common stock. We are required to establish and maintain internal control over financial reporting, disclosure controls, and to comply with other requirements of Sarbanes-Oxley and the rules promulgated by the SEC thereunder. Our management, including our President, cannot guarantee that our internal controls and disclosure controls will prevent all possible errors or all fraud. A control system, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. In addition, the design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints and the benefit of controls must be relative to their costs. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no system of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within the Company have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision-making can be faulty and that breakdowns can occur because of simple error or mistake. Further, controls can be circumvented by individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more persons, or by management override of the controls. The design of any system of controls also is based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions. Over time, a control may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or the degree of compliance with policies or procedures may deteriorate. Because of inherent limitations in a cost-effective control system, misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and may not be detected.
All of Covenant Holdings’ liabilities survived its acquisition by the Company and there may be undisclosed liabilities that could have a negative impact on our financial condition. Before the share exchange, certain due diligence activities on the Company and Covenant Holdings were performed. The due diligence process may not have revealed all liabilities (actual or contingent) of the Company and Covenant Holdings that existed or which may arise in the future relating to the Company’s activities before the consummation of the acquisition. Notwithstanding that Mr. Sidhu agreed to release and indemnify the Company of all liability related to the Company’s ownership interest in the mineral exploration rights in Canada, it is possible that claims for such liabilities may still be made against us, which we will be required to defend or otherwise resolve. The provisions and terms of the termination agreement may not be sufficient to protect us from claims and liabilities and any breaches of related representations and warranties. Any liabilities remaining from the Company’s pre-closing activities could harm our financial condition and results of operations.
New accounting standards could result in changes to our methods of quantifying and recording accounting transactions, and could affect our financial results and financial position. Changes to United States generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP, arise from new and revised standards, interpretations, and other guidance issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board, or FASB, the SEC, and others. The effects of such changes may include prescribing an accounting method where none had been previously specified, prescribing a single acceptable method of accounting from among several acceptable methods that currently exist, or revoking the acceptability of a current method and replacing it with an entirely different method, among others. Such changes could result in unanticipated effects on our results of operations, financial position, and other financial measures.
Risks Related to Doing Business in China.
We may have difficulty establishing adequate management, legal and financial controls in China. Historically, China has not adopted a Western style of management and financial reporting concepts and practices, as well as modern banking, computer and other control systems. We may have difficulty in hiring and retaining a sufficient number of qualified employees to work in China. As a result of these factors, we may experience difficulty in establishing management, legal and financial controls, collecting financial data and preparing financial statements, books of account and corporate records and instituting business practices that meet Western standards.
In December 2009, the board of directors of Chongqing Sysway, one of our wholly owned Chinese subsidiaries, declared and paid a $322,061 dividend to the original shareholders and management of the company without the authorization of Covenant’s board of directors. In a December 2009 meeting of the Chongqing Sysway board, the board resolved to declare a dividend payment to the original shareholders and management of the company based on 2007 earnings on the assumption that it was permissible. Upon our receipt of a report from our independent accountants, we determined that this payment was outside the parameters of our acquisition agreement with Chongqing Sysway and had to be reversed. Moreover, the dividend exceeded the amount that Chongqing Sysway was permitted to pay under PRC law. The original shareholders and management of Chongqing Sysway executed a promissory note to repay the full $322,061 dividend to Chongqing Sysway by April 15, 2010. Due to the failure of the original shareholders and management to repay the dividend and the failure of Chongqing and its prior owners to cooperate with the Company in the preparation of the financial statement disclosures required under United States securities laws, the Company terminated its agreements with Chongqing Sysway and rescinded the Company’s acquisition of Chongqing. See “Prospectus Summary—Rescission of our Acquisition of Chonqing Sysway”.
Recent Chinese regulations relating to the establishment of offshore special purpose companies by Chinese residents and registration requirements for employee stock ownership plans or share option plans may subject our Chinese resident shareholders to personal liability and limit our ability to acquire companies in China or to inject capital into our subsidiaries in China, limit our Chinese subsidiaries’ ability to distribute profits to us, or otherwise materially and adversely affect us. The Chinese State Administration of Foreign Exchange (“SAFE”) issued a public notice in October 2005, requiring Chinese residents, including both legal persons and natural persons, to register with the competent local SAFE branch before establishing or controlling any company outside of China established for the purpose of acquiring any assets of or equity interest in companies in China and raising funds from overseas (referred to as an “offshore special purpose company”). In addition, any Chinese resident that is a shareholder of an offshore special purpose company is required to amend his or her SAFE registration with the local SAFE branch in the event of any increase or decrease of capital, transfer of shares, merger, division, equity investment or creation of any security interest over any assets located in China with respect to that offshore special purpose company. To further clarify the implementation of Circular 75, the SAFE issued Circular 124 and Circular 106 on November 24, 2005 and May 29, 2007, respectively. Under Circular 106, PRC subsidiaries of an offshore special purpose company are required to coordinate and supervise the filing of SAFE registrations by the offshore holding company’s shareholders who are Chinese residents in a timely manner. If these shareholders fail to comply, the Chinese subsidiaries are required to report to the local SAFE authorities. If the Chinese subsidiaries of the offshore parent company do not report to the local SAFE authorities, they may be prohibited from distributing their profits and proceeds from any reduction in capital, share transfer or liquidation to their offshore parent company, and the offshore parent company may be restricted in its ability to contribute additional capital into its Chinese subsidiaries. Moreover, failure to comply with the above SAFE registration requirements could result in liabilities under China law for evasion of foreign exchange restrictions. The failure or inability of these Chinese resident beneficial owners to comply with the applicable SAFE registration requirements may subject these beneficial owners or us to the fines, legal sanctions and restrictions described above.
On March 28, 2007, SAFE released detailed registration procedures for employee stock ownership plans or share option plans to be established by overseas listed companies and for individual plan participants. Any failure to comply with the relevant registration procedures may affect the effectiveness of our employee stock ownership plans or share option plans and subject the plan participants, the companies offering the plans or the relevant intermediaries, as the case may be, to penalties under PRC foreign exchange regime. These penalties may subject us to fines and legal sanctions, prevent us from being able to make distributions or pay dividends, as a result of which our business operations and our ability to distribute profits to our shareholders could be materially and adversely affected.
In addition, the National Development and Reform Commission (“NDRC”) promulgated a Rule in October 2004, or the NDRC Rule, which requires NDRC approvals for overseas investment projects made by PRC entities. The NDRC Rule also provides that approval procedures for overseas investment projects of PRC individuals must be implemented with reference to this rule. However, there exist extensive uncertainties in terms of interpretation of the NDRC Rule with respect to its application to a PRC individual’s overseas investment, and in practice, we are not aware of any precedents that a PRC individual’s overseas investment has been approved by the NDRC or challenged by the NDRC based on the absence of NDRC approval. Our current beneficial owners who are PRC individuals did not apply for NDRC approval for investment in us. We cannot predict how and to what extent this will affect our business operations or future strategy. For example, the failure of our shareholders who are PRC individuals to comply with the NDRC Rule may subject these persons or our PRC subsidiary to certain liabilities under PRC laws, which could adversely affect our business.
Chinese regulation of loans and direct investment by offshore holding companies to Chinese entities may delay or prevent us from using the proceeds of this offering to make loans or additional capital contributions to our operating subsidiaries, which could materially and adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to fund and expand our business. We may make loans to our subsidiaries, or we may make additional capital contributions to our subsidiaries. Any loans to our subsidiaries are subject to Chinese regulations. For example, loans by us to our subsidiaries in China, which are foreign-invested enterprises, to finance their activities cannot exceed statutory limits and must be registered with the SAFE.
We may also decide to finance our subsidiaries by means of capital contributions. These capital contributions must be approved by the Ministry of Commerce or its local counterpart. We cannot assure you that we will be able to obtain these government approvals on a timely basis, or if at all, with respect to future capital contributions by us to our subsidiaries. If we fail to receive such approvals, our ability to capitalize our Chinese operations may be negatively affected, which could adversely affect our liquidity and our ability to fund and expand our business.
A return to profit repatriation controls may limit the ability to expand business and reduce the attractiveness of investing in Chinese business opportunities. PRC law allows enterprises owned by foreign investors to remit their profits, dividends and bonuses earned in the PRC to other countries, and the remittance does not require prior approval by SAFE. SAFE regulations required extensive documentation and reporting, some of which was burdensome and slowed payments. If there is a return to payment restrictions and reporting, the ability of a Chinese company to attract investors will be reduced. Also, current investors may not be able to obtain the profits of the business in which they own for other reasons. Relevant PRC law and regulation permit payment of dividends only from retained earnings, if any, determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations. It is possible that the PRC tax authorities may require changes in the income of the company that may limit its ability to pay dividends and other distributions to shareholders. PRC law requires companies to set aside a portion of net income to fund certain reserves, which amounts are not distributable as dividends. These rules and possible changes could restrict our companies from repatriating funds to us, and ultimately, our shareholders as dividends.
The economy of China has been experiencing unprecedented growth and this has resulted in some inflation. If the Chinese government tries to control inflation by traditional means of monetary policy or returns to planned economic techniques, our business will suffer a reduction in sales growth and expansion opportunities. The rapid growth of the Chinese economy has resulted in higher levels of inflation. If the government tries to control inflation, it may have an adverse effect on the business climate and growth of private enterprise in the PRC. An economic slow down will have an adverse effect on our sales and may increase costs. On the other hand, if inflation is allowed to proceed unchecked, our companies’ costs would likely increase, and there can be no assurance that they would be able to increase their prices to an extent that would offset the increase in their expenses.
We are subject to international economic and political risks over which we have little or no control and may be unable to alter our business practice in time to avoid the possibility of reduced revenues. Our business is conducted in China. Doing business outside the United States, particularly in China, subjects us to various risks, including changing economic and political conditions, major work stoppages, exchange controls, currency fluctuations, armed conflicts and unexpected changes in United States and foreign laws relating to tariffs, trade restrictions, transportation regulations, foreign investments and taxation. We have no control over most of these risks and may be unable to anticipate changes in international economic and political conditions and, therefore, unable to alter our business practice in time to avoid the possibility of reduced revenues.
China’s economic policies could affect our business. Substantially all of our assets are located in China and all of our revenue is derived from our operations in China. Accordingly, our results of operations and prospects are subject, to a significant extent, to the economic, political and legal developments in China.
While China’s economy has experienced significant growth in the past twenty years, such growth has been uneven, both geographically and among various sectors of the economy. The Chinese government has implemented various measures to encourage economic growth and guide the allocation of resources. Some of these measures benefit the overall economy of China, but they may also have a negative effect on us. For example, operating results and financial condition may be adversely affected by government control over capital investments or changes in tax regulations. The economy of China has been changing from a planned economy to a more market-oriented economy. In recent years the Chinese government has implemented measures emphasizing the utilization of market forces for economic reform and the reduction of state ownership of productive assets, and the establishment of corporate governance in business enterprises; however, a substantial portion of productive assets in China are still owned by the Chinese government. In addition, the Chinese government continues to play a significant role in regulating industry development by imposing industrial policies. It also exercises significant control over China’s economic growth through the allocation of resources, the control of payment of foreign currency-denominated obligations, the setting of monetary policy and the provision of preferential treatment to particular industries or companies.
China could change its policies toward private enterprise or even nationalize or expropriate private enterprises. Our business is subject to significant political and economic uncertainties and may be affected by political, economic and social developments in China. Over the past several years, the Chinese government has pursued economic reform policies including the encouragement of private economic activity and greater economic decentralization. The Chinese government may not continue to pursue these policies or may significantly alter them to our detriment from time to time with little, if any, prior notice.
Changes in policies, laws and regulations or in their interpretation or the imposition of confiscatory taxation, restrictions on currency conversion, restrictions or prohibitions on dividend payments to stockholders, or devaluations of currency could cause a decline in the price of our common stock. Nationalization or expropriation could even result in the total loss of an investment in our stock.
The nature and application of many laws of China create an uncertain environment for business operations and they could have a negative effect on us. The legal system in China is a civil law system. Unlike the common law system, the civil law system is based on written statutes in which decided legal cases have little value as precedents. In 1979, China began to promulgate a comprehensive system of laws and has since introduced many laws and regulations to provide general guidance on economic and business practices in China and to regulate foreign investment. Progress has been made in the promulgation of laws and regulations dealing with economic matters such as corporate organization and governance, foreign investment, commerce, taxation and trade. The promulgation of new laws, changes of existing laws and the abrogation of local regulations by national laws could cause a decline in the price of our common stock. In addition, as these laws, regulations and legal requirements are relatively recent, their interpretation and enforcement involve significant uncertainty.
If certain exemptions within the PRC regarding withholding taxes are removed, our subsidiaries may be required to deduct Chinese corporate withholding taxes from any dividends that are paid to us, which will reduce the return on our investment. Under current PRC tax laws, regulations and rulings, Chinese companies are exempt from paying withholding taxes with respect to dividends paid to stockholders outside the PRC. If the foregoing exemption is eliminated, in the future our Chinese subsidiaries may be required to withhold such taxes on dividends paid to the Company.
The PRC legal system has inherent uncertainties that could limit the legal protections available to you. Most of the Company assets and all of our operations are in the PRC. The Chinese legal system is based on written statutes. Prior court decisions may be cited for reference but are not binding on subsequent cases and have limited precedential value. Since 1979, the Chinese legislative bodies have promulgated laws and regulations dealing with such economic matters as foreign investment, corporate organization and governance, commerce, taxation and trade. However, because these laws and regulations are relatively new, and because of the limited volume of published decisions and their non-binding nature, the interpretation and enforcement of these laws and regulations involve uncertainties. The laws in the PRC differ from the laws in the United States and may afford less protection to our shareholders. Unlike laws in the United States, the applicable laws of China do not specifically allow shareholders to sue the directors, supervisors, officers or other shareholders on behalf of the company to enforce a claim against these parties that the company has failed to enforce itself. Therefore, any action brought against the company or its officers and directors or its assets may be very difficult to pursue if not impossible. It is unlikely that any suit in the PRC would be able to be based on theories common in the United States or based on United States securities laws.
It will be extremely difficult to acquire jurisdiction and enforce liabilities against any officers, directors, advisory board members and assets based in China. As our executive officers, advisory board members and directors may be Chinese citizens, it may be difficult, if not impossible, to acquire jurisdiction over these persons in the event a lawsuit is initiated against us and/or our officers and directors by a shareholder or group of shareholders in the United States. Also, because our operating subsidiaries and assets are located in China, it may be extremely difficult or impossible for you to access those assets to enforce judgments rendered against us or our executive officers, advisory board members or directors by U.S. courts. In addition, the courts in China may not permit the enforcement of judgments arising out of U.S. federal and state corporate, securities or similar laws. Accordingly, U.S. investors may not be able to enforce judgments against us for violation of U.S. securities laws.
We may face judicial corruption in China. Another obstacle to foreign investment in China is corruption. There is no assurance that we will be able to obtain recourse in any legal disputes with suppliers, customers or other parties with whom we conduct business, if desired, through China’s poorly developed and sometimes corrupt judicial systems.
If relations between the United States and China worsen, investors may be unwilling to hold or buy our stock and our stock price may decrease. At various times during recent years, the United States and China have had significant disagreements over political and economic issues. Controversies may arise in the future between these two countries. Any political or trade controversies between the United States and China, whether or not directly related to our business, could reduce the price of our common stock.
Restrictions on currency exchange may limit our ability to receive and use our revenues effectively. The Renminbi Yuan (“RMB” or “Renminbi”) is currently convertible under the “current account,” which includes dividends, trade and service-related foreign exchange transactions, but not under the “capital account,” which includes foreign direct investment and loans. Currently, our Chinese subsidiaries may purchase foreign currencies for settlement of current account transactions, including payments of dividends to us, without the approval of SAFE. However, the relevant Chinese government authorities may limit or eliminate their ability to purchase foreign currencies in the future. Since a significant amount of our future revenues will be denominated in Renminbi, any existing and future restrictions on currency exchange may limit our ability to utilize revenues generated in Renminbi to fund our business activities outside China that are denominated in foreign currencies.
Foreign exchange transactions by our Chinese subsidiaries under the capital account continue to be subject to significant foreign exchange controls and require the approval of or need to register with Chinese governmental authorities, including SAFE. In particular, if our Chinese subsidiaries borrow foreign currency loans from us or other foreign lenders, these loans must be registered with SAFE, and if we finance our Chinese subsidiaries by means of additional capital contributions, these capital contributions must be approved by certain government authorities, including the NDRC, the Ministry of Commerce, or MOFCOM, or their respective local counterparts. These limitations could affect the ability of our Chinese subsidiaries to obtain foreign exchange through debt or equity financing.
Fluctuation in the value of the RMB may reduce the value of your investment. The change in value of the RMB against the U.S. dollar, Euro and other currencies is affected by, among other things, changes in China’s political and economic conditions. On July 21, 2005, the PRC government changed its decade-old policy of pegging the value of the RMB to the U.S. dollar. Under the current policy, the RMB is permitted to fluctuate within a narrow and managed band against a basket of certain foreign currencies. This change in policy has resulted in a greater fluctuation range between RMB and the U.S. dollar. There remains significant international pressure on China to adopt a more flexible and more market-oriented currency policy that allows a greater fluctuation in the exchange rate between the RMB and the U.S. dollar. Accordingly, we expect that there will be increasing fluctuations in the RMB exchange rate against the U.S. dollar in the near future. Any significant revaluation of the RMB may have a material adverse effect on the value of, and any dividends paid on, our common stock in U.S. dollar terms.
We face risks associated with currency exchange rate fluctuations; any adverse fluctuation may adversely affect our operating margins. Almost all of our revenues are denominated in Renminbi. Conducting business in currencies other than US dollars subjects us to fluctuations in currency exchange rates that could have a negative impact on our reported operating results. Fluctuations in the value of the US dollar relative to other currencies impact our revenues, cost of revenues and operating margins and result in foreign currency translation gains and losses. If the exchange rate of the Renminbi is affected by lowering its value as against the US dollar, our reported profitability when stated in US dollars will decrease. Historically, we have not engaged in exchange rate hedging activities and have no current intention of doing so.
Risks Related to Our Securities
We may need additional capital to execute our business plan and fund operations and may not be able to obtain such capital on acceptable terms or at all. Capital requirements are difficult to plan in our rapidly changing industry. We expect that we will need additional capital to fund our future growth.
Our ability to obtain additional capital on acceptable terms or at all is subject to a variety of uncertainties, including:
|
·
|
Investors’ perceptions of, and demand for, companies in our industries;
|
|
·
|
Investors’ perceptions of, and demand for, companies operating in the PRC;
|
|
·
|
Conditions of the U.S. and other capital markets in which we may seek to raise funds;
|
|
·
|
Our future results of operations, financial condition and cash flows;
|
|
·
|
Governmental regulation of foreign investment in companies in particular countries;
|
|
·
|
Economic, political and other conditions in the United States, the PRC, and other countries; and
|
|
·
|
Governmental policies relating to foreign currency borrowings.
|
We may be required to pursue sources of additional capital through various means, including joint venture projects and debt or equity financings. There is no assurance that we will be successful in locating a suitable financing transaction in a timely fashion or at all. In addition, there is no assurance that we will be successful in obtaining the capital we require by any other means. Future financings through equity investments are likely to be dilutive to our existing shareholders. Also, the terms of securities we may issue in future capital transactions may be more favorable for our new investors. Newly issued securities may include preferences, superior voting rights, the issuance of warrants or other derivative securities, and the issuances of incentive awards under equity employee incentive plans, which may have additional dilutive effects. Further, we may incur substantial costs in pursuing future capital and/or financing, including investment banking fees, legal fees, accounting fees, printing and distribution expenses and other costs. We may also be required to recognize non-cash expenses in connection with certain securities we may issue, such as convertible notes and warrants, which will adversely impact our results of operations or financial condition.
If we cannot raise additional funds on favorable terms or at all, we may not be able to carry out all or parts of our strategy to maintain our growth and competitiveness or to fund our operations. If the amount of capital we are able to raise from financing activities, together with our revenues from operations, is not sufficient to satisfy our capital needs, even to the extent that we reduce our operations accordingly, we may be required to cease operations.
The market price of our common stock may be volatile, which could cause the value of your investment to decline or could subject us to securities class action litigation. Many factors could cause the market price of our common stock to rise and fall, including the following:
|
·
|
variations in our or our competitors’ actual or anticipated operating results;
|
|
·
|
variations in our or our competitors’ growth rates;
|
|
·
|
recruitment or departure of key personnel;
|
|
·
|
changes in the estimates of our operating performance or changes in recommendations by any securities analyst that follows our stock;
|
|
·
|
substantial sales of our common stock; or
|
|
·
|
changes in accounting principles.
|
Market volatility, as well as general economic, market or potential conditions, could reduce the market price of our common stock in spite of our operating performance. In the past, following periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities, securities class action litigation often has been brought against that company. Due to the potential volatility of our stock price, we therefore may be the target of securities litigation in the future. Securities litigation could result in substantial costs and divert management’s attention and resources from our business.
Shares of our common stock lack a significant trading market. Shares of our common stock are not eligible as yet for trading on any national securities exchange. Our common stock may be quoted in the over-the-counter market on the OTC Bulletin Board. These markets are highly illiquid. Although we intend to apply for listing of our common stock on an exchange, there can be no assurance if and when the initial listing criteria could be met or if such application would be granted, or that the trading of the common stock will be sustained. There is no assurance that an active trading market in our common stock will develop, or if such a market develops, that it will be sustained. In addition, there is a greater chance for market volatility for securities that are quoted on the OTC Bulletin Board as opposed to securities that trade on a national exchange. This volatility may be caused by a variety of factors, including the lack of readily available quotations, the absence of consistent administrative supervision of “bid” and “ask” quotations and generally lower trading volume. As a result, an investor may find it more difficult to dispose of, or to obtain accurate quotations as to the market value of, the common stock, or to obtain coverage for significant news events concerning us, and the common stock would become substantially less attractive for margin loans, for investment by financial institutions, as consideration in future capital raising transactions or other purposes. If our common stock is not quoted on the OTC Bulletin Board, we will have no right to cause Southridge to purchase our common stock under the Equity Credit Agreement.
Because the Company became public by means of a share exchange, we may not be able to attract the attention of major brokerage firms. There may be risks associated with our becoming public through a share exchange. Securities analysts of major brokerage firms may not provide coverage of us because there is no incentive to brokerage firms to recommend the purchase of our common stock. No assurance can be given that brokerage firms will, in the future, want to conduct any secondary offerings on our behalf.
Future sales of shares of our common stock by our shareholders could cause our stock price to decline. We cannot predict the effect, if any, that market sales of shares of our common stock or the availability of shares of common stock for sale will have on the market price prevailing from time to time. If our stockholders sell substantial amounts of our common stock in the public market upon the effectiveness of a registration statement, or upon the expiration of any holding period under Rule 144, such sales could create a circumstance commonly referred to as an “overhang” and in anticipation of which the market price of our common stock could fall. The existence of an overhang, whether or not sales have occurred or are occurring, also could make more difficult our ability to raise additional financing through the sale of equity or equity-related securities in the future at a time and price that we deem reasonable or appropriate. Our outstanding shares of common stock will be freely tradable upon the earlier of (i) effectiveness of a registration statement covering such shares; and (ii) the date on which such shares may be sold without registration pursuant to Rule 144 under the Securities Act and the sale of such shares could have a negative impact on the price of our common stock.
We may issue additional shares of our capital stock or debt securities to raise capital or complete acquisitions, which would reduce the equity interest of our shareholders. Our articles of incorporation authorize the issuance of up to 100,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $.00001 per share, and up to 100,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $.00001 per share. There are approximately 90,141,091 authorized and unissued shares of our common stock and 100,000,000 shares of our preferred stock that have not been reserved and are available for future issuance. Although we have no commitments as of the date of this offering to issue our securities, we may issue a substantial number of additional shares of our common stock, to complete a business combination or to raise capital. The issuance of additional shares of our common stock:
|
·
|
may significantly reduce the equity interest of our existing shareholders; and
|
|
·
|
may adversely affect prevailing market price for our common stock.
|
We currently do not intend to pay dividends on our common stock and, consequently, your only opportunity to achieve a return on your investment is if the price of our common stock appreciates. We do not expect to pay dividends on shares of our common stock in the foreseeable future. In addition, because we are a holding company, our ability to pay cash dividends on shares of our common stock may be limited by restrictions on our ability to obtain sufficient funds through dividends from our subsidiaries. Subject to these restrictions, the payment of cash dividends in the future, if any, will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend upon such factors as earnings levels, capital requirements, our overall financial condition and any other factors deemed relevant by our Board of Directors. Consequently, your only opportunity to achieve a return on your investment in the Company will be if the market price of our common stock appreciates.
Risks Related to Acquisition of Chinese Companies.
Under the agreement pursuant to which we acquired Hainan Jien, our continued ownership of such company will depend upon our ability to raise additional funds to contribute to Hainan Jien. We have agreed to contribute $2.5 million to Hainan Jien. It has agreed to extend the deadline for such contribution until June 30, 2010. Our ownership of the capital stock of Hainan Jien will not be registered in China and will not be recognized by the Chinese government or courts until such capital contribution is completed. In the event that we are unable to raise the funds necessary to make the contribution by that date, the original Chinese equity owners of Hainan Jien would have a claim for breach of the agreement. One remedy for such breach might be rescission of such agreement and the transfer of the ownership of such company back to the original Chinese owners, though the Company could negotiate a further extension of its original understanding, provided Hainan Jien agrees to such extension. In the event the original shareholders Hainan Jien are permitted to invoke such remedy, the Company would have no operating business and minimal assets.
China’s government and courts do not recognize the ownership of the stock of a Chinese company by a foreign corporation until the ownership of the stock is recorded on the records of the applicable government agency. If the Company has committed to make a capital contribution to a Chinese company or to take other actions in connection with the acquisition of an equity interest in such company, the Company may be unable to cause its ownership of the stock of such company to be registered as required by China law until such capital contribution or other actions have been completed. Traditionally, the shares of stock or other equity interests in the Chinese company are held in trust for the benefit of the acquiring company until all of the acquiring company’s obligations under the acquisition agreements have been completed and the ownership of the shares by the acquiring company are registered with the government. As a result, the Company may not have the same ability to control the actions of any Chinese company that it acquires until all of the Company’s obligations under the acquisition agreements have been completed.
Risks attendant to acquisitions. The Company has acquired all of the outstanding equity interests in a Chinese company. Other Chinese companies will be sought as investment targets, and there is no limit as to the number of Chinese companies that we may acquire. Because the Company has yet to engage in any definitive negotiations with any such target companies, there is no available information regarding these companies. Acquisitions involve a number of special risks, including: failure of the acquired business to achieve expected results; diversion of management’s attention; failure to retain key personnel of the acquired business; the need by the acquired business to obtain additional financing which if necessary and available, could increase leverage, dilute equity, or both; the potential negative effect on the financial statements of the Company from the increase in goodwill and other intangibles; and the high cost and expenses of completing acquisitions and risks associated with unanticipated events or liabilities. These risks could have a material adverse effect on the business, results of operations and financial condition of the Company.
The Company expects to face competition for acquisition candidates, which may limit the number of opportunities to acquire companies and may lead to higher acquisition prices. The Company cannot assure investors that it will be able to identify, acquire, or manage profitably additional businesses or to integrate successfully any acquired businesses into its existing business without substantial costs, delays or other operational or financial difficulties. In addition, the Company may inadvertently assume unknown liabilities in acquisitions that it has completed or plans to complete. The Company’s assumption of unknown liabilities in acquisitions may harm the financial condition and operating results of the Company. Acquisitions may be structured in such a manner that would result in the assumption of unknown liabilities not disclosed by the seller or not discovered during pre-acquisition due diligence. These obligations and liabilities could harm the financial condition and operating results of the Company.
Market risks. An investor in a private equity transaction (such as the Company’s acquisition of the Chinese technology companies) generally determines the terms of the investment based upon financial projections for the target company. Projected operating results for such companies will normally be based primarily on judgments of the management of those companies. In all cases, projections are only estimates of future results based upon assumptions made at the time the projections are developed. There can be no assurance that the projected results will be obtained, and actual results may vary significantly from the projections. General economic conditions or other factors that are not predictable can have a material adverse impact on the reliability of projections. For any given investment, total loss of invested capital is possible.
Risks Related to the Organization and Operations of the Company.
Revenues of the Company. The Company is a holding company and does not conduct any business operations. The Company must rely on capital that it raises from the sale of stock and dividends paid by its Chinese subsidiaries to fund the Company’s operating expenses. Therefore, there can be no assurances that the Company will have the funds available to satisfy its obligations. We currently expect that the earnings and cash flow of our subsidiaries will primarily be retained and used by us in their operations. Therefore, it is unlikely that the Company will declare or pay cash dividends or make distributions to our shareholders. See “Risks Related to our Securities—We currently do not intend to pay dividends on our common stock, and, consequently, your only opportunity to achieve a return on your investment is if the price of our common stock appreciates.”
This prospectus contains forward-looking statements that reflect our current expectations and views of future events. The forward looking statements are contained principally in the sections entitled “Prospectus Summary,” “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and “Business.” Known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors, including those listed under “Risk Factors,” may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from those expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements.
You can identify some of these forward-looking statements by words or phrases such as “may,” “will,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “aim,” “estimate,” “intend,” “plan,” “believe,” “is/are likely to,” “potential,” “continue” or other similar expressions. We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about future events and financial trends that we believe may affect our financial condition, results of operations, business strategy and financial needs. These forward-looking statements include statements relating to:
|
·
|
our goals and strategies;
|
|
·
|
our expansion plans;
|
|
·
|
our future business development, financial conditions and results of operations;
|
|
·
|
our expectations regarding demand for our products;
|
|
·
|
our expectations regarding keeping and strengthening our relationships with key customers;
|
|
·
|
our ability to stay abreast of market trends and technological advances;
|
|
·
|
our ability to effectively protect our intellectual property rights and not infringe on the intellectual property rights of others;
|
|
·
|
our ability to attract and retain quality employees;
|
|
·
|
our ability to pursue strategic acquisitions and alliances;
|
|
·
|
competition within our operating subsidiaries’ industries in China;
|
|
·
|
general economic and business conditions in the regions in which we sell our products;
|
|
·
|
relevant government policies and regulations relating to our holding company and operating subsidiaries’ industries; and
|
|
·
|
market acceptance of our products.
|
These forward-looking statements involve various risks and uncertainties. Although we believe that our expectations expressed in these forward-looking statements are reasonable, our expectations may later be found to be incorrect. Our actual results could be materially different from our expectations. Important risks and factors that could cause our actual results to be materially different from our expectations are generally set forth in “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” “Business,” and other sections in this prospectus. You should read thoroughly this prospectus and the documents that we refer to with the understanding that our actual future results may be materially different from and worse than what we expect. We qualify all of our forward-looking statements by these cautionary statements. Other sections of this prospectus include additional factors which could adversely impact our business and financial performance.
This prospectus contains statistical data that we obtained from various publicly available private resources and government publications. Statistical data in these publications also include projections based on a number of assumptions. The market for surveillance and/or software integration services may not grow at the rate projected by market data, or at all. The failure of this market to grow at the projected rate may have a material adverse effect on our business and the market price of our securities. Furthermore, if any one or more of the assumptions underlying the market data is later found to be incorrect, actual results may differ from the projections based on these assumptions. You should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements.
Unless otherwise indicated, information in this prospectus concerning economic conditions and our industry is based on information from independent industry analysts and publications, as well as our estimates. Except where otherwise noted, our estimates are derived from publicly available information released by third party sources, as well as data from our internal research, and are based on such data and our knowledge of our industry, which we believe to be reasonable. None of the independent industry publication market data cited in this prospectus was prepared on our or our subsidiaries’ behalf.
The forward-looking statements made in this prospectus relate only to events or information as of the date on which the statements are made in this prospectus. Except as required by law, we undertake no obligation to update or revise publicly any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, after the date on which the statements are made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. You should read this prospectus and the documents that we refer to in this prospectus and have filed as exhibits to the registration statement, of which this prospectus is a part, completely and with the understanding that our actual future results may be materially different from what we expect.
Unless otherwise specified in the applicable prospectus supplement, we intend to use a portion of the net proceeds from the sale of our securities offered by this prospectus to make the required capital contributions to Hainan Jien. Any additional net proceeds will be used for general corporate purposes, including, without limitation, the reduction or refinancing of debt or other corporate obligations, capital investment in targeted Chinese operating companies pursuant to our strategy described in “Our Business,” and general working capital needs.
As of the date of this prospectus, we cannot specify with certainty all of the particular uses for the net proceeds we will have upon completion of this offering. Accordingly, our management will have broad discretion in the application of net proceeds, if any.
Market Information
On February 3, 2010, our common stock became eligible for quotation on the OTC.BB under the symbol “CVGC.” The following table sets forth the range of the high and low bid prices per share of our common stock for each quarter (or portion thereof) beginning on February 3, 2010 and ending on June 24, 2010 as reported by the OTC Bulletin Board. These quotations represent inter-dealer prices, without retail mark-up, markdown, or commission and may not represent actual transactions.
|
High
|
Low
|
|||||||
|
First Quarter 2010 (January 1, 2010 – March 31, 2010)
|
$ | 2.70 | $ | 1.10 | ||||
|
Second Quarter (April 1, 2010 – June 24, 2010)
|
$ | 3.10 | $ | 2.25 | ||||
There is no established trading market for our common stock. As with most stocks that begin trading on the OTC.BB, it will take time for a significant active trading market in our common stock to develop. There can be no assurance that a significant active trading market in our common stock will develop, or if such a market develops, that it will be sustained.
Pursuant to the registration rights agreement that we entered into with Southridge, we have agreed to register under the Securities Act all of the shares of our common stock that we issue to Southridge under the Equity Credit Agreement. The number of shares that we issue to Southridge will depend upon the market price for our common stock at the various times that we elect to sell shares to Southridge under the Equity Credit Agreement and our capital needs. In addition, we have agreed to register under the Securities Act the shares issuable upon the exercise of the warrants to purchase 300,000 shares of our common stock that we have issued to Southridge.
As of June 24, 2010, there were 9,858,909 shares of our common stock outstanding.
Holders
As of June 24, 2010, there were 80 shareholders of record of our common stock. Because some of our shares of common stock are held in street or nominee name, it is believed that there are a substantial number of additional beneficial owners of our common stock.
Dividend Policy
We have not paid any cash dividends on our common stock to date, and we have no intention of paying cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Whether we will declare and pay dividends in the future will be determined by our board of directors at their discretion, subject to certain limitations imposed under Nevada corporate law. In addition, our ability to pay dividends may be affected by the foreign exchange controls in China. See “RISK FACTORS—Risks Relating to Doing Business in China—Restrictions on currency exchange may limit our ability to receive and use our revenues effectively;” and “RISK FACTORS—Risks Related to Our Securities—We currently do not intend to pay dividends on our common stock, and, consequently, your only opportunity to achieve a return on your investment is if the price of our common stock appreciates.” The timing, amount and form of dividends, if any, will depend on, among other things, our results of operations, financial condition, cash requirements and other factors deemed relevant by our board of directors.
AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Safe Harbor Declaration
The comments made throughout this prospectus should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and the notes thereto, and other financial information appearing elsewhere in this document. In addition to historical information, the following discussion and other parts of this document contain certain forward-looking information. When used in this discussion, the words, “believes,” “anticipates,” “expects,” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Such statements are subject to certain risks and uncertainties, which could cause actual results to differ materially from projected results, due to a number of factors beyond our control. Covenant does not undertake to publicly update or revise any of its forward-looking statements, even if experience or future changes show that the indicated results or events will not be realized. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date hereof. Readers are also urged to carefully review and consider the various factors that affect the Company’s business that are described in this section and elsewhere in this prospectus.
Overview
We are a holding company primarily engaged in the business of acquiring equity interests in private companies based and operating in the PRC and providing these companies with support, including administrative, legal, accounting and marketing assistance, and an infusion of capital with the long term goal of preparing them to become public companies in their own right. We believe that equity investments in China present one of the most attractive global investment opportunities available in the coming four to seven years. We plan to focus on growth company acquisitions located in China.
We were incorporated in the State of Nevada on November 8, 2006 under the name Everest Resources Corp. as a development stage corporation that intended to engage in the exploration of gold. On December 24, 2009, we changed our name to Covenant Group of China Inc. and acquired all of the capital stock of Covenant Holdings, a privately held company incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware and engaged in the business of acquiring equity interests in private Chinese operating companies and providing these companies with strategic support. The acquisition of the capital stock of Covenant Holdings was accomplished on December 24, 2009, pursuant to the terms of a share exchange agreement by and among the Company, Covenant Holdings and all of the shareholders of Covenant Holdings. Upon the closing of the share exchange, each of the Covenant Holdings shareholders exchanged their respective shares of Covenant Holdings, on a one-for-one basis, for 9,380,909 shares of the Company’s common stock. As a result of the share exchange, Covenant Holdings became a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company.
Prior to our acquisition of Covenant Holdings, we were in the development stage and had minimal business operations. We had no interest in any property, but had the right to conduct mineral exploration activities on 471 acres located in southern British Columbia, Canada pursuant to an agreement with the former majority shareholder of the Company, Gary Sidhu. In connection with the acquisition of Covenant Holdings, Mr. Sidhu terminated the Company’s mineral exploration rights, and he agreed to surrender 5,000,000 shares of the Company’s common stock in exchange for $100,000 and a promissory note from the Company in the principal amount of $190,000, $90,000 of which the Company has prepaid. Mr. Sidhu surrendered 4,500,000 shares of our common stock and agreed to surrender his remaining 500,000 shares upon full payment of the promissory note by the Company. On March 25, 2010, Mr. Sidhu and the Company entered into an agreement pursuant to which Mr. Sidhu agreed to cancel the promissory note and surrender his remaining 500,000 shares in exchange for the Company issuing to him 300,000 shares of common stock of the Company. On May 13, 2010, Mr. Sidhu and the Company entered into an agreement pursuant to which Mr. Sidhu agreed to reduce the number of shares that he will receive from 300,000 to 70,000. See “Prospectus Summary” in this prospectus.
There was no significant activity from June 10, 2009 through December 31, 2009, except for the acquisitions of our two operating subsidiaries, Hainan Jien and Chongqing Sysway. On June 24, 2009, Covenant Holdings entered into a stock acquisition and reorganization agreement with Hainan Jien and its stockholders. Pursuant to the terms of this agreement, Covenant Holdings acquired 100% of the capital stock of Jien, representing 100% of the company’s outstanding equity interests, in exchange for 1,350,000 shares of a public shell’s common stock. For purposes of this acquisition, the common stock of the shell company that would acquire all of the rights and obligations of Covenant Holdings was valued at $1.76 per share, which was determined by the volume weighted average stock price for the first day of trading of the Company’s common stock plus all private sales of Covenant Holdings’ common stock prior to the completion of the reverse merger with the Company. Jien was incorporated in Hainan Province, China in 1999. Jien specializes in the design and installation of security and surveillance infrastructure to protect financial institutions and government agencies, and it also implements “intelligent construction” projects for commercial customers.
On June 24, 2009, Covenant Holdings entered into a stock acquisition and reorganization agreement with Chongqing Sysway and its stockholders. Pursuant to the terms of this agreement, Covenant Holdings acquired 100% of the capital stock of Sysway, representing 100% of the company’s outstanding equity interests, in exchange for 1,400,000 shares of a public shell’s common stock. For purposes of this acquisition, the common stock of the shell company that would acquire all of the rights and obligations of Covenant Holdings was valued at $1.76 per share, which was determined in the same manner as in the acquisition of Hainan Jien. Chongqing Sysway was incorporated in 1999 in Chongqing City, Sichuan Province, PRC, as a State Owned Enterprise (“SOE”). Since 2005 Chongqing Sysway has operated as a private enterprise mainly engaged in systems integration services, including computer systems installation, website design, and system firewall setup, particularly for the tobacco industry.
Under the stock acquisition and reorganization agreement between the Company and Hainan Jien, the Company has agreed to make a capital contribution of $2,500,000 to Hainan Jien by June 30, 2010. The Company is not relying on any of the proceeds from the sale of shares under the Equity Credit Agreement to provide the funding for the $2,500,000 that the Company is required to contribute to Hainan Jien by June 30, 2010. The Company intends to complete a private placement of convertible preferred stock by June 30, 2010 that will provide the Company with sufficient net proceeds to make the required capital contribution to Hainan Jien.
Rescission of our Acquisition of Chongqing Sysway
On April 30, 2010, the Board of Directors of the Company voted to terminate and rescind the stock acquisition and reorganization agreement with Chongqing Sysway due to several breaches of such agreement by Chongqing Sysway, including the failure of the prior owners of Chongqing to repay a dividend paid to them by Chongqing Sysway in excess of that permitted under the agreement and under China law and the failure of Chongqing Sysway and its prior owners to cooperate with the Company in the preparation of the financial statement disclosures required under United States securities laws.
As a result of the termination and rescission of the agreement, the Company has transferred all of the shares of capital stock of Chongqing Sysway to the prior owners of Chongqing Sysway and the 1,400,000 shares of common stock of the Company issued in exchange for the shares of capital stock of Chongqing Sysway have been returned to the Company and treated as treasury shares. The intent of this transaction is to return the Company, Chongqing Sysway, and the prior owners of the capital stock of Chongqing Sysway to their status prior to the completion of the acquisition by the Company of the capital stock of Chongqing Sysway on December 24, 2009.
Because the assets and liabilities Chongqing Sysway as of December 31, 2009 and March 31, 2009 and the results of operations of Chongqing Sysway for the periods then ended are included in the consolidated financial statements of the Company as of such dates and for such periods, this Managements Discussion and Analysis includes information relating to Chongqing Sysway as of such dates and for such periods. Anyone considering purchasing shares of the Company’s common stock should understand, however, that the Company no longer owns any interest in Chongqing Sysway.
Critical Accounting Policies
While our significant accounting policies are more fully described in Note 2 to our consolidated financial statements, we believe the following accounting policies are the most critical to aid you in fully understanding and evaluating this management discussion and analysis.
Basis of Presentation
The Company’s financial statements are prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“US GAAP”).
Principle of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Covenant Holdings, Hainan Jien, and Chongqing Sysway, but all intercompany transactions and account balances are eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates
In preparing the financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, management makes estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the dates of the financial statements, as well as the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting year. Significant estimates, required by management, include the recoverability of long-lived assets and the valuation of inventories. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Accounts Receivable and Retentions Receivable
The Company’s policy is to maintain reserves for potential credit losses on accounts receivable. Management reviews the composition of accounts receivable and analyzes historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customer payment patterns to evaluate the adequacy of these reserves. We have retentions receivable for product quality assurance; our retention rate varies from 3% to 5% of the sales price with variable terms from 1 year to 3 years.
Inventories
Jien’s inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market with cost determined on a first in, first out basis. Chongqing Sysway’s inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market with cost determined on a Specific Identification Method.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred; additions, renewals and betterments are capitalized. When property and equipment are retired or otherwise disposed of, the related cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from the respective accounts, and any gain or loss is included in operations. Depreciation of property and equipment is provided using the straight-line method for substantially all assets with 5% salvage value and estimated lives ranging from 3 to 25 years as follows:
|
Buildings
|
20-25 years
|
|
Leasehold improvements
|
Shorter of lease term or 10 years
|
|
Vehicles
|
5-10 years
|
|
Office Equipment
|
3-5 years
|
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the fair value of the consideration transferred over the net of the acquisition date amount of identifiable assets acquired and the liability assumed. In accordance with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 142, Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets (“Statement No. 142”), codified in Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 350, goodwill is not amortized but is tested for impairment annually, or when circumstances indicate a possible impairment may exist. Impairment testing is performed at a reporting unit level. An impairment loss generally would be recognized when the carrying amount of the reporting unit exceeds the fair value of the reporting unit, with the fair value of the reporting unit determined using a discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis. A number of significant assumptions and estimates are involved in the application of the DCF analysis to forecast operating cash flows, including the discount rate, the internal rate of return, and projections of realizations and costs to produce. Management considers historical experience and all available information at the time the fair values of its reporting units are estimated.
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s revenue recognition policies are in compliance with Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Staff Accounting Bulletin (SAB) 104 (codified in FASB ASC Topic 480). Revenue is recognized at the date of shipment to customers when a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and collectability is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are recorded as unearned revenue.
The Company records its revenue when certain milestones as defined in the service contract are reached. These service contracts have clear milestones and deliverables with distinct values assigned to each milestone. The milestones do not require the delivery of multiple elements as noted in Emerging Issues Task Force (EITF) Issue 00-21 “Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables” (EITF No. 00-21) (codified in FASB ASC Topic 605). In accordance with SAB No. 104, the Company treats each milestone as an individual revenue agreement and only recognizes revenue for each milestone when all the conditions of SAB 104 defined earlier are met.
Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of products and services, net of value-added tax (“VAT”). All of Chongqing Sysway’s products and services that are sold and provided in the PRC are subject to a Chinese VAT of 17% of the gross sales price. This VAT may be offset by any VAT paid by the company on raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing their finished product. Chongqing Sysway recorded VAT payable and VAT receivable net of payments in the financial statements. The VAT tax return is filed offsetting the payables against the receivables.
Hainan Jien is qualified as a small business so that all of its products sold or services provided in the PRC are subject to a fixed VAT rate of 4% of the gross sales price regardless of the VAT paid. Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of goods or services, net of VAT. This VAT cannot be offset by any VAT paid by Hainan Jien on raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing their finished products.
The standard warranty of Hainan Jien is provided to its customers and is not considered an additional service; rather it is considered an integral part of the product and services’ sale. Hainan Jien believes that the existence of its standard product warranty in a sales contract does not constitute a deliverable in the arrangement and thus there is no need to apply the EITF No. 00-21 separation and allocation model for a multiple deliverable arrangement. SFAS No. 5 specifically addresses the accounting for standard warranties, and neither SAB No. 104 nor EITF No. 00-21 supersedes SFAS No. 5 (codified in FASB ASC Topic Warranty). The Company believes that accounting for its standard warranty pursuant to SFAS No. 5 does not impact revenue recognition because the cost of honoring the warranty can be reliably estimated.
Chongqing Sysway provides post-contract support (PCS). Maintenance revenues from ongoing customer support services are billed on an annual basis with the revenue being deferred and recognized ratably over the maintenance period. Chongqing Sysway does not charge for PCS services separately for the first year from the date the product is sold. The Company believes that this type of PCS does not have to be accounted for as a separate unit in accordance with guidance provided by AICPA Statement of Position (SOP) 97-2 (codified in FASB ASC Topic 985).
Cost of Revenue
Cost of goods sold consists primarily of material costs, labor costs, and related overhead which are directly attributable to the production of the service. Write-down of inventory to lower of cost or market is also recorded in cost of goods sold.
Foreign Currency Translation and Transactions and Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The accompanying consolidated financial statements are presented in United States Dollars (“USD”). The Company’s functional currency is the USD, while the Company’s wholly-owned Chinese subsidiaries’ functional currency is the Renminbi (“RMB”). The functional currencies of the Company’s foreign operations are translated into USD for balance sheet accounts using the current exchange rates in effect as of the balance sheet date and for revenue and expense accounts using the weighted-average exchange rate during the fiscal year. The translation adjustments are recorded as a separate component of stockholders’ equity, captioned accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). Gains and losses resulting from transactions denominated in foreign currencies are included in other income (expense) in the consolidated statements of operations. There have been no significant fluctuations in the exchange rate for the conversion of RMB to USD after the balance sheet date.
We use SFAS No. 130, “Reporting Comprehensive Income” (codified in FASB ASC Topic 220). Comprehensive income is comprised of net income and all changes to the statements of stockholders’ equity, except those due to investments by stockholders, changes in paid-in capital and distributions to stockholders. Comprehensive income for the period ended September 30, 2009 included net income and foreign currency translation adjustments.
Segment Reporting
SFAS No. 131, “Disclosures about Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information” (codified in FASB ASC Topic 280), requires use of the “management approach” model for segment reporting. The management approach model is based on the way a company’s management organizes segments within the company for making operating decisions and assessing performance. Reportable segments are based on products and services, geography, legal structure, management structure, or any other manner in which management disaggregates a company.
SFAS 131 has no effect on the Company’s financial statements as substantially all of the Company’s operations are conducted in one industry segment. The Company consists of one reportable business segment. All of the Company’s assets are located in the PRC.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
For the three months ended March 31, 2010 and the comparative period of 2009
The following table presents the actual consolidated results of operations of Covenant Group of China for the three months ended March 31, 2010 as compared to the pro forma consolidated results of operations of Covenant Group of China for the period from January 1, 2009 through March 31, 2009 as if the acquisition of JIEN occurred on January 1, 2009, indicated as a percentage of net sales.
|
For Three Months Ended March 31,
|
||||||||||
|
2010
|
2009 (Pro Forma)
|
|||||||||
|
|
$ |
% of Sales
|
|
$ |
% of Sales
|
|||||
| Sales |
1,425,941
|
2,028,041
|
||||||||
|
Cost of sales
|
1,006,965
|
71%
|
1,575,432
|
78%
|
||||||
|
Gross Profit
|
418,976
|
29%
|
452,609
|
22%
|
||||||
|
Operating Expenses
|
260,416
|
18%
|
144,529
|
7%
|
||||||
|
Income from Operations
|
158,560
|
11%
|
308,080
|
15%
|
||||||
|
Other Income (Expenses), net
|
(432,262)
|
(30)%
|
(1,302)
|
0%
|
||||||
|
Net Loss
|
(273,702)
|
(19)%
|
306,778
|
15%
|
||||||
NET REVENUES
Net revenues for the three months ended March 31, 2010 were $1,425,941, as compared to net revenues of $2,028,041 for the comparative period of 2009, a decrease of $602,100, or approximately 30%. This decrease was mainly attributed to Jien obtaining several large projects for government agencies in the beginning of 2009, such as Rural Credit Cooperative Branches Supervisory Control System and Hainan Province Medical School. We believe the recovery of the Chinese economy through the central government’s effective economic stimulation programs creates an active environment for Jien’s business, which we predict, combined with the strengthening of Jien’s own sales force, will bring Jien more new projects throughout 2010 despite the decrease in sales for the first quarter of 2010.
COST OF REVENUES
Cost of revenue includes material costs, labor costs, and related overhead, which are directly attributable to our provided services. For the three months ended March 31, 2010, cost of revenues amounted to $1,006,965, or approximately 71% of net revenues, as compared to cost of revenues of $1,575,432, or approximately 78% of net revenues for the comparative period of 2009.
The decrease in cost of revenue as a percentage to net revenue was attributed to the effective control of cost of equipment and other materials purchased to complete contracts and overhead cost by our subsidiaries’ management. The cost of each project varies based on the nature of each project.
GROSS PROFIT
Gross profit for the three months ended March 31, 2010 was $418,976, as compared to $452,609 for the comparative period of year 2009, a decrease of $33,633 or approximately 7%. Gross profit margin was 29% for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and 22% for the comparative period of 2009. This increase in gross profit margin was due to some government projects generated in the first quarter of 2010, which usually have relatively higher profit margins, as well as successful negotiations with customers on contact price and related terms.
OPERATING EXPENSES
Operating expenses consisted of selling, general and administrative expenses totaling $260,416 for the three months ended March 31, 2010, compared to $144,529 for the comparative period of 2009, an increase of $115,887 or 80%. The increase in operating expenses was primarily due to increased expenses in audit, legal, and consulting fees arising from the Company being a public company in 2010 as a result of the reverse merger at the end of 2009.
The operating expense for Jien was approximately $82,039 for the quarter ended March 31, 2010, as compared to $144,529 for the same period of 2009, a decrease of $62,490 or 43%. This decrease was mainly attributed to the efficient control of costs and expenses by Jien’s management, as well as the decreased tax rate on net sales from 3% in 2009 to 1.76% in 2010.
NET INCOME
For the three months ended March 31, 2010, the Company realized a net loss of $273,702 as compared to net income of $306,778 for the comparative period of 2009, a decrease of $580,480, or approximately 189%. This decrease in net income was mainly due to a one-time, non-cash expense of $428,000 resulting from the settlement of a note payable to one of the Company’s shareholders in exchange for the issuance of 300,000 shares of the Company’s common stock.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
For the Three Months Ended March 31, 2010 and the comparative period of 2009
As of March 31, 2010, we had cash and cash equivalents of $1,273,928, of which the Company directly held $25,209, Covenant Holdings held $303, Pandaz Delaware held $5,570 and Jien held $1,242,666. Other current assets were $2,233,561 and current liabilities were $1,672,237. Total working capital was $1,835,252 at March 31, 2010, and the ratio of current assets to current liabilities was 2.1:1.
The following table presents the actual summary of cash provided by or used in each of the indicated types of activities of Covenant Group of China for the three months ended March 31, 2010 as compared to the pro forma summary of cash provided by or used in each of the indicated types of activities of Covenant Group of China for the three months ended March 31, 2009 as if the acquisition of Jien occurred on January 1, 2009.
|
2010
|
(Pro Forma)
2009
|
|||||||
|
Cash provided by (used in):
|
||||||||
|
Operating Activities
|
$
|
112,993
|
$
|
310,684
|
||||
|
Investing Activities
|
(32,848)
|
-
|
||||||
|
Financing Activities
|
224,260
|
-
|
||||||
Net cash flow generated by operating activities was $112,993 during the three months ended March 31, 2010, as compared to net cash flow provided by operating activities of $310,684 for the comparative period of 2009. The decrease in net cash flow generated by operating activities during the three months ended March 31, 2010 was mainly due to decreased net income and decreased accounts payable outstanding, which was partially offset by the quick repayment of accounts receivable.
Net cash flow used in investing activities was $32,848 in the three months ended March 31, 2010, compared to net cash used in investing activities of $0 in the comparative period of 2009. The cash was used mainly for the acquisition of fixed assets.
Net cash flow provided by financing activities was $224,260 in the three months ended March 31, 2010 as compared to net cash provided by financing activities of $0 in the comparative period of 2009. The increased cash flow provided by financing activities is primarily due to a short-term bank loan received by Jien in the first quarter of 2010.
Over the next 12 to 18 months, the Company anticipates to engage in capital expenditures primarily through its subsidiary, Jien. Accordingly, Jien plans to utilize this capital to invest in expanding branch offices, to initiate an acquisition program, to purchase equipment to expand production and research and development, and for general working capital purposes. Total costs for these initiatives are projected to be $2 to $2.5 million. Direct capital expenditures by the Company at the holding company level are expected to be minimal and will involve primarily the purchase of computers and communications equipment. The anticipated sources of funding for all capital needs will be either through the sale of a series of convertible preferred stock of the Company, the sale of common stock under the Equity Credit Agreement or through the organic growth of Jien.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
On February 25, 2010, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2010-09 Subsequent Events Topic 855, “Amendments to Certain Recognition and Disclosure Requirements,” effective immediately. The amendments in the ASU remove the requirement for an SEC filer to disclose a date through which subsequent events have been evaluated in both issued and revised financial statements. Revised financial statements include financial statements revised as a result of either correction of an error or retrospective application of US GAAP. The FASB believes these amendments remove potential conflicts with the SEC’s literature. Subsequent events have been evaluated through the date the financial statements were issued.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have not entered into any other financial guarantees or other commitments to guarantee the payment obligations of any third parties. We have not entered into any derivative contracts that are indexed to our shares and classified as stockholder’s equity or that are not reflected in our consolidated financial statements. Furthermore, we do not have any retained or contingent interest in assets transferred to an unconsolidated entity that serves as credit, liquidity or market risk support to such entity. We do not have any variable interest in any unconsolidated entity that provides financing, liquidity, market risk or credit support to us or engages in leasing, hedging or research and development services with us.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Comparison of Six Months Ended December 31, 2009 and 2008
Hainan Jien
|
Six Months Ended
December 31, 2009
|
Six Months Ended
December 31, 2008
|
|||||||||||||||
| $ |
% of Sales
|
$ |
% of Sales
|
|||||||||||||
|
Sales
|
3,732,408 | 2,447,750 | ||||||||||||||
|
Cost of sales
|
2,938,921 | 79 | % | 1,774,608 | 72 | % | ||||||||||
|
Gross Profit
|
793,487 | 21 | % | 673,142 | 28 | % | ||||||||||
|
Operating Expenses
|
362,606 | 9 | % | 326,040 | 14 | % | ||||||||||
|
Income from Operations
|
430,881 | 12 | % | 347,102 | 14 | % | ||||||||||
|
Other Income, net
|
3,091 | 0 | % | 13,649 | 1 | % | ||||||||||
|
Income tax expense
|
- | - | - | - | ||||||||||||
|
Net Income
|
433,972 | 12 | % | 360,751 | 15 | % | ||||||||||
NET REVENUES
Net revenues for the six months ended December 31, 2009 were $3,732,408, as compared to net revenue of $2,447,750 for the comparative period of 2008, an increase of $1,284,658, or approximately 52%. This increase in revenue was due to the recovery of China economy as a result of effective central government’s economic stimulation programs, as well as strengthening in our own sales force, hiring more sales people and establishing a solid relationship with the government bureau, which enabled us to obtain two large contracts with Hainan Province Medical School.
COST OF REVENUES
Cost of revenue includes material costs, labor costs, and related overhead which are directly attributable to the production of the service. For the six months ended December 31, 2009, cost of revenues amounted to $2,938,921, or approximately 79% of net revenues, as compared to cost of revenues of $1,774,608, or approximately 72% of net revenues for the comparative period of 2008.
The increase in cost of revenue as a percentage of sales was due to tight budget control by customers, as we lowered our sales price on certain contracts in order to obtain more contracts. We believe our cost of revenues as a percentage of net revenue will decrease as the Chinese economy recovers.
GROSS PROFIT
Gross profit for the six months ended December 31, 2009 was $793,487, as compared to $673,142 for the comparative period of year 2008, an increase of $120,345 or approximately 18%. Gross profit margin was 21% for the six months ended December 31, 2009, and 28% for the comparative period of 2008. This decrease in gross profit margin was due to increased cost of revenues as described above.
OPERATING EXPENSES
Operating expenses consisting of selling, general and administrative expenses totaled $362,606 for the six months ended December 31, 2009, compared to $326,040 for the comparative period of 2008, an increase of $36,566 or 11%. The increase in operating expenses was mainly due to a proportional increase in payroll, insurance, and employee welfare and travel expenses with our increased sales and production.
NET INCOME
For the six months ended December 31, 2009, net income was $433,972 as compared to $360,751 for the comparative period of 2008, an increase of $73,221, or approximately 20%. This increase in net income was attributable to the growth in revenue. The decrease of net income as a percentage to net revenue from 15% for the six months ended December 31, 2008 to 12% for the six months ended December 31, 2009 was mainly due to increased project costs as a result of strict budget control by our customers. Despite this, we actually lowered our operating expenses as a percentage of net revenue for the six months ended December 31, 2009 to 9% as compared to 14% for the six months ended December 31, 2008. Our management believes that net income will continue to increase as we continue to increase our sales, offer better quality products and services and control our project costs.
Chongqing Sysway
|
Six Months Ended
December 31, 2009
|
Six Months Ended
December 31, 2008
|
|||||||||||||||
| $ |
% of Sales
|
$ |
% of Sales
|
|||||||||||||
|
Sales
|
2,795,522 | 3,287,207 | ||||||||||||||
|
Cost of sales
|
1,976,946 | 71 | % | 2,594,582 | 79 | % | ||||||||||
|
Gross Profit
|
818,576 | 29 | % | 692,625 | 21 | % | ||||||||||
|
Operating Expenses
|
382,200 | 13 | % | 375,357 | 11 | % | ||||||||||
|
Income from Operations
|
436,376 | 16 | % | 317,268 | 10 | % | ||||||||||
|
Other Income, net
|
771 | 0 | % | 10,670 | 0 | % | ||||||||||
|
Income tax expense
|
113,094 | 4 | % | 97,365 | 3 | % | ||||||||||
|
Net Income
|
324,053 | 12 | % | 230,573 | 7 | % | ||||||||||
NET REVENUES
Net revenues for the six months ended December 31, 2009 were $2,795,522, as compared to net revenue of $3,287,207 for the comparative period of 2008, a decrease of $491,685, or approximately 15%. This decrease in revenue was mainly attributable to obtaining several large projects in 2008; while in the same period of 2009 we obtained fewer contracts due to an overall slowing in our industry in the regions that we serve.
COST OF REVENUES
Cost of revenue includes material costs, labor costs, and related overhead which are directly attributable to the production of the service. For the six months ended December 31, 2009, cost of revenues amounted to $1,976,946, or approximately 71% of net revenues, as compared to cost of revenues of $2,594,582, or approximately 79% of net revenues for the comparative period of 2008.
The decrease in cost of revenue as percentage of sales is attributable to effective control by management of material costs.
GROSS PROFIT
Gross profit for the six months ended December 31, 2009 was $818,576, as compared to $692,625 for the comparative period of year 2008, an increase of $125,951 or approximately 18%. Gross profit margin was 29% for the six months ended December 31, 2009, and 21% for the comparative period of 2008. This increase in gross profit margin was due to the increased revenue from software and technique supports, which usually have relatively higher profit margin, although we had less revenue for system installation for the six months ended December 31, 2009.
OPERATING EXPENSES
Operating expenses consisting of selling, general and administrative expenses totaled $$382,200 for the six months ended December 31, 2009, compared to $375,357 for the comparative period of 2008, an increase of $6,843 or 2%.
NET INCOME
For the six months ended December 31, 2009, net income was $324,053 as compared to $230,573 for the comparative period of 2008, an increase of $93,480, or approximately 41%. This increase in net income was attributable to economy of scale combined with growth of higher profit business on software and technique supports. Our management believes that net income will continue to increase as we continue to increase our sales, offer better quality products and services and control our project costs.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Comparison of Six Months Ended December 31, 2009 and 2008
Hainan Jien
The following is a summary of cash provided by or used in each of the indicated types of activities during the six months ended December 31, 2009 as compared to the six months ended December 31, 2008.
|
Six Months Ended
December 31, 2009
|
Six Months Ended
December 31, 2008
|
|||||||
|
Cash provided by (used in):
|
||||||||
|
Operating Activities
|
$ | 43,729 | $ | (54,199 | ) | |||
|
Investing Activities
|
- | (41,598 | ) | |||||
|
Financing Activities
|
5,563 | 2,194 | ||||||
Net cash flow generated by operating activities was $43,729 in the six months ended December 31, 2009, as compared to net cash flow used in operating activities of $54,199 for the comparative period of 2008. The increase in net cash flow generated in operating activities during 2009 was mainly due to increased net income and decreased account receivables and increased account payables during the operating period compared to the comparative period of 2008.
Net cash flow used in investing activities was $0 in the six months ended December 31, 2009, compared to net cash used in investing activities of $41,598 in the comparative period of 2008. Cash flow used in investing activities was mainly for the acquisition of fixed assets.
Net cash flow provided by financing activities was $5,563 in the six months ended December 31, 2009 as compared to net cash generated by financing activities of $2,194 in the comparative period of 2008. The increased cash flow provided by financing activities was primarily due to a short term loan.
Chongqing Sysway
The following is a summary of cash provided by or used in each of the indicated types of activities during the six months ended December 31, 2009 as compared to the six months ended December 31, 2008.
|
Six Months Ended
December 31, 2009
|
Six Months Ended
December 31, 2008
|
|||||||
|
Cash provided by (used in):
|
||||||||
|
Operating Activities
|
$ | 701,421 | $ | (30,448 | ) | |||
|
Investing Activities
|
(10,444 | ) | (6,389 | ) | ||||
|
Financing Activities
|
(322,108 | ) | - | |||||
Net cash flow generated by operating activities was $701,421 in the six months ended December 31, 2009, as compared to net cash flow used in operating activities of $30,448 for the comparative period of 2008. The increase in net cash flow generated in operating activities during 2009 was mainly due to increased net income, payment received for retention receivables, and less payment made for account payables during the operating period compared with the comparative period of 2008.
Net cash flow used in investing activities was $10,444 in the six months ended December 31, 2009, compared to net cash used in investing activities of $6,389 in the comparative period of 2008. Cash flow used in investing activities was mainly for the acquisition of fixed assets for $10,993, net of $549 proceeds from disposal of fixed assets.
Net cash flow used in financing activities was $322,108 in the six months ended December 31, 2009 as compared to net cash generated by financing activities of $0 in the comparative period of 2008. The increased cash flow used in financing activities was primarily due to $322,108 of cash dividend to certain shareholders, which later on has been determined as due from shareholders and to be paid back by these shareholders in March of 2010.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Year Ended December 31, 2009 compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2008
Hainan Jien
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||||||||||
| $ |
% of Sales
|
$ |
% of Sales
|
|||||||||||||
|
Sales
|
6,758,243 | 5,554,357 | ||||||||||||||
|
Cost of sales
|
5,239,587 | 78 | % | 4,403,810 | 79 | % | ||||||||||
|
Gross Profit
|
1,518,656 | 22 | % | 1,150,547 | 21 | % | ||||||||||
|
Operating Expenses
|
592,105 | 9 | % | 489,260 | 9 | % | ||||||||||
|
Income from Operations
|
926,551 | 13 | % | 661,287 | 12 | % | ||||||||||
|
Other Income, net
|
(1,421 | ) | 0 | % | (3,849 | ) | 0 | % | ||||||||
|
Income tax expense
|
- | - | - | - | ||||||||||||
|
Net Income
|
925,130 | 13 | % | 657,438 | 12 | % | ||||||||||
NET REVENUES
Net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2009 were $6,758,243, as compared to net revenue of $5,554,357 for the year of 2008, an increase of $1,203,886, or approximately 22%. This increase in revenue was due to gradual recovery of the China economy as a result of the government’s effective economic stimulation policies, as well as strengthening of our own sales force and expanding our sales channels, which enabled us to obtain several major contracts from financial markets and a government agency.
COST OF REVENUES
Cost of revenue includes material costs, labor costs, and related overhead which are directly attributable to the production of the service. For the year ended December 31, 2009, cost of revenues amounted to $5,239,587 or approximately 78% of net revenues as compared to cost of revenues of $4,403,810, or approximately 79% of net revenues, in 2008.
The decrease in cost of revenues as a percentage of sales was attributable to effective management control of cost of materials and overhead costs. We purchased equipment and other materials from several primary suppliers, and we have purchase contracts with these suppliers in an effort to ensure a steady supply of equipment and other materials.
GROSS PROFIT
Gross profit for the year ended December 31, 2009 was $1,518,656, as compared to $1,150,547 for 2008, an increase of $368,109 or approximately 32%. Gross profit margin was 22% for 2009 and 21% for 2008. This increase in gross profit margin was due to increased revenue from several higher profit projects as a result of strengthening of our own sales force.
OPERATING EXPENSES
Operating expenses consisting of selling, general and administrative expenses totaled $592,105 for the year ended December 31, 2009, compared to $489,260 for 2008, an increase of $102,845 or 21%. The increase in operating expenses was primarily due to a one-time write-off of equipment installed on a project that was terminated prior to completion, an increase in the allowance for doubtful accounts, an increase in rental expense, an in crease in depreciation on leasehold renovations and an increase in the sales tax expense due to increases in Jien’s sales.
NET INCOME
For the year ended December 31, 2009, net income was $925,130 as compared to $657,438 for the year of 2008, an increase of $267,692, or approximately 41%. This increase in net income was attributable to economy of scale combined with growth in revenue and efficiency of operations. Our management believes that net income will continue to increase as we continue to increase our sales, offer better quality products and services and control our project costs.
Chongqing Sysway
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||||||||||
| $ |
% of Sales
|
$ |
% of Sales
|
|||||||||||||
|
Sales
|
5,132,554 | 4,924,438 | ||||||||||||||
|
Cost of sales
|
3,819,460 | 74 | % | 3,826,264 | 78 | % | ||||||||||
|
Gross Profit
|
1,313,094 | 26 | % | 1,098,174 | 22 | % | ||||||||||
|
Operating Expenses
|
665,894 | 13 | % | 645,944 | 13 | % | ||||||||||
|
Income from Operations
|
647,200 | 13 | % | 452,230 | 9 | % | ||||||||||
|
Other Income, net
|
653 | 0 | % | 195,749 | 4 | % | ||||||||||
|
Income tax expense
|
169,577 | 3 | % | 181,060 | 3 | % | ||||||||||
|
Net Income
|
478,276 | 10 | % | 466,919 | 10 | % | ||||||||||
NET REVENUES
Net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2009 were $5,132,554, as compared to net revenue of $4,924,438 for 2008, an increase of $208,116, or approximately 4%. This increase in revenue was due to a gradual recovery of the economy as a result of the Chinese government’s effective economic stimulation policies, as well as strengthening of our own sales force.
COST OF REVENUES
Cost of revenue includes material costs, labor costs, and related overhead which are directly attributable to the production of services. For the year ended December 31, 2009, cost of revenues amounted to $3,819,460 or approximately 74% of net revenues as compared to cost of revenues of $3,826,264, or approximately 78% of net revenues in 2008.
The decrease in cost of revenues as a percentage of sales was attributable to effective management control of the cost of materials and overhead costs. We purchase equipment and related materials from several primary suppliers, and we have purchase contracts with these suppliers in an effort to ensure a steady supply of equipment and related materials.
GROSS PROFIT
Gross profit for the year ended December 31, 2009 was $1,313,094, as compared to $1,098,174 for 2008, an increase of $214,920 or approximately 20%. Gross profit margin was 26% for 2009 and 22% for 2008. This increase in gross profit margin was due to increased revenue from software and technique supports, which have relatively higher profit margin.
OPERATING EXPENSES
Operating expenses consisting of selling, general and administrative expenses totaled $665,894 for the year ended December 31, 2009, compared to $645,944 for 2008, an increase of $19,950 or 3%. The slight increase in operating expenses was primarily due to an increase in payroll and increased costs associated with obtaining CMMI certification, offset by a reduction in research and development costs incurred in 2008 that were not incurred in 2009.
NET INCOME
For the year ended December 31, 2009, net income was $478,276 as compared to $466,918 for 2008, an increase of $11,358, or approximately 2%. This slight increase in net income was mainly due to increased sales and efficiency on cost and expenses control.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Year Ended December 31, 2009 Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2008
Hainan Jien
The following is a summary of cash provided by or used in each of the indicated types of activities during the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008:
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Cash provided by (used in):
|
||||||||
|
Operating Activities
|
$ | 654,054 | $ | (177,704 | ) | |||
|
Investing Activities
|
- | (59,858 | ) | |||||
|
Financing Activities
|
37,623 | (1,200 | ) | |||||
Net cash flow generated by operating activities was $654,054 in 2009, as compared to net cash flow used in operating activities of $177,704 in 2008. The increase in net cash flow generated by operating activities during 2009 was mainly due to increases in net income and customer deposits, less payment on certain prepaid expenses and other payables during the period, as well as an increase in accounts payables as a result of the better utilization of trade credits, partially offset by the increase in accounts receivable as a result of increased sales.
Net cash flow used in investing activities was $0 in 2009, compared to net cash used in investing activities of $59,858 in 2008. The cash used in investing activities was for the purchase of fixed assets.
Net cash flow provided by financing activities was $37,623 in 2009 as compared to net cash used in financing activities of $1,200 in 2008. The increased cash flow from financing activities in 2009 was primarily provided by the proceeds from a bank loan.
Chongqing Sysway
The following is a summary of cash provided by or used in each of the indicated types of activities during the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008:
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Cash provided by (used in):
|
||||||||
|
Operating Activities
|
$ | 702,166 | $ | (476,069 | ) | |||
|
Investing Activities
|
(15,794 | ) | (18,374 | ) | ||||
|
Financing Activities
|
(322,061 | ) | (129,952 | ) | ||||
Net cash flow generated by operating activities was $702,166 in 2009, as compared to net cash flow used in operating activities of $476,070 in 2008. The increase in net cash flow generated by operating activities during 2009 was mainly due to an increase in accounts payable as a result of the better utilization of trade credits, partially offset by the increase in accounts receivable as a result of increased sales.
Net cash flow used in investing activities was $15,794 in 2009, compared to net cash used in investing activities of $18,374 in 2008. The cash used in investing activities was for the purchase of fixed assets.
Net cash flow used in financing activities was $322,061 in 2009 as compared to net cash used in financing activities of $129,951 in 2008. The increased cash flow used in financing activities in 2009 was primarily due to a $322,061 cash dividend paid to certain shareholders of Chongqing Sysway. Net cash used in financing activities in 2008 was mainly attributable to the repayment of a short term loan.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In August 2009, the FASB issued an Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) regarding measuring liabilities at fair value. This ASU provides additional guidance clarifying the measurement of liabilities at fair value in circumstances in which a quoted price in an active market for the identical liability is not available; under those circumstances, a reporting entity is required to measure fair value using one or more of valuation techniques, as defined. This ASU is effective for the first reporting period, including interim periods, beginning after the issuance of this ASU. The adoption of this ASU did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
On June 10, 2009, the Company adopted Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2009-01, “Topic 105 - Generally Accepted Accounting Principles - amendments based on Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 168 , “The FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ and the Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles” (“ASU No. 2009-01”). ASU No. 2009-01 re-defines authoritative GAAP for nongovernmental entities to be only comprised of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ (“Codification”) and, for SEC registrants, guidance issued by the SEC. The Codification is a reorganization and compilation of all then-existing authoritative GAAP for nongovernmental entities, except for guidance issued by the SEC. The Codification is amended to effect non-SEC changes to authoritative GAAP. Adoption of ASU No. 2009-01 only changed the referencing convention of GAAP in Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In May 2009, the FASB issued SFAS No. 165, “Subsequent Events” (“SFAS 165”) codified in FASB ASC Topic 855-10-05, which provides guidance to establish general standards of accounting for and disclosures of events that occur after the balance sheet date but before financial statements are issued or are available to be issued. SFAS 165 also requires entities to disclose the date through which subsequent events were evaluated as well as the rationale for why that date was selected. SFAS 165 is effective for interim and annual periods ending after June 15, 2009, and accordingly, the Company adopted this pronouncement during the second quarter of 2009. SFAS 165 requires that public entities evaluate subsequent events through the date that the financial statements are issued.
In April 2009, the FASB issued FSP No. SFAS 107-1 and APB 28-1, “Interim Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments,” which is codified in FASB ASC Topic 825-10-50. This FSP essentially expands the disclosure about fair value of financial instruments that were previously required only annually to also be required for interim period reporting. In addition, the FSP requires certain additional disclosures regarding the methods and significant assumptions used to estimate the fair value of financial instruments. These additional disclosures are required beginning with the quarter ending June 30, 2009. This FSP had no material impact on the Company’s financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
FASB ASC 820-10 establishes a framework for measuring fair value and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. The changes to current practice resulting from the application of this standard relate to the definition of fair value, the methods used to measure fair value, and the expanded disclosures about fair value measurements. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007; however, it provides a one-year deferral of the effective date for non-financial assets and non-financial liabilities, except those that are recognized or disclosed in the financial statements at fair value at least annually. The Company adopted this standard for financial assets and financial liabilities and nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities disclosed or recognized at fair value on a recurring basis (at least annually) as of June 10, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on its financial statements.
FASB ASC 820-10 provides additional guidance for Fair Value Measurements when the volume and level of activity for the asset or liability has significantly decreased. This standard is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on its financial statements.
FASB ASC 805 establishes principles and requirements for how an acquirer recognizes and measures in its financial statements the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree and the goodwill acquired. This standard also establishes disclosure requirements to enable the evaluation of the nature and financial effects of the business combination. This standard was adopted by the Company beginning June 10, 2009 and will change the accounting for business combinations on a prospective basis.
FASB ASC 350-30 and 275-10 amend the factors that should be considered in developing renewal or extension assumptions used to determine the useful life of a recognized intangible asset. This standard is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is prohibited. The adoption of this standard did not have any impact on the Company’s financial statements.
FASB ASC 825-10 requires disclosures about the fair value of financial instruments for interim reporting periods. This standard is effective for interim reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
FASB ASC 320-10 amends the other-than-temporary impairment guidance for debt and equity securities. This standard is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on its financial statements.
As of December 31, 2009, the FASB has issued Accounting Standards Updates (ASU) through No. 2009-17. None of the ASUs have had an impact on the Company’s financial statements.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted
As of December 31, 2009, there are no recently issued accounting standards not yet adopted which would have a material effect on the Company’s financial statements.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have not entered into any other financial guarantees or other commitments to guarantee the payment obligations of any third parties. We have not entered into any derivative contracts that are indexed to our shares and classified as stockholder’s equity or that are not reflected in our consolidated financial statements. Furthermore, we do not have any retained or contingent interest in assets transferred to an unconsolidated entity that serves as credit, liquidity or market risk support to such entity. We do not have any variable interest in any unconsolidated entity that provides financing, liquidity, market risk or credit support to us or engages in leasing, hedging or research and development services with us.
Overview
We are a holding company engaged in the business of acquiring equity interests in private companies based and operating in China and providing these companies with support, including administrative, legal, accounting and marketing assistance. We also plan to provide these companies with an infusion of capital with the long term goal of preparing them to become public companies in their own right. We believe that equity investments in China present one of the most attractive global investment opportunities available in the coming four to seven years. Accordingly, the Company plans to focus on growth company acquisitions located in China. The local Chinese equity markets are highly concentrated, serving only a small fraction of the local corporate market.
Our initial focus is on information technology (“IT”) companies that are well positioned to capitalize on opportunities created by the government’s new policies or which are serving industrial sectors that are a target of the government’s economic development policies. IT spending growth in emerging markets such as China is nearly double that of western economies, and IT is considered to be a major factor in promoting GDP growth, balancing economic development, expanding the business base and accelerating the growth of a consumer class. IT spending is expected to increase in China from $73.0 billion in 2008 to $127.0 billion in 2013. China Information Technology Report Q4 2009 (by Business Monitor International, as published on October 15, 2009 by www.marketresearch.com). Our initial portfolio acquisitions of Chongqing Sysway and Hainan Jien were in furtherance of this focus. Jien specializes in the design and installation of security and surveillance systems. We terminated our agreements with Chongqing Sysway and rescinded our acquisition of its capital stock on April 30, 2010. See “Prospectus Summary—Rescission of our Acquisition of Chongqing Sysway”.
As the Chinese government’s long-term economic plan is also focused on developing consumer consumption, we intend to selectively review potential investment opportunities in small-to-medium size Chinese enterprises (“SMEs”) in sectors beyond IT that will benefit from the impact of these economic policies and that fit our strategic objectives.
We are committed to employing a rigorous, targeted investment approach to the growth of the Company and our acquisition of operating companies in China. We do not intend to invest in Chinese development stage companies that lack proven technologies, market acceptance or a demonstrated business model. We will target companies where the technology risk is limited and there is a normal business risk of expansion and execution of a business plan. In most cases, target companies will have an established market presence and base of revenue with a management team committed to, and capable of, executing a successful growth strategy.
We believe that we are positioned to work with Chinese growth companies in gaining access to the U.S. capital markets while simultaneously assisting such enterprises with becoming public companies in their own right. Although the Company is not a private equity firm in the traditional sense, emergent trends in private equity investment in China indicate there is increasing demand for growth capital for companies in light of the Chinese government’s economic initiatives and the country’s rapidly expanding consumer base. Private equity investment in China is expected to boom in the next few years. Specifically, it is predicted that China should experience a 30% rise in such investment during the 2009-2011 period (China’s Private Equity Boom, by Shaun Rein, Business Week, July 16, 2008). As a basis for comparison, investors allocated $20.5 billion to China in 2008 compared to $5 billion invested in 2005. This surge, according to Business Week, is supported by four pillars: the growth of the Chinese middle class; the global competitiveness of Chinese firms; the tightening of credit for smaller Chinese firms; and the Chinese stock market. Nevertheless, the success of our business will primarily be characterized by the investment opportunity that China presents and the positioning of our portfolio companies to capitalize on such opportunity within their respective industries.
We were incorporated as Everest Resources Corp. on November 8, 2006 in Nevada. Since December 24, 2009, our principal place of business has been based in Pennsylvania. As a result of a share exchange transaction, we changed our name to Covenant Group of China Inc. on December 24, 2009.
Our Operating Subsidiaries
Chongqing Sysway
Chongqing Sysway is a developer of advanced information systems and collaboration software, and it is also a systems integrator for manufacturers in the Chinese tobacco industry. It operates in Sichuan province and the Chongqing Central region of China. Chongqing is the portal to the southwest region of China and a key city in the PRC government’s urbanization strategy.
On April 30, 2010, the Board of Directors of the Company voted to terminate and rescind the stock acquisition and reorganization agreement with Chongqing Sysway due to several breaches of such agreement by Chongqing, including the failure of the prior owners of Chongqing to repay a dividend paid to them by Chongqing in excess of that permitted under the agreement and under China law and the failure of Chongqing and its prior owners to cooperate with the Company in the preparation of the financial statement disclosures required under United States securities laws.
As a result of the termination and rescission of the agreement, the Company has transferred all of the shares of capital stock of Chongqing to the prior owners of Chongqing and the 1,400,000 shares of common stock of the Company issued in exchange for the shares of capital stock of Chongqing have been returned to the Company and treated as treasury shares. The intent of this transaction is to return the Company, Chongqing, and the prior owners of the capital stock of Chongqing to their status prior to the completion of the acquisition by the Company of the capital stock of Chongqing on December 24, 2009.
Hainan Jien
Hainan Jien is a hi-tech integrated firm based in Haikou City, Hainan Province and is engaged in professional intelligent construction (“IC”) for modernized buildings, installation of surveillance networks and the development and expansion of IT for enterprises. Jien provides surveillance and IC services to a variety of market sectors such as manufacturing, finance, securities, hotel, postal services, aviation, government, and residential. Its business currently focuses on providing the following services to its customers:
|
·
|
Installation of security and surveillance systems (such as monitoring systems, alarm systems, access management, one-card pass technology and visual intercom);
|
|
·
|
TV engineering (cable and satellite television and communal antennae applications);
|
|
·
|
BAS automation and self-control engineering;
|
|
·
|
Integrated wiring, IC and queuing systems;
|
|
·
|
Communication engineering (telephone, wireless intercom and computer network systems); and
|
|
·
|
Energy-saving city applications (installation of public lighting systems)
|
As mentioned, Hainan Jien is centrally involved in the implementation of IC projects for commercial customers. IC construction involves designing and building structures with an integrated technology plan, which includes equipment management automation systems, fire warning systems, communication systems, security systems, and business support systems. IC systems, combined with advanced building structures and internal and external operating systems, make the functionality of buildings more comfortable, safe and energy-efficient. Moreover, with Jien’s understanding of IC projects, it embraces the North American concept of “green buildings,” through its implementation of sophisticated communications, network and security systems. According to national statistics, in 2006, the IC market was reported to comprise $23 billion of the total $260 billion construction industry in China. During the first half 2008, China’s output value of construction hit $331.0 billion. In a survey of 1,400 construction companies, it was estimated that approximately 45% of these enterprises have implemented initiatives surrounding the development and expansion of IT, or “informatization.”
In 2005, China Security and Protection Magazine, published by The Ministry of Public Security of the PRC, ranked Hainan Jien as one of China’s top 100 security and surveillance enterprises. Since then, JIEN is one of only two companies in Hainan province that hold a 3111 Project Initiative Certification—the “Safe City” Certification issued by the China Security and Protection Industry Association—to participate in the government’s Safe City Projects. The 3111 Project is the initial phase of the Safe City Project, which is an ongoing nationwide initiative sponsored by the Ministry of Public Security to enhance general security in China’s cities, which includes the implementation of new surveillance cameras in high-traffic areas throughout a total of approximately 660 cities. These security systems will be integrated and networked together both regionally and nationally to ensure safety and security for citizens and to help deploy public services in the most timely and effective manner possible. Contracts for this project are typically a year or more in duration and are signed and paid for by both the national and local governments.
Looking to the future, China has a much broader ten-year program to deploy a system of high-tech surveillance and tracking known as “golden shield.” The goal of this program is to deploy a nation-wide system that will enable law enforcement to monitor all highways and streets. It is estimated that the internal-security market will reach $33 billion by 2010. The Left Coaster, Police State 2.0, http://www.theleftcoaster.com/archives/012630.php. Additionally, Hainan Jien is also regionally well positioned to benefit from future growth. Recently, the provincial government of Hainan Island announced a twenty-year construction development plan to build out Hainan as an “International Tourism Island” in accordance with the Chinese Central Government’s strategic vision. See Industry Overview—Hainan Jien.
Pandaz LLC
On January 13, 2010, the Company acquired the assets of a small technology company under a wholly owned subsidiary, Pandaz LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, in exchange for $25,000. The assets are intangible in nature and primarily consist of rights to trade names, domain names, and all object code and source code to operate an Internet site deploying automobile search capabilities for consumers. The Pandaz LLC technology is currently in the development stage, and the Company plans to further develop this technology and the Pandaz LLC business model tentatively for the Chinese consumer auto market.
Our Business Operations
Hainan Jien
Hainan Jien’s business operations can primarily be separated into two facets: project implementation and post-sale service. Project implementation begins with customer interviews by our marketing personnel to ascertain project information and customer demands. After Jien completes a full assessment of the customer’s needs, it then designs a project unique to our customer’s application. Typically, a bidding process results and upon the signing of a contract, Jien’s implementation team builds out the project at the customer’s facility.
Post-sale service primarily involves honoring warranty commitments pursuant to Hainan Jien’s contracts with its customers. The warranty period for work performed under its contracts is usually one to three years, which is consistent with industry standards. As part of the post-sale service process, Jien provides a toll-free number available to its customers for consultation with its specialists. Hainan Jien’s technical support is equipped to respond to both hardware and software malfunctions on both an emergency and normal basis. Depending on the proximity of the implementation site relative to its Haikou City headquarters, Jien has the capability to either provide an engineer onsite or provide the customer with long-distance support. Hainan Jien’s commitment to assisting its customers with any post-sale matters is a key component to its competitive strategy, given its business of introducing and implementing new IC and surveillance technologies to the China market.
Industry Overview
China, In General
The Chinese economy can largely be characterized by its continued growth despite the recent global economic slowdown. As the Chinese continue to execute on a long-term strategy to develop a planned, market-driven economy, the country’s output continues to increase, as evidenced by GDP growth of 8.7% for 2009, while such output is increasingly being utilized to service domestic demand. This fact can be largely illustrated by the growth of the middle class. The Chinese middle class has already reached at least 250 million people and is expected to be in excess of 600 million by 2015. We expect this growth in the middle class and its consequent consumer behavior to become a theme for some of our investment activities.
As part of the growth of the middle class, China has also witnessed a marked transition of its population from rural areas to urban areas. Today, the urban population of China is approximately 585 million and it is expected to grow by over 300 million within 15 years. There are 51 cities in China with a population over 1 million. In comparison, there are only 9 of such cities in the United States. This trend will likely generate growing demand for infrastructure, social services, transportation systems, environmental and pollution control, as well as demand for consumer products and services ranging from household appliances to entertainment.
In order to connect these large urban centers and assure the rapid and efficient movement of manufactured goods between cities and food and produce into the cities, there has resulted an unprecedented level of investment in transportation infrastructure. This development of the transportation infrastructure includes 5 main north-south super highways and 4 main east-west superhighways and will result in there being 85,000 km of highways in China by the end of 2010, which is 12% longer than the total length of the highways currently in the U.S. Rail projects include plans for 280 bullet trains connecting major population centers. Additionally, China’s domestic production of cars and trucks exceeded U.S. production in 2009 and is expected to reach 15 million units per year by 2012.
The Chinese economy is rapidly and fundamentally transforming itself and the country under the guidance and through the policies of the Chinese Communist Party and the Central Government. Their policies are in pursuit of long-term goals and are not reoriented or refocused in response to short-term issues. The policies themselves are based on the principle of having a “harmonious society” through developing the health and wealth of the people through “market socialism,” which entails policies to assure market stability and economic growth.
A recent example of such policymaking was evidenced by China’s fourth quarter 2008 economic stimulus plan of $586 billion (4 trillion RMB). While the stimulus plan facilitated growth during the global economic distress of 2009, its focus on internal investment, industrial output and consumption has permitted sustained growth even as the Central Government has implemented more conservative policies to relieve inflationary pressures. For example, for 2009:
|
·
|
China’s consumer spending has expanded 15.1% on a year-to-year basis (Source: NuWire Investor, China Set for Double Digit Growth in 2010, http://www.nuwireinvestor.com/articles/china-set-for-double-digit-growth-in-2010-54183.aspx);
|
|
·
|
Spending will increase by 50% in China’s top 25 cities in the next 5 years (Source: Proactive Investors UK, Latest Figures Spark Further Optimism in China’s Speedy Economic Recovery and Future Prospects, http://www.proactiveinvestors.co.uk/companies/news/9360/latest-figures-spark-further-optimism-in-chinas-speedy-economic-recovery-and-future-prospects-9360.html);
|
|
·
|
Fixed asset investment has increased 33.4% since January 2009 (Source: NuWire Investor, China Set for Double Digit Growth in 2010, http://www.nuwireinvestor.com/articles/china-set-for-double-digit-growth-in-2010-54183.aspx);
|
|
·
|
Industrial output increased 9.4% during the first 10 months of 2009 (Source: Westender, China Goes Shopping, http://www.westender.com.au/news/718);
|
|
·
|
Producer price index (PPI wholesale level) dropped 6.5% (Source: Xinhua News Agency, China’s CPI Falls 1.1% in First Nine Months, PPI down 6.5%, http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2009-10/22/content_12295654.htm);
|
|
·
|
Consumer price index (CPI) dropped 1.1% (Source: Xinhua News Agency, China’s CPI Falls 1.1% in First Nine Months, PPI down 6.5%, http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2009-10/22/content_12295654.htm).
|
In light of the foregoing, our strategy was also influenced by the following key macro topics:
|
·
|
China’s New Economic Policy. The hallmarks of China’s policy are to: (i) significantly increase spending and implement substantial tax cuts by reducing the value-added tax and adopting preferential tax policies for SMEs; (ii) increase bank liquidity and continue to reduce interest rates; (iii) implement comprehensive industrial restructuring and facilitate the merger and reorganization of enterprises; and (iv) promote innovation in science and technology.
|
|
·
|
Chinese Economy has Significant Reserves. China has a substantial $2.3 trillion in foreign exchange reserves, up from $1.96 trillion at January 1, 2009, to keep the economy at its currently planned 8% plus growth level. In addition, China maintains a significant 35% savings rate, resulting in approximately $3.0 trillion in individual bank savings.
|
|
·
|
Major International Market Participants are Investing in China. Warren Buffet, Jim Rogers, the John Templeton Fund, the Carlyle Group, Temasek Holdings, and Cargill are investing in China. Goldman Sachs, also an investor in China, estimates that China’s GDP growth will be 8.3% in 2009 and 10.5% in 2010. Goldman Sachs predicts that China will surpass the U.S. economy by 2027. Optimism about China stretches across a wide range of American investors.
|
|
·
|
Foreign Direct and Private Equity Investment. Foreign Direct investment increased 23.6% from 2007 to 2008 from $74.8 billion to $92.4 billion, though there were 10,357 less projects. China’s private equity market, according to Business Week, should register 30%-plus growth for the next three years, with 2009 targeted for $15.0 billion. China’s Private Equity Boom, by Shaun Rein, Business Week, July 16, 2008. The larger projects and large companies receive the majority of these investments. This market reality, together with the lack of bank loans for small non-government companies, work to create an opportunity for aggressive equity investing in selected SMEs. SMEs suffer from budget constraints and limited resources to hire qualified people. They typically do not have access to credit or adequate budgets for R&D purposes.
|
|
·
|
Current Chinese Regulatory Environment. The current attitude of Chinese regulators toward large financial transactions is one of caution as evidenced by the fact that the central government has stymied recent deals involving Goldman Sachs and The Carlyle Group. Consequently, new investment strategies, including bridge loans, private investment in public equity transactions and mezzanine financings, are being used in China by both international and local private equity funds, with local funds offering RMB-denominated funds.
|
Chinese IT Industry, In General
IT opportunities are abundant in China since the introduction of the PRC government’s adoption of the “scientific concept” policy model. This model features fostering domestic economic growth and social progress. Important to this initiative is the Chinese concept of “informationization,” which centers on the development and expansion of IT in China. Informationization, recognized as a key component of the Central Government’s national strategy, is the process whereby the Chinese government advocates and supports the movement of the country from an industrial-based society to a technical and information-based society. Presentation of Xiaofan Zhao, Director General for the Department of IT Application Promotion, State Counsel Informationization Office, PRC. Accordingly, the informationization concept includes plans for the development of e-commerce, e-government, electronic content management, security and industrial IT applications in China.
On a broader level, according to PRC officials during the 17th Party Congress held in October 2007, the Party will aggressively redefine its present economic policy of promoting external growth in export-driven businesses to a new model of expansion in domestic investment and consumption within China. This is part of a new five-year economic plan to move from a planned economy to a market driven economy and to become integrated into global market systems.
Consequently, China’s IT market is expected to exceed global expectations during 2009-2013, according to the China Information Technology Report Q4 2009 (by Business Monitor International, as published on October 15, 2009 by www.marketresearch.com). Growth in 2009 will remain in single digits due to overall economic growth. The Chinese stimulus program and the rural electronics subsidiary programs are expected to raise IT spending from $78.0 billion in 2009 to $124.0 billion by 2013. Computer sales are projected to move from $52.0 billion to $80.0 billion in 2013. Software sales increased from $8.8 billion in 2008 to almost $10.0 billion in 2009. IT services will reach $16.4 billion in 2009, and this sector is expected to achieve a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 135% between 2009 and 2013.
China’s Banking Regulatory Commission (CBRC) is compelling banks to emphasize mitigating IT risk. The nation’s commercial banks lag far behind international competitors, according to China Construction Bank, in the application of risk measures to limit regional credit risk, which expands market risks and operational risks, thereby jeopardizing domestic risk management as well as global risk management.
The Chinese capital market, which is the fourth largest in the world, currently lacks advanced risk management procedures, and the country’s retail brokerage business is plagued with inconsistencies. In the last three years, over twenty firms have been closed down as the CBRC imposed stricter supervision of the retail market. Consequently, the opportunity for domestically-developed IT-based transaction systems with full risk and security features will be in great demand as Chinese investors move into the global markets.
The Company recognizes the favorable operating conditions that are unfolding in the Chinese economy in a number of Chinese industries using advanced IT. In addition to the security and surveillance, tobacco, and financial services industries, there are great opportunities in the automotive, retail consumer, energy reduction, alternate fuel, and carbon emissions markets. All of these industries are heavily reliant on software and supported by the government through policy statements. Individual state-authorized committees implement such policies. The implementation process is expressly identified in five and ten year plans.
China, operating under its new scientific concept policy model, has established an economic structure that is highly favorable for investing in Chinese information technology companies. This is primarily due to the fact that this industry is characterized by a number of growth drivers, including the vast rural market, government spending and demand from the internet and communications industries. Consequently, informationization among SMEs is a government priority, as the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) has already invested over $743.0 million in 2008 and will add credit loans and guarantee credit to SMEs. Additionally, rapidly growing internet adoption across China and the demand for IT-enabled business solutions create the potential for a lucrative market for IT-security development.
Special Economic Zones
The PRC offers investors a complex system of incentives at the national, regional and local levels. Party members have great influence at the regional and local levels where they live, impacting regional business activities and seeking employment for locals. There are special economic zones, hundreds of development zones and designated inland cities that vie for foreign investment. One of our subsidiaries, Jien, is located in a special economic zone in Hainan, China, where there is access to a large high-tech employee pool. China also has numerous national science parks, many focused on commercializing technology research developed in Chinese universities. PRC policy is to encourage investors to fund the introduction, innovation and development of technology, and invest in technology intensive projects in order to promote and facilitate technology companies.
Government and Small Business IT Markets
Investment in technology solutions is growing at exponential rates in two areas of opportunity for the Company. One opportunity is the government, regional and local IT markets. The other is the large independent small business market (SMEs with 1,000 or less employees and less than $45.0 million in revenue). By the end of 2008, China’s 9.7 million SMEs accounted for 99% of the number of enterprises, 60% of the GDP and provided jobs for 80% of the urban population.
The market for IT is flourishing in the SME market. In this area, Chinese companies will invest $28 billion, excluding communications, through 2010, according to the China Center of Information Industry Development (CCID). In general, the SME market will invest more in high-end IT infrastructure and services, seeking to increase their competitive advantage.
The SMEs operating environment has been historically tougher than the larger government-invested companies because of a lack of financing. SMEs depend on commercial loans, which are difficult to obtain, and government subsidies to fund their expansion and are too small to list their companies on national exchanges to raise necessary capital. As result, China recently launched a new exchange called ChiNext for small companies to enhance economic growth and to increase employment.
China joined the World Trade Organization on November 26, 2001. Since then, China has removed or relaxed various restrictions on financial regulations. The China Ministry of Finance modified its banking regulation principles “to grant more operational freedom to financial institutions and to tighten up supervision of the financial situation.” Financial liberalization has accelerated the integration of the global financial system, stimulated the innovation of financial technology and products, and improved operational efficiency. However, due to the intense competition in the financial markets, various types of operational risks faced by financial institutions increased substantially. In order to realize comprehensive operational efficiency and improve and sustain competitiveness, financial institutions have to strengthen their operational soundness, identify and quantify various risks in advance, and establish and carry out an effective risk management system.
Hainan Jien
Hainan—International Tourism Island
On February 7, 2010, Hainan Province announced a comprehensive, twenty-year economic and social development plan to execute on the Chinese government’s strategic vision to develop the island of Hainan, the country’s major beach holiday destination, as an “International Tourism Island.” The central goal of this plan is to promote the balanced economic development of the island through urban and rural modernization and improving social welfare programs and infrastructure, while at all times assuring that these development efforts are pursued with care for the environment. A key element to the execution of this goal will be the utilization of modern and intelligent construction practices to realize the build-out of state-of-the-art road transport infrastructure, housing, leisure, education and medical facilities, as called for in the plan. In addition, the province is planning to construct a major rapid transit system linking the four main areas of the island and to invest 2.64 billion RMB ($386 million) in its power grid as part of these initiatives. Source: http://english.bitf.org.cn/node_516350.htm; http://english.bitf.org.cn/2010-02/11/content_3393203.htm.
Surveillance System Market
The electronic market research company, iSuppli Corporation, estimates that the Chinese security and surveillance equipment market will withstand the impact of the economic recession and make further expansion during and after 2009 due to investments by the Chinese government in the security and surveillance industry, as well as due to the expanding home security system business. iSuppli also forecasts that the Chinese security industry will reach $18.9 billion by the end of 2009, an increase of 7.5% over the $17.5 billion spent in 2008. As this market expands to its capacity of $26.5 billion by 2013, a CAGR of 8.6% is expected from 2008 to 2013.
Growth in this market has been, and continues to be, driven by:
|
·
|
increased demand for security and surveillance products within China by a new customer group composed of various smaller industries and organizations, such as residential estates, factories and shopping centers;
|
|
·
|
preparation for the 2010 World’s Expo in Shanghai by the PRC government: while the expenditure on security and surveillance during the 2008 Olympics reached $300 million, the expenditure on security and surveillance infrastructure for the 2010 World’s Expo in Shanghai is expected to reach $3.0 billion;
|
|
·
|
3111 Project, the “Safe City Project” (See page 49 for a further discussion of the Safe City Project); and
|
|
·
|
the demand for IC.
|
Activity in the IC industry is influenced by annual investment in construction, public infrastructure, and the modernization of existing systems and related hardware. As new and better technologies are created, the scale of technological improvements will affect demand and, as a result, economically feasible break-through designs in IC will have a larger effect in stimulating demand than marginal improvements at elite prices, due to:
|
·
|
In recent years, China’s GDP growth rate has remained high (according to a report from China National Statistics Bureau, China’s GDP growth rate in 2006, 2007, 2008 and 2009 was 11.6%, 11.9%, 9.0 %, and 8.7%, respectively. Source: http://info.secu.hc360.com; http://www.cnn.com/2010/BUSINESS/01/20/china.GDP.annual/index.html;
|
|
·
|
Growth in construction: according to national statistics, as of 2008, China’s total output value in the construction industry exceeds $886 billion (RMB 6114.4 billion). The IC industry has significant growth potential, and IC is considered China’s key economic development industry. Currently, the percentage of new construction comprised of IC is as follows: America, 70%; Japan, 60%; and China, 10%. However, in China, this figure is expected to rise to around 33% in 2012.
|
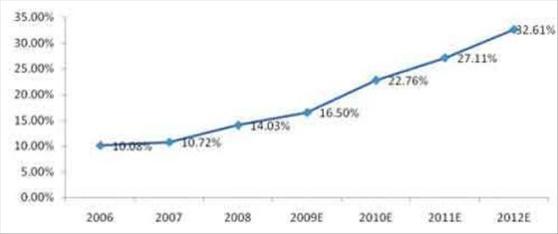
Source: http://info.secu.hc360.com; and
|
·
|
Market demand forecast: according to the nation’s “11th Five-Year Plan,” the growth rate of the construction market is expected to remain at or above 10% through 2010. Annual growth rate of the IC industry is expected to be higher than the construction market itself, which could reach 20% before 2010. Source: http://www.topenergy.org. Based on the above estimates, the management of JIEN believes that annual investment in the IC industry can be estimated as shown below:
|
|
US Dollars
|
(in billions)
|
|||||||||||
|
Year
|
2008
|
2009* | 2010* | |||||||||
|
Intelligent Construction Market
|
$ | 18.4 | $ | 23 | $ | 28.75 | ||||||
_____________________
*Estimated
Security Service
The role of software in China’s network security products industry will likely increase, and the network security service industry will also likely see dynamic growth. CCID Consulting Co. Ltd. (“CCID Consulting”), China’s leading research, consulting and IT outsourcing service provider, has reported that with the actualization of the ‘‘Administrative Measures for the Graded Protection of Information Security,’’ the pivotal industries are paying more attention to their network security strategic plan. Demand from the telecom, finance and energy industries, as well as government network security services, has grown rapidly.
In addition, CCID Consulting reported that the Chinese electronic security industry scale reached $7.52 (RMB 51.38 billion) in 2008, an increase of 22.5% compared to 2007. By 2009, the industry scale is predicted to reach $8.38 billion (RMB 57.13 billion), an increase of 11.2% over 2008. In 2011, the overall market is expected to reach $12.23 billion (RMB 83.58 billion). In general, this market is expected to develop in the following directions: rapid rise of security service demands and increased proportion of software in security products; expansion in mobile applications; and emergence of related security products. Source: http://www.ccidconsulting.com.
Network security demands, such as security consulting, security management monitoring and grade evaluation, have become the important driving forces of this market and frequent accidents have compelled SME’s to devote more funds to network security.
Products
Hainan Jien designs and installs security and surveillance infrastructure to protect financial institutions and government agencies and implements systems for IC projects for commercial customers. JIEN’s security and surveillance business is primarily sourced from the Chinese government’s “Safe City Project” 3111 Project initiative. To this end, the company specializes in the installation of security and surveillance systems in various public areas, from city-wide surveillance systems and traffic surveillance systems to critical government locations, cyber cafes, bars and discotheques. With regard to the IC services offered by Hainan Jien, the company focuses IC projects on three distinct areas:
|
·
|
Intelligent Building (“IBC”): Hainan Jien is one of the biggest providers of intelligent building services in Hainan Province. Hainan’s economy has seen rapid growth since the State Council approved Hainan as an “International Tourism Island.” The 2009 provincial GDP is 164.66 billion RMB, an increase of 11.7% compared with that of 2008 (which is a 3% higher growth rate than the national GDP). The province’s recent rapid development will be beneficial to the growth of Hainan’s industries and residents and, consequently, for the demand for intelligent buildings. Thus, we estimate that demand for Jien’s intelligent building services will increase correspondingly. Source: http://www.hainan.gov.cn/data/zfwj/2010/02/2502/.
|
|
·
|
Intelligent Housing: The development of Hainan as an International Tourism Island will likely promote the development of real estate in the region. It is predicted that housing opportunities in Hainan will soon open to the whole world. Accordingly, it is estimated that there are currently over 100 nation-wide enterprises specializing in real estate development in Hainan, culminating in an investment total of 100 billion RMB.
|
|
·
|
Intelligent Hotel: Hainan, also known as “China’s Hawaii,” is quickly becoming a global tourist destination. Approximately forty internationally and regionally recognized hotel brands have built new hotels in the province, such as Sheraton, Shangri-La, and Hilton. Since the approval of Hainan as an International Tourism Island and in accord with the requirements of the Outline of the Eleventh Five-year Plan of National Economy and Social Development, Hainan will look to build thirty additional five-star resort hotels in the next three years. With the development and popularization of the Intelligent Hotel systems line, the company hopes to obtain strong market share in this field as it grows.
|
Below is a graphical representation of a typical IC project performed by Hainan Jien:
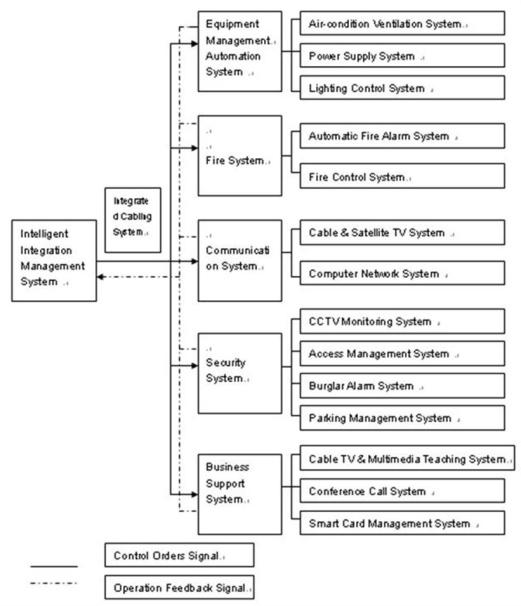
Competitive Advantages
Our Investment Strategy and Management Team
At the holding company level, we believe the following strengths will allow us to effectively execute our investment strategy.
We look to invest primarily in “unique growth companies” in China.
Through our research and due diligence, we focus primarily on “unique growth companies” as our potential investment targets. These businesses and technologies either participate in or focus on serving industrial sectors that are supported by the PRC’s five and ten year plans for internal economic development. As a result, our operating subsidiaries will operate in business environments supported by the Central and local governments and recognized as important to the economic expansion of China, thereby positioning our subsidiaries for expansive growth upon the successful execution of their business plans.
We will hold significant ownership stakes in our operating subsidiaries.
We intend to hold a significant equity stake in each of our operating subsidiaries. As a result, we will have a vested interest in the successful growth of our operating subsidiaries. Our management team at the holding company level, both in the U.S. and China, will lend its expertise and resources to facilitate the sustained growth of our subsidiaries as well as assist these businesses in gaining access to necessary capital for growth. Moreover, this strategy will allow for centralized control over the reporting obligations of our subsidiaries to ensure their regulatory compliance in the US markets and sound corporate governance.
Our Board and management possess extensive experience both in China and in the U.S. capital markets.
Our subsidiaries will benefit from the guidance and resources available to them at the holding company level. It is the goal of our Board, management and advisory board to work closely with our operating subsidiaries in assisting them with compliance requirements they will encounter as component parts of a U.S. public company, while simultaneously providing them access to necessary growth capital that will allow them to meet expanding market opportunities in China and ultimately generate a return to our investors. To this end, members of our Board and senior management are prepared to lend their years of experience with and knowledge of raising funds in the U.S. capital markets as well as their extensive management experience with U.S. public companies. Beyond this strength, our Board, management and advisory board members bring their experience with and understanding of China, its business culture, its economic opportunities, and its government to the development of the Company and the potential growth of our subsidiaries. Consequently, through our holding company structure, we are effectively situated as to serve as the key liaison between our subsidiaries and the U.S. investor.
Based on our research and experiences in China and the U.S. capital markets, we have a targeted investment strategy that focuses on quality operating companies.
In light of the vast investment opportunities in a rapidly developing economy such as China’s, we have the opportunity to be selective in the operating companies we choose to invest in. Consequently, we can utilize our experience in China and in the U.S. capital markets to invest in companies that have the greatest potential to generate sustained growth for the Company and eventually become standalone public entities. We have established the following investment criteria for our investment in or acquisition of target companies:
|
·
|
Focus on “unique growth companies”—i.e. businesses and technologies that participate in, or focus on, serving industrial sectors that are supported by the PRC’s five and ten year plans for internal economic development.
|
|
·
|
Investment will provide the Company with a substantial position in special growth companies.
|
|
·
|
These special growth companies should also:
|
|
–
|
Benefit from the support of both the local and regional government;
|
|
–
|
Be privately owned—i.e. there should not be an ownership stake held by the government;
|
|
–
|
Be free from competition with any government enterprise;
|
|
–
|
Have demonstrated profitable organic growth for 2-3 years;
|
|
–
|
Exhibit a well established and growing customer base, market penetration and operating infrastructure;
|
|
–
|
Have an effective and proven management team which is willing to make a multi-year contractual commitment to the execution of the business plan;
|
|
–
|
Be able to provide comprehensive financial statements; and
|
|
–
|
Be willing to commit to a program of establishing a system of sound corporate governance in accordance with U.S. public market standards and comply with all local laws and regulations as well as U.S. securities laws and exchange listing requirements. This will include adopting a code of conduct and U.S. accounting standards.
|
Jien’s Competitive Strengths in the IT Industry in China
We believe the following strengths differentiate Jien from its competitors, enabling Jien to attain a leadership position in the IT market in China.
Strong Solution and Service Development Capability
An experienced senior management team, most of whom have computer science, mathematics or engineering backgrounds, lead the solution development efforts of Jien. Accordingly, Jien is well regarded in its field. In addition to being ranked as a national top 100 security and surveillance provider, Hainan Jien is one of three security and surveillance firms that are First Grade National Certified, a certification issued by the Public Ministry Security Bureau that allows Hainan Jien to implement all levels of security projects nationwide. Jien uses component-based platforms in the software development process that enables it to redeploy relevant modules for future solutions or to repackage them as stand-alone standardized solutions.
The primary goal of the research efforts of Jien is to develop solutions that may be strategically implemented and commercialized. As an investment in long-term growth, Jien funds and operates its own research and development that focuses on core technologies underlying solutions and solution protocols, staffed with engineers dedicated to the research conducted by the centers. Jien is committed to research and development, and its focus on commercializing research results enables it to work toward becoming a leader in the competitive Chinese IT market, with the ability to provide a broad range of quality software solutions and the potential for sustained long-term growth.
Proven Management with a Successful Business Record
The senior management team of Jien consists of computer scientists and engineers with extensive management experience in the IT industry ranging from 16 years to 25 years. This management team has complementary skills in the areas of software development, operations, finance, and sales and marketing. Under the leadership of this management team, Jien has substantially expanded its operations and solution lines, and achieved significant revenue growth.
Market Positioning
Hainan Jien is positioned in a high growth region in China. Hainan Province, the location of Hainan Jien, recorded 2009 GDP at $24 billion and a year-on-year growth rate of 11.7%. Source: http://www.hainan.gov.cn/data/zfwj/2010/02/2502/. Additionally, the province was approved by the PRC State Council to establish itself as an International Tourism Island, whereby a series of incentive policies will be applied to the region. Such momentum is likely to boost infrastructure investment and property development and, consequently, the service market supporting such initiatives. In working to attain its status as a top security and surveillance firm and IC services leader in the province, it is Hainan Jien’s goal to take a primary role in Hainan’s development and benefit from the region’s accelerated development.
Recognition within the Industry
Hainan Jien is highly regarded by the certifying bodies its industry. In China, recognition by independent public and private industry experts of a firm’s product or service is regarded by commercial, governmental and retail customers as assurance of the quality of a firm’s offerings and is am important basis upon which to compete. Jien’s certifications and honors are as follows:
|
HAINAN JIEN
|
||
|
Certification & Honors
|
Certification Body
|
Certification Date
|
|
Security and surveillance certificate level 1
|
Public security bureau, Hainan Province
|
October 2009
|
|
Member of the Procurement Center of the Central People’s Government
|
Procurement Center of the Central People’s Government
|
March 2008
|
|
Computer Information System Integration Level 2
|
Hainan Development Bureau
|
April 2007
(valid for 3 years)
|
|
Certificate in intelligent construction design and installation level 2
|
Department of Construction, Hainan Province
|
April 2007
|
|
Member of Hainan Software Industry Association
|
Hainan Software Industry Association
|
2007
|
|
Commercial Credit Qualification Certificate
|
Hainan Guoli Credit Certification Center
|
June 2007
|
|
Quality Certification of IS09001:2000
|
China Quality Certification Centre
|
April 2007
(valid for 3 years)
|
|
Authentication Certificate of Commercial Credit AAA
|
Commercial Credit Administration of Hainan Province
|
August 2006
|
|
Greatest Grow Up of 100 Enterprise for China Public Security & Safety Industry
|
A Subordinate of The Ministry of Public Security of PRC
|
January 2005
|
Manufacturing and Project Implementation
Jien implements a dual phase project support and implementation process for its surveillance and IC services. The cornerstone of the project support phase is the accurate design of projects tailored to customer specifications in advance of project implementation. After a customer submits to us a project request, Jien validates the request to ensure it is in accordance with its capacity and capabilities, with the goal of assigning the proposal to one of its project designers. Once the proposal is submitted to a project designer, the designer is then responsible for developing a written and graphical design plan for submission to Jien’s customer. After second level review of the design and internal approval, the final project design proposal is submitted to the customer for review.
Upon acceptance of the project proposal by the customer and entry into a written contract setting forth the scope of work to be performed, the implementation phase begins with Hainan Jien’s management appointing a project manager to oversee preparation for the project both internally and with the customer, allocation of staff to the project worksite and construction. Once onsite, the project staff receives, inspects and lays all necessary wiring, followed by their receipt, inspection and installation of all required equipment. The project manager also works with the customer to assess the need for additional sub-projects tangential to the installation. To the extent such additional projects are required, the original contact is modified accordingly and the project manager oversees such further projects’ development and installation onsite. After all installation work is complete and the project staff runs a thorough inspection of the system, Jien ensures the installation is in accord with the customer’s specifications, making any required adjustments, and finally assisting the customer with the data transfer into the new system, if necessary.
Sales and Marketing
Hainan Jien’s Marketing Department is divided according to business scope among the following five industry sales centers: finance, government, real estate, hotel and small projects.
Jien’s marketing program is centered on a general-manager-responsibility system. Originally, Jien’s Deputy General Manager was responsible for the overall marketing for the company, having jurisdiction over the five industry sales centers. However, over the past two years of operations, the company has experienced rapid market growth. As a result, the company’s General Manager is now responsible for the government industry while its Deputy General Manager is responsible for the financial industry. Jien’s Marketing Director is in charge of the real estate industry while its Deputy Marketing Director heads the company’s hotel sales division. Hainan Jien’s general marketing staff manages sales for all small projects.
The company also adopts a partnership-sale method, whereby the company works with independent contractors who assist it with negotiations with potential customers on projects. Jien has a profit sharing relationship with its independent contractors based on the success of negotiations. The company’s independent contractors are located in all of the company’s sales centers. There is currently ten contractor marketing staff in Jien’s three sales centers, with its Haikou Center having six people, its Sanya Center having two people and its Hubei Province Center having two people. Advertising is primarily accomplished through face-to-face meetings with potential customers, Internet and e-mail communications, government conferences and scheduled meetings with Jien’s independent contractors.
Finally, Hainan Jien’s Post-Sale Service Department specializes in customer service. Jien has established a 7-day, 24-hour service system where customers can communicate with its Post-Sale Service Department through mobile phone, telephone, Tencent QQ and E-mail. As an added redundancy, the company’s Marketing and General Office Departments also have the capabilities of carrying out customer support functions.
Suppliers
Jien purchases its products based on customer demand, product performance and brand. Suppliers for the company’s project implementations vary due to different systems and the products demanded by its customers. Based on the size of a given project, some of Jien’s suppliers for large-size equipment will send their technical staff to the project site to support the company during the installation according to the company’s specifications. If quality problems occur, Jien’s suppliers generally assess the seriousness of the problem based on the difficulties communicated by Jien’s on-site technical staff. Generally, the company’s suppliers are available for technical guidance to assist its technicians with troubleshooting customers’ systems. If hardware problems occur with the company’s projects, suppliers normally provide on-the-spot support or spare products. Consistent with the company’s own warranty commitments to its customers, Jien’s suppliers normally provide free maintenance or replacement for their products within Jien’s warranty periods (1 to 3 years).
Customers
Hainan Jien’s 10 largest customers during 2009 are as shown in the chart below:
|
Clients
|
$000s |
% of Total Revenue
|
||||||
|
Hainan Medical College
|
$ | 1,269 | 18.99 | |||||
|
Hainan South Sea Technology Co., Ltd.
|
1,154 | 17.62 | ||||||
|
Hainan Land and Resources Bureau
|
733 | 10.97 | ||||||
|
Hainan Rural Credit Cooperatives
|
721 | 10.78 | ||||||
|
Hainan Green Wind Real Estate Co., Ltd.
|
617 | 9.23 | ||||||
|
Hainan Vocational and Technical College
|
544 | 8.14 | ||||||
|
Hainan Haiyun Industry Co., Ltd.
|
493 | 7.37 | ||||||
|
Hainan Jingrui Real Estate Co., Ltd.
|
425 | 6.35 | ||||||
|
Jindi Real Estate Co., Ltd., Luoniu Shan Group
|
330 | 4.94 | ||||||
|
Hainan Olympics Real Estate Co., Ltd.
|
67 | 1.00 | ||||||
|
TOTAL
|
$ | 6,352 | 95.02 | |||||
Hainan Jien’s customers are from various areas of Hainan Province and parts of Hubei Province. The company has no business overseas. Jien’s largest customers are primarily from government sector, the financial industry and real estate. Among our three largest customers, Jien has had a relationship with Hainan Medical College for two years, Hainan South Sea Technology Development Co., Ltd. for four years and Hainan Provincial Land and Resources Bureau for one year.
Research and Development
Hainan Jien’s research and development staff has developed a proprietary software system: Information Management System (“IMS”). The IMS system assists the company with the management of the exploration of market opportunities, production, logistics and internal project approval.
Jien is presently working on the requirements program for the IMS system. Thereafter, the continued steps for development of the technology are as follows: internal project approval; development of technology solutions; software coding; software testing; submission of a report of software property to the State Intellectual Property Office for property registration. The company plans to complete the IMS system and finish all of the registration processes before November 30, 2010.
Intellectual Property
Jien currently has intellectual property rights to an automatic spit plate machine. In 2010, Jien plans to apply for one additional patent through the State Intellectual Property Office for its IMS energy-saving construction management software system.
Employees
At March 31, 2010, we employed approximately 75 full time employees. Our holding company employed 2 full time employees and 2 part-time employees. Hainan Jien, employed 75 full time employees.
Covenant Employee Breakdown
|
Department
|
Holding Company
|
Hainan Jien
|
TOTAL
|
|||||||||
|
Management
|
2 | 6 | 8 | |||||||||
|
All administration
|
0 | 3 | 3 | |||||||||
|
Sales/Post-Sale Service
|
0 | 11 | 11 | |||||||||
|
Design/Implementation
|
0 | 53 | 53 | |||||||||
|
Total
|
2 | 73 | 75 | |||||||||
Government and Environmental Regulation
Previously, the Hainan government has given Hainan Jien preferential tax treatment due to its industry. However, a unified taxation policy has since been implemented throughout the nation, eliminating any tax reduction benefits for the company. Despite this, with the national designation of Hainan Province as an International Tourism Island, Jien expects preferential policies and incentives to be introduced to the region.
Competition
There are currently two US listed companies in China’s financial IT service sector recognized as leaders due to their size and financial strength, thereby posing competition to Jien. Those companies are:
|
·
|
Longtop, a NYSE listed company (LFT), which operates in similar business fields covering hardware, software and service support primarily for the financial services industry. Longtop’s total revenues for the 6 months ended September 2009 were $71.3 million, an increase of 50.1% over the corresponding period of 2008. Software development revenues represented 86% of the total revenues. Longtop estimates revenue to increase to $158.0 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010, up from $106.3 million for the fiscal year March 31, 2009, with software development responsible for $137.0 million of the revenues.
|
|
·
|
Yucheng Technologies, a NASDAQ listed company (YTEC), is a leading IT service provider to the Chinese banking industry. Yucheng’s exclusive focus on the banking sector allows it to provide high value software in the form of customized solutions. In its report for the third quarter 2009, Yucheng Technologies stated that 2009 revenues, primarily driven by software solutions, increased by 60% and confirmed that it will have revenue for the year in the range of $69-$72 million.
|
Our Corporate Information
Our principal offices are located at Two Bala Plaza, Suite 300, Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania 19004. Our telephone number is (610) 660-7828. Our website is http://www.covenantchina.com. The information contained on our website is not a part of this prospectus.
Jien’s headquarters and manufacturing facilities are located in the northern part of Hainan Province, Haikou City. The Municipal Administration of State-Owned Land has granted us the right to use the land in Haikou City until January 2012. The total area of our facility is approximately 1,100 square meters and our monthly rent is 24 RMB per square meter ($3,865 per month), payable in monthly installments.
From time to time, we may become involved in various lawsuits and legal proceedings that may arise in the ordinary course of business. However, litigation is subject to inherent uncertainties, and an adverse result in these or other matters may arise from time to time that may have an adverse affect on our business, financial conditions, or operating results. We are currently not aware of any such legal proceedings or claims that will have, individually or in the aggregate, a material adverse affect on our business, financial condition or operating results.
Executive Officers and Directors
As of June 24, 2010, the directors and executive officers of Covenant were:
|
Name
|
Age
|
Position
|
||
|
Fredric W. Rittereiser
|
73
|
Chairman of the Board of Directors
|
||
|
Kenneth Wong
|
53
|
President and Director
|
||
|
K. Ivan F. Gothner
|
51
|
Director
|
||
|
Justin D. Csik
|
27
|
General Counsel, Chief Financial Officer and Secretary
|
Our directors hold office for one-year terms and until their successors have been elected and qualified. Our officers are elected annually by the board of directors and serve at the discretion of the Board. Messrs. Rittereiser, Wong and Gothner were appointed as directors on December 24, 2009.
Biographies
Fredric Rittereiser, Chairman of the Board of Directors
Mr. Rittereiser was a founder of Covenant Holdings in 2009. He has over 40 years of capital markets experience as a senior executive at various Wall Street firms, and he has extensive experience working with US public companies with China-based operations. From 2007 to 2009, he served on the Board of Directors of AgFeed Industries, Inc., one of the largest hog producers in the PRC, and he is currently Chairman of the Strategic Affairs Committee for AgFeed Industries, a non-board position. From October 1996 until retiring in 2002, Mr. Rittereiser served as Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer of Ashton Technology Group, Inc., a company specializing in development and commercialization of online transaction systems for the financial industry. He was also a founder of Ashton Technology.
Prior to his principal role at Ashton Technology, Mr. Rittereiser served as a special consultant to Booz Allen and Hamilton, a global strategy and technology-consulting group, from 1991 to 1993. Previously, he was the former President and Chief Operating Officer of Instinet Corporation since 1983, which became one of the world’s leading electronic securities trading firms. Under his leadership, the company evolved into a highly efficient continuous electronic communications network or ECN that allowed institutions and dealers to negotiate securities trades anonymously. Mr. Rittereiser successfully negotiated the sale of Instinet to the Reuters Group in 1987. From 1973 until 1980, he served as the NASD representative on the National Market System Committee responsible for negotiated rates, developing market linkages in the U.S., promoting price competition and endorsing NASDAQ as the electronic market for growth companies and new issues.
Mr. Rittereiser was also a founder of Gomez Advisors, Inc., TH Lehman Inc., and he was a member of the board of directors of the International Heritage Mutual Fund.
Kenneth Wong, President and Director.
Mr. Wong was a founder of Covenant Holdings in 2009. He is also President, owner and founder of CIG Asia, Ltd., a Philadelphia, Pennsylvania-based national property and casualty insurance brokerage firm. From 2004-2007, Mr. Wong, as an appointee of President George W. Bush, served as a commissioner on the President’s Advisory Commission for Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders. In 2010, Mr. Wong was appointed to the Chairmanship of the National U.S. Hong Kong Business Association (“NUSHKBA”). NUSHKBA is a member of the Hong Kong Business Association Worldwide, which is affiliated with the Hong Kong Trade and Development Council. Mr. Wong also serves on the Executive Board of Directors of the Hong Kong Business Association Worldwide. Mr. Wong received a BA from Pennsylvania State University in sociology and political science.
K. Ivan F. Gothner, Director
Mr. Gothner was a founder of Covenant Holdings in 2009. In 1993, he founded Adirondack Partners, LLC, a private merchant-banking firm that focuses on serving small and mid-size growth companies, and has since served as Adirondack Partners’ Managing Director. Prior to founding Adirondack Partners, Mr. Gothner was Senior Vice President of Barclays Bank from 1990 to 1992, responsible for establishing an investment banking unit to serve small and mid-sized companies. Mr. Gothner joined Kleinwort Benson Limited in 1986, and from 1987 to 1990 he served as a Senior Vice President of the firm and General Manager of the KB Mezzanine Fund, L.P., a specialized fund which invested in equity and junior capital of small and mid-sized businesses. Currently, Mr. Gothner serves on the Board of Directors of ArtID, LLC and AgFeed Industries, Inc. (where he is also Chairman of the Audit Committee and Compensation Committee and a member of the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee). Mr. Gothner received a Bachelor’s of Art from Columbia College in political science and economics and a MIA from Columbia University’s School of International Affairs in international economic policy and finance.
Justin D. Csik, General Counsel, Chief Financial Officer and Corporate Secretary
Mr. Csik joined Covenant Holdings in October 2009. Mr. Csik is a practicing attorney with a background in accounting and economics. Upon being admitted to the state bars of Pennsylvania and New Jersey in 2008, Mr. Csik was a corporate finance associate with Buchanan Ingersoll & Rooney PC from 2008 to 2009. While at Buchanan Ingersoll, he worked on a variety of securities regulatory, transactional and corporate governance matters. He was also a member of his firm’s China practice group, where he assisted clients with legal issues unique to U.S. public companies with primarily China-based operations. Prior to joining Buchanan Ingersoll, Mr. Csik worked for Deloitte & Touche LLP for an extended audit and assurance internship in 2004. During his time with Deloitte, he worked on the major phases of financial statement audits for a variety of public and privately-held clients, which included substantive account testing and SEC reporting. Mr. Csik received his Bachelor of Science in accountancy and economics from Villanova University in 2005, graduating magna cum laude. In 2008, Mr. Csik received his Juris Doctor degree from Rutgers School of Law—Camden.
The Board of Directors and Committees
Currently, Messrs. Rittereiser and Gothner qualify as “independent” directors, but Mr. Wong does not qualify as an “independent” director, as that term is defined by applicable listing standards of The NASDAQ Stock Market and SEC rules. As a requirement to listing the Company’s common stock on The NASDAQ Capital Market or other exchange, the Company intends to add independent directors. The board’s composition (and that of its committees) will be subject to the corporate governance provisions of its primary trading market, including the requirement for appointment of independent directors in accordance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, and regulations adopted by the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant thereto.
Audit Committee
We intend to establish an audit committee of the board of directors, which will consist of independent directors, of which at least one director will qualify as a qualified financial expert as defined in the regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission. The audit committee’s duties would be to recommend to our board of directors the engagement of independent auditors to audit our financial statements and to review our accounting and auditing principles. The audit committee would review the scope, timing and fees for the annual audit and the results of audit examinations performed by the internal auditors and independent public accountants, including their recommendations to improve the system of accounting and internal control. The audit committee would at all times be composed exclusively of directors who are, in the opinion of our board of directors, free from any relationship that would interfere with the exercise of independent judgment as a committee member and who possess an understanding of financial statements and generally accepted accounting principles.
Compensation Committee
We intend to establish a compensation committee of the board of directors. The compensation committee would review and approve our salary and benefits policies, including compensation of executive officers. The compensation committee would also administer any stock option plans that we may adopt and recommend and approve grants of stock options under such plans.
Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee
We intend to establish a nominating and corporate governance committee of the board of directors to assist in the selection of director nominees, approve director nominations to be presented for shareholder approval at our annual meeting of shareholders and fill any vacancies on our board of directors, consider any nominations of director candidates validly made by shareholders, and review and consider developments in corporate governance practices.
Code of Conduct
Our board of directors plans to adopt a Code of Conduct, which will apply to all directors, officers and employees. The purpose of the Code is to promote honest and ethical conduct.
Compensation of Our Executive Officers
To date, Mr. Wong has not been compensated as President of Covenant Holdings. However, he is currently in negotiations with the Company regarding his future compensation as President of the Company. Mr. Csik has been compensated by Covenant Holdings at the rate of $5,000 per month ($60,000 per year) since joining Covenant Holdings in October 2009. Neither Mr. Wong nor Mr. Csik is a party to a written employment agreement or other compensatory arrangement with the Company. The advisability of entering into these agreements with the Company executives and the terms of any such agreement is a continuing source of discussion within the Company.
Summary Compensation Table
The following table shows the compensation of each of our named executives and highest compensated individuals in 2009. Our named executives are: our president, Mr. Wong; and our general counsel, chief financial officer and secretary, Mr. Csik; and our two most highly compensated individuals are: Song Xiaozhong; and Song Guangwei. Prior to the appointment of Messrs. Wong and Csik on December 24, 2009, Mr. Mohan Singh served as our president, principal executive officer, secretary, treasurer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer and sole member of our board of directors prior to his resignation on December 24, 2009, and his summary compensation information is also described in the following table.
|
Name and Principal Position
|
Year
|
Salary
|
Bonus
|
Option Awards
|
Total Compensation
|
|||||||||||||
|
Kenneth Wong
|
2009
|
$ | 0 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||
|
President
|
2008
|
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||
|
2007
|
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||
|
Justin D. Csik
|
2009
|
15,000 | 0 | 0 | 15,000 | |||||||||||||
|
General Counsel, Chief Financial Officer and Corporate Secretary
|
2008
|
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||
|
2007
|
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||
|
Song Xiaozhong
|
2009
|
26,352.39 | * | 0 | 0 | 26,352.39 | * | |||||||||||
|
Chairman, Chongqing Sysway
|
2008
|
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||
|
2007
|
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||
|
Song Guangwei
|
2009
|
17,568.26 | * | 0 | 0 | 17,568.26 | * | |||||||||||
|
Board Member, Deputy General Manager, Chongqing Sysway
|
2008
|
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||
|
2007
|
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||
|
Wang Junfeng
|
2009
|
4,392 | * | 0 | 0 | 4,392 | * | |||||||||||
|
Deputy General Manager, Hainan Jien
|
2008
|
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||
|
2007
|
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||
|
Wang Chaoshuai
|
2009
|
4,392 | * | 0 | 0 | 4,392 | * | |||||||||||
|
Manager, branch office in Sanya City, Hainan Province, Hainan Jien
|
2008
|
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||
|
2007
|
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||
|
Mohan Singh
|
2009
|
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||||||
|
President, Principal Executive Officer, Secretary, Treasurer, Principal Financial Officer, Principal Accounting Officer
|
2008
|
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||||||
|
2007
|
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
______________________________
*Reflects amounts paid in RMB and converted to US Dollars at the prevailing exchange rate of .1464 (RMB to USD) on March 22, 2010
Compensation paid to our named executives in 2008 consisted solely of cash salary and bonus. However, in the future, our named executive officers may be eligible to receive other forms of compensation.
Historically, we have not provided our named executives with perquisites or other personal benefits. Additionally, we do not provide any company-sponsored retirement benefits or deferred compensation programs to any employee (other than a mandatory state pension scheme in which all of our employees in the People’s Republic of China participate) because it is not customary to provide such benefits and programs in the PRC.
Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End
As of December 31, 2008, there were no outstanding equity awards held by executive officers of our company.
Stock Incentive Plans
The Company has no stock option or other equity incentive plans.
Director Compensation
The following table provides information concerning the compensation of our non-executive directors for the period from January 1, 2009 through December 31, 2009.
|
Name
|
Fees Earned or Paid in Cash ($)
|
Option Awards ($)
|
Total ($)
|
|||||||||
|
Fredric W. Rittereiser
|
$ | 0 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | ||||||
|
K. Ivan F. Gothner
|
0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
We do not currently compensate our directors for acting as such, although we may do so in the future, including with cash and/or equity. We reimburse our directors for reasonable expenses incurred in connection with their service as directors.
The following tables set forth certain information as of June 24, 2010 regarding the number of shares of common stock beneficially owned by (i) each person or entity known to us to own more than 5% of our common stock; (ii) our named executive officers; (iii) our directors; and (iv) all of our executive officers and directors as a group.
Unless otherwise indicated, each of the shareholders named in the table below has sole voting and investment power with respect to such shares of common stock. Except as otherwise indicated, the address of each of the shareholders listed below is: c/o Covenant Group of China Inc., Two Bala Plaza, Suite 300, Bala Cynwyd, PA 19004.
Except as otherwise noted, the individual or his or her family members had sole voting and investment power with respect to such shares. The percentages of beneficial ownership set forth below are based on 9,858,909 shares of our common stock issued and outstanding as of June 24, 2010.
|
Name of Beneficial Owner:
|
Number of Shares Beneficially Owned(1)
|
Percentage
Beneficially Owned(2)
|
||||||
|
Ma Bing Feng
|
810,000 | 7.1% | ||||||
|
HaiNan JIEN Intelligent Engineering Co.
Floor 6, No. 38 DaTong Road,
Fortune Centre,
Haikou City, Hainan Province, China 570102
|
||||||||
|
Sheng Zhou/Sunrise Capital International, Inc./Good Energy Enterprise, Ltd.
Unit 2309-2310, South Tower,
World Trade Centre, Huanshi Road,
Guangzhou, China 510095
|
1,100,909 | 9.6% | ||||||
|
Directors and Executive Officers:
|
||||||||
|
Fredric Rittereiser
|
0 | * | ||||||
|
Kenneth Wong
|
300,000 | 3.0 | ||||||
|
K. Ivan F. Gothner
|
250,000 | 2.5 | ||||||
|
Justin D. Csik
|
100,000 | 1.0 | ||||||
|
All Directors and named Executive Officers as a group
(4 persons)
|
650,000 | 6.6 | ||||||
______________________________
|
(1)
|
Beneficial ownership has been determined in accordance with Rule 13d-3 under the Exchange Act. Unless otherwise noted, we believe that each person named in the table has sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of common stock beneficially owned by such person.
|
|
(2)
|
Based on 9,858,909 shares of common stock issued and outstanding as of June 24, 2010.
|
Southridge, as a selling stockholder, may sell the securities registered under this prospectus:
|
·
|
through underwriting syndicates represented by one or more managing underwriters;
|
|
·
|
to or through underwriters or dealers;
|
|
·
|
through agents;
|
|
·
|
directly to one or more purchasers;
|
|
·
|
through a block trade in which the broker or dealer engaged to handle the block trade will attempt to sell the securities as agent, but may position and resell a portion of the block as principal to facilitate the transaction; or
|
|
·
|
Through a combination of any of these methods of sale.
|
Each applicable prospectus supplement used in connection with any offering of the shares covered by this prospectus will include the following information with respect to such offering:
|
·
|
the terms of the offering;
|
|
·
|
the names of any underwriters, dealers or agents;
|
|
·
|
the name or names of any managing underwriter or underwriters;
|
|
·
|
the purchase price of the shares;
|
|
·
|
the net proceeds from the sale of the shares;
|
|
·
|
any over-allotment options under which underwriters may purchase additional shares;
|
|
·
|
any delayed delivery arrangements;
|
|
·
|
any underwriting discounts or commissions or agency fees and other items constituting underwriters’ or agents’ compensation;
|
|
·
|
any discounts, commissions, or concessions allowed or reallowed or paid to dealers;
|
|
·
|
any commissions paid to agents; and
|
|
·
|
any securities exchanges or markets on which the shares may be listed.
|
Any initial public offering price and any discounts or concessions allowed or reallowed or paid to dealers may be changed from time to time.
Southridge may, from time to time, authorize underwriters acting as its agents to offer and sell the securities upon the terms and conditions as are set forth in the applicable prospectus supplement. We will include the name or names of any underwriters and the purchase price of the securities in a prospectus supplement relating to the securities. Any underwritten offering may be on a best efforts or a firm commitment basis. The obligations, if any, of the underwriter to purchase any securities will be subject to certain conditions.
If agents are used in an offering, the names of the agents and the terms of the agency will be specified in a prospectus supplement. Unless otherwise indicated in a prospectus supplement, the agents will act on a best-efforts basis for the period of their appointment.
If a dealer is used in an offering of securities, Southridge may sell the securities to the dealer as principal. We will include the name or names of any dealers and the purchase price of the securities in a prospectus supplement relating to the securities. The dealer may then resell the securities to the public at varying prices to be determined by the dealer at the time of sale. Any public offering price and any discounts or concessions allowed, re-allowed, or paid to dealers may be changed from time to time and will be described in a prospectus supplement relating to the securities.
Southridge, or any underwriter, dealer or agent, may distribute the securities from time to time in one or more transactions at:
|
·
|
a fixed price or prices, which may be changed;
|
|
·
|
at market prices prevailing at the time of sale;
|
|
·
|
at prices related to prevailing market prices; or
|
|
·
|
at negotiated prices.
|
Any of these prices may represent a discount from the prevailing market prices.
To the extent permitted by and in accordance with Regulation M under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), in connection with an offering an underwriter may engage in over-allotments, stabilizing transactions, short covering transactions and penalty bids. Over-allotments involve sales in excess of the offering size, which creates a short position. Stabilizing transactions permit bids to purchase the underlying security so long as the stabilizing bids do not exceed a specified maximum. Short covering transactions involve purchases of the securities in the open market after the distribution is completed to cover short positions. Penalty bids permit the underwriters to reclaim a selling concession from a dealer when the securities originally sold by the dealer are purchased in a covering transaction to cover short positions. Those activities may cause the price of the securities to be higher than it would be otherwise. If commenced, the underwriters may discontinue any of these activities at any time. We will describe any of these activities in the prospectus supplement.
Southridge may authorize underwriters, dealers or agents to solicit offers by certain institutions to purchase the securities at the public offering price under delayed delivery contracts. If Southridge uses delayed delivery contracts, we will disclose that Southridge is using them in the prospectus supplement and will tell you when Southridge will demand payment and delivery of the securities under the delayed delivery contracts. These delayed delivery contracts will be subject only to the conditions set forth in the applicable prospectus supplement. We will indicate in our prospectus supplement the commission that underwriters and agents soliciting purchases of the securities under delayed delivery contracts will be entitled to receive.
In connection with the sale of the securities and as further set forth in an applicable prospectus supplement, underwriters may receive compensation from Southridge or from purchasers of the securities for whom they may act as agents, in the form of discounts, concessions or commissions. Underwriters may sell the securities to or through dealers, and these dealers may receive compensation in the form of discounts, concessions or commissions from the underwriters and/or commissions from the purchasers for whom they may act as agents. Underwriters, dealers and agents that participate in the distribution of the securities may be deemed to be underwriters, and any discounts or commissions they receive from Southridge, and any profit on the resale of the securities they realize, may be deemed to be underwriting discounts and commissions under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”). The prospectus supplement will identify any underwriter or agent and will describe any compensation they receive from Southridge.
It is possible that one or more underwriters may make a market in our securities, but underwriters will not be obligated to do so and may discontinue any market making at any time without notice. Therefore, we can give no assurance about the liquidity of our securities that may be sold pursuant to this prospectus.
Under agreements we may enter into, we may indemnify underwriters, dealers and agents who participate in the distribution of the securities against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act.
Certain of the underwriters, dealers and agents and their affiliates may be customers of, engage in transactions with, and perform services for us and our subsidiaries from time to time in the ordinary course of business. Any such relationships will be disclosed in an applicable prospectus supplement.
If indicated in the prospectus supplement, Southridge will authorize underwriters or other persons acting as its agents to solicit offers by institutions to purchase securities from Southridge pursuant to contracts providing for payment and delivery on a future date. Institutions with which Southridge may make these contracts include commercial and savings banks, insurance companies, pension funds, investment companies, educational and charitable institutions and others. The obligations of any purchaser under any such contract will be subject to the condition that the purchase of the securities shall not at the time of delivery be prohibited under the laws of the jurisdiction to which the purchaser is subject. The underwriters and other agents will not have any responsibility with regard to the validity or performance of these contracts.
In compliance with guidelines of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, or FINRA, the maximum consideration or discount to be received by any FINRA member or independent broker dealer may not exceed 8.0% of the aggregate amount of the securities offered pursuant to this prospectus and any applicable prospectus supplement.
Equity Credit Agreement
This prospectus relates to sales of our common stock to Southridge pursuant to the Equity Credit Agreement, to the issuance of the Southridge Warrant and the issuance of shares of our common stock upon exercise of the Southridge Warrant.
We will not receive any proceeds for the sale by Southridge of the shares of common stock. In the event that a holder exercises the warrants for cash, we will receive the aggregate exercise price paid by such holder.
The shares of common stock owned, or which may be acquired by Southridge, may be offered and sold by Southridge from time to time as market conditions permit on the OTC.BB or otherwise at prices and terms then prevailing or at prices related to the then current market price, or in negotiated transactions. These shares may be sold by one or more of the following methods:
|
·
|
a block trade in which a broker or dealer so engaged will attempt to sell the shares as agent but may position and resell a portion of the block as principal to facilitate the transaction;
|
|
·
|
purchases by a broker or dealer as principal and resale by such broker or dealer for its account pursuant to this prospectus;
|
|
·
|
ordinary brokerage transactions and transactions in which the broker solicits purchasers;
|
|
·
|
privately negotiated transactions between sellers and purchasers without a broker/dealer;
|
|
·
|
a combination of any of the aforementioned methods of sale; or
|
|
·
|
any other method permitted by applicable law.
|
When making sales, brokers or dealers engaged by Southridge may arrange for other brokers or dealers to participate. These brokers or dealers may receive commissions or discounts from Southridge in amounts to be negotiated.
Southridge will be deemed to be an “underwriter” and any broker/dealers who act in connection with the sale of the shares by Southridge may be deemed to be “underwriters” within the meaning of Section 2(11) of the Securities Act of 1933, and any commissions received by them and profit on any resale of the shares as principal may be deemed to be underwriting discounts and commissions under the Securities Act.
We have advised Southridge that it will be deemed to be an underwriter, and any securities brokers/dealers or others who sell our shares on behalf of Southridge that they may be deemed to be statutory underwriters. We have also advised Southridge that in the event of a “distribution” of our shares, Southridge, any “affiliated purchasers,” and any broker/dealer or other person who participates in such distribution are subject to Rule 102 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”) until their participation in such distribution is completed. Rule 102 makes it unlawful for any person who is participating in a distribution to bid for or purchase stock of the same class as is the subject of the distribution. A “distribution” is defined in Rule 102 as an offering of securities “that is distinguished from ordinary trading transactions by the magnitude of the offering and the presence of special selling efforts and selling methods.” We have also advised Southridge that Rule 101 under the Exchange Act prohibits any “stabilizing bid” or “stabilizing purchase” for the purpose of pegging, fixing or stabilizing the price of the common stock in connection with the distribution of the shares.
The shares of common stock that may be sold to Southridge and the Southridge Warrant have been registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission to enable Southridge to sell the common stock in the public market. However, we have no obligation to:
|
·
|
assist or cooperate with Southridge in the offering or disposition of shares purchased by it;
|
|
·
|
obtain a commitment from an underwriter relating to any sale of shares by Southridge; or
|
|
·
|
include the shares in any underwritten offering.
|
The following description of our securities and provisions of our articles of incorporation and bylaws is only a summary. You should refer to our articles of incorporation and bylaws, a copy of each has been filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part. The following discussion is qualified in its entirety by reference to such exhibits.
Authorized Capital Stock
The total number of authorized shares that we may issue is 100,000,000 shares of common stock with a par value of $0.00001 per share and 100,000,000 shares of preferred stock with a par value of $0.00001 per share. We have no other authorized classes of stock.
Capital Stock Issued and Outstanding
As of June 24, 2010, 9,858,909 shares of common stock were issued and outstanding and held of record by 80 shareholders.
Description of Common Stock
The holders of common stock are entitled to one vote per share. Our Articles of Incorporation do not provide for cumulative voting. The holders of our common stock are entitled to receive ratably such dividends, if any, as may be declared by our board of directors out of legally available funds; however, the current policy of our board of directors is to retain earnings, if any, for operations and growth. Upon liquidation, dissolution or winding-up, the holders of our common stock are entitled to share ratably in all assets that are legally available for distribution. The holders of our common stock have no preemptive, subscription, redemption or conversion rights.
Description of the Southridge Warrant
The warrants included in this offering provide the holder with the right to purchase an aggregate of 300,000 shares of our common stock at an initial exercise price of $2.00 per share during the period commencing upon issuance and ending on the fifth anniversary thereof, subject to the terms and conditions set forth in the form of warrant. The following is a brief summary of certain provisions of the warrant, does not purport to be complete, and is qualified by reference in its entirety to the form of warrant which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part.
Exercise
The warrants may be exercised at any time after their issuance and on or before the fifth anniversary of their issuance by delivering to the Company a duly executed facsimile copy of the form of notice of exercise attached to the warrant certificate together with the aggregate exercise price for the number of shares being acquired. The warrants may also be exercised by means of a “cashless exercise” in accordance with the formula set forth in the warrant. In that case, the holder of the warrants would receive only the number of shares of common stock resulting from the application of that formula. Subject to certain exceptions set forth in the warrant certificate, the warrants are subject to a limitation on exercise in circumstances that would result in the holder having beneficial ownership of more than 4.99% of the outstanding shares of the Company’s common stock after giving effect to the exercise of such warrants.
Certificates for shares purchased upon exercise of the warrants will be credited to the holder’s prime broker with the Depository Trust Company through its Deposit Withdrawal System if the Company is then a participant in such system and the shares of common stock are then eligible for resale without volume or manner-of-sale limitations under Rule 144 promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933. Otherwise, the warrant holder will receive physical delivery of certificates for the purchased shares.
Exercise Price
The exercise price of the warrants is initially $2.00 per share. This initial exercise price and the number of shares issuable upon exercise of the warrants are subject to adjustment in the event of common stock dividends, subdivisions, combinations, and reclassifications, the issuance of rights to purchase common stock issued to holders of common stock, and the distribution to the holders of common stock of indebtedness, assets or rights to purchase other securities.
Market Information
On February 10, 2010, shares of our common stock began trading on the OTC.BB under the trading symbol “CVGC”. Since March 22, 2010, our average daily trading volume has been less than 10,000 shares per day. As with most stocks that begin trading on the OTC.BB, it will take time for a significant active trading market in our common stock to develop. There can be no assurance that a significant active trading market in our common stock will develop, or if such a market develops, that it will be sustained.
The audited financial statements of Covenant Group of China Inc. as of December 31, 2009 were audited by Morison Cogen, LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, to the extent set forth in its report and are included herein in reliance upon the authority of this firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
The validity of our common stock offered hereby will be passed upon for us by Holland & Hart, LLP, Reno, Nevada.
On December 24, 2009, we dismissed Manning Elliott LLP (“Manning Elliott”) as our independent accountants. Manning Elliott had previously been engaged as the principal accountant to audit our financial statements. The reason for the dismissal of Manning Elliott is that, following the consummation of the share exchange on December 24, 2009, (i) the former shareholders of Covenant Holdings own a significant amount of the outstanding shares of our common stock and (ii) our primary business became the business previously conducted by Covenant Holdings. The independent registered public accountant of Covenant Holdings for US accounting purposes was the firm of Morison Cogen LLP (“Morison Cogen”). We believe that it is in our best interest to have Morison Cogen continue to work with our business, and we therefore retained Morison Cogen as our new principal independent registered accounting firm, effective as of December 24, 2009. Morison Cogen is located at 150 Monument Road, Suite 500, Bala Cynwyd, PA 19004. The decision to change accountants was approved by our board of directors on December 24, 2009.
The report of Manning Elliott on our financial statements for the period from November 8, 2006 (inception) through our fiscal year ended June 30, 2009 did not contain an adverse opinion or disclaimer of opinion, nor was it qualified or modified as to uncertainty, audit scope or accounting principles, except that the report was qualified as to our ability to continue as a going concern.
From our inception through December 23, 2009, there were no disagreements with Manning Elliott on any matter of accounting principles or practices, financial statement disclosure, or auditing scope or procedure which, if not resolved to the satisfaction of Manning Elliott, would have caused it to make reference to the matter in connection with its reports.
From our inception through December 24, 2009, we did not consult Morison Cogen regarding either: (i) the application of accounting principles to a specific completed or contemplated transaction, or the type of audit opinion that might be rendered on our financial statements; or (ii) any matter that was the subject of a disagreement.
We have made the contents of our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 31, 2009 available to Manning Elliott and requested it to furnish us a letter addressed to the SEC as to whether Manning Elliott agrees or disagrees with, or wishes to clarify our expression of, our views, or containing any additional information. A copy of Manning Elliott’s letter to the SEC is included as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part.
The Nevada Revised Statutes provide that a director or officer is not individually liable to the corporation or its shareholders or creditors for any damages as a result of any act or failure to act in his capacity as a director or officer unless it is proven that his act or failure to act constituted a breach of his fiduciary duties as a director or officer and his breach of those duties involved intentional misconduct, fraud or a knowing violation of law. The Articles of Incorporation or an amendment thereto may, however, provide for greater individual liability. Furthermore, directors may be jointly and severally liable for the payment of certain distributions in violation of Chapter 78 of the Nevada Revised Statutes.
This provision is intended to afford directors and officers protection against and to limit their potential liability for monetary damages resulting from suits alleging a breach of the duty of care by a director or officer. As a consequence of this provision, shareholders of our company will be unable to recover monetary damages against directors or officers for action taken by them that may constitute negligence or gross negligence in performance of their duties unless such conduct meets the requirements of Nevada law to impose such liability. The provision, however, does not alter the applicable standards governing a director’s or officer’s fiduciary duty and does not eliminate or limit the right of our company or any shareholder to obtain an injunction or any other type of non-monetary relief in the event of a breach of fiduciary duty.
The Nevada Revised Statutes also provide that under certain circumstances, a corporation may indemnify any person for amounts incurred in connection with a pending, threatened or completed action, suit or proceeding in which he is, or is threatened to be made, a party by reason of his being a director, officer, employee or agent of the corporation or serving at the request of the corporation as a director, officer, employee or agent of another corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust or other enterprise, if such person (a) is not liable for a breach of fiduciary duty involving intentional misconduct, fraud or a knowing violation of law or such greater standard imposed by the corporation’s articles of incorporation; or (b) acted in good faith and in a manner which he reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interests of the corporation, and, with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, had no reasonable cause to believe his conduct was unlawful. Additionally, a corporation may indemnify a director, officer, employee or agent with respect to any threatened, pending or completed action or suit by or in the right of the corporation to procure a judgment in its favor, if such person (a) is not liable for a breach of fiduciary duty involving intentional misconduct, fraud or a knowing violation of law or such greater standard imposed by the corporation’s articles of incorporation; or (b) acted in good faith and in a manner which he reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interests of the corporation, however, indemnification may not be made for any claim, issue or matter as to which such a person has been adjudged by a court to be liable to the corporation or for amounts paid in settlement to the corporation, unless the court determines that the person is fairly and reasonably entitled to indemnity for such expenses as the court deems proper. To the extent that a director, officer, employee or agent of a corporation has been successful on the merits or otherwise in defense of any action, suit or proceeding referred to above, or in defense of any claim, issue or matter therein, the corporation shall indemnify him against expenses, including attorneys’ fees, actually and reasonably incurred by him in connection with the defense.
Our Bylaws provide, among other things, that a director, officer, employee or agent of the corporation will be indemnified against all expense, liability, and loss (including attorneys’ fees, judgments, fines, taxes, penalties and amounts paid or to be paid in settlement) reasonably incurred or suffered in connection with any threatened, pending, or completed action suit, or proceeding, whether civil, criminal, administrative, or investigative provided that he or she either is not liable pursuant to Nevada Revised Statutes 78.138 (relating to liability of directors and officers to the corporation in certain instances) or acted in good faith and in a manner reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interests of the corporation and, in the case of a criminal proceeding, had no reasonable cause to believe that his or her conduct was unlawful.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act of 1933 may be permitted to directors, officers, or persons controlling the Company pursuant to the foregoing provisions, the Company has been informed that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is therefore unenforceable.
This prospectus is part of a Registration Statement on Form S-1 we have filed with the SEC. We have not included in this prospectus all of the information contained in the registration statement, and you should refer to our registration statement and its exhibits for further information.
We file annual, quarterly, and special reports, proxy statements, and other information with the SEC. You may read and copy any document we file at the SEC’s public reference room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. Copies of these materials may also be obtained from the SEC at prescribed rates by writing to the Public Reference Section of the SEC, 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. You may obtain information about the operation of the SEC public reference room in Washington, D.C. by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. Our filings are also available to the public from commercial document retrieval services and at the website maintained by the SEC at http://www.sec.gov.
Our Web site address is http://www.covenantchina.com. The information on our Web site is not incorporated into this prospectus.
-68-
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC.
Consolidated Financial Statements
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
Interim Financial Statements of Covenant Group of China Inc. (Unaudited)
|
|
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets (As of March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009)
|
F-3
|
|
Consolidated Statement of Operations and Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) (Three months ended March 31, 2010)
|
F-4
|
|
Consolidated Statement of Cash Flow (Three months ended March 31, 2010)
|
F-5
|
|
Notes to Consolidated Interim Financial Statements
|
F-6
|
|
Audited Financial Statements of Covenant Group of China Inc.
|
|
|
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
|
F-20
|
|
Consolidated Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2009
|
F-21
|
|
Consolidated Statement of Income and Other Comprehensive Income from inception (June 10, 2009) to December 31, 2009
|
F-22
|
|
Consolidated Statement of Stockholders’ Equity from inception (June 10, 2009) to December 31, 2009
|
F-23
|
|
Consolidated Statement of Cash Flow from inception (June 10, 2009) to December 31, 2009
|
F-24
|
|
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
|
F-25
|
|
Audited Financial Statements of Chongqing HongSheng Sysway Information Industry Co., Inc.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
|
F-41
|
|
Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2008 and 2007
|
F-43
|
|
Statement of Income and Other Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007
|
F-44
|
|
Statement of Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007
|
F-45
|
|
Statement of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007
|
F-46
|
|
Notes to Condensed Financial Statements
|
F-47
|
|
Audited Financial Statements of Hainan Jien Intelligent EngineeringCo., Inc.
|
|
|
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
|
F-58
|
|
Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2008 and 2007
|
F-60
|
|
Statements of Operations and Other Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007
|
F-61
|
|
|
|
|
Statement of Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007
|
F-62
|
|
Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007
|
F-63
|
|
Notes to Condensed Financial Statements
|
F-64
|
|
Interim Financial Statements of Chongqing HongSheng Sysway Information Industry Co., Inc. (Unaudited)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Condensed Balance Sheets (As of June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008)
|
F-73
|
|
Condensed Statements of Operations and Other Comprehensive Income (Six months ended June 30, 2009 and 2008)
|
F-74
|
|
Condensed Statements of Cash Flow (Six months ended June 30, 2009 and 2008)
|
F-75
|
|
Notes to Condensed Interim Financial Statements
|
F-76
|
|
Interim Financial Statements of Hainan Jien Intelligent Engineering Co., Inc. (Unaudited)
|
|
|
Condensed Balance Sheets (As of June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008)
|
F-82
|
|
Condensed Statements of Operations and Other Comprehensive Income (Six months ended June 30, 2009 and 2008)
|
F-83
|
|
Condensed Statements of Cash Flow (Six months ended June 30, 2009 and 2008)
|
F-84
|
|
Notes to Condensed Interim Financial Statements
|
F-85
|
|
Interim Financial Statements of Covenant Group Holdings, Inc. (Unaudited)
|
|
|
Consolidated Balance Sheet (As of September 30, 2009)
|
F-92
|
|
Consolidated Statement of Operations and Other Comprehensive Income (from inception (June 10, 2009) to September 30, 2009))
|
F-93
|
|
Consolidated Statement of Stockholders’ Equity (from inception (June 10, 2009) to September 30, 2009))
|
F-94
|
|
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flow (from inception (June 10, 2009) to September 30, 2009))
|
F-95
|
|
Notes to Consolidated Interim Financial Statements
|
F-96
|
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET
|
|
March 31, 2010
|
December 31, 2009
|
||||||
|
ASSETS
|
(Unaudited)
|
(Audited)
|
||||||
|
CURRENT ASSETS
|
||||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalent
|
$
|
1,273,928
|
$
|
969,271
|
||||
|
Accounts receivable, net
|
1,492,206
|
2,156,112
|
||||||
|
Retentions receivable
|
268,105
|
344,428
|
||||||
|
Other receivables
|
171,897
|
234,066
|
||||||
|
Prepayment and deposits
|
37,543
|
98,537
|
||||||
|
Inventories
|
263,810
|
102,950
|
||||||
|
Total current assets
|
3,507,489
|
3,905,364
|
||||||
|
NON-CURRENT ASSETS
|
||||||||
|
Retentions receivable
|
236,731
|
146,451
|
||||||
|
Property, plant and equipment, net
|
27,702
|
21,794
|
||||||
|
Goodwill
|
572,020
|
572,020
|
||||||
|
Intangible assets
|
25,000
|
-
|
||||||
|
Total non-current assets
|
861,453
|
740,265
|
||||||
|
Assets of discontinued operations
|
-
|
4,162,726
|
||||||
|
Total assets
|
$
|
4,368,942
|
$
|
8,808,355
|
||||
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES
|
||||||||
|
Short term loans
|
$
|
261,928
|
$
|
37,638
|
||||
|
Note payable
|
-
|
100,000
|
||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
440,208
|
983,656
|
||||||
|
Unearned revenue
|
192,479
|
155,432
|
||||||
|
Taxes payable
|
18,570
|
9,980
|
||||||
|
Other payables and accrued liabilities
|
280,658
|
438,774
|
||||||
|
Dividend payable
|
478,394
|
478,260
|
||||||
|
Total current liabilities
|
1,672,237
|
2,203,740
|
||||||
|
Liabilities of discontinued operations
|
-
|
1,616,586
|
||||||
|
Total liabilities
|
1,672,237
|
3,820,326
|
||||||
|
STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
Common stock, $0.00001 par value, 20,000,000 shares
authorized, 11,280,909 shares issued and 9,880,909 shares
outstanding as of March 31, 2010, and 11,480,909 shares
issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2009 respectively
|
113
|
115
|
||||||
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
6,100,020
|
5,572,018
|
||||||
|
Statutory surplus reserve
|
67,737
|
67,737
|
||||||
|
Accumulated deficit
|
(681,174
|
)
|
(647,735
|
)
|
||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss
|
(1,938
|
)
|
(4,106
|
)
|
||||
|
5,484,758
|
4,988,029
|
|||||||
|
Less: treasury stock, at cost; 1,400,000 shares of common stock
|
(2,788,053
|
)
|
-
|
|||||
|
Total stockholders' equity
|
2,696,705
|
4,988,029
|
||||||
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
$
|
4,368,942
|
$
|
8,808,355
|
||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF OPERATION AND OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(Unaudited)
|
NET SALES
|
$
|
1,425,941
|
||
|
COST OF SALES
|
1,006,965
|
|||
|
GROSS PROFIT
|
418,976
|
|||
|
OPERATING EXPENSES
|
||||
|
Selling expenses
|
16,093
|
|||
|
General and administrative expenses
|
244,323
|
|||
|
Total Operating Expenses
|
260,416
|
|||
|
INCOME FROM OPERATIONS
|
158,560
|
|||
|
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSES)
|
||||
|
Other income
|
199
|
|||
|
Other expense
|
(202
|
)
|
||
|
Loss on settlement of debt
|
(428,000
|
)
|
||
|
Interest expense
|
(4,259
|
)
|
||
|
Total Other Expenses, net
|
(432,262
|
)
|
||
|
NET LOSS
|
(273,702
|
)
|
||
|
OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
|
||||
|
Foreign currency translation
|
2,168
|
|||
|
COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
|
$
|
(271,534
|
)
|
|
|
BASIC AND DILUTED WEIGHTED AVERAGE SHARES OUTSTANDING
|
10,063,131
|
|||
|
BASIC AND DILUTED NET LOSS PER SHARE
|
$
|
0.00
|
||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOW
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||
|
$
|
(273,702
|
)
|
||
|
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash
|
||||
|
provided by operating activities:
|
||||
|
Depreciation and amortization
|
1,832
|
|||
|
Change in allowance for doubtful accounts
|
(10,301
|
)
|
||
|
Loss on disposal of fixed assets
|
115
|
|||
|
Loss on settlement of debt
|
428,000
|
|||
|
(Increase) decrease in current assets:
|
||||
|
Accounts receivable
|
674,750
|
|||
|
Retentions receivable
|
(13,819
|
)
|
||
|
Other receivables
|
62,229
|
|||
|
Prepayment and deposits
|
61,016
|
|||
|
Inventory
|
(160,817
|
)
|
||
|
Increase (decrease) in current liabilities:
|
||||
|
Accounts payable
|
(543,674
|
)
|
||
|
Unearned revenue
|
37,001
|
|||
|
Accrued liabilities and other payables
|
(158,224
|
)
|
||
|
Taxes payable
|
8,587
|
|||
|
Net cash provided by operating activities
|
112,993
|
|||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||
|
Acquisition of property & equipment
|
(32,848
|
)
|
||
|
Net cash used in investing activities
|
(32,848
|
)
|
||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||
|
Proceeds from short term loans
|
224,260
|
|||
|
Net cash provided by financing activities
|
224,260
|
|||
|
EFFECT OF EXCHANGE RATE CHANGE ON CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
252
|
|||
|
NET INCREASE IN CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
304,657
|
|||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF PERIOD
|
969,271
|
|||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, END OF PERIOD
|
$
|
1,273,928
|
||
|
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information:
|
||||
|
Cash paid during the period for:
|
||||
|
Income tax paid
|
$
|
18,578
|
||
|
Interest paid
|
$
|
681
|
||
|
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash investing activities:
|
||||
|
Net assets of discontinued operations
|
$
|
2,788,053
|
||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
1. ORGANIZATION AND DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
Covenant Group of China Inc. (Covenant Group or the Company) (FKA: Everest Resources Corp.) was incorporated in the State of Nevada on November 8, 2006. On December 24, 2009, Covenant Group entered into and closed on a share exchange agreement with Covenant Group Holdings Inc. (Covenant Holdings), a privately held company incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware. Pursuant to the share exchange agreement, Covenant Group acquired all of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Covenant Holdings in exchange for 9,380,909 shares of common stock. Prior to the acquisition of Covenant Holdings, the Company was in the development stage and had minimal business operations.
Covenant Holdings was formed in the State of Delaware on June 10, 2009 to acquire equity interests in private Chinese operating companies and providing these companies with strategic support. The total number of Covenant Holdings shares authorized for issuance is 20,000,000 with $0.00001 par value. Covenant Holdings identified companies that focus on IT applications in Government mandated areas such as communications and media, government manufacturing and security and surveillance. There was no significant activity from June 10, 2009 through December 31, 2009 except for two acquisitions.
On June 24, 2009, Covenant Holdings entered into a stock acquisition and reorganization agreement with Hainan Jien Intelligent Engineering Co. Ltd. (Jien) and its stockholders. Pursuant to the terms of the agreement, Covenant Holdings acquired 100% of the common stock of Jien, representing 100% of its outstanding equity interests, in exchange for 1,350,000 shares of a public shell's common stock, which would acquire all of the rights and obligations of Covenant Holdings. The acquisition stock price was initially valued at a provisional amount of $2 per share, which was the stock price for Covenant Holdings’ prior private capital raises. The Company changed its valuation stock price to $1.76 per share, which was determined by the volume weighted average stock price for the first day of trading of the Company’s common stock plus all private sales of Covenant Holdings’ common stock prior to the completion of the reverse merger with the Company. Jien was incorporated in Hainan Province, People’s Republic of China in 1999. Jien specializes in the design and installation of security and surveillance infrastructure to protect financial institutions and government agencies, and it also implements IC projects for commercial customers.
On June 24, 2009, Covenant Holdings entered into a stock acquisition and reorganization agreement with Chongqing Sysway Information Technology Co. Ltd. (Chongqing Sysway) and its stockholders. Pursuant to the terms of the agreement, Covenant Holdings acquired 100% of the common stock of Chongqing Sysway, representing 100% of its outstanding equity interests, in exchange for 1,400,000 shares of a public shell's common stock, which would acquire all of the rights and obligations of Covenant Holdings. The acquisition stock price was initially valued at a provisional amount of $2 per share, which was the stock price for Covenant Holdings’ prior private capital raises. The Company changed its valuation stock price to $1.76 per share, which was determined by the volume weighted average stock price for the first day of trading of the Company’s common stock plus all private sales of Covenant Holdings’ common stock prior to the completion of the reverse merger with the Company. Chongqing Sysway was incorporated in Chongqing City, Sichuan Province, PRC, in 1999 as a State Owned Enterprise (SOE). Since 2005, Chongqing Sysway has operated as a private enterprise mainly engaged in systems integration services, including computer system installation, website design, and system firewall setup, particularly for the tobacco industry.
For accounting purposes, the effective acquisition date of Jien and Chongqing Sysway is deemed to be July 1, 2009 as the results of any activity from June 24, 2009 through June 30, 2009 were deemed to be immaterial to the financial statements taken as a whole.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
On December 24, 2009, Covenant Holdings entered into a share exchange agreement with Covenant Group. Covenant Group agreed to exchange 9,380,909 shares of its common stock, on a one-for-one basis, for each share of Covenant Holdings shares held of record on the date of the closing. Concurrent with the share exchange agreement, one of Covenant Group’s shareholders agreed to cancel 4,500,000 shares out of 6,600,000 of the total issued and outstanding shares of Covenant Group in exchange for the immediate payment of $100,000. He further agreed to cancel an additional 500,000 shares upon Covenant Holdings’ payment of the principal due on a note issued to the shareholder in the amount of $190,000, which, together with the $100,000 payment, represented the consideration for the acquisition of the shell company. As of December 31, 2009, $90,000 of the $190,000 note payable was paid. During the first quarter of 2010, the 500,000 shares were cancelled and the Company issued 300,000 shares to this shareholder in lieu of the payment for the note payable of $100,000. In May of 2010, the Company and this shareholder agreed to revise and reduce the 300,000 shares to 70,000 shares. The Share Exchange was being accounted for as a "reverse acquisition," since the Covenant Holdings shareholders own a majority of the outstanding shares of the Company's common stock immediately following the share exchange. Covenant Holdings was deemed to be the accounting acquiror in the reverse acquisition. Consequently, the assets and liabilities and the historical operations that were reflected in the financial statements prior to the share exchange were those of Covenant Holdings and were recorded at the historical cost basis of Covenant Holdings. The consolidated financial statements after completion of the share exchange would include the assets and liabilities of the Company and Covenant Holdings, and the historical operations of Covenant Holdings and operations of the Company from the closing date of the share exchange. As a result of the issuance of the shares of the Company’s common stock pursuant to the share exchange, a change in control of the Company occurred on the date of the consummation of the share exchange.
The Company's Board of Directors decided on April 30, 2010, to terminate and rescind the Acquisition Agreement with Chongqing Sysway due to several breaches of the agreement by Chongqing Sysway, including the failure of the prior owners of Chongqing Sysway to repay a dividend paid to them by Chongqing Sysway in excess of that permitted under the agreement and under China law and the failure of Chongqing Sysway and its prior owners to cooperate with the Company in the preparation of its financial statement disclosures required under United States securities laws. As a result of the termination and rescission of the agreement, the Company will transfer all of the shares of capital stock of Chongqing Sysway to the prior owners of Chongqing Sysway, and the 1,400,000 shares of common stock of the Company issued in exchange for the shares of capital stock of Chongqing Sysway will be returned to the Company and treated as treasury shares. The intent of this transaction is to return the Company, Chongqing Sysway, and the prior owners of the capital stock of Chongqing Sysway to their status prior to the completion of the acquisition by the Company of the capital stock of Chongqing Sysway on December 24, 2009.
On January 12, 2010, the Company formed a wholly owned subsidiary – Pandaz LLC, a Delaware LLC (Pandaz Delaware). On January 13, 2010, Pandaz Delaware entered into an asset purchase agreement with The Pandaz LLC, a Nevada LLC, for certain assets and intellectual property associated with an automobile dealer and customer interface, vehicle search function and automobile purchasing website that the company is tentatively looking to implement in China. The total purchase consideration was $25,000, of which, $10,000 was paid as the forgiveness of a bridge loan that the Company provided to the seller on January 7, 2010 and $15,000 was paid as a one-time cash payment.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principle of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Covenant Holdings, Covenant Group, Pandaz Delaware and Jien. All intercompany transactions and account balances are eliminated in consolidation.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying unaudited financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles for interim financial information and with the instructions for Form 10-Q and Rule 8-03 of Regulation S-X. Accordingly, they do not include all of the information and footnotes required by generally accepted accounting principles for complete financial statements. In the opinion of management, all adjustments (consisting of normal recurring accruals) considered necessary for a fair presentation have been included. Operating results for the three months ended March 31, 2010 are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected for the year ending December 31, 2010.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
Use of Estimates
In preparing the financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, management makes estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the dates of the financial statements, as well as the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting year. Significant estimates, required by management, include the recoverability of long-lived assets and the valuation of inventories. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
For purposes of the statement of cash flows, the Company considers all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
Accounts and Retentions Receivable
The Company’s policy is to maintain reserves for potential credit losses on accounts receivable. Management reviews the composition of accounts receivable and analyzes historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customer payment patterns to evaluate the adequacy of these reserves. Based on historical collection activity, the Company had allowances of $4,505 at March 31, 2010 and $78,356 at December 31, 2009.
At March 31, 2010, the Company had retentions receivable for product quality assurance of $504,836. At December 31, 2009, the Company had $490,879 of retentions receivable. The retention rate varies from 3% to 5% of the sales price, with variable terms from 1 year to 3 years. $268,105 and $344,428 of the retentions receivable at March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively, are current and due within one year; $236,731 and $146,451 of the retentions receivable are treated as long term assets at March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively.
Inventories
Jien’s inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market with cost determined on a first-in, first-out basis.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred; additions, renewals and betterments are capitalized. When property and equipment are retired or otherwise disposed of, the related cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from the respective accounts, and any gain or loss is included in operations. Depreciation of property and equipment is provided using the straight-line method for substantially all assets with 5% salvage value and estimated lives ranging from 3 to 25 years as follows:
|
Building
|
20 - 25 years
|
|
Leasehold improvements
|
Shorter of lease term or 10 years
|
|
Vehicle
|
5 - 10 years
|
|
Office Equipment
|
3 - 5 years
|
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Long-lived assets, which include property, plant and equipment and intangible assets, are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable.
Recoverability of long-lived assets to be held and used is measured by comparing the carrying amount of an asset to the estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its estimated undiscounted future cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset. Fair value is generally determined using the asset’s expected future discounted cash flows or market value, if readily determinable. Based on its review, the Company believes that, as of March 31, 2010, there were no significant impairments of its long-lived assets.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the fair value of the consideration transferred over the net of the acquisition date amount of identifiable assets acquired and the liability assumed. In accordance with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 142, Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets (“Statement No. 142”), codified in Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 350, goodwill is not amortized but is tested for impairment annually, or when circumstances indicate a possible impairment may exist. Impairment testing is performed at a reporting unit level. An impairment loss generally would be recognized when the carrying amount of the reporting unit exceeds the fair value of the reporting unit, with the fair value of the reporting unit determined using a discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis. A number of significant assumptions and estimates are involved in the application of the DCF analysis to forecast operating cash flows, including the discount rate, the internal rate of return, and projections of realizations and costs to produce. Management considers historical experience and all available information at the time the fair values of its reporting units are estimated.
Warranties
The Company offers a warranty to its customers on its products for a period from three months to three years depending on the contract terms negotiated with the customers; most of warranty term is one year. The Company accrues for warranty costs based on estimates of the costs that may be incurred under its warranty obligations. The warranty expense and related accrual is included in the Company's selling expenses and other payables respectively, and is recorded at the time revenue is recognized. Factors that affect the Company's warranty liability include the number of sold equipment, its estimates of anticipated rates of warranty claims, costs per claim and estimated support labor costs and the associated overhead. The Company periodically assesses the adequacy of its recorded warranty liabilities and adjusts the amounts as necessary. The Company’s warranty expense was immaterial for the three months ended March 31, 2010.
Income Taxes
The Company utilizes Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (SFAS) No. 109, “Accounting for Income Taxes,” codified in FASB ASC Topic 740, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Under this method, deferred income taxes are recognized for the tax consequences in future years of differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their financial reporting amounts at each period end based on enacted tax laws and statutory tax rates applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to affect taxable income. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
The Company adopted the provisions of FASB Interpretation No. 48, Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes (codified in FASB ASC Topic 740) on June 10, 2009. As a result of the implementation of FIN 48, the Company made a comprehensive review of its portfolio of tax positions in accordance with recognition standards established by FIN 48. As a result of the implementation of Interpretation 48, the Company recognized no material adjustments to liabilities or stockholders equity. When tax returns are filed, it is highly certain that some positions taken would be sustained upon examination by the taxing authorities, while others are subject to uncertainty about the merits of the position taken or the amount of the position that would be ultimately sustained. The benefit of a tax position is recognized in the financial statements in the period during which, based on all available evidence, management believes it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including the resolution of appeals or litigation processes, if any. Tax positions taken are not offset or aggregated with other positions. Tax positions that meet the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold are measured as the largest amount of tax benefit that is more than 50 percent likely of being realized upon settlement with the applicable taxing authority. The portion of the benefits associated with tax positions taken that exceeds the amount measured as described above is reflected as a liability for unrecognized tax benefits in the accompanying balance sheets along with any associated interest and penalties that would be payable to the taxing authorities upon examination.
Interest associated with unrecognized tax benefits are classified as interest expense and penalties are classified in selling, general and administrative expenses in the statements of income. The adoption of FIN 48 did not have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
Covenant Holdings had a US net operating loss of $818,290 at March 31, 2010 and $690,724 at December 31, 2009. A 100% valuation allowance has been established due to the uncertainty of its realization.
Covenant Group of China and Pandaz Delaware had US net operating loss of $16,918 and $8,400 at March 31, 2010, respectively.
Jien is qualified as a small business in the construction industry in the PRC. The Company is subject to a 1.76% and 3% tax rate on net sales for 2010 and 2009. Since the tax is based on sales, under US GAAP, it is not an income tax. Accordingly, $25,695 was recorded as general and administrative expense for the three months ended March 31, 2010.
The following table reconciles the U.S. statutory rates to the Company’s consolidated effective tax rate for the three months ended at March 31, 2010:
|
U.S. statutory rates
|
$
|
(93,059)
|
||
|
Foreign tax rate less than U.S. statutory rate
|
(27,645)
|
|||
|
Unrecognized tax benefit on US operating loss
|
51,980
|
|||
|
Non tax deductible expense for US company
|
145,520
|
|||
|
Foreign income exempt from foreign income tax
|
(76,796)
|
|||
|
Income tax expense
|
$
|
-
|
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) consist of the following:
| U.S. net operating loss | ||||
|
Deferred tax asset
|
||||
|
U.S. net operating loss
|
$
|
51,980
|
||
|
Less valuation allowance
|
(51,980)
|
|||
|
Net deferred tax asset
|
$
|
-
|
The valuation allowance for deferred tax assets as of March 31, 2010 was $286,826. The change in the total valuation for the three months ended March 31, 2010 was an increase of $51,980. The deferred tax asset arose from the net operating loss generated at the US parent company level. In assessing the realization of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which the net operating losses and temporary differences become deductible. Management considered projected future taxable income and tax planning strategies in making this assessment. The value of the deferred tax assets was offset by a valuation allowance, due to the current uncertainty of the future realization of the deferred tax assets.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
Revenue Recognition
The Company's revenue recognition policies are in compliance with Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Staff Accounting Bulletin (SAB) 104 (codified in FASB ASC Topic 480). Revenue is recognized at the date of shipment to customers when a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and collectability is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are recorded as unearned revenue.
The Company records its revenue when certain milestones as defined in the service contract are reached. These service contracts have clear milestones and deliverables with distinct values assigned to each milestone. The milestones do not require the delivery of multiple elements as noted in Emerging Issues Task Force (EITF) Issue 00-21 “Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables” (EITF No. 00-21) (codified in FASB ASC Topic 605). In accordance with SAB No. 104, the Company treats each milestone as an individual revenue agreement and only recognizes revenue for each milestone when all the conditions of SAB 104 defined earlier are met. Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of goods and services, net of value-added tax (VAT).
Jien is qualified as a small business so that all of the Company’s products sold or services provided in the PRC are subject to a fixed VAT rate of 4% of the gross sales price regardless of the VAT paid for 2010. Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of goods or services, net of VAT. This VAT cannot be offset by VAT paid by the Company on equipment and other materials included in the cost of completing contracts with customers.
The standard warranty of Jien is provided to its customers and is not considered an additional service; rather it is considered an integral part of the product and services’ sale. The Company believes that the existence of its standard product warranty in a sales contract does not constitute a deliverable in the arrangement and thus there is no need to apply the EITF 00-21(codified in FASB ASC Topic 605) separation and allocation model for a multiple deliverable arrangement. FAS 5 (codified in FASB ASC Topic Warranty) specifically addresses the accounting for standard warranties, and neither SAB 104 nor EITF 00-21 supersedes FAS 5. The Company believes that accounting for its standard warranty pursuant to FAS 5 does not impact revenue recognition because the cost of honoring the warranty can be reliably estimated.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of goods sold consists primarily of material costs, labor costs, and related overhead which are directly attributable to the production of the service. Write-down of inventory to lower of cost or market is also recorded in cost of goods sold.
Basic and Diluted Earnings (Loss) per Share (EPS)
Basic EPS is computed by dividing income available to common shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted EPS is similarly computed, except that the denominator is increased to include the number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding if the potential common shares had been issued and if the additional common shares were dilutive. Diluted net earnings per share are based on the assumption that all dilutive convertible shares and stock options were converted or exercised. Dilution is computed by applying the treasury stock method. Under this method, options and warrants are assumed to have been exercised at the beginning of the period (or at the time of issuance, if later), and as if funds obtained thereby were used to purchase common stock at the average market price during the period. Since the company does not have any outstanding options or warrants, the basic and diluted EPS are the same.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to credit risk consist primarily of accounts receivable and other receivables. The Company does not require collateral or other security to support these receivables. The Company conducts periodic reviews of its clients' financial condition and customer payment practices to minimize collection risk on accounts receivable.
The operations of the Company are located in the PRC. Accordingly, the Company's business, financial condition, and results of operations may be influenced by the political, economic, and legal environments in the PRC, as well as by the general state of the PRC economy.
Statement of Cash Flows
In accordance with SFAS No. 95, “Statement of Cash Flows,” codified in FASB ASC Topic 230, cash flows from the Company's operations are calculated based upon the local currencies. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the statement of cash flows may not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the balance sheet.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
For certain of the Company’s financial instruments, including cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, other receivables, accounts payable, accrued liabilities and short-term debt, the carrying amounts approximate their fair values due to their short maturities.
ASC Topic 820, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures,” requires disclosure of the fair value of financial instruments held by the Company. ASC Topic 825, “Financial Instruments,” defines fair value, and establishes a three-level valuation hierarchy for disclosures of fair value measurement that enhances disclosure requirements for fair value measures. The carrying amounts reported in the consolidated balance sheets for receivables and current liabilities each qualify as financial instruments and are a reasonable estimate of their fair values because of the short period of time between the origination of such instruments and their expected realization and their current market rate of interest. The three levels of valuation hierarchy are defined as follows:
|
·
|
Level 1 inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
|
|
|
·
|
Level 2 inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, and inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument.
|
|
|
·
|
Level 3 inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and significant to the fair value measurement.
|
The Company analyzes all financial instruments with features of both liabilities and equity under ASC 480, “Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity,” and ASC 815.
As of March 31, 2010, the Company did not have any financial instruments that are required to be presented on the balance sheet at fair value.
Foreign Currency Translation and Transactions
The accompanying consolidated financial statements are presented in United States Dollars (“USD”). The Company’s functional currency is the USD, while the Company’s wholly-owned Chinese subsidiaries’ functional currency is the Renminbi (“RMB”). The functional currencies of the Company’s foreign operations are translated into USD for balance sheet accounts using the current exchange rates in effect as of the balance sheet date and for revenue and expense accounts using the weighted-average exchange rate during the fiscal year. The translation adjustments are recorded as a separate component of stockholders’ equity, captioned accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). Gains and losses resulting from transactions denominated in foreign currencies are included in other income (expense) in the consolidated statements of operations. There have been no significant fluctuations in the exchange rate for the conversion of RMB to USD after the balance sheet date.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The Company uses SFAS 130 “Reporting Comprehensive Income” (codified in FASB ASC Topic 220). Comprehensive income is comprised of net income and all changes to the statements of stockholders’ equity, except those due to investments by stockholders, changes in paid-in capital and distributions to stockholders. Comprehensive income for the three months ended March 31, 2010 included net income and foreign currency translation adjustments.
Segment Reporting
SFAS No. 131, "Disclosures about Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information," codified in FASB ASC Topic 280, requires use of the “management approach” model for segment reporting. The management approach model is based on the way a company's management organizes segments within the company for making operating decisions and assessing performance. Reportable segments are based on products and services, geography, legal structure, management structure, or any other manner in which management disaggregates a company.
SFAS 131 has no effect on the Company's financial statements as substantially all of the Company's operations are conducted in one industry segment. The Company consists of one reportable business segment. All of the Company's assets are located in the PRC and its principal market is in the PRC.
New Accounting Pronouncements
On February 25, 2010, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2010-09 Subsequent Events Topic 855, “Amendments to Certain Recognition and Disclosure Requirements,” effective immediately. The amendments in the ASU remove the requirement for an SEC filer to disclose a date through which subsequent events have been evaluated in both issued and revised financial statements. Revised financial statements include financial statements revised as a result of either correction of an error or retrospective application of US GAAP. The FASB believes these amendments remove potential conflicts with the SEC’s literature. Subsequent events have been evaluated through the date the financial statements were issued.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted
As of March 31, 2010, there are no recently issued accounting standards not yet adopted which would have a material effect on the Company’s financial statements.
3. INVENTORY
Inventory consisted of the following at March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009:
|
2010
|
2009
|
|||||||
|
Raw Material
|
$
|
52,204
|
$
|
20,056
|
||||
|
Work in Process
|
211,606
|
82,894
|
||||||
|
Total
|
$
|
263,810
|
$
|
102,950
|
||||
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
4. ACQUISITION
On June 24, 2009, Covenant Holdings entered into stock acquisition and reorganization agreements with Jien and Chongqing Sysway (note 1). For convenience of reporting the acquisition for accounting purposes, July 1, 2009 has been designated as the acquisition date.
The following table summarizes the fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of acquisition.
|
Jien
|
Chongqing Sysway
|
Total
|
||||||||||
|
Cash
|
$
|
710,552
|
$
|
44,098
|
$
|
754,650
|
||||||
|
Accounts receivable
|
2,420,881
|
1,380,413
|
3,801,294
|
|||||||||
|
Retention receivable
|
271,770
|
1,084,047
|
1,355,817
|
|||||||||
|
Prepaid expenses
|
238,275
|
-
|
238,275
|
|||||||||
|
Advance to suppliers
|
-
|
1,661
|
1,661
|
|||||||||
|
Other receivables
|
154,237
|
132,186
|
286,423
|
|||||||||
|
Inventory
|
134,087
|
83,858
|
217,945
|
|||||||||
|
Property and equipment
|
45,102
|
37,265
|
82,367
|
|||||||||
|
Intangible assets-core software
|
-
|
152,256
|
152,256
|
|||||||||
|
Goodwill
|
572,020
|
902,303
|
1,474,323
|
|||||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
(1,442,990
|
)
|
(991,463
|
)
|
(2,434,453
|
)
|
||||||
|
Other current liabilities
|
(182,370
|
)
|
(25,499
|
)
|
(207,869
|
)
|
||||||
|
Unearned revenue
|
(108,245
|
)
|
-
|
(108,245
|
)
|
|||||||
|
Tax payable
|
(405,263
|
)
|
(337,125
|
)
|
(742,388
|
)
|
||||||
|
Short term loan
|
(32,056
|
)
|
-
|
(32,056
|
)
|
|||||||
|
Purchase price
|
$
|
2,376,000
|
$
|
2,464,000
|
$
|
4,840,000
|
||||||
The fair value of the consideration transferred was initially valued at a provisional amount of $2 per share, which was the stock price for Covenant Holdings’ prior private capital raises. The Company changed its valuation stock price to $1.76 per share, which was determined by the volume weighted average stock price for the first day of trading of the Company’s common stock plus all private sales of Covenant Holdings’ common stock prior to the completion of the reverse merger with the Company. The excess of the fair value of the consideration transferred over the net of the acquisition date amounts of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed was allocated to goodwill.
The Company's Board of Directors decided on April 30, 2010 to terminate and rescind the Acquisition Agreement with Chongqing Sysway due to several breaches of the agreement by Chongqing Sysway, including the failure of the prior owners of Chongqing Sysway to repay a dividend paid to them by Chongqing Sysway in excess of that permitted under the agreement and under China law and the failure of Chongqing Sysway and its prior owners to cooperate with the Company in the preparation of its financial statement disclosures required under United States securities laws.
The following pro forma consolidated results of operations of the Company for the three months ended March 31, 2009 presents the consolidated operations of the Company as if the acquisition of Jien occurred on January 1, 2009.
|
For the
Three months
Ended
March 31, 2009
|
||||
|
Net revenue
|
$
|
2,028,041
|
||
|
Cost of revenue
|
(1,575,432
|
)
|
||
|
Gross profit
|
452,609
|
|||
|
Total operating expenses
|
(144,529)
|
|||
|
Income from operations
|
308,080
|
|||
|
Non-operating expenses
|
(1,302)
|
|||
|
Income tax
|
-
|
|||
|
Net income
|
$
|
306,778
|
||
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
5. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property and equipment consisted of the following at March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009:
|
2010
|
2009
|
|||||||
|
Vehicle
|
$
|
7,336
|
$
|
-
|
||||
|
Office equipment
|
30,618
|
32,876
|
||||||
|
Leasehold Improvement
|
12,254
|
12,251
|
||||||
|
Subtotal
|
50,208
|
45,127
|
||||||
|
Less: Accumulated depreciation
|
(22,506
|
)
|
(23,333
|
)
|
||||
|
$
|
27,702
|
$
|
21,794
|
|||||
Depreciation expense for the three months ended March 31, 2010 was $1,832.
6. OTHER RECEIVABLES
Other receivables consisted of the following at March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009:
|
2010
|
2009
|
|||||||
|
Short term advance to third parties
|
$
|
109,778
|
$
|
180,043
|
||||
|
Advance to staffs
|
60,654
|
42,307
|
||||||
|
Deposit
|
1,465
|
11,716
|
||||||
|
$
|
171,897
|
$
|
234,066
|
|||||
7. INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Intangible assets of $25,000 at March 31, 2010 mainly consisted of website operating software with vehicle search function, manufacture’s code and dealer interface capabilities for the amount of $15,000 and intellectual property for technical information for the amount of $10,000, which were purchased by Pandaz Delaware during the three months ended March 31, 2010. The amortization for the intangible assets for the three months ended March 31, 2010 was immaterial.
8. TAX PAYABLE
Tax payable consisted of the following at March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009:
|
2010
|
2009
|
|||||||
|
Income tax payable
|
$
|
45,718
|
$
|
38,590
|
||||
|
Business tax payable
|
(14,220
|
)
|
(26,346
|
)
|
||||
|
Other taxes payable
|
(12,928
|
)
|
(2,264
|
)
|
||||
|
$
|
18,570
|
$
|
9,980
|
|||||
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
9. ACCRUED LIABILITIES AND OTHER PAYABLES
Accrued liabilities and other payables consisted of the following at March 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009:
|
2010
|
2009
|
|||||||
|
Warranty provision
|
$
|
44,094
|
$
|
48,475
|
||||
|
Short term advance from third parties
|
132,695
|
216,031
|
||||||
|
Sales and business tax payable
|
103,869
|
174,268
|
||||||
|
$
|
280,658
|
$
|
438,774
|
|||||
10. COMMON STOCK
Effective November 10, 2009, the Company and the lender of the three bridge loans have agreed to cancel the promissory note of $399,870. In lieu of principal and interest payments due to the lender, the Company issued 200,909 shares of the Company’s common stock to the lender.
Pursuant to the confidential private placement memorandum dated November 24, 2009, the Company was offering to sell up to 750,000 shares at $2.00 per share, with a minimum purchase of 10,000 Shares per investor, requiring a minimum investment of $20,000, with a minimum total quantity of 150,000 Shares ($300,000) that must be subscribed for by all investors to affect a closing and avoid termination of the Offering. At December 16, 2009, the Company sold 200,000 shares through the private placement, which were converted into publicly-traded securities upon the Company’s merger with a public shell company on December 24, 2009.
During the first quarter of 2010, one shareholder cancelled 500,000 shares of the Company’s stock that was originally held as collateral for a note arising from the share exchange transaction on December 24, 2009 with an outstanding balance of $100,000. The Company issued 300,000 shares to this shareholder in lieu of the payment for the note payable of $100,000 (Note 14).
11. DIVIDEND PAYABLE
The Company declared a 30% dividend of Jien’s 2008 net income to Jien’s original shareholders and management as part of the acquisition agreement dated June 24, 2009. The dividend declared for Jien was $200,608, and has been recorded as a dividend payable at December 31, 2009. As part of the acquisition agreement, the Company also agreed to pay the original shareholders and management of Jien a 30% dividend on 2009 year end profits. The dividend was declared and was recorded as a dividend payable for Jien in the amount of $277,653, which was the retained earnings that were available for declaring a dividend at December 31, 2009.
At March 31, 2010, the dividend payable was approximately $478,000.
12. MAJOR CUSTOMERS
Three customers accounted for 85% of the total sales for the three months ended March 31, 2010, and these three customers accounted for 39%, 28% and 17%, respectively. At March 31, 2010, the total receivable balance due from these customers was $757,677.
Two suppliers accounted for 76% of the total purchases for the three months ended March 31, 2010 and these two vendors accounted for 63% and 13%, respectively. At March 31, 2010, the total payable due to these vendors was $253,322.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
13. SHORT TERM LOANS
During the three months ended March 31, 2010, the Company borrowed $261,928 (RMB 1,788,000) from Shenzhen Development Bank. The loan bears interest at 5.59% per year and is due on June 26, 2010. This loan is collateralized by $393,971 (RMB 2,689,360) of accounts receivable.
At December 31, 2009, the Company had borrowed $37,600 from Shenzhen Development Bank with interest at 5.832% per year, due in February of 2010; this loan was paid in full upon maturity.
14. NOTE PAYABLE
At December 31, 2009, note payable represented the $100,000 remaining balance from a $190,000 promissory note issued to a former majority shareholder of Covenant Group plus cash consideration for the acquisition of the shell company. This note was settled by issuing the shareholder 300,000 common shares of the Company with a fair value of $528,000, resulting in a loss on settlement of $428,000. In May of 2010, the Company and this shareholder agreed to revise and reduce the 300,000 shares to 70,000 shares.
15. STATUTORY RESERVES
Pursuant to the corporate law of the PRC effective January 1, 2006, PRC subsidiaries of the Company are required to maintain a statutory reserve by appropriating from its after-tax profit before declaration or payment of dividends. The statutory reserve represents restricted retained earnings.
Surplus reserve fund
The PRC subsidiaries of the Company are required to transfer 10% of their net income, as determined under PRC accounting rules and regulations, to a statutory surplus reserve fund until such reserve balance reaches 50% of the Company’s registered capital. The Company had $67,737 in this reserve at March 31, 2010.
The surplus reserve fund is non-distributable other than during liquidation and can be used to fund previous years’ losses, if any, and may be utilized for business expansion or converted into share capital by issuing new shares to existing shareholders in proportion to their shareholding or by increasing the par value of the shares currently held by them, provided that the remaining reserve balance after such issue is not less than 25% of the registered capital.
Common welfare fund
Common welfare fund is a voluntary fund to which the Company can elect to transfer 5% to 10% of its net income. The Company did not make any contribution to this fund for the period since business inception through March 31, 2010.
This fund can only be utilized on capital items for the collective benefit of the Company’s employees, such as construction of dormitories, cafeteria facilities, and other staff welfare facilities. This fund is non-distributable other than upon liquidation.
Pursuant to the "Circular of the Ministry of Finance (MOF) on the Issue of Corporate Financial Management after the Corporate Law Enforced" (No.67 [2006]), effective on April 1, 2006, issued by the MOF, companies transferred the balance of SCWF (Statutory Common Welfare Fund) as of December 31, 2005 to Statutory Surplus Reserve. Any deficit in the SCWF was charged in turn to Statutory Surplus Reserve, additional paid-in capital and undistributed profit of previous years. If a deficit still remains, it should be transferred to retained earnings and be reduced to zero by a transfer from after tax profit of following years. At December 31, 2005, the Company did not have a deficit in the SCWF.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
16. COMMITMENTS
Jien leased its office under a long term, non-cancelable, and renewable operating lease agreement on November 8, 2007, with an expiration date of November 7, 2009. Upon expiration, the Company renewed the lease for a period from November 8, 2009 to November 7, 2012, with monthly rent of approximately $3,600 (RMB 24,509). Annual rental expense is approximately $43,200 for the years ended December 31, 2010 and 2011, and approximately $36,000 for 2012. For the three months ended March 31, 2010, the rental expense was $10,770.
17. DISPOSAL OF SUBSIDIARY
The Company records discontinued operations if both of the following conditions are met: (a) the operations and cash flows of the component have been (or will be) eliminated from the ongoing operations of the Company as a result of the disposal transaction and (b) the Company will not have any significant continuing involvement in the operations of the component after the disposal transaction. During a period in which a component of the Company either has been disposed of or is classified as held for sale, the income statement of the Company for current and prior periods shall report the results of operations of the component, including any gain or loss recognized in accordance with SFAS No. 144 “Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets,” (codified in FASB ASC Topic 360) in discontinued operations. The results of operations of a component classified as held for sale shall be reported in discontinued operations in the period(s) in which they occur. The results of discontinued operations, less applicable income taxes (benefit), shall be reported as a separate component of income before extraordinary items and the cumulative effect of accounting changes (if applicable).
The Company's Board of Directors decided on April 30, 2010 to terminate and rescind the Acquisition Agreement with Chongqing Sysway due to several breaches of the agreement by Chongqing Sysway, including the failure of the prior owners of Chongqing Sysway to repay a dividend paid to them by Chongqing Sysway in excess of that permitted under the agreement and under China law and the failure of Chongqing Sysway and its prior owners to cooperate with the Company in the preparation of the financial statement disclosures required under United States securities laws.
As a result of the termination and rescission of the agreement, the Company will transfer all of the shares of capital stock of Chongqing Sysway to the prior owners of Chongqing Sysway, and the 1,400,000 shares of common stock of the Company issued in exchange for the shares of capital stock of Chongqing Sysway will be returned to the Company and treated as treasury shares. The intent of this transaction is to return the Company, Chongqing Sysway, and the prior owners of the capital stock of Chongqing Sysway to their status prior to the completion of the acquisition by the Company of the capital stock of Chongqing Sysway on December 24, 2009. For convenience of reporting for accounting purposes, January 1, 2010 has been designated as the date of rescission.
The assets and liabilities of Chongqing Sysway have been reclassified at December 31, 2009 as assets of discontinued operations and liabilities of discontinued operations.
Identifiable net assets Chongqing Sysway as of December 31, 2009 were as follows:
|
Cash & cash equivalents
|
$
|
413,093
|
||
|
Accounts receivable, net
|
1,456,008
|
|||
|
Other current assets
|
1,159,231
|
|||
|
Goodwill
|
902,303
|
|||
|
Other noncurrent assets
|
232,091
|
|||
|
Total assets
|
$
|
4,162,726
|
||
|
Accounts payable
|
$
|
829,444
|
||
|
Tax payable
|
536,633
|
|||
|
Dividend payable
|
242,851
|
|||
|
Other current liabilities
|
7,658
|
|||
|
Total liabilities
|
$
|
1,616,586
|
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2010
(unaudited)
18. CONTINGENCIES
The Company’s operations in the PRC are subject to specific considerations and significant risks not typically associated with companies in North America and Western Europe. These include risks associated with, among others, the political, economic and legal environments and foreign currency exchange. The Company’ s results may be adversely affected by changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, currency conversion and remittance abroad, and rates and methods of taxation, among other things.
The Company’s sales, purchases and expenses transactions are denominated in RMB, and all of the Company’s assets and liabilities are also denominated in RMB. The RMB is not freely convertible into foreign currencies under the current law. In China, foreign exchange transactions are required by law to be transacted only by authorized financial institutions. Remittances in currencies other than RMB may require certain supporting documentation in order to affect the remittance.
19. EQUITY CREDIT AGREEMENT
On January 31, 2010, the Company entered into an equity credit agreement with an institutional investor providing the Company with the right, but not the obligation, to issue shares of its common stock at any time and from time to time during the next two years for gross proceeds of up to $20,000,000. The Company may require the investor to purchase shares of its common stock from time to time under the equity credit agreement by delivering a put notice specifying the total purchase price for the shares to be purchased. The investment amount may not be greater than the lesser of (a) $1,000,000 or (b) 300% of the average dollar volume (closing bid price times the volume on the OTC Bulletin Board for a trading day) for the 20 trading days preceding the put notice. The purchase price per share for the shares to be purchased for the investment amount will be 94% of the lowest closing bid price on the OTC Bulletin Board during the five trading days following the put notice.
The Company also agreed to issue to the investor warrants to purchase an additional 300,000 shares of its common stock during a five year period at an exercise price of $2.00 per share. The warrant will be issued to the investor upon the effectiveness of a registration statement on Form S-1 to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The warrant will be exercisable in whole or in part upon issuance and will remain exercisable for a five year period.
The Company also entered into a registration rights agreement as part of the transaction. The registration rights agreement requires the Company to prepare promptly, and file with the SEC within 60 days, the registration statement for the resale of the shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of the warrant.
As of March 31, 2010, the Company has not made any requirements to the investor.
20. SUBSEQUENT EVENT
On April 22, 2010, the company entered into a bridge loan agreement to obtain $120,000 in short-term financing from a private investor. In addition, 200,000 restricted common stock shares were issued to this investor in connection with this financing. The entire principal balance will be payable in full three months from April 22, 2010.
On May 13, 2010, the Company and the Company’s shareholder (the $100,000 note holder as described in Note 1 and Note 14) entered into a Second Amendment to the Share Cancellation and Loan Agreement, whereby the shareholder agreed to reduce the 300,000 shares to 70,000 shares as settlement of the debt.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Covenant Group of China, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of Covenant Group of China, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2009, and the related consolidated statements of income and comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity and cash flows for the period from June 10, 2009 (date of inception) through December 31, 2009. The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audit included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2009, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for the period from June 10, 2009 (date of inception) through December 31, 2009, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
/s/Morison Cogen LLP
Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania
March 31, 2010
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET
DECEMBER 31, 2009
|
ASSETS
|
||||
|
CURRENT ASSETS
|
||||
|
Cash and cash equivalent
|
$ | 1,382,364 | ||
|
Accounts receivable, net
|
3,612,120 | |||
|
Retentions receivable
|
888,491 | |||
|
Other receivables
|
298,599 | |||
|
Prepayment and deposits
|
147,256 | |||
|
Inventories
|
265,099 | |||
|
Due from shareholders
|
339,767 | |||
|
Total current assets
|
6,933,696 | |||
|
NON-CURRENT ASSETS
|
||||
|
Retentions receivable
|
201,065 | |||
|
Property, plant and equipment, net
|
62,166 | |||
|
Intangible assets, net
|
137,105 | |||
|
Goodwill
|
1,474,323 | |||
|
Total non-current assets
|
1,874,659 | |||
|
Total assets
|
8,808,355 | |||
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
||||
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES
|
||||
|
Short term loans
|
37,638 | |||
|
Note payable
|
100,000 | |||
|
Accounts payable
|
1,813,100 | |||
|
Unearned revenue
|
160,146 | |||
|
Taxes payable
|
546,613 | |||
|
Other payables and accrued liabilities
|
441,718 | |||
|
Dividend payable
|
721,111 | |||
|
Total current liabilities
|
3,820,326 | |||
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
||||
|
Common stock, $0.00001 par value, 20,000,000
shares authorized, 11,480,909 shares issued
and outstanding as of December 31, 2009
|
115 | |||
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
5,572,018 | |||
|
Statutory surplus reserve
|
67,737 | |||
|
Accumulated deficit
|
(647,735 | ) | ||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss
|
(4,106 | ) | ||
|
Total stockholders’ equity
|
4,988,029 | |||
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
8,808,355 | |||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF INCOME AND OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
FROM INCEPTION (JUNE 10, 2009) TO DECEMBER 31, 2009
|
NET SALES
|
$ | 6,527,930 | ||
|
COST OF SALES
|
4,915,867 | |||
|
GROSS PROFIT
|
1,612,063 | |||
|
OPERATING EXPENSES
|
||||
|
Selling expenses
|
143,801 | |||
|
General and administrative expenses
|
1,001,729 | |||
|
Total Operating Expenses
|
1,145,530 | |||
|
INCOME FROM OPERATIONS
|
466,533 | |||
|
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSES)
|
||||
|
Other income
|
5,102 | |||
|
Acquisition related costs
|
(290,000 | ) | ||
|
Interest income
|
482 | |||
|
Interest expense
|
(1,722 | ) | ||
|
Total Other Expenses, net
|
(286,138 | ) | ||
|
INCOME FROM OPERATION
|
180,395 | |||
|
INCOME TAX EXPENSE
|
(113,094 | ) | ||
|
NET INCOME
|
67,301 | |||
|
OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
|
||||
|
Foreign currency translation
|
(3,955 | ) | ||
|
COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
|
63,346 | |||
|
BASIC AND DILUTED WEIGHTED AVERAGE SHARES OUTSTANDING
|
8,940,718 | |||
|
BASIC AND DILUTED NET EARNINGS PER SHARE
|
$ | 0.01 | ||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
FROM INCEPTION (JUNE 10, 2009) TO DECEMBER 31, 2009
|
Common Stock
|
Paid in | Statutory | Other Comprehensive | Accumulated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Shares
|
Amount
|
Capital
|
Reserves
|
Income
|
Deficit
|
Total
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at inception (June 10, 2009)
|
- | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of funders’ shares
|
6,230,000 | 62 | (62 | ) | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Recapitalization on reverse acquisition
|
2,100,000 | 21 | (21 | ) | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Shares issued in private placement
|
200,000 | 2 | 399,998 | - | - | - | 400,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Loans converted into shares
|
200,909 | 2 | 399,868 | - | - | - | 399,870 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net income for the period
|
- | - | - | - | - | 67,301 | 67,301 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Acquisition of subsidiaries at June 24, 2009
|
2,750,000 | 28 | 4,772,335 | 67,737 | - | - | 4,840,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dividend declared
|
- | - | - | - | - | (715,036 | ) | (715,036 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation loss
|
- | - | - | - | $ | (4,106 | ) | - | (4,106 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2009
|
11,480,909 | $ | 115 | $ | 5,572,018 | $ | 67,737 | $ | (4,106 | ) | $ | (647,735 | ) | $ | 4,988,029 | |||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOW
FROM INCEPTION (JUNE 10, 2009) TO DECEMBER 31, 2009
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 67,301 | ||
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities:
|
||||
|
Depreciation and amortization
|
46,079 | |||
|
Change in allowance for doubtful accounts
|
50,378 | |||
|
Loss on disposal of fixed assets
|
291 | |||
|
Increase(decrease) in current assets, net of effect of acquisition:
|
||||
|
Accounts receivable
|
140,776 | |||
|
Retentions receivable
|
266,887 | |||
|
Other receivables
|
(12,016 | ) | ||
|
Prepayment and deposits
|
92,771 | |||
|
Inventories
|
(47,017 | ) | ||
|
Increase(decrease) in current liabilities, net of effect of acquisition:
|
||||
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses
|
(622,418 | ) | ||
|
Taxes payable
|
(196,097 | ) | ||
|
Unearned revenue
|
51,822 | |||
|
Other payables
|
233,640 | |||
|
NET CASH PROVIDED BY OPERATING ACTIVITIES
|
72,397 | |||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||
|
Cash acquired at acquisition
|
754,562 | |||
|
Purchase of property, plant and equipment
|
(10,993 | ) | ||
|
Proceeds from disposal assets
|
89 | |||
|
NET CASH PROVIDED BY INVESTING ACTIVITIES
|
743,658 | |||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||
|
Note payable
|
100,000 | |||
|
Short term loans
|
5,563 | |||
|
Due from shareholders
|
(339,628 | ) | ||
|
Issuance of common stock
|
799,870 | |||
|
NET CASH PROVIDED BY FINANCING ACTIVITIES
|
565,805 | |||
|
EFFECT OF EXCHANGE RATE ON CASH
|
504 | |||
|
NET INCREASE IN CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
1,382,364 | |||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF PERIOD
|
- | |||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, END OF PERIOD
|
$ | 1,382,364 | ||
|
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information:
|
||||
|
Cash paid during the period for:
|
||||
|
Income tax paid
|
$ | 298,811 | ||
|
Interest paid
|
$ | 1,370 | ||
|
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash financing activities:
|
||||
|
Dividend declared
|
$ | 721,111 | ||
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
|
||||
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2009
1. ORGANIZATION AND DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
Covenant Group of China Inc. (Covenant Group or the Company) (FKA: Everest Resources Corp.) was incorporated in the State of Nevada on November 8, 2006. On December 24, 2009, Covenant Group entered into and closed on a share exchange agreement with Covenant Group Holdings Inc (Covenant Holdings), a privately held company incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware. Pursuant to the share exchange agreement, Covenant Group acquired all of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Covenant Holdings in exchange for 9,380,909 shares of common stock. Prior to the acquisition of Covenant Holdings, the Company was engaged in the development stage and had minimal business operations.
Covenant Holdings was formed in the State of Delaware on June 10, 2009 to acquire equity interests in private Chinese operating companies and providing these companies with strategic support. The total number of Covenant Holdings shares authorized for issuance is 20,000,000 with $0.00001 par value. Covenant Holdings has identified companies with synergies in businesses and management that focus on IT software specifically in the financial markets in China, as well as Government mandated areas such as communications and media, government manufacturing and security and surveillance. There was no significant activity from June 10, 2009 through December 31, 2009 except for the two acquisitions.
On June 24, 2009, Covenant Holdings entered into a stock acquisition and reorganization agreement with Hainan Jien Intelligent Engineering Co. Ltd. (Jien) and its stockholders. Pursuant to the terms of the agreement, Covenant Holdings acquired 100% of the common stock of Jien, representing 100% of its outstanding equity interests, in exchange for 1,350,000 shares of a public shell’s common stock, which would acquire all of the rights and obligations of Covenant Holdings. The acquisition stock price was initially valued at a provisional amount of $2 per share, which was the stock price for Covenant Holdings’ prior private capital raises. The Company changed its valuation stock price to $1.76 per share, which was determined by the volume weighted average stock price for the first day of trading of the Company’s common stock plus all private sales of Covenant Holdings’ common stock prior to the completion of the reverse merger with the Company. Jien was incorporated in Hainan Province, People’s Republic of China in 1999. Jien specializes in the design and installation of security and surveillance infrastructure to protect financial institutions and government agencies, and it also implements IC projects for commercial customers.
On June 24, 2009, Covenant Holdings entered into a stock acquisition and reorganization agreement with the Chongqing Sysway Information Technology Co. Ltd. (Chongqing Sysway) and its stockholders Pursuant to the terms of the agreement, Covenant Holdings acquired 100% of the common stock of Sysway, representing 100% of its outstanding equity interests, in exchange for 1,400,000 shares of a public shell’s common stock, which would acquire all of the rights and obligations of Covenant Holdings. The acquisition stock price was initially valued at a provisional amount of $2 per share, which was the stock price for Covenant Holdings’ prior private capital raises. The Company changed its valuation stock price to $1.76 per share, which was determined by the volume weighted average stock price for the first day of trading of the Company’s common stock plus all private sales of Covenant Holdings’ common stock prior to the completion of the reverse merger with the Company. Chongqing Sysway was incorporated in the Chongqing City, Sichuan Province, PRC, in 1999 as a State Owned Enterprise (SOE). In 2005, the two SOE shareholders sold their ownership shares to the other original minority shareholders, and since then, Chongqing Sysway began to operate as a private enterprise mainly engaged in systems integration services, including computer system installation, website design, and system firewall setup, particularly for tobacco industry.
For accounting purposes, the effective acquisition date of Jien and Chongqing Sysway is deemed to be July 1, 2009 as the results of any activity from June 24, 2009 through June 30, 2009 were deemed to be immaterial to the financial statements taken as a whole.
On December 24, 2009, Covenant Holdings entered into a share exchange agreement with Covenant Group. Covenant Group agreed to exchange 9,380,909 shares of its common stock, on a one-for-one basis, for each share of Covenant Holdings shares held of record on the date of the closing. Concurrent with the share exchange agreement, one of Covenant Group’s shareholders agreed to cancel 4,500,000 shares out of 6,600,000 of the total issued and outstanding shares of Covenant Group in exchange for the immediate payment of $100,000. He further agreed to cancel an additional 500,000 shares upon Covenant Holdings’ payment of the principal due on a note issued to the shareholder in the amount of $190,000, which, together with the $100,000 payment, represented the consideration for the acquisition of the shell company. As of December 31, 2009, $90,000 of the $190,000 note payable was paid. The Share Exchange was being accounted for as a “reverse acquisition,” since the Covenant Holdings shareholders own a majority of the outstanding shares of the Company’s common stock immediately following the share exchange. Covenant Holdings was deemed to be the accounting acquiror in the reverse acquisition. Consequently, the assets and liabilities and the historical operations that were reflected in the financial statements prior to the share exchange were those of Covenant Holdings and were recorded at the historical cost basis of Covenant Holdings. The consolidated financial statements after completion of the share exchange would include the assets and liabilities of the Company and Covenant Holdings, historical operations of Covenant Holdings and operations of the Company from the closing date of the share exchange. As a result of the issuance of the shares of the Company’s common stock pursuant to the share exchange, a change in control of the Company occurred on the date of the consummation of the share exchange.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principle of Consolidation
The Consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Covenant Holdings, Jien, and Chongqing Sysway, All intercompany transactions and account balances are eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates
In preparing the financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, management makes estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the dates of the financial statements, as well as the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting year. Significant estimates, required by management, include the recoverability of long-lived assets and the valuation of inventories. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
For purposes of the statement of cash flows, the Company considers all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
Accounts and Retentions Receivable
The Company’s policy is to maintain reserves for potential credit losses on accounts receivable. Management reviews the composition of accounts receivable and analyzes historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customer payment patterns to evaluate the adequacy of these reserves. Based on historical collection activity, the Company had allowances of $78,356 at December 31, 2009.
At December 31, 2009, the Company had retentions receivable for product quality assurance of $1,089,556. The retention rate varies from 3% to 5% of the sales price with variable terms from 1 year to 3 years. $888,491 of the retentions receivable at December 31, 2009 are current and due within one year and $201,065 of the retentions receivable are noncurrent.
Inventories
Jien’s inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market with cost determined on a first in, first out basis. Chongqing Sysway’s inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market with cost determined on a specific identification method.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred; additions, renewals and betterments are capitalized. When property and equipment are retired or otherwise disposed of, the related cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from the respective accounts, and any gain or loss is included in operations. Depreciation of property and equipment is provided using the straight-line method for substantially all assets with 5% salvage value and estimated lives ranging from 3 to 25 years as follows:
|
Building
|
20 - 25 years
|
|
Leasehold improvements
|
Shorter of lease term or 10 years
|
|
Vehicle
|
5 - 10 years
|
|
Office Equipment
|
3 - 5 years
|
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Long-lived assets, which include property, plant and equipment and intangible assets, are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable.
Recoverability of long-lived assets to be held and used is measured by comparing of the carrying amount of an asset to the estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its estimated undiscounted future cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the assets. Fair value is generally determined using the asset’s expected future discounted cash flows or market value, if readily determinable. Based on its review, the Company believes that, as of December 31, 2009, there were no significant impairments of its long-lived assets.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the fair value of the consideration transferred over the net of the acquisition date amount of identifiable assets acquired and the liability assumed. In accordance with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 142, Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets (“Statement No. 142”), codified in Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 350, goodwill is not amortized but is tested for impairment annually, or when circumstances indicate a possible impairment may exist. Impairment testing is performed at a reporting unit level. An impairment loss generally would be recognized when the carrying amount of the reporting unit exceeds the fair value of the reporting unit, with the fair value of the reporting unit determined using a discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis. A number of significant assumptions and estimates are involved in the application of the DCF analysis to forecast operating cash flows, including the discount rate, the internal rate of return, and projections of realizations and costs to produce. Management considers historical experience and all available information at the time the fair values of its reporting units are estimated.
Warranties
The Company offers warranty to its customers on its products for a period from three months to three years depending on the contract terms negotiated with the customers; most of warranty term is one year. The Company accrues for warranty costs based on estimates of the costs that may be incurred under its warranty obligations. The warranty expense and related accrual is included in the Company’s selling expenses and other payable respectively, and is recorded at the time revenue is recognized. Factors that affect the Company’s warranty liability include the number of sold equipment, its estimates of anticipated rates of warranty claims, costs per claim and estimated support labor costs and the associated overhead. The Company periodically assesses the adequacy of its recorded warranty liabilities and adjusts the amounts as necessary. The Company’s warranty expense was immaterial for the period since business inception through December 31, 2009.
Income Taxes
The Company utilizes Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (SFAS) No. 109, “Accounting for Income Taxes,” codified in FASB ASC Topic 740, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Under this method, deferred income taxes are recognized for the tax consequences in future years of differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their financial reporting amounts at each period end based on enacted tax laws and statutory tax rates applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to affect taxable income. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
The Company adopted the provisions of FASB Interpretation No. 48, Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes (codified in FASB ASC Topic 740) on June 10, 2009. As a result of the implementation of FIN 48, the Company made a comprehensive review of its portfolio of tax positions in accordance with recognition standards established by FIN 48. As a result of the implementation of Interpretation 48, the Company recognized no material adjustments to liabilities or stockholders equity. When tax returns are filed, it is highly certain that some positions taken would be sustained upon examination by the taxing authorities, while others are subject to uncertainty about the merits of the position taken or the amount of the position that would be ultimately sustained. The benefit of a tax position is recognized in the financial statements in the period during which, based on all available evidence, management believes it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including the resolution of appeals or litigation processes, if any. Tax positions taken are not offset or aggregated with other positions. Tax positions that meet the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold are measured as the largest amount of tax benefit that is more than 50 percent likely of being realized upon settlement with the applicable taxing authority. The portion of the benefits associated with tax positions taken that exceeds the amount measured as described above is reflected as a liability for unrecognized tax benefits in the accompanying balance sheets along with any associated interest and penalties that would be payable to the taxing authorities upon examination.
Interest associated with unrecognized tax benefits are classified as interest expense and penalties are classified in selling, general and administrative expenses in the statements of income. The adoption of FIN 48 did not have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
Covenant Holdings has US net operating loss of $690,724 at December 31, 2009. A 100% valuation allowance has been established due to the uncertainty of its realization.
Jien is qualified as a small business in the construction industry in PRC. The Company is subject to a 3% tax rate on net sales for 2009. Since the tax is based on sales, under US GAAP, it is not an income tax. Accordingly, $108,315 was recorded as general and administrative expense for the period ended December 31, 2009.
Chongqing Sysway is governed by the Income Tax Law of the PRC concerning the private-run enterprises in Hi-Tech Zone, which are generally subject to tax at a statutory rate of 25% on income reported in the statutory financial statements after appropriated tax adjustments.
The following table reconciles the U.S. statutory rates to the Company’s consolidated effective tax rate for the period since inception of business through December 31, 2009:
|
U.S. statutory rates
|
$ | 61,335 | ||
|
Foreign tax rate less than U.S. statutory rate
|
(74,594 | ) | ||
|
Unrecognized tax benefit on US operating loss
|
234,846 | |||
|
Foreign income exempt from foreign income tax
|
(108,493 | ) | ||
|
Income tax expense
|
$ | 113,094 | ||
|
Income tax expense consists of the following:
|
||||
|
Current
|
||||
|
Federal
|
$ | - | ||
|
State
|
- | |||
|
Foreign
|
113,094 | |||
|
Total current
|
113,094 | |||
|
Deferred
|
||||
|
Federal
|
- | |||
|
State
|
- | |||
|
Foreign
|
- | |||
|
Total deferred
|
- | |||
|
Income tax expense
|
$ | 113,094 | ||
|
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) consist of the following:
|
||||
|
U.S. net operating loss
|
||||
|
Deferred tax asset
|
||||
|
U.S. net operating loss
|
$ | 234,846 | ||
|
Less valuation allowance
|
$ | (234,846 | ) | |
|
Net deferred tax asset
|
$ | - |
The valuation allowance for deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2009 was $234,846. The change in the total valuation for the period ended December 31, 2009 was an increase of $234,846. The deferred tax asset arose from the net operating loss generated at the US parent company level. In assessing the realization of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which the net operating losses and temporary differences become deductible. Management considered projected future taxable income and tax planning strategies in making this assessment. The value of the deferred tax assets was offset by a valuation allowance, due to the current uncertainty of the future realization of the deferred tax assets.
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s revenue recognition policies are in compliance with Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Staff Accounting Bulletin (SAB) 104 (codified in FASB ASC Topic 480). Revenue is recognized at the date of shipment to customers when a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and collectability is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are recorded as unearned revenue.
The Company records its revenue when certain milestones as defined in the service contract are reached. These service contracts have clear milestones and deliverables with distinct values assigned to each milestone. The milestones do not require the delivery of multiple elements as noted in Emerging Issues Task Force (EITF) Issue 0021 “Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables” (EITF No. 0021) (codified in FASB ASC Topic 605). In accordance with SAB No. 104, the Company treats each milestone as an individual revenue agreement and only recognizes revenue for each milestone when all the conditions of SAB 104 defined earlier are met.
Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of goods and services, net of value-added tax (VAT). Chongqing Sysway’s products that are sold and services that are provided in the PRC are subject to Chinese value-added tax of 17% of the gross sales price. This VAT may be offset by VAT paid by the Company on raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing their finished product. The Company recorded VAT payable and VAT receivable net of payments in the financial statements. The VAT tax return is filed offsetting the payables against the receivables.
Jien is qualified as a small business so that all of the Company’s products sold or services provided in the PRC are subject to a fixed VAT rate of 4% of the gross sales price regardless of the VAT paid for 2009. Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of goods or services, net of VAT. This VAT cannot be offset by VAT paid by the Company on raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing their finished.
The standard warranty of Jien is provided to its customers and is not considered an additional service; rather it is considered an integral part of the product and services’ sale. The Company believes that the existence of its standard product warranty in a sales contract does not constitute a deliverable in the arrangement and thus there is no need to apply the EITF 00-21 (codified in FASB ASC Topic 605) separation and allocation model for a multiple deliverable arrangement. FAS 5 (codified in FASB ASC Topic Warranty) specifically address the accounting for standard warranties and neither SAB 104 nor EITF 00-21 supersedes FAS 5. The Company believes that accounting for its standard warranty pursuant to FAS 5 does not impact revenue recognition because the cost of honoring the warranty can be reliably estimated.
Chongqing Sysway provides post-contract support (PCS). Maintenance revenues from ongoing customer support services are billed on an annual basis with the revenue being deferred and recognized ratably over the maintenance period. Chongqing Sysway does not charge for PCS services separately for the first year from the date the product is sold, accordingly, the Company believes that this type of PCS does not have to be accounted for as a separate unit in accordance with guidance provided by AICPA Statement of Position (SOP) 97-2, codified in FASB ASC Topic 985.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of goods sold consists primarily of material costs, labor costs, and related overhead which are directly attributable to the production of the service. Write-down of inventory to lower of cost or market is also recorded in cost of goods sold.
Basic and Diluted Earnings per Share (EPS)
Basic EPS is computed by dividing income available to common shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted EPS is similarly computed, except that the denominator is increased to include the number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding if the potential common shares had been issued and if the additional common shares were dilutive. Diluted net earnings per share are based on the assumption that all dilutive convertible shares and stock options were converted or exercised. Dilution is computed by applying the treasury stock method. Under this method, options and warrants are assumed to have been exercised at the beginning of the period (or at the time of issuance, if later), and as if funds obtained thereby were used to purchase common stock at the average market price during the period. Since the company does not have any outstanding option or warrants, the basic and diluted EPS are the same.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to credit risk consist primarily of accounts receivable and other receivables. The Company does not require collateral or other security to support these receivables. The Company conducts periodic reviews of its clients’ financial condition and customer payment practices to minimize collection risk on accounts receivable.
The operations of the Company are located in the PRC. Accordingly, the Company’s business, financial condition, and results of operations may be influenced by the political, economic, and legal environments in the PRC, as well as by the general state of the PRC economy.
Statement of Cash Flows
In accordance with SFAS No. 95, “Statement of Cash Flows,” codified in FASB ASC Topic 230, cash flows from the Company’s operations are calculated based upon the local currencies. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the statement of cash flows may not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the balance sheet.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
For certain of the Company’s financial instruments, including cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, other receivables, accounts payable, accrued liabilities and short-term debt, the carrying amounts approximate their fair values due to their short maturities.
ASC Topic 820, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures,” requires disclosure of the fair value of financial instruments held by the Company. ASC Topic 825, “Financial Instruments,” defines fair value, and establishes a three-level valuation hierarchy for disclosures of fair value measurement that enhances disclosure requirements for fair value measures. The carrying amounts reported in the consolidated balance sheets for receivables and current liabilities each qualify as financial instruments and are a reasonable estimate of their fair values because of the short period of time between the origination of such instruments and their expected realization and their current market rate of interest. The three levels of valuation hierarchy are defined as follows:
|
·
|
Level 1 inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
|
|
·
|
Level 2 inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, and inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument.
|
|
·
|
Level 3 inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and significant to the fair value measurement.
|
The Company analyzes all financial instruments with features of both liabilities and equity under ASC 480, “Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity,” and ASC 815.
As of December 31, 2009, the Company did not identify any assets and liabilities that are required to be presented on the balance sheet at fair value.
Foreign Currency Translation and Transactions
The accompanying consolidated financial statements are presented in United States Dollars (“USD”). The Company’s functional currency is the USD, while the Company’s wholly-owned Chinese subsidiaries’ functional currency is the Renminbi (“RMB”). The functional currencies of the Company’s foreign operations are translated into US$ for balance sheet accounts using the current exchange rates in effect as of the balance sheet date and for revenue and expense accounts using the weighted-average exchange rate during the fiscal year. The translation adjustments are recorded as a separate component of stockholders’ equity, captioned accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). Gains and losses resulting from transactions denominated in foreign currencies are included in other income (expense) in the consolidated statements of operations. There have been no significant fluctuations in the exchange rate for the conversion of RMB to USD after the balance sheet date.
Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The Company uses SFAS 130 “Reporting Comprehensive Income” (codified in FASB ASC Topic 220). Comprehensive income is comprised of net income and all changes to the statements of stockholders’ equity, except those due to investments by stockholders, changes in paid-in capital and distributions to stockholders. Comprehensive income for the period since inception of business through December 31, 2009 included net income and foreign currency translation adjustments.
Segment Reporting
SFAS No. 131, “Disclosures about Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information,” codified in FASB ASC Topic 280, requires use of the “management approach” model for segment reporting. The management approach model is based on the way a company’s management organizes segments within the company for making operating decisions and assessing performance. Reportable segments are based on products and services, geography, legal structure, management structure, or any other manner in which management disaggregates a company.
SFAS 131 has no effect on the Company’s financial statements as substantially all of the Company’s operations are conducted in one industry segment. The Company consists of one reportable business segment. All of the Company’s assets are located in the PRC and its principal market is in the PRC.
New Accounting Pronouncements
In August 2009, the FASB issued an Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) regarding measuring liabilities at fair value. This ASU provides additional guidance clarifying the measurement of liabilities at fair value in circumstances in which a quoted price in an active market for the identical liability is not available; under those circumstances, a reporting entity is required to measure fair value using one or more of valuation techniques, as defined. This ASU is effective for the first reporting period, including interim periods, beginning after the issuance of this ASU. The adoption of this ASU did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
On June 10, 2009, the Company adopted Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2009-01, “Topic 105 - Generally Accepted Accounting Principles - amendments based on Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 168 , “The FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ and the Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles” (“ASU No. 2009-01”). ASU No. 2009-01 re-defines authoritative GAAP for nongovernmental entities to be only comprised of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ (“Codification”) and, for SEC registrants, guidance issued by the SEC. The Codification is a reorganization and compilation of all then-existing authoritative GAAP for nongovernmental entities, except for guidance issued by the SEC. The Codification is amended to effect non-SEC changes to authoritative GAAP. Adoption of ASU No. 2009-01 only changed the referencing convention of GAAP in Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In May 2009, the FASB issued SFAS No. 165, “Subsequent Events” (“SFAS 165”) codified in FASB ASC Topic 855-10-05, which provides guidance to establish general standards of accounting for and disclosures of events that occur after the balance sheet date but before financial statements are issued or are available to be issued. SFAS 165 also requires entities to evaluate the subsequent events through the dates the financial statements are issued. SFAS 165 is effective for interim and annual periods ending after June 15, 2009, and accordingly, the Company adopted this pronouncement during the second quarter of 2009. The Company evaluated subsequent events through the date that the financial statements were issued.
In April 2009, the FASB issued FSP No. SFAS 107-1 and APB 28-1, “Interim Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments,” which is codified in FASB ASC Topic 825-10-50. This FSP essentially expands the disclosure about fair value of financial instruments that were previously required only annually to also be required for interim period reporting. In addition, the FSP requires certain additional disclosures regarding the methods and significant assumptions used to estimate the fair value of financial instruments. These additional disclosures are required beginning with the quarter ending June 30, 2009. This FSP had no material impact on the Company’s financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
FASB ASC 820-10 establishes a framework for measuring fair value and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. The changes to current practice resulting from the application of this standard relate to the definition of fair value, the methods used to measure fair value, and the expanded disclosures about fair value measurements. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007; however, it provides a one-year deferral of the effective date for non-financial assets and non-financial liabilities, except those that are recognized or disclosed in the financial statements at fair value at least annually. The Company adopted this standard for financial assets and financial liabilities and nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities disclosed or recognized at fair value on a recurring basis (at least annually) as of June 10, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on its financial statements.
FASB ASC 820-10 provides additional guidance for Fair Value Measurements when the volume and level of activity for the asset or liability has significantly decreased. This standard is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on its financial statements.
FASB ASC 805 establishes principles and requirements for how an acquirer recognizes and measures in its financial statements the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree and the goodwill acquired. This standard also establishes disclosure requirements to enable the evaluation of the nature and financial effects of the business combination. This standard was adopted by the Company beginning June 10, 2009 and will change the accounting for business combinations on a prospective basis.
FASB ASC 350-30 and 275-10 amend the factors that should be considered in developing renewal or extension assumptions used to determine the useful life of a recognized intangible asset. This standard is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is prohibited. The adoption of this standard did not have any impact on the Company’s financial statements.
FASB ASC 825-10 requires disclosures about the fair value of financial instruments for interim reporting periods. This standard is effective for interim reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
FASB ASC 320-10 amends the other-than-temporary impairment guidance for debt and equity securities. This standard is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on its financial statements.
As of December 31, 2009, the FASB has issued Accounting Standards Updates (ASU) through No. 2009-17. None of the ASUs have had an impact on the Company’s financial statements.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted
As of December 31, 2009, there are no recently issued accounting standards not yet adopted which would have a material effect on the Company’s financial statements.
3. INVENTORY
Inventory consisted of the following at December 31, 2009:
|
Raw material
|
$ | 34,273 | ||
|
Work in process
|
230,826 | |||
| $ | 265,099 |
4. ACQUISITION
On June 24, 2009, Covenant Holdings entered into stock acquisition and reorganization agreements with Jien and Chongqing Sysway (note 1).
The operating results of these two acquires, Jien and Chongqing Sysway are included in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations from the acquisition date. For convenience of reporting the acquisition for accounting purposes, July 1, 2009 has been designated as the acquisition date.
The following table summarizes the fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of acquisition.
|
Jien
|
Chongqing Sysway
|
Total
|
||||||||||
|
Cash
|
$ | 710,552 | $ | 44,098 | $ | 754,650 | ||||||
|
Accounts receivable
|
2,420,881 | 1,380,413 | 3,801,294 | |||||||||
|
Retention receivable
|
271,770 | 1,084,047 | 1,355,817 | |||||||||
|
Prepaid expenses
|
238,275 | - | 238,275 | |||||||||
|
Advance to suppliers
|
- | 1,661 | 1,661 | |||||||||
|
Other receivables
|
154,237 | 132,186 | 286,423 | |||||||||
|
Inventory
|
134,087 | 83,858 | 217,945 | |||||||||
|
Property and equipment
|
45,102 | 37,265 | 82,367 | |||||||||
|
Intangible assets-core software
|
- | 152,256 | 152,256 | |||||||||
|
Goodwill
|
572,020 | 902,303 | 1,474,323 | |||||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
(1,442,990 | ) | (991,463 | ) | (2,434,453 | ) | ||||||
|
Other current liabilities
|
(182,370 | ) | (25,499 | ) | (207,869 | ) | ||||||
|
Unearned revenue
|
(108,245 | ) | - | (108,245 | ) | |||||||
|
Tax payable
|
(405,263 | ) | (337,125 | ) | (742,388 | ) | ||||||
|
Short term loan
|
(32,056 | ) | - | (32,056 | ) | |||||||
|
Purchase price
|
$ | 2,376,000 | $ | 2,464,000 | $ | 4,840,000 | ||||||
The fair value of the consideration transferred was initially valued at a provisional amount of $2 per share, which was the stock price determined at $2 per share for the proposed capital raise. The Company changed its valuation on stock price to $1.76 per share that was determined at volume weighted average stock price for the first day of trading of the Company upon completion of the reverse merge. The excess of the fair value of the consideration transferred over the net of the acquisition date amounts of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed was allocated to goodwill.
The following pro forma consolidated results of operations of the Company for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 presents the consolidated operations of the Covenant as if the acquisition of Jien and Chongqing Sysway occurred on January 1, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
|
For the Years Ended December 31,
Pro forma Consolidated
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Net revenue
|
$ | 11,890,797 | 10,478,795 | |||||
|
Cost of revenue
|
(9,059,047 | ) | (8,230,074 | |||||
|
Gross profit
|
2,831,750 | 2,248,721 | ||||||
|
Total operating expenses
|
(1,658,724 | ) | (1,135,204 | ) | ||||
|
Income from operations
|
1,173,026 | 1,113,517 | ||||||
|
Non-operating income (expenses)
|
(290,768 | ) | 191,899 | |||||
|
Income tax
|
(169,576 | ) | (181,060 | ) | ||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 712,682 | $ | 1,124,356 | ||||
5. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property and equipment consisted of the following at December 31, 2009:
|
Vehicle
|
$ | 8,979 | ||
|
Office equipment
|
71,799 | |||
|
Leasehold Improvement
|
12,251 | |||
|
Subtotal
|
93,029 | |||
|
Less: Accumulated depreciation
|
(30,863 | ) | ||
| $ | 62,166 |
Depreciation expense for the period since business inception through December 31, 2009 was $ 30,851.
6. OTHER RECEIVABLES
Other receivables consisted of the following at December 31, 2009:
|
Short term advance to third parties
|
$ | 180,043 | ||
|
VAT tax payable from late received purchase invoices
|
25,034 | |||
|
Advance to staffs
|
71,630 | |||
|
Retention for sales contracts
|
2,819 | |||
|
Tax rebate
|
7,356 | |||
|
Deposits
|
11,717 | |||
| $ | 298,599 |
7. DUE FROM SHAREHOLDERS
Due from shareholders primarily represents a dividend paid by Chongqing Sysway to its original shareholders in the amount of $322,061. This dividend amount was in excess of Chongqing Sysway’s distributable reserves by approximately $230,000 and beyond that which the original shareholders of Chongqing Sysway were entitled to under the stock acquisition agreements the Company entered into with the original shareholders of Jien and Chongqing Sysway. The original Chongqing Sysway shareholders have agreed to repay the full $322,061 dividend to Chongqing Sysway by April 15, 2010 and have executed a non-interest bearing promissory note in the favor of Chongqing Sysway to this effect.
8. INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Intangible assets mainly consisted of computer core software that was developed by the Company for sale. The Company amortizes the software over 5 years. Amortization expense of intangible assets for the period from business inception through December 31, 2009 was approximately $15,228. Annual amortization expense for the next five years is expected to be as follows:
|
2010
|
2011
|
2012
|
2013
|
2014
|
||||||||||||||
| $ | 30,460 | $ | 30,460 | $ | 30,460 | $ | 30,460 | $ | 15,230 | |||||||||
9. TAX PAYABLE
Tax payable consisted of the following at December 31, 2009:
|
Income tax payable
|
$ | 383,327 | ||
|
Value added tax payable
|
151,462 | |||
|
Sales and business tax payable
|
(6,707 | ) | ||
|
Other taxes payable
|
18,530 | |||
| $ | 546,613 |
10. ACCRUED LIABILITIES AND OTHER PAYABLES
Accrued liabilities and other payables consisted of the following at December 31, 2009:
|
Warranty provision
|
$ | 48,475 | ||
|
Short term cash advance from third parties
|
216,031 | |||
|
Sales and business tax payable
|
177,212 | |||
| $ | 441,718 |
11. COMMON STOCK
Effective November 10, 2009, the Company and the lender of the three bridge loans have agreed to cancel the promissory note of $399,870. In lieu of principal and interest payments due to the lender, the Company issued 200,909 shares of the Company’s common stock to the lender.
Pursuant to the confidential private placement memorandum dated November 24, 2009, the Company was offering to sell up to 750,000 shares at $2.00 per share, with a minimum purchase of 10,000 Shares per investor, requiring a minimum investment of $20,000, with a minimum total quantity of 150,000 Shares ($300,000) that must be subscribed for by all investors to affect a closing and avoid termination of the Offering. At December 16, 2009, the Company sold 200,000 shares through the private placement, which were converted into publicly-traded securities upon the Company’s merger with a public shell company on December 24, 2009.
12. DIVIDEND PAYABLE
The Company declared 30% dividend of Jien and Chongqing Sysway’s 2008 net income to Jien and Chongqing Sysway’s original shareholders and management as part of the acquisition agreement dated June 24, 2009. The dividend declared for Jien and Chongqing Sysway was $200,608 and $151,614, respectively, and has been recorded as dividend payable at December 31, 2009.
As part of the acquisition agreement, the Company also agreed to pay the original shareholders and management of Jien and Chongqing Sysway a 30% dividend on 2009 year end profits. The dividend declared and was recorded as dividend payable for Jien was $277,653; and $91,237 for Chongqing Sysway which was the retained earnings that were available for declaring at December 31, 2009.
13. MAJOR CUSTOMERS
Four customers accounted for 54% of the total sales for the period since business inception through December 31, 2009, each customer accounted for 19%, 13%, 11%, and 11%, respectively. At December 31, 2009, the total receivable balance due from these customers was $ 902,761.
Three suppliers accounted for 56% of the total purchases for the period since business inception through December 31, 2009, each vendor accounted for 23%, 23% and 10%, respectively. At December 31, 2009, the total payable due to these vendors was $ 893,686.
14. SHORT TERM LOANS
During the year ended December 31, 2009, the Company borrowed $37,600 (RMB 257,000) from Shenzhen Development Bank. The loan bears interest at 5.832 per year and is due in February 2010. The loan was paid off subsequent to December 31, 2009.
15. NOTE PAYABLE
Note payable represented $100,000 remaining balance from a $190,000 promissory note issued to the former shareholder of Covenant Group for cash consideration for the acquisition of the shell company.
16. STATUTORY RESERVES
Pursuant to the corporate law of the PRC effective January 1, 2006, PRC subsidiaries of the Company are required to maintain one statutory reserve by appropriating from its after-tax profit before declaration or payment of dividends. The statutory reserve represents restricted retained earnings.
Surplus reserve fund
The PRC subsidiaries of the Company are only required to transfer 10% of its net income, as determined under PRC accounting rules and regulations, to a statutory surplus reserve fund until such reserve balance reaches 50% of the Company’s registered capital. The Company had $67,737 in this reserve at December 31, 2009.
The surplus reserve fund is non-distributable other than during liquidation and can be used to fund previous years’ losses, if any, and may be utilized for business expansion or converted into share capital by issuing new shares to existing shareholders in proportion to their shareholding or by increasing the par value of the shares currently held by them, provided that the remaining reserve balance after such issue is not less than 25% of the registered capital.
Common welfare fund
Common welfare fund is a voluntary fund that the Company can elect to transfer 5% to 10% of its net income to this fund. The Company did not make any contribution to this fund for the period since business inception through December 31, 2009.
This fund can only be utilized on capital items for the collective benefit of the Company’s employees, such as construction of dormitories, cafeteria facilities, and other staff welfare facilities. This fund is non-distributable other than upon liquidation.
Pursuant to the “Circular of the Ministry of Finance (MOF) on the Issue of Corporate Financial Management after the Corporate Law Enforced” (No.67 [2006]), effective on April 1, 2006, issued by the MOF, companies transferred the balance of SCWF (Statutory Common Welfare Fund) as of December 31, 2005 to Statutory Surplus Reserve. Any deficit in the SCWF was charged in turn to Statutory Surplus Reserve, additional paid-in capital and undistributed profit of previous years. If a deficit still remains, it should be transferred to retained earnings and be reduced to zero by a transfer from after tax profit of following years. At December 31, 2005, the Company did not have a deficit in the SCWF.
17. COMMITMENTS
Jien leased its office under long term, non-cancelable, and renewable operating lease agreements on November 8, 2007 with expiration date on November 7, 2009. Upon expiration, the Company renewed the lease for a period from November 8, 2009 to November 7, 2012, with monthly rent of approximately $3,600 (RMB 24,509). Annual rental expense is approximately $43,200 for the years ended December 31, 2010 and 2011, and approximately $36,000 for 2012.
Chongqing Sysway leased its office under one year, non-cancelable, and renewable operating lease agreement on December 1, 2007 with expiration date on November 30, 2008. After the lease expiration, the Company leases this office month-by-month with monthly rent of approximately $2,530 (RMB 17,232).
Total rental expense for the period since business inception through December 31, 2009 was approximately $43,839.
18. CONTINGENCIES
The Company’s operations in the PRC are subject to specific considerations and significant risks not typically associated with companies in the North America and Western Europe. These include risks associated with, among others, the political, economic and legal environments and foreign currency exchange. The Company’ s results may be adversely affected by changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, currency conversion and remittance abroad, and rates and methods of taxation, among other things.
The Company’s sales, purchases and expenses transactions are denominated in RMB and all of the Company’s assets and liabilities are also denominated in RMB. The RMB is not freely convertible into foreign currencies under the current law. In China, foreign exchange transactions are required by law to be transacted only by authorized financial institutions. Remittances in currencies other than RMB may require certain supporting documentation in order to affect the remittance.
19. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On January 31, 2010, the Company entered into an equity credit agreement with an institutional investor providing the Company with the right, but not the obligation, to issue shares of its common stock at any time and from time to time during the next two years for gross proceeds of up to $20,000,000. The Company may require the investor to purchase shares of its common stock from time to time under the equity credit agreement by delivering a put notice specifying the total purchase price for the shares to be purchased. The investment amount may not be greater than the lesser of (a) $1,000,000 or (b) 300% of the average dollar volume (closing bid price times the volume on the OTC Bulletin Board for a trading day) for the 20 trading days preceding the put notice. The purchase price per share for the shares to be purchased for the investment amount will be 94% of the lowest closing bid price on the OTC Bulletin Board during the five trading days following the put notice.
The Company also agreed to issue to the investor warrants to purchase an additional 300,000 shares of its common stock during a five year period at an exercise price of $2.00 per share. The warrant will be issued to the investor upon the effectiveness of a registration statement on Form S-1 to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The warrant will be exercisable in whole or in part upon issuance and will remain exercisable for a five year period.
The Company also entered into a registration rights agreement as part of the transaction. The registration rights agreement requires the Company to prepare promptly, and file with the SEC within 60 days, the registration statement for the resale of the shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of the warrant.
On January 12, 2010, the Company formed a wholly owned subsidiary – Pandaz LLC, a Delaware LLC (Pandaz Delaware). On January 13, 2010, Pandaz Delaware entered into an asset purchase agreement with The Pandaz LLC, a Nevada LLC, for purchasing certain assets and intellectual property associated with s dealer and customer interface, vehicle search function and automobile purchasing website that the company is tentatively looking to implement in China through one of the subsidiaries. The total purchase consideration was $25,000, of which, $10,000 was paid as the forgiveness of a bridge loan that the Company provided to the seller on January 7, 2010, and $15,000 was paid as a one-time cash payment.
CHONGQING SYSWAY ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2008 and 2007
Contents
| Page | ||||
| Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firms | F-41 - F-42 | |||
| Financial Statements: | ||||
| Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 | F-43 | |||
| Statements of Operations for the Years Ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 | F-44 | |||
| Statements of Shareholders’ Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 | F-45 | |||
| Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 | F-46 | |||
| Notes to Financial Statements | F-47 - F-56 | |||
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and
Stockholders of Chongqing Sysway Electronic Technology Co., Ltd
We have audited the accompanying balance sheet of Chongqing Sysway Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. (“the Company”) as of December 31, 2008, and the related statements of operations and comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity and cash flows for the year then ended. The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit.
We have conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audit included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2008, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year then ended, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States.
/s/ Morison Cogen, LLP
Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania
November 16, 2009
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the shareholders of Chongqing Sysway Electronic Co., Ltd.
We have audited the balance sheet of Chongqing Sysway Electronic Co., Ltd. (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2007 and the related statements of operations and other comprehensive income (loss), shareholders equity and cash flows for the year then ended. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2007 and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year then ended in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
/s/ Goldman Parks Kurland Mohidin LLP
Encino, California
April 17, 2008
F-42
CHONGQING SYSWAY INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD
BALANCE SHEETS
AS OF
DECEMBER 31, 2008 and 2007
(AUDITED)
|
ASSETS
|
December 31, 2008
|
December 31, 2007
|
||||||
|
CURRENT ASSETS
|
||||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents
|
$ | 48,588 | $ | 640,003 | ||||
|
Accounts receivable, net
|
932,910 | 2,065,124 | ||||||
|
Retentions receivable
|
49,610 | - | ||||||
|
Advance to Suppliers
|
33,213 | 14,538 | ||||||
|
Other receivables
|
207,298 | 101,812 | ||||||
|
Inventory
|
267,789 | 31,452 | ||||||
|
Total current assets
|
1,539,408 | 2,852,929 | ||||||
|
RETENTIONS RECEIVABLE
|
42,358 | 69,015 | ||||||
|
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, net
|
39,282 | 114,826 | ||||||
|
TOTAL ASSETS
|
$ | 1,621,048 | $ | 3,036,770 | ||||
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES
|
||||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
$ | 157,115 | $ | 2,054,445 | ||||
|
Taxes payable
|
206,568 | 76,858 | ||||||
|
Accrued liabilities and other payables
|
17,885 | 93,491 | ||||||
|
Advance from related party
|
- | 75,398 | ||||||
|
Short-term Loan
|
- | 48,327 | ||||||
|
Total current liabilities
|
381,568 | 2,348,519 | ||||||
|
CONTINGENCIES AND COMMITMENTS
|
||||||||
|
STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
Paid in capital
|
1,208,240 | 1,208,240 | ||||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income
|
104,271 | 49,916 | ||||||
|
Accumulated deficit
|
(73,031 | ) | (569,905 | ) | ||||
|
Total stockholders' equity
|
1,239,480 | 688,251 | ||||||
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
$ | 1,621,048 | $ | 3,036,770 | ||||
F-43
CHONGQING SYSWAY INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD
STATEMENTS OF INCOME AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
FOR THE YEARS ENDED
DECEMBER 31, 2008 and 2007
(AUDITED)
|
YEARS ENDED
|
||||||||
|
DECEMBER 31,
|
||||||||
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
|
Net sales
|
$ | 4,924,438 | $ | 4,013,972 | ||||
|
Cost of goods sold
|
(3,826,264 | ) | (3,050,588 | ) | ||||
|
Gross profit
|
1,098,174 | 963,384 | ||||||
|
Operating expenses
|
||||||||
|
Selling expenses
|
(159,949 | ) | (143,754 | ) | ||||
|
General and administrative expenses
|
(456,040 | ) | (386,912 | ) | ||||
|
Total operating expenses
|
(615,989 | ) | (530,666 | ) | ||||
|
Income from operations
|
482,185 | 432,718 | ||||||
|
Non-operating income (expenses)
|
||||||||
|
Interest expense
|
(1,011 | ) | (3,236 | ) | ||||
|
Reversal of provision for bad debt
|
161,805 | - | ||||||
|
Tax rebate
|
26,245 | - | ||||||
|
Other income
|
6,838 | 1,317 | ||||||
|
Subsidy income
|
1,872 | 57,591 | ||||||
|
Total non-operating income
|
195,749 | 55,672 | ||||||
|
Income before income tax
|
677,934 | 488,390 | ||||||
|
Income tax expense
|
(181,060 | ) | - | |||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 496,874 | $ | 488,390 | ||||
|
Other comprehensive item
|
||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation
|
54,355 | 32,523 | ||||||
|
Comprehensive Income
|
$ | 551,229 | $ | 520,913 | ||||
F-44
CHONGQING SYSWAY INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD
STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
FOR THE YEARS ENDED
DECEMBER 31, 2008 and 2007
(AUDITED)
|
Paid in capital
|
Other comprehensive income
|
Accumulated deficit
|
Total
|
|||||||||||||
|
Balance at January 1, 2007
|
$ | 1,208,240 | $ | 17,393 | $ | (1,058,295 | ) | $ | 167,338 | |||||||
|
Net income for the year
|
- | - | 488,390 | 488,390 | ||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation gain
|
- | 32,523 | - | 32,523 | ||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2007
|
1,208,240 | 49,916 | (569,905 | ) | 688,251 | |||||||||||
|
Net income for the year
|
- | - | 496,874 | 496,874 | ||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation gain
|
- | 54,355 | - | 54,355 | ||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2008
|
$ | 1,208,240 | $ | 104,271 | $ | (73,031 | ) | $ | 1,239,480 | |||||||
F-45
CHONGQING SYSWAY INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOW
FOR THE YEARS ENDED
DECEMBER 31, 2008 and 2007
(AUDITED)
|
YEARS ENDED
|
||||||||
|
DECEMBER 31,
|
||||||||
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 496,874 | $ | 488,390 | ||||
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash
|
||||||||
|
provided by operating activities:
|
||||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization
|
18,591 | 15,544 | ||||||
|
Change in allowance for doubtful accounts
|
(161,805 | ) | 127,495 | |||||
|
(Gain) / loss on disposal of fixed assets
|
(4,551 | ) | 610 | |||||
|
(Increase) decrease in current assets:
|
||||||||
|
Accounts receivable
|
1,412,786 | (1,753,474 | ) | |||||
|
Retentions receivable
|
(18,017 | ) | (66,191 | ) | ||||
|
Advance to suppliers
|
(17,415 | ) | (13,556 | ) | ||||
|
Other receivables
|
(10,783 | ) | (16,347 | ) | ||||
|
Inventory
|
(230,494 | ) | 2,741 | |||||
|
Increase (decrease) in current liabilities:
|
||||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
(2,003,216 | ) | 1,814,222 | |||||
|
Unearned revenue
|
- | (32,462 | ) | |||||
|
Accrued liabilities and other payables
|
(80,595 | ) | (95,218 | ) | ||||
|
Taxes payable
|
122,556 | 47,329 | ||||||
|
Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities
|
(476,069 | ) | 519,083 | |||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||||||
|
Acquisition of property & equipment
|
(18,374 | ) | (8,641 | ) | ||||
|
Net cash used in investing activities
|
(18,374 | ) | (8,641 | ) | ||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||||||
|
Short-term loan
|
(50,759 | ) | (11,707 | ) | ||||
|
Advance from related party
|
(79,193 | ) | - | |||||
|
Net cash used in financing activities
|
(129,952 | ) | (11,707 | ) | ||||
|
EFFECT OF EXCHANGE RATE CHANGE ON CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
32,980 | 29,111 | ||||||
|
NET (DECREASE) INCREASE IN CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
(591,415 | ) | 527,846 | |||||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF YEAR
|
640,003 | 112,157 | ||||||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, END OF YEAR
|
$ | 48,588 | $ | 640,003 | ||||
|
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information:
|
||||||||
|
Cash paid during the period for:
|
||||||||
|
Income tax paid
|
$ | 5,240 | $ | - | ||||
|
Interest paid
|
$ | 1,011 | $ | 3,692 | ||||
|
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash investing activities:
|
||||||||
|
Other receivable for fixed assets sold
|
$ | 86,281 | $ | - | ||||
F-46
CHONGQING SYSWAY INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2008 and 2007
(Audited)
1. ORGANIZATION AND DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
Chongqing Sysway Information Technology Co., Ltd. (the “Company” or “Chongqing Sysway”) was incorporated in the Chongqing City, Sichuan Province, People’s Republic of China (“PRC”) in 1999 as a State Owned Enterprise (“SOE”). In 2005, the two SOE shareholders sold their ownership shares among other original minority shareholders and since then, Chongqing Sysway began to operate as a private enterprise mainly engaged in system integration services including computer system installation, website design, system firewall setup, etc., particularly for tobacco industry.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Use of Estimates
In preparing the financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, management makes estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the dates of the financial statements, as well as the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting year. Significant estimates, required by management, include the recoverability of long-lived assets and the valuation of inventories. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
For purposes of the statement of cash flows, the Company considers all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents
Accounts and Retentions Receivable
The Company’s policy is to maintain reserves for potential credit losses on accounts receivable. Management reviews the composition of accounts receivable and analyzes historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customer payment patterns to evaluate the adequacy of these reserves. Based on historical collection activity, the Company had $0 and $154,053 bad debt allowance at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
At December 31, 2008 and 2007, the Company had retentions receivable for product quality assurance in the amount of $91,968 and $69,015, respectively. The retention rate varies from 3% to 5% of the sales price with variable terms from 1 year to 3 years. At December 31, 2008, $49,610 of the retentions receivable are current and due within one year, and $42,358 of the retentions receivable are noncurrent. At December 31, 2007, $0 of the retentions receivable are current and due within one year, and $69,015 of the retentions receivable are noncurrent.
Inventories
Inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market with cost determined on a Specific Identification Method.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred; additions, renewals and betterments are capitalized. When property and equipment are retired or otherwise disposed of, the related cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from the respective accounts, and any gain or loss is included in operations. Depreciation of property and equipment is provided using the straight-line method for substantially all assets with estimated lives ranging from 3 to 20 years as follows:
Building 25 years
Vehicle 10 years
Office Equipment 3-5 years
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Long-lived assets, which include property, plant and equipment and intangible assets, are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable.
Recoverability of long-lived assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to the estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its estimated undiscounted future cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the assets. Fair value is generally determined using the asset’s expected future discounted cash flows or market value, if readily determinable. Based on its review, the Company believes that, as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, there were no significant impairments of its long-lived assets.
Income Taxes
The Company utilizes SFAS No. 109, “Accounting for Income Taxes,” which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Under this method, deferred income taxes are recognized for the tax consequences in future years of differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their financial reporting amounts at each period end based on enacted tax laws and statutory tax rates applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to affect taxable income. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
The Company adopted the provisions of FASB Interpretation No. 48, Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes, on January 1, 2007. As a result of the implementation of FIN 48, the Company made a comprehensive review of its portfolio of tax positions in accordance with recognition standards established by FIN 48. As a result of the implementation of Interpretation 48, the Company recognized no material adjustments to liabilities or stockholders equity. When tax returns are filed, it is highly certain that some positions taken would be sustained upon examination by the taxing authorities, while others are subject to uncertainty about the merits of the position taken or the amount of the position that would be ultimately sustained. The benefit of a tax position is recognized in the financial statements in the period during which, based on all available evidence, management believes it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including the resolution of appeals or litigation processes, if any. Tax positions taken are not offset or aggregated with other positions. Tax positions that meet the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold are measured as the largest amount of tax benefit that is more than 50 percent likely of being realized upon settlement with the applicable taxing authority. The portion of the benefits associated with tax positions taken that exceeds the amount measured as described above is reflected as a liability for unrecognized tax benefits in the accompanying balance sheets along with any associated interest and penalties that would be payable to the taxing authorities upon examination. Interest associated with unrecognized tax benefits are classified as interest expense and penalties are classified in selling, general and administrative expenses in the statements of income. The adoption of FIN 48 did not have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
Revenue Recognition
The Company's revenue recognition policies are in compliance with Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Staff Accounting Bulletin (“SAB”) 104. Sales revenue is recognized at the date of shipment to customers when a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and collectibility is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are recorded as unearned revenue.
The Company records its revenue when certain milestones as defined in the service contract are reached. These service contracts have clear milestones and deliverables with distinct values assigned to each milestone. The milestones do not require the delivery of multiple elements as noted in Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”) Issue 00-21 “Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables” ("EITF No. 00-21"). In accordance with SAB No. 104, the Company treats each milestone as an individual revenue agreement and only recognizes revenue for each milestone when all the conditions of SAB 104 defined earlier are met.
Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of products and services, net of value-added tax (“VAT”). All of the Company’s products and service that are sold and provided in the PRC are subject to Chinese value-added tax of 17% of the gross sales price. This VAT may be offset by VAT paid by the Company on raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing their finished product. The Company recorded VAT payable and VAT receivable net of payments in the financial statements. The VAT tax return is filed offsetting the payables against the receivables. Sales and purchases are recorded net of VAT collected and paid as the Company acts as an agent for the government.
The Company provides post-contract support (PCS). Maintenance revenues from ongoing customer support services are billed on an annual basis with the revenue being deferred and recognized ratably over the maintenance period. The Company does not charge for PCS services separately for the first year from the date the product is sold. The Company believes that this type of PCS does not have to be accounted for as a separate unit in accordance with guidance provided by AICPA Statement of Position (SOP) 97-2. During the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, cost of providing such services during the first year from the date of sale was approximately $8,600 and $6,500, respectively. The Company charges PCS services through a separate contact after the first year of the sale, the revenue from the PCS services was $72,000 and $0 for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of goods sold consists primarily of material costs, labor costs, and related overhead which are directly attributable to the production of the service. Write-down of inventory to lower of cost or market is also recorded in cost of goods sold.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to credit risk consist primarily of accounts receivable and other receivables. The Company does not require collateral or other
security to support these receivables. The Company conducts periodic reviews of its clients' financial condition and customer payment practices to minimize collection risk on accounts receivable.
The operations of the Company are located in the PRC. Accordingly, the Company's business, financial condition, and results of operations may be influenced by the political, economic, and legal environments in the PRC, as well as by the general state of the PRC economy.
Statement of Cash Flows
In accordance with SFAS No. 95, “Statement of Cash Flows,” cash flows from the Company's operations are calculated based upon the local currencies. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the statement of cash flows may not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the balance sheet.
Basic and Diluted Net Income per Share
The Company is a limited company formed under the laws of the PRC. Like limited liability companies (LLC) in the United States, limited liability companies in the PRC do not issue shares to the owners. The owners however, are called shareholders. Ownership interest is determined in proportion to capital contributed. Accordingly, earnings per share data are not presented.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
SFAS No. 107, “Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments,” requires that the Company disclose estimated fair values of financial instruments. The carrying amounts reported in the statements of financial position for current assets and current liabilities qualifying as financial instruments are a reasonable estimate of fair value.
Foreign Currency Translation and Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The Company’s functional currency is the Renminbi (“RMB”). For financial reporting purposes, RMB has been translated into United States dollars ("USD") as the reporting currency. Assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate in effect at the balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are translated at the average rate of exchange prevailing during the reporting period. Translation adjustments arising from the use of different exchange rates from period to period are included as a component of stockholders' equity as "Accumulated other comprehensive income". Gains and losses resulting from foreign currency transactions are included in income. There has been no significant fluctuation in exchange rate for the conversion of RMB to USD after the balance sheet date.
The Company uses Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 130 (SFAS 130) “Reporting Comprehensive Income”. Comprehensive income is comprised of net income and all changes to the statements of stockholders’ equity, except those due to investments by stockholders, changes in paid-in capital and distributions to stockholders. Comprehensive income for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 included net income and foreign currency translation adjustments.
Segment Reporting
SFAS No. 131, "Disclosures about Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information" requires use of the “management approach” model for segment reporting. The management approach model is based on the way a company's management organizes segments within the company for making operating decisions and assessing performance. Reportable segments are based on products and services, geography, legal structure, management structure, or any other manner in which management disaggregates a company.
SFAS 131 has no effect on the Company's financial statements as substantially all of the Company's operations are conducted in one industry segment. The Company consists of one reportable business segment. All of the Company's assets are located in the PRC.
New Accounting Pronouncements
The Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
In May 2008, FASB issued SFAS No. 162, “The Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles.” SFAS 162 identifies the sources of accounting principles and the framework for selecting the principles to be used in the preparation of financial statements of nongovernmental entities that are presented in conformity with USA GAAP in the United States (the GAAP hierarchy). SFAS 162 adoption did not have an impact on the Company’s financial statements.
Determination of the Useful Life of Intangible Assets
In April 2008, the FASB issued FASB Staff Position FAS 142-3, “Determination of the Useful Life of Intangible Assets” (“FSP FAS 142-3”). FSP FAS 142-3 amends the factors that should be considered in developing renewal or extension assumptions used to determine the useful life of a recognized intangible asset under SFAS No. 142, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets” (“SFAS 142”), and requires additional disclosures. The objective of FSP FAS 142-3 is to improve the consistency between the useful life of a recognized intangible asset under SFAS 142 and the period of expected cash flows used to measure the fair value of the asset under SFAS No. 141 (R), “Business Combinations” (“SFAS 141(R)”), and other accounting principles generally accepted in the USA. FSP FAS 142-3 applies to all intangible assets, whether acquired in a business combination or otherwise and shall be effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The guidance for determining the useful life of intangible assets shall be applied prospectively to intangible assets acquired after the effective date. The disclosure requirements apply prospectively to all intangible assets recognized as of, and subsequent to, the effective date. Early adoption is prohibited. FSP FAS 142-3 is not currently applicable to the company.
Disclosures about Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
In March 2008, the FASB issued SFAS No. 161, “Disclosures about Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities an amendment of FASB Statement No. 133.” This Statement changes the disclosure requirements for derivative instruments and hedging activities. Entities are required to provide enhanced disclosures about (a) how and why an entity uses derivative instruments, (b) how derivative instruments and related hedged items are accounted for under Statement 133 and its related interpretations, and (c) how derivative instruments and related hedged items affect an entity’s financial position, financial performance, and cash flows. SFAS 161 is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning on or after November 15, 2008. SFAS 161 is not currently applicable to the company.
Fair value of measurements
On January 1, 2008, the Company adopted SFAS No. 157, “Fair Value Measurements,” SFAS 157 defines fair value, establishes a three-level valuation hierarchy for disclosures of fair value measurement and enhances disclosures requirements for fair value measurements. The three levels are defined as follow:
|
|
Level 1 inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
|
|
|
Level 2 inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, and inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument.
|
|
|
Level 3 inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and significant to the fair value measurement.
|
As of December 31, 2008, the Company did not identify any assets and liabilities that are required to be presented on the balance sheet at fair value.
Non-Controlling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements - An Amendment of ARB No. 51
In December 2007, FASB issued SFAS No. 160, "Non-controlling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements - An Amendment of ARB No. 51." SFAS 160 establishes new accounting and reporting standards for the non-controlling interest in a subsidiary and for the deconsolidation of a subsidiary. Specifically, this statement requires the recognition of a non-controlling interest (minority interest) as equity in the consolidated financial statements and separate from the parent’s equity. The amount of net income attributable to the non-controlling interest will be included in consolidated net income on the face of the income statement. SFAS 160 clarifies that changes in a parent’s ownership interest in a subsidiary that do not result in deconsolidation are equity transactions if the parent retains its controlling financial interest. In addition, this statement requires that a parent recognize a gain or loss in net income when a subsidiary is deconsolidated. Such gain or loss will be measured using the fair value of the non-controlling equity investment on the deconsolidation date. SFAS 160 also includes expanded disclosure requirements regarding the interests of the parent and its non-controlling interest. SFAS 160 is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning on or after December 15, 2008. The Company expects SFAS 160 will have an impact on accounting for business combinations, but the effect is dependent upon acquisitions at that time.
Business Combinations
SFAS 141 (Revised 2007), Business Combinations (SFAS 141(R)), is effective for the Company for business combinations for which the acquisition date is on or after January 1, 2009. SFAS 141(R) changes how the acquisition method is applied in accordance with SFAS 141. The primary revisions to this Statement require an acquirer in a business combination to measure assets acquired, liabilities assumed, and any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree at the acquisition date, at their fair values as of that date, with limited exceptions specified in the Statement. This Statement also requires the acquirer in a business combination achieved in stages to recognize the identifiable assets and liabilities, as well as the noncontrolling interest in the acquiree, at the full amounts of their fair values (or other amounts determined in accordance with the Statement). Assets acquired and liabilities assumed arising from contractual contingencies as of the acquisition date are to be measured at their acquisition-date fair values, and assets or liabilities arising from all other contingencies as of the acquisition date are to be measured at their acquisition-date fair value, only if it is more likely than not that they meet the definition of an asset or a liability in FASB Concepts Statement No. 6, Elements of Financial Statements. This Statement significantly amends other Statements and authoritative guidance, including FASB Interpretation No. 4, Applicability of FASB Statement No. 2 to Business Combinations Accounted for by the Purchase Method, and now requires the capitalization of research and development assets acquired in a business combination at their acquisition-date fair values, separately from goodwill. FASB Statement No. 109, Accounting for Income Taxes, was also amended by this Statement to require the acquirer to recognize changes in the amount of its deferred tax benefits that are recognizable because of a business combination either in income from continuing operations in the period of the combination or directly in contributed capital, depending on the circumstances. The Company expects SFAS 141R will have a significant impact on accounting for business combinations, but the effect is dependent upon acquisitions at that time.
Accounting for Non-Refundable Advance Payments for Goods or Services Received for Use in Future Research and Development Activities
In June 2007, FASB issued FASB Staff Position No. EITF 07-3, “Accounting for Nonrefundable Advance Payments for Goods or Services Received for use in Future Research and Development Activities,” which addresses whether non-refundable advance payments for goods or services that used or rendered for research and development activities should be expensed when the advance payment is made or when the research and development activity has been performed. EITF 07-03 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. The adoption of EITF 07-03 is not expected to have a significant impact on the Company’s financial statements.
3. INVENTORY
Inventory consisted of computer parts and supplementary parts in the amount of $ 267,789 and $ 31,452 at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
4. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property and equipment consisted of the following at December 31, 2008 and December 31, 2007 was as below:
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
|
Vehicle
|
51,210 | 47,981 | ||||||
|
Office and Equipment
|
267,437 | 233,078 | ||||||
|
Building
|
-- | 130,539 | ||||||
| 318,647 | 411,598 | |||||||
|
Less: Accumulated depreciation
|
(279,365 | ) | (296,772 | ) | ||||
| $ | 39,282 | 114,826 | ||||||
The Company disposed its office building for $87,789 during 2008 (see note 6). Depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 was $ 18,480 and $15,544, respectively.
5. MAJOR CUSTOMERS AND VENDORS
Four customers accounted for 67% and 69% of the Company’s net revenue for year 2008 and 2007, respectively. For year 2008, each customer accounted for about 23%, 19%, 13% and 12% of the sales. For year 2007, each customer accounted for about 24%, 17%, 14% and 14% of the sales. At December 31, 2008 and 2007, the total receivable balance due from these customers was $162,266 and $1,718,812, respectively.
One and four vendors provided 62% and 73% of the Company’s purchase of raw materials for year 2008 and 2007, respectively. For year 2007, each vendor accounted for about 22%, 20%, 20% and 11% of the purchases. At December 31, 2008, the account payable to this vendor was $ 0. At December 31 2007, the total payable to these vendors was $1,859,183.
6. OTHER RECEIVABLES
Other receivables consisted of the following at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively:
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
|
Advance to staff
|
$ | 44,914 | 6,737 | |||||
|
Advance to third parties
|
1,683 | 34,340 | ||||||
|
Tax rebate and retention for sales contract
|
15,593 | -- | ||||||
|
Receivable on disposal of asset
|
87,789 | -- | ||||||
|
Receivable for VAT paid but purchase invoices not yet received
|
57,319 | 60,735 | ||||||
| $ | 207,298 | 101,812 | ||||||
7. TAX PAYABLE
Tax payable consisted of the following at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively:
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
|
Value added tax payable
|
$ | 2,328 | 38,799 | |||||
|
Business tax payable
|
23,751 | 32,658 | ||||||
|
Income tax payable
|
178,663 | -- | ||||||
|
Other taxes payable
|
1,826 | 5,401 | ||||||
| $ | 206,568 | 76,858 | ||||||
8. ACCRUED LIABILITIES AND OTHER PAYABLES
Accrued liabilities and other payables consisted of the following at December 31, 2008 and December 31, 2007, respectively:
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
|
Accrued salary and welfare
|
$ | 15,969 | 24,293 | |||||
|
Other accrued expense
|
782 | 2,315 | ||||||
|
Other payable
|
1,134 | 66,883 | ||||||
| $ | 17,885 | 93,491 | ||||||
9. ADVANCE FROM RELATED PARTY
Advance from related party represented loan from the Company’s shareholder with no interest bearing, payable upon demand. At December 31, 2008 and 2007, advance from related party was $0 and $75,398, respectively.
10. INCOME TAXES
The Company is governed by the Income Tax Law of the PRC concerning the private-run enterprises in Hi-Tech Zone, and is subject to tax at a statutory rate of 25% for 2008 and 15% for 2007 on income reported in the statutory financial statements after appropriated tax adjustments.
The income tax provision consists of the following at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively:
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
|
Current
|
$ | 181,060 | 73,258 | |||||
|
Change in deferred tax asset
|
- | - | ||||||
|
Change in valuation allowance
|
- | - | ||||||
|
Benefit of NOL carryforward
|
- | (73,258 | ) | |||||
| $ | 181,060 | - | ||||||
The following is a reconciliation of the tax derived by applying the PRC statutory rate of 25% and 15% for 2008 and 2007 to the earnings before income taxes and comparing that to the recorded income tax provision:
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
|
Tax provision at PRC statutory rate
|
25.0 | % | 15.0 | % | ||||
|
Other income taxes
|
1.7 | % | - | |||||
|
Benefit of NOL carryforward
|
- | (15.0 | )% | |||||
| 26.7 | % | - | ||||||
The company adopted FIN 48 effective January 1, 2007 which did not require an accrual for uncertain tax positions as of January 1, 2007. There was no change in unrecognized tax benefits and accrual for uncertain tax positions as of December 31, 2007 and 2008.
11. SHORT-TERM LOAN
On April 25, 2006, the Company’s President entered a 5 years, 4% interest rate bank loan with maturity on April 25, 2011 for the amount of approximately $65,000 (RMB 500,000) under his personal name on behalf of the Company and for the use of the Company’s operation. This Company used its building as collateral for this loan and the Company repaid principal and interest monthly. This loan was paid in full during 2008.
12. STATUTORY RESERVES
Pursuant to the new corporate law of the PRC effective January 1, 2006, the Company is now only required to maintain one statutory reserve by appropriating from its after-tax profit before declaration or payment of dividends. The statutory reserve represents restricted retained earnings.
Surplus reserve fund
The Company is now only required to transfer 10% of its net income, as determined under PRC accounting rules and regulations, to a statutory surplus reserve fund until such reserve balance reaches 50% of the Company’s registered capital.
The surplus reserve fund is non-distributable other than during liquidation and can be used to fund previous years’ losses, if any, and may be utilized for business expansion or converted into share capital by issuing new shares to existing shareholders in proportion to their shareholding or by increasing the par value of the shares currently held by them, provided that the remaining reserve balance after such issue is not less than 25% of the registered capital. The Company did not make any reserve to this fund in 2008 and 2007 as the Company has accumulated deficit for both years.
Common welfare fund
Common welfare fund is a voluntary fund that the Company can elect to transfer 5% to 10% of its net income to this fund. The Company did not make any contribution to this fund for the year ended December 31, 2008 and 2007.
This fund can only be utilized on capital items for the collective benefit of the Company’s employees, such as construction of dormitories, cafeteria facilities, and other staff welfare facilities. This fund is non-distributable other than upon liquidation.
Pursuant to the "Circular of the Ministry of Finance (MOF) on the Issue of Corporate Financial Management after the Corporate Law Enforced" (No.67 [2006]), effective on April 1, 2006, issued by the MOF, companies transferred the balance of SCWF (Statutory Common Welfare Fund) as of December 31, 2005 to Statutory Surplus Reserve. Any deficit in the SCWF was charged in turn to Statutory Surplus Reserve, additional paid-in capital and undistributed profit of previous years. If a deficit still remains, it should be transferred to retained earnings and be reduced to zero by a transfer from after tax profit of following years. At December 31, 2005, the Company did not have a deficit in the SCWF.
13. COMMITMENTS
The Company leased its office under one year, non-cancelable, and renewable operating lease agreement on December 1, 2007 with expiration date on November 30, 2008; at maturity, the Company renewed the lease for additional one year expiring on November 30, 2009. The Company will lease this office month-by-month after November 30, 2009.
Total rental expense for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 were approximately $28,466 and $27,217, respectively.
14. CONTINGENCIES
The Company’s operations in the PRC are subject to specific considerations and significant risks not typically associated with companies in the North America and Western Europe. These include risks associated with, among others, the political, economic and legal environments and foreign currency exchange. The Company’ s results may be adversely affected by changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, currency conversion and remittance abroad, and rates and methods of taxation, among other things.
The Company’s sales, purchases and expenses transactions are denominated in RMB and all of the Company’s assets and liabilities are also denominated in RMB. The RMB is not freely convertible into foreign currencies under the current law. In China, foreign exchange transactions are required by law to be transacted only by authorized financial institutions. Remittances in currencies other than RMB may require certain supporting documentation in order to affect the remittance.
HAINAN JIEN INTELLIGENT ENGINEERING CO., LTD
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2008 and 2007
Contents
| Page | ||||
| Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firms | F-58 - F-59 | |||
| Financial Statements: | F-60 | |||
| Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 | F-61 | |||
| Statements of Operations for the Years Ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 | F-62 | |||
| Statements of Shareholders’ Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 | F-63 | |||
| Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 | F-64 - F-72 | |||
To the Board of Directors and
Stockholders of Hainan Jien Intelligent Engineering Co., Ltd.
We have audited the accompanying balance sheet of Hainan Jien Intelligent Engineering Co., Ltd. (“the Company”) as of December 31, 2008, and the related statements of operations and comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity and cash flows for the year then ended. The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit.
We have conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audit included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2008, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year then ended, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States.
/s/ Morison Cogen, LLP
Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania
November 16, 2009
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the shareholders of Hainan Jien Intelligent Engineering Co. Ltd.
We have audited the balance sheet of Hainan Jien Intelligent Engineering Co. Ltd. (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2007 and the related statements of income and other comprehensive income, shareholders equity and cash flows for year then ended. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2007 and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year then ended in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
/s/ Goldman Parks Kurland Mohidin LLP
Encino, California
April 15, 2008
HAINAN JIEN INTELLIGENT ENGINEERING CO., LTD.
BALANCE SHEETS
AS OF
DECEMBER 31, 2008 and 2007
(AUDITED)
|
ASSETS
|
December 31, 2008
|
December 31, 2007
|
||||||
|
CURRENT ASSETS
|
||||||||
|
Cash & cash equivalents
|
$ | 68,101 | $ | 291,129 | ||||
|
Restricted cash
|
3,449 | - | ||||||
|
Accounts receivable, net
|
1,415,415 | 651,288 | ||||||
|
Retentions receivable
|
53,716 | 98,395 | ||||||
|
Prepaid expenses
|
257,306 | - | ||||||
|
Other receivables
|
108,333 | 143,929 | ||||||
|
Inventory
|
118,800 | 17,134 | ||||||
|
Total current assets
|
2,025,120 | 1,201,875 | ||||||
|
RETENTIONS RECEIVABLE
|
202,666 | 98,886 | ||||||
|
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, net
|
78,919 | 37,219 | ||||||
|
TOTAL ASSETS
|
$ | 2,306,705 | $ | 1,337,980 | ||||
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES
|
||||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
$ | 409,221 | $ | 349,966 | ||||
|
Unearned revenue
|
268,725 | - | ||||||
|
Tax payable
|
235,774 | 334,329 | ||||||
|
Other payables and accrued liabilities
|
80,740 | 50,129 | ||||||
|
Total current liabilities
|
994,460 | 734,424 | ||||||
|
CONTINGENCIES AND COMMITMENTS
|
||||||||
|
STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
Paid in capital
|
120,824 | 120,824 | ||||||
|
Statutory reserve
|
67,737 | 44,738 | ||||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income
|
83,016 | 31,765 | ||||||
|
Retained earnings
|
1,040,668 | 406,229 | ||||||
|
Total stockholders' equity
|
1,312,245 | 603,556 | ||||||
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
$ | 2,306,705 | $ | 1,337,980 | ||||
F-60
HAINAN JIEN INTELLIGENT ENGINEERING CO., LTD.
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
FOR YEARS ENDED
DECEMBER 31, 2008 and 2007
(AUDITED)
|
YEARS ENDED
|
||||||||
|
DECEMBER 31
|
||||||||
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
|
Net sales
|
$ | 5,554,357 | $ | 3,580,253 | ||||
|
Cost of goods sold
|
(4,403,810 | ) | (2,732,574 | ) | ||||
|
Gross profit
|
1,150,547 | 847,679 | ||||||
|
Operating expenses
|
||||||||
|
Selling expenses
|
(103,774 | ) | (15,351 | ) | ||||
|
General and administrative expenses
|
(385,486 | ) | (346,918 | ) | ||||
|
Total operating expenses
|
(489,260 | ) | (362,269 | ) | ||||
|
Income from operations
|
661,287 | 485,410 | ||||||
|
Non-operating income (expenses)
|
||||||||
|
Interest income
|
189 | 102 | ||||||
|
Interest expense
|
(2,937 | ) | (723 | ) | ||||
|
Other income
|
547 | 6,551 | ||||||
|
Other expenses
|
(1,648 | ) | (2,778 | ) | ||||
|
Total non-operating income (expenses)
|
(3,849 | ) | 3,152 | |||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 657,438 | $ | 488,562 | ||||
|
Other comprehensive item
|
||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation
|
51,251 | 26,990 | ||||||
|
Comprehensive Income
|
$ | 708,689 | $ | 515,552 | ||||
F-61
HAINAN JIEN INTELLIGENT ENGINEERING CO., LTD.
STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
FOR YEARS ENDED
DECEMBER 31, 2008 and 2007
(AUDITED)
|
Paid in capital
|
Statutory reserves
|
Other comprehensive income
|
(Accumulated deficit) / Retained earnings
|
Total
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at January 1, 2007
|
$ | 120,824 | $ | - | $ | 4,775 | $ | (37,595 | ) | $ | 88,004 | |||||||||
|
Net income for the year
|
- | - | - | 488,562 | 488,562 | |||||||||||||||
|
Transfer to statutory reserves
|
- | 44,738 | - | (44,738 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation gain
|
- | - | 26,990 | - | 26,990 | |||||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2007
|
120,824 | 44,738 | 31,765 | 406,229 | 603,556 | |||||||||||||||
|
Net income for the year
|
- | - | - | 657,438 | 657,438 | |||||||||||||||
|
Transfer to statutory reserves
|
- | 22,999 | - | (22,999 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation gain
|
- | - | 51,251 | - | 51,251 | |||||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2008
|
$ | 120,824 | $ | 67,737 | $ | 83,016 | $ | 1,040,668 | $ | 1,312,245 | ||||||||||
F-62
HAINAN JIEN INTELLIGENT ENGINEERING CO., LTD.
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOW
FOR YEARS ENDED
DECEMBER 31, 2008 and 2007
(AUDITED)
|
YEARS ENDED
|
|||||||||
|
DECEMBER 31,
|
|||||||||
|
2008
|
2007
|
||||||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES:
|
|||||||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 657,438 | $ | 488,562 | |||||
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash
|
|||||||||
|
(used in) provided by operating activities:
|
|||||||||
|
Depreciation
|
21,286 | 13,638 | |||||||
|
Change in allowance for doubtful accounts
|
27,487 | - | |||||||
|
(Increase) decrease in current assets:
|
|||||||||
|
Restricted cash
|
(3,394 | ) | - | ||||||
|
|
Accounts receivable
|
(736,318 | ) | (570,299 | ) | ||||
|
|
Retentions receivable
|
(45,095 | ) | (174,676 | ) | ||||
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other receivables
|
(208,649 | ) | (32,745 | ) | ||||
|
|
Inventory
|
(98,914 | ) | (11,249 | ) | ||||
|
Increase (decrease) in current liabilities:
|
|||||||||
|
|
Accounts payable
|
35,132 | 213,128 | ||||||
|
|
Unearned revenue
|
264,449 | - | ||||||
|
|
Other payables and accrued liabilities
|
28,004 | 34,326 | ||||||
|
|
Tax payable
|
(119,130 | ) | 173,530 | |||||
|
Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities
|
(177,704 | ) | 134,215 | ||||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES:
|
|||||||||
|
Acquisition of property & equipment
|
(59,858 | ) | (1,531 | ) | |||||
|
Net cash used in investing activities
|
(59,858 | ) | (1,531 | ) | |||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES:
|
|||||||||
|
Due to (from) related parties
|
(1,200 | ) | 100,565 | ||||||
|
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities
|
(1,200 | ) | 100,565 | ||||||
|
EFFECT OF EXCHANGE RATE CHANGE ON CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
15,734 | 13,080 | |||||||
|
NET (DECREASE) INCREASE IN CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
(223,028 | ) | 246,329 | ||||||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF YEAR
|
291,129 | 44,800 | |||||||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, END OF YEAR
|
$ | 68,101 | $ | 291,129 | |||||
|
Supplemental Cash flow data:
|
|||||||||
|
Interest paid
|
$ | 2,985 | $ | 1,344 | |||||
F-63
HAINAN JIEN INTELLIGENT ENGINEERING CO., LTD.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2008 and 2007
(Audited)
1. ORGANIZATION AND DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
Hainan Jien Intelligent Engineering Co. Ltd. (the “Company” or “Jien”) was incorporated in the Hainan Province, People’s Republic of China (“PRC”) in 1999. Jien is engaged in providing full service of design and installation of intelligentized equipment for business and residential communities.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in conformity with US GAAP. The Company’s functional currency is the Chinese Renminbi; however, the accompanying financial statements have been translated and presented in United States Dollars ($).
Use of Estimates
In preparing financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, management makes estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the dates of the financial statements, as well as the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting year. Significant estimates, required by management, include the recoverability of long-lived assets and the valuation of inventories. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
For purposes of the statement of cash flows, the Company considers all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. As of December 31, 2008, the Company maintained total restricted cash of $3,449 in a bank account, represented cash deposit from a customer for partial settlement of retention receivable that is due in 2011. The restricted cash will be released in 2011 after the retention period expires.
Accounts and Retentions Receivable
The Company’s policy is to maintain reserves for potential credit losses on accounts receivable. Management reviews the composition of accounts receivable and analyzes historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customer payment patterns to evaluate the adequacy of these reserves. Based on historical collection activity, the Company made allowance of approximately $27,931 and $1,692 at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
At December 31, 2008 and 2007, the Company had retentions receivable for product quality assurance in the amount of $256,832 and $197,281, respectively. The retention rate varies from 3% to 5% of the sales price with variable terms from 1 year to 3 years. At December 31, 2008, $53,716 of the retentions receivable are current and due within one year, and $202,666 of the retentions receivable are noncurrent. At December 31, 2007, $98,395 of the retentions receivable are current and due within one year, and $98,886 of the retentions receivable are noncurrent.
Inventories
Inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market with cost determined on a first in, first out basis.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred; additions, renewals and betterments are capitalized. When property and equipment are retired or otherwise disposed of, the related cost and accumulated depreciation is removed from the respective accounts, and any gain or loss is included in operations. Depreciation of property and equipment is provided using the straight-line method for substantially all assets with a 5% salvage value and estimated lives ranging from 5 to 20 years as follows:
Building 20 years
Leasehold improvements Shorter of lease term or 10 years
Vehicle 5 years
Office Equipment 5 years
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Long-lived assets, which include property, plant and equipment and intangible assets, are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable.
Recoverability of long-lived assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to the estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its estimated undiscounted future cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the assets. Fair value is generally determined using the asset’s expected future discounted cash flows or market value, if readily determinable. Based on its review, the Company believes that, as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, there were no significant impairments of its long-lived assets.
Warranties
The Company offers warranty to its customers on its products for a period from three months to three years depending on the contract terms negotiated with the customers; most of warranty term is one year. The Company accrues for warranty costs based on estimates of the costs that may be incurred under its warranty obligations. The warranty expense and related accrual is included in the Company's selling expenses and other payable respectively, and is recorded at the time revenue is recognized. Factors that affect the Company's warranty liability include the number of sold equipment, its estimates of anticipated rates of warranty claims, costs per claim and estimated support labor costs and the associated overhead. The Company periodically assesses the adequacy of its recorded warranty liabilities and adjusts the amounts as necessary.
The Company's warranty reserve at December 31, 2008 was as follows:
|
Beginning balance
|
$
|
-
|
||
|
Provisions made
|
73,715
|
|||
|
Changes in estimates
|
-
|
|||
|
Actual costs incurred
|
(28,943)
|
|||
|
Ending balance, included in other payables and accrued expenses
|
$
|
44,772
|
Income Taxes
The Company utilizes SFAS No. 109, “Accounting for Income Taxes,” which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Under this method, deferred income taxes are recognized for the tax consequences in future years of differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their financial reporting amounts at each period end based on enacted tax laws and statutory tax rates applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to affect taxable income. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
When tax returns are filed, it is highly certain that some positions taken would be sustained upon examination by the taxing authorities, while others are subject to uncertainty about the merits of the position taken or the amount of the position that would be ultimately sustained. The benefit of a tax position is recognized in the financial statements in the period during which, based on all available evidence, management believes it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including the resolution of appeals or litigation processes, if any. Tax positions taken are not offset or aggregated with other positions. Tax positions that meet the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold are measured as the largest amount of tax benefit that is more than 50 percent likely of being realized upon settlement with the applicable taxing authority. The portion of the benefits associated with tax positions taken that exceeds the amount measured as described above is reflected as a liability for unrecognized tax benefits in the accompanying balance sheets along with any associated interest and penalties that would be payable to the taxing authorities upon examination. Interest associated with unrecognized tax benefits are classified as interest expense and penalties are classified in selling, general and administrative expenses in the statements of income. At December 31, 2008 and 2007, the Company did not take any uncertain positions that would necessitate recording of tax related liability.
Revenue Recognition
The Company's revenue recognition policies are in compliance with Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Staff Accounting Bulletin (“SAB”) 104. Sales revenue is recognized at the date of shipment to customers when a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and collectibility is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are recorded as unearned revenue.
The Company records its revenue when certain milestones as defined in the service contract are reached. These service contracts have clear milestones and deliverables with distinct values assigned to each milestone. The milestones do not require the delivery of multiple elements as noted in Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”) Issue 00-21 “Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables” ("EITF No. 00-21"). In accordance with SAB No. 104, the Company treats each milestone as an individual revenue agreement and only recognizes revenue for each milestone when all the conditions of SAB 104 defined earlier are met.
The Company is qualified as a small business so that all of the Company’s products sold or services provided in the PRC are subject to a fixed low value-added tax (“VAT”) of 4% of the gross sales price regardless of the VAT paid. Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of goods or services, net of VAT. This VAT cannot be offset by VAT paid by the Company on raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing their finished.
VAT deducted from sales was $ 8,357 and $ 39,039 for the year ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. Sales are recorded net of VAT collected as the Company acts as an agent for the government.
The standard warranty of the Company is provided to its customers and is not considered an additional service; rather it is considered an integral part of the product and services’ sale. The Company believes that the existence of its standard product warranty in a sales contract does not constitute a deliverable in the arrangement and thus there is no need to apply the EITF 00-21 separation and allocation model for a multiple deliverable arrangement. FAS 5 specifically address the accounting for standard warranties and neither SAB 104 nor EITF 00-21 supersedes FAS 5. The Company believes that accounting for its standard warranty pursuant to FAS 5 does not impact revenue recognition because the cost of honoring the warranty can be reliably estimated.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of goods sold consists primarily of material costs, labor costs, and related overhead which are directly attributable to the production of the service. Write-down of inventory to lower of cost or market is also recorded in cost of goods sold.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to credit risk consist primarily of accounts receivable and other receivables. The Company does not require collateral or other security to support these receivables. The Company conducts periodic reviews of its clients' financial condition and customer payment practices to minimize collection risk on accounts receivable.
The operations of the Company are located in the PRC. Accordingly, the Company's business, financial condition, and results of operations may be influenced by the political, economic, and legal environments in the PRC, as well as by the general state of the PRC economy.
Statement of Cash Flows
In accordance with SFAS No. 95, “Statement of Cash Flows,” cash flows from the Company's operations is calculated based upon local currencies. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the statement of cash flows may not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the balance sheet.
Basic and Diluted Net Income per Share
The Company is a limited company formed under the laws of the PRC. Like limited liability companies (LLC) in the United States, limited liability companies in the PRC do not issue shares to the owners. The owners however, are called shareholders. Ownership interest is determined in proportion to capital contributed. Accordingly, earnings per share data are not presented.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
SFAS No. 107, “Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments,” requires the Company disclose estimated fair values of financial instruments. The carrying amounts reported in the statements of financial position for current assets and current liabilities qualifying as financial instruments are a reasonable estimate of fair value.
Foreign Currency Translation and Comprehensive Income
The Company’s functional currency is the Renminbi (“RMB”). For financial reporting purposes, RMB has been translated into United States dollars ("USD") as the reporting currency. Assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate in effect at the balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are translated at the average rate of exchange prevailing during the reporting period. Translation adjustments arising from the use of different exchange rates from period to period are included as a component of stockholders' equity as "Accumulated other comprehensive income". Gains and losses resulting from foreign currency transactions are included in income. There has been no significant fluctuation in exchange rate for the conversion of RMB to USD after the balance sheet date.
The Company uses SFAS 130 “Reporting Comprehensive Income”. Comprehensive income is comprised of net income and all changes to the statements of stockholders’ equity, except those due to investments by stockholders, changes in paid-in capital and distributions to stockholders. Comprehensive income for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 included net income and foreign currency translation adjustments.
Segment Reporting
SFAS No. 131, "Disclosures about Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information" requires use of the “management approach” model for segment reporting. The management approach model is based on the way a company's management organizes segments within the company for making operating decisions and assessing performance. Reportable segments are based on products and services, geography, legal structure, management structure, or any other manner in which management disaggregates a company.
SFAS 131 has no effect on the Company's financial statements as substantially all of the Company's operations are conducted in one industry segment. The Company consists of one reportable business segment. All of the Company's assets are located in the PRC.
New Accounting Pronouncements
The Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
In May 2008, FASB issued SFAS No. 162, “The Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles.” SFAS 162 identifies the sources of accounting principles and the framework for selecting the principles to be used in the preparation of financial statements of nongovernmental entities that are presented in conformity with USA GAAP in the United States (the GAAP hierarchy). SFAS 162 adoption did not have an impact on the Company’s financial statements.
Determination of the Useful Life of Intangible Assets
In April 2008, the FASB issued FASB Staff Position FAS 142-3, “Determination of the Useful Life of Intangible Assets” (“FSP FAS 142-3”). FSP FAS 142-3 amends the factors that should be considered in developing renewal or extension assumptions used to determine the useful life of a recognized intangible asset under SFAS No. 142, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets” (“SFAS 142”), and requires additional disclosures. The objective of FSP FAS 142-3 is to improve the consistency between the useful life of a recognized intangible asset under SFAS 142 and the period of expected cash flows used to measure the fair value of the asset under SFAS No. 141 (R), “Business Combinations” (“SFAS 141(R)”), and other accounting principles generally accepted in the USA. FSP FAS 142-3 applies to all intangible assets, whether acquired in a business combination or otherwise and shall be effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The guidance for determining the useful life of intangible assets shall be applied prospectively to intangible assets acquired after the effective date. The disclosure requirements apply prospectively to all intangible assets recognized as of, and subsequent to, the effective date. Early adoption is prohibited. FSP FAS 142-3 is not currently applicable to the company.
Disclosures about Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
In March 2008, the FASB issued SFAS No. 161, “Disclosures about Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities an amendment of FASB Statement No. 133.” This Statement changes the disclosure requirements for derivative instruments and hedging activities. Entities are required to provide enhanced disclosures about (a) how and why an entity uses derivative instruments, (b) how derivative instruments and related hedged items are accounted for under Statement 133 and its related interpretations, and (c) how derivative instruments and related hedged items affect an entity’s financial position, financial performance, and cash flows. SFAS 161 is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning on or after November 15, 2008. SFAS 161 is not currently applicable to the company.
Fair value of measurements
On January 1, 2008, the Company adopted SFAS No. 157, “Fair Value Measurements,” SFAS 157 defines fair value, establishes a three-level valuation hierarchy for disclosures of fair value measurement and enhances disclosures requirements for fair value measurements. The three levels are defined as follow:
|
|
Level 1 inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
|
|
|
Level 2 inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, and inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument.
|
|
|
Level 3 inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and significant to the fair value measurement.
|
As of December 31, 2008, the Company did not identify any assets and liabilities that are required to be presented on the balance sheet at fair value.
Non-Controlling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements - An Amendment of ARB No. 51
In December 2007, FASB issued SFAS No. 160, "Non-controlling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements - An Amendment of ARB No. 51." SFAS 160 establishes new accounting and reporting standards for the non-controlling interest in a subsidiary and for the deconsolidation of a subsidiary. Specifically, this statement requires the recognition of a non-controlling interest (minority interest) as equity in the consolidated financial statements and separate from the parent’s equity. The amount of net income attributable to the non-controlling interest will be included in consolidated net income on the face of the income statement. SFAS 160 clarifies that changes in a parent’s ownership interest in a subsidiary that do not result in deconsolidation are equity transactions if the parent retains its controlling financial interest. In addition, this statement requires that a parent recognize a gain or loss in net income when a subsidiary is deconsolidated. Such gain or loss will be measured using the fair value of the non-controlling equity investment on the deconsolidation date. SFAS 160 also includes expanded disclosure requirements regarding the interests of the parent and its non-controlling interest. SFAS 160 is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning on or after December 15, 2008. The Company expects SFAS 160 will have an impact on accounting for business combinations, but the effect is dependent upon acquisitions at that time.
Business Combinations
SFAS 141 (Revised 2007), Business Combinations (SFAS 141(R)), is effective for the Company for business combinations for which the acquisition date is on or after January 1, 2009. SFAS 141(R) changes how the acquisition method is applied in accordance with SFAS 141. The primary revisions to this Statement require an acquirer in a business combination to measure assets acquired, liabilities assumed, and any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree at the acquisition date, at their fair values as of that date, with limited exceptions specified in the Statement. This Statement also requires the acquirer in a business combination achieved in stages to recognize the identifiable assets and liabilities, as well as the noncontrolling interest in the acquiree, at the full amounts of their fair values (or other amounts determined in accordance with the Statement). Assets acquired and liabilities assumed arising from contractual contingencies as of the acquisition date are to be measured at their acquisition-date fair values, and assets or liabilities arising from all other contingencies as of the acquisition date are to be measured at their acquisition-date fair value, only if it is more likely than not that they meet the definition of an asset or a liability in FASB Concepts Statement No. 6, Elements of Financial Statements. This Statement significantly amends other Statements and authoritative guidance, including FASB Interpretation No. 4, Applicability of FASB Statement No. 2 to Business Combinations Accounted for by the Purchase Method, and now requires the capitalization of research and development assets acquired in a business combination at their acquisition-date fair values, separately from goodwill. FASB Statement No. 109, Accounting for Income Taxes, was also amended by this Statement to require the acquirer to recognize changes in the amount of its deferred tax benefits that are recognizable because of a business combination either in income from continuing operations in the period of the combination or directly in contributed capital, depending on the circumstances. The Company expects SFAS 141R will have a significant impact on accounting for business combinations, but the effect is dependent upon acquisitions at that time.
Accounting for Non-Refundable Advance Payments for Goods or Services Received for Use in Future Research and Development Activities
In June 2007, FASB issued FASB Staff Position No. EITF 07-3, “Accounting for Nonrefundable Advance Payments for Goods or Services Received for use in Future Research and Development Activities,” which addresses whether non-refundable advance payments for goods or services that used or rendered for research and development activities should be expensed when the advance payment is made or when the research and development activity has been performed. EITF 07-03 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. The adoption of EITF 07-03 is not expected to have a significant impact on the Company’s financial statements.
Inventory at December 31, 2008 and 2007 consisted of raw material and work in process as follows.
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
Inventory
|
2008
|
2007
|
||||||
|
Raw material
|
$ | 37,224 | 17,134 | |||||
|
Work in process
|
81,576 | -- | ||||||
| $ | 118,800 | 17,134 | ||||||
4. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property and equipment consisted of the following at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively:
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
|
Leasehold Improvement
|
$ | 100,692 | -- | |||||
|
Office equipment
|
41,615 | 76,343 | ||||||
|
Less: Accumulated depreciation
|
(63,388 | ) | (39,124 | ) | ||||
| $ | 78,919 | 37,219 | ||||||
Depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 was $ 21,286 and $13,638, respectively.
5. PREPAID EXPENSES
Prepaid expenses consisted of prepayments to vendors for materials and parts for the projects which have not commenced at balance sheet date. Prepaid expenses were $257,306 and $0 at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
6. OTHER RECEIVABLES
Other receivables consisted of prepayment to vendors and sub-contractors and cash advances to employees for normal business purposes such as travelling expense. At December 31, 2008 and 2007, the amount was $108,333 and $143,929, respectively.
7. MAJOR CUSTOMERS AND VENDORS
Four major customers accounted for 80% of the Company’s net revenue for 2008, each customer accounted for approximately 52%, 11%, 9% and 8% of net sales. At December 31, 2008, the total receivable balance due from these customers was $ 1,149,240.
Four major customers accounted for 65% of the Company’s net revenue for 2007, each customer accounted for approximately 25%, 18%, 12%, and 10% of net sales. At December 31, 2007, the total receivable balance due from these customers was $591,060.
Two major vendors provided 83% and 25% of the Company’s purchases of raw materials for year 2008 and 2007. The Company had total accounts payable to these two vendors of $ 360,262 and $54,780 at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
8. TAX PAYABLE
Tax payable consisted of the following at December 31, 2008 and 2007 as follows:
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
|
Income tax payable
|
$ | 147,620 | 215,898 | |||||
|
Value added tax payable
|
648 | 57,829 | ||||||
|
Business tax payable
|
83,370 | 54,726 | ||||||
|
Other taxes payable
|
4,136 | 5,876 | ||||||
| $ | 235,774 | 334,329 | ||||||
9. OTHER PAYABLES AND ACCRUED LIABILITIES
Other payables and accrued liabilities consisted of the following at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively:
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
|
Payable to Subcontractors
|
$
|
17,482
|
$
|
-
|
||||
|
Salary and welfare payable
|
4,258
|
17,562
|
||||||
|
Payable to employees for expense reimburse
|
12,100
|
-
|
||||||
|
Warranty reserve
|
44,772
|
-
|
||||||
|
Deposit from customers for construction
|
-
|
28,509
|
||||||
|
Other payables
|
2,128
|
4,058
|
||||||
|
Total
|
$
|
80,740
|
$
|
50,129
|
||||
10. UNEARNED REVENUE
Unearned revenue represented amounts received from customers but services has not been provided or completed. As of December 31, 2008 and 2007, the amount was $ 268,725 and $0, respectively.
11. INCOME TAXES
The Company is governed by the Income Tax Law of the PRC concerning the private-run enterprises in special district, which are generally subject to tax at a statutory rate of 15% before year 2008 on income reported in the statutory financial statements after appropriated tax adjustments.
The Company is qualified as a small business in the construction industry in PRC. The Company was subject to 2.7% and 2.4% tax rate on net sales in 2008 and 2007, respectively. The tax rate will increase to 3% of net sales in 2009. Since the tax is based on sales, under US GAAP, it is not income tax. Accordingly, $ 144,973 and $ 85,926 have been recorded as general and administrative expense for 2008 and 2007 respectively.
12. STATUTORY RESERVES
Pursuant to the new corporate law of the PRC effective January 1, 2006, the Company is now only required to maintain one statutory reserve by appropriating from its after-tax profit before declaration or payment of dividends. The statutory reserve represents restricted retained earnings.
Surplus reserve fund
The Company is now only required to transfer 10% of its net income, as determined under PRC accounting rules and regulations, to a statutory surplus reserve fund until such reserve balance reaches 50% of the Company’s registered capital. For the year ended December 31 2008, the Company transferred approximately $23,000 to the reserve as the amount reached 50% of the Company’s registered capital. For the year ended December 31, 2007, the Company made $44,738 to this reserve.
The surplus reserve fund is non-distributable other than during liquidation and can be used to fund previous years’ losses, if any, and may be utilized for business expansion or converted into share capital by issuing new shares to existing shareholders in proportion to their shareholding or by increasing the par value of the shares currently held by them, provided that the remaining reserve balance after such issue is not less than 25% of the registered capital.
Common welfare fund
Common welfare fund is a voluntary fund that the Company can elect to transfer 5% to 10% of its net income to this fund. The Company did not make any contribution to this fund for the year ended December 31, 2008 and 2007.
This fund can only be utilized on capital items for the collective benefit of the Company’s employees, such as construction of dormitories, cafeteria facilities, and other staff welfare facilities. This fund is non-distributable other than upon liquidation.
Pursuant to the "Circular of the Ministry of Finance (MOF) on the Issue of Corporate Financial Management after the Corporate Law Enforced" (No.67 [2006]), effective on April 1, 2006, issued by the MOF, companies transferred the balance of SCWF (Statutory Common Welfare Fund) as of December 31, 2005 to Statutory Surplus Reserve. Any deficit in the SCWF was charged in turn to Statutory Surplus Reserve, additional paid-in capital and undistributed profit of previous years. If a deficit still remains, it should be transferred to retained earnings and be reduced to zero by a transfer from after tax profit of following years. At December 31, 2005, the Company did not have a deficit in the SCWF.
13. COMMITMENTS
The Company leased its office under long term, non-cancelable, and renewable operating lease agreements on November 8, 2007 with expiration date on November 7, 2009. The Company will pay the rents month-by-month after the expiration date.
Future minimum rental payments required under this operating lease though November 7, 2009 is $ 35,202. Total rental expense for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 were approximately $14,000 and $5,000, respectively.
14. CONTINGENCIES
The Company’s operations in the PRC are subject to specific considerations and significant risks not typically associated with companies in the North America and Western Europe. These include risks associated with, among others, the political, economic and legal environments and foreign currency exchange. The Company’ s results may be adversely affected by changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, currency conversion and remittance abroad, and rates and methods of taxation, among other things.
The Company’s sales, purchases and expenses transactions are denominated in RMB and all of the Company’s assets and liabilities are also denominated in RMB. The RMB is not freely convertible into foreign currencies under the current law. In China, foreign exchange transactions are required by law to be transacted only by authorized financial institutions. Remittances in currencies other than RMB may require certain supporting documentation in order to affect the remittance.
CHONGQING SYSWAY INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD
CONDENSED BALANCE SHEETS
AS OF
JUNE 30, 2009 and DECEMBER 31, 2008
|
JUNE 30, 2009
|
DECEMBER 31, 2008
|
|||||||
|
ASSETS
|
(Unaudited)
|
(Audited)
|
||||||
|
CURRENT ASSETS
|
||||||||
|
Cash & cash equivalents
|
$ | 44,098 | $ | 48,588 | ||||
|
Accounts receivable, net
|
1,380,413 | 932,910 | ||||||
|
Retentions receivable
|
1,084,047 | 49,610 | ||||||
|
Advance to supplier
|
1,661 | 33,213 | ||||||
|
Other receivables
|
132,186 | 207,298 | ||||||
|
Inventory
|
83,858 | 267,789 | ||||||
|
Intangible assets
|
152,257 | - | ||||||
|
Total current assets
|
2,878,520 | 1,539,408 | ||||||
|
RETENTIONS RECEIVABLE
|
- | 42,358 | ||||||
|
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, net
|
37,265 | 39,282 | ||||||
|
TOTAL ASSETS
|
$ | 2,915,785 | $ | 1,621,048 | ||||
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES
|
||||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
$ | 991,463 | $ | 157,115 | ||||
|
Tax payable
|
337,125 | 206,568 | ||||||
|
Accrued liabilities and other payables
|
25,499 | 17,885 | ||||||
|
Total current liabilities
|
1,354,087 | 381,568 | ||||||
|
CONTINGENCIES AND COMMITMENTS
|
||||||||
|
STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
Paid in capital
|
1,360,497 | 1,208,240 | ||||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income
|
104,782 | 104,271 | ||||||
|
Retained earnings (accumulated deficit)
|
96,419 | (73,031 | ) | |||||
|
Total stockholders' equity
|
1,561,698 | 1,239,480 | ||||||
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
$ | 2,915,785 | $ | 1,621,048 | ||||
F-73
CHONGQING SYSWAY INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
FOR THE SIX MONTHS ENDED
JUNE 30, 2009 and 2008
(UNAUDITED)
|
FOR SIX MONTHS ENDED
|
||||||||
|
JUNE 30, 2009
|
JUNE 30, 2008
|
|||||||
|
(Unaudited)
|
(Unaudited)
|
|||||||
|
Net sales
|
$ | 2,337,032 | $ | 1,637,231 | ||||
|
Cost of goods sold
|
(1,842,514 | ) | (1,231,682 | ) | ||||
|
Gross profit
|
494,518 | 405,549 | ||||||
|
Operating expenses
|
||||||||
|
Selling expenses
|
(75,784 | ) | (61,465 | ) | ||||
|
General and administrative expenses
|
(192,682 | ) | (194,381 | ) | ||||
|
Total operating expenses
|
(268,466 | ) | (255,846 | ) | ||||
|
Income from operations
|
226,052 | 149,703 | ||||||
|
Non-operating income (expenses)
|
||||||||
|
Interest income
|
43 | 176 | ||||||
|
Interest expense
|
31 | (995 | ) | |||||
|
Reversal of bad debt provision in prior years
|
- | 159,210 | ||||||
|
Subsidy income
|
- | 25,824 | ||||||
|
Other income
|
- | 1,558 | ||||||
|
Other expenses
|
(192 | ) | (695 | ) | ||||
|
Total non-operating income (expenses)
|
(118 | ) | 185,078 | |||||
|
Income before income tax expense
|
225,934 | 334,781 | ||||||
|
Income tax expense
|
56,483 | 83,696 | ||||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 169,451 | $ | 251,085 | ||||
|
Other comprehensive item
|
||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation
|
511 | 50,990 | ||||||
|
Comprehensive Income
|
$ | 169,962 | $ | 302,075 | ||||
F-74
CHONGQING SYSWAY INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOW
FOR THE SIX MONTHS ENDED
JUNE 30, 2009 and 2008
(UNAUDITED)
|
FOR SIX MONTHS ENDED
|
||||||||
|
JUNE 30, 2009
|
JUNE 30, 2008
|
|||||||
|
(Unaudited)
|
(Unaudited)
|
|||||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 169,451 | $ | 251,085 | ||||
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash
|
||||||||
|
provided by operating activities:
|
||||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization
|
7,382 | 8,959 | ||||||
|
Change in allowance for doubtful accounts
|
- | (159,210 | ) | |||||
|
(Increase) decrease in current assets:
|
||||||||
|
Accounts receivable
|
(447,082 | ) | 808,915 | |||||
|
Retention receivable
|
(991,927 | ) | 71,326 | |||||
|
Advance to suppliers
|
31,561 | (50,913 | ) | |||||
|
Other receivable
|
75,187 | (2,967 | ) | |||||
|
Inventory
|
184,015 | (83,051 | ) | |||||
|
Increase (decrease) in current liabilities:
|
||||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
834,189 | (1,253,646 | ) | |||||
|
Accrued liabilities and other payable
|
7,606 | (50,122 | ) | |||||
|
Tax payable
|
130,460 | 23,085 | ||||||
|
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities
|
842 | (436,539 | ) | |||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||||||
|
Acquisition of property & equipment
|
(5,350 | ) | (11,890 | ) | ||||
|
Net cash used in investing activities
|
(5,350 | ) | (11,890 | ) | ||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||||||
|
Short-term loan
|
- | (49,945 | ) | |||||
|
Advance from related parties
|
- | (77,922 | ) | |||||
|
Net cash used in financing activities
|
- | (127,867 | ) | |||||
|
EFFECT OF EXCHANGE RATE CHANGE ON CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
18 | 21,712 | ||||||
|
NET DECREASE IN CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
(4,490 | ) | (554,584 | ) | ||||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF PERIOD
|
48,588 | 640,003 | ||||||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, END OF PERIOD
|
$ | 44,098 | $ | 85,419 | ||||
F-75
CHONGQING SYSWAY INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2009 (UNAUDITED) and DECEMBER 31, 2008 (AUDITED)
1. ORGANIZATION AND DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
Chongqing Sysway Information Technology Co., Ltd. (the “Company” or “Chongqing Sysway”) was incorporated in the Chongqing City, Sichuan Province, People’s Republic of China (“PRC”) in 1999 as a State Owned Enterprise (“SOE”). In 2005, the two SOE shareholders sold their ownership shares among other original minority shareholders and since then, Chongqing Sysway began to operate as a private enterprise mainly engaged in system integration services including computer system installation, website design, system firewall setup, etc., particularly for tobacco industry.
The unaudited condensed financial statements have been prepared by the Company, pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission. The information furnished herein reflects all adjustments (consisting of normal recurring accruals and adjustments) which are, in the opinion of management, necessary to fairly present the operating results for the respective periods. Certain information and footnote disclosures normally present in annual financial statements prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America have been omitted pursuant to such rules and regulations. The results for the six months ended June 30, 2009 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the full year ending December 31, 2009.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in conformity with US GAAP. The Company’s functional currency is the Chinese Renminbi; however, the accompanying financial statements have been translated and presented in United States Dollars ($).
Accounts and Retentions Receivable
The Company’s policy is to maintain reserves for potential credit losses on accounts receivable. Management reviews the composition of accounts receivable and analyzes historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customer payment patterns to evaluate the adequacy of these reserves. Based on historical collection activity, the Company had $0 bad debt allowance at June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively.
At June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008, the Company had retentions receivable for product quality assurance in the amount of $1,084,047 and $91,968, respectively. The retention rate varies from 3% to 5% of the sales price with variable terms from 1 year to 3 years.
Revenue Recognition
The Company's revenue recognition policies are in compliance with Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Staff Accounting Bulletin (“SAB”) 104, (codified in FASB ASC Topic 480). Sales revenue is recognized at the date of shipment to customers when a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and collectibility is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are recorded as unearned revenue.
The Company records its revenue when certain milestones as defined in the service contract are reached. These service contracts have clear milestones and deliverables with distinct values assigned to each milestone. The milestones do not require the delivery of multiple elements as noted in Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”) Issue 00-21 “Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables” ("EITF No. 00-21"), (codified in FASB ASC Topic 605). In accordance with SAB No. 104, the Company treats each milestone as an individual revenue agreement and only recognizes revenue for each milestone when all the conditions of SAB 104 defined earlier are met.
Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of products and services, net of value-added tax (“VAT”). All of the Company’s products and service that are sold and provided in the PRC are subject to Chinese value-added tax of 17% of the gross sales price. This VAT may be offset by VAT paid by the Company on raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing their finished product. The Company recorded VAT payable and VAT receivable net of payments in the financial statements. The VAT tax return is filed offsetting the payables against the receivables. Sales and purchases are recorded net of VAT collected and paid as the Company acts as an agent for the government.
The Company provides post-contract support (PCS). Maintenance revenues from ongoing customer support services are billed on an annual basis with the revenue being deferred and recognized ratably over the maintenance period. The Company does not charge for PCS services separately for the first year from the date the product is sold. The Company believes that this type of PCS does not have to be accounted for as a separate unit in accordance with guidance provided by AICPA Statement of Position (SOP) 97-2, codified in FASB ASC Topic 985. The Company charges PCS services through a separate contact after the first year of the sale.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of goods sold consists primarily of material costs, labor costs, and related overhead which are directly attributable to the production of the service. Write-down of inventory to lower of cost or market is also recorded in cost of goods sold.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to credit risk consist primarily of accounts receivable and other receivables. The Company does not require collateral or other security to support these receivables. The Company conducts periodic reviews of its clients' financial condition and customer payment practices to minimize collection risk on accounts receivable.
The operations of the Company are located in the PRC. Accordingly, the Company's business, financial condition, and results of operations may be influenced by the political, economic, and legal environments in the PRC, as well as by the general state of the PRC economy.
Basic and Diluted Net Income per Share
The Company is a limited company formed under the laws of the PRC. Like limited liability companies (LLC) in the United States, limited liability companies in the PRC do not issue shares to the owners. The owners however, are called shareholders. Ownership interest is determined in proportion to capital contributed. Accordingly, earnings per share data are not presented.
New Accounting Pronouncements
On June 10, 2009, the Company adopted Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2009-01, “Topic 105 - Generally Accepted Accounting Principles - amendments based on Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 168 , “The FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ and the Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles” (“ASU No. 2009-01”). ASU No. 2009-01 re-defines authoritative GAAP for nongovernmental entities to be only comprised of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ (“Codification”) and, for SEC registrants, guidance issued by the SEC. The Codification is a reorganization and compilation of all then-existing authoritative GAAP for nongovernmental entities, except for guidance issued by the SEC. The Codification is amended to effect non-SEC changes to authoritative GAAP. Adoption of ASU No. 2009-01 only changed the referencing convention of GAAP in Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In May 2009, the FASB issued SFAS No. 165, “Subsequent Events” (“SFAS 165”) codified in FASB ASC Topic 855-10-05, which provides guidance to establish general standards of accounting for and disclosures of events that occur after the balance sheet date but before financial statements are issued or are available to be issued. SFAS 165 also requires entities to disclose the date through which subsequent events were evaluated as well as the rationale for why that date was selected. SFAS 165 is effective for interim and annual periods ending after June 15, 2009, and accordingly, the Company adopted this pronouncement during the second quarter of 2009. SFAS 165 requires that public entities evaluate subsequent events through the date that the financial statements are issued.
In April 2009, the FASB issued FSP No. SFAS 107-1 and APB 28-1, “Interim Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments,” which is codified in FASB ASC Topic 825-10-50. This FSP essentially expands the disclosure about fair value of financial instruments that were previously required only annually to also be required for interim period reporting. In addition, the FSP requires certain additional disclosures regarding the methods and significant assumptions used to estimate the fair value of financial instruments. These additional disclosures are required beginning with the quarter ending June 30, 2009.
FASB ASC 820-10 establishes a framework for measuring fair value and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. The changes to current practice resulting from the application of this standard relate to the definition of fair value, the methods used to measure fair value, and the expanded disclosures about fair value measurements. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007; however, it provides a one-year deferral of the effective date for non-financial assets and non-financial liabilities, except those that are recognized or disclosed in the financial statements at fair value at least annually. The Company adopted this standard for financial assets and financial liabilities and nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities disclosed or recognized at fair value on a recurring basis (at least annually) as of January 1, 2008. The Company adopted the standard for nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities on January 1, 2008. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on its financial statements.
FASB ASC 805 establishes principles and requirements for how an acquirer recognizes and measures in its financial statements the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree and the goodwill acquired. This standard also establishes disclosure requirements to enable the evaluation of the nature and financial effects of the business combination. This standard was adopted by the Company beginning January 1, 2009 and will change the accounting for business combinations on a prospective basis.
FASB ASC 810-10 requires all entities to report noncontrolling (minority) interests in subsidiaries as equity in the consolidated financial statements. The standard establishes a single method of accounting for changes in a parent’s ownership interest in a subsidiary that does not result in deconsolidation and expands disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008 and interim periods within those fiscal years. This standard is not currently applicable to the Company.
FASB ASC 815-10 is effective January 1, 2009. This standard requires enhanced disclosures about derivative instruments and hedging activities to allow for a better understanding of their effects on an entity’s financial position, financial performance, and cash flows. Among other things, this standard requires disclosures of the fair values of derivative instruments and associated gains and losses in a tabular formant. This standard is not currently applicable to the Company since the Company does not have derivative instruments or hedging activity.
FASB ASC 350-30 and 275-10 amend the factors that should be considered in developing renewal or extension assumptions used to determine the useful life of a recognized intangible asset. This standard is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is prohibited. The adoption of this standard did not have any impact on the Company’s financial statements.
FASB ASC 260-10 provides that unvested share-based payment awards that contain nonforfeitable rights to dividends or dividend equivalents (whether paid or unpaid) are participating securities and shall be included in the computation of earnings per share pursuant to the two-class method. This standard is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company does not currently have any share-based awards that would qualify as participating securities. Therefore, application of this standard is not expected to have an effect on the Company's financial reporting.
FASB ASC 470-20 will be effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. The standard includes guidance that convertible debt instruments that may be settled in cash upon conversion should be separated between the liability and equity components, with each component being accounted for in a manner that will reflect the entity's nonconvertible debt borrowing rate when interest costs are recognized in subsequent periods. This standard is currently not applicable to the Company since the Company does not have any convertible debt.
FASB ASC 815-10 and 815-40 are effective for financial statements for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The standard addresses the determination of whether an instrument (or an embedded feature) is indexed to an entity’s own stock, which is the first part of the scope exception for the purpose of determining whether the instrument is classified as an equity instrument or accounted for as a derivative instrument which would be recognized either as an asset or liability and measured at fair value. The standard shall be applied to outstanding instruments as of the beginning of the fiscal year in which this standard is initially applied. Any debt discount that was recognized when the conversion option was initially bifurcated from the convertible debt instrument shall continue to be amortized. The cumulative effect of the change in accounting principles shall be recognized as an adjustment to the opening balance of retained earnings. This standard is currently not applicable to the Company.
FASB ASC 825-10 requires disclosures about the fair value of financial instruments for interim reporting periods. This standard is effective for interim reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
FASB ASC 820-10 provides additional guidance for Fair Value Measurements when the volume and level of activity for the asset or liability has significantly decreased. This standard is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on its financial statements.
FASB ASC 320-10 amends the other-than-temporary impairment guidance for debt and equity securities. This standard is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on its financial statements.
3. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property and equipment consisted of the following at June, 2009 and December 31, 2008 was as below:
|
June 30,
2009
|
December 31,
2008
|
|||||||
|
Vehicle
|
$ | 51,230 | 51,210 | |||||
|
Office and Equipment
|
272,894 | 267,437 | ||||||
|
Building
|
-- | -- | ||||||
| 324,124 | 318,647 | |||||||
|
Less: Accumulated depreciation
|
(286,859 | ) | (279,365 | ) | ||||
| $ | 37,265 | 39,282 | ||||||
The Company disposed its office building for $87,823 during 2008 (see note 5). Depreciation expense for the six months ended June 30, 2009 and 2008 was $7,382 and $8,959, respectively.
4. MAJOR CUSTOMERS AND VENDORS
Three customers accounted for 94% and 76% of the Company’s net revenue for six months ended at June 30, 2009 and 2008, respectively. For the six months ended June 30, 2009, each customer accounted for about 61%, 22% and 11% of the sales. For the six months ended June 30, 2008, each customer accounted for about 35%, 31% and 10% of the sales. At June 30, 2009 the total receivable balance due from these customers was $2,075,170.
Two and one vendor provided 75% and 87% of the Company’s purchase of raw materials for the six months ended June 30, 2009 and 2008, respectively. For the six months ended at June 30, 2009, each vendor accounted for about 66% and 9% of the purchases. At June 30, 2009 the account payable to these vendors was $ 879,983.
5. OTHER RECEIVABLES
Other receivables consisted of the following at June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively:
|
June 30,
2009
|
December 31,
2008
|
|||||||
|
Advance to staff
|
$ | 11,330 | 44,914 | |||||
|
Advance to third parties
|
9,002 | 1,683 | ||||||
|
Tax rebate and retention for sales contract
|
13,843 | 15,593 | ||||||
|
Receivable on disposal of asset
|
87,823 | 87,789 | ||||||
|
Receivable for VAT paid but purchase invoices not yet received
|
10,188 | 57,319 | ||||||
| $ | 132,186 | 207,298 | ||||||
6. INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Intangible assets mainly consisted of computer core software that was developed by the Company for sale. The Company recorded the value of the software for $152,257 at June 30, 2009. The Company amortizes the software over 5 years.
7. TAX PAYABLE
Tax payable consisted of the following at June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively:
|
June 30,
2009
|
December 31,
2008
|
|||||||
|
Value added tax payable
|
$ | 9,568 | 2,328 | |||||
|
Business tax payable
|
84,186 | 23,751 | ||||||
|
Income tax payable
|
234,357 | 178,663 | ||||||
|
Other taxes payable
|
9,014 | 1,826 | ||||||
| $ | 337,125 | 206,568 | ||||||
8. INCOME TAXES
The Company is governed by the Income Tax Law of the PRC concerning the private-run enterprises in Hi-Tech Zone, and is subject to tax at a statutory rate of 25% for both 2009 and 2008 on income reported in the statutory financial statements after appropriated tax adjustments.
9. CONTINGENCIES
The Company’s operations in the PRC are subject to specific considerations and significant risks not typically associated with companies in the North America and Western Europe. These include risks associated with, among others, the political, economic and legal environments and foreign currency exchange. The Company’ s results may be adversely affected by changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, currency conversion and remittance abroad, and rates and methods of taxation, among other things.
The Company’s sales, purchases and expenses transactions are denominated in RMB and all of the Company’s assets and liabilities are also denominated in RMB. The RMB is not freely convertible into foreign currencies under the current law. In China, foreign exchange transactions are required by law to be transacted only by authorized financial institutions. Remittances in currencies other than RMB may require certain supporting documentation in order to affect the remittance.
HAINAN JIEN INTELLIGENT ENGINEERING CO., LTD.
CONDENSED BALANCE SHEETS
AS OF
JUNE 30, 2009 and DECEMBER 31, 2008
|
JUNE 30, 2009
|
DECEMBER 31, 2008
|
|||||||
|
ASSETS
|
(Unaudited)
|
(Audited)
|
||||||
|
CURRENT ASSETS
|
||||||||
|
Cash & cash equivalents
|
$ | 710,552 | $ | 68,101 | ||||
|
Restricted cash
|
- | 3,449 | ||||||
|
Accounts receivable, net
|
2,420,881 | 1,415,415 | ||||||
|
Retentions receivable
|
271,770 | 53,716 | ||||||
|
Prepaid expenses
|
238,275 | 257,305 | ||||||
|
Other receivables
|
154,237 | 108,333 | ||||||
|
Inventory
|
134,087 | 118,800 | ||||||
|
Total current assets
|
3,929,802 | 2,025,119 | ||||||
|
RETENTIONS RECEIVABLE
|
- | 202,666 | ||||||
|
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, net
|
45,102 | 78,919 | ||||||
|
TOTAL ASSETS
|
$ | 3,974,904 | $ | 2,306,704 | ||||
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES
|
||||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
$ | 1,442,990 | $ | 409,221 | ||||
|
Tax payable
|
405,263 | 235,774 | ||||||
|
Accrued liabilities and other payables
|
182,371 | 80,740 | ||||||
|
Unearned revenue
|
- | 268,725 | ||||||
|
Advance from related party
|
108,245 | - | ||||||
|
Short-term loan
|
32,056 | - | ||||||
|
Total current liabilities
|
2,170,925 | 994,460 | ||||||
|
CONTINGENCIES AND COMMITMENTS
|
||||||||
|
STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
Paid in capital
|
120,824 | 120,824 | ||||||
|
Statutory reserve
|
67,737 | 67,737 | ||||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income
|
83,591 | 83,015 | ||||||
|
Retained earnings
|
1,531,827 | 1,040,668 | ||||||
|
Total stockholders' equity
|
1,803,979 | 1,312,244 | ||||||
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
$ | 3,974,904 | $ | 2,306,704 | ||||
F-82
HAINAN JIEN INTELLIGENT ENGINEERING CO., LTD.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
FOR SIX MONTHS ENDED
JUNE 30, 2009 and 2008
(UNAUDITED)
|
FOR THE SIX MONTHS ENDED
|
||||||||
|
JUNE 30, 2009
|
JUNE 30, 2008
|
|||||||
|
(Unaudited)
|
(Unaudited)
|
|||||||
|
Net sales
|
$ | 3,025,835 | $ | 3,106,608 | ||||
|
Cost of goods sold
|
(2,300,666 | ) | (2,629,202 | ) | ||||
|
Gross profit
|
725,169 | 477,406 | ||||||
|
Operating expenses
|
||||||||
|
Selling expenses
|
(2,502 | ) | (20,123 | ) | ||||
|
General and administrative expenses
|
(226,998 | ) | (143,098 | ) | ||||
|
Total operating expenses
|
(229,500 | ) | (163,221 | ) | ||||
|
Income from operations
|
495,669 | 314,185 | ||||||
|
Non-operating income (expenses)
|
||||||||
|
Interest income
|
12 | - | ||||||
|
Interest expense
|
(83 | ) | - | |||||
|
Other income
|
20 | - | ||||||
|
Other expenses
|
(4,461 | ) | (17,498 | ) | ||||
|
Total non-operating expenses
|
(4,512 | ) | (17,498 | ) | ||||
|
Net income
|
491,157 | 296,687 | ||||||
|
Other comprehensive item
|
||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation
|
576 | 60,022 | ||||||
|
Comprehensive Income
|
$ | 491,733 | $ | 356,709 | ||||
F-83
HAINAN JIEN INTELLIGENT ENGINEERING CO., LTD.
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOW
FOR SIX MONTHS ENDED
JUNE 30, 2009 and 2008
(UNAUDITED)
|
FOR THE SIX MONTHS ENDED
|
||||||||
|
JUNE 30, 2009
|
JUNE 30, 2008
|
|||||||
|
(Unaudited)
|
(Unaudited)
|
|||||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 491,157 | $ | 296,687 | ||||
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash
|
||||||||
|
provided by operating activities:
|
||||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization
|
33,844 | 8,568 | ||||||
|
Change in allowance for doubtful accounts
|
27,939 | 1,749 | ||||||
|
(Increase) decrease in current assets:
|
||||||||
|
Accounts receivable
|
(1,032,728 | ) | (2,499,527 | ) | ||||
|
Retention receivable
|
(15,285 | ) | 203,885 | |||||
|
Prepayment
|
19,130 | (40,027 | ) | |||||
|
Other receivable
|
(45,855 | ) | 26,392 | |||||
|
Inventory
|
(15,238 | ) | (155,681 | ) | ||||
|
Increase (decrease) in current liabilities:
|
||||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
1,033,487 | 2,014,353 | ||||||
|
Unearned revenue
|
(268,800 | ) | - | |||||
|
Accrued liabilities and other payable
|
101,587 | (15,181 | ) | |||||
|
Tax payable
|
169,376 | 39,025 | ||||||
|
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities
|
498,614 | (119,757 | ) | |||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||||||
|
Acquisition of property & equipment
|
- | (18,601 | ) | |||||
|
Net cash used in investing activities
|
- | (18,601 | ) | |||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||||||
|
Short-term loan
|
32,052 | (2,125 | ) | |||||
|
Advance from related parties
|
108,232 | (1,181 | ) | |||||
|
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities
|
140,284 | (3,306 | ) | |||||
|
EFFECT OF EXCHANGE RATE CHANGE ON CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
3,553 | 14,370 | ||||||
|
NET INCREASE (DECREASE) IN CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
642,451 | (127,294 | ) | |||||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF PERIOD
|
68,101 | 291,129 | ||||||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, END OF PERIOD
|
$ | 710,552 | $ | 163,835 | ||||
F-84
HAINAN JIEN INTELLIGENT ENGINEERING CO., LTD.
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2009 (UNAUDITED) and DECEMBER 31, 2008 (AUDITED)
1. ORGANIZATION AND DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
Hainan Jien Intelligent Engineering Co. Ltd. (the “Company” or “Jien”) was incorporated in the Hainan Province, People’s Republic of China (“PRC”) in 1999. Jien is engaged in providing full service of design and installation of intelligentized equipment for business and residential communities.
The unaudited condensed financial statements have been prepared by the Company, pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission. The information furnished herein reflects all adjustments (consisting of normal recurring accruals and adjustments) which are, in the opinion of management, necessary to fairly present the operating results for the respective periods. Certain information and footnote disclosures normally present in annual financial statements prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America have been omitted pursuant to such rules and regulations. The results for the six months ended June 30, 2009 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the full year ending December 31, 2009.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in conformity with US GAAP. The Company’s functional currency is the Chinese Renminbi; however, the accompanying financial statements have been translated and presented in United States Dollars ($).
Accounts and Retentions Receivable
The Company’s policy is to maintain reserves for potential credit losses on accounts receivable. Management reviews the composition of accounts receivable and analyzes historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customer payment patterns to evaluate the adequacy of these reserves. Based on historical collection activity, the Company made allowance of approximately $27,942 and $27,931 at June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively.
At June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008, the Company had retentions receivable for product quality assurance in the amount of $271,770 and$256,832, respectively. The retention rate varies from 3% to 5% of the sales price with variable terms from 1 year to 3 years.
Revenue Recognition
The Company's revenue recognition policies are in compliance with Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Staff Accounting Bulletin (“SAB”) 104, (codified in FASB ASC Topic 480). Sales revenue is recognized at the date of shipment to customers when a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and collectibility is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are recorded as unearned revenue.
The Company records its revenue when certain milestones as defined in the service contract are reached. These service contracts have clear milestones and deliverables with distinct values assigned to each milestone. The milestones do not require the delivery of multiple elements as noted in Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”) Issue 00-21 “Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables” ("EITF No. 00-21"), (codified in FASB ASC Topic 605). In accordance with SAB No. 104, the Company treats each milestone as an individual revenue agreement and only recognizes revenue for each milestone when all the conditions of SAB 104 defined earlier are met.
The Company is qualified as a small business so that all of the Company’s products sold or services provided in the PRC are subject to a fixed low value-added tax (“VAT”) of 4% of the gross sales price regardless of the VAT paid. Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of goods or services, net of VAT. This VAT cannot be offset by VAT paid by the Company on raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing their finished. Sales are recorded net of VAT collected as the Company acts as an agent for the government.
The standard warranty of the Company is provided to its customers and is not considered an additional service; rather it is considered an integral part of the product and services’ sale. The Company believes that the existence of its standard product warranty in a sales contract does not constitute a deliverable in the arrangement and thus there is no need to apply the EITF 00-21 separation and allocation model for a multiple deliverable arrangement. FAS 5 specifically address the accounting for standard warranties and neither SAB 104 nor EITF 00-21 supersedes FAS 5 (codified in FASB ASC Topic Warranty). The Company believes that accounting for its standard warranty pursuant to FAS 5 does not impact revenue recognition because the cost of honoring the warranty can be reliably estimated.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of goods sold consists primarily of material costs, labor costs, and related overhead which are directly attributable to the production of the service. Write-down of inventory to lower of cost or market is also recorded in cost of goods sold.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to credit risk consist primarily of accounts receivable and other receivables. The Company does not require collateral or other security to support these receivables. The Company conducts periodic reviews of its clients' financial condition and customer payment practices to minimize collection risk on accounts receivable.
The operations of the Company are located in the PRC. Accordingly, the Company's business, financial condition, and results of operations may be influenced by the political, economic, and legal environments in the PRC, as well as by the general state of the PRC economy.
Basic and Diluted Net Income per Share
The Company is a limited company formed under the laws of the PRC. Like limited liability companies (LLC) in the United States, limited liability companies in the PRC do not issue shares to the owners. The owners however, are called shareholders. Ownership interest is determined in proportion to capital contributed. Accordingly, earnings per share data are not presented.
New Accounting Pronouncements
On June 10, 2009, the Company adopted Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2009-01, “Topic 105 - Generally Accepted Accounting Principles - amendments based on Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 168 , “The FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ and the Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles” (“ASU No. 2009-01”). ASU No. 2009-01 re-defines authoritative GAAP for nongovernmental entities to be only comprised of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ (“Codification”) and, for SEC registrants, guidance issued by the SEC. The Codification is a reorganization and compilation of all then-existing authoritative GAAP for nongovernmental entities, except for guidance issued by the SEC. The Codification is amended to effect non-SEC changes to authoritative GAAP. Adoption of ASU No. 2009-01 only changed the referencing convention of GAAP in Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In May 2009, the FASB issued SFAS No. 165, “Subsequent Events” (“SFAS 165”) codified in FASB ASC Topic 855-10-05, which provides guidance to establish general standards of accounting for and disclosures of events that occur after the balance sheet date but before financial statements are issued or are available to be issued. SFAS 165 also requires entities to disclose the date through which subsequent events were evaluated as well as the rationale for why that date was selected. SFAS 165 is effective for interim and annual periods ending after June 15, 2009, and accordingly, the Company adopted this pronouncement during the second quarter of 2009. SFAS 165 requires that public entities evaluate subsequent events through the date that the financial statements are issued.
In April 2009, the FASB issued FSP No. SFAS 107-1 and APB 28-1, “Interim Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments,” which is codified in FASB ASC Topic 825-10-50. This FSP essentially expands the disclosure about fair value of financial instruments that were previously required only annually to also be required for interim period reporting. In addition, the FSP requires certain additional disclosures regarding the methods and significant assumptions used to estimate the fair value of financial instruments. These additional disclosures are required beginning with the quarter ending June 30, 2009.
FASB ASC 820-10 establishes a framework for measuring fair value and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. The changes to current practice resulting from the application of this standard relate to the definition of fair value, the methods used to measure fair value, and the expanded disclosures about fair value measurements. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007; however, it provides a one-year deferral of the effective date for non-financial assets and non-financial liabilities, except those that are recognized or disclosed in the financial statements at fair value at least annually. The Company adopted this standard for financial assets and financial liabilities and nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities disclosed or recognized at fair value on a recurring basis (at least annually) as of January 1, 2008. The Company adopted the standard for nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities on January 1, 2008. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on its financial statements.
FASB ASC 805 establishes principles and requirements for how an acquirer recognizes and measures in its financial statements the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree and the goodwill acquired. This standard also establishes disclosure requirements to enable the evaluation of the nature and financial effects of the business combination. This standard was adopted by the Company beginning January 1, 2009 and will change the accounting for business combinations on a prospective basis.
FASB ASC 810-10 requires all entities to report noncontrolling (minority) interests in subsidiaries as equity in the consolidated financial statements. The standard establishes a single method of accounting for changes in a parent’s ownership interest in a subsidiary that does not result in deconsolidation and expands disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008 and interim periods within those fiscal years. This standard is not currently applicable to the Company.
FASB ASC 815-10 is effective January 1, 2009. This standard requires enhanced disclosures about derivative instruments and hedging activities to allow for a better understanding of their effects on an entity’s financial position, financial performance, and cash flows. Among other things, this standard requires disclosures of the fair values of derivative instruments and associated gains and losses in a tabular formant. This standard is not currently applicable to the Company since the Company does not have derivative instruments or hedging activity.
FASB ASC 350-30 and 275-10 amend the factors that should be considered in developing renewal or extension assumptions used to determine the useful life of a recognized intangible asset. This standard is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is prohibited. The adoption of this standard did not have any impact on the Company’s financial statements.
FASB ASC 260-10 provides that unvested share-based payment awards that contain nonforfeitable rights to dividends or dividend equivalents (whether paid or unpaid) are participating securities and shall be included in the computation of earnings per share pursuant to the two-class method. This standard is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company does not currently have any share-based awards that would qualify as participating securities. Therefore, application of this standard is not expected to have an effect on the Company's financial reporting.
FASB ASC 470-20 will be effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. The standard includes guidance that convertible debt instruments that may be settled in cash upon conversion should be separated between the liability and equity components, with each component being accounted for in a manner that will reflect the entity's nonconvertible debt borrowing rate when interest costs are recognized in subsequent periods. This standard is currently not applicable to the Company since the Company does not have any convertible debt.
FASB ASC 815-10 and 815-40 are effective for financial statements for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The standard addresses the determination of whether an instrument (or an embedded feature) is indexed to an entity’s own stock, which is the first part of the scope exception for the purpose of determining whether the instrument is classified as an equity instrument or accounted for as a derivative instrument which would be recognized either as an asset or liability and measured at fair value. The standard shall be applied to outstanding instruments as of the beginning of the fiscal year in which this standard is initially applied. Any debt discount that was recognized when the conversion option was initially bifurcated from the convertible debt instrument shall continue to be amortized. The cumulative effect of the change in accounting principles shall be recognized as an adjustment to the opening balance of retained earnings. This standard is currently not applicable to the Company.
FASB ASC 825-10 requires disclosures about the fair value of financial instruments for interim reporting periods. This standard is effective for interim reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
FASB ASC 820-10 provides additional guidance for Fair Value Measurements when the volume and level of activity for the asset or liability has significantly decreased. This standard is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on its financial statements.
FASB ASC 320-10 amends the other-than-temporary impairment guidance for debt and equity securities. This standard is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on its financial statements.
3. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property and equipment consisted of the following at June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively:
|
June 30,
2009
|
December 31,
2008
|
|||||||
|
Leasehold Improvement
|
$ | 41,632 | 100,692 | |||||
|
Office equipment
|
100,731 | 41,615 | ||||||
|
Less: Accumulated depreciation
|
(97,261 | ) | (63,388 | ) | ||||
| $ | 45,102 | 78,919 | ||||||
Depreciation expense for the six months ended June 30, 2009 and 2008 was $33,844 and $8,568, respectively.
4. PREPAID EXPENSES
Prepaid expenses consisted of prepayments to vendors for materials and parts for the projects which have not commenced at balance sheet date. Prepaid expenses were $ 238,275 and $ 257,305 at June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively.
5. OTHER RECEIVABLES
Other receivables consisted of prepayment to sub-contractors and cash advances to employees for normal business purposes such as travelling expense. At June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008, the amount was $ 154,237 and $108,333, respectively.
6. MAJOR CUSTOMERS AND VENDORS
Six major customers accounted for 93% of the Company’s net revenue for the six months ended June 30, 2009, each customer accounted for approximately 24%, 19%, 18%, 11% 11% and 10% of net sales. At June 30, 2009, the total receivable balance due from these customers was $1,869,938.
Three major customers accounted for 89% of the Company’s net revenue for the six months ended June 30, 2008, each customer accounted for approximately 55%, 19% and 15% of net sales.
Five and three major vendors provided 68% and 92% of the Company’s purchases of raw materials for the six months ended June 30, 2009 and 2008, respectively. For the six months ended June 30, 2009, each customer accounted for 17%, 16%, 13%, 12% and 10% of the purchases. And for the six months ended June 30, 2008, each customer accounted for 54%, 26% and 12% of the purchases. The Company had total accounts payable to these vendors of $369,297 at June 30, 2009.
7. TAX PAYABLE
Tax payable consisted of the following at June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008 was as follows:
|
June 30,
2009
|
December 31,
2008
|
|||||||
|
Income tax payable
|
$ | 250,421 | 147,620 | |||||
|
Value added tax payable
|
6,509 | 648 | ||||||
|
Business tax payable
|
136,240 | 83,370 | ||||||
|
Other taxes payable
|
12,093 | 4,136 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 405,263 | 235,774 | |||||
8. OTHER PAYABLES AND ACCRUED LIABILITIES
Other payables and accrued liabilities consisted of the following at June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively:
|
June 30, 2009
|
December 31,
2008
|
|||||||
|
Payable to Subcontractors
|
$
|
73,745
|
$
|
17,482
|
||||
|
Salary and welfare payable
|
4,349
|
4,258
|
||||||
|
Payable to employees for expense reimburse
|
37,635
|
12,100
|
||||||
|
Warranty reserve
|
45,375
|
44,772
|
||||||
|
Deposit from customers for construction
|
1,444
|
-
|
||||||
|
Accrued expenses
|
14,350
|
|||||||
|
Other payables
|
5,473
|
2,128
|
||||||
|
Total
|
$
|
182,371
|
$
|
80,740
|
||||
9. ADVANCE FROM RELATED PARTY
Advance from related party represented loan from the Company’s shareholder with no interest, payable upon demand. At June 30, 2009 and December 31, 2008, advance from related party was $108,245 and $0, respectively.
10. SHORT TERM LOAN
In June of 2009, the Company obtained a short term loan from Shenzhen Development Bank for the amount of approximately $32,056, interest rate at 5.832% per annum, with maturity date due within five months from the borrowing date. The Company repaid the loan on November 7, 2009.
11. INCOME TAXES
The Company is qualified as a small business in the construction industry in PRC. The Company was subject to 2.7% and 2.4% tax rate on net sales in 2008 and 2007, respectively. The tax rate will increase to 3% of net sales in 2009. Since the tax is based on sales, under US GAAP, it is not income tax. Accordingly, $80,506 and $17,756 have been recorded as general and administrative expense for the six months ended June 30, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
12. CONTINGENCIES
The Company’s operations in the PRC are subject to specific considerations and significant risks not typically associated with companies in the North America and Western Europe. These include risks associated with, among others, the political, economic and legal environments and foreign currency exchange. The Company’ s results may be adversely affected by changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, currency conversion and remittance abroad, and rates and methods of taxation, among other things.
The Company’s sales, purchases and expenses transactions are denominated in RMB and all of the Company’s assets and liabilities are also denominated in RMB. The RMB is not freely convertible into foreign currencies under the current law. In China, foreign exchange transactions are required by law to be transacted only by authorized financial institutions. Remittances in currencies other than RMB may require certain supporting documentation in order to affect the remittance.
|
COVENANT GROUP HOLDINGS INC.
|
||||
|
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET
|
||||
|
SEPTEMBER 30, 2009
|
||||
|
(UNAUDITED)
|
||||
|
ASSETS
|
||||
|
CURRENT ASSETS
|
||||
|
Cash & cash equivalents
|
$ | 1,004,006 | ||
|
Accounts receivable, net
|
4,508,514 | |||
|
Retentions receivable
|
1,173,291 | |||
|
Prepayment
|
126,454 | |||
|
Other receivables
|
372,218 | |||
|
Inventory
|
295,189 | |||
|
Intangible assets
|
144,705 | |||
|
Total current assets
|
7,624,377 | |||
|
NON-CURRENT ASSETS
|
||||
|
Retentions receivable
|
190,921 | |||
|
Property and equipment, net
|
68,387 | |||
|
Goodwill
|
2,134,323 | |||
|
Total non-current assets
|
2,393,631 | |||
|
TOTAL ASSETS
|
$ | 10,018,008 | ||
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES
|
||||
|
Accounts payable
|
$ | 3,052,343 | ||
|
Unearned revenue
|
35,621 | |||
|
Tax payable
|
645,782 | |||
|
Accrued liabilities and other payables
|
192,116 | |||
|
Dividend payable
|
346,293 | |||
|
Short-term loans
|
485,973 | |||
|
Total current liabilities
|
4,758,128 | |||
|
CONTINGENCIES AND COMMITMENTS
|
||||
|
STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||
|
Common stock, $0.00001 par value, 20,000,000
shares authorized, 6,230,000 shares issued
and outstanding as of September 30, 2009
|
62 | |||
|
Paid in capital
|
5,170,401 | |||
|
Statutory reserve
|
87,915 | |||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income
|
1,502 | |||
|
Retained earnings
|
- | |||
|
Total stockholders' equity
|
5,259,880 | |||
|
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
$ | 10,018,008 | ||
|
COVENANT GROUP HOLDINGS INC.
|
||||
|
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF INCOME AND OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
|
||||
|
FROM INCEPTION (JUNE 10, 2009) TO SEPTEMBER 30, 2009
|
||||
|
(UNAUDITED)
|
||||
|
Net sales
|
$ | 2,957,242 | ||
|
Cost of goods sold
|
(2,325,551 | ) | ||
|
Gross profit
|
631,691 | |||
|
Operating expenses
|
||||
|
Selling expenses
|
(38,050 | ) | ||
|
General and administrative expenses
|
(455,312 | ) | ||
|
Total operating expenses
|
(493,362 | ) | ||
|
Income from operations
|
138,329 | |||
|
Non-operating income (expenses)
|
||||
|
Interest income
|
157 | |||
|
Interest expense
|
(762 | ) | ||
|
Other income
|
1,203 | |||
|
Other expenses
|
(14 | ) | ||
|
Total non-operating income
|
584 | |||
|
Income before income tax
|
138,913 | |||
|
Income tax expense
|
(34,242 | ) | ||
|
Net income
|
104,671 | |||
|
Other comprehensive item
|
||||
|
Foreign currency translation
|
1,502 | |||
|
Comprehensive Income
|
$ | 106,173 | ||
F-93
|
COVENANT GROUP HOLDINGS INC.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
FROM INCEPTION (JUNE 10, 2009) TO SEPTEMBER 30, 2009
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(UNAUDITED)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Common stock
|
Other comprehensive income
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Shares
|
Amount
|
Paid in capital
|
Statutory reserves
|
Retained earnings
|
Total
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at inception (June 10, 2009)
|
- | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of funders' shares
|
6,230,000 | 62 | (62 | ) | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net income for the period
|
- | - | - | - | - | 104,671 | 104,671 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Acquisition of subsidiaries
at June 24, 2009
|
- | - | 5,432,263 | 67,737 | - | - | 5,500,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dividend declared
|
- | - | (261,800 | ) | - | - | (84,493 | ) | (346,293 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Transfer to statutory reserves
|
- | - | - | 20,178 | - | (20,178 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation gain
|
- | - | - | - | 1,502 | - | 1,502 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at September 30, 2009
|
6,230,000 | $ | 62 | $ | 5,170,401 | $ | 87,915 | $ | 1,502 | $ | - | $ | 5,259,880 | |||||||||||||||
|
COVENANT GROUP HOLDINGS INC.
|
||||
|
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOW
|
||||
|
FROM INCEPTION (JUNE 10, 2009) TO SEPTEMBER 30, 2009
|
||||
|
(UNAUDITED)
|
||||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 104,671 | ||
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash
|
||||
|
provided by operating activities:
|
||||
|
Depreciation and amortization
|
23,096 | |||
|
Change in allowance for doubtful accounts
|
27,406 | |||
|
(Increase) decrease in current assets, net of effect of acquisition:
|
||||
|
Accounts receivable
|
(732,806 | ) | ||
|
Retentions receivable
|
(7,818 | ) | ||
|
Advance to suppliers
|
- | |||
|
Other receivable
|
(84,674 | ) | ||
|
Prepayment
|
112,574 | |||
|
Inventory
|
(77,128 | ) | ||
|
Increase (decrease) in current liabilities, net of effect of acquisition:
|
||||
|
Accounts payable
|
616,675 | |||
|
Unearned revenue
|
(72,649 | ) | ||
|
Tax payable
|
(96,893 | ) | ||
|
Accrued liabilities and other payable
|
(15,837 | ) | ||
|
Net cash used in operating activities
|
(203,383 | ) | ||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||
|
Cash acquired from acquisition
|
754,650 | |||
|
Acquisition of property & equipment
|
(1,470 | ) | ||
|
Net cash provide by investing activities
|
753,180 | |||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES:
|
||||
|
Proceeds from Short-term loans
|
453,888 | |||
|
Net cash provided by financing activities
|
453,888 | |||
|
EFFECT OF EXCHANGE RATE CHANGE ON CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
321 | |||
|
NET INCREASE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS
|
1,004,006 | |||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF PERIOD
|
- | |||
|
CASH & CASH EQUIVALENTS, END OF PERIOD
|
$ | 1,004,006 | ||
|
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information:
|
||||
|
Cash paid during the period for:
|
||||
|
Income tax paid
|
$ | 113,082 | ||
|
Interest paid
|
$ | 627 | ||
|
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash financing activities:
|
||||
|
Dividend declared
|
$ | 346,293 | ||
F-95
COVENANT GROUP HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
SEPTEMBER 30, 2009
(UNAUDITED)
1. ORGANIZATION AND DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
Covenant Group Holdings Inc. (Covenant or the Company), was formed in the State of Delaware in June 10, 2009 to acquire Technology companies in Mainland China. The total number of shares authorized to issue is 20,000,000 with $0.0001 par value, there was no shares issued as of September 30, 2009. Covenant is engaged in identifying companies with synergies in businesses and management that focus on IT software specifically in the financial markets in China as well as Government mandated areas such as the Communications and Media, Government Manufacturing and Security and Surveillance industries. There was no significant activity from June 10, 2009 through June 30, 2009 except for the two acquisitions.
On June 24, 2009(Effective Date), Covenant entered into a stock acquisition and reorganization agreement with the Hainan Jien Intelligent Engineering Co. Ltd. (Jien) and its stockholders. Pursuant to the terms of the Agreement, Covenant acquired 100% of the common stock, Jien representing 100% of the outstanding equity interests in exchange for 1,350,000 shares of a public shell's common stock, the shell company whom shall acquire all of the rights and obligations of Covenant, valued at a provisional amount of $2 per share (Note 4), which is the stock price determined at $2 per share for the proposed capital raise (Stock Consideration). Jien was incorporated in the Hainan Province, People’s Republic of China (PRC) in 1999. Jien is engaged in providing full service of design and installation of intelligentized equipment for business and residential communities.
On June 24, 2009 (Effective Date), Covenant entered into a stock acquisition and reorganization agreement with the Chongqing Sysway Information Technology Co. Ltd. (Chongqing Sysway) and its stockholders. Pursuant to the terms of the Agreement, Covenant acquired 100% of the common stock of Chongqing Sysway, representing 100% of the outstanding equity interest in exchange for 1,400,000 shares of a public shell's common stock, the shell company whom shall acquire all of the rights and obligations of Covenant, valued at a provisional amount of $2 per share (Note 4), which is the stock price determined at $2 per share for the proposed capital raise (Stock Consideration). Chongqing Sysway was incorporated in the Chongqing City, Sichuan Province, PRC, in 1999 as a State Owned Enterprise (SOE). In 2005, the two SOE shareholders sold their ownership shares among other original minority shareholders and since then, Chongqing Sysway began to operate as a private enterprise mainly engaged in system integration services including computer system installation, website design, and system firewall setup, particularly for tobacco industry.
The unaudited financial statements have been prepared by the Company, pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission. The information furnished herein reflects all adjustments (consisting of normal recurring accruals and adjustments) which are, in the opinion of management, necessary to fairly present the operating results for the respective periods. Certain information and footnote disclosures normally present in annual financial statements prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America have been omitted pursuant to such rules and regulations. The results for the period from business inception through September 30, 2009 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the full year ending December 31, 2009.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principle of Consolidation
The Consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Covenant, Jien, and Chongqing Sysway, All intercompany transactions and account balances are eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates
In preparing the financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, management makes estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the dates of the financial statements, as well as the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting year. Significant estimates, required by management, include the recoverability of long-lived assets and the valuation of inventories. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
For purposes of the statement of cash flows, the Company considers all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
Accounts and Retentions Receivable
The Company’s policy is to maintain reserves for potential credit losses on accounts receivable. Management reviews the composition of accounts receivable and analyzes historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customer payment patterns to evaluate the adequacy of these reserves. Based on historical collection activity, the Company had allowances of $55,368 at September 30, 2009.
At September 30, 2009 the Company had retentions receivable for product quality assurance of $1,364,212. The retention rate varies from 3% to 5% of the sales price with variable terms from 1 year to 3 years. $1,173,291 of the retentions receivable at September 30, 2009 are current and due within one year, and $190,921 of the retentions receivable are noncurrent.
Inventories
Jien’s inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market with cost determined on a first in, first out basis. Chongqing Sysway’s inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market with cost determined on a specific identification method.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred; additions, renewals and betterments are capitalized. When property and equipment are retired or otherwise disposed of, the related cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from the respective accounts, and any gain or loss is included in operations. Depreciation of property and equipment is provided using the straight-line method for substantially all assets with 5% salvage value and estimated lives ranging from 3 to 25 years as follows:
Building 20 - 25 years
Leasehold improvements Shorter of lease term or 10 years
Vehicle 5 - 10 years
Office Equipment 3 - 5 years
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Long-lived assets, which include property, plant and equipment and intangible assets, are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable.
Recoverability of long-lived assets to be held and used is measured by comparing of the carrying amount of an asset to the estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its estimated undiscounted future cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the assets. Fair value is generally determined using the asset’s expected future discounted cash flows or market value, if readily determinable. Based on its review, the Company believes that, as of September 30, 2009, there were no significant impairments of its long-lived assets.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the fair value of the consideration transferred over the net of the acquisition date amount of identifiable assets acquired and the liability assumed. In accordance with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 142, Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets (“Statement No. 142”), codified in Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 350, goodwill is not amortized but is tested for impairment annually, or when circumstances indicate a possible impairment may exist. Impairment testing is performed at a reporting unit level. An impairment loss generally would be recognized when the carrying amount of the reporting unit exceeds the fair value of the reporting unit, with the fair value of the reporting unit determined using a discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis. A number of significant assumptions and estimates are involved in the application of the DCF analysis to forecast operating cash flows, including the discount rate, the internal rate of return, and projections of realizations and costs to produce. Management considers historical experience and all available information at the time the fair values of its reporting units are estimated.
Warranties
The Company offers warranty to its customers on its products for a period from three months to three years depending on the contract terms negotiated with the customers; most of warranty term is one year. The Company accrues for warranty costs based on estimates of the costs that may be incurred under its warranty obligations. The warranty expense and related accrual is included in the Company's selling expenses and other payable respectively, and is recorded at the time revenue is recognized. Factors that affect the Company's warranty liability include the number of sold equipment, its estimates of anticipated rates of warranty claims, costs per claim and estimated support labor costs and the associated overhead. The Company periodically assesses the adequacy of its recorded warranty liabilities and adjusts the amounts as necessary. The Company’s warranty expense was immaterial for the period since business inception through September 30, 2009.
Income Taxes
The Company utilizes Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (SFAS) No. 109, “Accounting for Income Taxes,” codified in FASB ASC Topic 740, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Under this method, deferred income taxes are recognized for the tax consequences in future years of differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their financial reporting amounts at each period end based on enacted tax laws and statutory tax rates applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to affect taxable income. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
The Company adopted the provisions of FASB Interpretation No. 48, Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes (codified in FASB ASC Topic 740) on June 10, 2009. As a result of the implementation of FIN 48, the Company made a comprehensive review of its portfolio of tax positions in accordance with recognition standards established by FIN 48. As a result of the implementation of Interpretation 48, the Company recognized no material adjustments to liabilities or stockholders equity. When tax returns are filed, it is highly certain that some positions taken would be sustained upon examination by the taxing authorities, while others are subject to uncertainty about the merits of the position taken or the amount of the position that would be ultimately sustained. The benefit of a tax position is recognized in the financial statements in the period during which, based on all available evidence, management believes it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including the resolution of appeals or litigation processes, if any. Tax positions taken are not offset or aggregated with other positions. Tax positions that meet the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold are measured as the largest amount of tax benefit that is more than 50 percent likely of being realized upon settlement with the applicable taxing authority. The portion of the benefits associated with tax positions taken that exceeds the amount measured as described above is reflected as a liability for unrecognized tax benefits in the accompanying balance sheets along with any associated interest and penalties that would be payable to the taxing authorities upon examination.
Interest associated with unrecognized tax benefits are classified as interest expense and penalties are classified in selling, general and administrative expenses in the statements of income. The adoption of FIN 48 did not have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
Covenant has US net operating loss of $144,466 at September 30, 2009. A 100% valuation allowance has been established due to the uncertainty of its realization.
Jien is qualified as a small business in the construction industry in PRC. The Company is subject to a 4% tax rate on net sales for 2009. Since the tax is based on sales, under US GAAP, it is not an income tax.
Chongqing Sysway is governed by the Income Tax Law of the PRC concerning the private-run enterprises in Hi-Tech Zone, which are generally subject to tax at a statutory rate of 25% on income reported in the statutory financial statements after appropriated tax adjustments.
The following table reconciles the U.S. statutory rates to the Company’s consolidated effective tax rate for the period since inception of business through September 30, 2009:
|
U.S. statutory rates
|
|
$
|
56,876
|
|
|
Foreign tax rate less than U.S. statutory rate
|
|
(28,057)
|
|
|
|
Unrecognized tax benefit on US operating loss
|
49,118
|
|||
|
Foreign income exempt from foreign income tax
|
(43,695)
|
|||
|
Income tax expense
|
|
$
|
$ 34,242
|
|
Income tax expense consists of the following:
|
Current
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
|
State
|
-
|
|||
|
Foreign
|
34,242
|
|||
|
Total current
|
34,242
|
|||
|
Deferred
|
||||
|
Federal
|
-
|
|||
|
State
|
-
|
|||
|
Foreign
|
-
|
|||
|
Total deferred
|
-
|
|||
|
Income tax expense
|
$
|
34,242
|
||
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) consist of the following:
U.S. net operating loss
|
Deferred tax asset
|
||||
|
U.S. net operating loss
|
$
|
49,118
|
||
|
Less valuation allowance
|
(49,118)
|
|||
|
Net deferred tax asset
|
$
|
-
|
The valuation allowance for deferred tax assets as of September 30, 2009 was $49,118. The change in the total valuation for the period ended September 30, 2009 was an increase of $49,118. The deferred tax asset arose from the net operating loss generated at the US parent company level. In assessing the realization of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependant upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which the net operating losses and temporary differences become deductible. Management considered projected future taxable income and tax planning strategies in making this assessment. The value of the deferred tax assets was offset by a valuation allowance, due to the current uncertainty of the future realization of the deferred tax assets.
Revenue Recognition
The Company's revenue recognition policies are in compliance with Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Staff Accounting Bulletin (SAB) 104 (codified in FASB ASC Topic 480). Revenue is recognized at the date of shipment to customers when a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and collectibility is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are recorded as unearned revenue.
The Company records its revenue when certain milestones as defined in the service contract are reached. These service contracts have clear milestones and deliverables with distinct values assigned to each milestone. The milestones do not require the delivery of multiple elements as noted in Emerging Issues Task Force (EITF) Issue 00-21 “Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables” (EITF No. 00-21) (codified in FASB ASC Topic 605). In accordance with SAB No. 104, the Company treats each milestone as an individual revenue agreement and only recognizes revenue for each milestone when all the conditions of SAB 104 defined earlier are met.
Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of goods and services, net of value-added tax (VAT). Chongqing Sysway’s products that are sold and services that are provided in the PRC are subject to Chinese value-added tax of 17% of the gross sales price. This VAT may be offset by VAT paid by the Company on raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing their finished product. The Company recorded VAT payable and VAT receivable net of payments in the financial statements. The VAT tax return is filed offsetting the payables against the receivables.
Jien is qualified as a small business so that all of the Company’s products sold or services provided in the PRC are subject to a fixed VAT rate of 4% of the gross sales price regardless of the VAT paid for 2009. Sales revenue represents the invoiced value of goods or services, net of VAT. This VAT cannot be offset by VAT paid by the Company on raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing their finished.
The standard warranty of Jien is provided to its customers and is not considered an additional service; rather it is considered an integral part of the product and services’ sale. The Company believes that the existence of its standard product warranty in a sales contract does not constitute a deliverable in the arrangement and thus there is no need to apply the EITF 00-21(codified in FASB ASC Topic 605) separation and allocation model for a multiple deliverable arrangement. FAS 5 (codified in FASB ASC Topic Warranty) specifically address the accounting for standard warranties and neither SAB 104 nor EITF 00-21 supersedes FAS 5. The Company believes that accounting for its standard warranty pursuant to FAS 5 does not impact revenue recognition because the cost of honoring the warranty can be reliably estimated.
Chongqing Sysway provides post-contract support (PCS). Maintenance revenues from ongoing customer support services are billed on an annual basis with the revenue being deferred and recognized ratably over the maintenance period. Chongqing Sysway does not charge for PCS services separately for the first year from the date the product is sold. The Company believes that this type of PCS does not have to be accounted for as a separate unit in accordance with guidance provided by AICPA Statement of Position (SOP) 97-2, codified in FASB ASC Topic 985.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of goods sold consists primarily of material costs, labor costs, and related overhead which are directly attributable to the production of the service. Write-down of inventory to lower of cost or market is also recorded in cost of goods sold.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to credit risk consist primarily of accounts receivable and other receivables. The Company does not require collateral or other security to support these receivables. The Company conducts periodic reviews of its clients' financial condition and customer payment practices to minimize collection risk on accounts receivable.
The operations of the Company are located in the PRC. Accordingly, the Company's business, financial condition, and results of operations may be influenced by the political, economic, and legal environments in the PRC, as well as by the general state of the PRC economy.
Statement of Cash Flows
In accordance with SFAS No. 95, “Statement of Cash Flows,” codified in FASB ASC Topic 230, cash flows from the Company's operations are calculated based upon the local currencies. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the statement of cash flows may not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the balance sheet.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
SFAS No. 107, “Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments,” codified in FASB ASC Financial Instruments, Topic 825, requires that the Company disclose estimated fair values of financial instruments. The carrying amounts reported in the statements of financial position for current assets and current liabilities qualifying as financial instruments are a reasonable estimate of fair value.
Foreign Currency Translation and Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The Company’s functional currency is the Renminbi (RMB). For financial reporting purposes, RMB has been translated into United States dollars (USD) as the reporting currency. Assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate in effect at the balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are translated at the average rate of exchange prevailing during the reporting period. Translation adjustments arising from the use of different exchange rates from period to period are included as a component of stockholders' equity as "Accumulated other comprehensive income". Gains and losses resulting from foreign currency transactions are included in income. There has been no significant fluctuation in exchange rate for the conversion of RMB to USD after the balance sheet date.
The Company uses SFAS 130 “Reporting Comprehensive Income” (codified in FASB ASC Topic 220). Comprehensive income is comprised of net income and all changes to the statements of stockholders’ equity, except those due to investments by stockholders, changes in paid-in capital and distributions to stockholders. Comprehensive income for the period since inception of business through September 30, 2009 included net income and foreign currency translation adjustments.
Segment Reporting
SFAS No. 131, "Disclosures about Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information," codified in FASB ASC Topic 280, requires use of the “management approach” model for segment reporting. The management approach model is based on the way a company's management organizes segments within the company for making operating decisions and assessing performance. Reportable segments are based on products and services, geography, legal structure, management structure, or any other manner in which management disaggregates a company.
SFAS 131 has no effect on the Company's financial statements as substantially all of the Company's operations are conducted in one industry segment. The Company consists of one reportable business segment. All of the Company's assets are located in the PRC.
New Accounting Pronouncements
On June 10, 2009, the Company adopted Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2009-01, “Topic 105 - Generally Accepted Accounting Principles - amendments based on Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 168 , “The FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ and the Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles” (“ASU No. 2009-01”). ASU No. 2009-01 re-defines authoritative GAAP for nongovernmental entities to be only comprised of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ (“Codification”) and, for SEC registrants, guidance issued by the SEC. The Codification is a reorganization and compilation of all then-existing authoritative GAAP for nongovernmental entities, except for guidance issued by the SEC. The Codification is amended to effect non-SEC changes to authoritative GAAP. Adoption of ASU No. 2009-01 only changed the referencing convention of GAAP in Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In May 2009, the FASB issued SFAS No. 165, “Subsequent Events” (“SFAS 165”) codified in FASB ASC Topic 855-10-05, which provides guidance to establish general standards of accounting for and disclosures of events that occur after the balance sheet date but before financial statements are issued or are available to be issued. SFAS 165 also requires entities to disclose the date through which subsequent events were evaluated as well as the rationale for why that date was selected. SFAS 165 is effective for interim and annual periods ending after June 15, 2009, and accordingly, the Company adopted this pronouncement during the second quarter of 2009. SFAS 165 requires that public entities evaluate subsequent events through the date that the financial statements are issued. The Company has evaluated subsequent events through December 7, 2009.
In April 2009, the FASB issued FSP No. SFAS 107-1 and APB 28-1, “Interim Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments,” which is codified in FASB ASC Topic 825-10-50. This FSP essentially expands the disclosure about fair value of financial instruments that were previously required only annually to also be required for interim period reporting. In addition, the FSP requires certain additional disclosures regarding the methods and significant assumptions used to estimate the fair value of financial instruments. These additional disclosures are required beginning with the quarter ending June 30, 2009. This FSP had no material impact on the Company’s financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
FASB ASC 820-10 establishes a framework for measuring fair value and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. The changes to current practice resulting from the application of this standard relate to the definition of fair value, the methods used to measure fair value, and the expanded disclosures about fair value measurements. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007; however, it provides a one-year deferral of the effective date for non-financial assets and non-financial liabilities, except those that are recognized or disclosed in the financial statements at fair value at least annually. The Company adopted this standard for financial assets and financial liabilities and nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities disclosed or recognized at fair value on a recurring basis (at least annually) as of January 1, 2008. The Company adopted the standard for nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities on June 10, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on its financial statements.
FASB ASC 820-10 provides additional guidance for Fair Value Measurements when the volume and level of activity for the asset or liability has significantly decreased. This standard is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on its financial statements.
FASB ASC 805 establishes principles and requirements for how an acquirer recognizes and measures in its financial statements the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree and the goodwill acquired. This standard also establishes disclosure requirements to enable the evaluation of the nature and financial effects of the business combination. This standard was adopted by the Company beginning June 10, 2009 and will change the accounting for business combinations on a prospective basis.
FASB ASC 810-10 requires all entities to report noncontrolling (minority) interests in subsidiaries as equity in the consolidated financial statements. The standard establishes a single method of accounting for changes in a parent’s ownership interest in a subsidiary that does not result in deconsolidation and expands disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. This standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008 and interim periods within those fiscal years. This standard is not currently applicable to the Company.
FASB ASC 815-10 is effective January 1, 2009. This standard requires enhanced disclosures about derivative instruments and hedging activities to allow for a better understanding of their effects on an entity’s financial position, financial performance, and cash flows. Among other things, this standard requires disclosures of the fair values of derivative instruments and associated gains and losses in a tabular formant. This standard is not currently applicable to the Company since the Company does not have derivative instruments or hedging activity.
FASB ASC 350-30 and 275-10 amend the factors that should be considered in developing renewal or extension assumptions used to determine the useful life of a recognized intangible asset. This standard is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is prohibited. The adoption of this standard did not have any impact on the Company’s financial statements.
FASB ASC 260-10 provides that unvested share-based payment awards that contain nonforfeitable rights to dividends or dividend equivalents (whether paid or unpaid) are participating securities and shall be included in the computation of earnings per share pursuant to the two-class method. This standard is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company does not currently have any share-based awards that would qualify as participating securities. Therefore, application of this standard is not expected to have an effect on the Company's financial reporting.
FASB ASC 470-20 will be effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. The standard includes guidance that convertible debt instruments that may be settled in cash upon conversion should be separated between the liability and equity components, with each component being accounted for in a manner that will reflect the entity's nonconvertible debt borrowing rate when interest costs are recognized in subsequent periods. This standard is currently not applicable to the Company since the Company does not have any convertible debt.
FASB ASC 815-10 and 815-40 are effective for financial statements for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The standard addresses the determination of whether an instrument (or an embedded feature) is indexed to an entity’s own stock, which is the first part of the scope exception for the purpose of determining whether the instrument is classified as an equity instrument or accounted for as a derivative instrument which would be recognized either as an asset or liability and measured at fair value. The standard shall be applied to outstanding instruments as of the beginning of the fiscal year in which this standard is initially applied. Any debt discount that was recognized when the conversion option was initially bifurcated from the convertible debt instrument shall continue to be amortized. The cumulative effect of the change in accounting principles shall be recognized as an adjustment to the opening balance of retained earnings. This standard is currently not applicable to the Company.
FASB ASC 825-10 requires disclosures about the fair value of financial instruments for interim reporting periods. This standard is effective for interim reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
FASB ASC 320-10 amends the other-than-temporary impairment guidance for debt and equity securities. This standard is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The adoption of this standard did not have a material effect on its financial statements.
As of September 30, 2009, the FASB has issued Accounting Standards Updates (ASU) through No. 2009-12. None of the ASUs have had an impact on the Company’s financial statements.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted
As of September 30, 2009, there are no recently issued accounting standards not yet adopted which would have a material effect on the Company’s financial statements.
Inventory at September 30, 2009 was mainly working in process, raw material including computer parts, supplementary parts in the amount of $295,189.
4. ACQUISITION OF SUBSIDIARIES AND GOODWILL
On June 24, 2009, Covenant entered into stock acquisition and reorganization agreements with Jien and Chongqing Sysway (note 1).
The operating results of these two acquires, Jien and Chongqing Sysway are included in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations from the acquisition date. For convenience of reporting the acquisition for accounting purposes, June 30, 2009 has been designated as the acquisition date.
The following table summarizes the fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of acquisition.
|
Jien
|
Chongqing Sysway
|
Total
|
||||||||||
|
Cash
|
$ | 710,552 | $ | 44,098 | $ | 754,650 | ||||||
|
Accounts receivable
|
2,420,881 | 1,380,413 | 3,801,294 | |||||||||
|
Retention receivable
|
271,770 | 1,084,047 | 1,355,817 | |||||||||
|
Prepaid expenses
|
238,275 | - | 238,275 | |||||||||
|
Advance to suppliers
|
- | 1,661 | 1,661 | |||||||||
|
Other receivables
|
154,237 | 132,186 | 286,423 | |||||||||
|
Inventory
|
134,087 | 83,858 | 217,945 | |||||||||
|
Property and equipment
|
45,102 | 37,265 | 82,367 | |||||||||
|
Intangible assets-core software
|
- | 152,256 | 152,256 | |||||||||
|
Goodwill
|
896,020 | 1,238,303 | 2,134,323 | |||||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
(1,442,990 | ) | (991,463 | ) | (2,434,453 | ) | ||||||
|
Other current liabilities
|
(182,370 | ) | (25,499 | ) | (207,869 | ) | ||||||
|
Unearned revenue
|
(108,245 | ) | - | (108,245 | ) | |||||||
|
Tax payable
|
(405,263 | ) | (337,125 | ) | (742,388 | ) | ||||||
|
Short term loan
|
(32,056 | ) | - | (32,056 | ) | |||||||
|
Purchase price
|
$ | 2,700,000 | $ | 2,800,000 | $ | 5,500,000 | ||||||
The fair value of the consideration transferred is provisionally based on $2 per share that is reflected in the proposed capital raise. The final valuation will be based on either the price per share reflected in the proposed capital raise or the price per share in the open market once the reverse merge into a U.S. public shell is consummated. Whichever the management of the Company believes is most representative of the fair value of its common stock.
The company has not finalized the determination of whether identifiable intangible assets exists and thus the excess of the fair value of the consideration transferred over the net of the acquisition date amounts of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed is allocated to goodwill.
The following pro forma financial information presents the consolidated operations of the Company as if the Jien and Chongqing Sysway acquisitions had occurred on January 1, 2009.
|
For the nine months ended
September 30, 2009
|
Pro forma Consolidated
|
|||
|
Net Revenue
|
$ | 8,320,065 | ||
|
Cost of Revenue
|
(6,468,690 | ) | ||
|
Gross Profit
|
1,851,375 | |||
|
Operating expenses
|
(991,311 | ) | ||
|
Income from operations
|
860,064 | |||
|
Non-operating expenses
|
(4,047 | ) | ||
|
Income tax expense
|
(90,723 | ) | ||
|
Net income
|
$ | 765,294 | ||
The following pro forma financial information presents the consolidated operations of Jien and Chongqing Sysway for the three months ended September 30, 2008 as to provide comparative operating results to the consolidated operations of Covenant since business inception through September 30, 2009 which includes the operating results of Jien and Chongqing Sysway since acquisition.
|
For the three months ended
September 30, 2008
|
Pro forma Consolidated
|
|||
|
Net Revenue
|
$ | 3,196,590 | ||
|
Cost of Revenue
|
(2,582,522 | ) | ||
|
Gross Profit
|
614,068 | |||
|
Operating expenses
|
(292,138 | ) | ||
|
Income from operations
|
321,930 | |||
|
Non-operating income
|
3,453 | |||
|
Income tax expense
|
(45,483 | ) | ||
|
Net income
|
$ | 279,900 | ||
5. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property and equipment consisted of the following at September 30, 2009:
|
Vehicle
|
$ | 8,978 | ||
|
Office equipment
|
62,646 | |||
|
Leasehold Improvement
|
12,249 | |||
|
Subtotal
|
83,873 | |||
|
Less: Accumulated depreciation
|
(15,486 | ) | ||
| $ | 68,387 |
Depreciation expense for the period since business inception through September 30, 2009 was approximately $ 15,400.
6. OTHER RECEIVABLES
Other receivables consisted of the following at September 30, 2009:
|
Short term advance to third parties
|
$ | 184,507 | ||
|
Receivable on disposal of office building
|
87,861 | |||
|
Advance to staffs
|
63,883 | |||
|
Advance to subcontractors
|
18,976 | |||
|
Tax rebate
|
7,355 | |||
|
Deposits
|
9,636 | |||
| $ | 372,218 |
7. INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Intangible assets mainly consisted of computer core software that was developed by the Company for sale. The Company amortizes the software over 5 years. Amortization expense of intangible assets for the period from business inception through September 30, 2009 was approximately $7,600.
8. TAX PAYABLE
Tax payable consisted of the following at September 30, 2009:
|
Income tax payable
|
$ | 432,778 | ||
|
Value added tax payable
|
970 | |||
|
Sales and business tax payable
|
194,171 | |||
|
Other taxes payable
|
17,863 | |||
| $ | 645,782 |
9. ACCRUED LIABILITIES AND OTHER PAYABLES
Accrued liabilities and other payables mainly consisted of accrued payroll, welfare payable, payable for after-sales service, short term cash advances from third parties and payables for the Company’s construction deposits in the aggregate of $ 192,116 at September 30, 2009.
10. DIVIDEND PAYABLE
The Company declared 30% dividend of Jien and Chongqing Sysway’s 2008 net income to Jien and Chongqing Sysway’s original shareholders and management as part of the acquisition agreement dated June 24, 2009. The dividend declared for Jien and Chongqing Sysway was $197,231 and $149,062, respectively, and has been recorded as dividend payable at September 30, 2009.
As part of the acquisition agreement, the Company also agreed to pay the original shareholders and management of Jien and Chongqing Sysway a 30% dividend on 2009 year end profits.
11. MAJOR CUSTOMERS AND VENDORS
Five customers accounted for 83% of the total sales for the period since business inception through September 30, 2009, each customer accounted for 21%, 21%, 17%, 13% and 11%, respectively. At September 30, 2009, the total receivable balance due from these customers was $ 2,448,498.
Three suppliers accounted for 61% of the total purchases for the period since business inception through September 30, 2009, each vendor accounted for 35%, 17% and 9%, respectively. At September 30, 2009, the total payable due to these vendors was $ 1,609,324.
12. SHORT TERM LOANS
Since June of 2009, Jien obtained several short term loans from Shenzhen Development Bank for the aggregate amount of approximately $86,000, interest rate at 5.832% per annum, with various maturity dates. Jien repaid approximately $32,000 on November 7, 2009, and the remaining is due to be repaid on or before the end of February 2010.
In September of 2009, Covenant entered three bridge loan agreements with one lender for the aggregate amount of $399,870 for financing certain startup expenditures. These three bridge loans bear interest rate of 6% per annum, principal and interest will be payable in full six months from the loan agreement date. These bridge loans may be prepaid at any time, in whole or in part, without interest, penalty or premium of any kind. Effective November 10, 2009, these bridge loans have been converted into the investment into the Company by issuing total 200,909 shares of the Company’s common stock to the lender.
13. STATUTORY RESERVES
Pursuant to the new corporate law of the PRC effective January 1, 2006, the Company is now only required to maintain one statutory reserve by appropriating from its after-tax profit before declaration or payment of dividends. The statutory reserve represents restricted retained earnings.
Surplus reserve fund
The Company is now only required to transfer 10% of its net income, as determined under PRC accounting rules and regulations, to a statutory surplus reserve fund until such reserve balance reaches 50% of the Company’s registered capital. The Company had $87,915 in this reserve at September 30, 2009.
The surplus reserve fund is non-distributable other than during liquidation and can be used to fund previous years’ losses, if any, and may be utilized for business expansion or converted into share capital by issuing new shares to existing shareholders in proportion to their shareholding or by increasing the par value of the shares currently held by them, provided that the remaining reserve balance after such issue is not less than 25% of the registered capital.
Common welfare fund
Common welfare fund is a voluntary fund that the Company can elect to transfer 5% to 10% of its net income to this fund. The Company did not make any contribution to this fund for the period since business inception through September 30, 2009.
This fund can only be utilized on capital items for the collective benefit of the Company’s employees, such as construction of dormitories, cafeteria facilities, and other staff welfare facilities. This fund is non-distributable other than upon liquidation.
Pursuant to the "Circular of the Ministry of Finance (MOF) on the Issue of Corporate Financial Management after the Corporate Law Enforced" (No.67 [2006]), effective on April 1, 2006, issued by the MOF, companies transferred the balance of SCWF (Statutory Common Welfare Fund) as of December 31, 2005 to Statutory Surplus Reserve. Any deficit in the SCWF was charged in turn to Statutory Surplus Reserve, additional paid-in capital and undistributed profit of previous years. If a deficit still remains, it should be transferred to retained earnings and be reduced to zero by a transfer from after tax profit of following years. At December 31, 2005, the Company did not have a deficit in the SCWF.
14. COMMITMENTS
Jien leased its office under long term, non-cancelable, and renewable operating lease agreements on November 8, 2007 with expiration date on November 7, 2009. The Company pays the rents month-by-month after the expiration date.
Chongqing Sysway leased its office under one year, non-cancelable, and renewable operating lease agreement on December 1, 2007 with expiration date on November 30, 2008; at maturity, the Company renewed the lease for additional one year expiring on November 30, 2009. The Company leases this office month-by-month after November 30, 2009.
Total rental expense for the period since business inception through September 30, 2009 was approximately $14,000.
15. CONTINGENCIES
The Company’s operations in the PRC are subject to specific considerations and significant risks not typically associated with companies in the North America and Western Europe. These include risks associated with, among others, the political, economic and legal environments and foreign currency exchange. The Company’ s results may be adversely affected by changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, currency conversion and remittance abroad, and rates and methods of taxation, among other things.
The Company’s sales, purchases and expenses transactions are denominated in RMB and all of the Company’s assets and liabilities are also denominated in RMB. The RMB is not freely convertible into foreign currencies under the current law. In China, foreign exchange transactions are required by law to be transacted only by authorized financial institutions. Remittances in currencies other than RMB may require certain supporting documentation in order to affect the remittance.
16. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
Effective November 10, 2009, the Company and the lender of the three bridge loans have agreed to cancel the promissory note of $399,870. In lieu of principal and interest payments due to the lender, the Company agreed to issue 200,909 shares of the Company’s common stock to the lender.
Based on confidential private placement memorandum dated November 24, 2009, the Company is offering to sell up to 750,000 Shares at $2.00 per share, with a minimum purchase of 10,000 Shares per investor, requiring a minimum investment of $20,000, with a minimum total quantity of 150,000 Shares ($300,000) that must be subscribed for by all investors to affect a closing and avoid termination of the Offering. The Company will pay commissions or finder’s fees on sales through broker-dealers or finders in an amount not to exceed 8% of the purchase price of such sales (excluding expenses).
The Offering will continue until the earlier of when all Shares offered are sold or such time as the Company elects to terminate the offering, which shall be no later than January 31, 2010 (which date may be extended by the Company at its sole election for up to an additional one month). The shares issued to investors through the private placement will be converted into publicly-traded securities upon the Company’s contemplated merger with a public shell company. At December 16, 2009, the Company sold 200,000 shares through the private placement.
On December 24, 2009, Covenant entered into a share exchange agreement with Everest Resources Corp. (Everest) for 1 to 1 share exchange of 9,380,909 shares of Covenant’s outstanding shares, whereby Covenant shareholders became the majority owners of Everest after the reverse merge. The acquisition of Covenant by Everest has been accounted for as recapitalization of Covenant as Covenant’s shareholders will be the majority shareholders and have control of the Company.
COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC.
$20,600,000
SHARES OF COMMON STOCK AND WARRANTS
PRELIMINARY PROSPECTUS
July , 2010
You should rely only on the information contained in this prospectus and any applicable prospectus supplement. We have not authorized any other person to provide you with different information. If anyone provides you with different or inconsistent information, you should not rely on it. We are not making an offer to sell these securities in any jurisdiction where the offer or sale is not permitted. You should not assume that the information contained in this prospectus or any applicable prospectus supplement is accurate as of any date other than the date on the front cover of this prospectus or the prospectus supplement, regardless of the date of delivery of this prospectus or any applicable prospectus supplement or any sale of a security.
Until ________, 201_, all dealers effecting transactions in these securities, whether or not participating in this offering, may be required to deliver a prospectus. This is in addition to the obligation of dealers to deliver a prospectus when acting as underwriters.
Part II
INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
Item 13. Other Expenses of Issuance and Distribution
The following is an estimate of the expenses that will be incurred by the Company in connection with the issuance and distribution of the securities being registered.
The following table sets forth the estimated costs and expenses of the Company in connection with the offering described in the registration statement.
|
SEC Registration Fee
|
$ | 5,348 | ||
|
Accounting Fees and Expenses
|
$ | 65,000 | ||
|
Legal Fees and Expenses
|
$ | 25,000 | ||
|
Printing and Engraving
|
$ | 2,500 | ||
|
Miscellaneous
|
$ | 15,000 | ||
|
Total
|
$ | 112,848 |
Item 14. Indemnification of Directors and Officers
Section 78.138 of the Nevada Revised Statutes provides that a director or officer is not individually liable to the corporation or its shareholders or creditors for any damages as a result of any act or failure to act in his capacity as a director or officer unless it is proven that (1) his act or failure to act constituted a breach of his fiduciary duties as a director or officer and (2) his breach of those duties involved intentional misconduct, fraud or a knowing violation of law.
This provision is intended to afford directors and officers protection against and to limit their potential liability for monetary damages resulting from suits alleging a breach of the duty of care by a director or officer. As a consequence of this provision, shareholders of our company will be unable to recover monetary damages against directors or officers for action taken by them that may constitute negligence or gross negligence in performance of their duties unless such conduct falls within one of the foregoing exceptions. The provision, however, does not alter the applicable standards governing a director’s or officer’s fiduciary duty and does not eliminate or limit the right of our company or any shareholder to obtain an injunction or any other type of non-monetary relief in the event of a breach of fiduciary duty.
Item 15. Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
On April 22, the Company issued 200,000 shares of common stock to Sui Generis Capital Partners, LLC in connection with obtaining a $120,000 bridge loan from Sui Generis Capital Partners, LLC. The issuance of such shares was exempt from the registration requirements of the Securities Act pursuant to the exemption provided under Section 4(2) of the Securities Act.
On December 24, 2009, the Company entered into a share cancellation and loan agreement with Gary Sidhu, whereby Mr. Sidhu received a promissory note from the Company in the principal amount of $190,000, $90,000 of which the Company has prepaid. On March 25, 2010, Mr. Sidhu and the Company entered into an agreement pursuant to which Mr. Sidhu agreed to cancel the promissory note and surrender his remaining 500,000 shares of the Company’s common stock in exchange for the Company issuing to him 300,000 shares of common stock of the Company. The issuance of such shares was exempt from the registration requirements of the Securities Act pursuant to the exemption provided under Section 4(2) of the Securities Act. On May 13, 2010, Mr. Sidhu and the Company entered into an agreement pursuant to which Mr. Sidhu agreed to reduce the number of shares issued to him from 300,000 to 70,000.
On December 24, 2009, pursuant to the terms of a share exchange agreement dated December 24, 2009, by and among the Company, Covenant Holdings and the Covenant Holdings shareholders, all of the outstanding shares of Covenant Holdings were exchanged for an aggregate of 9,380,909 shares of common stock of the Company. The issuance of such shares was exempt from the registration requirements of the Securities Act pursuant to the exemption provided under Section 4(2) of the Securities Act.
On December 3, 2009, Covenant Holdings raised $400,000 in exchange for the issuance of 200,000 shares of Covenant Holdings common stock to an offshore investor pursuant to a private placement offering. The issuance of such shares was exempt from the registration requirements of the Securities Act pursuant to the exemption provided under Regulation S promulgated under the Securities Act.
In September 2009, Covenant Holdings entered into three bridge loan agreements with an offshore investor in the aggregate amount of $399,870 for financing certain startup expenditures. On November 10, 2009, Covenant Holdings and the offshore investor entered into a loan termination and subscription agreement whereby the bridge loans were retired in exchange for 200,909 shares of Covenant Holdings’ common stock. The issuance of such shares was exempt from the registration requirements of the Securities Act pursuant to the exemption provided under Regulation S promulgated under the Securities Act.
Item 16. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
The following is a complete list of Exhibits filed as part of this Registration Statement:
(a) Exhibits
|
Exhibit Number
|
Description
|
|
2.1
|
Share Exchange Agreement by and among Covenant Group Holdings Inc., Covenant Group of China Inc. (formerly Everest Resources Corp.), and the Shareholders of Covenant Group Holdings Inc., dated as of December 24, 2009. (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of the Registrant filed on December 31, 2009)
|
|
3.1
|
Articles of Incorporation of Covenant Group of China Inc. (formerly Everest Resources Corp.) (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registration Statement on Form SB-2 of the Registrant filed on August 30, 2007)
|
|
3.2
|
Certificate of Amendment to the Articles of Incorporation of Covenant Group of China Inc. (formerly Everest Resources Corp.) (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3(i).1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of the Registrant filed on December 31, 2009)
|
|
3.3
|
Bylaws of Covenant Group of China Inc. (formerly Everest Resources Corp.) (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registration Statement on Form SB-2 of the Registrant filed on August 30, 2007)
|
|
3.4
|
Amendment to Bylaws of Covenant Group of China Inc. (formerly Everest Resources Corp.) (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3(ii).2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of the Registrant filed on December 31, 2009)
|
|
4.1
|
Specimen Stock Certificate of Covenant Group of China Inc. (formerly Everest Resources Corp.) (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of the Registrant filed on December 31, 2009)
|
|
4.2
|
Form of Common Stock Purchase Warrant (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of the Registrant filed on February 4, 2010)
|
|
5.1
|
Opinion of Holland & Hart LLP*
|
|
10.1
|
Stock Acquisition and Reorganization Agreement dated as of June 24, 2009, between Covenant Group Holdings Inc. and Chongqing HongSheng Information Sysway Industry Co, Ltd. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of the Registrant filed on December 31, 2009)
|
|
Exhibit Number
|
Description
|
|
10.2
|
Stock Acquisition and Reorganization Agreement dated as of June 24, 2009, between Covenant Group Holdings Inc. and Hainan JIEN Intelligent Engineering Co. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of the Registrant filed on December 31, 2009)
|
|
10.3
|
Promissory Note of Covenant Group Holdings Inc. in favor of Gary Sidhu in the principal amount of $190,000 (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Current Report on Form 10-K of the Registrant filed on December 31, 2009)
|
|
10.4
|
Registration Rights Agreement dated January 31, 2010 between Covenant Group of China Inc. and Southridge Partners II, LP (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of the Registrant filed on February 4, 2010)
|
|
10.5
|
Equity Credit Agreement dated January 31, 2010 between Covenant Group of China Inc. and Southridge Partners II, LP (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of the Registrant filed on February 4, 2010)
|
|
10.6
|
Share Entrustment Agreement dated March 26, 2010 among Covenant Group of China Inc., Chongqing HongSheng Information Sysway Industry Co, Ltd., Shi Quansheng, Song Xiaozhong, Song Guangwei and Yuan Rui**
|
|
10.7
|
Share Entrustment Agreement dated March 22, 2010 among Covenant Group of China Inc., Hainan JIEN Intelligent Engineering Co., Ma Bing Feng and Dai Qing Hua**
|
|
10.8
|
Amendment to the Share Cancellation and Loan Agreement among Covenant Group of China Inc., Covenant Group Holdings Inc, and Gary Sidhu**
|
|
10.9
|
Promissory Note of Shi Quansheng, Song Xiaozhong, Song Guangwei and Yuan Rui in favor of Chongqing HongSheng Information Sysway Industry Co, Ltd. in the principal amount of 2,200,000 RMB dated March, 23, 2010**
|
|
10.10
|
Second Amendment to Share Cancellation and Loan Agreement among Covenant Group of China Inc., Covenant Group Holdings Inc, and Gary Sidhu (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of the Registrant filed on May 17, 2010)
|
|
10.11
|
Amendment to Equity Credit Agreement between Covenant Group of China Inc. and Southridge Partners II, LP (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of the Registrant filed on May 17, 2010)
|
|
10.12
|
Bridge Loan Agreement dated as of April 22, 2010, by and between Covenant Group of China Inc. and Sui Generis Capital Partners LLC (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of the Registrant filed on May 17, 2010)
|
|
10.13
|
Engineering and Construction Contract dated November 5, 2008, by and between Hainan Jien Intelligent Engineering Co. Ltd. And Hainan Province Medical School**
|
|
10.14
|
Engineering and Construction Contract dated May 22, 2008, by and between Hainan Jien Intelligent Engineering Co. Ltd. And Hainan Province Medical School**
|
| 10.15 | Bridge Loan Agreement dated as of June 10, 2010, between Covenant Group of China, Inc. and Walston Dupont Global Advisors LLC |
|
16.1
|
Letter from Manning Elliott LLP dated December 31, 2009 (Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 16.1 to the Current Report on Form 10-K of the Registrant filed on December 31, 2009)
|
|
21
|
List of subsidiaries of the Company**
|
|
23.1
|
Consent of Holland & Hart LLP (included in Exhibit 5.1)*
|
|
23.2
|
Consent of Morison Cogen LLP, independent registered public accounting firm
|
|
*to be filed by amendment
|
|
|
**Previously filed.
|
|
Item 17. Undertakings
The undersigned Registrant hereby undertakes:
(1) To file, during any period in which offers or sales are being made, a post-effective amendment to this Registration Statement:
(i) To include any prospectus required by Section 10(a)(3) of the Securities Act of 1933;
(ii) To reflect in the prospectus any facts or events arising after the effective date of the Registration Statement (or the most recent post-effective amendment thereof) which, individually or in the aggregate, represent a fundamental change in the information set forth in the Registration Statement;
(iii) To include any material information with respect to the plan of distribution not previously disclosed in the Registration Statement or any material change to such information in the Registration Statement.
(2) That, for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each such post-effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
(3) To remove from registration by means of a post-effective amendment any of the securities being registered which remain unsold at the termination of the offering.
(4) That, for the purpose of determining liability under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser:
(i) If the undersigned Registrant is relying on Rule 430B:
(A) Each prospectus filed by the Registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(3) shall be deemed to be part of the registration statement as of the date the filed prospectus was deemed part of and included in the registration statement; and
(B) Each prospectus required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424(b)(2), (b)(5), or (b)(7) as part of a registration statement in reliance on Rule 430B relating to an offering made pursuant to Rule 415(a)(1)(i), (vii), or (x) for the purpose of providing the information required by section 10(a) of the Securities Act of 1933 shall be deemed to be part of and included in the registration statement as of the earlier of the date such form of prospectus is first used after effectiveness or the date of the first contract of sale of securities in the offering described in the prospectus. As provided in Rule 430B, for liability purposes of the issuer and any person that is at that date an underwriter, such date shall be deemed to be a new effective date of the registration statement relating to the securities in the registration statement to which that prospectus relates, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof. Provided however, that no statement made in a registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into the registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract of sale prior to such effective date, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or prospectus that was part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately prior to such effective date; or
(ii) If the undersigned Registrant is subject to Rule 430C, each prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b) as part of a registration statement relating to an offering, other than registration statements relying on Rule 430B or other than prospectuses filed in reliance on Rule 430A, shall be deemed to be part of and included in the registration statement as of the date it is first used after effectiveness. Provided however, that no statement made in a registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into the registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract of sale prior to such first use, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or prospectus that was part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately prior to such date of first use.
(5) That, for the purpose of determining liability of the undersigned Registrant under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser in the initial distribution of the securities, the undersigned Registrant undertakes that in a primary offering of securities of the undersigned Registrant pursuant to this registration statement, regardless of the underwriting method used to sell the securities to the purchaser, if the securities are offered or sold to such purchaser by means of any of the following communications, the undersigned Registrant will be a seller to the purchaser and will be considered to offer or sell such securities to such purchaser:
(i) Any preliminary prospectus or prospectus of the undersigned Registrant relating to the offering required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424;
(ii) Any free writing prospectus relating to the offering prepared by or on behalf of the undersigned Registrant or used or referred to by the undersigned Registrant;
(iii) The portion of any other free writing prospectus relating to the offering containing material information about the undersigned Registrant or its securities provided by or on behalf of the undersigned Registrant; and
(iv) Any other communication that is an offer in the offering made by the undersigned Registrant to the purchaser.
(6) Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act of 1933 may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the Registrant pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, the Registrant has been informed that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act of 1933 and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the Registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the Registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the Registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question of whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act of 1933 and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
(7) The undersigned Registrant hereby undertakes that:
(i) For purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, the information omitted from the form of prospectus filed as a part of this registration statement in reliance upon Rule 430A and contained in a form of prospectus filed by the registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(1) or (4) or 497(h) under the Securities Act shall be deemed to be part of this registration statement as of the time it was declared effective.
(ii) For the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each post-effective amendment that contains a form of prospectus shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, the registrant has duly caused this Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the city of Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania, on the date indicated below.
| COVENANT GROUP OF CHINA INC. | |||
|
Date: July 2, 2010
|
By:
|
/s/ Kenneth Wong | |
| Kenneth Wong | |||
| President | |||
|
Date: July 2, 2010
|
By:
|
/s/ Justin D. Csik | |
| Justin D. Csik | |||
| Chief Financial Officer | |||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement has been signed below by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
Signature
|
Title
|
Date
|
|
|
/s/ Fredric Rittereiser
|
Chairman of the Board
|
July 2, 2010
|
|
|
Fredric Rittereiser
|
|||
|
/s/ Kenneth Wong
|
Director and President
|
July 2, 2010
|
|
|
Kenneth Wong
|
|||
|
/s/ K. Ivan F. Gothner
|
Director
|
July 2, 2010
|
|
|
K. Ivan F. Gothner
|
II-6
