Attached files
UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| [ X ] | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 | |||
| For the fiscal year ended | December 31, 2009 | |||
| OR | ||||
| [ ] | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 | |||
| For the transition period from | to | |||
Commission file number 0-23367
BIRNER DENTAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| COLORADO | 84-1307044 | |||
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (IRS Employer | |||
| Identification No.) |
| 3801 EAST FLORIDA AVENUE, SUITE 508 | ||||
| DENVER, COLORADO | 80210 | |||
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (303) 691-0680
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |||
| Common Stock, without par value | Nasdaq Capital Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
(Title of Class)
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes [ ] No [ X ]
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes [ ] No [ X ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes [ X ] No [ ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Date File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such Files). Yes [ ] No [ ]
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. [ ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer | [ ] | Accelerated filer | [ ] | Non-accelerated filer | [ ] | Smaller reporting company | [ X ] |
| (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes [ ] No [ X ]
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the registrant’s classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date.
| Class | Shares Outstanding as of March 29, 2010 | |||
| Common Stock, without par value | 1,865,532 |
The aggregate market value of the registrant’s voting stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant computed by reference to the last reported sale price of its Common Stock as of June 30, 2009, the last business day of the registrant’s most recent completed second fiscal quarter, was $12,761,150. This calculation assumes that the registrant’s executive officers, directors and persons owning 5% or more of the outstanding Common Stock as of such date may be affiliates of the registrant and that 886,191 shares of Common Stock are held by non-affiliates.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
The information required by Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K (Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14) is incorporated by reference from the registrant’s definitive proxy statement for the 2010 Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A within 120 days from December 31, 2009.
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K (“Annual Report”) of Birner Dental Management Services, Inc. (the “Company”), which are not historical in nature, are forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward-looking statements include statements in Item 1, “Business,” Item 1A, “Risk Factors,” Item 5, “Market for the Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities” and Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” regarding, for example, the intent, belief or current expectations of the Company or its officers with respect to the development or acquisition of additional dental practices and the successful integration of such practices into the Company’s network, recruitment of additional dentists, funding of the Company’s expansion, capital expenditures and payment or nonpayment of dividends.
Investors and prospective investors are cautioned that any such forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and involve risks and uncertainties. Such forward-looking statements involve certain risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from anticipated results. These risks and uncertainties include regulatory constraints, changes in laws or regulations concerning the practice of dentistry or dental practice management companies, the availability of suitable new markets and suitable locations within such markets, changes in the Company’s operating or expansion strategy, failure to consummate or successfully integrate proposed developments or acquisitions of dental practices, the ability of the Company to manage effectively an increasing number of dental practices, the general economy of the United States and the specific markets in which the Company’s dental practices are located or are proposed to be located, trends in the health care, dental care and managed care industries, as well as the risk factors set forth in Item 1A, “Risk Factors,” of this Annual Report, and other factors as may be identified from time to time in the Company’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission or in the Company’s press releases.
EXPLANATORY NOTE
In this Annual Report, the Company is restating its previously issued audited statements of income for each of the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2008 and its unaudited consolidated statements of income for each of the quarters of the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2009. The restated consolidated statements of income can be found in Item 8, “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data,” of this Annual Report.
The Company’s previously filed annual reports on Form 10-K and quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, earnings press releases and other similar communications for the restated periods as described above will not be amended and should not be relied upon. Therefore, the consolidated statements of income, reports of the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm and related financial information contained in such previously filed reports should not be relied upon. Similarly, related press releases and reports describing the Company’s financial results for the aforementioned periods should no longer be relied upon.
2
Birner Dental Management Services, Inc.
Form 10-K
Table of Contents
| Part | Item(s) | Page | |
| I. | 1. | Business | 4 |
| 1A. | Risk Factors | 12 | |
| 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments | 19 | |
| 2. | Properties | 20 | |
| 3. | Legal Proceedings | 22 | |
| 4. | Reserved | 22 | |
| II. | 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities | 23 |
| 6. | Selected Financial Data | 26 | |
| 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 26 | |
| 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure About Market Risk | 39 | |
| 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | 40 | |
| 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure | 68 | |
| 9A. | Controls and Procedures | 68 | |
| 9B. | Other Information | 69 | |
| III. | 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance | 70 |
| 11. | Executive Compensation | 70 | |
| 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters | 70 | |
| 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence | 70 | |
| 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services | 70 | |
| IV. | 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules | 71 |
| Signatures | 72 |
3
PART I
ITEM 1. Business.
General
The Company is a dental business service organization devoted to servicing geographically dense dental practice networks in select markets, currently including Colorado, New Mexico and Arizona. With 45 affiliated dental practices (“Offices”) in Colorado and ten in New Mexico, the Company believes that its affiliated Offices comprise the largest provider of dental care in Colorado and New Mexico. The Company currently provides business services to 65 Offices, of which 38 were acquired and 27 were developed internally (“de novo Offices”). The Company provides a solution to the needs of dentists, patients, and third-party payors by allowing the Company’s affiliated dentists to provide high-quality, efficient dental care in patient-friendly, family practice settings. Dentists practicing at the various locations provide comprehensive general dentistry services, and the Company offers specialty dental services through affiliated specialists at some of its locations.
Restatement of Certain Financial Information
On March 10, 2010, management and the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors of the Company concluded that the Company’s previously issued audited statements of income for each of the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2008 and its unaudited consolidated statements of income for each of the quarters of the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2009 should be restated. The restatements are a result of a change in accounting relating to the consolidation of the Company’s managed professional corporations (“P.C.s”).
In prior periods, the Company had been consolidating its managed P.C.s under the consolidation by contract method as originally set forth in Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”) 97-02 and the related Staff interpretation of EITF 97-02 since its initial public offering in 1998. The consolidation by contract method as described in EITF 97-02 has a very narrow scope, and the Company believed that it fit within that scope precisely. In 2009, the Staff of the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) reviewed and issued comments pertaining to the Company’s Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008. In the course of reviewing the SEC’s accounting comments, management of the Company examined the application of the consolidation methodology of Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification Topic 810-10, “Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities” (“ASC Topic 810-10”), to the consolidation of its affiliated P.C.s. ASC Topic 810-10 provides that variable interest entity, or VIE, accounting should be considered before consideration of consolidation by contract. Based on its review of ASC Topic 810-10, management began the process of analyzing whether its managed P.C.s should be consolidated under the VIE model and made submissions to the SEC to determine whether VIE accounting under ASC Topic 810-10 was appropriate. After thorough consideration of the questions and comments raised by the SEC in the SEC review process and discussions with the SEC staff regarding the issue, on March 10, 2010, the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors of the Company, in consultation with management and the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, concluded that treatment of the Company’s managed P.C.s as variable interest entities is the appropriate treatment under ASC Topic 810-10. See Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” and Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements.
The restatements affect the Company’s previously reported revenue and expenses for clinical salaries and benefits paid to dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants. As a result, the Company’s reported revenue increased by the amounts paid to dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants. Clinical salaries and benefits increased by the same dollar amounts as the increase in revenue. The restatements have no impact on the following items:
- Contribution from dental offices
- Operating income
- Net income
- Earnings per share
- Consolidated balance sheets
- Consolidated statements of shareholders equity and comprehensive income
- Consolidated statements of cash flows
- Adjusted EBITDA
4
In connection with the restatements as described in this Annual Report, management of the Company re-evaluated the effectiveness of its disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting. As a result of this re-evaluation, management determined that there was a control deficiency that constituted a material weakness in the Company’s internal controls. The material weakness is a result of a lack of controls to identify variable interest entities and the consolidation of variable interest entities under generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). Accordingly, additional enhancements to the control environment have been implemented in 2010 to ensure that controls related to these material weaknesses are strengthened and will operate effectively. See Item 9A, “Controls and Procedures.”
Dental Services Industry
According to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (“CMS”), dental expenditures in the U.S. increased from $38.9 billion in 1993 to an estimated $101.2 billion in 2008. CMS also projects that dental expenditures will reach approximately $180.4 billion by 2019, representing an increase of approximately 78.3% over 2008 dental expenditures. The Company believes this growth is driven by (i) an increase in the number of people covered by third-party payment arrangements and the resulting increase in their utilization of dental services, (ii) an increasing awareness of the benefits of dental treatments, (iii) the retention of teeth into later stages of life, (iv) the general aging of the population, as older patients require more extensive dental services, and (v) a growing awareness of and demand for preventative and cosmetic services.
Traditionally, most dental patients have paid for dental services themselves rather than through third-party payment arrangements such as indemnity insurance, preferred provider plans or managed dental plans. More recently, factors such as increased consumer demand for dental services and the desire of employers to provide enhanced benefits for their employees have resulted in an increase in third-party payment arrangements for dental services. Recent market trends, including the rise of third-party payment arrangements, have contributed to the increased consolidation of practices in the dental services industry and to the formation of dental practice management companies. The Company believes that the percentage of people covered by third-party payment arrangements will continue to increase due in part to the popularity of such arrangements.
Patient Services
The Company’s affiliated Offices seek to develop long-term relationships with patients. Dentists practicing at the Offices provide comprehensive general dentistry services, including crowns and bridges, fillings (including gold, porcelain and composite inlays/onlays), and aesthetic procedures such as porcelain veneers and bleaching. In addition, dental hygienists provide cleanings and periodontal services including root planing and scaling. If appropriate, the patient is offered specialty dental services, such as orthodontics, oral surgery, pediatrics, endodontics and periodontics, which are available at certain of the Offices. Affiliated specialists rotate through certain Offices to provide these services. By offering a broad range of dental services within a single practice, the Company is able to distinguish itself from its competitors and realize operating efficiencies and economies of scale through higher utilization of its facilities.
The Company Dentist Philosophy
The Company seeks to develop long-term relationships with its dentists by building the practice at each of its Offices around a managing dentist. The Company’s dental practice management model provides managing dentists a leadership role and ability to practice in a style they are most accustomed to without the capital commitment and the administrative burdens such as billing/collections, payroll, accounting, and marketing. This gives the managing dentists the ability to focus primarily on providing high-quality dental care to their patients, team building, and developing long-term relationships with patients and staff by building trust and providing a friendly, relaxed atmosphere in their Office. The managing dentist exercises their clinical judgment in matters of patient care. In addition, managing dentists have a financial incentive to improve the operating performance of their Offices through a bonus system based upon the operating performance of the Office.
When the revenues of an Office justify expansion, associate dentists can be added to the team. Depending on performance and abilities, an associate dentist may be given the opportunity to become a managing dentist.
5
Dental Practice Management Model
The Company’s dental practice management model is designed to achieve its goal of providing personalized, high-quality dental care in a patient-friendly setting similar to that found in a traditional private dental practice. The Company’s dental practice management model consists of the following components:
Recruiting of Dentists. The Company seeks dentists with excellent skills and experiences, who are sensitive to patient needs, interested in establishing long-term patient relationships and are motivated by financial incentives to enhance Office operating performance. The Company believes that practicing in its network of Offices offers dentists advantages over a solo or smaller group practice, including relief from the burden of most administrative responsibilities and the resulting ability to focus more time on practicing dentistry. Other advantages include relief from capital commitments, a compensation structure that rewards productivity, employee benefits such as health insurance, a 401(k) plan, continuing education, paid holidays and vacation, and payment of professional membership fees and malpractice insurance. The Company seeks to recruit managing dentists with three or more years of practice experience, although from time to time the Company recruits associate dentists graduating from residency programs.
The Company advertises for dentists in national and regional dental journals, local market newspapers, professional conferences and directly at dental schools with strong residency programs. In addition, the Company’s existing affiliated dentists provide a good referral source for recruiting future dentists.
Training of Non-Dental Employees. The Company has developed a formalized training program for non-dental employees, which is conducted by the Company’s staff. This program includes training in patient interaction, scheduling, use of computer systems, office procedures and protocols, and third-party payment arrangements. The Company also offers formalized mandatory training programs for employees regarding occupational safety and environmental issues, state dental practice law, state and local regulations, and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) to ensure compliance with government regulations. Additionally, the Company encourages its employees to attend continuing education seminars as a supplement to the Company’s formalized training program. Company regional directors meet with senior management and administrative staff to review pertinent and timely topics and generate ideas that can be shared with all Offices. Management believes that its training program and ongoing meetings with employees have contributed to the success of the Offices.
Staffing Model. The Company’s staffing model attempts to maximize profitability in the Offices by adjusting personnel according to an Office’s revenue level. Staffing at mature Offices varies based on the number of treatment rooms, but generally includes one to three dentists, two to four dental assistants, one to three dental hygienists, one to three hygiene assistants and two to five front office personnel. Staffing at de novo Offices typically consists initially of one dentist, one dental assistant and one front office person. As the patient base builds at an Office, additional staff is added to accommodate the growth. The Company currently has a staff of four regional directors in Colorado, one regional director for New Mexico and one regional director for Arizona. Regional directors are responsible for between ten and 15 Offices, overseeing operations, training and development of non-dental employees, recruitment and implementing the Company’s dental practice management model.
Management Information Systems. The Company has a networked management information system through which it receives uniform data that is analyzed to measure and improve operating performance in the Offices. The Company’s system enables it to maintain on-line contact with each of its Offices and allows it to monitor the Office’s performance with real-time data relating to patient and insurance information, treatment plans, scheduling, revenues and collections. The Company provides each Office with monthly operating and financial data, which is analyzed and used to improve the Office’s performance.
Advertising and Marketing. The Company seeks to increase patient volume at its Offices through television, radio, internet and print advertising and other marketing techniques. The Company’s advertising efforts are primarily aimed at increasing patient awareness and emphasize the high-quality care provided, as well as the timely, individualized attention received from the Company’s affiliated dentists. During 2009, the Company used radio advertising in Colorado Springs, Colorado and Albuquerque, New Mexico. During 2008, the Company did not use television, radio, or print advertising and relied on Yellow Page and internet advertising.
Purchasing/Vendor Relationships. The Company has negotiated arrangements with a number of its more significant vendors, including dental laboratory and supply providers, to reduce unit costs. By aggregating supply purchasing and laboratory usage, the Company believes that it has received favorable pricing compared to solo or
6
smaller group practices. The Company purchased $2.2 million of dental supplies from Henry Schein and incurred $617,000 in laboratory expenses from Pro Dental Laboratory during 2009. The Company’s system of centralized buying and distribution on an as-needed basis reduces the storage of inventory and supplies at the Offices.
Payor Mix
The Company’s payors include indemnity insurers, preferred provider plans, managed dental care plans, and uninsured cash patients. The Company negotiates managed care contracts and preferred provider networks on behalf of the Offices, and each Office enters into a contract with the various managed care plans.
Capitated managed dental care plans accounted for 21.7% of the Company’s revenue in 2009 compared to 22.9% in 2008 (including revenue from associated co-payments).
Expansion Program
Between its formation in May 1995 and 2001, the Company acquired 42 practices, including six practices that have been consolidated with existing Offices and one practice that was closed during 2004. Of those acquired practices (including the six practices consolidated with existing Offices and the one practice closed during 2004), 34 were located in Colorado, five were located in New Mexico, and three were located in Arizona. Although the Company has acquired and integrated several group practices, many of the Company’s acquisitions have been solo dental practices. The Company has developed 28 de novo Offices (including one practice that was consolidated with an existing Office). During 2006, the Company opened four de novo Offices; two in Phoenix, Arizona and one each in the Denver, Colorado and Albuquerque, New Mexico markets. No new Offices were opened during 2007. During 2008, the Company opened one de novo Office in Longmont, Colorado. During 2009, the Company acquired two practices in Tucson, Arizona and one practice in Denver, Colorado. In February 2010, the Company opened a de novo Office in the Albuquerque, New Mexico market.
The Company expects to increase revenue in existing markets by enhancing the operating performance of its existing Offices and through select de novo Offices, acquisitions and other development activity. Enhancing operating performance will principally be accomplished through the expansion of specialty services and the aggressive recruitment of additional dentists and dental hygienists to further utilize existing physical capacity in the Offices. Additionally, the Company has remodeled certain Offices to expand the number of treatment rooms in an Office so that more patients can be treated. Also, the Company continues to look for potential future development sites for de novo Offices and evaluates potential acquisition candidates.
Affiliation Model
Relationship with Professional Corporations (P.C.s)
Each Office is operated by a P.C. which is owned by one of six different licensed dentists affiliated with the Company. The Company’s President, Mark A. Birner, DDS, is one of the six dentists and individually owns 52 P.C.s. The Company has entered into agreements with the owners of the P.C.s which provide that upon the death, disability, incompetence or insolvency of the owner, a loss of the owner’s license to practice dentistry, a termination of the owner’s employment by the P.C. or (in the case of Dr. Birner) the Company, a conviction of the owner for a criminal offense, or a breach by the P.C. of the Management Agreement (as defined below) with the Company, or a determination by the Company in its sole discretion that it is in it’s best interest, the Company may require the owner to sell their shares in the P.C. for a nominal amount to a third-party designated by the Company. These agreements also prohibit the owner from transferring or pledging the shares in the P.C.s except to parties approved by the Company who agree to be bound by the terms of the agreements. Upon a transfer of the shares to another party, the owner agrees to resign all positions held as an officer or director of the P.C.
Management Agreements with Affiliated Offices
The Company derives all of its revenue from its management agreements with the P.C.s (the “Management Agreements”). Under each of the Management Agreements, the Company provides business and marketing services to the Offices, including (i) providing capital, (ii) designing and implementing marketing programs, (iii) negotiating for the purchase of supplies, (iv) staffing, (v) recruiting, (vi) training of non-dental personnel, (vii) billing and collecting patient fees, (viii) arranging for certain legal and accounting services, and (ix) negotiating with managed care organizations. The P.C. is responsible for, among other things, (i) supervision of all dentists,
7
dental hygienists and dental assistants, (ii) ensuring compliance with all laws, rules and regulations relating to dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants, and (iii) maintaining proper patient records. The Company has made, and intends to make in the future, loans to the P.C.s to fund their acquisition of dental assets from third parties in order to comply with state dental practice laws. Because the Company’s financial statements are consolidated with the financial statements of the P.C.s, these loans are eliminated in consolidation.
Under the typical Management Agreement, the P.C. pays the Company a management fee equal to the Adjusted Gross Center Revenue of the P.C. less compensation paid to the dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants employed at the Office of the P.C. Adjusted Gross Center Revenue is comprised of all fees and charges booked each month by or on behalf of the P.C. as a result of dental services provided to patients at the Office, less any adjustments for uncollectible accounts, professional courtesies and other activities that do not generate a collectible fee. The Company’s costs include all direct and indirect costs, overhead and expenses relating to the Company’s provision of management services to the Office under the Management Agreement, including (i) salaries, benefits and other direct costs of Company employees who work at the Office (other than dentists’, dental hygienists’ and dental assistants’ salaries), (ii) direct costs of all Company employees or consultants who provide services to or in connection with the Office, (iii) utilities, janitorial, laboratory, supplies, advertising and other expenses incurred by the Company in carrying out its obligations under the Management Agreement, (iv) depreciation expense associated with the P.C.’s assets and the assets of the Company used at the Office, and the amortization of intangible asset value relating to the Office, (v) interest expense on indebtedness incurred by the Company to finance any of its obligations under the Management Agreement, (vi) general and malpractice insurance expenses, lease expenses and dentist recruitment expenses, (vii) personal property and other taxes assessed against the Company’s or the P.C.’s assets used in connection with the operation of the Office, (viii) out-of-pocket expenses of the Company’s personnel related to mergers or acquisitions involving the P.C., (ix) corporate overhead charges or any other expenses of the Company including the P.C.’s pro rata share of the expenses of the accounting and computer services provided by the Company, and (x) a collection reserve in the amount of 5.0% of Adjusted Gross Center Revenue. As a result, substantially all costs associated with the provision of dental services at the Office are borne by the Company, except for the compensation of the dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants who work at the Office. This enables the Company to manage the profitability of the Offices. Each Management Agreement is for a term of 40 years. Each Management Agreement generally may be terminated by the P.C. only for cause, which includes a material default by or bankruptcy of the Company. Upon expiration or termination of a Management Agreement by either party, the P.C. must satisfy all obligations it has to the Company.
The Company plans to continue to use the current form of its Management Agreement to the extent possible. However, the terms of the Management Agreement are subject to change to comply with existing or new regulatory requirements or to enable the Company to compete more effectively.
Employment Agreements
Dentists practicing at the Offices have entered into employment agreements or independent contractor agreements with a P.C. The majority of these agreements can be terminated by either party without cause with 90 days notice. The agreements typically contain non-competition provisions for a period ranging from three to five years following their termination within a specified geographic area, usually a specified number of miles from the associated Office, and restrict solicitation of patients and employees. Managing dentists receive compensation based upon a specified amount per hour worked or a percentage of production attributable to their work, or a bonus based upon the operating performance of the Office. Associate dentists are compensated based upon a specified amount per hour or monthly guarantee or a percentage of production attributable to their work. Specialists are compensated based upon an hourly or monthly guarantee or a percentage of their own work.
As of December 31, 2009, the Company had 87 general dentists, 38 specialists and 66 dental hygienists who were employed by the P.C.s, and 374 non-dental employees.
Competition
The dental services industry is highly fragmented, consisting primarily of solo and smaller group practices. The dental practice management segment of this industry is highly competitive and is expected to become more competitive. In this regard, the Company expects that the provision of multi-specialty dental services at convenient locations will become increasingly more common. The Company is aware of several dental practice management companies that are operating in its markets, including Dental One, Bright Now, Pacific Dental, American Dental Partners, Inc. and Dental Health Centers of America. Companies with dental practice management businesses
8
similar to that of the Company, which currently operate in other parts of the country, may begin targeting the Company’s existing markets for expansion. Such competitors may have a greater financial track record and soundness, superior affiliation models, a better reputation of existing affiliated practices, more management expertise or otherwise enjoy competitive advantages, which may make it difficult for the Company to compete against them.
The business of providing general and specialty dental services is highly competitive in the markets in which the Company operates. The Company believes it competes with other providers of dental and specialty services on the basis of factors such as brand name recognition, convenience, cost and the quality and range of services provided. Competition may include practitioners who have more established practices and reputations. The Company also competes against established practices in the retention and recruitment of general dentists, specialists, dental hygienists and other personnel. If the availability of such individuals begins to decline in the Company’s markets, it may become more difficult to attract and retain qualified personnel to sufficiently staff the existing Offices or to meet the staffing needs of the Company’s planned expansion.
Government Regulation
The practice of dentistry is regulated at both the state and federal levels, and the regulation of health care-related companies is increasing. There can be no assurance that the regulatory environment in which the Company or the P.C.s operate will not change significantly in the future. The laws and regulations of all states in which the Company operates impact the Company’s operations but do not currently materially restrict the Company’s operations in those states. In addition, state and federal laws regulate health maintenance organizations and other managed care organizations for which dentists may be providers. In connection with its operations in existing markets and expansion into new markets, the Company may become subject to additional laws, regulations and interpretations or enforcement actions. The laws regulating health care are broad and subject to varying interpretations, and there is currently a lack of case law construing such statutes and regulations. The ability of the Company to operate profitably will depend in part upon the ability of the Company and the P.C.s to operate in compliance with applicable health care regulations.
Although the Company believes its operations as currently conducted are in material compliance with existing applicable laws and regulations, there can be no assurance that the Company’s contractual arrangements will not be successfully challenged as violating applicable laws and regulations or that the enforceability of such arrangements will not be limited as a result of such laws and regulations. In addition, there can be no assurance that the business structure under which the Company operates, or the advertising strategy the Company employs, will not be deemed to constitute the unlicensed practice of dentistry, or the operation of an unlicensed clinic or health care facility or a violation of a state dental practice act. The Company has not sought judicial or regulatory interpretations with respect to the manner in which it conducts its business. There can be no assurance that a review of the business of the Company and the P.C.s by courts or regulatory authorities will not result in a determination that could materially and adversely affect their operations or that the regulatory environment will not change so as to restrict the Company’s existing or future operations. In the event that any legislative measures, regulatory provisions or rulings or judicial decisions restrict or prohibit the Company from carrying on its business or from expanding its operations to certain jurisdictions, structural and organizational modifications of the Company’s organization and arrangements may be required which could have a material adverse effect on the Company, or the Company may be required to cease operations.
State Regulation
The laws of many states, including Colorado and New Mexico, permit a dentist to conduct a dental practice only as an individual, a member of a partnership or an employee of a professional corporation, limited liability company or limited liability partnership. These laws typically prohibit, either by specific provision or as a matter of general policy, non-dental entities, such as the Company, from practicing dentistry, from employing dentists and, in certain circumstances, dental hygienists or dental assistants, or from otherwise exercising control over the provision of dental services. Under the Management Agreements, the P.C.s control all clinical aspects of the practice of dentistry and the provision of dental services at the Offices, including the exercise of independent professional judgment regarding the diagnosis or treatment of any dental disease, disorder or physical condition. Persons to whom dental services are provided at the Offices are patients of the P.C.s and not of the Company. The Company does not employ the dentists who provide dental services at the Offices nor does the Company have or exercise any control or direction over the manner or methods in which dental services are performed or interfere in any way with the exercise of professional judgment by the dentists.
9
Many states, including Colorado, limit the ability of a person other than a licensed dentist, to own or control dental equipment or offices used in a dental practice. Some states allow leasing of equipment and office space to a dental practice under a bona fide lease, if the equipment and office remain under the control of the dentist. Some states, including New Mexico, require all advertisements to be in the name of the dentist. A number of states, including Arizona, Colorado and New Mexico, also regulate the content of advertisements of dental services. In addition, Arizona, Colorado and New Mexico and many other states impose limits on the tasks that may be delegated by dentists to dental hygienists and dental assistants. Some states require entities designated as “clinics” to be licensed, and may define clinics to include dental practices that are owned or controlled in whole or in part by non-dentists. These laws and their interpretations vary from state to state and are enforced by the courts and by regulatory authorities with broad discretion.
Many states have fraud and abuse laws which are similar to the federal fraud and abuse law described below, and which in many cases apply to referrals for items or services reimbursable by any third-party payor, not just by Medicare and Medicaid. A number of states, including Arizona, Colorado and New Mexico, prohibit the submitting of false claims for dental services.
Many states, including Colorado and New Mexico, also prohibit “fee-splitting” by dentists with any party except other dentists in the same professional corporation or practice entity. In most cases, these laws have been construed to apply to the practice of paying a portion of a fee to another person for referring a patient or otherwise generating business, and not to prohibit payment of reasonable compensation for facilities and services (other than the generation of referrals), even if the payment is based on a percentage of the practice’s revenues, but some courts have found that the percentage allocation of fees to a practice management company to be impermissible “fee splitting.”
Many states also have laws prohibiting paying or receiving any remuneration, direct or indirect, that is intended to include referrals for health care items or services, including dental items and services.
In addition, there are certain regulatory risks associated with the Company’s role in negotiating and administering managed care contracts. The application of state insurance laws to third party payor arrangements, other than fee-for-service arrangements, is an unsettled area of law with little guidance available. As the P.C.s contract with third-party payors, on a capitation or other basis under which the relevant P.C. assumes financial risk, the P.C.s may become subject to state insurance laws. Specifically, in some states, regulators may determine that the Company or the P.C.s are engaged in the business of insurance, particularly if they contract on a financial-risk basis directly with self-insured employers or other entities that are not licensed to engage in the business of insurance. In Arizona, Colorado and New Mexico, the P.C.s currently only contract on a financial-risk basis with entities that are licensed to engage in the business of insurance and thus are not subject to the insurance laws of those states. To the extent that the Company or the P.C.s are determined to be engaged in the business of insurance, the Company may be required to change the method of payment from third-party payors and the Company’s revenue may be materially and adversely affected.
Federal Regulation
Federal laws generally regulate reimbursement, billing and self-referral practices under Medicare and Medicaid programs. Because the P.C.s currently receive a minimal amount of revenue under Medicare or Medicaid, the impact of these laws on the Company to date has been negligible. There can be no assurance, however, that the P.C.s will not have patients in the future covered by these laws, or that the scope of these laws will not be expanded in the future, and if expanded, such laws or interpretations of the laws could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition and operating results.
Federal regulations also allow state licensing boards to revoke or restrict a dentist’s license in the event the dentist defaults in the payment of a government-guaranteed student loan, and further allow the Medicare program to offset overdue loan payments against Medicare income due to the defaulting dentist’s employer. The Company cannot assure compliance by dentists with the payment terms of their student loans, if any.
Revenue of the P.C.s or the Company from all insurers, including governmental insurers, is subject to significant regulation. Some payors limit the extent to which dentists may assign their revenue from services rendered to beneficiaries. Under these “reassignment” rules, the Company may not be able to require dentists to assign their third-party payor revenue unless certain conditions are met, such as acceptance by dentists of assignment of the
10
payor receivable from patients, reassignment to the Company of the sole right to collect the receivables, and written documentation of the assignment. In addition, governmental payment programs such as Medicare and Medicaid limit reimbursement for services provided by dental assistants and other ancillary personnel to those services which were provided “incident to” a dentist’s services. Under these “incident to” rules, the Company may not be able to receive reimbursement for services provided by certain members of the Company’s Offices’ staff unless certain conditions are met, such as requirements that services must be of a type commonly furnished in a dentist’s office and must be rendered under the dentist’s direct supervision and that clinical Office staff must be employed by the dentist or the P.C. The Company does not currently derive a significant portion of its revenue under such programs.
The operations of the Offices are also subject to compliance with regulations promulgated by OSHA relating to such matters as heat sterilization of dental instruments and the use of barrier techniques such as masks, goggles and gloves. The operation of the Offices are also subject to compliance with regulations promulgated by the EPA relating to such matters as hazardous waste disposal. The Company incurs expenses on an ongoing basis relating to OSHA and EPA monitoring and compliance.
Health care providers, including the Company, are required to comply with the electronic data security and privacy requirements of HIPAA. HIPAA delegates enforcement authority to the CMS Office for Civil Rights. Recent changes to HIPAA implemented by the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 have extended the direct application of many HIPAA provisions to business associates of covered entities, and now permit state attorneys general to pursue civil actions under HIPAA. Violations of HIPAA could result in civil penalties of up to $1,500,000 per type of violation in each calendar year and criminal penalties of up to $250,000 per violation and/or up to ten years in prison per violation. As of December 31, 2009, the Company believes that it was in full compliance with all requirements of HIPAA and there has been no material impact on the Company due to the implementation of these regulations.
Insurance
The Company believes that its existing insurance coverage is adequate to protect it from the risks associated with the ongoing operation of its business. This coverage includes property and casualty, general liability, workers compensation, director’s and officer’s corporate liability, employment practices liability, excess liability and professional liability insurance for the Company and for dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants at the Offices.
Seasonality
The Company’s past financial results have fluctuated somewhat due to seasonal variations in the dental service industry, with revenue typically lower in the fourth calendar quarter. The Company expects this seasonal fluctuation to continue in the future.
Trademark
The Company is the registered owner of the PERFECT TEETH® trademark in the United States. The Company uses the PERFECT TEETH name to distinguish the Company’s Offices from other dental offices in the markets in which it operates. Also, the Company promotes brand awareness and generates demand through marketing and advertising utilizing the PERFECT TEETH name. The trademark is effective until 2018 when it will be subject to renewal.
Company Website
Information related to the Company’s filings with the SEC can be found on the Company’s website at www.bdms-perfectteeth.com. The Company’s website is not a part of, or incorporated by reference in, this Annual Report.
11
ITEM 1A. Risk Factors.
General economic conditions and other factors outside of the Company’s control may affect the Company’s stock price and results of operations.
The market price of the Common Stock could be subject to wide fluctuations in response to quarterly variations in operating results of the Company or its competitors, developments in the industry or changes in general economic conditions. A recessionary economic cycle, higher levels of unemployment, higher consumer debt levels, higher tax rates and other changes in tax laws or other economic factors could adversely affect consumer demand for the Company’s services and in particular, discretionary or elective dental services, which could adversely affect the Company’s results of operations. In addition, current or worsening economic conditions could adversely affect the Company’s collection of accounts receivable.
The majority of the Company’s affiliated dental Offices are located in Colorado and the Offices in Colorado generated 72%, 73% and 71% of the Company’s total revenue for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively. Adverse changes or conditions affecting the Colorado market such as healthcare reform, changes in laws and regulations and governmental investigations, may have a particularly significant impact on the business of our affiliated dentists and our business, financial condition and results of operations. The Company’s current concentration in the Colorado market as well as the Company’s strategy of focused expansion in areas in and around the Company’s existing markets increases the risk that adverse economic or regulatory developments in this market may have a material and adverse impact on the Company’s operations.
The Company’s operations and growth strategy place significant demands on management.
The Company’s ability to compete effectively depends upon its ability to hire, train, and assimilate additional management and other employees, and its ability to expand, improve, and effectively utilize its operating, management, marketing and financial systems to accommodate its expanded operations. Any failure by the Company’s management to effectively anticipate, implement, and manage the changes required to sustain the Company’s growth may have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition, and operating results. See Item 1. “Business – Expansion Program.”
The success of the Company depends on the continued services of three members of the Company’s senior management, its Chief Executive Officer, Fred Birner, its President, Mark Birner, D.D.S., and its Chief Financial Officer, Treasurer and Secretary, Dennis Genty. The Company believes its future success will depend in part upon its ability to attract and retain qualified management personnel. Competition for such personnel is intense and the Company competes for qualified personnel with numerous other employers, some of which have greater financial and other resources than the Company. The loss of the services of one or more members of the Company’s senior management or the failure to add or retain qualified management personnel could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition and operating results.
The Company is heavily dependent upon the recruitment and retention of dentists and other personnel.
The Company believes that the profitability and operations of its Offices and its expansion strategy depend on the availability and successful recruitment and retention of dentists, dental assistants, dental hygienists, specialists, and other personnel. The Company may not be able to recruit or retain dentists and other personnel for its Offices, which may have a material adverse effect on the Company’s expansion strategy and its business, financial condition and operating results. See Item 1. “Business - Dental Practice Management Model.”
The Company is not the owner of the P.C.s and is heavily dependent on its affiliated dentists and management agreements.
The Company receives management fees for services provided to the P.C.s under Management Agreements. The Company owns most of the non-dental operating assets of the Offices but does not employ or contract with dentists, dental hygienists or dental assistants, or control the provision of dental care. The Company’s revenue is dependent on the revenue generated by the P.C.s. Therefore, effective and continued performance of dentists providing services for the P.C.s is essential to the Company’s long-term success. Under each Management Agreement, the Company pays substantially all of the operating and non-operating expenses associated with the provision of dental
12
services except for the salaries and benefits of the dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants and principal and interest payments of loans made to the P.C. by the Company. Any material loss of revenue by the P.C.s would have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition, and operating results, and any termination of a Management Agreement (which is permitted in the event of a material default or bankruptcy by either party) could have such an effect. In the event of a breach of a Management Agreement by a P.C., there can be no assurance that the legal remedies available to the Company will be adequate to compensate the Company for its damages resulting from such breach. See Item 1. “Business - Affiliation Model.”
The Company operates in a competitive market, which may reduce gross profit margins and market share.
The dental practice management segment of the dental services industry is highly competitive and is expected to become increasingly more competitive. Several dental practice management companies operate in the Company’s markets. A number of companies with dental practice management businesses similar to that of the Company currently operate in other parts of the country and may enter the Company’s existing markets in the future. As the Company seeks to expand its operations into new markets, it is likely to face competition from dental practice management companies, which already have established a strong business presence in such locations. The Company’s competitors may have a greater financial track record and soundness, a better reputation of existing affiliated practices, more management expertise or otherwise enjoy competitive advantages, which may make it difficult for the Company to compete against them or to acquire additional Offices on terms acceptable to the Company. See Item 1. “Business - Competition.”
The business of providing general dental and specialty dental services is highly competitive in the markets in which the Company operates. Competition for providing dental services may include practitioners who have more established practices and reputations. The Company competes against established practices in the retention and recruitment of general dentists, specialists, dental hygienists and other personnel. If the availability of such dentists, specialists, dental hygienists and other personnel begins to decline in the Company’s markets, it may become more difficult to attract qualified dentists, specialists, dental hygienists and other personnel. There is no assurance that the Company will be able to compete effectively against other existing practices or against new single or multi-specialty dental practices that enter its markets, or to compete against such practices in the recruitment and retention of qualified dentists, specialists, dental hygienists and other personnel. See Item 1. “Business - Competition.”
The Company is exposed to uncertainty and risks associated with de novo Office development.
The Company utilizes internal and external resources to identify locations in suitable markets for the development of de novo Offices. Identifying locations in suitable geographic markets and negotiating leases can be a lengthy and costly process. Furthermore, the Company will need to provide each de novo Office with the appropriate equipment, furnishings, materials and supplies and other capital resources. Additionally, de novo Offices must be staffed with one or more dentists. Because a de novo Office may be staffed with a dentist with no previous patient base, significant advertising and marketing expenditures may be required to attract patients. There can be no assurance that a de novo Office will become profitable for the Company. See Item 1. “Business - Expansion Program.”
The Company may need additional capital and there is no guarantee additional financing would be available.
Implementation of the Company’s expansion strategy has required significant capital resources. Such resources will be needed to establish additional de novo Offices and maintain or upgrade the Company’s management information systems, and for the effective integration, operation and expansion of the Offices. In addition, during 2009 the Company began the capital intensive process of converting the traditional x-ray systems in the Offices to digital x-ray systems. The Company historically has primarily used cash and promissory notes as consideration in acquisitions of dental practices and intends to continue to do so. If the Company’s capital requirements over the next several years exceed cash flow generated from operations and borrowings available under the Company’s existing bank line of credit (the “Credit Facility”) or any successor credit facility, the Company may need to issue additional equity securities or incur additional debt. If additional funds are raised through the issuance of equity securities, dilution to the Company’s existing shareholders may result. Additional debt or non-Common Stock equity financings could be required to the extent that the Common Stock fails to maintain a market value sufficient to warrant its use for future financing needs. If additional funds are raised through the incurrence of debt, such debt instruments will likely contain restrictive financial, maintenance and security covenants. The Company may not be able to obtain additional required capital on satisfactory terms, if at all. The failure to raise the funds necessary to finance the expansion of the Company’s operations or the Company’s other capital requirements could have a material and adverse effect on the Company’s ability to pursue its strategy and on its business, financial condition
13
and operating results. See Item 7. “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources.”
The Company’s ability to pay dividends is restricted by several factors.
The Company began paying a quarterly cash dividend in 2004, and increased the quarterly cash dividend in February 2005, January 2006, January 2007, January 2008 and March 2010. However, the payment of dividends in the future is subject to the discretion of the Company’s Board of Directors, and various factors may prevent the Company from paying dividends or may require the Company to reduce the dividends. Such factors include the Company’s financial position, capital requirements and liquidity, the existence of a stock repurchase program, any loan agreement restrictions, state corporate law restrictions, results of operations and other factors the Company’s Board of Directors may consider relevant.
The Company is subject to federal, state and other laws and regulations that could give rise to substantial liabilities or otherwise adversely affect its cost, manner or feasibility of doing business.
The practice of dentistry is regulated at both the state and federal levels. There can be no assurance that the regulatory environment in which the Company or the P.C.s operate will not change significantly in the future. In addition, state and federal laws regulate health maintenance organizations and other managed care organizations for which dentists may be providers. In general, regulation of health care companies is increasing. In connection with its operations in existing markets and expansion into new markets, the Company may become subject to additional laws, regulations and interpretations or enforcement actions. The laws regulating health care are broad and subject to varying interpretations, and there is currently a lack of case law construing such statutes and regulations. The ability of the Company to operate profitably will depend in part upon the ability of the Company to operate in compliance with applicable health care regulations.
The laws of many states, including Colorado and New Mexico, permit a dentist to conduct a dental practice only as an individual, a member of a partnership or an employee of a professional corporation, limited liability company or limited liability partnership. These laws typically prohibit, either by specific provision or as a matter of general policy, non-dental entities, such as the Company, from practicing dentistry, from employing dentists and, in certain circumstances, dental hygienists or dental assistants, or from otherwise exercising control over the provision of dental services.
Many states, including Colorado, limit the ability of a person other than a licensed dentist to own or control dental equipment or offices used in a dental practice. In addition, Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, and many other states impose limits on the tasks that may be delegated by dentists to dental hygienists and dental assistants. Some states, including Arizona, Colorado and New Mexico, regulate the content of advertisements of dental services. Some states require entities designated as “clinics” to be licensed, and may define clinics to include dental practices that are owned or controlled in whole or in part by non-dentists. These laws and their interpretations vary from state to state and are enforced by the courts and by regulatory authorities with broad discretion.
Many states, including Colorado and New Mexico, also prohibit “fee-splitting” by dentists with any party except other dentists in the same professional corporation or practice entity. In most cases, these laws have been construed as applying to the practice of paying a portion of a fee to another person for referring a patient or otherwise generating business, and not to prohibit payment of reasonable compensation for facilities and services (other than the generation of referrals), even if the payment is based on a percentage of the practice’s revenues, but some courts have found that the percentage allocation of fees to a practice management company to be impermissible “fee splitting.”
Regulatory uncertainties could adversely affect the Company’s business and operations.
Many states have fraud and abuse laws, which apply to referrals for items or services reimbursable by any third-party payor, not just by Medicare and Medicaid. A number of states, including Arizona, Colorado and New Mexico, prohibit the submitting of false claims for dental services.
In addition, there are certain regulatory risks associated with the Company’s role in negotiating and administering managed care contracts. The application of state insurance laws to third party payor arrangements, other than fee-for-service arrangements, is an unsettled area of law with little guidance available. Specifically, in some states, regulators may determine that the P.C.s are engaged in the business of insurance, particularly if they contract on a
14
financial-risk basis directly with self-insured employers or other entities that are not licensed to engage in the business of insurance. If the P.C.s are determined to be engaged in the business of insurance, the Company may be required to change the method of payment from third-party payors and the Company’s business, financial condition and operating results may be materially and adversely affected.
Federal laws generally regulate reimbursement and billing practices under Medicare and Medicaid programs. The federal fraud and abuse statute prohibits, among other things, the payment, offer, solicitation or receipt of any form of remuneration, directly or indirectly, in cash or in kind to induce or in exchange for (i) the referral of a person for services reimbursable by Medicare or Medicaid, or (ii) the purchasing, leasing, ordering or arranging for or recommending the purchase, lease or order of any item, good, facility or service which is reimbursable under Medicare or Medicaid. Because the P.C.s receive a minimal amount of revenue under Medicare and Medicaid, the impact of these laws on the Company to date has been negligible. There can be no assurance, however, that the P.C.s will not have patients in the future covered by these laws, or that the scope of these laws will not be expanded in the future, and if expanded, such laws or interpretations there under could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition and operating results.
Health care providers, including the Company, are required to comply with the electronic data security and privacy requirements of HIPAA. HIPAA delegates enforcement authority to the CMS Office for Civil Rights. Recent changes to HIPAA implemented by the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 have extended the direct application of many HIPAA provisions to business associates of covered entities, and now permit state attorneys general to pursue civil actions under HIPAA. Violations of HIPAA could result in civil penalties of up to $1,500,000 per type of violation in each calendar year and criminal penalties of up to $250,000 per violation and/or up to ten years in prison per violation. As of December 31, 2009, the Company believes that it was in full compliance with all requirements of HIPAA and there has been no material impact on the Company due to the implementation of these regulations.
Although the Company believes that its operations as currently conducted are in material compliance with applicable laws, there can be no assurance that the Company’s contractual arrangements will not be successfully challenged as violating applicable fraud and abuse, self-referral, false claims, fee-splitting, insurance, facility licensure or certificate-of-need laws or that the enforceability of such arrangements will not be limited as a result of such laws. In addition, there can be no assurance that the business structure under which the Company operates, or the advertising strategy the Company employs, will not be deemed to constitute the unlicensed practice of dentistry, or the operation of an unlicensed clinic or health care facility or a violation of a state dental practice act. The Company has not sought judicial or regulatory interpretations with respect to the manner in which it conducts its business. There can be no assurance that a review of the business of the Company and the P.C.s by courts or regulatory authorities will not result in a determination that could materially and adversely affect their operations or that the regulatory environment will not change so as to restrict the Company’s existing or future operations. In the event that any legislative measures, regulatory provisions or rulings or judicial decisions restrict or prohibit the Company from carrying on its business or from expanding its operations to certain jurisdictions, structural and organizational modifications of the Company’s organization and arrangements may be required, which could have a material adverse effect on the Company, or the Company may be required to cease operations or change the way it conducts business. See Item 1. “Business - Government Regulation.”
The Company’s failure to effectively evaluate and integrate acquisitions may have negative effects on the Company’s results of operations and financial condition.
The Company has completed 45 dental practice acquisitions, six of which have been consolidated into existing Offices and one of which was closed during 2004. The success of future acquisitions will depend on several factors, including the following:
-
Ability to Identify Suitable Dental Practices. Identifying appropriate acquisition candidates and negotiating and consummating acquisitions can be a lengthy and costly process. Furthermore, the Company may compete for acquisition opportunities with companies that have greater resources than the Company. There can be no assurance that suitable acquisition candidates will be identified or that acquisitions will be consummated on terms favorable to the Company, on a timely basis or at all. If a planned acquisition fails to occur or is delayed, the Company’s quarterly financial results may be materially lower than expectations, resulting in a decline, perhaps substantial, in the market price of its Common Stock. In addition, increasing consolidation in the dental management services industry may result in an increase in purchase prices required to be paid by the Company to acquire dental practices.
15
-
Ability to Integrate Dental Practices. The integration of acquired dental practices into the Company’s networks is a difficult, costly and time consuming process which, among other things, requires the Company to attract and retain competent and experienced management and administrative personnel and to implement and integrate reporting and tracking systems, management information systems and other operating systems. In addition, such integration may require the expansion of accounting controls and procedures and the evaluation of certain personnel functions. There can be no assurance that substantial unanticipated problems, costs or delays associated with such integration efforts or with such acquired practices will not occur. There also can be no assurance that the Company will be able to successfully integrate acquired practices in a timely manner or at all, or that any acquired practices will have a positive impact on the Company’s results of operations and financial condition.
The health care industry’s cost-containment initiatives may reduce per patient profit margins.
The health care industry, including the dental services market, is experiencing a trend toward cost containment, as payors seek to impose lower reimbursement rates upon providers. The Company believes that this trend will continue and will increasingly affect the provision of dental services. This may result in a reduction in per-patient and per-procedure revenue from historical levels. Significant reductions in payments to dentists or other changes in reimbursement by payors for dental services may have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition and operating results.
A portion of the Company’s revenue is derived from capitated payment arrangements, which have terms that may adversely affect the Company’s results of operations and financial condition.
In 2009, the Company derived approximately 12.3% of its revenue from capitated managed dental care contracts, and 9.4% of its revenue from associated co-payments. Under a capitated managed dental care contract, the dental practice provides dental services to the members of the plan and receives a fixed monthly capitation payment for each plan member covered for a specific schedule of services regardless of the quantity or cost of services to the participating dental practice which is obligated to provide them, and may receive a co-pay for each service provided. This arrangement shifts the risk of utilization of such services to the dental group practice that provides the dental services. Because the Company assumes responsibility under its Management Agreements for all aspects of the operation of the dental practices other than the practice of dentistry and thus bears all costs of the provision of dental services at the Offices other than compensation and benefits of dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants, the risk of over-utilization of dental services at the Offices under capitated managed dental care plans is effectively shifted to the Company. In contrast, under traditional indemnity insurance arrangements, the insurance company reimburses reasonable charges that are billed for the dental services provided.
Risks associated with capitated managed dental care contracts include principally (i) the risk that the capitation payments and any associated co-payments do not adequately cover the costs of providing the dental services, (ii) the risk that one or more of the P.C.s may be terminated as an approved provider by managed dental care plans with which they contract, (iii) the risk that the Company will be unable to negotiate future capitation arrangements on satisfactory terms with managed care dental plans, and (iv) the risk that large subscriber groups will terminate their relationship with such managed dental care plans which would reduce patient volume and capitation and co-payment revenue. There can be no assurance that the Company will be able to negotiate future capitation arrangements on behalf of P.C.s on satisfactory terms or at all, or that the fees offered in current capitation arrangements will not be reduced to levels unsatisfactory to the Company. Moreover, to the extent that costs incurred by the Company’s affiliated dental practices in providing services to patients covered by capitated managed dental care contracts exceed the revenue under such contracts, the Company’s business, financial condition and operating results may be materially and adversely affected. See Item 1. “Business - Payor Mix.”
If federal or state regulations change to require licensure, the Company’s business model may be adversely affected.
Federal and state laws regulate insurance companies and certain other managed care organizations. Many states, including Colorado, also regulate the establishment and operation of networks of health care providers. In most states, these laws do not apply to discounted-fee-for-service arrangements. These laws also do not generally apply to networks that are paid on a capitated basis, unless the entity with which the network provider is contracting is not a licensed health insurer or other managed care organization. There are exceptions to these rules in some states. For example, certain states require a license for a capitated arrangement with any party unless the risk-bearing entity is a
16
professional corporation that employs the professionals. The Company believes its current activities do not constitute the provision of insurance in Arizona, Colorado or New Mexico, and thus, it is in compliance with the insurance laws of these states with respect to the operation of its Offices. There can be no assurance that these laws will not be changed or that interpretations of these laws by the regulatory authorities in those states, or in the states in which the Company expands, will not require licensure or a restructuring of some or all of the Company’s operations. In the event that the Company is required to become licensed under these laws, the licensure process can be lengthy and time consuming and, unless the regulatory authority permits the Company to continue to operate while the licensure process is progressing, the Company could experience a material adverse change in its business while the licensure process is pending. In addition, many of the licensing requirements mandate strict financial and other requirements, which the Company may not immediately be able to meet. Further, once licensed, the Company would be subject to continuing oversight by and reporting to the respective regulatory agency. The regulatory framework of certain jurisdictions may limit the Company’s expansion into, or ability to continue operations within, such jurisdictions if the Company is unable to modify its operational structure to conform to such regulatory framework. Any limitation on the Company’s ability to expand could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition and operating results.
The Company may see increased costs or lower revenue arising from health care reform.
In March 2010, Congress passed, and the President signed, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act. This act may have a significant impact on health care providers, insurers and others associated with the health care industry, including the Company. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this comprehensive act on its business. Federal and state governments may propose other health care initiatives and revisions to the health care and health insurance systems. It is uncertain what legislative programs, if any will be adopted in the future, or what action Congress or state legislatures may take regarding other health care reform proposals or legislation. In addition, changes in the health care industry, such as the growth of managed care organizations and provider networks, may result in lower payments for the services of the Company’s managed practices.
The substantial value of its intangible assets may impair the Company’s results of operations and financial condition.
At December 31, 2009, intangible assets on the Company’s consolidated balance sheet were $12.8 million, representing 60.4% of the Company’s total assets at that date. If the Company completes additional acquisitions, the Company expects the amount allocable to intangible assets on its balance sheet will increase, which will increase the Company’s amortization expense. In the event of any sale or liquidation of the Company or a portion of its assets, the value of the Company’s intangible assets may not be realized. In addition, the Company evaluates whether events and circumstances have occurred indicating that any portion of the remaining balance of the amount allocable to the Company’s intangible assets may not be recoverable. When factors indicate that the amount allocable to the Company’s intangible assets should be evaluated for possible impairment, the Company may be required to reduce the carrying value of such assets. Any future determination requiring the write off of a significant portion of unamortized intangible assets could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition and operating results.
Professional liability may produce unforeseen expenses and lower operating results.
In recent years, dentists have become subject to an increasing number of lawsuits alleging malpractice. Some of these lawsuits involve large claims and significant defense costs. Any suits involving the Company or dentists at the Offices, if successful, could result in substantial damage awards that may exceed the limits of the Company’s insurance coverage. The Company provides practice management services; it does not engage in the practice of dentistry or control the practice of dentistry by the dentists or their compliance with regulatory requirements directly applicable to providers. There can be no assurance, however, that the Company will not become subject to litigation in the future as a result of the dental services provided at the Offices. The Company maintains professional liability insurance for itself and provides for professional liability insurance covering dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants at the Offices. While the Company believes it has adequate liability insurance coverage, there can be no assurance that the coverage will be adequate to cover losses or that coverage will continue to be available upon terms satisfactory to the Company. In addition, certain types of risks and liabilities, including penalties and fines imposed by governmental agencies, are not covered by insurance. Malpractice insurance, moreover, can be expensive and varies from state to state. Successful malpractice claims could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition and operating results. See Item 1, “Business - Insurance.”
17
Non-competition covenants and other arrangements with the Company’s affiliated dentists may not be enforceable.
The Management Agreements require the P.C.s to enter into employment agreements with dentists which include non-competition provisions typically for three to five years after termination of employment within a specified geographic area, usually a specified number of miles from the relevant Office, and restrict solicitation of employees and patients. Covenants not to compete are generally not favored by courts. In Colorado, covenants not to compete are prohibited by statute with certain exceptions. Permitted covenants not to compete are enforceable in Colorado only to the extent their terms are reasonable in both duration and geographic scope and meet other statutory and common law requirements. Arizona and New Mexico courts have enforced covenants not to compete if their terms are found to be reasonable and meet other statutory and common law requirements. It is thus uncertain whether a court will enforce a covenant not to compete in those states in a given situation. In addition, there is little judicial authority regarding whether a practice management agreement will be viewed as the type of protectable business interest that would permit it to enforce such a covenant or to require a P.C. to enforce such covenants against dentists formerly employed by the P.C. Since the intangible value of a Management Agreement depends primarily on the ability of the P.C. to preserve its business, which could be harmed if employed dentists went into competition with the P.C., a determination that the covenants not to compete contained in the employment agreements between the P.C. and its employed dentists are unenforceable could have a material adverse impact on the Company. See Item 1. “Business - Affiliation Model- Employment Agreements.” In addition, the Company is a party to various agreements with managing dentists who own the P.C.s, which restrict the dentists’ ability to transfer the shares in the P.C.s. See Item 1, “Business - Affiliation Model - Relationship with P.C.s.” There can be no assurance that these agreements will be enforceable in a given situation. A determination that these agreements are not enforceable could have a material adverse effect on the Company.
Seasonality could affect revenue during the latter part of the fiscal year.
The Company’s past financial results have fluctuated somewhat due to seasonal variations in the dental service industry, with revenue typically lower in the fourth calendar quarter. The Company expects this seasonal fluctuation to continue in the future.
The Company relies on a single bank for its Credit Facility, and the Credit Facility contains financial and other covenants that may limit its flexibility.
The Company’s $7.0 million Credit Facility is with a single bank. The Company historically has renewed the Credit Facility and extended the term of the Credit Facility for one additional year annually in the spring and intends to continue this practice in the spring of 2010. In 2009, the bank agreed to extend the Credit Facility but required adjustments to increase the interest rate. Although the Company has utilized this bank for its financing needs for over ten years, there can be no assurances that due to the current environment this bank will not change the terms of the Credit Facility or cease to continue to extend credit to the Company. In addition, the Credit Facility contains financial covenants that require the Company to maintain debt to Adjusted EBITDA and operating cash flow to fixed charges ratios. The Credit Facility also contains other restrictive covenants regarding the incurrence of additional debt, liens, transactions with affiliates, mergers, consolidations and sales of assets and changes in management. These restrictions could limit the Company’s ability to obtain future financing, make capital expenditures, withstand the current or future economic downturns or otherwise take advantage of business opportunities that may arise, any of which could place the Company at a competitive disadvantage relative to its competitors that have less debt and are not subject to such restrictions.
The Company’s inability or failure to protect its intellectual property could have a negative impact on its operating results.
The Company owns one trademark registration (PERFECT TEETH®) that it currently uses and considers to be material to the successful operation of its business. If the Company is unable to protect or preserve the value of this trademark, or other proprietary rights for any reason, its brand and reputation could be impaired or diluted and the Company may see a decline in revenues.
Events or rumors relating to the Company’s brand names could significantly impact its business.
Recognition of the Company’s PERFECT TEETH ® brand name and the association of the brand with quality, comprehensive dental care is an integral part of its business. Any events or rumors that cause patients to no longer
18
associate the brand with quality, comprehensive dental care may materially adversely affect the value of the brand name and demand for dental services at the Offices.
If the Company fails to establish and maintain proper and effective internal controls, the Company’s ability to produce accurate financial statements on a timely basis could be impaired, which would adversely affect its operating results, financial condition and stock price.
Ensuring that the Company has adequate internal financial and accounting controls and procedures in place to produce accurate financial statements on a timely basis is a costly and time-consuming effort that needs to be reevaluated frequently. Failure by the Company to maintain effective internal financial and accounting controls would cause its financial reporting to be unreliable, could have a material adverse effect on its business, operating results, financial condition and cash flows, and could cause the trading price of its Common Stock to fall dramatically. Due to the failure to account for the consolidation of its affiliated P.C.s under the variable interest entity model, there was a material weakness in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008 and 2009. As a result of this material weakness, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer determined that, as of December 31, 2008 and 2009, the Company’s internal controls over financial reporting were not effective to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of the Company’s financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external reporting in accordance with GAAP.
The restatement of the consolidated statements of income has subjected the Company to significant costs and additional risks and uncertainties.
As previously disclosed in a Form 8-K filed March 12, 2010 and as discussed in this Annual Report, the Company decided to restate its previously issued audited consolidated statements of income for each of the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2008 and its unaudited consolidated statements of income for each of the quarters of the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2009. This restatement has subjected the Company to substantial unanticipated costs in the form of accounting and legal fees, in addition to the substantial diversion of time and attention of the Company’s Audit Committee, its Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, and other executive officers in dealing with the restatements. Although the restatements are complete, the Company can give no assurance that it will not incur additional costs associated with the restatements. The restatements also may lead to claims from shareholders and regulators, which may subject the Company to significant costs and diversion of management time.
Nasdaq has stock market listing standards for share prices and market capitalization, and failure to comply with the standards may result in the Company being de-listed from Nasdaq.
The Company’s Common Stock is thinly-held and trades with low volume. If the Company is unable to maintain Nasdaq listing standards, the Company may be forced to de-list with Nasdaq.
ITEM 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
Not applicable to smaller reporting companies.
19
ITEM 2. Properties.
Offices and Facilities
The Company’s corporate headquarters are located at 3801 E. Florida Avenue, Suite 508, Denver, Colorado, in approximately 9,500 square feet occupied under a lease that expires October 31, 2010. The Company believes that this space is adequate for its current needs. The Company also leases real estate at the location of each Office under leases ranging in term from one to five years with options to renew the leases for specific periods subsequent to their original terms. The Company believes the facilities at each of its Offices are adequate for their current level of business. The Company generally anticipates leasing and developing de novo Offices in its current markets rather than significantly expanding the size of its existing Offices.
As of the date of this Annual Report, the Company managed a total of 65 Offices with 45 in Colorado, ten in New Mexico, and ten in Arizona. The Offices typically are located either in shopping centers, professional office buildings or stand-alone buildings. The majority of the de novo Offices are located in supermarket-anchored shopping centers. The Offices have from four to 19 treatment rooms and range in size from 1,200 square feet to 7,400 square feet.
20
Location of Offices
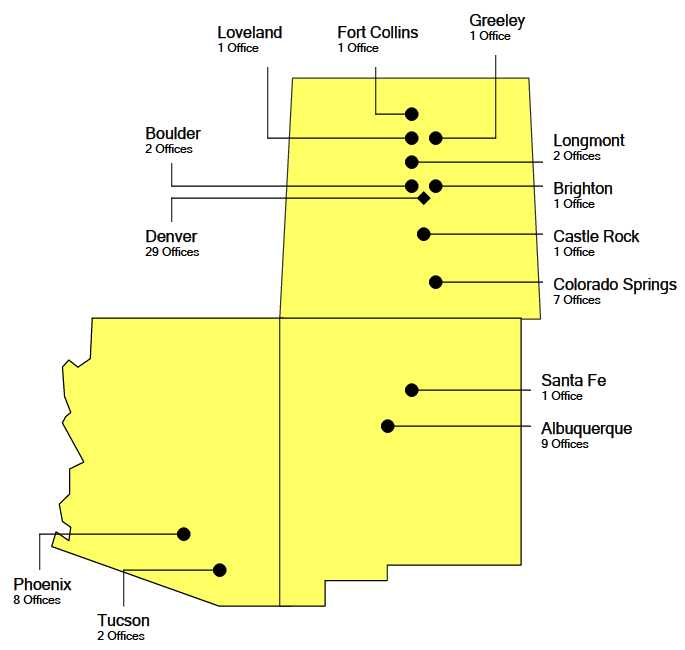
21
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS.
From time to time, the Company is subject to litigation incidental to its business. Such claims, if successful, could result in damage awards exceeding, perhaps substantially, applicable insurance coverage. The Company is not presently a party to any material litigation.
ITEM 4. RESERVED.
22
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES.
Price Range of Common Stock
The Common Stock is quoted on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “BDMS”. The following table sets forth, for the period indicated, the range of high and low sales prices per share of Common Stock, as reported on The Nasdaq Capital Market.
| HIGH | LOW | ||||||
| 2008 | |||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 22.10 | $ | 19.00 | |||
| Second Quarter | 20.00 | 14.00 | |||||
| Third Quarter | 17.37 | 13.34 | |||||
| Fourth Quarter | 14.00 | 10.00 | |||||
| 2009 | |||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 12.25 | $ | 10.01 | |||
| Second Quarter | 15.95 | 10.26 | |||||
| Third Quarter | 18.05 | 12.99 | |||||
| Fourth Quarter | 17.15 | 11.00 | |||||
At March 29, 2010, the last reported sale price of the Company’s Common Stock was $17.13 per share. As of the same date, there were 1,865,532 shares of Common Stock outstanding held by approximately 195 holders of record and approximately 431 beneficial owners.
Dividend Policy
The Company declared the following quarterly cash dividends in 2008 and 2009.
| Date Dividend Paid | Quarterly Dividend Paid per Share | |
| April 11, 2008; July 11, 2008; October 10, 2008; January 9, 2009 | 0.17 | |
| April 10, 2009; July 10, 2009; October 9, 2009; January 8, 2010 | 0.17 | |
On March 12, 2010, the Company announced that its Board of Directors approved an increase in the quarterly dividend to $.20 per share. The payment of dividends in the future is subject to the discretion of the Company’s Board of Directors, and various factors may prevent the Company from paying dividends or require the Company to reduce the dividends. Such factors include the Company’s financial position, capital requirements and liquidity, the existence of a stock repurchase program, any loan agreement restrictions, state corporate law restrictions, results of operations and such other factors the Company’s Board of Directors may consider relevant.
23
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer
The following chart provides information regarding Common Stock repurchases by the Company during the period October 1, 2009 through December 31, 2009.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
| Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased | Average Price Paid per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs (1) | Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs | ||||||||||||
| October 1, 2009 through October 31, 2009 | 2,300 | $ | 15.66 | 1,300 | $ | 334,284 | ||||||||||
| November 1, 2009 through November 30, 2009 | 1,500 | $ | 14.96 | 1,500 | $ | 311,841 | ||||||||||
| December 1, 2009 through December 31, 2009 | 10,806 | $ | 15.33 | 8,056 | $ | 688,351 | ||||||||||
| Total | 14,606 | $ | 15.34 | 10,856 |
| (1) |
The stock repurchase program has been ongoing for more than five years and there are no expiration dates on any of the plans. Common Stock repurchases may be made from time to time as the Company’s management deems appropriate. |
24
Performance Graph*
The following line graph compares the percentage change from December 31, 2004 through December 31, 2009 for (i) the Common Stock, (ii) the Nasdaq Composite Index, (iii) the S&P Healthcare Sector, (iv) the S&P 500 Composite Index and (v) American Dental Partners. Historical stock price performance is not necessarily indicative of future stock price performance.
Comparison of 5-Year Cumulative Total Return **
Assumes Initial Investment of $100

| Description | 12/31/2004 | 12/31/2005 | 12/31/06 | 12/31/07 | 12/31/08 | 12/31/2009 | ||||||||||||||||||
| BIRNER DENTAL | $ | 100.00 | $ | 210.17 | $ | 203.71 | $ | 235.72 | $ | 130.03 | $ | 202.07 | ||||||||||||
| NASDAQ Composite - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Returns | 100.00 | 104.89 | 121.46 | 128.13 | 80.73 | 102.08 | ||||||||||||||||||
| S&P - Healthcare | 100.00 | 106.48 | 114.50 | 122.84 | 94.84 | 113.53 | ||||||||||||||||||
| S&P 500 Index - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Returns | 100.00 | 104.89 | 121.46 | 128.13 | 80.73 | 102.08 | ||||||||||||||||||
| American Dental Partners | 100.00 | 143.03 | 149.45 | 79.35 | 54.91 | 101.99 |
*This Section is not “soliciting material,” is not deemed “filed” with the Securities and Exchange Commission and is not to be incorporated by reference in any filing of the Company under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, whether made before or after the date hereof and irrespective of any general incorporation language in any such filing.
**Total return based on $100 initial investment and reinvestment of dividends.
25
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA.
Not applicable to smaller reporting companies.
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS.
General
The following discussion and analysis relates to factors that have affected the consolidated results of operations and financial condition of the Company for the three years ended December 31, 2009. Reference is made to the Company’s consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto included elsewhere in this Annual Report. This discussion and analysis contains forward-looking statements. Discussions containing such forward-looking statements may be found in the material set forth below and under Item 1, “Business,” Item 5, “Market for the Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities” as well as in this Annual Report generally. Investors and prospective investors are cautioned that any such forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and involve risks and uncertainties. Actual events or results may differ materially from those discussed in the forward-looking statements as a result of various factors, including, without limitation the risk factors set forth in Item 1A, “Risk Factors.” The Company undertakes no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
Overview
The Company was formed as a Colorado corporation in May 1995, and currently provides dental practice management services to 65 Offices in Colorado, New Mexico, and Arizona staffed by 87 dentists and 38 specialists. The Company has acquired 45 practices (six of which were consolidated into existing Offices and one of which was closed during 2004) and opened 28 de novo Offices (one of which was consolidated into an existing Office). The Company derives all of its revenue from its Management Agreements with the P.C.s. In addition, the Company assumes a number of responsibilities when it acquires a new practice or develops a de novo Office, which are set forth in the Management Agreement, as described below. The Company expects to expand in existing markets primarily by enhancing the operating performance of its existing Offices, by developing de novo Offices and by making acquisitions.
Restatement of Certain Financial Information
On March 10, 2010, management and the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors of the Company concluded that the Company’s previously issued audited statements of income for each of the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2008 and its unaudited consolidated statements of income for each of the quarters of the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2009 should be restated. The restatements are a result of a change in accounting relating to the consolidation of the Company’s managed P.Cs.
In prior periods, the Company had been consolidating its managed P.C.s under the consolidation by contract method as originally set forth in EITF 97-02 and the related Staff interpretation of EITF 97-02 since its initial public offering in 1998. The consolidation by contract method as described in EITF 97-02 has a very narrow scope, and the Company believed that it fit within that scope precisely. In 2009, the Staff of the SEC reviewed and issued comments pertaining to the Company’s Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008. In the course of reviewing the SEC’s accounting comments, management of the Company examined the application of the consolidation methodology of ASC Topic 810-10 to the consolidation of its affiliated P.C.s. ASC Topic 810-10 provides that variable interest entity, or VIE, accounting should be considered before consideration of consolidation by contract. Based on its review of ASC Topic 810-10, management began the process of analyzing whether its managed P.C.s should be consolidated under the VIE model and made submissions to the SEC to determine whether VIE accounting under ASC Topic 810-10 was appropriate. After thorough consideration of the questions and comments raised by the SEC in the SEC review process and discussions with the SEC staff regarding the issue, on March 10, 2010, the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors of the Company, in consultation with management and the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, concluded that treatment of the Company’s managed P.C.s as variable interest entities is the appropriate treatment under ASC Topic 810-10. See Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements.
26
The restatements affect the Company’s previously reported revenue and expenses for clinical salaries and benefits paid to dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants. As a result, the Company’s reported revenue increased by the amounts paid to dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants. Clinical salaries and benefits increased by the same dollar amounts as the increase in revenue. The restatements have no impact on the following items:
- Contribution from dental offices
- Operating income
- Net income
- Earnings per share
- Consolidated balance sheets
- Consolidated statements of shareholders equity and comprehensive income
- Consolidated statements of cash flows
- Adjusted EBITDA
In connection with the restatements as described in this Annual Report, management of the Company re-evaluated the effectiveness of its disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting. As a result of this re-evaluation, management determined that there was a control deficiency that constituted a material weakness in the Company’s internal controls. The material weakness is a result of a lack of controls to identify variable interest entities and the consolidation of variable interest entities under GAAP. Accordingly, additional enhancements to the control environment have been implemented in 2010 to ensure that controls related to these material weaknesses are strengthened and will operate effectively. See Item 9A, “Controls and Procedures.”
Components of Revenue and Expenses
Revenue represents the revenue of the Offices, reported at estimated realizable amounts, received from third-party payors and patients for dental services rendered at the Offices, net of contractual and other adjustments. Substantially all of the Company’s patients are insured under third-party payor agreements. The Company’s billing system generates contractual adjustments for each patient encounter based on fee schedules for the patient’s insurance plan. The services provided are attached to the patient’s fee schedule based on the insurance the patient has at the time the service is provided. Therefore, the revenue that is recorded by the billing system is based on insurance contractual amounts. Additionally, each patient at the time of service signs a form agreeing that the patient is ultimately responsible for the contracted fee if the insurance company does not pay the fee for any reason.
Direct expenses consist of clinical salaries and benefits paid to dentists, dental hygienist and dental assistants and the expenses incurred by the Company in connection with managing the Offices, including salaries and benefits of other employees at the Offices, supplies, laboratory fees, occupancy costs, advertising and marketing, depreciation and amortization and general and administrative expenses (including office supplies, equipment leases, management information systems and other expenses related to dental practice operations). The Company also incurs personnel and administrative expenses in connection with maintaining a corporate function that provides management, administrative, marketing, development and professional services to the Offices.
Under each of the Management Agreements, the Company provides business and marketing services at the Offices, including (i) providing capital, (ii) designing and implementing advertising and marketing programs, (iii) negotiating for the purchase of supplies, (iv) staffing, (v) recruiting, (vi) training of non-dental personnel, (vii) billing and collecting patient fees, (viii) arranging for certain legal and accounting services, and (ix) negotiating with managed care organizations. The P.C. is responsible for, among other things, (i) supervision of all dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants, (ii) complying with all laws, rules and regulations relating to dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants, and (iii) maintaining proper patient records. The Company has made, and intends to make in the future, loans to P.C.s to fund their acquisition of dental assets from third parties in order to comply with state dental practice laws. Because the Company’s financial statements are consolidated with the financial statements of the P.C.s, these loans are eliminated in consolidation.
Under the typical Management Agreement, the P.C. pays the Company a management fee equal to the Adjusted Gross Center Revenue of the P.C. less compensation paid to the dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants employed at the Office of the P.C. Adjusted Gross Center Revenue is comprised of all fees and charges booked each month by or on behalf of the P.C. as a result of dental services provided to patients at the Office, less any adjustments for uncollectible accounts, professional courtesies and other activities that do not generate a collectible fee. The Company’s costs include all direct and indirect costs, overhead and expenses relating to the Company’s
27
provision of management services to the Office under the Management Agreement, including (i) salaries, benefits and other direct costs of Company employees who work at the Office, (ii) direct costs of all Company employees or consultants who provide services to or in connection with the Office, (iii) utilities, janitorial, laboratory, supplies, advertising and other expenses incurred by the Company in carrying out its obligations under the Management Agreement, (iv) depreciation expense associated with the P.C.’s assets and the assets of the Company used at the Office, and the amortization of intangible asset value relating to the Office, (v) interest expense on indebtedness incurred by the Company to finance any of its obligations under the Management Agreement, (vi) general and malpractice insurance expenses, lease expenses and dentist recruitment expenses, (vii) personal property and other taxes assessed against the Company’s or the P.C.’s assets used in connection with the operation of the Office, (viii) out-of-pocket expenses of the Company’s personnel related to mergers or acquisitions involving the P.C., (ix) corporate overhead charges or any other expenses of the Company including the P.C.’s pro rata share of the expenses of the accounting and computer services provided by the Company, and (x) a collection reserve in the amount of 5.0% of Adjusted Gross Center Revenue. As a result, substantially all costs associated with the provision of dental services at the Office are borne by the Company, except for the compensation of the dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants who work at the Office. This enables the Company to manage the profitability of the Offices. Each Management Agreement is for a term of 40 years. Each Management Agreement generally may be terminated by the P.C. only for cause, which includes a material default by or bankruptcy of the Company. Upon expiration or termination of a Management Agreement by either party, the P.C. must satisfy all obligations it has to the Company.
Revenue is derived principally from fee-for-service revenue and revenue from capitated managed dental care plans. Fee-for-service revenue consists of P.C. revenue received from indemnity dental plans, preferred provider plans and direct payments by patients not covered by any third-party payment arrangement. Managed dental care revenue consists of P.C. revenue received from capitated managed dental care plans, including capitation payments and patient co-payments. Capitated managed dental care contracts are between dental benefits organizations and the P.C.s. Under the Management Agreements, the Company negotiates and administers these contracts on behalf of the P.C.s. Under a capitated managed dental care contract, the dental group practice provides dental services to the members of the dental benefits organization and receives a fixed monthly capitation payment for each plan member covered for a specific schedule of services regardless of the quantity or cost of services to the participating dental group practice obligated to provide them. This arrangement shifts the risk of utilization of these services to the dental group practice providing the dental services. Because the Company assumes responsibility under the Management Agreements for all aspects of the operation of the dental practices (other than the practice of dentistry) and thus bears all costs of the P.C.s associated with the provision of dental services at the Office (other than compensation of dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants), the risk of over-utilization of dental services at the Office under capitated managed dental care plans is effectively shifted to the Company. In addition, dental group practices participating in a capitated managed dental care plan often receive supplemental payments for more complicated or elective procedures. In contrast, under traditional indemnity insurance arrangements, the insurance company pays whatever reasonable charges are billed by the dental group practice for the dental services provided. See Item 1. “Business - Payor Mix.”
The Company seeks to increase its fee-for-service revenue by increasing the patient volume at existing Offices through effective advertising and marketing programs, adding additional specialty services, by opening de novo Offices and by making select acquisitions of dental practices. The Company seeks to supplement this fee-for-service revenue with revenue from contracts with capitated managed dental care plans. Although the Company’s fee-for-service business generally provides a greater margin than its capitated managed dental care business, capitated managed dental care business increases facility utilization and dentist productivity. The relative percentage of the Company’s revenue derived from fee-for-service business and capitated managed dental care contracts varies from market to market depending on the availability of capitated managed dental care contracts in any particular market and the Company’s ability to negotiate favorable contractual terms. In addition, the profitability of capitated managed dental care revenue varies from market to market depending on the level of capitation payments and co-payments in proportion to the level of benefits required to be provided.
The Company’s policy is to collect any patient co-payments at the time the service is provided. If the patient owes additional amounts that are not covered by insurance, Offices collect by sending monthly invoices, placing phone calls and sending collection letters. Interest at 18% APR is charged on all account balances greater than 60 days old. Patient accounts receivable in excess of $50 that are over 120 days and that appear are not collectible are written off as bad debt and sent to an outside collections agency.
28
Results of Operations
The Company has grown primarily through the ongoing development of a dense dental practice network and the implementation of its dental practice management model. Revenue was $59.4 million in 2007, $59.0 million in 2008 and $59.6 million in 2009. Contribution from the dental Offices was $8.7 million in 2007, $7.3 million in 2008 and $7.8 million in 2009. Net income was $2.4 million in 2007, $1.8 million in 2008 and $1.9 million in 2009. The Company attributes its decrease in revenue, contribution from dental Offices and net income in 2008 to a general weakness in the economy in the Company’s markets as reflected by a reduced number of new patient visits and patient procedures, and in particular fewer crown and bridge procedures. For 2009, same store revenue (based on 60 Offices) decreased by $316,000 from 2008. The Company attributes this decrease to continued general weakness in the economy in the Company’s markets as reflected by reduced number of new patient visits and patient procedures, and in particular fewer crown and bridge procedures.
For the year ended December 31, 2009, revenue increased to $59.6 million compared to $59.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, an increase of $557,000 or 0.9%. This increase was attributable to an increase in same store (based on 60 Offices) specialty dentistry revenue of $641,000, $598,000 in revenue from two Offices acquired in Tucson, Arizona in the fourth quarter of 2009 and $276,000 of additional revenue from a de novo Office that opened in May 2008, offset by a decrease in same store general dentistry revenue of $957,000.
For the year ended December 31, 2008, revenue decreased to $59.0 million compared to $59.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2007, a decrease of $371,000 or 0.6%. This decrease was attributable to a decrease in same store (based on 60 Offices) general dentistry revenue of $1.4 million offset by an increase in same store specialty dentistry revenue of $875,000, general dentistry revenue from a de novo Office that opened in May 2009 of $105,000 and specialty dentistry revenue from the de novo Office of $81,000.
The Company’s earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization and non cash expense associated with stock-based compensation (“Adjusted EBITDA”) increased $101,000 or 1.5% to $6.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 from $6.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2008. Approximately $73,000 of the $101,000 increase in Adjusted EBITDA from 2008 to 2009 is related to the two acquisitions in Tucson, Arizona in the fourth quarter of 2009. Excluding the acquisitions, Adjusted EBITDA was mostly flat from 2008 to 2009 and down from 2007 mostly due to the continued general weakness in the economy in its markets. Although Adjusted EBITDA is not a GAAP measure of performance or liquidity, the Company believes that it may be useful to an investor in evaluating the Company’s ability to meet future debt service, capital expenditures and working capital requirements. However, investors should not consider these measures in isolation or as a substitute for operating income, cash flows from operating activities or any other measure for determining the Company’s operating performance or liquidity that is calculated in accordance with GAAP. In addition, because Adjusted EBITDA is not calculated in accordance with GAAP, it may not necessarily be comparable to similarly titled measures employed by other companies. A reconciliation of Adjusted EBITDA to net income can be made by adding depreciation and amortization expense - Offices, depreciation and amortization expense – corporate, stock-based compensation expense, interest expense/(income), net, and income tax expense to net income as in the table below.
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||
| RECONCILIATION OF ADJUSTED EBITDA: | |||||||||||
|
Net income |
$ | 2,435,107 | $ | 1,790,409 | $ | 1,925,066 | |||||
|
Add back: |
|||||||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization - Offices |
2,541,995 | 2,445,956 | 2,423,788 | ||||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization - corporate |
110,270 | 96,366 | 86,809 | ||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
729,394 | 731,607 | 902,409 | ||||||||
|
Interest expense, net |
365,140 | 282,267 | 174,582 | ||||||||
|
Income tax expense |
1,650,342 | 1,414,962 | 1,350,301 | ||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 7,832,248 | $ | 6,761,567 | $ | 6,862,955 | |||||
29
At December 31, 2009, the Company’s total assets of $21.3 million included $12.8 million of identifiable intangible assets related to the Management Agreements. At that date, the Company’s total shareholders’ equity was $7.6 million. The Company’s retained earnings as of December 31, 2009 were approximately $7.5 million and the Company had a working capital deficit on that date of approximately $2.1 million. During 2009, the Company had capital expenditures of $1.1 million, acquired three dental Offices for $1.4 million and purchased approximately $930,000 of Common Stock while decreasing total bank debt by approximately $1.6 million.
The Company’s revenue from capitated managed dental care plans (including revenue associated with co-payments) was 21.7% of total revenue in 2009, compared to 22.9% in 2008 and 22.3% in 2007.
The following table sets forth the percentages of revenue represented by certain items reflected in the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Income. The information that follows should be read in conjunction with the Company’s consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto.
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2007 (Restated) |
2008 (Restated) |
2009 | ||||||||||
| Revenue | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||
| Direct expenses: | ||||||||||||
|
Clinical salaries and benefits |
56.2 | 58.0 | 57.7 | |||||||||
|
Dental supplies |
3.9 | 4.0 | 3.7 | |||||||||
|
Laboratory fees |
4.4 | 4.6 | 4.4 | |||||||||
|
Occupancy |
7.7 | 8.1 | 8.3 | |||||||||
|
Advertising and marketing |
1.1 | 0.7 | 0.8 | |||||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization |
4.3 | 4.1 | 4.1 | |||||||||
|
General and administrative |
7.7 | 8.0 | 7.9 | |||||||||
| 85.4 | 87.7 | 86.9 | ||||||||||
| Contribution from dental offices | 14.6 | 12.3 | 13.1 | |||||||||
| Corporate expenses: | ||||||||||||
|
General and administrative |
6.9 | (1) | 6.2 | (1) | 7.2 | (1) | ||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization |
0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | |||||||||
| Operating income | 7.5 | 5.9 | 5.8 | |||||||||
| Interest expense, net | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.3 | |||||||||
| Income before income taxes | 6.9 | 5.4 | 5.5 | |||||||||
| Income tax expense | 2.8 | 2.4 | 2.3 | |||||||||
| Net income | 4.1 | % | 3.0 | % | 3.2 | % | ||||||
| (1) |
Corporate expenses - general and administrative includes $324,120 of equity compensation for a stock award and $405,274 of stock-based compensation expense pursuant to ASC Topic 718 for the year ended December 31, 2007, $731,607 of stock- based compensation expense pursuant to ASC Topic 718 for the year ended December 31, 2008 and $657,033 of stock- based compensation expense pursuant to ASC Topic 718 and $245,376 related to a long-term incentive program for the year ended December 31, 2009. |
30
Year Ended December 31, 2009 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2008
Revenue
Revenue increased to $59.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 compared to $59.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, an increase of $557,000 or 0.9%. This increase is attributable to an increase in same store (based on 60 Offices) specialty dentistry revenue of $641,000, $598,000 in revenue from Offices acquired during the fourth quarter of 2009 and $276,000 of additional revenue from a de novo Office that opened in May 2008 offset by a decrease in same store general dentistry revenue of $957,000.
Direct Expenses
Clinical salaries and benefits. Clinical salaries and benefits increased to $34.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 compared to $34.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, an increase of $109,000 or 0.3%. This increase is primarily attributable to an increase in specialty dentist wages of $359,000, general dentist wages of $128,000 and health insurance of $247,000 offset by reduced administrative wages of $227,000, dental hygienist wages of $168,000, dental assistant wages of $148,000, workers compensation insurance of $40,000 and payroll taxes of $34,000. As a percentage of revenue, clinical salaries and benefits decreased to 57.7% in 2009 from 58.0% in 2008.
Dental supplies. Dental supplies decreased to $2.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 compared to $2.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, a decrease of $140,000 or 5.9%. This decrease is attributable to three factors: (1) fewer new dentists requesting initial dental supply inventories; (2) a 3% rebate from the Company’s primary dental supply vendor that will be effective through 2010; and (3) a concentrated effort that began in January 2009 to reduce dental supply expense through the implementation of a new process for the monthly dental supply budget. As a percentage of revenue, dental supplies decreased to 3.7% in 2009 from 4.0% in 2008.
Laboratory fees. Laboratory fees decreased to $2.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 compared to $2.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, a decrease of $107,000 or 3.9%. This decrease is primarily due to lower laboratory fees that were negotiated with the Company’s significant vendors in December 2008. As a percentage of revenue, laboratory fees decreased to 4.4% in 2009 from 4.6 % in 2008.
Occupancy. Occupancy expenses increased to $4.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 from $4.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, an increase of $145,000 or 3.0%. This increase was due to increased rental payments resulting from the renewal of Office leases at current market rates for Offices whose leases expired subsequent to 2008 as well as $52,000 from two Offices acquired during the fourth quarter of 2009 and $35,000 additional occupancy expense from a de novo Office that opened in May 2008. As a percentage of revenue, occupancy expense increased to 8.3 % in 2009 from 8.1 % in 2008.
Advertising and marketing. Advertising and marketing expenses increased to $463,000 for the year ended December 31, 2009 from $433,000 for the year ended December 31, 2008, an increase of $29,000 or 6.8%. This increase is attributable to a radio advertising campaign the Company initiated in May 2009 in its Denver and Colorado Springs, Colorado and Albuquerque, New Mexico markets. The cost of the campaign was $118,000 for the year. In addition to the radio advertising, the Company also started advertising on the internet and spent $25,000 in 2009. The radio and internet advertising campaigns were partially offset by a decrease of $112,000 for yellow page advertising as a result of the Company’s negotiation of more favorable rates. As a percentage of revenue, advertising and marketing increased to 0.8% in 2009 from 0.7% in 2008.
Depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization expenses incurred at the Offices remained constant at $2.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008. As a percentage of revenue, depreciation and amortization remained constant at 4.1% in 2009 and 2008.
General and administrative. General and administrative expenses attributable to the Offices remained constant at $4.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008. As a percentage of revenue, Office general and administrative expenses decreased to 7.9% in 2009 from 8.0% in 2008.
31
Contribution from Dental Offices
As a result of the increased revenue and flat direct expenses, contribution from dental Offices increased to $7.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 from $7.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, an increase of $557,000 or 7.7 %. As a percentage of revenue, contribution from dental Offices increased to 13.1% in 2009 from 12.3% in 2008.
Corporate Expenses
Corporate expenses - general and administrative. Corporate expenses - general and administrative increased to $4.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 from $3.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, an increase of $604,000 or 16.4%. This increase is primarily attributable to an increase in executive bonuses of $174,000 and $472,000 accrued for a long-term incentive plan for the executives. As a percentage of revenue, corporate expenses - general and administrative increased to 7.2% in 2009 compared to 6.2% in 2008.
Corporate expenses - depreciation and amortization. Corporate expenses - depreciation and amortization decreased to 87,000 for the year ended December 31, 2009 from $96,000 for the year ended December 31, 2008, a decrease of $10,000 or 9.9%. This decrease was primarily the result of older assets becoming fully depreciated somewhat offset by the addition of new depreciable assets. As a percentage of revenue, corporate expenses - depreciation and decreased to 0.1% in 2009 compared to 0.2% in 2008.
Operating Income
As a result of the above, operating income decreased to $3.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 from $3.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, a decrease of $38,000 or 1.1%. As a percentage of revenue, operating income decreased to 5.8% in 2009 from 5.9% in 2008.
Interest Expense/(Income), Net
Interest expense, net decreased to $175,000 for the year ended December 31, 2009 from $282,000 for the year ended December 31, 2008, a decrease of $108,000 or 38.2%. This decrease in interest expense is attributable to a reduction in the principal amount of the term loan related to the “dutch auction” tender offer on October 5, 2006 (the “Term Loan”) and reduced borrowings on the Credit Facility. As a percentage of revenue, interest expense, net decreased to 0.3% in 2009 from 0.5% in 2008.
Net Income
As a result of the above, the Company’s net income was $1.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 compared to net income of $1.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, an increase of $135,000 or 7.5%. As a percentage of revenue, net income increased to 3.2% in 2009 from 3.0% in 2008. Net income for the year ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 was net of income tax expense of $1.4 million.
Year Ended December 31, 2008 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2007
Revenue
Revenue decreased to $59.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to $59.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2007, a decrease of $371,000 or 0.6%. This decrease is attributable to a decrease in same store (based on 60 Offices) revenue from general dentistry of $1,432,000 offset by an increase in same store revenue from specialty dentistry of $875,000 along with a de novo Office the Company opened in May 2008 generating $186,000 in revenue. The Company attributes the decrease in revenue to general weakness in the economy in the Company’s markets as reflected by a reduced number of patient procedures and in particular fewer crown and bridge procedures.
Direct Expenses
Clinical salaries and benefits. Clinical salaries and benefits increased to $34.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to $33.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2007, an increase of $880,000 or 2.6%. This increase is primarily attributable to an increase in specialty dentist wages of $354,000, health insurance
32
of $212,000, dental hygiene wages of $144,000, payroll taxes of $131,000, accrued vacation of $84,000 and general wage increases granted during 2008 offset by a decrease in general dentist wages of $147,000. As a percentage of revenue, clinical salaries and benefits increased to 58.0% in 2008 from 56.2% in 2007.
Dental supplies. Dental supplies increased to $2.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to $2.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2007, an increase of $55,000 or 2.4%. This increase includes a $24,000 initial supply purchase for a de novo Office opened during 2008. As a percentage of revenue, dental supplies increased to 4.0% in 2008 from 3.9% in 2007.
Laboratory fees. Laboratory fees increased to $2.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to $2.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2007, an increase of $108,000 or 4.1%. This increase is primarily related to overall increased material costs for crowns and bridges and an increased number of implant procedures, which carry an increased laboratory fee. As a percentage of revenue, laboratory fees increased to 4.6% in 2008 from 4.4% in 2007.
Occupancy. Occupancy expenses increased to $4.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 from $4.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2007, an increase of $198,000 or 4.3%. This increase was due to increased rental payments resulting from the renewal of Office leases at current market rates for Offices whose leases expired subsequent to 2007 as well as $43,000 from the addition of one de novo Office opened during 2008. As a percentage of revenue, occupancy expense increased to 8.1% in 2008 from 7.7% in 2007.
Advertising and marketing. Advertising and marketing expenses decreased to $433,000 for the year ended December 31, 2008 from $678,000 for the year ended December 31, 2007, a decrease of $245,000 or 36.1%. This decrease is attributable to a shift away from television and print advertising in 2007 that the Company did not conduct in 2008. As a percentage of revenue, advertising and marketing decreased to 0.7% in 2008 from 1.1% in 2007.
Depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization expenses incurred at the Offices decreased to $2.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 from $2.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2007, a decrease of $96,000 or 3.8%. This decrease was primarily the result of 2007 including amortization expense of $104,000 at one Office in order to recognize an impairment charge that was necessary in order to write down its value to market. As a percentage of revenue, depreciation and amortization decreased to 4.1% in 2008 from 4.3% in 2007.
General and administrative. General and administrative expenses attributable to the Offices increased to $4.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 from $4.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2007, an increase of $139,000 or 3.0%. This increase was primarily related to increased bad debt expense of $70,000 and increased repairs and maintenance of $58,000. As a percentage of revenue, Office general and administrative expenses increased to 8.0% in 2008 from 7.7% in 2007.
Contribution from Dental Offices
As a result of the decreased revenue and increased direct expenses, contribution from dental Offices decreased to $7.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 from $8.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2007, a decrease of $1.4 million or 16.2%. As a percentage of revenue, contribution from dental Offices decreased to 12.3% in 2008 from 14.6% in 2007.
Corporate Expenses
Corporate expenses - general and administrative. Corporate expenses - general and administrative decreased to $3.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 from $4.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2007, a decrease of $432,000 or 10.5%. This decrease is primarily attributable to a reduction in executive bonuses of $507,000. As a percentage of revenue, corporate expenses - general and administrative decreased to 6.2 % in 2008 compared to 6.9% in 2007.
Corporate expenses - depreciation and amortization. Corporate expenses - depreciation and amortization decreased to 96,000 for the year ended December 31, 2008 from $110,000 for the year ended December 31, 2007, a decrease of $14,000 or 12.6%. This decrease was primarily the result of older assets becoming fully depreciated somewhat offset by the addition of new depreciable assets. As a percentage of revenue, corporate expenses - depreciation and amortization remained constant at 0.2% in 2008 and 2007.
33
Operating Income
As a result of the above, operating income decreased to $3.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 from $4.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2007, a decrease of $963,000 or 21.6%. As a percentage of revenue, operating income decreased to 5.9% in 2008 from 7.5% in 2007.
Interest Expense/(Income), Net
Interest expense, net decreased to $282,000 for the year ended December 31, 2008 from $365,000 for the year ended December 31, 2007, a decrease of $83,000 or 22.7%. This decrease in interest expense is attributable to a reduction in the principal amount of the Term Loan combined with reduced interest rates. As a percentage of revenue, interest expense, net decreased to 0.5% in 2008 from 0.6% in 2007.
Net Income
As a result of the above, the Company’s net income was $1.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to net income of $2.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2007, a decrease of $645,000 or 26.5%. As a percentage of revenue, net income decreased to 3.0% in 2008 from 4.1% in 2007. Net income for the year ended December 31, 2008 was net of income tax expense of $1.4 million while net income for the year ended December 31, 2007 was net of income tax expense of $1.7 million.
Critical Accounting Policies
The Company’s financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, which require the Company to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and the related disclosures. A summary of those significant accounting policies can be found in the notes to consolidated financial statements. The estimates used by management are based upon the Company’s historical experiences combined with management’s understanding of current facts and circumstances. Certain of the Company’s accounting policies are considered critical as they are both important to the portrayal of the Company’s financial condition and the results of its operations and require significant or complex judgments on the part of management. Management has not determined how reported amounts would differ based on the application of different accounting policies. Management has also not determined the likelihood that materially different amounts could be reported under different conditions or using different assumptions. Management believes that the following represent the critical accounting policies of the Company as described in Financial Reporting Release No. 60, “Cautionary Advice Regarding Disclosure About Critical Accounting Policies”, which was issued by the SEC:
Variable Interest Entities
The Company prepares its consolidated financial statements in accordance with ASC 810, which provides for consolidation of variable interest entities of which the Company is the primary beneficiary. The Company has concluded that the P.C.s meet the definition of variable interest entities as defined by this standard and that the Company is the primary beneficiary of these variable interest entities. The Company concluded that the P.C.s meet the definition of variable interest entities because the equity investment at risk by each P.C. owner, which generally has not been more than $100, is not sufficient on a quantitative or qualitative basis to support each P.C.’s activities without additional financial support from the Company, which is provided through (i) the Company’s advancement of operating costs on behalf of the P.C.s and forgoing any amounts due the Company from the P.C.s under the Management Agreements when the P.C.s lack sufficient cash flow to pay the management fees in full and (ii) the Company’s capital investments in facilities and dental equipment used by the P.C.s in the operation of their dental practices. The Company determined that it is the primary beneficiary, as defined in ASC 810-10-38, of the P.C.s because (i) it absorbs losses of the P.C.s by forgoing the management fees, (ii) through the Management Agreements, the Company has the power to direct the activities of the P.C.s that most significantly impact the P.C.s’ economic performance, provides business and marketing services at the Offices, including providing capital, payment of all Center Expenses (as defined in the Management Agreements), designing and implementing marketing programs, negotiating for the purchase of supplies, staffing, recruiting, training of non-dental personnel, billing and collecting patient fees, arranging for certain legal and accounting services, and negotiating with managed care organizations, and (iii) no other party provides financial support to the P.C.s, and the P.C.s have no independent ability to support themselves. Accordingly, the net assets and results of operations of the P.C.s are included in the consolidated financial statements of the Company, and all transactions between the P.C.s and the Company, such as the management fees the Company charges, have been eliminated.
Impairment of Intangible and Long-lived Assets
At December 31, 2009, intangible assets on the Company’s consolidated balance sheet were $12.8 million, representing 60.4% of the Company’s total assets at that date. The Company's dental practice acquisitions involve the purchase of tangible and intangible assets and the assumption of certain liabilities of the acquired Offices. As part of the purchase price allocation, the Company allocates the purchase price to the tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed, based on estimated fair market values. Identifiable intangible assets include the Management Agreement. The Management Agreement represents the Company's right to manage the Offices during the 40-year term of the agreement. The assigned value of the Management Agreement is amortized using the straight-line method over a period of 25 years. The Company reviews the recorded amount of intangible assets and other long-lived assets for impairment for each Office whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying
34
amount of the assets may not be recoverable. If this review indicates that the carrying amount of the assets may not be recoverable as determined based on the undiscounted cash flows of each Office, whether acquired or developed, the carrying value of the asset is reduced to fair value. Among the factors that the Company will continually evaluate are unfavorable changes in each Office, relative market share and local market competitive environment, current period and forecasted operating results, cash flow levels of Offices and the impact on the revenue earned by the Company, and the legal and regulatory factors governing the practice of dentistry. As of December 31, 2007, the Company determined that intangible assets were overstated by approximately $104,000. This amount was determined by comparing the intangible asset and property and equipment value at one Office to an independent appraised value for that Office. As a result, the Company recognized an impairment charge of $104,000 in amortization expense in December 2007.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
The Company’s allowance for doubtful accounts reflects a reserve that reduces customer accounts receivable to the net amount estimated to be collectible. Estimating the credit-worthiness of customers and the recoverability of customer accounts requires management to exercise considerable judgment. In estimating uncollectible amounts, management considers factors such as general economic and industry-specific conditions, historical customer performance and anticipated customer performance. While management considers the Company’s processes to be adequate to effectively quantify its exposure to doubtful accounts, changes in economic, industry or specific customer conditions may require the Company to adjust its allowance for doubtful accounts.
Deferred Income Taxes
Deferred income taxes are recognized for the expected tax consequences in future years for differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their financial reporting amounts, based upon enacted tax laws and statutory tax rates applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to affect taxable income. The Company’s significant deferred tax assets are related to accruals not currently deductible, allowance for doubtful accounts and depreciation expense for tax which is less than depreciation expense for books. The Company has not established a valuation allowance to reduce deferred tax assets as the Company expects to fully recover these amounts in future periods. The Company’s significant deferred tax liability is the result of intangible asset amortization expense for tax being greater than the intangible asset amortization expense for books. Management reviews and adjusts those estimates annually based upon the most current information available. However, because the recoverability of deferred taxes is directly dependent upon the future operating results of the Company, actual recoverability of deferred taxes may differ materially from management’s estimates.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The Company finances its operations and growth through a combination of cash provided by operating activities and a Credit Facility.
Net cash provided by operating activities was $5.7 million, $5.6 million and $5.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2009, the Company’s cash provided by operating activities excluding net income and non-cash items consisted primarily of an increase in accounts payable, accrued expenses and accrued payroll of $739,000 and a decrease in deferred charges and other assets of $7,000, offset by an increase in accounts receivable (net of provision for doubtful accounts) of $844,000, a decrease of income taxes payable of $104,000 and an increase in prepaid expenses and other assets of $15,000. During the year ended December 31, 2008, the Company’s cash provided by operating activities excluding net income and non-cash items consisted primarily of a decrease in prepaid expenses and other assets of $202,000, a decrease in deferred charges and other assets of $11,000 and an increase in income taxes payable/receivable of $398,000, offset by a decrease in accounts payable, accrued expenses and accrued payroll of $263,000, an increase in accounts receivable (net of provision for doubtful accounts) of $597,000, and a decrease in other long-term obligations of $32,000. During the year ended December 31, 2007, the Company’s cash provided by operating activities excluding net income and non-cash items consisted primarily of an increase in accounts payable, accrued expenses and accrued payroll of $22,000, a decrease in deferred charges and other assets of $10,000, offset by an increase in accounts receivable (net of provision for doubtful accounts) of $569,000, a decrease in income taxes payable/receivable of $141,000, an increase in prepaid expenses and other assets of $23,000 and a decrease in other long-term obligations of $35,000.
35
Net cash used in investing activities was $714,000, $1.1 million and $2.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2009, the Company invested $1.4 million to acquire three dental Offices and loaned $192,000 in connection with one of the acquisitions. The Company also invested $1.1 million to purchase additional property and equipment including $299,000 to move one of its existing Offices and $186,000 to install digital x-rays at four Offices. Additionally, the Company invested $148,000 in the development of a de novo Office. During the year ended December 31, 2008, the Company invested $754,000 in the purchase of additional property and equipment including $155,000 in a new time collection system for its payroll system and $159,000 for a major remodel of one of its existing Offices. Additionally, the Company invested $372,000 in the development of a de novo Office. During the year ended December 31, 2007, the Company invested $667,000 in the purchase of additional property and equipment and $48,000 in the development of de novo Offices.
For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, net cash used in financing activities was $4.9 million, $4.2 million and $3.4 million, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2009, net cash used in financing activities was comprised of $457,000 of proceeds from the exercise of Common Stock options and $1,000 from the tax benefit of Common Stock options exercised. This was offset by $930,000 for the purchase of Common Stock, $1.3 million for the payment of Common Stock dividends, $706,000 to pay down the Credit Facility and $920,000 to pay down the Term Loan. For the year ended December 31, 2008, net cash used in financing activities was comprised of a $2.1 million increase in borrowings under the Credit Facility, $327,000 of proceeds from the exercise of Common Stock options and $11,000 from the tax benefit of Common Stock options exercised. This was offset by $4.4 million for the purchase of Common Stock, $1.4 million for the payment of Common Stock dividends, and $920,000 to pay down the Term Loan. For the year ended December 31, 2007, net cash used in financing activities was comprised of $1.3 million of proceeds from the exercise of Common Stock options and $955,000 from the tax benefit of Common Stock options exercised. This was offset by $4.1 million for the purchase of Common Stock, $1.2 million for the payment of Common Stock dividends, $920,000 to pay down the Term Loan, a $798,000 decrease in borrowings under the Credit Facility and $34,000 in repayments of long-term debt.
On June 30, 2009, the Company amended its Credit Facility. The amended Credit Facility extends the expiration of the credit agreement from May 31, 2010 to May 31, 2011. The Credit Facility allows the Company to borrow, on a revolving basis, an aggregate principal amount not to exceed $7.0 million at either, or a combination of, the lender’s Base Rate or at LIBOR plus a LIBOR rate margin, at the Company’s option. The Base Rate computes interest at the higher of the lender’s “prime rate” or the Federal Funds Rate plus a margin. The amendment adjusted the Base Rate margin from 0.5% to 2.5%. The LIBOR option computes interest at the LIBOR rate as of the date such LIBOR rate loan was made plus a LIBOR rate margin. The amendment states that the LIBOR rate is the higher of 1.5% or the LIBOR rate and the margin is adjusted from 1.25% to 3.875%. As of December 31, 2009, the Company’s LIBOR borrowing rate was 5.375% and the Base Rate borrowing rate was 5.75%. Management believes that the LIBOR and Base Rate margins increased as a result of the lender’s increased cost of funds and not because of the Company’s credit quality. A commitment fee on the average daily unused amount of the revolving loan commitment during the preceding quarter is also assessed and increased from 0.25% to 0.40% as of June 1, 2009 as a result of the amendment. The Company may prepay any Base Rate loan at any time and any LIBOR rate loan upon not less than three business days prior written notice given to the lender, but the Company is responsible for any loss or cost incurred by the lender in liquidating or employing deposits required to fund or maintain the LIBOR rate loan. At December 31, 2009, the Company had $3.7 million outstanding and $3.3 million available for borrowing under the Credit Facility. This consisted of $2.0 million outstanding under the LIBOR rate option and $1.7 million outstanding under the Base Rate option. The Credit Facility requires the Company to comply with certain covenants and financial ratios. At December 31, 2009, the Company was in full compliance with all of its covenants under the Credit Facility.
In October 2006, the Company accepted for payment, at a purchase price of $21.75 per share, 212,396 shares of its Common Stock that were properly tendered and not withdrawn pursuant to the Company’s “dutch auction” tender offer. The 212,396 shares purchased were comprised of 175,000 shares the Company offered to purchase and 37,396 shares that were purchased pursuant to the Company's right to purchase up to an additional 2% of the outstanding shares as of August 31, 2006, without extending the tender offer in accordance with applicable securities laws. These shares represented approximately 9.2% of the shares outstanding as of September 30, 2006. The tender offer was funded by a $4.6 million Term Loan. Under the Term Loan, $2.3 million was borrowed at a fixed interest rate of 7.05% and the remaining $2.3 million was borrowed at a floating interest rate of LIBOR plus 1.5%. The principal amount borrowed will be paid quarterly in 20 equal payments of approximately $230,000 plus interest beginning December 31, 2006. The Term Loan matures on September 30, 2011.
36
The Company has paid the following quarterly cash dividends.
| Date Dividend Paid | Quarterly Dividend Paid per Share | |
| April 11, 2008; July 11, 2008; October 10, 2008; January 9, 2009 | 0.17 | |
| April 10, 2009; July 10, 2009; October 9, 2009; January 8, 2010 | 0.17 |
The Company believes that cash generated from operations and borrowings under its Credit Facility will be sufficient to fund its anticipated working capital needs, capital expenditures and dividend payments for at least the next 12 months. In order to meet its long-term liquidity needs, the Company may need to issue additional equity and debt securities, subject to market and other conditions. There can be no assurance that such additional financing will be available on terms acceptable to the Company or at all. The failure to raise the funds necessary to finance its future cash requirements could adversely affect the Company’s ability to pursue its strategy and could negatively affect its operations in future periods. See Item 1A, “Risk Factors - Need for Additional Capital; Uncertainty of Additional Financing” in this Annual Report.
The Company from time to time may purchase its Common Stock on the open market or in privately negotiated transactions. During 2007, the Company, in 27 separate transactions, repurchased 196,791 shares of its Common Stock for a total consideration of approximately $4.1 million at prices ranging from $18.50 to $24.33 per share. In August 2007, the Company repurchased 100,000 shares at a price of $20.75 per share through a private transaction that was approved by the Board of Directors. In December 2007, the Company repurchased 49,204 shares at a price of $21.00 per share through a private transaction that was approved by the Board of Directors. During 2008, the Company, in 47 separate transactions, repurchased 292,538 shares of its Common Stock for total consideration of approximately $4.4 million at prices ranging from $10.47 to $21.00 per share. In February 2008, the Company repurchased 3,210 shares at $21.00 per share in a private transaction that was approved by the Board of Directors. During 2009, the Company, in 108 separate transactions repurchased 61,702 shares of its Common Stock for total consideration of approximately $930,000 at prices ranging at prices ranging from $10.02 to $17.00 per share. As of December 31, 2009, approximately $688,000 of the previously authorized amount was available for these purchases.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In September 2006, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for fair value measurements and disclosures which defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value and expands disclosures related to assets and liabilities measured at fair value. In February 2008, the FASB issued additional authoritative guidance for fair value measurements which delayed the effective date of the authoritative guidance for fair value measurements to fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2008 for all nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities that are recognized or disclosed at fair value in the financial statements on a nonrecurring basis. The Company adopted all of the provisions of the authoritative guidance for fair value measurements on January 1, 2008 with the exception of the application of the guidance to non-recurring nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities which the Company adopted on January 1, 2009. The adoption did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In December 2007, the FASB issued revised authoritative guidance for business combinations which establishes principles and requirements for how an acquirer in a business combination transaction recognizes and measures in its financial statements the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, and any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree at the acquisition date. The provisions of the guidance also establish disclosure requirements which will enable financial statement users to evaluate the nature and financial effects of the business combination. In April 2009, the FASB issued additional authoritative guidance for business combinations relating to the initial recognition and measurement, subsequent measurement and accounting and disclosures of assets and liabilities that arise from contingencies in a business combination. The authoritative guidance for business combinations is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. The Company adopted all of the provisions of the authoritative guidance for business combinations on January 1, 2009. The adoption resulted in the recording of contingent liabilities associated with the Company’s acquisitions of dental Offices during the year ended December 31, 2009.
In December 2007, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for consolidations which states that accounting and reporting for minority interests will be recharacterized as noncontrolling interests and classified as a component of equity. The guidance also establishes reporting requirements that provide sufficient disclosures that clearly identify and distinguish between the interests of the parent and the interests of the noncontrolling owners. The guidance
37
applies to all entities that prepare consolidated financial statements, except not-for-profit organizations, but will affect only those entities that have an outstanding noncontrolling interest in one or more subsidiaries or that deconsolidate a subsidiary. This guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. The Company adopted this guidance as of January 1, 2009. The adoption did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In March 2008, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for derivatives and hedging which requires companies with derivative instruments to disclose information that should enable financial statement users to understand how and why a company uses derivative instruments, how derivative instruments and related hedged items are accounted for under the guidance, and how derivative instruments and related hedged items affect a company’s financial position, financial performance and cash. This guidance is effective for fiscal years and interim periods beginning after November 15, 2008. The Company adopted this guidance on January 1, 2009. The adoption requires the Company to make additional disclosures but did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In April 2008, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for intangibles – goodwill and other which amends the factors that should be considered in developing renewal or extension assumptions used to determine the useful life of a recognized intangible asset under the guidance. This guidance also requires enhanced disclosures concerning a company’s treatment of costs incurred to renew or extend the term of a recognized intangible asset. This guidance is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. The Company adopted this guidance on January 1, 2009, but it did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
In June 2008, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for earnings per share. The guidance addresses whether instruments granted in share-based payment transactions may be participating securities prior to vesting and, therefore, need to be included in the earnings allocation in computing basic earnings per share pursuant to the two-class method of the guidance for earnings per share. This guidance is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008 and interim periods within those years. The adoption of this guidance did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In April 2009, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for fair value measurements and disclosures. This guidance provides companies with guidelines on how to determine fair value measurements when the volume and level of activity for an asset or liability have significantly decreased and how to identify transactions that are not orderly. This guidance was effective for the Company beginning with its reporting period ended June 30, 2009 and did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In April 2009, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for interim disclosures for financial instruments. This guidance amends prior authoritative guidance by requiring disclosures of the fair value of financial instruments included within the scope of the prior guidance whenever a public company issues summarized financial information for interim reporting periods. This guidance was effective for the Company beginning with its reporting period ended June 30, 2009 and did not have a material effect on its consolidated financial statements. The Company has provided the additional disclosures required in Note 2.
In May 2009, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for subsequent events which provides rules on recognition and disclosure for events and transactions occurring after the balance sheet date but before the financial statements are issued or available to be issued. This guidance was effective for the Company beginning with its reporting period ended June 30, 2009 and shall be applied prospectively. The adoption of this statement did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In June 2009, the FASB issued ASC 810-10-65-2, Amendments to FASB ASC 810-10-05-8A. This statement prescribes a qualitative model for identifying whether a company has a controlling financial interest in a VIE and eliminates the quantitative model prescribed by ASC Topic 810-10. The new model identifies two primary characteristics of a controlling financial interest: (1) provides a company with the power to direct significant activities of the VIE, and (2) obligates a company to absorb losses of and/or provides rights to receive benefits from the VIE. ASC 810-10-65-2 requires a company to reassess on an ongoing basis whether it holds a controlling financial interest in a VIE. A company that holds a controlling financial interest is deemed to be the primary beneficiary of the VIE and is required to consolidate the VIE. This statement is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2009. In connection with its review of ASC Topic 810-10, which resulted in its conclusion that treatment of the Company’s managed P.C.s as variable interest entities is the appropriate treatment under ASC Topic 810-10 as discussed above, the Company’s management also analyzed ASC 810-10-65-2 and concluded that ASC
38
810-10-65-2 applies to the Company and that it will consolidate its managed P.C.s under ASC 810-10-65-2 effective January 1, 2010.
In July 2009, the FASB established the FASB Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) as the source of authoritative accounting principles recognized by the FASB to be applied by nongovernmental entities in the preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP. Rules and interpretive releases of the SEC under authority of federal securities laws are also sources of authoritative GAAP for SEC registrants. The ASC supersedes all existing non-SEC accounting and reporting standards and is not intended to change GAAP. The use of the ASC was effective for financial statements issued for periods ending after September 15, 2009.
In August 2009, the FASB issued new accounting guidance to provide clarification on measuring liabilities at fair value when a quoted price in an active market is not available. This new guidance became effective on July 1, 2009. The Company adopted this guidance on July 1, 2009, but it did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In January 2010, the FASB issued new accounting guidance relating to improving disclosures about fair value measurement. The new accounting guidance requires new disclosures and clarifies certain existing disclosure requirements about fair value measurements. A reporting entity is required to disclose significant transfers in and out of Level 1 and Level 2 fair value measurements, to describe the reasons for the transfers and to present separately information about purchases, sales, issuances and settlements for fair value measurements using significant unobservable inputs. This new accounting guidance is effective on January 1, 2010, except for the disclosures about purchases, sales, issuances and settlements in the roll forward of activity in Level 3 fair value measurements, which is effective on January 1, 2011 and early adoption is permitted. The Company does not believe this guidance will have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURE ABOUT MARKET RISK.
Not applicable to smaller reporting companies.
39
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Birner Dental Management Services, Inc. and subsidiaries’ consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2008 and 2009 and for each of the three years ended December 31, 2009:
| Page | |
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | 41 |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets | 42 |
| Consolidated Statements of Income | 43 |
| Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity and Comprehensive Income | 44 |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | 45 |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | 47 |
40
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors
Birner Dental Management Services, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Birner Dental Management Services, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the related consolidated statements of income, shareholders’ equity and comprehensive income, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2009. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Birner Dental Management Services, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2009, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
As discussed in Note 14, the Company restated its consolidated statements of income for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007.
We were not engaged to examine management’s assessment of the effectiveness of Birner Dental Management Services, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, included in Item 9A of this report on Form 10-K and, accordingly, we do not express an opinion thereon.
HEIN & ASSOCIATES LLP
Denver, Colorado
March 30, 2010
41
BIRNER DENTAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| December 31, | |||||||
| ASSETS | 2008 | 2009 | |||||
| CURRENT ASSETS: | |||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 1,234,991 | $ | 779,622 | |||
|
Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $290,688 and $371,762, respectively |
2,875,732 | 3,124,160 | |||||
|
Deferred tax asset |
195,091 | 195,170 | |||||
|
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
418,653 | 433,222 | |||||
|
Total current assets |
4,724,467 | 4,532,174 | |||||
| PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, net | 3,887,919 | 3,532,011 | |||||
| OTHER NONCURRENT ASSETS: | |||||||
|
Intangible assets, net |
10,621,918 | 12,842,285 | |||||
|
Deferred charges and other assets |
160,289 | 153,734 | |||||
|
Notes receivable |
- | 191,557 | |||||
|
Total assets |
$ | 19,394,593 | $ | 21,251,761 | |||
| LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||
| CURRENT LIABILITIES: | |||||||
|
Accounts payable |
$ | 1,551,851 | $ | 1,934,468 | |||
|
Accrued expenses |
1,462,258 | 1,716,395 | |||||
|
Accrued payroll and related expenses |
1,714,550 | 1,795,968 | |||||
|
Income taxes payable |
371,569 | 267,160 | |||||
|
Current maturities of long-term debt |
920,000 | 920,000 | |||||
|
Total current liabilities |
6,020,228 | 6,633,991 | |||||
| LONG-TERM LIABILITIES: | |||||||
|
Deferred tax liability, net |
618,913 | 526,036 | |||||
|
Long-term debt, net of current maturities |
5,988,202 | 4,362,024 | |||||
|
Other long-term obligations |
259,678 | 2,112,395 | |||||
|
Total liabilities |
12,887,021 | 13,634,446 | |||||
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES | |||||||
| SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY: | |||||||
|
Preferred Stock, no par value, 10,000,000 shares authorized; none outstanding |
- | - | |||||
|
Common Stock, no par value, 20,000,000 shares authorized; 1,863,587 and 1,858,135 shares issued and outstanding, respectively |
- | 164,255 | |||||
|
Treasury Stock purchased in excess of Common Stock basis |
(266,786 | ) | - | ||||
|
Retained earnings |
6,817,449 | 7,475,212 | |||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(43,091 | ) | (22,152 | ) | |||
|
Total shareholders' equity |
6,507,572 | 7,617,315 | |||||
|
Total liabilities and shareholders' equity |
$ | 19,394,593 | $ | 21,251,761 | |||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated balance sheets.
42
BIRNER DENTAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2007 (Restated) |
2008 (Restated) |
2009 | ||||||||||
| REVENUE: | $ | 59,386,817 | $ | 59,016,250 | $ | 59,573,559 | ||||||
| DIRECT EXPENSES: | ||||||||||||
|
Clinical salaries and benefits |
33,362,065 | 34,242,025 | 34,351,138 | |||||||||
|
Dental supplies |
2,316,044 | 2,370,866 | 2,230,807 | |||||||||
|
Laboratory fees |
2,615,017 | 2,722,607 | 2,615,246 | |||||||||
|
Occupancy |
4,599,981 | 4,798,133 | 4,943,088 | |||||||||
|
Advertising and marketing |
678,488 | 433,496 | 462,861 | |||||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization |
2,541,995 | 2,445,956 | 2,423,788 | |||||||||
|
General and administrative |
4,593,316 | 4,731,822 | 4,718,548 | |||||||||
| 50,706,906 | 51,744,905 | 51,745,476 | ||||||||||
|
Contribution from dental offices |
8,679,911 | 7,271,345 | 7,828,083 | |||||||||
| CORPORATE EXPENSES: | ||||||||||||
|
General and administrative |
4,119,052 | (1) | 3,687,341 | (1) | 4,291,325 | (1) | ||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization |
110,270 | 96,366 | 86,809 | |||||||||
| OPERATING INCOME | 4,450,589 | 3,487,638 | 3,449,949 | |||||||||
|
Interest expense (income), net |
365,140 | 282,267 | 174,582 | |||||||||
| INCOME BEFORE INCOME TAXES | 4,085,449 | 3,205,371 | 3,275,367 | |||||||||
|
Income tax expense |
1,650,342 | 1,414,962 | 1,350,301 | |||||||||
| NET INCOME | $ | 2,435,107 | $ | 1,790,409 | $ | 1,925,066 | ||||||
|
Net income per share of Common Stock - Basic |
$ | 1.16 | $ | 0.88 | $ | 1.03 | ||||||
|
Net income per share of Common Stock - Diluted |
$ | 1.08 | $ | 0.86 | $ | 1.02 | ||||||
|
Cash dividends per share of Common Stock |
$ | 0.60 | $ | 0.68 | $ | 0.68 | ||||||
|
Weighted average number of shares of Common Stock and dilutive securities: |
||||||||||||
|
Basic |
2,092,448 | 2,024,794 | 1,863,596 | |||||||||
|
Diluted |
2,258,108 | 2,085,889 | 1,895,441 | |||||||||
| (1) |
Corporate expenses - general and administrative includes $324,120 of equity compensation for a stock award and $405,274 of stock-based compensation expense pursuant to ASC Topic 718 for the year ended December 31, 2007, $731,607 of stock-based compensation expense pursuant to ASC Topic 718 for the year ended December 31, 2008 and $657,033 of stock-based compensation expense pursuant to ASC Topic 718 and $245,376 related to a long-term incentive program for the year ended December 31, 2009. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
43
BIRNER DENTAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
| Common Stock | Treasury Stock Purchased in excess of Common Stock Basis | Other Comprehensive Income | Retained Earnings | Shareholders' Equity | |||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| BALANCES, January 1, 2007 | 2,132,461 | $ | 4,191,349 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 5,207,184 | $ | 9,398,533 | ||||||||||||
|
Common Stock options exercised |
187,770 | 1,293,925 | - | - | - | 1,293,925 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Purchase and retirement of Common Stock |
(196,791 | ) | (4,141,188 | ) | - | - | - | (4,141,188 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
Tax benefit of Common Stock options exercised |
- | 955,035 | - | - | - | 955,035 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Dividends declared on Common Stock |
- | - | - | - | (1,256,797 | ) | (1,256,797 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
- | 729,394 | - | - | - | 729,394 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Other comprehensive loss |
- | - | - | (34,156 | ) | - | (34,156 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
Net income, year-ended December 31, 2007 |
- | - | - | 2,435,107 | 2,435,107 | 2,435,107 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive income |
- | - | - | 2,400,951 | - | - | |||||||||||||||||
| BALANCES, December 31, 2007 | 2,123,440 | $ | 3,028,515 | $ | - | $ | (34,156 | ) | $ | 6,385,494 | $ | 9,379,853 | |||||||||||
|
Common Stock options exercised |
32,685 | 326,788 | - | - | - | 326,788 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Purchase and retirement of Common Stock |
(292,538 | ) | (4,098,041 | ) | (266,786 | ) | - | - | (4,364,827 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
Tax benefit of Common Stock options exercised |
- | 11,131 | - | - | - | 11,131 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Dividends declared on Common Stock |
- | - | - | - | (1,358,454 | ) | (1,358,454 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
- | 731,607 | - | - | - | 731,607 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Other comprehensive loss |
- | - | - | (8,935 | ) | - | (8,935 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
Net income, year-ended December 31, 2008 |
- | - | - | 1,790,409 | 1,790,409 | 1,790,409 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive income |
- | - | - | 1,781,474 | - | - | |||||||||||||||||
| BALANCES, December 31, 2008 | 1,863,587 | $ | - | $ | (266,786 | ) | $ | (43,091 | ) | $ | 6,817,449 | $ | 6,507,572 | ||||||||||
|
Common Stock options exercised, net |
56,250 | 190,480 | 266,786 | - | - | 457,266 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Purchase and retirement of Common Stock |
(61,702 | ) | (929,900 | ) | - | - | - | (929,900 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
Tax benefit of Common Stock options exercised |
- | 1,266 | - | - | - | 1,266 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Dividends declared on Common Stock |
- | - | - | - | (1,267,303 | ) | (1,267,303 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
- | 902,409 | - | - | - | 902,409 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Other comprehensive income |
- | - | - | 20,939 | - | 20,939 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Net income, year-ended December 31, 2009 |
- | - | - | 1,925,066 | 1,925,066 | 1,925,066 | |||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive income |
- | - | - | 1,946,005 | - | - | |||||||||||||||||
| BALANCES, December 31, 2009 | 1,858,135 | $ | 164,255 | $ | - | $ | (22,152 | ) | $ | 7,475,212 | $ | 7,617,315 | |||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
44
BIRNER DENTAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||
|
Net income |
$ | 2,435,107 | $ | 1,790,409 | $ | 1,925,066 | |||||
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|||||||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization |
2,652,265 | 2,542,322 | 2,510,597 | ||||||||
|
Stock compensation expense |
729,394 | 731,607 | 902,409 | ||||||||
|
Loss on disposition of property |
- | 885 | - | ||||||||
|
Provision for doubtful accounts |
664,304 | 730,129 | 695,573 | ||||||||
|
Provision for (benefit from) deferred income taxes |
(94,937 | ) | 64,320 | (92,956 | ) | ||||||
|
Changes in assets and liabilities net of effects from acquisitions: |
|||||||||||
|
Accounts receivable |
(568,932 | ) | (597,313 | ) | (844,000 | ) | |||||
|
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
(23,082 | ) | 201,712 | (14,569 | ) | ||||||
|
Deferred charges and other assets |
10,173 | 11,398 | 6,555 | ||||||||
|
Accounts payable |
296,922 | (393,569 | ) | 382,617 | |||||||
|
Accrued expenses |
(134,256 | ) | (127,972 | ) | 275,076 | ||||||
|
Accrued payroll and related expenses |
(140,293 | ) | 258,073 | 81,418 | |||||||
|
Income taxes payable/receivable |
(140,833 | ) | 398,386 | (104,409 | ) | ||||||
|
Other long-term obligations |
(35,284 | ) | (31,588 | ) | 4,717 | ||||||
|
Net cash provided by operating activities |
5,650,548 | 5,578,799 | 5,728,094 | ||||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||
|
Notes receivable - related parties, net |
- | - | (191,557 | ) | |||||||
|
Capital expenditures |
(666,648 | ) | (753,952 | ) | (1,080,514 | ) | |||||
|
Acquisition of dental centers |
- | - | (1,398,335 | ) | |||||||
|
Development of new dental centers |
(47,707 | ) | (371,969 | ) | (148,208 | ) | |||||
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
(714,355 | ) | (1,125,921 | ) | (2,818,614 | ) | |||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||
|
Advances - line of credit |
20,101,330 | 23,597,356 | 17,369,169 | ||||||||
|
Repayments - line of credit |
(20,899,230 | ) | (21,473,665 | ) | (18,075,347 | ) | |||||
|
Repayments - term loan |
(920,000 | ) | (920,000 | ) | (920,000 | ) | |||||
|
Repayment of long-term debt |
(33,561 | ) | - | - | |||||||
|
Proceeds from exercise of Common Stock options |
1,293,925 | 326,788 | 457,266 | ||||||||
|
Purchase and retirement of Common Stock |
(4,141,188 | ) | (4,364,828 | ) | (929,900 | ) | |||||
|
Tax benefit of Common Stock options exercised |
955,035 | 11,132 | 1,266 | ||||||||
|
Common Stock cash dividends |
(1,216,540 | ) | (1,358,820 | ) | (1,267,303 | ) | |||||
|
Net cash used in financing activities |
(4,860,229 | ) | (4,182,037 | ) | (3,364,849 | ) | |||||
| NET INCREASE (DECREASE) IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | 75,964 | 270,841 | (455,369 | ) | |||||||
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, beginning of period | 888,186 | 964,150 | 1,234,991 | ||||||||
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, end of period | $ | 964,150 | $ | 1,234,991 | $ | 779,622 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
45
BIRNER DENTAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(UNAUDITED)
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||
| SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION: | |||||||||||
|
Cash paid during the year for interest |
$ | 462,787 | $ | 329,185 | $ | 212,423 | |||||
|
Cash paid during the year for income taxes |
$ | 931,076 | $ | 956,586 | $ | 1,546,407 | |||||
| NON-CASH ITEMS: | |||||||||||
|
Gain/(loss) recognized on interest rate swap (net of taxes) |
$ | (34,156 | ) | $ | (8,935 | ) | $ | 20,939 | |||
|
Contingent liability assumed related to office acquistions |
$ | - | $ | - | $ | 1,848,000 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these condensed consolidated financial statements.
46
BIRNER DENTAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| (1) | DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS AND ORGANIZATION |
Birner Dental Management Services, Inc., a Colorado corporation (the ''Company''), was incorporated in May 1995 and provides business services to dental group practices. As of December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, the Company managed 60, 61 and 64 dental practices (collectively referred to as the ''Offices''), respectively. The Company provides business services, which are designed to improve the efficiency and profitability of the dental practices. These Offices are organized as professional corporations (“P.C.s”) and the Company provides its business services to the Offices under long-term management agreements (the ''Management Agreements'').
The Company has grown primarily through acquisitions and de novo developments. The following table highlights the Company’s growth through December 31, 2009 as follows:
| Acquisitions | De Novo Developments | Office Consolidations/Closings | |||
| 2001 and Prior | 42 | 18 | (6) | ||
| 2002 | - | - | - | ||
| 2003 | - | - | - | ||
| 2004 | - | 2 | (1) | ||
| 2005 | - | 2 | - | ||
| 2006 | - | 4 | (1) | ||
| 2007 | - | - | - | ||
| 2008 | - | 1 | - | ||
| 2009 | 3 | - | - | ||
| Total | 45 | 27 | (8) |
The Company's operations and expansion strategy depend, in part, on the availability of dentists, dental hygienists and other professional personnel and the ability to hire and assimilate additional management and other employees to accommodate expanded operations.
| (2) | SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
Basis of Presentation/Basis of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared on the accrual basis of accounting. These financial statements present the financial position and results of operations of the Company and the Offices, which are under the control of the Company. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in the consolidation. Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to the presentation used in 2009. Such reclassification had no effect on net income. As noted in Note 14, the Company restated its consolidated income statements for 2007 and 2008 to record revenue and clinical salaries on a gross basis. The restatement had no effect on contribution from dental offices, operating income, net income, earnings per share, the consolidated balance sheets, the consolidated statements of shareholders’ equity and comprehensive income or the consolidated statements of cash flows.
The Company treats Offices as consolidated subsidiaries where it has a long-term and unilateral controlling financial interest over the assets and operations of the Offices. The Company has obtained control of substantially all of the Offices via the Management Agreements. The Company is a business service organization and does not engage in the practice of dentistry or the provision of dental hygiene services. These services are provided by licensed professionals. Certain key features of these arrangements either enable the Company at any time and in its sole discretion to cause a change in the shareholder of the P.C. (i.e., ''nominee shareholder'') or allow the Company to
47
vote the shares of stock held by the owner of the P.C. and to elect a majority of the board of directors of the P.C. The accompanying statements of income reflect revenue, which is the amount billed to patients less contractual adjustments. Direct expenses consist of all the expenses incurred in operating the Offices and paid by the Company. Under the Management Agreements, the Company assumes responsibility for the management of most aspects of the Offices' business (the Company does not engage in the practice of dentistry or the provision of dental hygiene services), including personnel recruitment and training, comprehensive administrative business and marketing support and advice, and facilities, equipment, and support personnel as required to operate the practice.
The Company prepares its consolidated financial statements in accordance with ASC 810, which provides for consolidation of variable interest entities of which the Company is the primary beneficiary. The Company has concluded that the P.C.s meet the definition of variable interest entities as defined by this standard and that the Company is the primary beneficiary of these variable interest entities. The Company concluded that the P.C.s meet the definition of variable interest entities because the equity investment at risk by each P.C. owner, which generally has not been more than $100, is not sufficient on a quantitative or qualitative basis to support each P.C.’s activities without additional financial support from the Company, which is provided through (i) the Company’s advancement of operating costs on behalf of the P.C.s and forgoing any amounts due the Company from the P.C.s under the Management Agreements when the P.C.s lack sufficient cash flow to pay the management fees in full and (ii) the Company’s capital investments in facilities and dental equipment used by the P.C.s in the operation of their dental practices. The Company determined that it is the primary beneficiary, as defined in ASC 810-10-38, of the P.C.s because (i) it absorbs losses of the P.C.s by forgoing the management fees, (ii) through the Management Agreements, the Company has the power to direct the activities of the P.C.s that most significantly impact the P.C.s’ economic performance, provides business and marketing services at the Offices, including providing capital, payment of all Center Expenses (as defined in the Management Agreements), designing and implementing marketing programs, negotiating for the purchase of supplies, staffing, recruiting, training of non-dental personnel, billing and collecting patient fees, arranging for certain legal and accounting services, and negotiating with managed care organizations, and (iii) no other party provides financial support to the P.C.s, and the P.C.s have no independent ability to support themselves. Accordingly, the net assets and results of operations of the P.C.s are included in the consolidated financial statements of the Company, and all transactions between the P.C.s and the Company, such as the management fees the Company charges, have been eliminated.
Revenue
Revenue is generally recognized when services are provided and are reported at estimated net realizable amounts due from insurance companies, preferred provider and health maintenance organizations (i.e., third-party payors) and patients for services rendered, net of contractual and other adjustments. Dental services are billed and collected by the Company in the name of the Offices.
Revenue under certain third-party payor agreements is subject to audit and retroactive adjustments. To management's knowledge, there are no material claims, disputes or other unsettled matters that exist concerning third-party reimbursements.
During 2007, 2008 and 2009, 12.2%, 12.8% and 12.3%, respectively, of the Company's revenue was derived from capitated managed dental care contracts. Under these contracts, the Offices receive a fixed monthly payment for each covered plan member for a specific schedule of services regardless of the quantity or cost of services provided by the Offices. Additionally, the Offices may receive co-pays from the patient for certain services provided. Revenue from the Company’s capitated managed dental care contracts is recognized as earned on a monthly basis.
Substantially all of the Company’s patients are insured under third-party payor agreements. The Company’s billing system generates contractual adjustments for each patient encounter based on fee schedules for the patient’s insurance plan. The services provided are attached to the patient’s fee schedule based on the insurance the patient has at the time the service is provided. Therefore, the revenue that is recorded by the billing system is based on insurance contractual amounts. Additionally, each patient at the time of service signs a form agreeing that the patient is ultimately responsible for the contracted fee if the insurance company does not pay the fee for any reason.
Contribution From Dental Offices
The ''Contribution from dental offices'' represents the excess of revenue from the operations of the Offices over direct expenses associated with operating the Offices. Revenue and direct expenses relate exclusively to business activities associated with the Offices. The contribution from dental offices provides an indication of the level of earnings generated from the operation of the Offices to cover corporate expenses, interest expense charges and income taxes.
Advertising and Marketing
Costs of advertising, promotion and marketing are expensed as incurred.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
For purposes of the consolidated balance sheets and statements of cash flows, cash and cash equivalents include money market accounts and all highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less. From time to time the Company may have cash at one bank in excess of the federally insured amount. As of December 31, 2009, the Company did not have cash at one bank in excess of the federally insured amount.
48
Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable represents receivables from patients and other third-party payors for dental services provided. Such amounts are recorded net of contractual allowances and other adjustments at the time of billing. In those instances when payment is not received at the time of service, the Offices record receivables from their patients, most of whom are local residents and are insured under third-party payor agreements. In addition, the Company has estimated allowances for uncollectible accounts. The Company’s allowance for doubtful accounts reflects a reserve that reduces customer accounts receivable to the net amount estimated to be collectible. Accounts are normally considered delinquent after 120 days. However, estimating the credit-worthiness of customers and the recoverability of customer accounts requires management to exercise considerable judgment. In estimating uncollectible amounts, management considers factors such as general economic and industry-specific conditions, historical customer performance and anticipated customer performance. Management continually monitors and periodically adjusts the allowances associated with these receivables.
The Company’s policy is to collect any patient co-payments at the time the service is provided. If the patient owes additional amounts that are not covered by insurance, Offices collect by sending monthly invoices, placing phone calls and sending collection letters. Interest at 18% APR is charged on all account balances greater than 60 days old. Patient accounts receivable in excess of $50 that are over 120 days and that appear are not collectible are written off as bad debt and sent to an outside collections agency.
Notes Receivable
Notes receivable were created as part of a dental Office acquisition. One note has a standard principal and interest monthly amortization payment schedule and a maturity date of October 29, 2013 and the second note has a balloon payment (both accrued interest and principal) due on October 29, 2013. Both notes bear interest of 6% which is accrued monthly. If a note is uncollectable, an allowance for doubtful accounts would be created.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost or fair market value at the date of acquisition, net of accumulated depreciation. Property and equipment are depreciated using the straight-line method over their useful lives of five years and leasehold improvements are amortized over the remaining life of the leases. Depreciation was $1,768,893, $1,762,316 and $1,723,631 for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively.
Intangible Assets
The Company's dental practice acquisitions involve the purchase of tangible and intangible assets and the assumption of certain liabilities of the acquired Offices. As part of the purchase price allocation, the Company allocates the purchase price to the tangible and identifiable intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed, based on estimated fair market values. Identifiable intangible assets include the Management Agreement. The Management Agreement represents the Company's right to manage the Offices during the 40-year term of the agreement. The assigned value of the Management Agreement is amortized using the straight-line method over a period of 25 years. Amortization was $883,372, $780,006 and $786,966 for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively.
The Management Agreements cannot be terminated by the related professional corporation without cause, consisting primarily of bankruptcy or material default by the Company.
Impairment of Long-Lived and Intangible Assets
In the event that facts and circumstances indicate that the carrying value of long-lived and intangible assets may be impaired, an evaluation of recoverability would be performed. If an evaluation were required, the estimated future undiscounted cash flows associated with the asset would be compared to the asset’s carrying amount to determine if a write-down to market value or discounted cash flow value would be required. As of December 31, 2007, the Company determined that intangible assets associated with one Office should be written down approximately $104,000. This amount was determined by comparing the intangible asset and property and equipment value at the Office to an independent appraised value for that Office. As a result, the Company recognized an impairment charge of $104,000 as amortization expense in December 2007.
49
Contingent Liabilities
As part of the dental Office acquisitions completed in the fourth quarter of 2009, the Company has recorded contingent liabilities to recognize an estimated amount to be paid as part of the acquisition agreements. These contingent liabilities were initially recorded at estimated fair value, are payable after four years from the acquisition date and are calculated at a multiple of then trailing twelve-months operating cash flows. The Company remeasures the contingent liability to fair value each reporting date until the contingency is resolved. The changes in fair value are recognized in earnings.
Concentrations of Credit Risk
Financial instruments, which potentially subject the Company to concentration of credit risk, are primarily cash and cash equivalents and accounts receivable. The Company maintains its cash balances in the form of bank demand deposits and money market accounts with financial institutions that management believes are creditworthy. The Company may be exposed to credit risk generally associated with healthcare and retail companies. The Company established an allowance for uncollectible accounts based upon factors surrounding the credit risk of specific customers, historical trends and other information. The Company has no significant financial instruments with off-balance sheet risk of accounting loss.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period.
The application of accounting policies requires the use of judgment and estimates. As it relates to the Company, estimates and forecasts are required to determine purchase price allocations for acquisitions, any impairment of assets, allowances for bad debts, deferred tax asset valuation reserves, if any, contingent liabilities, deferred revenue and employee benefit-related liabilities.
Matters that are subject to judgments and estimation are inherently uncertain, and different amounts could be reported using different assumptions and estimates. Management uses its best estimates and judgments in determining the appropriate amount to reflect in the financial statements, using historical experience and all available information. The Company also uses outside experts where appropriate. The Company applies estimation methodologies consistently from year to year.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes (Note 10) pursuant to ASC Topic 740, “Accounting for Income Taxes,'' which requires the use of the asset and liability method of computing deferred income taxes. The objective of the asset and liability method is to establish deferred tax assets and liabilities for the temporary differences between the book basis and the tax basis of the Company's assets and liabilities at enacted tax rates expected to be in effect when such amounts are realized or settled.
Earnings Per Share
The Company calculates earnings per share in accordance with ASC Topic 260, “Earnings Per Share.” The standard requires presentation of two categories of EPS – basic EPS and diluted EPS. Basic EPS excludes dilution and is computed by dividing income available to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding for the year. Diluted EPS reflects the potential dilution that could occur if securities or other contracts to issue Common Stock were exercised or converted into Common Stock or resulted in the issuance of Common Stock that then shared in the earnings of the Company.
50
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Income | Weighted Average Shares | Per Share Amount | Net Income | Weighted Average Shares | Per Share Amount | Net Income | Weighted Average Shares | Per Share Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic EPS | $ | 2,435,107 | 2,092,448 | $ | 1.16 | $ | 1,790,409 | 2,024,794 | $ | 0.88 | $ | 1,925,066 | 1,863,596 | $ | 1.03 | |||||||||||||
| Effect of Diluive Stock Options | - | 165,660 | (0.08 | ) | - | 61,095 | (0.02 | ) | - | 31,845 | (0.01 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Diluted EPS: | $ | 2,435,107 | 2,258,108 | $ | 1.08 | $ | 1,790,409 | 2,085,889 | $ | 0.86 | $ | 1,925,066 | 1,895,441 | $ | 1.02 | |||||||||||||
The difference between basic earnings per share and diluted earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009 relates to the effect of 165,660, 61,095 and 31,845 shares, respectively, of dilutive shares of Common Stock from stock options which are included in total shares for the diluted calculation determined under the treasury stock method as prescribed by ASC Topic 718, “Compensation – Stock Compensation.” For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009 options to purchase 13,700, 277,079 and 289,389 shares, respectively, of the Company’s Common Stock were not included in the computation of dilutive income per share because their effect was anti-dilutive.
Comprehensive Income
ASC Topic 220, “Reporting Comprehensive Income,” established standards for reporting and displaying comprehensive income and its components in a full set of general purpose financial statements. In addition to net income, comprehensive income includes all changes in equity during a period, except those resulting from investments by and distributions to owners. In 2007 and 2008, the Company recognized, on its balance sheet, approximately $34,000 and $9,000, respectively, of other comprehensive loss to mark down the value of a cash flow hedge net of taxes. In 2009, the Company recognized, on its balance sheet, approximately $21,000 of other comprehensive income to mark up the value of the cash flow hedge net of taxes.
Costs of Start-up Activities
Start-up costs and organization costs are expensed as they are incurred.
Segment Reporting
The Company operates in one business segment, which is to provide business services to dental practices. The Company currently provides business services to Offices in the states of Arizona, Colorado and New Mexico. All aspects of the Company’s business are structured on a practice-by-practice basis. Financial analysis and operational decisions are made at the individual Office level. The Company does not evaluate performance criteria based upon geographic location, type of service offered or source of revenue.
Stock-Based Compensation Plans
The Company follows ASC Topic 718 to account for stock-based compensation plans. Under ASC Topic 718, the Company is required to measure the cost of employee services received in exchange for stock options and similar awards based on the grant date fair value of the award and recognize this cost in the income statement over the period during which an employee is required to provide service in exchange for the award.
The Company recognizes compensation expense on a straight line basis over the requisite service period of the award. Total stock-based compensation expense included in the Company’s statement of income for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009 was approximately $405,000, $732,000 and $902,000, respectively. In 2009, the stock-based compensation expense consisted of $657,000 related to stock options and $245,000 related to restricted stock units granted under a long-term incentive program (“LTIP”). The LTIP was adopted by the Board of Directors on June 3, 2009 and provides for long-term performance-based cash and stock opportunities for the executive officers of the Company. Total stock-based compensation expense was recorded as a component of corporate general and administrative expense.
51
The Black-Scholes option-pricing model was used to estimate the option fair values. The option-pricing model requires a number of assumptions, of which the most significant are expected stock price volatility, the expected pre-vesting forfeiture rate, expected dividend rate and the expected option term (the amount of time from the grant date until the options are exercised or expire). Expected volatility was calculated based upon actual historical stock price movements over the most recent periods ending December 31, 2009 equal to the expected option term. Expected pre-vesting forfeitures were estimated based on actual historical pre-vesting forfeitures over the most recent periods ending December 31, 2009 for the expected option term. The expected option term in 2007 was calculated using the “simplified” method permitted by Staff Accounting Bulletin 107. The expected option term in 2008 and 2009 was calculated based on historical experience.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In September 2006, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for fair value measurements and disclosures which defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value and expands disclosures related to assets and liabilities measured at fair value. In February 2008, the FASB issued additional authoritative guidance for fair value measurements which delayed the effective date of the authoritative guidance for fair value measurements to fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2008 for all nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities that are recognized or disclosed at fair value in the financial statements on a nonrecurring basis. The Company adopted all of the provisions of the authoritative guidance for fair value measurements on January 1, 2008 with the exception of the application of the guidance to non-recurring nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities which the Company adopted on January 1, 2009. The adoption did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In December 2007, the FASB issued revised authoritative guidance for business combinations which establishes principles and requirements for how an acquirer in a business combination transaction recognizes and measures in its financial statements the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, and any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree at the acquisition date. The provisions of the guidance also establish disclosure requirements which will enable financial statement users to evaluate the nature and financial effects of the business combination. In April 2009, the FASB issued additional authoritative guidance for business combinations relating to the initial recognition and measurement, subsequent measurement and accounting and disclosures of assets and liabilities that arise from contingencies in a business combination. The authoritative guidance for business combinations is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. The Company adopted all of the provisions of the authoritative guidance for business combinations on January 1, 2009. The adoption resulted in the recording of contingent liabilities associated with the Company’s acquisitions of dental Offices during the year ended December 31, 2009.
In December 2007, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for consolidations which states that accounting and reporting for minority interests will be recharacterized as noncontrolling interests and classified as a component of equity. The guidance also establishes reporting requirements that provide sufficient disclosures that clearly identify and distinguish between the interests of the parent and the interests of the noncontrolling owners. The guidance applies to all entities that prepare consolidated financial statements, except not-for-profit organizations, but will affect only those entities that have an outstanding noncontrolling interest in one or more subsidiaries or that deconsolidate a subsidiary. This guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. The Company adopted this guidance as of January 1, 2009. The adoption did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In March 2008, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for derivatives and hedging which requires companies with derivative instruments to disclose information that should enable financial statement users to understand how and why a company uses derivative instruments, how derivative instruments and related hedged items are accounted for under the guidance, and how derivative instruments and related hedged items affect a company’s financial position, financial performance and cash. This guidance is effective for fiscal years and interim periods beginning after November 15, 2008. The Company adopted this guidance on January 1, 2009. The adoption requires the Company to make additional disclosures but did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In April 2008, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for intangibles – goodwill and other which amends the factors that should be considered in developing renewal or extension assumptions used to determine the useful life of a recognized intangible asset under the guidance. This guidance also requires enhanced disclosures concerning a company’s treatment of costs incurred to renew or extend the term of a recognized intangible asset. This guidance is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. The Company adopted this guidance on January 1, 2009, but it did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
52
In June 2008, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for earnings per share. The guidance addresses whether instruments granted in share-based payment transactions may be participating securities prior to vesting and, therefore, need to be included in the earnings allocation in computing basic earnings per share pursuant to the two-class method of the guidance for earnings per share. This guidance is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008 and interim periods within those years. The adoption of this guidance did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In April 2009, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for fair value measurements and disclosures. This guidance provides companies with guidelines on how to determine fair value measurements when the volume and level of activity for an asset or liability have significantly decreased and how to identify transactions that are not orderly. This guidance was effective for the Company beginning with its reporting period ended June 30, 2009 and did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In April 2009, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for interim disclosures for financial instruments. This guidance amends prior authoritative guidance by requiring disclosures of the fair value of financial instruments included within the scope of the prior guidance whenever a public company issues summarized financial information for interim reporting periods. This guidance was effective for the Company beginning with its reporting period ended June 30, 2009 and did not have a material effect on its consolidated financial statements. The Company has provided the additional disclosures required in Note 2.
In May 2009, the FASB issued authoritative guidance for subsequent events which provides rules on recognition and disclosure for events and transactions occurring after the balance sheet date but before the financial statements are issued or available to be issued. This guidance was effective for the Company beginning with its reporting period ended June 30, 2009 and shall be applied prospectively. The adoption of this statement did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In June 2009, the FASB issued ASC 810-10-65-2, Amendments to FASB ASC 810-10-05-8A. This statement prescribes a qualitative model for identifying whether a company has a controlling financial interest in a VIE and eliminates the quantitative model prescribed by ASC Topic 810-10. The new model identifies two primary characteristics of a controlling financial interest: (1) provides a company with the power to direct significant activities of the VIE, and (2) obligates a company to absorb losses of and/or provides rights to receive benefits from the VIE. ASC 810-10-65-2 requires a company to reassess on an ongoing basis whether it holds a controlling financial interest in a VIE. A company that holds a controlling financial interest is deemed to be the primary beneficiary of the VIE and is required to consolidate the VIE. This statement is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2009. In connection with its review of ASC Topic 810-10, which resulted in its conclusion that treatment of the Company’s managed P.C.s as variable interest entities is the appropriate treatment under ASC Topic 810-10 as discussed in Note 14, the Company’s management also analyzed ASC 810-10-65-2 and concluded that ASC 810-10-65-2 applies to the Company and that it will consolidate its managed P.C.s under ASC 810-10-65-2 effective January 1, 2010.
In July 2009, the FASB established the FASB Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) as the source of authoritative accounting principles recognized by the FASB to be applied by nongovernmental entities in the preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP. Rules and interpretive releases of the SEC under authority of federal securities laws are also sources of authoritative GAAP for SEC registrants. The ASC supersedes all existing non-SEC accounting and reporting standards and is not intended to change GAAP. The use of the ASC was effective for financial statements issued for periods ending after September 15, 2009.
In August 2009, the FASB issued new accounting guidance to provide clarification on measuring liabilities at fair value when a quoted price in an active market is not available. This new guidance became effective on July 1, 2009. The Company adopted this guidance on July 1, 2009, but it did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In January 2010, the FASB issued new accounting guidance relating to improving disclosures about fair value measurement. The new accounting guidance requires new disclosures and clarifies certain existing disclosure requirements about fair value measurements. A reporting entity is required to disclose significant transfers in and out of Level 1 and Level 2 fair value measurements, to describe the reasons for the transfers and to present separately information about purchases, sales, issuances and settlements for fair value measurements using significant unobservable inputs. This new accounting guidance is effective on January 1, 2010, except for the disclosures about
53
purchases, sales, issuances and settlements in the roll forward of activity in Level 3 fair value measurements, which is effective on January 1, 2011 and early adoption is permitted. The Company does not believe this guidance will have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
| (3) | ACQUISITIONS |
With each Office acquisition, the Company enters into a contractual arrangement, including a Management Agreement, which has a term of 40 years. Pursuant to these contractual arrangements the Company provides all business and marketing services at the Offices, other than the provision of dental services, and it has long-term and unilateral control over the assets and business operations of each Office. Accordingly, acquisitions are considered business combinations and are accounted as such.
2009 Acquisitions
On September 30, 2009, the Company acquired all of the assets except for accounts receivable of an Arizona partnership and entered into a Management Agreement to manage the practice for a purchase price of $350,000, all payable in cash, and an estimated fair value of contingent liabilities of $718,000 assumed in this acquisition. These contingent liabilities were recorded as of the date of acquisition and are payable after four years from the acquisition date and are calculated at a multiple of then trailing twelve-month operating cash flows. The purchase price was allocated as follows: $315,000 to intangible assets and $35,000 to fixed assets.
On October 29, 2009, the Company acquired all of the assets of an Arizona partnership and entered into a Management Agreement to manage the practice for a purchase price of $700,000, all payable in cash, and an estimated fair value of contingent liabilities of $850,000 assumed in this acquisition. These contingent liabilities were recorded as of the date of acquisition and are payable after four years from the acquisition date and are calculated at a multiple of then trailing twelve-month operating cash flows. The purchase price was allocated as follows: $530,000 to intangible assets, $100,000 to accounts receivable and $70,000 to fixed assets.
On December 30, 2009, the Company acquired all of the assets except for accounts receivable of a Colorado partnership and entered into a Management Agreement to manage the practice for a purchase price of $340,000, all payable in cash, and an estimated fair value of contingent liabilities of $280,000 assumed in this acquisition. These contingent liabilities were recorded as of the date of acquisition and are payable after four years from the acquisition date and are calculated at a multiple of then trailing twelve-month operating cash flows. The purchase price was allocated as follows: $306,000 to intangible assets and $34,000 to fixed assets.
The fair values of the acquisitions were based on significant inputs not observable in the market and are therefore defined as level 3 inputs under ASC Topic 820. Key assumptions include the estimate for the fair value of the contingent liabilities.
The following unaudited pro forma financial information represents the combined results for the Company and the three dental Office acquisitions from 2009 for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 as if the acquisitions had occurred on January 1, 2009 and January 1, 2008. The pro forma financial information is not intended to represent or be indicative of the consolidated results of operations or financial condition of the Company that would have been reported had the acquisitions been completed as of the dates presented, and should not be taken as representative of the future consolidated results of operations or financial condition of the Company.
| For the years ended December 31, | |||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | ||||||
| Revenue | 63,077,187 | 62,887,409 | |||||
| Operating income | 3,787,421 | 3,644,192 | |||||
| Net income | 1,957,987 | 2,038,281 | |||||
The three dental Offices acquired contributed approximately $598,000 to revenue, $62,000 to operating income and $36,000 to net income during the fourth quarter and year-ended December 31, 2009.
54
| (4) | PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT |
Property and equipment consist of the following:
| December 31, | |||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | ||||||
| Dental equipment | $ | 6,326,917 | $ | 6,568,775 | |||
| Furniture and fixtures | 1,274,620 | 1,349,841 | |||||
| Leasehold improvements | 8,156,458 | 8,628,827 | |||||
| Computer equipment, software and related items | 1,928,638 | 2,229,458 | |||||
| Instruments | 988,817 | 1,077,003 | |||||
| 18,675,450 | 19,853,904 | ||||||
| Less - accumulated depreciation | (14,787,531 | ) | (16,321,893 | ) | |||
| Property and equipment, net | $ | 3,887,919 | $ | 3,532,011 | |||
Depreciation expense was $1,762,893, $1,762,316 and $1,723,631 for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively.
| (5) | INTANGIBLE ASSETS |
Intangible assets consist of Management Agreements:
| Amortization Period | December 31, | ||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | ||||||||
| Management Agreements | 25 years | $ | 18,740,290 | $ | 21,747,623 | ||||
| Less - accumulated amortization | (8,118,372 | ) | (8,905,338 | ) | |||||
| Intangible assets, net | $ | 10,621,918 | $ | 12,842,285 | |||||
Amortization expense was $883,372, $780,005 and $786,966 for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively.
The estimated aggregate amortization expense on the Management Agreements for each of the five succeeding fiscal years is as follows:
| 2010 | $ | 875,234 | |
| 2011 | 875,234 | ||
| 2012 | 875,234 | ||
| 2013 | 875,234 | ||
| 2014 | 856,996 | ||
| $ | 4,357,932 |
55
| (6) | DEBT |
Debt consists of the following:
| December 31, | |||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | ||||||
|
Revolving credit agreement with a bank not to exceed $7.0 million, at either, or a combination of, the lender’s Base Rate (3.25% at December 31, 2008) or a LIBOR rate Plus 1.25% (3.08% at December 31, 2008), collateralized by the Company’s accounts receivable and Management Agreements, due in May 2010. |
$ | 4,378,202 | - | ||||
|
Revolving credit agreement with a bank not to exceed $7.0 million, at either, or a combination of, the lender’s Base Rate (5.75% at December 31, 2009) or the higher of the LIBOR rate or 1.5% plus 3.875% (5.375% at December 31, 2009), collateralized by the Company's accounts receivable and Management Agreement, due in May 2011. |
- | 3,672,024 | |||||
|
$4.6 million Term Loan with a bank, $2.3 million of which was borrowed at a fixed rate of 7.05% and the remainder was borrowed at a floating interest rate of LIBOR plus 1.5% (1.73% at December 31, 2009), with principal to be repaid in 20 equal quarterly payments of approximately $230,000 plus interest beginning December 31, 2006, collateralized by the Company's accounts receivable and Management Agreements, matures on September 30, 2011. |
2,530,000 | 1,610,000 | |||||
| 6,908,202 | 5,282,024 | ||||||
| Less - current maturities | (920,000 | ) | (920,000 | ) | |||
| Long-term debt, net of current maturities | $ | 5,988,202 | $ | 4,362,024 | |||
Credit Facility
On June 30, 2009, the Company amended its bank line of credit (“Credit Facility”). The amended Credit Facility extends the expiration of the credit agreement from May 31, 2010 to May 31, 2011. The Credit Facility allows the Company to borrow, on a revolving basis, an aggregate principal amount not to exceed $7.0 million at either, or a combination of, the lender’s Base Rate or at LIBOR plus a LIBOR rate margin, at the Company’s option. The Base Rate computes interest at the higher of the lender’s “prime rate” or the Federal Funds Rate plus a margin. The amendment adjusted the Base Rate margin from 0.5% to 2.5%. The LIBOR option computes interest at the LIBOR rate as of the date such LIBOR rate loan was made plus a LIBOR rate margin. The amendment states that the LIBOR rate is the higher of 1.5% or the LIBOR rate and the margin is adjusted from 1.25% to 3.875%. As of December 31, 2009, the Company’s LIBOR borrowing rate was 5.375% and the Base Rate borrowing rate was 5.75%. Management believes that the LIBOR and Base Rate margins increased as a result of the lender’s increased cost of funds and not because of the Company’s credit quality. A commitment fee on the average daily unused amount of the revolving loan commitment during the preceding quarter is also assessed and increased from 0.25% to 0.40% as of June 1, 2009 as a result of the amendment. The Company may prepay any Base Rate loan at any time and any LIBOR rate loan upon not less than three business days prior written notice given to the lender, but the Company is responsible for any loss or cost incurred by the lender in liquidating or employing deposits required to fund or maintain the LIBOR rate loan. The Credit Facility expires on May 31, 2011. The Company historically has renewed the Credit Facility and extended the term of the Credit Facility for one additional year annually in the spring and intends to continue this practice in the spring of 2010. At December 31, 2009, the Company had $3.7 million outstanding and $3.3 million available for borrowing under the Credit Facility. This consisted of $2.0 million outstanding under the LIBOR rate option and $1.7 million outstanding under the Base Rate option. The Credit
56
Facility requires the Company to comply with certain covenants and financial ratios. At December 31, 2009, the Company was in full compliance with all of its covenants under the Credit Facility.
Term Loan
In October 2006, the Company entered into a $4.6 million term loan (“Term Loan”). Under the Term Loan, $2.3 million was borrowed at a fixed interest rate of 7.05% and the remaining $2.3 million was borrowed at a floating interest rate of LIBOR plus 1.5%. As of December 31, 2009, the floating rate was 1.73%. The principal amount borrowed is repaid quarterly in 20 equal payments of $230,000 plus interest beginning December 31, 2006. The Term Loan matures on September 30, 2011. As of December 31, 2009, $805,000 was outstanding at the fixed rate of 7.05% and $805,000 was outstanding at the LIBOR plus 1.5% floating rate. The Term Loan requires the Company to comply with certain covenants and financial ratios. At December 31, 2009, the Company was in full compliance with all of its covenants under the Term Loan.
The interest rate on one-half of the principal amount of the Term Loan has been fixed with a fixed-for-floating interest rate swap. The Company has elected to designate this fixed-for-floating interest rate swap as a cash flow hedge under ASC Topic 815, “Derivatives and Hedging.”
Scheduled Maturities
The scheduled maturities of debt are as follows:
| Year | Amount | |||
| 2010 | $ | 920,000 | ||
| 2011 | 4,362,024 | |||
| $ | 5,282,024 |
| (7) | SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY |
Treasury Stock
The Company from time to time may purchase its Common Stock on the open market or in privately negotiated transactions. During 2007, the Company, in 27 separate transactions, repurchased 196,791 shares of its Common Stock for a total consideration of approximately $4.1 million at prices ranging from $18.50 to $24.33 per share. In August 2007, the Company repurchased 100,000 shares at $20.75 per share in a private transaction that was approved by the Board of Directors. In December 2007, the Company repurchased 49,204 shares at $21.00 per share in a private transaction that was approved by the Board of Directors. During 2008, the Company, in 47 separate transactions, repurchased 292,538 shares of its Common Stock for total consideration of approximately $4.4 million at prices ranging from $10.47 to $21.00 per share. In February 2008, The Company repurchased 3,210 shares at $21.00 per share in a private transaction that was approved by the Board of Directors. During 2009, the Company, in 108 separate transactions repurchased 61,702 shares of its Common Stock for total consideration of approximately $930,000 at prices ranging at prices ranging from $10.02 to $17.00 per share. As of December 31, 2009, approximately $688,000 of the previously authorized amount was available for these purchases.
Due to the Company’s repurchases of common stock at prices higher than the original issue price, the Company’s Common Stock balance would have been reduced to a negative $266,786 as of December 31, 2008. The Company reclassified this negative balance to treasury stock purchased in excess of Common Stock basis on the balance sheet as of December 31, 2008.
Stock-Based Compensation Plans
At the Company’s June 2005 annual meeting of shareholders, the shareholders approved the 2005 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2005 Plan”). The 2005 Plan was amended at the June 2007 annual meeting of shareholders to reserve 425,000 shares of Common Stock for issuance and was amended again at the June 2009 annual meeting of
57
shareholders to reserve 625,000 share of Common Stock for issuance. The 2005 Plan provides for the grant of incentive stock options, restricted stock, restricted stock units and stock grants to employees (including officers and employee-directors) and non-statutory stock options to employees, directors and consultants. The objectives of this plan include attracting and retaining the best personnel and providing for additional performance incentives by providing employees with the opportunity to acquire Common Stock. As of December 31, 2009, there were 242,898 shares available for issuance under the 2005 Plan. The exercise price of the stock options issued under the 2005 Plan is equal to the market price, or market price plus 10% for shareholders who own greater than 10% of the Company, at the date of grant. These stock options expire seven years, or five years for shareholders who own greater than 10% of the Company, from the date of the grant and vest annually over a service period ranging from three to five years. The 2005 Plan is administered by a committee of two or more outside directors from the Company’s Board of Directors (the “Committee”). The Committee determines the eligible individuals to whom awards under the 2005 Plan may be granted, as well as the time or times at which awards will be granted, the number of shares to be granted to any eligible individual, the life of any award, and any other terms and conditions of the awards in addition to those contained in the 2005 Plan. As of December 31, 2009, there were 177,972 vested options, 128,711 unvested options and 60,000 vested restricted shares outstanding under the 2005 Plan.
The Employee Stock Option Plan (the ''Employee Plan'') was adopted by the Board of Directors effective as of October 30, 1995, and as amended on September 4, 1997, February 28, 2002, and June 8, 2004, reserved 479,250 shares of Common Stock for issuance. The Employee Plan provided for the grant of incentive stock options to employees (including officers and employee-directors) and non-statutory stock options to employees, directors and consultants. The Employee Plan expired by its terms on October 30, 2005. As of December 31, 2009, there were 86,568 vested options and no unvested options outstanding under the Employee Plan.
The Company uses the Black-Scholes pricing model to estimate the fair value of each option granted with the following weighted average assumptions:
| For years ended December 31, | |||||||||||||
| Valuation Assumptions | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | ||||||||||
| Expected life | 4.5 | (1) | 3.7 | (2) | 3.2 | (2) | |||||||
| Risk-free interest rate (3) | 4.71 | % | 2.11 | % | 1.30 | % | |||||||
| Expected volatility (4) | 58 | % | 58 | % | 69 | % | |||||||
| Expected dividend yield | 3.07 | % | 4.06 | % | 6.33 | % | |||||||
| Expected forfeiture (5) | 5.37 | % | 4.81 | % | 4.97 | % | |||||||
| (1) | The expected life, in years, of stock options is estimated using the simplified-method calculation. | |
| (2) | The expected life, in years, of stock options is estimated based on historical experience. | |
| (3) | The risk-free interest rate is based on U.S. Treasury bills whose term is consistent with the expected life of the stock options. | |
| (4) | The expected volatility is estimated based on historical and current stock price data for the Company. | |
| (5) | Forfeitures are estimated based on historical experience. | |
58
A summary of stock option activity as of December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, and changes during the years then ended, are presented below:
| Number of Options/Warrants | Weighted-Average Exercise Price | Range of Exercise Prices | Weighted-Average Remaining Contractual Term (years) | Aggregate Intrinsic Value(thousands) | |||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2006 | 563,235 | $ | 11.63 | $ | 4.80 - $19.75 | 3.7 | $ | 6,550 | |||||||||||
Granted |
20,000 | $ | 21.49 | $ | 19.50 - $21.85 | ||||||||||||||
Exercised |
187,769 | $ | 6.89 | $ | 4.80 - $17.61 | ||||||||||||||
Canceled |
18,333 | $ | 14.74 | $ | 9.66 - $17.61 | ||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2007 | 377,133 | $ | 14.36 | $ | 5.50 - $21.85 | 3.7 | $ | 2,677 | |||||||||||
Granted |
147,000 | $ | 17.63 | $ | 10.20 - $21.00 | ||||||||||||||
Exercised |
32,685 | $ | 10.00 | $ | 5.50 - $19.54 | ||||||||||||||
Canceled |
24,932 | $ | 17.15 | $ | 12.50 - $20.02 | ||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2008 | 466,516 | $ | 15.55 | $ | 7.88 - $21.85 | 3.8 | $ | 273 | |||||||||||
Granted |
19,000 | $ | 10.75 | $ | 10.75 - $10.75 | ||||||||||||||
Exercised |
61,765 | $ | 8.77 | $ | 7.86 - $14.81 | ||||||||||||||
Canceled |
30,500 | $ | 16.76 | $ | 11.50 - $21.75 | ||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2009 | 393,251 | $ | 16.28 | $ | 9.66 - $21.85 | 3.2 | $ | 879 | |||||||||||
| Exercisable at December 31, 2007 | 213,688 | $ | 12.25 | $ | 5.50 - $19.75 | 2.8 | $ | 1,963 | |||||||||||
| Exercisable at December 31, 2008 | 254,986 | $ | 13.87 | $ | 7.88 - $21.85 | 2.2 | $ | 262 | |||||||||||
| Exercisable at December 31, 2009 | 264,540 | $ | 16.01 | $ | 9.66 - $21.85 | 2.3 | $ | 611 |
The weighted average grant date fair value of options granted was $9.02, $6.35 and $3.70 per option during the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively. Net cash proceeds from the exercise of stock options during the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009 were $1,294,000, $327,000 and $457,000, respectively. The associated income tax benefit from stock options exercised during the year ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, was $955,000, $11,000 and $1,000, respectively. As of the date of exercise, the total intrinsic value of options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009 was $2.7 million, $245,000 and $423,000, respectively. As of December 31, 2009, there was $600,000 of total unrecognized compensation expense related to non-vested stock options, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of 1.2 years.
In October 2009, an officer of the Company exercised 8,682 options at an exercise price of $9.75 on a cashless basis. A net of 3,167 shares of Common Stock were issued to the officer, as the Company effectively repurchased 5,515 shares of Common Stock to pay the total exercise cost of $84,649. The value of the Common Stock used to determine the net shares to be issued upon the cashless exercise was $15.35 per share, which was the closing price of the Company’s Common Stock on the date of the transaction.
59
The following table summarizes information about the options outstanding at December 31, 2009:
| Options Outstanding | Options Exercisable | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Range of Exercise Prices | Number of Options Outstanding at December 31, 2009 | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Number of Options Exercisable at December 31, 2009 | Weighted Average Exercise Price | |||||||||||||||||
| $ | 8.74 — 10.92 | 90,318 | 2.2 | $ | 10.00 | 64,652 | 9.76 | |||||||||||||||
| 10.93 — 13.11 | 50,250 | 4.0 | 12.00 | 31,584 | 12.30 | |||||||||||||||||
| 13.12 — 15.29 | 12,333 | 4.6 | 14.22 | 8,333 | 14.52 | |||||||||||||||||
| 17.49 — 19.66 | 135,850 | 2.2 | 18.66 | 118,134 | 18.76 | |||||||||||||||||
| 19.67 — 21.85 | 104,500 | 4.9 | 20.93 | 41,837 | 20.98 | |||||||||||||||||
| $ | 6.56 — 21.85 | 393,251 | 3.2 | $ | 16.28 | 264,540 | $ | 16.01 | ||||||||||||||
Restricted Stock
On July 1, 2005, the Company granted 60,000 shares of restricted Common Stock to the Company’s Chairman and Chief Executive Officer. All of the compensation expense related to the restricted stock grant was recognized as of December 31, 2008.
| (8) | LONG-TERM INCENTIVE PROGRAM |
On June 3, 2009, the Compensation Committee of the Company adopted the LTIP. The LTIP, which operates under the 2005 Plan, provides for long-term performance-based cash and stock opportunities for the executive officers of the Company. Details of the LTIP are as follows:
The Company’s executive officers may earn an aggregate of up to $1,050,000 in cash and up to 80,000 shares of Common Stock of the Company. The Company issued restricted stock units with respect to the 80,000 shares. Frederic W. Birner, the Company’s Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, Dennis N. Genty, the Company’s Chief Financial Officer, and Mark A. Birner, D.D.S., the Company’s President, may earn up to 50%, 25% and 25% of the foregoing amounts, respectively. Of the foregoing amounts, 24%, 33% and 43% can be earned in each of 2009, 2010 and 2011, respectively.
The executive officers may earn the foregoing amounts through achievement by the Company of performance targets related to patient revenue growth, practice additions, adjusted EBITDA margin and earnings per share growth. The executive officers will earn 100% of the amounts allocated to a particular year if the Company exceeds all four of the annual performance targets, 90% if the Company exceeds three of the four annual performance targets, 66.7% if the Company exceeds two of the four annual performance targets, and 0% if the Company achieves fewer than two of the four annual performance targets. The Compensation Committee will review each of the performance targets annually and will administer the LTIP.
All amounts vest only if the executive officer is employed by the Company on December 31, 2011 and will be payable during the first quarter of 2012.
For the year ended December 31, 2009, the Company accrued approximately $227,000 related to the cash portion and recorded $245,000 of stock-based compensation for the equity portion, respectively, of the LTIP.
60
| (9) | COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
Operating Lease Obligations
The Company leases office space under leases accounted for as operating leases. The original lease terms are generally one to five years with options to renew the leases for specific periods subsequent to their original terms. Rent expense for these leases totaled $3,697,399, $3,891,143 and $3,968,865 for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008, and 2009, respectively.
Future minimum lease commitments for operating leases with remaining terms of one or more years are as follows:
| Years ending December 31, | |||
| 2010 | $ | 3,134,459 | |
| 2011 | 2,341,568 | ||
| 2012 | 1,804,333 | ||
| 2013 | 1,211,474 | ||
| 2014 | 571,506 | ||
| Thereafter | 168,508 | ||
| $ | 9,231,848 | ||
Certain of the Company’s office space leases are structured to include scheduled and specified rent increases over the lease term. From time to time the Company receives incentives from the landlord including tenant improvement discounts and periods of free rent. The Company recognizes the effects of these rent escalations, tenant improvement discounts and periods of free rent on a straight-line basis over the lease terms.
Contingent Liabilities
As part of the dental Office acquisitions completed in the fourth quarter of 2009, the Company has recorded contingent liabilities to recognize an estimated amount to be paid as part of the acquisition agreement. These contingent liabilities were initially recorded at estimated fair values are payable after four years from the acquisition date and are calculated at a multiple of then trailing twelve-months operating cash flows. The Company remeasures the contingent liability to fair value each reporting date until the contingency is resolved. The changes in fair value are recognized in earnings. As of December 31, 2009, the Company has recorded $1.8 million of contingent liabilities which are payable starting in September 2013.
Litigation
From time to time the Company is subject to litigation incidental to its business, which could include litigation as a result of the dental services provided at the Offices, although the Company does not engage in the practice of dentistry or control the practice of dentistry. The Company maintains general liability insurance for itself and provides for professional liability insurance to the dentists, dental hygienists and dental assistants at the Offices. Management believes the Company is not presently a party to any material litigation.
| (10) | INCOME TAXES |
The Company accounts for income taxes through recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future income tax consequences of events, which have been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the difference between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse.
61
Income tax expense for the years ended December 31 consists of the following:
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||
| Current: | |||||||||||
|
Federal |
$ | 1,737,943 | $ | 1,167,494 | $ | 1,267,220 | |||||
|
State |
130,503 | 183,149 | 177,800 | ||||||||
| 1,868,446 | 1,350,643 | 1,445,020 | |||||||||
| Deferred: | |||||||||||
|
Federal |
(191,493 | ) | 67,829 | (86,144 | ) | ||||||
|
State |
(26,611 | ) | (3,510 | ) | (8,575 | ) | |||||
| (218,104 | ) | 64,319 | (94,719 | ) | |||||||
| Total income tax expense | $ | 1,650,342 | $ | 1,414,962 | $ | 1,350,301 |
The Company's effective tax rate differs from the statutory rate due to the impact of the following (expressed as a percentage of income before income taxes):
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||
| Statutory federal income tax expense | 34.0 | % | 34.0 | % | 34.0 | % | |||||
| State income tax expense | 3.5 | 4.0 | 3.0 | ||||||||
| Effect of permanent differences - | |||||||||||
|
Travel and entertainment expenses |
0.3 | 0.5 | 0.5 | ||||||||
|
Share based compensation |
2.9 | 5.6 | 5.0 | ||||||||
| Other | (0.3 | ) | - | (1.3 | ) | ||||||
| 40.4 | % | 44.1 | % | 41.2 | % |
Temporary differences comprise the deferred tax assets and liabilities in the consolidated balance sheets as follows:
| December 31, | |||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | ||||||
| Deferred tax assets current: | |||||||
|
Accruals not currently deductible |
$ | 84,629 | $ | 87,512 | |||
|
Allowance for doubtful accounts |
110,462 | 107,658 | |||||
| 195,091 | 195,170 | ||||||
| Deferred tax assets long-term: | |||||||
|
Depreciation for tax under books |
1,182,869 | 1,256,348 | |||||
|
Stock option compensation |
89,785 | 332,612 | |||||
| 1,272,654 | 1,588,960 | ||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities long-term: | |||||||
|
Intangible asset amortization for tax over books |
(1,891,567 | ) | (2,114,996 | ) | |||
| (1,891,567 | ) | (2,114,996 | ) | ||||
| Net deferred tax asset (liability) | $ | (423,822 | ) | $ | (330,866 | ) | |
Deferred income taxes are recognized for the expected tax consequences in future years for differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their financial reporting amounts, based upon enacted tax laws and statutory tax rates applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to affect taxable income. The Company’s significant deferred tax assets are related to: Accruals not currently deductible, allowance for doubtful accounts and
62
depreciation expense for tax which is less than depreciation expense for books, the tax effect of the deferred revenue adjustment and stock option timing differences between book and tax. The Company has not established a valuation allowance to reduce deferred tax assets as the Company expects to fully recover these amounts in future periods. The Company’s significant deferred tax liability is the result of intangible asset amortization expense for tax being greater than the intangible asset amortization expense for books. Management reviews and adjusts those estimates annually based upon the most current information available. However, because the recoverability of deferred taxes is directly dependent upon the future operating results of the Company, actual recoverability of deferred taxes may differ materially from management’s estimates.
In 2007, 2008 and 2009, tax benefits associated with the exercise of stock options reduced taxes payable by approximately $955,000, $11,000 and $1,000, respectively, and increased equity by the same amount.
The Company is aware of the risk that the recorded deferred tax assets may not be realizable. However, management believes that it will obtain the full benefit of the deferred tax assets on the basis of its evaluation of the Company’s anticipated profitability over the period of years that the temporary differences are expected to become tax deductions. It believes that sufficient book and taxable income will be generated to realize the benefit of these tax assets.
Effective January 1, 2007, the Company adopted the provisions of ASC Topic 740, “Accounting for Income Taxes,” which clarifies the accounting for uncertainty in income taxes recognized in a company’s financial statements. ASC Topic 740 requires a company to determine whether it is more likely than not that a tax position will be sustained upon examination based upon the technical merits of the position. If the more-likely-than-not threshold is not met, a company must measure the tax position to determine the amount to recognize in the financial statements. The application of income tax law and regulations is inherently complex and subject to change. The Company is required to make many subjective assumptions and judgments regarding its income tax exposures. Changes in these subjective assumptions and judgments can materially affect amounts recognized in the Company’s financial statements.
At the adoption date of January 1, 2007 and at December 31, 2009, the Company had no unrecognized tax benefits which would affect the effective tax rate if recognized, and as of December 31, 2009, the Company had no accrued interest or penalties related to uncertain tax positions.
On initial application, ASC Topic 740 was applied to all tax positions for which the statute of limitations remained open. The tax years 2006-2009 remain open to examination by taxing jurisdictions to which the Company is subject.
| (11) | BENEFIT PLANS |
Profit Sharing 401(k)/Stock Bonus Plan
The Company has a 401(k)/stock bonus plan, which was established April 1, 1997. Eligible employees may make voluntary contributions to the plan. Effective November 1, 2005, the Company announced that it would start matching 20% of the first 6% of each employee’s contribution. Effective April 1, 2007, the Company announced that it would increase this match to 40% of the first 6% of each employee’s contribution. The Company contributed $191,000, $207,000 and $197,000 towards the plan for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively. In addition, the Company may make profit sharing contributions during certain years, which may be made, at the Company's discretion, in cash or in Common Stock of the Company. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, the Company did not make any profit sharing contributions.
Other Company Benefits
The Company provides a health and welfare benefit plan to all regular full-time employees. The plan includes health and life insurance and a cafeteria plan. In addition, regular full-time and regular part-time employees are entitled to certain dental benefits.
| (12) | DISCLOSURES ABOUT FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS |
ASC Topic 825, ''Disclosures About Fair Value of Financial Instruments,'' requires disclosure about the fair value of financial instruments. Carrying amounts for all financial instruments included in current assets and current liabilities
63
approximate estimated fair values due to the short maturity of those instruments. The fair values of the Company's note payable are based on similar rates currently available to the Company. The Company believes the fair value approximates book value for the note receivable. As of December 31, 2007 and 2008, the Company recognized, on its balance sheet, approximately $34,000 and $9,000 (net of taxes), respectively, of other comprehensive loss to mark down the value of the Company’s interest rate swap designated as a cash flow hedge. In 2009, the Company recognized, on its balance sheet, approximately $21,000 (net of taxes) of other comprehensive income to mark up the value of the cash flow hedge. As required by ASC Topic 820, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures,” the Company calculated the value of the cash flow hedge using Level II inputs.
| (13) | SUBSEQUENT EVENTS |
On February 16, 2010, the Company opened a de novo Office located in Bernalillo, New Mexico. The Company now has ten Offices in the Albuquerque and Santa Fe, New Mexico markets.
On March 12, 2010, the Company announced that its Board of Directors approved an increase in the amount of the quarterly cash dividend from $.17 per share to $.20 per share.
As discussed in the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 12, 2010 and elsewhere in this Annual Report, the Company has restated its previously issued audited statements of income for each of the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2008 and its unaudited consolidated statements of income for each of the quarters of the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2009.
| (14) | RESTATEMENT OF CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
The Company had been consolidating its managed professional corporations under the consolidation by contract method as originally set forth prior to codification in Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”) 97-02 and the related Staff interpretation of EITF 97-02 since its initial public offering in 1998. The consolidation by contract method as described in EITF 97-02 has a very narrow scope, and the Company believed that it fit within that scope precisely. The Staff of the SEC reviewed and issued comments pertaining to the Company’s Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008. In the course of reviewing the SEC’s accounting comments, management of the Company examined the application of the consolidation methodology of ASC Topic 810-10 to the consolidation of its managed professional corporations. ASC Topic 810-10 contains a sentence providing that variable interest entity, or VIE, accounting should be considered before consideration of consolidation by contract. Based on its review of ASC Topic 810-10, the Company began the process of analyzing whether its managed professional corporations should be consolidated under the VIE model and made submissions to the SEC to determine whether VIE accounting under ASC Topic 810-10 was appropriate. After thorough consideration of the questions and comments raised by the SEC in the SEC review process and discussions with the SEC staff regarding the issue, on March 10, 2010, the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors of the Company, in consultation with management and the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, concluded that treatment of the Company’s managed professional corporations as variable interest entities is the appropriate treatment under ASC Topic 810-10.
64
The following is a summary of the significant effects of the restatements on the Company’s consolidated statements of income for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2007 and 2008. See Note 15 for the effects on the previously issued quarterly financial statements. The restatement has no impact on
-
Contribution from dental offices
-
Operating income
-
Net income
-
Earnings per share
-
Consolidated balance sheets
-
Consolidated statements of shareholders equity and comprehensive income
-
Consolidated statements of cash flows
Consolidated Statements of Income
| Year Ended Dec. 31, 2007 | |||||||||||
| Line Item | As Previously Reported | Adjustments | As Restated | ||||||||
| REVENUE (1) | $ | 35,282,984 | $ | 24,103,833 | $ | 59,386,817 | |||||
| DIRECT EXPENSES: | |||||||||||
| Clinical salaries and benefits | $ | 9,258,232 | $ | 24,103,833 | $ | 33,362,065 | |||||
| DIRECT EXPENSES | $ | 26,603,073 | $ | 24,103,833 | $ | 50,706,906 | |||||
| Year Ended Dec. 31, 2008 | |||||||||||
| Line Item | As Previously Reported | Adjustments | As Restated | ||||||||
| REVENUE (1) | $ | 34,522,861 | $ | 24,493,389 | $ | 59,016,250 | |||||
| DIRECT EXPENSES: | |||||||||||
| Clinical salaries and benefits | $ | 9,748,636 | $ | 24,493,389 | $ | 34,242,025 | |||||
| DIRECT EXPENSES | $ | 27,251,516 | $ | 24,493,389 | $ | 51,744,905 | |||||
(1) Previously reported as NET REVENUE
65
| (15) | QUARTERLY RESULTS OF OPERATIONS (UNAUDITED) |
As discussed in Note 14, revenue and clinical salaries and benefits have been restated. There were no changes to contribution from dental offices, net income or net income per share of common stock. The following summarizes certain quarterly results of operations:
| Revenue as Previously Reported (1) | Revenue Restated | Clinical Salaries and Benefits as Previously Reported | Clinical Salaries and Benefits Restated | Direct Expenses as Previously Reported | Direct Expenses Restated | ||||||||
| 2007 quarter ended: | |||||||||||||
| 31-Mar-07 | $ | 9,446,584 | $ | 15,730,055 | $ | 2,452,112 | $ | 8,735,583 | $ | 6,762,102 | $ | 13,045,573 | |
| 30-Jun-07 | 9,027,811 | 15,101,800 | 2,384,027 | 8,458,016 | 6,805,328 | 12,879,317 | |||||||
| 30-Sep-07 | 8,640,137 | 14,726,411 | 2,271,625 | 8,357,899 | 6,562,237 | 12,648,511 | |||||||
| 31-Dec-07 | 8,168,452 | 13,828,551 | 2,150,468 | 7,810,567 | 6,473,406 | 12,133,505 | |||||||
| $ | 35,282,984 | $ | 59,386,817 | $ | 9,258,232 | $ | 33,362,065 | $ | 26,603,073 | $ | 50,706,906 | ||
| 2008 quarter ended: | |||||||||||||
| 31-Mar-08 | $ | 8,946,997 | $ | 15,254,252 | $ | 2,667,975 | $ | 8,975,230 | $ | 6,979,031 | $ | 13,286,286 | |
| 30-Jun-08 | 8,793,229 | 14,916,479 | 2,491,642 | 8,614,892 | 7,046,156 | 13,169,406 | |||||||
| 30-Sep-08 | 8,763,895 | 14,976,112 | 2,351,310 | 8,563,527 | 6,806,399 | 13,018,616 | |||||||
| 31-Dec-08 | 8,018,740 | 13,869,407 | 2,237,709 | 8,088,376 | 6,419,930 | 12,270,597 | |||||||
| $ | 34,522,861 | $ | 59,016,250 | $ | 9,748,636 | $ | 34,242,025 | $ | 27,251,516 | $ | 51,744,905 | ||
| 2009 quarter ended: | |||||||||||||
| 31-Mar-09 | $ | 9,040,511 | $ | 15,341,714 | $ | 2,576,545 | $ | 8,877,748 | $ | 6,832,084 | $ | 13,133,287 | |
| 30-Jun-09 | 8,886,727 | 15,216,028 | 2,421,007 | 8,750,308 | 6,755,193 | 13,084,494 | |||||||
| 30-Sep-09 | 8,496,084 | 14,690,693 | 2,376,929 | 8,571,538 | 6,745,685 | 12,940,294 | |||||||
| 31-Dec-09 (2) | 14,325,124 | 8,151,544 | 12,587,401 | ||||||||||
| $ | 26,423,322 | $ | 59,573,559 | $ | 7,374,481 | $ | 34,351,138 | $ | 20,332,962 | $ | 51,745,476 |
(1) Previously reported as NET REVENUE
(2) Not restated
66
| Contribution From Dental Offices | Net Income | Net Income Per Share of Common Stock-Diluted | |||||
| 2007 quarter ended: | |||||||
| 31-Mar-07 | $ | 2,684,483 | $ | 780,579 | $ | 0.34 | |
| 30-Jun-07 | 2,222,483 | 611,941 | 0.26 | ||||
| 30-Sep-07 | 2,077,900 | 635,040 | 0.28 | ||||
| 31-Dec-07 | 1,695,045 | 407,547 | 0.19 | ||||
| $ | 8,679,911 | $ | 2,435,107 | $ | 1.08 | ||
| 2008 quarter ended: | |||||||
| 31-Mar-08 | $ | 1,967,966 | $ | 517,557 | $ | 0.24 | |
| 30-Jun-08 | 1,747,015 | 450,198 | 0.21 | ||||
| 30-Sep-08 | 1,957,496 | 500,147 | 0.24 | ||||
| 31-Dec-08 | 1,598,868 | 322,507 | 0.17 | ||||
| $ | 7,271,345 | $ | 1,790,409 | $ | 0.86 | ||
| 2009 quarter ended: | |||||||
| 31-Mar-09 | $ | 2,208,427 | $ | 677,026 | $ | 0.36 | |
| 30-Jun-09 | 2,131,534 | 519,593 | 0.27 | ||||
| 30-Sep-09 | 1,750,399 | 365,550 | 0.19 | ||||
| 31-Dec-09 | 1,737,723 | 362,897 | 0.19 | ||||
| $ | 7,828,083 | $ | 1,925,066 | $ | 1.02 |
67
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE.
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
As discussed in the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 12, 2010 and elsewhere in this Annual Report, the Company has restated its previously issued audited statements of income for each of the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2008 and its unaudited consolidated statements of income for each of the quarters of the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2009.
In connection with the restatement, the Company carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s management, including the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended), as of December 31, 2008 and 2009.
Based on their evaluation of the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting at December 31, 2008, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer previously had concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting were effective. In light of the restatement as discussed in this Annual Report, including Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have now concluded that, at December 31, 2008, the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting were not effective due to a material weakness in the Company’s internal controls over financial reporting. The material weakness is a result of a lack of controls to identify variable interest entities and the accurate reporting of the consolidation of variable interest entities under GAAP. In addition, because the material weakness related to variable interest entity accounting continued to exist through December 31, 2009, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, at December 31, 2009, the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were not effective.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
The Company’s management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and directors; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on our financial statements.
Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”).
As discussed above, as a result of the material weakness of a lack of controls to identify variable interest entities and the accurate reporting of the consolidation of variable interest entities under GAAP, management has concluded that, as of December 31, 2009, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was not effective.
This Annual Report does not include an attestation report of the Company’s registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting. Management’s report was not subject to attestation by the Company’s registered public accounting firm pursuant to temporary rules of the SEC that permit the Company to provide only management’s report in this Annual Report.
68
Remediation of the Material Weakness
In the first quarter of 2010, the Company implemented controls to more readily identify variable interest entities and to consolidate such variable interest entities properly under GAAP. These controls include a review by the Company’s Chief Financial Officer of any new material contracts to compare the terms of such contracts to the requirements for consolidation under variable interest entity accounting. The Company may also consider implementing a control that would engage outside consultants if additional resources are needed to address any issues regarding variable interest entity accounting or other new accounting pronouncements in the future. The Company will analyze and test the effectiveness of the new controls as of March 31, 2010.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
As the material weaknesses noted above were not identified until 2010, there were no specific remediation actions during the fourth fiscal quarter of 2009 which materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION.
None.
69
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE.
The information required by this Item 10 is incorporated in this Annual Report by reference to the applicable information set forth in the Company’s definitive proxy statement for the 2010 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which will be filed no later than 120 days after the close of the 2009 fiscal year with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION.
The information required by this Item 11 is incorporated in this Annual Report by reference to the applicable information set forth in the Company’s definitive proxy statement for the 2010 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which will be filed no later than 120 days after the close of the 2009 fiscal year with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS.
The information required by this Item 12 is incorporated in this Annual Report by reference to the applicable information set forth in the Company’s definitive proxy statement for the 2010 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which will be filed no later than 120 days after the close of the 2009 fiscal year with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE.
The information required by this Item 13 is incorporated in this Annual Report by reference to the applicable information set forth in the Company’s definitive proxy statement for the 2010 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which will be filed no later than 120 days after the close of the 2009 fiscal year with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES.
The information required by this Item 14 is incorporated in this Annual Report by reference to the applicable information set forth in the Company’s definitive proxy statement for the 2010 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which will be filed no later than 120 days after the close of the 2009 fiscal year with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
70
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES.
| (a) | (1) | Financial Statements: |
|
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | ||
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets - | ||
|
As of December 31, 2008 and 2009 | ||
|
Consolidated Statements of Income - | ||
|
Years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009 | ||
|
Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity and Comprehensive Income - | ||
|
Years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009 | ||
|
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows - | ||
|
Years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009 | ||
|
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | ||
| (2) | Financial Statement Schedules: | |
|
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm on Schedule | ||
|
II - Valuation and Qualifying Accounts - | ||
|
Three Years Ended December 31, 2009 |
Because the Company is primarily a holding company and all subsidiaries are wholly owned, only consolidated statements are being filed. Schedules other than those listed above are omitted because of the absence of the conditions under which they are required or because the information is included in the financial statements or notes to the financial statements.
| (b) | The Exhibit Index lists the exhibits filed with this Annual Report. |
71
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
BIRNER DENTAL MANAGEMENT SERVICES, INC.
a Colorado corporation
| /s/ Frederic W.J. Birner | Chairman of the Board, Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) | March 31, 2010 | ||
| Frederic W.J. Birner |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| /s/ Frederic W.J. Birner | Chairman of the Board, Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) | March 31, 2010 | ||
| Frederic W.J. Birner | ||||
| /s/ Dennis N. Genty | Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and Treasurer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | March 31, 2010 | ||
| Dennis N. Genty | ||||
| /s/ Mark A. Birner | President and Director | March 31, 2010 | ||
| Mark A. Birner, D.D.S. | ||||
| /s/ Brooks G. O’Neil | Director | March 31, 2010 | ||
| Brooks G. O’Neil | ||||
| /s/ Paul E. Valuck | Director | March 31, 2010 | ||
| Paul E. Valuck D.D.S. | ||||
| /s/ Thomas D. Wolf | Director | March 31, 2010 | ||
| Thomas D. Wolf |
72
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
We have audited in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements of Birner Dental Management Services, Inc. for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 included in this Form 10-K and have issued our report thereon dated March 30, 2010. Our audits were made for the purpose of forming an opinion on the basic financial statements taken as a whole. This Schedule II - Valuation and Qualifying Accounts is the responsibility of the Company’s management and is presented for purposes of complying with the Securities and Exchange Commission’s rules and is not part of the basic financial statements. The information included in this schedule for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 has been subjected to the auditing procedures applied in the audits of the basic financial statements and, in our opinion, fairly states in all material respects the financial data required to be set forth therein in relation to the basic financial statements taken as a whole.
HEIN & ASSOCIATES LLP
Denver, Colorado
March 30, 2010
73
Birner Dental Management Services, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Financial Statement Schedule
II – Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
| Description | Balance at beginning of period | Charged to costs and expenses | Deductions(2) | Balance at end of period | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | $ | 290,688 | $ | 695,573 | (1) | $ | 614,499 | $ | 371,762 | |||||||
| 2008 | $ | 291,827 | $ | 730,149 | $ | 731,288 | $ | 290,688 | ||||||||
| 2007 | $ | 288,513 | $ | 664,304 | $ | 660,990 | $ | 291,827 |
(1) Approximately $81,000 of this amount is related to one of the dental Office acquisitions.
(2) Charges to the account are for the purpose for which the reserves were created.
74
Index of Exhibits
| Exhibit Number | Description of Document |
| 3.1 |
Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC File No. 333-36391), as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 25, 1997. |
| 3.2 |
Amended and Restated Bylaws, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC File No. 333-36391), as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on |
| 4.1 |
Specimen Stock Certificate, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC File No. 333-36391), as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 25, 1997. |
| 10.1 |
Form of Indemnification Agreement entered into between the Registrant and its Directors and Executive Officers, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC File No. 333-36391), as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 25, 1997. |
| 10.2 |
Form of Restricted Stock Agreement and Grant Notice under 2005 Equity Incentive Plan, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 000-23367), as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on July 19, 2005. |
| 10.3 |
Birner Dental Management Services, Inc. 2005 Equity Incentive Plan, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 99 of the Company’s Definitive Proxy Statement filed with the Securities Exchange Commission on April 27, 2005. |
| 10.14 |
Form of Managed Care Contract with Prudential, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.14 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC File No. 333-36391), as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 25, 1997. |
| 10.15 |
Form of Managed Care Contract with PacifiCare, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC File No. 333-36391), as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 25, 1997. |
| 10.18 |
Form of Management Agreement, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.18 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC File No. 333-36391), as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 25, 1997. |
| 10.20 |
Form of Stock Transfer and Pledge Agreement, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.20 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC File No. 333-36391), as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 25, 1997. |
| 10.23 |
Birner Dental Management Services, Inc. 1995 Employee Stock Option Plan, including forms of Incentive Stock Option Agreement and Non-statutory Stock Option Agreement under the Employee Plan, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC File No. 333-36391), as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 25, 1997. |
| 10.25 |
Profit Sharing 401(k)/Stock Bonus Plan of the Registrant, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.25 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC File No. 333-36391), as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 25, 1997. |
| 10.26 |
Form of Stock Transfer and Pledge Agreement with Mark Birner, D.D.S., incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.26 of Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC File No. 333-36391), as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 7, 1997. |
| 10.43 |
Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated August 7, 2003 between the Registrant and KeyBank National Association, incorporated herein as Exhibit 10.43 to the Company’s Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2003. |
| 10.49 |
Seventh Amendment to the Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated June 30, 2009 between the Registrant and KeyBank National Association, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company’s Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2009. |
| 23* | Hein & Associates LLP consent dated March 30, 2010. |
| 31.1* | |
| 31.2* | |
| 32.1* |
Certification of Form 10-K report pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
* Filed with this Form 10-K.
75
